JS Tutorial
Js versions, js functions, js html dom, js browser bom, js web apis, js vs jquery, js graphics, js examples, js references, javascript destructuring, destructuring assignment syntax.
The destructuring assignment syntax unpack object properties into variables:
It can also unpack arrays and any other iterables:

Object Destructuring
The order of the properties does not matter:
Destructuring is not destructive.
Destructuring does not change the original object.
Object Default Values
For potentially missing properties we can set default values:
Object Property Alias
String destructuring.
One use for destructuring is unpacking string characters.
Destructuring can be used with any iterables.
Advertisement
Array Destructuring
We can pick up array variables into our own variables:
Skipping Array Values
We can skip array values using two or more commas:
Array Position Values
We can pick up values from specific index locations of an array:
The Rest Property
You can end a destructuring syntax with a rest property.
This syntax will store all remaining values into a new array:
Destructuring Maps
Swapping javascript variables.
You can swap the values of two variables using a destructuring assignment:

COLOR PICKER

Contact Sales
If you want to use W3Schools services as an educational institution, team or enterprise, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Top Tutorials
Top references, top examples, get certified.
- JS Tutorial
- JS Exercise
- JS Interview Questions
- JS Operator
- JS Projects
- JS Examples
- JS Free JS Course
- JS A to Z Guide
- JS Formatter
JavaScript Object assign() Method
The Object.assign() method is used to copy the values and properties from one or more source objects to a target object. It invokes getters and setters since it uses both [[Get]] on the source and [[Set]] on the target.
Parameters:
- target : It is the target object to which values and properties have to be copied.
- sources : It is the source object from which values and properties have to be copied.
Return Value:
Object.assign() returns the target object.
Example 1: In this example, the properties of the object “obj1” i.e. { a: 10 } is copied to the target object “new_obj”.
Output:
Example 2: In this example, the properties of three source objects “obj1, obj2, obj3” are copied to the target object “new_obj”. The value of any pre-existing key-value pair that existed in the previous object will be over-written. For example, obj1.b which has a value of 10 will now be overwritten with obj2.b which has a value of 20
Output :
Example 3: In this example, the properties of three source objects “obj1, obj2, obj3” are copied to the target object “new_obj” and the target object gets the overwritten values.
Explanation:
In the above code the properties are overwritten by other objects that have the same properties later in the same order of parameters.
Applications:
- Object.assign() is used for cloning an object, to merge objects with the same properties.
Errors and Exceptions :
- A TypeError is raised if the property is non-writable.
- The target object can be changed only if the properties are added before the error is raised.
- Object.assign() does not throw on null or undefined source values
We have a complete list of JavaScript Object methods, to check those please go through this JavaScript Object Complete Reference article.
Supported Browsers:
- Google Chrome
JavaScript Object assign() Method- FAQs
How does the assign() method work.
The assign() method copies the properties of one or more source objects into a target object. Properties in the target object are overwritten by properties in the source objects if they have the same key.
Does the assign() method modify the target object?
Yes, the assign() method modifies the target object. It copies properties from the source objects directly into the target object.
How does Object.assign() handle properties that are not enumerable?
Object.assign() only copies enumerable properties from source objects to the target object. Non-enumerable properties are ignored.
How does the assign() method handle null or undefined source objects?
If a source object is null or undefined , it is ignored and skipped during the property copying process. No properties are copied from null or undefined sources.
What are some common use cases for the assign() method?
Common use cases for the assign() method include: Merging multiple objects into one. Cloning an object (shallow copy). Adding properties to an existing object. Combining default settings with user-defined settings.
Similar Reads
- Web Technologies
- JavaScript-Methods
- javascript-object
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
JavaScript Object Destructuring, Spread Syntax, and the Rest Parameter – A Practical Guide

