- New QB365-SLMS
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject How do Organisms Reproduce Chapter Case Study Questions 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Cbse 10th standard science subject how do organisms reproduce case study questions 2021.
10th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
A newly married couple does not want have children for few years. They consulted a doctor who advised them barrier method and chemical method of birth control. Yet another couple who already have two children and are middle aged also consulted doctor for some permanent solution to avoid unwanted pregnancy. Doctor advised them surgical method of birth control. (i) What are the barrier methods of birth control?
(ii) How physical barrier prevent pregnancy? (a) They kill the sperms (b) They kill the ovum (c) They prevent sperms from meeting the ovum (d) They prevent intercourse (iii) How chemical methods prevent pregnancy? (a) Vaginal pills contain chemical called spermicides which kill the sperms (b) Oral pills prevent ovulation so there will be no fertilisation (c) Oral pills stop menstruation in females (d) Both (a) and (b) (iv) Select the correct statement regarding surgical method of birth control. (a) It involves termination of pregnancies in women particularly after eight weeks of conception (b) Small portion of sperm duct or vas deferences in males is removed by surgical operation and both cut ends are ligated properly (c) Small portion of oviducts in females is removed by surgical operation and cut ends are ligated (d) Both (b) and (c) (v) Select the correct statement regarding birth control methods. (a) Barrier method of birth control also protects the couple from sexually transmitted diseases (b) Some women experience unpleasant side effects on taking oral pills because of change in hormonal balance in body (c) Surgical method in males is called vasectomy and in females is called tubectomy (d) All of these
A married woman used a device X made of common metal for preventing pregnancy. This device was put into her uterus by some trained medical professional. Unfortunately she got pregnant after two months of insertion of device. She was in shock to learn that her birth control device has failed. (i) What is the name of birth control device used by the woman?
(ii) Which metal is commonly used for making device X?
(iii) How does device X prevent pregnancy? (a) It prevents ovulation (b) It prevents copulation (c) It suppresses fertilising capacity of sperm (d) None of these (iv) Why do you think the woman got pregnant even after using device X? (a) Device X might have got expelled without the knowledge of woman (b) Device X might be defective and was not working from the beginning (c) Device X could have been destroyed by the uterine fluid (d) None of these (v) Select the correct statement regarding device X. (a) Device X is very effective in preventing sexually transmitted diseases (b) Device X can be inserted in uterus by woman herself (c) Device X prevents menstrual cycle in women (d) Device X can cause heavy painful and longer duration periods or menstruation
X, Y and Z are sexually reproducing organisms. Fertilisation occurs either in external medium (water) or inside the body of organism. Thus two types of gametic fusion are external fertlisation and internal fertilisation. X undergoes external fertilisation whereas Y and Z undergo internal fertilisation. X and Y both release their eggs outside their body. (i) Select the option that correctly identifies organisms X, Y and Z.
(ii) Select the correct statement regarding organisms X and Y. (a) Y produces large number of eggs where X produces single egg at a time. (b) Fertilisation in case of X occurs in water but fertilisation occurs inside the body of Y. (c) X could be a reptile whereas Y could be fish or amphibian. (d) Eggs of X are covered by hard calcareous shell whereas eggs ofY are covered in jelly. (iii) Select the incorrect statement regarding organisms Y and Z. (a) Y is oviparous whereas Z is viviparous. (b) Zygote develops to complete baby in the bodies of organism Y and Z. (c) Y could be a bird or reptile whereas Z could be a mammal. (d) Both Y and Z copulate with their female counterparts to transfer sperms in their bodies. (iv) Select the correct match. (a) Eggs with calcareous shells - Parrot, King Cobra, Salmon (b) Eggs with jelly covering - Toad, Eagle, Lizard (c) Eggs without shell - Cat, Dog, Human (d) Eggs produced in large numbers at a time - Rohu, Human, Python (v) Why are eggs of animal X covered in jelly? (a) To keep the eggs moist and offer some protection from predators (b) To prevent the egg from breaking (c) To prevent fertilisation of eggs (d) All of these
Menstrual cycle is the cycle of events taking place in female reproductive organs, under the control of sex hormones, in every 28 days. At an interval of 28 days, a single egg is released from either of two ovaries. Regular menstrual cycle stopped abruptly in a married women. She got herself tested and was happy to discover that she is pregnant with her first baby. (i) Why menstruation stops in a pregnant female? (a) The egg gets fertilised so need not to be expelled out of body (b) Ovulation stops during pregnancy and so do menstruation (c) Thick uterine lining is needed for proper development of embryo, so that it is retained (d) All of these (ii) Select the correct sequence of acts that leads to pregnancy in a female. A. Fertilisation of egg B. Ovulation C. Formation of zygote D. Implantation
(iii) How is a zygote different from embryo? (a) Zygote is formed by repeated division of embryo (b) Zygote is formed by fusion of sperm and egg whereas embryo is formed by fusion of zygote with other zygote (c) Zygote is single celled but embryo is multicellular (d) Zygote is formed by fertilisation but embryo is formed without fertilisation (iv) What change takes place in the uterus of a pregnant female? (a) Uterine lining becomes thick and vascular (b) Placenta develops which links the embryo to mother through umbilical cord (c) Uterus lining containing lots of blood capillaries breaks down (d) Both (a) and (b) (v) Select the correct statement. (a) The average duration of human pregnancy is about nine months (b) The time period from fertilisation up to the birth of baby is called gestation (c) If doctor finds any anomaly in the developing fetus then he may terminate pregnancy at an early stage, known as abortion (d) All of these
X, Y and Z are three sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). X and Z are caused by bacteria whereas Y is caused by virus P. Virus P lowers the immunity of a person and leads to an incurable disease. X starts as painless sores on genitals rectum or mouth. Z causes painful urination and abnormal discharge from genitals. (i) Select the option that correctly identifies disease X, Y and Z?
