How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree?
Earning a Ph.D. from a U.S. grad school typically requires nearly six years, federal statistics show.
How Long It Takes to Get a Ph.D. Degree

Caiaimage | Tom Merton | Getty Images
A Ph.D. is most appropriate for someone who is a "lifelong learner."
Students who have excelled within a specific academic discipline and who have a strong interest in that field may choose to pursue a Ph.D. degree. However, Ph.D. degree-holders urge prospective students to think carefully about whether they truly want or need a doctoral degree, since Ph.D. programs last for multiple years.
According to the Survey of Earned Doctorates, a census of recent research doctorate recipients who earned their degree from U.S. institutions, the median amount of time it took individuals who received their doctorates in 2017 to complete their program was 5.8 years. However, there are many types of programs that typically take longer than six years to complete, such as humanities and arts doctorates, where the median time for individuals to earn their degree was 7.1 years, according to the survey.
Some Ph.D. candidates begin doctoral programs after they have already obtained master's degrees, which means the time spent in grad school is a combination of the time spent pursuing a master's and the years invested in a doctorate. In order to receive a Ph.D. degree, a student must produce and successfully defend an original academic dissertation, which must be approved by a dissertation committtee. Writing and defending a dissertation is so difficult that many Ph.D. students drop out of their Ph.D. programs having done most of the work necessary for degree without completing the dissertation component. These Ph.D. program dropouts often use the phrase " all but dissertation " or the abbreviation "ABD" on their resumes.
According to a comprehensive study of Ph.D. completion rates published by The Council of Graduate Schools in 2008, only 56.6% of people who begin Ph.D. programs earn Ph.D. degrees.
Ian Curtis, a founding partner with H&C Education, an educational and admissions consulting firm, who is pursuing a Ph.D. degree in French at Yale University , says there are several steps involved in the process of obtaining a Ph.D. Students typically need to fulfill course requirements and pass comprehensive exams, Curtis warns. "Once these obligations have been completed, how long it takes you to write your dissertation depends on who you are, how you work, what field you're in and what other responsibilities you have in life," he wrote in an email. Though some Ph.D. students can write a dissertation in a single year, that is rare, and the dissertation writing process may last for several years, Curtis says.
Curtis adds that the level of support a Ph.D. student receives from an academic advisor or faculty mentor can be a key factor in determining the length of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. program. "Before you decide to enroll at a specific program, you’ll want to meet your future advisor," Curtis advises. "Also, reach out to his or her current and former students to get a sense of what he or she is like to work with."
Curtis also notes that if there is a gap between the amount of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. and the amount of time a student's funding lasts, this can slow down the Ph.D. completion process. "Keep in mind that if you run out of funding at some point during your doctorate, you will need to find paid work, and this will leave you even less time to focus on writing your dissertation," he says. "If one of the programs you’re looking at has a record of significantly longer – or shorter – times to competition, this is good information to take into consideration."
He adds that prospective Ph.D. students who already have master's degrees in the field they intend to focus their Ph.D. on should investigate whether the courses they took in their master's program would count toward the requirements of a Ph.D. program. "You’ll want to discuss your particular situation with your program to see whether this will be possible, and how many credits you are likely to receive as the result of your master’s work," he says.

How to Write M.D.-Ph.D. Application Essays
Ilana Kowarski May 15, 2018

Emmanuel C. Nwaodua, who has a Ph.D. degree in geology, says some Ph.D. programs require candidates to publish a paper in a first-rate, peer-reviewed academic journal. "This could extend your stay by a couple of years," he warns.
Pierre Huguet, the CEO and co-founder of H&C Education, says prospective Ph.D. students should be aware that a Ph.D. is designed to prepare a person for a career as a scholar. "Most of the jobs available to Ph.D. students upon graduation are academic in nature and directly related to their fields of study: professor, researcher, etc.," Huguet wrote in an email. "The truth is that more specialization can mean fewer job opportunities. Before starting a Ph.D., students should be sure that they want to pursue a career in academia, or in research. If not, they should make time during the Ph.D. to show recruiters that they’ve traveled beyond their labs and libraries to gain some professional hands-on experience."
Jack Appleman, a business writing instructor, published author and Ph.D. candidate focusing on organizational communication with the University at Albany—SUNY , says Ph.D. programs require a level of commitment and focus that goes beyond what is necessary for a typical corporate job. A program with flexible course requirements that allow a student to customize his or her curriculum based on academic interests and personal obligations is ideal, he says.
Joan Kee, a professor at the University of Michigan with the university's history of art department, says that the length of time required for a Ph.D. varies widely depending on what subject the Ph.D. focuses on. "Ph.D. program length is very discipline and even field-specific; for example, you can and are expected to finish a Ph.D, in economics in under five years, but that would be impossible in art history (or most of the humanities)," she wrote in an email.
Kee adds that humanities Ph.D. programs often require someone to learn a foreign language, and "fields like anthropology and art history require extensive field research." Kee says funding for a humanities Ph.D. program typically only lasts five years, even though it is uncommon for someone to obtain a Ph.D. degree in a humanities field within that time frame. "Because of this, many if not most Ph.D. students must work to make ends meet, thus further prolonging the time of completion," she says.
Jean Marie Carey, who earned her Ph.D. degree in art history and German from the University of Otago in New Zealand, encourages prospective Ph.D. students to check whether their potential Ph.D. program has published a timeline of how long it takes a Ph.D. student to complete their program. She says it is also prudent to speak with Ph.D. graduates of the school and ask about their experience.
Online Doctoral Programs: What to Expect
Ronald Wellman March 23, 2018

Kristin Redington Bennett, the founder of the Illumii educational consulting firm in North Carolina, encourages Ph.D. hopefuls to think carefully about whether they want to become a scholar. Bennett, who has a Ph.D. in curriculum and assessment and who previously worked as an assistant professor at Wake Forest University , says a Ph.D. is most appropriate for someone who is a "lifelong learner." She says someone contemplating a Ph.D. should ask themselves the following questions "Are you a very curious person... and are you persistent?"
Bennett urges prospective Ph.D. students to visit the campuses of their target graduate programs since a Ph.D. program takes so much time that it is important to find a school that feels comfortable. She adds that aspiring Ph.D. students who prefer a collaborative learning environment should be wary of graduate programs that have a cut-throat and competitive atmosphere, since such students may not thrive in that type of setting.
Alumni of Ph.D. programs note that the process of obtaining a Ph.D. is arduous, regardless of the type of Ph.D. program. "A Ph.D. is a long commitment of your time, energy and financial resources, so it'll be easier on you if you are passionate about research," says Grace Lee, who has a Ph.D. in neuroscience and is the founder and CEO of Mastery Insights, an education and career coaching company, and the host of the Career Revisionist podcast.
"A Ph.D. isn't about rehashing years of knowledge that is already out there, but rather it is about your ability to generate new knowledge. Your intellectual masterpiece (which is your dissertation) takes a lot of time, intellectual creativity and innovation to put together, so you have to be truly passionate about that," Lee says.
Curtis says a prospective Ph.D. student's enthusiasm for academic work, teaching and research are the key criteria they should use to decide whether to obtain a Ph.D. degree. "While the time it takes to complete a doctorate is an understandable concern for many, my personal belief is that time is not the most important factor to consider," he says. "Good Ph.D. programs provide their students with generous stipends, health care and sometimes even subsidized housing."
Erin Skelly, a graduate admissions counselor at the IvyWise admissions consulting firm, says when a Ph.D. students struggles to complete his or her Ph.D. degree, it may have more to do with the student's academic interests or personal circumstances than his or her program.
"The time to complete a Ph.D. can depend on a number of variables, but the specific discipline or school would only account for a year or two's difference," she wrote in an email. "When a student takes significantly longer to complete a Ph.D. (degree), it's usually related to the student's coursework and research – they need to take additional coursework to complete their comprehensive exams; they change the focus of their program or dissertation, requiring extra coursework or research; or their research doesn't yield the results they hoped for, and they need to generate a new theory and conduct more research."
Skelly warns that the average completion time of a Ph.D. program may be misleading in some cases, if the average is skewed based on one or two outliers. She suggests that instead of focusing on the duration of a particular Ph.D. program, prospective students should investigate the program's attritition and graduation rates.
"It is worthwhile to look at the program requirements and the school's proposed timeline for completion, and meet current students to get their input on how realistic these expectations for completion are," Skelly says. "That can give you an honest idea of how long it will really take to complete the program."
Searching for a grad school? Access our complete rankings of Best Graduate Schools.
Tags: graduate schools , education , students
You May Also Like
What to ask law students and alumni.
Gabriel Kuris April 22, 2024

Find a Strong Human Rights Law Program
Anayat Durrani April 18, 2024

Environmental Health in Medical School
Zach Grimmett April 16, 2024

How to Choose a Law Career Path
Gabriel Kuris April 15, 2024

Questions Women MBA Hopefuls Should Ask
Haley Bartel April 12, 2024

Law Schools With the Highest LSATs
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 11, 2024

MBA Programs That Lead to Good Jobs
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 10, 2024

B-Schools With Racial Diversity
Sarah Wood April 10, 2024

Law Schools That Are Hardest to Get Into
Sarah Wood April 9, 2024

Ask Law School Admissions Officers This
Gabriel Kuris April 9, 2024


Research Voyage
Research Tips and Infromation
How Long Should Be PhD Dissertation? Unlocking The Mystery of PhD Thesis Length

