

Teaching the Research Paper Part 1: Introducing the Research Paper and Preparing Students for the Assignment

There are three things every teacher should do before taking their students to the computer lab to research information for their research papers: teach the difference between reliable and unreliable sources, check to make sure every student has a self-generated research question, and help prepare students with key phrases and words to search.
Whenever I begin teaching the research paper , I always share with my students the story of how I wrote my Master’s thesis paper. It was a 50 page paper with 50 different sources.
I don’t do this to toot my own horn. I don’t do this to scare my students away from post-secondary education. I don’t do this to make the students feel like their research assignment is petty and small. I do this so that I can explain the process of research to them and so that they know I was once in their shoes.
So how exactly do you write a 50-page research paper that has 50 unique, credible sources? One source at a time.
Teaching the Research Paper: 3 Critical Steps to Take
Teaching the research paper: find credible sources.
When teaching the research paper to my secondary ELA students, I first show them about research and credible sources. Before students can even begin looking for their sources, they have to know how to distinguish between reliable and unreliable sources. Being able to do so is the first step in finding a reliable source.

Once I feel my students have a firm understanding of the sources they will be looking at, we then dive into the research topic, and the students select their issues related to the main topic.
Teaching the Research Paper: Create Questions
One of the critical parts of teaching the research paper to students is having them come up with their self-generated research questions. To do this, I encourage students to work collaboratively and talk about their research topics.
Students can work in small groups to see what their peers would like to know about that matter.
Working in small groups first provides extra support for EL and struggling students. From there, students come up with their questions to answer. There is also a graphic organizer in my Research Paper Writing resource that is especially helpful during this process.
Teaching the Research Paper: Brainstorm Key Words
Once students have a self-generated question, it is time to get students to think about keywords and phrases they will use in their search for sources. All too often I see students typing precise, wordy questions into a search engine. This only creates frustration for the students as well as the teacher.
Taking half a class to discuss keywords and phrases helps students tremendously, and it even speeds up the research process because students can find credible sources a lot easier. When teaching keywords and phrases to my students, I encourage them to type no more than four words into the search engine. I tell them that they must think of the most important words directly related to their topic.
To help students think about keywords and phrases they can use in the search engine, have them think about hashtags for their research topic. This fun, easy, and engaging strategy will get students thinking about what to research and what is explicitly related to their subject.
Teaching the Research Paper: A Research Paper Writing Instructional Unit
Take the stress out of teaching your students how to write a research paper with this complete research writing unit ! This comprehensive and complete research paper writing unit will help you teach your students how to write a research paper. Now available in print + digital!
This step-by-step resource teaches your students the eight steps of research writing, and it includes every single thing you could need for a successful research writing unit! Plus, it is updated for 9th edition MLA!
The editable teaching presentation (which comes in both PowerPoint and Google Slides®) is ideal for direct instruction and includes multiple days of guided instruction! The research writing presentation introduces students to the eight steps for completing a research project: selecting topics, generating questions, brainstorming, researching and gathering credible information, organizing and outlining, writing the first draft, peer editing, and finalizing the paper.
Research Paper Teaching Unit
Take the stress out of teaching your students how to write a research paper with this complete research writing unit ! This comprehensive and complete research paper writing unit will help you teach your students how to write a research paper. Now available in print + digital!
Read more about teaching the research paper
Read more about research in the classroom with Part 2 which covers research paper topics and Part 3 which includes using Google Apps for research.
THANK YOU! I've had to sit through some painfully tedious COLLEGE classes because so many students aren't learning this in K12 that we're required to take classes on things like how to do a search. I greatly appreciate those of you who are teaching these important skills!
Is there a part 2?
Hi Deena, Thank you for reaching out. Yes. There is a part 2 and a part 3. I will link them to this post!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