In JavaScript, we use objects to store multiple values as a complex data structure. There are hardly any JavaScript applications that do not deal with objects.
Web developers commonly extract values from an object property to use further in programming logic. With ES6, JavaScript introduced object destructuring to make it easy to create variables from an object's properties.
In this article, we will learn about object destructuring by going through many practical examples. We will also learn how to use the spread syntax and the rest parameter . I hope you enjoy it.
Object Destructuring in JavaScript
We create objects with curly braces {…} and a list of properties. A property is a key-value pair where the key must be a string or a symbol, and the value can be of any type, including another object.
Here we have created a user object with three properties: name, address, and age. The real need in programming is to extract these property values and assign them to a variable.
For example, if we want to get the value of the name and age properties from the user object, we can do this:
This is undoubtedly a bit more typing. We have to explicitly mention the name and age property with the user object in dot(.) notation, then declare variables accordingly and assign them.
We can simplify this process using the new object destructuring syntax introduced in ES6.
JavaScript Object Destructuring is the syntax for extracting values from an object property and assigning them to a variable. The destructuring is also possible for JavaScript Arrays.
By default, the object key name becomes the variable that holds the respective value. So no extra code is required to create another variable for value assignment. Let's see how this works with examples.
Basic Object Destructuring Example
Let's take the same user object that we referred to above.
The expression to extract the name property value using object destructuring is the following:
As you see, on the left side of the expression, we pick the object property key ( name in this case) and place it inside the {} . It also becomes the variable name to hold the property value.
The right side of the expression is the actual object that extracts the value. We also mention the keywords, const , let and so on to specify the variable's scope.
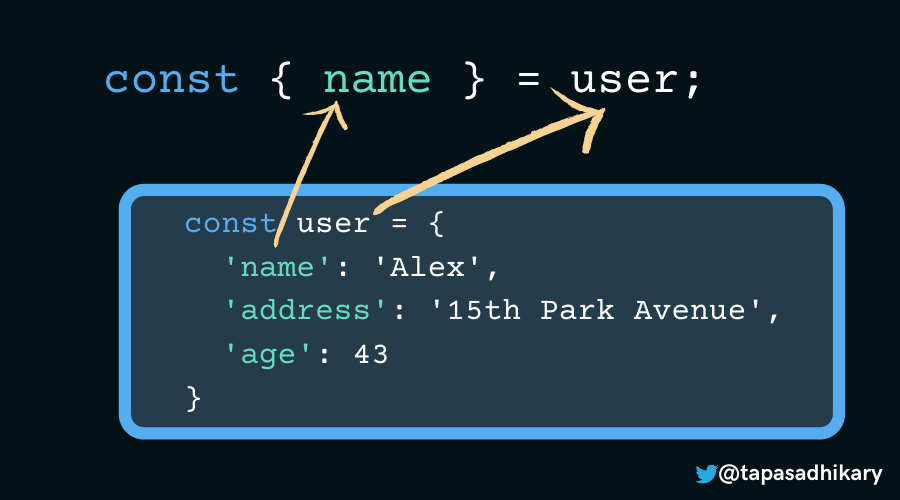
So, how do we extract values from more than one object property? Simple – we keep adding the object keys inside the {} with commas separating them. In the example below, we destructure both the name and age properties from the user object.
Variable Declaration Rule
The keywords let and const are significant in object destructuring syntax. Consider the example below where we have omitted the let or const keyword. It will end up in the error, Uncaught SyntaxError: Unexpected token '=' .
What if we declare the variable in advance and then try to destructure the same name's key from the object? Nope, not much luck here either. It is still syntactically incorrect.
In this case, the correct syntax is to put the destructuring expression inside parenthesis ( (...) ).
Please note that the parenthesis are required when you want to omit the let or const keyword in the destructuring expression itself.

Add a New Variable & Default Value
We can add a new variable while destructuring and add a default value to it. In the example below, the salary variable is non-existent in the user object. But we can add it in the destructuring expression and add a default value to it.
The alternative way to do the above is this:
There is a considerable advantage to the flexibility of adding a variable with a default value. The default value of this new variable is not necessarily going to be any constant value always. We can compute the value of it from other destructured property values.
Let's take a user object with two properties, first_name and last_name . We can now compute the value of a non-existent full_name using these two properties.
Isn't that elegant and useful!
Add Aliases
You can give an alias name to your destructured variables. It comes in very handy if you want to reduce the chances of variable name conflicts.
In the example below, we have specified an alias name for the property address as permanentAddress .
Please note, an attempt to access the variable address here will result in this error:
Nested Object Destructuring
An object can be nested. This means that the value of an object property can be another object, and so on.
Let's consider the user object below. It has a property called department with the value as another object. But let's not stop here! The department has a property with the key address whose value is another object. Quite a real-life scenario, isn't it?
How do we extract the value of the department property? Ok, it should be straight-forward by now.
And here's the output when you log department :

