

20 Email Marketing Case Studies: Examples & Results to Learn From
How would you like to read the best email marketing case studies ever published?
More importantly, how would you like to copy the best practices for email marketing campaigns that are based on real-world examples and not just theory?
Below, you’ll find a list of the top email marketing case studies along with the results and key findings from each example. By studying these email marketing case study examples and applying the lessons learned in your own email campaigns, you can hopefully achieve similar results as an email marketer.
Table of Contents
Top Email Marketing Case Studies
Getting 1,300 monthly donations – watsi email marketing case study.
In this case study, you’ll learn how Watsi crafted an email marketing campaign encouraging new and existing users to sign up for its Universal Fund. Using seven test-driven tools helped this organization knock huge campaigns out of the park. Learn how Watsi used email to make people feel more special, take customization to the next level, earn 1,300 monthly donations, and more.
Collecting 100,000 Emails In One Week – Tim Ferris Show Email Marketing Case Study
This email marketing case study has it all: tips, templates, and code to create a successful email campaign. Discover how Harry’s, a men’s grooming brand, launched its brand and how it collected nearly 100,000 email addresses in one week. You’ll learn everything they did so you can try to replicate the results.
The Science Behind Obama’s Campaign Emails – Bloomberg Email Marketing Case Study
Obama’s election success proved the true power of digital marketing, including powerful email campaigns. Most of the $690 million dollars Obama raised online came from fundraising emails. In this article, you’ll learn about the rigorous experimentation by a large team of analysts and the strategies that made the campaign so successful.
The Amazon Email Experience – Vero Email Marketing Case Study
In this case study on email marketing by Vero, you’ll get a complete analysis of Amazon’s email experience for the user. It takes you from the initial subscriber welcome message, to email receipts, shipping updates, thank you content, invites, Black Friday deals, the review email, and more. There are loads of data and useful tips you can gain and use for your own email campaigns in this post.
Boost Open Rates By 3X & CTR By 2X – Digital Marketer Email Marketing Case Study
How would you like to instantly boost your open rates by 3X and your click-through rates (CTR) by 2X with the next email you send to your list? Digital Marketer shows you 11 strategies you can use right now based on its own research and data to achieve similar results.
Increasing Reach, Impact & Subscriber Satisfaction – Content Marketing Institute Email Marketing Case Study
This article by Content Marketing Institute contains a breakdown of several case study examples for email marketing. Inside, you’ll learn about using list segmentation as well as advice on measuring and optimizing your email delivery performance. Popular brands discussed include SalesForce, Xerox, Noodles Company, and more.
Birchbox Boost Conversions By 25% – Braze Email Marketing Case Study
This is one of the top email marketing case studies that prove why you shouldn’t send out a one-size-fits-all message to your mailing list. It’s a short case study on email marketing, but you’ll learn quickly how Braze helped Birchbox use custom attributes culled from data gathered on customer behavior to switch from generic email content to a more personalized strategy that delivered better results: a 25% boost in conversion rates and 16% increase in open rates.
109% Revenue Lift for Dell with GIFs – MarketingSherpa Email Marketing Case Study
This is one of the best email marketing case studies available that shows the true power of using GIFs in your daily, weekly, or monthly newsletter campaigns. Discover how Dell lifted revenue by 109% with GIF-centered email effort.
$40,000 In Sales Without Annoying Subscribers – Yaro Starak Email Marketing Case Study
Here’s a complete breakdown of how Yaro Starak generated $40,00 in sales without annoying his subscribers during new product launches. It contains lots of tips, tricks, and expert advice on how (and when) to send consecutive emails, usiing videos in the campaign, creating a sense of urgency to buy now, and more.
$800,000 for Charity Water By Increasing Email Frequency – Money Journal Email Marketing Case Study
There are numerous email marketing strategies you can use to increase revenue for your business. However, not all email campaigns have to be heavily focused on giving customer discounts or free stuff to generate more money. This is especially true for non-profit organizations. Check out this case study to learn how Charity Water increased revenue by $800,000 by taking an unconventional approach to their follow-up emails that takes their audience on a journey.
Nanoleaf Recovers 30% of Abandonded Carts – Rejoiner Email Marketing Case Study
Are you an ecommerce brand, online retailer, course seller, or other type of website that uses a cart for the checkout process? If so, then this case study by Rejoiner will give you actionable tips to try based on data from Nanoleaf, which recovered 30% of sales with abandoned cart follow-up emails.
70+ Calls for a B2B Company with Cold Emailing – Growforce Email Marketing Case Study
Cold email marketing can be one of the best converting channels when done right. And this article will help you improve your cold emailing results. Read it to find out some of the top cold email best practices, get an example email sequence, and learn a powerful extra step you can use for marketing automation that works.
From Starting Blocks to Total Clarity – Email Marketing Heroes Case Study
Email Marketing Heroes is a podcast that offers free email marketing tips and a membership program to help business owners improve their email campaigns. In this blog post (and podcast), you’ll learn how one member got instant positive results by emailing her list more regularly, setting up automated email campaigns, and including links in a specific part of each message.
Hammock Increased Open Rate 48% with Shorter Emails – MarketingSherpa Email Marketing Case Study
Hammock is a B2B company that turned its traditional, content-heavy email newsletter into what they refer to as an “un-newsletter.” Discover how “The Idea Email” increased email open rates by 48% by focusing on one central topic and containing 350 words or less.
A/B Testing for Success – VWO Email Marketing Case Study
Most digital marketers don’t think about A/B testing their email marketing campaigns. However, year after year, email marketing delivers the highest return on investment (ROI) across all acquisition channels. In this article, you’ll learn how to incorporate A/B testing best practices, methodologies, and mental models to increase open rates, click-through rates (CTR), conversions, and more.
Building a Welcome Series from Scratch – HelpScout Email Marketing Case Study
This is not your typical case study on email marketing; however, it’s an important article to read if you need help setting up a good welcome series for your business. HelpScout takes you from the first email to the last you send to new subscribers while also describing the goal of each email message in the campaign.
600 Email Subscribers With 2 Blog Posts – Jacob McMillen Email Marketing Case Study
Want to know how to combine the power of SEO, blogging, and email marketing to get new subscribers on your list? Jacob McMillen teaches you all that and more in this case study. Learn how he used ConvertKit on a new blog along with SumoMe Pro popups, and a special SEO content writing technique to get 600 email subscribers from just two blog posts. Includes step-by-step instructions for you to copy this exact strategy for your website and email campaigns.
8 Steps to Building a Tripwire Email Funnel – Data Driven Marketing Email Case Study
If you’re serious about email marketing, then you need to have a good tripwire in place to make more sales from your new subscribers. Inside this guide, you’ll find a complete strategy for building an effective tripwire funnel that converts more subscribers into customers as well as using a follow up email sequence to capture the non-buyers.
10 Tripwire Examples – Autogrow Email Marketing Case Study
After reading the last previous guide on setting up an email tripwire funnel, you may want to look at this page to get proven examples of case studies that worked for this type of email marketing.
56% Rise In Open Rates with Emojis In Subject Lines – Campaign Monitor Email Marketing Case Study
A famous email campaign case study released by Experian revealed that 56% of unique open rates increased for brands that used emojis in their subject lines. In this article, Campaign Monitor offers valuable tips for using emojis like a pro email marketer.
What Is an Email Marketing Case Study?
An email marketing case study explains the process a business went through with a client to help them achieve specific results with an email campaign. Email marketing case studies provide a detailed examination of particular strategies within a real-world context to prove how effective it was for the client.
Are Case Studies Good for Email Marketing?
Case studies are good for email marketing because you can learn how to create email campaigns more effectively. Instead of just studying the theory of email marketing, you can learn from real email strategy campaigns to find out what methods deliver a higher return on investment.
Read More Marketing Case Studies
Here’s a list of more case studies you can use to improve your marketing campaigns:
- SEO case studies
- PPC case studies
- Content marketing case studies
- Digital marketing case studies
- Social media marketing case studies
- Affiliate marketing case studies

Email Marketing Case Study Examples Summary
I hope you enjoyed this list of the best email marketing case studies that are based on real-world results and not just theory.
As you discovered, the email marketing case study examples above demonstrated many different ways to implement an effective email campaign. By studying the key findings from these examples, and applying the methods learned to your own business and email newsletters, you can hopefully achieve the same positive outcome with your email marketing efforts.
New email success case studies are being published every month and I’ll continue to update this list as they become available. So keep checking back to read the current sources of information on email marketing.
All in one marketing cloud software for modern marketing teams.
Marketing powered by your data warehouse.
Help Center
Help articles for Vero Connect and Vero Cloud users.
Developer Guide
Setup and configuration guide for engineering users.
API Reference
Documentation of API endpoints and implementation.
Insights on enhancing product-first email and push messaging campaigns.
- Template Library
- Liquid Guide
- Integrations
- Sign up for free
9 Great Email Marketing Case Studies (and Counting)
- News and Updates Updated August 2020 Posted: August 2015
On this page
Transparency is hot right now, but not in email marketing.
You can see how many Twitter followers a brand has. Lots of businesses blog about their audience growth. And some newsletters share their subscriber count as social proof .
But no one talks about open and click rates, ROI or impact on the bottom line. It’s taboo in the email world.
That makes it really hard to find email marketing case studies. If you want inspiration for your own campaigns, there aren’t many options. You can:
- Read blogs like this one 🙂
- Dive into ReallyGoodEmails.com
- Sign up for newsletters and products to receive their emails
Other than that, all you can do is test your assumptions relentlessly.
We’d like to make it a little easier to read stories about great email campaigns so we collected some of our favorites. Here is the criteria for the case studies we included:
- They are real case studies, not a best practices pieces.
- They include quotes or data from the campaign creators.
That sounds simple until you start exploring the web for stories that meet those two rules. We’d like to add to this list so if you know of a great email story, let us know in the comments.
Together, these posts are long enough to be a book. So we turned them into one.
Download an .epub file
What Startups Can Learn from Watsi’s Wildly Successful Email Campaign
Read it | Share it | Save it
This story is too nuanced to accurately summarize but here’s a primer.
Watsi is the first non-profit to be part of Y Combinator. They crowdsource healthcare funding for people all over the world. To drive recurring revenue, they broke out their monthly donation feature into its own product and launched it separately.
They used email to source early feedback, used social proof to create buzz and built a personalized newsletter to keep users informed about their donations.
Here’s a snippet from this post:
Part of showing people what they’re getting is investing in communications where you aren’t asking for anything. Instead, you’re thanking people for their business or their participation. You’re acknowledging your end of the deal where you’re committed to delighting and surprising them. This is something that for-profit startups tend to neglect – the importance of not just sending a receipt for a purchase, but honing that interaction to make customers feel something more.
Email marketing is isn’t a channel – it’s one layer of a customer-centric company. This case study reveals how complex (and truly valuable) it is to use email to grow a business.
Building a Newsletter Welcome Series from Scratch
Help Scout’s signature flair is purpose .
As they considered how to welcome to new subscribers – and there are more than 51,000 – they knew that aligning business goals with a great experience was key. They pulled it off by ensuring each email sought to achieve a single, measurable goal.
Each of the five emails in the sequence is explained in detail, including the intended purpose and suggestions based on their own learnings.
How The Skimm’s passionate readership helped its newsletter grow to 1.5 million subscribers
Building a profitable business with email is very different than using email to build a profitable business.
Watsi, for example, uses email to support their product. In The Skimm’s case, the email is the product. When newsletters become a business, it’s worth paying careful attention to their strategy. (We detailed an example of this in our Death to the Stock Photo case study .)
The Skimm’s email newsletter reaches 1.5 million daily. That growth has been fueled by an intense understanding of their target reader and an community that is eager to help. There are more than 6,000 “ Skimm’bassadors ” actively spreading the word about this business.
There’s a lot to learn here but if you take just one lesson, let it be this:
The Skimm focuses on women ages 22-34 in big cities throughout the country. They are busy, they’re on the go. It’s a professional audience. And we looked at what they do first thing in the morning. Your alarm goes off, you grab your phone, and you read emails from friends and family first. It really made sense to us to introduce a product that fit in with that routine. And email is very much in the routines of the demo that we’re going after.
There’s no need to reinvent the wheel. Meet your target audience where they’re already active.
How to Gather 100,000 Emails in One Week
I hope you’re noticing a trend in these case studies: Pulling off a wildly successful email campaign isn’t easy.
Even when the goals are simple, the logistics tend to get messy. The smartest companies dig in anyway.
In Harry’s case, they used a landing page to gather 100,000 emails in the week leading up their launch. As a shaving company, they are competing against institutions like Gillette. The only way to outsell them is to out-maneuver them.
Harry’s drove traffic to a landing page, asked for a signup, then used a referral mechanism to incentivize people to share the product. Those who referred friends earned free products. They gave away a ton of free razors that week but it cost way less than broadcasting the upcoming launch on traditional advertising channels.
This post gets into the nitty gritty of driving the traffic, managing the flood of interest and actually delivering the free products.
The Art and Science of Turning Free Trials Into Happy Customers
If you’re a small startup, you’ll be able to relate to this story.
Alex Smith runs marketing at ContactMonkey . As a growing company with a small team, it became too difficult to onboard new customers one at a time. So Alex created a series of events in the application that trigger emails or pause existing campaigns.
The result was not only happier customers, but faster growth. Once the triggers were in place, ContactMonkey was able to guarantee that each customer received the right messaging at the right time.
This post shares the exact emails and triggers ContactMonkey uses to onboarding their users, along with some ideas for blurring the lines between CRM and email marketing.
The Science Behind Those Obama Campaign E-Mails
I think this line will pique your interest about Obama’s last campaign: “Most of the $690 million Obama raised online came from fundraising e-mails.”
The Obama campaign famously used a casual, conversational in tone in the email subject lines. The most famous subject line was simply “Hey.” Another – “I will be outspent” – raised $2.6 million on its own.
Source: Slideshare
This didn’t happen by accident. The folks behind the campaigns tested incessantly, sometimes playing with a dozen or more variations on a single email. Here’s one of the most interesting findings revealed by digital analytics directo Amelia Showalter:
…these triumphs were fleeting. There was no such thing as the perfect e-mail; every breakthrough had a shelf life. “Eventually the novelty wore off, and we had to go back and retest,” says Showalter.
They bottled lightening over and over through rigorous testing and exceptional copywriting. The viral effect was manufactured, not serendipitous.
What We Learned From A Week Of Prototyping A Newsletter In Public
When Buzzfeed began developing a daily email newsletter, the editors turned to Facebook for feedback. They shared their prototypes ( here’s an example ) with their own friends. They made each iteration of the newsletter public to ensure they could patch any holes before launch.
Interestingly, editor Millie Tran said the most useful part of this exercise was the intense focus on the product/market fit:
The most valuable thing about this exercise was that it allowed us to avoid getting too emotionally attached to any one idea early on and to keep tweaking and adjusting the product to be better.
As we’ve written before, email is an extension of your product and should be treated with the appropriate care.
Buzzfeed also wrote a follow-up to this post about using email to test early versions of their mobile app.
Learning vs. Selling
This is a personal story based on my experience here at Vero. Last year, we created 14-step campaign to welcome new subscribers to the blog. The open rates were decent and we heard some positive feedback from customers about the campaign.
Then we nuked it.
Because it a) wasn’t helping us convert readers into customers and b) it wasn’t helping us learn about our readers. We replaced the entire campaign with a single email.
Tons of people replied and we’ve been able to shape our content and emails to match our readers’ challenges and needs. The lesson is here to create opportunities to learn before you try to sell your product.
The Most Successful E-mail I Ever Wrote
A single email can change a business.
Derek Sivers, founder of CD Baby, realized this after he created this masterpiece of a shipping confirmation email :
Source: Smashing Magazine
The email went viral. At the time, no one put any effort into their transactional emails . The personal touch resonated with a lot of people.
That one silly e-mail, sent out with every order, has been so loved that if you search Google for “private CD Baby jet” you’ll get over 20,000 results. Each one is somebody who got the e-mail and loved it enough to post on their website and tell all their friends. That one goofy e-mail created thousands of new customers.
Simon Schmid calls this finesse the “personality layer.” Here are a number of other examples.
A few more case studies from the Vero archives:
- TripAdvisor’s Unfair Email Marketing Advantage
- How Amazon Dominates E-Commerce with Email
- How Death to the Stock Photo Built a Profitable Business with Email
- Why Product Hunt’s Emails Are So Addictive
- Evernote’s Simple But Useful Onboarding Emails
And here’s a few suggestions from readers:
- How The New York Times gets a 70 percent open rate on its newsletters
Want to send more personalized mobile and email messages to your users?
Customer story.
How Vero helps Plann cater to the needs of an agile startup that's scaling up quickly
Check out Vero , customer engagement software designed for product marketers. Message your users based on what they do (or don't do) in your product.
Consider signing up for a free trial. No credit card required.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Business Ideas
- Business Opportunities
- Entrepreneurs
- Startup News
- Startup Intro
- Write For Us
- Startup Directories List
- Contributors

How to Get Support When Launching a Small Business
How to measure your financial health, how to make your business billing process more efficient, understanding interest rates for florida commercial financing, 3 important aspects of a successful glamping business, 7 things you need to do before starting a gift shop…, a step by step guide to becoming a travel agent for…, how to make working from home easier, 8 most profitable writing niches and how to choose the best…, 5 tips for retaining top talent within your organization, 6 things you need to know about crm as an upcoming…, restaurant essentials: a guide for new business owners, a quick primer on your debt-to-income ratio, how to plan a business trip to san francisco, buying a fedex store vs fedex routes: which is better to…, 5 steps to launch your own travel agent business, 5 strategies to bring in new customers to your small business, exploring sentiment analysis marketing – understanding your audience like never before, revolutionizing media publishing and affiliate marketing with ai technologies, boosting your sales team: a roadmap to attract and retain top…, 5 steps to help you reach your business’s target audience, label printing machine: unleash your brand’s creative potential, building financial wellness through employee benefit programs, joshua burgin explains how to be a great leader, 8 benefits of product serialization to your manufacturing business, the evolution of business skills specialization over the years, 3 things to know before visiting toronto on a business trip, from startups to large corporations: making the right choice for video…, why is it worth it to do business in germany, 3 things you need to know before starting an online business, a step-by-step guide to start a recruitment agency (2023 -2024), strava’s path to $1.5b valuation and 100m+ users, infinite uptime has successfully secured an additional $18.85 million in funding, understanding more about space id token, how the automotive industry is changing production procedures in 2023, japan startup unveils space viewing tour on affordable balloon flight, email marketing case studies: unveiling successful campaigns and insights.

Email marketing remains a powerful tool for businesses to connect with their target audience and achieve remarkable results.
In this article, we will delve into real-life case studies of businesses that have leveraged email marketing to attain impressive outcomes.
By examining these success stories, we can uncover the strategies and tactics that contributed to their achievements, offering valuable insights for aspiring marketers.
Case Study 1: Clothing Retailer’s Personalization Powerhouse
A well-known clothing retailer implemented a highly personalized email marketing campaign that led to a substantial increase in customer engagement and sales. The key to their success lay in collecting and leveraging customer data effectively.
By segmenting their subscriber list based on demographics, browsing history, and previous purchases, they tailored their email content to match each recipient’s preferences. They utilized dynamic content to showcase personalized product recommendations, discounts, and exclusive offers.
This level of personalization fostered a strong sense of relevance and urgency, resulting in a significant boost in open rates, click-through rates, and overall conversions.
Insights: Collecting and utilizing customer data to deliver personalized content is crucial for maximizing email marketing success . Effective segmentation, dynamic content, and targeted offers are key elements to enhance engagement and drive conversions.
Protip: Segmentation becomes easier when you have the right target audience’s email list. GetEmail.io is a one-stop service to help you find every professional’s email address. Its Chrome extension can help you find bulk email addresses even on platforms like Gmail, LinkedIn as well as Salesforce!
Case Study 2: E-commerce Startup’s Cart Recovery Triumph
An e-commerce startup struggling with abandoned carts implemented a cart recovery email campaign that yielded remarkable results. By integrating automation and behavioral triggers, they sent timely and personalized emails to customers who had left items in their carts without completing the purchase.
These emails included persuasive copy, compelling visuals, and a clear call to action to encourage recipients to return and complete their purchases.
Furthermore, the company offered exclusive incentives, such as discounts or free shipping, to entice customers back to their website. As a result, the startup experienced a substantial increase in cart recovery rates, ultimately boosting revenue and improving customer loyalty.
Insights: Utilizing automation and behavioral triggers to implement cart recovery email campaigns can effectively reclaim lost revenue. Persuasive copy, compelling visuals, and enticing incentives play a vital role in driving customers to complete their purchases.
Case Study 3: Software Provider’s Onboarding Success
A software provider implemented a well-crafted email onboarding series to educate and engage new users. They designed a sequence of emails that guided users through the onboarding process, providing step-by-step instructions, useful tips, and video tutorials to help users maximize the software’s capabilities.
However, they incorporated interactive elements, such as surveys or quizzes, to gather valuable feedback and further tailor their messaging. This comprehensive onboarding campaign significantly reduced user churn and increased product adoption, leading to higher customer satisfaction and long-term loyalty.
Insights: An effective onboarding email series can enhance user adoption, reduce churn, and foster customer loyalty. Providing valuable resources, and interactive elements, and seeking user feedback are key components of a successful onboarding campaign.
Conclusion:
These real-life case studies demonstrate the power of email marketing when implemented strategically.
By understanding and applying these insights, businesses can harness the potential of email marketing to achieve impressive results, foster customer relationships, and drive business growth in the digital age.
Subscribe For Growth Hacks, and Business Ideas
Email address:

Content Team Writer
The content Team Writer is one of the writers from our team of content writers. The Business Goals blog is expanding day by day and we need more writers and brand ambassadors for promoting our media website. If you are interested contact your portfolio through the Write for Us page.
- Content Team Writer https://www.thebusinessgoals.com/author/guest-author/ The Future of Urban Property Management: Selecting a Property Management Company
- Content Team Writer https://www.thebusinessgoals.com/author/guest-author/ The Ultimate Guide to Choosing Blackbriar Backpacks for Sports and Travelling
- Content Team Writer https://www.thebusinessgoals.com/author/guest-author/ Building Financial Wellness Through Employee Benefit Programs
- Content Team Writer https://www.thebusinessgoals.com/author/guest-author/ Exploring Sentiment Analysis Marketing - Understanding Your Audience Like Never Before
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Boosting your sales team: a roadmap to attract and retain top talent, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
The future of urban property management: selecting a property management company, the ultimate guide to choosing blackbriar backpacks for sports and travelling, what is an ip license and why does your business need one, most popular.
The Importance of Regular Roof Maintenance for Commercial Properties
Startup Studio Insider Founder Shares How Startup Studios Are A Successfully Proven Business Model
Defining Entrepreneurial Creativity in Creative Entrepreneurship
What Insurance Cover Is Best For Couriers?
How to Start a Vending Machine Business in New Jersey (2023)

Most Viewed
How to define a target markets with examples, what is a venture capitalist – an insight into the world..., top characteristics of an entrepreneur to follow for success, ‘understanding the difference between venture capital vs private equity.’, trending now.
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Write for Us
Are You An Entrepreneur?
Join our mailing list for growth.
- Sendlane Blog
- Customer Stories
- Books & Guides
- Template Center
- Request a Demo
Featured Resources

Abandoned Cart Email Funnel: Best Tactics & Examples

8 Inspiring Website Pop-Up Examples to Boost Your Sales

BigCommerce Merchant, Rx Smart Gear Implements a Multi-channel Revenue Strategy w/ Sendlane’s Email & SMS Automation
Search results for “ ”

Introducing: Sendlane Forms

7 eCommerce Trends to Watch Out For in 2024

Our 2023 Year in Review!
%20(1).png)
A Review Of Gmail’s 2024 Deliverability Changes: What You Need To Know
%20(1).png)
A Deep Dive into Gmail’s 2024 Engaged Sending Changes
.jpg)
How to Create Evergreen Content to Warm Up Customers

How to Monitor Performance Using Revenue Attribution

Practical Pop-Up Tips for Website Owners
.jpg)
eCommerce Product Reviews: Why They Matter and How to Get Them
.jpg)
Product Reviews: Why They’re Crucial for eCommerce Success

6 Pro Tips for Handling Online Negative Reviews

Online Review Monitoring: The Ultimate Guide with Tools and Tips
.jpg)
How to Create the Perfect Website Pop-Up Message: Step-by-Step

How to Collect Reviews Using Apps

5 Easy Examples to Respond to Positive Reviews

Feedback Request Emails + Examples

8 Tips To Get Positive Online Reviews
.png)
Top 15 Email Subject Lines For Review Requests

How To Respond to Negative Reviews: 8 Effective Negative Review Response Examples

How to Write a Customer Feedback Email + Real Example Templates

Top 4 Product Review Software to Consider in 2023
.png)
How to Ask for Reviews with Request Emails + Examples

5 Best Ratings and Reviews Platforms to Try in 2023

Introducing Sendlane Reviews: Fully Integrated Reviews Collection, Management & Display

How to Ask for Product Reviews: Tips, Strategies, and Templates

How to Use AI to Automate the Customer Feedback Experience

Why Attribution Is Critical for DTC Marketers (+ 7 Key Metrics to Track)
.png)
6 Cost-effective SMS Strategies for Retention and ROI

Less Budget, More Strategy: Effective Email & SMS Leveraging Intent & UGC

6 Best eCommerce Reviews Platforms
.png)
5 eCommerce Email Marketing Templates to Drive More Sales

How To Add Product Reviews To Your Shopify Store
.png)
A Complete Guide to eCommerce Reviews Management
.png)
How to Use Chat GPT with Email Marketing

How to Create Custom Emails for WooCommerce + Templates
.png)
4 Product Reviews Templates for eCommerce
.png)
How To Implement AI in Email Marketing + Top Tools

Email Marketing Strategy For Fashion Brands in 2023
.png)
6 Ways to Improve Your eCommerce Emails in 2023

Email Marketing Best Practices for Pet Brands in 2023
.png)
Upsell Emails Best Practices for eCommerce in 2023

5 Must-Try Marketing Automation Tools for eCommerce in 2023

How to Build an Email Marketing Strategy for Beauty Brands in 2023
.png)
Email Marketing for Electronics and Gadgets Stores in 2023
.png)
How to Create Personalized Emails for eCommerce
%20(1).png)
Email Clipping Explained: How to Avoid it & Improve Deliverability
.png)
8 Email Marketing Examples for Food and Beverage Brands

15 Best eCommerce Email Examples to Grow your Business

20+ Product Launch Email Subject Lines That Get Results

6 Best Triggered Email Examples for Your Automation

How to Segment Emails Based on Buyer Persona: Step By Step

8 Email Automation Ideas for eCommerce Success

10 Best Email Marketing Automation Software for Business Growth

10 Best Types of Emails To Boost eCommerce Sales

How to Use Email And SMS Marketing to Grow Your eCommerce Store

8 Steps to Build an eCommerce Marketing Plan in 2023
.png)
8 Marketing Automation Software for your Business

5 Powerful Email Sequences to Boost eCommerce Sales

SMS Marketing Automation: Best Practices & Software

SMS Marketing Strategy: Examples & Best Practices

The Best Strategies to Improve Abandoned Cart SMS + Examples

The Ultimate Guide to eCommerce Marketing Automation

5 Essential Email Automation Tools for 2023

What is Omnichannel eCommerce Strategy & Examples for 2023

The 7 Best SMS Apps for Shopify in 2023

Abandoned Cart Text Messages For Shopify

How To Choose The Best Email Marketing Software

Introducing Sendlane’s Back-in-Stock Notifications
.png)
10 SMS Marketing Ideas to Boost eCommerce Sales
.png)
The 7 Best Alternatives to Mailchimp for 2023

The 6 Best SMS Automation Software of 2023
%20(1).png)
Thrive in a Recession: 3 Strategies for your Email and SMS Marketing

A Complete Guide to SMS Marketing for eCommerce
%20(1).png)
Top Cart Abandoned Rate Reasons & Statistics for 2023

Getting Started With eCommerce Email Marketing: 5 Tips For Success

The 6 Best Email Marketing Software for B2C

The 11 Best Practices for eCommerce Marketing Automation
.png)
The 5 Best SMS Marketing Software Platforms

Our 2022 Year in Review!

