Free Contingency Plan Templates
By Joe Weller | March 25, 2021 (updated October 2, 2024)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Contingency plans offer organizations a proactive strategy for resuming daily functions and operations following unforeseen events. We’ve compiled the most useful contingency plan templates and tips on using them for various industries.
On this page, you'll find free contingency plan templates, including a simple contingency plan template , a software contingency plan template , a business contingency plan template , and a project management contingency plan template . Plus, learn how to use a contingency plan template .

Simple Contingency Plan Template

Use this simple contingency plan template to help your organization return to daily operations after unforeseen circumstances. Find sections for business impact analysis (BIA), recovery strategies, plan development, and testing and exercises. By completing these areas, you can stress-test your contingency plan. Assign contingency plan tasks to team members. Share the document with stakeholders to keep everyone apprised of the organization’s fail-safe contingency plan.
Download a Simple Contingency Plan Template for Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet | Google Docs
For more resources on emergency response and contingency planning, see “ Free Risk Management Plan Templates .”
Simple Contingency Plan Presentation Template
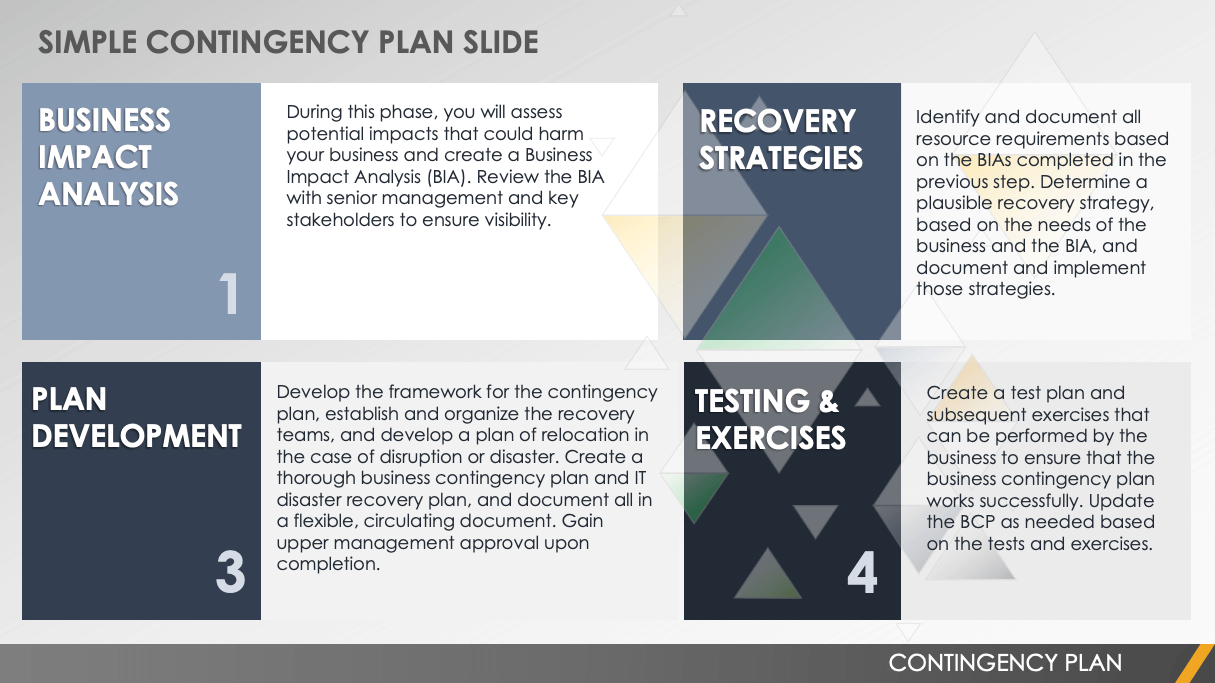
Use this simple contingency plan presentation template to highlight the details of your contingency plan to your team members and other stakeholders. Slides include details for business impact analysis (BIA), recovery strategies, contingency plan development, and plan testing and exercises. It also includes a comprehensive version history slide including your presentation plan’s version, approved by, revision date, descriptions of changes, author, prepared by, and approved by sections. Keep everyone in the loop with this easy-to-use contingency plan presentation template.