SUBSCRIBE NOW

How to Write a Research Paper
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Research Paper Fundamentals
How to choose a topic or question, how to create a working hypothesis or thesis, common research paper methodologies, how to gather and organize evidence , how to write an outline for your research paper, how to write a rough draft, how to revise your draft, how to produce a final draft, resources for teachers .
It is not fair to say that no one writes anymore. Just about everyone writes text messages, brief emails, or social media posts every single day. Yet, most people don't have a lot of practice with the formal, organized writing required for a good academic research paper. This guide contains links to a variety of resources that can help demystify the process. Some of these resources are intended for teachers; they contain exercises, activities, and teaching strategies. Other resources are intended for direct use by students who are struggling to write papers, or are looking for tips to make the process go more smoothly.
The resources in this section are designed to help students understand the different types of research papers, the general research process, and how to manage their time. Below, you'll find links from university writing centers, the trusted Purdue Online Writing Lab, and more.
What is an Academic Research Paper?
"Genre and the Research Paper" (Purdue OWL)
There are different types of research papers. Different types of scholarly questions will lend themselves to one format or another. This is a brief introduction to the two main genres of research paper: analytic and argumentative.
"7 Most Popular Types of Research Papers" (Personal-writer.com)
This resource discusses formats that high school students commonly encounter, such as the compare and contrast essay and the definitional essay. Please note that the inclusion of this link is not an endorsement of this company's paid service.
How to Prepare and Plan Out Writing a Research Paper
Teachers can give their students a step-by-step guide like these to help them understand the different steps of the research paper process. These guides can be combined with the time management tools in the next subsection to help students come up with customized calendars for completing their papers.
"Ten Steps for Writing Research Papers" (American University)
This resource from American University is a comprehensive guide to the research paper writing process, and includes examples of proper research questions and thesis topics.
"Steps in Writing a Research Paper" (SUNY Empire State College)
This guide breaks the research paper process into 11 steps. Each "step" links to a separate page, which describes the work entailed in completing it.
How to Manage Time Effectively
The links below will help students determine how much time is necessary to complete a paper. If your sources are not available online or at your local library, you'll need to leave extra time for the Interlibrary Loan process. Remember that, even if you do not need to consult secondary sources, you'll still need to leave yourself ample time to organize your thoughts.
"Research Paper Planner: Timeline" (Baylor University)
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment.
"Research Paper Planner" (UCLA)
UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
There's a reason teachers spend a long time talking about choosing a good topic. Without a good topic and a well-formulated research question, it is almost impossible to write a clear and organized paper. The resources below will help you generate ideas and formulate precise questions.
"How to Select a Research Topic" (Univ. of Michigan-Flint)
This resource is designed for college students who are struggling to come up with an appropriate topic. A student who uses this resource and still feels unsure about his or her topic should consult the course instructor for further personalized assistance.
"25 Interesting Research Paper Topics to Get You Started" (Kibin)
This resource, which is probably most appropriate for high school students, provides a list of specific topics to help get students started. It is broken into subsections, such as "paper topics on local issues."
"Writing a Good Research Question" (Grand Canyon University)
This introduction to research questions includes some embedded videos, as well as links to scholarly articles on research questions. This resource would be most appropriate for teachers who are planning lessons on research paper fundamentals.
"How to Write a Research Question the Right Way" (Kibin)
This student-focused resource provides more detail on writing research questions. The language is accessible, and there are embedded videos and examples of good and bad questions.
It is important to have a rough hypothesis or thesis in mind at the beginning of the research process. People who have a sense of what they want to say will have an easier time sorting through scholarly sources and other information. The key, of course, is not to become too wedded to the draft hypothesis or thesis. Just about every working thesis gets changed during the research process.
CrashCourse Video: "Sociology Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is tailored to sociology students, it is applicable to students in a variety of social science disciplines. This video does a good job demonstrating the connection between the brainstorming that goes into selecting a research question and the formulation of a working hypothesis.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement for an Analytical Essay" (YouTube)
Students writing analytical essays will not develop the same type of working hypothesis as students who are writing research papers in other disciplines. For these students, developing the working thesis may happen as a part of the rough draft (see the relevant section below).
"Research Hypothesis" (Oakland Univ.)
This resource provides some examples of hypotheses in social science disciplines like Political Science and Criminal Justice. These sample hypotheses may also be useful for students in other soft social sciences and humanities disciplines like History.
When grading a research paper, instructors look for a consistent methodology. This section will help you understand different methodological approaches used in research papers. Students will get the most out of these resources if they use them to help prepare for conversations with teachers or discussions in class.
"Types of Research Designs" (USC)
A "research design," used for complex papers, is related to the paper's method. This resource contains introductions to a variety of popular research designs in the social sciences. Although it is not the most intuitive site to read, the information here is very valuable.
"Major Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is a bit on the dry side, it provides a comprehensive overview of the major research methodologies in a format that might be more accessible to students who have struggled with textbooks or other written resources.
"Humanities Research Strategies" (USC)
This is a portal where students can learn about four methodological approaches for humanities papers: Historical Methodologies, Textual Criticism, Conceptual Analysis, and the Synoptic method.
"Selected Major Social Science Research Methods: Overview" (National Academies Press)
This appendix from the book Using Science as Evidence in Public Policy , printed by National Academies Press, introduces some methods used in social science papers.
"Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: 6. The Methodology" (USC)
This resource from the University of Southern California's library contains tips for writing a methodology section in a research paper.
How to Determine the Best Methodology for You
Anyone who is new to writing research papers should be sure to select a method in consultation with their instructor. These resources can be used to help prepare for that discussion. They may also be used on their own by more advanced students.
"Choosing Appropriate Research Methodologies" (Palgrave Study Skills)
This friendly and approachable resource from Palgrave Macmillan can be used by students who are just starting to think about appropriate methodologies.
"How to Choose Your Research Methods" (NFER (UK))
This is another approachable resource students can use to help narrow down the most appropriate methods for their research projects.
The resources in this section introduce the process of gathering scholarly sources and collecting evidence. You'll find a range of material here, from introductory guides to advanced explications best suited to college students. Please consult the LitCharts How to Do Academic Research guide for a more comprehensive list of resources devoted to finding scholarly literature.
Google Scholar
Students who have access to library websites with detailed research guides should start there, but people who do not have access to those resources can begin their search for secondary literature here.
"Gathering Appropriate Information" (Texas Gateway)
This resource from the Texas Gateway for online resources introduces students to the research process, and contains interactive exercises. The level of complexity is suitable for middle school, high school, and introductory college classrooms.
"An Overview of Quantitative and Qualitative Data Collection Methods" (NSF)
This PDF from the National Science Foundation goes into detail about best practices and pitfalls in data collection across multiple types of methodologies.
"Social Science Methods for Data Collection and Analysis" (Swiss FIT)
This resource is appropriate for advanced undergraduates or teachers looking to create lessons on research design and data collection. It covers techniques for gathering data via interviews, observations, and other methods.
"Collecting Data by In-depth Interviewing" (Leeds Univ.)
This resource contains enough information about conducting interviews to make it useful for teachers who want to create a lesson plan, but is also accessible enough for college juniors or seniors to make use of it on their own.
There is no "one size fits all" outlining technique. Some students might devote all their energy and attention to the outline in order to avoid the paper. Other students may benefit from being made to sit down and organize their thoughts into a lengthy sentence outline. The resources in this section include strategies and templates for multiple types of outlines.
"Topic vs. Sentence Outlines" (UC Berkeley)
This resource introduces two basic approaches to outlining: the shorter topic-based approach, and the longer, more detailed sentence-based approach. This resource also contains videos on how to develop paper paragraphs from the sentence-based outline.
"Types of Outlines and Samples" (Purdue OWL)
The Purdue Online Writing Lab's guide is a slightly less detailed discussion of different types of outlines. It contains several sample outlines.
"Writing An Outline" (Austin C.C.)
This resource from a community college contains sample outlines from an American history class that students can use as models.
"How to Structure an Outline for a College Paper" (YouTube)
This brief (sub-2 minute) video from the ExpertVillage YouTube channel provides a model of outline writing for students who are struggling with the idea.
"Outlining" (Harvard)
This is a good resource to consult after completing a draft outline. It offers suggestions for making sure your outline avoids things like unnecessary repetition.
As with outlines, rough drafts can take on many different forms. These resources introduce teachers and students to the various approaches to writing a rough draft. This section also includes resources that will help you cite your sources appropriately according to the MLA, Chicago, and APA style manuals.
"Creating a Rough Draft for a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
This resource is useful for teachers in particular, as it provides some suggested exercises to help students with writing a basic rough draft.
Rough Draft Assignment (Duke of Definition)
This sample assignment, with a brief list of tips, was developed by a high school teacher who runs a very successful and well-reviewed page of educational resources.
"Creating the First Draft of Your Research Paper" (Concordia Univ.)
This resource will be helpful for perfectionists or procrastinators, as it opens by discussing the problem of avoiding writing. It also provides a short list of suggestions meant to get students writing.
Using Proper Citations
There is no such thing as a rough draft of a scholarly citation. These links to the three major citation guides will ensure that your citations follow the correct format. Please consult the LitCharts How to Cite Your Sources guide for more resources.
Chicago Manual of Style Citation Guide
Some call The Chicago Manual of Style , which was first published in 1906, "the editors' Bible." The manual is now in its 17th edition, and is popular in the social sciences, historical journals, and some other fields in the humanities.
APA Citation Guide
According to the American Psychological Association, this guide was developed to aid reading comprehension, clarity of communication, and to reduce bias in language in the social and behavioral sciences. Its first full edition was published in 1952, and it is now in its sixth edition.
MLA Citation Guide
The Modern Language Association style is used most commonly within the liberal arts and humanities. The MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing was first published in 1985 and (as of 2008) is in its third edition.
Any professional scholar will tell you that the best research papers are made in the revision stage. No matter how strong your research question or working thesis, it is not possible to write a truly outstanding paper without devoting energy to revision. These resources provide examples of revision exercises for the classroom, as well as tips for students working independently.
"The Art of Revision" (Univ. of Arizona)
This resource provides a wealth of information and suggestions for both students and teachers. There is a list of suggested exercises that teachers might use in class, along with a revision checklist that is useful for teachers and students alike.
"Script for Workshop on Revision" (Vanderbilt University)
Vanderbilt's guide for leading a 50-minute revision workshop can serve as a model for teachers who wish to guide students through the revision process during classtime.
"Revising Your Paper" (Univ. of Washington)
This detailed handout was designed for students who are beginning the revision process. It discusses different approaches and methods for revision, and also includes a detailed list of things students should look for while they revise.
"Revising Drafts" (UNC Writing Center)
This resource is designed for students and suggests things to look for during the revision process. It provides steps for the process and has a FAQ for students who have questions about why it is important to revise.
Conferencing with Writing Tutors and Instructors
No writer is so good that he or she can't benefit from meeting with instructors or peer tutors. These resources from university writing, learning, and communication centers provide suggestions for how to get the most out of these one-on-one meetings.
"Getting Feedback" (UNC Writing Center)
This very helpful resource talks about how to ask for feedback during the entire writing process. It contains possible questions that students might ask when developing an outline, during the revision process, and after the final draft has been graded.
"Prepare for Your Tutoring Session" (Otis College of Art and Design)
This guide from a university's student learning center contains a lot of helpful tips for getting the most out of working with a writing tutor.
"The Importance of Asking Your Professor" (Univ. of Waterloo)
This article from the university's Writing and Communication Centre's blog contains some suggestions for how and when to get help from professors and Teaching Assistants.
Once you've revised your first draft, you're well on your way to handing in a polished paper. These resources—each of them produced by writing professionals at colleges and universities—outline the steps required in order to produce a final draft. You'll find proofreading tips and checklists in text and video form.
"Developing a Final Draft of a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
While this resource contains suggestions for revision, it also features a couple of helpful checklists for the last stages of completing a final draft.
Basic Final Draft Tips and Checklist (Univ. of Maryland-University College)
This short and accessible resource, part of UMUC's very thorough online guide to writing and research, contains a very basic checklist for students who are getting ready to turn in their final drafts.
Final Draft Checklist (Everett C.C.)
This is another accessible final draft checklist, appropriate for both high school and college students. It suggests reading your essay aloud at least once.
"How to Proofread Your Final Draft" (YouTube)
This video (approximately 5 minutes), produced by Eastern Washington University, gives students tips on proofreading final drafts.
"Proofreading Tips" (Georgia Southern-Armstrong)
This guide will help students learn how to spot common errors in their papers. It suggests focusing on content and editing for grammar and mechanics.
This final set of resources is intended specifically for high school and college instructors. It provides links to unit plans and classroom exercises that can help improve students' research and writing skills. You'll find resources that give an overview of the process, along with activities that focus on how to begin and how to carry out research.
"Research Paper Complete Resources Pack" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, rubrics, and other resources is designed for high school students. The resources in this packet are aligned to Common Core standards.
"Research Paper—Complete Unit" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, notes, PowerPoints, and other resources has a 4/4 rating with over 700 ratings. It is designed for high school teachers, but might also be useful to college instructors who work with freshmen.
"Teaching Students to Write Good Papers" (Yale)
This resource from Yale's Center for Teaching and Learning is designed for college instructors, and it includes links to appropriate activities and exercises.
"Research Paper Writing: An Overview" (CUNY Brooklyn)
CUNY Brooklyn offers this complete lesson plan for introducing students to research papers. It includes an accompanying set of PowerPoint slides.
"Lesson Plan: How to Begin Writing a Research Paper" (San Jose State Univ.)
This lesson plan is designed for students in the health sciences, so teachers will have to modify it for their own needs. It includes a breakdown of the brainstorming, topic selection, and research question process.
"Quantitative Techniques for Social Science Research" (Univ. of Pittsburgh)
This is a set of PowerPoint slides that can be used to introduce students to a variety of quantitative methods used in the social sciences.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1902 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,034 quotes across 1902 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!


Writing Research Papers

This research writing unit of study is designed to guide your students through the research writing process.
This is a free writing unit of study from the curriculum corner..
This research writing collection includes mini lessons, anchor charts and more.
Mention the words “research writing” in an intermediate classroom and you might be met with moans & groans or perhaps even see fear in the eyes of some students.
In all seriousness though, writing can be intimidating for many children in our classrooms.
Guided and focused your mini-lessons can be helpful for students. Also, the more examples you can get students to interact with, the more they will understand the expectations. Finally, the more modeling that you do for them, the more they can view writing as less overwhelming.
Download the free resources to accompany this unit of study at the bottom of this post.

Lesson Ideas for Writing Research Papers:
Lesson 1: Noticings
- Begin by getting your students familiar with what research writing looks like.
- Have them work in pairs or small groups to read pieces of research writing. They will record their “noticings” about the writing.
- Then, come together in a community circle to discuss and create a class anchor chart.
- You will find a blank anchor chart and one with noticings already recorded.
- Here is a link we found that contains some student-created examples of research writing: Student Writing Models . Simply scroll through the grade levels for different samples.
Lesson 2: Opinion vs. Facts
- Begin with a brief review of opinions vs. facts.
- Use the six paragraphs we share in our resources to give your students some practice differentiating between the two.
- Each of the paragraphs contains both opinions and facts.
- Students will read the paragraphs and record the facts and opinions from their paragraph onto the recording page.