(ii) Identify virus P from the given paragraph. (a) Human papilloma virus (b) Human adenovirus (c) Human immunodeficiency virus (d) Human cytomegalovirus (iii) What are the symptoms of disease Y? (a) Weight loss (b) Fever or night sweats (c) Fatigue and weakness infections (d) All of these (iv) Select the incorrect statement regarding diseases X and Y. (a) Both X and Y can spread from infected mother to unborn baby during pregnancy (b) Both X and Y can spread from infected partner to healthy partner by unprotected sex (c) Y can also spread through use of contaminated needles and blood transfusion (d) None of these. (v) How can disease Y be prevented? (a) By following polygamy and having protected sex (b) Use of sterilised needles for injecting medicines, blood tests, etc (c) Collecting blood from unknown donors without background check by blood bank professionals (d) All of these.
*****************************************
Cbse 10th standard science subject how do organisms reproduce case study questions 2021 answer keys.
(i) (d): In barrier methods of preventing pregnancy, the physical devices such as condom and diaphragm are used. Condoms are rubber tubes used by males whereas diaphragm are rubber cups used by females. (ii) (c): Physical barriers prevent the sperm from meeting the ovum by acting as a barrier between them. (iii) (d): Chemical methods of birth control include oral pills and vaginal pills. Oral pills are combination of estrogen and progesterone which prevent ovulation (release of egg during monthly cycle), so they prevent fertilisation. Vaginal pills are inserted in vagina before intercourse and release spermicides which kill sperms. (iv) (d) (v) (d)
(i) (b) : Intrauterine device is placed inside the uterus by a doctor or a trained nurse. Copper T is a common intra-uterine device. (ii) (b) iii) (c) (iv) (a): Intra-uterine devices are highly effective in preventing unwanted pregnancies. But they come with one disadvantage, that is they can get expelled anytime without the knowledge of women. Couple continue active sexual life thinking that their birth control device is still in action. (v) (d) : Intra-uterine devices do not protect against sexually transmitted diseases. Periods may become heavier, longer and more painful and there are chances of pelvic infection.
(i) (b) (ii) (b): X could be fish or amphibian whereas Y could be bird or reptile. Animals like fish or amphibian produce large number of eggs and sperms which fuse in external medium like water. Animals like birds or reptiles produce few eggs at a time. They lay fertilised eggs which are protected by outermost hard calcareous shell. (iii) (b): Development of zygote takes place outside the body of Y inside the laid egg whereas zygote develops into complete baby inside the body of female Z. (iv) (c): Cat, dog and human undergo internal fertilisation so their eggs are not covered by calcareous shell or jelly covering. (v) (a)
(i) (d) (ii) (b): First of all ovulation takes place. Then the eggs get fertilised by sperm. This leads to formation of zygote. Zygote divides to form few celled embryo which gets embedded at the proper site in the thick lining of uterus. This is called implantation. (iii) (c) : Zygote is formed by fusion of sperm and egg i.e., fertilisation. It is single celled and it gives rise to embryo by repeated cell divisions. (iv) (d): After implantation, a disc like tissue develops between thick uterine wall and embryo, called placenta. Placenta links the embryo to the mother through umbilical cord. All the requirements of the developing fetus like nutrition, respiration, excretion etc., are met from mother's body through placenta.This is because in placenta, embryo's blood vessels lie in close association with mother's blood vessels. (v) (d)
(i) (b) : X could be Syphilis, Y could be AIDS and Z could be gonorrhoea. (ii) (c): Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) cause immunodeficiency syndrome a condition characterised by progressive failure of immune system allowing life threatening conditions. (iii) (d) iv) (d) (v) (b): Sterilised needles are free from any kinds of germs.
Related 10th Standard CBSE Science Materials
10th standard cbse syllabus & materials, cbse 10th maths probability chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths statistics chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths surface areas and volumes chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths areas related to circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths some applications of trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths introduction to trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths coordinate geometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths triangles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths arithmetic progressions chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th maths quadratic equations chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th social science the making of a global world chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science nationalism in india chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science the rise of nationalism in europe chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths pair of linear equation in two variables chapter case study question with answers.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

10th Standard CBSE Study Materials

10th Standard CBSE Subjects
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Case Study Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce
Please refer to Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce Case Study Questions with answers provided below. We have provided Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science for all chapters as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS examination guidelines. These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year. Please practise these case study based Class 10 Science Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations.
Case Study Questions Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce
Case/Passage – 1
When the branches of a plant growing in the field are pulled towards the ground and a part of them is covered with moistsoil (leaving the tips of the branches exposed above the ground), then after sometime new roots develop from the parts of branches buried in the soil. On cutting these branches from the parent plant, new plants are produced from the cut parts of branches which had developed roots.
Question: Name any two plants which are grown for their flowers and propagated by this method.
Jasmine and China rose
Question: What type of branches should a plant have to be able to be propagated by this method?
Slender branches (Thin branches)
Question: What is this method of propagation of plants known as?
Layering
Question: Name one plant which gets propagated by this method naturally by forming runners (soft horizontal stems running above the ground)
LStrawberry
Question: Name any two plants which are grown for their fruits and propagated by this method.
Lemon and Guava
Case/Passage – 2
When an insect sits on the flower of a plant then some particles, present on the top of little stalks in the flower get stick to its body hair. When this insect now sits on the flower of another similar plant, then particles attached to the hair of insect are shifted to top of a flask-shaped organ at the centre of a flower. This particle grows a long tube B from the top of flask-shaped organ through which C moves down and reaches the bottom of the flask-shaped organ. Here C fuses with the nucleus of D, present in structure E. The fusion of C and D forms a new cell F which grows and develops into a seed of the plant.
