Case Study Analysis: Examples + How-to Guide & Writing Tips
A case study analysis is a typical assignment in business management courses. The task aims to show high school and college students how to analyze a current situation, determine what problems exist, and develop the best possible strategy to achieve the desired outcome.
Many students feel anxious about writing case analyses because being told to analyze a case study and provide a solution can seem like a big task. That is especially so when working with real-life scenarios. However, you can rest assured writing a case analysis paper is easier than you think. Just keep reading this article and you will find case study examples for students and the advice provided by Custom-writing experts!
- 👣 Main Steps
- 🕵 Preparing the Case

🔬 Analyzing the Case
- 📑 Format & Structure
- 🙅 Things to Avoid
- 🏁 Conclusion
🔗 References
👣 writing a case study analysis: main steps.
Business management is built on case analysis. Every single economic result shows that the methods and instruments employed were either well-timed and expedient, in the event of success, or not, in case of failure. These two options indicate whether the strategy is efficient (and should be followed) or requires corrections (or complete change). Such an approach to the case study will make your writing piece more proficient and valuable for the reader. The following steps will direct your plan for writing a case study analysis.
Step 1: Preliminary work
- Make notes and highlight the numbers and ideas that could be quoted.
- Single out as many problems as you can, and briefly mark their underlying issues. Then make a note of those responsible. In the report, you will use two to five of the problems, so you will have a selection to choose from.
- Outline a possible solution to each of the problems you found. Course readings and outside research shall be used here. Highlight your best and worst solution for further reference.
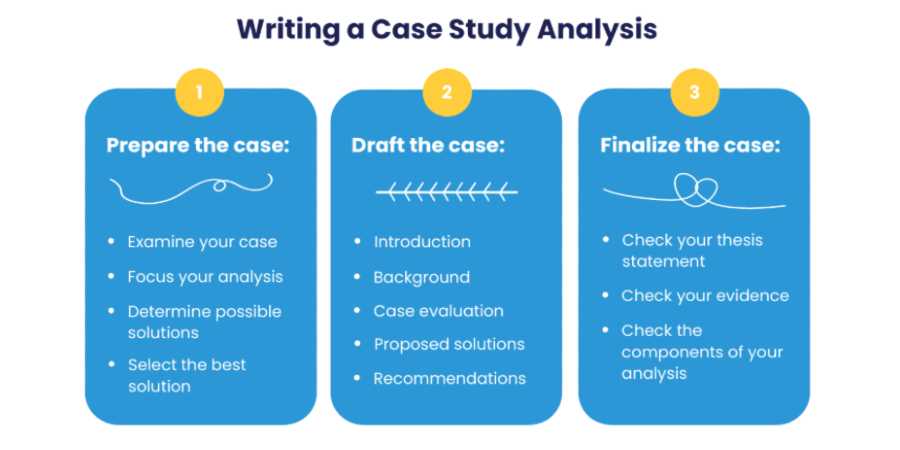
Step 2: Drafting the Case
- Provide a general description of the situation and its history.
- Name all the problems you are going to discuss.
- Specify the theory used for the analysis.
- Present the assumptions that emerged during the analysis, if any.
- Describe the detected problems in more detail.
- Indicate their link to, and effect on, the general situation.
- Explain why the problems emerged and persist.
- List realistic and feasible solutions to the problems you outlined, in the order of importance.
- Specify your predicted results of such changes.
- Support your choice with reliable evidence (i.e., textbook readings, the experience of famous companies, and other external research).
- Define the strategies required to fulfill your proposed solution.
- Indicate the responsible people and the realistic terms for its implementation.
- Recommend the issues for further analysis and supervision.
Step 3: Finalizing the Case
Like any other piece of writing, a case analysis requires post-editing. Carefully read it through, looking for inconsistencies and gaps in meaning. Your purpose is to make it look complete, precise, and convincing.
🕵 Preparing a Case for Analysis
Your professor might give you various case study examples from which to choose, or they may just assign you a particular case study. To conduct a thorough data analysis, you must first read the case study. This might appear to be obvious. However, you’d be surprised at how many students don’t take adequate time to complete this part.
Read the case study very thoroughly, preferably several times. Highlight, underline, flag key information, and make notes to refer to later when you are writing your analysis report.
If you don’t have a complete knowledge of the case study your professor has assigned, you won’t conduct a proper analysis of it. Even if you make use of a business case study template or refer to a sample analysis, it won’t help if you aren’t intimately familiar with your case study.
You will also have to conduct research. When it comes to research, you will need to do the following:
- Gather hard, quantitative data (e.g. 67% of the staff participated in the meeting).
- Design research tools , such as questionnaires and surveys (this will aid in gathering data).
- Determine and suggest the best specific, workable solutions.
It would be best if you also learned how to analyze a case study. Once you have read through the case study, you need to determine the focus of your analysis. You can do this by doing the following:
| Identify | E.g., the loss of brand identity as a problem faced by Starbucks |
| Analyze of the existing problem | |
| Establish between the various factors | Starbucks’ brand image – possible sources of influence: |
| Formulate to address the problem | |
Compare your chosen solutions to the solutions offered by the experts who analyzed the case study you were given or to online assignments for students who were dealing with a similar task. The experts’ solutions will probably be more advanced than yours simply because these people are more experienced. However, don’t let this discourage you; the whole point of doing this analysis is to learn. Use the opportunity to learn from others’ valuable experience, and your results will be better next time.
If you are still in doubt, the University of South Carolina offers a great guide on forming a case study analysis.
📑 Case Analysis Format & Structure
When you are learning how to write a case study analysis, it is important to get the format of your analysis right. Understanding the case study format is vital for both the professor and the student. The person planning and handing out such an assignment should ensure that the student doesn’t have to use any external sources .
In turn, students have to remember that a well-written case analysis provides all the data, making it unnecessary for the reader to go elsewhere for information.
Regardless of whether you use a case study template, you will need to follow a clear and concise format when writing your analysis report. There are some possible case study frameworks available. Still, a case study should contain eight sections laid out in the following format:
- Describe the purpose of the current case study;
- Provide a summary of the company;
- Briefly introduce the problems and issues found in the case study
- Discuss the theory you will be using in the analysis;
- Present the key points of the study and present any assumptions made during the analysis.
- Present each problem you have singled out;
- Justify your inclusion of each problem by providing supporting evidence from the case study and by discussing relevant theory and what you have learned from your course content;
- Divide the section (and following sections) into subsections, one for each of your selected problems.
- Present a summary of each problem you have identified;
- Present plausible solutions for each of the problems, keeping in mind that each problem will likely have more than one possible solution;
- Provide the pros and cons of each solution in a way that is practical.
- Conclusion . This is a summary of your findings and discussion.
- Decide which solution best fits each of the issues you identified;
- Explain why you chose this solution and how it will effectively solve the problem;
- Be persuasive when you write this section so that you can drive your point home;
- Be sure to bring together theory and what you have learned throughout your course to support your recommendations.
- Provide an explanation of what must be done, who should take action, and when the solution should be carried out;
- Where relevant, you should provide an estimate of the cost in implementing the solution, including both the financial investment and the cost in terms of time.
- References. While you generally do not need to refer to many external sources when writing a case study analysis, you might use a few. When you do, you will need to properly reference these sources, which is most often done in one of the main citation styles, including APA, MLA, or Harvard. There is plenty of help when citing references, and you can follow these APA guidelines , these MLA guidelines , or these Harvard guidelines .
- Appendices. This is the section you include after your case study analysis if you used any original data in the report. These data, presented as charts, graphs, and tables, are included here because to present them in the main body of the analysis would be disruptive to the reader. The University of Southern California provides a great description of appendices and when to make use of them.
When you’ve finished your first draft, be sure to proofread it. Look not only for potential grammar and spelling errors but also for discrepancies or holes in your argument.
You should also know what you need to avoid when writing your analysis.
🙅 Things to Avoid in Case Analysis
Whenever you deal with a case study, remember that there are some pitfalls to avoid! Beware of the following mistakes:
- Excessive use of colloquial language . Even though it is a study of an actual case, it should sound formal.
- Lack of statistical data . Give all the important data, both in percentages and in numbers.
- Excessive details. State only the most significant facts, rather than drowning the reader in every fact you find.
- Inconsistency in the methods you have used . In a case study, theory plays a relatively small part, so you must develop a specific case study research methodology.
- Trivial means of research . It is critical that you design your own case study research method in whatever form best suits your analysis, such as questionnaires and surveys.
It is useful to see a few examples of case analysis papers. After all, a sample case study report can provide you with some context so you can see how to approach each aspect of your paper.
👀 Case Study Examples for Students
It might be easier to understand how a case study analysis works if you have an example to look at. Fortunately, examples of case studies are easy to come by. Take a look at this video for a sample case study analysis for the Coca-Cola Company.
If you want another example, then take a look at the one below!
Business Case Analysis: Example
CRM’s primary focus is customers and customer perception of the brand or the company. The focus may shift depending on customers’ needs. The main points that Center Parcs should consider are an increase in customer satisfaction and its market share. Both of these points will enhance customer perception of the product as a product of value. Increased customer satisfaction will indicate that the company provides quality services, and increased market share can reduce the number of switching (or leaving) customers, thus fostering customer loyalty.
Case Study Topics
- Equifax case study: the importance of cybersecurity measures.
- Study a case illustrating ethical issues of medical research.
- Examine the case describing the complications connected with nursing and residential care.
- Analyze the competitive strategy of Delta Airlines .
- Present a case study of an ethical dilemma showing the conflict between the spirit and the letter of the law.
- Explore the aspects of Starbucks’ marketing strategyin a case study.
- Research a case of community-based clinic organization and development.
- Customer service of United Airlines: a case study .
- Analyze a specific schizophrenia case and provide your recommendations.
- Provide a case study of a patient with hyperglycemia.
- Examine the growth strategy of United Healthcare.
- Present a case study demonstrating ethical issues in business.
- Study a case of the 5% shareholding rule application and its impact on the company.
- Case study of post-traumatic stress disorder .
- Analyze a case examining the issues of cross-cultural management .
- Write a case study exploring the ethical issues the finance manager of a long-term care facility can face and the possible reaction to them.
- Write a case study analyzing the aspects of a new president of a firm election.
- Discuss the specifics of supply chain management in the case of Tehindo company.
- Study a case of a life crisis in a family and the ways to cope with it.
- Case study of Tea Leaves and More: supply chain issues.
- Explore the case of ketogenic diet implementation among sportspeople.
- Analyze the case of Webster Jewelry shop and suggest some changes.
- Examine the unique aspects of Tea and More brand management.
- Adidas case study: an ethical dilemma .
- Research the challenges of Brazos Valley Food Bank and suggest possible solutions.
- Describe the case of dark web monitoring for business.
- Study a case of permissive parenting style .
- Case study of Starbucks employees.
- Analyze a case of workplace discrimination and suggest a strategy to avoid it.
- Examine a case of the consumer decision-making process and define the factors that influence it.
- Present a case study of Netflix illustrating the crucial role of management innovation for company development.
- Discuss a case describing a workplace ethical issue and propose ways to resolve it.
- Case study of the 2008 financial crisis: Graham’s value investing principles in the modern economic climate.
- Write a case study analyzing the harmful consequences of communication issues in a virtual team.
- Analyze a case that highlights the importance of a proper functional currency choice.
- Examine the case of Hitachi Power Systems management.
- Present a case study of medication research in a healthcare facility.
- Study the case of Fiji Water and the challenges the brand faces.
- Research a social problem case and suggest a solution.
- Analyze a case that reveals the connection between alcohol use and borderline personality disorder.
- Transglobal Airline case study: break-even analysis.
- Examine the case of Chiquita Brands International from the moral and business ethics points of view.
- Present a case study of applying for Social Security benefits.
- Study the case of a mass hacker attack on Microsoft clients and suggest possible ways to prevent future attacks.
- Case study of leadership effectiveness.
- Analyze a case presenting a clinical moral dilemma and propose ways to resolve it.
- Describe the case of Cowbell Brewing Company and discuss the strategy that made them successful.
- Write a case study of WeWork company and analyze the strengths and weaknesses of its strategy.
- Case study of medical ethical decision-making.
- Study the case of The Georges hotel and suggest ways to overcome its managerial issues.
🏁 Concluding Remarks
Writing a case study analysis can seem incredibly overwhelming, especially if you have never done it before. Just remember, you can do it provided you follow a plan, keep to the format described here, and study at least one case analysis example.
If you still need help analyzing a case study, your professor is always available to answer your questions and point you in the right direction. You can also get help with any aspect of the project from a custom writing company. Just tackle the research and hand over the writing, write a rough draft and have it checked by a professional, or completely hand the project off to an expert writer.
Regardless of the path you choose, you will turn in something of which you can be proud!
✏️ Case Study Analysis FAQ
Students (especially those who study business) often need to write a case study analysis. It is a kind of report that describes a business case. It includes multiple aspects, for example, the problems that exist, possible solutions, forecasts, etc.
There should be 3 main points covered in a case study analysis:
- The challenge(s) description,
- Possible solutions,
- Outcomes (real and/or foreseen).
Firstly, study some examples available online and in the library. Case study analysis should be a well-structured paper with all the integral components in place. Thus, you might want to use a template and/or an outline to start correctly.
A case study analysis is a popular task for business students. They typically hand it in the format of a paper with several integral components:
- Description of the problem
- Possible ways out
- Results and/or forecasts
Students sometimes tell about the outcome of their research within an oral presentation.
- Case Study: Academia
- Windows of vulnerability: a case study analysis (IEEE)
- A (Very) Brief Refresher on the Case Study Method: SAGE
- The case study approach: Medical Research Methodology
- Strengths and Limitations of Case Studies: Stanford University
- A Sample APA Paper: Radford University
- How to Write a Case Study APA Style: Seattle PI
- The Case Analysis: GVSU
- How to Outline: Purdue OWL
- Incorporating Interview Data: UW-Madison Writing Center
- Share to Facebook
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

If you are a student, you might need to learn how to write a literature review at some point. But don’t think it’s the same as the book review or other types of academic writing you had to do in high school! A literature review is a close examination of...

So, have you been recently assigned a research project? Or, even worse, is it already due soon? The following research paper hacks will help you do it in record time. In the article, you’ll see ten things you can do to conduct a study and compose a piece like a...

Eating a delicacy, watching a good movie, and proving a point to an audience are the three things that make life seem better. Today, you’ll deal with the last one. You’re about to become a professional at public speaking and attention grabbing. Here, you can learn how to write a...
![example of analysis of case study Library Research Paper: Example & Writing Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/library-with-books-284x122.jpeg)
What is a library research paper? It’s nothing more than an academic writing project that summarizes the information on a specific topic taken from primary and secondary sources. There are numerous library research examples you can find online. But to complete this assignment, you should simply follow these essential steps:...
![example of analysis of case study Research Analysis Paper: How to Analyze a Research Article [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/opened-book-library-table-284x153.jpg)
Do you need to write a research analysis paper but have no idea how to do that? Then you’re in the right place. While completing this type of assignment, your key aim is to critically analyze a research article. An article from a serious scientific journal would be a good...
![example of analysis of case study American Antiquity Style Guide: Citation Rules & Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/education-concept-books-laptop-library-284x153.jpg)
American Antiquity is a professional quarterly journal, which contains various papers on the American archeology. It is incredibly popular among archeologists and the students majoring in history. The organization adopted the rules of The Society for American Archaeology (SAA) citation style. As a result: The journal includes numerous references that...

The most tedious and time-consuming part of any school or college written assignment is the bibliography. Sometimes, it can even be challenging! For example, if you’re confused by the variety of citation styles. That is why Custom-Writing experts prepared a brief guide about creating a perfect bibliography for a project....

An appendix is the part of the paper that contains supplementary material. The information from an appendix in paper writing is not essential. If the readers ignore this part, they still have to get the paper’s idea. Appendices help the readers to understand the research better. They might be useful...

Writing an abstract is one of the skills you need to master to succeed in your studies. An abstract is a summary of an academic text. It contains information about the aims and the outcomes of the research. The primary purpose of an abstract is to help readers understand what...

So you have to write a literature review. You find your favorite novel and then start analyzing it. This is how it’s usually done, right? It’s not. You have to learn the elements of literature review and how to deal with them.
![example of analysis of case study How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step [2024 Upd.]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/research-charts-284x153.jpg)
Only two words, but you already feel a chill down your spine. A research paper is no joke. It’s a super detailed piece of academic writing where you analyze a chosen issue in-depth. The main aim of such torture is to show how knowledgeable you are and that your opinion...

A research proposal is a text that suggests a topic or research problem, justifies the need to study it, and describes the ways and methods of conducting the study. Scholars usually write proposals to get funding for their research. In their turn, students might have to do that to get...
Quite an impressive piece The steps and procedures outlined here are well detailed and the examples facilitates understanding.
it was very helpful. I have an assessment to write where in I need to mention different effective components that are needed to compile a high quality case study assessment.
It is very important and helpful.
Thanks a lot. A knowledge shared with a structured template. Stay the course
Thanks for this valuable knowledge.I loved this. keep sharing. to know more about click Air India Case Study – Why Air India failed ?
This is going to be a great help in my monthly analysis requirements for my subject. Thank you so much.
Thank you very much for this insightful guidelines… It has really been a great tool for writing my project. Thanks once again.
This article was very helpful, even though I’ll have a clearer mind only after I do the case study myself but I felt very much motivated after reading this, as now I can at least have a plan of what to do compared to the clueless me I was before I read it. I hope if I have any questions or doubts about doing a case study I can clear it out here.
- Design for Business
- Most Recent
- Presentations
- Infographics
- Data Visualizations
- Forms and Surveys
- Video & Animation
- Case Studies
- Digital Marketing
- Design Inspiration
- Visual Thinking
- Product Updates
- Visme Webinars
- Artificial Intelligence
15 Real-Life Case Study Examples & Best Practices

Written by: Oghale Olori

Case studies are more than just success stories.
They are powerful tools that demonstrate the practical value of your product or service. Case studies help attract attention to your products, build trust with potential customers and ultimately drive sales.
It’s no wonder that 73% of successful content marketers utilize case studies as part of their content strategy. Plus, buyers spend 54% of their time reviewing case studies before they make a buying decision.
To ensure you’re making the most of your case studies, we’ve put together 15 real-life case study examples to inspire you. These examples span a variety of industries and formats. We’ve also included best practices, design tips and templates to inspire you.
Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
What is a case study, 15 real-life case study examples, sales case study examples, saas case study examples, product case study examples, marketing case study examples, business case study examples, case study faqs.
- A case study is a compelling narrative that showcases how your product or service has positively impacted a real business or individual.
- Case studies delve into your customer's challenges, how your solution addressed them and the quantifiable results they achieved.
- Your case study should have an attention-grabbing headline, great visuals and a relevant call to action. Other key elements include an introduction, problems and result section.
- Visme provides easy-to-use tools, professionally designed templates and features for creating attractive and engaging case studies.
A case study is a real-life scenario where your company helped a person or business solve their unique challenges. It provides a detailed analysis of the positive outcomes achieved as a result of implementing your solution.
Case studies are an effective way to showcase the value of your product or service to potential customers without overt selling. By sharing how your company transformed a business, you can attract customers seeking similar solutions and results.
Case studies are not only about your company's capabilities; they are primarily about the benefits customers and clients have experienced from using your product.
Every great case study is made up of key elements. They are;
- Attention-grabbing headline: Write a compelling headline that grabs attention and tells your reader what the case study is about. For example, "How a CRM System Helped a B2B Company Increase Revenue by 225%.
- Introduction/Executive Summary: Include a brief overview of your case study, including your customer’s problem, the solution they implemented and the results they achieved.
- Problem/Challenge: Case studies with solutions offer a powerful way to connect with potential customers. In this section, explain how your product or service specifically addressed your customer's challenges.
- Solution: Explain how your product or service specifically addressed your customer's challenges.
- Results/Achievements : Give a detailed account of the positive impact of your product. Quantify the benefits achieved using metrics such as increased sales, improved efficiency, reduced costs or enhanced customer satisfaction.
- Graphics/Visuals: Include professional designs, high-quality photos and videos to make your case study more engaging and visually appealing.
- Quotes/Testimonials: Incorporate written or video quotes from your clients to boost your credibility.
- Relevant CTA: Insert a call to action (CTA) that encourages the reader to take action. For example, visiting your website or contacting you for more information. Your CTA can be a link to a landing page, a contact form or your social media handle and should be related to the product or service you highlighted in your case study.

Now that you understand what a case study is, let’s look at real-life case study examples. Among these, you'll find some simple case study examples that break down complex ideas into easily understandable solutions.
In this section, we’ll explore SaaS, marketing, sales, product and business case study examples with solutions. Take note of how these companies structured their case studies and included the key elements.
We’ve also included professionally designed case study templates to inspire you.
1. Georgia Tech Athletics Increase Season Ticket Sales by 80%

Georgia Tech Athletics, with its 8,000 football season ticket holders, sought for a way to increase efficiency and customer engagement.
Their initial sales process involved making multiple outbound phone calls per day with no real targeting or guidelines. Georgia Tech believed that targeting communications will enable them to reach more people in real time.
Salesloft improved Georgia Tech’s sales process with an inbound structure. This enabled sales reps to connect with their customers on a more targeted level. The use of dynamic fields and filters when importing lists ensured prospects received the right information, while communication with existing fans became faster with automation.
As a result, Georgia Tech Athletics recorded an 80% increase in season ticket sales as relationships with season ticket holders significantly improved. Employee engagement increased as employees became more energized to connect and communicate with fans.
Why Does This Case Study Work?
In this case study example , Salesloft utilized the key elements of a good case study. Their introduction gave an overview of their customers' challenges and the results they enjoyed after using them. After which they categorized the case study into three main sections: challenge, solution and result.
Salesloft utilized a case study video to increase engagement and invoke human connection.
Incorporating videos in your case study has a lot of benefits. Wyzol’s 2023 state of video marketing report showed a direct correlation between videos and an 87% increase in sales.
The beautiful thing is that creating videos for your case study doesn’t have to be daunting.
With an easy-to-use platform like Visme, you can create top-notch testimonial videos that will connect with your audience. Within the Visme editor, you can access over 1 million stock photos , video templates, animated graphics and more. These tools and resources will significantly improve the design and engagement of your case study.
Simplify content creation and brand management for your team
- Collaborate on designs , mockups and wireframes with your non-design colleagues
- Lock down your branding to maintain brand consistency throughout your designs
- Why start from scratch? Save time with 1000s of professional branded templates
Sign up. It’s free.

