- Collections
- Strategy / Business Plan
- Problem solving

Problem Solving Presentation Templates
Present the problem-solving processes effectively with our premade problem solving powerpoint templates and google slides themes. crafted to guide you from problem identification to resolution, these free templates breathe life into complex strategies. they feature creative, fully editable infographics, like puzzles and light bulb designs..

- Analytical Thinking: Breaking down a problem into smaller parts to understand its nature.
- Creative Thinking: Thinking outside the box to find unique and effective solutions.
- Decision Making: Choosing the best course of action among different alternatives.
- Team Collaboration: Working together to generate diverse perspectives and solutions.
- Communicate the problem statement clearly to stakeholders.
- Exhibit potential solutions and their implications.
- Rally teams around a unified strategy.
- Track progress and outcomes.
In such scenarios, the design and layout of your presentation matter as much as its content. And this is where Slide Egg steps in!
- Diverse Designs: From representing problem identification, business solutions, problem-solving techniques, and strategies to process steps, our slides have it all.
- Creative Infographics: Our slides are adorned with multicolor infographics like puzzle pieces, human brains, ladders, bulbs, stars, magnifiers, locks, and keys to captivate your audience.
- User-Friendly: Our problem solution slides offers 100% editable features, allowing you to tailor the content to fit your narrative seamlessly.
- Cost-Efficient: For those on a budget, we provide free problem and solution slides so you can experience the quality of our offerings.
Become an expert with SlideEgg
How To Build A Problem Solving PowerPoint
We're here to help you, what is problem solving presentation templates.
Problem Solving Presentation Templates is a set of pre-designed PowerPoint slides that you can use to present and explain problem-solving strategies. The templates provide visuals and text that you can use to describe the problem-solving process, from identifying the problem to finding a solution.
Where can we use these Problem Solving Slides?
You can use these Problem Solving Slides for corporate meetings, educational classes, team-building events, or workshops. You can also use them to help facilitate brainstorming sessions and critical thinking activities.
How can I make Problem Solving PPT Slides in a presentation?
Start by creating a slide that outlines the problem. This should include the problem statement and a brief description of the context. Including brainstorming, researching, listing potential solutions, analyzing the data, and finally arriving at a solution. Suppose you want to create slides by yourself. Visit Tips and tricks for detailed instructions.
Who can use Problem Solving Presentation Templates?
Anyone can use Problem Solving PPT Templates to present a problem-solving strategy or process visually engagingly. These templates can be used by professionals, educators, students, business owners, and anyone looking to share a problem-solving approach with an audience.
Why do we need Problem Solving Presentation Slides?
Presenting a problem-solving Presentation slide helps illustrate complex concepts and issues. It can also engage an audience, provide visual context and simplify data. Problem-solving slides can convey ideas and solutions effectively and explore different solutions and alternatives.
Where can I find free Problem Solving Presentation Templates?
Many websites offer free Problem Solving Presentation Templates. Slide egg is one of the best PowerPoint providers. Our websites have uniquely designed templates that allow you to share the problem and help to track progress towards a solution.
- Preferences

Solving Workplace Problems - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

Solving Workplace Problems
Welcome. solving workplace problems. presented by. lynne couture ... attain higher levels of organizational performance. solve even the most complex problems ... – powerpoint ppt presentation.
- Purpose To introduce you to the purpose and scope of Solving Workplace Problems
- Improve process performance
- Correct process deficiencies
- Attain higher levels of organizational performance
- Solve even the most complex problems-step-by-step
- Provide a common language for solving workplace problems
- Define/discuss Problem Solving Tools
- Take an assessment
- Discuss the Problem Solving Process
- Overview SWP skill steps, objectives, design, and audience
- Complete some exercises
- Overview behavioral modeling and job-specific skill practice
- Payoff Youll be in a better position to assess the potential value of SWP for your organization.
- Any leader who is responsible for improving performance and finding solutions to complex problems with his/her people
- Senior Executives
- Department Heads
- Functional (IT, HR, etc.) Managers
- Sales Managers
- Team Leaders
- First Level Supervisors
- Why are sales declining?
- How do we get more people participating in meetings?
- Why isnt our team winning more games?
- How can we get a new product to market faster?
- Why are we getting so many defects from production line 10?
- Patients waiting too long to see emergency room physician
- Manufacturing
- Manufacturing not meeting production targets
- Donors not giving as much as prior year
- Parents are not attending school meetings
- Follow an orderly, step-by-step problem-solving process
- Write problem statements that clearly define problems encountered in work situations
- Assess the contexts of problems
- Analyze the likely root causes of problems
- Involve team members in evaluating the root causes and possible solutions
- Create plans to implement solutions to problems
- Agree and support implementation
- Introduction OpeningPre-TestObjectives Introductions/ExpectationsBenefitsKey Terms Awareness ExerciseContent Teach-backsAction VerbsProblem-Solving ToolsProblem Solving ExercisesCase Study Exercise.
- Job-Specific Practice Worksheet CreationIntroductionSkill PracticeDiscuss
- Summarize and Close Post-Test Summary... Application Job Aids and Tools
- Interesting Hold the learners attention and motivate learning.
- Important They say, This is really going to help me!
- Relevant -- The content and skills have immediate utility.
- Active Learning Lots active of involvement throughout program.
- Skill-Based They can do something when they are done.
- Essential Skills of Leadership
- Maintain Team Member Self-Esteem.
- Focus on Behavior.
- Encourage Team Member Participation.
- Essential Skills of Communicating
- Create a Climate of Open Communication.
- Design Clear, Concise Messages.
- Manage Nonverbal Behaviors Effectively.
- Listen to Communicate.
- I am more committed because I have participated.
- I have a proven 5 step process to follow and a common language that everyone understands
- I focus my energy on the most important things results.
- I will perform and judge my work against a clear, measurable standard.
- My team leader will have a more objective standard to observe, coach and evaluate my performance.
- Controllable Factors
- Uncontrollable Factors
- Constraints
- Rating System
- Rational, Systematic
- Contextual Approach
- Dissolution
- Write a problem statement
- Determine the magnitude
- Determine your authority
- Decision to act
- What is the problem?
- How do you know it is a problem?
- Where has this problem occurred?
- When has it occurred?
- Identify whom to involve
- List symptoms
- List possible causes
- Generate alternative solutions
- Identify criteria for evaluating alternatives
- Weigh the alternatives
- Evaluate resources
- Assign responsibilities
- List tasks and completion dates
- Identify whom to inform
- Identify feedback that will be used to measure progress
- Identify what criteria you will use to determine if the solution is a success.
- Determine what follow-up will be required for implementation success
- More tuned to the way things are done these days.
- Appeals to a broader audience beyond first-level team leaders.
- Use of a five-step process to effectively solve problems
- Provides a common language
- Essential Skills of Communication
- Developing Performance Goals Standards
- Providing Performance Feedback
- Managing Complaints
- Improving Work Habits
- Effective Discipline
- Resolving Conflict
- Coaching Job Skills
- Supporting Change
- Communicating Up
- Hiring Winning Talent (Classroom and Online)
- Leading Successful Projects (Classroom)
- Motivating Team Members (Classroom)
- Solving Workplace Problems (Classroom)
- Retaining Winning Talent (Coming Soon)
- Using Financial Data (Coming Soon)
- Ethics Matter (Coming Soon)
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.


- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Solving Workplace Problems
Published by Milton Ramsey Modified over 5 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Solving Workplace Problems"— Presentation transcript:

Building Relationships

Working With Others Teamwork

Assignment 2 Case Study. Criteria Weightage - 60 % Due Date – 11 th October 2012 Length of Analysis – 2500 words Leverage % including appendices,

Supervisory Skill Builders Handling Problems and Conflicts.

Acting Like a Professional

Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. McGraw-Hill Technology Education Logic and Problem Solving Advanced Computer Programming.

During an Interview: It’s Show Time

Chapter 11 Management Skills

Investigating Your Career

Chapter 9.2 Working With Others Chapter 9.2 Working With Others Lesson 9.2 Teamwork Lesson 9.2 Teamwork.

Chapter 16 Problem Solving and Decision Making. Objectives After reading the chapter and reviewing the materials presented the students will be able to:

Brainstorm Solutions Problem Solving Module Session 4.

2009 Your Opinion Our Future SurveyClarify and Prioritize Clarify & Prioritize Tool Root Cause The 5 Why’s Control & Employee Impact 4 Block Cost & Ease.

Quality Tools. Decision Tree When to use it Use it when making important or complex decisions, to identify the course of action that will give the best.

Desirable Employee Qualities

Chapter 1 You and the World of WorkSucceeding in the World of Work The Changing Workplace 1.2 SECTION OPENER / CLOSER INSERT BOOK COVER ART Section 1.2.

/0604 © Business & Legal Reports, Inc. BLR’s Training Presentations Effective Decision-Making Strategies.

/0904 © Business & Legal Reports, Inc. BLR’s Training Presentations Creative Problem-Solving.

1 The importance of Team Working and Personal Attributes.

© BLR ® —Business & Legal Resources 1408 Problem Solving For Employees.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Problem Solving Activities
All the Problem Solving Activities on this page help you and your group collaboratively tackle seemingly impossible issues.
If you are looking to build consensus around a difficult problem it is likely a tool or process on this page can help you.
[…] Problem Solving […]
Excelent summary thanks so much for this purposeful help
Session expired
Please log in again. The login page will open in a new tab. After logging in you can close it and return to this page.
Enter your email to receive your FREE tools & activities.
We will never share your email address with anyone.

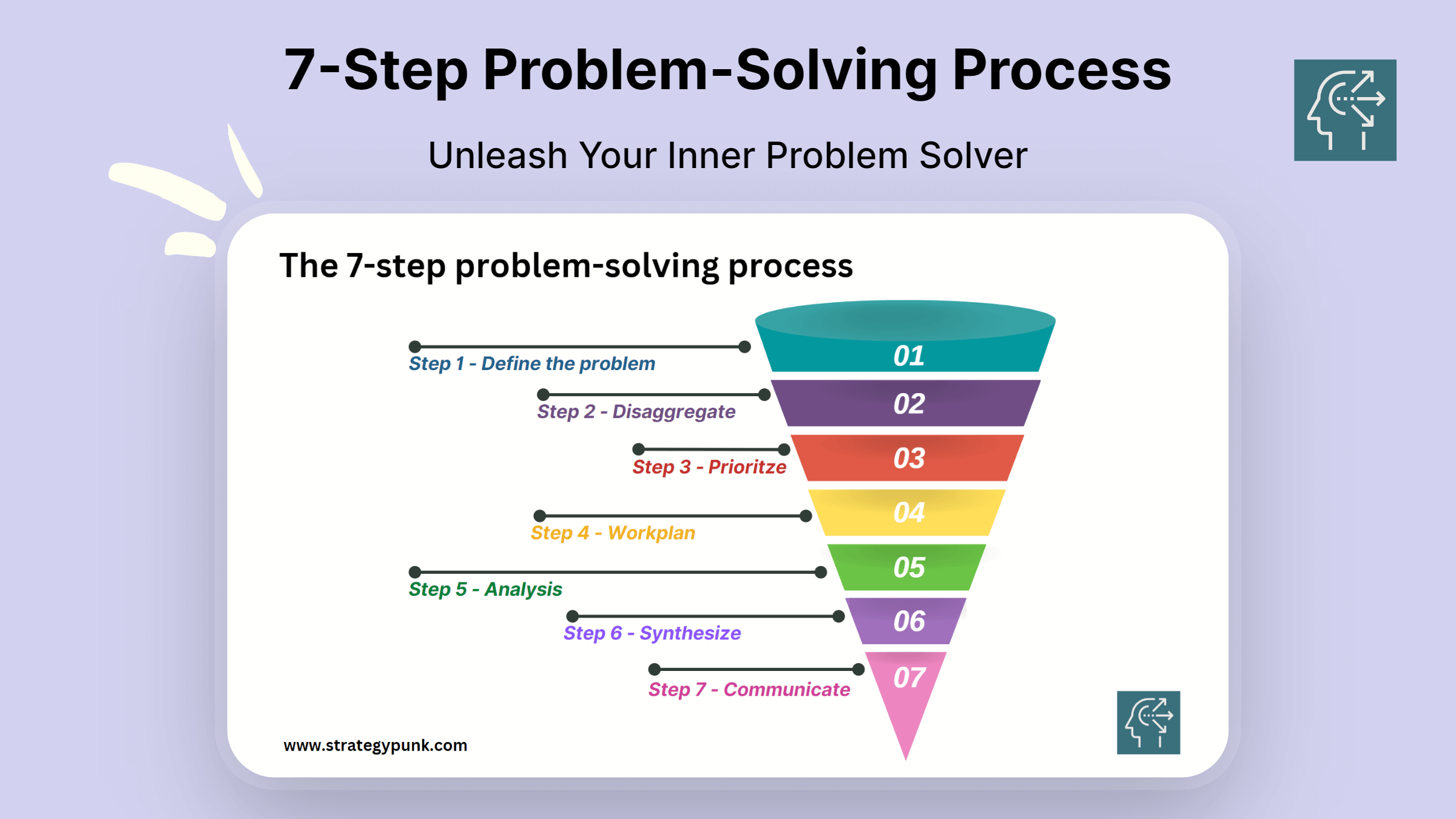
Master the 7-Step Problem-Solving Process for Better Decision-Making
Discover the powerful 7-Step Problem-Solving Process to make better decisions and achieve better outcomes. Master the art of problem-solving in this comprehensive guide. Download the Free PowerPoint and PDF Template.