Embarking on the journey of a PhD is a scholarly endeavour that demands not only intellectual prowess but also a deep commitment to contributing valuable insights to the academic world. At the heart of this rigorous pursuit lies the dissertation, a magnum opus that serves as the pinnacle of one’s academic achievement. Yet, as aspiring scholars delve into the realms of research and knowledge creation, a pivotal question looms large: How long should a Ph.D. dissertation be?
The optimal length of a Ph.D. dissertation is a strategic equilibrium, determined by the intricate interplay of research complexity, disciplinary norms, and institutional guidelines, emphasizing quality over mere quantity.
In the intricate tapestry of academia, the length of a dissertation is a nuanced consideration, influenced by a myriad of factors ranging from disciplinary norms to the intricacies of research design. In this exploration, we embark on a journey to unravel the complexities surrounding dissertation length, understanding the guiding principles, and offering insights into how aspiring doctoral candidates can strike the delicate balance between depth and brevity.
Join us as we navigate the academic landscape, demystifying the expectations, uncovering the variances across disciplines, and providing practical tips for crafting a dissertation that stands as a testament to scholarly excellence. Whether you’re at the threshold of your doctoral journey or guiding others through its twists and turns, this discourse aims to shed light on the intricacies of dissertation length, empowering you to embark on this intellectual odyssey with confidence and purpose.
Introduction
A. defining the purpose.
- B. The Dissertation's Role in Academic Knowledge
C. Emphasizing Thorough Research and Original Contributions
A. exploring institutional guidelines, b. specific requirements and length expectations, c. the importance of adherence, a. acknowledging disciplinary differences, b. examples of varied expectations, c. emphasizing disciplinary norms, a. research complexity, b. data collection and analysis, c. literature review, d. methodology, a. emphasizing the importance of balance, b. strategies for maintaining focus and relevance, c. encouraging quality over quantity, a. effective time management, b. techniques for concise writing, c. value of feedback from advisors and peers.
Embarking on a PhD journey is akin to setting sail into uncharted waters of knowledge, with the dissertation standing tall as the crowning achievement. It’s not just a document; it’s a testament to years of intellectual toil, research finesse, and a contribution to the vast expanse of human understanding. But as scholars immerse themselves in the sea of research, a question inevitably surfaces: How long should a Ph.D. dissertation be?
Significance Unveiled
A Ph.D. dissertation is more than a lengthy document; it’s a scholarly masterpiece that not only encapsulates an individual’s intellectual prowess but adds a unique brushstroke to the grand canvas of academia. It’s a beacon of knowledge, guiding future researchers and shaping the trajectory of scholarly discourse. Understanding its significance is the first step toward unlocking the secrets of its length.
Navigating Length: A Delicate Balancing Act
Determining the appropriate length for a Ph.D. dissertation is no mere formality. It’s a delicate dance between providing comprehensive insights and maintaining reader engagement. Striking this balance is crucial, as the length not only influences how the research is perceived but also reflects the researcher’s ability to weave a compelling narrative without unnecessary verbosity.
Factors in the Equation
The length of a dissertation is a dynamic variable influenced by a multitude of factors. From the complexity of the research question to the intricacies of data collection, each element plays a role. It’s a symphony where the depth of the literature review, the intricacy of the methodology, and the nature of the chosen discipline all contribute to the final crescendo of the dissertation length.
Purpose of a PhD Dissertation
At the heart of the Ph.D. journey lies the dissertation, a formidable endeavour that goes beyond being a mere academic requirement. It serves as the cornerstone of a scholar’s intellectual legacy, encapsulating years of research, critical thinking, and a commitment to advancing knowledge in a specific field. The purpose of a Ph.D. dissertation extends far beyond a graduation requirement; it is a scholarly rite of passage that marks one’s entry into the ranks of contributing intellectuals.
B. The Dissertation’s Role in Academic Knowledge
The dissertation, in essence, is a torchbearer of academic knowledge. It doesn’t merely regurgitate existing information but actively contributes to the ongoing conversation within a field. Picture it as a puzzle piece that, when seamlessly integrated, enriches the larger mosaic of human understanding. Its role is not just to summarize what is known but to illuminate uncharted territories, challenging established paradigms and paving the way for new insights.
Example: In the field of environmental science, a Ph.D. dissertation might delve into the impact of climate change on a specific ecosystem, offering novel findings that reshape our understanding of ecological resilience. It becomes a pivotal contribution that informs future research and policy decisions.
Thorough research is the bedrock upon which a meaningful dissertation stands. It involves meticulously exploring existing literature, methodologies, and gaps in knowledge. This isn’t a cursory glance but a deep dive into the scholarly ocean, where each wave of information contributes to the construction of a comprehensive understanding.
Original contributions are the soul of a Ph.D. dissertation. It’s not just about rehashing what’s already known but about introducing something new and transformative. This could be a novel research methodology, a groundbreaking theory, or empirical findings that challenge existing theories.
Example: In the realm of psychology, a Ph.D. dissertation might involve the development of a new therapeutic approach for a specific mental health condition, backed by both a comprehensive review of existing literature and empirical evidence from original studies. This not only adds to the academic discourse but also has tangible implications for clinical practice.
University Guidelines PhD Dissertation Length: Navigating the Academic Framework
In academia, each university sets the stage with its own set of guidelines governing the composition and expectations of a Ph.D. dissertation. These guidelines serve as the rulebook, providing a roadmap for aspiring scholars to traverse the challenging terrain of research and writing. Understanding these guidelines is akin to deciphering the code that unlocks the door to doctoral success.
Dive into the particulars, and you’ll find that universities often outline specific requirements and expectations regarding the length of a dissertation. These may range from prescribed word counts for each section to broader expectations for the overall document. Some institutions might emphasize brevity, while others encourage a more expansive exploration. Unravelling these expectations is not just a bureaucratic formality; it’s a strategic move that ensures your work aligns with the academic standards set by your institution.
Example: Imagine a university that places a strong emphasis on concise and focused dissertations. Here, the guidelines may state a maximum word count for each chapter, encouraging a streamlined and impactful presentation of research findings. Adhering to these specifics ensures that your dissertation not only meets the academic standards but also resonates with the evaluators who appreciate clarity and precision.
While the allure of academic freedom may tempt scholars to chart their own course, adherence to institutional guidelines is paramount. It’s not just a matter of compliance; it’s a strategic decision that aligns your work with the expectations of the academic community. Universities set guidelines with a purpose – to maintain standards, ensure consistency, and facilitate fair evaluation. Ignoring these guidelines can inadvertently hinder the reception of your dissertation, potentially overshadowing the brilliance of your research with concerns about adherence to academic norms.
Disciplinary Variances: Navigating the Length Spectrum
In the vast landscape of academia, one size certainly does not fit all, especially when it comes to the length of Ph.D. dissertations. It’s crucial to acknowledge and appreciate the dynamic nature of disciplinary differences, where each field has its own set of expectations, traditions, and scholarly norms. Understanding this diversity is the key to crafting a dissertation that resonates within the specific academic community to which it belongs.
Let’s take a stroll through different academic landscapes to grasp the breadth of expectations. In the sciences, precision and brevity often reign supreme. A molecular biology dissertation, for instance, may prioritize concise methodology and results chapters, with an emphasis on data interpretation. Contrast this with a dissertation in the humanities, where the richness of language and the depth of literary analysis might lead to a more extensive exploration of concepts.
Example: In engineering, a Ph.D. dissertation might lean towards a succinct presentation of methodologies, experimental results, and their implications for the field. Meanwhile, in the realm of philosophy, a dissertation could be characterized by a more expansive engagement with existing literature and a thorough philosophical exploration of the research question.
The beauty of academia lies in its diversity, but this very diversity requires scholars to be attuned to the norms of their specific discipline. What might be considered a concise and impactful dissertation in one field could be seen as lacking depth in another. Recognizing these norms is not just a matter of fitting in; it’s a strategic decision that ensures your work aligns with the expectations of your academic peers.
Understanding disciplinary norms is like speaking the language of your scholarly community. It’s about knowing when to be succinct and when to elaborate, when to prioritize methodology and when to delve deep into theoretical frameworks.
Factors Influencing PhD Dissertation Length
1. Impact of Research Question Complexity
The complexity of your research question is like the compass guiding the depth and breadth of your dissertation. Intricate inquiries often demand more comprehensive exploration, delving into multiple facets and dimensions. For instance, a research question investigating the genetic determinants of a rare disease may necessitate an extensive review of existing literature, detailed methodologies, and intricate analyses to uncover meaningful insights.
2. Examples of Research Topics
Consider the following examples to illustrate the point:
- Less Complex: An analysis of consumer behavior in response to a specific marketing strategy might require a detailed but more straightforward exploration.
- More Complex: On the other hand, a study examining the intersection of artificial intelligence and ethical considerations in healthcare may demand a multifaceted investigation into both technological and ethical dimensions, significantly impacting the length of the dissertation.
1. Influence of Data Nature and Quantity
The nature and amount of data collected cast a profound shadow on dissertation length. A project relying on extensive datasets, intricate statistical analyses, or comprehensive case studies inherently demands a more extended exploration. In contrast, qualitative research might be more concise but equally impactful in unraveling complex phenomena.
2. Role of Statistical Analysis, Case Studies, or Qualitative Research
Consider the following scenarios:
- Statistical Analysis: A dissertation delving into the economic impact of climate change policies might involve sophisticated statistical models and require an in-depth presentation of results and their implications.
- Qualitative Research: Conversely, a dissertation employing qualitative interviews to explore the lived experiences of individuals facing a specific social challenge may present findings in a more narrative form.
1. Significance of a Comprehensive Literature Review
A robust literature review acts as the scaffolding for your dissertation, providing the theoretical foundation and context for your research. The broader and more complex the field, the more extensive the literature review. For instance, exploring a niche area within a rapidly evolving field, like emerging technologies, may demand a more thorough literature review to capture the latest developments and debates.
2. Contribution to Overall Length
Consider this:
- A dissertation in environmental science, investigating the impact of urbanization on biodiversity, might necessitate a detailed exploration of existing literature on ecology, urban planning, and biodiversity conservation.
1. Impact of Detailed Research Methodology
The methodology section is the blueprint of your research, and its level of detail significantly influences the length of your dissertation. A dissertation with a meticulous methodology section is like a well-constructed building, providing a clear roadmap for readers to understand the research process.
2. Need for Clarity and Precision in Research Design
For example:
- A dissertation in public health aiming to assess the effectiveness of a health intervention might require a detailed explanation of the study design, participant recruitment strategies, and data collection methods to ensure the study’s validity and reliability.
Balancing Depth and Brevity: Crafting a Dissertation Masterpiece
In the symphony of scholarly writing, achieving harmony between depth and brevity is a skill that distinguishes a stellar dissertation. While delving deep into the nuances of your research is essential, presenting it with conciseness ensures that your audience remains engaged. The challenge lies in striking the right balance, where the richness of content is not sacrificed on the altar of brevity.
- Clear Research Objectives: Begin with well-defined research objectives that serve as the North Star for your dissertation. This clarity guides your writing, preventing unnecessary tangents and ensuring each section contributes directly to your overarching goals. Example: In a dissertation exploring the impact of mindfulness-based interventions on stress reduction, clear objectives would center around understanding the effectiveness of specific mindfulness techniques and their implications for stress management.
- Thematic Structure: Organize your dissertation thematically, ensuring each chapter has a clear purpose and contributes to building a cohesive narrative. This not only aids readability but also enhances the overall impact of your research. Example: In a literature review, grouping studies thematically—such as by intervention type or outcome measures—provides a structured and focused presentation of existing research, avoiding a scattered and disjointed narrative.
- Rigorous Editing: Approach your writing with a discerning eye during the editing process. Trim unnecessary words, sentences, or sections that do not directly contribute to the core message of your dissertation. Be ruthless in maintaining relevance. Example: In the methodology section, focus on explaining key decisions and processes, omitting redundant details that do not influence the study’s validity or replicability.
- Depth of Analysis: Instead of inundating your dissertation with an abundance of superficial analyses, delve deep into a few key points. Thoroughly explore the significance and implications of your findings, providing a nuanced understanding of your research. Example: In a discussion section, rather than covering multiple tangential points, focus on the most critical aspects of your results, analyzing their theoretical and practical implications in detail.
- Precision in Language: Choose words judiciously to convey your ideas with precision. Aim for clarity without unnecessary embellishments, ensuring that each sentence adds value to your argument. Example: In the introduction, use concise language to clearly articulate the research gap, the significance of the study, and the specific research questions without unnecessary elaboration.
- Selectivity in Citations: While a comprehensive literature review is vital, selectively cite studies that directly contribute to your research context. Avoid an exhaustive list that overwhelms readers with unnecessary details. Example: In a literature review on educational interventions for students with learning disabilities, selectively cite studies that showcase diverse approaches and methodologies, providing a nuanced understanding of the existing landscape.
As we navigate the delicate equilibrium between depth and brevity, remember that a well-crafted dissertation is not measured by its length but by the impact of its scholarly contributions. Join us as we explore the art of balancing substance with succinctness, ensuring your dissertation stands as a masterpiece in the annals of academic inquiry.
Tips for Managing PhD Dissertation Length: Navigating the Dissertation Writing Process
- Setting Realistic Milestones: Break down the dissertation-writing process into manageable milestones. Establish realistic timelines for each section, considering the complexity and time required for research, writing, and revisions. Example: Allocate a specific time frame for conducting literature reviews, data analysis, and drafting each chapter. This ensures steady progress and prevents last-minute rushes.
- Regular Progress Checks: Monitor your progress regularly and adjust your schedule as needed. If a particular section is taking longer than anticipated, evaluate the reasons and recalibrate your timeline accordingly. Example: If data analysis is proving more time-consuming than expected, revisit your research plan and, if necessary, adjust your writing schedule for subsequent chapters.
- Balancing Research and Writing: Strive for a balance between conducting research and writing. While research is crucial, allocate dedicated time for translating findings into written content to avoid a backlog of information. Example: If you’re conducting experiments, allocate specific writing sessions to summarize and interpret the results, ensuring a continuous flow of progress.
Visit my article on ” How to Manage Research Time” for managing PhD time.
- Clarity in Expression: Aim for clarity in your writing. Express complex ideas in straightforward language, avoiding unnecessary jargon or convoluted sentences that can inflate the word count without adding substance. Example: Instead of using complex terminology in a theoretical framework, opt for clear and precise language that conveys the theoretical concepts without unnecessary embellishments.
- Economical Word Choices: Choose words judiciously. Opt for strong, impactful words that convey your message succinctly. Trim redundant phrases and eliminate words that don’t contribute directly to your argument. Example: Instead of saying “due to the fact that,” use the more concise “because” to convey the same meaning with fewer words.
- Strategic Use of Figures and Tables: Incorporate visuals strategically to convey information efficiently. Figures and tables can often replace lengthy textual explanations, providing a visual representation of data or concepts. Example: Instead of describing a complex set of results in paragraphs, present key findings in a well-designed table, allowing readers to grasp the information at a glance.
- Early and Regular Feedback: Share drafts of your work with advisors and peers early in the writing process. Their feedback can identify potential issues and guide revisions, preventing the need for extensive rewrites later. Example: Submit a draft of your literature review to your advisor before completing the entire chapter. Early feedback can help refine your approach and ensure you’re on the right track.
- Objective External Perspectives: Advisors and peers offer valuable external perspectives. They can identify areas where your explanation may be unclear or where additional details may be necessary. Example: If your research methodology is intricate, seek feedback from a peer who is not intimately familiar with your topic. Their questions and comments can reveal where additional clarification is needed for a broader audience.
- Critical Review for Redundancy: Advisors and peers can help identify redundant sections or unnecessary details. A fresh set of eyes can pinpoint areas where content can be streamlined without compromising the depth of your argument. Example: If two sections of your dissertation cover similar ground, feedback from others can highlight the need to merge or eliminate redundant content, improving the overall flow.
Visit my articles related to PhD , Exciting Careers after PhD .
The journey through the complexities of determining the length of a Ph.D. dissertation reveals a delicate interplay of factors crucial to its scholarly impact. From understanding the significance of this academic endeavour to navigating institutional guidelines and disciplinary variances, the pursuit of balance between depth and brevity emerges as a paramount challenge.
As researchers, we must navigate the intricate landscapes of research complexity, data analysis, literature review, and methodology while maintaining a steadfast commitment to quality over quantity. The tips offered for effective time management, concise writing, and the judicious seeking of feedback underscore the strategic nature of dissertation crafting.
Ultimately, the dissertation is not just an academic requirement but a scholarly legacy—a testament to our intellectual contributions and a beacon guiding future inquiry. In this conclusion, let us recognize that the true measure of a dissertation’s success lies not solely in its length but in its enduring impact on the trajectory of knowledge within our respective fields.
Upcoming Events
- Visit the Upcoming International Conferences at Exotic Travel Destinations with Travel Plan
- Visit for Research Internships Worldwide

