

Generations of Computer 1st to 5th Explained with Pictures.
The history of computer technology is often used to refer to the origin of all the different generations of computers . From first to fifth each computer generation is characterized by significant technological development in their components, memory , and elements which essentially changed the way these devices work.
Several periods of generation from over the years advanced the technological evolution leads to the creation of today’s modern computer with more complex, more powerful, and increased capability and functionality.
Introduction to Computer Generations
This development period of electronic computing technology is called Computer Generation. There are five generations of computers identified, although the sixth generation could be in development now in the early 21st century.
During the evolutionary timeline, each generation of computers has improved a lot by undergoing considerable changes in their size, type, and functionality.
By analyzing them, one can trace the evolution of computer technology, to see how the computer industry has changed over the years and how great capabilities and software progress has been made by humankind in under a hundred years , as a result, the creation of different generations.
At present, the computer is playing a significant part in human existence because today’s digital computer is being used for every work in each field. If someday an issue occurs in the computer or the server is down, at that point all the work stops. This is how significant it is for technology development!
In this article, I will introduce you to all the generations of computers with pictures by explaining the complete information about their characteristics , names, components , and examples too.
Generations of Computer From 1st to 5th
Let’s discover the series of computer generations in the following list:
1st Generation of Computer (1940-1956)
This first generation of computers was based on vacuum tube technology used for calculations, storage, and control, invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming. The vacuum tubes and diode valves were the chief components of the first generations of computers.

First-generation computers relied on the lowest-level machine language, in order to perform operations, and could only solve a single problem at a point of time.
Magnetic drums were used as the memory in these computers (were very slow in speed). The punched and magnetic tapes were used for the input and output function of the computer in order to display on prints even the results weren’t 100% accurate.

Also, the first generation of computers available was based on the 8-bit microprocessor.
The disadvantages of 1st gen computers are that they were very enormous in size and heavy in weight (made of thousands of vacuum tubes ) , occupying large rooms. Also, once they were kept in one place it was difficult to transfer. Another con like using a decimal number system and many switches and cables.
In addition, they were also very expensive to operate with using a large amount of electricity, the vacuum tubes produced large amounts of heat, so an air conditioner was required for the proper functioning unless a lot of heat can cause a malfunction.
The advantage of the first generation of computers is that they could calculate in milliseconds (about five thousand sums per second.)
The computers of first-generation were managed to use in different fields like weather forecasting, solving mathematical problems, energy tasks, also in space research, military, and other scientific tasks.
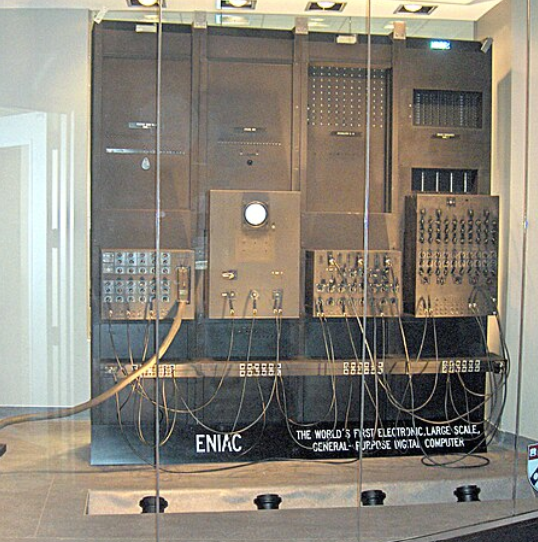
In the first generation of computers, the first computer of the world named “ENIAC” (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was discovered by John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert in the year between 1943 to 1945.
ENIAC used panel-to-panel wiring and switches for programming, occupied more than 1,000 square feet, used about 18,000 vacuum tubes, and weighed 30 tons.
Characteristics of the 1st Generation of Computer:
- Vacuum tubes and diode valves were used as the main electronic component in the first generation computers.
- Punch cards, paper tape utilized for input and output operations.
- Magnetic drums used for storage.
- Huge in size and weight with a lot of power consumption.
- Very expensive in price also not reliable.
- Computers were programmed with low-level machine language also has low operating speed.
Examples of the first generation of computers are ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer) EDSEC (Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator), EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer), (Electronic delay storage automatic calculator), IBM -701 and IBM 650.
ENIAC, the first general-purpose electronic digital computer . This computer about 18,000 vacuum tubes used for the calculation result in huge in size, occupied more than 1,000 square feet, and weighed 30 tons. These were the harbingers of today’s digital computers. This first computing machine was designed by people J. P. Eckert, W. Mosley, J. W. Mauchly.
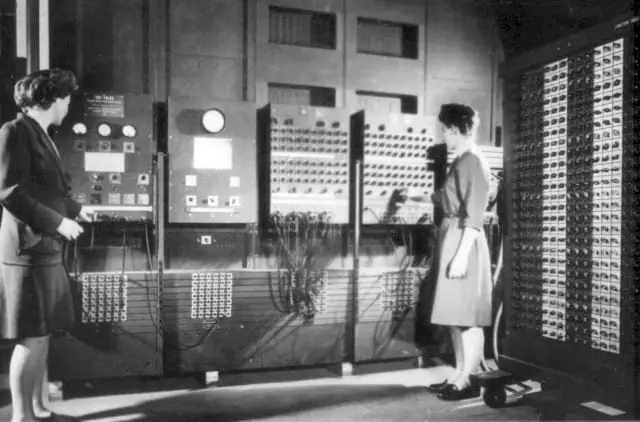
2nd Generation of Computer (1956-1964)
The second generation of computers replaced the vacuum tubes with a reliable component called transistors for manufacturing of computers was invented by William Shockley in 1947.
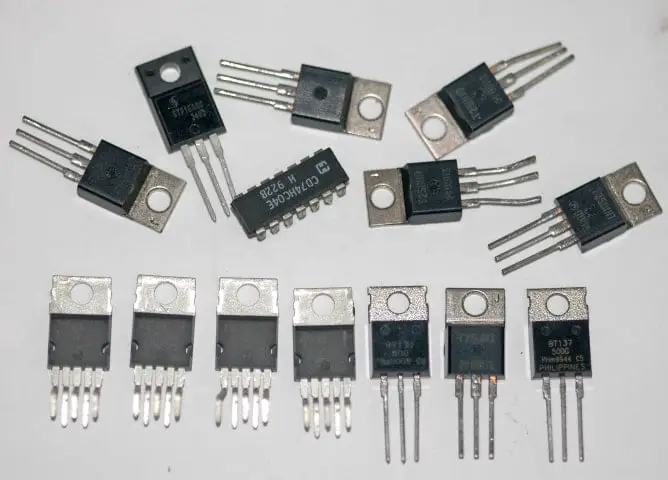

The transistors were the revolution in the computer field because this component advantaged the 2nd gen computer by increasing the performance, operating speed (hundreds of thousands of operations per second), as well as decreasing the electricity consumption of the computers.
Transistors were far superior to the vacuum tube, allowing computers to get faster, cheaper, more energy-efficient made and possible to reduce the size of computing equipment and ultimately heat reduced and reliability improved.
Computers of second-generation are characterized by the use of the first high-level programming languages, allowing programmers to specify instructions in words. At this time, early versions of COBOL, ALGOL, SNOBOL, and FORTRAN languages were developed .
These were the first computers to store their instructions in their memory, which went from a magnetic drum to magnetic core technology. During this period, the first computer game name “ Spacewar ” was seen on a PDP-1 computer.

Do you know~ that the oldest abacus was a computing machine designed to calculate thousands of years ago, which is still used in schools today to do calculations.
Also, the concept of Central Processing Unit (CPU), multi-programming operating systems, programming language, memory, and input and output units (I / O units) were developed in the timeline of second-generation computers.
The major disadvantages of Second-generation computers were they still relied on punch cards for input and hard copies for output as well as still it was difficult to move the computers for the reason they were enough large and even some computers needed ACs.

This second generation of computers was first used in the fields like the atomic energy industry and nuclear power plants and other commercial fields.
Characteristics of the 2nd Generation of Computer:
- Computers based on transistors instead of vacuum tubes.
- Magnetic Tape was used to store data.
- Relatively small in size and reduced weight with low energy consumption than 1st gen computers.
- Faster, reliable, and less expensive than the first generation.
- Use of storage devices, printers, and operating systems, etc.
- Higher-level languages like COBOL, ALGOL, SNOBOL, and FORTRAN were developed and used.
Examples of the second generation of computers include IBM 1620, CDC 1604, IBM 7094, UNIVAC 1108, IBM 620, CDC 3600, IBM 4044, Honeywell 400, IBM 1401 Mainframe, and PDP-1 minicomputer. IBM was actively working, producing transistor versions of its computers.
3rd Generation of Computer (1964-1971)
The third generation appeared in the form of integrated circuits (invented by Jack Kilby from 1958 to 1964). An IC (integrated circuit) is consists of many small transistors mounted on chips , which are called semiconductors.
This synchronized chip became an important foundation for the third generation computers when scientists combined hundreds of transistors fit in this circuit result in a more powerful electronic segment called an integrated circuit.
Multiprogramming was implemented (this is when there are several executable programs in memory) at the same time that it diminished their manufacturing costs. In the mid-60s. IBM improved the term “computer architecture”. By the end of the 60s. mini-computers appeared.
This revolutionary innovation allowed to expansion of the processing capacity and memory of the machines.
Instead of punch cards and prints, users interacted via keyboards and monitors , and interacted with an operating system, allowing the device to run various applications at once with a central program that monitored the memory.

As you can see, the first appearance of computer monitors fell on the second generation of computers. The invention belongs to the company IBM, which in 1964 released the commercial display station IBM-2250.
it was used in the system/360 series. The model had a vector monochrome display measuring 12×12 inches, with a resolution of 1024×1024 pixels and a refresh rate of 40 Hz. This invention revolutionized today’s different types of monitors including LCD, LED, OLED monitors.
The invention of IC incredibly decreased the size of computers and made it easy for transportation from one place to another. The working speed and efficiency of this generation of computers were much faster than the previous generation and even cheaper.
High-end languages such as PASCAL, BASIC, FORTRAN – II TO IV, COBOL, ALGOL developed in this generation.
For the first time, they got access to a mass audience allowed computers to penetrate into different spheres of human activity since they were smaller and cheaper. Along these, they turned out to be more specialized (i.e., there were different computers for different tasks).
The 3rd generation of computers was the initial move towards the miniaturization of computers and quickly expanded their scope: control, automation of scientific experiments, data transmission, etc. In addition to being used in the manufacture of radios, TVs, and other similar devices .
Characteristics of the 3rd Generation of Computer:
- In this generation, computers based on Integrated Circuit was more powerful than the transistor.
- The size of the computers was likewise little because the size of the IC being more modest than the circuit size of the transistors.
- More reliable, inexpensive, faster, energy-efficient, as well as very light in weight than 2nd gen computers.
- The first Computer Mouse and Keyboard were appeared and used in the 3rd generation of computers
- Use of new versions of high-level languages like BASIC, COBOL, FORTRAN, PASCAL, and ALGOL
- Available for a mass audience and made it possible for general purpose usage.
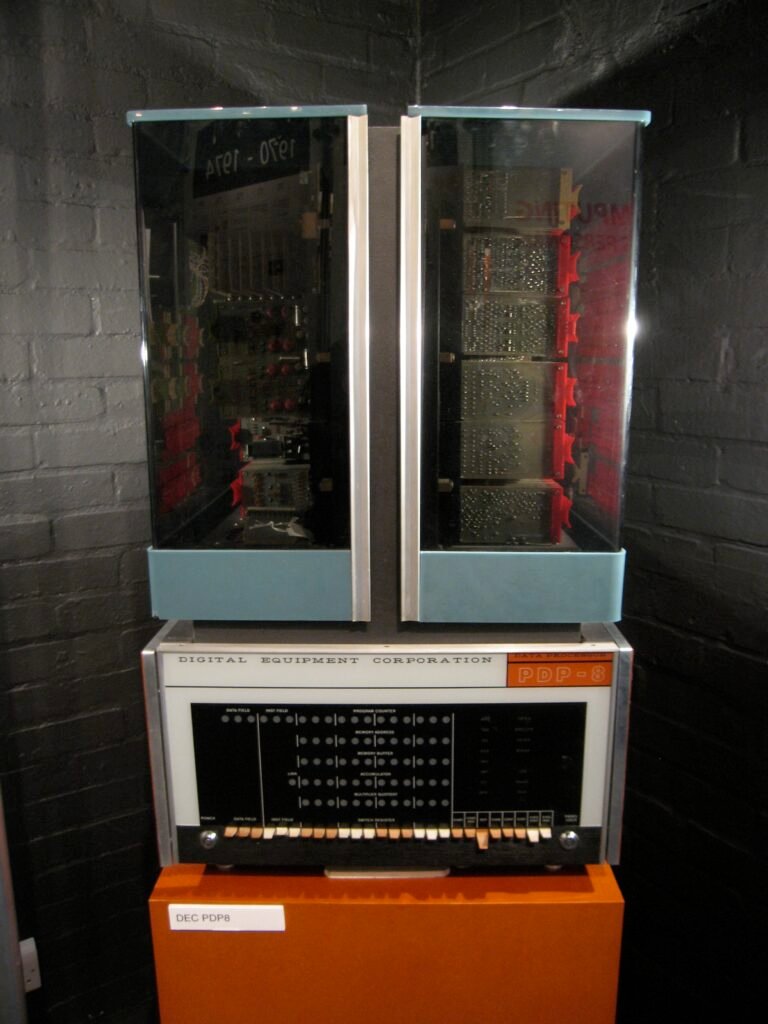
Some of the most popular models of the 3rd generation of computers were the ICL 2903, ICL 1900, TDC-B16, IBM 360 and 370, Honeywell 6000, UNIVAC 1108, PDP-8, and PDP-11, which were ideal in their handling multiprocessing capabilities, reliability, and flexibility than previous generations.
4th Generation of Computer (1971-2010)
The microprocessor brought the fourth generation of computers, as thousands of integrated circuits equivalent to about millions of transistors were assembled and brought the whole central processing unit and other fundamental elements of the machine into a small chip called a microprocessor fitted on the CPU socket.
These computers used Very Large Scale Integrated circuits technology also called VLSI technology. After the invention, the microprocessor began to used in computing machines in the fourth and fifth generations of computers.
Within the framework of the considered generation in 1971, the first microprocessor appeared as an unexpected result of Intel’s work on calculator circuits and further development of minicomputers ( PDP-11 ).
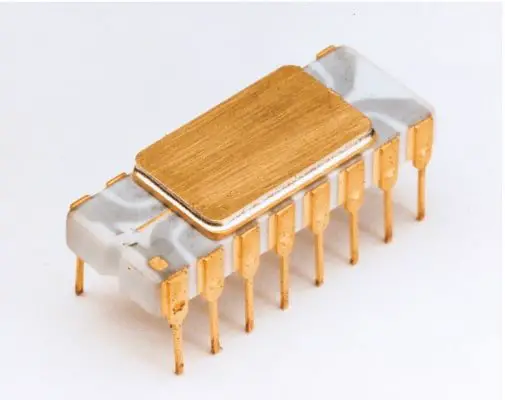
The first personal computer and a microcomputer was “ ALTAIR ” developed by the company MITS in 1974. Also, the first microprocessor was the Intel 4004, manufactured in 1971, initially for an electronic calculator. Whereas the computers of the first generation filled an entire room, while now the 4th generation ‘microprocessors’ fit in the palm of the hand.
This generation of computers used an operating system based on the graphical user interface (GUI), which means these numbers were very easy to perform mathematical and logical tasks.
The computers started to utilize high-speed memory systems on integrated circuits with a capacity of several megabytes. Computer performance has increased significantly (hundreds of millions of operations per second).
The high-level language like C, C ++, Java, PHP, Python, Visual Basic, was utilized to compose programs in the computers of the fourth generation.