Download a Simple Contingency Plan Template for PowerPoint
To learn more, read this comprehensive guide on contingency planning.
Software Contingency Plan Template
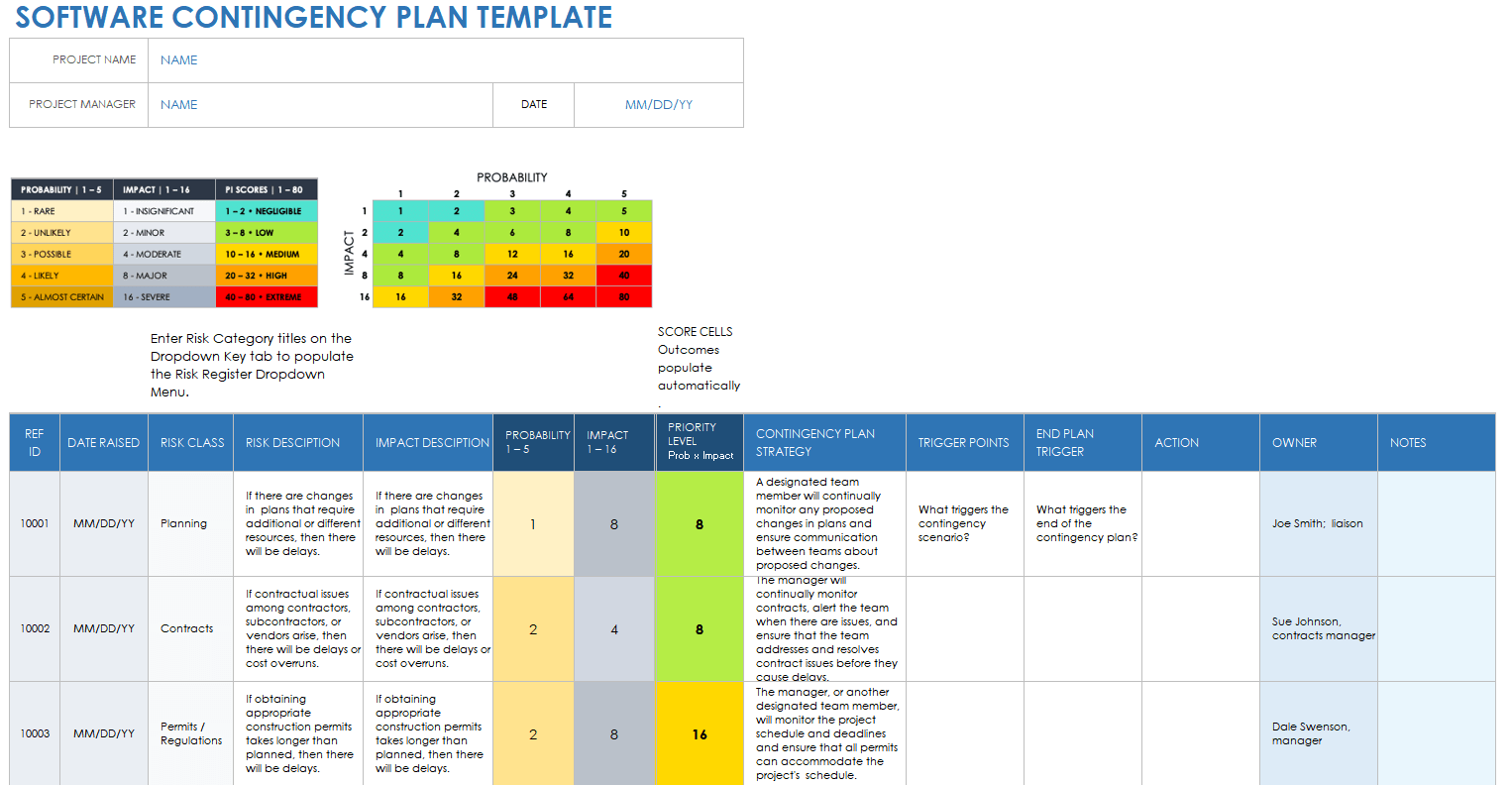
Use this software contingency plan template to identify, describe, and categorize risks, create an impact level and impact description, and create a contingency plan for each, in order to mitigate risks. For each risk, the template also includes a Trigger Points column (e.g., “What triggers the contingency scenario?”) and End Plan Trigger column (e.g., “What triggers the end of the contingency plan?”), so that team members understand the need for the contingency plan. Software project managers can use this template to create contingency plans related to data security, user privacy, geographically discrete data centers, or apply it to software development and software testing.