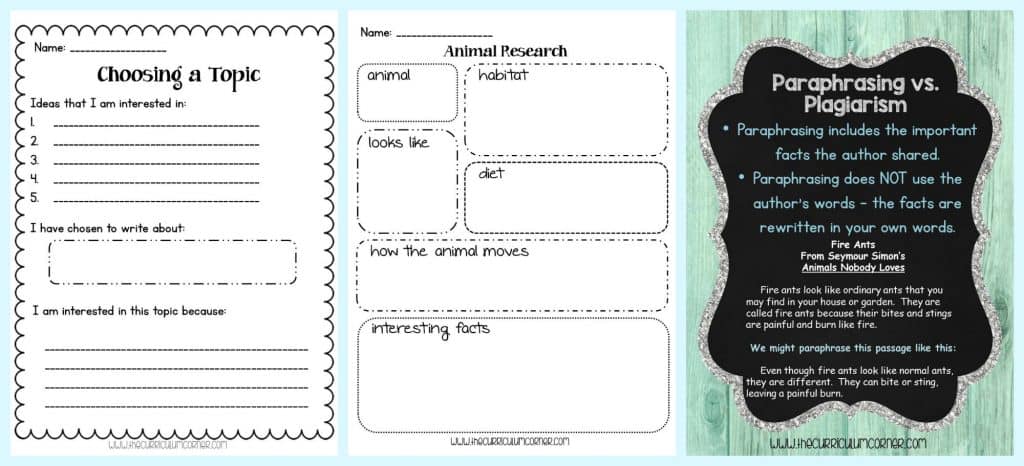
Lesson 3: Choosing a Topic
- We know that providing choice will allow for greater engagement and success. We want to help students to narrow their choices by giving them some guidance.
- Gather students and begin a discussion about choosing a research topic.
- Ask them to think of topics they already know a little about, have interest in or is important/relevant to their lives.
- You might pose the question “Why is that important in research writing?” and discuss their thoughts.
- For this lesson we have provided a page where students can individually brainstorm topics. You can circulate the room during this process to help students to narrow their topic.
- If you feel your class may need help to narrow their choices, think about giving them a broad topic, such as animals, and then have them choose a sub-topics from the bigger umbrella topic.
- If you feel like your students need an added level of support you might think about creating an anchor chart from a class brainstorming session about possible appropriate topics and then display this in your room.
Lesson 4: Where to Find Accurate Information about a Topic
- Help students to begin to understand where they might find accurate information about their topics.
- Where are the places you can begin to look for information about your topic?
- Why would the copyright date on a book be important in doing research?
- Is everything on the internet true?
- Why is it important for your research to contain accurate information?
- Where do you begin to look for information that will accurate
- One way to help students think through appropriate sites on the internet is to pass out the ten cards provided in our resources.
- Have students read the cards and discuss what kind of a website it is.
- Talk about whether they know or have heard of the sites. Would they consider the sites “trusted” enough to gain knowledge about their topics. Then have them talk about why or why not these sites would be trusted.
Lesson 5: Double Check Your Facts
- We want our students to get into the habit of double checking their facts. This will help ensure what they are learning is correct.
- To do this, you might want them to practice this skill. In this lesson use the page provided to have each student find and record a fact about a topic of their choice on the internet.
- The page then has students write where they found the fact, and also has them list a corresponding fact from a different source.
- Finally they determine if the facts are the same or different. You may have to further the lesson by discussing approximations. For example one site might say that an animal can weigh up to 1,500 pounds, while another might state that the animal weighs between 1,200 and 1,500 pounds.
- You will need to talk about how those facts might both be accurate even though they are stated differently. If they seem to check out, then help students generalize the information for a research paper.

Lesson 6: Taking Notes
- Sometimes giving students resources and a blank sheet of notebook paper can be too overwhelming. You have students who simply copy everything from the text or you have others who have no idea where to start.
- We need to guide them to read to pull out facts & relevant information.
- For this lesson we have provided various templates for note-taking. Whatever method or template you choose for helping your students learn to take notes, model it several times in front of the class Demonstrating for them how to write the notes as they read about a topic will be helpful.
- After initial teaching, you may find that you need to pull small groups for extra practice. Some might need a one-on-one conference.
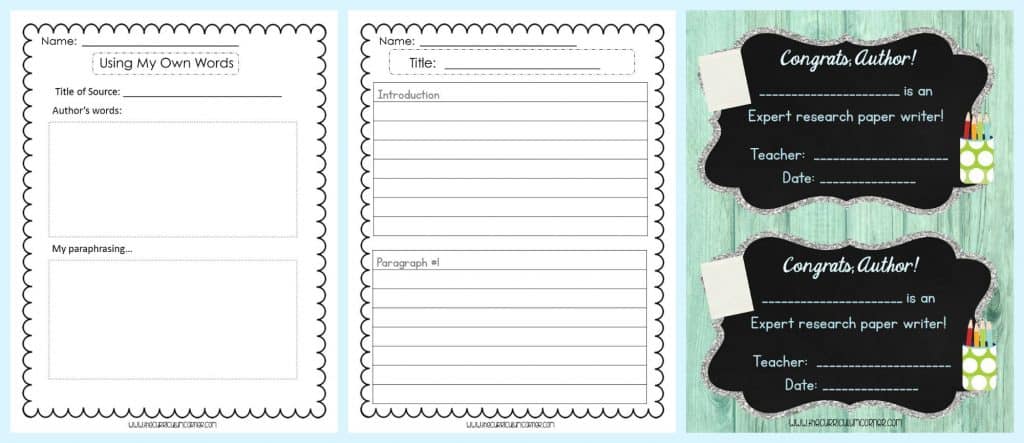
Lesson 7: Paraphrasing vs. Plagiarism
- Students will need to learn how to paraphrase their research. This will help them avoid plagiarizing words from their resources.
- Discuss why plagiarizing is something that they shouldn’t do in their writing because it is “stealing” another’s words.
- Tell the students that there is a way to use another author’s ideas in an appropriate way without copying their words. First, they need to paraphrase and then they need to cite the source where they found the information.
- Display the anchor chart “What is Paraphrasing” and discuss the definition.
- Next, pass out copies of “My Own Words” to pairs of students. Explain that their task will be to find a paragraph or passage in a nonfiction book. They will paraphrase the author’s words, keeping the same ideas.
- Finally, gather students together to share their paraphrasing efforts. Each pair of students can read the paragraph/passage from the book and then the paraphrasing that they wrote. Discuss the words and decisions the students made in their paraphrasing.
Lesson 8: Word Choice in Research Writing
- To help students think about making their writing more interesting, have them brainstorm words that could add voice to their writing.
- After working independently on the word choice page provided, have them meet with partners. They can talk about nouns, verbs and adjectives that relate to their topic.
Lesson 9: Writing Sketch
- This graphic organizer can be used for students to plan their writing.
- If your writers are more advanced you might choose to skip this step, It could be a big help for students who have taken notes and have too many facts.
- Be sure to model how to write the facts & ideas from your notes onto your planner. Students will see first hand how to make sure to only add what is relevant and important to their writing.
- Some questions you can pose: What will be the focus of each paragraph in your research writing? What do you want to include from your notes? Why is it important to the research? What facts don’t quite fit into the paragraphs you’ve decided upon? Should you change some of the paragraphs so that they better support the research and what you want your readers to learn?
- Once the planner is finished, they can use it as a guide to help their writing stay focused.
Lesson 10: Writing Introductions to Research
- Teach students how to think about their introduction as a way to grab their readers’ attention.
- Our anchor chart has some ideas to get writers started. You might also extend the anchor chart to include ideas from your students. (We have included some blank anchor charts at the very bottom of the download.)
- Discuss the parts that need to be included in the introductory paragraph first. Then, move on to some of the ways that might engage readers. As always be sure to model how you would go about writing an introductory paragraph using your Writing Sketch.
Lesson 11: Developing Your Paragraphs
- Next, help students stay focused and develop complete paragraphs.The next graphic organizer will get them to think through the specifics of each paragraph.
- Again, this may not be needed for all of the students in your classroom, but it might be something to think about using with all of them for at least their very first attempts at writing research papers.
- Model how to use the Writing Sketch planner to develop their paragraphs more fully on this organizer.
Lesson 12: Writing a Conclusion to Research
Providing a solid concluding paragraph is also something that needs modeled for your students.
Use the anchor chart with ideas to get you started with the modeling of this as well.
***If you would like for your students to write their first drafts on something that continues to support organization for them, you will find guided lined paper.
Lesson 13: Research Rendezvous Celebration
We love ending a unit of study with a celebration.
For this particular celebration, you might invite students to bring in a visual to help illustrate their topic.
Invite parents and other special adults from your building to the celebration and think about providing a snack.
You can also print out our “Congrats Author!” certificates to give to each student during the celebration.

All the research writing resources described above can be found in one download here:
Writing a Research Paper Resources
As with all of our resources, The Curriculum Corner creates these for free classroom use. Our products may not be sold. You may print and copy for your personal classroom use. These are also great for home school families!
You may not modify and resell in any form. Please let us know if you have any questions.
Dulce Hernandez
Thursday 8th of April 2021
Thank you so much. I tutor non-English speakers from K-9th grade. These resources are a God send!!
Monday 25th of May 2020
I cant download it, where do you download it?
Jill & Cathy
Wednesday 2nd of September 2020
Here is the link: https://www.thecurriculumcorner.com/thecurriculumcorner456/wp-content/pdf/writing/research/researchwriting.pdf
Graphic Organizer for Research Papers - The Curriculum Corner 4-5-6
Tuesday 19th of November 2019
[…] You might also like our unit of study for writing research papers:How to Write a Research Paper […]
Planning a Dynamic Writing Workshop - The Curriculum Corner 123
Thursday 14th of November 2019
[…] Writing Research Papers […]
Language Arts in the Middle School and High School Years
Thursday 11th of May 2017
[…] The middle school years can also be a good time to introduce writing a short research paper if your student is ready. Introduce how to do research, how to make an outline, and how to write a short research paper, including how to cite sources. Here’s a website that has a free introduction to writing research papers: https://www.thecurriculumcorner.com/thecurriculumcorner456/writing-research-papers/. […]
Engage Every Learner.®

- Facebook Page - VariQuest
- Twitter - All Tweets
- Youtube - All Videos
- VariQuest Blog
[Lesson Plan] How to Write a Research Paper: The Research Process
- Share this Article