11 Best Email and SMS Marketing Platforms

The Best Email Marketing Software For eCommerce in 2023

10+ Best SMS Templates To Grow Your eCommerce Store

Shop Our Customers: The 2022 Holiday Gift Guide

Abandoned Cart Email Flow: Steps and Best Practices

A SMS Marketing Guide for WooCommerce & Top Tools

12 Best Email Marketing Campaigns to Try in 2023

The 6 Best Ways To Generate eCommerce Leads in 2023

5 Tips to Create Conversion-Worthy Emails w/ The Template Center

The Best Email Marketing Metrics for eCommerce in 2023

5 Steps to Improve Email Deliverability

How to Implement an eCommerce Product Launch Strategy

Out-of-The-Box Automation: Sendlane's New Pre-Built Funnels

How Does Email Automation Work?

7 Effective eCommerce Customer Retention Strategies

The 5 Best Email Apps for Shopify in 2023

5 Best Email Marketing Tools for WooCommerce

5 eCommerce Remarketing Strategies to Boost Sales

A Complete Guide To SMS Marketing for BigCommerce

The Best Email Marketing Software For BigCommerce

6 Holiday Email and SMS Mistakes—and How to Avoid Them

10+ Abandoned Cart Text Message Examples & Templates

11 SMS Examples to Sell More This Holiday Season

The 5 Best Alternatives to Klaviyo for eCommerce

Sendlane’s New Email Builder: Create Engaging & Personalized Emails Faster
.png)
Co-Creating Made Easy: Introducing New Roles & User Permissions

How To Build An eCommerce Omnichannel Marketing Strategy

4 Examples of Last Chance Email Subject Lines We Love

Ultimate Guide to Browse Abandonment Emails: Definitions, Tactics, and Examples

7 Clever Ways to Ask and Increase Online Reviews

Why Online Reviews Are Needed (And How to Get Started)

Email Marketing Tips & Examples for Fashion Brands

5 Email Design Trends to Inspire You in 2023

6 Email Design Tips to Increase Engagement (and Conversions!)

6 Ways Email & SMS Are Changing The Customer Experience

3 Ways To Unite Your Email & SMS Strategy in Sendlane
7 Automation Ideas for BigCommerce Brands

The Future of Social Commerce for Online Vendors

11 Steps to Increase Your BigCommerce Store's Conversion Rate

Today's Best Web3 Opportunities for eCommerce Brands

5 Examples of Summer Email & SMS Campaigns To Increase Sales

How to Start an eCommerce Subscription Business in Six Steps (2023)

Why Subscription eCommerce is Worth Trying (With 7 Examples)

Email and SMS Strategies for Successful Cause Marketing Campaigns on BigCommerce

How BigCommerce Merchants Can Maximize Their Loyalty Program

4 Ways To Boost Customer Retention with Email Marketing

5 Ways Data Feed Management Unlocks Omnichannel Success

How to Maximize Email Marketing for Your Dropshipping Business

4 Essential SMS Marketing Trends to Try in 2023

How Can Marketing Automation Help Your BigCommerce Web Store?

5 Ways to Optimize Your CX w/ Deep-Data for BigCommerce

Top 12 BigCommerce Apps That Increase Store Traffic

4 Creative SMS Marketing Campaigns to Inspire You

6 BigCommerce Apps for Your Multi-storefront Tech Stack

5 SMS Marketing Strategies for Flawless Customer Service

5 Best SMS Marketing Examples for eCommerce That We Love

5 Steps to Developing Brand Awareness in Email & SMS Marketing

6 eCommerce Email Marketing Case Studies for 2023

5 Reasons Why Email Marketing Is Important For eCommerce

Deep-Data for BigCommerce: Drive More Sales w/ Email & SMS

eCommerce Automation: Benefits, Strategies & Examples

Top 10 Tips for Effective SMS Marketing

4 Essential eCommerce Marketing Trends for 2023

Marketing Automation: What it is, Examples & Best Practices

7 Strategies to Kickstart Your SMS Marketing for Shopify Stores

10 Clever eCommerce Marketing Strategies to try in 2023

Best Subject Lines for Abandoned Cart Emails

8 SMS Marketing Benefits & Tips

Six Effortless Ways to Grow Your SMS Marketing List
.jpeg)
The New Sendlane SMS/MMS Marketing (+ 8 Best Practices)

eCommerce Automation: How to Streamline Your eCommerce Store

How to Use Sendlane's API v.2 & Custom Integrations

Our 2021 Year in Review!
.png)
Sendlane + Justuno: Drive More Conversions with Custom Opt-Ins

The 8-Part BigCommerce Store Launch Preplist

Lists v. Tags v. Segments: When, How & Why to Use Them

How Shopify Stores Boost Their AOV with Post-purchase Upsells

How to Leverage UGC in eCommerce Marketing (+ Examples)

An 8-Step Prep-list for Launching a New WooCommerce Store

6 Strategies to Nurture Leads Post Holiday Season

7 Ways to Leverage Social Media to Grow Your eCom Email List

The 9-Step Guide to Launching a New Shopify Store

9 Ways to Grow Your Email List in Sendlane as a Digital Retailer

Your BFCM Email Marketing Strategy (Timing, Cadence, and Copy)

The 5-Step eCommerce Holiday Marketing Prep-list

6 Best Ways to Manage Contacts Inside Sendlane Audience

The New Sendlane Audience: A 360-Degree View of Customer Data

5 Tried & Tested Ways to Increase Sales on Shopify

How to Send Abandoned Cart Emails on WooCommerce + Conversion Tips

We’ve Raised $20M! Announcing Sendlane’s Official Series A!

The 3 Top Revenue-Generating Automations to Build in Sendlane

What to Actually Do as an Email Marketer for IOS 15

8 eCommerce Email Marketing Campaigns To Increase ROI

7 Tips for Creating Dynamic Abandoned Cart Emails for Shopify

How to Make Your First Sale on Shopify in 2023

The Top 3 Ways to Generate Revenue Using Sendlane

The eCommerce Explosion: Stats to Drive Growth in 2021

Omnichannel Marketing: 5 Strategies to Drive Growth in 2021

10 Abandoned Cart Email Templates To Help Bring Customers Back

6 Ways to Use Sendlane Campaigns to Increase Email ROI

How to Manage Multiple eCommerce Stores in One Platform
.png)
7 New Product Announcement Email Examples & Templates

5 Ways to Retarget Shoppers w/ Sendlane's FB Audience Integration

5 Promotional Email Examples to Inspire Your Next Campaign

8 Best Ways to Segment Your Contacts in Sendlane
.png)
Buyer Persona For eCommerce: How To Identify It + Examples
Sendlane Beacon: 5 Best Practices for Website Tracking

12 Lead Nurturing Email Examples to Create a Winning Campaign
.png)
3 Pro Tips to Optimize Your Emails Using Sendlane Experiments

8 Tactics for a Great Digital Customer Experience Strategy
.png)
A Tour of Sendlane Automations
.jpeg)
12 Strategies to Increase CLTV with Email Marketing

How to Deliver Amazing Customer Experiences with Sendlane’s WooCommerce Integration

6 Email Subject Line Best Practices for eCommerce in 2023
.png)
How to Turn First-Time Shoppers into Repeat Customers with Sendlane’s Miva Integration

8 Ways to Boost Average Order Value + Examples

8 Email Acquisition Strategies For Growing Your Email List

3 Tips to Boost eCommerce Sales and ROI with Sendlane’s ClickBank Integration

How to Design and Optimize Your eCommerce Checkout Flow

4 Ways to Use Sendlane's Shopify Integration to Deliver Personalized Customer Experiences

How to Use Email Coupons to Drive Sales (Best Practices & Examples)

Our 2020 Year in Review!

3 Outstanding Customer Loyalty Programs & What You Can Learn From Them

How to Map The Buyer's Journey Through Email to Sell More Effectively

4 Ways to Reduce Your Shopping Cart Abandonment

5 Automated Email Workflows for eCommerce To Boost ROI

Sendlane Holiday Party 2016

Our 2016 Year in Review!
.png)
To Clean or Not to Clean – The Official Case Study of List Cleaning

5 Examples of Simple & Effective Email Marketing Campaigns
.png)
3 Powerful Tips for Creating Perfect Marketing Emails

Our 2017 Year in Review!

The Email Curse Word Database

Sendlane Team Trip 2018 – Cabo San Lucas

Sendlane on the Bay! - San Diego Patriot Jet Boat

Sendlane Summer Kick Off BBQ & Pool Party

How Effective Email Marketing Grows Your Ecommerce Business

5 Best Product Launch Email Template & Examples

5 Creative Ways to Sign Off Your Emails

9 Promotional Emails Your Contacts Will Love
.png)
10 Black Friday & Cyber Monday Email Marketing Examples

Happy Thanksgiving From The Sendlane Team!

8 Email Marketing Strategies Starbucks Uses to Gain Customer Loyalty

5 eCommerce Email Marketing Segmentation Strategies

Four Powerful Pitch Styles to Engage & Persuade Your Audience

7 Tips to Drive Last Minute Christmas Sales Through Email
Sendlane Holiday Party 2018!

How to Make Your Next Launch a Massive Success (Phase 1 - The Warm-Up)

How to Make Your Next Launch a Massive Success (Phase 2 - The Reveal)

How to Make Your Next Launch a Massive Success (Phase 3 – The Release)

Happy New Year! Our 2018 Year in Review

Building a Customer Feedback Email Template (+ 7 Examples)

5 Artificial Intelligence Use Cases in Email Marketing for 2023

Five Ways to Improve Your Email UX for More Impact
.png)
5 Emails You Can Send Current Customers to Keep Them Buying

Our Story - The Vision of Sendlane

Why Shopify No Longer Works With Mailchimp

Four Ways to Boost Referrals With Email Marketing

The #1 Reason To Leave Your Email Marketing Provider (It's Not What You Think)

16 Product Update Emails Examples (+ How To Guide for 2023)

9 Best Practices for Writing Effective SMS Campaigns

Sendlane's Annual Team Building Trip 2019 - Puerto Vallarta, Mexico

12 FOMO Marketing Techniques to Boost Your Email Conversions

Sendlane Named One of Inc. Magazine's Best Workplaces in 2019

5 Abandoned Cart Emails & How to Make Them Work

How to Upsell & Cross-sell Customers: 4 Ways to Boost Sales

How Shopify Builds Credibility With Customers Using Email

How Top Content Creators Fuel Their Biz with Marketing Automation

Introducing — The Marketing Automation Hustle Podcast

Text-Based vs Image-Based Emails: Which is Best For You?

Social Media vs. Email Marketing: 5 Reasons Why Email Wins

8 Ways to Successfully Align Your Social Media & Email Marketing

6 Tips to Generate More Sales From Order Confirmation Emails

How to Create an eCommerce Cross-Channel Marketing Strategy

Sendlane is #610 On The Inc. 5,000 List!

11 Easy Ways to Make Your SMS Marketing More Powerful

5 Messages to Practice Effective Lifecyle Email Marketing

4 Reasons Your Email Marketing Isn't Working + Tips to Boost ROI

Privy - Build Smart Opt-in Forms To Grow Your Email List

3 High ROI Methods For Blending Email With The Rest of Your eCommerce Marketing

eCommerce Email Marketing in 2020: What's Staying and What's Changing
2019 - Our Year in Review

CCPA: What Is It and Who Does It Apply To

3 Strategies to Increase Brand Awareness Using Email Marketing

Segment Your New Contacts Immediately (& Automatically!) With Tags

3 eCommerce Welcome Email Examples and What You Can Learn From Them

5 Emails for Your Post-Purchase Automation (+ Examples)

Sendlane + Miva: The Ultimate eCommerce Duo

10 Best Strategies For Increasing Email Opt-Ins

35 Email Marketing Stats to Drive Your Business Forward in 2020

6 Emails You Need to Create a Product Launch Email Campaign

How to Measure Customer Satisfaction With Automated Post-Purchase Email Funnels

3 Automated SMS Texts Every eCommerce Store Should Send

Sendlane + OneClickUpsell - The Shopify App You Need to Boost Your eCommerce Sales
.png)
How Nurture Leads with Customer Education Emails

Introducing Sendlane Experiments - Multivariate Testing

3 Ways to Create an Automated Customer Experience With Email

Hey Shopify… Meet Sendlane!
.png)
Blue Bottle Coffee Advertising: Case Study on Email Marketing

Zapier & Sendlane – Better Together!
.png)
Right On Track: 8 Vital eCommerce Email Metrics You Can't Ignore

Introducing Deep-Data for WooCommerce!
.png)
How Email Retargeting Works & 3 Strategies to Win More Sales
.png)
How Segmentation Supercharges Your Email Marketing and The Stats to Prove It

Product Recommendations Email Best Practices & Examples
.png)
3 Emails Every eCommerce Sales Funnel Needs (with examples)
.png)
The ROI Segment Trifecta! 3 Segments Your Online Store Needs

How to Boost Email Performance Using Automated List Hygiene
.png)
Why List Hygiene Is The Key Ingredient For Increased Email Engagement & Success

How to Use Tags to Organize and Segment Your Sendlane Contacts
.png)
How to Use Machine Learning Open Predictability to Skyrocket Email Performance

How to Create Eye-Catching Emails with Sendlane’s Email Builder
.png)
Best Practices For Email Marketing During the Pandemic

How to Use Custom Fields to Create Hyper-Personalized Emails

The Ultimate Growth Hack: Hyper-Personalized Email Marketing (and How To Do It)

The Ultimate Guide to Email Marketing Tagging

Retarget Your Shoppers with Sendlane's Facebook Custom Audience Integration
.png)
5 Emails For Your Abandoned Cart Funnel That'll Recover Sales
.png)
3 Strategies to Convert Traffic into Leads Before Cyber Monday

How to Build Email Marketing Funnels for eCommerce

The Ultimate Guide to SMS and MMS Marketing

The Essential Email Copywriting Guide

Skybound Entertainment Uses Segmentation and Personalization to Increase Email Open-Rates to 80% With Sendlane
Subscribe to Sendlane Newsletter
Stay up-to-date with the best email automation practices and latest marketing news.
Subscribe to The eCommerce Hustle
- Email Marketing

If your business is looking to improve its email marketing strategy, there is a lot to be gained from diving into the analytics of every completed campaign. It’s also helpful to study other companies’ campaigns that had positive outcomes, as they can offer inspiration for your future projects!
The following eCommerce email marketing case studies showcase three instances where a good email content based on a marketing strategyl marketing strategy yielded positive returns. These campaigns all incorporated the Sendlane platform to achieve these results, the details of which we’ll touch on here.
Read all of our fantastic customer case studies such as Starbucks' email marketing and how they use it to gain customer loyalty.
1. MAD TASTY’s Successful Mid-Pandemic Journey into eCommerce
The hemp-extract beverage company MAD TASTY is the perfect example of a brand that was quick to pivot when COVID hit, subsequently transitioning their operations in order to remain competitive in a relatively niche industry. Here’s how they did it, and how email marketing paved the way.
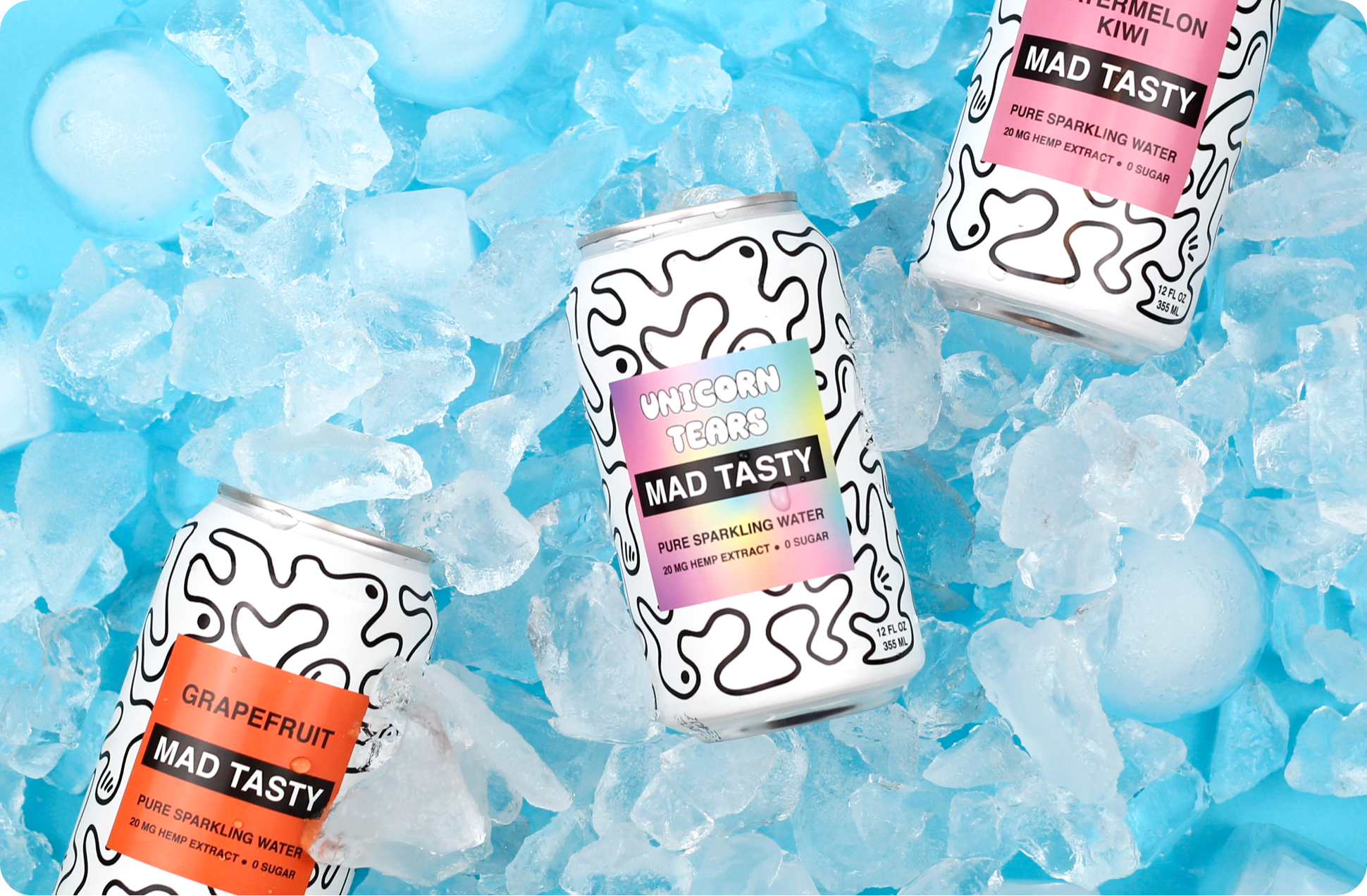

Background and shift to email marketing
OneRepublic frontman Ryan Tedder is the pen and voice behind some of the biggest pop hits in the world, including Apologize with Timbaland, Counting Stars, and Good Life. Six years ago he was at a crossroads in terms of his mental health, with skyrocketing anxiety levels brought on by exhaustion. It was then that he tried CBD for the first time.
After seeing positive results fairly quickly, he started work on a retail store presenting clean CBD products to the US market. When expert marketer Leila Khoury was brought in to grow customer awareness and revenue, she noticed that they weren’t tapping into email marketing nearly enough. She foresaw possibilities to scale the business by building a new, well-nurtured audience base online by investing in an eCommerce email marketing software.
Making the switch
As recently as the end of 2019, MAD TASTY was still predominantly a physical business without much of an eCommerce presence. While their team was sending email campaigns to customers, it was with a provider that didn’t offer much support.
A recommendation from another business in the same industry soon brought Sendlane into the mix. Enthralled by the deep-data integration we offered, the brand was impressed by how we were able to help them get to know their core customers on a much deeper level; we facilitated them in quickly creating audience segments for more personalized targeting. Being able to automate much of the process — effectively freeing up resources for other COVID-related challenges — was an added bonus.
Sendlane’s impact
Aside from showing the commercial power of email marketing to the MAD TASTY team for the first time, Sendlane was the formal channel through which the company could help transition their business online and encourage their customers to buy their CBD products through their web and increase their sales.
The switch meant that their marketing department spent less time generating mailer designs, automating much of the process right from day one. Their customers were now able to buy products online and learn more about new releases directly from MAD TASTY, leading to better sales and growing the brand’s popularity over the last two years.
2. Rx Smart Gear Implements a Multi-channel Revenue Strategy
Another case study to take note of showcases the strength of leveraging a multi-channel revenue strategy with unified email and SMS marketing. Rx Smart Gear — a world-leading fitness brand — was hopeful in turning SMS marketing into their next highest revenue source. The results were nothing short of astounding.

Shifting focus to SMS marketing
The team at RXSG already knew about the importance of email marketing. The channel is responsible for 15% of their total revenue and plays a key role in delivering personalized customer experiences.
But most ESPs they used lacked comprehensive employee training, reliable customer support, and integrations with their favorite apps. RXSG was looking for an all-in-one solution that not only enabled them to implement campaigns easily, but also helped their employees understand automations.
A roll of the dice
Marketing expert Ericka Arguedas knew they needed a tool that would easily integrate with their current tech stack so their team could leverage data for a unified client experience.
After searching for a while, RXSG came across Sendlane — the best email marketing solution for their needs. The platform’s intuitive and powerful email and SMS features made it easy to implement a multi-channel strategy. Plus, the transition was a breeze thanks to their dedicated Customer Success & Implementation managers! Together, they were able to integrate their BigCommerce store and apps like Justuno to start funneling data under one roof.
How Sendlane helped
Before making the switch, the RXSG team was unsure how automations worked. But the Sendlane support team quickly went to work teaching Ericka and team how to build email and SMS automations from scratch.
With Sendlane, RXSG was able to boost their revenue and click rates by enriching customer profiles with relevant emails and valuable data using the Justuno integration to segment and send high-converting email & SMS.
To top it off, the RXSG team was also able to reach new customers to subscribe easily through multiple channels by implementing automated email & SMS campaigns.
//[inject:ad-personalized-email]
3. Skybound Entertainment Increase Open Rates by 80%
Skybound Entertainment is a business born out of a single comic book that was adapted into a long-standing hit TV series. The Walking Dead might have taken a long time to develop a loyal fanbase, but today it is at a point where it is generating high revenue volumes for the company. This has allowed them to invest in new projects as well as improve their existing marketing efforts, with a prominent focus on generating eCommerce sales.

A slow start for email engagement
Having never really prioritized email marketing as part of their customer value and growth strategy, Skybound Entertainment wasn’t too fussy about the provider they worked with. However, once their audience started to grow exponentially, it became obvious that they were going to need marketing automation software that could help them better manage their email master list. They were hoping to find a provider that could save them both time and energy so they could focus on developing the business in other areas.
Big master list, no segments
Despite having grown their email lists to two million subscribers, they were still receiving low engagement on their email marketing campaigns. The problem was clear: their existing provider did not have a feature in place to break their master list into different audience segments that could be targeted individually with different messages.
Mass emails to a bulk audience consisting of people with very different interests are typically coupled with low open and engagement rates. Once Sendlane was brought in, we were able to help update the existing master list. The result was better targeting, with open rates skyrocketing to as much as 80% (that’s four out of every five recipients) for some campaigns.
4. Grey Ghost Gear’s Email Revenue Attribution Jumps From 1.8% to 34%+ After Switching To Sendlane

It started with an unexpected change to their pricing plan. Then, the changes to their Terms of Service and the ESP’s updates surrounding GDPR required them to jump through multiple hoops before they could send out a single campaign.
Understandably, it was starting to be too much to deal with. That was when Ryan began to look at the revenue they were generating after these changes, which became the turning point in starting a search for a new email marketing platform.
Sendlane's solution
Ryan began putting together a list of must-haves Grey Ghost Gear would need from another email marketing platform. Aside from making it easier to actually send emails, there were a few more boxes that needed ticking.
At the top of the list was better deliverability to help increase CTR and, ultimately, revenue. Next, the need for top-notch customer service with a more one-on-one feel. Lastly, the new platform had to incorporate intelligent email marketing automations — something that was entirely non-existent on their current ESP at the time.
Soon enough, Ryan came across Sendlane and signed up for a free trial. From the first call with Sendlane’s customer service team, Ryan was impressed by the level of insight and help the team members gave. It was a refreshing change of pace from what he and his team at Grey Ghost Gear were accustomed to.
5. Strawberry Hill Baking Company Drives $42,000+ Revenue During Holiday Campaigns with Sendlane

Because of his tech background, Marc is a big believer in the importance of innovation in products. He knew from experience products that stopped innovating couldn’t keep up with customers' needs.
Initially, they started using Constant Contact as an email provider. Then they moved through a few other tools, including Klaviyo, trying to find an ESP that didn't come with a steep learning curve without losing eCommerce capabilities like automation and SMS.
As he started his search, Marc eventually stumbled across Sendlane. After giving it a try, he fell in love with the important marketing features like browser behavior tracking and ease of use.
When Sendlane recently added SMS to the platform, Marc went to work using Sendlane’s email and SMS opt-in features to collect content and grow their list. Their SMS list increased to 2500+ in just a couple of months right in time for Black Friday and Holiday season shopping.
6. Wellgrove Health Harnesses Sendlane's Intuitive Platform to Create Powerful Marketing Automations

Dustin, President of Boundary Bend Wellness, has always known two things: That olives are a powerful antioxidant he swears by, and email marketing is the name of the game in eCommerce business.
After coming on board with the company, Dustin started diving deep into the areas of business that were generating revenue.
As they started pushing out various email marketing campaigns on their current platform, he found that the interface was hard to navigate, the open-rates weren’t anything to write home about, and the email automation features were non-existent.
Wellgrove continued to work on growing their brand. All the while, Dustin kept an eye out for a new email marketing platform worth trying out. At the suggestion of a developer he worked with, he signed up for a free trial with Sendlane and soon enough was on a call with an Account Manager.
Our platform’s influence
Our platform’s role was predominantly to do housekeeping on the existing email list (which at that point had been cut down to 200,000 people after a re-engagement campaign). From the new segments, the Skybound Entertainment team was able to better study their audience, adapt their thinking, and come up with new ideas to keep their target audience interested and engaged.
On top of helping them streamline the way they spoke to their audience, the Skybound team also gained a trusted supplier in the process. We do our best to understand the individual needs of each and every one of our clients, aligning these with the visions they have for growing and expanding their operations over time.
These case studies have showcased the effectiveness of email marketing for eCommerce-focused businesses. If yours is looking to grow its revenue from online sales, it might be a good time to think about making the switch to Sendlane. We love working with all different industries and business sizes, from startups to major brands. We are here to introduce efficient marketing automation into your operations, saving you time and allowing you to redirect company resources wherever else they might be needed.
Partner with Sendlane and it won’t be long before it’s smooth sailing for your email marketing strategy and campaigns, leaving room for your team to focus on generating inspiring content ideas for the audience segments you’re targeting. Get in touch with us today to find out more about how we can help you get there!
Share article link
Subscribe to our blog.

