- Literary Terms
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Write an Essay

I. What is an Essay?
An essay is a form of writing in paragraph form that uses informal language, although it can be written formally. Essays may be written in first-person point of view (I, ours, mine), but third-person (people, he, she) is preferable in most academic essays. Essays do not require research as most academic reports and papers do; however, they should cite any literary works that are used within the paper.
When thinking of essays, we normally think of the five-paragraph essay: Paragraph 1 is the introduction, paragraphs 2-4 are the body covering three main ideas, and paragraph 5 is the conclusion. Sixth and seventh graders may start out with three paragraph essays in order to learn the concepts. However, essays may be longer than five paragraphs. Essays are easier and quicker to read than books, so are a preferred way to express ideas and concepts when bringing them to public attention.
II. Examples of Essays
Many of our most famous Americans have written essays. Benjamin Franklin, Thomas Paine, and Thomas Jefferson wrote essays about being good citizens and concepts to build the new United States. In the pre-Civil War days of the 1800s, people such as:
- Ralph Waldo Emerson (an author) wrote essays on self-improvement
- Susan B. Anthony wrote on women’s right to vote
- Frederick Douglass wrote on the issue of African Americans’ future in the U.S.
Through each era of American history, well-known figures in areas such as politics, literature, the arts, business, etc., voiced their opinions through short and long essays.
The ultimate persuasive essay that most students learn about and read in social studies is the “Declaration of Independence” by Thomas Jefferson in 1776. Other founding fathers edited and critiqued it, but he drafted the first version. He builds a strong argument by stating his premise (claim) then proceeds to give the evidence in a straightforward manner before coming to his logical conclusion.
III. Types of Essays
A. expository.
Essays written to explore and explain ideas are called expository essays (they expose truths). These will be more formal types of essays usually written in third person, to be more objective. There are many forms, each one having its own organizational pattern. Cause/Effect essays explain the reason (cause) for something that happens after (effect). Definition essays define an idea or concept. Compare/ Contrast essays will look at two items and show how they are similar (compare) and different (contrast).
b. Persuasive
An argumentative paper presents an idea or concept with the intention of attempting to change a reader’s mind or actions . These may be written in second person, using “you” in order to speak to the reader. This is called a persuasive essay. There will be a premise (claim) followed by evidence to show why you should believe the claim.
c. Narrative
Narrative means story, so narrative essays will illustrate and describe an event of some kind to tell a story. Most times, they will be written in first person. The writer will use descriptive terms, and may have paragraphs that tell a beginning, middle, and end in place of the five paragraphs with introduction, body, and conclusion. However, if there is a lesson to be learned, a five-paragraph may be used to ensure the lesson is shown.
d. Descriptive
The goal of a descriptive essay is to vividly describe an event, item, place, memory, etc. This essay may be written in any point of view, depending on what’s being described. There is a lot of freedom of language in descriptive essays, which can include figurative language, as well.
IV. The Importance of Essays
Essays are an important piece of literature that can be used in a variety of situations. They’re a flexible type of writing, which makes them useful in many settings . History can be traced and understood through essays from theorists, leaders, artists of various arts, and regular citizens of countries throughout the world and time. For students, learning to write essays is also important because as they leave school and enter college and/or the work force, it is vital for them to be able to express themselves well.
V. Examples of Essays in Literature
Sir Francis Bacon was a leading philosopher who influenced the colonies in the 1600s. Many of America’s founding fathers also favored his philosophies toward government. Bacon wrote an essay titled “Of Nobility” in 1601 , in which he defines the concept of nobility in relation to people and government. The following is the introduction of his definition essay. Note the use of “we” for his point of view, which includes his readers while still sounding rather formal.