Recent Posts
- How to End Your Academic/Research Internship?
- PhD or Industry Job? A Comprehensive Career Guide
- Post Doc Positions in India
- 04 Reasons for Outsourcing Academic Conference Management
- How to Put Research Grants on Your CV ?
- All Blog Posts
- Research Career
- Research Conference
- Research Internship
- Research Journal
- Research Tools
- Uncategorized
- Research Conferences
- Research Journals
- Research Grants
- Internships
- Research Internships
- Email Templates
- Conferences
- Blog Partners
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Research Voyage
Design by ThemesDNA.com

How Long is a Dissertation for a PhD?
How long is a dissertation? This is one of the most common questions asked by current or aspiring doctoral students.

A dissertation is an extensive research project that contributes fresh knowledge to the author’s field. Many doctoral programs require students to write, defend, and revise a dissertation to earn their degrees.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
This article explores the average length of a dissertation and various factors that affect the scope of these papers.
How Long Is a Dissertation?

For most graduate students, the dissertation is the longest and most time-consuming paper they write throughout their education. This project aims to address a research question in the student’s field and build on existing bodies of scholarship.
Additionally, the dissertation showcases the student’s mastery of research methodologies. Because a dissertation must accomplish several goals, they tend to be ambitious and lengthy.
Most dissertations are 100 to 250 pages long. But many factors impact the length of a dissertation, including:
- Academic field . Each discipline has different norms regarding dissertation content and length. For instance, literature dissertations often include extended close readings of texts, while science dissertations focus more on data analysis and research design. As a result, humanities dissertations are typically longer.
- Institutional requirements . Most colleges and universities specify a minimum number of pages for the dissertation. You can ask your academic advisor or the graduate studies office about specific dissertation guidelines.
- Topic complexity . Broad or complex research questions may require more data and analysis to answer, resulting in a longer dissertation.
- Individual writing style . Some doctoral students enjoy writing elaborate and detailed sentences, while others prefer to get straight to the point.
- Research methodologies . The approaches and methods used in the research can dramatically affect the length of the dissertation. For example, some dissertations include case studies, which may require lengthy explanations and analyses. Others use quantitative research methods and may include a number of charts and figures.
- Committee feedback . Graduate students typically write their dissertations under the supervision of a faculty committee. These professors may recommend adding or cutting material during revision, impacting the dissertation’s final length.
- Future goals . Some doctoral students plan to revise their dissertation and publish it as an academic monograph after graduation. Writing a longer dissertation gives them more material to adapt for their book.
Reading dissertations from your department and field can give you a better sense of the typical length.
How Long Are Dissertations by Discipline?

The answer to “how long is a doctoral dissertation?” varies by field. In some disciplines, it’s common for graduate students to spend several years writing extensive manuscripts. Other fields produce shorter dissertations of approximately 100 pages.
Here are a few examples of dissertation norms for different disciplines:
- Arts : Students studying art and creative writing may produce a creative dissertation. These projects typically consist of a theoretical introduction and a creative project, such as a poetry collection or a series of paintings. Creative dissertations may have fewer than 100 written pages, but the artistic elements can still be time-consuming.
- Chemistry : These dissertations typically range from 100 to 150 pages. They typically describe experimental methodologies and draw conclusions from the author’s findings.
- Computer science : Dissertations in this field are generally 50 to 150 pages long and often include quantitative data and algorithms.
- English : PhD students in this field frequently write lengthy literature reviews and provide in-depth analyses of novels and other texts. English dissertations may range from 200 to 350 pages.
Faculty in your discipline can help you understand dissertation expectations.
Average Dissertation Length Per Chapter

Dissertations typically have similar components and structures across disciplines. Here are six common chapters and their average lengths:
- Introduction : The first chapter introduces the primary research topic and explains its relevance to the field. The introduction also provides a brief overview of the investigation method. Most introductions are 10 to 25 pages long.
- Literature review : This chapter situates the project within the broader discipline. The author analyzes existing sources already written on their research topic and identifies biases or gaps that their own project remedies. Humanities dissertations tend to have 20 to 30 page literature reviews, while STEM dissertations devote 10 to 20 pages to this component.
- Methodology : The third chapter typically focuses on the methods and techniques used to gather data. Ideally, this description should contain all the details that another researcher would need to duplicate the experiment and verify the results. The methodology chapter ranges from 15 to 25 pages, depending on the complexity of the research.
- Findings : This section analyzes the collected data and discusses the results of the research project. It often includes charts, diagrams, and other data visualizations illustrating the findings. This chapter could be 20 to 50 pages, depending on the number of images and the amount of text needed to thoroughly examine the results.
- Discussion : This chapter explains the significance of the results. The author may also compare their findings to previously published scholarship. The discussion is typically 15 to 25 pages.
- Conclusion : The author summarizes their findings, acknowledges the limitations of their research, and suggests avenues for future studies. Most conclusions consist of 15 to 20 pages.
Some dissertations deviate from this format. For instance, English dissertations may devote several chapters to critical analyses of different genres or authors.
What Is a Dissertation?

A dissertation is a lengthy written document that a doctoral student produces based on their original research. This project demonstrates the student’s expertise in their area of specialty and contributes to existing knowledge in the field.
Dissertations typically fall into one of two categories. Empirical dissertations require students to collect and analyze data. For instance, a psychology student may interview people about their mental health, while a marketing student could interpret sales data.
Theoretical dissertations focus on analyzing existing scholarship and secondary sources. For example, a literature student might research psychoanalysis and apply this approach to superhero comics.
How Many Pages Is a Dissertation?

The length of a dissertation varies by discipline, institution, and research project. Some dissertations can be as short as 50 pages, while others may total 400 pages. But the average dissertation ranges from 100 pages to 250 pages.
Dissertations in the humanities and social sciences are typically the most extensive. These projects often include detailed analyses, case studies, and literature reviews. By contrast, dissertations in STEM fields like economics and mathematics are often 150 pages or less.
Students in these disciplines frequently use mathematical formulas and data visualizations to prove their findings, resulting in less text.
Why Are Dissertations So Long?