StrategyPunk
Introduction
Mastering the art of problem-solving is crucial for making better decisions. Whether you're a student, a business owner, or an employee, problem-solving skills can help you tackle complex issues and find practical solutions. The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process is a proven method that can help you approach problems systematically and efficiently.
The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process involves steps that guide you through the problem-solving process. The first step is to define the problem, followed by disaggregating the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Next, you prioritize the features and create a work plan to address each. Then, you analyze each piece, synthesize the information, and communicate your findings to others.
By following this process, you can avoid jumping to conclusions, overlooking important details, or making hasty decisions. Instead, you can approach problems with a clear and structured mindset, which can help you make better decisions and achieve better outcomes.
In this article, we'll explore each step of the 7-Step Problem-Solving Process in detail so you can start mastering this valuable skill. You can download the process's free PowerPoint and PDF templates at the end of the blog post .
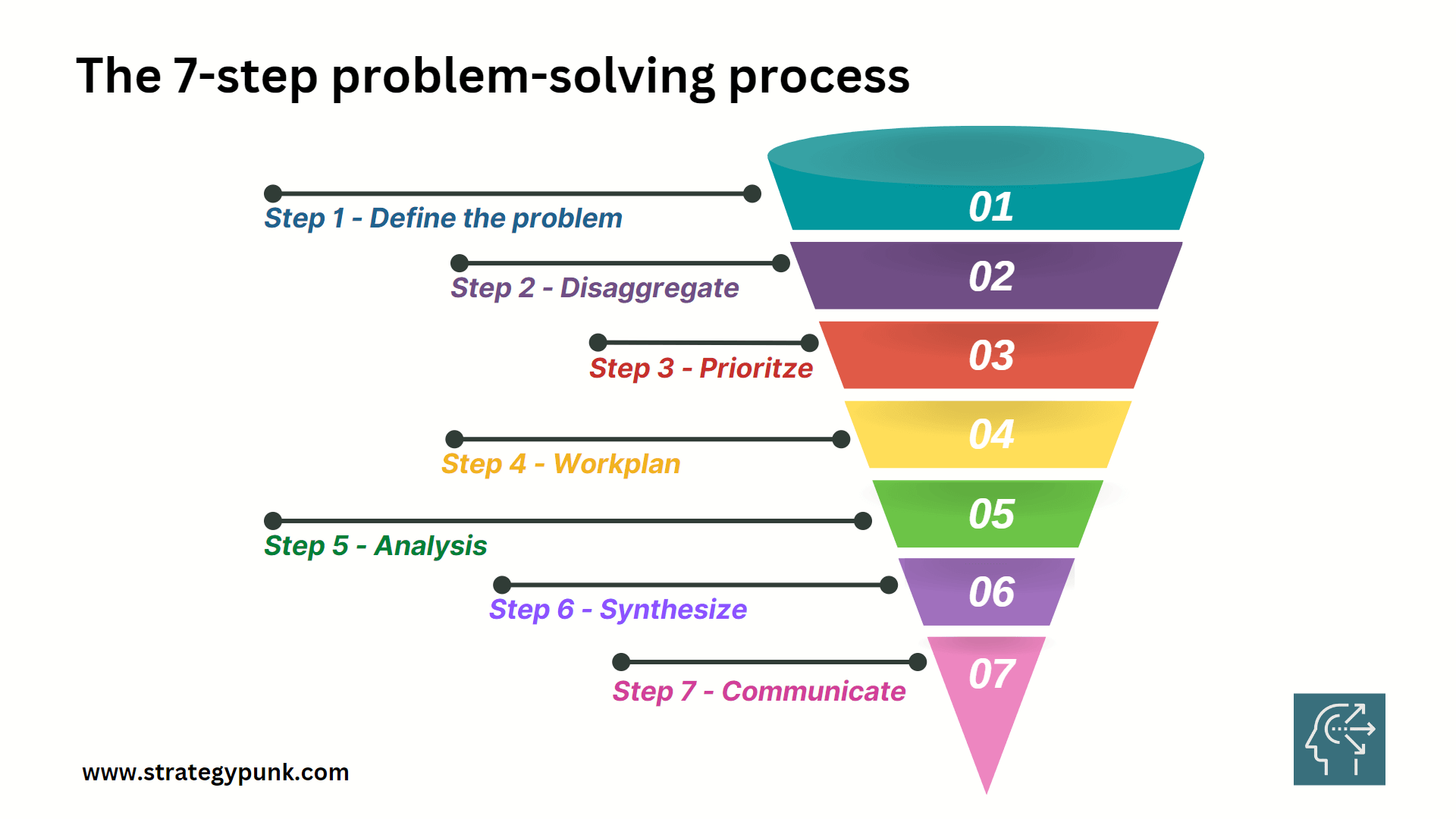
Step 1: Define the Problem
The first step in the problem-solving process is to define the problem. This step is crucial because finding a solution is only accessible if the problem is clearly defined. The problem must be specific, measurable, and achievable.
One way to define the problem is to ask the right questions. Questions like "What is the problem?" and "What are the causes of the problem?" can help. Gathering data and information about the issue to assist in the definition process is also essential.
Another critical aspect of defining the problem is identifying the stakeholders. Who is affected by it? Who has a stake in finding a solution? Identifying the stakeholders can help ensure that the problem is defined in a way that considers the needs and concerns of all those affected.
Once the problem is defined, it is essential to communicate it to all stakeholders. This helps ensure that everyone is on the same page and that there is a shared understanding of the problem.
Step 2: Disaggregate
After defining the problem, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is to disaggregate the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Disaggregation helps break down the problem into smaller pieces that can be analyzed individually. This step is crucial in understanding the root cause of the problem and identifying the most effective solutions.
Disaggregation can be achieved by breaking down the problem into sub-problems, identifying the contributing factors, and analyzing the relationships between these factors. This step helps identify the most critical factors that must be addressed to solve the problem.
A tree or fishbone diagram is one effective way to disaggregate a problem. These diagrams help identify the different factors contributing to the problem and how they are related. Another way is to use a table to list the other factors contributing to the situation and their corresponding impact on the issue.
Disaggregation helps in breaking down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. It helps understand the relationships between different factors contributing to the problem and identify the most critical factors that must be addressed. By disaggregating the problem, decision-makers can focus on the most vital areas, leading to more effective solutions.
Step 3: Prioritize
After defining the problem and disaggregating it into smaller parts, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is prioritizing the issues that need addressing. Prioritizing helps to focus on the most pressing issues and allocate resources more effectively.
There are several ways to prioritize issues, including:
- Urgency: Prioritize issues based on their urgency. Problems that require immediate attention should be addressed first.
- Impact: Prioritize issues based on their impact on the organization or stakeholders. Problems with a high impact should be given priority.
- Resources: Prioritize issues based on the resources required to address them. Problems that require fewer resources should be dealt with first.
Considering their concerns and needs, it is important to involve stakeholders in the prioritization process. This can be done through surveys, focus groups, or other forms of engagement.
Once the issues have been prioritized, it is essential to develop a plan of action to address them. This involves identifying the required resources, setting timelines, and assigning responsibilities.
Prioritizing issues is a critical step in problem-solving. By focusing on the most pressing problems, organizations can allocate resources more effectively and make better decisions.
Step 4: Workplan
After defining the problem, disaggregating, and prioritizing the issues, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is to develop a work plan. This step involves creating a roadmap that outlines the steps needed to solve the problem.
The work plan should include a list of tasks, deadlines, and responsibilities for each team member involved in the problem-solving process. Assigning tasks based on each team member's strengths and expertise ensures the work is completed efficiently and effectively.
Creating a work plan can help keep the team on track and ensure everyone is working towards the same goal. It can also help to identify potential roadblocks or challenges that may arise during the problem-solving process and develop contingency plans to address them.
Several tools and techniques can be used to develop a work plan, including Gantt charts, flowcharts, and mind maps. These tools can help to visualize the steps needed to solve the problem and identify dependencies between tasks.
Developing a work plan is a critical step in the problem-solving process. It provides a clear roadmap for solving the problem and ensures everyone involved is aligned and working towards the same goal.
Step 5: Analysis
Once the problem has been defined and disaggregated, the next step is to analyze the information gathered. This step involves examining the data, identifying patterns, and determining the root cause of the problem.
Several methods can be used during the analysis phase, including:
- Root cause analysis
- Pareto analysis
- SWOT analysis
Root cause analysis is a popular method for identifying the underlying cause of a problem. This method involves asking a series of "why" questions to get to the root cause of the issue.
Pareto analysis is another method that can be used during the analysis phase. This method involves identifying the 20% of causes responsible for 80% of the problems. By focusing on these critical causes, organizations can make significant improvements.
Finally, SWOT analysis is a valuable tool for analyzing the internal and external factors that may impact the problem. This method involves identifying the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to the issue.
Overall, the analysis phase is critical for identifying the root cause of the problem and developing practical solutions. Organizations can gain a deeper understanding of the issue and make informed decisions by using a combination of methods.
Step 6: Synthesize
Once the analysis phase is complete, it is time to synthesize the information gathered to arrive at a solution. During this step, the focus is on identifying the most viable solution that addresses the problem. This involves examining and combining the analysis results for a clear and concise conclusion.
One way to synthesize the information is to use a decision matrix. This involves creating a table that lists the potential solutions and the essential criteria for making a decision. Each answer is then rated against each standard, and the scores are tallied to arrive at a final decision.
Another approach to synthesizing the information is to use a mind map. This involves creating a visual representation of the problem and the potential solutions. The mind map can identify the relationships between the different pieces of information and help prioritize the solutions.
During the synthesis phase, it is vital to remain open-minded and consider all potential solutions. Involving all stakeholders in the decision-making process ensures that everyone's perspectives are considered.