Download a Software Contingency Plan Template for Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Read this guide to contingency planning to find tips for improving your contingency preparedness.
Information Technology (IT) Service Contingency Plan Template
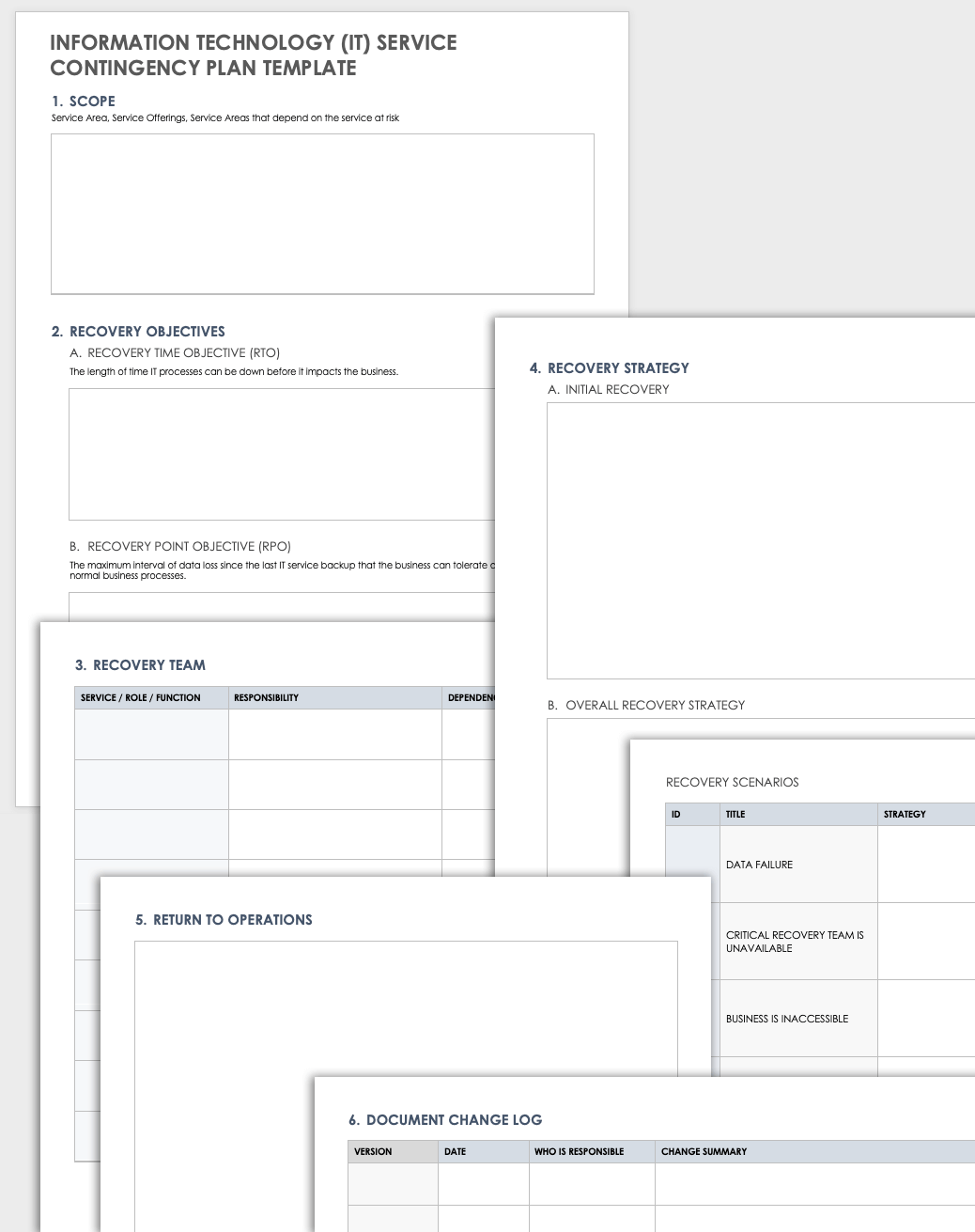
This easy-to-fill template focuses on keeping IT operations up and running in the event of a disruption. Use this template to document details of the scope, recovery objectives, recovery team, recovery strategy, and return-to-plan strategy of your IT department’s contingency plan. Be fully prepared for any incidents that cause downtime by using the proactive steps in this all-inclusive IT service continuity planning template.