Dissertations are typically the most extended assignments that students complete in graduate school. Several factors contribute to their length, including:
- Depth of research . Doctoral students can spend several years researching their topic and analyzing data. This extensive work often takes hundreds of pages to summarize and explain.
- Literature review . Most fields have extensive bodies of scholarship, so students spend many pages analyzing sources and contextualizing their projects.
- Bibliography . Dissertations often cite dozens or even hundreds of sources, resulting in lengthy bibliographies.
Also, colleges often require dissertations to include additional materials like abstracts and tables of content.
What’s the Difference Between a Dissertation vs. Thesis?
Depending on the type of graduate program you enroll in, you may be required to write a dissertation or thesis. Here are the main differences between a thesis vs. dissertation .
If you want to develop your own concepts or theories, a dissertation can help you accomplish this goal.
What’s the Difference Between a Capstone vs. Dissertation?
There are doctorate programs with no dissertation. Like some online doctoral programs in education without dissertation requirements, they have a capstone project instead. Here’s a comparison of a dissertation vs. capstone .
Your career goals can help determine if a capstone or dissertation is right for you.
How Long Is a Dissertation for a PhD Degree?

People often wonder, “How long is a PhD dissertation?” These projects are typically 100 to 250 pages long, though dissertations on complex topics may total more than 400 pages.
Writing a dissertation allows you to develop advanced expertise on your chosen research topic. Many students also publish portions of their dissertations as peer-reviewed articles and share their findings at conferences. These activities enhance your CV and may make you more competitive for academic jobs.
You can kickstart your doctoral journey today by researching accredited online programs in your field.


How Long Does it Take To Get A PhD? Doctorate Degree Timeline
Starting a PhD means you’re ready for a big academic adventure, full of tough challenges and exciting discoveries.
If you’re thinking about going for it, you’re probably wondering just how much time you’ll need to commit to this big goal.
For full-time PhD students, the journey typically take 3-6 years. However, if you’re juggling other commitments and opt for a part-time PhD, the timeline can extend to 7 years to complete, sometimes more.
This article breaks down what the PhD journey looks like, what can make it longer or shorter, and some tips on how to make it through.
If you’re curious about how long it’ll take to add ‘Dr.’ before your name, you’re in the right place. Let’s dive into the world of PhD timelines!
How Long Does It Take To Get A PhD?
The answer here isn’t straightforward, as it hinges on various factors, including:
- the discipline,
- the institution, and
- whether you’re a full-time or part-time student.
For full-time PhD students, the journey typically take 3-6 years. However, if you’re juggling other commitments and opt for a part-time PhD, the timeline can extend to 7 years to complete, sometimes more.

Distance learning PhD programs offer flexibility but similarly require a substantial time commitment, often mirroring the length of part-time studies.
The heart of a doctoral program is the dissertation, a rigorous research project that demands an in-depth exploration of your chosen field. This phase alone can take several months to years, significantly influencing the overall length of your PhD journey.
Beyond the dissertation, coursework, exams, and sometimes teaching responsibilities add layers to the doctoral experience.
The requirements for a PhD vary widely across disciplines and institutions. For instance, a doctorate in the sciences might involve extensive lab work, potentially extending the time to completion.
In contrast, a doctorate in the arts could hinge more on coursework and creative output, leading to variations in the timeline.
Does A Doctorate Degree Take Longer Than Masters?
A doctorate degree typically takes longer to complete than a master’s degree.
While a master’s program can often be completed in 1-2 years of full-time study, a doctoral program usually requires 4-6 years, depending on the:
- research complexity, and
- whether the student is enrolled full-time or part-time.
The doctoral journey is more than just additional coursework; it involves conducting original research, writing a comprehensive dissertation, and often teaching or engaging in professional development activities.
The dissertation phase, which requires students to contribute new knowledge to their field, is particularly time-consuming and can extend the duration of a PhD program significantly.
The time it takes to complete a doctorate can be influenced by your
- research topic,
- funding availability, and
- the level of support from advisors and faculty.
Master’s programs are typically more structured, with a clearer set of coursework requirements and a shorter thesis or capstone project, leading to a quicker path to graduation.

Why Does It Take So Long To Finish Doctoral Program?
Starting a doctoral program is a significant commitment, often taking longer than anticipated. If you wonder why it takes so long, here are a couple of reasons you can think about:
Extensive Coursework
Initially, you might think coursework in your PhD study is just a continuation of your previous studies.
Doctoral level courses are a different beast. They demand not just understanding but the ability to critically analyze and apply complex concepts.
Each course can feel like a mini research project, requiring more than just classroom attendance. This phase lays the foundation but is time-consuming.
The Dissertation
The heart of your doctoral journey is your dissertation. This isn’t just a long essay or an extended research paper. It’s an original contribution to your field, requiring:
- exhaustive research,
- experimentation, and
Some students find their research path straightforward, while others may hit unexpected roadblocks or need to pivot their focus, extending the time required.
Part-Time Study
Many PhD candidates choose a part-time path due to work, family, or other commitments. While this flexibility is crucial for many, it stretches the duration of the program.
What a full-time student might complete in 4-6 years, part-time students might take 7 years or more to finish.
Funding and Resources
Access to funding and resources can significantly impact the timeline. Some projects require extensive fieldwork, specialised equipment, or access to rare materials. Delays in funding or accessing necessary resources can stall progress.
If funding is an issue, consider applying for work outside of the university. You can also try your luck with the university, as a research or teaching assistant , or more.

Academic Publishing
As part of the doctoral process, many students are encouraged or required to publish their findings.
However, the process of submitting to academic journals, undergoing peer review, and possibly revising and resubmitting, is lengthy.
This step is crucial for the academic community but adds time to the doctoral timeline. If may help to start writing and publishing work earlier to ensure you have enough time to finish.
Faculty Supervision and Mentorship
The relationship with your advisor or supervisory committee is pivotal. These mentors gatekeep your studies, as they:
- guide your research,
- provide feedback, and
- approve your progress.
Scheduling conflicts, feedback loops, and the iterative nature of research can add semesters or even years to your timeline.
Personal Growth and Professional Development
Beyond the academic requirements, doctoral students often engage in teaching, attend conferences, and network within their academic community. These activities contribute to your professional development but also extend your time in the program.
Factors That Influence The Time To Get A PhD
The time it takes to complete PhD is influenced by a multitude of factors, each significant in its own right. Let’s delve deeper into these elements to understand the intricacies of the PhD voyage.
The Scope of Research :
The ambition of your research can significantly dictate the duration of your PhD. Some projects will need more time and commitment, especially if they:
- Demand extensive fieldwork,
- elaborate experiments, or
- groundbreaking theoretical developments.
Imagine embarking on a quest that not only seeks answers but also questions the very foundations of your field. Such endeavours are thrilling but inherently time-consuming, often extending the PhD journey beyond the typical timeframe.
Program Structure and Requirements
The architecture of a PhD program—its coursework, qualifying exams, and other prerequisites—lays the groundwork for your academic expedition.
Programs with a heavy load of initial coursework aim to equip you with a broad foundation, yet this can elongate the path to your actual dissertation work.
Mode of Study
The decision between full-time and part-time study is pivotal. A full-time commitment allows you to immerse yourself in research, ideally hastening progress.
Yet, life’s obligations may necessitate a part-time route, extending the journey but offering flexibility.
Distance learning, with its inherent flexibility, caters to those balancing diverse commitments, yet this mode, too, can stretch the timeline, particularly if it lacks the immediacy and intensity of on-campus engagement.
Quality of Supervision
The symbiotic relationship with your advisor is the compass guiding your research voyage. An advisor who is both a mentor and a critic, offering timely and constructive feedback, can expedite your journey.
Less engaged supervision may leave you adrift, prolonging the process as you navigate the academic waters largely on your own.
Worse still, if you are unlucky enough, you may end up with supervisors that not only does not help you, but actively attempt to make your study life difficult. These nightmare scenarios do exist, and you should be aware of them.
Financial Stability
The financial underpinnings of your PhD endeavor are more critical than often acknowledged. Consistent funding allows you to dedicate yourself fully to your research, free from financial distractions.
Conversely, the absence of stable support might necessitate part-time employment, diluting focus and extending the timeline.
Resource Availability
Access to specialized resources—be it state-of-the-art laboratories, rare archival collections, or cutting-edge software—can be the wind in your PhD sails.
Limited or delayed access to these essential tools, however, can stall progress, turning what could be a swift journey into a prolonged odyssey.
If you found yourself in a position without the right resources to complete your PhD, consider to propose your university to allow you to work with other universities with what you need. If this is not possible, you can always transfer university, although this would mean more work.
Publishing Requirements
The adage “publish or perish” holds particularly true in the realm of PhD studies. The process of getting your research published, from initial submission to eventual acceptance, is fraught with delays and revisions. Each publication cycle can add months to your timeline,
Yet these publications are crucial stepping stones towards establishing your academic credibility. In fact, some universities want you to publish papers to graduate.
Personal Life and Circumstances
The journey towards a PhD is not undertaken in academic isolation. Life, with its unforeseen challenges and responsibilities, continues.
Personal circumstances can impact your ability to devote time and energy to your studies, necessitating pauses or a reduction in research intensity.
These issues can range from situation such as:
- such as health issues,
- family commitments, or
- significant life events

Tips To Earn Your Doctoral Degree Fast
Earning a doctoral degree is a significant academic endeavor, often perceived as a marathon rather than a sprint. However, with strategic planning and focused effort, you can navigate this journey more swiftly than you might expect.
Here are some tips to help you earn your doctoral degree faster, drawing from the experiences and strategies of successful PhD candidates.
Choose Your Program Wisely
The structure of the PhD program you choose can greatly influence how long it takes to complete your degree. Programs that allow you to start your dissertation research early, even while completing your coursework, can save you a considerable amount of time.
Some program are designed to integrate dissertation work with coursework, enabling a more seamless transition into the research phase.
Opt for Full-Time Study If Possible
While part-time PhD programs offer flexibility for working professionals, full-time study allows for a more immersive research experience.
Dedicating all your working hours to your doctoral research can expedite the process, reducing the time it takes to get your PhD significantly.
Secure Adequate Funding
Financial stability is key to focusing fully on your research without the distraction of part-time work. Look for:
- scholarships,
- grants, and
- funding opportunities from your institution.
You can also try to secure funding from external sources like the National Science Foundation.
Secure funding not only supports your financial needs but also often comes with academic resources that can accelerate your research progress.
Develop a Strong Relationship with Your Advisor
Your advisor is your guide through the PhD process. A supportive advisor can provide invaluable feedback, help you navigate academic challenges, and keep you on track.
Regular meetings and clear communication with your advisor can help you refine your research direction and avoid time-consuming pitfalls.
Focus Your Research
A well-defined research question can provide a clear path forward. The more focused your research, the less likely you are to get bogged down in unmanageable amounts of data or tangential studies.
It’s about depth rather than breadth; delving deeply into a specific area can lead to significant contributions to your field and a quicker path to completion.

Take Advantage of Existing Research and Resources
Don’t reinvent the wheel. Building on existing research and utilizing available resources can save you time. This includes:
- leveraging datasets,
- using established methodologies, and c
- ollaborating with other researchers.
Access to resources like specialized labs or archives, as provided by your institution, can also streamline the research process.
Stay Organized and Manage Your Time Effectively
Good time management is crucial. Set realistic goals, create a timeline for your research and writing, and stick to it.
Tools like Gantt charts can help you visualize your PhD timeline, including key milestones like coursework completion, comprehensive exams, and dissertation chapters.