2. WeightWatchers Completely Revamped their Enterprise Sales Process with HubSpot

WeightWatchers, a 60-year-old wellness company, sought a CRM solution that increased the efficiency of their sales process. With their previous system, Weightwatchers had limited automation. They would copy-paste message templates from word documents or recreate one email for a batch of customers.
This required a huge effort from sales reps, account managers and leadership, as they were unable to track leads or pull customized reports for planning and growth.
WeightWatchers transformed their B2B sales strategy by leveraging HubSpot's robust marketing and sales workflows. They utilized HubSpot’s deal pipeline and automation features to streamline lead qualification. And the customized dashboard gave leadership valuable insights.
As a result, WeightWatchers generated seven figures in annual contract value and boosted recurring revenue. Hubspot’s impact resulted in 100% adoption across all sales, marketing, client success and operations teams.
Hubspot structured its case study into separate sections, demonstrating the specific benefits of their products to various aspects of the customer's business. Additionally, they integrated direct customer quotes in each section to boost credibility, resulting in a more compelling case study.
Getting insight from your customer about their challenges is one thing. But writing about their process and achievements in a concise and relatable way is another. If you find yourself constantly experiencing writer’s block, Visme’s AI writer is perfect for you.
Visme created this AI text generator tool to take your ideas and transform them into a great draft. So whether you need help writing your first draft or editing your final case study, Visme is ready for you.
3. Immi’s Ram Fam Helps to Drive Over $200k in Sales

Immi embarked on a mission to recreate healthier ramen recipes that were nutritious and delicious. After 2 years of tireless trials, Immi finally found the perfect ramen recipe. However, they envisioned a community of passionate ramen enthusiasts to fuel their business growth.
This vision propelled them to partner with Shopify Collabs. Shopify Collabs successfully cultivated and managed Immi’s Ramen community of ambassadors and creators.
As a result of their partnership, Immi’s community grew to more than 400 dedicated members, generating over $200,000 in total affiliate sales.
The power of data-driven headlines cannot be overemphasized. Chili Piper strategically incorporates quantifiable results in their headlines. This instantly sparks curiosity and interest in readers.
While not every customer success story may boast headline-grabbing figures, quantifying achievements in percentages is still effective. For example, you can highlight a 50% revenue increase with the implementation of your product.
Take a look at the beautiful case study template below. Just like in the example above, the figures in the headline instantly grab attention and entice your reader to click through.
Having a case study document is a key factor in boosting engagement. This makes it easy to promote your case study in multiple ways. With Visme, you can easily publish, download and share your case study with your customers in a variety of formats, including PDF, PPTX, JPG and more!

4. How WOW! is Saving Nearly 79% in Time and Cost With Visme
This case study discusses how Visme helped WOW! save time and money by providing user-friendly tools to create interactive and quality training materials for their employees. Find out what your team can do with Visme. Request a Demo
WOW!'s learning and development team creates high-quality training materials for new and existing employees. Previous tools and platforms they used had plain templates, little to no interactivity features, and limited flexibility—that is, until they discovered Visme.
Now, the learning and development team at WOW! use Visme to create engaging infographics, training videos, slide decks and other training materials.
This has directly reduced the company's turnover rate, saving them money spent on recruiting and training new employees. It has also saved them a significant amount of time, which they can now allocate to other important tasks.
Visme's customer testimonials spark an emotional connection with the reader, leaving a profound impact. Upon reading this case study, prospective customers will be blown away by the remarkable efficiency achieved by Visme's clients after switching from PowerPoint.
Visme’s interactivity feature was a game changer for WOW! and one of the primary reasons they chose Visme.
“Previously we were using PowerPoint, which is fine, but the interactivity you can get with Visme is so much more robust that we’ve all steered away from PowerPoint.” - Kendra, L&D team, Wow!
Visme’s interactive feature allowed them to animate their infographics, include clickable links on their PowerPoint designs and even embed polls and quizzes their employees could interact with.
By embedding the slide decks, infographics and other training materials WOW! created with Visme, potential customers get a taste of what they can create with the tool. This is much more effective than describing the features of Visme because it allows potential customers to see the tool in action.
To top it all off, this case study utilized relevant data and figures. For example, one part of the case study said, “In Visme, where Kendra’s team has access to hundreds of templates, a brand kit, and millions of design assets at their disposal, their team can create presentations in 80% less time.”
Who wouldn't want that?
Including relevant figures and graphics in your case study is a sure way to convince your potential customers why you’re a great fit for their brand. The case study template below is a great example of integrating relevant figures and data.
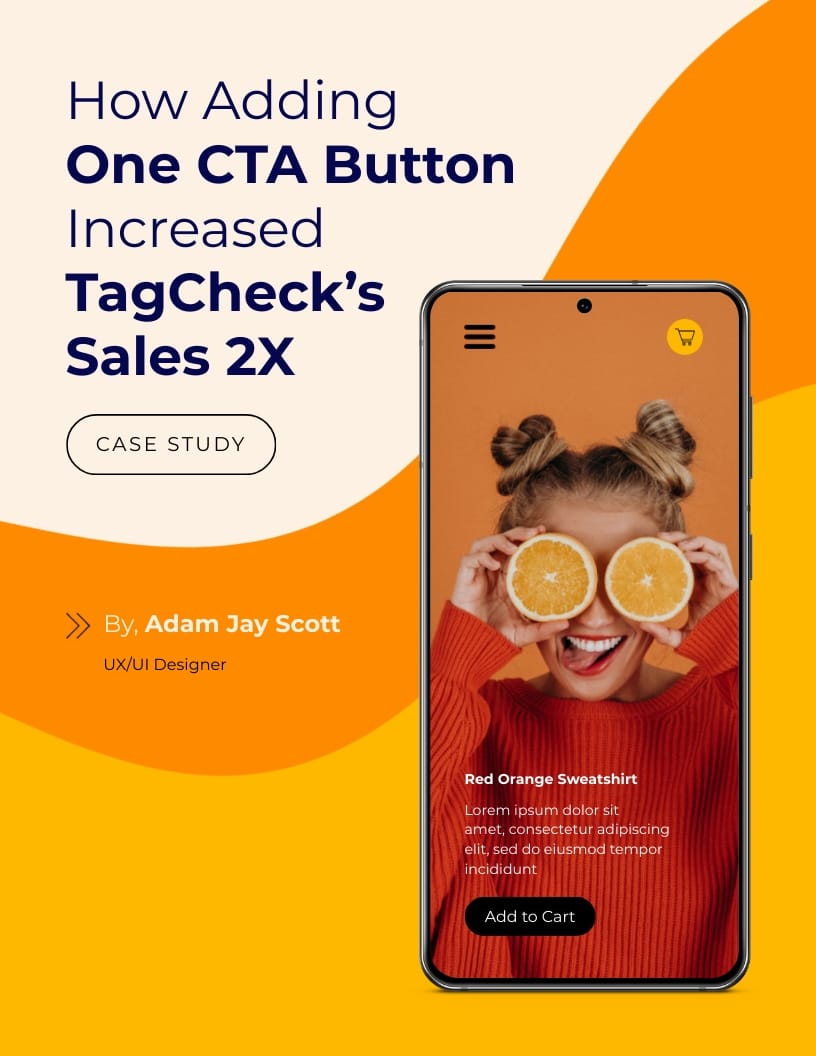
This colorful template begins with a captivating headline. But that is not the best part; this template extensively showcases the results their customer had using relevant figures.
The arrangement of the results makes it fun and attractive. Instead of just putting figures in a plain table, you can find interesting shapes in your Visme editor to take your case study to the next level.
5. Lyte Reduces Customer Churn To Just 3% With Hubspot CRM

While Lyte was redefining the ticketing industry, it had no definite CRM system . Lyte utilized 12–15 different SaaS solutions across various departments, which led to a lack of alignment between teams, duplication of work and overlapping tasks.
Customer data was spread across these platforms, making it difficult to effectively track their customer journey. As a result, their churn rate increased along with customer dissatisfaction.
Through Fuelius , Lyte founded and implemented Hubspot CRM. Lyte's productivity skyrocketed after incorporating Hubspot's all-in-one CRM tool. With improved efficiency, better teamwork and stronger client relationships, sales figures soared.
The case study title page and executive summary act as compelling entry points for both existing and potential customers. This overview provides a clear understanding of the case study and also strategically incorporates key details like the client's industry, location and relevant background information.
Having a good summary of your case study can prompt your readers to engage further. You can achieve this with a simple but effective case study one-pager that highlights your customer’s problems, process and achievements, just like this case study did in the beginning.
Moreover, you can easily distribute your case study one-pager and use it as a lead magnet to draw prospective customers to your company.
Take a look at this case study one-pager template below.

This template includes key aspects of your case study, such as the introduction, key findings, conclusion and more, without overcrowding the page. The use of multiple shades of blue gives it a clean and dynamic layout.
Our favorite part of this template is where the age group is visualized.
With Visme’s data visualization tool , you can present your data in tables, graphs, progress bars, maps and so much more. All you need to do is choose your preferred data visualization widget, input or import your data and click enter!
6. How Workato Converts 75% of Their Qualified Leads

Workato wanted to improve their inbound leads and increase their conversion rate, which ranged from 40-55%.
At first, Workato searched for a simple scheduling tool. They soon discovered that they needed a tool that provided advanced routing capabilities based on zip code and other criteria. Luckily, they found and implemented Chili Piper.
As a result of implementing Chili Piper, Workato achieved a remarkable 75–80% conversion rate and improved show rates. This led to a substantial revenue boost, with a 10-15% increase in revenue attributed to Chili Piper's impact on lead conversion.
This case study example utilizes the power of video testimonials to drive the impact of their product.
Chili Piper incorporates screenshots and clips of their tool in use. This is a great strategy because it helps your viewers become familiar with how your product works, making onboarding new customers much easier.
In this case study example, we see the importance of efficient Workflow Management Systems (WMS). Without a WMS, you manually assign tasks to your team members and engage in multiple emails for regular updates on progress.
However, when crafting and designing your case study, you should prioritize having a good WMS.
Visme has an outstanding Workflow Management System feature that keeps you on top of all your projects and designs. This feature makes it much easier to assign roles, ensure accuracy across documents, and track progress and deadlines.
Visme’s WMS feature allows you to limit access to your entire document by assigning specific slides or pages to individual members of your team. At the end of the day, your team members are not overwhelmed or distracted by the whole document but can focus on their tasks.
7. Rush Order Helps Vogmask Scale-Up During a Pandemic

Vomask's reliance on third-party fulfillment companies became a challenge as demand for their masks grew. Seeking a reliable fulfillment partner, they found Rush Order and entrusted them with their entire inventory.
Vomask's partnership with Rush Order proved to be a lifesaver during the COVID-19 pandemic. Rush Order's agility, efficiency and commitment to customer satisfaction helped Vogmask navigate the unprecedented demand and maintain its reputation for quality and service.
Rush Order’s comprehensive support enabled Vogmask to scale up its order processing by a staggering 900% while maintaining a remarkable customer satisfaction rate of 92%.
Rush Order chose one event where their impact mattered the most to their customer and shared that story.
While pandemics don't happen every day, you can look through your customer’s journey and highlight a specific time or scenario where your product or service saved their business.
The story of Vogmask and Rush Order is compelling, but it simply is not enough. The case study format and design attract readers' attention and make them want to know more. Rush Order uses consistent colors throughout the case study, starting with the logo, bold square blocks, pictures, and even headers.
Take a look at this product case study template below.
Just like our example, this case study template utilizes bold colors and large squares to attract and maintain the reader’s attention. It provides enough room for you to write about your customers' backgrounds/introductions, challenges, goals and results.
The right combination of shapes and colors adds a level of professionalism to this case study template.

8. AMR Hair & Beauty leverages B2B functionality to boost sales by 200%

With limits on website customization, slow page loading and multiple website crashes during peak events, it wasn't long before AMR Hair & Beauty began looking for a new e-commerce solution.
Their existing platform lacked effective search and filtering options, a seamless checkout process and the data analytics capabilities needed for informed decision-making. This led to a significant number of abandoned carts.
Upon switching to Shopify Plus, AMR immediately saw improvements in page loading speed and average session duration. They added better search and filtering options for their wholesale customers and customized their checkout process.
Due to this, AMR witnessed a 200% increase in sales and a 77% rise in B2B average order value. AMR Hair & Beauty is now poised for further expansion and growth.
This case study example showcases the power of a concise and impactful narrative.
To make their case analysis more effective, Shopify focused on the most relevant aspects of the customer's journey. While there may have been other challenges the customer faced, they only included those that directly related to their solutions.
Take a look at this case study template below. It is perfect if you want to create a concise but effective case study. Without including unnecessary details, you can outline the challenges, solutions and results your customers experienced from using your product.
Don’t forget to include a strong CTA within your case study. By incorporating a link, sidebar pop-up or an exit pop-up into your case study, you can prompt your readers and prospective clients to connect with you.

9. How a Marketing Agency Uses Visme to Create Engaging Content With Infographics

SmartBox Dental , a marketing agency specializing in dental practices, sought ways to make dental advice more interesting and easier to read. However, they lacked the design skills to do so effectively.
Visme's wide range of templates and features made it easy for the team to create high-quality content quickly and efficiently. SmartBox Dental enjoyed creating infographics in as little as 10-15 minutes, compared to one hour before Visme was implemented.
By leveraging Visme, SmartBox Dental successfully transformed dental content into a more enjoyable and informative experience for their clients' patients. Therefore enhancing its reputation as a marketing partner that goes the extra mile to deliver value to its clients.
Visme creatively incorporates testimonials In this case study example.
By showcasing infographics and designs created by their clients, they leverage the power of social proof in a visually compelling way. This way, potential customers gain immediate insight into the creative possibilities Visme offers as a design tool.
This example effectively showcases a product's versatility and impact, and we can learn a lot about writing a case study from it. Instead of focusing on one tool or feature per customer, Visme took a more comprehensive approach.
Within each section of their case study, Visme explained how a particular tool or feature played a key role in solving the customer's challenges.
For example, this case study highlighted Visme’s collaboration tool . With Visme’s tool, the SmartBox Dental content team fostered teamwork, accountability and effective supervision.
Visme also achieved a versatile case study by including relevant quotes to showcase each tool or feature. Take a look at some examples;
Visme’s collaboration tool: “We really like the collaboration tool. Being able to see what a co-worker is working on and borrow their ideas or collaborate on a project to make sure we get the best end result really helps us out.”
Visme’s library of stock photos and animated characters: “I really love the images and the look those give to an infographic. I also really like the animated little guys and the animated pictures. That’s added a lot of fun to our designs.”
Visme’s interactivity feature: “You can add URLs and phone number links directly into the infographic so they can just click and call or go to another page on the website and I really like adding those hyperlinks in.”
You can ask your customers to talk about the different products or features that helped them achieve their business success and draw quotes from each one.
10. Jasper Grows Blog Organic Sessions 810% and Blog-Attributed User Signups 400X
Jasper, an AI writing tool, lacked a scalable content strategy to drive organic traffic and user growth. They needed help creating content that converted visitors into users. Especially when a looming domain migration threatened organic traffic.
To address these challenges, Jasper partnered with Omniscient Digital. Their goal was to turn their content into a growth channel and drive organic growth. Omniscient Digital developed a full content strategy for Jasper AI, which included a content audit, competitive analysis, and keyword discovery.
Through their collaboration, Jasper’s organic blog sessions increased by 810%, despite the domain migration. They also witnessed a 400X increase in blog-attributed signups. And more importantly, the content program contributed to over $4 million in annual recurring revenue.
The combination of storytelling and video testimonials within the case study example makes this a real winner. But there’s a twist to it. Omniscient segmented the video testimonials and placed them in different sections of the case study.
Video marketing , especially in case studies, works wonders. Research shows us that 42% of people prefer video testimonials because they show real customers with real success stories. So if you haven't thought of it before, incorporate video testimonials into your case study.
Take a look at this stunning video testimonial template. With its simple design, you can input the picture, name and quote of your customer within your case study in a fun and engaging way.
Try it yourself! Customize this template with your customer’s testimonial and add it to your case study!

11. How Meliá Became One of the Most Influential Hotel Chains on Social Media

Meliá Hotels needed help managing their growing social media customer service needs. Despite having over 500 social accounts, they lacked a unified response protocol and detailed reporting. This largely hindered efficiency and brand consistency.
Meliá partnered with Hootsuite to build an in-house social customer care team. Implementing Hootsuite's tools enabled Meliá to decrease response times from 24 hours to 12.4 hours while also leveraging smart automation.
In addition to that, Meliá resolved over 133,000 conversations, booking 330 inquiries per week through Hootsuite Inbox. They significantly improved brand consistency, response time and customer satisfaction.
The need for a good case study design cannot be over-emphasized.
As soon as anyone lands on this case study example, they are mesmerized by a beautiful case study design. This alone raises the interest of readers and keeps them engaged till the end.
If you’re currently saying to yourself, “ I can write great case studies, but I don’t have the time or skill to turn it into a beautiful document.” Say no more.
Visme’s amazing AI document generator can take your text and transform it into a stunning and professional document in minutes! Not only do you save time, but you also get inspired by the design.
With Visme’s document generator, you can create PDFs, case study presentations , infographics and more!
Take a look at this case study template below. Just like our case study example, it captures readers' attention with its beautiful design. Its dynamic blend of colors and fonts helps to segment each element of the case study beautifully.

12. Tea’s Me Cafe: Tamika Catchings is Brewing Glory

Tamika's journey began when she purchased Tea's Me Cafe in 2017, saving it from closure. She recognized the potential of the cafe as a community hub and hosted regular events centered on social issues and youth empowerment.
One of Tamika’s business goals was to automate her business. She sought to streamline business processes across various aspects of her business. One of the ways she achieves this goal is through Constant Contact.
Constant Contact became an integral part of Tamika's marketing strategy. They provided an automated and centralized platform for managing email newsletters, event registrations, social media scheduling and more.
This allowed Tamika and her team to collaborate efficiently and focus on engaging with their audience. They effectively utilized features like WooCommerce integration, text-to-join and the survey builder to grow their email list, segment their audience and gather valuable feedback.
The case study example utilizes the power of storytelling to form a connection with readers. Constant Contact takes a humble approach in this case study. They spotlight their customers' efforts as the reason for their achievements and growth, establishing trust and credibility.
This case study is also visually appealing, filled with high-quality photos of their customer. While this is a great way to foster originality, it can prove challenging if your customer sends you blurry or low-quality photos.
If you find yourself in that dilemma, you can use Visme’s AI image edit tool to touch up your photos. With Visme’s AI tool, you can remove unwanted backgrounds, erase unwanted objects, unblur low-quality pictures and upscale any photo without losing the quality.
Constant Contact offers its readers various formats to engage with their case study. Including an audio podcast and PDF.
In its PDF version, Constant Contact utilized its brand colors to create a stunning case study design. With this, they increase brand awareness and, in turn, brand recognition with anyone who comes across their case study.
With Visme’s brand wizard tool , you can seamlessly incorporate your brand assets into any design or document you create. By inputting your URL, Visme’s AI integration will take note of your brand colors, brand fonts and more and create branded templates for you automatically.
You don't need to worry about spending hours customizing templates to fit your brand anymore. You can focus on writing amazing case studies that promote your company.
13. How Breakwater Kitchens Achieved a 7% Growth in Sales With Thryv

Breakwater Kitchens struggled with managing their business operations efficiently. They spent a lot of time on manual tasks, such as scheduling appointments and managing client communication. This made it difficult for them to grow their business and provide the best possible service to their customers.
David, the owner, discovered Thryv. With Thryv, Breakwater Kitchens was able to automate many of their manual tasks. Additionally, Thryv integrated social media management. This enabled Breakwater Kitchens to deliver a consistent brand message, captivate its audience and foster online growth.
As a result, Breakwater Kitchens achieved increased efficiency, reduced missed appointments and a 7% growth in sales.
This case study example uses a concise format and strong verbs, which make it easy for readers to absorb the information.
At the top of the case study, Thryv immediately builds trust by presenting their customer's complete profile, including their name, company details and website. This allows potential customers to verify the case study's legitimacy, making them more likely to believe in Thryv's services.
However, manually copying and pasting customer information across multiple pages of your case study can be time-consuming.
To save time and effort, you can utilize Visme's dynamic field feature . Dynamic fields automatically insert reusable information into your designs. So you don’t have to type it out multiple times.
14. Zoom’s Creative Team Saves Over 4,000 Hours With Brandfolder

Zoom experienced rapid growth with the advent of remote work and the rise of the COVID-19 pandemic. Such growth called for agility and resilience to scale through.
At the time, Zoom’s assets were disorganized which made retrieving brand information a burden. Zoom’s creative manager spent no less than 10 hours per week finding and retrieving brand assets for internal teams.
Zoom needed a more sustainable approach to organizing and retrieving brand information and came across Brandfolder. Brandfolder simplified and accelerated Zoom’s email localization and webpage development. It also enhanced the creation and storage of Zoom virtual backgrounds.
With Brandfolder, Zoom now saves 4,000+ hours every year. The company also centralized its assets in Brandfolder, which allowed 6,800+ employees and 20-30 vendors to quickly access them.
Brandfolder infused its case study with compelling data and backed it up with verifiable sources. This data-driven approach boosts credibility and increases the impact of their story.
Bradfolder's case study goes the extra mile by providing a downloadable PDF version, making it convenient for readers to access the information on their own time. Their dedication to crafting stunning visuals is evident in every aspect of the project.
From the vibrant colors to the seamless navigation, everything has been meticulously designed to leave a lasting impression on the viewer. And with clickable links that make exploring the content a breeze, the user experience is guaranteed to be nothing short of exceptional.
The thing is, your case study presentation won’t always sit on your website. There are instances where you may need to do a case study presentation for clients, partners or potential investors.
Visme has a rich library of templates you can tap into. But if you’re racing against the clock, Visme’s AI presentation maker is your best ally.