Research-writing has changed a lot over the years, and with the prominence of artificial intelligence, those changes are only going to continue.
As students learn the important skill of responsibly researching for their writing, we at VariQuest have put together a 42-page booklet, split into two parts (to make it easier to digest and teach!) and this first part focuses on the research portion of the process.
From choosing a topic, to learning to paraphrase, to writing a thesis, these lessons are designed in a writers'-workshop-style to immerse students in every important step of writing a research paper. Using the example of The Great Barrier Reef, each lesson is paired with a handful of helpful printables - including anchor charts, discussion-prompts, and more!
Previous Article
![lesson plan writing a research paper [Lesson Plan] How to Write a Research Paper: The Writing Process](https://content.cdntwrk.com/mediaproxy?url=https%3A%2F%2Finfo.variquest.com%2Fhubfs%2FeBook%2FHow%2520to%2520Write%2520a%2520Research%2520Paper%2Fhow%2520to%2520write%2520a%2520research%2520paper%2520part%25202%2520blog%2520header.png%23keepProtocol&size=1&version=1708632756&sig=7a7f992b8eb3202d5b559b3528dee055&default=hubs%2Ftilebg-blogs.jpg)
We ask Google, we ask Alexa, we ask Siri...but what questions and answers do we need to find, ours...
Next Article
![lesson plan writing a research paper [Lesson Plan] Artificial Intelligence for the Writing Classroom](https://content.cdntwrk.com/mediaproxy?url=https%3A%2F%2Finfo.variquest.com%2Fhubfs%2FeBook%2FHow%2520to%2520Write%2520a%2520Research%2520Paper%2Fartificial%2520intelligence%2520writing%2520classroom%2520blog%2520header.png%23keepProtocol&size=1&version=1708632757&sig=1c98b19f762d343b74c8fc180604f91f&default=hubs%2Ftilebg-blogs.jpg)
There are so many questions when it comes to Artificial Intelligence (AI) and how it will affect h...
Most Recent Articles
![lesson plan writing a research paper [Lesson Plan] SEL Photo Activities for Grades 5-7](https://content.cdntwrk.com/mediaproxy?url=https%3A%2F%2Finfo.variquest.com%2Fhubfs%2FLesson_Plan_PDFs%2FSEL%2520Photo%2520Activities%2520header.png%23keepProtocol&size=1&version=1712432018&sig=36043467659cdc58fd01a7c4e0b4e10f&default=hubs%2Ftilebg-blogs.jpg)
At a time when our world and nation are struggling with division and conflicting ideology - empathy and compassion are important concepts to teach our future generations, so they can...
![lesson plan writing a research paper [Lesson Plan] Pi Day Activities for Upper-Elementary and Middle School Students](https://content.cdntwrk.com/mediaproxy?url=https%3A%2F%2Finfo.variquest.com%2Fhubfs%2FLesson_Plan_PDFs%2FPi%2520Day%2520Activities%2520Blog%2520Header.png%23keepProtocol&size=1&version=1710189992&sig=ab49c07260f67fe83b83f01a871ed392&default=hubs%2Ftilebg-blogs.jpg)
Circumference, diameter, radius, apple, cherry, rhubarb?! "Pi Day" is celebrated annually on March 14th (Get it - 3.14?!) and we're here to help you celebrate! According to piday.org,...

According to Neil Fleming's popular "VARK" model of learning types/styles, there are 4 main learning styles - including visual, auditory, reading/writing, and kinesthetic. Other models...
![lesson plan writing a research paper [Lesson Plan] Menu Math for Grades 3-6](https://content.cdntwrk.com/mediaproxy?url=https%3A%2F%2Finfo.variquest.com%2Fhubfs%2FHeader%2520Images%2Fmenu%2520math%2520header.png%23keepProtocol&size=1&version=1708632754&sig=fc5bd7de33f25f58a6ff8d497a3d009e&default=hubs%2Ftilebg-blogs.jpg)
Real-world-application learning is where learning takes real flight! We're so proud when our students master a concept, but even more proud when they can apply it to their everyday lives....
![lesson plan writing a research paper [Lesson Plan] Celebrate the Chinese New Year 2024!](https://content.cdntwrk.com/mediaproxy?url=https%3A%2F%2Finfo.variquest.com%2Fhubfs%2FCarman%2FCNY%25201-2018%2F%25E6%2581%25AD%25E5%2596%259C%25E7%2599%25BC%25E8%25B2%25A1.png%23keepProtocol&size=1&version=1708632755&sig=962e55db413d547df717013426c08ef8&default=hubs%2Ftilebg-blogs.jpg)
Chinese New Year, also known as the Spring Festival, has been celebrated for thousands of years. It is one of the most important holidays widely celebrated in many Asian countries and...
![lesson plan writing a research paper [Free Holiday Printables] You've Been SOCKED!](https://content.cdntwrk.com/mediaproxy?url=https%3A%2F%2Finfo.variquest.com%2Fhubfs%2FHeader%2520Images%2Fyouve%2520been%2520socked%2520blog%2520header.png%23keepProtocol&size=1&version=1708632755&sig=fe271a837ddc50d0b0edfaa323d32280&default=hubs%2Ftilebg-blogs.jpg)
While everyone has different holiday traditions and celebrates this time of year in different ways - we can all agree that spreading kindness and joy is one of the best! We've put...
We ask google, we ask alexa, we ask siri...but what questions and answers do we need to find, ourselves the skill of writing a research paper doesn't just develop writing skills or..., there are so many questions when it comes to artificial intelligence (ai) and how it will affect humankind in the future. at its best, it can help us learn and understand even more about....
![lesson plan writing a research paper [Downloads] Classroom Coloring Activities for Fall Holidays](https://content.cdntwrk.com/mediaproxy?url=https%3A%2F%2Finfo.variquest.com%2Fhubfs%2Ffall%2520coloring%2520blog%2520header.png%23keepProtocol&size=1&version=1708632757&sig=d3323da683a8b5bf05557420031fd2e5&default=hubs%2Ftilebg-blogs.jpg)
When the season of fall arrives, you're celebrating being done with the first few weeks of the school year, and outside the colors of the environment are changing. What better way to...

Trying to figure out how to best spend your Career & Technical Education funding - or use other funding for career & technical education programs? Let's take a look at some options.

Sensory paths are not only fun for elementary education because they help get the wiggles out, but they help with learning too! At VariQuest®, we feel passionately about visual and...
![lesson plan writing a research paper [Lesson Plan] Building Community With Kindness](https://content.cdntwrk.com/mediaproxy?url=https%3A%2F%2Finfo.variquest.com%2Fhubfs%2FHeader%2520Images%2Fbuilding%2520community%2520with%2520kindness%2520email%2520header.png%23keepProtocol&size=1&version=1692198532&sig=78399484e4c0b8174887d25918c70a9c&default=hubs%2Ftilebg-blogs.jpg)
In the 1960s, The Beach Boys scored a hit with the song, Be True to Your School about being proud of the school you go to and defending it to others. Are you proud of the school you...
![lesson plan writing a research paper [Download] Engage Every Learner® Content Fall 2023 Expansion Pack](https://content.cdntwrk.com/mediaproxy?url=https%3A%2F%2Finfo.variquest.com%2Fhubfs%2Fimages%2FeContent%2520Screenshots%2FFall%25202023%2520Release%2520Banner%25201200X400.png%23keepProtocol&size=1&version=1691693048&sig=27c99d424a13eed4e3bc55ebd2ca7b92&default=hubs%2Ftilebg-blogs.jpg)
We're deep into the back-to-school season, which means you're making your plans for the year - and as we do every spring and fall, we're bringing you a brand new expansion pack for your...
![lesson plan writing a research paper [Printable] My Logins and References Notebook Inserts](https://content.cdntwrk.com/mediaproxy?url=https%3A%2F%2Finfo.variquest.com%2Fhubfs%2FHeader%2520Images%2Fmy%2520logins%2520and%2520references%2520blog%2520header.png%23keepProtocol&size=1&version=1689778862&sig=e728eacac23bc55826da0f1cd1af5247&default=hubs%2Ftilebg-blogs.jpg)
In this midst of the back-to-school shopping season, teachers, parents, and students alike are purchasing tools they will need to be successful in the coming school year. And using...

You can't escape reading about Artificial Intelligence (AI) advancements and how they are changing the world every day. From self-driving cars to robotics to digital assistants and...
![lesson plan writing a research paper [Download] Writing With Caution Classroom Poster and Activities](https://content.cdntwrk.com/mediaproxy?url=https%3A%2F%2Finfo.variquest.com%2Fhubfs%2FHeader%2520Images%2Fwriting%2520with%2520caution%2520poster%2520header.png%23keepProtocol&size=1&version=1686837986&sig=38d5bd4d93ebd2148488bd7c71770535&default=hubs%2Ftilebg-blogs.jpg)
THERE (not their, or they're) is no way around it - homophones are tricky...and the English language is full of them!
![lesson plan writing a research paper [Printable] Don't Keep it Bottled Up Compliment Cards](https://content.cdntwrk.com/mediaproxy?url=https%3A%2F%2Finfo.variquest.com%2Fhubfs%2FHeader%2520Images%2Fcompliment%2520cards%2520email%2520blog%2520header.png%23keepProtocol&size=1&version=1684332412&sig=a06221ee156b84fe65c26454d21df39b&default=hubs%2Ftilebg-blogs.jpg)
What does a compliment cost? Nothing! When you give someone a compliment, not only are you making them feel better, you get a little happiness boost from the good deed as well. Teaching...

Through the use of various digital tools that promote the process of visual learning, teachers are changing the way knowledge is conveyed to students. This type of learning makes the...
![lesson plan writing a research paper [Printables] When I Feel Upset I Can...](https://content.cdntwrk.com/mediaproxy?url=https%3A%2F%2Finfo.variquest.com%2Fhubfs%2FHeader%2520Images%2Fwhen%2520I%2520feel%2520upset%2520blog%2520header.png%23keepProtocol&size=1&version=1680617177&sig=8b9176a1117838902c37bcfe5f537a78&default=hubs%2Ftilebg-blogs.jpg)
When big feelings take over, it's tough to take a step back before exerting an emotional response to a perceived issue. As students learn and grow in their social-emotional development,...