But, let's go one more nested level down. How do we extract the value of the address property of the department ? Now, this may sound a bit tricky. However, if you apply the same object destructuring principles, you'll see that it's similar.
Here's the output when you log address :

In this case, department is the key we focus on and we destructure the address value from it. Notice the {} around the keys you want to destructure.
Now it's time to take it to the next level. How do we extract the value of city from the department's address? Same principle again!
The output when you log city is "Bangalore".
It can go any level nested down.
The rule of thumb is to start with the top-level and go down in the hierarchy until you reach the value you want to extract.
Dynamic Name Property
Many times you may not know the property name (key) of an object while destructuring it. Consider this example. We have a user object:
Now the method getValue(key) takes a property key name and should return the value of it.
So, how do we write the definition of the getValue(key) method using the destructuring syntax?
Well, the syntax is very much the same as creating aliases. As we don't know the key name to hard-code in the destructuring syntax, we have to enclose it with square brackets ( [...] ).
Destructure to the Function Parameter
This one is my favorites, and it practically reduces lots of unnecessary code. You may want just a couple of specific property values to pass as a parameter to the function definition, not the entire object. Use object destructuring to function parameter in this case.
Let's take the user object example once again.
Suppose we need a function to return a string using the user's name and age. Say something like Alex is 43 year(s) old! is the return value when we call this:
We can simply use destructuring here to pass the name and age values, respectively, to the function definition. There is no need to pass the entire user object and then extract the values from it one by one. Please have a look:
Destructure Function Return Value
When a function returns an object and you are interested in specific property values, use destructuring straight away. Here is an example:
It is similar to the basic object destructuring we saw in the beginning.
Destructure in Loops
You can use object destructuring with the for-of loop. Let's take an array of user objects like this:
We can extract the property values with object destructuring using the for-of loop.
This is the output:

The Console object
In JavaScript, console is a built-in object supported by all browsers. If you have noticed, the console object has many properties and methods, and some are very popular, like console.log() .

Using the destructuring object syntax, we can simplify the uses of these methods and properties in our code. How about this?
Spread Syntax in JavaScript
The Spread Syntax (also known as the Spread Operator) is another excellent feature of ES6. As the name indicates, it takes an iterable (like an array) and expands (spreads) it into individual elements.
We can also expand objects using the spread syntax and copy its enumerable properties to a new object.
Spread syntax helps us clone an object with the most straightforward syntax using the curly braces and three dots {...} .
With spread syntax we can clone, update, and merge objects in an immutable way. The immutability helps reduce any accidental or unintentional changes to the original (Source) object.
The Object Destructuring and Spread syntaxes are not the same thing in JavaScript.
Create a Clone of an Object
We can create a cloned instance of an object using the spread syntax like this:
You can alternatively use object.assign() to create a clone of an object. However, the spread syntax is much more precise and much shorter.
The spread syntax performs a shallow copy of the object. This means that none of the nested object instances are cloned.
Add Properties to Objects
We can add a new property (key-value pair) to the object using the spread syntax . Note that the actual object never gets changed. The new property gets added to the cloned object.
In the example below, we are adding a new property ( salary ) using the spread syntax.
Update Properties
We can also update an existing property value using the spread syntax. Like the add operation, the update takes place on the object's cloned instance, not on the actual object.
In the example below, we are updating the value of the age property:
Update Nested Objects
As we have seen, updating an object with the spread syntax is easy, and it doesn't mutate the original object. However, it can be a bit tricky when you try to update a nested object using the spread syntax. Let's understand it with an example.
We have a user object with a property department . The value of the department property is an object which has another nested object with its address property.
Now, how can we add a new property called, number with a value of, say, 7 for the department object? Well, we might try out the following code to achieve it (but that would be a mistake):
As you execute it, you will realize that the code will replace the entire department object with the new value as, {'number': 7} . This is not what we wanted!