“We will speak of nobility, first as a portion of an estate, then as a condition of particular persons. A monarchy, where there is no nobility at all, is ever a pure and absolute tyranny; as that of the Turks. For nobility attempers sovereignty, and draws the eyes of the people, somewhat aside from the line royal. But for democracies, they need it not; and they are commonly more quiet, and less subject to sedition, than where there are stirps of nobles. For men’s eyes are upon the business, and not upon the persons; or if upon the persons, it is for the business’ sake, as fittest, and not for flags and pedigree. We see the Switzers last well, notwithstanding their diversity of religion, and of cantons. For utility is their bond, and not respects. The united provinces of the Low Countries, in their government, excel; for where there is an equality, the consultations are more indifferent, and the payments and tributes, more cheerful. A great and potent nobility, addeth majesty to a monarch, but diminisheth power; and putteth life and spirit into the people, but presseth their fortune. It is well, when nobles are not too great for sovereignty nor for justice; and yet maintained in that height, as the insolency of inferiors may be broken upon them, before it come on too fast upon the majesty of kings. A numerous nobility causeth poverty, and inconvenience in a state; for it is a surcharge of expense; and besides, it being of necessity, that many of the nobility fall, in time, to be weak in fortune, it maketh a kind of disproportion, between honor and means.”
A popular modern day essayist is Barbara Kingsolver. Her book, “Small Wonders,” is full of essays describing her thoughts and experiences both at home and around the world. Her intention with her essays is to make her readers think about various social issues, mainly concerning the environment and how people treat each other. The link below is to an essay in which a child in an Iranian village she visited had disappeared. The boy was found three days later in a bear’s cave, alive and well, protected by a mother bear. She uses a narrative essay to tell her story.
VI. Examples of Essays in Pop Culture
Many rap songs are basically mini essays, expressing outrage and sorrow over social issues today, just as the 1960s had a lot of anti-war and peace songs that told stories and described social problems of that time. Any good song writer will pay attention to current events and express ideas in a creative way.
A well-known essay written in 1997 by Mary Schmich, a columnist with the Chicago Tribune, was made into a popular video on MTV by Baz Luhrmann. Schmich’s thesis is to wear sunscreen, but she adds strong advice with supporting details throughout the body of her essay, reverting to her thesis in the conclusion.

VII. Related Terms
Research paper.
Research papers follow the same basic format of an essay. They have an introductory paragraph, the body, and a conclusion. However, research papers have strict guidelines regarding a title page, header, sub-headers within the paper, citations throughout and in a bibliography page, the size and type of font, and margins. The purpose of a research paper is to explore an area by looking at previous research. Some research papers may include additional studies by the author, which would then be compared to previous research. The point of view is an objective third-person. No opinion is allowed. Any claims must be backed up with research.
VIII. Conclusion
Students dread hearing that they are going to write an essay, but essays are one of the easiest and most relaxed types of writing they will learn. Mastering the essay will make research papers much easier, since they have the same basic structure. Many historical events can be better understood through essays written by people involved in those times. The continuation of essays in today’s times will allow future historians to understand how our new world of technology and information impacted us.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
What is Essay? Definition, Usage, and Literary Examples
Essay definition, history of the essay, types of essays, notable essayists, examples of literary essays, further resources on essays, related terms.
An essay (ES-ey) is a nonfiction composition that explores a concept, argument, idea, or opinion from the personal perspective of the writer. Essays are usually a few pages, but they can also be book-length. Unlike other forms of nonfiction writing, like textbooks or biographies, an essay doesn’t inherently require research. Literary essayists are conveying ideas in a more informal way.
The word essay comes from the Late Latin exigere , meaning “ascertain or weigh,” which later became essayer in Old French. The late-15th-century version came to mean “test the quality of.” It’s this latter derivation that French philosopher Michel de Montaigne first used to describe a composition.
Michel de Montaigne first coined the term essayer to describe Plutarch’s Oeuvres Morales , which is now widely considered to be a collection of essays. Under the new term, Montaigne wrote the first official collection of essays, Essais , in 1580. Montaigne’s goal was to pen his personal ideas in prose . In 1597, a collection of Francis Bacon’s work appeared as the first essay collection written in English. The term essayist was first used by English playwright Ben Jonson in 1609.