The advent of the first personal computers in the mid-70s gave every common user the same computing resources that enormous computers had during the 60s. These computers were made more modest, faster, and less expensive can undoubtedly be put on a table or desk. Which marked the so-called era of personal computers .
Peripheral devices examples , such as mice, joysticks, handheld devices, etc., were developed during this 4th generation. Computers could be connected together in a network to share information with each other, this has played an important role in the birth and development of LAN, Ethernet, and the Internet .

The most popular companies in the world like Intel and AMD were rising. Then again, companies like Microsoft and Apple introduced their operating systems ‘Windows’ and ‘Macintosh’ in the generation of this computer. Because of which the act of multimedia started.
This is the era where personal computers were born, an idea that actually persists today. Also, these were the generation of DEC’s (Digital Equipment Corporation) minicomputers.
Characteristics of the 4th Generation of Computer:
- Computers based on microprocessors and VLSI technology .
- The computers of 4th gen were small in size, lightweight, and almost portable computers.
- The integrating of multi cores in processors like Dual core , Octa core, etc has began.
- The processing speed of this computer generation was much faster and reliable than the previous three generations.
- The size and cost of power supply units has reduced.
- Use of languages like C, C ++, .Net, Java, PHP, Python , Visual Basic.
- Use of GUI Based OS with more memory capacity.
- Accessible to the Internet .
- Due to the low cost of these computers, they were available to every common man.
Desktops, Laptops, Workstations, Tablets, Chromebooks , and Smartphones, are examples of the fourth generation of computers.
Good to Know~ Alan Turing is the father of modern computers born in England in 1912.
5th Generation of Computer (2010-At Present)
Artificial intelligence is the name of the fifth as well as the latest generation of computers based on ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) technology is the process of integrating or embedding millions of transistors on a single silicon microchip.

Computing in the 5th computer generation is versatile made portable, powerful, lightweight, innovative, comfortable with low electricity consumption . Because of the Internet’s advantages , it extended its limits of use to limits never before suspected.
The main objective of the latest fifth-generation computing and effort made by computer researchers is to make them smart by incorporating Artificial Intelligence so as to develop devices that respond to the input of natural language and are capable of learning and self-organizing even in 2022 it is under development.
This new information technology has greatly increased the size and working ability of the microprocessor, which has prompted the use of computers in the various fields of Entertainment, Accounting, Educational institutes , Film-making, Traffic-control, Business applications , and Hospitals, Engineering, Researches, Defense, etc.
That’s why a computer of the 5th generation is also known as the AI (Artificial Intelligence) generation of computers.
Some computers are being intended to do all the work themselves as a human act, behave, and communicate. The best example of this is an Artificial Intelligence (AI) based computing machine in the 5th generation of computers “ Sophia ” a robot.
Characteristics of the 5th Generation of Computer:
- The main focus on AI-based computers.
- Computers made of microprocessors based on ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) technology.
- The processing speed is quite high can perform billions of calculations in a second.
- Computers are portable, cheap, reliable, fast, and available in various forms and sizes like a Desktop, Laptop, Smartphone, Smartwatches, etc.
- Invention of the operating system such as Windows, Macintosh and ChromeOS of Chromebooks .
- Multimedia has evolved in this generation by combining Sound, Graphics, or Picture and Text.
- Development of Internet of Things.
Computers of the fifth generation are being made to think like us. For which continuous advancement of technologies like Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things, Robotics, etc. Although the examples of AI computing software such as Chatbots, Windows Cortana, Google Assistant, Apple Siri, Speech recognition, that are being used today.
Classification of the computer by generations
| ) | . | |||
| ) | ||||
| ) | ||||
| ) | ||||
| ) |
Factors/Reasons for the development of computer generations:
There below are the general factors associated with the development and change in the generations of electronic computers:
- Improvement of the element base,
- Downsizing,
- Technological progress (increased performance, speed, and memory)
- Reduced cost,
- Development of software ,
- Changes in architecture, expansion of the range of tasks solved by computers,
- Simplification and standardization of hardware.
- Changing the way of interaction between the user and the computer.
How many generations of computers have there been?
There are 5 computer generations till now i.e. vacuum tubes, transistors, integrated circuits, microprocessors, and the last one is artificial intelligence. 6th generation yet to come may be either in the form of quantum computers or developing the existing artificial intelligence technology to a greater extent.
What is the 6th generation of computers?
Electronic computers are usually divided into five generations now and the 6th generation is still in development but has the potential to give birth to the sixth generation of computers may be in the form of quantum computing.
Which is the current modern generation of computers today?
The technologies based on artificial intelligence are the current and the latest generation of computers(5th GEN) today.
What is the historical development of computers according to generation?
In accordance with the methodology for assessing the development of computer technology, the first generation was considered to be vacuum tube computers, the second – transistor computers, the third – computers on integrated circuits, the fourth – using microprocessors, and the fifth generation computers is based on the artificial intelligence.
What is the generation of a colossus computer?
Colossus computer was the first generation of the computer developed and designed by Tommy Flowers at Bletchley Park in the year 1944 with the purpose of cracking Hitler’s codes.
The sixth will also discover in the future since there are some flaws of technology in this generation that will be revived or resolved in the upcoming generation.
It takes much time and research to publish such an article ” Generation of Computer 1st to 5th “ If you liked the insights of the article you can support us by sharing this post on social networks.
Share this Post !
Similar Posts

What to do When RAM is Fully Used? Is it Good?

Why is My Keyboard and Mouse is Not Working? (9 Ways to Fix)

Logo appears but your computer Doesn’t start? Here’s why!

What Is the Red Light On The Bottom Of The Mouse?
26 thoughts on “generations of computer 1st to 5th explained with pictures.”.
yes that awesome
You’re welcome. And I’m happy to hear that you enjoyed this information!
This the best platform for student to learn from very gradual, this information is really helpful
It was so wonderful and interesting thank you so much
Hi Rachel, you’re welcome. And I’m happy to hear that you enjoyed this information!
You have explained the generation of computers very well, by reading this article anyone will understand about the generation of computers.
You’re welcome. Glad you learned some new & informative stuff.
Yes you right sir
Thanks for DIGITALWORLD839.COM for publication of the topics on computers
Wow it helped a lot
Hi Angel, you’re welcome. And I’m happy to hear that you found this information helpful!
You’re welcome, Asif.
Thank you so much
You’re welcome, Zamzam.
thank you! you help me a lot
Very informative and really precise on the subjects. Thanks.
This’s really helped me with my school project. Thanks so much!
It’s outstanding To much details given by the writer
Well understood!
well understood! thank you
That sounds nice It’ll boost the academic performance of computer student?
Thanks i found this platform very interesting
Thanks for the information it’s really useful
That’s great
thank so much for the help much appreciated.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Generation of Computers 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th
The Generation of Computer tells about the evolution of technology to distinguish the computers in terms of varying hardware and software. Know everything about the Generation of Computers 1st to 5th.
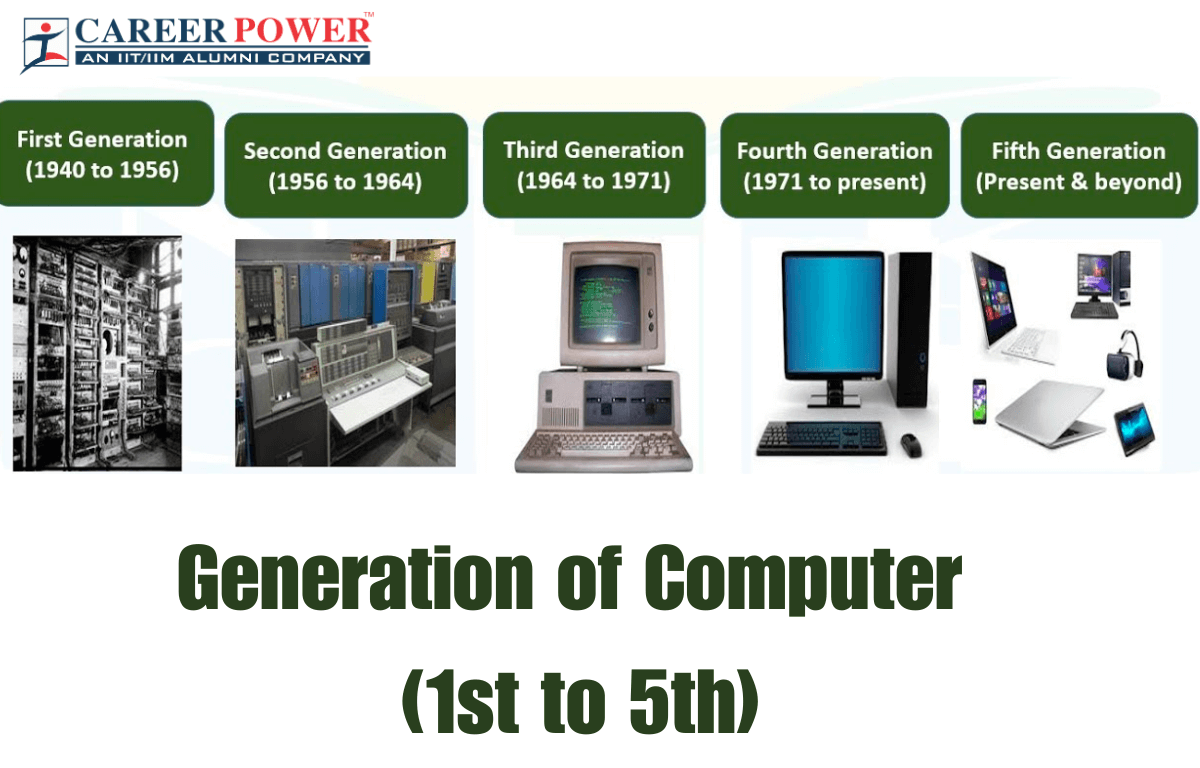
Table of Contents
For many decades we have relied on computers and now they have become an inseparable part of our lives. We cannot imagine our lives without computers are they have made our work easier. These computers have gone through changes over time and have you ever really wondered what a computer actually is? Today we use Laptops for our office work, and tablets for day-to-day calculations or entertainment purposes. These indicate that computers have evolved and undergone changes in their structure, functions and speed over time.
What is the Evolution of the computer?
The evolution of computers started around the 16th century. The evolution of the computer is the process of transforming the oldest vacuum tube-based system to the current model system of today’s computers. Long ago, the early primitive people were trailblazers in the use of counting tools, making use of objects like sticks, stones, and bones for their counting needs. The computer we see today has faced many changes, for the betterment via the history of computers . It has continuously improved itself in terms of speed, accuracy, size, and price to urge the form of the computer we have today. Here we have discussed the 5 generations of computers and their characteristics.
Generation of Computer
In computers, we use the term “generation” to show the evolution of technology. Earlier, the generation term was used to distinguish the computers in terms of varying hardware but now it all together includes the hardware and software which makes up a computer system. After centuries of evolution that began in the 16th century, the contemporary computer has taken its current form. There are 5 Generations of computers and all of them have been discussed below along with their features.
| 1st Generation | 1940 – 1956 | Vacuum Tube Based |
| 2nd Generation | 1956 – 1963 | Transistor Based |
| 3rd Generation | 1964 – 1971 | Integrated Circuit Based |
| 4th Generation | 1971 – Present | Microprocessor Based |
| 5th Generation | Present – Future | Artificial Intelligence Based |
1. First Generation Computers
The 1st Generation Computers were introduced using the technology of vacuum tubes which can control the flow of electronics in a vacuum. These tubes are usually used in switches, amplifiers, radios, televisions, etc. The First Generation of Computer was very heavy and large and were not ideal for programming. They used basic programming and didn’t have an operating system, which made it tough for users to do programming on them. The 1st Generation Computers required a big room dedicated to them and also consumed a lot of electricity.
Some examples of main first-generation computers are-
- ENIAC: Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer, built by J. Presper Eckert and John V. Mauchly which contained 18,000 vacuum tubes.
- EDVAC: Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer, designed by Von Neumann.
- UNIVAC: Universal Automatic Computer, developed by Eckert and Mauchly in 1952.
Characteristics of 1st Generation Computers
- These computers were designed using vacuum tubes.
- Programming in these computers was done using machine languages.
- The main memory of 1st Generation Computers consisted of magnetic tapes and magnetic drums.
- Paper tapes and Punched cards were used as input/output devices in these computers.
- These computers were very huge but worked very slowly.
- Examples of 1st Generation Computers are IBM 650, IBM 701, ENIAC, UNIVAC1, etc.
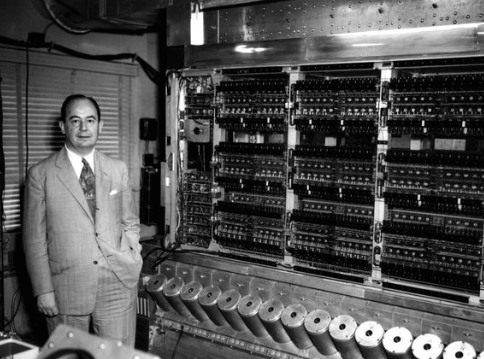
2. Second Generation Computers
The Second Generation of Computers revolutionized as it started using the technology of transistors instead of bulky vacuum tubes. Transistors are devices made of semiconductor materials that open or close a circuit. These transistors were invented in the Bell Labs which made the Second Generation Computer powerful and faster than the previous ones. Transistors made these computers smaller and generated less heat compared to the vacuum tubes they replaced. The Second Generation of Computers also introduced the use of CPU, memory and input/output units. The programming languages used for the second-generation computers were FORTRAN (1956), ALGOL (1958), and COBOL (1959).