Download an Information Technology (IT) Service Contingency Plan Template for Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Google Docs | Smartsheet
IT Service Contingency Plan Presentation Template
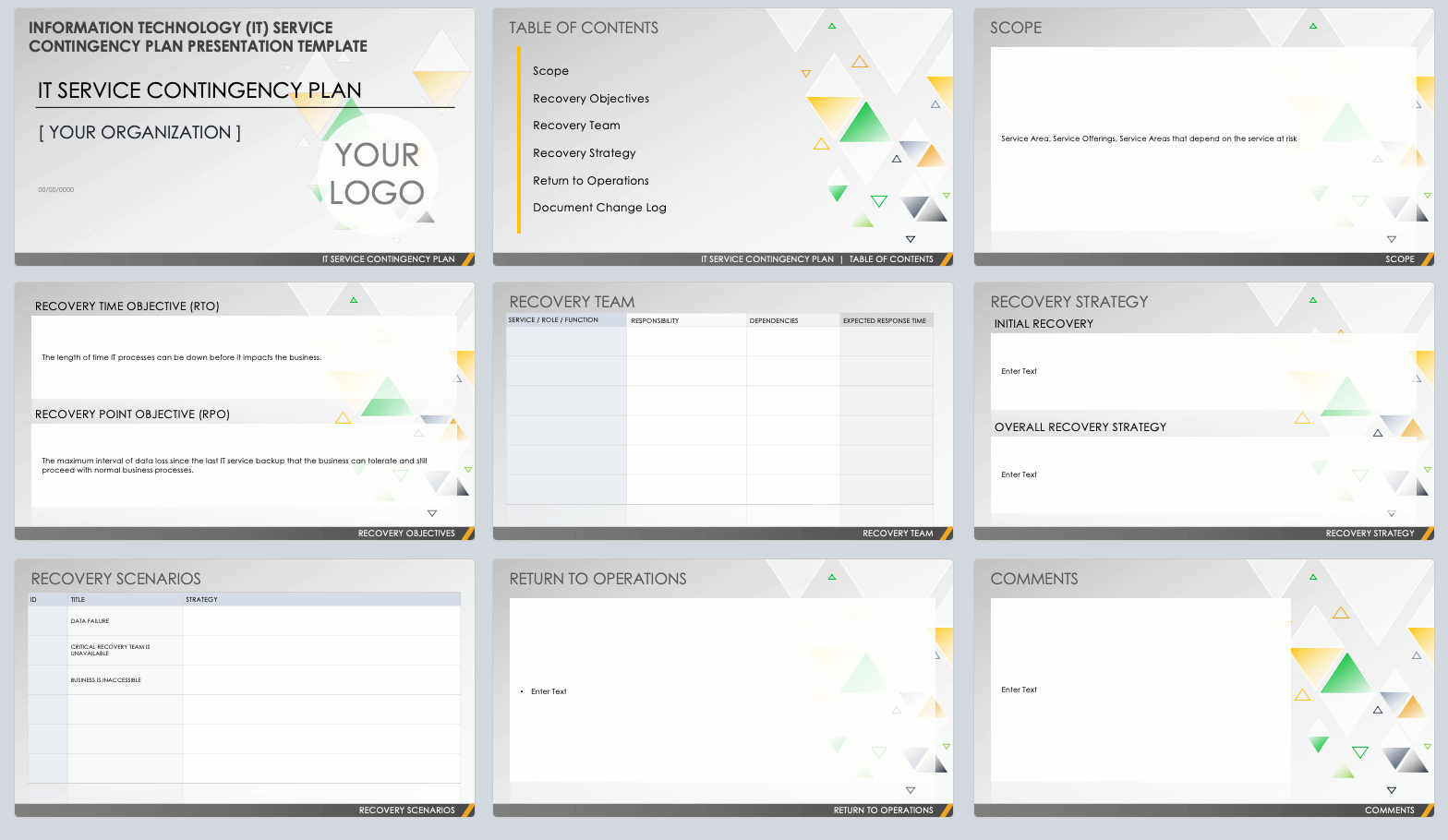
This easy-to-use information technology (IT) contingency plan presentation template is the perfect solution for presenting your IT contingency plan to key stakeholders. Slides include scope (service area, service offerings, and service areas that depend on the service at risk), recovery objectives (recovery time objectives, RTO; and recovery point objective, RPO), recovery team (service / role / function, responsibility, dependencies, and expected response time), and recovery strategy (initial recovery and overall recovery strategy). Easily gain buy-in from team members, management and other stakeholders with the all-in-one, IT-specific solution for outlining and refining your IT department’s service contingency plan.