As educators, we know one of the more challenging times in a secondary-aged student's life can be preparing for adulthood after high school. This can be especially true for students with...
- Share this Hub
- Try for free

Writing Research Papers Lesson Plans
- Most Popular
- Most Recent

ELA Common Core Lesson Plans

- Create Characters Lesson Plan
- Creative Writing Lesson Plan: Using Details
- How to Write a Cause and Effect Essay
- How to Write a Conclusion for an Essay Lesson Plan
- How to Write a Persuasive Essay
- How to Write a Reflective Essay
- How to Write an Article Critique and Review
- How to Write an Introduction to an Essay
- How to Write a Problem Solution Essay
- Lesson Plan: Effective Sentence Structure
- Lesson Plan: Improve Writing Style with Improved Sentence Structure
- Logical Fallacies Lesson Plan with Summary & Examples
- Teaching Active and Passive Voice
- Teaching How to Revise a Rough Draft
- Teaching Instructional Articles: How to Write Instructions
- Teaching Word Choice: Using Strong Verbs
- Using Imagery Lesson Plan
- Writing for Audience and Purpose
- Writing Transitions Lesson
- Analyzing Humor in Literature Lesson Plan
- Analyzing Shakespeare Strategies
- Fun Reading Lesson Plan
- How to Write a Literary Analysis.
- How to Annotate and Analyze a Poem
- Lesson Plan for Teaching Annotation
- Literary Terms Lesson Plan
- Literature Exemplars – Grades-9-10
- Teaching Short Story Elements
- Using Short Stories to Teach Elements of Literature
- Bill of Rights Lesson Plan
- Fun Ideas for Teaching Language
- Comma Rules: How to Use Commas
- Difference between Denotation and Connotation
- Effective Word Choice Lesson Plan
- Fun Grammar Review Game or Vocabulary & Language Arts
- Lesson Plans for Substitute Teachers and Busy English Teachers
- Lesson Plan: Creating the Perfect Title
- 4.08 – Lesson Plan: Using Semicolons Correctly
- Pronoun-Antecedent Agreement Lesson Plan
- Sentence Combining Made Easy Lesson Plan
- Strategies for Teaching Vocabulary
- Using Tone Effectively Lesson Plan
- 4.12 – Word Choice Lesson Plan: Eliminate and Replace “To Be” Verbs
- Using Voice in Writing Effectively Lesson Plan
- Speaking & Listening
- Teacher Guide Central
Easy Research Paper Lesson Plan

I got many strange looks while eating razors and drinking cow urine.
Get 5 Short Story Lesson Plans Now!
We specialize in teacher-ready lesson plans.
I will never give away, trade or sell your email address. You can unsubscribe at any time.
Luckily I came up with a research paper lesson plan that wouldn’t cause me to want to lick a curling iron while stepping on Lego pieces. I now share this lesson plan for writing a research paper with you. It also serves as a research skills lesson plan.
ELA Common Core Standards for Writing a Research Paper Lesson Plan

- Common Core Writing Standard 2 . Write informative/explanatory texts to examine and convey complex ideas, concepts, and information clearly and accurately through the effective selection, organization, and analysis of content.
- W.9-10.5 Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on addressing what is most significant for a specific purpose and audience. (Editing for conventions should demonstrate command of L.9-10.1-3.)
- W.9-10.7 Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects to answer a question (including a self-generated question) or solve a problem; narrow or broaden the inquiry when appropriate; synthesize multiple sources on the subject, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation.
- W.9-10.8 Gather relevant information from multiple authoritative print and digital sources, using advanced searches effectively; assess the usefulness of each source in answering the research question; integrate information into the text selectively to maintain the flow of ideas, avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format for citation.
- W.9-10.9 Draw evidence from literary or informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research.
- L.9-10.3a Write and edit work so that it conforms to the guidelines in a style manual (e.g., MLA Handbook, Turabian’s Manual for Writers) appropriate for the discipline and writing type.
Keep it simple.
This particular research skills lesson plan’s purpose is to give students confidence. The teacher takes them through the steps. It may take a week or two. The materials I used for my research paper unit involves The Odyssey . I utilized the text book and web sources.

If you’d rather get struck in the forehead by a boulder thrown by a Cyclops than read another research paper, keep reading.
Step 1 : Instruct students how to create a works cited page. Include examples on your works cited page. Numerous handouts exist online. Here’s one I use: Citation Expectations .
Step 2 : Students will now take notes on a specific topic. This works best if it’s aligned thematically with a unit you’re about to begin. Before taking the first note, instruct students to write down the citation information in MLA format. For example, we were about to begin The Odyssey , so I found introductory material in our text book for them to read and take Cornell Notes on. By the end of day 1, they had one page of Cornell Notes, properly cited.
Step 3: At this point you’re simply repeating step 2. For this day I found another article in the text book about epic poems. At the end of day 2, students had 2 pages of Cornell Notes with citation information in MLA format.
It takes a hero to teach research to high-school students.
Step 4 : We’re doing the same thing, except you’ll want to mix in a different type of citation. I used The Hero’s Journey video from TedEd. If you checkout my Hero’s Journey Resource Page , there’s a video and a few other things. By the end of day 3, students have three pages of notes and three sources properly cited in MLA format.
Step 5: One more time. For these notes, I find a source online and project it on a screen. For this exercise, I used a document on epic conventions from Carson-Newman University. In addition to learning about epic conventions, we learned that Carson-Newman University is in Tennessee. Now you know. Each student now has 4 pages of notes, all with the correct MLA citation.
*Obviously, you can modify the assignment to suit the ability and needs of your students. I prefer to keep it simple and focus on the technical aspects of research papers.*
Step 6: Put together the works cited page. Refer to the Citations Expectations or just Google it. I recommend the Purdue OWL website. I revert back to 1973 and make students hand write their works cited page in class as a rough draft. Despite teaching for 17 years, I’m still amazed at the number of times I can repeat something and still have 2/3 of students do the exact opposite.

Step 8: Instruct students to write the rough draft in class. Emphasize the importance of citing in the correct format.
Step 9: They’re on their own. You’ve gone through it step-by-step. Make the final draft due in a few days.
Here’s how I assess the mini-research paper.
- *MLA Works Cited Page: 40 pts. The works cited page must be absolutely perfect to get 40 points. Take off a point or two for typos and other minor errors. Errors in overall quality–excluding a source, not double spacing, wrong size font, no title, not indenting correctly are major errors and will be treated as major errors in the scoring.
- Direct Citation of Sources: 35 pts. I require a minimum of 3 directly cited sources. Either it’s done right or it isn’t. It must be perfect to get the full 35 points. All mistakes are penalized. Major mistakes–not including a page number, not including an author, not setting the citation up in context–are penalized accordingly.
- Spelling, Mechanics, Grammar, etc: 15 pts . The key here is not to look stupid. One of the challenges of a research paper is establishing credibility. Any mistake in this area requires a penalty.
- Content: 10 pts. This is the opposite of what I usually do. The major objective of this assignment is to teach technical research writing skills. Once the basic skills of research writing are complete, I can then focus on content.
*According to MLA, you should only include works in the works cited page that you actually cite. For this assignment, however, it’s a good idea to make them cite all the sources you go over in class.
Last Updated on March 25, 2016 by Trenton Lorcher
Return to top of page
Copyright © 2024 | By: WebsiteRedesign.nz
Jump to navigation
- Inside Writing
- Teacher's Guides
- Student Models
- Writing Topics
- Minilessons
- Shopping Cart
- Inside Grammar
- Grammar Adventures
- CCSS Correlations
- Infographics
Sign up or login to use the bookmarking feature.
Writing a Research Paper
After fully engaging your sources, you have plenty of remarkable information to convey to your reader. The problem may be figuring out where to begin. What do you share first?
The following activities will suggest many starting points and ending points and other points in between. The strategies below will prime the pump of your ideas, getting them to flow easily into your first draft.
Writing the Beginning Paragraph
Your first job in writing a research paper is to catch your reader's interest. You can experiment with a number of strategies to form an interesting lead sentence.
Write a lead sentence.
Try out some of these strategies for introducing your research paper. Read the examples for ideas. Make a copy of this Google doc or download a Word template .
"Do things. Be sane. Don't fritter away your time; create, act, take a place wherever you are, and be somebody; get action.” —Theodore Roosevelt, Sr.
Teddy Roosevelt transformed himself from an asthmatic weakling to a brawler who won in Cuba and Panama, in Washington and on Mount Rushmore.
As they charged up San Juan Hill into the teeth of machine-gun fire, Teddy Roosevelt turned to a fellow soldier and shouted, "Holy Godfrey, what fun!"
Are heroes born, or are they made?
© 2024 Thoughtful Learning. Copying is permitted.
k12.thoughtfullearning.com
Please log in to save materials. Log in
- Resource Library
- Argumentative Paper
- Research Paper
- Social Issue
Argumentative Paper Format
Social issue topics paper information, types of papers: argument/argumentative, writing and intro and conclusion, writing the body of your paper, writing an argumentative research paper lesson plan 10.