Caitlin Hutchinson
Head of Marketing
Related articles

The 2021 eCommerce Email Marketing Playbook Part 2

Mastering Customer Acquisition & Retention in 2021
Better features. better support. better customer experience., no more guessing; make data-driven decisions at a glance, find hidden growth opportunities in your shopify customers, turn sales into reviews & reviews into more sales. all for free., uncover what your customers really want, create winning campaigns faster with personalized email marketing, unified email & sms marketing for bigcommerce, everything your brand needs to achieve greatness with sms, truly unified email & sms marketing for ecommerce, drive significant roi for your online store, the ultimate guide to maximizing cltv for digital retailers.

The eCommerce Segmentation Handbook

The Definitive Guide to Abandoned Cart Emails for eCommerce

The Big Book of eCommerce Email Funnels

Your 2021 Guide to eCommerce Holiday Marketing

The Digital Retailer’s Email Copywriting Handbook

The Future of eCommerce in 2022

The Digital Retailer's Guide to Modern SMS/MMS Marketing

Increase Revenue and Retention by Mastering the Digital Customer Experience

The BigCommerce Experience: Omnichannel Marketing Strategies for a Post-Cookie World

The Shopify Experience: A Merchant & Marketer's Guide to Scaling eCommerce Growth

Unlock Your Marketing Automation Powers
Get started with your free 14-day test drive.
All our PRO level features at your fingertips.
See it for yourself
- SMS Marketing
- Deep-Data Integrations
- Multivariable Segmentation
- Real-Time Analytics
- Multivariate Testing
- Sendlane Beacon
- Commerce Roundtable
- Webinars & Events
- eBooks & Guides
- The Sendlane Blog
- The Knowledge Base
- Partner With Sendlane
- Sendlane vs. Klaviyo
- Sendlane vs. Mailchimp
Why Sendlane?
- Drive Sales
Copyright © 2024, Sendlane — built in San Diego, CA
Stay up to date with the latest strategies & eCom news!

- Free Resources

Email Marketing: 4 quick case studies to help you get higher open rates and more online sales

This article was originally published in the MarketingSherpa email newsletter .
In the day-to-day trenches of sending email after email to your list, it can be easy to overlook a crucial fundamental for each email you send – does it have a clear objective? And have you executed on that objective?
To help you nail down that objective, you can watch The Goal of an Email is to Get a Click: How to improve a direct sales email by clarifying the objective from MarketingExperiments (MarketingSherpa’s sister publication).
And once you have solidified that objective, spark your next great email marketing idea by reading these quick case studies to discover how your peers have improved their email performance.
Quick Case Study #1: Camera and electronics retailer increases average order value 25% with personalization
Adorama was concerned its broadcast emails might be suffering from fatigue and could benefit from personalization. The challenge was finding a solution that would speak to customers more directly and boost response without being overly burdensome and complex.
Creative Sample #1: Camera and electronics retailer’s email before personalization

“ Alchemy Worx created banners to be inserted on top of the broadcast emails referencing brands recipients had previously purchased: Canon, Sony and Nikon,” said Allan Levy, CEO, Alchemy Worx.
Copy in the banners said the offer specifically included products for those brand buyers. The team split tested the template with brand-specific banners against a template that had no banner but was otherwise identical to them. Both the messages with and without banners were sent to tens of thousands of recipients, making the results statistically significant.
The specific tailored banners brought the customers who received these e-mails to landing pages for an exclusive sale for buyers of that brand, where their product preferences were served to them as top choices and priority items up top. The general audience was sent to a random assortment of products.
“For example, the Sony customer was directed to a page that had Sony items positioned at the top, while Nikon customers were brought to a page with Nikon items at the top, and so on. Many photographers live in a specific camera ecosystem so it was critical to speak to them directly through their interests,” Levy said.
Creative Sample #2: Camera and electronics retailer’s email after personalization

“Finding an easy way to personalize emails for our repeat customers was critical in helping to drive continued success and bring in additional revenue,” said Gvantsa Green, Vice President of Marketing, Adorama. “While it sounds so simple, it makes all the difference to customers and can help increase order volume and engagement for brands. By promoting those brand names which consumers were familiar with and comfortable with at the top of our e-mails, we were able to turn around statistically significant results that were enough to make personalized, branded banners a regular part of Adorama’s e-mail program moving forward”
The template with the banners achieved an 18.25% boost in revenue per mailing, a 25.33% lift in average order value and a 20% increase in engagement metrics over the template without banners.
“Through testing, you can develop a simple, easily executable way to personalize any email program and significantly boost key performance metrics. With the clear positive effects it has on email performance, it is important to identify ways to incorporate various forms of personalization into our everyday communications with customers,” Levy advised.
Quick Case Study #2: Job search website for voiceover actors increases welcome drip campaign open rate from 22.49% to 27.42%
Each month, 50,000 people receive drip campaigns from Voices.com . While open rates were decent, the team felt there was some low-hanging fruit.
To organize the work, the team’s Email Channel Specialist Jenna Hass organized all the copy into a single Google Doc and grabbed screenshots of what each email looked like. “This really hits home when you see each email as chapters in a story. Honestly, some emails seemed out of order, which we needed to fix, too,” said David Ciccarelli, Chief Executive Officer, Voices.com.
The team held a two-hour working session to focus on the drip campaign. They started with the purpose of the entire email sequence, which they defined as establishing trust, building a relationship and educating their audience on how to get started.
The first change, which took less than five minutes, was changing the sender from a generic email address – [email protected] – to the company’s Customer Experience Manager Silvana Cordoba. This small change alone improved open rates from 28.75% to 43.63% for the first email, and the average open rate increased from 22.49% to 27.42% for the four-email welcome series. “We were shocked, but in hindsight, emails that come from a person are routed to Gmail’s primary inbox and avoid the often-overlooked [Promotions] inbox. It’s likely that other email service providers treat messages in a similar manner.”
Then, the team moved some emails that were sent later in the drip series to earlier on in the sequence to correct the order. In a couple of instances, two emails were combined and they even cut an email out entirely. “Be ruthless with the intent to deliver value with each message,” Ciccarelli said.
They also read the copy out loud. “While the longest part of our session, it was certainly worth it. We found dated terms, concepts that lacked context and mixed metaphors. Edit in line and re-read out loud. Once it sounds good, it’ll be received well by your prospect or customer,” he said. Visually they aimed to make each image have stronger messaging than the stock images used prior. Better copy and better design with refreshed hero images improved click through rates as well.
Creative Sample #3: Email sequence for job search website for voice over actors

Quick Case Study #3: Farm pivots to subscription product after retail locations close in pandemic, increases online sales more than 500% with email marketing
Soluna Garden Farm is a small farm in Massachusetts specializing in herbs, flowers, tea, and spices. “Prior to the pandemic, most of our sales were in-person – at our retail store, our stall in the Boston Public Market, and other area farmers’ markets,” said Amy Hirschfeld, Co-owner, Soluna Garden Farm.
When COVID-19 closed down those options, the farm did not have a single retail outlet to sell its products. They started a new subscription offering to get farm products to customers even during the pandemic and announced it with an email campaign.
They had steadily grown the email list for years and had a regular newsletter and email marketing but pivoted to speak to an online-first audience. The very first email caused the farm to sell out – what normally would have taken a season to sell in-person was accounted for in a single day thanks to email marketing.
The team continued to promote the subscription through email marketing and are now seeing open rates of almost 25% and click rates over 10%. The success led the team to redesign the farm’s website making it easier for customers to not only find the farm online, but also subscribe to its email list and buy products online.
“Our story shows the value of connecting and staying in touch with customers online,” Hirschfeld said. During the second quarter of 2020 when the pandemic hit and the farm had to close both retail locations, online sales increased by more than 500% because the farm was able to reach customers through its email list.
“Without our email list, I'm not sure if we would have survived. My advice to other small businesses powering on through the pandemic would be to do whatever you can to keep growing your list,” Hirschfeld said.
Quick Case Study #4: Software platform switches to plain text emails, increases open rate to 60%
“Our emails were arriving at the promotional tab in Gmail, which reduced our open rate,” said Borja Prieto, Head of Growth, FROGED . The software platform had around a 30% open rate with a 10% to 15% clickthrough rate (CTRs).
The team tried to use plain text emails with very simple calls to action – plain old-school links. The same email started to get around a 60% open rate and 35% CTR.
“Send plain-text emails from a real person within the company and use his/her signature. What the recipient receives is like a one-to-one email, and if you manage to send very personalized content, you'll win,” Prieto advised.
Related Resources
Email Messaging On-demand Certification Course – Learn how to get immediate results form MECLABS Institute’s email optimization methodology
Email Marketing Chart: Why consumers unsubscribe from brands’ email
Email Marketing: 5 tactics to personalize your email message for better results
MarketingSherpa Quick Guide to Email Marketing – 10 tactics to personalize your message for better results
Improve Your Marketing
Join our thousands of weekly case study readers.
Enter your email below to receive MarketingSherpa news, updates, and promotions:
Note: Already a subscriber? Want to add a subscription? Click Here to Manage Subscriptions
Get Better Business Results With a Skillfully Applied Customer-first Marketing Strategy

The customer-first approach of MarketingSherpa’s agency services can help you build the most effective strategy to serve customers and improve results, and then implement it across every customer touchpoint.
Get headlines, value prop, competitive analysis, and more.
Marketer Vs Machine

Marketer Vs Machine: We need to train the marketer to train the machine.
Free Marketing Course

Become a Marketer-Philosopher: Create and optimize high-converting webpages (with this free online marketing course)
Project and Ideas Pitch Template

A free template to help you win approval for your proposed projects and campaigns
Six Quick CTA checklists

These CTA checklists are specifically designed for your team — something practical to hold up against your CTAs to help the time-pressed marketer quickly consider the customer psychology of your “asks” and how you can improve them.
Infographic: How to Create a Model of Your Customer’s Mind
You need a repeatable methodology focused on building your organization’s customer wisdom throughout your campaigns and websites. This infographic can get you started.
Infographic: 21 Psychological Elements that Power Effective Web Design

To build an effective page from scratch, you need to begin with the psychology of your customer. This infographic can get you started.
Receive the latest case studies and data on email, lead gen, and social media along with MarketingSherpa updates and promotions.
- Your Email Account
- Customer Service Q&A
- Search Library
- Content Directory:
Questions? Contact Customer Service at [email protected]
© 2000-2024 MarketingSherpa LLC, ISSN 1559-5137 Editorial HQ: MarketingSherpa LLC, PO Box 50032, Jacksonville Beach, FL 32240
The views and opinions expressed in the articles of this website are strictly those of the author and do not necessarily reflect in any way the views of MarketingSherpa, its affiliates, or its employees.

Email Marketing Wins: Real Case Studies and Success Stories!
by PanGrow | Nov 22, 2023

In the world of digital marketing, email marketing stands out as a super effective tool, whether you’re selling to other businesses (B2B) or directly to consumers (B2C). When you consider various email marketing case studies, you will find that diligent and intelligent efforts in this area never go to waste.
Sure, there are other ways to get people interested in your business, but email has some awesome benefits that really stand out, especially when you compare it to social media and search engines. They say that for every dollar you invest in email marketing, you can expect a whopping $39.40 in return. That’s a pretty amazing return on investment!
But here’s the thing: just sending emails here and there isn’t enough. You’ve got to make sure that people are actually opening and reading your emails. If they’re not opening them, your goals won’t be met. So, it’s super important to focus on getting the best possible email open rate.
In the competitive digital world, mastering email marketing is like having a superpower. It’s not just about sending messages; it’s about making sure people open them, pay attention, and connect with your business. As you navigate the digital landscape, making your emails stand out and ensuring people open them is key to long-term success and building strong connections with your audience.
Let’s explore a few email marketing case studies that had some tough challenges. They used email marketing in a smart way to not only deal with these challenges but also find great success.
HubSpot – Personalization Powerhouse

Company Background:
Founded in 2006, HubSpot stands as a prominent platform for inbound marketing and sales solutions. Catering to a diverse user base, HubSpot faced the challenge of delivering personalized content to a broad audience.
Challenge :
The challenge for HubSpot was to connect with users on an individual level in a landscape flooded with generic emails. How could they make their communications more relevant and engaging for each unique subscriber?
Overcoming with Email Marketing:
HubSpot tackled this challenge head-on by leveraging the power of personalization in email marketing. Using sophisticated data analytics, they delved into user behaviour, preferences, and interactions. Armed with this information, HubSpot crafted highly tailored email campaigns, recommending personalized content, providing targeted product suggestions, and offering exclusive discounts based on users’ past engagements.
For instance, if a user frequently engaged with blog posts on a specific topic, HubSpot would send curated emails featuring related content. This strategy significantly boosted user engagement, as recipients felt that the content was specifically tailored to their needs and preferences.
HubSpot implemented dynamic content in emails, allowing them to display different content to different segments of their audience. This level of personalization not only enhanced the user experience but also contributed to increased conversion rates and customer loyalty.
Amazon’s Retail E-commerce Marketing

Background:
Amazon, founded in 1994, initially started as an online bookstore and has evolved into one of the world’s most influential e-commerce and cloud-computing giants. As an e-commerce behemoth, Amazon faced the substantial challenge of helping users navigate and discover relevant products within the immense array of options available on its platform.
The Challenge:
The challenge for Amazon was twofold. First, users could easily feel overwhelmed by the sheer volume of products available, leading to decision fatigue and potentially reducing the likelihood of a purchase. Second, with such an extensive inventory, there was a risk that users might not find products that genuinely aligned with their preferences and needs.
Overcoming the Challenge:
Amazon ingeniously tackled this challenge by leveraging the power of recommendations through email marketing. Recognizing the value of data-driven insights, Amazon implemented sophisticated algorithms to analyze each customer’s browsing history, past purchases, and overall engagement on the platform.
Using this wealth of data, Amazon crafted targeted and personalized email campaigns. These emails were designed to suggest products tailored specifically to each customer’s interests, preferences, and purchase history. For example, if a customer frequently browsed or purchased electronics, they might receive emails featuring the latest gadgets, accessories, or related items.
By delivering content that resonated with individual customers, Amazon significantly increased the likelihood of them discovering and purchasing products aligned with their interests.
Mailmodo’s Pain Point Resolution

Mailmodo, a marketing platform, provides email marketing case studies of how their clients have successfully resolved pain points and discovered new growth avenues through email marketing. Their email marketing case studies highlight the power of personalization, automation, and segmentation in driving engagement and conversions.
By tailoring email content to specific audience segments, businesses have been able to deliver highly relevant messages that resonate with their subscribers. This approach has led to increased open rates, click-through rates, and ultimately, higher conversions.
Mailmodo’s case studies exemplify the impact of leveraging email marketing tools to address customer pain points and drive business growth.
How did Zillow do it?

Zillow, a prominent real estate and rental marketplace, is dedicated to providing consumers with valuable data. With an extensive database of property listings and user information, Zillow faced the challenge of effectively presenting this data in an engaging and actionable way.
Zillow needed to overcome the challenge of delivering relevant information to its users, ensuring that it was both useful and compelling enough to drive them to take action. With such a vast amount of data available, finding a personalized approach to engage users was crucial.
Zillow leveraged its user data to send personalized, data-driven emails to its audience. These emails included tailored home recommendations and market trends based on each user’s search history and preferences. By utilizing the power of personalization and data-driven insights, Zillow aimed to deliver content that resonated with its users and encouraged them to take action.
The implementation of personalized, data-driven emails yielded remarkable results for Zillow. Users responded positively, with a significant increase in engagement observed. More users clicked through the emails to view properties and utilized various services offered by Zillow. This heightened engagement demonstrated the effectiveness of using data to drive email marketing campaigns. By delivering timely and relevant content, Zillow successfully captured the attention of its audience and motivated them to take further action on its platform.
Dollar Shave Club: Humor and Personality for Retention

Dollar Shave Club, founded in 2011, disrupted the shaving industry with its subscription-based model that delivers razors and grooming products to customers’ doors.
In a competitive market, differentiating the brand and retaining customers were significant challenges. Dollar Shave Club needed a strategy that went beyond the transactional nature of their business.
Dollar Shave Club infused humor and personality into its email campaigns. From witty subject lines to entertaining content, the brand made every email a delightful experience for subscribers. This approach not only distinguished the brand from competitors but also fostered a sense of community among its subscribers, contributing to higher customer retention rates.
Don’t be afraid to inject personality and humour into your email campaigns. It can make your brand more relatable and memorable, fostering a stronger connection with your audience.
Starbucks: A Brew of Personalization and Customer Loyalty

Starbucks, a global coffee giant, had the challenge of keeping its customers engaged and loyal in an extremely competitive market.
With a vast customer base, Starbucks needed to ensure that its marketing efforts were personal and engaging to each customer. They had to ensure their promotions were reaching the right people at the right time.
Starbucks leveraged email marketing to send personalized offers based on customers’ purchase history and preferences. They used data from their loyalty program to segment their customers and deliver highly targeted emails. For instance, a customer who frequently purchases a particular drink would receive promotions related to that drink.
Starbucks’ personalized email marketing efforts resulted in increased customer loyalty and higher sales. Customers appreciated the personalized touch, which made them feel valued and understood. This case study showcases the power of personalization in email marketing.
Grammarly: Nurturing Leads with Educational Content

Grammarly, launched in 2009, is a writing assistant tool that helps users improve their writing skills and enhance the clarity of their communication.
With a user base spanning a wide range of writing abilities, Grammarly faced the challenge of catering to diverse needs. Lead conversions into loyal customers requires a strategic approach.
Grammarly used email marketing for lead nurturing. Their emails included valuable tips on improving writing skills, insights into premium features, and success stories from users who benefited from the tool. By providing educational content, Grammarly not only kept users engaged but also positioned itself as an indispensable tool for anyone looking to enhance their writing.
These email marketing case studies collectively emphasize that email marketing is not merely a communication tool; it’s a dynamic force that can drive engagement, build trust, and foster meaningful connections with an audience. The common thread among these achievements is the strategic utilization of data, personalization, transparency, and education to create impactful and resonant email campaigns.
Know about the latest email marketing trends in today’s digital world. Visit our website and work on the strategies that drive results!
Fill the form below to request a callback.
By submitting this form, I agree that the Terms of Service and Privacy Policy .
- Digital Marketing
- Apps & Website