Characteristics of Second-Generation Computers
- The Second Generation computers used the technology of Transistors.
- Machine language and Assembly Languages were used for these computers.
- Magnetic core and magnetic tape/disk were used for memory storage.
- The Second Generation Computers were smaller in size, consumed less power and generated less heat.
- Magnetic tape and punched cards were used as input/output devices.
- Some of the examples are PDP-8, IBM1400 series, IBM 7090 and 7094, UNIVAC 1107, CDC 3600, etc.

3. Third Generation Computers
The evolution of Third Generation Computers took place with a shift from transistors to integrated circuits also called IC. The Third Generation of Computers was very fast and reliable. The ICs used in these computers were made from silicons and were called silicon chips. A single IC has many transistors, registers, and capacitors built on one thin slice of silicon. This generation of computers has increased memory space and efficiency. Higher-level languages like BASIC (Beginners All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) were used and the Minicomputers were introduced in this era.
Characteristics of Third-Generation Computers
- These computers were built using Integrated Circuits (ICs).
- High-level programming languages were used for programming on these computers.
- Large magnetic core and magnetic tape/disk were used for memory storage.
- Magnetic tape, monitor, keyboard, printer, etc were used as input/ output devices .
- Some of the examples of Third Generation Computers are IBM 360, IBM 370, PDP-11, NCR 395, B6500, UNIVAC 1108, etc.

4. Fourth Generation Computers
The period from 1972 to 2010 is considered the period of the fourth generation of computers. Microprocessor technology was used to develop the Fourth Generation of Computers. The foremost advantage of these computers is that the microprocessor can contain all the circuits required to perform arithmetic, logic, and control functions on one chip. In the Fourth Generation, computers became very small in size and also became portable.
Technologies like multiprocessing, multiprogramming, time-sharing, operating speed, and virtual memory were also introduced by then. During the fourth generation, private computers and computer networks became a reality.
Characteristics of Fourth-Generation Computers
- The Fourth Generation Computers have been developed using the technology of Very-large-scale integration (VLSI) and the microprocessor (VLSI has thousands of transistors on a single microchip).
- Semiconductor memory such as RAM, ROM , etc was used for memory storage.
- Input/output devices such as pointing devices, optical scanning, keyboard, monitor, printer, etc were introduced.
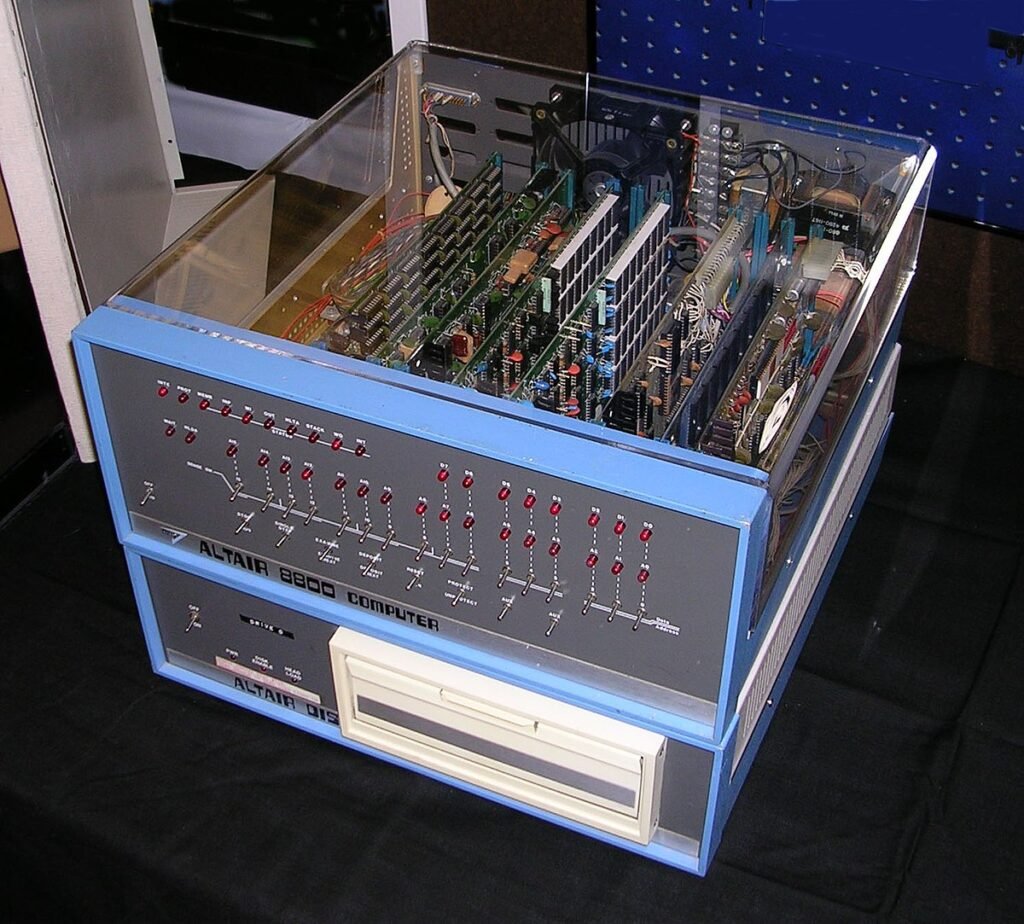
- Some examples of Fourth Generation Computers are IBM PC, STAR 1000, APPLE II, Apple Macintosh, Alter 8800, etc.

5. Fifth Generation Of Computers
The Fifth Generation of Computers has been built using the technology called Artificial Intelligence (AI). This technology encourages computers to behave like humans. Some of the applications of AI have been seen in features like voice recognition, entertainment, etc. The speed of the Fifth Generation of Computers is the highest while the sizes are the smallest. A big improvement has been noticed so far over the years in the various generations of computers in the aspect of speed, accuracy dimensions, etc.
Characteristics of Fifth Generation of Computers
- The 5th Generation Computers have been built based on artificial intelligence, use the Ultra Large-Scale Integration (ULSI) technology and parallel processing method (ULSI has millions of transistors on a single microchip and the Parallel processing method uses two or more microprocessors to run tasks simultaneously).
- These computers understand natural language (human language).
- The Fifth-generation computers are portable and smaller in size.
- Trackpad (or touchpad), touchscreen, pen, speech input (recognize voice/speech), light scanner, printer, keyboard, monitor, mouse, etc are used as Input/Output devices.
- Examples of 5th Generation Computers are Desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, etc.

History of Computer Generation
The word ‘computer’ was first used in the 16th century for a person who used to do calculations until the 20th century. Women were hired as human computers to carry out all forms of calculations and computations. By the end of the 19th century, the word ‘computer’ was used for the machines that did calculations. Nowadays we use the word for the programmable digital devices that run on electricity.
Before computers were invented, sticks, stones, and bones were used as counting tools. With the evolution of human intellect and the advancement of technology, more computing devices were produced. There are mechanical calculators used by humans before computers. Some of the most famous mechanical calculators are:
- Pascal’s Calculator
- Stepped Reckoner
- Arithmometer
- Comptometer & Comptograph
Difference Engine
Analytical engine.
- The Millionaire
Below we have discussed briefly the early-age computing devices used by mankind.
The Chinese are said to have discovered the Abacus some 4,000 years ago. The abacus was built using a wooden rack having metal rods with beads mounted on them. To perform the arithmetic calculations, beads were moved by the abacus operator according to some rules.
Napier’s Bones
John Napier invented Napier’s Bones which was a manually operated calculating device. John used 9 different ivory strips or bones marked with numbers to multiply and divide with the help of this calculating tool. The Napier’s Bone was also the first calculating tool to use decimal points.
First-generation calculator or machine for calculations that was ever developed in the history of mankind was named Pascaline. A French mathematician-philosopher Blaise Pascal invented the Pascaline between 1642 and 1644. This was the very first invention of such kind and therefore only had the options of addition and subtraction and that too by entering the numbers by manipulating its dials.
Stepped Reckoner or Leibnitz wheel
A German mathematician-philosopher Gottfried Wilhelm Leibnitz developed the Stepped Reckoner or Leibnitz wheel in 1673. This machine was technically an upgrade of Pascal’s invention. The Stepped Reckoner or Leibnitz wheel was a digital mechanical calculator that was made of fluted drums instead of gears.
Charles Babbage, known as the “Father of Modern Computer designed the Difference engine in the early 1820s. The Difference Engine was a mechanical computer that could perform simple calculations. It was a steam-driven calculating machine designed to solve tables of numbers like logarithm tables.
The Analytical Engine was also developed by Charles Babbage in the 1830s. This calculating machine was a mechanical computer that used punch cards as input. These machines were capable of solving any mathematical problem and storing information as a permanent memory.
Tabulating Machine
Herman Hollerith, an American statistician invented the Tabulating Machine in the 1890s which was a mechanical tabulator based on punch cards that was capable of tabulating statistics and recording or sorting data or information.
Differential Analyzer
The Differential Analyzer was the first electronic computer introduced in the United States in 1930. It was an analog device invented by Vannevar Bush. This machine could perform 25 calculations in a few minutes.
The major changes in the history of computers began in 1937 when Howard Aiken aimed to invent a machine that could perform calculations of larger numbers. In 1944, IBM and Harvard partnered to build the Mark I computer. The Mark 1 was the first programmable digital computer.
Sharing is caring!
Generation of Computers- FAQs
Q1. what is a generation.
In computers, we use the term "generation" to show the evolution of technology. Earlier, the generation term was used to distinguish the computers in terms of varying hardware but now it all together includes the hardware and software which makes up a computer system.
Q2. How many generations of computer are there?
There are a total of 5 generation of computer that exist in the world.
Q3. What technology is used behind the Fifth Generation of Computers?
Artificial Intelligence is used to build the Fifth Generation of Computers.
Q4. Who invented Vacuum Tubes?
The Vacuum Tubes were invented by Lee De Forest.
Q5. Who invented 2nd generation computer?
The 2nd generation computer were invented by Walter H. Brattain (1902-1987), John Bardeen (1908-1991), and William B at at Bell Labs. The second generation computers are based upon transistors, not on vacuum tubes.
Q6. Which computer introduced the concept of the mouse and graphical user interface (GUI)?
Apple Macintosh introduced the concept of the mouse and graphical user interface (GUI)
Q7. Which computer is considered the first true personal computer?
Altair 8800 the first true personal computer.
Q8. Give a few examples of first generation computers?
Examples of First generation computer includes the following computers: 1. ENIAC: Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer. 2. EDVAC: Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer. 3. UNIVAC: Universal Automatic Computer.
Q9: Name the programing language used in the second generation computers.
The second Generation computer used FORTRAN (1956), ALGOL (1958), and COBOL (1959) as programing languages.
As Team Lead- Content Writer, I take on leadership within our content creation team, overseeing the development of error-free educational content. My primary responsibility is to produce and analyse high-quality content educating and informing the aspirants about upcoming government exams published on our website. I have more than 6 years experience in content writing wherein 3.5 years of experience in ed-tech content writing.

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- CUET Result 2024
- CUET Answer Key 2024 Out
- CUET Exam Analysis 2024
- NEET Result 2024
- NEET Answer Key 2024
- NEET Cut Off 2024
- NEET Toppers List 2024 Out
- NEET Syllabus 2025
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2024
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 English Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2024
- CBSE Class 10 English Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 SST Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Hindi Syllabus
Latest Posts
Important exams.
- JEE Mains 2025
- JEE Advanced 2024
- NIMCET 2024
- AP EAMCET 2024
- TS EAMCET 2024
- AP ECET 2024
- TS ECET 2024
- TS PGECET 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- AP Polycet 2024
- TS Polycet 2024
- JEECUP 2024
- Bihar Polytechnic 2024
- Jharkhand Polytechnic 2024
- Responsible Disclosure Program
- Cancellation & Refunds
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Unit 7. Evolution of computers
Topic A: Computer generations
Click play on the following audio player to listen along as you read this section.
Basic Terms

Vacuum tube – an electronic device that controls the flow of electrons in a vacuum. It used as a switch, amplifier, or display screen in many older model radios, televisions, computers, etc.

Transistor – an electronic component that can be used as an amplifier or as a switch. It is used to control the flow of electricity in radios, televisions, computers, etc.
Integrated circuit (IC) – a small electronic circuit printed on a chip (usually made of silicon) that contains many its own circuit elements (e.g. transistors, diodes , resistors, etc.).

Microprocessor – an electronic component held on an integrated circuit that contains a computer’s central processing unit (CPU) and other associated circuits.

CPU (central processing unit) – It is often referred to as the brain or engine of a computer where most of the processing and operations take place (CPU is part of a microprocessor).

Magnetic drum – a cylinder coated with magnetic material, on which data and programs can be stored.
Magnetic core – uses arrays of small rings of magnetized material called cores to store information.

Machine language – a low-level programming language comprised of a collection of binary digits (ones and zeros) that the computer can read and understand.
Assembly language is like the machine language that a computer can understand, except that assembly language uses abbreviated words (e.g. ADD, SUB, DIV…) in place of numbers (0s and 1s).