Question: What are these particles? Name the process by which these particles are transfered from one flower to other flower of another similar plant.
These particles are known as pollen grains; cross pollination
Question: What is C which moves down through the tube B?
C is male gamete.pollen grains; cross pollination
Question: What is the name of tube B?
Pollen-tube
Question: What is F?
F is fertilised egg (zygote).
Question: Name D and E.
D is female gamete (ovum or egg); E is ovule
Case/Passage – 3
The male reproductive system consists of portions which produce the germ-cells and other portions that deliver the germ-cells to the site of fertilisation. The formation of germ-cells or sperms takes place in the testes. These are located outside the abdominal cavity in scrotum because sperm formation requires a lower temperature than the normal body temperature. We have discussed the role of the testes in the secretion of the hormone, testosterone, in the previous chapter. In addition to regulating the formation of sperms, testosterone brings about changes in appearance seen in boys at the time of puberty. The sperms formed are delivered through the vas deferens which unites with a tube coming from the urinary bladder. The urethra thus forms a common passage for both the sperms and urine. Along the path of the vas deferens, glands like the prostate and the seminal vesicles add their secretions so that the sperms are now in a fluid which makes their transport easier and this fluid also provides nutrition. The sperms are tiny bodies that consist of mainly genetic material and a long tail that helps them to move towards the female germ-cell.
Question: The seminiferous tubules of the testes are lined by the germinal epithelium consisting of (a) sertoli cells (b) cells of germinal epithelium (c) cells of Leydig or interstitial cells (d) secondary spermatocytes
Question: The seminiferous tubules of the testes are lined by the germinal epithelium consisting of (a) spermatids (b) cells of Sertoli (c) spermatogonium (d) spermatocytes
Question: In man, Cryptorchidism is the condition when (a) testes do not descent into the scrotum (b) there are two testes in each scrotum (c) testis degenerates in the scrotum (d) testis enlarges in the scrotum
Question: Another name for Bulbourethral gland is (a) Meibomian gland (b) Prostate gland (c) Perineal gland (d) Cowper’s gland
Question: Which of these is an accessory reproductive gland in male mammals (a) Inguinal gland (b) Prostate gland (c) Mushroom-shaped gland (d) Gastric gland
Case/Passage – 4
The male reproductive system consist of portions which produce the germ-cells and other portions that deliver the germ-cells to the site of fertilisation. Testes are located outside the abdominal cavity in scrotum because sperm formation requires a lower temperature than normal body temperature. It also has a role of secretion of male sex hormone which brings changes in appearance seen in boys at the time of puberty. Vas deferens unites wih a tube coming from urinary bladder. Urethra is a common passage for sperms and urine. Prostate gland and seminal vesicles add their secretions so that sperms are now in fluid.
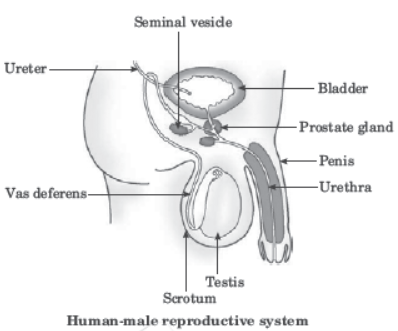
Question. Testes are located outside the abdominal cavity in scrotum because (a) sperms formation requires higher temperature than body temperature (b) sperms formation requires lower temperature than body temperature (c) it is easier to transport sperms from the scrotum (d) None of these
Question. Which of the following statement is incorrect? (a) Sperms and urine has a common passage from urethra. (b) Sperms have long tail that helps them to move forward. (c) Sperms contain genetic material. (d) Sperms formation requires 1–3°C higher temperature than normal body temperature.
Question. What is the nature of semen? (a) slightly acidic (b) Neutral (c) Slightly basic (d) Strongly basic
Question. Name the sex hormone associated with males. (a) Testosterone (b) Progesterone (c) Oestrogen (d) None of these
Question. Which of the following statements is incorrect ? (a) Sperms are present in a fluid (b) Fluid provides nutrition to sperms (c) Fluid makes easier transportation of sperms (d) Fluid helps to bind the sperms together
Case/Passage – 5
Study the table related to sex ratio of females/1000 males in different states and answer the questions that follow:
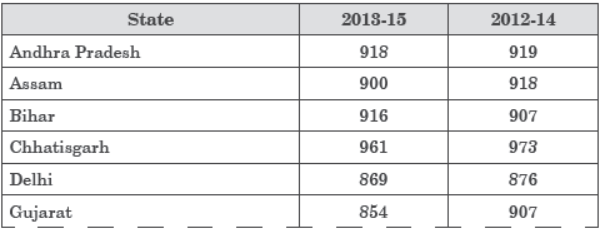
Question. Which test is responsible for female foeticide? (a) UV-Spectroscopy (b) Ultrasound (c) MRI (d) X-Ray
Question. Which state of India has lowest sex ratio in 2013-15? (a) Punjab (b) Odisha (c) Haryana (d) Delhi
Question. Which of the following state improves sex ratio in 2013-15 from 2012-14? (a) Delhi (b) Karnataka (c) Bihar (d) Kerala
Question. Name the state which has males to female ratio to maximum extent in 2013-15. (a) Haryana (b) Kerala (c) West Bengal (d) Uttar Pradesh
Question. What is major cause of less females than males in India? (a) Male Foeticide (b) Female Foeticide (c) Natural (d) None of these
Class 10 Science How Do The Organism… Exam Questions
Question. List four categories of contraceptive methods. State in brief two advantages of adopting such preventive methods. Answer : Four categories of contraceptive methods are: a. Barrier method (Condoms) b. Surgical method (Vasectomy in males and Tubectomy in females) c. Withdrawal method d. Calendar method e. Hormonal method f. IUCD/Copper-T/Loop (any four) Two advantages: a. Helps in maintaining health of women. b. Helps in preventing STDs especially AIDS. c. Helps in birth control.