Email Marketing for B2B: Best Practices and Case Studies

The vast expanse of the digital world is teeming with communication channels, each clamoring for a slice of the engagement pie. However, standing tall amidst this digital cacophony is the often-underestimated titan: email marketing. Within the B2B sector, its potency is unrivaled.
With tailored strategies steeped in empirical data, the potential for creating lasting partnerships, cementing trust, and driving sustainable growth is immense. This guide is an odyssey into the multifaceted realm of “Email Marketing for B2B”. It is a confluence of best practices, saturated with up-to-date statistics, and illuminated by enlightening case studies that offer real-world exemplars of success.
- Table of Contents
What is B2B email marketing?
B2B email marketing, which stands for Business-to-Business email marketing, represents a significant avenue for businesses communicating with other enterprises. Statistics have consistently underscored its importance. According to a recent study by the Content Marketing Institute, 87% of B2B marketers cite email as one of their top free organic distribution channels.
This form of marketing diverges from B2C (Business-to-Consumer) email marketing, in which businesses directly target individual consumers. Given the intricate nature of B2B transactions—with longer sales cycles and multiple decision-makers involved—the efficacy of email as a channel becomes evident. Data from Campaign Monitor indicates that B2B email campaigns see a 23% higher click-through rate than B2C campaigns, highlighting the engaged nature of this audience.
The driving force behind B2B email marketing is fostering and nurturing business relationships. The content tends to be more comprehensive and value-oriented, aiming to solve specific industry challenges or provide insights. This approach aligns with findings from HubSpot, which revealed that 71% of B2B buyers during the awareness stage of the buying cycle value content that explores industry trends.
Segmentation is another strong suit of B2B email marketing. Advanced email marketing tools now allow businesses to dissect their audience based on diverse parameters, ensuring targeted communication. For instance, a Mailchimp study found that segmented email campaigns have a 14.37% higher open rate compared to non-segmented campaigns.
However, while B2B email marketing can be an engine of growth, it also demands careful navigation. The rise in data protection standards, like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), mandates a more conscientious approach to collecting and managing data. Non-compliance can be costly, with GDPR fines potentially reaching up to 4% of a company’s annual global revenue.
Additionally, there’s an overarching need for quality in B2B email communications. Ascend2’s research highlights that 51% of email marketers consider enriching content quality as their number one strategy for optimizing email performance. This means that while frequency is essential, sending high-value, well-researched emails can lead to better engagement and, ultimately, conversion.
In the grand scheme, B2B email marketing isn’t just about sending emails—it’s about building lasting, valuable relationships with business partners, stakeholders, and potential clients. And as data consistently demonstrates, it remains a linchpin in the B2B communication strategy, driving engagement, trust, and business growth.
- Emails: The Conduits of Constructive Conversations
Within the B2B space, emails have evolved beyond their conventional image of mere communication instruments.
Today, they serve as nuanced platforms initiating and nurturing meaningful dialogues. When rightly employed, emails can decode and cater to specific client needs, offering solutions tailored like a well-fitted suit.
A recently conducted in-depth survey revealed an eye-opening fact: 60% of B2B decision-makers place paramount importance on receiving customized email content. They believe that such tailored interactions hold the promise of addressing their specific challenges, thereby echoing their business aspirations and concerns.
- Crafting the Quintessential Digital Handshake
Navigating the B2B landscape requires more than just expertise; it demands the establishment of trust and the portrayal of unyielding professionalism.
Every email sent from a B2B entity isn’t just a message; it’s a reflection of that organization’s ethos and competence. It’s akin to a digital handshake – the first point of contact that could make or break potential collaborations.
It’s no surprise then that a study highlighted how nearly half (47%) of B2B recipients form their initial impressions about a partnership based on their maiden email interactions. Such statistics emphasize the pivotal role that email plays in shaping business trajectories.
Let’s delve into the importance of using B2B-specific strategies for email marketing in the B2B space.
State of Technology 2024
Humanity's Quantum Leap Forward
Explore 'State of Technology 2024' for strategic insights into 7 emerging technologies reshaping 10 critical industries. Dive into sector-wide transformations and global tech dynamics, offering critical analysis for tech leaders and enthusiasts alike, on how to navigate the future's technology landscape.
Why B2B Emails Require B2B Strategies: Data-Driven Analysis of Email Marketing for B2B
Email marketing is a formidable force in the business world, but a one-size-fits-all approach is not the answer. Specifically, Email Marketing for B2B occupies a niche of its own, demanding a distinct approach backed by robust data. Let’s deeply analyze, using concrete statistics, why B2B emails call for tailored B2B strategies.
- 1. Distinct Audience Profiles
B2B and B2C markets primarily differ in their target audiences. While B2C email campaigns often cater to individual consumers, looking to invoke an emotional purchase reaction, Email Marketing for B2B targets a varied group of stakeholders. Gartner’s research illuminates this by highlighting that a typical B2B buying decision involves between six to ten decision-makers. This means that each email sent in a B2B context must resonate with multiple roles, from technicians to CEOs, each bringing their unique perspectives and concerns to the table. Simply put, the diversity in the B2B audience profile mandates a more nuanced approach than its B2C counterpart.
- 2. Prolonged Sales Cycles
Decisions in the B2B sector are not driven by impulse. The Harvard Business Review states that B2B sales cycles have increased by 22% over the past five years.
When crafting strategies for Email Marketing for B2B, this protracted decision-making timeline cannot be ignored. Emails must be designed to nurture leads patiently, providing consistent value over extended periods. This might involve offering insights, addressing concerns, or introducing potential solutions at various stages of the decision-making process.
- 3. Value-driven Content is Paramount
While discounts or limited-time offers might be the highlight of B2C emails, B2B communications have a different priority: value. Demand Gen Report showed that 96% of B2B buyers actively seek content from industry thought leaders during their purchase journey.
In light of this, Email Marketing for B2B must consistently disseminate insightful, actionable, and high-quality content. This isn’t just about showcasing products or services, but about establishing credibility, demonstrating expertise, and fostering trust.
- 4. Imperative for Personalization
Understanding and addressing audience-specific needs is a hallmark of successful B2B email campaigns. The Content Marketing Institute found that 90% of top-performing B2B content marketers place audience informational needs above all else. In the B2B realm, emails need to transcend generic communications. Personalized email campaigns should reflect a deep understanding of the recipient’s industry, challenges, and goals, making each interaction meaningful and relevant.
- 5. Segmentation as the Cornerstone
With personalization comes the need for adept segmentation. The multifaceted roles within B2B decision-making units make segmentation crucial. According to Mailchimp, segmented email campaigns have a 14.31% higher open rate than non-segmented ones. For Email Marketing for B2B, this means categorizing contacts based on various criteria like industry, position, past interactions, and potential needs, ensuring that the content they receive aligns with their specific profiles.
- 6. The High Stakes of B2B Transactions
B2B deals often involve considerable sums and longer-term commitments compared to typical B2C transactions. McKinsey’s research indicates that, for B2B buyers, the end-to-end experience of a transaction can be valued up to 2x more than price or branding. This underscores the need for Email Marketing for B2B strategies to focus on building trust, showcasing reliability, and emphasizing long-term value over quick discounts or superficial engagements.
- 7. Compliance and Regulatory Landscape
In the digital age, data protection and privacy have taken center stage. Regulatory frameworks like GDPR are not just guidelines but mandated laws. ITProPortal’s survey revealed that a staggering 90% of B2B entities elevated their cybersecurity budgets in the wake of GDPR.
Thus, B2B email strategies must prioritize stringent adherence to data regulations, not only to avoid substantial fines but also to maintain trustworthiness in the eyes of clients and partners.
- 8. Building Long-term Relationships
B2B interactions aren’t just about one-off transactions. Salesforce’s study found that 79% of business buyers believe it’s essential to engage with salespeople perceived as trusted advisors, not merely sales reps. This highlights the importance of relationship-building in Email Marketing for B2B. Each email should not just aim for a sale but should strive to deepen the relationship, offer value, and foster mutual growth.
- 9. An Iterative Approach
The B2B landscape is dynamic, with technological advancements and industry shifts constantly reshaping it. Forrester’s data suggests that businesses adopting an iterative and feedback-driven approach in their B2B strategies witness a 10% increase in annual revenue. This means Email Marketing for B2B should not be static; regular feedback loops, analysis of campaign data, and agile adjustments are imperative for sustained success.
- 10. Integration with Broader B2B Strategies
No marketing tool should operate in isolation, especially in the interconnected digital world. B2B email campaigns gain heightened efficacy when integrated with other channels, be it content marketing, webinars, or social media. SiriusDecisions emphasizes this interconnectedness, stating that a harmonized integration of marketing channels in B2B can lead to a significant uptick in overall engagement and conversion rates.
While email remains a potent tool across both B2B and B2C domains, the strategies governing them differ substantially. Recognizing and acting upon these nuances is the key to unlocking the immense potential of Email Marketing for B2B
- The ROI Narrative: Beyond Just Numbers
Return on Investment (ROI) isn’t a new term in the world of business. However, when it comes to B2B email marketing, the ROI story narrates a tale of phenomenal success and unmatched effectiveness.
Emails, when strategically designed and executed, promise returns that are often multiple times the initial investment. Recent data-driven research showcased that B2B email marketing campaigns, on average, fetch an ROI that is 38 times the initial spend. These aren’t mere numbers; they’re testaments to the raw power and potential that email marketing harnesses within the B2B space.
15 B2B Email Marketing Best Practices
- 1. Segmentation of Your Audience
Segmenting email lists is the cornerstone of proficient Email Marketing for B2B. It means grouping your contacts based on shared characteristics like job roles, industries, or stages in the buying cycle.
According to Campaign Monitor, segmented email campaigns drive a 760% increase in revenue. The more refined your segments, the more personalized your messaging can become, which in turn enhances engagement.
Additionally, understanding the behavior of different segments allows B2B marketers to send emails at optimal times, leading to improved open rates. It’s imperative for businesses to leverage data-driven insights to refine and perfect their segmentation strategies continuously.
- 2. Personalize the Content
Beyond starting an email with the recipient’s name, true personalization tailors content to the individual’s preferences, past interactions, and needs. DemandGen reports that personalized emails improve click-through rates by an average of 14% and conversions by 10%.
In the realm of Email Marketing for B2B, where the buying process is longer and often involves multiple decision-makers, personalization can build a stronger rapport and speed up decision-making. By leveraging data analytics, businesses can pinpoint what content is most appealing to individual contacts and tailor their emails accordingly.
- 3. Responsive Design
The rise of mobile technology has made responsive email design non-negotiable. Adobe’s studies indicate that about 40% of B2B professionals check their email on a mobile device first. Hence, emails that don’t display correctly on mobile devices can lead to lost opportunities.
Furthermore, in Email Marketing for B2B, where emails might contain detailed graphics, charts, or crucial CTA buttons, ensuring readability and functionality across devices is paramount. Implementing responsive design not only ensures content appears correctly but also enhances user experience, promoting higher engagement rates.
- 4. Optimize Email Frequency
While staying top-of-mind is essential, bombarding contacts with daily emails can be counterproductive. A study from MarketingSherpa found that 86% of professionals prefer to receive promotional emails at least monthly, while only 15% wish to receive them daily.
Recognizing the right balance in Email Marketing for B2B ensures that content remains welcome and not perceived as spam. Businesses should monitor unsubscription rates and feedback to determine the optimal email frequency for their audience.
- 5. Use Engaging Subject Lines
The subject line often determines whether an email gets opened or discarded. In fact, Convince & Convert found that 35% of recipients open emails based on the subject line alone.
Crafting engaging, relevant, and curiosity-piquing subject lines is therefore vital in Email Marketing for B2B. A/B testing different subject lines can provide insights into what resonates most with your audience, allowing for continuous refinement.
- 6. Leverage Automation
Automation, when used judiciously, can streamline email campaigns and ensure timely engagement. For instance, welcome emails can be automated for new subscribers.
Research from Invesp indicates that welcome emails generate 320% more revenue on a per-email basis than other promotional emails. By automating such processes in Email Marketing for B2B, businesses can engage contacts at crucial touchpoints without manual intervention.
- 7. Prioritize Quality Over Quantity
In the realm of Email Marketing for B2B, the focus should invariably be on the depth and relevance of your content rather than sheer volume.
While sending out numerous emails might seem like an excellent way to capture attention, it often leads to diminishing returns. Ascend2’s research underscores the importance of quality, indicating that 51% of email marketers consider high-quality content as their paramount strategy for improving engagement rates.
In B2B marketing, where the target audience is often swamped with numerous business emails daily, the content’s value becomes a distinctive factor. A well-researched, relevant, and actionable email will not only garner attention but also position your brand as a thought leader, aiding decision-makers in their purchasing journey.
- 8. Maintain a Clean Email List
Every efficient Email Marketing for B2B strategy underlines the importance of a clean email list. Dormant or non-responsive contacts can skew your metrics, giving a distorted view of your campaign’s success.
By regularly weeding out such contacts, businesses ensure that their messages reach genuinely interested parties, thereby boosting engagement. Additionally, with regulations like GDPR emphasizing user consent and data privacy, maintaining a clean list ensures compliance and protects businesses from potential legal ramifications.
Thus, an updated email list is not just about efficiency but also about building trust and adhering to best practices.
- 9. Measure and Iterate
The dynamism of the digital landscape demands continuous analysis and adaptation. A successful Email Marketing for B2B strategy relies heavily on real-time metrics such as open rates, click-through rates, and most importantly, conversion rates.
Gartner’s statistics, which suggest a potential 15-20% ROI increase from data-driven marketing, validate this approach. By closely monitoring these metrics, businesses can identify which strategies are working and which areas require improvement, thereby fine-tuning their campaigns for optimal results.
- 10. Integrate with Other Marketing Channels
Isolation is the enemy of holistic digital marketing. Email campaigns should seamlessly integrate with other marketing endeavors, be it social media promotions , content marketing strategies, or PPC campaigns.
Such integration not only provides consistency in messaging but also amplifies the reach and impact of your campaigns. As per the Data & Marketing Association, synergizing campaigns across multiple channels can bolster engagement rates by a significant 37%. This statistic reinforces the idea that a unified marketing front is often more effective than disparate efforts.
- 11. Create Visually Appealing Emails
A picture speaks a thousand words, and in the world of email marketing, this adage rings exceptionally true. While well-crafted content is vital, complementing it with relevant imagery or infographics can significantly enhance user engagement.
Brain Rules’ research highlights the potency of visual aids, noting that people retain a staggering 65% of information when paired with an appropriate image, as opposed to a mere 10% without it. For B2B marketers, this implies the importance of presenting data, product information, or even testimonials in a visually captivating manner.
- 12. Ensure Compliance with GDPR and Other Regulations
In today’s digital age, data privacy is paramount. Regulatory measures like GDPR are not mere guidelines but mandatory practices that businesses need to integrate into their operations.
Non-compliance doesn’t just tarnish a brand’s reputation but can also result in hefty penalties. Especially in Email Marketing for B2B, where communication often involves decision-makers from various regions and sectors, adhering to data protection standards is non-negotiable. It’s a testament to a business’s commitment to ethical practices and respect for its stakeholders.
- 13. Utilize A/B Testing
The diverse nature of B2B audiences means that there’s no one-size-fits-all strategy. What resonates with one segment might not work for another. Here’s where A/B testing becomes invaluable.
By testing variations in emails, from subject lines to visual elements, businesses can discern what resonates best with their audience. HubSpot’s findings accentuate this point, noting a potential 40% lead generation boost for marketers leveraging A/B testing. Such an approach ensures that businesses are always in tune with their audience’s preferences, leading to more impactful campaigns.
- 14. Encourage Feedback and Interaction
Emails should foster two-way communication. Instead of just disseminating information, B2B emails should encourage recipients to share feedback, ask questions, or even challenge the content.
Econsultancy’s study reveals that businesses that actively seek and act upon feedback witness up to a 15% surge in customer satisfaction. Such interactions not only provide businesses with fresh insights but also fortify relationships, positioning the brand as one that values its stakeholders’ opinions.
- 15. Stay Updated with Trends and Best Practices
The digital landscape is ever-evolving, with new tools, platforms, and strategies emerging continually. For businesses invested in Email Marketing for B2B, staying abreast of these changes is imperative. Adapting to new technologies or methodologies ensures that their campaigns remain effective, relevant, and competitive.
Moreover, a commitment to continuous learning and evolution is indicative of a brand’s dedication to excellence, a trait highly valued in the B2B sector.
By embracing and implementing these nuanced practices, B2B businesses can craft email marketing strategies that are not just effective but also sustainable. It paves the way for building robust relationships, driving meaningful engagement, and ultimately, achieving substantial growth.
Illuminating Case Studies in B2B Email Marketing
- Adobe’s Emphasis on Interactive Emails
Adobe, a major player in the creative software industry, has increasingly incorporated interactivity into its email campaigns. Recognizing that B2B decision-makers are inundated with emails, Adobe sought to make their communications stand out. Using features like sliders, collapsible menus, and animated CTAs, Adobe reported a substantial increase in engagement rates, emphasizing the need for innovation in email formats.
- Maersk’s Success with Storytelling
Maersk, a global leader in shipping, successfully employed storytelling in its email campaigns. Rather than simply promoting their services, Maersk shared stories of global trade, the people involved, and the impact of their operations. This human-centric approach led to a 70% increase in unique opens and a click-through rate that surpassed industry standards.
- Cisco’s Video-Centric Approach
Cisco, the tech giant, understood early on the power of video in email marketing. Given that including video in an email can lead to a 200-300% increase in click-through rate (according to HubSpot), Cisco’s strategy to incorporate product demonstrations, client testimonials, and educational content in video format within their emails proved to be a masterstroke in engagement.
- IBM’s Cognitive Content Approach
IBM leveraged its AI powerhouse, Watson, to craft ‘cognitive content’ for email marketing. Recognizing the importance of hyper-personalization, they fed their AI system with data on customer interactions and preferences. Watson then created content that catered specifically to the reader’s interests. This tech-driven approach saw IBM’s engagement rates surge, with certain campaigns experiencing a click-through rate boost of over 50%.
- General Electric’s Interactive Emails
General Electric (GE) has been at the forefront of merging innovation with marketing. Their email campaigns often included embedded interactive elements like quizzes and surveys, giving the reader not just information but an immersive experience. This engagement-centric strategy led to a marked increase in open rates and more importantly, longer email interaction times.
- Dropbox’s Simplistic Engagement
Dropbox, known for its minimalist design approach, used this same philosophy in its B2B email campaigns. With a clear call to action, ample white space, and concise content, Dropbox’s emails were a testament to the adage “less is more”. Their strategy was validated with an above-average industry open rate and a substantial boost in user onboarding from email links.
- Airbnb’s Use of User-Generated Content
While Airbnb is a B2C company, their B2B outreach to potential hosts employed a genius strategy. They curated user-generated stories of current hosts, showcasing the financial and social benefits of joining the Airbnb community. By giving potential B2B partners a glimpse into real success stories, Airbnb saw a spike in new host sign-ups through email campaigns.
- Microsoft’s Emphasis on Webinars
Given the often complex nature of Microsoft’s products for businesses, the tech giant regularly utilized email marketing to promote webinars. These webinars would delve deep into product utilities, benefits, and demonstrations. Microsoft’s emails, promoting these webinars, were structured with clear CTAs and benefits of attending, leading to packed sessions every time they hosted one.
- Oracle’s Drip Campaigns for New Products
Oracle, a heavyweight in the B2B tech space, employed drip campaigns effectively whenever they launched new products or updates. These sequences would start by introducing the product, followed by deep dives, case studies, and eventually, a sales-focused pitch. By educating the potential client incrementally, Oracle ensured that by the campaign’s end, the lead was well-informed and more likely to convert.
All these case studies underline the adaptability and power of email marketing in the B2B realm. Each brand, with its unique challenges and audience, found innovative ways to leverage emails for better engagement and conversion.
As we reflect upon the vast landscape of Email Marketing for B2B, it becomes evident that this domain is much more than just digital correspondence; it’s an intricate tapestry of strategy, personalization, and continuous evolution. B2B relationships are built upon trust, knowledge, and consistent value provision.
Through the numerous best practices we’ve delved into, from harnessing the potency of segmentation to the imperative of GDPR compliance , we recognize a common theme: intentionality. Every email sent in the B2B realm should be more than just a message; it should be a purposeful step towards solidifying a lasting business relationship.
Moreover, the case studies serve as tangible evidence of the transformative power of adept B2B email campaigns. Real-world businesses, irrespective of their industry niches, have harnessed the prowess of emails to not just communicate but to connect deeply. These success stories are not outliers but exemplars for any B2B entity striving to amplify their email marketing ROI. They highlight the symbiotic relationship between a business’s understanding of its audience and the consequent email strategies they employ.
As we stand on the cusp of an era where digital interactions are becoming increasingly central to business operations, the significance of Email Marketing for B2B cannot be understated.
However, with its vast potential comes the responsibility of harnessing it ethically, effectively, and with the genuine intent of adding value.
To any B2B enterprise looking to scale new heights, the roadmap is clear: invest in understanding your audience, be diligent in curating high-quality content, be open to iterative learning, and above all, remember that in the world of B2B, relationships are paramount. As we’ve learned, with the right strategies in place, email becomes not just a communication tool but a powerful bridge to lasting business partnerships.
- 1.What distinguishes B2B email marketing from B2C email marketing?
B2B email marketing primarily targets companies, professionals, or decision-makers, focusing on value propositions, long-term relationships, and solutions to complex business challenges. In contrast, B2C email marketing directly targets consumers, emphasizing promotional offers, product features, and emotional engagement.
- 2. Why are B2B email campaign best practices important?
Best practices ensure that B2B email campaigns are effective, relevant, and compliant with regulations. By adhering to best practices, businesses can enhance their email deliverability, engagement rates, and ultimately, their ROI, while nurturing long-lasting relationships with their audience.
- 3.Can you provide examples of successful B2B email marketing case studies?
Certainly! There are numerous instances where companies have leveraged email marketing to boost their brand awareness, lead generation, and sales conversions. Examples include software companies offering exclusive whitepapers, manufacturers sharing product demonstrations, or consulting firms showcasing client testimonials. Each case study provides insights into the strategies employed and the results achieved.
- 4. How important is content quality in Email Marketing for B2B?
Content quality is paramount. A study by Ascend2 found that enriching content quality was the most effective strategy for increasing email engagement for 51% of email marketers. B2B recipients expect high-value, informative content that aids their decision-making process.
- 5. How often should B2B companies send out marketing emails?
The frequency depends on the business’s goals, the nature of the content, and the preferences of the audience. While regular touchpoints can foster engagement, it’s essential to avoid overwhelming recipients. Balancing frequency with value-driven content ensures optimal engagement and minimizes the risk of unsubscriptions.
- 6. Are there specific regulations B2B email marketers should be aware of?
Yes, B2B email marketers must be compliant with regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the CAN-SPAM Act. These regulations mandate practices like obtaining explicit consent before sending emails and including clear opt-out mechanisms. Non-compliance can lead to hefty penalties and damage to brand reputation.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 1 / 5. Vote count: 1
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Related Post
Top email marketing trends to watch in 2024, the important role of ai in email marketing in the digital age, how outsourcing email marketing can boost your business, crafting the perfect email marketing funnel, email and sms marketing tips for your contracting business, tips for creating email marketing strategy in 2024, table of contents.
Expand My Business is Asia's largest marketplace platform which helps you find various IT Services like Web and App Development, Digital Marketing Services and all others.
- IT Staff Augmentation
- Data & AI
- E-commerce Development
Article Categories
- Technology 586
- Business 302
- Digital Marketing 239
- Social Media Marketing 125
- E-Commerce 117
- Website Development 95
Copyright © 2024 Mantarav Private Limited. All Rights Reserved.

Case Studies , Email & SMS Marketing
Case Study: Email Marketing Done Right
March 14, 2023

Email marketing is one of the most effective and affordable ways for small businesses to reach potential customers and build relationships.
For one, email marketing is a cost-effective way for small businesses to reach leads and customers. It’s much cheaper than traditional marketing methods, such as direct mail or print advertising, and it requires very little time and effort.
Email marketing is also easy to track and analyze. You can measure the success of your campaigns by looking at open rates, click-through rates and conversions. This allows you to make adjustments to your campaigns to ensure they are as effective as possible.
Last but certainly not least, email marketing is an excellent way to build relationships with potential customers. You can use email campaigns to introduce your brand and products, offer discounts, and stay in touch with customers. This helps to create a loyal customer base who will be more likely to purchase from you in the future.
Email marketing is an essential tool for small businesses looking to grow. It’s cost-effective, easy to track, and can help you reach a wider audience and build relationships with potential customers. With the right strategy, email marketing can be an invaluable asset for your business.
Online store builds strong connections with email marketing
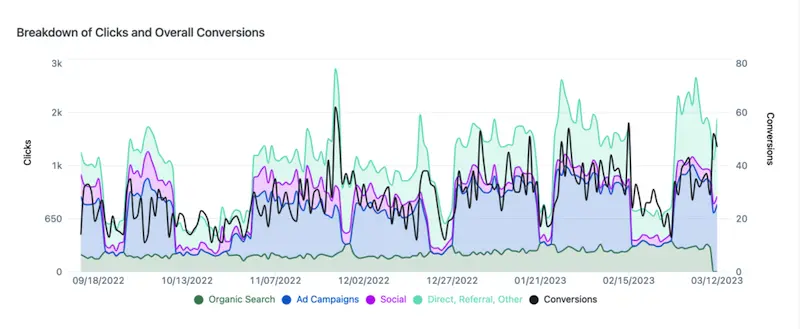
One online store saw just how valuable an effective email marketing strategy can be when it comes to converting leads and building loyal customer relationships.
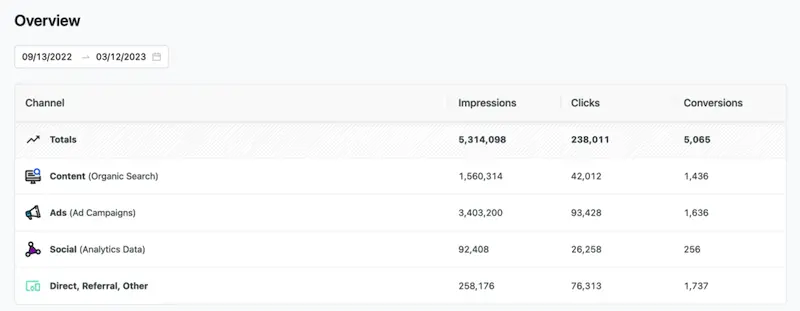
Over the past six months, they’ve seen millions of impressions, hundreds of thousands of clicks and thousands of conversions. And, while email can’t compare in terms of direct conversions to other channels, like organic and paid search, it has a huge impact on their ability to nurture leads and customers.

They’ve also seen their email marketing success grow over time, with a 589% increase in sessions and a 389% increase in goal conversions.

How did they do it?
This online store first launched their email journey back in September, and it has allowed them to stay top of mind with leads and customers ever since.

They built their automated email journey to ensure regular points of contact with their leads and customers. At the beginning of the journey, contacts are more frequent, while leads and customers farther down in the journey get emails less frequently.
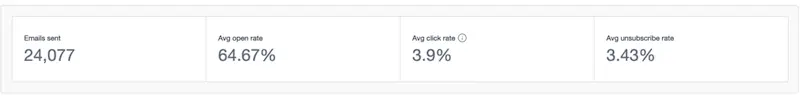
With compelling subject lines, proactive email listing management and valuable content, they drove higher-than-average open rates.

And, one of the best parts of their email marketing strategy is that it allows them to get even more value from their blog posts. By sending out their posts as emails, they saved time while also nurturing leads and customers.
Plus, thanks to automation, they were able to send out tens of thousands emails without taking any time from their schedule.
Email marketing is one of the most effective and affordable ways for small businesses to reach potential customers and build relationships. And, while it may never be your premier source of success, it can play a major role in your ability to convert leads and stay top of mind with customers.
Build, manage and grow your small business with Marketing 360®
Marketing 360® is a singular platform that offers everything you need to build a modern, professional website , launch ads on popular channels , manage all of your contacts, projects and deals , schedule out social media posts , monitor your SEO performance and so much more, plus the marketing team you need to grow your business .
See our plans and pricing.
Account M36997 Screenshots taken on 3/13/23
*Results are based on past client performance. Individual account performance may vary. Results are not guaranteed.
Get Plans and Pricing Below

Case Studies , Reputation Management
Case Study: Property Management Uses Reputation Management to Learn About Customer Satisfaction

Email & SMS Marketing
The Benefits of Text Message Marketing for Real Estate Agents

Case Studies
Case Study: Furniture Store Sees Conversion Rates Skyrocket

7 Email Marketing Tips for Photographers

SMS Marketing Compliance: What You Need to Know

Case Studies , Social Media Marketing
Case Study: Furniture Store Boosts Visibility With Social Media Giveaway
Get the know-how to get ahead.
Get business, marketing and sales tips written by experienced industry practitioners. 100% free. Cancel anytime.
- Email address *

TechBullion
Case study: how 3 businesses achieved success with email marketing..

In the ever-evolving landscape of digital marketing, email marketing remains a powerful and versatile tool for businesses to connect with their audience. When utilized effectively, email marketing can yield impressive results, and in this case study, we’ll delve into the stories of three diverse businesses that leveraged email marketing to achieve remarkable success.
Email marketing is more than just sending out promotional emails; it’s about building meaningful relationships with your audience, providing value, and nurturing leads through personalized communication. Each of these businesses approached email marketing uniquely, tailoring their strategies to fit their specific goals and target audiences. Let’s explore how these companies harnessed the potential of email marketing and achieved substantial growth.
Introduction
E-commerce excellence, business overview:.
Company A is an online clothing retailer with a strong presence in the fashion industry. Their main objectives were to increase sales, reduce cart abandonment rates, and build a loyal customer base.
Email Marketing Strategy:
Company A implemented a multi-faceted email marketing strategy . They began by segmenting their email list based on customer preferences, shopping behavior, and demographics. This segmentation allowed them to send highly personalized emails, promoting products and offers that were most relevant to individual recipients.
They also utilized automated email sequences. For instance, when a customer abandoned their cart, they would receive a series of reminder emails with enticing incentives, such as discounts or free shipping. Additionally, they sent out weekly newsletters that featured new arrivals, fashion tips, and exclusive promotions.
By tailoring their emails to specific customer segments, Company A saw a significant increase in their open and click-through rates. They also noticed a considerable reduction in cart abandonment rates. Over the course of a year, their email marketing efforts contributed to a 40% increase in sales. Moreover, the loyal customer base they cultivated through personalized communication became a valuable asset for the company’s long-term growth.
B2B Brilliance
Company B is a B2B software solutions provider specializing in project management software. They aimed to generate leads, establish thought leadership in their industry, and ultimately increase their conversion rate.
Company B adopted a content-rich email marketing approach. They focused on creating informative and educational content that catered to the pain points of their target audience. This content included blog posts, whitepapers, webinars, and case studies.
To build their email list, they offered valuable resources such as e-books in exchange for email subscriptions. Their newsletters featured a curated selection of their latest content, alongside industry news and tips for improving project management.
Company B’s email marketing strategy successfully positioned them as thought leaders in their industry. Their email list grew steadily, and their open rates remained consistently high. Over the course of two years, their email marketing campaigns resulted in a 30% increase in lead generation, which translated into a 20% increase in their conversion rate. Their email marketing efforts not only attracted new clients but also nurtured existing leads into loyal customers.
Local Services Triumph
Company C is a local home renovation and repair service provider. Their primary objectives were to increase brand awareness, gain new customers, and boost customer retention.
Company C focused on creating a sense of community and trust through email marketing. They began by sending out personalized welcome emails to new customers, expressing gratitude for choosing their services. These emails also included tips on home maintenance and renovation ideas.
To boost customer retention, they implemented a loyalty program, where customers could earn rewards and discounts through repeat bookings. They sent regular newsletters with seasonal offers, DIY home improvement tips, and customer success stories.
Company C’s personalized and community-centric approach to email marketing led to a significant increase in customer loyalty. Their retention rates improved, with many customers becoming repeat clients due to the loyalty program and valuable content they received via email. This resulted in a 25% increase in annual revenue within two years of implementing their email marketing strategy.
The success stories of these three businesses demonstrate the incredible potential of email marketing when employed strategically. Regardless of the industry or business type, email marketing can be a powerful tool for achieving various objectives, such as boosting sales, lead generation, establishing thought leadership, and increasing customer loyalty.
The common thread among these case studies is the emphasis on personalization, valuable content, and consistent engagement. Building strong relationships with your audience is at the heart of email marketing success. By understanding your customers’ needs, segmenting your email list, and delivering content that resonates, you can achieve impressive results with email marketing, just like these businesses did.
In today’s digital age, email marketing continues to be a fundamental component of a comprehensive digital marketing strategy. The success stories of these businesses serve as a testament to the enduring power of email marketing in achieving tangible, long-lasting results. As you embark on your own email marketing journey, take inspiration from these case studies and remember that the key to success lies in understanding your audience and delivering value through every email you send.

Recommended for you

Trending Stories

Amazon CEO Ignores Regulators After A Botched iRobot Acquisition
Andy Jassy, Amazon CEO, criticised authorities yesterday for their growing obstruction of mergers, citing...

HKMA Warns Public Against Fraudulent Digital Currency Claims
The public has been alerted to be wary of fraudulent schemes purporting to be...

TiK Tok Tagged “A Weapon Of War” Calls For Its Ban
Palantir advisor Jacob Helberg and investor Vinod Khosla wrote an open letter to senators...