Step 7: Communicate
After synthesizing the information, the next step is communicating the findings to the relevant stakeholders. This is a crucial step because it helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page and that the decision-making process is transparent.
One effective way to communicate the findings is through a well-organized report. The report should include the problem statement, the analysis, the synthesis, and the recommended solution. It should be clear, concise, and easy to understand.
In addition to the report, a presentation explaining the findings is essential. The presentation should be tailored to the audience and highlight the report's key points. Visual aids such as tables, graphs, and charts can make the presentation more engaging.
During the presentation, it is essential to be open to feedback and questions from the audience. This helps ensure everyone agrees with the recommended solution and addresses concerns or objections.
Effective communication is vital to ensuring the success of the decision-making process. By communicating the findings clearly and concisely, stakeholders can make informed decisions and work towards a common goal.
The 7-step problem-solving process is a powerful tool for helping individuals and organizations make better decisions. By following these steps, individuals can identify the root cause of a problem, prioritize potential solutions, and develop a clear plan of action. This process can be applied to various scenarios, from personal challenges to complex business problems.
Through disaggregation, individuals can break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. By prioritizing potential solutions, individuals can focus their efforts on the most impactful actions. The work step allows individuals to develop a clear action plan, while the analysis step provides a framework for evaluating possible solutions.
The synthesis step combines all the information gathered to develop a comprehensive solution. Finally, the communication step allows individuals to share their answers with others and gather feedback.
By mastering the 7-step problem-solving process, individuals can become more effective decision-makers and problem-solvers. This process can help individuals and organizations save time and resources while improving outcomes. With practice, individuals can develop the skills to apply this process to a wide range of scenarios and make better decisions in all areas of life.
7-Step Problem-Solving Process PPT Template
Free powerpoint and pdf template, executive summary: the 7-step problem-solving process.
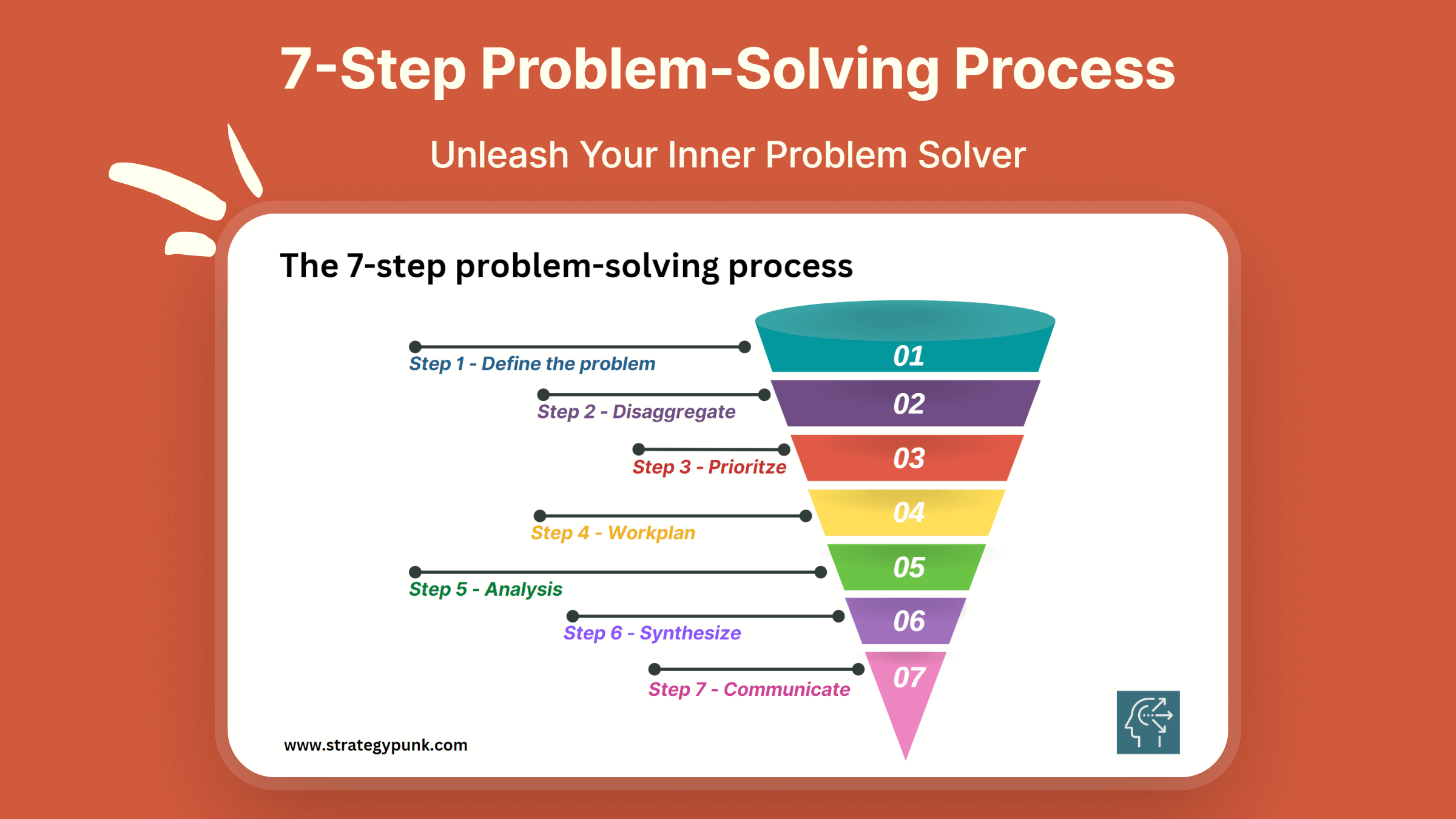
The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process is a robust and systematic method to help individuals and organizations make better decisions by tackling complex issues and finding practical solutions. This process comprises defining the problem, disaggregating it into smaller parts, prioritizing the issues, creating a work plan, analyzing the data, synthesizing the information, and communicating the findings.
By following these steps, individuals can identify the root cause of a problem, break it down into manageable components, and prioritize the most impactful actions. The work plan, analysis, and synthesis steps provide a framework for developing comprehensive solutions, while the communication step ensures transparency and stakeholder engagement.
Mastering this process can improve decision-making and problem-solving capabilities, save time and resources, and improve outcomes in personal and professional contexts.
Sign up for StrategyPunk
Every Organization Needs a Strategy. Unlock Free Insights and Templates to Master Yours. Join 5000+ Leaders Today.
No spam. Unsubscribe anytime.
7-Step Problem-Solving Process PDF Template
7-step problem-solving process powerpoint template.