Question. List any two modes of asexual reproduction. Under which mode of reproduction is vegetative propagation placed and why? List two advantages of vegetative propagation. Answer : Two modes of asexual reproduction are fission Regeneration Vegetative propagation is placed under asexual reproduction as reproduction happens from any part of a plant. It may be either leaf, shoot or root. Advantages are: a. The plants bear flowers and fruits earlier than those propagated sexually. b. Plants have lost capacity to form seeds hence they are propagated vegetatively.
Question. Study the diagram given below: (Image 94) a. Identify the process. b. Which organism uses the above method of reproduction? c. How is the above method different from the process of fragmentation? or In context of reproduction of species, state the main difference between fission and fragmentation. Also give one example of each. Answer : a. Binary fission. b. Amoeba. c. Binary fission occurs in unicellular organisms only. In fragmentation the body of a simple multicellular organism breaks down into many ‘fragments’. All cells undergo division and the organism develops from each fragment.
Question. a. Identify the asexual method of reproduction in each of the following organisms: (i) Rose (ii) Yeast (iii) Planaria b. What is fragmentation? Name a multicellular organism which reproduces by this method. Answer : a. (i) Vegetative propagation by stem. (ii) Budding (iii) Regeneration b. Fragmentation is a asexual method of reproduction in which an organism simply breaks up into smaller pieces/ fragments upon maturation. These pieces or fragments grow into new individuals. Spirogyra is the multicellular organism with relatively simple body organisation which reproduces through this simple method of reproduction, i.e., fragmentation.
Question. a. Give one example each of sexually transmitted diseases in each of following cases (i) Bacterial infections (ii) Viral infections b. How can spread of these diseases be prevented? or Name one sexually transmitted disease each caused due to bacterial infection and viral infection. How can they be prevented? Answer : a. Bacterial infections: Syphilis, Gonorrhoea. Viral infections: Warts, AIDS, Hepatitis B, Herpes. b. Spread of these diseases can be prevented by using physical barrier, avoiding sex with multiple partners.
Question. DNA content has the tendency to double itself during sexual reproduction due to combining of the genetic materials from the two parents. How the problem of DNA doubling can be solved to maintain the consistency of the genetic material throughout the species? or “The chromosome number of the sexually reproducing parents and their offsprings is the same”. Justify the statement. Answer : DNA doubling is always followed by cell division. Due to this special cell division, gametes form with half the content of DNA and single set of chromosomes. These gamete fuse to form zygote on fertilization. Thus the characteristic number of chromosome and the normal DNA content for a cell is regained. Thus the consistency of the genetic material throughout the species is maintained and for the same reason the chromosome number of the sexually reproducing parents and their offsprings is the same.
Question. Explain the structure of the female reproductive system of humans. Answer : Female Reproductive System consists of ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina. a. Ovaries are located inside the abdominal cavity, near the kidney. It performs two functions: • Produce female germ – cells/eggs. Every month one egg is produced • Secrete hormones like Estrogens which stimulate the development of secondary sexual characteristics at puberty. b. Fallopian Tubes carry the egg from ovary to the womb; egg gets fertilized in the oviducts only if it meets a sperm. c. Uterus is a elastic bag like structure. The fertilized egg, the zygote gets implanted in the fining of uterus and develops into an embiyo. d. Vagina (Birth Canal) receives the sperms as well as child is borne through it.
Question. Give the functions of the following in the process of reproduction: a. Pollen tube. b. ovary, c. Stigma. Answer : a. Pollen tube carries male gamete from stigma to ovule. b. Ovary has ovule and forms fruit to protect and dispersal of seeds c. Stigma receives pollen during pollination.
Question. Justify the following statements: a. Variation is beneficial for the species over a period of time. b. New offsprings produced are similar to their parents but not identical. c. Binary fission is different in Amoeba and Leishmania. Answer : a. Variations help a population in the process of natural selection and accumulation of adaptations in a population. It leads to evolution of a species. b. Offspring, especially when produced sexually, have minor differences or variations among themselves hence they may not look identical. By virtue of them being from same species they look similar. c. Binary fission in Amoeba is in any plane but in Leishmania it is in a fixed plane.
Question. a. Give the functions of: (i) Stigma (ii) Ovary b. State in brief the formation of seed in a flower. Answer : a. (i) The sticky terminal part of the carpel is called stigma. It receives pollen. (ii) The swollen bottom part of the carpel is called ovary. It contains female germ cells which form seed after fertilization. b. After fertilization, the zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule. The ovule develops a tough coat and is gradually converted into a seed.
Question. In the diagram of human male reproductive system given below:
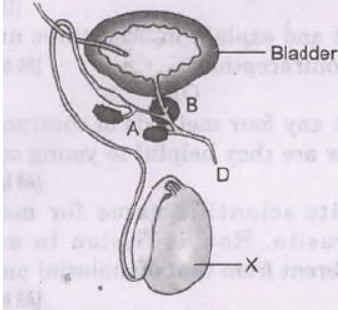
a. Label parts A and B. b. Name the hormone produced by organ “X’. What is the role of this hormone in human male? c. Mention the name of substances that are transported by tubes (i) C and (ii) D. Answer : a. A – seminal vesicle, B – prostate gland. b. Testosterone: It controls gamete formation/ secondary sex organs/ accessory glands. c. C – sperms, D – sperms/semen and urine.