Get Your PhD Without Taking Too Much Time – Possible
The journey to obtaining a PhD is a unique blend of personal commitment, academic rigor, and research innovation.
While the timeline can vary widely, most candidates find themselves immersed in their studies and research for anywhere from 4 to 6 years. Exceptions can happen, and you may finish earlier or later.
Key factors like your field of study, the nature of your research, and your personal life circumstances play significant roles in shaping your individual journey.
Remember, earning a PhD is more than just a race to the finish line; it’s a profound journey of learning, discovery, and personal growth. Embrace the journey, stay focused, and the day you earn the title of ‘Doctor’ will be a milestone to remember.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider

How to Write a PhD Research Proposal
- Applying to a PhD
- A research proposal summarises your intended research.
- Your research proposal is used to confirm you understand the topic, and that the university has the expertise to support your study.
- The length of a research proposal varies. It is usually specified by either the programme requirements or the supervisor upon request. 1500 to 3500 words is common.
- The typical research proposal structure consists of: Title, Abstract, Background and Rationale, Research Aims and Objectives, Research Design and Methodology, Timetable, and a Bibliography.
What is a Research Proposal?
A research proposal is a supporting document that may be required when applying to a research degree. It summarises your intended research by outlining what your research questions are, why they’re important to your field and what knowledge gaps surround your topic. It also outlines your research in terms of your aims, methods and proposed timetable .
What Is It Used for and Why Is It Important?
A research proposal will be used to:
- Confirm whether you understand the topic and can communicate complex ideas.
- Confirm whether the university has adequate expertise to support you in your research topic.
- Apply for funding or research grants to external bodies.
How Long Should a PhD Research Proposal Be?
Some universities will specify a word count all students will need to adhere to. You will typically find these in the description of the PhD listing. If they haven’t stated a word count limit, you should contact the potential supervisor to clarify whether there are any requirements. If not, aim for 1500 to 3500 words (3 to 7 pages).
Your title should indicate clearly what your research question is. It needs to be simple and to the point; if the reader needs to read further into your proposal to understand your question, your working title isn’t clear enough.
Directly below your title, state the topic your research question relates to. Whether you include this information at the top of your proposal or insert a dedicated title page is your choice and will come down to personal preference.
2. Abstract
If your research proposal is over 2000 words, consider providing an abstract. Your abstract should summarise your question, why it’s important to your field and how you intend to answer it; in other words, explain your research context.
Only include crucial information in this section – 250 words should be sufficient to get across your main points.
3. Background & Rationale
First, specify which subject area your research problem falls in. This will help set the context of your study and will help the reader anticipate the direction of your proposed research.
Following this, include a literature review . A literature review summarises the existing knowledge which surrounds your research topic. This should include a discussion of the theories, models and bodies of text which directly relate to your research problem. As well as discussing the information available, discuss those which aren’t. In other words, identify what the current gaps in knowledge are and discuss how this will influence your research. Your aim here is to convince the potential supervisor and funding providers of why your intended research is worth investing time and money into.
Last, discuss the key debates and developments currently at the centre of your research area.
4. Research Aims & Objectives
Identify the aims and objectives of your research. The aims are the problems your project intends to solve; the objectives are the measurable steps and outcomes required to achieve the aim.
In outlining your aims and objectives, you will need to explain why your proposed research is worth exploring. Consider these aspects:
- Will your research solve a problem?
- Will your research address a current gap in knowledge?
- Will your research have any social or practical benefits?
If you fail to address the above questions, it’s unlikely they will accept your proposal – all PhD research projects must show originality and value to be considered.
5. Research Design and Methodology
The following structure is recommended when discussing your research design:
- Sample/Population – Discuss your sample size, target populations, specimen types etc.
- Methods – What research methods have you considered, how did you evaluate them and how did you decide on your chosen one?
- Data Collection – How are you going to collect and validate your data? Are there any limitations?
- Data Analysis – How are you going to interpret your results and obtain a meaningful conclusion from them?
- Ethical Considerations – Are there any potential implications associated with your research approach? This could either be to research participants or to your field as a whole on the outcome of your findings (i.e. if you’re researching a particularly controversial area). How are you going to monitor for these implications and what types of preventive steps will you need to put into place?
6. Timetable
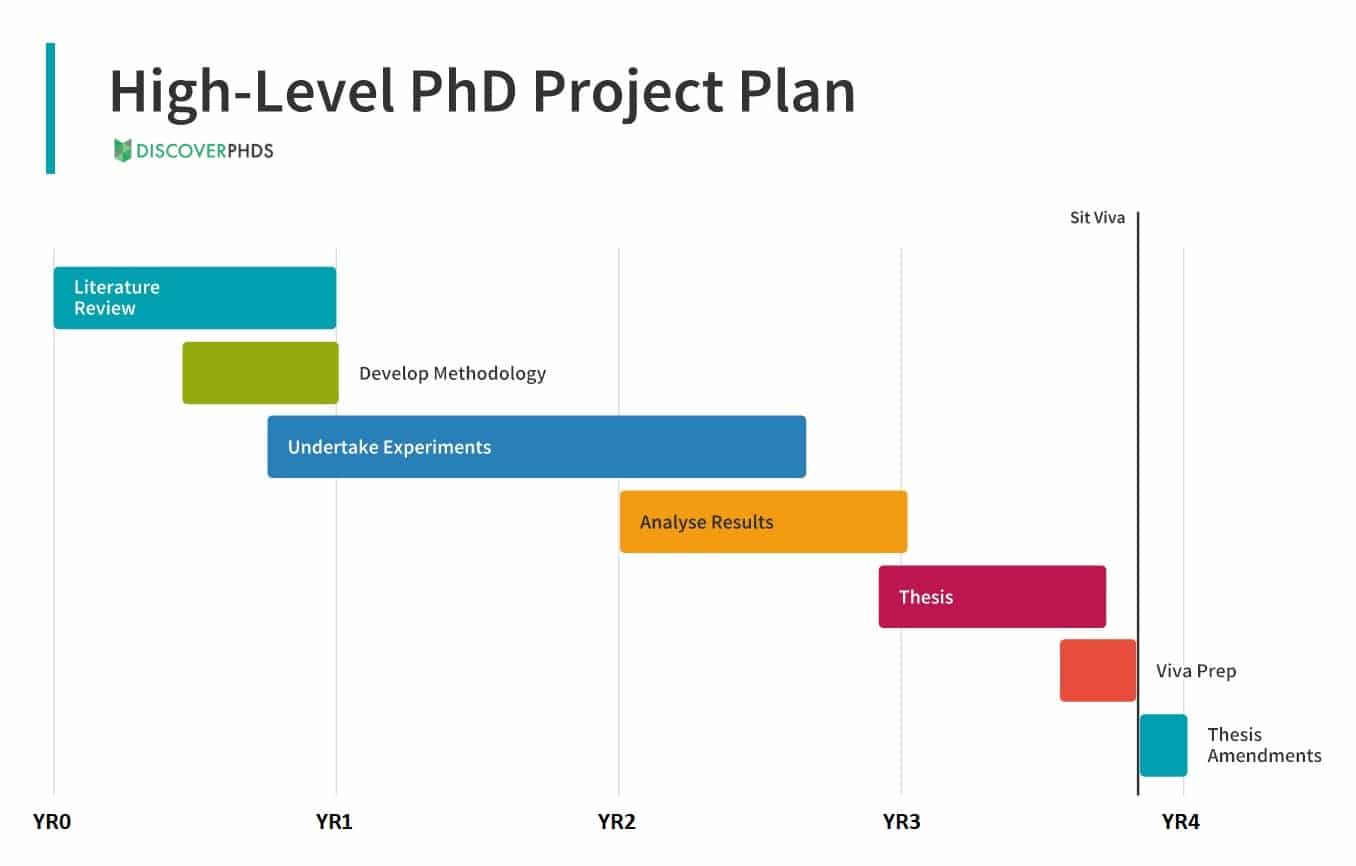
We’ve outlined the various stages of a PhD and the approximate duration of a PhD programme which you can refer to when designing your own research study.
7. Bibliography
Plagiarism is taken seriously across all academic levels, but even more so for doctorates. Therefore, ensure you reference the existing literature you have used in writing your PhD proposal. Besides this, try to adopt the same referencing style as the University you’re applying to uses. You can easily find this information in the PhD Thesis formatting guidelines published on the University’s website.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Questions & Answers
Here are answers to some of the most common questions we’re asked about the Research Proposal:
Can You Change a Research Proposal?
Yes, your PhD research proposal outlines the start of your project only. It’s well accepted that the direction of your research will develop with time, therefore, you can revise it at later dates.
Can the Potential Supervisor Review My Draft Proposal?
Whether the potential supervisor will review your draft will depend on the individual. However, it is highly advisable that you at least attempt to discuss your draft with them. Even if they can’t review it, they may provide you with useful information regarding their department’s expertise which could help shape your PhD proposal. For example, you may amend your methodology should you come to learn that their laboratory is better equipped for an alternative method.
How Should I Structure and Format My Proposal?
Ensure you follow the same order as the headings given above. This is the most logical structure and will be the order your proposed supervisor will expect.
Most universities don’t provide formatting requirements for research proposals on the basis that they are a supporting document only, however, we recommend that you follow the same format they require for their PhD thesis submissions. This will give your reader familiarity and their guidelines should be readily available on their website.
Last, try to have someone within the same academic field or discipline area to review your proposal. The key is to confirm that they understand the importance of your work and how you intend to execute it. If they don’t, it’s likely a sign you need to rewrite some of your sections to be more coherent.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