Artificial intelligence (AI) – an area of computer science that deals with the simulation and creation of intelligent machines or intelligent behave in computers (they think, learn, work, and react like humans).
First Generation of Computers
Classification of generations of computers.
The evolution of computer technology is often divided into five generations.
| Generations of computers | Generations timeline | Evolving hardware |
|---|---|---|
| First generation | 1940s-1950s | Vacuum tube based |
| Second generation | 1950s-1960s | Transistor based |
| Third generation | 1960s-1970s | Integrated circuit based |
| Fourth generation | 1970s-present | Microprocessor based |
| Fifth generation | The present and the future | Artificial intelligence based |
The main characteristics of first generation of computers (1940s-1950s)

- Main memory – magnetic drums and magnetic tapes
- Programming language – machine language

- Speed and size – very slow and very large in size (often taking up entire room).
- Input/output devices – punched cards and paper tape.
- Examples – ENIAC, UNIVAC1, IBM 650, IBM 701, etc.
- Quantity – there were about 100 different vacuum tube computers produced between 1942 and1963.
Second Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of second generation of computers (1950s-1960s).
- Memory – magnetic core and magnetic tape / disk

- Power and size – low power consumption, generated less heat, and smaller in size (in comparison with the first generation computers).
- Speed – improvement of speed and reliability (in comparison with the first generation computers).
- Input/output devices – punched cards and magnetic tape.
- Examples – IBM 1401, IBM 7090 and 7094, UNIVAC 1107, etc.
Third Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of third generation of computers (1960s-1970s).
- Memory – large magnetic core, magnetic tape / disk

- Size – smaller, cheaper, and more efficient than second generation computers (they were called minicomputers).
- Speed – improvement of speed and reliability (in comparison with the second generation computers).

- Examples – IBM 360, IBM 370, PDP-11, UNIVAC 1108, etc.
Fourth Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of fourth generation of computers (1970s-present).

- VLSI– thousands of transistors on a single microchip.
- RAM (random-access memory) – a type of data storage (memory element) used in computers that temporary stores of programs and data (volatile: its contents are lost when the computer is turned off).

- A mix of both third- and fourth-generation languages
- Size – smaller, cheaper and more efficient than third generation computers.
- Speed – improvement of speed, accuracy, and reliability (in comparison with the third generation computers).

- Network – a group of two or more computer systems linked together.
- Examples – IBM PC, STAR 1000, APPLE II, Apple Macintosh, etc.

Fifth Generation of Computers
The main characteristics of fifth generation of computers (the present and the future).

- ULSI – millions of transistors on a single microchip
- Parallel processing method – use two or more microprocessors to run tasks simultaneously.
- Language – understand natural language (human language).
- Power – consume less power and generate less heat.
- Speed – remarkable improvement of speed, accuracy and reliability (in comparison with the fourth generation computers).
- Size – portable and small in size, and have a huge storage capacity.

- Example – desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, etc.

The computer – this amazing technology went from a government/business-only technology to being everywhere from people’s homes, work places, to people’s pockets in less than 100 years.

an electronic device that controls the flow of electrons in a vacuum. It used as a switch, amplifier, or display screen in many older model radios, televisions, computers, etc.
an electronic component that can be used as an amplifier or as a switch. It is used to control the flow of electricity in radios, televisions, computers, etc.
a small electronic circuit printed on a chip (usually made of silicon) that contains many its own circuit elements (e.g. transistors, diodes, resistors, etc.).
an electronic component held on an integrated circuit that contains a computer's central processing unit (CPU) and other associated circuits.
The brain or engine of a computer, where most of the processing and operations take place.
a cylinder coated with magnetic material, on which data and programs can be stored.
uses arrays of small rings of magnetized material called cores to store information.
a low-level programming language comprised of a collection of binary digits (ones and zeros) that the computer can read and understand.
a physical device that is used to store data, information, and programs in a computer.
an area of computer science that deals with the simulation and creation of intelligent machines or intelligent behave in computers (they think, learn, work, and react like humans).
Key Concepts of Computer Studies Copyright © 2020 by Meizhong Wang is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

The Evolution Of Computer | Generations of Computer
The development of computers has been a wonderful journey that has covered several centuries and is defined by a number of inventions and advancements made by our greatest scientists. Because of these scientists, we are using now the latest technology in the computer system.
Now we have Laptops , Desktop computers , notebooks , etc. which we are using today to make our lives easier, and most importantly we can communicate with the world from anywhere around the world with these things.
So, In today’s blog, I want you to explore the journey of computers with me that has been made by our scientists.
Note: If you haven’t read our History of Computer blog then must read first then come over here
let’s look at the evolution of computers/generations of computers
COMPUTER GENERATIONS
Computer generations are essential to understanding computing technology’s evolution. It divides computer history into periods marked by substantial advancements in hardware, software, and computing capabilities. So the first period of computers started from the year 1940 in the first generation of computers. let us see…
Table of Contents
Generations of computer
The generation of classified into five generations:
- First Generation Computer (1940-1956)
- Second Generation Computer (1956-1963)
- Third Generation Computer(1964-1971)
- Fourth Generation Computer(1971-Present)
- Fifth Generation Computer(Present and Beyond)
| Computer Generations | Periods | Based on |
|---|---|---|
| First-generation of computer | 1940-1956 | Vacuum tubes |
| Second-generation of computer | 1956-1963 | Transistor |
| Third generation of computer | 1964-1971 | Integrated Circuit (ICs) |
| Fourth-generation of computer | 1971-present | Microprocessor |
| Fifth-generation of computer | Present and Beyond | AI (Artificial Intelligence) |
1. FIRST GENERATION COMPUTER: Vacuum Tubes (1940-1956)

The first generation of computers is characterized by the use of “Vacuum tubes” It was developed in 1904 by the British engineer “John Ambrose Fleming” . A vacuum tube is an electronic device used to control the flow of electric current in a vacuum. It is used in CRT(Cathode Ray Tube) TV , Radio , etc.

The first general-purpose programmable electronic computer was the ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) which was completed in 1945 and introduced on Feb 14, 1946, to the public. It was built by two American engineers “J. Presper Eckert” and “John V Mauchly” at the University of Pennsylvania.

The ENIAC was 30-50 feet long, 30 tons weighted, contained 18000 vacuum tubes, 70,000 registers, and 10,000 capacitors, and it required 150000 watts of electricity, which makes it very expensive.
Later, Eckert and Mauchly developed the first commercially successful computer named UNIVAC(Univeral Automatic Computer) in 1952 .
Examples are ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer), UNIVAC-1 (Univeral Automatic Computer-1)

- These computers were designed by using vacuum tubes.
- These generations’ computers were simple architecture.
- These computers calculate data in a millisecond.
- This computer is used for scientific purposes.
DISADVANTAGES
- The computer was very costly.
- Very large.
- It takes up a lot of space and electricity
- The speed of these computers was very slow
- It is used for commercial purposes.
- It is very expensive.
- These computers heat a lot.
- Cooling is needed to operate these types of computers because they heat up very quickly.
2. SECOND GENERATION COMPUTER: Transistors (1956-1963)
The second generation of computers is characterized by the use of “Transistors” and it was developed in 1947 by three American physicists “John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley” .

A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals or open or close a circuit. It was invented in Bell labs, The transistors became the key ingredient of all digital circuits, including computers.
The invention of transistors replaced the bulky electric tubes from the first generation of computers.
Transistors perform the same functions as a Vacuum tube , except that electrons move through instead of through a vacuum. Transistors are made of semiconducting materials and they control the flow of electricity.
It is smaller than the first generation of computers, it is faster and less expensive compared to the first generation of computers. The second-generation computer has a high level of programming languages, including FORTRAN (1956), ALGOL (1958), and COBOL (1959).
Examples are PDP-8 (Programmed Data Processor-8), IBM1400 (International business machine 1400 series), IBM 7090 (International business machine 7090 series), CDC 3600 ( Control Data Corporation 3600 series)

ADVANTAGES:
- It is smaller in size as compared to the first-generation computer
- It used less electricity
- Not heated as much as the first-generation computer.
- It has better speed
DISADVANTAGES:
- It is also costly and not versatile
- still, it is expensive for commercial purposes
- Cooling is still needed
- Punch cards were used for input
- The computer is used for a particular purpose
3. THIRD GENERATION COMPUTER: Integrated Circuits (1964-1971)
The Third generation of computers is characterized by the use of “Integrated Circuits” It was developed in 1958 by two American engineers “Robert Noyce” & “Jack Kilby” . The integrated circuit is a set of electronic circuits on small flat pieces of semiconductor that is normally known as silicon. The transistors were miniaturized and placed on silicon chips which are called semiconductors, which drastically increased the efficiency and speed of the computers.
These ICs (integrated circuits) are popularly known as chips. A single IC has many transistors, resistors, and capacitors built on a single slice of silicon.
This development made computers smaller in size, low cost, large memory, and processing. The speed of these computers is very high and it is efficient and reliable also.
These generations of computers have a higher level of languages such as Pascal PL/1, FORTON-II to V, COBOL, ALGOL-68, and BASIC(Beginners All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) was developed during these periods.
Examples are NCR 395 (National Cash Register), IBM 360,370 series, B6500

- These computers are smaller in size as compared to previous generations
- It consumed less energy and was more reliable
- More Versatile
- It produced less heat as compared to previous generations
- These computers are used for commercial and as well as general-purpose
- These computers used a fan for head discharge to prevent damage
- This generation of computers has increased the storage capacity of computers
- Still, a cooling system is needed.
- It is still very costly
- Sophisticated Technology is required to manufacture Integrated Circuits
- It is not easy to maintain the IC chips.
- The performance of these computers is degraded if we execute large applications.
4. FOURTH GENERATION OF COMPUTER: Microprocessor (1971-Present)
The fourth generation of computers is characterized by the use of “Microprocessor”. It was invented in the 1970s and It was developed by four inventors named are “Marcian Hoff, Masatoshi Shima, Federico Faggin, and Stanley Mazor “. The first microprocessor named was the “Intel 4004” CPU, it was the first microprocessor that was invented.

A microprocessor contains all the circuits required to perform arithmetic, logic, and control functions on a single chip. Because of microprocessors, fourth-generation includes more data processing capacity than equivalent-sized third-generation computers. Due to the development of microprocessors, it is possible to place the CPU(central processing unit) on a single chip. These computers are also known as microcomputers. The personal computer is a fourth-generation computer. It is the period when the evolution of computer networks takes place.
Examples are APPLE II, Alter 8800

- These computers are smaller in size and much more reliable as compared to other generations of computers.
- The heating issue on these computers is almost negligible
- No A/C or Air conditioner is required in a fourth-generation computer.
- In these computers, all types of higher languages can be used in this generation
- It is also used for the general purpose
- less expensive
- These computers are cheaper and portable
- Fans are required to operate these kinds of computers
- It required the latest technology for the need to make microprocessors and complex software
- These computers were highly sophisticated
- It also required advanced technology to make the ICs(Integrated circuits)
5. FIFTH GENERATION OF COMPUTERS (Present and beyond)
These generations of computers were based on AI (Artificial Intelligence) technology. Artificial technology is the branch of computer science concerned with making computers behave like humans and allowing the computer to make its own decisions currently, no computers exhibit full artificial intelligence (that is, can simulate human behavior).

In the fifth generation of computers, VLSI technology and ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) technology are used and the speed of these computers is extremely high. This generation introduced machines with hundreds of processors that could all be working on different parts of a single program. The development of a more powerful computer is still in progress. It has been predicted that such a computer will be able to communicate in natural spoken languages with its user.
In this generation, computers are also required to use a high level of languages like C language, c++, java, etc.
Examples are Desktop computers, laptops, notebooks, MacBooks, etc. These all are the computers which we are using.

- These computers are smaller in size and it is more compatible
- These computers are mighty cheaper
- It is obviously used for the general purpose
- Higher technology is used
- Development of true artificial intelligence
- Advancement in Parallel Processing and Superconductor Technology.
- It tends to be sophisticated and complex tools
- It pushes the limit of transistor density.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many computer generations are there.
Mainly five generations are there:
First Generation Computer (1940-1956) Second Generation Computer (1956-1963) Third Generation Computer(1964-1971) Fourth Generation Computer(1971-Present) Fifth Generation Computer(Present and Beyond)
Which things were invented in the first generation of computers?
Vacuum Tubes
What is the fifth generation of computers?
The Fifth Generation of computers is entirely based on Artificial Intelligence. Where it predicts that the computer will be able to communicate in natural spoken languages with its user.
What is the latest computer generation?
The latest generation of computers is Fifth which is totally based on Artificial Intelligence.
Who is the inventor of the Integrated Circuit?
“Robert Noyce” and “Jack Bily”
What is the full form of ENIAC ?
ENIAC Stands for “Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer” .
Related posts:
- What is a Computer System and Its Types?|Different types of Computer System
- How does the Computer System Work| With Diagram, Input, Output, processing
- The History of Computer Systems and its Generations
- Different Applications of Computer Systems in Various Fields | Top 12 Fields
- Explain Von Neumann Architecture?
- What are the input and Output Devices of Computer System with Examples
- What is Unicode and ASCII Code
- What is RAM and its Types?
- What is the difference between firmware and driver? | What are Firmware and Driver?
- What is Hardware and its Types
4 thoughts on “The Evolution Of Computer | Generations of Computer”
It is really useful thanks
Glad to see
it is very useful information for the students of b.sc people who are seeing plz leave a comment to related post thank u
Love to see that this post is proving useful for the students.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Definitions
- How to Buy XRP in 2024
- How to Buy Bitcoin in 2024
- How to Buy Shiba Inu in 2024
- Crypto Gambling
- Crypto Casinos
- Crash Gambling
- Crypto Sports Betting
What are the Five Generations of Computers? (1st to 5th)
Reviewed by Web Webster
We’ve come a long way since the first generation of computer, with new generation of computers bringing significant advances in speed and power to computing tasks. Learn about each of the five generations of computers and major technology developments that have led to the computer technology that we use today.
The history of computer development is a computer science topic that is often used to reference the different generations of computing devices . Each computer generation is characterized by a major technological development that fundamentally changed the way computers operate.
Each major developments from the 1940s to the present day (5th generation of computer) has introduced smaller, cheaper, more powerful, and more efficient computing machines. This technology has minimized storage and increased portability.
In this definition...
What Are the 5 Generations of Computers?
In this Webopedia Study Guide, you’ll learn more about each of the five generations of computers and the advances in technology that have led to the development of the many computing devices we use today.
Our journey through the five generations of computers starts in 1940 with vacuum tube circuitry and goes to the present day and beyond with artificial intelligence (AI) systems and devices.
Let’s take a look…
5 generations of computers checklist, getting started: key terms to know.
- First Generation: Vacuum Tubes
- Second Generation: Transistors
- Third Generation: Integrated Circuits
- Fourth Generation: Microprocessors
- Fifth Generation: Artificial Intelligence
The following technology definitions will help you to better understand the five generations of computing:
- Microprocessor
- Magnetic drums
- Integrated circuit
- Semiconductor
- Nanotechnology
- Machine language
- Assembly language
- Artificial intelligence