15. How Cents of Style Made $1.7M+ in Affiliate Sales with LeadDyno

Cents of Style had a successful affiliate and influencer marketing strategy. However, their existing affiliate marketing platform was not intuitive, customizable or transparent enough to meet the needs of their influencers.
Cents of Styles needed an easy-to-use affiliate marketing platform that gave them more freedom to customize their program and implement a multi-tier commission program.
After exploring their options, Cents of Style decided on LeadDyno.
LeadDyno provided more flexibility, allowing them to customize commission rates and implement their multi-tier commission structure, switching from monthly to weekly payouts.
Also, integrations with PayPal made payments smoother And features like newsletters and leaderboards added to the platform's success by keeping things transparent and engaging.
As a result, Cents of Style witnessed an impressive $1.7 million in revenue from affiliate sales with a substantial increase in web sales by 80%.
LeadDyno strategically placed a compelling CTA in the middle of their case study layout, maximizing its impact. At this point, readers are already invested in the customer's story and may be considering implementing similar strategies.
A well-placed CTA offers them a direct path to learn more and take action.
LeadDyno also utilized the power of quotes to strengthen their case study. They didn't just embed these quotes seamlessly into the text; instead, they emphasized each one with distinct blocks.
Are you looking for an easier and quicker solution to create a case study and other business documents? Try Visme's AI designer ! This powerful tool allows you to generate complete documents, such as case studies, reports, whitepapers and more, just by providing text prompts. Simply explain your requirements to the tool, and it will produce the document for you, complete with text, images, design assets and more.
Still have more questions about case studies? Let's look at some frequently asked questions.
How to Write a Case Study?
- Choose a compelling story: Not all case studies are created equal. Pick one that is relevant to your target audience and demonstrates the specific benefits of your product or service.
- Outline your case study: Create a case study outline and highlight how you will structure your case study to include the introduction, problem, solution and achievements of your customer.
- Choose a case study template: After you outline your case study, choose a case study template . Visme has stunning templates that can inspire your case study design.
- Craft a compelling headline: Include figures or percentages that draw attention to your case study.
- Work on the first draft: Your case study should be easy to read and understand. Use clear and concise language and avoid jargon.
- Include high-quality visual aids: Visuals can help to make your case study more engaging and easier to read. Consider adding high-quality photos, screenshots or videos.
- Include a relevant CTA: Tell prospective customers how to reach you for questions or sign-ups.
What Are the Stages of a Case Study?
The stages of a case study are;
- Planning & Preparation: Highlight your goals for writing the case study. Plan the case study format, length and audience you wish to target.
- Interview the Client: Reach out to the company you want to showcase and ask relevant questions about their journey and achievements.
- Revision & Editing: Review your case study and ask for feedback. Include relevant quotes and CTAs to your case study.
- Publication & Distribution: Publish and share your case study on your website, social media channels and email list!
- Marketing & Repurposing: Turn your case study into a podcast, PDF, case study presentation and more. Share these materials with your sales and marketing team.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of a Case Study?
Advantages of a case study:
- Case studies showcase a specific solution and outcome for specific customer challenges.
- It attracts potential customers with similar challenges.
- It builds trust and credibility with potential customers.
- It provides an in-depth analysis of your company’s problem-solving process.
Disadvantages of a case study:
- Limited applicability. Case studies are tailored to specific cases and may not apply to other businesses.
- It relies heavily on customer cooperation and willingness to share information.
- It stands a risk of becoming outdated as industries and customer needs evolve.
What Are the Types of Case Studies?
There are 7 main types of case studies. They include;
- Illustrative case study.
- Instrumental case study.
- Intrinsic case study.
- Descriptive case study.
- Explanatory case study.
- Exploratory case study.
- Collective case study.
How Long Should a Case Study Be?
The ideal length of your case study is between 500 - 1500 words or 1-3 pages. Certain factors like your target audience, goal or the amount of detail you want to share may influence the length of your case study. This infographic has powerful tips for designing winning case studies
What Is the Difference Between a Case Study and an Example?
Case studies provide a detailed narrative of how your product or service was used to solve a problem. Examples are general illustrations and are not necessarily real-life scenarios.
Case studies are often used for marketing purposes, attracting potential customers and building trust. Examples, on the other hand, are primarily used to simplify or clarify complex concepts.
Where Can I Find Case Study Examples?
You can easily find many case study examples online and in industry publications. Many companies, including Visme, share case studies on their websites to showcase how their products or services have helped clients achieve success. You can also search online libraries and professional organizations for case studies related to your specific industry or field.
If you need professionally-designed, customizable case study templates to create your own, Visme's template library is one of the best places to look. These templates include all the essential sections of a case study and high-quality content to help you create case studies that position your business as an industry leader.
Get More Out Of Your Case Studies With Visme
Case studies are an essential tool for converting potential customers into paying customers. By following the tips in this article, you can create compelling case studies that will help you build trust, establish credibility and drive sales.
Visme can help you create stunning case studies and other relevant marketing materials. With our easy-to-use platform, interactive features and analytics tools , you can increase your content creation game in no time.
There is no limit to what you can achieve with Visme. Connect with Sales to discover how Visme can boost your business goals.
Easily create beautiful case studies and more with Visme

Trusted by leading brands
Recommended content for you:

Create Stunning Content!
Design visual brand experiences for your business whether you are a seasoned designer or a total novice.
About the Author
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on May 8, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyze the case, other interesting articles.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
| Research question | Case study |
|---|---|
| What are the ecological effects of wolf reintroduction? | Case study of wolf reintroduction in Yellowstone National Park |
| How do populist politicians use narratives about history to gain support? | Case studies of Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán and US president Donald Trump |
| How can teachers implement active learning strategies in mixed-level classrooms? | Case study of a local school that promotes active learning |
| What are the main advantages and disadvantages of wind farms for rural communities? | Case studies of three rural wind farm development projects in different parts of the country |
| How are viral marketing strategies changing the relationship between companies and consumers? | Case study of the iPhone X marketing campaign |
| How do experiences of work in the gig economy differ by gender, race and age? | Case studies of Deliveroo and Uber drivers in London |
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
TipIf your research is more practical in nature and aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as you solve it, consider conducting action research instead.
Unlike quantitative or experimental research , a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
Example of an outlying case studyIn the 1960s the town of Roseto, Pennsylvania was discovered to have extremely low rates of heart disease compared to the US average. It became an important case study for understanding previously neglected causes of heart disease.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience or phenomenon.
Example of a representative case studyIn the 1920s, two sociologists used Muncie, Indiana as a case study of a typical American city that supposedly exemplified the changing culture of the US at the time.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews , observations , and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data.
Example of a mixed methods case studyFor a case study of a wind farm development in a rural area, you could collect quantitative data on employment rates and business revenue, collect qualitative data on local people’s perceptions and experiences, and analyze local and national media coverage of the development.
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis , with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyze its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved September 27, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/case-study/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is action research | definition & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

Due to recent expansions in US sanctions against Russia and Belarus as well as existing country-level sanctions in Iran, North Korea, Syria, Cuba, and the Crimea region (each a “sanctioned country”), Zapier will no longer be able to provide services in any sanctioned country starting September 12, 2024. These sanctions prohibit US companies from offering certain IT and enterprise software services in a sanctioned region.
Starting September 12, 2024, Zapier customers will no longer be able to access Zapier services from a sanctioned country. We understand this may be inconvenient and appreciate your understanding as we navigate these regulatory requirements.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Basic Research – Types, Methods and Examples

Quasi-Experimental Research Design – Types...

Phenomenology – Methods, Examples and Guide

Correlational Research – Methods, Types and...
How to Write a Case Study Analysis
Step-By-Step Instructions
Lucy Lambriex/Getty Images
- Student Resources
- Business Degree Options
- Choosing A Business School
- Business School Admissions
- MBA Programs & Rankings
- Business Careers and Internships
- Homework Help
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Distance Learning
When writing a business case study analysis , you must first have a good understanding of the case study . Before you begin the steps below, read the business case carefully, taking notes all the while. It may be necessary to read the case several times to get all of the details and fully grasp the issues facing the group, company, or industry.
As you are reading, do your best to identify key issues, key players, and the most pertinent facts. After you are comfortable with the information, use the following step-by-step instructions (geared toward a single-company analysis) to write your report. To write about an industry, just adapt the steps listed here to discuss the segment as a whole.
Step 1: Investigate the Company’s History and Growth
A company’s past can greatly affect the present and future state of the organization. To begin, investigate the company’s founding, critical incidents, structure, and growth. Create a timeline of events, issues, and achievements. This timeline will come in handy for the next step.
Step 2: Identify Strengths and Weaknesses
Using the information you gathered in step one, continue by examining and making a list of the value creation functions of the company. For example, the company may be weak in product development but strong in marketing. Make a list of problems that have occurred and note the effects they have had on the company. You should also list areas where the company has excelled. Note the effects of these incidents as well.
You're essentially conducting a partial SWOT analysis to get a better understanding of the company's strengths and weaknesses. A SWOT analysis involves documenting things like internal strengths (S) and weaknesses (W) and external opportunities (O) and threats (T).
Step 3: Examine the External Environment
The third step involves identifying opportunities and threats within the company’s external environment. This is where the second part of the SWOT analysis (the O and the T) comes into play. Special items to note include competition within the industry, bargaining powers, and the threat of substitute products. Some examples of opportunities include expansion into new markets or new technology. Some examples of threats include increasing competition and higher interest rates.
Step 4: Analyze Your Findings
Using the information in steps 2 and 3, create an evaluation for this portion of your case study analysis. Compare the strengths and weaknesses within the company to the external threats and opportunities. Determine if the company is in a strong competitive position, and decide if it can continue at its current pace successfully.
Step 5: Identify Corporate-Level Strategy
To identify a company’s corporate-level strategy, identify and evaluate the company’s mission , goals, and actions toward those goals. Analyze the company’s line of business and its subsidiaries and acquisitions. You also want to debate the pros and cons of the company strategy to determine whether or not a change might benefit the company in the short or long term.
Step 6: Identify Business-Level Strategy
Thus far, your case study analysis has identified the company’s corporate-level strategy. To perform a complete analysis, you will need to identify the company’s business-level strategy. (Note: If it is a single business, without multiple companies under one umbrella, and not an industry-wide review, the corporate strategy and the business-level strategy are the same.) For this part, you should identify and analyze each company’s competitive strategy, marketing strategy, costs, and general focus.
Step 7: Analyze Implementations
This portion requires that you identify and analyze the structure and control systems that the company is using to implement its business strategies. Evaluate organizational change, levels of hierarchy, employee rewards, conflicts, and other issues that are important to the company you are analyzing.
Step 8: Make Recommendations
The final part of your case study analysis should include your recommendations for the company. Every recommendation you make should be based on and supported by the context of your analysis. Never share hunches or make a baseless recommendation.
You also want to make sure that your suggested solutions are actually realistic. If the solutions cannot be implemented due to some sort of restraint, they are not realistic enough to make the final cut.
Finally, consider some of the alternative solutions that you considered and rejected. Write down the reasons why these solutions were rejected.
Step 9: Review
Look over your analysis when you have finished writing. Critique your work to make sure every step has been covered. Look for grammatical errors , poor sentence structure, or other things that can be improved. It should be clear, accurate, and professional.
Business Case Study Analysis Tips
Keep these strategic tips in mind:
- Know the case study backward and forward before you begin your case study analysis.
- Give yourself enough time to write the case study analysis. You don't want to rush through it.
- Be honest in your evaluations. Don't let personal issues and opinions cloud your judgment.
- Be analytical, not descriptive.
- Proofread your work, and even let a test reader give it a once-over for dropped words or typos that you no longer can see.
- What to Expect From MBA Classes
- How to Get Good Grades in Business School
- How to Read a Lot of Dry Text Quickly
- Components of a Business Plan
- Tips for New MBA Students
- Tips for Working on Group Projects
- Marketing Plan for a Business Venture
- MBA Case Studies From Top Business Schools
- How to Write and Format a Business Case Study
- Business Case Competitions: Purpose, Types and Rules
- Business Majors: Finance
- GRE vs. GMAT: Which Test Should MBA Applicants Take?
- What You Can Do With an MBA
- Chicago Booth MBA Programs and Admissions
- MBA Math Skills Every Business Student Needs
- GMAT Exam Structure, Timing, and Scoring
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study research paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or more subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in the Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- The case represents an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- The case provides important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- The case challenges and offers a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in current practice. A case study analysis may offer an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- The case provides an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings so as to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- The case offers a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for an exploratory investigation that highlights the need for further research about the problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of east central Africa. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a rural village of Uganda can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community. This example of a case study could also point to the need for scholars to build new theoretical frameworks around the topic [e.g., applying feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation].
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work.
In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What is being studied? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis [the case] you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why is this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would involve summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to investigate the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your use of a case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in relation to explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular case [i.e., subject of analysis] and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that constitutes your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; and, c) what were the consequences of the event in relation to the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experiences they have had that provide an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of their experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using them as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem [e.g., why is one politician in a particular local election used to show an increase in voter turnout from any other candidate running in the election]. Note that these issues apply to a specific group of people used as a case study unit of analysis [e.g., a classroom of students].
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, historical, cultural, economic, political], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, explain why you are studying Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research suggests Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut off? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should clearly support investigation of the research problem and linked to key findings from your literature review. Be sure to cite any studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for examining the problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your analysis of the case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is common to combine a description of the results with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings Remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations revealed by the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research if that is how the findings can be interpreted from your case.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and any need for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) reiterate the main argument supported by the findings from your case study; 2) state clearly the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in or the preferences of your professor, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented as it applies to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were engaged with social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood more in terms of managing access rather than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis that leave the reader questioning the results.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent] knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical [context-dependent] knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: Jun 3, 2024 9:44 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
Sales CRM Terms
What is Case Study Analysis? (Explained With Examples)
Oct 11, 2023

Case Study Analysis is a widely used research method that examines in-depth information about a particular individual, group, organization, or event. It is a comprehensive investigative approach that aims to understand the intricacies and complexities of the subject under study. Through the analysis of real-life scenarios and inquiry into various data sources, Case Study Analysis provides valuable insights and knowledge that can be used to inform decision-making and problem-solving strategies.
1°) What is Case Study Analysis?
Case Study Analysis is a research methodology that involves the systematic investigation of a specific case or cases to gain a deep understanding of the subject matter. This analysis encompasses collecting and analyzing various types of data, including qualitative and quantitative information. By examining multiple aspects of the case, such as its context, background, influences, and outcomes, researchers can draw meaningful conclusions and provide valuable insights for various fields of study.
When conducting a Case Study Analysis, researchers typically begin by selecting a case or multiple cases that are relevant to their research question or area of interest. This can involve choosing a specific organization, individual, event, or phenomenon to study. Once the case is selected, researchers gather relevant data through various methods, such as interviews, observations, document analysis, and artifact examination.
The data collected during a Case Study Analysis is then carefully analyzed and interpreted. Researchers use different analytical frameworks and techniques to make sense of the information and identify patterns, themes, and relationships within the data. This process involves coding and categorizing the data, conducting comparative analysis, and drawing conclusions based on the findings.
One of the key strengths of Case Study Analysis is its ability to provide a rich and detailed understanding of a specific case. This method allows researchers to delve deep into the complexities and nuances of the subject matter, uncovering insights that may not be captured through other research methods. By examining the case in its natural context, researchers can gain a holistic perspective and explore the various factors and variables that contribute to the case.
1.1 - Definition of Case Study Analysis
Case Study Analysis can be defined as an in-depth examination and exploration of a particular case or cases to unravel relevant details and complexities associated with the subject being studied. It involves a comprehensive and detailed analysis of various factors and variables that contribute to the case, aiming to answer research questions and uncover insights that can be applied in real-world scenarios.
When conducting a Case Study Analysis, researchers employ a range of research methods and techniques to collect and analyze data. These methods can include interviews, surveys, observations, document analysis, and experiments, among others. By using multiple sources of data, researchers can triangulate their findings and ensure the validity and reliability of their analysis.
Furthermore, Case Study Analysis often involves the use of theoretical frameworks and models to guide the research process. These frameworks provide a structured approach to analyzing the case and help researchers make sense of the data collected. By applying relevant theories and concepts, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying factors and dynamics at play in the case.
1.2 - Advantages of Case Study Analysis
Case Study Analysis offers numerous advantages that make it a popular research method across different disciplines. One significant advantage is its ability to provide rich and detailed information about a specific case, allowing researchers to gain a holistic understanding of the subject matter. Additionally, Case Study Analysis enables researchers to explore complex issues and phenomena in their natural context, capturing the intricacies and nuances that may not be captured through other research methods.
Moreover, Case Study Analysis allows researchers to investigate rare or unique cases that may not be easily replicated or studied through experimental methods. This method is particularly useful when studying phenomena that are complex, multifaceted, or involve multiple variables. By examining real-world cases, researchers can gain insights that can be applied to similar situations or inform future research and practice.
Furthermore, this research method allows for the analysis of multiple sources of data, such as interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which can contribute to a comprehensive and well-rounded examination of the case. Case Study Analysis also facilitates the exploration and identification of patterns, trends, and relationships within the data, generating valuable insights and knowledge for future reference and application.
1.3 - Disadvantages of Case Study Analysis
While Case Study Analysis offers various advantages, it also comes with certain limitations and challenges. One major limitation is the potential for researcher bias, as the interpretation of data and findings can be influenced by preconceived notions and personal perspectives. Researchers must be aware of their own biases and take steps to minimize their impact on the analysis.
Additionally, Case Study Analysis may suffer from limited generalizability, as it focuses on specific cases and contexts, which might not be applicable or representative of broader populations or situations. The findings of a case study may not be easily generalized to other settings or individuals, and caution should be exercised when applying the results to different contexts.
Moreover, Case Study Analysis can require significant time and resources due to its in-depth nature and the need for meticulous data collection and analysis. This can pose challenges for researchers working with limited budgets or tight deadlines. However, the thoroughness and depth of the analysis often outweigh the resource constraints, as the insights gained from a well-conducted case study can be highly valuable.
Finally, ethical considerations also play a crucial role in Case Study Analysis, as researchers must ensure the protection of participant confidentiality and privacy. Researchers must obtain informed consent from participants and take measures to safeguard their identities and personal information. Ethical guidelines and protocols should be followed to ensure the rights and well-being of the individuals involved in the case study.
2°) Examples of Case Study Analysis
Real-world examples of Case Study Analysis demonstrate the method's practical application and showcase its usefulness across various fields. The following examples provide insights into different scenarios where Case Study Analysis has been employed successfully.
2.1 - Example in a Startup Context
In a startup context, a Case Study Analysis might explore the factors that contributed to the success of a particular startup company. It would involve examining the organization's background, strategies, market conditions, and key decision-making processes. This analysis could reveal valuable lessons and insights for aspiring entrepreneurs and those interested in understanding the intricacies of startup success.
2.2 - Example in a Consulting Context
In the consulting industry, Case Study Analysis is often utilized to understand and develop solutions for complex business problems. For instance, a consulting firm might conduct a Case Study Analysis on a company facing challenges in its supply chain management. This analysis would involve identifying the underlying issues, evaluating different options, and proposing recommendations based on the findings. This approach enables consultants to apply their expertise and provide practical solutions to their clients.
2.3 - Example in a Digital Marketing Agency Context
Within a digital marketing agency, Case Study Analysis can be used to examine successful marketing campaigns. By analyzing various factors such as target audience, message effectiveness, channel selection, and campaign metrics, this analysis can provide valuable insights into the strategies and tactics that contribute to successful marketing initiatives. Digital marketers can then apply these insights to optimize future campaigns and drive better results for their clients.
2.4 - Example with Analogies
Case Study Analysis can also be utilized with analogies to investigate specific scenarios and draw parallels to similar situations. For instance, a Case Study Analysis could explore the response of different countries to natural disasters and draw analogies to inform disaster management strategies in other regions. These analogies can help policymakers and researchers develop more effective approaches to mitigate the impact of disasters and protect vulnerable populations.
In conclusion, Case Study Analysis is a powerful research method that provides a comprehensive understanding of a particular individual, group, organization, or event. By analyzing real-life cases and exploring various data sources, researchers can unravel complexities, generate valuable insights, and inform decision-making processes. With its advantages and limitations, Case Study Analysis offers a unique approach to gaining in-depth knowledge and practical application across numerous fields.
About the author

Arnaud Belinga

"i wrote this article"
Try my sales crm software (people love it) 👇.
DISCOVER BREAKCOLD CRM
Related Articles

What is the 80-20 rule? (Explained With Examples)

What is the ABCD Sales Method? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Accelerated Sales Cycle? (Explained With Examples)

What is Account-Based Marketing (ABM)? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Account Manager? (Explained With Examples)

What is Account Mapping? (Explained With Examples)