- Youth Program
- Wharton Online
How the PhD Program Works
Program Overview
Completing your doctorate at Wharton requires 5 years of full-time study. The first 2 years in the program prepare you for admission to candidacy by taking courses, qualifying exams, and starting research projects. In the last few years, you are primarily conducting research full-time including writing and defending your doctoral dissertation.
Admission to candidacy.
You begin by taking courses required for your program of study. All programs requires a preliminary exam, which may be either oral or written.
Some programs may have further requirements, such as an additional exam or research paper. If you enter with a master’s degree or other transfer credit, you may satisfy the formal course requirements more quickly.
Beginning the Wharton PhD Curriculum How the first two years of the Wharton program helped students discover their interests, learn the tools of the profession, and fuel their passion for teaching.
The Doctoral Dissertation
Upon successful completion of coursework and passing a preliminary examination, you are admitted to candidacy for the dissertation phase of your studies.
Your doctoral dissertation should contain original research that meets standards for published scholarship in your field. You are expected to be an expert in the topic you choose to research.
You are admitted to candidacy for the dissertation phase of your studies upon successful completion of coursework and passing a preliminary examination, but you can start thinking about and working on research of relevance at any time.
The dissertation process culminates with a “defense,” in which you defend the proposal orally before your dissertation committee.
While working on your dissertation, you interact extensively with Wharton faculty. Together with interested faculty, you create your own research community that includes your dissertation advisor and dissertation committee.
Policies and Procedures
Get more detailed explanation of course requirements, academic standards, the Teacher Development Program, time limits, and dissertation procedures and requirements.
Sample Program Sequence
Years 1 & 2.
Coursework Examination Research Papers Research Activities Field-Specific Requirements
Directed Reading & Research Admission to Candidacy Formulation of Research Topic
Years 4 & 5
Continued Research Oral Examination Dissertation
Hear From Our Doctoral Community
Conducting ground-breaking research at wharton, what brought this cdc researcher to wharton's phd program, the diverse skill set you need to become a professor.
Graduate School
Ph.d. requirements.
- Academics & Research
- Programs & Requirements
Brown University awards more than 200 doctor of philosophy degrees annually.
The Brown Ph.D. is primarily a research degree. Teaching is an important part of many doctoral programs, and many departments require candidates for the Ph.D. to have teaching experience.
Brown University offers substantial financial support to doctoral students. All incoming doctoral students are guaranteed five years of support, which includes a stipend, full tuition remission, health-services fee, and a health-insurance subsidy. Doctoral students in the Humanities and Social Sciences are guaranteed six years of support. All promises of student support are subject to students making satisfactory academic progress, as determined by their programs of study. Please see related links for additional details regarding the University's commitment to doctoral education.
Ph.D. Funding
Funding guarantee, four general requirements for the doctor of philosophy.
The candidate must be formally admitted to his or her degree program.
The normal residency requirement is the equivalent of three Academic Years of full-time study beyond the bachelor's degree. Students who enter a PhD program at Brown already holding a master’s degree in a related field have a residency requirement equivalent to two Academic Years of full-time study upon entering the PhD program at Brown. Use of a previously earned master’s degree to reduce PhD residency requirements is contingent upon approval of the program Director of Graduate Study. Graduate work done at other institutions and not used in fulfillment of the requirements for any doctoral degree elsewhere may, on the approval of the program Director of Graduate Study, be counted in fulfillment of up to, but not exceeding, one year of the residency requirement. A student who desires credit for work done elsewhere should file a timely application with the program Director of Graduate Study; transfer credit forms are available through the Office of the Registrar .
A student is advanced to candidacy for the Ph.D. when he or she has completed satisfactorily all the requirements, departmental and general, requisite to beginning work on the dissertation. Candidacy is determined by the department or program of study and certified by the Registrar. Most departments require a preliminary examination before advancing any student to candidacy. Most departments also require a final examination or defense. The examination is conducted by professors in the department and by such other members of the faculty as may be appointed.
The candidate must present a dissertation on a topic related to his or her area of specialization that presents the results of original research and gives evidence of excellent scholarship. The dissertation must be approved by the professor or committee under whose direction it is written and by the Graduate Council. All requirements for the Ph.D. must be completed within five years after advancement to candidacy.
Faculty Member Leaves Brown
If a faculty member working with a doctoral student leaves Brown for any reason before that student has completed his or her degree requirements, it may not always be possible for that faculty member to continue working with the student as an advisor. In such cases, departments will work with students to help them locate a new advisor.
Additional Requirements
Individual departments and programs may have additional requirements regarding the number of courses to be taken, proficiency in foreign languages, special examinations, and theses. The department should be consulted for specific information.
- Crimson Careers
- For Employers
- Harvard College
- Harvard Kenneth C. Griffin Graduate School of Arts & Sciences
- Harvard Extension School
- Premed / Pre-Health
- Families & Supporters
- Faculty & Staff
- Prospective Students
- First Generation / Low Income
- International Students
- Students of Color
- Students with Disabilities
- Undocumented Students
- Explore Interests & Make Career Decisions
- Create a Resume/CV or Cover Letter
- Expand Your Network
- Engage with Employers
- Search for a Job
- Find an Internship
- January Experiences (College)
- Find & Apply for Summer Opportunities Funding
- Prepare for an Interview
- Negotiate an Offer
- Apply to Graduate or Professional School
- Access Resources
- AI for Professional Development and Exploration
- Arts & Entertainment
- Business & Entrepreneurship
- Climate, Sustainability, Environment, Energy
- Government, Int’l Relations, Education, Law, Nonprofits
- Life Sciences & Health
- Technology & Engineering
- Still Exploring
- Talk to an Advisor
How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree?
- Share This: Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on Facebook Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on LinkedIn Share How Long Does It Take to Get a Ph.D. Degree? on X
Earning a Ph.D. from a U.S. grad school typically requires nearly six years, federal statistics show.