First Generation: Vacuum Tubes (1940–1956)
The first generation of computer systems used vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for main memory , and they were often enormous, taking up entire rooms. These computers were very expensive to operate, and in addition to using a great deal of electricity, the first computers generated a lot of heat, which was often the cause of malfunctions. The maximum internal storage capacity was 20,000 characters.
First generation computers relied on machine language , the lowest-level programming language understood by computers, to perform operations, and they could only solve one problem at a time. It would take operators days or even weeks to set up a new problem. Input was based on punched cards and paper tape, and output was displayed on printouts.
It was in this generation that the Von Neumann architecture was introduced, which displays the design architecture of an electronic digital computer. Later, the UNIVAC and ENIAC computers, invented by J. Presper Eckert, became examples of first generation computer technology. The UNIVAC was the first commercial computer delivered to a business client, the U.S. Census Bureau in 1951.
Recommended Reading: Webopedia’s ENIAC definition
Second Generation: Transistors (1956–1963)
The world would see transistors replace vacuum tubes in the second generation of computer. The transistor was invented at Bell Labs in 1947 but did not see widespread use in computers until the late 1950s. This generation of computers also included hardware advances like magnetic core memory, magnetic tape, and the magnetic disk.
The transistor was far superior to the vacuum tube, allowing computers to become smaller, faster, cheaper, more energy-efficient, and more reliable than their first-generation predecessors. Though the transistor still generated a great deal of heat that subjected the computer to damage, it was a vast improvement over the vacuum tube. A second-generation computer still relied on punched cards for input and printouts for output .
When Did Computers Start Using Assembly Languages?
Second-generation computers moved from cryptic binary language to symbolic, or assembly , languages, which allowed programmers to specify instructions in words. High-level programming languages were also being developed at this time, such as early versions of COBOL and FORTRAN . These were also the first computers that stored their instructions in their memory, which moved from a magnetic drum to magnetic core technology.
The first computers of this generation were developed for the atomic energy industry.
Third Generation: Integrated Circuits (1964–1971)
The development of the integrated circuit was the hallmark of the third generation of computers. Transistors were miniaturized and placed on silicon chips , called semiconductors , which drastically increased the speed and efficiency of computers.
Instead of punched cards and printouts, users would interact with a third-generation computer through keyboards, monitors, and interfaces with an operating system , which allowed the device to run many different applications at one time with a central program that monitored the memory. Computers, for the first time, became accessible to a mass audience because they were smaller and cheaper than their predecessors.
Did You Know… ? Integrated circuit (IC) chips are small electronic devices made out of semiconductor material. The first integrated circuit was developed in the 1950s by Jack Kilby of Texas Instruments and Robert Noyce of Fairchild Semiconductor.
Fourth Generation: Microprocessors (1971–Present)
The microprocessor ushered in the fourth generation of computers, as thousands of integrated circuits were built onto a single silicon chip. The technology in the first generation that filled an entire room could now fit in the palm of the hand. The Intel 4004 chip, developed in 1971, integrated all the components of the computer, from the central processing unit and memory to input/output controls, on a single chip.
In 1981, IBM introduced its first personal computer for the home user, and in 1984 Apple introduced the Macintosh. Microprocessors also moved out of the realm of desktop computers and into many areas of life as more and more everyday products began to use the microprocessor chip.
As these small computers became more powerful, they could be linked together to form networks, which eventually led to the development of the Internet. Each fourth-generation computer also saw the computer development of GUIs , the mouse , and handheld technology.
Fifth Generation: Artificial Intelligence (Present and Beyond)
The fifth generation of computer technology, based on artificial intelligence, is still in development. However, there are some applications, such as voice recognition , that are being used today. The use of parallel processing and superconductors is helping to make artificial intelligence a reality. This is also so far the prime generation for packing a large amount of storage into a compact and portable device.
Quantum computation and molecular and nanotechnology will radically change the face of computers in years to come. The goal of fifth-generation computing is to develop devices that will respond to natural language input and are capable of learning and self-organization.
The History of Windows Operating Systems
Related Links
- IBM 704 Vacuum Tube Assembly
- UNIVAC I History
- Vintage Computer Chip Collectibles, The Transistor
- ENIAC Museum Online
- IBM Advanced Computing Systems Timeline

Vangie Beal is a freelance business and technology writer covering Internet technologies and online business since the late '90s.
Generations of Computer Explained

Understanding the computer generations and their evolution is not only captivating but also essential for comprehending the technological advancements that shaped the modern digital world.
Now, it’s hard to imagine a world without computers, isn’t it?
From supercomputers and sophisticated smartphones to tablets and other devices, computers are everywhere and have become vital to our lives.
In this article, I’ll talk about all five computer generations, how they evolved, each of their characteristics, and the predictions for the highly anticipated sixth generation of computers.
Let’s dive in!
Generations of Computers and Their Evolution

Here is an overview of the 5 generations of computers and their evolution.
First Generation
In the 1940s, a remarkable event unfolded before the world’s eyes – the birth of the first generation of computers. These pioneer machines relied on vacuum tubes, large electronic components that controlled the flow of electricity.
However, vacuum tubes had significant drawbacks. They were power-hungry, produced substantial heat, and often encountered frequent failures.
The ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), as a prominent example from this era, vividly illustrates these challenges.
Second Generation
In the late 1950s, computing experienced a remarkable advancement through the development of transistors. These small, solid-state devices replaced vacuum tubes, resulting in more compact and reliable computers.
The introduction of transistors, led to significant improvements in size reduction, power efficiency, and heat generation.
This breakthrough marked the emergence of the second generation of computers, exemplified by notable models like IBM 1401 and UNIVAC 1107.
Third Generation
During the 1960s, computers entered their third generation by introducing integrated circuits (ICs). The ICs transformed computer technology by consolidating numerous transistors and electronic components onto a single silicon chip.
This innovative development significantly reduced computer sizes while simultaneously enhancing computational power.
Some outstanding examples from this era of computers include the IBM System/360 series and DEC PDP-8.
Fourth Generation
In the late 1970s, a significant development occurred in the field of computing – the emergence of microprocessors. It marked the fourth generation of computers.
As a result, personal computers (PCs) and graphical user interfaces (GUIs) were born, transforming computing and making it accessible to both individuals and businesses alike.
Some notable machines from this era include the Apple II, IBM PC, and Commodore 64.
Fifth Generation
In the 1990s, computers witnessed a significant transformation with the emergence of the fifth generation.
This era was characterized by the development of artificial intelligence (AI) and parallel processing. It signaled the arrival of supercomputers equipped with enormous processing capabilities, driving progress in weather prediction, scientific exploration, and data interpretation.
Now that we know what advancements paved the way for transitioning one computer generation to another, let’s understand each generation in detail.
First Generation: Vacuum Tube Computers (1940s – mid-1950s)

During the 1940s to the mid-1950s, a significant milestone in history unfolded with the emergence of the first generation of computers. These machines, fueled by vacuum tubes, announced the beginning of digital computing.
Vacuum tube computers, or first-generation computers, relied on delicate and bulky vacuum tubes for processing and storing data. The electronic components controlled the flow of electrical signals.
While these machines may seem primitive by today’s standards, they were at the forefront of technology during their time.
Key Features
- Size: Vacuum tube computers were massive. They occupied entire rooms and required special cooling systems to prevent overheating.
- Computational Power: While these computers may seem slow by today’s standards, they marked significant progress in automating calculations. This advancement allowed for the execution of complex computations that were unimaginable before.
- Memory: In the early stages of memory development, magnetic drums, and punched cards were utilized to establish basic data storage and retrieval capabilities.
- Programming: Programming these machines was an uphill task that involved physically rewiring the circuits. This made software development time-consuming.
Significance and Legacy
The vacuum tube computers paved the way for subsequent generations. They showcased the potential of automated computing despite their size and limitations. These early machines demonstrated the feasibility of digital calculations, inspiring researchers to explore ways to make computers more efficient, compact, and accessible.
To overcome the limitations of vacuum tube computers, such as their large size, high heat generation, and frequent failures, researchers began searching for alternatives. This pursuit led to the development of transistors in the late 1950s, which marked the beginning of the second generation of computing.
Second Generation: Transistors (Late 1950s – Mid 1960s)

As the 1950s transitioned into the 1960s, a remarkable shift occurred in the computing landscape. This transformative era introduced the second generation of computers.
With the emergence of transistors, these sleek devices replaced bulky vacuum tubes and ushered in an era of enhanced efficiency and accessibility in computing technology.
The second generation of computers utilized transistors, compact solid-state devices that replaced the energy-consuming vacuum tubes of the initial generation. This transition resulted in significant advancements across various computing aspects, progressing the way for notable progress.
- Size: Transistor-based computers revolutionized the computing landscape by being significantly smaller and more space-efficient. This breakthrough liberated computing from the constraints of large, cumbersome rooms.
- Computational Power: Transistors have transformed computing, empowering computers to perform calculations faster and significantly enhancing their processing capabilities.
- Reliability: Transistors, unlike vacuum tubes, offered increased reliability and durability. This significant improvement resulted in reduced breakdowns and maintenance requirements.
- Energy Efficiency: Transistors are an efficient alternative to vacuum tubes. By consuming considerably less power, they reduce energy consumption and generate less heat.
- Programming: During this era, the development of high-level programming languages such as FORTRAN and COBOL brought about a significant change. These languages simplified software development and made it more accessible to a wider audience.
The adoption of transistors brought about a monumental shift in computing. It enhanced the overall efficiency of computers and paved the way for diverse applications across various fields. This pivotal generation set the stage for the development of smaller, more versatile, and commercially viable computers.
However, the limitations of transistors eventually led to the third generation of computers, driven by the emergence of integrated circuits (ICs).
Third Generation: Integrated Circuits (1960s – 1970s)

During the 1960s, computers experienced a remarkable leap in their evolution.
It was the emergence of the third generation that marked this era, characterized by groundbreaking innovation in integrated circuits (ICs).
ICs are tiny electronic components, carefully carved onto silicon chips that further revolutionized the world of computing. ICs not only minimized computer size but also enhanced computational abilities.
Furthermore, ICs combined multiple transistors and electronic components on a single silicon chip. This opened the way for groundbreaking advancement in computing.
- Size: The integration of components onto silicon chips profoundly impacted computer size. This advancement enabled computers to be housed on a single desk or occupy an even smaller space.
- Computational power: The use of integrated circuits significantly enhanced computational power. This allowed computers to efficiently and swiftly execute complex tasks with greater efficiency.
- Reliability: You’ll find that integrated circuits are more reliable than previous technologies. This leads to reduced downtime and maintenance requirements.
- Energy efficiency: These circuits consumed significantly less power, contributing to a reduction in energy costs and heat generation.
- Memory: During the third generation, advanced forms of memory emerged. These included core memory and semiconductor memory, revolutionizing data storage and retrieval capabilities. This allowed for more efficient and effective handling of information.
- Programming: High-level programming languages have constantly evolved, resulting in increased accessibility and efficiency in software development.
The integration of circuits was an inventive move. It transformed the field of computing, replacing large and complex machines into smaller, more powerful, and user-friendly systems.
With this development, computers became widely accessible for various purposes, including business, research, and personal tasks, expanding beyond their initial use in scientific or military applications.
Due to changing demands and the rapid pace of technological advancements led to the evolution of the fourth generation of computers. It was marked by the arrival of microprocessors, which brought together the central processing unit (CPU) onto just one chip.
Fourth Generation: Microprocessors (Late 1970s – 1990s)

In the late 1970s, a pioneering advancement in computing emerged as the fourth generation arrived. This era brought a sophisticated technology known as microprocessors.
Microprocessors are integrated circuits that host the central processing unit (CPU) on a single chip and bring innovative computer design. They achieved this by integrating the CPU, memory, and control circuits onto a single chip. This miniaturization provided benefits in terms of processing power, energy efficiency, and portability.
Consequently, it paved the way for personal computers and transformed the digital landscape.
- Size: The CPU being integrated onto a single chip had a tremendous impact on reducing the size of computers. This made them compact enough to fit on a desktop conveniently.
- Computational power: Microprocessors offered efficiency in computing by significantly enhancing computational capabilities. This breakthrough allowed computers to execute tasks more swiftly and handle increasingly intricate calculations.
- Energy efficiency: Microprocessors were designed to be more energy-efficient than their predecessors. Therefore, they consume less power and generate less heat.
- Personal computing: Personal computers (PCs) emerged during the fourth generation. It changed the way we used to do computing. This is also where computer accessibility increased. Even individuals and smaller businesses could easily access computers to run their operations.
- Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs): Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) changed how people interacted with computers by replacing complex command-line interfaces with intuitive visual interactions.
The introduction of microprocessors transformed computing, making it accessible beyond research labs. Individuals and businesses both started using personal computers in their homes and offices. This technological breakthrough laid the foundation for a digital revolution.
Advancements in microprocessor technology, along with the increasing demand for enhanced connectivity and networking capabilities, played a significant role in introducing the fifth generation of computers.
Fifth Generation: Artificial Intelligence and Beyond (1990s – Present)

The fifth generation of computers spans from the 1990s to today. The 1990s era was marked by the emergence of the fifth generation of computers. It introduced innovative, highly sophisticated concepts like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) and merged them with other digital technologies like parallel processing, natural language processing (NLP), etc.
This profoundly influenced the modern computing landscape in ways that were previously unforeseen. This phase also transformed human interactions with machines and ignited an unprecedented wave of innovation across multiple industries.
As a result of integrating AI and other advanced computational technologies resulted in the emergence of supercomputers, high-performance computing, and the internet. And now, you can enjoy computing faster with energy efficiency while accessing the internet to perform various tasks.
- Size: Computers have undergone significant advancements, becoming smaller and more portable. This has led to enhanced accessibility of technology for both individuals and businesses.
- Computational power : Integrating AI and advancements in hardware has resulted in a remarkable surge in processing power. This increased capacity has facilitated the execution of intricate calculations and thorough data analysis.
- Memory: Storage capacities have experienced significant growth, enabling the seamless collection and analysis of vast amounts of data.
- Programming: AI-driven applications and tools have emerged, making complex coding processes simpler and enabling automation in various tasks. The era is witnessing the usage of programming languages like Python, Java, C, etc.
The integration of AI in the fifth generation has brought a great technological shift in various industries. It has opened up the way for advancements in machine learning, natural language processing, and robotics, reshaping both professional and personal lives.
So, are you prepared to witness the unfolding of a remarkable future? The anticipation surrounding the sixth generation of computers is immense.
Sixth Generation: The Future