Question. What happens when: a. APlanaria is cut into three different pieces, b. Leaf of the Bryophyllum with notches fall on the soil. c. Testosterone is released in the male reproductive system. Answer : a. Three new Planaria will form due to regeneration. b. New plantlets will form from these buds helping the plant to propagate vegetatively. c. The male shows masculine features and attains fertility. Sperm starts forming in testis.
Question. What is vegetative propagation? List two advantages and two disadvantages of vegetative propagation. Answer : Method of producing new plants from vegetative parts like roots, stem and leaves is called vegetative propagation. Advantages are: a. The plants bear flowers and fruits earlier than those propagated sexually. b. Plants have lost capacity to form seeds hence they are propagated vegetatively. Disadvantages are: a. Such plants are genetically similar to parent plants and are vulnerable to infections and diseases. b. They do not have variations therefore do not adapt well to changing environment, the plant species does not evolve.
Question. List three techniques to prevent pregnancy. Which of them is not meant for males? How does the use of such techniques have an impact on health and prosperity of a family? or List any four methods of contraception used by humans. How does their use have a direct effect on the health and prosperity of a family? Answer : Three techniques to prevent pregnancy: a. Mechanical barrier — male or female. b. Taking oral pills/i-pill/saheli – changing the hormonal balance of the body so that eggs are not released. c. Use of the loop or the Copper-T. d. Surgical method – tubectomy / vasectomy Use of hormonal preparations is not meant for males. Effect on Health and Prosperity: a. Health of women is maintained b. Parents can give more attention to children c. More resources can be made available.
Question. What is the effect of DNA copying, which is not perfectly ccurate, on the reproduction process? How does the amount of DNA remain constant though each new generation is a combination of DNA copies of two individuals? Answer : a. DNA copying leads to more variations in the offspring. b. Sexually reproducing organisms have special lineage of cells which have only half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. c. When such germ cells fused, a new individual is formed with the same amount of DNA as that of parent.
Question. Differentiate between the following: a. Placenta and uterus b. Unisexual and bisexual flowers c. Fertilization and germination Answer : a. Placenta and uterus : The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called placenta. After fertilization, embryo gets attached to the walls of uterus. b. Unisexual flowers contain either stamens or carpels. Bisexual flowers contain both stamens and carpels. c. Fertilization and germination : The fusion of male gamete with female gamete leading to the formation of zygote is known as fertilization. The growth of embryo (present in the seed) into seedling under appropriate conditions is known as germination.
Question. A part of the male reproductive system is shown below. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
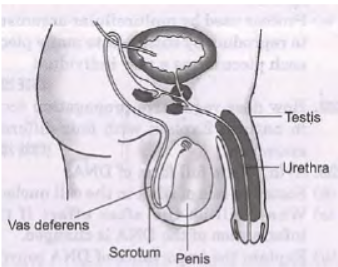
a. Two part have been incorrectly labelled. Identify them. b. Give the function of urethra. c. Which hormone is released by testis? Answer : a. Testis, penis. b. Urethra serves as a common passage for both sperms and urine. c. Testosterone.
Question. List six specific characteristics of sexual reproduction. Answer : C haracteristics of sexual reproduction: a. Two parents are involved. b. Two dissimilar gametes are formed by meiosis. c. Variations are produced. d. Occurs in all the higher and some of the lower organisms. e. Fertilization / fusion of gametes leading to zygote formation.
Question. List four points of significance of reproductive health in a society. Name any two areas related to reproductive health which have improved over the past 50 years in our country. Answer : Significance: a. Prevent STDs. b. Advantage of small family. c. Less mortality among new-borns. d. Reduces the cases of maternal mortality. Areas which have improved: a. Family Planning. b. Decrease in STD cases.
Question. Mention one function each of the following parts with respect to the female reproductive system: a. Vagina b. Ovary Answer : a. The uterus open into vagina through the cervix. The sperms enter through the vaginal passage during sexual intercourse. b. One egg (female gamete) is produced every month by one of the ovaries.
Question. List and explain in brief three methods of contraception. or List any four methods of contraception. How are they helpful to young couples? Answer : Four methods of contraception: a. Condoms b. Copper-T c. Diaphragm d. Oral pills All these help in family planning as it helps in keeping gap between two children. They help in proper utilization of family resources.
Question. Write scientific name for malarial parasite. How is fission in amoeba different from that of malarial parasite? Answer : a. Plasmodium, b. Fission in amoeba produces two daughter cells – binary fission. Fission in Plasmodium produce many daughter cells – multiple fission,
Question. a. Give the functions of the following: 1. Pollen tube 2. Ovary b. List any two changes observed in the body of a female during puberty. Answer : a. (i) Transfer of male gamete. (ii) Production of female gamete. b. (i) Growth of mammary glands. (ii) Onset of menstrual cycle.
Question. What is meant by DNA copying? Mention its importance in reproduction. Answer : Cells use chemical reactions to build copies of their DNA. This creates two copies of the DNA in a reproducing cell. DNA copying is accompanied by the creation of an additional cellular apparatus to facilitate the DNA copies to separate with its own cellular apparatus. DNA copying gives rise to some inbuilt tendency for variation during reproduction which is the basis for evolution.
Question. a. What are sexually transmitted diseases? Name any one which is caused by bacteria and one caused by viral infection. b. Mention any two methods to avoid such diseases. Answer : a. Diseases that spread through the sexual contact are called sexually transmitted diseases. (i) Gonorrhoea or syphilis is caused by bacteria. (ii) Warts, HTV, AIDS is caused by virus. b. (i) Use of condoms on penis.
(ii) Use covering on vagina.