How do we fix that? We need to spread the properties of the nested object as well as add/update it. Here is the correct syntax that will add a new property number with the value 7 to the department object without replacing its value:
The output is the following:

Combine (or Merge) two Objects
The last practical use of the spread syntax in JavaScript objects is to combine or merge two objects. obj_1 and obj_2 can be merged together using the following syntax:
Note that this way of merging performs a shallow merge . This means that if there is a common property between both the objects, the property value of obj_2 will replace the property value of obj_1 in the merged object.
Let's take the user and department objects to combine (or merge) them together.
Merge the objects using the spread syntax, like this:
The output will be the following:

If we change the department object like this:
Now try to combine them and observe the combined object output:
The output will be:

The name property value of the user object is replaced by the name property value of the department object in the merged object output. So be careful of using it this way.
As of now, you need to implement the deep-merge of objects by yourself or make use of a library like lodash to accomplish it.
The Rest Parameter in JavaScript
The Rest parameter is kind of opposite to the spread syntax. While spread syntax helps expand or spread elements and properties, the rest parameter helps collect them together.
In the case of objects, the rest parameter is mostly used with destructuring syntax to consolidate the remaining properties in a new object you're working with.
Let's look at an example of the following user object:
We know how to destructure the age property to create a variable and assign the value of it. How about creating another object at the same time with the remaining properties of the user object? Here you go:

In the output we see that the age value is 43 . The rest parameter consolidated the rest of the user object properties, name and address , in a separate object.
To summarize,
- Object destructuring is new syntax introduced in ES6. It helps create variables by extracting the object's properties in a much simpler way.
- If you are working with (or planning to use) a framework/library like angular , react , or vue , you will be using a lot of object destructuring syntax.
- Object destructuring and Spread syntax are not the same thing.
- Spread syntax (also known as the Spread Operator) is used to copy the enumerable properties of an object to create a clone of it. We can also update an object or merge with another object using the spread syntax.
- The Rest parameter is kind of the opposite of the Spread syntax. It helps to consolidate (or collect) the remaining object properties into a new object while destructuring is done.
Destructuring assignment
The two most used data structures in JavaScript are Object and Array .
- Objects allow us to create a single entity that stores data items by key.
- Arrays allow us to gather data items into an ordered list.
However, when we pass these to a function, we may not need all of it. The function might only require certain elements or properties.
Destructuring assignment is a special syntax that allows us to “unpack” arrays or objects into a bunch of variables, as sometimes that’s more convenient.
Destructuring also works well with complex functions that have a lot of parameters, default values, and so on. Soon we’ll see that.
Array destructuring
Here’s an example of how an array is destructured into variables:
Now we can work with variables instead of array members.
It looks great when combined with split or other array-returning methods:
As you can see, the syntax is simple. There are several peculiar details though. Let’s see more examples to understand it better.
It’s called “destructuring assignment,” because it “destructurizes” by copying items into variables. However, the array itself is not modified.
It’s just a shorter way to write:
Unwanted elements of the array can also be thrown away via an extra comma:
In the code above, the second element of the array is skipped, the third one is assigned to title , and the rest of the array items are also skipped (as there are no variables for them).
…Actually, we can use it with any iterable, not only arrays:
That works, because internally a destructuring assignment works by iterating over the right value. It’s a kind of syntax sugar for calling for..of over the value to the right of = and assigning the values.
We can use any “assignables” on the left side.
For instance, an object property:
In the previous chapter, we saw the Object.entries(obj) method.
We can use it with destructuring to loop over the keys-and-values of an object:
The similar code for a Map is simpler, as it’s iterable:
There’s a well-known trick for swapping values of two variables using a destructuring assignment:
Here we create a temporary array of two variables and immediately destructure it in swapped order.
We can swap more than two variables this way.
The rest ‘…’
Usually, if the array is longer than the list at the left, the “extra” items are omitted.
For example, here only two items are taken, and the rest is just ignored:
If we’d like also to gather all that follows – we can add one more parameter that gets “the rest” using three dots "..." :
The value of rest is the array of the remaining array elements.
We can use any other variable name in place of rest , just make sure it has three dots before it and goes last in the destructuring assignment.
Default values
If the array is shorter than the list of variables on the left, there will be no errors. Absent values are considered undefined:
If we want a “default” value to replace the missing one, we can provide it using = :
Default values can be more complex expressions or even function calls. They are evaluated only if the value is not provided.
For instance, here we use the prompt function for two defaults:
Please note: the prompt will run only for the missing value ( surname ).
Object destructuring
The destructuring assignment also works with objects.
The basic syntax is:
We should have an existing object on the right side, that we want to split into variables. The left side contains an object-like “pattern” for corresponding properties. In the simplest case, that’s a list of variable names in {...} .
For instance:
Properties options.title , options.width and options.height are assigned to the corresponding variables.
The order does not matter. This works too:
The pattern on the left side may be more complex and specify the mapping between properties and variables.
If we want to assign a property to a variable with another name, for instance, make options.width go into the variable named w , then we can set the variable name using a colon:
The colon shows “what : goes where”. In the example above the property width goes to w , property height goes to h , and title is assigned to the same name.
For potentially missing properties we can set default values using "=" , like this:
Just like with arrays or function parameters, default values can be any expressions or even function calls. They will be evaluated if the value is not provided.
In the code below prompt asks for width , but not for title :
We also can combine both the colon and equality:
If we have a complex object with many properties, we can extract only what we need:
The rest pattern “…”
What if the object has more properties than we have variables? Can we take some and then assign the “rest” somewhere?
We can use the rest pattern, just like we did with arrays. It’s not supported by some older browsers (IE, use Babel to polyfill it), but works in modern ones.
It looks like this:
In the examples above variables were declared right in the assignment: let {…} = {…} . Of course, we could use existing variables too, without let . But there’s a catch.
This won’t work:
The problem is that JavaScript treats {...} in the main code flow (not inside another expression) as a code block. Such code blocks can be used to group statements, like this:
So here JavaScript assumes that we have a code block, that’s why there’s an error. We want destructuring instead.
To show JavaScript that it’s not a code block, we can wrap the expression in parentheses (...) :
Nested destructuring
If an object or an array contains other nested objects and arrays, we can use more complex left-side patterns to extract deeper portions.
In the code below options has another object in the property size and an array in the property items . The pattern on the left side of the assignment has the same structure to extract values from them:
All properties of options object except extra which is absent in the left part, are assigned to corresponding variables:
Finally, we have width , height , item1 , item2 and title from the default value.
Note that there are no variables for size and items , as we take their content instead.
Smart function parameters
There are times when a function has many parameters, most of which are optional. That’s especially true for user interfaces. Imagine a function that creates a menu. It may have a width, a height, a title, an item list and so on.
Here’s a bad way to write such a function:
In real-life, the problem is how to remember the order of arguments. Usually, IDEs try to help us, especially if the code is well-documented, but still… Another problem is how to call a function when most parameters are ok by default.
That’s ugly. And becomes unreadable when we deal with more parameters.
Destructuring comes to the rescue!
We can pass parameters as an object, and the function immediately destructurizes them into variables:
We can also use more complex destructuring with nested objects and colon mappings:
The full syntax is the same as for a destructuring assignment:
Then, for an object of parameters, there will be a variable varName for the property incomingProperty , with defaultValue by default.
Please note that such destructuring assumes that showMenu() does have an argument. If we want all values by default, then we should specify an empty object:
We can fix this by making {} the default value for the whole object of parameters:
In the code above, the whole arguments object is {} by default, so there’s always something to destructurize.
Destructuring assignment allows for instantly mapping an object or array onto many variables.
The full object syntax:
This means that property prop should go into the variable varName and, if no such property exists, then the default value should be used.
Object properties that have no mapping are copied to the rest object.
The full array syntax:
The first item goes to item1 ; the second goes into item2 , and all the rest makes the array rest .
It’s possible to extract data from nested arrays/objects, for that the left side must have the same structure as the right one.
We have an object:
Write the destructuring assignment that reads:
- name property into the variable name .
- years property into the variable age .
- isAdmin property into the variable isAdmin (false, if no such property)
Here’s an example of the values after your assignment:
The maximal salary
There is a salaries object:
Create the function topSalary(salaries) that returns the name of the top-paid person.
- If salaries is empty, it should return null .
- If there are multiple top-paid persons, return any of them.
P.S. Use Object.entries and destructuring to iterate over key/value pairs.
Open a sandbox with tests.
Open the solution with tests in a sandbox.
Lesson navigation
- © 2007—2024 Ilya Kantor
- about the project
- terms of usage
- privacy policy
- Skip to main content
- Skip to search
- Skip to select language
- Sign up for free
- Remember language
Assignment (=)
Baseline widely available.
This feature is well established and works across many devices and browser versions. It’s been available across browsers since July 2015 .
- See full compatibility
- Report feedback
The assignment ( = ) operator is used to assign a value to a variable or property. The assignment expression itself has a value, which is the assigned value. This allows multiple assignments to be chained in order to assign a single value to multiple variables.
A valid assignment target, including an identifier or a property accessor . It can also be a destructuring assignment pattern .
An expression specifying the value to be assigned to x .
Return value
The value of y .
Thrown in strict mode if assigning to an identifier that is not declared in the scope.
Thrown in strict mode if assigning to a property that is not modifiable .
Description
The assignment operator is completely different from the equals ( = ) sign used as syntactic separators in other locations, which include:
- Initializers of var , let , and const declarations
- Default values of destructuring
- Default parameters
- Initializers of class fields
All these places accept an assignment expression on the right-hand side of the = , so if you have multiple equals signs chained together:
This is equivalent to:
Which means y must be a pre-existing variable, and x is a newly declared const variable. y is assigned the value 5 , and x is initialized with the value of the y = 5 expression, which is also 5 . If y is not a pre-existing variable, a global variable y is implicitly created in non-strict mode , or a ReferenceError is thrown in strict mode. To declare two variables within the same declaration, use:
Basic assignment and chaining
Value of assignment expressions.
The assignment expression itself evaluates to the value of the right-hand side, so you can log the value and assign to a variable at the same time.
Unqualified identifier assignment
The global object sits at the top of the scope chain. When attempting to resolve a name to a value, the scope chain is searched. This means that properties on the global object are conveniently visible from every scope, without having to qualify the names with globalThis. or window. or global. .
Because the global object has a String property ( Object.hasOwn(globalThis, "String") ), you can use the following code:
So the global object will ultimately be searched for unqualified identifiers. You don't have to type globalThis.String ; you can just type the unqualified String . To make this feature more conceptually consistent, assignment to unqualified identifiers will assume you want to create a property with that name on the global object (with globalThis. omitted), if there is no variable of the same name declared in the scope chain.
In strict mode , assignment to an unqualified identifier in strict mode will result in a ReferenceError , to avoid the accidental creation of properties on the global object.
Note that the implication of the above is that, contrary to popular misinformation, JavaScript does not have implicit or undeclared variables. It just conflates the global object with the global scope and allows omitting the global object qualifier during property creation.
Assignment with destructuring
The left-hand side of can also be an assignment pattern. This allows assigning to multiple variables at once.
For more information, see Destructuring assignment .
Specifications
Browser compatibility.
BCD tables only load in the browser with JavaScript enabled. Enable JavaScript to view data.
- Assignment operators in the JS guide
- Destructuring assignment