The dawn of the sixth generation of computers is upon us, indicating a technological revolution that holds the power to reshape our very existence. This innovative era promises to revolutionize computing through quantum technology, advanced nanotechnology, and increasingly sophisticated artificial intelligence.
This will open the door to unimaginable possibilities.
Key Advancements
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computers are extraordinary machines that have the power to perform calculations at mind-boggling speeds, surpassing what traditional computers can achieve. They open pathways toward tackling intricate scientific problems, revolutionizing cryptography, and much more.
- Nanotechnology: Did you know that manipulating matter at the atomic and molecular scale can provide extraordinary results? It would allow us to create computer components so small yet incredibly powerful, enhancing miniaturization and efficiency.
- Biocomputing: Integrating computers with biological systems has the potential to benefit various fields, including medicine, data storage, and processing.
Potential Impact
The innovations of the sixth generation could offer immense opportunities across various fields, including IT, manufacturing, cybersecurity, healthcare, climate modeling, and artificial intelligence. The potential is boundless, from simulating molecular behavior for drug discovery to fortifying cybersecurity with quantum encryption.
Final Words
As we come to the end of our exploration through the different generations of computers, you’ve seen how these machines have changed over time.
From the big computers that used vacuum tubes in the past to the smart ones that use AI today, things have really changed a lot. Computers used to be huge, and now they are much smaller. They can do much more complex tasks now, like helping us talk to each other worldwide.
The next generation of computers could use even more sophisticated technologies to make them super powerful, allowing you to do amazing stuff.
So, even though we’ve seen a lot of changes already, there’s still more to come. Keep watching because computers will keep getting cooler and doing things we might not even imagine yet!
Related Articles
- 12 Emerging IT Automation Trends to Keep an Eye on
- Computer Networking Introduction for Beginners

- Basics of Computer Science Tutorial
- Basics of Computer Science - Home
- Fundamental Concept
- Role of Computer in Today’s World
- Computer System
- Programming Languages
- Hardware and Software
- Analog and Digital
- Operating System
- Types of Computer
- Computer Networking Terminology
- Computer Applications
Generations of Computer
- Data Processing
- Computer Networking
- Computer Related Jobs
- Electronic Commerce
- Software Programming
- Algorithm Flowchart
- Mobile Computer
- Windows Desktop Elements
- Computer Multimedia
- Computer Security
- Computer Threat
- Computer Virus
- Computer Science: Abbreviations
- Computer Science: Development
- Computer Science: Innovators
- Short-cut Keys
- Useful Resources
- Online Quiz
- Online Test
- Quick Guide
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
The development of computer systems is normally discussed as the development over different generations.
With the succession of different generations, came the advancement in computer technology.
Computer Generations
Let us now discuss the development in Computer Technology over the different generations.
First Generation
The period 1940 to 1956, roughly considered as the First Generation of Computer.
The first generation computers were developed by using vacuum tube or thermionic valve machine.
The input of this system was based on punched cards and paper tape; however, the output was displayed on printouts.
The first generation computers worked on binary-coded concept (i.e., language of 0-1). Examples: ENIAC, EDVAC, etc.

Second Generation
The period 1956 to 1963 is roughly considered as the period of Second Generation of Computers.
The second generation computers were developed by using transistor technology.
In comparison to the first generation, the size of second generation was smaller.
In comparison to computers of the first generation, the computing time taken by the computers of the second generation was lesser.

Third Generation
The period 1963 to 1971 is roughly considered as the period of Third Generation of computers.
The third generation computers were developed by using the Integrated Circuit (IC) technology.

In comparison to the computers of the second generation, the size of the computers of the third generation was smaller.
In comparison to the computers of the second generation, the computing time taken by the computers of the third generation was lesser.
The third generation computer consumed less power and also generated less heat.
The maintenance cost of the computers in the third generation was also low.
The computer system of the computers of the third generation was easier for commercial use.
Fourth Generation
The period 1972 to 2010 is roughly considered as the fourth generation of computers.
The fourth generation computers were developed by using microprocessor technology.

By coming to fourth generation, computer became very small in size, it became portable.
The machine of fourth generation started generating very low amount of heat.
It is much faster and accuracy became more reliable.
The production cost reduced to very low in comparison to the previous generation.
It became available for the common people as well.
Fifth Generation
The period 2010 to till date and beyond, roughly considered as the period of fifth generation of computers.
By the time, the computer generation was being categorized on the basis of hardware only, but the fifth generation technology also included software.
The computers of the fifth generation had high capability and large memory capacity.
Working with computers of this generation was fast and multiple tasks could be performed simultaneously.
Some of the popular advanced technologies of the fifth generation include Artificial intelligence, Quantum computation, Nanotechnology, Parallel processing, etc.


How many generations of computers are there?
Computer generations are based on when major technological changes in computers occurred, like going from vacuum tubes to transistors. As of 2024, there are five generations of the computer.
Review each of the generations below for more information and examples of computers and technology that fall into each generation.
First generation (1940 - 1956)
Second generation (1956 - 1963), third generation (1964 - 1971), fourth generation (1971 - 2010), fifth generation (2010 to present), sixth generation (future generations).

The first generation of computers used vacuum tubes as a major piece of technology. Vacuum tubes were widely used in computers from 1940 through 1956 . Vacuum tubes were larger components and resulted in first-generation computers being quite large in size, taking up a lot of space in a room. Some first-generation computers took up an entire room.
The ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) is a great example of a first-generation computer. It consisted of nearly 20,000 vacuum tubes, 10,000 capacitors , and 70,000 resistors . It weighed over 30 tons and took up a lot of space, requiring a large room to house it. Other examples of first-generation computers include the EDSAC (Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator), IBM 701 , and Manchester Mark 1 .

The second generation of computers used transistors instead of vacuum tubes. Transistors were widely used in computers from 1956 to 1963 . Transistors were smaller than vacuum tubes and allowed computers to be smaller in size, faster in speed, and cheaper to build.
The first computer to use transistors was the TX-0 and was introduced in 1956. Other computers that used transistors include the IBM 7070, Philco Transac S-1000, and RCA 501.
The third generation of computers introduced used IC (Integrated Circuit) in computers. Using IC's in computers helped reduce the size of computers even more than second-generation computers, and also made them faster.
Nearly all computers since the mid to late 1960s have utilized IC's. While the third generation is considered by many people to have spanned from 1964 to 1971 , IC's are still used in computers today. Over 45 years later, today's computers have deep roots going back to the third generation.
The fourth generation of computers took advantage of the invention of the microprocessor, commonly known as a CPU (Central Processing Unit). Microprocessors, with integrated circuits, helped make it possible for computers to fit easily on a desk and for the introduction of the laptop.
Early computers to use a microprocessor include the Altair 8800 , IBM 5100 , and Micral. Today's computers still use a microprocessor, despite the fourth generation being considered to have ended in 2010 .

The fifth generation of computers is beginning to use AI (Artificial Intelligence), an exciting technology with many potential applications around the world. Leaps have been made in AI technology and computers, but there is still room for much improvement.
One of the more well-known examples of AI in computers is IBM's Watson, which was featured on the TV show Jeopardy as a contestant. Other more recent examples include ChatGPT and the introduction of and AI PCs .
As of 2024 , most still consider us to be in the fifth generation as AI continues to develop. One possible contender for a future sixth generation is the quantum computer . However, until quantum computing becomes more developed and widely used, it is still only a promising idea.
Some people also consider nanotechnology to be part of the sixth generation. Like quantum computing, nanotechnology is largely still in its infancy and requires more development before becoming widely used.
With a new generation of computers it's also possible how we interact with a computer may also change. New ways of how we may interact with the next generation of computers include only using our voice , AR ( Augmented Reality ), VR ( Virtual Reality ), or MR ( Mixed Reality ).
Related information
- When was the first computer invented?
- Who is the father of the computer?
- Computer history and timeline.
- Computer history questions and answers.
- See our generation definition for related links and information.

- Computer Fundamentals
- Interview Q
Computer Components
Computer memory.
Computer Network
Computer Virus
Number systems, shortcut keys.
Interview Questions
| The first counting device was used by the primitive people. They used sticks, stones and bones as counting tools. As human mind and technology improved with time more computing devices were developed. Some of the popular computing devices starting with the first to recent ones are described below; The history of computer begins with the birth of abacus which is believed to be the first computer. It is said that Chinese invented Abacus around 4,000 years ago. It was a wooden rack which has metal rods with beads mounted on them. The beads were moved by the abacus operator according to some rules to perform arithmetic calculations. Abacus is still used in some countries like China, Russia and Japan. An image of this tool is shown below; It was a manually-operated calculating device which was invented by John Napier (1550-1617) of Merchiston. In this calculating tool, he used 9 different ivory strips or bones marked with numbers to multiply and divide. So, the tool became known as "Napier's Bones. It was also the first machine to use the decimal point. Pascaline is also known as Arithmetic Machine or Adding Machine. It was invented between 1642 and 1644 by a French mathematician-philosopher Biaise Pascal. It is believed that it was the first mechanical and automatic calculator. Pascal invented this machine to help his father, a tax accountant. It could only perform addition and subtraction. It was a wooden box with a series of gears and wheels. When a wheel is rotated one revolution, it rotates the neighboring wheel. A series of windows is given on the top of the wheels to read the totals. An image of this tool is shown below; It was developed by a German mathematician-philosopher Gottfried Wilhelm Leibnitz in 1673. He improved Pascal's invention to develop this machine. It was a digital mechanical calculator which was called the stepped reckoner as instead of gears it was made of fluted drums. See the following image; In the early 1820s, it was designed by Charles Babbage who is known as "Father of Modern Computer". It was a mechanical computer which could perform simple calculations. It was a steam driven calculating machine designed to solve tables of numbers like logarithm tables. This calculating machine was also developed by Charles Babbage in 1830. It was a mechanical computer that used punch-cards as input. It was capable of solving any mathematical problem and storing information as a permanent memory. It was invented in 1890, by Herman Hollerith, an American statistician. It was a mechanical tabulator based on punch cards. It could tabulate statistics and record or sort data or information. This machine was used in the 1890 U.S. Census. Hollerith also started the Hollerith?s Tabulating Machine Company which later became International Business Machine (IBM) in 1924. It was the first electronic computer introduced in the United States in 1930. It was an analog device invented by Vannevar Bush. This machine has vacuum tubes to switch electrical signals to perform calculations. It could do 25 calculations in few minutes. The next major changes in the history of computer began in 1937 when Howard Aiken planned to develop a machine that could perform calculations involving large numbers. In 1944, Mark I computer was built as a partnership between IBM and Harvard. It was the first programmable digital computer. A generation of computers refers to the specific improvements in computer technology with time. In 1946, electronic pathways called circuits were developed to perform the counting. It replaced the gears and other mechanical parts used for counting in previous computing machines. In each new generation, the circuits became smaller and more advanced than the previous generation circuits. The miniaturization helped increase the speed, memory and power of computers. There are five generations of computers which are described below; The first generation (1946-1959) computers were slow, huge and expensive. In these computers, vacuum tubes were used as the basic components of CPU and memory. These computers were mainly depended on batch operating system and punch cards. Magnetic tape and paper tape were used as output and input devices in this generation; Some of the popular first generation computers are; ( Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) ( Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer) ( Universal Automatic Computer)The second generation (1959-1965) was the era of the transistor computers. These computers used transistors which were cheap, compact and consuming less power; it made transistor computers faster than the first generation computers. In this generation, magnetic cores were used as the primary memory and magnetic disc and tapes were used as the secondary storage. Assembly language and programming languages like COBOL and FORTRAN, and Batch processing and multiprogramming operating systems were used in these computers. Some of the popular second generation computers are; The third generation computers used integrated circuits (ICs) instead of transistors. A single IC can pack huge number of transistors which increased the power of a computer and reduced the cost. The computers also became more reliable, efficient and smaller in size. These generation computers used remote processing, time-sharing, multi programming as operating system. Also, the high-level programming languages like FORTRON-II TO IV, COBOL, PASCAL PL/1, ALGOL-68 were used in this generation. Some of the popular third generation computers are; The fourth generation (1971-1980) computers used very large scale integrated (VLSI) circuits; a chip containing millions of transistors and other circuit elements. These chips made this generation computers more compact, powerful, fast and affordable. These generation computers used real time, time sharing and distributed operating system. The programming languages like C, C++, DBASE were also used in this generation. Some of the popular fourth generation computers are; In fifth generation (1980-till date) computers, the VLSI technology was replaced with ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration). It made possible the production of microprocessor chips with ten million electronic components. This generation computers used parallel processing hardware and AI (Artificial Intelligence) software. The programming languages used in this generation were C, C++, Java, .Net, etc. Some of the popular fifth generation computers are; |

- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share

Learn Latest Tutorials
Transact-SQL
Reinforcement Learning
R Programming
React Native
Python Design Patterns
Python Pillow
Python Turtle
Preparation

Verbal Ability

Company Questions
Trending Technologies
Artificial Intelligence
Cloud Computing
Data Science
Machine Learning
B.Tech / MCA
Data Structures
Operating System
Compiler Design
Computer Organization
Discrete Mathematics
Ethical Hacking
Computer Graphics
Software Engineering
Web Technology
Cyber Security
C Programming
Control System
Data Mining
Data Warehouse

- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to secondary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Computer Notes
- Computer Fundamental
- Computer Memory
- DBMS Tutorial
- Operating System
- Computer Networking
- C Programming
- C++ Programming
- Java Programming
- C# Programming
- SQL Tutorial
- Management Tutorial
- Computer Graphics
- Compiler Design
- Style Sheet
- JavaScript Tutorial
- Html Tutorial
- Wordpress Tutorial
- Python Tutorial
- PHP Tutorial
- JSP Tutorial
- AngularJS Tutorial
- Data Structures
- E Commerce Tutorial
- Visual Basic
- Structs2 Tutorial
- Digital Electronics
- Internet Terms
- Servlet Tutorial
- Software Engineering
- Interviews Questions
- Basic Terms
- Troubleshooting
Header Right
History of computer | generation of computer.
By Dinesh Thakur
Each generation of computer is characterized by a major technological development that fundamentally changed the way computers operate, resulting in increasingly smaller, cheaper, more powerful and more efficient and reliable devices.
The various generations of computers an listed below :
(i) First Generation (1946-1954) : In 1946 there was no ‘best’ way of storing instructions and data in a computer memory . There were four competing technologies for providing computer memory : electrostatic storage tubes, acoustic delay lines ( mercury or nickel ), magnetic drums (and disks?), and magnetic core storage.
The digital computes using electronic valves (Vacuum tubes) are known as first generation computers. the first ‘computer’ to use electronic valves (ie. vacuum tubes). The high cost of vacuum tubes prevented their use for main memory. They stored information in the form of propagating sound waves.
The vacuum tube consumes a lot of power. The Vacuum tube was developed by Lee DeForest in 1908. These computers were large in size and writing programs on them was difficult. Some of the computers of this generation were:
Mark I : The IBM Automatic Sequence Controlled Calculator (ASCC) , called the Mark I by Harvard University , was an electro-mechanical computer . Mark I is the first machine to successfully perform a long services of arithmetic and logical operation . Mark I is the First Generation Computer . it was the first operating machine that could execute long computations automatically . Mark I computer which was built as a partnership between Harvard and IBM in 1944 . This was the first programmable digital computer made in the U.S. But it was not a purely electronic computer. Instead the Mark I was constructed out of switches, relays, rotating shafts, and clutches. The machine weighed 5 tons, incorporated 500 miles of wire, was 8 feet tall and 51 feet long, and had a 50 ft rotating shaft running its length, turned by a 5 horsepower electric motor.
ENIAC: It was the first general-purpose electronic computer built in 1946 at University of Pennsylvania, USA by John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert . The completed machine was announced to the public the evening of February 14, 1946 . It was named Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator (ENIAC) . ENIAC contained 17,468 vacuum tubes, 7,200 crystal diodes, 1,500 relays, 70,000 resistors, 10,000 capacitors and around 5 million hand-soldered joints. It weighed more than 30 short tons (27 t), was roughly 8 by 3 by 100 feet (2.4 m × 0.9 m × 30 m), took up 1800 square feet (167 m2), and consumed 150 kW of power. Input was possible from an IBM card reader , and an IBM card punch was used for output. These cards could be used to produce printed output offline using an IBM accounting machine, such as the IBM 405 . Today your favorite computer is many times as powerful as ENIAC, still size is very small.
EDVAC: It stands for Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer and was developed in 1950 .it was to be a vast improvement upon ENIAC, it was binary rather than decimal , and was a stored program computer. The concept of storing data and instructions inside the computer was introduced here. This allowed much faster operation since the computer had rapid access to both data and instructions. The other advantage of storing instruction was that computer could do logical decision internally.
The EDVAC was a binary serial computer with automatic addition, subtraction, multiplication, programmed division and automatic checking with an ultrasonic serial memory. EDVAC’s addition time was 864 microseconds and its multiplication time was 2900 microseconds (2.9 milliseconds).
The computer had almost 6,000 vacuum tubes and 12,000 diodes, and consumed 56 kW of power. It covered 490 ft² (45.5 m²) of floor space and weighed 17,300 lb (7,850 kg).
EDSAC: It stands for Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Computer and was developed by M.V. Wilkes at Cambridge University in 1949 . Two groups of individuals were working at the same time to develop the first stored-program computer. In the United States, at the University of Pennsylvania the EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer) was being worked on. In England at Cambridge, the EDSAC (Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Computer) was also being developed. The EDSAC won the race as the first stored-program computer beating the United States’ EDVAC by two months. The EDSAC performed computations in the three millisecond range. It performed arithmetic and logical operations without human intervention. The key to the success was in the stored instructions which it depended upon solely for its operation. This machine marked the beginning of the computer age. EDSAC is the first computer is used to store a program
UNIVAC-1 : Ecker and Mauchly produced it in 1951 by Universal Accounting Computer setup. it was the first commercial computer produced in the United States. It was designed principally by J. Presper Eckert and John Mauchly, the inventors of the ENIAC.
The machine was 25 feet by 50 feet in length, contained 5,600 tubes, 18,000 crystal diodes, and 300 relays. It utilized serial circuitry, 2.25 MHz bit rate, and had an internal storage capacity 1,000 words or 12,000 characters.
It utilized a Mercury delay line , magnetic tape, and typewriter output . The UNIVAC was used for general purpose computing with large amounts of input and output.
Power consumption was about 120 kva. Its reported processing speed was 0.525 milliseconds for arithmetic functions, 2.15 milliseconds for multiplication and 3.9 Milliseconds for division.
The UNIVAC was also the first computer to come equipped with a magnetic tape unit and was the first computer to use buffer memory .
Other Important Computers of First Generation
Some other computers of this time worth mentioning are the Whirlwind, developed at Massachussets Institute of Technology, and JOHNNIAC, by the Rand Corporation. The Whirlwind was the first computer to display real time video and use core memory. The JOHNNIAC was named in honor of Jon Von Neumann. Computers at this time were usually kept in special locations like government and university research labs or military compounds.
Limitations of First Generation Computer
Followings are the major drawbacks of First generation computers.
1. They used valves or vacuum tubes as their main electronic component.
2. They were large in size, slow in processing and had less storage capacity.
3. They consumed lots of electricity and produced lots of heat.
4. Their computing capabilities were limited.
5. They were not so accurate and reliable.
6. They used machine level language for programming.
7. They were very expensive.
Example: ENIAC, UNIVAC, IBM 650 etc
(ii) Second Generation (1955-1964) : The second-generation computer used transistors for CPU components & ferrite cores for main memory & magnetic disks for secondary memory. They used high-level languages such as FORTRAN (1956), ALGOL (1960) & COBOL (1960 – 1961) . I/O processor was included to control I/O operations.
Around 1955 a device called Transistor replaced the bulky Vacuum tubes in the first generation computer. Transistors are smaller than Vacuum tubes and have higher operating speed. They have no filament and require no heating. Manufacturing cost was also very low. Thus the size of the computer got reduced considerably.
It is in the second generation that the concept of Central Processing Unit (CPU), memory, programming language and input and output units were developed. The programming languages such as COBOL, FORTRAN were developed during this period. Some of the computers of the Second Generation were
1. IBM 1620 : Its size was smaller as compared to First Generation computers and mostly used for scientific purpose.
2. IBM 1401 : Its size was small to medium and used for business applications.
3. CDC 3600 : Its size was large and is used for scientific purposes.
1. Transistors were used instead of Vacuum Tube.
2. Processing speed is faster than First Generation Computers (Micro Second)
3. Smaller in Size (51 square feet)
4. The input and output devices were faster.
Example: IBM 1400 and 7000 Series, Control Data 3600 etc.
(iii) Third Generation (1964-1977) : By the development of a small chip consisting of the capacity of the 300 transistors . These ICs are popularly known as Chips . A single IC has many transistors, registers and capacitors built on a single thin slice of silicon . So it is quite obvious that the size of the computer got further reduced. Some of the computers developed during this period were IBM-360, ICL-1900, IBM-370, and VAX-750 . Higher level language such as BASIC (Beginners All purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) was developed during this period. Computers of this generation were small in size, low cost, large memory and processing speed is very high. Very soon ICs Were replaced by LSI (Large Scale Integration) , which consisted about 100 components. An IC containing about 100 components is called LSI.
1. They used Integrated Circuit (IC) chips in place of the transistors.
2. Semi conductor memory devices were used.
3. The size was greatly reduced, the speed of processing was high, they were more accurate and reliable.
4. Large Scale Integration (LSI) and Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) were also developed.
5. The mini computers were introduced in this generation.
6. They used high level language for programming.
Example: IBM 360, IBM 370 etc.
(iv) Fourth Generation : An IC containing about 100 components is called LSI (Large Scale Integration) and the one, which has more than 1000 such components, is called as VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) . It uses large scale Integrated Circuits (LSIC) built on a single silicon chip called microprocessors. Due to the development of microprocessor it is possible to place computer’s central processing unit (CPU) on single chip. These computers are called microcomputers. Later very large scale Integrated Circuits (VLSIC) replaced LSICs. Thus the computer which was occupying a very large room in earlier days can now be placed on a table. The personal computer (PC) that you see in your school is a Fourth Generation Computer Main memory used fast semiconductors chips up to 4 M bits size. Hard disks were used as secondary memory. Keyboards, dot matrix printers etc. were developed. OS-such as MS-DOS, UNIX, Apple’s Macintosh were available. Object oriented language, C++ etc were developed.
1. They used Microprocessor (VLSI) as their main switching element.
2. They are also called as micro computers or personal computers.
3. Their size varies from desktop to laptop or palmtop.
4. They have very high speed of processing; they are 100% accurate, reliable, diligent and versatile.
5. They have very large storage capacity.
Example: IBM PC, Apple-Macintosh etc.
(v) Fifth Generation (1991- continued) : 5th generation computers use ULSI (Ultra-Large Scale Integration) chips. Millions of transistors are placed in a single IC in ULSI chips. 64 bit microprocessors have been developed during this period. Data flow & EPIC architecture of these processors have been developed. RISC & CISC , both types of designs are used in modern processors. Memory chips and flash memory up to 1 GB, hard disks up to 600 GB & optical disks up to 50 GB have been developed. fifth generation digital computer will be Artificial intelligence .
You’ll also like:
- Definition of Computer | Meaning of computer
- History of C? Why we use C programming language
- What is the History of E-Commerce?
- History of Java
- History of HTML

Dinesh Thakur is a Freelance Writer who helps different clients from all over the globe. Dinesh has written over 500+ blogs, 30+ eBooks, and 10000+ Posts for all types of clients.
For any type of query or something that you think is missing, please feel free to Contact us .
Basic Course
- Database System
- Management System
- Electronic Commerce
Programming
- Structured Query (SQL)
- Java Servlet
World Wide Web
- Java Script
- HTML Language
- Cascading Style Sheet
- Java Server Pages
Generations of Computers
The section on computer awareness is a fairly new section of banking exams. So from this section, the topic on generations of computers is of prime importance. Here in this article, we will discuss the various generations of computers and the reasons that are important. Let us see!
Suggested Videos
A computer is basically an electronic machine that can process information. However, the “ process ” could be anything. For example, it could be the addition or any other arithmetic operation . Otherwise, it could be just the instruction to group a given set of data or to ungroup it. Today’s computers have the power to carry out billions of calculations in a second and return results that are very accurate and reliable. How did it all happen? Where did it all start?
Click here to learn everything you need to know about the English Language .
The computers of today find their roots in the second half of the twentieth century. Later as time progressed, we saw many technological improvements in physics and electronics . This has eventually led to revolutionary developments in the hardware and software of computers. In other words, soon the computer started to evolve. Each such technological advancement marks a generation of computers. Let us begin with the first one.

First Generation Of Computers
Computers developed between 1946 – 1959, are the first generation of computers. They were large and limited to basic calculations. They consisted of large devices like the vacuum tubes. The input method of these computers was a machine language known as the 1GL or the first generation language. The physical methods of using punch cards, paper tape, and magnetic tape were used to enter data into these computers.
Be updated and don’t get stuck in an exam. Prepare your General Awareness topics here.
Examples of the first generation computers include ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC, IBM-701, and IBM-650. These computers were large and very unreliable. They would heat up and frequently shut down and could only be used for very basic computations.
Second Generation Of Computers
Computers developed between 1959-1965 the second generation computers. These computers were more reliable and in place of vacuum tubes, used transistors. This made them far more compact than the first generation computers. The input for these computers were higher level languages like COBOL, FORTRAN etc. In these computers, primary memory was stored on the magnetic cores and magnetic tape and they used magnetic disks as secondary storage devices.
Examples of the second generation computers include IBM 1620, IBM 7094, CDC 1604, CDC 3600, UNIVAC 1108. As a result, they worked on AC and therefore were faster than their predecessors.
Having trouble with concepts like DBMS? Have an important exam soon? Click here and start your preparations now!
Third Generation Of Computers
Computers developed during the period of 1965 – 1971, the third generation of computers. These computers differed from the first and the second generations simply by the fact that a new circuit element like IC’s (Integrated Circuits) was used. An integrated circuit is a small device that can contain thousands and thousands of devices like transistors, resistances and other circuit elements that make up a computer. Jack Kilby is credited with the invention of the Integrated Circuit or the IC chips. With the invention of IC’s, it became possible to fit thousands of circuit elements into a small region and hence the size of the computers eventually became smaller and smaller.
Another salient feature of these computers was that they were much more reliable and consumed far less power. The input languages for such computers were COBOL, FORTRAN-II up to FORTRAN-IV, PASCAL, ALGOL-68, BASIC, etc. These languages were much better and could represent more information. Consequently more and more complex calculations are possible
Examples of the third generation computers include IBM-360 series, Honeywell-6000 series, PDP (Personal Data Processor), and IBM-370/168.
Find all the topics of Reasoning Ability here!
Fourth Generation Of Computers
Fourth Generation of computers was between 1971 – 1980. These computers used the VLSI technology or the Very Large Scale Integrated (VLSI) circuits technology. Therefore they were also known as the microprocessors. Intel was the first company to develop a microprocessor. The first “personal computer” or PC developed by IBM, belonged to this generation. VLSI circuits had almost about 5000 transistors on a very small chip and were capable of performing many high-level tasks and computations. These computers were thus very compact and thereby required a small amount of electricity to run.
Examples are STAR 1000, CRAY-X-MP(Super Computer), DEC 10, PDP 11, CRAY-1. This generation of computers had the first “supercomputers” that could perform many calculations accurately. They were also used in networking and also used higher and more complicated languages as their inputs. The computer languages like languages like C, C+, C++, DBASE etc. were the input for these computers.
Want to see how smart you are? Want to exercise your brain? Click here for a wonderfully explained and lucid section of Reasoning Ability.
Fifth Generation Of Computers
This is the present generation of computers and is the most advanced one. The generation began somewhere around 1981 and is the present generation of computers. The methods of input include the modern high-level languages like Python, R, C#, Java etc. These are extremely reliable and employ the ULSI or the Ultra Large Scale Integration technology. These computers are at the frontiers of the modern scientific calculations and are used to develop the Artificial Intelligence or AI components that will have the ability to think for themselves.
Examples include: Intel P 4, i 3 – i10, AMD Athlon, etc.
We have the most complete syllabus of quantitative aptitude in one place for you! Click here
Check Your Awareness
Q 1: The language used in ENIAC:
A) C B) C++ C) 1 GL D) Python
Ans: Basically ENIAC was a first generation computer and therefore the correct option is 1 GL.
Q 2: Which among these will have VLSI?
A) DEC 10 B) PDP 11 C) CRAY-1 D) All of these.
Ans: Earlier VLSI or the very large scale integration was employed in the fourth generation of computers. All of these above examples are from the fourth generation and therefore the answer is D.
Practice Questions
Q 1: You can use Java in which of these following generations:
Ans: D is the correct option.
Q 2: The ULSI technology is present in which generation of computers:
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Basics of Computers
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- Basic Computer Terminology
- Computer Abbreviations
- Computer Languages
- Basic Internet Knowledge and Protocols
- History of Computers
- Basic Computer Knowledge – Practice Problems
- Computer Organization
- Input and Output (I/O) Devices
- Hardware and Software
One response to “Hardware and Software”
THANKS ,THIS IS THE VERY USEFUL KNOWLEDGE
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial
Computer Fundamental Tutorial
This Computer Fundamental Tutorial covers everything from basic to advanced concepts, including computer hardware, software, operating systems, peripherals, etc. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced professional, this tutorial is designed to enhance your computer skills and take them to the next level.