Redefine “INFLUENCE”:Miss W in TOKEN2049 Dubai
As we navigate through the epoch of digital innovation, Miss W Global is charting...

Dunkin’s Strategy: Billboards to Buzz in Multichannel Marketing
In my years of exploring the ins and outs of effective marketing strategies, I’ve...

Samsung To Reveal $44 Billion US Chip Initiative
Samsung Electronics is getting ready to unveil a US$44 billion (RM209.79 billion) investment in...

Generative AI for companies is here – here’s what you need to know
Companies are increasingly drawn to the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) platforms to transform...

Enhance Your Crypto Project’s Reach on Telegram Using Telega.io
Navigating the crypto landscape requires a keen edge and innovative tools, especially for web3...


Litepips: Navigating the Forex Trading Landscape with Precision and Insight
In the ever-fluctuating realm of the forex market, where opportunities and risks walk hand...

10X Exchange Token ALGT Pulls Investors from PEPE and SHIB
Algotech (ALGT) token has made headlines in the crypto news by delivering 10x returns...

The Launch of Fitbyte Token (FIB): Bridging Real World Assets with the Digital Economy
In the swiftly evolving landscape of cryptocurrency, a new entrant, the Fitbyte Token (FIB),...

Bitcoin Cash Halving Hints At Bitcoin’s $42K Post-Event Dip
A $5 billion potential sell-off by BTC miners and the post-halving decline of Bitcoin...

China remains Vital For U.S. Chipmakers Amid Rising Tensions
In spite of Beijing’s efforts to become self-sufficient in the semiconductor industry and Washington’s...

Transforming Industries: Deep Manishkumar Dave’s Leadership in Smart Manufacturing & IoT Revolution
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, the convergence of Smart Manufacturing and the Internet...

Navigating the Social Media Landscape: Strategies for Effective Brand Presence
In the ever-evolving realm of social media, establishing a strong brand presence is essential...

Meta is Introducing New Features to Blur Nudity Images on Instagram to Protect Teens.
Meta is introducing new features to blur nudity images on Instagram to protect teens....

Apple to Allow Repairers to Use Old Apple Parts in Repairs
Apple plans to expand repair options with support for used genuine parts Takeaway Points...

Sequence Partners with Google to Streamline Web3 Gaming Development
In the ever-evolving landscape of gaming technology, the integration of Web3 has emerged as...

Bitcoin and Beyond: The Essential Crypto News Guide
Cryptocurrency represents a significant shift in the financial landscape, heralding a new age of...

Sygnum Bank Partners with Matter Labs to Tokenise $50M Reserves for Enhanced Transparency
Sygnum Bank has announced a strategic partnership with Matter Labs to tokenise $50 million...
Like Us On Facebook
Latest interview.
Technology White-label Solution for Programmatic Advertising; Interview With Anastasia-Nikita Bansal, CEO of Teqblaze
Hey there! I’m Niki. More than six years ago, I started my journey in AdTech, initially as a project manager at Smarty...
Latest Press Release

NTT DATA and Reiz Tech Announce New Venture to Target DACH
The joint venture – LITIT — built on previous collaborative successes of its parent companies, aims to transform the IT landscape of...
Pin It on Pinterest
18 Ways to Use Case Studies in Your Email Marketing
We’re always talking about how case studies are one of the hardest-working types of content.
They can help you:
- Build brand awareness
- Present solutions that solve your audience’s pain
- Grease the wheels for decision making
- Showcase results that inspire new leads
But did you know that email marketing is the perfect channel for sharing your stories?
With hard numbers , big results, and a gripping story, case studies leap out of the inbox. And with email’s special features like segmenting and sequences, you can send that persuasive pop to the right person at just the right time to gain a new customer.
Try these 18 ways to leverage your case study content and amp up your opens, clicks, and sales.
18 Ways to Leverage Case Study Content in Email
1. Audience satisfaction. Your subscribers invited you to their inbox because they want to know more about how you solve their problems. Case studies answer their questions in an irresistibly sticky format.
Questions such as:
- Do you help customers in their industry or niche?
- Can you ease the challenges that are giving them heartburn?
- Does your solution have the features they desperately need?
- Will your results persuade their decision makers?
2. Gated lead magnets. Use a case study as an opt-in to grow your email list.
3. Metrics in subject lines . Putting the most impressive metrics in your subject lines snags attention. This could be something like:
- “__% higher (metric) in ____(time). Interested?”
- “What could you do with __% more ____?”
- “How to get XX% more traffic for your ______”
- “[Case study] How XYZ Company got _____ (result)”
Here’s an example (and see how that headline pops?):
4. Quotes in subject lines. As above, but with your best customer quotes :
- “I wish I’d known about XYZ Company sooner….”
- “XYZ Company totally saved our bacon….”
5. Segmenting. Hand-picked case studies are the epitome of personalized persuasion. Send custom-fit stories to each avatar or segment based on:
- Pain points
Case studies can also enhance segmentation in reverse. You can tag readers who click on the story and follow up later with related offers and content.
6. Welcome sequences. Rev up new subscribers by following your lead magnet with an exciting story that’s connected to their goal.
7. Nurture sequences. Deepen your connection to subscribers by telling a story about how you solved the pain they’re feeling right now.
8. Drip email series. Build up tension and craft cliffhangers with a drip email series designed around a case study. For example:
- Email #1: discuss the frustrating problem
- Email #2: give hope with the solution
- Email #3: relieve the pain with results and a CTA.
9. Onboarding sequences. Help new customers set up your solution by sharing a study that demonstrates an interesting implementation.
10. Sales sequences. With hard-hitting details, case studies bring the perfect content as your readers progress through the later stages of the buyer’s journey:
- Consideration: showcase how your solution compares to competitors
- Decision-making: confirm your value with impressive results.
11. Upselling. Use the success story to pitch a premium service or add-on product to existing customers.
Use the success story to pitch a premium service or add-on product to existing customers.
12. Newsletters. Repurpose your case studies as newsletter articles, or send teasers with links to download or view. This could be something as simple as:
“We helped a _______ company shorten its app development process by 12 months, giving it an important market differentiator for the next insurance open enrollment period. Find out how we did it here.” <link to case study>
13. Re-engage dormant clients. Send an email that teases a scroll-stopping win and link to the full story.
14. Before and after examples. Convince on-the-fence prospects by spelling out exactly what life was like before and how much better life is after your solution.
15. Competitor comparisons. Craft a sequence about why one (or more!) customers decided to switch from a competitor’s product to yours.
16. Cold email outreach. Include case studies as a wow-worthy demonstration of your capability.
17. Media pitches. Pitch journalists, editors, or media outlets and reel them in with concrete metrics and customer quotes.
18. Email signatures. Include a link to your case study page or a specific case study so that everyone you interact with will passively encounter your social proof.
Here’s a quick illustration:

When you combine the irresistible drama and hard results of your case studies with the personalized experience of email, you get persuasive power that’s hard to beat.
So give some of these email plays a try—and get your case studies working harder and driving more wins.
Want to talk about leveraging case studies in your email marketing?
Contact us and we’ll help you get started.
Laurie Zottmann
Staff writer.
The only thing Laurie loves more than unforgettable stories is helping readers accomplish stuff that matters. When it comes to solving pesky business problems and capturing B2B audiences, nothing lights up the whole marquee like a heroic case study.
Ya, you like that? Well, there’s more where that came from!
Should you send case study interview questions in advance.
Sending your case study interview questions to your interviewee in advance sounds like a no-brainer, doesn’t it? And certainly, if you type “should you send case study interview questions in advance” into Google, that’s the boilerplate advice everyone gives. But is that truly good advice? Or does it depend on the situation? At Case Study Buddy, we’ve conducted (literally) hundreds and hundreds of case study interviews, and we’re continually testing new and better ways of conducting them. And the answer...
Best AI Case Study Examples in 2024 (And a How-To Guide!)
Who has the best case studies for AI solutions? B2B buyers’ heads are spinning with the opportunities that AI makes possible. But in a noisy, technical space where hundreds of new AI solutions and use cases are popping up overnight, many buyers don’t know how to navigate these opportunities—or who they can trust. Your customers are as skeptical as they are excited, thinking… “I’m confused by the complexity of your technology.” “I’m unsure whether there’s clear ROI.” “I’m concerned about...
How to Write Cybersecurity Case Studies
When it comes to case studies, cybersecurity poses special challenges. The cybersecurity landscape is saturated with solutions—and so sales and marketing teams have never been hungrier for customer success stories they can share as proof of their product’s abilities. But cybersecurity clients are very reluctant to be featured. They don’t want to talk about the time they almost got hacked, they don’t want to disclose the details of their setup and risk more attacks, and they just plain don’t want...
Let’s tell your stories together.
Get in touch to start a conversation.
🎉 Case Study Buddy has been acquired by Testimonial Hero 🎉 Learn more at testimonialhero.com
28 Case Study Examples Every Marketer Should See
Published: March 08, 2023
Putting together a compelling case study is one of the most powerful strategies for showcasing your product and attracting future customers. But it's not easy to create case studies that your audience can’t wait to read.

In this post, we’ll go over the definition of a case study and the best examples to inspire you.

What is a case study?
A case study is a detailed story of something your company did. It includes a beginning — often discussing a conflict, an explanation of what happened next, and a resolution that explains how the company solved or improved on something.
A case study proves how your product has helped other companies by demonstrating real-life results. Not only that, but marketing case studies with solutions typically contain quotes from the customer. This means that they’re not just ads where you praise your own product. Rather, other companies are praising your company — and there’s no stronger marketing material than a verbal recommendation or testimonial. A great case study is also filled with research and stats to back up points made about a project's results.
There are myriad ways to use case studies in your marketing strategy . From featuring them on your website to including them in a sales presentation, a case study is a strong, persuasive tool that shows customers why they should work with you — straight from another customer. Writing one from scratch is hard, though, which is why we’ve created a collection of case study templates for you to get started.
Fill out the form below to access the free case study templates.

Free Case Study Templates
Showcase your company's success using these three free case study templates.
- Data-Driven Case Study Template
- Product-Specific Case Study Template
- General Case Study Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
There’s no better way to generate more leads than by writing case studies . But without case study examples to draw inspiration from, it can be difficult to write impactful studies that convince visitors to submit a form.
Marketing Case Study Examples
To help you create an attractive and high-converting case study, we've put together a list of some of our favorites. This list includes famous case studies in marketing, technology, and business.
These studies can show you how to frame your company offers in a way that is both meaningful and useful to your audience. So, take a look, and let these examples inspire your next brilliant case study design.
These marketing case studies with solutions show the value proposition of each product. They also show how each company benefited in both the short and long term using quantitative data. In other words, you don’t get just nice statements, like "This company helped us a lot." You see actual change within the firm through numbers and figures.
You can put your learnings into action with HubSpot's Free Case Study Templates . Available as custom designs and text-based documents, you can upload these templates to your CMS or send them to prospects as you see fit.

1. " How Handled Scaled from Zero to 121 Locations with the Help of HubSpot ," by HubSpot

What's interesting about this case study is the way it leads with the customer. That reflects a major HubSpot cornerstone, which is to always solve for the customer first. The copy leads with a brief description of why the CEO of Handled founded the company and why he thought Handled could benefit from adopting a CRM. The case study also opens up with one key data point about Handled’s success using HubSpot, namely that it grew to 121 locations.
Notice that this case study uses mixed media. Yes, there is a short video, but it's elaborated upon in the other text on the page. So while your case studies can use one or the other, don't be afraid to combine written copy with visuals to emphasize the project's success.
Key Learnings from the HubSpot Case Study Example
- Give the case study a personal touch by focusing on the CEO rather than the company itself.
- Use multimedia to engage website visitors as they read the case study.
2. " The Whole Package ," by IDEO

Here's a design company that knows how to lead with simplicity in its case studies. As soon as the visitor arrives at the page, they’re greeted with a big, bold photo and the title of the case study — which just so happens to summarize how IDEO helped its client. It summarizes the case study in three snippets: The challenge, the impact, and the outcome.
Immediately, IDEO communicates its impact — the company partnered with H&M to remove plastic from its packaging — but it doesn't stop there. As the user scrolls down, the challenge, impact, and progress are elaborated upon with comprehensive (but not overwhelming) copy that outlines what that process looked like, replete with quotes and intriguing visuals.
Key Learnings from the IDEO Case Study Example
- Split up the takeaways of your case studies into bite-sized sections.
- Always use visuals and images to enrich the case study experience, especially if it’s a comprehensive case study.
3. " Rozum Robotics intensifies its PR game with Awario ," by Awario
In this case study, Awario greets the user with a summary straight away — so if you’re feeling up to reading the entire case study, you can scan the snapshot and understand how the company serves its customers. The case study then includes jump links to several sections, such as "Company Profile," "Rozum Robotics' Pains," "Challenge," "Solution," and "Results and Improvements."
The sparse copy and prominent headings show that you don’t need a lot of elaborate information to show the value of your products and services. Like the other case study examples on this list, it includes visuals and quotes to demonstrate the effectiveness of the company’s efforts. The case study ends with a bulleted list that shows the results.
Key Learnings from the Awario Robotics Case Study Example
- Create a table of contents to make your case study easier to navigate.
- Include a bulleted list of the results you achieved for your client.
4. " Chevrolet DTU ," by Carol H. Williams

If you’ve worked with a company that’s well-known, use only the name in the title — like Carol H. Williams, one of the nation’s top advertising agencies, does here. The "DTU," stands for "Discover the Unexpected." It generates interest because you want to find out what the initials mean.
They keep your interest in this case study by using a mixture of headings, images, and videos to describe the challenges, objectives, and solutions of the project. The case study closes with a summary of the key achievements that Chevrolet’s DTU Journalism Fellows reached during the project.
Key Learnings from the Carol H. Williams Case Study Example
- If you’ve worked with a big brand before, consider only using the name in the title — just enough to pique interest.
- Use a mixture of headings and subheadings to guide users through the case study.
5. " How Fractl Earned Links from 931 Unique Domains for Porch.com in a Single Year ," by Fractl

Fractl uses both text and graphic design in their Porch.com case study to immerse the viewer in a more interesting user experience. For instance, as you scroll, you'll see the results are illustrated in an infographic-design form as well as the text itself.
Further down the page, they use icons like a heart and a circle to illustrate their pitch angles, and graphs to showcase their results. Rather than writing which publications have mentioned Porch.com during Fractl’s campaign, they incorporated the media outlets’ icons for further visual diversity.
Key Learnings from the Fractl Case Study Example
- Let pictures speak for you by incorporating graphs, logos, and icons all throughout the case study.
- Start the case study by right away stating the key results, like Fractl does, instead of putting the results all the way at the bottom.
6. " The Met ," by Fantasy
What's the best way to showcase the responsiveness and user interface of a website? Probably by diving right into it with a series of simple showcases— which is exactly what Fantasy does on their case study page for the Metropolitan Museum of Art. They keep the page simple and clean, inviting you to review their redesign of the Met’s website feature-by-feature.
Each section is simple, showing a single piece of the new website's interface so that users aren’t overwhelmed with information and can focus on what matters most.
If you're more interested in text, you can read the objective for each feature. Fantasy understands that, as a potential customer, this is all you need to know. Scrolling further, you're greeted with a simple "Contact Us" CTA.
Key Learnings from the Fantasy Case Study Example
- You don’t have to write a ton of text to create a great case study. Focus on the solution you delivered itself.
- Include a CTA at the bottom inviting visitors to contact you.
7. " Rovio: How Rovio Grew Into a Gaming Superpower ," by App Annie
If your client had a lot of positive things to say about you, take a note from App Annie’s Rovio case study and open up with a quote from your client. The case study also closes with a quote, so that the case study doesn’t seem like a promotion written by your marketing team but a story that’s taken straight from your client’s mouth. It includes a photo of a Rovio employee, too.
Another thing this example does well? It immediately includes a link to the product that Rovio used (namely, App Annie Intelligence) at the top of the case study. The case study closes with a call-to-action button prompting users to book a demo.
Key Learnings from the App Annie Case Study Example
- Feature quotes from your client at the beginning and end of the case study.
- Include a mention of the product right at the beginning and prompt users to learn more about the product.
8. " Embracing first-party data: 3 success stories from HubSpot ," by Think with Google

Google takes a different approach to text-focused case studies by choosing three different companies to highlight.
The case study is clean and easily scannable. It has sections for each company, with quotes and headers that clarify the way these three distinct stories connect. The simple format also uses colors and text that align with the Google brand.
Another differentiator is the focus on data. This case study is less than a thousand words, but it's packed with useful data points. Data-driven insights quickly and clearly show how the value of leveraging first-party data while prioritizing consumer privacy.
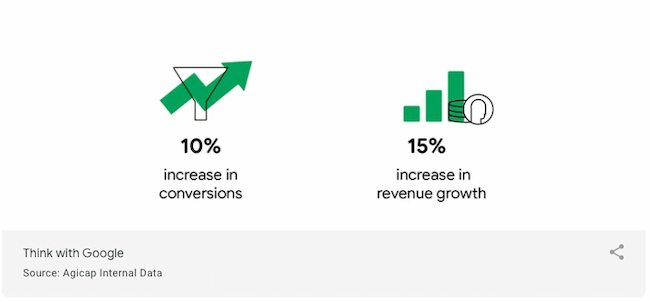
Key Learnings from the Think with Google Case Study Example
- A case study doesn’t need to be long or complex to be powerful.
- Clear data points are a quick and effective way to prove value.
9. " In-Depth Performance Marketing Case Study ," by Switch

Switch is an international marketing agency based in Malta that knocks it out of the park with this case study. Its biggest challenge is effectively communicating what it did for its client without ever revealing the client’s name. It also effectively keeps non-marketers in the loop by including a glossary of terms on page 4.
The PDF case study reads like a compelling research article, including titles like "In-Depth Performance Marketing Case Study," "Scenario," and "Approach," so that readers get a high-level overview of what the client needed and why they approached Switch. It also includes a different page for each strategy. For instance, if you’d only be interested in hiring Switch for optimizing your Facebook ads, you can skip to page 10 to see how they did it.
The PDF is fourteen pages long but features big fonts and plenty of white space, so viewers can easily skim it in only a few minutes.
Key Learnings from the Switch Case Study Example
- If you want to go into specialized information, include a glossary of terms so that non-specialists can easily understand.
- Close with a CTA page in your case study PDF and include contact information for prospective clients.
10. " Gila River ," by OH Partners

Let pictures speak for you, like OH Partners did in this case study. While you’ll quickly come across a heading and some text when you land on this case study page, you’ll get the bulk of the case study through examples of actual work OH Partners did for its client. You will see OH Partners’ work in a billboard, magazine, and video. This communicates to website visitors that if they work with OH Partners, their business will be visible everywhere.
And like the other case studies here, it closes with a summary of what the firm achieved for its client in an eye-catching way.
Key Learnings from the OH Partners Case Study Example
- Let the visuals speak by including examples of the actual work you did for your client — which is especially useful for branding and marketing agencies.
- Always close out with your achievements and how they impacted your client.
11. " Facing a Hater ," by Digitas
Digitas' case study page for Sprite’s #ILOVEYOUHATER campaign keeps it brief while communicating the key facts of Digitas’ work for the popular soda brand. The page opens with an impactful image of a hundred people facing a single man. It turns out, that man is the biggest "bully" in Argentina, and the people facing him are those whom he’s bullied before.
Scrolling down, it's obvious that Digitas kept Sprite at the forefront of their strategy, but more than that, they used real people as their focal point. They leveraged the Twitter API to pull data from Tweets that people had actually tweeted to find the identity of the biggest "hater" in the country. That turned out to be @AguanteElCofler, a Twitter user who has since been suspended.
Key Learnings from the Digitas Case Study Example
- If a video was part of your work for your client, be sure to include the most impactful screenshot as the heading.
- Don’t be afraid to provide details on how you helped your client achieve their goals, including the tools you leveraged.
12. " Better Experiences for All ," by HermanMiller

HermanMiller sells sleek, utilitarian furniture with no frills and extreme functionality, and that ethos extends to its case study page for a hospital in Dubai.
What first attracted me to this case study was the beautiful video at the top and the clean user experience. User experience matters a lot in a case study. It determines whether users will keep reading or leave. Another notable aspect of this case study is that the video includes closed-captioning for greater accessibility, and users have the option of expanding the CC and searching through the text.
HermanMiller’s case study also offers an impressive amount of information packed in just a few short paragraphs for those wanting to understand the nuances of their strategy. It closes out with a quote from their client and, most importantly, the list of furniture products that the hospital purchased from the brand.
Key Learnings from the HermanMiller Case Study Example
- Close out with a list of products that users can buy after reading the case study.
- Include accessibility features such as closed captioning and night mode to make your case study more user-friendly.
13. " Capital One on AWS ," by Amazon
Do you work continuously with your clients? Consider structuring your case study page like Amazon did in this stellar case study example. Instead of just featuring one article about Capital One and how it benefited from using AWS, Amazon features a series of articles that you can then access if you’re interested in reading more. It goes all the way back to 2016, all with different stories that feature Capital One’s achievements using AWS.
This may look unattainable for a small firm, but you don’t have to go to extreme measures and do it for every single one of your clients. You could choose the one you most wish to focus on and establish a contact both on your side and your client’s for coming up with the content. Check in every year and write a new piece. These don’t have to be long, either — five hundred to eight hundred words will do.
Key Learnings from the Amazon AWS Case Study Example
- Write a new article each year featuring one of your clients, then include links to those articles in one big case study page.
- Consider including external articles as well that emphasize your client’s success in their industry.
14. " HackReactor teaches the world to code #withAsana ," by Asana

While Asana's case study design looks text-heavy, there's a good reason. It reads like a creative story, told entirely from the customer's perspective.
For instance, Asana knows you won't trust its word alone on why this product is useful. So, they let Tony Phillips, HackReactor CEO, tell you instead: "We take in a lot of information. Our brains are awful at storage but very good at thinking; you really start to want some third party to store your information so you can do something with it."
Asana features frequent quotes from Phillips to break up the wall of text and humanize the case study. It reads like an in-depth interview and captivates the reader through creative storytelling. Even more, Asana includes in-depth detail about how HackReactor uses Asana. This includes how they build templates and workflows:
"There's a huge differentiator between Asana and other tools, and that’s the very easy API access. Even if Asana isn’t the perfect fit for a workflow, someone like me— a relatively mediocre software engineer—can add functionality via the API to build a custom solution that helps a team get more done."
Key Learnings from the Asana Example
- Include quotes from your client throughout the case study.
- Provide extensive detail on how your client worked with you or used your product.
15. " Rips Sewed, Brand Love Reaped ," by Amp Agency

Amp Agency's Patagonia marketing strategy aimed to appeal to a new audience through guerrilla marketing efforts and a coast-to-coast road trip. Their case study page effectively conveys a voyager theme, complete with real photos of Patagonia customers from across the U.S., and a map of the expedition. I liked Amp Agency's storytelling approach best. It captures viewers' attention from start to finish simply because it's an intriguing and unique approach to marketing.
Key Learnings from the Amp Agency Example
- Open up with a summary that communicates who your client is and why they reached out to you.
- Like in the other case study examples, you’ll want to close out with a quantitative list of your achievements.
16. " NetApp ," by Evisort
Evisort opens up its NetApp case study with an at-a-glance overview of the client. It’s imperative to always focus on the client in your case study — not on your amazing product and equally amazing team. By opening up with a snapshot of the client’s company, Evisort places the focus on the client.
This case study example checks all the boxes for a great case study that’s informative, thorough, and compelling. It includes quotes from the client and details about the challenges NetApp faced during the COVID pandemic. It closes out with a quote from the client and with a link to download the case study in PDF format, which is incredibly important if you want your case study to be accessible in a wider variety of formats.
Key Learnings from the Evisort Example
- Place the focus immediately on your client by including a snapshot of their company.
- Mention challenging eras, such as a pandemic or recession, to show how your company can help your client succeed even during difficult times.
17. " Copernicus Land Monitoring – CLC+ Core ," by Cloudflight
Including highly specialized information in your case study is an effective way to show prospects that you’re not just trying to get their business. You’re deep within their industry, too, and willing to learn everything you need to learn to create a solution that works specifically for them.
Cloudflight does a splendid job at that in its Copernicus Land Monitoring case study. While the information may be difficult to read at first glance, it will capture the interest of prospects who are in the environmental industry. It thus shows Cloudflight’s value as a partner much more effectively than a general case study would.
The page is comprehensive and ends with a compelling call-to-action — "Looking for a solution that automates, and enhances your Big Data system? Are you struggling with large datasets and accessibility? We would be happy to advise and support you!" The clean, whitespace-heavy page is an effective example of using a case study to capture future leads.
Key Learnings from the Cloudflight Case Study Example
- Don’t be afraid to get technical in your explanation of what you did for your client.
- Include a snapshot of the sales representative prospects should contact, especially if you have different sales reps for different industries, like Cloudflight does.
18. " Valvoline Increases Coupon Send Rate by 76% with Textel’s MMS Picture Texting ," by Textel

If you’re targeting large enterprises with a long purchasing cycle, you’ll want to include a wealth of information in an easily transferable format. That’s what Textel does here in its PDF case study for Valvoline. It greets the user with an eye-catching headline that shows the value of using Textel. Valvoline saw a significant return on investment from using the platform.
Another smart decision in this case study is highlighting the client’s quote by putting it in green font and doing the same thing for the client’s results because it helps the reader quickly connect the two pieces of information. If you’re in a hurry, you can also take a look at the "At a Glance" column to get the key facts of the case study, starting with information about Valvoline.
Key Learnings from the Textel Case Study Example
- Include your client’s ROI right in the title of the case study.
- Add an "At a Glance" column to your case study PDF to make it easy to get insights without needing to read all the text.
19. " Hunt Club and Happeo — a tech-enabled love story ," by Happeo

In this blog-post-like case study, Happeo opens with a quote from the client, then dives into a compelling heading: "Technology at the forefront of Hunt Club's strategy." Say you’re investigating Happeo as a solution and consider your firm to be technology-driven. This approach would spark your curiosity about why the client chose to work with Happeo. It also effectively communicates the software’s value proposition without sounding like it’s coming from an in-house marketing team.
Every paragraph is a quote written from the customer’s perspective. Later down the page, the case study also dives into "the features that changed the game for Hunt Club," giving Happeo a chance to highlight some of the platform’s most salient features.
Key Learnings from the Happeo Case Study Example
- Consider writing the entirety of the case study from the perspective of the customer.
- Include a list of the features that convinced your client to go with you.
20. " Red Sox Season Campaign ," by CTP Boston
What's great about CTP's case study page for their Red Sox Season Campaign is their combination of video, images, and text. A video automatically begins playing when you visit the page, and as you scroll, you'll see more embedded videos of Red Sox players, a compilation of print ads, and social media images you can click to enlarge.
At the bottom, it says "Find out how we can do something similar for your brand." The page is clean, cohesive, and aesthetically pleasing. It invites viewers to appreciate the well-roundedness of CTP's campaign for Boston's beloved baseball team.
Key Learnings from the CTP Case Study Example
- Include a video in the heading of the case study.
- Close with a call-to-action that makes leads want to turn into prospects.
21. " Acoustic ," by Genuine