Student Learning Objectives
As a result of meeting the requirements in this course, you will be able to:
1. Employ a variety of approaches to analyze and interpret texts. (PLG 1) (Gen Ed Goal 1 a)
2. Respond to texts, in discussion and writing assignments, demonstrating an understanding of rhetorical strategies employed in the texts. (PLG 2) (Gen Ed Goal 1a, b; 6 a, b)
3. Incorporate the fundamentals of academic essay writing such as gathering ideas, developing and clearly stating theses, organizing, drafting, revising, and editing. (PLG 3) (Gen Ed Goal 1 c, d)
4. Compose essays in several rhetorical modes, such as description, comparison/contrast, and argument. (PLG 3) (Gen Ed Goal 1c, d)
5. Move from personal responses to formal academic essays, including appropriate, properly formatted evidence from outside sources. (PLG 4, 5) (Gen Ed Goal 1 c)
6. Accurately incorporate the ideas of others using summary, paraphrase, and direct quotation. (PLG 4, 5) (Gen Ed Goal 1 c; 6 b)
7. Incorporate the academic requirements, tools, and techniques of research through the resources of contemporary information science. (PLG 6) (Gen Ed Goal 4 a, b, c, d)
8. Employ current MLA style for text presentation, in-text citations, and Works Cited pages for essays and research papers. (PLG 5, 6) (Gen Ed Goal 4 a, b, c, d)
9. Write an argumentative research paper accurately incorporating material from outside sources. (PLG 4, 5, 6) (Gen Ed Goal 1 a, b, c, d; 4 a, b, c, d; 6 a, b)
Course Requirements
You will be required to do the following:
- Write at least four multi-paragraph assignments of at least 500 words.
(Meets student learning objectives 1-5)
- Write at least one in-class essay.
(Meets student learning objectives 2-5)
- Complete other writing exercises such as summaries, journals, reading responses, reading comprehension questions, quizzes on reading assignments, letters, resumes, etc.
(Meets student learning objectives 1-6)
- Read, interpret, and analyze a variety of texts.
(Meets student learning objectives 1, 2)
- Conduct independent research and write a 5-7-page research paper, using MLA style.
(Meets student learning objectives 6-9)
- Submit papers that adhere to MLA manuscript requirements and which demonstrate effective proofreading and editing.
(Meets student learning objectives 1-9)
- Participate in class discussions and other in-class (individual or group) activities necessary to produce quality expository prose.
(Meets student learning objectives 2-7)
Version History
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
Online Guide to Writing and Research
The research process, explore more of umgc.
- Online Guide to Writing
Planning and Writing a Research Paper
Mastering the complex academic skill of writing a research paper will prepare you to enter the discourse community of your chosen area of study with excitement and confidence. Writing a research paper can seem like a daunting task, but if you take the time in the pages ahead to learn how to break the writing process down, you will be amazed at the level of comfort and control you feel when preparing your assignment.
Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . © 2022 UMGC. All links to external sites were verified at the time of publication. UMGC is not responsible for the validity or integrity of information located at external sites.
Table of Contents: Online Guide to Writing
Chapter 1: College Writing
How Does College Writing Differ from Workplace Writing?
What Is College Writing?
Why So Much Emphasis on Writing?
Chapter 2: The Writing Process
Doing Exploratory Research
Getting from Notes to Your Draft
Introduction
Prewriting - Techniques to Get Started - Mining Your Intuition
Prewriting: Targeting Your Audience
Prewriting: Techniques to Get Started
Prewriting: Understanding Your Assignment
Rewriting: Being Your Own Critic
Rewriting: Creating a Revision Strategy
Rewriting: Getting Feedback
Rewriting: The Final Draft
Techniques to Get Started - Outlining
Techniques to Get Started - Using Systematic Techniques
Thesis Statement and Controlling Idea
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Freewriting
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Summarizing Your Ideas
Writing: Outlining What You Will Write
Chapter 3: Thinking Strategies
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone: Style Through Vocabulary and Diction
Critical Strategies and Writing
Critical Strategies and Writing: Analysis
Critical Strategies and Writing: Evaluation
Critical Strategies and Writing: Persuasion
Critical Strategies and Writing: Synthesis
Developing a Paper Using Strategies
Kinds of Assignments You Will Write
Patterns for Presenting Information
Patterns for Presenting Information: Critiques
Patterns for Presenting Information: Discussing Raw Data
Patterns for Presenting Information: General-to-Specific Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Specific-to-General Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Summaries and Abstracts
Supporting with Research and Examples
Writing Essay Examinations
Writing Essay Examinations: Make Your Answer Relevant and Complete
Writing Essay Examinations: Organize Thinking Before Writing
Writing Essay Examinations: Read and Understand the Question
Chapter 4: The Research Process
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Ask a Research Question
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Cite Sources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Collect Evidence
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Decide Your Point of View, or Role, for Your Research
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Draw Conclusions
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Find a Topic and Get an Overview
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Manage Your Resources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Outline
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Survey the Literature
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Work Your Sources into Your Research Writing
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Human Resources
Research Resources: What Are Research Resources?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Electronic Resources
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Print Resources
Structuring the Research Paper: Formal Research Structure
Structuring the Research Paper: Informal Research Structure
The Nature of Research
The Research Assignment: How Should Research Sources Be Evaluated?
The Research Assignment: When Is Research Needed?
The Research Assignment: Why Perform Research?
Chapter 5: Academic Integrity
Academic Integrity
Giving Credit to Sources
Giving Credit to Sources: Copyright Laws
Giving Credit to Sources: Documentation
Giving Credit to Sources: Style Guides
Integrating Sources
Practicing Academic Integrity
Practicing Academic Integrity: Keeping Accurate Records
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Paraphrasing Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Quoting Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Summarizing Your Sources
Types of Documentation
Types of Documentation: Bibliographies and Source Lists
Types of Documentation: Citing World Wide Web Sources
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - APA Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - CSE/CBE Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - Chicago Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - MLA Style
Types of Documentation: Note Citations
Chapter 6: Using Library Resources
Finding Library Resources
Chapter 7: Assessing Your Writing
How Is Writing Graded?
How Is Writing Graded?: A General Assessment Tool
The Draft Stage
The Draft Stage: The First Draft
The Draft Stage: The Revision Process and the Final Draft
The Draft Stage: Using Feedback
The Research Stage
Using Assessment to Improve Your Writing
Chapter 8: Other Frequently Assigned Papers
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Article and Book Reviews
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Reaction Papers
Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Adapting the Argument Structure
Writing Arguments: Purposes of Argument
Writing Arguments: References to Consult for Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Anticipate Active Opposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Determine Your Organization
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Develop Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Introduce Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - State Your Thesis or Proposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Write Your Conclusion
Writing Arguments: Types of Argument
Appendix A: Books to Help Improve Your Writing
Dictionaries
General Style Manuals
Researching on the Internet
Special Style Manuals
Writing Handbooks
Appendix B: Collaborative Writing and Peer Reviewing
Collaborative Writing: Assignments to Accompany the Group Project
Collaborative Writing: Informal Progress Report
Collaborative Writing: Issues to Resolve
Collaborative Writing: Methodology
Collaborative Writing: Peer Evaluation
Collaborative Writing: Tasks of Collaborative Writing Group Members
Collaborative Writing: Writing Plan
General Introduction
Peer Reviewing
Appendix C: Developing an Improvement Plan
Working with Your Instructor’s Comments and Grades
Appendix D: Writing Plan and Project Schedule
Devising a Writing Project Plan and Schedule
Reviewing Your Plan with Others
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
- Career & Technical Education (CTE)
- Lesson Plans & Activities
- Professional Development
- Student Engagement
- Student Achievement
- School Funding
- Special Education
![lesson plan writing a research paper [Lesson Plan] How to Write a Research Paper: The Research Process](https://info.variquest.com/hubfs/eBook/How%20to%20Write%20a%20Research%20Paper/how%20to%20write%20a%20research%20paper%20blog%20header.png)
By: VariQuest Visual and Kinesthetic Learning Suite on November 8th, 2023
Print/Save as PDF
[Lesson Plan] How to Write a Research Paper: The Research Process
Lessons/Activities/Templates | Academic Subject: English Language Arts | Grade Level: Secondary (7-12) | Grade Level: Intermediate (3-6)

As students learn the important skill of responsibly researching for their writing, we at VariQuest have put together a 42-page booklet, split into two parts (to make it easier to digest and teach!) and this first part focuses on the research portion of the process.
From choosing a topic, to learning to paraphrase, to writing a thesis, these lessons are designed in a writers'-workshop-style to immerse students in every important step of writing a research paper. Using the example of The Great Barrier Reef, each lesson is paired with a handful of helpful printables - including anchor charts, discussion-prompts, and more!
Part 1 of How to Write a Research Paper explores the research portion of the writing process, guiding students in grades 5-7 through independently gathering information to write a paper on a chosen topic. Developed in partnership with Cathy Henry of The Curriculum Corner , students will come away with plenty of research and sources to begin part 2 of the journey - The Writing Process.
In this activity you'll find:
- Lessons 1-9 of the How to Write a Research Paper Unit focused on the research part of the process
- Downloadable posters, activity cards, awards, & more!
- An assessment rubric to review final papers

Ready for Part 2? Download that here!
Want to learn more about how the VariQuest® Visual and Kinesthetic Learning Suite can help you save time and precious funding dollars to create lesson supports, bulletin board displays, and student-based enterprise materials for your school? Contact us today for a no-obligation demonstration with one of our expert education consultants. You'll be amazed at what our solutions can do for you!


Research Writing (Grades 4-6)
Our Research Writing lesson plan for grades 4-6 teaches students how to write a thoroughly researched and factually accurate five paragraph essay. Students write an essay based on research they conduct in order to practice this type of writing.
Description
Additional information.
Our Research Writing Lesson Plan for grades 4-6 teaches students about the importance of researching and reporting findings accurately and effectively. Being able to clearly and accurately inform and communicate findings through writing is a valuable skill that students will need in many areas of their lives. Gathering and summarizing key information will also be a powerful tool for academic reading and writing throughout upper grades and higher education. In this lesson, students are asked to use the information they have learned to research and write a research paper from start to finish, including brainstorming and outlining.
At the end of the lesson, students will have written an essay based on a topic of their choosing with sources cited.
Thank you for submitting a review!
Your input is very much appreciated. Share it with your friends so they can enjoy it too!
Great Resource
Awesome! I was encouraged to find this as I develop my own writing curriculum for my homeschooled middle schoolers.

Nice resource
I haven't used this resource yet, but at first glance it looks helpful!
Research Writing
I have not started this with my child yet, but I have looked over the information. I am really looking forward to using this. Very informative.
I absolutely love the blended
I absolutely love the blended lesson plan structure that accommodates for all types of learners. you all ROCK!!!
Excellent curriculum
Lots of subjects and ways to teach kids. Love the packets
Related products

Careers: Archaeologist

Man o’ Wars

Meriwether Lewis and William Clark
Make your life easier with our lesson plans, stay up-to-date with new lessons.