(CAIAIMAGE/TOM MERTON/GETTY IMAGES)
A Ph.D. is most appropriate for someone who is a “lifelong learner.”
Students who have excelled within a specific academic discipline and who have a strong interest in that field may choose to pursue a Ph.D. degree. However, Ph.D. degree-holders urge prospective students to think carefully about whether they truly want or need a doctoral degree, since Ph.D. programs last for multiple years.
According to the Survey of Earned Doctorates, a census of recent research doctorate recipients who earned their degree from U.S. institutions, the median amount of time it took individuals who received their doctorates in 2017 to complete their program was 5.8 years. However, there are many types of programs that typically take longer than six years to complete, such as humanities and arts doctorates, where the median time for individuals to earn their degree was 7.1 years, according to the survey.
Some Ph.D. candidates begin doctoral programs after they have already obtained master’s degrees, which means the time spent in grad school is a combination of the time spent pursuing a master’s and the years invested in a doctorate. In order to receive a Ph.D. degree, a student must produce and successfully defend an original academic dissertation, which must be approved by a dissertation committtee. Writing and defending a dissertation is so difficult that many Ph.D. students drop out of their Ph.D. programs having done most of the work necessary for degree without completing the dissertation component. These Ph.D. program dropouts often use the phrase “ all but dissertation ” or the abbreviation “ABD” on their resumes.
According to a comprehensive study of Ph.D. completion rates published by The Council of Graduate Schools in 2008, only 56.6% of people who begin Ph.D. programs earn Ph.D. degrees.
Ian Curtis, a founding partner with H&C Education, an educational and admissions consulting firm, who is pursuing a Ph.D. degree in French at Yale University , says there are several steps involved in the process of obtaining a Ph.D. Students typically need to fulfill course requirements and pass comprehensive exams, Curtis warns. “Once these obligations have been completed, how long it takes you to write your dissertation depends on who you are, how you work, what field you’re in and what other responsibilities you have in life,” he wrote in an email. Though some Ph.D. students can write a dissertation in a single year, that is rare, and the dissertation writing process may last for several years, Curtis says.
[ READ: What Is a Doctorate or a Doctoral Degree? ]
Curtis adds that the level of support a Ph.D. student receives from an academic advisor or faculty mentor can be a key factor in determining the length of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. program. “Before you decide to enroll at a specific program, you’ll want to meet your future advisor,” Curtis advises. “Also, reach out to his or her current and former students to get a sense of what he or she is like to work with.”
Curtis also notes that if there is a gap between the amount of time it takes to complete a Ph.D. and the amount of time a student’s funding lasts, this can slow down the Ph.D. completion process. “Keep in mind that if you run out of funding at some point during your doctorate, you will need to find paid work, and this will leave you even less time to focus on writing your dissertation,” he says. “If one of the programs you’re looking at has a record of significantly longer – or shorter – times to competition, this is good information to take into consideration.”
Pierre Huguet, the CEO and co-founder of H&C Education, says prospective Ph.D. students should be aware that a Ph.D. is designed to prepare a person for a career as a scholar. “Most of the jobs available to Ph.D. students upon graduation are academic in nature and directly related to their fields of study: professor, researcher, etc.,” Huguet wrote in an email. “The truth is that more specialization can mean fewer job opportunities. Before starting a Ph.D., students should be sure that they want to pursue a career in academia, or in research. If not, they should make time during the Ph.D. to show recruiters that they’ve traveled beyond their labs and libraries to gain some professional hands-on experience.”
Jack Appleman, a business writing instructor, published author and Ph.D. candidate focusing on organizational communication with the University at Albany—SUNY , says Ph.D. programs require a level of commitment and focus that goes beyond what is necessary for a typical corporate job. A program with flexible course requirements that allow a student to customize his or her curriculum based on academic interests and personal obligations is ideal, he says.
[ READ: Ph.D. Programs Get a Lot More Practical. ]
Joan Kee, a professor at the University of Michigan with the university’s history of art department, says that the length of time required for a Ph.D. varies widely depending on what subject the Ph.D. focuses on. “Ph.D. program length is very discipline and even field-specific; for example, you can and are expected to finish a Ph.D, in economics in under five years, but that would be impossible in art history (or most of the humanities),” she wrote in an email.
Jean Marie Carey, who earned her Ph.D. degree in art history and German from the University of Otago in New Zealand, encourages prospective Ph.D. students to check whether their potential Ph.D. program has published a timeline of how long it takes a Ph.D. student to complete their program. She says it is also prudent to speak with Ph.D. graduates of the school and ask about their experience.
Bennett urges prospective Ph.D. students to visit the campuses of their target graduate programs since a Ph.D. program takes so much time that it is important to find a school that feels comfortable. She adds that aspiring Ph.D. students who prefer a collaborative learning environment should be wary of graduate programs that have a cut-throat and competitive atmosphere, since such students may not thrive in that type of setting.
[ READ: 4 Fields Where Doctorates Lead to Jobs. ]
Alumni of Ph.D. programs note that the process of obtaining a Ph.D. is arduous, regardless of the type of Ph.D. program. “A Ph.D. is a long commitment of your time, energy and financial resources, so it’ll be easier on you if you are passionate about research,” says Grace Lee, who has a Ph.D. in neuroscience and is the founder and CEO of Mastery Insights, an education and career coaching company, and the host of the Career Revisionist podcast.
“A Ph.D. isn’t about rehashing years of knowledge that is already out there, but rather it is about your ability to generate new knowledge. Your intellectual masterpiece (which is your dissertation) takes a lot of time, intellectual creativity and innovation to put together, so you have to be truly passionate about that,” Lee says.
Erin Skelly, a graduate admissions counselor at the IvyWise admissions consulting firm, says when a Ph.D. students struggles to complete his or her Ph.D. degree, it may have more to do with the student’s academic interests or personal circumstances than his or her program.
“The time to complete a Ph.D. can depend on a number of variables, but the specific discipline or school would only account for a year or two’s difference,” she wrote in an email. “When a student takes significantly longer to complete a Ph.D. (degree), it’s usually related to the student’s coursework and research – they need to take additional coursework to complete their comprehensive exams; they change the focus of their program or dissertation, requiring extra coursework or research; or their research doesn’t yield the results they hoped for, and they need to generate a new theory and conduct more research.”
Skelly warns that the average completion time of a Ph.D. program may be misleading in some cases, if the average is skewed based on one or two outliers. She suggests that instead of focusing on the duration of a particular Ph.D. program, prospective students should investigate the program’s attritition and graduation rates.
“It is worthwhile to look at the program requirements and the school’s proposed timeline for completion, and meet current students to get their input on how realistic these expectations for completion are,” Skelly says. “That can give you an honest idea of how long it will really take to complete the program.”
Searching for a grad school? Access our complete rankings of Best Graduate Schools.
Psychology (Quantitative Research Methods), PHD
On this page:, at a glance: program details.
- Location: Tempe campus
- Second Language Requirement: No
Program Description
Degree Awarded: PHD Psychology (Quantitative Research Methods)
The PhD program in psychology with a concentration in quantitative research methods offers an immersive education in advanced statistical techniques and research methodologies that are employed in the conduct of both basic and applied psychological research.
A collaborative, interdisciplinary approach to research empowers students to deepen their understanding and tackle key issues, such as exploring the limits of existing methods, pushing the methodological frontiers forward, evaluating the effectiveness of established and emerging methodologies, and improving the robustness of psychological research through innovative measurements and analytical methods.
What sets this program apart is its distinguished, award-winning faculty, known for their expertise and dedication to training the next generation of psychological methodologists. Alongside the faculty, students gain practical experience and master techniques in the areas of measurement, study design, data analysis, statistical modeling, and evaluation of the utility of new and existing methods.
Graduates of this program emerge as experts in quantitative research who are prepared to make meaningful contributions to the field by developing and applying sophisticated statistical and methodological solutions to address pressing research issues.
Quantitative Faculty Research Labs
Degree Requirements
84 credit hours, a written comprehensive exam, an oral comprehensive exam, a prospectus and a dissertation
Required Core (3 or 4 credit hours) PSY 502 Professional Issues in Psychology (3) or PSY 531 Multiple Regression in Psychological Research (4)
Concentration (3 credit hours) PSY 533 Structural Equation Modeling (3)
Other Requirements (31 credit hours) PSY 530 Intermediate Statistics (4) PSY 532 Analysis of Multivariate Data (3) PSY 534 Psychometric Methods (3) PSY 536 Statistical Methods in Prevention Research (3) PSY 537 Longitudinal Growth Modeling (3) PSY 538 Advanced Structural Equation Modeling (3) PSY 539 Multilevel Models for Psychological Research (3) PSY 540 Missing Data Analysis (3) PSY 543 Statistical Mediation Analysis (3) PSY 555 Experimental and Quasi-experimental Designs for Research (3)
Electives (22 or 23 credit hours)
Research (12 credit hours)
Culminating Experience (12 credit hours) PSY 799 Dissertation (12)
Additional Curriculum Information Electives are determined in consultation with the student's supervisory committee.
Other requirements courses may be substituted for other courses based on consultation with the student's supervisory committee.
Admission Requirements
Applicants must fulfill the requirements of both the Graduate College and The College of Liberal Arts and Sciences.
Applicants are eligible to apply to the program if they have earned a bachelor's or master's degree from a regionally accredited institution.
Applicants must have a minimum cumulative GPA of 3.00 (scale is 4.00 = "A") in the last 60 hours of their first bachelor's degree program or a minimum cumulative GPA of 3.00 (scale is 4.00 = "A") in an applicable master's degree program.
All applicants must submit:
- graduate admission application and application fee
- official transcripts
- SlideRoom application and fee
- statement of purpose form
- curriculum vitae or resume
- three letters of recommendation
- proof of English proficiency
Additional Application Information An applicant whose native language is not English must provide proof of English proficiency regardless of their current residency.
ASU does not accept the GRE® General Test at home edition.
To apply to the doctoral program, applicants must follow the instructions on the doctoral program admissions instructions and checklist. It is strongly recommended that applicants download and print the instructions and checklist to ensure completion of the application process and that all required supplemental forms are included.
The Department of Psychology application process is completed online through ASU's graduate admission services, which includes the application form and official transcripts. Application to the Department of Psychology doctoral programs is also completed via SlideRoom, for processing of supplemental application materials. The SlideRoom account requires an additional fee.
Applicants must submit three academic letters of recommendation from faculty members who know the student well. Three letters are required, but four letters of recommendation may be submitted.
Next Steps to attend ASU
Learn about our programs, apply to a program, visit our campus, application deadlines, career opportunities.
Quantitative psychologists possess advanced statistical and methodological expertise applicable to various research challenges. While rooted in psychology, their skills find broad applications in fields such as education, heath, neuroscience and marketing. Graduates of the doctorate in psychology (quantitative research methods) program excel in interdisciplinary collaboration and effective communication of complex ideas.
Potential careers induce roles as:
- consultants
- data scientists
- policy analysts
- psychology professors
- psychometricians
- research scientists
Program Contact Information
If you have questions related to admission, please click here to request information and an admission specialist will reach out to you directly. For questions regarding faculty or courses, please use the contact information below.
- [email protected]
- 480/727-4561
- Harvard Business School →
- Doctoral Programs →
PhD Programs
- Accounting & Management
- Business Economics
- Health Policy (Management)
- Organizational Behavior
- Technology & Operations Management
Students in our PhD programs are encouraged from day one to think of this experience as their first job in business academia—a training ground for a challenging and rewarding career generating rigorous, relevant research that influences practice.
Our doctoral students work with faculty and access resources throughout HBS and Harvard University. The PhD program curriculum requires coursework at HBS and other Harvard discipline departments, and with HBS and Harvard faculty on advisory committees. Faculty throughout Harvard guide the programs through their participation on advisory committees.
How do I know which program is right for me?
There are many paths, but we are one HBS. Our PhD students draw on diverse personal and professional backgrounds to pursue an ever-expanding range of research topics. Explore more here about each program’s requirements & curriculum, read student profiles for each discipline as well as student research , and placement information.
The PhD in Business Administration grounds students in the disciplinary theories and research methods that form the foundation of an academic career. Jointly administered by HBS and GSAS, the program has five areas of study: Accounting and Management , Management , Marketing , Strategy , and Technology and Operations Management . All areas of study involve roughly two years of coursework culminating in a field exam. The remaining years of the program are spent conducting independent research, working on co-authored publications, and writing the dissertation. Students join these programs from a wide range of backgrounds, from consulting to engineering. Many applicants possess liberal arts degrees, as there is not a requirement to possess a business degree before joining the program
The PhD in Business Economics provides students the opportunity to study in both Harvard’s world-class Economics Department and Harvard Business School. Throughout the program, coursework includes exploration of microeconomic theory, macroeconomic theory, probability and statistics, and econometrics. While some students join the Business Economics program directly from undergraduate or masters programs, others have worked in economic consulting firms or as research assistants at universities or intergovernmental organizations.
The PhD program in Health Policy (Management) is rooted in data-driven research on the managerial, operational, and strategic issues facing a wide range of organizations. Coursework includes the study of microeconomic theory, management, research methods, and statistics. The backgrounds of students in this program are quite varied, with some coming from public health or the healthcare industry, while others arrive at the program with a background in disciplinary research
The PhD program in Organizational Behavior offers two tracks: either a micro or macro approach. In the micro track, students focus on the study of interpersonal relationships within organizations and the effects that groups have on individuals. Students in the macro track use sociological methods to examine organizations, groups, and markets as a whole, including topics such as the influence of individuals on organizational change, or the relationship between social missions and financial objectives. Jointly administered by HBS and GSAS, the program includes core disciplinary training in sociology or psychology, as well as additional coursework in organizational behavior.
Accounting & Management
Business economics , health policy (management) , management , marketing , organizational behavior , strategy , technology & operations management .
- Search This Site All UCSD Sites Faculty/Staff Search Term
- Living in San Diego
- Culture of Belonging
- Departments
- Land Acknowledgement
- Pathway Programs
- MD & Combined Programs
- Physician Assistant Education
- Graduate Programs (MS & PhD)
- Residency & Fellowship Programs
- Education & Training Facilities
- Continuing Professional Development
- Medical Education & Technology
- Research Centers & Institutes
- Student Opportunities
- Requests for Clinical Data
- UC San Diego Health
- Clinical Trials
- Training Facilities
- Residents & Fellows
- Faculty & Staff
- School of Medicine
Graduate Programs
Science informs medicine and medicine informs science. School of Medicine offers several master's and Ph.D.-level graduate programs for students interested in pursuing careers in health and biomedical sciences research. Our graduate students conduct their thesis work in faculty labs, where their basic, translational and clinical research advances our understanding of human development and disease. Our master's degree and Ph.D. students also contribute to the development of new diagnostics and therapeutics in cardiology, neurology, cancer, diabetes, infectious diseases and more.
Master of Science (M.S.)
- Master's in Clinical Research
Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.)
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Biomedical Sciences
- Neurosciences
- Independent PhD: Medical students may also pursue advanced training leading to a M.A., M.S. or Ph.D. in the Biomedical Sciences Program independent of the Medical Scientist Training Program, or in any of the UC San Diego general campus science or engineering programs. Information is available from relevant departments and faculty.
Joint Programs with San Diego State University
- Au.D. in Audiology
- Ph.D. in Clinical Psychology
- Ph.D. in Interdisciplinary Research on Substance Use
Medical Scientist Training Program
Are you interested in pursuing a joint MD/PhD program? Explore the Medical Scientist Training Program (MSTP) at School of Medicine.
Learn more about MSTP
Skip to Content
PhD students earn major NSF graduate research fellowships
Three Electrical, Computer and Energy Engineering graduate students have received 2024 National Science Foundation (NSF) Graduate Research Fellowships for their promising quantum and metameterial antennas research.
This year, the NSF awarded 27 students from CU Boulder , including 18 from the College of Engineering and Applied Science with the 2024 graduate research fellowship, a prestigious award recognizing students in a wide variety of STEM disciplines, exploring some of the most pressing issues of our time.
Each recipient will receive three years of financial support, including an annual stipend of $37,000, as well as professional development and research opportunities.

Aliza Siddiqui
Advisor: Joshua Combes Lab: Combes Group
Bio: Siddiqui is a first-year PhD student with a research concentration in Quantum Engineering and Architecture. She graduated from Louisiana State University, home of the Tigers, with a degree in computer science.
My proposal involves creating a new benchmarking/testing framework for the next generation of error-corrected quantum computers. Given the noise of physical qubits, recent work has suggested combining the state of several physical qubits to create a logical qubit. I will collaborate with Dr. Josh Combes and Sandia National Labs for my PhD. Through this work, the quantum community will have a tool-kit that will help us determine how well a quantum computer performs, diagnose what and where the issues are and create solutions to realize full-scale, error-corrected quantum systems.