There are many ways to categorize essays. Aldous Huxley, a leading essayist, determined that there are three major groups: personal and autobiographical, objective and factual, and abstract and universal. Within these groups, several other types can exist, including the following:
- Academic Essays : Educators frequently assign essays to encourage students to think deeply about a given subject and to assess the student’s knowledge. As such, an academic essay employs a formal language and tone, and it may include references and a bibliography. It’s objective and factual, and it typically uses a five-paragraph model of an introduction, two or more body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Several other essay types, like descriptive, argumentative, and expository, can fall under the umbrella of an academic essay.
- Analytical Essays : An analytical essay breaks down and interprets something, like an event, piece of literature, or artwork. This type of essay combines abstraction and personal viewpoints. Professional reviews of movies, TV shows, and albums are likely the most common form of analytical essays that people encounter in everyday life.
- Argumentative/Persuasive Essays : In an argumentative or persuasive essay, the essayist offers their opinion on a debatable topic and refutes opposing views. Their goal is to get the reader to agree with them. Argumentative/persuasive essays can be personal, factual, and even both at the same time. They can also be humorous or satirical; Jonathan Swift’s A Modest Proposal is a satirical essay arguing that the best way for Irish people to get out of poverty is to sell their children to rich people as a food source.
- Descriptive Essays : In a descriptive essay, the essayist describes something, someone, or an event in great detail. The essay’s subject can be something concrete, meaning it can be experienced with any or all of the five senses, or abstract, meaning it can’t be interacted with in a physical sense.
- Expository Essay : An expository essay is a factual piece of writing that explains a particular concept or issue. Investigative journalists often write expository essays in their beat, and things like manuals or how-to guides are also written in an expository style.
- Narrative/Personal : In a narrative or personal essay, the essayist tells a story, which is usually a recounting of a personal event. Narrative and personal essays may attempt to support a moral or lesson. People are often most familiar with this category as many writers and celebrities frequently publish essay collections.
- James Baldwin, “ Notes of a Native Son ”
- Joan Didion, “ Goodbye To All That ”
- George Orwell, “ Shooting an Elephant ”
- Ralph Waldo Emerson, “ Self-Reliance ”
- Virginia Woolf, " Three Guineas "
1. Michel De Montaigne, “Of Presumption”
De Montaigne’s essay explores multiple topics, including his reasons for writing essays, his dissatisfaction with contemporary education, and his own victories and failings. As the father of the essay, Montaigne details characteristics of what he thinks an essay should be. His writing has a stream-of-consciousness organization that doesn’t follow a structure, and he expresses the importance of looking inward at oneself, pointing to the essay’s personal nature.
2. Virginia Woolf, “A Room of One’s Own”
Woolf’s feminist essay, written from the perspective of an unknown, fictional woman, argues that sexism keeps women from fully realizing their potential. Woolf posits that a woman needs only an income and a room of her own to express her creativity. The fictional persona Woolf uses is meant to teach the reader a greater truth: making both literal and metaphorical space for women in the world is integral to their success and wellbeing.
3. James Baldwin, “Everybody’s Protest Novel”
In this essay, Baldwin argues that Harriet Beecher Stowe’s novel Uncle Tom’s Cabin doesn’t serve the black community the way his contemporaries thought it did. He points out that it equates “goodness” with how well-assimilated the black characters are in white culture:
Uncle Tom’s Cabin is a very bad novel, having, in its self-righteous, virtuous sentimentality, much in common with Little Women. Sentimentality […] is the mark of dishonesty, the inability to feel; […] and it is always, therefore, the signal of secret and violent inhumanity, the mask of cruelty.
This essay is both analytical and argumentative. Baldwin analyzes the novel and argues against those who champion it.
Top Writing Tips offers an in-depth history of the essay.