What is Account-Based Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Ad Targeting? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Addressable Market? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Adoption Curve? (Explained With Examples)

What is an AE (Account Executive)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Affiliate Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is AI in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is an AI-Powered CRM? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Alternative Close? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Annual Contract Value? (ACV - Explained With Examples)

What are Appointments Set? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Assumptive Close? (Explained With Examples)

What is Automated Outreach? (Explained With Examples)

What is Average Revenue Per Account (ARPA)? (Explained With Examples)

What is B2B (Business-to-Business)? (Explained With Examples)

What is B2G (Business-to-Government)? (Explained With Examples)

What is B2P (Business-to-Partner)? (Explained With Examples)

What is BANT (Budget, Authority, Need, Timing)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Behavioral Economics in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Benchmark Data? (Explained With Examples)

What is Benefit Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What are Benefit Statements? (Explained With Examples)

What is Beyond the Obvious? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Bootstrapped Startup? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Bottom of the Funnel (BOFU)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Bounce Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Brand Awareness? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Break-Even Point? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Breakup Email? (Explained With Examples)

What is Business Development? (Explained With Examples)

What are Business Insights? (Explained With Examples)

What is Business Process Automation? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Buyer Persona? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Buyer's Journey? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Buying Cycle? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Buying Signal? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Buying Team? (Explained With Examples)

What is a C-Level Executive? (Explained With Examples)

What is Call Logging? (Explained With Examples)

What is Call Recording? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Call-to-Action (CTA)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Challenger Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Chasing Lost Deals? (Explained With Examples)

What is Churn Prevention? (Explained With Examples)

What is Churn Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Click-Through Rate (CTR)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Client Acquisition? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Closing Ratio? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Ben Franklin Close? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cognitive Bias in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cognitive Dissonance in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cold Calling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cold Outreach? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Competitive Advantage? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Competitive Analysis? (Explained With Examples)

What is Competitive Positioning? (Explained With Examples)

What is Conceptual Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Closing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Negotiation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Prospecting? (Explained With Examples)

What is Consultative Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Content Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Content Syndication? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Conversion Funnel? (Explained With Examples)

What is Conversion Optimization? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Conversion Path? (Explained With Examples)

What is Conversion Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cost-Per-Click (CPC)? (Explained With Examples)

What is a CRM (Customer Relationship Management)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cross-Cultural Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Cross-Sell Ratio? (Explained With Examples)

What is Cross-Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer-Centric Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer-Centric Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Journey Mapping? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Customer Journey? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Profiling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Customer Retention? (Explained With Examples)

What is Dark Social? (Explained With Examples)

What is Data Enrichment? (Explained With Examples)

What is Data Segmentation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Database Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What are Decision Criteria? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Decision Maker? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Decision-Making Unit (DMU)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Demand Generation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Digital Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Direct Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Discovery Call? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Discovery Meeting? (Explained With Examples)

What are Discovery Questions? (Explained With Examples)

What is Door-to-Door Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Drip Campaign? (Explained With Examples)

What is Dunning? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Early Adopter? (Explained With Examples)

What is Elevator Pitch? (Explained With Examples)

What is Email Hygiene? (Explained With Examples)

What is Email Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Emotional Intelligence Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Engagement Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Engagement Rate? (Explained With Examples)

What is Engagement Strategy? (Explained With Examples)

What is Feature-Benefit Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Field Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Follow-Up? (Explained With Examples)

What is Forecast Accuracy? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Funnel? (Explained With Examples)

What is Gamification in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Gatekeeper Strategy? (Explained With Examples)


What is Gatekeeper? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Go-to Market Strategy? (Explained With Examples)

What is Growth Hacking? (Explained With Examples)

What is Growth Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Guerrilla Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is High-Ticket Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Holistic Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Ideal Customer Profile (ICP)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inbound Lead Generation? (Explained With Examples)

What is an Inbound Lead? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inbound Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inbound Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Influencer Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inside Sales Representative? (Explained With Examples)

What is Inside Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Insight Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Key Account? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Key Performance Indicator (KPI)? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Landing Page? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Database? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Lead Enrichment? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Generation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Nurturing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Qualification? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lead Scoring? (Explained With Examples)

What are LinkedIn InMails? (Explained With Examples)

What is LinkedIn Sales Navigator? (Explained With Examples)

What is Lost Opportunity? (Explained With Examples)

What is Market Positioning? (Explained With Examples)

What is Market Research? (Explained With Examples)

What is Market Segmentation? (Explained With Examples)

What is MEDDIC? (Explained With Examples)

What is Middle Of The Funnel (MOFU)? (Explained With Examples)

What is Motivational Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is a MQL (Marketing Qualified Lead)? (Explained With Examples)

What is MRR Growth? (Explained With Examples)

What is MRR (Monthly Recurring Revenue)? (Explained With Examples)

What is N.E.A.T. Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Neil Rackham's Sales Tactics? (Explained With Examples)

What is Networking? (Explained With Examples)

What is NLP Sales Techniques? (Explained With Examples)

What is the Net Promotion Score? (NPS - Explained With Examples)

What is Objection Handling Framework? (Explained With Examples)

What is On-Hold Messaging? (Explained With Examples)

What is Onboarding in Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Online Advertising? (Explained With Examples)

What is Outbound Sales? (Explained With Examples)

What is Pain Points Analysis? (Explained With Examples)

What is Permission Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Personality-Based Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Persuasion Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Pipeline Management? (Explained With Examples)

What is Pipeline Velocity? (Explained With Examples)

What is Predictive Lead Scoring? (Explained With Examples)

What is Price Negotiation? (Explained With Examples)

What is Price Objection? (Explained With Examples)

What is Price Sensitivity? (Explained With Examples)

What is Problem-Solution Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Product Knowledge? (Explained With Examples)

What is Product-Led-Growth? (Explained With Examples)

What is Prospecting? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Qualified Lead? (Explained With Examples)

What is Question-Based Selling? (Explained With Examples)

What is Referral Marketing? (Explained With Examples)

What is Relationship Building? (Explained With Examples)

What is Revenue Forecast? (Explained With Examples)

What is a ROI? (Explained With Examples)

What is Sales Automation? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Bonus Plan? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Champion? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Collateral? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Commission Structure Plan? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales CRM? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Cycle? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Demo? (Explained With Examples)

What is Sales Enablement? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Flywheel? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Funnel? (Explained With Examples)

What are Sales KPIs? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Meetup? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Pipeline? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Pitch? (Explained With Examples)

What is a Sales Playbook? (Explained With Examples)
Try breakcold now, are you ready to accelerate your sales pipeline.
Join over +1000 agencies, startups & consultants closing deals with Breakcold Sales CRM
Get Started for free
Sales CRM Features
Sales Pipeline Software
Sales Lead Tracking
CRM with social media integrations
Social Selling Software
Contact Management
CRM Unified Email LinkedIn Inbox
Breakcold works for many industries
CRM for Agencies
CRM for Startups
CRM for Consultants
CRM for Small Business
CRM for LinkedIn
CRM for Coaches
Sales CRM & Sales Pipeline Tutorials
The 8 Sales Pipeline Stages
The Best CRMs for Agencies
The Best CRMs for Consultants
The Best LinkedIn CRMs
How to close deals in 2024, not in 2010
CRM automation: from 0 to PRO in 5 minutes
LinkedIn Inbox Management
LinkedIn Account-Based Marketing (2024 Tutorial with video)
Tools & more
Sales Pipeline Templates
Alternatives
Integrations
CRM integration with LinkedIn
© 2024 Breakcold
Privacy Policy
Terms of Service
The Ultimate Guide on Writing an A+ Case Study Analysis + 15 Examples

Struggle with writing a case study analysis? You are in the right place! Below, we will show you nuts and bolts of this type of paper, how to write it, and share 15 distinct essay examples. Plus, you will find the case study checklist to keep your writing on track.
What is a Case Study Analysis?
Case study analysis topics.
- Important Aspects
You might ask, what is a case study analysis ? With this type of work, you take an actual situation from a specific discipline, such as business or education. The goal is to find a solution, analyze the outcomes of the situation, or evaluate it.

Case study analysis does not target one specific theory or piece of knowledge. It requires a universal application of several theories and methods for research and review. Hence, it can be helpful for many disciplines at once. If you need to look at some examples, head over to our essay database .
There are several steps you need to take for a successful analysis depending on the type of your case study. Here are the most critical universal points:
- Analyze the problem from different perspectives. Use the theories and methods you have learned about in the classroom.
- Devise a series of solutions or outcomes. You need to analyze their advantages and weaknesses.
- Provide the best solution according to your analysis. You must present solid arguments for why you have suggested it.
- Demonstrate well-grounded research in your case study analysis You should not make claims without proof.
- Provide credible references for any theory that you mention in your analysis. You do not want your work to be discarded because of plagiarism.
If you want to start the business in the future, case study analysis is essential for your education. It can give you a taste of what your career is might include.
Are you panicking because you have never written anything like this before? Don’t worry! After going through the guidelines in this article, you will get a better sense of what is required from you. It will not seem as scary anymore. 😊
- Business ethics: the case study
- Comparing Johnson and Johnson and Pfizer vaccines
- Theories of criminal law
- Recklessness as a symptom of antisocial personality disorder
- Differences between nursing care & residential care
- Strengths and weaknesses of Microsoft Corporation
- Farming the Cerrado : advantages and disadvantages of soybean farming in Brazil
- McKinsey opioid scandal: the case study
- General Electric vs. General Motors
- How much longer will Lake Mead last?
- Organizational issues of the City Centre Hospital
- How to use fact patterns to your advantage
- Prevention and control of sexually transmitted infections
- The role of gender in the workplace
- Blue ocean market: Uber case study
- Five stages of a child’s development
- The importance of health history in treating severe pain
- How does Equifax protect personal data?
- Adidas and healthy lifestyle promotion
- Long-term value for the organization as a result of high-quality customer service
- The missions of community-based clinics
- Operations management: Apple case study
- Emergency management of Fournier’s gangrene
- The outcome of the Hamdi v. Rumsfeld case
- What are the seven principles of ethics in research?
- Tea Leaves and More : issues and solutions
- The effect of transformational leadership on employee productivity
- Inventory management as a solution for understocking and overstocking
- Strength and conditioning training: the case study
- History of Nike corporation
- Positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia
- Anxiety-related habits during post-traumatic stress disorder
- The issue of Starbucks employees wearing union pins
- How does Delta Airlines increase its competitive advantage?
- Why was Anne Hutchinson a threat to authorities?
15 Case Study Analysis Examples
We have prepared 15 examples of case study analysis, so you can get an idea of how they should look. The disciplines are broad and there is something here for everyone. Check out the table below!
| # | Name | Description | Highlight |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Yolanda Pinellas developed necrosis as a result of infiltration during intravenous therapy, because of hospital malpractice. | This is a good example of analysis of contributing factors. | |
| 2 | This case study focuses on a situation when parents are against vaccination, but nurses feel it is necessary for the children’s wellbeing. | This is an example of how ethical case studies should be handled. | |
| 3 | The Clayton facility faces losses, according to its recent financial report, but their market analysis indicates that the situation will not go on for long. | This is a financial case study with its nuances. It would be good to take into account if you are dealing with a case study in finance. | |
| 4 | This case study focuses on the Amish population and their usage of non-traditional medicine. | This analysis discusses the case on several levels. | |
| 5 | As a company that is a part of NASA’s space program, TechFite is worried about its cybersecurity as it is a likely target of espionage. | This one proposes a process outline based on a framework. It includes bulleted lists to make the information more digestable. | |
| 6 | The analysis of this case study is evaluating a training program in Braun Oral B Ireland using Kirkpatrick’s model. | This study will be a helpful example for you if you are looking to analyze your topic through a certain model. | |
| 7 | Banner Health is a non-profit care organization that wants to address both its citizens’ physical and mental health needs. This case study takes a look at their strategic plan. | This one implements a comparison tactic that highlights the strengths and weaknesses of the case. | |
| 8 | This case study analyzes the models of transformational change in Zurich UK Life and General Motors. | This is a very long analysis. You can learn how to keep extensive texts engaging for your audience. | |
| 9 | Zalora is a company that works in the apparel industry and it wants to enter the online economic environment. | This case study includes a big section dedicated to recommendations and reflections. If your case study requires you to recommend solutions, you should check this out. | |
| 10 | This case study example analyzes the practices behind Hot Topic’s success. | This is a quick success analysis that you can check out if you need to write a broader version. | |
| 11 | Taylor needs to convince Bob that using bar codes is helpful as Bob refuses to accept it. | This is a role-playing case study that uses made-up characters to discuss a certain topic. | |
| 12 | This case focuses on the bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers, an investment banking institution. | This is a very detailed case study that explores the deep history of the topic and introduces information in a captivating manner using graphs and lists. | |
| 13 | This case study uses Jean Piaget’s work to understand the cognitive development of children. | This is a detailed psychological research. It is an example of how a case study in behavioral analysis should be structured. | |
| 14 | The case study focuses on analyzing the weaknesses of Simmons brought by the change of its CEO. | This case study performs a quality analysis of resources and sustainability. | |
| 15 | HUB produces organic beer and sells it in Oregon. They want to advance in terms of market share and profit as part of their future development. | SWOT, PESTLE, Peter’s five forces and VRIO analysis are implemented in this case study. |
Let’s concentrate on the format for case study analysis!
Case Study Analysis: Format
In this section, we will get you acquainted with different types of case studies. We will focus on the difference between multiple and single case study analysis. Additionally, we will show you how to organize all of your ideas into an outline. Hence, your work will be understandable and complete.
- Types of Case Studies
There are several distinct types of case studies , each with its nuances. The choice will depend on the needs of your investigation. We will focus on Illustrative, Exploratory, Cumulative, and Critical Instance studies. Let’s explore each of them one by one.
- Illustrative Case Studies Illustrative case studies are the most common type. They are very descriptive, and the main goal is to help you understand the situation. You are typically given one or two instances of an event. Illustrative case studies answer two questions: What is happening? Why is it happening? The case study is explained in great detail, including location, key players, roles, influence, and involvement. The focus of illustrative case studies is to maintain the reader’s interest. Hence, the language should be understandable, but it should not be oversimplified. It is not preferred to quote more than two instances as the case study might become too complicated.
- Exploratory Case Studies Exploratory case studies are mainly used in Social Sciences. They tend to focus on real-life contexts for situations. They are implemented before a large-scale investigation to help develop the case for more advanced research processes. Exploratory case studies aim to research a specific topic in detail to help you reach a complete understanding of it. You need to identify questions that can later be answered as part of a more extensive examination. Your initial research might reveal very persuasive details. However, it is crucial to remember that concluding before the large-scale investigation is counterproductive.
- Cumulative Case Studies The idea of a cumulative case study is to gather information and details from many data sources to claim a general phenomenon. Cumulative case studies eliminate the need for additional and expensive new studies, which are simply repetitions of the old ones. If you properly analyze all of the case study data that exists, you will realize that everything you are looking for is already there. However, it is essential to look at the existing research from a new perspective to ensure it fits the current challenges and needs.
- Critical Instance Case Studies Critical instance case studies are similar to cumulative but work oppositely. Instead of defining a general phenomenon based on little research, it tries to understand a specific case based on generalized findings. Critical instance case studies help answer cause and effect questions. The adequate specification of your evaluation question is the most crucial part of your analysis.
- Single vs. Multiple Case Study
Your case study can either include a single case or multiple cases . In this section, we will discuss the benefits of both:
- Single Case Study Single case studies are less expensive and do not take as much time. When examining one case, it is easier to put all of your energy into it and get a deeper understanding of the subject. Since the study is more careful, you can look at one thing from many different perspectives. Usually, in a single case study, the case is more critical and unique , and it is possible to focus on a more longitudinal research.
- Multiple Case Study When studying several cases, you can understand the critical similarities and differences among them. If you base your research on many cases, it will be more robust and reliable. Such analysis allows you to form broader research questions. Hence, you can end up with a more convincing theory.
Now, let’s talk about the backbone of every study: the outline!

Case Study Outline
Before writing any paper, you should first prepare an outline. It not only makes your job easier but also enhances the organization of your paper. You should put all of your ideas down and try to understand which order and format will best suit your analysis.
We have tried to simplify the process by preparing a sample outline for your case study analysis. It will help you understand what your paper should include.
- Introduction Firstly, you should introduce your reader to the case, assuming they have no prior knowledge. Describe all the challenges and mention the most important details.
- Answers to the Questions There will probably be some questions about your case. It would be best if you answered all of them in an organized manner. Make sure not to make it too obvious. Answer them in such a way that it seems like a part of your analysis.
- Challenges Though you talk about the challenges in your introduction a little bit, it is essential to go into more detail within the main paragraphs to make sure your readers understand them. It will improve the comprehension of solutions later.
- Solutions Introduce each solution you have devised. Evaluate those based on different theories and mechanisms. All of your propositions need to be solid and well-designed. Your case study evaluation should be informative and engaging.
- Final Statement In this part of your paper, you should state which solution best fits the case according to your broader analysis. You should compare it with the others and explain why you have chosen it.
- Conclusion The conclusion is the last thing you need to write. There is nothing specific that should be included. Make sure that your paper comes to a logical end.
- References Of course, you need to reference all of the theories and practices mentioned in your paper for your analysis to be solid and well-grounded. The style of your references will depend on the format assigned by your instructor.
This is how a typical case study analysis should look like. We mentioned this format for you to imagine the standard thought process that goes into making outlines. First, organize your research and divide it into parts to achieve an exciting and compelling paper. The type of case study analysis with which you are dealing also matters.
Now, here’s how you start writing!
How to Write Case Study Analysis: Important Aspects
In this section, you will find everything you need to kickstart writing your paper. Firstly, we will go through the things you need to have ready before you start. Then, we will show you how to do adequate research. Finally, we will give you a case study checklist to make it easier to complete the tasks throughout your analysis.
Before You Start
It is vital to choose an appropriate case study topic first. It should be exciting and relevant to your area of study. Once you select your topic, you need to choose an applicable case study . There are several criteria that you need to keep in mind in your search of a case study:
- The case study should complement your topic of research For example, if the topic you have chosen is related to marketing, it would be weird if your case study was about banking. However, a case study about how a famous company handles its marketing would be very acceptable.
- The case study should apply to the phenomena that you have chosen to research Make sure that the way the company handles its marketing can be generalized to benefit other companies. It needs to be universally reusable.
- The case study cannot be outdated You need to know that you can apply the outcome of your research to the modern world. Everything needs to be analyzed from the perspective of today.
- Decide whether you need a single or multiple case study You can go through the comparison above once again. Try to understand which one suits your topic best.
Do you already have the topic? Let’s get your researching skills up to date!