Download an Information Technology (IT) Service Contingency Plan Template for PowerPoint | Google Slides | Smartsheet
Business Contingency Plan Template
Keep tabs on your organization’s comprehensive business contingency plan (BCP) with this distinctive business contingency plan template. It guides you through your business function recovery priorities, relocation strategy, alternate business site, recovery plan, recovery phase, records and backup details, restoration plan, recovery teams, and recovery procedures. This BCP template is useful for determining accurate planning and courses of action to ensure the success of your business’s contingency plan.
Download a Business Contingency Plan Template for Microsoft Word | Google Docs | PowerPoint | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet
Business Contingency Framework Template

This one-page template features a broad-strokes framework for performing a business impact analysis (BIA), along with working out your recovery strategy, plan development, and testing and exercises. You’re never far from the big-picture vision of your business contingency plan with this efficient one-page business contingency framework template, available in Microsoft Word, PDF, Google Docs and Slides, and presentation-friendly PowerPoint formats.
Download a Business Contingency Framework Template for Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Google Docs | Google Slides | PowerPoint
For more resources on business contingency planning, see “ Free Business Continuity Plan Templates .”
Project Management Contingency Plan Template
This project management contingency plan template is ideal for creating a comprehensive contingency plan for any type of project. The template enables you to create a high-level executive summary of your project’s contingency plan, including risk evaluation, a synopsis of your risk-prevention mitigation strategies process, and roles and responsibilities. Use this template to define risks and their events or triggers, consider budgetary implications, and define your potential plans of action.
Download a Project Management Contingency Plan Template for Excel | Google Sheets
Visit our article on contingency planning in project management for more information.

Small Business Contingency Plan Template
It’s critical for small businesses to have a comprehensive contingency plan that team members can reference in the event of a debilitating event or emergency. Designed specifically for small businesses, this template uses a pre-built, all-inclusive contingency plan to provide guidance for modestly sized organizations. Take the guesswork out of creating a contingency plan from scratch, and leverage the advantages of this small-business-specific template.
Download a Small Business Contingency Plan Template for Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Google Docs
For more resources on emergency response and contingency planning, check out our roundup of disaster recovery plan templates .
Contingency Plan Checklist Template
This two-part, fully customizable contingency plan checklist template contains a pre-built contingency plan checklist based on disaster-recovery steps, and a step-by-step, linear recovery procedure section. Use the latter section to ensure that everyone is aware of your contingency plan, if there is an event or occurrence that triggers the need to implement your plan. Then, use the checklist section to ensure that all steps in your contingency plan are in place, should you need to execute your contingency plan.
Download a Contingency Plan Checklist Template for Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Google Docs
What Is a Contingency Plan Template?
A contingency plan template provides a step-by-step process to communicate actionable items in the event of a disaster or disruption. The document takes the guesswork out of emergency planning, so you can protect resources, minimize interruptions, and identify go-to team contacts.
You can begin the contingency planning process by completing a contingency plan template so that you’re adequately prepared. By recording accurate and thorough information to ready yourself for an emergency, you can determine your priorities, relocation strategy, and recovery plan details. A contingency plan also helps you plan your organization’s recovery phases, work to ensure records backup, create a restoration plan, establish a recovery team, and assign roles to key individuals.
When to Use a Contingency Plan
You should use a contingency plan if there is the risk of an unexpected event that could impact your project’s success. A contingency plan is a backup plan that outlines steps for you to take in case the original plan encounters unforeseen obstacles.