The Harvard Writing Center offers tips on outlining an essay.
We at SuperSummary have an excellent essay writing resource guide .
- Academic Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Expository Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Persuasive Essay

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
The 31 Literary Devices You Must Know
General Education

Need to analyze The Scarlet Letter or To Kill a Mockingbird for English class, but fumbling for the right vocabulary and concepts for literary devices? You've come to the right place. To successfully interpret and analyze literary texts, you'll first need to have a solid foundation in literary terms and their definitions.
In this article, we'll help you get familiar with most commonly used literary devices in prose and poetry. We'll give you a clear definition of each of the terms we discuss along with examples of literary elements and the context in which they most often appear (comedic writing, drama, or other).
Before we get to the list of literary devices, however, we have a quick refresher on what literary devices are and how understanding them will help you analyze works of literature.
What Are Literary Devices and Why Should You Know Them?
Literary devices are techniques that writers use to create a special and pointed effect in their writing, to convey information, or to help readers understand their writing on a deeper level.
Often, literary devices are used in writing for emphasis or clarity. Authors will also use literary devices to get readers to connect more strongly with either a story as a whole or specific characters or themes.
So why is it important to know different literary devices and terms? Aside from helping you get good grades on your literary analysis homework, there are several benefits to knowing the techniques authors commonly use.
Being able to identify when different literary techniques are being used helps you understand the motivation behind the author's choices. For example, being able to identify symbols in a story can help you figure out why the author might have chosen to insert these focal points and what these might suggest in regard to her attitude toward certain characters, plot points, and events.
In addition, being able to identify literary devices can make a written work's overall meaning or purpose clearer to you. For instance, let's say you're planning to read (or re-read) The Lion, the Witch, and the Wardrobe by C.S. Lewis. By knowing that this particular book is a religious allegory with references to Christ (represented by the character Aslan) and Judas (represented by Edmund), it will be clearer to you why Lewis uses certain language to describe certain characters and why certain events happen the way they do.
Finally, literary techniques are important to know because they make texts more interesting and more fun to read. If you were to read a novel without knowing any literary devices, chances are you wouldn't be able to detect many of the layers of meaning interwoven into the story via different techniques.
Now that we've gone over why you should spend some time learning literary devices, let's take a look at some of the most important literary elements to know.
List of Literary Devices: 31 Literary Terms You Should Know
Below is a list of literary devices, most of which you'll often come across in both prose and poetry. We explain what each literary term is and give you an example of how it's used. This literary elements list is arranged in alphabetical order.
An allegory is a story that is used to represent a more general message about real-life (historical) issues and/or events. It is typically an entire book, novel, play, etc.
Example: George Orwell's dystopian book Animal Farm is an allegory for the events preceding the Russian Revolution and the Stalinist era in early 20th century Russia. In the story, animals on a farm practice animalism, which is essentially communism. Many characters correspond to actual historical figures: Old Major represents both the founder of communism Karl Marx and the Russian communist leader Vladimir Lenin; the farmer, Mr. Jones, is the Russian Czar; the boar Napoleon stands for Joseph Stalin; and the pig Snowball represents Leon Trotsky.
Alliteration
Alliteration is a series of words or phrases that all (or almost all) start with the same sound. These sounds are typically consonants to give more stress to that syllable. You'll often come across alliteration in poetry, titles of books and poems ( Jane Austen is a fan of this device, for example—just look at Pride and Prejudice and Sense and Sensibility ), and tongue twisters.
Example: "Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers." In this tongue twister, the "p" sound is repeated at the beginning of all major words.
Allusion is when an author makes an indirect reference to a figure, place, event, or idea originating from outside the text. Many allusions make reference to previous works of literature or art.
Example: "Stop acting so smart—it's not like you're Einstein or something." This is an allusion to the famous real-life theoretical physicist Albert Einstein.