- Lesson Plans
- For Teachers
© 2024 Learn Bright. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions. Privacy Policy.
- Sign Up for Free

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
C.1.1 Formatting a Research Paper
Learning objectives.
- Identify the major components of a research paper written using American Psychological Association (APA) style.
- Apply general APA style and formatting conventions in a research paper.
In this chapter, you will learn how to use APA style , the documentation and formatting style followed by the American Psychological Association, as well as MLA style , from the Modern Language Association. There are a few major formatting styles used in academic texts, including AMA, Chicago, and Turabian:
- AMA (American Medical Association) for medicine, health, and biological sciences
- APA (American Psychological Association) for education, psychology, and the social sciences
- Chicago —a common style used in everyday publications like magazines, newspapers, and books
- MLA (Modern Language Association) for English, literature, arts, and humanities
- Turabian —another common style designed for its universal application across all subjects and disciplines
While all the formatting and citation styles have their own use and applications, in this chapter we focus our attention on the two styles you are most likely to use in your academic studies: APA and MLA.
If you find that the rules of proper source documentation are difficult to keep straight, you are not alone. Writing a good research paper is, in and of itself, a major intellectual challenge. Having to follow detailed citation and formatting guidelines as well may seem like just one more task to add to an already-too-long list of requirements.
Following these guidelines, however, serves several important purposes. First, it signals to your readers that your paper should be taken seriously as a student’s contribution to a given academic or professional field; it is the literary equivalent of wearing a tailored suit to a job interview. Second, it shows that you respect other people’s work enough to give them proper credit for it. Finally, it helps your reader find additional materials if he or she wishes to learn more about your topic.
Furthermore, producing a letter-perfect APA-style paper need not be burdensome. Yes, it requires careful attention to detail. However, you can simplify the process if you keep these broad guidelines in mind:
- Work ahead whenever you can. You can consult the chapter, “ Writing from Research: What Will I Learn? “ from the original version of this textbook ( intentionally omitted ), which includes tips for keeping track of your sources early in the research process, which will save time later on.
- Get it right the first time. Apply APA guidelines as you write, so you will not have much to correct during the editing stage. Again, putting in a little extra time early on can save time later.
- Use the resources available to you. In addition to the guidelines provided in this chapter, you may wish to consult the APA website at http://www.apa.org or the Purdue University Online Writing lab at http://owl.english.purdue.edu , which regularly updates its online style guidelines.
- Consult the Fanshawe College Library website section “ ACADEMIC WRITING & CITATION ” for additional resources on research and citation.
General Formatting Guidelines
This chapter provides detailed guidelines for using the citation and formatting conventions developed by the American Psychological Association, or APA. Writers in disciplines as diverse as astrophysics, biology, psychology, and education follow APA style. The major components of a paper written in APA style are listed in the following box.
These are the major components of an APA-style paper:
Body, which includes the following:
- Headings and, if necessary, subheadings to organize the content
- In-text citations of research sources
- References page
All these components must be saved in one document, not as separate documents.
The title page of your paper includes the following information:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Name of the institution with which the author is affiliated
- Header at the top of the page with the paper title (in capital letters) and the page number (If the title is lengthy, you may use a shortened form of it in the header.)
List the first three elements in the order given in the previous list, centered about one third of the way down from the top of the page. Use the headers and footers tool of your word-processing program to add the header, with the title text at the left and the page number in the upper-right corner. Your title page should look like the following example.

The next page of your paper provides an abstract , or brief summary of your findings. An abstract does not need to be provided in every paper, but an abstract should be used in papers that include a hypothesis. A good abstract is concise—about one hundred fifty to two hundred fifty words—and is written in an objective, impersonal style. Your writing voice will not be as apparent here as in the body of your paper. When writing the abstract, take a just-the-facts approach, and summarize your research question and your findings in a few sentences.
Below is a sample paper written by a student named Jorge, who researched the effectiveness of low-carbohydrate diets. Read Jorge’s abstract. Note how it sums up the major ideas in his paper without going into excessive detail.
To view the original draft of this paper, you can review the chapter entitled, “ Creating a Rough Draft for a Research Paper ” from the original version of this textbook ( intentionally omitted ).

Write an abstract summarizing your paper. Briefly introduce the topic, state your findings, and sum up what conclusions you can draw from your research. Use the word count feature of your word-processing program to make sure your abstract does not exceed one hundred fifty words.
Depending on your field of study, you may sometimes write research papers that present extensive primary research, such as your own experiment or survey. In your abstract, summarize your research question and your findings, and briefly indicate how your study relates to prior research in the field.
Margins, Pagination, and Headings
APA style requirements also address specific formatting concerns, such as margins, pagination, and heading styles, within the body of the paper. Review the following APA guidelines.
Use these general guidelines to format the paper:
- Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch.
- Use double-spaced text throughout your paper.
- Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point).
- Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section. Page numbers appear flush right within your header.
- Section headings and subsection headings within the body of your paper use different types of formatting depending on the level of information you are presenting. Additional details from Jorge’s paper are provided.

Begin formatting the final draft of your paper according to APA guidelines. You may work with an existing document or set up a new document if you choose. Include the following:
- Your title page
- The abstract you created in “Exercise 1”
- Correct headers and page numbers for your title page and abstract
APA style uses section headings to organize information, making it easy for the reader to follow the writer’s train of thought and to know immediately what major topics are covered. Depending on the length and complexity of the paper, its major sections may also be divided into subsections, sub-subsections, and so on. These smaller sections, in turn, use different heading styles to indicate different levels of information. In essence, you are using headings to create a hierarchy of information.
The following heading styles used in APA formatting are listed in order of greatest to least importance:
- Section headings use centered, boldface type. Headings use title case, with important words in the heading capitalized.
- Subsection headings use left-aligned, boldface type. Headings use title case.
- The third level uses left-aligned, indented, boldface type. Headings use a capital letter only for the first word, and they end in a period.
- The fourth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are boldfaced and italicized.
- The fifth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are italicized and not boldfaced.
Visually, the hierarchy of information is organized as indicated in Table C.1.1 “Section Headings” .
Table C.1.1 Section Headings
A college research paper may not use all the heading levels shown in Table C.1.1 “Section Headings” , but you are likely to encounter them in academic journal articles that use APA style. For a brief paper, you may find that level 1 headings suffice. Longer or more complex papers may need level 2 headings or other lower-level headings to organize information clearly. Use your outline to craft your major section headings and determine whether any subtopics are substantial enough to require additional levels of headings.
Working with the document you developed in “Exercise 2” , begin setting up the heading structure of the final draft of your research paper according to APA guidelines. Include your title and at least two to three major section headings, and follow the formatting guidelines provided above. If your major sections should be broken into subsections, add those headings as well. Use your outline to help you.
Because Jorge used only level 1 headings, his Exercise 3 would look like the following:
Citation Guidelines
In-text citations.
Throughout the body of your paper, include a citation whenever you quote or paraphrase material from your research sources. The purpose of citations is twofold: to give credit to others for their ideas and to allow your reader to follow up and learn more about the topic if desired. Your in-text citations provide basic information about your source; each source you cite will have a longer entry in the references section that provides more detailed information.
In-text citations must provide the name of the author or authors and the year the source was published. (When a given source does not list an individual author, you may provide the source title or the name of the organization that published the material instead.) When directly quoting a source, it is also required that you include the page number where the quote appears in your citation.
This information may be included within the sentence or in a parenthetical reference at the end of the sentence, as in these examples.
Epstein (2010) points out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Here, the writer names the source author when introducing the quote and provides the publication date in parentheses after the author’s name. The page number appears in parentheses after the closing quotation marks and before the period that ends the sentence.
Addiction researchers caution that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (Epstein, 2010, p. 137).
Here, the writer provides a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence that includes the author’s name, the year of publication, and the page number separated by commas. Again, the parenthetical citation is placed after the closing quotation marks and before the period at the end of the sentence.
As noted in the book Junk Food, Junk Science (Epstein, 2010, p. 137), “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive.”
Here, the writer chose to mention the source title in the sentence (an optional piece of information to include) and followed the title with a parenthetical citation. Note that the parenthetical citation is placed before the comma that signals the end of the introductory phrase.
David Epstein’s book Junk Food, Junk Science (2010) pointed out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Another variation is to introduce the author and the source title in your sentence and include the publication date and page number in parentheses within the sentence or at the end of the sentence. As long as you have included the essential information, you can choose the option that works best for that particular sentence and source.
Citing a book with a single author is usually a straightforward task. Of course, your research may require that you cite many other types of sources, such as books or articles with more than one author or sources with no individual author listed. You may also need to cite sources available in both print and online and nonprint sources, such as websites and personal interviews.
The rest of this chapter provides extensive guidelines for citing a variety of source types.
Writing at Work
APA is just one of several different styles with its own guidelines for documentation, formatting, and language usage. Depending on your field of interest, you may be exposed to additional styles, such as the following:
- MLA style. Determined by the Modern Languages Association and used for papers in literature, languages, and other disciplines in the humanities.
- Chicago style. Outlined in the Chicago Manual of Style and sometimes used for papers in the humanities and the sciences; many professional organizations use this style for publications as well.
- Associated Press (AP) style. Used by professional journalists.
References List
The brief citations included in the body of your paper correspond to the more detailed citations provided at the end of the paper in the references section. In-text citations provide basic information—the author’s name, the publication date, and the page number if necessary—while the references section provides more extensive bibliographical information. Again, this information allows your reader to follow up on the sources you cited and do additional reading about the topic if desired.
The specific format of entries in the list of references varies slightly for different source types, but the entries generally include the following information:
- The name(s) of the author(s) or institution that wrote the source
- The year of publication and, where applicable, the exact date of publication
- The full title of the source
- For books, the city of publication
- For articles or essays, the name of the periodical or book in which the article or essay appears
- For magazine and journal articles, the volume number, issue number, and pages where the article appears
- For sources on the web, the URL where the source is located
The references page is double spaced and lists entries in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. If an entry continues for more than one line, the second line and each subsequent line are indented five spaces. Review the following example.