Sometimes, simple is key. Genuine's case study for Acoustic is straightforward and minimal, with just a few short paragraphs, including "Reimagining the B2B website experience," "Speaking to marketers 1:1," and "Inventing Together." After the core of the case study, we then see a quote from Acoustic’s CMO and the results Genuine achieved for the company.
The simplicity of the page allows the reader to focus on both the visual aspects and the copy. The page displays Genuine's brand personality while offering the viewer all the necessary information they need.
- You don’t need to write a lot to create a great case study. Keep it simple.
- Always include quantifiable data to illustrate the results you achieved for your client.
22. " Using Apptio Targetprocess Automated Rules in Wargaming ," by Apptio
Apptio’s case study for Wargaming summarizes three key pieces of information right at the beginning: The goals, the obstacles, and the results.
Readers then have the opportunity to continue reading — or they can walk away right then with the information they need. This case study also excels in keeping the human interest factor by formatting the information like an interview.
The piece is well-organized and uses compelling headers to keep the reader engaged. Despite its length, Apptio's case study is appealing enough to keep the viewer's attention. Every Apptio case study ends with a "recommendation for other companies" section, where the client can give advice for other companies that are looking for a similar solution but aren’t sure how to get started.
Key Learnings from the Apptio Case Study Example
- Put your client in an advisory role by giving them the opportunity to give recommendations to other companies that are reading the case study.
- Include the takeaways from the case study right at the beginning so prospects quickly get what they need.
23. " Airbnb + Zendesk: building a powerful solution together ," by Zendesk
Zendesk's Airbnb case study reads like a blog post, and focuses equally on Zendesk and Airbnb, highlighting a true partnership between the companies. To captivate readers, it begins like this: "Halfway around the globe is a place to stay with your name on it. At least for a weekend."
The piece focuses on telling a good story and provides photographs of beautiful Airbnb locations. In a case study meant to highlight Zendesk's helpfulness, nothing could be more authentic than their decision to focus on Airbnb's service in such great detail.
Key Learnings from the Zendesk Case Study Example
- Include images of your client’s offerings — not necessarily of the service or product you provided. Notice how Zendesk doesn’t include screenshots of its product.
- Include a call-to-action right at the beginning of the case study. Zendesk gives you two options: to find a solution or start a trial.
24. " Biobot Customer Success Story: Rollins College, Winter Park, Florida ," by Biobot
Like some of the other top examples in this list, Biobot opens its case study with a quote from its client, which captures the value proposition of working with Biobot. It mentions the COVID pandemic and goes into detail about the challenges the client faced during this time.
This case study is structured more like a news article than a traditional case study. This format can work in more formal industries where decision-makers need to see in-depth information about the case. Be sure to test different methods and measure engagement .
Key Learnings from the Biobot Case Study Example
- Mention environmental, public health, or economic emergencies and how you helped your client get past such difficult times.
- Feel free to write the case study like a normal blog post, but be sure to test different methods to find the one that best works for you.
25. " Discovering Cost Savings With Efficient Decision Making ," by Gartner

You don't always need a ton of text or a video to convey your message — sometimes, you just need a few paragraphs and bullet points. Gartner does a fantastic job of quickly providing the fundamental statistics a potential customer would need to know, without boggling down their readers with dense paragraphs. The case study closes with a shaded box that summarizes the impact that Gartner had on its client. It includes a quote and a call-to-action to "Learn More."
Key Learnings from the Gartner Case Study Example
- Feel free to keep the case study short.
- Include a call-to-action at the bottom that takes the reader to a page that most relates to them.
26. " Bringing an Operator to the Game ," by Redapt

This case study example by Redapt is another great demonstration of the power of summarizing your case study’s takeaways right at the start of the study. Redapt includes three easy-to-scan columns: "The problem," "the solution," and "the outcome." But its most notable feature is a section titled "Moment of clarity," which shows why this particular project was difficult or challenging.
The section is shaded in green, making it impossible to miss. Redapt does the same thing for each case study. In the same way, you should highlight the "turning point" for both you and your client when you were working toward a solution.
Key Learnings from the Redapt Case Study Example
- Highlight the turning point for both you and your client during the solution-seeking process.
- Use the same structure (including the same headings) for your case studies to make them easy to scan and read.
27. " Virtual Call Center Sees 300% Boost In Contact Rate ," by Convoso

Convoso’s PDF case study for Digital Market Media immediately mentions the results that the client achieved and takes advantage of white space. On the second page, the case study presents more influential results. It’s colorful and engaging and closes with a spread that prompts readers to request a demo.
Key Learnings from the Convoso Case Study Example
- List the results of your work right at the beginning of the case study.
- Use color to differentiate your case study from others. Convoso’s example is one of the most colorful ones on this list.
28. " Ensuring quality of service during a pandemic ," by Ericsson
Ericsson’s case study page for Orange Spain is an excellent example of using diverse written and visual media — such as videos, graphs, and quotes — to showcase the success a client experienced. Throughout the case study, Ericsson provides links to product and service pages users might find relevant as they’re reading the study.
For instance, under the heading "Preloaded with the power of automation," Ericsson mentions its Ericsson Operations Engine product, then links to that product page. It closes the case study with a link to another product page.
Key Learnings from the Ericsson Case Study Example
- Link to product pages throughout the case study so that readers can learn more about the solution you offer.
- Use multimedia to engage users as they read the case study.
Start creating your case study.
Now that you've got a great list of examples of case studies, think about a topic you'd like to write about that highlights your company or work you did with a customer.
A customer’s success story is the most persuasive marketing material you could ever create. With a strong portfolio of case studies, you can ensure prospects know why they should give you their business.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August 2018 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

How to Write a Case Study: Bookmarkable Guide & Template

How to Market an Ebook: 21 Ways to Promote Your Content Offers
![case study on email marketing 7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/most%20popular%20types%20of%20content.jpg)
7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]
![case study on email marketing How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/listicle-1.jpg)
How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]
![case study on email marketing What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/business%20whitepaper.jpg)
What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]

What is an Advertorial? 8 Examples to Help You Write One

How to Create Marketing Offers That Don't Fall Flat

20 Creative Ways To Repurpose Content

16 Important Ways to Use Case Studies in Your Marketing

11 Ways to Make Your Blog Post Interactive
Showcase your company's success using these free case study templates.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
Direct mail to prospects and email to current customers? Modeling and field-testing multichannel marketing
- Original Empirical Research
- Open access
- Published: 05 August 2023
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Albert Valenti ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2887-7712 1 ,
- Shuba Srinivasan 2 ,
- Gokhan Yildirim 3 &
- Koen Pauwels 4 , 5
3125 Accesses
2 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Multichannel retailers need to understand how to allocate marketing budgets to customer segments and online and offline sales channels. We propose an integrated methodological approach to assess how email and direct mail effectiveness vary by channel and customer value segment. We apply this approach to an international beauty retailer in six countries and to an apparel retailer in the United States. We estimate multi-equation hierarchical linear models and find that sales responsiveness to email and direct mail varies by customer value segment. Specifically, direct mail drives customer acquisition in the offline channel, while email drives sales for both online and offline channels for current customer segments. A randomized field experiment with the beauty retailer provides causal support for the findings. The proposed reallocation of marketing resources would yield a revenue lift of 13.5% for the beauty retailer and 9.3% for the apparel retailer, compared with the 6.5% actual increase in the field experiment.
Similar content being viewed by others

How is retargeting related to purchase incidence, channel choice, and purchase quantity?
Tanya Mark, Tirtha Dhar, … Katherine N. Lemon

May I have your attention, please? An investigation on opening effectiveness in e-mail marketing
Julián Chaparro-Peláez, Ángel Hernández-García & Ángel-José Lorente-Páramo