Anachronism
An anachronism occurs when there is an (intentional) error in the chronology or timeline of a text. This could be a character who appears in a different time period than when he actually lived, or a technology that appears before it was invented. Anachronisms are often used for comedic effect.
Example: A Renaissance king who says, "That's dope, dude!" would be an anachronism, since this type of language is very modern and not actually from the Renaissance period.
Anaphora is when a word or phrase is repeated at the beginning of multiple sentences throughout a piece of writing. It's used to emphasize the repeated phrase and evoke strong feelings in the audience.
Example: A famous example of anaphora is Winston Churchill's "We Shall Fight on the Beaches" speech. Throughout this speech, he repeats the phrase "we shall fight" while listing numerous places where the British army will continue battling during WWII. He did this to rally both troops and the British people and to give them confidence that they would still win the war.

Anthropomorphism
An anthropomorphism occurs when something nonhuman, such as an animal, place, or inanimate object, behaves in a human-like way.
Example: Children's cartoons have many examples of anthropomorphism. For example, Mickey and Minnie Mouse can speak, wear clothes, sing, dance, drive cars, etc. Real mice can't do any of these things, but the two mouse characters behave much more like humans than mice.
Asyndeton is when the writer leaves out conjunctions (such as "and," "or," "but," and "for") in a group of words or phrases so that the meaning of the phrase or sentence is emphasized. It is often used for speeches since sentences containing asyndeton can have a powerful, memorable rhythm.
Example: Abraham Lincoln ends the Gettysburg Address with the phrase "...and that government of the people, by the people, for the people shall not perish from the Earth." By leaving out certain conjunctions, he ends the speech on a more powerful, melodic note.
Colloquialism
Colloquialism is the use of informal language and slang. It's often used by authors to lend a sense of realism to their characters and dialogue. Forms of colloquialism include words, phrases, and contractions that aren't real words (such as "gonna" and "ain't").
Example: "Hey, what's up, man?" This piece of dialogue is an example of a colloquialism, since it uses common everyday words and phrases, namely "what's up" and "man."
An epigraph is when an author inserts a famous quotation, poem, song, or other short passage or text at the beginning of a larger text (e.g., a book, chapter, etc.). An epigraph is typically written by a different writer (with credit given) and used as a way to introduce overarching themes or messages in the work. Some pieces of literature, such as Herman Melville's 1851 novel Moby-Dick , incorporate multiple epigraphs throughout.
Example: At the beginning of Ernest Hemingway's book The Sun Also Rises is an epigraph that consists of a quotation from poet Gertrude Stein, which reads, "You are all a lost generation," and a passage from the Bible.
Epistrophe is similar to anaphora, but in this case, the repeated word or phrase appears at the end of successive statements. Like anaphora, it is used to evoke an emotional response from the audience.
Example: In Lyndon B. Johnson's speech, "The American Promise," he repeats the word "problem" in a use of epistrophe: "There is no Negro problem. There is no Southern problem. There is no Northern problem. There is only an American problem."

A euphemism is when a more mild or indirect word or expression is used in place of another word or phrase that is considered harsh, blunt, vulgar, or unpleasant.
Example: "I'm so sorry, but he didn't make it." The phrase "didn't make it" is a more polite and less blunt way of saying that someone has died.
A flashback is an interruption in a narrative that depicts events that have already occurred, either before the present time or before the time at which the narration takes place. This device is often used to give the reader more background information and details about specific characters, events, plot points, and so on.
Example: Most of the novel Wuthering Heights by Emily Brontë is a flashback from the point of view of the housekeeper, Nelly Dean, as she engages in a conversation with a visitor named Lockwood. In this story, Nelly narrates Catherine Earnshaw's and Heathcliff's childhoods, the pair's budding romance, and their tragic demise.
Foreshadowing
Foreshadowing is when an author indirectly hints at—through things such as dialogue, description, or characters' actions—what's to come later on in the story. This device is often used to introduce tension to a narrative.