General Electric - McKinsey Nine Field Matrix (FREE Template)
GE-McKinsey Nine-Field Matrix: PowerPoint Template
PESTLE Analysis of Siemens AG (FREE PDF and PPT template)
Unlock Siemens AG's business environment with our detailed PESTLE analysis. Get free PowerPoint & PDF templates to create your own strategic assessment.
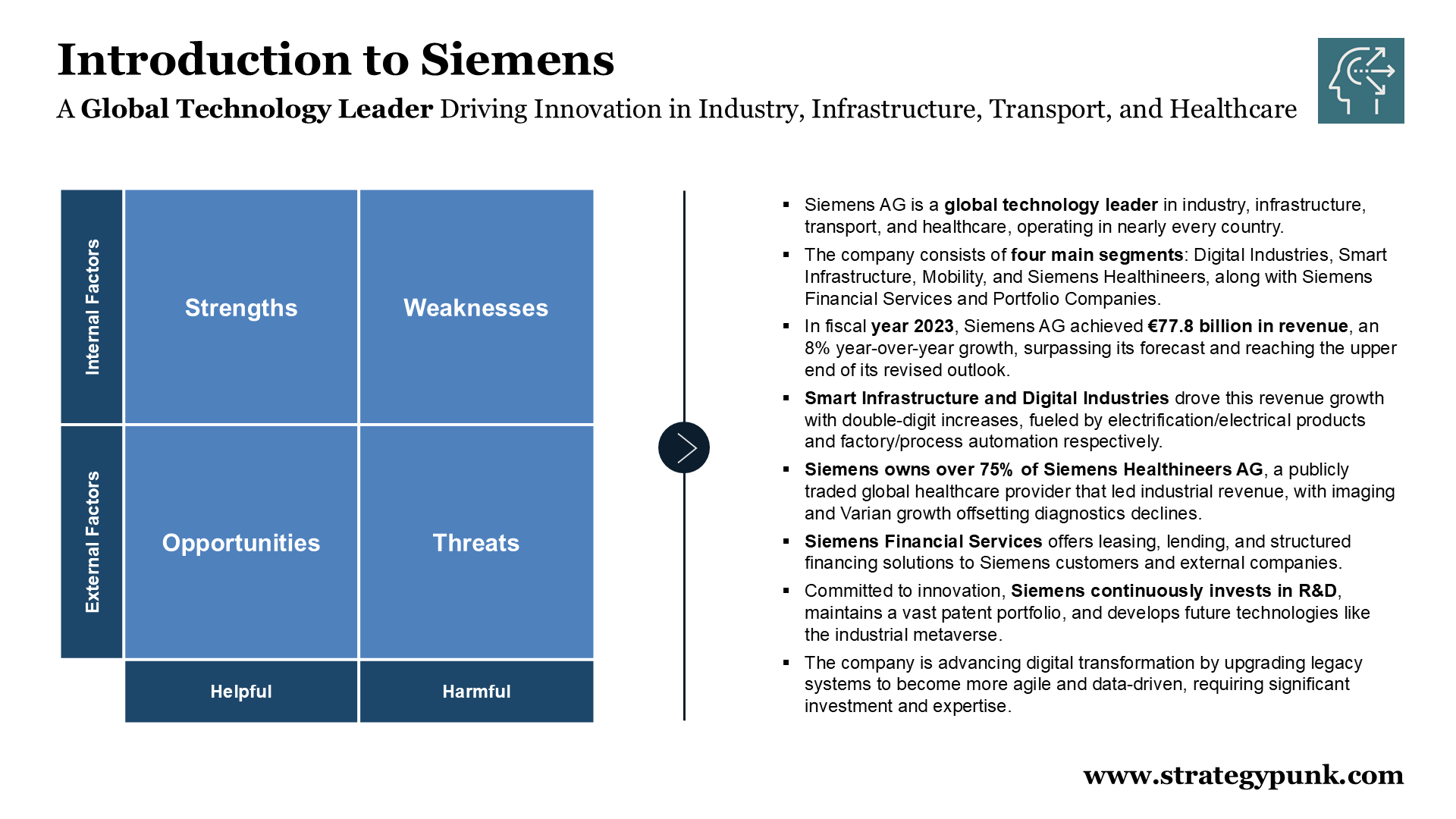
SWOT Analysis of Siemens AG (FREE PDF and PPT template)
Explore Siemens AG's SWOT Analysis for key insights. Download our free PDF and PPT templates to enhance your strategic planning.
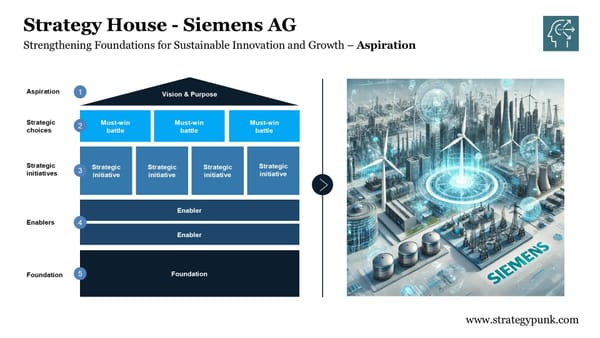
Digital Transformation by Design: The Siemens Strategy House
Applying the Strategy House to Siemens AG. Unlock Siemens's strategic framework with our analysis and free PDF.
7 Step Problem Solving Process Diagram for PowerPoint
The 7 Step Problem Solving Process Diagram for PowerPoint is a semi-circular template design. It illustrates an iterative process cycle including chevron arrows. Each of these arrow shapes outlines a sequence of the problem-solving method in seven stages. The stages include problem definition, disaggregation, prioritizing, work plan, analysis, synthesis, and communication. These stages are also known as the 7 steps to bullet-proof problem-solving model. This 7 step circular infographic and process flow diagram encapsulates all essential steps required to address an issue up to its resolution.
Finding and implementing a solution to any problem is a crucial skill required in all parts of life. It is considered one of the important job capabilities. The 7 steps process of problem-solving provides a foundation that is applicable for business as well as personal challenges. This process functions effectively with nearly all types of problem-solving tools and techniques.
The 7 Step Problem Solving Process Diagram for PowerPoint presents a semi-circle shape of connected chevron arrows. These arrows define the direction of the process sequence. The problem-solving diagram template can be used in educational/staff training and organizational problem-solving presentations. There are additional seven slides of the PowerPoint diagram template to carry detailed discussions about each stage. The users can customize colors and change the textual content of pre-design templates. The SlideModel diagram templates offer a 5 step version of problem solving process template. The users can choose from these templates based on the complexity of the problem and decision making strategies. Alternatively to this 7 step circular infographic template for PowerPoint, you can also download other 7 steps PowerPoint templates for your presentations or process flow PPT templates with creative slides and layouts.