COMMENTS
The Object.assign() static method copies all enumerable own properties from one or more source objects to a target object. It returns the modified target object.
The destructuring assignment syntax is a JavaScript expression that makes it possible to unpack values from arrays, or properties from objects, into distinct variables. The object and array literal expressions provide an easy way to create ad hoc packages of data.
The Object.assign() method copies properties from one or more source objects to a target object.
The destructuring assignment syntax unpack object properties into variables: let {firstName, lastName} = person; It can also unpack arrays and any other iterables:
Object.assign will assign all enumerable own properties of the second (and further) parameters to the first parameter, and will return the first parameter. So So const obj3 = Object.assign(obj2, obj1);
The Object.assign() method is used to copy the values and properties from one or more source objects to a target object. It invokes getters and setters since it uses both [[Get]] on the source and [[Set]] on the target.
JavaScript Object Destructuring is the syntax for extracting values from an object property and assigning them to a variable. The destructuring is also possible for JavaScript Arrays. By default, the object key name becomes the variable that holds the respective value. So no extra code is required to create another variable for value assignment.
JavaScript Object.assign() copies enumerable and own properties from a source object to a target object. It can be used to clone an object or merge objects.
Destructuring assignment allows for instantly mapping an object or array onto many variables. The full object syntax: let {prop : varName = defaultValue, ...rest} = object
The assignment (=) operator is used to assign a value to a variable or property. The assignment expression itself has a value, which is the assigned value. This allows multiple assignments to be chained in order to assign a single value to multiple variables.