In APA style, book and article titles are formatted in sentence case, not title case. Sentence case means that only the first word is capitalized, along with any proper nouns.
Key Takeaways
- Following proper citation and formatting guidelines helps writers ensure that their work will be taken seriously, give proper credit to other authors for their work, and provide valuable information to readers.
- Working ahead and taking care to cite sources correctly the first time are ways writers can save time during the editing stage of writing a research paper.
- APA papers usually include an abstract that concisely summarizes the paper.
- APA papers use a specific headings structure to provide a clear hierarchy of information.
- In APA papers, in-text citations usually include the name(s) of the author(s) and the year of publication.
- In-text citations correspond to entries in the references section, which provide detailed bibliographical information about a source.
Putting the Pieces Together Copyright © 2020 by Andrew Stracuzzi and André Cormier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Baltimore bridge collapse: a bridge engineer explains what happened, and what needs to change
Associate Professor, Civil Engineering, Monash University
Disclosure statement
Colin Caprani receives funding from the Department of Transport (Victoria) and the Level Crossing Removal Project. He is also Chair of the Confidential Reporting Scheme for Safer Structures - Australasia, Chair of the Australian Regional Group of the Institution of Structural Engineers, and Australian National Delegate for the International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering.
Monash University provides funding as a founding partner of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
When the container ship MV Dali, 300 metres long and massing around 100,000 tonnes, lost power and slammed into one of the support piers of the Francis Scott Key Bridge in Baltimore, the bridge collapsed in moments . Six people are presumed dead, several others injured, and the city and region are expecting a months-long logistical nightmare in the absence of a crucial transport link.
It was a shocking event, not only for the public but for bridge engineers like me. We work very hard to ensure bridges are safe, and overall the probability of being injured or worse in a bridge collapse remains even lower than the chance of being struck by lightning.
However, the images from Baltimore are a reminder that safety can’t be taken for granted. We need to remain vigilant.
So why did this bridge collapse? And, just as importantly, how might we make other bridges more safe against such collapse?
A 20th century bridge meets a 21st century ship
The Francis Scott Key Bridge was built through the mid 1970s and opened in 1977. The main structure over the navigation channel is a “continuous truss bridge” in three sections or spans.
The bridge rests on four supports, two of which sit each side of the navigable waterway. It is these two piers that are critical to protect against ship impacts.
And indeed, there were two layers of protection: a so-called “dolphin” structure made from concrete, and a fender. The dolphins are in the water about 100 metres upstream and downstream of the piers. They are intended to be sacrificed in the event of a wayward ship, absorbing its energy and being deformed in the process but keeping the ship from hitting the bridge itself.
The fender is the last layer of protection. It is a structure made of timber and reinforced concrete placed around the main piers. Again, it is intended to absorb the energy of any impact.
Fenders are not intended to absorb impacts from very large vessels . And so when the MV Dali, weighing more than 100,000 tonnes, made it past the protective dolphins, it was simply far too massive for the fender to withstand.
Read more: I've captained ships into tight ports like Baltimore, and this is how captains like me work with harbor pilots to avoid deadly collisions
Video recordings show a cloud of dust appearing just before the bridge collapsed, which may well have been the fender disintegrating as it was crushed by the ship.
Once the massive ship had made it past both the dolphin and the fender, the pier – one of the bridge’s four main supports – was simply incapable of resisting the impact. Given the size of the vessel and its likely speed of around 8 knots (15 kilometres per hour), the impact force would have been around 20,000 tonnes .
Bridges are getting safer
This was not the first time a ship hit the Francis Scott Bridge. There was another collision in 1980 , damaging a fender badly enough that it had to be replaced.
Around the world, 35 major bridge collapses resulting in fatalities were caused by collisions between 1960 and 2015, according to a 2018 report from the World Association for Waterborne Transport Infrastructure. Collisions between ships and bridges in the 1970s and early 1980s led to a significant improvement in the design rules for protecting bridges from impact.

Further impacts in the 1970s and early 1980s instigated significant improvements in the design rules for impact.
The International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering’s Ship Collision with Bridges guide, published in 1993, and the American Association of State Highway and Transporation Officials’ Guide Specification and Commentary for Vessel Collision Design of Highway Bridges (1991) changed how bridges were designed.
In Australia, the Australian Standard for Bridge Design (published in 2017) requires designers to think about the biggest vessel likely to come along in the next 100 years, and what would happen if it were heading for any bridge pier at full speed. Designers need to consider the result of both head-on collisions and side-on, glancing blows. As a result, many newer bridges protect their piers with entire human-made islands.
Of course, these improvements came too late to influence the design of the Francis Scott Key Bridge itself.
Lessons from disaster
So what are the lessons apparent at this early stage?
First, it’s clear the protection measures in place for this bridge were not enough to handle this ship impact. Today’s cargo ships are much bigger than those of the 1970s, and it seems likely the Francis Scott Key Bridge was not designed with a collision like this in mind.
So one lesson is that we need to consider how the vessels near our bridges are changing. This means we cannot just accept the structure as it was built, but ensure the protection measures around our bridges are evolving alongside the ships around them.

Second, and more generally, we must remain vigilant in managing our bridges. I’ve written previously about the current level of safety of Australian bridges, but also about how we can do better.
This tragic event only emphasises the need to spend more on maintaining our ageing infrastructure. This is the only way to ensure it remains safe and functional for the demands we put on it today.
- Engineering
- Infrastructure
- Urban infrastructure
- container ships
- Baltimore bridge collapse

Research Fellow – Beyond The Resource Curse

Audience Development Coordinator (fixed-term maternity cover)

Lecturer (Hindi-Urdu)

Director, Defence and Security

Opportunities with the new CIEHF

COMMENTS
Procedure [60 minutes]: Step 1: Begin the lesson plan with an image [3 minutes] Show the third slide of the PowerPoint presentation with a picture of stacked books and an apple on the top of the book that is titled "Education.". Begin to discuss the significance of the apple as. a very powerful fruit.
Lesson Plan 1: Research paper Writing: An Overview . Objectives: -SWBAT identify parts that comprise a scientific research paper -SWBAT understand some different ways scientists develop ideas for their research -SWBAT understand the advantages of conducting a literature search -SWBAT understand the process of writing a research paper
Students will use scaffolding to research and organize information for writing a research paper. A research paper scaffold provides students with clear support for writing expository papers that include a question (problem), literature review, analysis, methodology for original research, results, conclusion, and references.
1. Gathering Research. Students often need guidance in researching. I take them to our university library and help them use our library search engines. In doing non-profit research papers, I have my students look at the websites of the charities and find research papers about the problems the non-profits try to solve.
The research writing presentation introduces students to the eight steps for completing a research project: selecting topics, generating questions, brainstorming, researching and gathering credible information, organizing and outlining, writing the first draft, peer editing, and finalizing the paper.
CUNY Brooklyn offers this complete lesson plan for introducing students to research papers. It includes an accompanying set of PowerPoint slides. "Lesson Plan: How to Begin Writing a Research Paper" (San Jose State Univ.) This lesson plan is designed for students in the health sciences, so teachers will have to modify it for their own needs.
Lesson Ideas for Writing Research Papers: Lesson 1: Noticings. ... This graphic organizer can be used for students to plan their writing. If your writers are more advanced you might choose to skip this step, It could be a big help for students who have taken notes and have too many facts.
As students learn the important skill of responsibly researching for their writing, we at VariQuest have put together a 42-page booklet, split into two parts (to make it easier to digest and teach!) and this first part focuses on the research portion of the process. From choosing a topic, to learning to paraphrase, to writing a thesis, these ...
Original Research How would you test the idea you think makes the most sense? In order to test the ideas about (your topic) this researcher will (describe a suitable way to test your ideas: survey, experiment, model, interview, etc.) _____Results: (What happened?)List your results. You can attach a table, chart, or list of findings.
Consult reference materials to verify statements contained in realistic fiction selections. Browse our printable Writing Research Papers Lesson Plans resources for your classroom. Download free today!
Learn to write a research paper step-by-step with a process that involves determining the research purpose and question in the early stages, finding sources, taking notes, creating an outline, and ...
One of the challenges of a research paper is establishing credibility. Any mistake in this area requires a penalty. Content: 10 pts. This is the opposite of what I usually do. The major objective of this assignment is to teach technical research writing skills. Once the basic skills of research writing are complete, I can then focus on content.
Get Part 1: The Research Process here! From writing introductions and conclusions to proofreading to publishing, these lessons are designed in a writers'-workshop-style to guide students through all the important steps in writing a research paper. Using the example of The Great Barrier Reef, all lessons come paired with a handful of helpful ...
Try out some of these strategies for introducing your research paper. Read the examples for ideas. Make a copy of this Google doc or download a Word template. Start with a fascinating quotation. "Do things. Be sane. Don't fritter away your time; create, act, take a place wherever you are, and be somebody; get action.". —Theodore Roosevelt ...
Section 1. Student Learning Objectives. As a result of meeting the requirements in this course, you will be able to: 1. Employ a variety of approaches to analyze and interpret texts. (PLG 1) (Gen Ed Goal 1 a) 2. Respond to texts, in discussion and writing assignments, demonstrating an understanding of rhetorical strategies employed in the texts.
Writing a research paper can seem like a daunting task, but if you take the time in the pages ahead to learn how to break the writing process down, you will be amazed at the level of comfort and control you feel when preparing your assignment. Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783. This work is licensed under a Creative ...
Our Research Writing lesson plan for grades 3-4 teaches students how to write a thoroughly researched and factually accurate five paragraph essay. Students practice researching a topic, summarizing and citing their information, and consolidating it into paragraphs. Categories: Downloadable, Language Arts Tags: 3rd Grade, 4th Grade.
Developed in partnership with Cathy Henry of The Curriculum Corner, students will come away with plenty of research and sources to begin part 2 of the journey - The Writing Process. In this activity you'll find: Lessons 1-9 of the How to Write a Research Paper Unit focused on the research part of the process
Now play the video lesson How to Write an Outline for an Essay or Research Paper for the class, pausing at 00:53. Do any of the students know the differences between an alphanumeric outline and a ...
Our Research Writing lesson plan for grades 4-6 teaches students how to write a thoroughly researched and factually accurate five paragraph essay. Students write an essay based on research they conduct in order to practice this type of writing. Categories: Downloadable, Language Arts Tags: 4th Grade, 5th Grade, 6th Grade.
A Detailed Lesson Plan in English Grade 10. I. Objectives At the end of this lesson, the students will be able to: a. interpret the primary purpose of an academic research paper.; b. examine ways to get started with the writing process.; and c. explain the importance of research in daily lives
Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch. Use double-spaced text throughout your paper. Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point). Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section.
Published: March 26, 2024 11:59pm EDT. When the container ship MV Dali, 300 metres long and massing around 100,000 tonnes, lost power and slammed into one of the support piers of the Francis Scott ...