Question. a. How do organisms reproduced by fission? b. Write names of any two organisms which reproduce by this method. c. Differentiate between the fission of Leishmania and Plasmodium. Answer : a. Cell division takes place which leads to creation of new individuals. b. Bacteria, Protozoa. c. Leishmania — binary fission occurs in a definite orientation. Plasmodium — undergoes multiple fission,
Question. Give reasons: a. Wind acts as a pollinating agent. b. Variation is essential and beneficial to a species. c. Use of condoms prevents pregnancy. Answer : a. Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma. b. Helps in evolution and survival. c. Prevents fertilization – Barrier method.
Question. What are secondary sexual characters in humans? Name one such character of male and female. Answer : The characters which distinguish a male from female are called secondary sexual characters. Secondary sexual characters of male are moustache, beard, thick growth of hair on body, strong muscles and harsh voice. Secondary sexual characters of female are less hair on body, broad hips, development of breasts and soft voice.
Question. Name and explain the method by which Rhizopus reproduces. Answer : Rhizopus reproduces by spore formation. Method: It is a method of asexual reproduction.
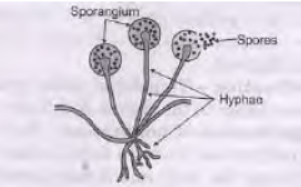
Spores are produced in a structure called sporangium.
Long Answer Questions
Question. Name the type of asexual reproduction demonstrated by the following organisms: a. Amoeba b. Rhizopus c. Planaria d. Plasmodium e. Bryophyllum Answer : a. Binary fission b. Spore formation c. Fragmentation d. Multiple fission e. Vegetative propagation
Question. Answer the following: a. How is zygote formed? b. State the function of placenta in the mother’s body. c. At what interval the egg is formed in human female ovary? d. Name two STDs caused by bacterial infection. e. Why is prenatal sex determination prohibited? Answer : a. Zygote is formed by the fusion of male and female gamete. b. Placenta is a special tissue through which the developing embryo/foetus gets nutrition from mother’s blood. It also transports wastes of the embryo into mother’s blood. c. Ovulation releases mature ovum from ‘ the ovary. It happens once during a menstrual cycle that is for roughly 28 days. d. STDs caused by bacterial infection are Gonorrhoea and Syphilis. e. Prenatal sex determination is misused and it may be the reason for female foeticide.
Question. How does vegetative propagation occur in nature? Explain with four different examples. Answer : There are many plants in which parts like the root, stem and leaves develop into new plants under appropriate conditions. This is called as vegetative propagation. Examples of vegetative propagation: a. Adventitious buds: In Bryophyllum, adventitious buds grow in the notches along the leaf margin, which when fall on the soil, develop into new plants. b. Cutting: A piece of stem, root, leaf or even a bulb scale is placed partly under moist soil which grows into a new plant, e.g., rose. c. Layering: A part of the stem is pulled out and buried in the soil. The layered stem grows into a new plant, e.g., Pudina. d. Grafting: In grafting, two parts from two different plants are joined together so that they can unite and grow into a new plant, e.g., sugarcane.
Question. a. (i) Write full form of DNA. (ii) State the role of DNA in the cell nucleus, (iii) What will be the after effect if the information of the DNA is changed. b. Explain the importance of DNA copying in reproduction. Answer : a. (i) Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid. (ii) Informational source for making proteins. (iii) Proteins will be changed. b. Its only due to DNA copying that body designs are similar because DNA cell nucleus carries information for making proteins if DNA copying will not take place then body design will change.
Question. a. Identify A,B,C and D in the given diagram and write their names.
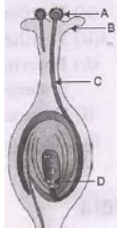
b. What is pollination? Explain its significance. c. Explain the process of fertilization in flowers. Name the parts of flower that develop after fertilization into (i) seed (ii) fruit Answer : a. A – pollen grain; B – stigma; C – Pollen tube, D – Female germ cell/Egg cell. b. Pollination – Transfer of pollen grains from anther to the stigma of a flower. Significance of pollination – Process of pollination leads to fertilization as it brings the male and female gametes together for fusion. c. After a pollen falls on a suitable stigma, the pollen tube grows out of the pollen grain and travels through the style to reach the ovule in the ovary. Here the male germ cell (carried by the pollen tube) fuses with the female germ cell to form a zygote.
Question. Define the following processes: a. Fertilization b. Menstruation c. Binary fission d. Vegetative propagation e. Regeneration Answer : a. The fusion of male gamete with female gamete is known as fertilization. b. Menstruation cycle takes place every month when egg is not fertilized. It lasts for about two to eight days and during this cycle the lining of uterus slowly breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucus. c. Binary fission is the splitting of nucleus into two daughter cells which can take place in any plane. It can be observed in Amoeba. d. When vegetative part of a plant like the root, stem or leaves develops into new plant under appropriate conditions, it is known as vegetative propagation. e. When body of an organism cuts into any number of pieces and each piece grows into a complete organism. This is known as regeneration. Hydra and Planaria reproduce through this process.
Question. a. Write the function of following parts in human female reproductive system: (i) Ovary (ii) Oviduct (iii) Uterus b. Describe in brief the structure and function of placenta. or Write the functions of the following in human female reproductive system: Ovary, oviduct, uterus How does the embryo get nourishment inside the mother’s body? Explain in brief. Answer : a. Functions of Ovary, oviduct, uterus Functions of Ovary (i) Production of female hormone, oestrogen and progesterone. (ii) Production of female gamete / egg /germ cell. Functions of Oviduct: (i) Transfer of female gamete from the ovary. (ii) Site of fertilization. Functions of Uterus: (i) Implantation of Zygote/ embryo. (ii) Nourishment of developing embryo. b. Placenta is a special disc like tissue embedded in the mother’s uterine wall and connected to the foetus / embryo. Placenta provides a large surface area for glucose and oxygen/nutrients to pass from the mother’s blood to the embryo/ foetus.