You must be logged in to download this file.
Favorite Add to Collection

Subscribe today and get immediate access to download our PowerPoint templates.
Related PowerPoint Templates

Consulting Proposal Slide Deck Template

DACI PowerPoint Template

Conflict Resolution PowerPoint Template

Corporate Presentation Slide Deck Template

CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING
Nov 16, 2014
1.72k likes | 4.26k Views
CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING. CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING. Introductions Purpose Learning Objectives. CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING. PURPOSE: To develop the awareness and the skills necessary to solve problems creatively. LEARNING OBJECTIVES. 1. Define creative problem solving.
Share Presentation
- creative thinking
- problem solving
- mental blocks
- mental block 3
- creative problem solving process

Presentation Transcript
CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING Optimist International
CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING • Introductions • Purpose • Learning Objectives Optimist International
CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING PURPOSE: To develop the awareness and the skills necessary to solve problems creatively. Optimist International
LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Define creative problem solving. 2. Be familiar with common mental blocks to creative thinking process. 3. Explore ways to be more creative. 4. Know the steps to the creative problem solving process. 5. Be familiar with: Brainstorming, Mind mapping and Multivoting 6. Apply tools to solve a problem. Optimist International
Workshop Outline • A. What is creative problem solving? • B. Why don’t we think creatively more often? • C. How can we be more creative? • D. What is the creative problem solving process? • E. What are some other specific creative problem solving tools and techniques? • F. Application of learning. Optimist International
CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING What is creative problem solving? Optimist International
Some Additional Thoughts • The creative person uses information to form new ideas. • The real key to creative problem solving is what you do with the knowledge. • Creative problem solving requires an attitude that allows you to search for new ideas and use your knowledge and experience. • Change perspective and use knowledge to make the ordinary extraordinary and the usual commonplace. Optimist International
DEFINITION Creative problem solving is - Optimist International
DEFINITION “Creative problem solving is - looking at the same thing as everyone else and thinking something different.” Adapted from a famous quote from a former Nobel prize winner, Albert Szent-Gyorgi. Optimist International
EXERCISE Optimist International
A SOLUTION Optimist International
LET’S TALK ABOUT: Why don’t we think creatively more often? What are the barriers that get in our way? Optimist International
BARRIERS THAT GET IN OUR WAY • Time • Why change? • Usually don’t need to be creative • Habit • Routine • Haven’t been taught to be creative What are some other barriers that get in our way? Optimist International
MENTAL BLOCKS Mental blocks are reasons (attitudes) why we don’t “think something different.” Optimist International
MENTAL BLOCKS 1. The _______ answer. 2. That’s not _________. 3. __________ the rules. 4. Be ______________. 5. ________ is frivolous. 6. That’s not my _____. 7. ________ ambiguity. 8. Don’t be _________. 9. __________is wrong. 10. I’m not __________. Optimist International
MENTAL BLOCK # 1 • The right answer. Only one? Optimist International
MENTAL BLOCK # 2 • The right answer. • That’s not logical. Optimist International
MENTAL BLOCK # 3 Why rules should be challenged: • 1. We make rules based on reasons that make a lot of sense. • 2. We follow these rules. • 3. Time passes, and things change. • 4. The original reasons for the generation of these rules may no longer exist, but because the rules are still in place, we continue to follow them. • The right answer. • That’s not logical. • Follow the rules. Optimist International
MENTAL BLOCK # 4 • The right answer. • That’s not logical. • Follow the rules. • Be practical. Optimist International
MENTAL BLOCK # 5 • The right answer. • That’s not logical. • Follow the rules. • Be practical. • Play is frivolous. “When do you get your best ideas?” Optimist International
MENTAL BLOCK # 6 • That’s not my area. Optimist International
MENTAL BLOCK # 7 • That’s not my area. • Avoid ambiguity. AMBIGUITY Optimist International
MENTAL BLOCK # 8 • That’s not my area. • Avoid ambiguity. • Don’t be foolish. Optimist International
MENTAL BLOCK # 9 • That’s not my area. • Avoid ambiguity. • Don’t be foolish. • To err is wrong. Optimist International
MENTAL BLOCK # 10 • That’s not my area. • Avoid ambiguity. • Don’t be foolish. • To err is wrong. • I’m not creative. Optimist International
BEING MORE CREATIVE How can we be more creative? Jot down at least 3 ideas that come to your mind. Optimist International
Golden Rules of Creative Thinking • Start small trying to discover new ways to be creative, ___________. • __________ to abandon the old, obsolete ways of doing things and explore new ways. • It is not possible to change the way we think about everything. ________ in which to try creative thinking techniques. • Understand that creative thinking requires __________, but it is worth it! • Remember that creative thinking is both _______ and__________!!! Optimist International
Golden Rules of Creative Thinking (Continued) • _________ on what you can reasonably do. Trying to do too many things at once compromises the effort and may take away from the results. • _________creative thinking for today as well as tomorrow. • Include other people in the creative thinking process with you. __________fosters creative thinking. • Include _______ and ______ in your creative thinking process as well as ___________. • Keep ________________. Optimist International
CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING PROCESS STEP 1. State what appears to be the problem. The real problem may not surface until facts have been gathered and analyzed. Therefore, start with what you assume to be the problem, that can later be confirmed or corrected. Optimist International
CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING PROCESS STEP 2. Gather facts, feelings and opinions. What happened? Where, when and how did it occur? What is it’s size, scope, and severity? Who and what is affected? Likely to happen again? Need to be corrected? May need to assign priorities to critical elements. Optimist International
CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING PROCESS STEP 3. Restate the problem. The real facts help make this possible, and provide supporting data. The actual problem may, or may not be the same as stated in Step 1. Optimist International
CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING PROCESS STEP 4. Identify alternative solutions. Generate ideas. Do not eliminate any possible solutions until several have been discussed. Optimist International
CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING PROCESS STEP 5. Evaluate alternatives. Which will provide the optimum solution? What are the risks? Are costs in keeping with the benefits? Will the solution create new problems? Optimist International
CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING PROCESS STEP 6. Implement the decision! Who must be involved? To what extent? How, when and where? Who will the decision impact? What might go wrong? How will the results be reported and verified? Optimist International
CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING PROCESS STEP 7. Evaluate the results. Test the solution against the desired results. Make revisions if necessary. Optimist International
10 Questions To Encourage Ideas • What if…? • How can we improve…? • How will the Optimist Member and/or the community benefit? • Are we forgetting anything? • What’s the next step? Optimist International
10 Questions To Encourage Ideas • What can we do better…? • What do you think about…? • What should we add? • What should we eliminate? • What other ideas do you have...? Optimist International
TOOLS & TECHNIQUES BRAINSTORMING Purpose: To generate a large number of ideas in a short period of time. Optimist International
BRAINSTORMING Rules for Brainstorming: • The more ideas the better! • No discussion • No idea is a bad idea • Build on one another’s ideas • Display all ideas Optimist International
BRAINSTORMING EXERCISE How Do We Motivate Our Local Optimist Club Members? Ideas: Freely record your ideas as they come to your mind. Optimist International
Re-state the question to keep the process going Remember Creative Thinking What did you mean by that?!!! BRAINSTORMING GUIDELINES 1. Practice question:How Do We Motivate Our Local Optimist Club Members? 2. Clarify understanding. Once all the ideas have been generated (it may take approximately 5 to 6 minutes),review ideas offered. Optimist International
Let’s combine ideas!!! Are wedone yet? BRAINSTORMING GUIDELINES 3. Combine items that are similar and/or eliminate duplicates. 4. Completion. Optimist International
TOOLS & TECHNIQUES - MULTIVOTING • Purpose: To help a group of people make a decision with which they are comfortable. • Definition: A way to vote to select the most important or popular items (alternatives) from a list. Optimist International
Multivoting List 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Revised List 1. 2. 3. MULTIVOTING Steps 1. Generate a list of items and number each item. 2. If two or more items seem similar, they may be combined. 3. If necessary, renumber the items. Optimist International
MULTIVOTING Steps (Continued) 4. Write down the numbers of the items you feel are the major cause of the problem. 5. Share your votes by a show of hands. 6. Eliminate those items with the fewest votes. 7. Repeat steps 3 (renumber) through 6 on the list of remaining items. Continue this process until only a few items remain. If a clear favorite does not emerge, the group may discuss the items listed and make a choice. Optimist International
MIND MAPPING • Definition : A visual picture of a group of ideas, concepts or issues. • Purpose : • Unblock our thinking. • See an entire idea or several ideas on one sheet of paper. • See how ideas relate to one another. • Look at things in a new and different way. • Look at an idea in depth. Optimist International
Motivating Members Methods How Think freely!! Mind Mapping Exercise 1. Initial Tumble of Ideas. • Over-sized blank sheet of paper. • Select word, phrase or problem statement to serve as a focus for discussion. • Print it in the middle of the paper. Enclose it in a box or oval. • Let a word pop out of your mind. Print it anywhere on the paper. • Underline it and connect the line with the problem statement (or key phrase or word) you are working. • Record the next idea and connect it to original focus point or the prior thought. • Continue printing and connecting words. Optimist International
Motivating Members People Helping Others Purpose Resources Results Methods Fun Learning How Mind Mapping Exercise EXAMPLE Optimist International
Mind Mapping Exercise-- Helpful Hints A • Keep your printing large and easy to read. • Feel free to use symbols and or pictures. • Have some fun using different colors. Optimist International
Have Fun Drawing Your Own Mind Map! COMPLETED MAP • Draw over clusters of similar thoughts that are associated with the main focus point. Have fun using a different color highlighter with each cluster of words. • How do the variety of ideas relate to one another? • Do you notice any common causes of the problem? What are the most important causes? • You are now ready to brainstorm solutions! Optimist International
- More by User