Case Study Research
When doing case study research, simply googling something rains down tons of sources full of information. However, most of those sources cannot be trusted, especially when writing an academic paper. The references are the most crucial part of such papers. If they are poor, then your essay has no reliable basis. Hence, you need to look for official sources, such as university websites or scholarly articles. Remember that Wikipedia is not a valid source !
Throughout the process, have your research question in mind. It is easy to get carried away and read every exciting article on the topic. Nonetheless, it would be best to have a specific goal to ensure your research is practical and not wasting your time.
Finally, keep your research up to date! Remember that you are looking for information that applies to the current world and its challenges. You need to look for modern solutions to the given problem.
We are almost there! Let’s make sure you can tick off every item in this checklist !
Checklist for Case Study Analysis
Go through this checklist. It will help you keep your case study research and writing on track.
- Choose the topic.
- Decide whether you are going to do single or multiple case study.
- Identify the type of your case study.
- They are relevant to the topic.
- Their outcome can be generalized to fit other cases within the same area of research.
- They are not outdated.
- Define a clear case study research question.
- Make sure that the sources of your research are credible and up to date.
- Identify the theories and methodologies you are going to use to analyze the case.
- Use more than one point of view to examine the case, and look at it from different perspectives.
- Have a clear outline of what you are going to include in your paper.
- Write and proofread your paper.
Have you completed every item on this list? Congratulations! You are done with your case study analysis!
❓ What is the difference between case study and case analysis?
Case study and case analysis both provide you with a topic and require extensive research. However, a case study must be taken from real life. For example, a student might analyze Coca-Cola’s financial results and come up with brilliant results that can significantly impact the company. If you send this kind of case study analysis to the company, you might even get a reward. Case analysis focuses more on problems and solutions, whereas case studies can include general research and evaluation.
❓ What are the stages of a case study?
There are four main stages of a case study:
- analyzing the case,
- identifying its challenges,
- devising a set of possible solutions or outcomes,
- evaluating those outcomes.
To ensure the success of your analysis, you should go over all of these stages with equal diligence.
❓ What is the purpose of a case study?
The purpose of a case study analysis is to describe a case in detail and identify the main issues with it. Afterwards, these issues need to be analyzed based on appropriate theories from the discipline that you have learned about in class. Finally, you need to recommend a list of actions that should be performed for that case.
❓ What are the qualities of a good case study?
Here are some qualities of a good case study:
- It is written in a formal, academic language with good grammar and coherent structure.
- All of the claims made in the case study have a reasonable basis and can be proven.
- The case study does not overload the readers with unnecessary information. It is clear and to the point.
- The information is passed to the reader in an organized manner. It has flow, and it is easy to keep up with the extensive academic research.
- What is a Case Study Analysis
- Illustrative Case Studies
- Exploratory Case Study Example
- Definition of Cumulative Case Studies
- Definition of Critical Instance Case Studies
- A Comparative Study of Single and Multiple Case Studies
- How to Choose an Applicable Study
- Case Study Checklist
Mindful Walking: Journey to Self-Discovery
Being productive at home: 25 tips for students & remote workers, the future is here: assistive technology for learning disabilities, dealing with failure: the guide on how to make the most of your mistakes, cybersecurity threats for students & how to fight them, dual degree vs. double major: what’s the difference & are they worth it.
Instant insights, infinite possibilities
What is case study research?
Last updated
8 February 2023
Reviewed by
Cathy Heath
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
Suppose a company receives a spike in the number of customer complaints, or medical experts discover an outbreak of illness affecting children but are not quite sure of the reason. In both cases, carrying out a case study could be the best way to get answers.
Organization
Case studies can be carried out across different disciplines, including education, medicine, sociology, and business.
Most case studies employ qualitative methods, but quantitative methods can also be used. Researchers can then describe, compare, evaluate, and identify patterns or cause-and-effect relationships between the various variables under study. They can then use this knowledge to decide what action to take.
Another thing to note is that case studies are generally singular in their focus. This means they narrow focus to a particular area, making them highly subjective. You cannot always generalize the results of a case study and apply them to a larger population. However, they are valuable tools to illustrate a principle or develop a thesis.
Analyze case study research
Dovetail streamlines case study research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- What are the different types of case study designs?
Researchers can choose from a variety of case study designs. The design they choose is dependent on what questions they need to answer, the context of the research environment, how much data they already have, and what resources are available.
Here are the common types of case study design:
Explanatory
An explanatory case study is an initial explanation of the how or why that is behind something. This design is commonly used when studying a real-life phenomenon or event. Once the organization understands the reasons behind a phenomenon, it can then make changes to enhance or eliminate the variables causing it.
Here is an example: How is co-teaching implemented in elementary schools? The title for a case study of this subject could be “Case Study of the Implementation of Co-Teaching in Elementary Schools.”
Descriptive
An illustrative or descriptive case study helps researchers shed light on an unfamiliar object or subject after a period of time. The case study provides an in-depth review of the issue at hand and adds real-world examples in the area the researcher wants the audience to understand.
The researcher makes no inferences or causal statements about the object or subject under review. This type of design is often used to understand cultural shifts.
Here is an example: How did people cope with the 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami? This case study could be titled "A Case Study of the 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami and its Effect on the Indonesian Population."
Exploratory
Exploratory research is also called a pilot case study. It is usually the first step within a larger research project, often relying on questionnaires and surveys . Researchers use exploratory research to help narrow down their focus, define parameters, draft a specific research question , and/or identify variables in a larger study. This research design usually covers a wider area than others, and focuses on the ‘what’ and ‘who’ of a topic.
Here is an example: How do nutrition and socialization in early childhood affect learning in children? The title of the exploratory study may be “Case Study of the Effects of Nutrition and Socialization on Learning in Early Childhood.”
An intrinsic case study is specifically designed to look at a unique and special phenomenon. At the start of the study, the researcher defines the phenomenon and the uniqueness that differentiates it from others.
In this case, researchers do not attempt to generalize, compare, or challenge the existing assumptions. Instead, they explore the unique variables to enhance understanding. Here is an example: “Case Study of Volcanic Lightning.”
This design can also be identified as a cumulative case study. It uses information from past studies or observations of groups of people in certain settings as the foundation of the new study. Given that it takes multiple areas into account, it allows for greater generalization than a single case study.
The researchers also get an in-depth look at a particular subject from different viewpoints. Here is an example: “Case Study of how PTSD affected Vietnam and Gulf War Veterans Differently Due to Advances in Military Technology.”
Critical instance
A critical case study incorporates both explanatory and intrinsic study designs. It does not have predetermined purposes beyond an investigation of the said subject. It can be used for a deeper explanation of the cause-and-effect relationship. It can also be used to question a common assumption or myth.
The findings can then be used further to generalize whether they would also apply in a different environment. Here is an example: “What Effect Does Prolonged Use of Social Media Have on the Mind of American Youth?”
Instrumental
Instrumental research attempts to achieve goals beyond understanding the object at hand. Researchers explore a larger subject through different, separate studies and use the findings to understand its relationship to another subject. This type of design also provides insight into an issue or helps refine a theory.
For example, you may want to determine if violent behavior in children predisposes them to crime later in life. The focus is on the relationship between children and violent behavior, and why certain children do become violent. Here is an example: “Violence Breeds Violence: Childhood Exposure and Participation in Adult Crime.”
Evaluation case study design is employed to research the effects of a program, policy, or intervention, and assess its effectiveness and impact on future decision-making.
For example, you might want to see whether children learn times tables quicker through an educational game on their iPad versus a more teacher-led intervention. Here is an example: “An Investigation of the Impact of an iPad Multiplication Game for Primary School Children.”
- When do you use case studies?
Case studies are ideal when you want to gain a contextual, concrete, or in-depth understanding of a particular subject. It helps you understand the characteristics, implications, and meanings of the subject.
They are also an excellent choice for those writing a thesis or dissertation, as they help keep the project focused on a particular area when resources or time may be too limited to cover a wider one. You may have to conduct several case studies to explore different aspects of the subject in question and understand the problem.
- What are the steps to follow when conducting a case study?
1. Select a case
Once you identify the problem at hand and come up with questions, identify the case you will focus on. The study can provide insights into the subject at hand, challenge existing assumptions, propose a course of action, and/or open up new areas for further research.
2. Create a theoretical framework
While you will be focusing on a specific detail, the case study design you choose should be linked to existing knowledge on the topic. This prevents it from becoming an isolated description and allows for enhancing the existing information.
It may expand the current theory by bringing up new ideas or concepts, challenge established assumptions, or exemplify a theory by exploring how it answers the problem at hand. A theoretical framework starts with a literature review of the sources relevant to the topic in focus. This helps in identifying key concepts to guide analysis and interpretation.
3. Collect the data
Case studies are frequently supplemented with qualitative data such as observations, interviews, and a review of both primary and secondary sources such as official records, news articles, and photographs. There may also be quantitative data —this data assists in understanding the case thoroughly.
4. Analyze your case
The results of the research depend on the research design. Most case studies are structured with chapters or topic headings for easy explanation and presentation. Others may be written as narratives to allow researchers to explore various angles of the topic and analyze its meanings and implications.
In all areas, always give a detailed contextual understanding of the case and connect it to the existing theory and literature before discussing how it fits into your problem area.
- What are some case study examples?
What are the best approaches for introducing our product into the Kenyan market?
How does the change in marketing strategy aid in increasing the sales volumes of product Y?
How can teachers enhance student participation in classrooms?
How does poverty affect literacy levels in children?
Case study topics
Case study of product marketing strategies in the Kenyan market
Case study of the effects of a marketing strategy change on product Y sales volumes
Case study of X school teachers that encourage active student participation in the classroom
Case study of the effects of poverty on literacy levels in children
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 22 August 2024
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
Main Tips On How To Write Case Study Analysis
Table of contents
- 1 What is a Case Study Analysis?
- 2 Difference Between Research Paper and Case Study
- 3 Types of Case Studies
- 4 Writing a Case Study Draft
- 5 How to Write a Case Study Outline
- 6 How to Write a Case Study
- 7 How to Analyze a Case Study
- 8.1 Tips for a Successful Case Analysis
- 9 How to Format a Case Study
- 10 How to Create a Title Page and Cite a Case Study
Many students struggle with how to do a case study analysis. Writing such an assignment is always daunting, as it requires you to analyze something and form conclusions based on your research.
It usually focuses on phenomena you can’t study in a typical way. Therefore, when writing such a text, you have to prepare thoughtfully. In the PapersOwl article, you will find out what this academic writing is and how to write a case analysis.
What is a Case Study Analysis?
A case study analysis is a form of writing that analyzes a specific situation, event, object, person, or even place. The said analysis should be written and structured to lead to a conclusion. Typically, you cannot analyze the subject of this essay via quantitative methods.
Note that such studies can be used in various fields and require the use of many theories that can give you a unique approach to the matter. For example, you can write a paper like this about social sciences, business, medicine, and many other fields. Each of these will require a particular approach.
Difference Between Research Paper and Case Study
Both research papers and case studies share common features, yet they also differ in several key aspects. Hence, knowing these parallels and distinctions, you will be able to learn how to write a case study assignment correctly.
A case study introduction can present the topic but does not require a citation of other similar works or the writer’s opinion. In contrast, a research paper requires citations right from the introduction, as it builds on the research of others.
Furthermore, authors of case studies should share their insights and perspectives on the case they study. A major difference is that research papers concentrate on a specific issue and use solid evidence. In contrast, case studies examine a subject in depth, offer detailed information, and help develop critical thinking skills.
Types of Case Studies
When it comes to writing case study analysis, there are five types you must learn to differentiate. That is important because whether you get such an assignment, you will have to understand the task first and then start with the writing.
Here are the types of case studies which you will encounter most often:
- Problem-oriented – this type focuses on real-life situations or theoretical issues and aims to solve them. For example, “World Hunger.”
- The second type is critical , also known as innate . The goal is to investigate a specific case, particularly its effects and what causes them – “Why Toys Remain Gender Stereotyped.”
Historical case studies focus on events from our past. The text should contain information about a specific historical period of this type. Your goal will be to provide different perspectives of an event and parallel them to current-day issues. An example of such a topic is “Racism During Ancient Times – Roman Empire.”
- The illustrative or Instrumental type focuses on describing a particular event. Here you have to explain the event’s outcome and what you have learned from it. A sample of such a topic is “The Effects of Dance Therapy in Depressed Adolescents.”
- Collective case studies are the fifth type. They include a collection of data about a specific case you will use to compare. E.g., “The Management Leadership at Work.”
- Exploratory Case Studies . This type often applies in new fields of study or in cases where little data exists. An example of this type is “Initial Insights into Behavioral Trends in Cryptocurrency Trading.”

Writing a Case Study Draft
Creating a rough draft is the foremost step to take while writing such a paper. It is an essential step you must take, no matter how experienced you are. By doing it, you will be able to get more creative. In addition, you can explore options and decide on what to focus on more precisely, which will eventually result in a higher grade for your work.
So, sit down in a quiet place, bring an old-fashioned pen and paper, and start drafting ideas. Read them briefly while sipping on your tea and edit. After you have decided where your focus will lay, you have to develop these ideas and thoughts a bit more, then pick the best one.
How to Write a Case Study Outline
Creating a case study outline is an essential step in the writing process using the case study research method. Here’s how you can structure this preparation effectively:
- Conduct Research: Begin by using academic search engines like Google Scholar, or refer to books and published materials to gather relevant data. This research will help clarify the structure of your case study and determine the main points that need addressing.
- Formulate Your Thesis Statement: Develop a clear thesis statement that will guide the narrative of your case study. This statement should be based on the specific topic you have chosen.
- Outline Preparation
- Review Case Details: Thoroughly review the case you are analyzing to ensure a deep understanding of the subject.
- Note-taking and Question Formulation: Write down important notes and questions that arise during your review. Highlight relevant facts and critical data points that will support your analysis.
- Identify Problems and Causes: Identify the main problems and consider what their causes might be. This includes figuring out who is responsible and how these problems impact the company.
- Preliminary Research: Perform initial research to discover if similar problems have occurred previously and how they were resolved. This can offer insights into possible solutions and strategies for your case study.
The outline for your case study paper is essential to your writing process. It lets your professor assess your understanding of the topic, the correctness of your format, and the structure of your paper. They can spot any potential problems with your work. Having an outline serves as a guide for both you and your professor, making it easier to plan and write your paper . With the help of a well-crafted outline, your professor can navigate your paper more easily and spot any issues before they arise. Writing a case study can be challenging, but having a strong outline makes the process simpler.
A case study outline will most likely consist of the following sections and information:
- Case study title;
- Student’s name;
- Educational instructor’s name;
- Course name.
Introduction/Summary
- It briefly overviews your case study, thesis statement, and essential findings.
Main Body Paragraphs – usually three to five
- Literature Review/Background Information;
- Method/Findings;
- Discussion/Solutions/Recommendations.
- Repeat a paraphrased version of your thesis;
- Summarize your case study key points;
- Finish with a statement that can recommend the audience to read further by giving them thoughts to contemplate and develop new ideas.
Reference List or Bibliography
- List all the sources of evidence used to create your case study in your educational organization’s required citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard, Turabian, etc.).
How to Write a Case Study
The way to write a case study is by strictly following the main idea of your thesis. You already know that a study’s main body consists of an introduction, literature review, method, discussion, and conclusion sections. Thus, all that is left is to focus on these parts and understand how to make them perfect.
- The Introduction/Summary: The introduction of a case study should start with a solid first sentence that will hook the reader. Afterward, you must explain the question you will be answering and why you are doing it. You should include some of the topic’s relevant history and details here. Also, you should explain how your case study will enrich the available information. Also, briefly summarize your literature review, which your findings will use as a base. Try to finish positively and make the reader see the benefits of reading your work.

- Background Information/Literature Review: Structure and present the data from your academic sources . This section will show the reader how vital your work is and the basis for it.
- Method/Findings: This part aims to explain the case you selected, how it connects to the issue, and why you chose them. You can also add what methods you use. Here you must note that the data collection methods are qualitative, not quantitative, for case studies. That means the data is not random but well-structured and chronically taken from interviews, focus groups, and other sources.
- Discussion/Solutions: Restate your thesis but rephrase it, then draw your conclusions from what you have discovered via your research and link to your statement. Inform the audience of your main findings and define why the results are relevant to the field. Think about the following questions:
Were the results unexpected? Why/Why not?
How do your findings compare to previous similar case studies in your literature review?
Do your findings correlate to previous results, or do they contradict them?
Are your findings helpful in deepening the current understanding of the topic?
Next, explore possible alternative explanations or interpretations of your findings. Be subjective and explain your paper’s limitations. End with some suggestions for further exploration based on the limits of your work.
- Conclusion: Inform the reader precisely why your case study and findings are relevant, and restate your thesis and main results. Give a summary of previous studies you reviewed and how you contributed to expanding current knowledge. The final should explain how your work can be helpful and implemented in future research.
Your instructor should have an excellent example they can show you, so feel free to ask. They will surely want to help you learn how to write a case study!

How to Analyze a Case Study
Analyzing a case study involves a structured approach that simulates real-life scenarios and is key to developing actionable insights. Here is a step-by-step guide adapted from Ellet, W. (2007) to help you effectively analyze a case study:
- Identify the Type of Case Study
Begin by determining the type of case study you are examining. This could be:
- Problems: Where something significant has occurred, and the cause is unknown.
- Decisions : Where a clear decision needs making, requiring options, criteria, and relevant evidence.
- Evaluations : Where you assess the effectiveness of a performance or outcome.
- Rules : These involve using quantitative methods to analyze a business area.
- Develop a Hypothesis
From the perspective of the protagonist, formulate a hypothesis to address the dilemma. Consider what you need to know about the situation:
- For problems: Understand the aspects, significance, and responsible parties.
- For decisions: Identify the options available, the stakes involved, and the decision-making criteria.
- For evaluations: Determine who or what is evaluated, the stakes, and the key evaluation criteria.
- Evidence and Alternatives
Evaluate your hypothesis by considering:
- The evidence supporting your hypothesis and any additional evidence needed.
- The weaknesses of your hypothesis and possible alternatives.
Writing a Case Analysis
Writing a case analysis involves a structured approach that enables you to communicate your understanding and analytical skills effectively. Here’s how you can craft your analysis to be insightful and comprehensive:
- Start with a Clear Definition or Position Statement
Begin your case analysis by stating your main conclusion, which serves as the answer to “What?” This initial statement should clearly outline what you have concluded from your analysis of the case.
- Build a Strong Argument with Evidence
Support your position statement with solid evidence, which answers “Why?” This evidence can be quantitative (numerical data) or qualitative (observations and interviews). The purpose here is to provide a foundation for your conclusions, showing how you arrived at them through logical reasoning.
- Outline a Chronological Action Plan
Detail the steps necessary to solve the problem, implement a decision, or enhance performance. This section answers “How?” and should include specific, realistic steps that address any major risks associated with your plan.

Tips for a Successful Case Analysis
- Aim to deliver concise and clear results of your analytical process rather than a simple summary or a complete transcript of your thoughts.
- Ensure your reader understands and is persuaded by your analysis by linking your conclusions directly to credible evidence.
- Discuss the advantages and also acknowledge any disadvantages of your conclusions to provide a balanced view.
How to Format a Case Study
Knowing how a case study analysis format should look is crucial. Therefore, you must know what the text structure should look like. The standard one contains about eight sections:
- Introduction/The Executive Summary: As the first part here, you have to hook the reader’s attention, so the introduction of the case study is the most important part of the writing. Then present them with a brief overview of your case study analyses and their findings. Make sure to form a good thesis statement , as this is the pivotal point of your work.
- Literary Review/Background information: Similarly to other papers, in this part, you have to write your most important facts or findings while identifying the case issue.
- Method/Findings/Discussion: This section can be written separately based on how your text flows. Here you will have to explore more about the case and its findings. Allow yourself to go into more detail instead of just briefly covering them.
- Solutions/Recommendations/Implementation Part: You have to discuss the answers you came up with. Basically, you say why they are fit to solve the case and how you think they can be used in practice. Note that you must write only realistic and practical solutions for the problem. It’s possible to write testable evidence that can support your recommendations.
- Conclusion: Here, you are supposed to cover your whole paper briefly and even repeat the thesis (rephrased). Make sure to highlight the critical points of your case study.
- References or Bibliography: This section must include the sources from which you collected data or whom you consulted. Usually, this part is on a separate page, and the listing should be according to your academic institution’s requirements.
- Appendices (include only if applicable): It is usual for some parts of your materials to be too lengthy or unfit for the other sections of the case study. Therefore, you have to include them here. That can be pictures, raw data of statistics, graphs, notes, etc. The appendix section is strictly for subsidiary materials, do not put the most relevant ones here.
- Author Note: Remember that all educational institutions have their requirement for a case study format. The abovementioned is an example; thus, you may see a section or another is missing, or there are additional ones.

How to Create a Title Page and Cite a Case Study
A case study in APA format for students can differ from one institution to another. So, knowing your college or school requirements is crucial before you start writing. Nonetheless, the general one should look like this:
- Title – A header no longer than nine words has “Case Study” and reflects the content and the idea behind it yet is engaging to read;
- Write your full name;
- The name of your course/class;
- Next is your professor or instructor name;
- The university/school name;
- The date of submission.
When citing in your paper, you must ensure it is done accurately and in your academic style. If you are unsure how to do it, research the requirements and google “How to do a case study analysis in Harvard”, for example. Note that short citations can be in your text, but longer ones should be in the bibliography section.
Hruby, A. (2018). Hruby, A., & Hu, F. B. (2015). The epidemiology of obesity: a big picture. Pharmacoeconomics, 33(7), 673-689. www.sciepub.com. http://www.sciepub.com/reference/254744
Case studies strive to analyze an event, location, case, or person. They can be similar to research papers, so you must pay close attention to the structure and what your professor has requested from you.
Finally, the process of writing can be overwhelming due to the many sections. However, if you take the process step by step and do your preparations properly, you will have an easy time writing the paper. You can also look for assistance online – many services offer to order case study online help . With the right kind of assistance, you can be sure that your paper is of high quality and is due on time!
Readers also enjoyed
WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
What is a case study?
Applications for case study research, what is a good case study, process of case study design, benefits and limitations of case studies.
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Case studies
Case studies are essential to qualitative research , offering a lens through which researchers can investigate complex phenomena within their real-life contexts. This chapter explores the concept, purpose, applications, examples, and types of case studies and provides guidance on how to conduct case study research effectively.

Whereas quantitative methods look at phenomena at scale, case study research looks at a concept or phenomenon in considerable detail. While analyzing a single case can help understand one perspective regarding the object of research inquiry, analyzing multiple cases can help obtain a more holistic sense of the topic or issue. Let's provide a basic definition of a case study, then explore its characteristics and role in the qualitative research process.
Definition of a case study
A case study in qualitative research is a strategy of inquiry that involves an in-depth investigation of a phenomenon within its real-world context. It provides researchers with the opportunity to acquire an in-depth understanding of intricate details that might not be as apparent or accessible through other methods of research. The specific case or cases being studied can be a single person, group, or organization – demarcating what constitutes a relevant case worth studying depends on the researcher and their research question .
Among qualitative research methods , a case study relies on multiple sources of evidence, such as documents, artifacts, interviews , or observations , to present a complete and nuanced understanding of the phenomenon under investigation. The objective is to illuminate the readers' understanding of the phenomenon beyond its abstract statistical or theoretical explanations.
Characteristics of case studies
Case studies typically possess a number of distinct characteristics that set them apart from other research methods. These characteristics include a focus on holistic description and explanation, flexibility in the design and data collection methods, reliance on multiple sources of evidence, and emphasis on the context in which the phenomenon occurs.
Furthermore, case studies can often involve a longitudinal examination of the case, meaning they study the case over a period of time. These characteristics allow case studies to yield comprehensive, in-depth, and richly contextualized insights about the phenomenon of interest.
The role of case studies in research
Case studies hold a unique position in the broader landscape of research methods aimed at theory development. They are instrumental when the primary research interest is to gain an intensive, detailed understanding of a phenomenon in its real-life context.
In addition, case studies can serve different purposes within research - they can be used for exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory purposes, depending on the research question and objectives. This flexibility and depth make case studies a valuable tool in the toolkit of qualitative researchers.
Remember, a well-conducted case study can offer a rich, insightful contribution to both academic and practical knowledge through theory development or theory verification, thus enhancing our understanding of complex phenomena in their real-world contexts.
What is the purpose of a case study?
Case study research aims for a more comprehensive understanding of phenomena, requiring various research methods to gather information for qualitative analysis . Ultimately, a case study can allow the researcher to gain insight into a particular object of inquiry and develop a theoretical framework relevant to the research inquiry.
Why use case studies in qualitative research?
Using case studies as a research strategy depends mainly on the nature of the research question and the researcher's access to the data.
Conducting case study research provides a level of detail and contextual richness that other research methods might not offer. They are beneficial when there's a need to understand complex social phenomena within their natural contexts.
The explanatory, exploratory, and descriptive roles of case studies
Case studies can take on various roles depending on the research objectives. They can be exploratory when the research aims to discover new phenomena or define new research questions; they are descriptive when the objective is to depict a phenomenon within its context in a detailed manner; and they can be explanatory if the goal is to understand specific relationships within the studied context. Thus, the versatility of case studies allows researchers to approach their topic from different angles, offering multiple ways to uncover and interpret the data .
The impact of case studies on knowledge development
Case studies play a significant role in knowledge development across various disciplines. Analysis of cases provides an avenue for researchers to explore phenomena within their context based on the collected data.