Example: Say you're reading a fictionalized account of Amelia Earhart. Before she embarks on her (what we know to be unfortunate) plane ride, a friend says to her, "Be safe. Wouldn't want you getting lost—or worse." This line would be an example of foreshadowing because it implies that something bad ("or worse") will happen to Earhart.
Hyperbole is an exaggerated statement that's not meant to be taken literally by the reader. It is often used for comedic effect and/or emphasis.
Example: "I'm so hungry I could eat a horse." The speaker will not literally eat an entire horse (and most likely couldn't ), but this hyperbole emphasizes how starved the speaker feels.
Imagery is when an author describes a scene, thing, or idea so that it appeals to our senses (taste, smell, sight, touch, or hearing). This device is often used to help the reader clearly visualize parts of the story by creating a strong mental picture.
Example: Here's an example of imagery taken from William Wordsworth's famous poem "I Wandered Lonely as a Cloud":
When all at once I saw a crowd, A host of golden Daffodils; Beside the Lake, beneath the trees, Fluttering and dancing in the breeze.
Irony is when a statement is used to express an opposite meaning than the one literally expressed by it. There are three types of irony in literature:
- Verbal irony: When someone says something but means the opposite (similar to sarcasm).
- Situational irony: When something happens that's the opposite of what was expected or intended to happen.
- Dramatic irony: When the audience is aware of the true intentions or outcomes, while the characters are not . As a result, certain actions and/or events take on different meanings for the audience than they do for the characters involved.
- Verbal irony: One example of this type of irony can be found in Edgar Allan Poe's "The Cask of Amontillado." In this short story, a man named Montresor plans to get revenge on another man named Fortunato. As they toast, Montresor says, "And I, Fortunato—I drink to your long life." This statement is ironic because we the readers already know by this point that Montresor plans to kill Fortunato.
- Situational irony: A girl wakes up late for school and quickly rushes to get there. As soon as she arrives, though, she realizes that it's Saturday and there is no school.
- Dramatic irony: In William Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet , Romeo commits suicide in order to be with Juliet; however, the audience (unlike poor Romeo) knows that Juliet is not actually dead—just asleep.

Juxtaposition
Juxtaposition is the comparing and contrasting of two or more different (usually opposite) ideas, characters, objects, etc. This literary device is often used to help create a clearer picture of the characteristics of one object or idea by comparing it with those of another.
Example: One of the most famous literary examples of juxtaposition is the opening passage from Charles Dickens' novel A Tale of Two Cities :
"It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness, it was the spring of hope, it was the winter of despair …"
Malapropism
Malapropism happens when an incorrect word is used in place of a word that has a similar sound. This misuse of the word typically results in a statement that is both nonsensical and humorous; as a result, this device is commonly used in comedic writing.
Example: "I just can't wait to dance the flamingo!" Here, a character has accidentally called the flamenco (a type of dance) the flamingo (an animal).
Metaphor/Simile
Metaphors are when ideas, actions, or objects are described in non-literal terms. In short, it's when an author compares one thing to another. The two things being described usually share something in common but are unalike in all other respects.
A simile is a type of metaphor in which an object, idea, character, action, etc., is compared to another thing using the words "as" or "like."
Both metaphors and similes are often used in writing for clarity or emphasis.
"What light through yonder window breaks? It is the east, and Juliet is the sun." In this line from Romeo and Juliet , Romeo compares Juliet to the sun. However, because Romeo doesn't use the words "as" or "like," it is not a simile—just a metaphor.
"She is as vicious as a lion." Since this statement uses the word "as" to make a comparison between "she" and "a lion," it is a simile.
A metonym is when a related word or phrase is substituted for the actual thing to which it's referring. This device is usually used for poetic or rhetorical effect .
Example: "The pen is mightier than the sword." This statement, which was coined by Edward Bulwer-Lytton in 1839, contains two examples of metonymy: "the pen" refers to "the written word," and "the sword" refers to "military force/violence."