What is Computer?
The computer is a super-intelligent electronic device that can perform tasks, process information, and store data. It takes the data as an input and processes that data to perform tasks under the control of a program and produces the output. A computer is like a personal assistant that follows instructions to get things done quickly and accurately. It has memory to store information temporarily so that the computer can quickly access it when needed.
Prerequisites for Computer Fundamentals
No prerequisites or prior knowledge required to learn computer fundamentals, Hence, this article on Computer Fundamentals is designed for absolute beginners.
Computer Fundamentals Tutorial Index
In the upcoming section you will get a topic wise categories for computer fundamental. So, explore the below section to learn the fundamentals of computer fundamentals.
Introduction To Computer Fundamentals
- What are Computer Fundamentals?
- Importance of Computer Fundamentals in Digital Age
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Computer
- Classification of Computers
- Application area of Computer
History and Evolution of Computers
- History of Computers
- The Origins of Computing
- First Generation – 1940-1956 Vacuum Tubes
- Second Generation – 1956-1963 Transistors
- Third Generation – 1964-1971 Integrated Circuits
- Fourth Generation – 1971-Present Microprocessors
- Fifth Generation – Present and Beyond Artificial Intelligence
Components of a Computer System
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Memory Units
Input Devices
Output devices.
- LCD Monitor
- LED Monitor
- QWERTY Keyboard
- AZERTY Keyboard
- DVORAK Keyboard
- Trackball Mouse
- Mechanical Mouse
- Optical Mouse
- Wireless Mouse
- Peripherals Devices
Computer Hardware
- Motherboard
- What are the Functions of a CPU?
- Program Execution in the CPU
- Difference Between ALU and CU
- Difference between System Unit and CPU
- Random Access Memory (RAM)
- SRAM Full Form
- DRAM Full Form
- Difference between Random Access Memory (RAM) and Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
- Random Access Memory (RAM) and Read Only Memory (ROM)
- Similarities of RAM and ROM
- Hard Disk Drives (HDD)
- Solid State Drives (SSD)
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
- Power Supply Unit (PSU)
- Computer Peripherals (Keyboard, Mouse, Monitor, etc.)
Computer Software
- Introduction to Software
- Types of Software
- Application Software
- System Software
- Utility Software
- What is Keyboard?
- What is Mouse?
- What is a Joystick?
- What is a light pen?
- What is Scanner?
- What is OCR?
- What is barcode reader?
- What is WebCam?
Data Storage and Memory
- What is a Storage Device?
- Types of Data Storage
- Optical Storage
- DVD-ROM Full Form
- DVD-RAM Full Form
- DVD-R Full Form
- DVD-RW Full Form
- Flash Drives
- Memory Cards
- Cloud Storage
Computer Short Cut Key
- Computer Keyboard Shortcut Keys
- Function Keys on keyboard
- Windows Shortcut Keys
- Keyboard Shortcuts for Ubuntu |
- Most Used Shortcuts of Turbo C++
- Important Questions for Computer Keyboard Shortcuts
- Computer Memory
- Register Memory
- Cache Memory
- Primary Memory
- Secondary Memory
Basics of Operating System
- What is Operating System?
- Evolution of Operating System
- Types of Operating Systems
- Operating System Services
- Functions of Operating System
Computer Security and Privacy
- What is Computer Security?
- Importance of Computer Security
- Common Security Threats
- Network Security Measures (Firewalls, Encryption)
- Access Control
- User Authentication
- Privacy Concerns and Data Protection
Computer Networks and Internet
- Introduction to Computer Networks
- Network Topologies (Star, Bus, Ring)
- Network Protocols (TCP/IP, HTTP, FTP)
- World Wide Web
Introduction to Programming
- What is Programming?
- A Categorical List of programming languages
- Language Processors: Assembler, Compiler and Interpreter
- Variables ( C , C++ , Java )
- Data Types ( C , C++ , Java )
- Operators ( C , C++ , Java )
- Control Structures (Conditionals, Loops)
- Functions and Procedures
Difference Between
- Difference between RAM and ROM
- Difference between Hard Disk and Floppy Disk
- Difference between CD-ROM and Magnetic Disks
- Difference between Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and Magnetic Ink Character Reader (MICR)
- Difference between Magnetic Disk and Optical Disk
- Difference between Hard Disk Drive (HDD) and Solid State Drive (SSD)
- Difference between CD and DVD
- Difference Between Blu-Ray and DVD
- Difference between Application Software and Utility Software
- Difference between Application Software and Operating System
- Difference between System Software and Application Software
- Difference between Barcode and QR Code
Functionalities of Computer
Any digital computer performs the following five operations:
- Step 1 − Accepts data as input.
- Step 2 − Saves the data/instructions in its memory and utilizes them as and when required.
- Step 3 − Execute the data and convert it into useful information.
- Step 4 − Provides the output.
- Step 5 − Have control over all the above four steps
The Evolution of Computers
A journey through the history of computers. We’ll start with the origins of computing and explore the milestones that led to the development of electronic computers.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| First Generation | 1946-1959 | Vacuum Tube-based |
| Second Generation | 1959-1965 | Transistor-based |
| Third Generation | 1965-1971 | Integrated Circuit based |
| Fourth Generation | 1971-1980 | VLSI microprocessor based |
| Fifth Generation | 1980-onwards | ULSI microprocessor based |
Applications of Computer Fundamentals
- Software Development: Computer fundamentals are fundamental to software development. Understanding programming languages, algorithms, data structures, and software design principles are crucial for developing applications, websites, and software systems. It forms the basis for creating efficient and functional software solutions.
- Network Administration : Computer fundamentals are essential for network administrators. They help set up and manage computer networks, configure routers and switches, troubleshoot network issues, and ensure reliable connectivity. Knowledge of computer fundamentals enables network administrators to maintain and optimize network performance.
- Cybersecurity : Computer fundamentals are at the core of cybersecurity. Understanding the basics of computer networks, operating systems, encryption techniques, and security protocols helps professionals protect systems from cyber threats. It enables them to identify vulnerabilities, implement security measures, and respond effectively to security incidents.
- Data Analysis : Computer fundamentals are necessary for data analysis and data science. Knowledge of programming, statistical analysis, and database management is essential to extract insights from large datasets. Understanding computer fundamentals helps in processing and analyzing data efficiently, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning : Computer fundamentals provide the foundation for AI and machine learning. Concepts such as algorithms, data structures, and statistical modelling are vital in training and developing intelligent systems. Understanding computer fundamentals allows professionals to create AI models, train them on large datasets, and apply machine learning techniques to solve complex problems.
Understanding computer fundamentals is essential for anyone looking to navigate the digital world confidently. This tutorial Computer fundamental has covered the basics of hardware, software, operating systems, and networking, providing you with a solid foundation. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to refresh your knowledge, mastering these core concepts will help you use technology more effectively and prepare you for more advanced studies in computing.
Computer Fundamentals Tutorial – FAQs
Q.1 how long does it take to learn computer fundamentals .
The time required to learn computer fundamentals can vary depending on your prior knowledge and the depth of understanding you aim to achieve. With consistent effort and dedication, one can grasp the basics within a few weeks or months. However, mastering computer fundamentals is an ongoing process as technology evolves.
Q.2 Are computer fundamentals only for technical professionals?
No, computer fundamentals are not limited to technical professionals. They are beneficial for anyone who uses computers in their personal or professional life. Basic computer skills are increasingly essential in various careers and everyday tasks.
Q.3 Can I learn computer fundamentals without any prior technical knowledge?
Absolutely! Computer fundamentals are designed to be beginner-friendly. You can start learning without any prior technical knowledge. There are numerous online tutorials, courses, and resources available that cater to beginners.
Q.4 How can computer fundamentals improve my job prospects?
Computer skills are highly sought after in today’s job market. Proficiency in computer fundamentals can enhance your employability by opening up job opportunities in various industries. It demonstrates your adaptability, problem-solving abilities, and ability to work with digital tools.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Computer Subject
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Second-generation computers moved from cryptic binary machine language to symbolic, or assembly, languages, which allowed programmers to specify instructions in words. High-level programming languages were also being developed at this time, such as early versions of COBOL and FORTRAN.
Introduction to Computer Generations. This development period of electronic computing technology is called Computer Generation. There are five generations of computers identified, although the sixth generation could be in development now in the early 21st century.. During the evolutionary timeline, each generation of computers has improved a lot by undergoing considerable changes in their size ...
Generations of Computer: The modern computer took its shape with the arrival of your time. It had been around the 16th century when the evolution of the computer started. The initial computer faced many changes, obviously for the betterment. It continuously improved itself in terms of speed, accuracy, size, and price to urge the form of the ...
The Fifth-generation computers are portable and smaller in size. Trackpad (or touchpad), touchscreen, pen, speech input (recognize voice/speech), light scanner, printer, keyboard, monitor, mouse, etc are used as Input/Output devices. Examples of 5th Generation Computers are Desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, etc.
Here are the five generations of computers: First Generation (1940s-1950s): The first computers used vacuum tubes for processing and magnetic drums for storage. They were large, expensive, and unreliable. Second Generation (1950s-1960s): The second generation of computers replaced vacuum tubes with transistors, making them smaller, faster, and ...
The main characteristics of first generation of computers (1940s-1950s) Main electronic component - vacuum tube. Main memory - magnetic drums and magnetic tapes. Programming language - machine language. Power - consume a lot of electricity and generate a lot of heat. Speed and size - very slow and very large in size (often taking up ...
Generations of computer. The generation of classified into five generations: 1. FIRST GENERATION COMPUTER: Vacuum Tubes (1940-1956) The first generation of computers is characterized by the use of "Vacuum tubes" It was developed in 1904 by the British engineer "John Ambrose Fleming".
Each computer generation is characterized by a major technological development that fundamentally changed the way computers operate. Each major developments from the 1940s to the present day (5th generation of computer) has introduced smaller, cheaper, more powerful, and more efficient computing machines. This technology has minimized storage ...
Generations of Computers and Their Evolution Here is an overview of the 5 generations of computers and their evolution. First Generation. In the 1940s, a remarkable event unfolded before the world's eyes - the birth of the first generation of computers. These pioneer machines relied on vacuum tubes, large electronic components ...
The period 1940 to 1956, roughly considered as the First Generation of Computer. The first generation computers were developed by using vacuum tube or thermionic valve machine. The input of this system was based on punched cards and paper tape; however, the output was displayed on printouts. The first generation computers worked on binary-coded ...
As of 2024, there are five generations of the computer. Review each of the generations below for more information and examples of computers and technology that fall into each generation. First generation (1940 - 1956) Second generation (1956 - 1963) Third generation (1964 - 1971) Fourth generation (1971 - 2010) Fifth generation (2010 to present)
a. First generation of computers. b. Second generation of computers. c. Third generation of computers. d. Fourth generation of computers. Solution: a. First-generation of computers. Explanation: ENIAC, UNIVAC-1, EDVAC, etc. are examples of the first generation of computers. Question 5: The _____ technology is used in fifth generation computers . a.
History of Computers Generation. The word 'computer' has a very interesting origin. It was first used in the 16th century for a person who used to compute, i.e. do calculations. The word was used in the same sense as a noun until the 20th century. Women were hired as human computers to carry out all forms of calculations and computations.
Generations of Computers Generation in computer terminology is a change in technology a computer is/was being used. Initially, the generation term was used to distinguish between varying hardware technologies. Nowadays, generation includes both hardware and software, which together make up an entire computer system.
The third generation computers used integrated circuits (ICs) instead of transistors. A single IC can pack huge number of transistors which increased the power of a computer and reduced the cost. The computers also became more reliable, efficient and smaller in size. These generation computers used remote processing, time-sharing, multi ...
Each generation of computer is characterized by a major technological development that fundamentally changed the way computers operate, resulting in increasingly smaller, cheaper, more powerful and more efficient and reliable devices.. The various generations of computers an listed below : (i) First Generation (1946-1954) : In 1946 there was no 'best' way of storing instructions and data ...
Functionalities of Computer. If we consider it in a very broad sense, any digital computer performs the following five operations: Step 1 − Accepts data as input. Step 2 − Saves the data/instructions in its memory and utilizes them as and when required. Step 3 − Execute the data and convert it into useful information. Step 4 − Provides ...
In these computers, primary memory was stored on the magnetic cores and magnetic tape and they used magnetic disks as secondary storage devices. Examples of the second generation computers include IBM 1620, IBM 7094, CDC 1604, CDC 3600, UNIVAC 1108. As a result, they worked on AC and therefore were faster than their predecessors.
assignment topic: generation of computer submitted to: sir attaulah submitted by: shams ullah roll no: 44 subject: computer science semester: bs 2 nd semester session: 2020-department of political science university of balochistan quetta table of content: 1: introduction 2: history of computer 3: characteristices of computer 4: generations of ...
Second generation computers were slow The third generation computer is very fast as compared to the second generation computer. Second generation were of small memory the third generation is large memory as compared to the second generation computer. Comparison of third and forth generation : Third generation Forth generation
Assignment Generations of Computer - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. The document discusses the five generations of computers from the 1940s to the 1980s. The first generation used vacuum tubes and were large, expensive, and unreliable. The second generation used transistors, making computers smaller, faster, and more reliable.
First-generation computers, which were created between the 1940s and 1950s, represented the start of the computers. These computers employed vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for storage. ... However, this problem can be reduced to graph coloring to achieve allocation and assignment. Therefore a good register allocat. 6 min read.
Functionalities of Computer. Any digital computer performs the following five operations: Step 1 − Accepts data as input. Step 2 − Saves the data/instructions in its memory and utilizes them as and when required. Step 3 − Execute the data and convert it into useful information. Step 4 − Provides the output.