This can result in the production of rich, practical insights that can be instrumental in both theory-building and practice. Case studies allow researchers to delve into the intricacies and complexities of real-life situations, uncovering insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Types of case studies
In qualitative research , a case study is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Depending on the nature of the research question and the specific objectives of the study, researchers might choose to use different types of case studies. These types differ in their focus, methodology, and the level of detail they provide about the phenomenon under investigation.
Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate approach for your research project and effectively achieving your research goals. Let's briefly look at the main types of case studies.
Exploratory case studies
Exploratory case studies are typically conducted to develop a theory or framework around an understudied phenomenon. They can also serve as a precursor to a larger-scale research project. Exploratory case studies are useful when a researcher wants to identify the key issues or questions which can spur more extensive study or be used to develop propositions for further research. These case studies are characterized by flexibility, allowing researchers to explore various aspects of a phenomenon as they emerge, which can also form the foundation for subsequent studies.
Descriptive case studies
Descriptive case studies aim to provide a complete and accurate representation of a phenomenon or event within its context. These case studies are often based on an established theoretical framework, which guides how data is collected and analyzed. The researcher is concerned with describing the phenomenon in detail, as it occurs naturally, without trying to influence or manipulate it.
Explanatory case studies
Explanatory case studies are focused on explanation - they seek to clarify how or why certain phenomena occur. Often used in complex, real-life situations, they can be particularly valuable in clarifying causal relationships among concepts and understanding the interplay between different factors within a specific context.

Intrinsic, instrumental, and collective case studies
These three categories of case studies focus on the nature and purpose of the study. An intrinsic case study is conducted when a researcher has an inherent interest in the case itself. Instrumental case studies are employed when the case is used to provide insight into a particular issue or phenomenon. A collective case study, on the other hand, involves studying multiple cases simultaneously to investigate some general phenomena.
Each type of case study serves a different purpose and has its own strengths and challenges. The selection of the type should be guided by the research question and objectives, as well as the context and constraints of the research.
The flexibility, depth, and contextual richness offered by case studies make this approach an excellent research method for various fields of study. They enable researchers to investigate real-world phenomena within their specific contexts, capturing nuances that other research methods might miss. Across numerous fields, case studies provide valuable insights into complex issues.
Critical information systems research
Case studies provide a detailed understanding of the role and impact of information systems in different contexts. They offer a platform to explore how information systems are designed, implemented, and used and how they interact with various social, economic, and political factors. Case studies in this field often focus on examining the intricate relationship between technology, organizational processes, and user behavior, helping to uncover insights that can inform better system design and implementation.
Health research
Health research is another field where case studies are highly valuable. They offer a way to explore patient experiences, healthcare delivery processes, and the impact of various interventions in a real-world context.

Case studies can provide a deep understanding of a patient's journey, giving insights into the intricacies of disease progression, treatment effects, and the psychosocial aspects of health and illness.
Asthma research studies
Specifically within medical research, studies on asthma often employ case studies to explore the individual and environmental factors that influence asthma development, management, and outcomes. A case study can provide rich, detailed data about individual patients' experiences, from the triggers and symptoms they experience to the effectiveness of various management strategies. This can be crucial for developing patient-centered asthma care approaches.
Other fields
Apart from the fields mentioned, case studies are also extensively used in business and management research, education research, and political sciences, among many others. They provide an opportunity to delve into the intricacies of real-world situations, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of various phenomena.
Case studies, with their depth and contextual focus, offer unique insights across these varied fields. They allow researchers to illuminate the complexities of real-life situations, contributing to both theory and practice.
Whatever field you're in, ATLAS.ti puts your data to work for you
Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti to turn your data into insights.
Understanding the key elements of case study design is crucial for conducting rigorous and impactful case study research. A well-structured design guides the researcher through the process, ensuring that the study is methodologically sound and its findings are reliable and valid. The main elements of case study design include the research question , propositions, units of analysis, and the logic linking the data to the propositions.
The research question is the foundation of any research study. A good research question guides the direction of the study and informs the selection of the case, the methods of collecting data, and the analysis techniques. A well-formulated research question in case study research is typically clear, focused, and complex enough to merit further detailed examination of the relevant case(s).
Propositions
Propositions, though not necessary in every case study, provide a direction by stating what we might expect to find in the data collected. They guide how data is collected and analyzed by helping researchers focus on specific aspects of the case. They are particularly important in explanatory case studies, which seek to understand the relationships among concepts within the studied phenomenon.
Units of analysis
The unit of analysis refers to the case, or the main entity or entities that are being analyzed in the study. In case study research, the unit of analysis can be an individual, a group, an organization, a decision, an event, or even a time period. It's crucial to clearly define the unit of analysis, as it shapes the qualitative data analysis process by allowing the researcher to analyze a particular case and synthesize analysis across multiple case studies to draw conclusions.
Argumentation
This refers to the inferential model that allows researchers to draw conclusions from the data. The researcher needs to ensure that there is a clear link between the data, the propositions (if any), and the conclusions drawn. This argumentation is what enables the researcher to make valid and credible inferences about the phenomenon under study.
Understanding and carefully considering these elements in the design phase of a case study can significantly enhance the quality of the research. It can help ensure that the study is methodologically sound and its findings contribute meaningful insights about the case.
Ready to jumpstart your research with ATLAS.ti?
Conceptualize your research project with our intuitive data analysis interface. Download a free trial today.
Conducting a case study involves several steps, from defining the research question and selecting the case to collecting and analyzing data . This section outlines these key stages, providing a practical guide on how to conduct case study research.
Defining the research question
The first step in case study research is defining a clear, focused research question. This question should guide the entire research process, from case selection to analysis. It's crucial to ensure that the research question is suitable for a case study approach. Typically, such questions are exploratory or descriptive in nature and focus on understanding a phenomenon within its real-life context.
Selecting and defining the case
The selection of the case should be based on the research question and the objectives of the study. It involves choosing a unique example or a set of examples that provide rich, in-depth data about the phenomenon under investigation. After selecting the case, it's crucial to define it clearly, setting the boundaries of the case, including the time period and the specific context.
Previous research can help guide the case study design. When considering a case study, an example of a case could be taken from previous case study research and used to define cases in a new research inquiry. Considering recently published examples can help understand how to select and define cases effectively.
Developing a detailed case study protocol
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
The protocol should also consider how to work with the people involved in the research context to grant the research team access to collecting data. As mentioned in previous sections of this guide, establishing rapport is an essential component of qualitative research as it shapes the overall potential for collecting and analyzing data.
Collecting data
Gathering data in case study research often involves multiple sources of evidence, including documents, archival records, interviews, observations, and physical artifacts. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the case. The process for gathering data should be systematic and carefully documented to ensure the reliability and validity of the study.
Analyzing and interpreting data
The next step is analyzing the data. This involves organizing the data , categorizing it into themes or patterns , and interpreting these patterns to answer the research question. The analysis might also involve comparing the findings with prior research or theoretical propositions.
Writing the case study report
The final step is writing the case study report . This should provide a detailed description of the case, the data, the analysis process, and the findings. The report should be clear, organized, and carefully written to ensure that the reader can understand the case and the conclusions drawn from it.
Each of these steps is crucial in ensuring that the case study research is rigorous, reliable, and provides valuable insights about the case.
The type, depth, and quality of data in your study can significantly influence the validity and utility of the study. In case study research, data is usually collected from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case. This section will outline the various methods of collecting data used in case study research and discuss considerations for ensuring the quality of the data.
Interviews are a common method of gathering data in case study research. They can provide rich, in-depth data about the perspectives, experiences, and interpretations of the individuals involved in the case. Interviews can be structured , semi-structured , or unstructured , depending on the research question and the degree of flexibility needed.
Observations
Observations involve the researcher observing the case in its natural setting, providing first-hand information about the case and its context. Observations can provide data that might not be revealed in interviews or documents, such as non-verbal cues or contextual information.
Documents and artifacts
Documents and archival records provide a valuable source of data in case study research. They can include reports, letters, memos, meeting minutes, email correspondence, and various public and private documents related to the case.

These records can provide historical context, corroborate evidence from other sources, and offer insights into the case that might not be apparent from interviews or observations.
Physical artifacts refer to any physical evidence related to the case, such as tools, products, or physical environments. These artifacts can provide tangible insights into the case, complementing the data gathered from other sources.
Ensuring the quality of data collection
Determining the quality of data in case study research requires careful planning and execution. It's crucial to ensure that the data is reliable, accurate, and relevant to the research question. This involves selecting appropriate methods of collecting data, properly training interviewers or observers, and systematically recording and storing the data. It also includes considering ethical issues related to collecting and handling data, such as obtaining informed consent and ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of the participants.
Data analysis
Analyzing case study research involves making sense of the rich, detailed data to answer the research question. This process can be challenging due to the volume and complexity of case study data. However, a systematic and rigorous approach to analysis can ensure that the findings are credible and meaningful. This section outlines the main steps and considerations in analyzing data in case study research.
Organizing the data
The first step in the analysis is organizing the data. This involves sorting the data into manageable sections, often according to the data source or the theme. This step can also involve transcribing interviews, digitizing physical artifacts, or organizing observational data.
Categorizing and coding the data
Once the data is organized, the next step is to categorize or code the data. This involves identifying common themes, patterns, or concepts in the data and assigning codes to relevant data segments. Coding can be done manually or with the help of software tools, and in either case, qualitative analysis software can greatly facilitate the entire coding process. Coding helps to reduce the data to a set of themes or categories that can be more easily analyzed.
Identifying patterns and themes
After coding the data, the researcher looks for patterns or themes in the coded data. This involves comparing and contrasting the codes and looking for relationships or patterns among them. The identified patterns and themes should help answer the research question.
Interpreting the data
Once patterns and themes have been identified, the next step is to interpret these findings. This involves explaining what the patterns or themes mean in the context of the research question and the case. This interpretation should be grounded in the data, but it can also involve drawing on theoretical concepts or prior research.
Verification of the data
The last step in the analysis is verification. This involves checking the accuracy and consistency of the analysis process and confirming that the findings are supported by the data. This can involve re-checking the original data, checking the consistency of codes, or seeking feedback from research participants or peers.
Like any research method , case study research has its strengths and limitations. Researchers must be aware of these, as they can influence the design, conduct, and interpretation of the study.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of case study research can also guide researchers in deciding whether this approach is suitable for their research question . This section outlines some of the key strengths and limitations of case study research.
Benefits include the following:
- Rich, detailed data: One of the main strengths of case study research is that it can generate rich, detailed data about the case. This can provide a deep understanding of the case and its context, which can be valuable in exploring complex phenomena.
- Flexibility: Case study research is flexible in terms of design , data collection , and analysis . A sufficient degree of flexibility allows the researcher to adapt the study according to the case and the emerging findings.
- Real-world context: Case study research involves studying the case in its real-world context, which can provide valuable insights into the interplay between the case and its context.
- Multiple sources of evidence: Case study research often involves collecting data from multiple sources , which can enhance the robustness and validity of the findings.
On the other hand, researchers should consider the following limitations:
- Generalizability: A common criticism of case study research is that its findings might not be generalizable to other cases due to the specificity and uniqueness of each case.
- Time and resource intensive: Case study research can be time and resource intensive due to the depth of the investigation and the amount of collected data.
- Complexity of analysis: The rich, detailed data generated in case study research can make analyzing the data challenging.
- Subjectivity: Given the nature of case study research, there may be a higher degree of subjectivity in interpreting the data , so researchers need to reflect on this and transparently convey to audiences how the research was conducted.
Being aware of these strengths and limitations can help researchers design and conduct case study research effectively and interpret and report the findings appropriately.

Ready to analyze your data with ATLAS.ti?
See how our intuitive software can draw key insights from your data with a free trial today.
Call/Text/Whatsapp:
+1 (888-687-4420)
24/7/365 Available
- College Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Expository Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Scholarship Essay
- Admission Essay
- Reflective Essay
- Nursing Essay
- Economics Essay
Assignments
- Term Papers
- Research Papers
- Case Studies
- Dissertation
- Presentation
- Editing Help
- Cheap Essay Writing
- How to Order
Writing A Case Study
Case Study Examples
Brilliant Case Study Examples and Templates For Your Help
15 min read
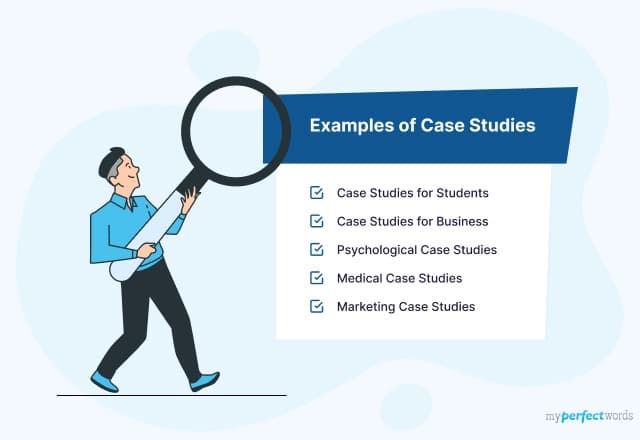
People also read
A Complete Case Study Writing Guide With Examples
Simple Case Study Format for Students to Follow
Understand the Types of Case Study Here
It’s no surprise that writing a case study is one of the most challenging academic tasks for students. You’re definitely not alone here!
Most people don't realize that there are specific guidelines to follow when writing a case study. If you don't know where to start, it's easy to get overwhelmed and give up before you even begin.
Don't worry! Let us help you out!
We've collected over 25 free case study examples with solutions just for you. These samples with solutions will help you win over your panel and score high marks on your case studies.
So, what are you waiting for? Let's dive in and learn the secrets to writing a successful case study.
- 1. An Overview of Case Studies
- 2. Case Study Examples for Students
- 3. Business Case Study Examples
- 4. Medical Case Study Examples
- 5. Psychology Case Study Examples
- 6. Sales Case Study Examples
- 7. Interview Case Study Examples
- 8. Marketing Case Study Examples
- 9. Tips to Write a Good Case Study
An Overview of Case Studies
A case study is a research method used to study a particular individual, group, or situation in depth. It involves analyzing and interpreting data from a variety of sources to gain insight into the subject being studied.
Case studies are often used in psychology, business, and education to explore complicated problems and find solutions. They usually have detailed descriptions of the subject, background info, and an analysis of the main issues.
The goal of a case study is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the subject. Typically, case studies can be divided into three parts, challenges, solutions, and results.
Here is a case study sample PDF so you can have a clearer understanding of what a case study actually is:
Case Study Sample PDF
How to Write a Case Study Examples
Learn how to write a case study with the help of our comprehensive case study guide.
Case Study Examples for Students
Quite often, students are asked to present case studies in their academic journeys. The reason instructors assign case studies is for students to sharpen their critical analysis skills, understand how companies make profits, etc.
Below are some case study examples in research, suitable for students:
|
Case Study Example in Software Engineering
Qualitative Research Case Study Sample
Software Quality Assurance Case Study
Social Work Case Study Example
Ethical Case Study
Case Study Example PDF
These examples can guide you on how to structure and format your own case studies.
Struggling with formatting your case study? Check this case study format guide and perfect your document’s structure today.
Business Case Study Examples
A business case study examines a business’s specific challenge or goal and how it should be solved. Business case studies usually focus on several details related to the initial challenge and proposed solution.
To help you out, here are some samples so you can create case studies that are related to businesses:
|
|
Here are some more business case study examples:
Business Case Studies PDF
Business Case Studies Example
Typically, a business case study discovers one of your customer's stories and how you solved a problem for them. It allows your prospects to see how your solutions address their needs.
Medical Case Study Examples
Medical case studies are an essential part of medical education. They help students to understand how to diagnose and treat patients.
Here are some medical case study examples to help you.
Medical Case Study Example
Nursing Case Study Example
Want to understand the various types of case studies? Check out our types of case study blog to select the perfect type.
Psychology Case Study Examples
Case studies are a great way of investigating individuals with psychological abnormalities. This is why it is a very common assignment in psychology courses.
By examining all the aspects of your subject’s life, you discover the possible causes of exhibiting such behavior.
For your help, here are some interesting psychology case study examples:
Psychology Case Study Example
Mental Health Case Study Example
Sales Case Study Examples
Case studies are important tools for sales teams’ performance improvement. By examining sales successes, teams can gain insights into effective strategies and create action plans to employ similar tactics.
By researching case studies of successful sales campaigns, sales teams can more accurately identify challenges and develop solutions.
Sales Case Study Example
Interview Case Study Examples
Interview case studies provide businesses with invaluable information. This data allows them to make informed decisions related to certain markets or subjects.
Interview Case Study Example
Marketing Case Study Examples
Marketing case studies are real-life stories that showcase how a business solves a problem. They typically discuss how a business achieves a goal using a specific marketing strategy or tactic.
They typically describe a challenge faced by a business, the solution implemented, and the results achieved.
This is a short sample marketing case study for you to get an idea of what an actual marketing case study looks like.
: ABC Solutions, a leading provider of tech products and services.
Engaging and informative content highlighting products and services. Incorporating real-world examples to showcase the impact of ABC Solutions. Utilizing analytics to refine content strategies. Aligning content with customer needs and pain points. Content marketing efforts led to a significant boost in brand visibility. Compelling narratives highlighting how products and services transformed businesses.
|
Here are some more popular marketing studies that show how companies use case studies as a means of marketing and promotion:
“Chevrolet Discover the Unexpected” by Carol H. Williams
This case study explores Chevrolet's “ DTU Journalism Fellows ” program. The case study uses the initials “DTU” to generate interest and encourage readers to learn more.
Multiple types of media, such as images and videos, are used to explain the challenges faced. The case study concludes with an overview of the achievements that were met.
Key points from the case study include:
- Using a well-known brand name in the title can create interest.
- Combining different media types, such as headings, images, and videos, can help engage readers and make the content more memorable.
- Providing a summary of the key achievements at the end of the case study can help readers better understand the project's impact.
“The Met” by Fantasy
“ The Met ” by Fantasy is a fictional redesign of the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City, created by the design studio Fantasy. The case study clearly and simply showcases the museum's website redesign.
The Met emphasizes the website’s features and interface by showcasing each section of the interface individually, allowing the readers to concentrate on the significant elements.
For those who prefer text, each feature includes an objective description. The case study also includes a “Contact Us” call-to-action at the bottom of the page, inviting visitors to contact the company.
Key points from this “The Met” include:
- Keeping the case study simple and clean can help readers focus on the most important aspects.
- Presenting the features and solutions with a visual showcase can be more effective than writing a lot of text.
- Including a clear call-to-action at the end of the case study can encourage visitors to contact the company for more information.
“Better Experiences for All” by Herman Miller
Herman Miller's minimalist approach to furniture design translates to their case study, “ Better Experiences for All ”, for a Dubai hospital. The page features a captivating video with closed-captioning and expandable text for accessibility.
The case study presents a wealth of information in a concise format, enabling users to grasp the complexities of the strategy with ease. It concludes with a client testimonial and a list of furniture items purchased from the brand.
Key points from the “Better Experiences” include:
- Make sure your case study is user-friendly by including accessibility features like closed captioning and expandable text.
- Include a list of products that were used in the project to guide potential customers.
“NetApp” by Evisort
Evisort's case study on “ NetApp ” stands out for its informative and compelling approach. The study begins with a client-centric overview of NetApp, strategically directing attention to the client rather than the company or team involved.
The case study incorporates client quotes and explores NetApp’s challenges during COVID-19. Evisort showcases its value as a client partner by showing how its services supported NetApp through difficult times.
- Provide an overview of the company in the client’s words, and put focus on the customer.
- Highlight how your services can help clients during challenging times.
- Make your case study accessible by providing it in various formats.
“Red Sox Season Campaign,” by CTP Boston
The “ Red Sox Season Campaign ” showcases a perfect blend of different media, such as video, text, and images. Upon visiting the page, the video plays automatically, there are videos of Red Sox players, their images, and print ads that can be enlarged with a click.
The page features an intuitive design and invites viewers to appreciate CTP's well-rounded campaign for Boston's beloved baseball team. There’s also a CTA that prompts viewers to learn how CTP can create a similar campaign for their brand.
Some key points to take away from the “Red Sox Season Campaign”:
- Including a variety of media such as video, images, and text can make your case study more engaging and compelling.
- Include a call-to-action at the end of your study that encourages viewers to take the next step towards becoming a customer or prospect.
“Airbnb + Zendesk” by Zendesk
The case study by Zendesk, titled “ Airbnb + Zendesk : Building a powerful solution together,” showcases a true partnership between Airbnb and Zendesk.
The article begins with an intriguing opening statement, “Halfway around the globe is a place to stay with your name on it. At least for a weekend,” and uses stunning images of beautiful Airbnb locations to captivate readers.
Instead of solely highlighting Zendesk's product, the case study is crafted to tell a good story and highlight Airbnb's service in detail. This strategy makes the case study more authentic and relatable.
Some key points to take away from this case study are:
- Use client's offerings' images rather than just screenshots of your own product or service.
- To begin the case study, it is recommended to include a distinct CTA. For instance, Zendesk presents two alternatives, namely to initiate a trial or seek a solution.
“Influencer Marketing” by Trend and WarbyParker
The case study "Influencer Marketing" by Trend and Warby Parker highlights the potential of influencer content marketing, even when working with a limited budget.
The “Wearing Warby” campaign involved influencers wearing Warby Parker glasses during their daily activities, providing a glimpse of the brand's products in use.
This strategy enhanced the brand's relatability with influencers' followers. While not detailing specific tactics, the case study effectively illustrates the impact of third-person case studies in showcasing campaign results.
Key points to take away from this case study are:
- Influencer marketing can be effective even with a limited budget.
- Showcasing products being used in everyday life can make a brand more approachable and relatable.
- Third-person case studies can be useful in highlighting the success of a campaign.
Marketing Case Study Template
Marketing Case Study Example
Now that you have read multiple case study examples, hop on to our tips.
Tips to Write a Good Case Study
Here are some note-worthy tips to craft a winning case study
- Define the purpose of the case study This will help you to focus on the most important aspects of the case. The case study objective helps to ensure that your finished product is concise and to the point.
- Choose a real-life example. One of the best ways to write a successful case study is to choose a real-life example. This will give your readers a chance to see how the concepts apply in a real-world setting.
- Keep it brief. This means that you should only include information that is directly relevant to your topic and avoid adding unnecessary details.
- Use strong evidence. To make your case study convincing, you will need to use strong evidence. This can include statistics, data from research studies, or quotes from experts in the field.
- Edit and proofread your work. Before you submit your case study, be sure to edit and proofread your work carefully. This will help to ensure that there are no errors and that your paper is clear and concise.
There you go!
We’re sure that now you have secrets to writing a great case study at your fingertips! This blog teaches the key guidelines of various case studies with samples. So grab your pen and start crafting a winning case study right away!
Having said that, we do understand that some of you might be having a hard time writing compelling case studies.
But worry not! Our expert case study writing service is here to take all your case-writing blues away!
With 100% thorough research guaranteed, we can craft an amazing case study within 24 hours!
Besides, if you're pressed for time, simply uttering the words just do my essay for me will get your essay done quickly and flawlessly!
So why delay? Let us help you shine in the eyes of your instructor!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

Case Study Analysis
Ai generator.