Mood is the general feeling the writer wants the audience to have. The writer can achieve this through description, setting, dialogue, and word choice .
Example: Here's a passage from J.R.R. Tolkien's The Hobbit: "It had a perfectly round door like a porthole, painted green, with a shiny yellow brass knob in the exact middle. The door opened on to a tube-shaped hall like a tunnel: a very comfortable tunnel without smoke, with panelled walls, and floors tiled and carpeted, provided with polished chairs, and lots and lots of pegs for hats and coats -- the hobbit was fond of visitors." In this passage, Tolkien uses detailed description to set create a cozy, comforting mood. From the writing, you can see that the hobbit's home is well-cared for and designed to provide comfort.
Onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia is a word (or group of words) that represents a sound and actually resembles or imitates the sound it stands for. It is often used for dramatic, realistic, or poetic effect.
Examples: Buzz, boom, chirp, creak, sizzle, zoom, etc.
An oxymoron is a combination of two words that, together, express a contradictory meaning. This device is often used for emphasis, for humor, to create tension, or to illustrate a paradox (see next entry for more information on paradoxes).
Examples: Deafening silence, organized chaos, cruelly kind, insanely logical, etc.
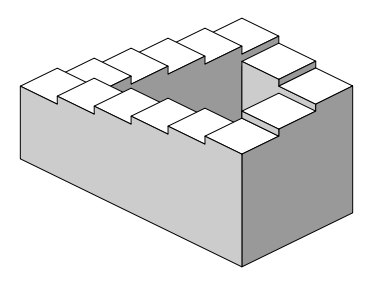
A paradox is a statement that appears illogical or self-contradictory but, upon investigation, might actually be true or plausible.
Note that a paradox is different from an oxymoron: a paradox is an entire phrase or sentence, whereas an oxymoron is a combination of just two words.
Example: Here's a famous paradoxical sentence: "This statement is false." If the statement is true, then it isn't actually false (as it suggests). But if it's false, then the statement is true! Thus, this statement is a paradox because it is both true and false at the same time.
Personification
Personification is when a nonhuman figure or other abstract concept or element is described as having human-like qualities or characteristics. (Unlike anthropomorphism where non-human figures become human-like characters, with personification, the object/figure is simply described as being human-like.) Personification is used to help the reader create a clearer mental picture of the scene or object being described.
Example: "The wind moaned, beckoning me to come outside." In this example, the wind—a nonhuman element—is being described as if it is human (it "moans" and "beckons").
Repetition is when a word or phrase is written multiple times, usually for the purpose of emphasis. It is often used in poetry (for purposes of rhythm as well).
Example: When Lin-Manuel Miranda, who wrote the score for the hit musical Hamilton, gave his speech at the 2016 Tony's, he recited a poem he'd written that included the following line:
And love is love is love is love is love is love is love is love cannot be killed or swept aside.
Satire is genre of writing that criticizes something , such as a person, behavior, belief, government, or society. Satire often employs irony, humor, and hyperbole to make its point.
Example: The Onion is a satirical newspaper and digital media company. It uses satire to parody common news features such as opinion columns, editorial cartoons, and click bait headlines.
A type of monologue that's often used in dramas, a soliloquy is when a character speaks aloud to himself (and to the audience), thereby revealing his inner thoughts and feelings.
Example: In Romeo and Juliet , Juliet's speech on the balcony that begins with, "O Romeo, Romeo! Wherefore art thou Romeo?" is a soliloquy, as she is speaking aloud to herself (remember that she doesn't realize Romeo's there listening!).
Symbolism refers to the use of an object, figure, event, situation, or other idea in a written work to represent something else— typically a broader message or deeper meaning that differs from its literal meaning.
The things used for symbolism are called "symbols," and they'll often appear multiple times throughout a text, sometimes changing in meaning as the plot progresses.