Question. Differentiate between: a. Pollen tube and Style b. Fission of Amoeba and Plasmodium c. Fragmentation and regeneration d. Bud of Hydra and bud of Bryophyllum e. Vegetative propagation and spore formation. Answer : a. Pollen tube forms and male gametes are carried by it to the ovule. Style is part of female part- carpel through which pollen tube passes. b. Amoeba shows binary fission where one cell splits into two equal halves. Plasmodium (malarial parasite) shows multiple fission where one cell divides into many daughter cells simultaneously. c. Fragmentation occurs in multi-cellular organisms with simple body organisation like Spirogyra (a filamentous alga). It involves breaking up of a filament into many fragments and each fragment growing into new individual. Regeneration is the ability to give rise to new individuals from the body parts of the parent individual, e.g., Hydra and Planaria, if their bodies get broken into many pieces, each piece is capable of regrowing into a complete individual. d. In Hydra, a bud is formed at a specific site by repeated cell division and develops into a tiny hydra. In Bryophyllum, vegetative buds arise from the notches of its leaves and develops into a new plantlet. e. Vegetative Propagation is the development of new plants from parts like root, leaf and stem under suitable conditions, e.g., Bryophyllum vegetative buds arise from the notches of its leaves. In potato, ginger, garlic etc. it occurs through stems. Spore formation: A spore is a special cell protected by thick coating. It is capable of germinating into a new plant when comes in contact with suitable and environment conditions and moist surface, e.g., in Rhizopus (bread mould), they are formed inside reproductive, bob¬like sacs called sporangia.
Question. What happens when a. Testosterone is released in the male reproductive system. b. Pollen grain falls on the stigma of flower. c. Egg fuses with the sperm cell. d. A Planaria is cut into three different pieces. e. Buds are formed on the notches of leaf of the Bryophyllum. Answer : a. The male shows masculine features and attains fertility/ sperm starts forming in testis. b. Pollen tube forms and male gametes are carried by it to the ovule. c. Fertilization occurs and a zygote forms. d. Three new Planaria will form due to regeneration. e. New plantlets will form from these buds helping the plant to propagate vegetatively.
Question. Explain what happens when: a. Testosterone is released in males. b. Pollen grain falls on the stigma of the flower. c. Egg fuses with sperm cell. d. Planaria is cut into many pieces. e. Buds are formed on the notches of the Bryophyllum leaf. Answer : a. (i) Formation of sperms, change in appearance. (ii) Thick hair growth on the face and voice begin to crack. b. A tube grows out of the pollen grain and travel through the style to reach the ovary. c. Zygote is formed (fertilization). d. Each piece grows into a complete organism. e. Buds may fall on the soil and develop into new plants.
Question. a. Identify the organisms A, B and the mode of asexual reproduction exhibited by them.
b. How will an organism be benefitted if it reproduces through spores? c. Mention the two asexual methods by which hydra can reproduce. Explain briefly any one such method. Answer : a. (i) Bryophyllum – vegetative propagation. (ii) Plasmodium – multiple fission. b. Spores are covered with thick walls that protect them until they come into contact with a moist surface. c. Budding and Regeneration. Budding : A bud develops as an outgrowth due to repeated cell division at a specific site, these buds develop into tiny individuals, mature and detach from the parent to become new individuals. Regeneration: Specialized cells divide to form large number of cells and undergo changes to become various cell types and tissues.
Question. a. Identify the organisms in figure A, B, C and D.
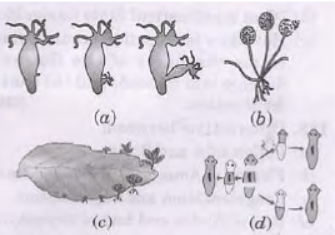
b. Identify the life process commonly shown in all the figures, c. How is this life process .advantageous to the organisms? Mention any two advantages. Answer : a. (A) Hydra (B) Rhizopus (C) Bryophyllum (D) Planaria b. Asexual mode of reproduction c. (i) Only one individual is required. (ii) Progeny is identical like parents (iii) Produced in large number (Any two)
Question. a. Draw a diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower and label on it sepals, petal, ovary and stigma. b. Write the names of male and female parts of a flower. Answer :
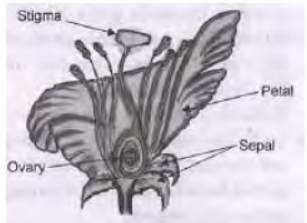
b. Male Part : Stamen; Female Part : Carpel/pistil
Question. a. List two reasons for the appearance of variations among the progeny formed by sexual reproduction.
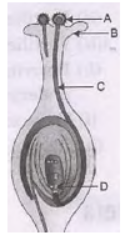
b. (i) Name the part marked A in the diagram. (ii) How does “A” reaches part B? (iii) State the importance of , the part C. (iv) What happens to the part marked D after fertilization is over? Answer : a. Sexual reproduction confers new characteristics on the offspring due to genetic recombination occurring during gamete formation in the sex organs. Moreover it involves union of two gametes coming from two parents which different genetic combination. Thus it ensures more diversity in characteristics. b. (i) Pollen (ii) Pollination (iii) Pollen tube carries male gametes to the ovule in ovary. (iv) Ovule turns into seeds.