Studying rare phenomena, through the use of case studies, is not an easy feat. Despite that, case studies have become popular in this age of information since they provide in-depth and detailed data about individuals and businesses. Furthermore, case studies have provided breakthrough information and have broken off several misconceptions in almost all fields of studies. How has this become achievable for researchers? Surely, they have used and followed the best templates from the expert ones. Scroll down to discover the best analysis template and example for you to start your own case study.
Case Study Analysis Examples and Templates
1. case study analysis template.

- Google Docs
Size: A4, US Letter
In most universities, it has become customary for students to critique certain researches. If you have been enrolled in a course that frequently requires you to examine researches, especially case studies, then you just found the right template to make your student life easier ! This case study analysis template will be of great help as it provides a detailed outline on how to thoroughly assess researches.
2. Case Study Report Template

Sometimes, businesses need to undergo proper scientific methods in order to assess organizational factors such as work productivity and employee retention. This is mostly done through case studies since they provide exhaustive accounts of what happened, what is happening, and what can happen to a company over a period of time. Using this case study report template not only provides you a comprehensive format but also a publishable one that can easily be understood by other readers.
3. Case Study Analysis of Company Practices

Size: 200.1 KB
Having a hard time writing down your case study? Refer to the above sample from Ashford University. It tackles how the human resources practices at Starbucks Coffee Company affects its reputation as this generation’s leading coffee shop. Moreover, the sample presents concise guidelines at every part of the analysis. From the title page down to the references section , this sample has got you covered!
4. Case Study and Analysis for Strategic Management

Size: 614.3 KB
Every successful business has a strategic management plan implemented behind it; however, these strategic plans do not last for a lifetime. Perhaps it is why Ikea, an international home products retailer, has conducted a case study of their existing strategic management plan and see if it will still be applicable given today’s different circumstances. Albarrak’s sample case study above showcases the objectives and strategies used by Ikea, their financial standing, their SWOT analysis, as well as the major issues that they have faced. A complete case study like the one above is just what every aspiring successful business needs.
5. Business Case Study Analysis

Size: 243.2 KB
Business courses often demand a lot of case analysis. If you are new to this type of analysis, you might want to check out the above template from Grand Valley State University. The sample provides extensive descriptions on what each part should contain. Additionally, what makes it different from other case analysis formats is that it gives guidelines on how you should arrange and caption the visual presentations that your paper requires.
6. Case Study Analysis Guide for Students

Size: 118.6 KB
Formulating your own complex format of a case study analysis might just consume your time and energy. That is why, sometimes, it’s better to go back to the basic layouts. After all, simplicity is the ultimate sophistication, right? This sample from James Cook University provides the format of the two basic kinds of case study analysis which are problem-based case studies and analyzing case studies with questions. Not only does this serve as an example but it also provides templates for both kinds of case studies.
7. Case Study Report in Official Government Format

Size: 105.4 KB
Case studies do not necessarily mean they are only about one person or a small group of people. Mostly, it is about singular or remarkable phenomena. If you’re looking for a sample case study analysis that includes compilations of different case studies, you’ve clicked on the right link. The above sample will walk you through four different case studies that relatively share the similar phenomenon. What makes this sample distinctive is that it is researched for the Australian government and has its own official format.
8. Market Competition Case Study

Size: 569.5 KB
There will always be competition in business. Nowadays, to keep up with the competition, companies turn to case studies. Above is a case study that presents how a company is doing against its competitors in the shoe market. If you are a business owner with multiple competitions, you might want to consider starting a case study with the help of the one provided above. Check them out; it’s always best to stay a step ahead!
9. Case Study and Analysis of Dabur India Limited

Size: 489 KB
Analyzing a case study can be demanding in a lot of aspects, and one of the best ways to give its demands is to learn from example. Above is an example of a case study about Dabur India Limited followed by an analysis of that same case study. Both documents are simple yet comprehensive and will greatly help you in beginning your own analyses of other case studies.
10. Three-page Case Study Analysis

Size: 1.5 MB
Different cases require different methods of analysis. Some cases need a meticulous process of analysis while some can be done even with few pages. If you’re analyzing a case study that can be summed up in only a handful of sheets, you might want to consider the samples above. What makes it different from other formats is that it provides compressed but all-inclusive solutions and recommendations to the problems stated in the case study.
11. ZARA Case Study Analysis

Size: 267.3 KB
Ever wondered how businesses manage to flourish despite the test of time? That may be because they have confidently trusted in case studies related to them. Above is a sample case study analysis of reputable fashion company ZARA. The sample showcases different types of analysis including the significant SWOT and PESTLE, which are hardly found in other case study analysis formats.
12. Case Study Analysis: The Diamond Industry

Size: 424.5 KB
Studying a broad field in the business industry can be overwhelming. The diamond industry, for instance, has a lot of related fields and terms such as the mining industry, markets, political geographies, etc. Of course, you have to take these terms into account, depending on your study. Luckily, a sample study on the said field from University of Chester is here to help you kick off your own case study analysis with its particular format and presentation of charts. Download it now.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
- Monash Online
Student Academic Success
- 1:1 Consultation 1:1 Consultation
- Study better Study better
- Build digital capabilities Build digital capabilities
- Understand assessments Understand assessments
- Excel at writing Excel at writing
- Enhance your thinking Enhance your thinking
- Present confidently Present confidently
- Collaborate with others Collaborate with others
- Improve your academic English Improve your academic English
- Maintain academic integrity Maintain academic integrity
- Advance your graduate studies Advance your graduate studies
- O-week workshops O-week workshops
- Let's Talk Assessments Let's Talk Assessments
- Set up for academic success Set up for academic success
- Writing classes Writing classes
- End of semester End of semester
- PhD writing workshops and courses PhD writing workshops and courses
- First Year Undergraduate Success First Year Undergraduate Success
- Graduate coursework success Graduate coursework success
- Academic Language Skills Analysis Academic Language Skills Analysis
- Mathematics skills analysis Mathematics skills analysis
- Orientation Orientation
- SAS cafe SAS cafe
- SAS pop up SAS pop up
- Written Feedback Written Feedback
- About us About us
- Skip to content
- Skip to navigation
Case study example
Atlanta public schools case study.
In 2011, an external investigation of the performance evaluation strategies of the Atlanta Public Schools System revealed that schools had been cheating to obtain high results. For this example case analysis, the student has identified the problems faced by the organisation, outlined factors that contributed to the problem, and proposed solutions and recommendations.
The following case analysis is annotated with tips and explanations in each section. Click the icons to display the annotations. Note that for your actual assignment you may not be required to include all sections in the example case analysis here – check your assignment instructions carefully.
This resource has demonstrated the main steps in producing a case study assignment.
These steps will help you to identify what has happened in a case situation, why it happened, and apply relevant theory. Remember that some case studies require you to evaluate and recommend solutions.
You will need to:
- identify the problems in a case, and
- analyse the problems.
You may also need to:
- develop and evaluate alternative solutions, and
- make recommendations for action.
Remember to check your assignment instructions carefully to determine the type of case study you are required to write. Some units may require you to follow a particular style or structure. Check unit information for templates or guides to ensure that you meet these expectations.
Kimberley, N. (2016). StudentQ Manual (6th ed.) . Faculty of Business and Economics, Monash University.
Van Weelden, S. J. & Busuttil, L. (2018). Student guide to the case method . Ivey Publishing.
Navigating this resource
You can navigate the pages in this resource by either clicking on the page links here or by clicking the navigation buttons below.
What is a case study
Six steps to approaching a case study, how to write up a case study, your feedback matters.
We want to hear from you! Let us know what you found most useful or share your suggestions for improving this resource.
Overview of Case Studies: Common Elements and Framework for Analysis
- First Online: 28 September 2024
Cite this chapter