Positioning the Postal Service for the Next Generation: An Overview of Market Research
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Multichannel retail is important for today’s marketers (Cui et al., 2021 ; Dekimpe, 2020 ), but it requires managers to allocate marketing budgets to channels and customer segments. Customer transactional data give retailers detailed information about existing customers’ purchase history, allowing them to prioritize customer segments by value. However, which segments are most responsive to which marketing action is unclear a priori (Zhang et al., 2014 ). For example, direct mail volume increased 46% between 2019 and 2022 (Gendusa, 2022 ), with growth in impressions (28%) outpacing digital ad impressions (10%) in 2021; yet direct mail is also very expensive and therefore often targeted to the highest-value segments (Sahni et al., 2017 ). Our survey of 351 marketing managers reveals that 46% believe that the most expensive marketing action should be targeted at the most valuable customers while 41% believe that all marketing should be sent to all customer types. Footnote 1 Consistent with these statements, most companies target emails to least valuable customer segments, including prospects, with its low cost as the primary reason (Levinson, 2019 ; Medlar, 2017 ), and target costly marketing actions to high-value customer segments. However, managers need to assess marketing response in multiple channels to understand which marketing actions produce the best returns and to make budgeting decisions on which actions to invest in and which customer segments to target.
Prior marketing research advises companies to allocate marketing actions to customer segments most receptive to them (Kamakura & Russell, 1989 ) and finds that customers’ past experience with the company’s offering does not necessarily mean greater responsiveness to marketing actions (Ascarza, 2018 ). First, some current customers may not peruse direct mail because they already know the firm and its offerings and prefer reminder emails. However, prospective customers (prospects hereinafter), for whom transactional data is not available, and light buyers might be more responsive to direct mail because of the rich information provided. How much these customers subsequently buy is an open question. Second, customers’ intrinsic preferences for email and direct mail may depend on the intensity of their interactions with the firm (i.e., email opening or direct mail browsing frequencies) differ among customers. Consistent with this argument, Return Path’s ( 2015 ) study suggests that email targeting should depend on customers’ engagement level. Third, recent legal developments such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), are removing up to 75% of third-party data from analysis, Indeed, direct mail “has greatly benefited from GDPR because it does not require consent from recipients” (PostGrid, 2022 ) while the use of emails may be impacted, making it more crucial to identify and target marketing-responsive customers instead of maximizing impressions (e.g., by emailing all customers) (Morris, 2019 ; Snyder, 2018 ).
Our research objective is therefore to address an important marketing-mix resource allocation problem for multichannel retailers. That is, we propose an integrated methodological approach to allocate online and offline marketing actions (in our case, email and direct mail), given the different responses in channels and customer segments, including prospects and dormant customers (i.e., those who have not purchased for a long time). To this end, we develop a decision-support system based on a systematic empirical modeling approach. We begin by describing the value of customers using the recency–frequency–monetary value–clumpiness (RFMC) model, which allows us to classify customers into value segments (Zhang et al., 2014 ). We then estimate multi-equation hierarchical linear models (HLMs) to assess the online and offline sales responsiveness to email and direct mail and customer value segment levels. When the data are from multinational retailers, we perform a meta-analysis of the estimates across countries for comparison. We use HLMs for out-of-sample sales prediction and marketing resource reallocation. Finally, we perform a field experiment to obtain the predicted benefits of the reallocation in a causal setting.
Specifically, we perform three empirical analyses. The first involves an international beauty retailer with data on every purchase transaction and all marketing communications for a four-year period for almost 85,000 customers randomly sampled from its six main markets: United States, Great Britain, Germany, France, Spain, and Italy. The second analysis involves a US apparel retailer with transactional data, online and offline channels, and marketing actions. In the third analysis, to evaluate our model-based results and provide causal inference support, we design and implement a randomized field experiment for the beauty retailer with all its 120,000 customers in Italy.
From a substantive perspective, our research is grounded in marketing managers’ challenges in multichannel retail, addressed with the empirics-first approach advocated by Golder et al. ( 2023 ) instead of starting from theory often borrowed from the founding disciplines (Kohli & Haenlein, 2021 ). Our work combines “conceptualization, research design and research execution” with “deep socialization with practice” (Stremersch, 2021 , p. 13) and challenges the current wisdom held by many high-level decision makers (Kohli & Haenlein, 2021 ). Following Lehmann ( 2020 ), we adopt an integrative modeling approach that blends data and theory by combining prediction and explanation for two specific retailers in six developed countries. In terms of prescriptive implications, we assess potential revenue improvements (e.g., Lemmens & Gupta, 2020 ) following Mantrala et al. ( 1992 ), who argue that the biggest gains are to be realized not by optimizing the total budget, but by doing a reallocation of the current budget. Consistent with this argument, we find that a reallocation of the marketing budget over customer value groups yields substantial revenue improvement. While the specific results are particularly relevant to the marketing actions and companies studied, our findings may encourage scholarly thinking about how they generalize to other contexts (Stremersch et al., 2023 ).
Research on multichannel response to direct mail and email
Within the rich literature on multichannel marketing response, we focus our review on the two marketing actions, direct mail and emails, that capture offline and online marketing in our contexts and on how marketing responsiveness differs by customer segments. Table 1 shows our study’s contributions and positions it within related marketing literature.
Direct mail effectiveness
Despite the growth of online marketing, multichannel retailers rely on direct mail given its ease of processing by consumers, ability to generate greater brand recall, and higher response rates than digital marketing communication (e.g., email, paid search, online display, social media). Direct mail, which accounts for more than one-third of direct marketing expenditures in many countries (Direct Marketing Association, 2015 ), can arouse interest in a firm’s products and result in purchase through short-term rewards (Roberts & Berger, 1999 ; Rust & Verhoef, 2005 ).
Several studies have shown that direct mail significantly affects behavior (Hill et al., 2006 ; Verhoef, 2003 ) and adoption of a new technological product (Prins & Verhoef, 2007 ; Risselada et al., 2014 ). Naik and Peters ( 2009 ) provide empirical evidence that direct mail directly drives online visits to enable car configurations. Valentini et al. ( 2011 ) find that direct mail by a multichannel retailer can drive new customers’ choice of shopping in either online or offline channels (for a review of omnichannel retail, see Timoumi et al., 2022 ). In the context of direct mail for charity donations, Seenivasan et al. ( 2016 ) conduct a field experiment that varies the framing of the message and find that monthly framing of the donation, including a story of an in-group person, yields better outcomes. Verhoef et al. ( 2007 ) argue that direct mail has high ease of use, can result in channel lock-in, and exhibits cross-channel synergy between direct mail search and web purchase. Danaher and Dagger ( 2013 ) cite direct mail as an effective tool to reach unaware consumers. In their comparison of the relative effectiveness of multiple marketing tools, they identify direct mail as the second most effective tool when considering dollar sales as the focal outcome and the most effective when profit is the focal outcome. At the same time, contradictory evidence in the business-to-business sector suggests that direct mail is not effective in driving sales (Wiesel et al., 2011 ).
Direct mail response varies for customer groups and marketing interventions, which can be explained by customer characteristics and past purchase history (Rust & Verhoef, 2005 ). Research has found that marketing response can differ among customer groups depending on demographics or recency–frequency–monetary (RFM) value metrics (Wedel & Kamakura, 2002 ). For example, marketing actions such as promotions are more effective for prospects (Van Heerde & Bijmolt, 2005 ) but do little for acquired customers and could even have negative effects (Anderson & Simester, 2004 ). Rust and Verhoef ( 2005 ) find that loyal customers might have reached their full value in the service relationship in terms of the number of financial services purchased and might be less likely to purchase additional services, despite receiving direct mail with a call for action. Mark et al. ( 2019 ) develop a dynamic segmentation model of channel choice and purchase frequency to assess the responsiveness of segments to direct mail and email. They find that direct mail is an effective tool at influencing purchases in both offline and online channels. However, none of these studies consider how response to direct mail might vary for prospects versus acquired customers over time, in online and offline channels, and assessed with consumer transactional data in an econometrics analysis or a randomized field experiment (see Table 1 ).
Email effectiveness
Emails are effective in driving sales response for several reasons. First, they enable marketers to reach their customers at a low cost. Chittenden and Rettie ( 2003 ) report that the total cost per 5000 customers for email campaigns is $26,500 versus $69,600 for direct mail, so email costs about 38% of direct mail. Second, emails provide information that motivates customers to visit the physical store (Tezinde et al., 2002 ). Emails drive sales (Danaher & Dagger, 2013 ), average spending (Kumar et al., 2014 ), and customer retention (Drèze & Bonfrer, 2008 ). Third, emails may generate faster responses and create an opportunity for interactive communication with customers; customers can respond to an email the moment they receive it on their computer or mobile device.
As to cross-channel effects, emails make it more convenient for customers to use the online (vs. offline) channel because they can land on the firm’s web page by clicking on the email links. Ansari et al. ( 2008 ) find that emails have a positive effect on online sales but a negative effect on offline sales. Sahni et al. ( 2017 ) conduct a post hoc analysis of experiments and show the aggregate-level effects of emails on expenditure. Similarly, Zhang et al. ( 2017 ) capture the average effect of a customer’s response to emails on purchase.
Finally, several meta-analyses find that marketing effectiveness varies across countries and that country effects moderate the elasticity of advertising (Sethuraman et al., 2011 ) and promotions (Kremer et al., 2008 ). Importantly, this evidence comes mostly from a comparison between mature and emerging markets, whereas our data are from mature markets. In addition, as Table 1 shows, these studies do not consider cross-channel effects of marketing actions, except for a few single-country works (Pauwels & Neslin, 2015 ; Valentini et al., 2011 ).
Direct mail and email comparison in consumer segment response
How do direct mail and email compare in consumer responses? In surveys, 70% of Americans find direct mail more personal than email (Direct Marketing Association, 2020 ). Consumers view direct mail as more believable, formal, and important and email as quicker, more informal, and spontaneous (Niblock, 2017 ). While 56% of consumers note that direct mail makes them feel valued, only 40% indicate such about email (Niblock, 2017 ). When delving deeper into why this is so, consumers report that direct mail is tangible and real (Bozeman, 2019 ) and, “as a physical object, provides the space and time needed to appreciate what the company sends” (Medlar, 2017 ).
Regarding differences among consumer segments, direct mail’s trustworthiness and ability to evoke feelings of being valued might be more important for prospects than for current customers. Only 44% of consumers could recall the brand right after seeing a digital ad, while 75% could recall it after receiving direct mail (Niblock, 2017 ). Consumers prefer to receive direct mail for brochures and catalogs (63% vs 21%) and welcome packs (62% vs 23%) but prefer emails for news and updates (62% vs 17%) and confirmation or follow-up messages (57% vs 21%) (Niblock, 2017 ). While direct mail “appeals to … prospects in a very different way – a more emotional way” (Medlar, 2017 ), email is read while at work or relaxing at home and “doesn’t feel the same … as opening a piece of direct mail does” (Bozeman, 2019 ). Moreover, the physicality of direct mail versus email provides the space to communicate more creatively (Levinson, 2019 ), which might be more appealing for prospects who know less about the company offering.
Contributions
This research makes substantive and methodological contributions to the marketing literature on multichannel resource allocation (see Table 1 ). First, from a substantive standpoint, it tackles an important marketing mix resource allocation problem facing multichannel retailers—namely, how to allocate online and offline marketing actions given the different responses in channels and customer segments, including prospect and dormant customers. This research is the first to show that sending direct mail—the most expensive marketing action—to the highest-value customers results in lower performance. Our model-based results in several countries and across retailers, confirmed by a field experiment, show that retailers should allocate direct mail for customer acquisition. From a practice perspective, our decision-support system is embedded in a beauty retailer’s decision processes (Lilien, 2011 ).
Second, from a methodological perspective, we adopt an integrated approach to assess the effectiveness of email and direct mail, per channel and segment. Inspired by the iterative model-experiment decision-making procedure (Hanssens & Pauwels, 2016 ), we also assess our model-based findings in a field experiment. Fischer et al. ( 2011 ) similarly propose a decision model to guide marketing resource allocation in a business-to-business health care setting by determining near-optimal marketing budgets at the country–product–marketing activity level in an Excel-supported environment. Our approach differs from theirs in three ways. First, they do not obtain insights into direct mail and email effectiveness for customer segments, which are of academic and managerial interest. Second, their approach lacks an experimental field test, which is helpful for normative implications that prescriptively guide marketing resource allocation. Third, they analyze their budget allocation estimations under the assumption of the specific response function that best represents the data in their study. Instead, we use more flexible econometric estimation techniques.
Methodological approach
Modeling requirements.
Our research objectives impose several methodological requirements. First, the modeling approach should allow for customer heterogeneity. An important decision is whether customer heterogeneity should be captured at the individual or segment level. We refer to aggregate segment-level models for three reasons: (1) we compare current customers with prospects and dormants, for whom historical purchase data are not available; (2) our objective is to support strategic decision-making on marketing resource allocation, and therefore we follow the literature on such models, which are typically at the aggregate level (e.g., Fischer et al., 2011 ; Hanssens et al., 2014 ; Srinivasan et al., 2016 ); and (3) targeting-related privacy concerns loom large when using consumer-level data, and scholars in the RFM tradition have advocated for summarizing consumer purchase histories and using data-compressed variables for modeling (e.g., Zhang et al., 2014 ).
Second, when confronted with email and direct mail campaigns, customer segments may exhibit different purchase behavior because of differences in overall consumption levels (i.e., intercept heterogeneity) and variations in their responses to email and direct mail campaigns (i.e., slope heterogeneity). These sources of variation are referred to as unobserved heterogeneity (Jain et al., 1994 ). Thus, our model should be flexible in accommodating unobserved heterogeneity among customer segments.
Third, we require a model that involves online and offline channels simultaneously and allows for cross-channel correlation. This enables us to account for channel variation in marketing responsiveness of each customer segment and consider the dependence between online and offline channels. These requirements lead us to estimate a multi-equation HLM (Leckie & Charlton, 2013 ) with two levels, with time-series observations nested within customer segments. Finally, because consumer segments could differ by country, we estimate our model separately for each country.
Thus, we develop and implement a multimethod modeling approach plus a field experiment to address retailers’ marketing problem. Table 2 outlines this approach, which combines customer value segmentation and cluster analysis (descriptive), econometric analyses through multi-equation HLMs (predictive), reallocation of marketing resources (prescriptive), and a field experimental study (causal).
Empirical methodology
Quantify customer value.
We quantify customer value with the RFMC approach because it only requires customer purchase history and can be readily implemented by managers (Zhang et al., 2014 ). Footnote 2 The RFMC approach is an extension of the traditional RFM, which is widely used for customer valuation (Gupta et al., 2006 ), and adds the clumpiness metric. Clumpiness is the degree of nonconformity to identical spacing in purchasing, and its addition helps achieve improved customer valuation and predictive accuracy (Zhang et al., 2014 ). We operationalize clumpiness using the entropy measure. Footnote 3
Create customer segments
We create customer segments according to the standardized RFMC metrics in each country using k-means cluster analysis, an approach preferred for large data sets (James et al., 2013 ). Footnote 4 We use the Euclidean distance as the dissimilarity measure (Gordon, 1999 ). As a starting point for the clusters’ centroids, we use the quantiles of the standardized RFMC values because we want to obtain clusters that reflect a customer value continuum. For example, for a four-cluster solution, the starting points are the 20%–40%–60%–80% values of each standardized RFMC metric. In consultation with the beauty retailer, we opted for a static segmentation to ensure managerial tractability and ease of implementation, given the firm’s annual marketing budget allocation. Importantly, we consider two additional customer segments, prospects and dormants, for which RFMC values cannot be computed because data are not existent or not available because they have not purchased for a long time.
Evaluate responsiveness to emails and direct mail
We estimate multi-equation HLMs to assess online and offline sales responsiveness to emails and direct mail by customer value segment (Leckie & Charlton, 2013 ). Specifically, for each country, we use a two-level structure in which time-series observations are nested within customer value segments (Auer & Papies, 2020 ; Rabe-Hesketh & Skrondal, 2008 ; Raudenbush & Bryk, 2002 ). Similar to Steenkamp and Geyskens ( 2014 ), we develop our model formulation for each level to arrive at the equation we estimate.
We include variables that vary with time as predictors in the level 1 formulation. Equations ( 1 ) and ( 2 ) include all the time-varying predictors (subscripts t and i denote time index and customer value segment index, respectively). Because we deal with time-series data, we specify a k th –order autoregressive terms to account for the autocorrelations in the residuals. Footnote 5 Thus, for both offline and online equations, we formulate level 1 as follows:
Across time within a customer value segment
where the superscripts off and on indicate that the coefficient is for the offline and online equation, respectively, OFF_SALES and ON_SALES stand for offline and online sales, and EMAIL and DIRECT_MAIL stand for email and direct mail. Moreover, DISC is the discount variable that controls for the applied promotions, and HOLIDAY is a categorical variable that captures the effect of major holidays. Footnote 6 The error terms, \({\varepsilon}_{ti}^{off}\) and \({\varepsilon}_{ti}^{on}\) , follow a bivariate normal distribution with zero mean and time-invariant variance–covariance matrix, \(\Omega =\left[\begin{array}{cc}{\sigma}_{off}^2& {\sigma}_{off, on}\\ {}{\sigma}_{on, off}& {\sigma}_{on}^2\end{array}\right]\) . Thus, Ω is nondiagonal; that is, the errors of the two equations are correlated (Leckie & Charlton, 2013 ).
The level 1 equations suggest that the intercepts and slopes of the email and direct mail variables vary across customer value segments. Level 2 includes these varying parameters from level 1 as dependent variables:
Across customer value segments
Equation ( 3 ) shows that overall offline sales in segment i are a function of a baseline ( \({\alpha}_{00}^{off}\Big)\) and a segment-specific intercept ( \({\alpha}_{0i}^{off}\) ). Similarly, Eq. ( 4 ) shows that overall online sales in segment j are a function of a baseline ( \({\alpha}_{00}^{on}\Big)\) and a segment-specific intercept ( \({\alpha}_{0i}^{on}\) ). Equations ( 5 )–( 8 ) specify the slopes of the email and direct mail variables as fixed across time and varying across segments. For example, the slope for email in the offline sales equation is a function of the overall effect ( \({\delta}_{00}^{off}\) ) and a segment-specific effect ( \({\delta}_{0i}^{off}\) ). Footnote 7
We combine the two levels in a single formulation, as shown in Eqs. ( 9 ) and ( 10 ):
Model Estimation
We estimate the model simultaneously using maximum likelihood for each country, allowing the errors of the equations to be correlated (Leckie & Charlton, 2013 ). We focus on the combined significance of the parameter estimates across countries using the meta-analytical test of added Z’s (Rosenthal, 1984 ), because our main interest is in the overall effects of online and offline marketing actions (ter Braak et al., 2014 ). This test allows us to derive more generalizable insights because it combines evidence of the six countries in our data. The effect size of the parameters are the weighted mean response elasticity parameters across countries. The weight is the inverse of the estimate’s standard error, normalized to 1. Thus, weighted coefficients can be interpreted as a reliability-weighted mean, with estimates with higher reliability (lower standard error) obtaining a higher weight (ter Braak et al., 2014 ).
Endogeneity
Our explanatory variables may not be strictly exogenous. For example, managers may set email and direct mail levels according to certain customer responsiveness. This type of endogeneity can be overcome by using exclusion restrictions. In the “Robustness checks” section, we derive these exclusion restrictions and explain how we use the control function (CF) approach to account for this source of endogeneity exploiting multi-country data (Papies et al., 2017 ; Wooldridge, 2015 ). In addition, we conducted a field experiment that assesses the causal effects.
Obtain out-of-sample predictions
We compare the forecast accuracy of the proposed HLMs with several benchmarks. We re-estimate the model parameters holding out 15% of the estimation period to evaluate prediction accuracy. We use three benchmarks commonly used by managers: random walk (i.e., the value in the previous period), last value in the estimation period, and mean of the country’s customer segment in the estimation period. We also use two machine learning models as benchmarks: random forests and support vector machines (Hennig-Thurau et al., 2015 ; Zhang & Chang, 2021 ). We evaluate the forecast accuracy with two measures: mean absolute error (MAE) and mean absolute percentage error (MAPE).
Reallocate optimally emails and direct mail
We (re)allocate emails and direct mail using the HLM estimates that incorporate customer value segments as drivers of marketing effectiveness, under the constraint of management’s maximum total number of emails and direct mail to avoid consumer fatigue and backlash (see Web Appendix A instead for a reallocation setup under the constraint of a total monetary budget). In doing so, we obtain the online and offline contributions in terms of sales increase per unit of email and direct mail per customer segment in each country (Dinner et al., 2014 ). For a given customer segment, we define the constrained resource allocation decision as
where Π is a differentiable profit function, m is the contribution margin (%), OFF _ SALES is offline sales, ON _ SALES is online sales, c em is the unit cost of emails (€), and c dm is the unit cost of direct mail (€). We note that the feasible region is compact by Eq. ( 11 ), and therefore Π attains a local maximum on the feasible region according to the Weierstrass theorem (Sundaram, 1996 ). Thus, the solution of this problem is characterized by the Karush–Kuhn–Tucker (KKT) conditions, which we develop in detail in Web Appendix B . Since the beauty retailer had upper bounds for both email and direct mail campaigns, the net returns of email ( NR em ) become:
Assuming c em is constant, we define NR em = FC em − c em , where FC em denotes the financial contribution of emails. Then, as the short-term elasticities of offline and online sales with respect to number of emails are \({\eta}_{off, em}=\frac{\partial OFF\_ SALES}{\partial EMAIL}\ \frac{EMAIL}{OFF\_ SALES}\) and \({\eta}_{on, em}=\frac{\partial ON\_ SALES}{\partial EMAIL}\ \frac{EMAIL}{ON\_ SALES}\) , we can define FC em as
Similarly, the financial contribution of direct mail is
International beauty retailer data
We obtained data from L’Occitane en Provence, an international natural and organic ingredient-based beauty and wellness products retailer. Its product portfolio includes skin care, hair care, fragrance, and body and bath offerings, and stores exclusively sell their own products. In addition to the brick-and-mortar stores, the company sells online through an e-commerce website for each country. These websites do not differ across countries, beyond the different languages.
The purchase transaction data, which cover four years between 2011 and 2014, include both online and offline transactions and discounts at purchase at the individual customer level for 84,110 customers. We randomly sampled customers from the firm’s six main countries: United States, Great Britain, Germany, France, Spain, and Italy. The data comprise prospect, dormant, and active customers.
The marketing communication data, which cover the years 2013 and 2014, contain all the online and offline communications from the retailer. The only online communication the retailer uses is email, and the data include whether and when the email was received, opened, and clicked. The only offline communication is direct mail, and the data include the start and end dates of the direct mail campaigns. According to the retailer’s management, the content is typically the same for both marketing actions; we employed two independent coders to confirm that this is the case for a sample of 385 emails and direct mail pieces from the United States and Great Britain (both were in English, the native language of the coders).
Beyond emails and direct mail, the company offers discounts, which we treat as a control variable in our model (Srinivasan et al., 2010 ). During the analysis period, the prices were the same in both the online and offline channels in each country. The firm has email and postal addresses for 42% and 65% of its customers, respectively. Footnote 8 In addition, the firm has the contact information of multiple prospects, who have shown interest in the brand at the point of sale or website but have not yet purchased from the firm.
Data operationalization
For the operationalization, we specify emails as an email sent, instead of “opened,” because emails sent represent a firm marketing decision. We operationalize the direct mail variable as 1 divided by the length of the campaign for each week of the campaign, because we do not know the exact day customers received the direct mail and thus must assume a constant impact throughout the campaign. We measure discount as the value amount of the discount (Wiesel et al., 2011 ). Finally, we test for seasonality by considering all periods, as in Srinivasan et al. ( 2004 ), but we find that seasonality occurs only for the Christmas period. We therefore create a dummy variable that takes the value of 1 between weeks 47 and 52 around the Christmas holiday. Table 3 provides descriptive statistics of the variables by country.
We aggregate the data at the weekly level to obtain a panel of customer transactions and marketing actions. We used 96 weeks of data for the calibration period to compute RFMC metrics and to create customer value segments. For the estimation of the HLMs, we used between 51 and 60 weeks, depending on data availability per country. These HLMs use log-transformed data to reduce skewness in the variables, to facilitate interpretation of the coefficients directly as elasticities, and to make comparisons among marketing actions, segments, and countries feasible; the estimated elasticities are the basis of the recommended effective marketing resource (re)allocation.
US apparel retailer data
We obtained data for a second retailer on all purchases and marketing communications for 23,891 randomly selected customers in the United States from 2010 to 2012. The retailer’s products, apparel and accessories targeted at women, are sold exclusively through company-owned brick-and-mortar stores or through the retailer’s own website. Similar to the beauty retailer, the retailer’s only online (offline) communication channel is email (direct mail). Moreover, this retailer has a different marketing approach than the beauty retailer; it allocates a larger proportion of emails to the medium- and high-value segments, while direct mail allocation is proportional to the size of the segments. Web Appendix C provides descriptive statistics.
Model-free evidence
We first explore the relationship between both direct mail and email and sales. We do so without imposing any structure in the data by examining the correlations at the individual customer level for the three predefined customer groups: prospects, dormants, and current customers.
As shown on Table 4 , the correlations between direct mail and sales are larger for prospects than for both dormants and current customers in four of the six countries (US, Great Britain, Germany, and Spain), while the correlation for prospects is of similar magnitude as for current customers in two countries (France and Italy). In contrast, for emails, the correlations with sales are mostly negative across these three customer groups and six countries and without a clear pattern of correlation magnitude. These results suggest that direct mail might be more effective for prospects.
Econometric analysis results
We begin with the results of the econometric analysis of the historical transaction data for both retailers. Then, we present several robustness checks where we: (1) specify a three-level cross-random-effects (CRE) model to evaluate sales variation drivers, (2) estimate a three-level HLM that combines all six countries, (3) estimate the HLM model with a Bayesian approach, and (4) assess endogeneity with the CF approach. We describe the field experiment design and results in the subsequent section.
International beauty retailer results
Customer value segments.
We compute customer value in terms of the RFMC metrics for each customer. With these metrics, we then create customer value segments using cluster analysis. Footnote 9 From the comparison of different cluster solutions (see Web Appendix D ), we obtain seven segments in the United States and Italy and six segments in Great Britain, Germany, France, and Spain. In each country, two segments consist of prospects and dormants, that is, customers who have never purchased from the retailer and customers who did not purchase during the two-year calibration period but have purchased before from the retailer. We label the other segments (i.e., consumers who made purchases during the calibration period) as nonrecent low value, recent low value, medium value, high value, and very high value. Table 5 reports the results of the cluster analysis. The table shows the breakdown of the customer value segments by country and the means and standard deviations of the RFMC metrics.
Prospects and dormants in combination represent at least half the customer base in all countries. However, there are notable country-specific differences: the United States has a larger proportion of prospects (38%) and a lower proportion of dormants (26%), while Great Britain has a larger proportion of dormants (40%) and a lower proportion of prospects (10%). The two low-value segments have similar levels of frequency, monetary value, and clumpiness but differ on the recency dimension. The recent low-value segment (nonrecent low-value segment) purchased, on average, eight weeks (one and half years) before the end of the calibration period. The United States (13%) and France (14%) have a lower proportion of these two segments. The medium-value segment mirrors the population average for the four metrics, while the high-value segments have large values of both frequency and monetary value. All countries are fairly similar in terms of the proportion of medium- and high-value customers, ranging from 25% to 30%, except the United States, which has a slightly lower representation of these customers (22%).
Effectiveness of direct mail and email
We estimate the HLMs with maximum likelihood estimation. All variables are stationary according to the augmented Dickey–Fuller and Levin–Lin–Chu panel unit-root tests (see Web Appendix E ). We check for homoskedasticity of the residuals (see Web Appendix F ). To determine the number of autoregressive terms, we test for residual autocorrelation, adding lags until the autocorrelation has been purged from the residuals; this resulted in two lags for the autoregressive terms. Our empirical findings suggest that random-effects components are not statistically significant in any of the six countries, and therefore a fixed-coefficients specification should be employed. Thus, in our models, we capture segment-level customer heterogeneity through the fixed-coefficients specification.
Table 6 presents the main results on the offline and online sales elasticities of email and direct mail for value segments consolidated across countries (ter Braak et al., 2014 ). Direct mail has positive and significant offline sales effects for prospects (.164, Z = 3.940, p < .05). The magnitude of the estimated direct mail elasticity is in line with expectations from previous research: Danaher and Dagger ( 2013 ) report .104 as an average direct mail elasticity. and Danaher et al. ( 2020 ) find catalog elasticities of .02 (online) to .03 (in-store). Email, by contrast, has positive and significant online sales effects for medium- and high-value segments (.432, Z = 1.793 and .478, Z = 1.764, both p < .1). We present the HLM estimation results for each country in Web Appendices H and I and the long-term elasticities in Web Appendix J .
In summary, we find important differences in the effectiveness of email and direct mail for channels and value segments. First, email has sales effects on medium- and high-value segments, while direct mail works only for prospects. Second, email has online sales effects, while direct mail has offline sales effects.
Out-of-sample forecasts
We compare the conditional forecast results for the last 15% of observations, for which the brand’s marketing-mix decisions are known. We obtain the forecasts from three traditional benchmarks (i.e., mean of customer value segment per country in the estimation period, the last period value in the estimation period, and a random walk) and from two machine learning models (i.e., random forest and support vector machines). As Table 7 shows, the best forecast accuracy comes from the HLM, given that it exploits the cross-sectional, time-series, and hierarchical structure of the data. Footnote 10
US apparel retailer results
For the second retailer, we compute the RFMC metrics for each individual customer at the weekly level for a calibration period of one year. We then segment the customer base according to the RFMC metrics into six segments to facilitate comparisons with the beauty retailer analysis. Table 8 shows that the proportion of customers in each segment is prospects (14%), dormants (7%), nonrecent low value (26%), recent low value (16%), medium value (34%), and high value (3%). We then evaluate the responsiveness to emails and direct mail in the estimation period consisting of 52 weeks.
Our results shown in Table 9 confirm the findings of the main analysis that own- and cross-channel effects of emails and direct mail vary by customer value segment. Specifically, direct mail has both offline and online effects for dormants (.02, p < .05; .05 p < 0.05, respectively), while email only has offline effects for both prospects and dormants (.12, p < .01; .14 p < 0.01, respectively). Notably, email shows only offline effects, and direct mail shows both offline and online effects.
Robustness checks
We test whether the results are robust to capturing country heterogeneity in a single main model, instead of having a separate model per each country. For the beauty retailer, first, we estimate three-level CRE models to evaluate the extent to which sales variation is explained by each possible level: time, customer value segment, and country. Second, we estimate a three-level HLM to incorporate country as a third level. We also present the robustness of our results to a Bayesian estimation and a CF approach.
Assessment of sales variation drivers
Similar to Hanssens et al. ( 2014 ), we estimate CRE models to examine the sales variation drivers. The CRE models show that for offline sales, customer value accounts for 90% of the explained variance, and country effects and time effects account for 8% and 2%, respectively. However, we find important differences for online sales—country effects explain as much as 50% of the explained variance, while customer value and time effects account for 42% and 8%, respectively. Thus, both country effects and customer value are essential to understand online sales variation, while customer value explains the majority of offline sales variation. All in all, the CRE results provide further empirical support for using multichannel marketing for customer value segments.
Analysis of countries jointly
Our model is flexible to allow resource allocation for customer segments at the global corporate level. That is, instead of six two-level HLMs, we estimate a three-level model, in which we constraint the number of segments to be the same in each country. This approach may be preferred by multinational retailers whose decisions for within-country allocations of expenditures between emails and direct mail are centralized. The number of optimal segments per country is six. The results are similar to the main results in both signs and significance. Specifically, the main finding that the most expensive marketing action, direct mail, is effective in driving customer acquisition of prospects in the offline channel holds (see Web Appendices K and L for details).
Bayesian estimation
To confirm that the results are not driven by the estimation procedure, we estimate the HLMs with a Bayesian approach for the main models and an alternative model with random intercepts, instead of fixed intercepts as in the main model. The results are similar to the main estimations in both signs and significance (see Web Appendix M ).
CF approach
The marketing communication variables might be correlated with the error term. Such endogeneity can be overcome using exclusion restrictions. We explore the possible estimate bias with a CF approach (Papies et al., 2017 ; Wooldridge, 2015 ), which is equivalent to the two-stage least squares approach for linear models but uses fitted values of the first stage as additional regressors in the second stage. To construct instruments for each country, we use the level of marketing in the other countries (Kuebler et al., 2018 ). The assumption is that country managers do not consider the sales levels of other countries when determining the marketing actions for a focal country (exclusion restriction). That is, managers set marketing actions levels expecting a response on the consumers they impact, i.e., customers in their country of responsibility and not in other countries. At the same time, managers follow similar strategies per segment across countries, and therefore marketing actions in the same segment may be correlated across countries (relevance condition). Indeed, the correlations between the instruments and the endogenous variables fall in the ranges of .88 and .94 for direct mail and .72 and .88 for email, supporting our assumption on the relevance condition.
The CF analysis largely confirms the main analysis results. The CF estimates coincide in terms of direction and significance with those of the main analysis, except for the effect of email on online sales for high-value customers in the United States (see Web Appendix N ). The instruments for the offline sales model are not significant (−.010, p > .1 and .064, p > .05, for direct mail and email, respectively), suggesting that the estimates of the offline sales model in the main analysis are not biased. However, the instruments for the online sales model are positive and significant (.112, p < .05 and .161, p < .05, for direct mail and email, respectively). When we account for this positive bias, the online equation results in a nonsignificant effect of emails for high-value customers in the United States. Moreover, the magnitude of the effect of email on online sales for high value customers in Italy and France is reduced but remains significant. All other results remain the same.
- Field experiment
Field experiment design
The main goal of the field experiment is to test the model-based findings on the differential effects of emails and direct mail by customer value segment in a controlled causal setting. We designed and implemented the experiment together with the marketing team of the beauty retailer between July and November 2017 in Italy. The four experimental cells are (1) control (no marketing), (2) only emails, (3) only direct mail, and (4) both emails and direct mail. To ensure a balanced proportion in each cell, we stratified each cell in the six customer value segments. To create the six segments, we obtained individual-customer purchase data spanning two years before the experiment. The field experiment took into account customers’ expressed preferences not to be contacted by certain channels and therefore was run on a sample of customers contactable by both channels, to avoid self-selection, to compare email and direct mail responsiveness in online and offline channels. Although a pure random assignment should result in each segment being equally represented in the four experimental cells in theory, proportionate stratification ensures that all segments are equally represented in each cell in practice (Duflo et al., 2007 ). This stratification is especially important because the total amount of direct mail was constrained for budgetary reasons to 33,000 pieces, and we wanted to ensure that high-value customers, who are a small fraction of the overall population, are proportionally represented in cells 3 and 4. The total sample consists of 122,394 customers (Table 10 ).
To evaluate the differential effects of the treatment groups, we specify a random-effects regression for customers in the prospect and dormant segments, because the treatment is exogenous (Chintagunta et al., 1991 ). For customers in the other four value segments, we specify a difference-in-differences regression, because the treatment is exogenous and customers in these segments purchased within the two-year period before the experiment. We run a separate regression per each segment, in which customer sales ( SALES ) vary per customer (index i ) and week (index t ). Equation ( 14 ) presents the random-effects regression and considers only the campaign period because prospects and dormants did not purchase before the experiment. Equation ( 15 ) presents the difference-in-differences regression and considers the campaign period and the two years prior.
where α i represents the customer-level intercept; CELL2 , CELL3 , and CELL4 capture whether the customer belongs to cells 2, 3, and 4, respectively; 𝛾 t represents time fixed effects; CAMPAIGN is a dummy variable that takes the value of 1 if the period belongs to the campaign and 0 otherwise; and ε it is the residual error. The coefficients of interest are β 2 , β 3 , and β 4 for Eq. ( 14 ) and β 5 , β 6 , and β 7 for Eq. ( 15 ).
Field experiment results
Figure 1 shows the results of the field experiment on the differential effectiveness of email and direct mail for different consumer value segments. First, we confirm that direct mail is only effective for prospects, with an elasticity of .132 ( p < .05), compared with the .164 estimate in the main analysis. Second, email is not effective for any of the segments, while it was significantly effective for medium- and high-value segments in the main analysis. Third, direct mail and email in combination (interaction effects) are effective for the medium-value segment (.011, p < .05), while the two marketing actions did not interact significantly in the main analysis; this effect, though significant, is small.
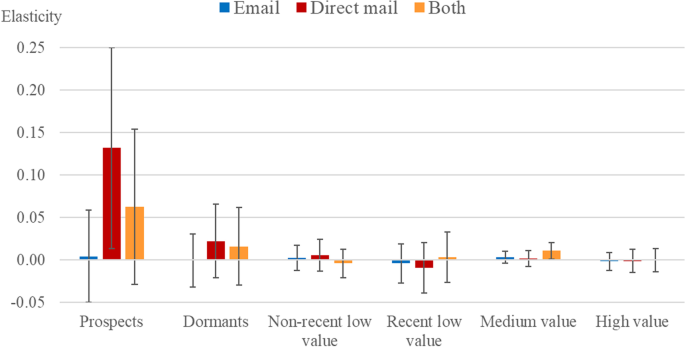
Email and direct mail effectiveness from field experiment for beauty retailer. Notes: Confidence level of error bars at p < .05.
Managerial implications
We calculate revenue lifts from (1) the econometric analysis of the beauty retailer data, (2) the econometric analysis of the apparel retailer, and (3) the field experiment. To calculate the financial contribution of emails and direct mail (Eqs. ( 12 ) and ( 13 )), we take the elasticity estimates from the empirical models and the mean levels of sales, emails, and direct mail per customer segment from the data. According to the beauty retailer’s annual report (L’Occitane, 2015 ), the cost of goods sold is 18%, and therefore we infer that the profit margin is 82%. Keeping the total number of emails and direct mail constrained in each country and holding the budget constant, Footnote 11 we assess how much the reallocation of marketing resources would improve the financial contribution.
Figure 2 compares the current allocation of marketing resources with the proposed reallocation and reports the sizes of the customer value segments (see Web Appendix O for details by country). For emails, the current allocation is proportional to the size of the customer value segments (i.e., “bigger gets more”; Corstjens & Merrihue, 2003 , p. 118); our reallocation proposes to reduce emails for prospects, dormants, and recent low-value segment and to increase them for nonrecent low-, medium-, and high-value segments, based on their response elasticities and segment sizes. For direct mail, the current allocation disproportionally considers the medium- and high-value segments and disregards prospects (i.e., the most expensive action for the most valuable customers); our reallocation suggests shifting direct mail to prospects. We evaluate the incremental revenue from the proposed reallocation by multiplying the financial contribution of the segment by the difference between the model-based proposed number of emails and direct mail and the actual number sent by the retailer based on the HLM.
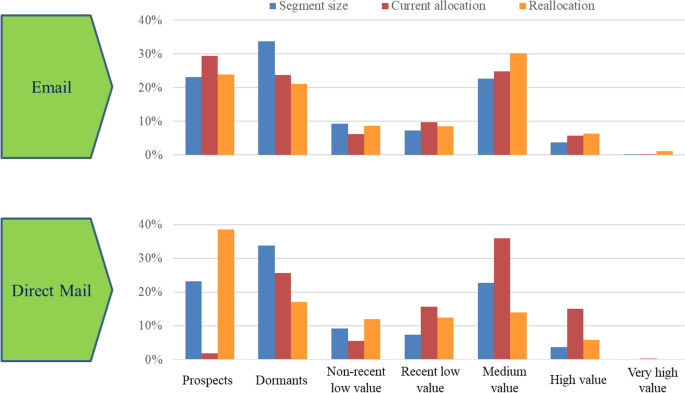
Effective reallocation of emails and direct mail for beauty retailer
Our reallocation of marketing actions would yield a sales lift of €340,000, 33% due to better allocation of emails and 67% due to better allocation of direct mail, which represents a 13.5% total revenue increase. Given the beauty retailer’s size, the global implementation of the proposed reallocations would amount to hundreds of millions of euros in incremental revenues. Footnote 12 For the apparel retailer, the effective reallocation of marketing actions would yield a sales lift of $26,000, 84% due to better allocation of emails and 16% due to better allocation of direct mail, which represents a 9.3% revenue increase.
Finally, we quantify the revenue lift potential with a marketing resource allocation that considers the field experiment estimates. We compute the revenue lift with respect to the status quo of the typical marketing allocation used by the retailer, as this condition is not present in our experimental cells ( CELL1 in the experiment receives no marketing, which is not business-as-usual). Collectively, the marketing resource reallocation from the field experiment findings lifts revenue by 6.5% with respect to business-as-usual, holding marketing costs constant. The business-as-usual allocation has a revenue impact lift of 1.6% with respect to the control group of no marketing actions. Thus, we expect that a chainwide implementation of these recommendations will result in a lift of between 6.5% (from the field experiment) and 13.5% (using HLMs) in revenue for the beauty retailer.
Communication of these insights to the beauty retailer helped management adopt data-driven analytical tools and blend quantitative approaches with managerial intuition (Roberts, 2000 ). As one member of the marketing team noted: “The different effectiveness of direct mail and email depending on the customer type was surprising to us. Rethinking about this finding, we have a deep and increasing interest in investing in direct mail activities for customer acquisition and inactive customers.” The model-based recommendations helped the retailer embrace scientific decision-support systems and provided an opportunity to use marketing analytical dashboards with hands-on practice. In the words of Delphine Fournier, customer relationship management manager of L’Occitane: “The combination of marketing science tools with experimentation gives us a new perspective in understanding marketing effectiveness and helps us improve our resource allocation tremendously” (ISMS Practice Prize, 2018 ). L’Occitane has since implemented this model-based decision-making procedure consisting of iterative, model experiment, phases (Hanssens & Pauwels, 2016 ), and embedded marketing science models into its decision processes (Kumar & Petersen, 2005 ; Lilien, 2011 ).
Conclusions
Understanding online and offline sales responsiveness to email and direct mail for multichannel retailers is essential for academics and practitioners. Accordingly, we propose a systematic approach to quantify how email and direct mail influence online and offline sales for different customer value segments across countries. We conduct an empirical analysis using data from a beauty retailer with 84,110 customers from six countries and run a field experiment with 122,000 customers in one country for the retailer. We replicate the econometric analysis for an apparel retailer. In addition, we conduct several robustness checks to assess the validity of our findings.
This research provides four key insights. First, direct mail drives customer acquisition in the offline channel, while email drives both online and offline sales across different customer segments. Second, the model performs considerably better than benchmarks (up to 50%) in forecasting sales for channels and countries. Third, a reallocation of the marketing budget for customer value groups shows substantial revenue improvement of 13.5% for the HLM-based analysis and a revenue lift of 6.5% in the field experiment. Our model can be readily applied to other settings, as indicated by the 9.3% calculated revenue improvement for the apparel retailer. Moreover, the results of the field experiment in one country provide causal support for our empirical model findings.
Our findings challenge common wisdom, though they are consistent with surveys on different consumer experiences with direct mail versus emails. Receiving an expensive direct mail is more likely than an email to attract the attention of customers who have never purchased or stopped purchasing a while ago (dormants). This interpretation fits the broader consumer behavior theory that affective reactions are critical (e.g., Hoch & Loewenstein, 1991 ; Shiv & Fedorikhin, 1999 ); we would also add that emotional appeals are especially important to attract the attention of and gain new customers, while current customers do not need them to the same degree.
We offer several important insights for retail managers operating in a multichannel context. To allocate marketing resources effectively, managers should pay close attention to the different responsiveness of customer value segments to emails and direct mail. Both customer value and country effects are relevant to understand the online sales variation, even among the similar Western countries we analyzed. Our methodology can help retailers forecast future sales and optimally allocate marketing resources. Several of our insights may inspire companies to reassess how they run their email and direct mail campaigns. First, a customer’s “high-value” status with the company does not mean greater responsiveness to marketing actions. In our analysis, we find that such customers are less responsive to the (very expensive) direct mail. Second, as newly penetrated countries typically have a higher share of prospective customers and light buyers, direct mail resources might best be allocated to such countries. Finally, customer privacy issues have become even more important with recent legal developments, such as the GDPR, raising the stakes for companies to identify and target responsive customers.
This research has limitations that suggest directions for future research. First, we did not examine the order of emails and direct mail; thus, future research could test the ideal sequencing of email and direct mail, as “email makes for the perfect follow up to a direct mail campaign” (Bozeman, 2019 ) and companies should “create a lasting first impression with direct mail [and] reinforce it with email marketing” (Niblock, 2017 ). Future research could also explore a continuous (discrete) time dynamic optimization model through which Hamiltonian (Bellman) equations would be specified. Second, our data do not include competitors’ marketing actions. However, for both retail data sets used, the own-brand products are sold exclusively by the companies in question, rendering competition only indirect. Furthermore, future research could quantify marketing’s power to build long-term brand equity or to upgrade customers to higher-value segments. Our methodology can also be applied beyond the studied developed Western markets (e.g., developing countries), the analyzed product categories, and the studied channels (e.g., mobile) or marketing actions (e.g., phone calls, text notifications). In this study, we propose and implement a generalizable methodology for marketing resource allocation, which can be applied by any multichannel (multinational) retailer, whether they sell products or services, and can accommodate any number of countries, sales and communication channels. Finally, we call for future research to examine other regions to determine whether the findings generalize to non-Western countries.
Survey with N = 351, average experience = 3.8 years. The remainder (13%) agreed with the statement, “The most expensive communication should be sent to the least valuable customers.”
Other data (e.g., demographics, preferences, needs, attitudes) were not available for our partner companies.
Zhang et al. ( 2014 ) propose four measures (entropy, second moment, log utility, and sum of three largest components) and show that entropy is the most robust with the best performance.
Marketers have a long history of working with both a priori segmentation and latent response segments (e.g., Kamakura & Russell, 1989 ). The latter requires observing marketing response and leaves explaining the observed response differences to other analyses (e.g., comparing a priori customer characteristics to make the latent segments addressable). By contrast, a priori segmentation uses variables the company can observe (e.g., demographics) and then shows how marketing responses differ between these segments. A priori segmentation has evolved from demographics to customer purchase histories such as RFMC, which drive marketing response and are actionable for the company (e.g., Zhang et al., 2014 ). The evolving convention in the RFMC literature and our discussion with managers led us to choose this segmentation.
We estimated a model with heterogenous autoregressive coefficients across segments to assess whether they varied by segment. The likelihood ratio test results suggested the homogenous autoregressive coefficients across segments for all countries, except France. For France, we based our decision on the information criteria (AIC and BIC) result (see Web Appendix G), which favored the homogenous autoregressive coefficients across segments.
We estimated a model with interaction terms between the marketing actions to test whether they showed synergistic effects. Since we did not find significant synergistic effects, we choose to keep a more parsimonious specification in the model specification.
For the segment-specific intercepts and slopes, we use the fixed-effects formulation. An alternative approach is to use a random-effects specification that treats parameters as realizations of random variables following a probability distribution. To determine which specification to follow, we estimate the model with random-effects and test the significance of the random components. Our results favor the use of fixed-effects specification. We discuss this finding in the results section. This choice is also consistent with the recommendation that the fixed-effects approach should be used when the data have a small number of groups (i.e., fewer than 10) (Snijders & Bosker, 2011 ; Steenkamp & Geyskens, 2014 ).
We randomly selected the data for the econometric analysis in each country from the full customer base. Therefore, some sampled customers might not be contactable. The field experiment addresses the potential self-selection issue: we only include in the experiment the 120,000-plus customers who are contactable by email and direct mail to assess their responsiveness to both channels.
To select the number of cluster solutions, we take into account model requirement constraints, statistical criteria, and managerial considerations. We examine the reduction of variance in the RFMC metrics explained by the different number of clusters in each country. To this end, we use the comparison criteria of within-sum-of-squares, proportional reduction variance (eta coefficient), and proportional reduction error (Makles, 2012 ).
We focus on over-time forecasting validation because the HLM exploits the time-series structure as well as the cross-sectional and hierarchical structure of the data. However, we also perform a k-fold cross-validation. The fivefold validation uses 80% of the customers in a segment to predict the other 20%, rotating this approach through the full sample five times. The results based on the fivefold specification indicate an MAE and a MAPE of .732 and .265 for the offline sales equation, respectively, and .670 and .606 for the online sales equation, respectively.
The reason companies do not totally skew toward emails is twofold: (1) the optimal allocation depends on the ratio of elasticities (e.g., Dorfman & Steiner, 1954 ; Wright, 2009 ), and (2) companies want to avoid losing consumer goodwill by exceeding an unknown annoyance level of emails. We worked with the client, which set a maximum of three emails per week (seven in the United States). If we had not worked with a limit, some segments would have received two emails a day (i.e., 14 in one week), which seemed excessive to the managers.
Following Fischer et al. ( 2011 ), we also evaluate the reallocation considering the growth potential per segment and country applying a segment size multiplier. We obtain the multiplier from the growth observed in each segment. The reallocation results that consider this growth remain practically the same.
Anderson, E. T., & Simester, D. I. (2004). Long-run effects of promotion depth on new versus established customers: Three field studies. Marketing Science, 23 (1), 4–20.
Article Google Scholar
Ansari, A., Mela, C. F., & Neslin, S. A. (2008). Customer channel migration. Journal of Marketing Research, 45 (1), 60–76.
Ascarza, E. (2018). Retention futility: Targeting high-risk customers might be ineffective. Journal of Marketing Research, 55 (1), 80–98.
Auer, J., & Papies, D. (2020). Cross-price elasticities and their determinants: A meta-analysis and new empirical generalizations. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 48 (3), 584–605.
Bozeman, R. (2019). Direct mail vs email – Optimize both through the customer journey. Retrieved April 6, 2021 from https://www.postalytics.com/blog/direct-mail-vs-email/ .
Chintagunta, P. K., Jain, C. D., & Vilcassim, N. J. (1991). Investigating heterogeneity in brand preferences in logit models for panel data. Journal of Marketing Research, 28 (4), 417–428.
Chittenden, L., & Rettie, R. (2003). An evaluation of e-mail marketing and factors affecting response. Journal of Targeting, Measurement and Analysis for Marketing, 11 (3), 203–217.
Corstjens, M., & Merrihue, J. (2003). Optimal marketing. Harvard Business Review, 81 (10), 114–121.
Google Scholar
Cui, T. H., Ghose, A., Halaburda, H., Iyengar, R., Pauwels, K., Sriram, S., Tucker, C., & Venkataraman, S. (2021). Informational challenges in omnichannel marketing: Remedies and future research. Journal of Marketing, 85 (1), 103–120.
Danaher, P. J., & Dagger, T. S. (2013). Comparing the relative effectiveness of advertising channels: A case study of a multimedia blitz campaign. Journal of Marketing Research, 50 (4), 517–534.
Danaher, P. J., Danaher, T. S., Smith, M. S., & Loaiza-Maya, R. (2020). Advertising effectiveness for multiple retailer-brands in a multimedia and multichannel environment. Journal of Marketing Research, 57 (3), 445–467.
Dekimpe, M. G. (2020). Retailing and retailing research in the age of big data analytics. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 37 (1), 3–14.
Dinner, I. M., Van Heerde, H. J., & Neslin, S. A. (2014). Driving online and offline sales: The cross-channel effects of traditional online display, and paid search advertising. Journal of Marketing Research, 51 (5), 527–545.
Direct Marketing Association (2015). National client email 2015. Research report. Retrieved April 6, 2021 from https://www.emailmonday.com/wp content/uploads/2015/04/National-client-email-2015-DMA.pdf .
Direct Marketing Association (UK) (2020). Marketer email tracker 2020. Research report. Retrieved April 6, 2021 from https://dma.org.uk/uploads/misc/marketer-email-tracker-2020.pdf .
Dorfman, R., & Steiner, P. O. (1954). Optimal advertising and optimal quality. American Economic Review, 44 (5), 826–836.
Drèze, X., & Bonfrer, A. (2008). Empirical investigation of the impact of communication timing on customer equity. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 22 (1), 36–50.
Duflo, E., Glennerster, R., & Kremer, M. (2007). Using randomization in development economics research: A toolkit. In T. P. Schultz & J. A. Strauss (Eds.), Handbook of development economics (Vol. 4, pp. 3895–3962). Elsevier.
Fischer, M., Albers, S., Wagner, N., & Frie, M. (2011). Practice prize winner. Dynamic marketing budget allocation across countries, products, and marketing activities. Marketing Science, 30 (4), 568–585.
Gendusa, J. (2022). 82 direct mail statistics you should know about in 2022, PostcardMania , Retrieved August 4, 2022 from https://www.postcardmania.com/blog/direct-mail-statistics-2022 .
Golder, P. N., Dekimpe, M. G., An, J. T., van Heerde, H. J., Kim, D. S., & Alba, J. W. (2023). Learning from data: An empirics-first approach to relevant knowledge generation. Journal of Marketing, 87 (3), 319–336.
Gordon, A. D. (1999). Classification . Chapman and Hall.
Book Google Scholar
Gupta, S., Hanssens, D., Hardie, B., Kahn, W., Kumar, V., Lin, N., Ravishanker, N., & Sriram, S. (2006). Modeling customer lifetime value. Journal of Service Research, 9 (2), 139–155.
Hanssens, D. M., & Pauwels, K. H. (2016). Demonstrating the value of marketing. Journal of Marketing, 80 (6), 173–190.
Hanssens, D. M., Pauwels, K. H., Srinivasan, S., Vanhuele, M., & Yildirim, G. (2014). Consumer attitude metrics for guiding marketing mix decisions. Marketing Science, 33 (4), 534–550.
Hennig-Thurau, T., Wiertz, C., & Feldhaus, F. (2015). Does Twitter matter? The impact of microblogging word of mouth on consumers’ adoption of new movies. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 43 (3), 375–394.
Hill, S., Provost, F., & Volinsky, C. (2006). Network-based marketing: Identifying likely adopters via consumer networks. Statistical Science, 21 (2), 256–276.
Hoch, S. J., & Loewenstein, G. F. (1991). Time-inconsistent preferences and consumer self-control. Journal of Consumer Research, 17 (4), 492–507.
ISMS Practice Prize (2018). Gary L. Lilien ISMS-MSI Practice Prize Videos. Retrieved April 6, 2021 from https://lilienpracticeprizevideos.org/category/2018/ .
Jain, D. C., Vilcassim, N. J., & Chintagunta., P.K. (1994). A Random-Coefficients Logit Brand-Choice Model Applied to Panel Data. Journal of Business and Economic Statistics, 12 (3), 317–328.
James, G., Witten, D., Hastie, T., & Tibshirani, R. (2013). An introduction to statistical learning . Springer.
Kamakura, W. A., & Russell, G. J. (1989). A probabilistic choice model for market segmentation and elasticity structure. Journal of Marketing Research, 26 (4), 379–390.
Kohli, A. K., & Haenlein, M. (2021). Factors affecting the study of important marketing issues: Implications and recommendations. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 38 (1), 1–11.
Kremer, S., Bijmolt, T., Leeflang, P., & Wieringa, J. (2008). Generalizations on the effectiveness of pharmaceutical promotional expenditures. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 25 (4), 234–246.
Kuebler, R., Pauwels, K., Yildirim, G., & Fandrich, T. (2018). App popularity: Where in the world are consumers most sensitive to price and user ratings. Journal of Marketing, 82 (5), 20–44.
Kumar, V., & Petersen, J. A. (2005). Using a customer-level marketing strategy to enhance firm performance: A review of theoretical and empirical evidence. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 33 (4), 504–519.
Kumar, V., Zhang, X., & Luo, A. (2014). Modeling customer opt-in and opt-out in a permission-based marketing context. Journal of Marketing Research, 51 (4), 403–419.
L’Occitane (2015). 2015 Annual results announcement. Retrieved April 6, 2021 from https://group.loccitane.com/investors/financial-information .
Leckie, G., & Charlton, C. (2013). Runmlwin: A program to run the MlwiN multilevel modeling software from within Stata. Journal of Statistical Software, 52 , 1–40.
Lehmann, D. R. (2020). The evolving world of research in marketing and the blending of theory and data. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 37 (1), 27–42.
Lemmens, A., & Gupta, S. (2020). Managing churn to maximize profits. Marketing Science, 39 (5), 956–973.
Levinson, I. (2019). E-mail versus direct mail: Which works better? Retrieved April 6, 2021 from https://www.businessknowhow.com/directmail/ideas/compare.html .
Lilien, G. L. (2011). Bridging the academic–practitioner divide in marketing decision models. Journal of Marketing, 75 (4), 196–210.
Makles, A. (2012). Stata tip 110: How to get the optimal k-means cluster solution. The Stata Journal, 12 (2), 347–351.
Mantrala, M. K., Sinha, P., & Zoltners, A. A. (1992). Impact of resource allocation rules on marketing investment-level decisions and profitability. Journal of Marketing Research, 29 (2), 162–175.
Mark, T., Bulla, J., Niraj, R., Bulla, I., & Schwarzwäller, W. (2019). Catalogue as a tool for reinforcing habits: Empirical evidence from a multichannel retailer. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 36 (4), 528–541.
Medlar, A. (2017). Direct mail vs. email: If you can only use one, which wins? Retrieved April 6, 2021 from https://www.enthusem.com/blog/direct-mail-vs.-email-if-you-can-only-use-one-which-wins .
Morris, G. (2019). Which EU countries accept B2B emails post-GDPR. Retrieved April 6, 2021 from https://www.leadiro.com/blog/gdpr-mapped .
Naik, P. A., & Peters, K. (2009). A hierarchical marketing communications model of online and offline media synergies. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 23 (4), 288–299.
Niblock, R. (2017). Infographic: Direct mail vs email. Retrieved April 6, 2021 from https://www.digitaldoughnut.com/articles/2017/february/infographic-direct-mail-vs-email .
Papies, D., Ebbes, P., & Van Heerde, H. J. (2017). Addressing endogeneity in marketing models. In P. Leeflang, J. Wieringa, T. Bijmolt, & K. Pauwels (Eds.), Advanced methods for modeling markets (pp. 581–627). Springer.
Chapter Google Scholar
Pauwels, K., & Neslin, S. A. (2015). Building with bricks and mortar: The revenue impact of opening physical stores in a multichannel environment. Journal of Retailing, 91 (2), 182–197.
PostGrid (2022). Everything you need to know about direct mail and GDPR. Retrieved April 6, 2021 from https://www.postgrid.com/gdpr-compliance-for-direct-mail/ .
Prins, R., & Verhoef, P. C. (2007). Marketing communication drivers of adoption timing of a new e-service among existing customers. Journal of Marketing, 71 (2), 169–183.
Rabe-Hesketh, S., & Skrondal, A. (2008). Multilevel and longitudinal modeling using Stata . Stata P.
Raudenbush, S., & Bryk, A. S. (2002). Hierarchical linear models: Applications and data analysis methods . Sage.
Return Path (2015). Frequency matters: The keys to optimizing email send frequency. Research report. Retrieved April 6, 2021 from http://returnpath.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/RP-Frequency-Report-FINAL.pdf .
Risselada, H., Verhoef, P. C., & Bijmolt, T. (2014). Dynamic effects of social influence and direct marketing on the adoption of high-technology products. Journal of Marketing, 78 (2), 52–68.
Roberts, J. H. (2000). The intersection of modelling potential and practice. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 17 (2/3), 127–134.
Roberts, M. L., & Berger, P. D. (1999). Direct marketing management . Prentice Hall International.
Rosenthal, R. (1984). Meta-analytic procedures for social science research . Sage.
Rossi, P. E. (2014). Even the rich can make themselves poor: A critical examination of IV methods in marketing applications. Marketing Science, 33 (5), 655–672.
Rust, R., & Verhoef, P. C. (2005). Optimizing the marketing interventions mix in intermediate-term CRM. Marketing Science, 24 (3), 477–489.
Sahni, N., Zou, D., & Chintagunta, P. K. (2017). Do targeted discount offers serve as advertising? Evidence from 70 field experiments. Management Science, 63 (8), 2397–2771.
Seenivasan, S., Sudhir, K., & Talukdar, D. (2016). Do store brands aid store loyalty. Management Science, 62 (3), 802–816.
Sethuraman, R., Tellis, G. J., & Briesch, R. (2011). How well does advertising work? Generalizations from meta-analysis of brand advertising elasticities. Journal of Marketing Research, 48 (3), 457–471.
Shiv, B., & Fedorikhin, A. (1999). Heart and mind in conflict: The interplay of affect and cognition in consumer decision making. Journal of Consumer Research, 26 (3), 278–292.
Snijders, T. A., & Bosker, R. J. (2011). Multilevel analysis: An introduction to basic and advanced multilevel modeling . Sage.
Snyder, J. (2018). Post GDPR, clients will own data and agencies must get creative. Retrieved April 6, 2021 from https://adexchanger.com/data-driven-thinking/post-gdpr-clients-will-own-data-and-agencies-must-get-creative/ .
Srinivasan, S., Pauwels, K., Hanssens, D. M., & Dekimpe, M. G. (2004). Do promotions benefit manufacturers, retailers, or both? Management Science, 50 (5), 617–629.
Srinivasan, S., Rutz, O. J., & Pauwels, K. (2016). Paths to and off purchase: Quantifying the impact of traditional marketing and online consumer activity. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 44 (4), 440–453.
Srinivasan, S., Vanhuele, M., & Pauwels, K. (2010). Mind-set metrics in market response models: An integrative approach. Journal of Marketing Research, 47 (4), 672–684.
Steenkamp, J.-B. E. M., & Geyskens, I. (2014). Manufacturer and retailer strategies to impact store brand share: Global integration, local adaptation, and worldwide learning. Marketing Science, 33 (1), 6–26.
Stremersch, S. (2021). The study of important marketing issues: Reflections. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 38 (1), 12–17.
Stremersch, S., Gonzalez, J., Valenti, A., & Villanueva, J. (2023). The value of context-specific studies for marketing. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 51 (1), 50–65.
Sundaram, R. K. (1996). A first course in optimization theory . Cambridge University Press.
ter Braak, A., Geyskens, I., & Dekimpe, M. G. (2014). Taking private labels upmarket: Empirical generalizations on category drivers of premium private label introductions. Journal of Retailing, 90 (2), 125–140.
Tezinde, T., Smith, B., & Murphy, J. (2002). Getting permission: Exploring factors affecting permission marketing. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 16 (4), 28–39.
Timoumi, A., Gangwar, M., & Mantrala, M. K. (2022). Cross-channel effects of omnichannel retail marketing strategies: A review of extant data-driven research. Journal of Retailing, 98 (1), 133–151.
Valentini, S., Montaguti, E., & Neslin, S. A. (2011). Decision process evolution in customer channel choice. Journal of Marketing, 75 (6), 72–86.
Van Heerde, H. J., & Bijmolt, T. (2005). Decomposing the promotional revenue bump for loyalty program members versus nonmembers. Journal of Marketing Research, 42 (4), 443–457.
Verhoef, P. C. (2003). Understanding the effect of customer relationship management efforts on customer retention and customer share development. Journal of Marketing, 67 (4), 30–45.
Verhoef, P. C., Neslin, S. A., & Vroomen, B. (2007). Multichannel customer management: Understanding the research-shopper phenomenon. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 24 (2), 129–148.
Wedel, M., & Kamakura, W. A. (2002). Introduction to the special issue on market segmentation. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 19 (3), 181–183.
Wiesel, T., Pauwels, K., & Arts, J. (2011). Marketing's profit impact: Quantifying online and offline funnel progression. Marketing Science, 30 (4), 604–611.
Wooldridge, J. M. (2015). Control function methods in applied econometrics. Journal of Human Resources, 50 (2), 420–445.
Wright, M. (2009). A new theorem for optimizing the advertising budget. Journal of Advertising Research, 49 (2), 164–169.
Zhang, J. Z., & Chang, C. W. (2021). Consumer dynamics: Theories, methods, and emerging directions. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 49 (1), 166–196.
Zhang, X., Kumar, V., & Cosguner, K. (2017). Dynamically managing a profitable email marketing program. Journal of Marketing Research, 54 (6), 851–866.
Zhang, Y., Bradlow, E. T., & Small, D. S. (2014). Predicting customer value using clumpiness: From RFM to RFMC. Marketing Science, 34 (2), 195–208.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Wharton Customer Analytics Initiative for providing the data sets used in this study and the management of L’Occitane en Provence for their collaboration in this project and for their feedback. We thank Eric Bradlow, Peter Fader, Dominique Hanssens, Gary Lilien, John Roberts, and Christian Schulze for their useful suggestions on this work. The first author is grateful for Boston University’s Questrom School of Business doctoral funding support.
Open Access funding provided thanks to the CRUE-CSIC agreement with Springer Nature.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
IESE Business School, University of Navarra, 08034, Barcelona, Spain
Albert Valenti
Questrom School of Business, Boston University, Boston, MA, 02215, USA
Shuba Srinivasan
Imperial College of London, London, SW7 2AZ, UK
Gokhan Yildirim
D’Amore-McKim School of Business, Northeastern University, Boston, MA, 02115, USA
Koen Pauwels
BI Norwegian Business School, Oslo, Norway
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Albert Valenti .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Marnik Dekimpe served as Area Editor for this article.
Supplementary Information
(DOCX 5562 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Valenti, A., Srinivasan, S., Yildirim, G. et al. Direct mail to prospects and email to current customers? Modeling and field-testing multichannel marketing. J. of the Acad. Mark. Sci. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-023-00962-2
Download citation
Received : 22 September 2021
Accepted : 28 June 2023
Published : 05 August 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-023-00962-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Marketing mix effectiveness
- Multichannel retailing
- Direct mail
- Hierarchical linear model
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