Creative Problem Solving
Our Problem Solving Training Program focuses on problem solving strategies and tools that help to analyze, structure and solve business issues. It is an important element in Management Skills training.
1.52k views • 19 slides

Brainstorming - Creative Problem Solving Method
Session objectives. What is brainstormingWhy and when use itHow to organise and lead a successful brainstorming sessionWhat mistakes are to be avoidedAdditional creative problem solving methods. What is brainstorming. ?The best way how to have a good idea is to have many ideas?Alex F. Osborne,
886 views • 22 slides

Problem Solving and Creative Thinking
Problem Solving and Creative Thinking. Problem Solving. What is a Problem? A problem arises when a living creature has a goal but does not know how this goal is to be reached.
2.32k views • 61 slides

Creative Problem Solving Across Cultures
Creative Problem Solving Across Cultures. The overall purpose of this exercise is for students to explore the how to use creative problem solving in various cultures. . Creativity Defined. Objectives. To determine the how country cultures influence creative problem solving.
657 views • 7 slides

Creative Problem Solving. Chapter 13. “ Make it a practice to keep on the lookout for novel and interesting ideas that others have used successfully. Your idea only has to be original in its adaptation to the problem you are working on.” —Thomas Alva Edison.
442 views • 13 slides

Creative Problem Solving. Mental Models. Steps to Engineering Goals. Foundation Mental models Knowledge creation model Creative problem solving process Superstructure Engineering design & problem solving Communication & teamwork Learning, innovation, & information management Roadway
406 views • 18 slides

CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING. Prof. Vidyanand Jha IIM Calcutta December 7, 2000. PROBLEM SOLVING. Problem - a discrepancy current state-desired state Decisions- Choices Two or more alternatives Decision Making process of choice making. General model of problem solving. Identify problem
806 views • 36 slides

789 views • 51 slides

Creative Problem Solving. Visualization. Visualization. “Seeing with the mind’s eye” can expand creative thinking and problem solving. Dorothy A. Sisk, Professor, Lamar University. Memory. Human Brain: Short-term memory Long-term memory Information processor
419 views • 14 slides

Creative Problem Solving. Adapted from “CPS For Kids” written by Bob Eberle and Bob Stanish.
383 views • 17 slides

Creativity and Creative Problem Solving
Creativity and Creative Problem Solving. Minder Chen Professor of MIS California State University Channel Islands [email protected]. Creativity and Innovation.
1.61k views • 90 slides

Creative Problem Solving. Innovation in Action. Creativity. The sum of two coins is $1.10. One of them is not a dime. What are the two coins? Dollar coin and a dime. Creativity. A year has 12 months, and some have 30 days, and some have 31 days. How many months have 28 days? All.
240 views • 10 slides

CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING. facilitated by Ruth E. Lawhorn 3/98. Creative Problem Solving is. Adding another ingredient to the usual “stew” of what do I do about whatever… (Source: original verse by Ruth E. Lawhorn). What is Problem Solving?.
330 views • 14 slides

Creative problem solving
Creative problem solving. The art and mindset of hacking. WHO?. ME. WHO?. ?. YOU. Hacking. Hacking. creative solution illegal computer access neat trick …. Right and wrong. Legality Ethics. Problem 1. Solve each equation by adding one straight line. history. Phreaks Morris Worm.
356 views • 12 slides

Creative Problem Solving. Adeyl Khan (Ayn) BPS 440. We are managers!. Why CPS? Tackle complex problems Encourage innovation Implement new solutions Is creativity the key to management success?. successful managers. The Goal: Understand CPS. Introduction to the essential skills
419 views • 11 slides

Creative Problem Solving. TRIZ. Problem Solving Methods. DMAIC – Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control DFSS – Design for Six Sigma PDCA – Plan, Do, Check, Act PDSA – Plan, Do, Study, Act TQM, PR, Kaizen, Pugh, WB, . . . . TRIZ – Theory of Inventive Problem Solving.
389 views • 15 slides

Creative Problem Solving. Brainstorming & Nominal Group Technique. Brainstorming :. Introduced by Alex Osborn, 1939 Creative problem-solving technique Atmosphere free of criticism All members must participate Implemented during the “solutions step” of the Standard Agenda.
832 views • 4 slides

Getting Unstuck: Creative Problem Solving
Getting Unstuck: Creative Problem Solving. Ken Abrams, Ph.D. You-Know. Objectives. Explore why we need to be creative and how to get that way Propose a method to leverage new technology to improve problem solving creativity. The Challenge. Think different!.
736 views • 39 slides
Our Creative Problem Solving course will help you to come up with many innovative ideas, to crafi those ideas and apply them in your own life. You will also develop your skills in creative expression, both verbally and visually and learn how to see problems from diGerent perspectives. The Creative Problem Solving course will equip you with a creative process that you can apply in academic and work contexts or when pursuing your own personal creative projects.
66 views • 3 slides

Techniques of Creative Problem Solving
Techniques of Creative Problem Solving. Contents. Introduction Techniques of creative problem solving Problem Decomposition Information Search Breaking Stereotyped response Unblocking Mutual Stimulation Imaging Fusing Ideating Exteremisation and dialectical Brainstorming
325 views • 25 slides

Innovation and Creative Problem Solving
Innovation and Creative Problem Solving. Prof. Maarja Kruusmaa Centre for Biorobotics www.biorobotics.ttu.ee. Course content. What is creativity? Creative and critical thinking, methods for boosting creativity. Creativity and engineering. How creative? How to assess creative solutions?
276 views • 6 slides

CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING. Problem Solving Techniques. Brainstorming Consensus Building Action Planning. Brainstorming.
518 views • 44 slides

IMAGES
VIDEO