- Catherine Atkin 6 &
- Kwi-Gon Kim 7
Part of the book series: Cities and Nature ((CITIES))
This chapter provides an overview and explanation of the elements of the thirteen case studies from Africa, South and Southeast Asia, South America and the Middle East. It introduces the reader to the elements of comprehensive climate risk management and green recovery planning covered by the case studies including flood risk assessment, green recovery planning and local context variables and adaptive conditions analysis. It sets the context for the reader’s review of the case studies and outlines the key learning questions readers should consider.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Stanford CodeX Climate Data Policy Initiative, Stanford, USA
Catherine Atkin
Seoul National University, Seoul, South Korea
Kwi-Gon Kim
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Catherine Atkin .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea (Republic of)
Climate Data Policy Initiative, Stanford CodeX Center for Legal Informatics, Palo Alto, CA, USA
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Atkin, C., Kim, KG. (2024). Overview of Case Studies: Common Elements and Framework for Analysis. In: Kim, KG., Atkin, C. (eds) Cross-Cultural Perspectives on Climate Change Adaptation. Cities and Nature. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-50365-8_7
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-50365-8_7
Published : 28 September 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-50364-1
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-50365-8
eBook Packages : Earth and Environmental Science Earth and Environmental Science (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.
Redirect Notice
Nih definition of clinical trial case studies.
The case studies provided below are designed to help you identify whether your study would be considered by NIH to be a clinical trial. Expect the case studies and related guidance to evolve over the upcoming year. For continuity and ease of reference, case studies will retain their original numbering and will not be renumbered if cases are revised or removed.
The simplified case studies apply the following four questions to determine whether NIH would consider the research study to be a clinical trial:
- Does the study involve human participants?
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention?
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants?
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome?
If the answer to all four questions is “yes,” then the clinical study would be considered a clinical trial according to the NIH definition.
General Case Studies
The study involves the recruitment of research participants who are randomized to receive one of two approved drugs. It is designed to compare the effects of the drugs on the blood level of a protein.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, the study involves human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to receive an intervention, one of two drugs.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of the drugs on the level of the protein in the participants’ blood.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, the level of a protein, is a health-related biomedical outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with condition Y to receive a drug that has been approved for another indication. It is designed to measure the drug’s effects on the level of a biomarker associated with the severity of condition Y.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to receive an intervention, the approved drug.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the drug’s effect on the level of the biomarker.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, the level of a biomarker, is a health-related biomedical outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with condition X to receive investigational compound A. It is designed to assess the pharmacokinetic properties of compound A.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to receive an intervention, compound A.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate how the body interacts with compound A
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, pharmacokinetic properties, is a health-related biomedical outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with disease X to receive an investigational drug. It is designed to assess safety and determine the maximum tolerated dose of the drug.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to receive an intervention, the investigational drug.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to assess safety and determine the maximum tolerated dose of the investigational drug.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, safety and maximum tolerated dose, is a health-related biomedical outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with disease X to receive a chronic disease management program. It is designed to assess usability and to determine the maximum tolerated dose of the chronic disease program (e.g., how many in-person and telemedicine visits with adequate adherence).
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to receive an intervention, the chronic disease management program.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to determine the maximum tolerated dose of the program to obtain adequate adherence.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, tolerable intensity and adequate adherence of the intervention, is a health-related outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with disease X to receive either an investigational drug or a placebo. It is designed to evaluate the efficacy of the investigational drug to relieve disease symptoms.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to receive an intervention, the investigational drug or placebo.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of the investigational drug on the participants’ symptoms.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, relief of symptoms, is a health-related outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with disease X to receive an investigational drug. It is designed to assess whether there is a change in disease progression compared to baseline. There is no concurrent control used in this study.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of the investigational drug on the subject’s disease progression.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, disease progression, is a health-related outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with disease X to test an investigational in vitro diagnostic device (IVD). It is designed to evaluate the ability of the device to measure the level of an antibody in blood.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, in this context the IVD would not be considered an intervention. The IVD is being used to test its ability to measure antibody levels, but not to test its effects on any health-related biomedical or behavioral outcomes.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with disease X to be evaluated with an investigational in vitro diagnostic device (IVD). The study is designed to evaluate how knowledge of certain antibody levels impacts clinical management of disease.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to an intervention, measurement of an antibody level, with the idea that knowledge of that antibody level might affect clinical management.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate how knowledge of the level of an antibody might inform treatment.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being measured, how blood antibody levels inform treatment, is a health-related outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of healthy volunteers who will be randomized to different durations of sleep deprivation (including no sleep deprivation as a control) and who will have stress hormone levels measured. It is designed to determine whether the levels of stress hormones in blood rise in response to different durations of sleep deprivation.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, the healthy volunteers are human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to an intervention, different durations of sleep deprivation followed by a blood draw.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to measure the effect of different durations of sleep deprivation on stress hormone levels.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, stress hormone levels, is a health-related biomedical outcome.
The study involves the analysis of de-identified, stored blood samples and de-identified medical records of patients with disease X who were treated with an approved drug. The study is designed to evaluate the level of a protein in the blood of patients that is associated with therapeutic effects of the drug.
- Does the study involve human participants? No, the study does not involve human participants because only de-identified samples and information are used.
The study involves the analysis of identifiable, stored blood samples and identified medical records of patients with disease X who were treated with an approved drug. The study is designed to evaluate the level of a protein in the blood of patients that is associated with therapeutic effects of the drug.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, patients are human participants because the blood and information are identifiable.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, secondary research with biospecimens or health information is not a clinical trial.
The study involves the recruitment of a healthy volunteers whose blood is drawn for genomic analysis. It is designed to identify the prevalence of a genetic mutation in the cohort and evaluate potential association between the presence of the mutation and the risk of developing a genetic disorder.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, sample collection (blood draw) is not an intervention in this context.
Physicians report that some patients being treated with drug A for disease X are also experiencing some improvement in a second condition, condition Y. The study involves the recruitment of research participants who have disease X and condition Y and are being treated with drug A. The participants are surveyed to ascertain whether they are experiencing an improvement in condition Y.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, participants are not prospectively assigned to receive an intervention as they are receiving drugs as part of their clinical care. The surveys are being used for measurement, not to modify a biomedical or behavioral outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of patients with disease X who are receiving one of three standard therapies as part of their clinical care. It is designed to assess the relative effectiveness of the three therapies by monitoring survival rates using medical records over a few years.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, there is no intervention. The therapies are prescribed as part of clinical care; they are not prospectively assigned for the purpose of the study. The study is observational.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with disease X vs. healthy controls and comparing these participants on a range of health processes and outcomes including genomics, biospecimens, self-report measures, etc. to explore differences that may be relevant to the development of disease X.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, the measures needed to assess the outcomes are not interventions in this context, as the study is not intended to determine whether the measures modify a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of healthy volunteers for a respiratory challenge study; participants are randomized to receive different combinations of allergens. The study evaluates the severity and mechanism of the immune response to different combinations of allergens introduced via inhalation.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, healthy volunteers are human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, healthy volunteers are prospectively assigned to randomly selected combinations of allergens.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is evaluating the effects of different combinations of allergens on the immune response in healthy individuals.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the study evaluates the severity and mechanism of the immune reaction to allergens, which are health-related biomedical outcomes.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) to evaluate the effects of an investigational drug on memory, and retention and recall of information.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, participants are prospectively assigned to receive the investigational drug.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is evaluating the effects of the drug on participants’ memory.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the study evaluates memory, and retention and recall of information in the context of AD.
The study involves the recruitment of individuals to receive a new behavioral intervention for sedentary behavior. It is designed to measure the effect of the intervention on hypothesized differential mediators of behavior change.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, participants are prospectively assigned to receive a behavioral intervention.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is evaluating the effects of the intervetion on mediators of behavior change.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, mediators of behavior change, are behavioral outcomes relevant to health.
The study involves the recruitment of patients with disease X to be evaluated with a new visual acuity task. It is designed to evaluate the ability of the new task to measure visual acuity as compared with the gold standard Snellen Test
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to an intervention, the new visual acuity test.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? No, the study is designed to evaluate the ability of the new visual acuity test to measure visual acuity as compared to the gold standard Snellen Test, but not to modify visual acuity.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with CHF who were hospitalized before or after implementation of the Medicare incentives to reduce re-hospitalizations. Morbidity, mortality, and quality of life of these participants are evaluated to compare the effects of these Medicare incentives on these outcomes.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, the intervention (incentives to reduce re-hospitalization) were assigned by Medicare, not by the research study.
The study involves the recruitment of healthcare providers to assess the extent to which being provided with genomic sequence information about their patients informs their treatment of those patients towards improved outcomes.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, both the physicians and the patients are human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, physicians are prospectively assigned to receive genomic sequence information, which is the intervention.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of intervening with physicians, on the treatment they provide to their patients.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related, biomedical, or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, the extent to which providing specific information to physicians informs the treatment of patients, is a health-related outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants with a behavioral condition to receive either an investigational behavioral intervention or a behavioral intervention in clinical use. It is designed to evaluate the effectiveness of the investigational intervention compared to the intervention in clinical use in reducing the severity of the obsessive compulsive disorder.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to an intervention, either the investigational intervention or an intervention in clinical use.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate whether the investigational intervention is as effective as the standard intervention, at changing behavior.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related, biomedical, or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, the interventions’ effectiveness in reducing the severity of the condition, is a health-related behavioral outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of physicians who will be randomly assigned to use a new app or an existing app, which cues directed interviewing techniques. The study is designed to determine whether the new app is better than the existing app at assisting physicians in identifying families in need of social service support. The number of community service referrals will be measured.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, both the physicians and the families are human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, physicians are prospectively assigned to use one of two apps, which are the interventions.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of intervening with physicians, on social service support referral for families.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related, biomedical, or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, the number of referrals, is a health-related outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of parents to participate in focus groups to discuss topics related to parental self-efficacy and positive parenting behaviors. It is designed to gather information needed to develop an intervention to promote parental self-efficacy and positive parenting behaviors.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, the parents are human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, a focus group is not an intervention.
The study involves the recruitment of healthy volunteers to test a new behavioral intervention. It is designed to evaluate the effect of a meditation intervention on adherence to exercise regimens and quality of life to inform the design of a subsequent, fully-powered trial.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, study participants are human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to a behavioral intervention.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on adherence, and quality of life.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, adherence and quality of life are health-related outcomes.
A study will test the feasibility a mobile phone app designed to increase physical activity. A group of sedentary individuals will use the app for a week while their interactions with the app are monitored. The number of interactions with the app will be measured, as well as any software issues. Participants will also complete a survey indicating their satisfaction with and willingness to use the app, as well as any feedback for improvement. The app’s effect on physical activity, weight, or cardiovascular fitness will not be evaluated.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, sedentary individuals will be enrolled.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? The participants will interact with the app for a week.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? No. While the participants’ interactions are monitored (steps or heart rate may be recorded in this process), the study is NOT measuring the effect of using the app ON the participant. The study is only measuring the usability and acceptability of the app, and testing for bugs in the software. The effect on physical activity is NOT being measured.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? N/A
The study involves the recruitment of healthy family members of patients hospitalized for disease X to test two CPR training strategies. Participants will receive one of two training strategies. The outcome is improved CPR skills retention.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, family members of patients are human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to one of two CPR educational strategies.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of educational strategies on CPR skills.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, retention of CPR skills is a health-related behavioral outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of research participants in three different communities (clusters) to test three CPR training strategies. The rate of out-of- hospital cardiac arrest survival will be compared.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to receive one of three types of CPR training, which is the intervention.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of different CPR training strategies on patient survival rates post cardiac arrest.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, out-of-hospital cardiac arrest survival is a health-related outcome.
A study involves the recruitment of school children to evaluate two different tools for monitoring food intake. Food consumption behavior will be measured by asking children to activate a pocket camera during meals and to use a diary to record consumed food. The accuracy of the two food monitoring methods in measuring energy intake will be assessed.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, children are human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, in this context the monitoring methods would not be considered an intervention. The study is designed to test the accuracy of two monitoring methods, but not to test the effect on any health-related biomedical or behavioral outcomes.
A study involves the recruitment of school children to evaluate two different tools for monitoring food intake. Food consumption behavior will be measured by asking children to activate a pocket camera during meals and to use a diary to record consumed food. Changes to eating behavior will be assessed.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to two food monitoring methods.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to determine whether using the monitoring methods changes eating behavior.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, eating behavior is a health-related outcome.
A study involves the recruitment of children at two schools to monitor eating behavior. Children’s food choices will be monitored using a remote food photography method. Food consumption and the accuracy of food monitoring methods will be assessed.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, the children participating in this study are human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, not in this context. The study involves observing and measuring eating behavior, but not modifying it. This is an observational study.
A study involves the recruitment of children at two schools to evaluate their preferences for graphics and colors used in healthy food advertisements. Children will be presented with multiple health advertisements and their preferences for graphics and colors will be assessed.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to see different advertisements.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the advertisements.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? No, preferences are not health-related biomedical or behavioral outcomes.
The study involves ambulatory patients who have new-onset stable angina and who are recruited from community practices. They are randomized to undergo CT angiography or an exercise stress test of the doctor’s choice. To keep the trial pragmatic, the investigators do not prescribe a protocol for how physicians should respond to test results. The study is designed to determine whether the initial test (CT angiography or stress test) affects long-term rates of premature death, stroke, or myocardial infarctions.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are randomized to undergo CT angiography or an exercise stress test.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to determine whether the initial test done affects long-term rates of certain clinical events.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, premature death, stroke, and myocardial infarction are health-related biomedical outcomes.
The study involves patients who present with stable angina to community practices. As part of their routine care some of their physicians refer them for CT angiography, while others refer them for exercise stress tests. The study is designed to see whether or not there's an association between the type of test that is chosen and long-term risk of death, stroke, or myocardial infarction.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, the intervention is not prospectively assigned by the investigators. Rather, the intervention, in this case diagnostic study, occurs as part of routine clinical care.
The investigators conduct a longitudinal study of patients with schizophrenia. Their physicians, as part of their standard clinical care, prescribe antipsychotic medication. The investigators conduct an imaging session before starting treatment; they repeat imaging 4-6 weeks later.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, not in this context. Antipsychotic medications are given as part of clinical care, not as part of a prospective, approved research protocol.
The investigators conduct a longitudinal study of patients with schizophrenia. Their physicians, as part of their standard clinical care, prescribe antipsychotic medication. As part of the research protocol, all participants will be prescribed the same dose of the antipsychotic medication. The investigators conduct an imaging session before starting treatment; they repeat imaging 4-6 weeks later.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, although participants are all receiving antipsychotic medication as part of their standard medical care, the dose of the antipsychotic medication is determined by the research protocol, rather than individual clinical need.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of a dose of antipsychotic medication on brain function.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome ? Yes, brain function measured by imaging is a health-related outcome.
The study involves recruitment of healthy volunteers who will wear a thermal compression device around their legs. This pilot study is designed to examine preliminary performance and safety of a thermal compression device worn during surgery. Investigators will measure core temperature, comfort, and presence of skin injury in 15-minute intervals.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, participants are assigned to wear a thermal compression device.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of the thermal compression device on participant core temperature, comfort, and presence of skin injury.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome ? Yes, participant core temperature, comfort, and presence of skin injury are health-related biomedical outcomes.
The study involves collection of data on hospitalizations for various acute illnesses among people who live close to a border between two states that have recently implemented different laws related to public health (e.g. smoking regulations, soda taxes). The investigators want to take advantage of this “natural experiment” to assess the health impact of the laws.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, the study involves human participants.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, the interventions were assigned by state laws and state of residence, not by the research study.
The study involves recruitment of healthy volunteers to engage in working memory tasks while undergoing transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) to induce competing local neuronal activity. The study is measuring task performance to investigate the neural underpinnings of working memory storage and processing.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, healthy volunteers are prospectively assigned to receive TMS stimulation protocols during a working memory task.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is evaluating the effects of local TMS stimulation on working memory performance and oscillatory brain activity in healthy individuals.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the study evaluates working memory processes, which are health-related biomedical outcomes.
The study involves recruitment of healthy volunteers to engage in a social valuation task while dopamine tone in the brain is manipulated using tolcapone, an FDA-approved medication. The study aims to understand the role of dopamine in social decision-making and to search for neural correlates of this valuation using fMRI.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, healthy volunteers are prospectively assigned to receive tolcapone during a social valuation task.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is evaluating the effects of modulating dopamine tone on social decision-making. Although this study uses an FDA-approved drug to modulate dopamine tone, the goal of this intervention is to understand the role of dopamine in a fundamental phenomenon (social valuation), and not to study the mechanism of action of the drug or its clinical effects.
The career development candidate proposes to independently lead a study to test a new drug A on patients with disease X. Patients will be randomized to a test and control group, with the test group receiving one dose of drug A per week for 12 months and controls receiving placebo. To assess presence, number, and type of any polyps, a colonoscopy will be performed. To assess biomarkers of precancerous lesions, colon mucosal biopsies will be collected. Complete blood count will be measured, and plasma will be stored for potential biomarker evaluation.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to receive an intervention, drug A or placebo.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of drug A and placebo on the presence and type of polyps.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, the presence and type of polyps, is a health-related biomedical outcome.
Ancillary Study to Case Study #42a: Some types of drug A being evaluated in Case Study #42a have been reported to impact renal function. An internal medicine fellow performs an ancillary study where stored plasma from Case Study #42a will be evaluated for multiple biomarkers of renal function.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, patients are human participants because the plasma and information are identifiable.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, because the assignment of participants to an intervention occurs as part of an existing, separately funded clinical trial. This proposal would be considered an ancillary study that is not an independent clinical trial.
Ancillary Study to Case Study #42a: An internal medicine fellow designs an independent ancillary trial where a subset of patients from the parent trial in Case Study #42a will also receive drug B, based on the assumption that a two-drug combination will work significantly better than a single drug at both improving renal function and reducing polyps. The test subjects will be evaluated for renal function via plasma clearance rates at 6 and 12 months after initiation of drugs A and B.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to receive an intervention, drugs A and B.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of drugs A and B on renal function.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the effect being evaluated, renal function, is a health-related biomedical outcome.
A group of healthy young adults will perform a Go/No-Go task while undergoing fMRI scans. The purpose of the study is to characterize the pattern of neural activation in the frontal cortex during response inhibition, and the ability of the participant to correctly withhold a response on no-go
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, healthy young adults will be enrolled in this study.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants will be prospectively assigned to perform a Go/No-Go task, which involves different levels of inhibitory control.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of the Go/No-Go task on neural activation in the frontal cortex. The study will measure inhibitory control and the neural systems being engaged. In this study, the Go/No-Go task is the independent variable, and behavioral performance and the associated fMRI activations are the dependent variables.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the neural correlates of inhibitory control and behavioral performance are health-related biomedical outcomes.
A group of adolescents will participate in a longitudinal study examining changes in executive function over the course of a normal school year. Color naming performance on the standard version of the Stroop test will be obtained. All measures will be compared at multiple time points during the school year to examine changes in executive function. The purpose is to observe changes in executive function and to observe if differences exist in the Stroop effect over the course of the school year for these adolescents.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, adolescents will be enrolled in this study.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, there is no intervention in this study and no independent variable manipulated. The adolescents are not prospectively assigned to an intervention, but instead the investigator will examine variables of interest (including the Stroop test) over time. The Stroop effect is used as a measurement of point-in-time data.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? No, there is no intervention. Performance on the Stroop test is a well-established measure of executive function and the test is not providing an independent variable of interest here. It is not being used to manipulate the participants or their environment. The purpose is simply to obtain a measure of executive function in adolescents over the course of the school year.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? N/A. No effect of an intervention is being evaluated.
A group of participants with social anxiety will perform an experimentally manipulated Stroop test. In this variant of the Stroop test, the stimuli presented are varied to include emotional and neutral facial expressions presented in different colors. Participants are instructed to name the colors of the faces presented, with the expectation that they will be slower to name the color of the emotional face than the neutral face. The purpose of the study is to examine the degree to which participants with social anxiety will be slower to process emotional faces than neutral faces.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, participants with social anxiety will be enrolled in this study.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants will be prospectively assigned to perform a modified Stroop test using different colored emotional/neutral faces to explore emotional processing in people with social anxiety. Note that the independent variable is the presentation of emotional vs neutral faces.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to measure the effect of emotional valence (i.e. emotional faces) on participant response time to name the color. The purpose is to determine whether the response time to emotional faces is exaggerated for people with social anxiety as compared to neutral faces. Note that the response time to name the colors is the dependent variable in this study.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the processing of emotional information is a health-related biomedical outcome.
The study involves healthy volunteers and compares temporal SNR obtained with a new fMRI pulse sequence with that from another sequence.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, in this context the different pulse sequences would not be considered an intervention. The pulse sequences are not being used to modify any biomedical or behavioral outcome; rather the investigator is comparing performance characteristics of the two pulse sequences.
The study is designed to demonstrate that a new imaging technology (e.g. MRI, PET, ultrasound technologies, or image processing algorithm) is equivalent to, or has better sensitivity/specificity than a standard of care imaging technology. Aim one will use the new imaging technology and the gold standard in ten healthy volunteers. Aim Two will use the new imaging technology and the gold standard before and after a standard care procedure in ten patients. In both aims the performance of the new technology will be compared to the gold standard. No clinical care decisions will be made based on the use of the device in this study.
- Does the study involve human participants? YES. Aim one will study ten healthy volunteers, and aim two will study ten patient volunteers.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, participants will be prospectively assigned to be evaluated with a new imaging technology and the gold standard technology.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? No, the study is not measuring the effect of the technologies ON the human subjects. The study is determining if the new technology is equivalent or better than the gold standard technology. No effect on the participant is being measured.
Institute or Center specific Case Studies
An investigator proposes to add secondary outcomes to an already funded clinical trial of a nutritional intervention. The trial is supported by other funding, but the investigator is interested in obtaining NIH funding for studying oral health outcomes. Participants in the existing trial would be assessed for oral health outcomes at baseline and at additional time points during a multi-week dietary intervention. The oral health outcomes would include measures of gingivitis and responses to oral health related quality of life questionnaires. Oral fluids would be collected for analysis of inflammatory markers and microbiome components.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, because the assignment of participants to an intervention (and the administration of the intervention) occur as part of an existing, separately funded clinical trial. This proposal would be considered an ancillary study that leverages an already existing clinical trial.
The goal of the project is to use functional neuroimaging to distinguish patients with temporomandibular disorders (TMD) who experience TMD pain through centralized pain processes from those with TMD related to peripheral pain. Pain processing in a study cohort of TMD patients and healthy controls will be measured through functional magnetic resonance neuroimaging (fMRI) following transient stimulation of pain pathways through multimodal automated quantitative sensory testing (MAST QST). TMD patients will receive study questionnaires to better correlate the extent to which TMD pain centralization influences TMD prognosis and response to standard of care peripherally targeted treatment (prescribed by physicians, independently of the study).
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, not in this context. The transient stimulation of pain pathways and the fMRI are being performed to measure and describe brain activity, but not to modify it.
An investigator proposes to perform a study of induced gingivitis in healthy humans, to study microbial colonization and inflammation under conditions of health and disease. During a 3-week gingivitis induction period, each study participant will use a stent to cover the teeth in one quadrant during teeth brushing. A contralateral uncovered quadrant will be exposed to the individual's usual oral hygiene procedures, to serve as a control. Standard clinical assessments for gingivitis will be made and biospecimens will be collected at the point of maximal induced gingivitis, and again after normal oral hygiene is resumed. Biospecimens will be assessed for microbial composition and levels of inflammation-associated chemokines.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are prospectively assigned to an intervention, abstaining from normal oral hygiene for a portion of the mouth, to induce gingivitis.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to evaluate the effect of the induced gingivitis on microbial composition and levels of inflammatory chemokines in oral samples.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, the microbial composition and chemokine levels in oral samples are health-related biomedical outcomes.
The study will enroll older adults with hearing loss, comparing the effectiveness of enhanced hearing health care (HHC) to usual HHC. In addition to routine hearing-aid consultation and fitting, participants randomized to enhanced HCC will be provided patient-centered information and education about a full range of hearing assistive technologies and services. Study outcomes include the utilization of technology or services, quality of life, communication abilities, and cognitive function.
- Does the study involve human participants? Yes, the study enrolls older adults with hearing loss.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, participants are randomized to receive enhanced HCC or usual HCC interventions.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study will evaluate enhanced HCC’s effectiveness in modifying participant behavior and biomedical outcomes.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, rate of technology/service utilization is a behavioral outcome and quality of life, communications, and cognition are biomedical outcomes that may be impacted by the interventions.
The study involves the recruitment of obese individuals who will undergo a muscle biopsy before and after either exercise training or diet-induced weight loss. Sarcolemmal 1,2-disaturated DAG and C18:0 ceramide species and mitochondrial function will be measured. Levels will be correlated with insulin sensitivity.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are assigned to either exercise training or a diet.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to compare the effects of the interventions on muscle metabolism.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, muscle metabolism/signaling is a health-related outcome.
The study involves the recruitment of participants with type 2 diabetes who will undergo a muscle biopsy before and after a fast to measure acetylation on lysine 23 of the mitochondrial solute carrier adenine nucleotide translocase 1 (ANT1). Levels will be related to rates of fat oxidation.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are assigned to undergo a fast.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to compare the effects of the fast on molecular parameters of metabolism.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, metabolism is a health-related outcome.
Insulin-resistant and insulin-sensitive nondiabetic adults who have a parent with type 2 diabetes will be followed over time to understand the role of mitochondrial dysfunction in the development of diabetes. Oral glucose tolerance tests will be performed annually to measure insulin sensitivity and glycemic status. Participants will also undergo a brief bout of exercise, and mitochondrial ATP synthesis rates will be measured by assessing the rate of recovery of phosphocreatine in the leg muscle, using 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, the participants are not assigned to an intervention; the OGTT and 31P MRS are measures.
Participants with chronic kidney disease will be recruited to receive one of two drug agents. After 6 weeks of therapy, subjects will undergo vascular function testing and have measures of oxidative stress evaluated in their plasma and urine. Results of the function testing and the oxidative stress biomarkers will be related to drug treatment.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are assigned to receive two different drugs.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to compare the effects of the drugs on vascular function.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, vascular function is a health-related outcome.
Participants with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease will be recruited to receive an oral curcumin therapy or placebo and the participants will undergo vascular function testing, renal imaging to assess kidney size, and assessment of oxidative stress biomarkers in urine and plasma after an ascorbic acid challenge. Changes in these outcomes will be related to oral therapy.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are assigned to receive medication or placebo.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? Yes, the study is designed to compare the effects of the drugs on vascular function and kidney size.
- Is the effect being evaluated a health-related biomedical or behavioral outcome? Yes, vascular function and kidney size are health-related outcomes.
Kidney transplant recipients will be recruited to undergo an experimental imaging procedure at several timepoints up to 4 months post-transplantation. Output from the images will be related to pathological assessments of the transplant as well as clinical measures of renal function.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? No, the participants are not assigned to receive an intervention. They undergo transplantation as part of their routine clinical care. The imaging procedure is a measure and not an intervention.
The study proposes the development of a novel probe to assess clearance of a nutritional metabolite in a given disease state. The probe is a GMP grade, deuterated, intravenously administered tracer and clearance is assessed by mass spectrometry analysis of serial blood draws. Participants will either receive a micronutrient supplement or will receive no supplementation. The clearance rate of the probe will be compared in the two groups, to understand the performance of the probe.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are assigned to receive either a micronutrient supplement or nothing.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? No, the intervention is being used to assess the performance of the probe and is not looking at an effect on the participant.
In order to assess the contribution of ingested glycolate to oxalate production, healthy participants will be recruited to a study involving the consumption of a controlled diet for three days, followed by an infusion of 13C2-glycolate. Blood and urine will be collected during the subsequent 24 hours to assess the amount of labeled glycolate in plasma and urine oxalate.
- Are the participants prospectively assigned to an intervention? Yes, the participants are assigned to receive a controlled diet for three days.
- Is the study designed to evaluate the effect of the intervention on the participants? No, the intervention (controlled diet) is being used to minimize exogenous dietary sources of oxalate in the participants prior to the labeled tracer infusion. The study will not be evaluating the effect of the diet on the participants.
- Decision Tool: Does Your Human Subjects Research Study Meet the NIH Definition of a Clinical Trial?
- NIH Definition of a Clinical Trial

COMMENTS
Briefly introduce the problems and issues found in the case study. Discuss the theory you will be using in the analysis; Present the key points of the study and present any assumptions made during the analysis. Findings. This is where you present in more detail the specific problems you discovered in the case study.
Identify the key problems and issues in the case study. Formulate and include a thesis statement, summarizing the outcome of your analysis in 1-2 sentences. Background. Set the scene: background information, relevant facts, and the most important issues. Demonstrate that you have researched the problems in this case study. Evaluation of the Case
To ensure you're making the most of your case studies, we've put together 15 real-life case study examples to inspire you. These examples span a variety of industries and formats. We've also included best practices, design tips and templates to inspire you. Let's dive in!
Case study is unbounded and relies on gathering external information; case analysis is a self-contained subject of analysis. The scope of a case study chosen as a method of research is bounded. However, the researcher is free to gather whatever information and data is necessary to investigate its relevance to understanding the research problem.
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
For example, the case study quotes the social media manager and project manager's insights regarding team-wide communication and access before explaining in greater detail. Takeaway: Highlight pain points your business solves for its client, and explore that influence in greater detail. 3. EndeavourX and Figma.
Defnition: A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation. It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied.
Step 4: Analyze Your Findings. Using the information in steps 2 and 3, create an evaluation for this portion of your case study analysis. Compare the strengths and weaknesses within the company to the external threats and opportunities. Determine if the company is in a strong competitive position, and decide if it can continue at its current ...
A case may include 1. irrelevant information 2. unstated information that the reader must infer 3. a nonlinear structure in which related evidence is scattered throughout the text How to Analyze a Case Study 1. Determine what type of case study you're reading. Types of case situations generally are:
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity.
The purpose of case study research is twofold: (1) to provide descriptive information and (2) to suggest theoretical relevance. Rich description enables an in-depth or sharpened understanding of the case. It is unique given one characteristic: case studies draw from more than one data source. Case studies are inherently multimodal or mixed ...
Case Study Analysis is a widely used research method that examines in-depth information about a particular individual, group, organization, or event. It is a comprehensive investigative approach that aims to understand the intricacies and complexities of the subject under study. Through the analysis of real-life scenarios and inquiry into ...
A case analysis in business is a study of a business problem. Anyone conducting a case analysis can use evidence to propose viable solutions to business problems, then provide recommendations on the best way to implement these solutions to produce the desired results. Related: Analytical Skills: Definitions and Examples
This is a financial case study with its nuances. It would be good to take into account if you are dealing with a case study in finance. 4. Knowledge Dissemination. This case study focuses on the Amish population and their usage of non-traditional medicine. This analysis discusses the case on several levels.
1. Select a case. Once you identify the problem at hand and come up with questions, identify the case you will focus on. The study can provide insights into the subject at hand, challenge existing assumptions, propose a course of action, and/or open up new areas for further research. 2.
In contrast, case studies examine a subject in depth, offer detailed information, and help develop critical thinking skills. Types of Case Studies. When it comes to writing case study analysis, there are five types you must learn to differentiate. That is important because whether you get such an assignment, you will have to understand the task ...
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
Case study protocol is a formal document capturing the entire set of procedures involved in the collection of empirical material . It extends direction to researchers for gathering evidences, empirical material analysis, and case study reporting . This section includes a step-by-step guide that is used for the execution of the actual study.
Example of Case Study Suitable for Students. Title: Energy Efficiency Upgrade: A Case Study of GreenTech Office. Introduction: GreenTech Office embarked on an energy efficiency upgrade to reduce its environmental impact. This case study delves into the facts and figures behind the initiative's success.
Above is a sample case study analysis of reputable fashion company ZARA. The sample showcases different types of analysis including the significant SWOT and PESTLE, which are hardly found in other case study analysis formats. 12. Case Study Analysis: The Diamond Industry. academia.edu.
Give students an opportunity to practice the case analysis methodology via an ungraded sample case study. Designate groups of five to seven students to discuss the case and the six steps in breakout sessions (in class or via Zoom). Ensure case analyses are weighted heavily as a grading component. We suggest 30-50 percent of the overall course ...
Atlanta public schools case study. In 2011, an external investigation of the performance evaluation strategies of the Atlanta Public Schools System revealed that schools had been cheating to obtain high results. For this example case analysis, the student has identified the problems faced by the organisation, outlined factors that contributed ...
Case study authors drew upon a variety of new and existing climate risk management frameworks and took an indicator approach to flood risk assessment. This analysis included an assessment of local context variables that impact vulnerability and adaptation capacity as well as the identification of high-impact flooding hazard reduction strategies.
Business Case Analysis Expectations, General Guidelines, and Example Updated Spring 2024 Submission of a Case Analysis is required for successful completion of this course. It is part of your Capstone experience. Read and understand the Expectations and Guidelines very carefully - Your grade will depend upon it. A Case Example has been provided at the end of this document.
Case #10a. The study involves the analysis of de-identified, stored blood samples and de-identified medical records of patients with disease X who were treated with an approved drug. ... No, sample collection (blood draw) is not an intervention in this context. This study is not a clinical trial. Keyword(s): Observational. Case #12. Physicians ...
We illustrate the method using a real-life case study drawn from an appraisal of pembrolizumab plus axitinib for treating advanced renal cell carcinoma in which the initial decision was informed by immature survival data. ... Breeze P. Estimating the expected value of sample information using the probabilistic sensitivity analysis sample: a ...