COMMENTS
Top Email Marketing Case Studies: 1. Getting 1,300 Monthly Donations Email Marketing Case Study 2. Collecting 100,000 Emails In One Week Example 3. The Science Behind Obama's Campaign Emails 4. The Amazon Email Experience 5. Boost Open Rates By 3X & CTR By 2X 6. Increasing Reach, Impact & Subscriber Satisfaction 7. Birchbox Boost Conversions By 25% 8. 109% Revenue Lift for Dell with GIFs 9 ...
3. WOŚP email marketing case study - use online marketing tools to collect information from your audience The Great Orchestra of Christmas Charity (Wielka Orkiestra Świątecznej Pomocy "WOŚP") - is a philanthropic foundation whose primary goal is providing health care, saving the lives of ill people, especially children, and promoting a healthy lifestyle, and preventive medicine.
Check out Vero, customer engagement software designed for product marketers. Message your users based on what they do (or don't do) in your product. It's really hard to find email marketing case studies. If you want inspiration, there aren't many options. But you can read blogs like this one :)
Case Study 1: The Rejuvenation of Customer Engagement — Constant Contact's Pivot to Personalization. Background: Constant Contact, a renowned email marketing platform, faced a challenge familiar to many in the industry: the need to re-engage a somewhat dormant customer base. They recognized that a one-size-fits-all approach was no longer ...
First step: The company crafted an email to their subscribers about using symbols in email content. The subject line read "Make your emails stand out with symbols.". Second step: This email performed fairly well, producing an open rate of 20.5%. Mailigen wanted to see if they could improve on that rate.
Email Marketing Templates: 9 Case Studies for Email Marketing Success. See the exact emails a high-growth ecommerce brand is using to engage, educate, and upsell new prospects. by Elise Dopson. ... Email marketing is one of the most profitable marketing channels for an ecommerce business. It's also one of the most time consuming.
Case Study 1: Clothing Retailer's Personalization Powerhouse. A well-known clothing retailer implemented a highly personalized email marketing campaign that led to a substantial increase in customer engagement and sales. The key to their success lay in collecting and leveraging customer data effectively.
2. Rx Smart Gear Implements a Multi-channel Revenue Strategy. Another case study to take note of showcases the strength of leveraging a multi-channel revenue strategy with unified email and SMS marketing. Rx Smart Gear — a world-leading fitness brand — was hopeful in turning SMS marketing into their next highest revenue source.
Hammock. Hammock, a creative agency, has its work cut out for it when it comes to email signups. Most agency email subscribers are B2B clients, and they already receive so much email from agency account managers, projects managers, and creatives that they would need a very compelling reason to read any more agency email.
Quick Case Study #3: Farm pivots to subscription product after retail locations close in pandemic, increases online sales more than 500% with email marketing Soluna Garden Farm is a small farm in Massachusetts specializing in herbs, flowers, tea, and spices.
These email marketing case studies collectively emphasize that email marketing is not merely a communication tool; it's a dynamic force that can drive engagement, build trust, and foster meaningful connections with an audience. The common thread among these achievements is the strategic utilization of data, personalization, transparency, and ...
Open rate: 47%. Click rate: 13%. And abandoned basket emails: Open rate: 38%. Click rate: 19%. The targets for these campaigns were 15% for the open rate and 3% for the click rate. Enter The Digitals and showcase your finest work, your team and your clients to the global digital marketing and ecommerce community.
Illuminating Case Studies in B2B Email Marketing Adobe's Emphasis on Interactive Emails. Adobe, a major player in the creative software industry, has increasingly incorporated interactivity into its email campaigns. Recognizing that B2B decision-makers are inundated with emails, Adobe sought to make their communications stand out.
Case Study: Email Marketing Done Right. Email marketing is one of the most effective and affordable ways for small businesses to reach potential customers and build relationships. For one, email marketing is a cost-effective way for small businesses to reach leads and customers. It's much cheaper than traditional marketing methods, such as ...
Regardless of the industry or business type, email marketing can be a powerful tool for achieving various objectives, such as boosting sales, lead generation, establishing thought leadership, and increasing customer loyalty. The common thread among these case studies is the emphasis on personalization, valuable content, and consistent engagement.
Drip email series. Build up tension and craft cliffhangers with a drip email series designed around a case study. For example: Email #1: discuss the frustrating problem. Email #2: give hope with ...
Use case studies in your email marketing. Case studies are particularly suited to email marketing when you have an industry-segmentable list. For example, if you have a case study from a client in the insurance industry, emailing your case study to your base of insurance-related contacts can be a really relevant addition to a lead nurturing ...
Email Marketing Templates: 9 Case Studies for Email Marketing Success. See the exact emails a high-growth ecommerce brand is using to engage, educate, and upsell new prospects. by Elise Dopson. ... Email marketing is one of the most profitable marketing channels for an ecommerce business. It's also one of the most time consuming.
AI's Role In The Future Marketing. Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to redefine email marketing, infusing it with a new level of engagement and accuracy. By 2030, AI could become an ...
Drip email series. Build up tension and craft cliffhangers with a drip email series designed around a case study. For example: Email #1: discuss the frustrating problem. Email #2: give hope with the solution. Email #3: relieve the pain with results and a CTA.
Conclusion. Case studies are powerful marketing tools. They tell your potential customers relatable stories, demonstrate your company's success, and help you build credibility. Case studies will help you reach your audience in a way that no sales pitch, email, newsletter, or advertisement will.
Open up with a summary that communicates who your client is and why they reached out to you. Like in the other case study examples, you'll want to close out with a quantitative list of your achievements. 16. " NetApp ," by Evisort. Evisort opens up its NetApp case study with an at-a-glance overview of the client.
Multichannel retailers need to understand how to allocate marketing budgets to customer segments and online and offline sales channels. We propose an integrated methodological approach to assess how email and direct mail effectiveness vary by channel and customer value segment. We apply this approach to an international beauty retailer in six countries and to an apparel retailer in the United ...
Through a detailed case study conducted at the American Institute of Business Experience Design, I illustrate MECCDAL's efficacy in augmenting business and marketing educational delivery mechanisms while fostering both collective and individual well-being alongside enhanced innovation and implementation competencies among students.
Introduction. As the demand for experiential, hands-on, and engaging learning experiences in marketing education continues to increase (Dahl, Peltier, & Schibrowsky, Citation 2018), the concept of play in the classroom remains elusive (Neck, Grossman, Winkel, & Stamp, Citation 2022).Playful learning experiences have been shown to be effective in developing disciplinary knowledge, critical ...