Question. Identify the following methods and giving one example of each: a. Process in which reproduction takes place by breaking up of parent into fragments. b. Process of dividing of organisms into many cells simultaneously. c. Process of reproduction by formation of bud on parent body. d. Process of reproduction by formation of spores. e. Process used by multicellular organisms to reproduce by cutting into many pieces each piece forms a new individual. Answer : a. Fragmentation, Spirogyra b. Multiple fission, Plasmodium c. Budding, Hydra d. Spore formation, Rhizopus e. Regeneration, Planaria.
Question. a. Draw a sectional view of human female reproductive system and label the part where: (i) Eggs develop (ii) Fertilization takes place (iii) Fertilized eggs get implanted. b. Describe in brief, the changes the uterus undergoes: (i) To receive the zygote (ii) If zygote is not formed. Answer : a.
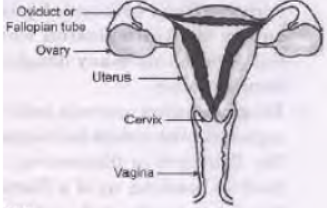
(i) Ovary (ii) Oviduct or fallopian tube (iii) Uterus or uterus wall b. (i) It becomes thicker due to development of blood vessels and glands in it. (ii) It gets peeled and shed off along with mucus, blood, dead ovum during menstruation
Question. List five distinguishing features between sexual and asexual types of reproductions in tabular form. Answer :
Question. a. Name the human male reproductive organ that produces sperms and also secretes a hormone. Write the functions of the secreted hormone. b. Name the parts of the human female reproductive system where (i) Fertilization takes place, (ii) Implantation of the fertilized egg occurs. Explain how the embryo gets nourishment inside the mother’s body. Answer : a Testis – secrete male hormone – testosterone. Functions : (i) Formation of sperms, (ii) Development of secondary sexual characters. b. (i) fallopian tube/oviduct. (ii) uterus.
Placenta is a special disc like tissue embedded in the mother’s uterine wall and connected to the foetus/embryo. Placenta provides a large surface area for glucose and oxygen/ nutrients to pass from the mother’s blood to the embryo/ foetus.


Related Posts

The Bangle Sellers Summary by Sarojini Naidu

Old Man at the Bridge Summary by Ernest Miller Hemingway

Case Study Chapter 2 Acids Bases Salts

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- Toppers Notes
- Most Repeated Question
- Diagram Based Question
- Study Planner
- Competency Based Questions
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- JEE Toppers Notes
- JEE Formula
- JEE Important Question
- JEE Mind Map
- JEE Integer-Numerical Type Question
- JEE Study Planner
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- BCECE Previous Year Paper
- JCECE Previous Year Paper
- LPU Mock Test
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- NEET Toppers Notes
- NEET Formula
- NEET Important Question
- NEET Assertion Reason Question
- NEET Study Planner
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Important Question
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- MBA General Knowledge
- CAT Mind Map
- CAT Study Planner
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions Class 10
Students who are studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to get the knowledge about the How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions. Case based questions are generally based on the seen passages from the chapter How Do Organisms Reproduce. Through solving the case based questions, students can understand each and every concept.
With the help of How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions, students don’t need to memorise each answer. As answers for these case studies are already available in the given passage. Questions are asked through MCQs so student’s won’t take time to mark the answers. These multiple choice questions can help students to score the weightage of How Do Organisms Reproduce.
How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions with Solutions
Selfstudys provides case studies for the Class 10 Science chapter How Do Organisms Reproduce with solutions. The Solutions can be helpful for students to refer to if there is a doubt in any of the case studies problems. The solutions from the Selfstudys website are easily accessible and free of cost to download. This accessibility can help students to download case studies from anywhere with the help of the Internet.
How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions with solutions are in the form of PDF. Portable Document Format (PDF) can be downloaded through any of the devices: smart phone, laptop. Through this accessibility, students don't need to carry those case based questions everywhere.
Features of How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions
Before solving questions, students should understand the basic details of How Do Organisms Reproduce. Here are the features of case based questions on How Do Organisms Reproduce are:
- These case based questions start with short or long passages. In these passages some concepts included in the chapter can be explained.
- After reading the passage, students need to answer the given questions. These questions are asked in the Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ).
- These case based questions are a type of open book test. These case based questions can help students to score well in the particular subject.
- These How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions can also be asked in the form of CBSE Assertion and Reason .
Benefits of Solving How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions
According to the CBSE board, some part of the questions are asked in the board exam question papers according to the case studies. As some benefits of solving How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions can be obtained by the students. Those benefits are:
- Through solving case studies students will be able to understand every concept included in the chapter How Do Organisms Reproduce
- Passages included in the case study are seen passages, so students don’t need to struggle for getting answers. As these questions and answers can be discussed by their concerned teacher.
- Through these students can develop their observation skills. This skill can help students to study further concepts clearly.
- Case studies covers all the concepts which are included in the How Do Organisms Reproduce
How to Download How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Based Questions?
Students studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to solve questions based on case study. It is necessary for students to know the basic idea of How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions. Students can obtain the basic idea of case based questions through Selfstudys website. Easy steps to download it are:
- Open Selfstudys website.
- Bring the arrow towards CBSE which is visible in the navigation bar.
- A pop-up menu will appear, Select case study from the list.
- New page will appear, select 10 from the list of classes.
- Select Science from the subject list.
- And in the new page, you can access the How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions.
Tips to solve How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Questions-
Students should follow some basic tips to solve How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions. These tips can help students to score good marks in CBSE Class 10 Science.
- Generally, the case based questions are in the form of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
- Students should start solving the case based questions through reading the given passage.
- Identify the questions and give the answers according to the case given.
- Read the passage again, so that you can easily answer the complex questions.
- Answer according to the options given below the questions provided in the How Do Organisms Reproduce Case Study Based Questions.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.


IMAGES
VIDEO