The following provides a list of typical scenarios where you should use a contingency plan:
- Risky or Uncertain Situations: When there are potential risks or uncertainties that could impact the success of your project, it's a good idea to have a contingency plan in place to mitigate those risks.
- Time-Sensitive Projects: When you have a tight deadline or critical timeline that you must meet, a contingency plan can help ensure that your project is completed on time, even if unexpected issues arise.
- Resource Limitations: When you have resource constraints, such as budget or personnel, a contingency plan can help you effectively allocate resources.
- Emergency Situations: When emergencies (e.g., natural disasters, pandemics, or other crises) can impact your ability to complete your project, a contingency plan can help you and your organization respond quickly and efficiently.
Overall, you should use a contingency plan whenever there is a potential risk or uncertainty that could impact the success of your project or goal, or when there is the possibility of emergencies. When unexpected events occur, it's always better to be proactively prepared by having a plan in place, instead of scrambling to come up with a solution.
Sections of a Contingency Plan Template:
While your contingency plan will vary to meet the needs of your project, below are the common elements of a contingency plan:
- Recovery Priorities: Enter contingency plan priorities, including recovering essential operations and restoring critical functions.
- Relocation Strategy: Add the relocation strategy when your contingency plan requires moving your primary services.
- Alternate Site: Document alternate site details when you determine the secondary site where you can continue operations.
- Recovery Plan: Enter the step-by-step recovery-plan details to get your organization operational again.
- Disaster Occurrence: Use this phase to identify what constitutes a disaster that requires your organization to activate the contingency plan.
- Plan Activation: In this phase, your organization puts your contingency plan into effect, which continues until your organization secures an alternate site and can relocate operations.
- Alternate Site Operation: Operations continue at the secondary facility until you can restore them at the original site.
- Transition to Primary Site: The organization prepares to move operations back to the original site.
- Records Backup: Enter contingency plan details about how you’ll back up records and make them accessible in the event of a disaster or disruption.
- Restoration Plan: Add your plan for ensuring that all operations, records, etc., are able to be operational in the event of a facility disruption or disaster.
- Recovery Teams: List the recovery team(s) and members. Assign contingency plan tasks based on job role and title.
- Recovery Procedures: Enter details of specific activities or tasks required to adequately recover normal and critical operations.
Additionally, a contingency plan template enables you to track changes to your plan through a section for version history, comprising the following data:
- Version: Enter the unique version number for the most up-to-date iteration of the plan.
- Approved By: Ensure that department heads or other stakeholders have approved the contingency plan.
- Revision Date: Provide the date when a substantial revision was made to your contingency plan.
- Description of Change: List details of the change(s) made to the plan.
- Author: Record the name of the plan’s primary author.
How to Create a Contingency Plan
When creating a contingency plan, be proactive, thorough, and adaptable. By anticipating potential risks and developing a well-documented plan of action, organizations can minimize the negative impact of unexpected events and ensure continuity of critical functions and key services.
Here are some key steps to follow when creating a contingency plan:
- Identify Potential Risks: First, identify potential risks or unexpected events that could impact the success of your project. Brainstorm with stakeholders and team members to identify as many potential risks as possible.
- Assess the Impact: Once you have identified potential risks, assess each risk’s potential impact. This will help you prioritize risks and determine which ones require immediate attention.
- Develop Response Strategies: Based on your impact assessment, develop response strategies for each potential risk. This may involve developing alternative solutions or workarounds, identifying additional resources, or establishing clear communication protocols.
- Assign Responsibilities: Determine who will be responsible for executing the contingency plan if and when it is necessary. Assign specific roles and responsibilities to stakeholders or team members to ensure that everyone knows what they’ll need to do.
- Establish Communication Protocols: Establish clear communication protocols so that team members and stakeholders know how to report potential risks or unexpected events and receive updates on the status of the contingency plan.
- Test and Refine Your Plan: Test the contingency plan periodically to ensure that it works effectively. Make adjustments as needed.
- Document Your Plan: Document the contingency plan in a clear and concise manner and make it easily accessible to all relevant parties.
Keep in mind that a contingency plan is only effective if you regularly review and update it to reflect changing circumstances and new risks that may arise.
Drive Results With Effective Contingency Planning in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

IMAGES
VIDEO