Example: In F. Scott Fitzgerald's 1925 novel The Great Gatsby , the green light that sits across from Gatsby's mansion symbolizes Gatsby's hopes and dreams .
A synecdoche is a literary device in which part of something is used to represent the whole, or vice versa. It's similar to a metonym (see above); however, a metonym doesn't have to represent the whole—just something associated with the word used.
Example: "Help me out, I need some hands!" In this case, "hands" is being used to refer to people (the whole human, essentially).
While mood is what the audience is supposed to feel, tone is the writer or narrator's attitude towards a subject . A good writer will always want the audience to feel the mood they're trying to evoke, but the audience may not always agree with the narrator's tone, especially if the narrator is an unsympathetic character or has viewpoints that differ from those of the reader.
Example: In an essay disdaining Americans and some of the sites they visit as tourists, Rudyard Kipling begins with the line, "Today I am in the Yellowstone Park, and I wish I were dead." If you enjoy Yellowstone and/or national parks, you may not agree with the author's tone in this piece.

How to Identify and Analyze Literary Devices: 4 Tips
In order to fully interpret pieces of literature, you have to understand a lot about literary devices in the texts you read. Here are our top tips for identifying and analyzing different literary techniques:
Tip 1: Read Closely and Carefully
First off, you'll need to make sure that you're reading very carefully. Resist the temptation to skim or skip any sections of the text. If you do this, you might miss some literary devices being used and, as a result, will be unable to accurately interpret the text.
If there are any passages in the work that make you feel especially emotional, curious, intrigued, or just plain interested, check that area again for any literary devices at play.
It's also a good idea to reread any parts you thought were confusing or that you didn't totally understand on a first read-through. Doing this ensures that you have a solid grasp of the passage (and text as a whole) and will be able to analyze it appropriately.
Tip 2: Memorize Common Literary Terms
You won't be able to identify literary elements in texts if you don't know what they are or how they're used, so spend some time memorizing the literary elements list above. Knowing these (and how they look in writing) will allow you to more easily pinpoint these techniques in various types of written works.
Tip 3: Know the Author's Intended Audience
Knowing what kind of audience an author intended her work to have can help you figure out what types of literary devices might be at play.
For example, if you were trying to analyze a children's book, you'd want to be on the lookout for child-appropriate devices, such as repetition and alliteration.
Tip 4: Take Notes and Bookmark Key Passages and Pages
This is one of the most important tips to know, especially if you're reading and analyzing works for English class. As you read, take notes on the work in a notebook or on a computer. Write down any passages, paragraphs, conversations, descriptions, etc., that jump out at you or that contain a literary device you were able to identify.
You can also take notes directly in the book, if possible (but don't do this if you're borrowing a book from the library!). I recommend circling keywords and important phrases, as well as starring interesting or particularly effective passages and paragraphs.
Lastly, use sticky notes or post-its to bookmark pages that are interesting to you or that have some kind of notable literary device. This will help you go back to them later should you need to revisit some of what you've found for a paper you plan to write.
What's Next?
Looking for more in-depth explorations and examples of literary devices? Join us as we delve into imagery , personification , rhetorical devices , tone words and mood , and different points of view in literature, as well as some more poetry-specific terms like assonance and iambic pentameter .
Reading The Great Gatsby for class or even just for fun? Then you'll definitely want to check out our expert guides on the biggest themes in this classic book, from love and relationships to money and materialism .
Got questions about Arthur Miller's The Crucible ? Read our in-depth articles to learn about the most important themes in this play and get a complete rundown of all the characters .
For more information on your favorite works of literature, take a look at our collection of high-quality book guides and our guide to the 9 literary elements that appear in every story !

These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Hannah received her MA in Japanese Studies from the University of Michigan and holds a bachelor's degree from the University of Southern California. From 2013 to 2015, she taught English in Japan via the JET Program. She is passionate about education, writing, and travel.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!

IMAGES
VIDEO