Dylan Meyer
Advisor: Scott Diddams Lab: Frequency Comb & Quantum Metrology Lab
Bio: Meyer is a first-year PhD student in the FCQM group. He received his undergraduate degree from the University of Alabama in Electrical Engineering.
My research proposal is the development of highly stable and robust millimeter wave time and frequency (T&F) transfer, supporting T&F transfer between atomic clocks. T&F transfer is used to create clock networks that are essential for positioning and navigation, such as GPS and essential infrastructure like the Internet and power grid. These technologies support up to $1 billion dollars of trade and financial transactions a day. In addition, these clock networks are capable of fundamental science experiments capable of probing new and exciting questions related to physics and geodesy.

Advisors: Cody Scarborough and Robert MacCurdy Lab Groups: EMRG and MAClab
Bio: Pham received their Bachelor's and Master's degrees in Electrical & Computer Engineering from the University of Oklahoma, where he conducted research on RF filters. After graduating, he worked for 3 years in industry as an RF engineer developing radar systems. He will begin his PhD this fall 2024.
My research proposal is on the application of multi-material additive manufacturing techniques for metamaterial antennas. Metamaterial antennas are capable of more sophisticated capabilities and unique form-factors compared to conventional antennas. By leveraging multi-material additive manufacturing, there are more degrees-of-freedom for the shape and composition of the metamaterials. This research would enhance the design flexibility and capabilities of next-generation antennas to meet the growing performance demands of future wireless systems.
Related Articles

ECEE students earn college undergraduate awards 2024

Innovation unveiled: ECEE students to showcase design projects

Zoya Popovic elected to the National Academy of Inventors
Apply Visit Give
Departments
- Ann and H.J. Smead Aerospace Engineering Sciences
- Chemical & Biological Engineering
- Civil, Environmental & Architectural Engineering
- Computer Science
- Electrical, Computer & Energy Engineering
- Paul M. Rady Mechanical Engineering
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomedical Engineering
- Creative Technology & Design
- Engineering Education
- Engineering Management
- Engineering Physics
- Environmental Engineering
- Integrated Design Engineering
- Materials Science & Engineering
Affiliates & Partners
- ATLAS Institute
- BOLD Center
- Colorado Mesa University
- Colorado Space Grant Consortium
- Discovery Learning
- Engineering Honors
- Engineering Leadership
- Entrepreneurship
- Herbst Program for Engineering, Ethics & Society
- Integrated Teaching and Learning
- Global Engineering
- Mortenson Center for Global Engineering
- National Center for Women & Information Technology
- Western Colorado University
Calorie restriction study reveals complexities in how diet impacts aging
Penn State researchers may have uncovered another layer of complexity in the mystery of how diet impacts aging. A new study led by researchers in the Penn State College of Health and Human Development examined how a person's telomeres -- sections of genetic bases that function like protective caps at the ends of chromosomes -- were affected by caloric restriction.
The team published their results in Aging Cell . Analyzing data from a two-year study of caloric restriction in humans, the researchers found that people who restricted their calories lost telomeres at different rates than the control group -- even though both groups ended the study with telomeres of roughly the same length. Restricting calories by 20% to 60% has been shown to promote longer life in many animals, according to previous research.
Over the course of human life, every time a person's cells replicate, some telomeres are lost when chromosomes are copied to the new cell. When this happens, the overall length of the cell's telomeres becomes shorter. After cells replicate enough times, the protective cap of telomeres completely dissipates. Then, the genetic information in the chromosome can become damaged, preventing future reproduction or proper function of the cell. A cell with longer telomeres is functionally younger than a cell with short telomeres, meaning that two people with the same chronological age could have different biological ages depending on the length of their telomeres.
Typical aging, stress, illness, genetics, diet and more can all influence how often cells replicate and how much length the telomeres retain, according to Idan Shalev, associate professor of biobehavioral health at Penn State. Shalev led the researchers who analyzed genetic samples from the national CALERIE study -- the first randomized clinical trial of calorie restriction in humans. Shalev and his team sought to understand the effect of caloric restriction on telomere length in people. Because telomere length reflects how quickly or slowly a person's cells are aging, examining telomere length could allow scientists to identify one way in which caloric restriction may slow aging in humans.
"There are many reasons why caloric restriction may extend human lifespans, and the topic is still being studied," said Waylon Hastings, who earned his doctorate in biobehavioral health at Penn State in 2020 and was lead author of this study. "One primary mechanism through which life is extended relates to metabolism in a cell. When energy is consumed within a cell, waste products from that process cause oxidative stress that can damage DNA and otherwise break down the cell. When a person's cells consume less energy due to caloric restriction, however, there are fewer waste products, and the cell does not break down as quickly."
The researchers tested the telomere length of 175 research participants using data from the start of the CALERIE study, one year into the study and the end of the study after 24 months of caloric restriction. Approximately two-thirds of study participants participated in caloric restriction, while one-third served as a control group.
During the study, results showed that telomere loss changed trajectories. Over the first year, participants who were restricting caloric intake lost weight, and they lost telomeres more rapidly than the control group. After a year, the weight of participants on caloric restriction was stabilized, and caloric restriction continued for another year. During the second year of the study, participants on caloric restriction lost telomeres more slowly than the control group. At the end of two years, the two groups had converged, and the telomere lengths of the two groups was not statistically different.
"This research shows the complexity of how caloric restriction affects telomere loss," Shalev said. "We hypothesized that telomere loss would be slower among people on caloric restriction. Instead, we found that people on caloric restriction lost telomeres more rapidly at first and then more slowly after their weight stabilized."
Shalev said the results raised a lot of important questions. For example, what would have happened to telomere length if data had been collected for another year? Study participants are scheduled for data collection at a 10-year follow-up, and Shalev said that he was eager to analyze those data when they become available.
Despite the ambiguity of the results, Shalev said there is promise for the potential health benefits of caloric restriction in humans. Previous research on the CALERIE data has demonstrated that caloric restriction may help reduce harmful cholesterol and lower blood pressure. For telomeres, the two-year timeline was not sufficient to show benefits, but those may still be revealed, according to Shalev and Hastings.
Three of Shalev's trainees, Hastings, current graduate student Qiaofeng Ye and former postdoctoral scholar Sarah Wolf, led the research under Shalev's guidance.
Hastings said the opportunity to lead this study was critical to his career.
"I was recently hired as an assistant professor in the Department of Nutrition at Texas A&M University, and I will begin that work in the fall semester," Hastings said. "Prior to this project, I had limited experience in nutrition. This project literally set the course of my career, and I am grateful to Dr. Shalev for trusting me with that responsibility."
Calen Ryan and Daniel Belsky of Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, Sai Krupa Das of Tufts University, Kim Huffman and William Kraus of Duke University School of Medicine, Michael Kobor and Julia MacIsaac of University of British Columbia, Corby Martin and Leanne Redman of Pennington Biomedical Research Center and Susan Racette of Arizona State University College of Health Solutions all contributed to this research.
The National Institute on Aging funded this research.
- Healthy Aging
- Diet and Weight Loss
- Human Biology
- Diseases and Conditions
- Epigenetics Research
- Cell Biology
- Chemical synapse
- Baldness treatments
- Insulin-like growth factor
- Double blind
- Immune system
- Biological tissue
- Endangered species
- Domestication
Story Source:
Materials provided by Penn State . Original written by Aaron Wagner. Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Waylon J. Hastings, Qiaofeng Ye, Sarah E. Wolf, Calen P. Ryan, Sai Krupa Das, Kim M. Huffman, Michael S. Kobor, William E. Kraus, Julia L. MacIsaac, Corby K. Martin, Susan B. Racette, Leanne M. Redman, Daniel W. Belsky, Idan Shalev. Effect of long‐term caloric restriction on telomere length in healthy adults: CALERIE™ 2 trial analysis . Aging Cell , 2024; DOI: 10.1111/acel.14149
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- This Alloy Is Kinky
- Giant Galactic Explosion: Galaxy Pollution
- Flare Erupting Around a Black Hole
- Two Species Interbreeding Created New Butterfly
- Warming Antarctic Deep-Sea and Sea Level Rise
- Octopus Inspires New Suction Mechanism for ...
- Cities Sinking: Urban Populations at Risk
- Puzzle Solved About Ancient Galaxy
- How 3D Printers Can Give Robots a Soft Touch
- Combo of Multiple Health Stressors Harming Bees
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.
Do women who live together get their periods together, or is it a myth?
What research says about the common assumption.

Is it true women who live together will menstruate at the same time?
Although some women believe this, the answer, experts say, is no, not really.
Menstrual synchrony, as it is known, does occur occasionally, but not because of proximity or the release of chemical pheromones, which has long been a popular theory. “It’s a mathematical coincidence,” says Jeffrey Schank, professor of psychology at the University of California at Davis, whose studies provide an explanation as to why women in close quarters sometimes menstruate at the same time. “In one sense, it’s a real experience, but it’s due to statistical characteristics of cycles, not nearness or any biological processes. It’s not pheromones or anything evolutionary. There’s no good evolutionary reason for it — there’s no evolutionary advantage to having babies at the same time.”
Women don’t always cycle at the same frequency, so irregularity can sometimes lead to menstruation occurring together, “but it’s statistical,” Schank says. “Cycles vary in length, and all this variability will lead to convergence and divergence.” Not all women menstruate on a regular schedule; while many have a 28-day cycle, others can have shorter, longer or very irregular ones.
Get Well+Being tips straight to your inbox

The belief that women sharing space had their periods together originated in a 1971 paper by psychologist Martha K. McClintock, who studied 135 women in a college dormitory and concluded that social interaction has a strong effect on the menstrual cycle, probably because of something physiological. Support for this so-called McClintock effect has persisted, despite many later studies that were inconsistent and failed to prove her hypothesis and challenged her methodology.
McClintock, professor emerita of psychology at the University of Chicago, says the science has changed since her original paper was published. She now believes that pheromones secreted from the armpits of women in close quarters changes the timing of ovulation, prompting simultaneous ovulation — not menstruation.“I am aware of all this focus on mathematics, but we’ve gone beyond that,” she says. “In the phrase ‘menstrual synchrony,’ scratch out ‘menstrual’ and put in ‘ovulation’.“
Social psychologist Leonard Weller, professor emeritus in the department of sociology and anthropology at Bar-Ilan University in Israel, conducted a series of small studies — about 15 by his count — in the 1990s with his son, Aron Weller, professor of psychology at Bar-Ilan, on menstrual synchrony. They found that sometimes women were in sync — and sometimes they weren’t. He agrees with Schank that the alignment in cycles was a mathematical coincidence.
“The majority opinion is that it is a mathematical coincidence,” Leonard Weller says. “If you plot the onset for each of two women over a period of time, you will probably find they will converge as well as become disparate, having nothing to do with pheromone influence. Also, assuming the normal menstrual cycle lasts about five days, two women will have some overlap in the timing of their cycles. This has nothing to do with synchrony.”
Noha Ahmed, an obstetrician-gynecology resident physician in D.C., speaking on behalf of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, remembers hearing about menstrual synchrony when she was in college, but says existing studies have been too varied and conducted in too small samples to support the idea.
“It can be hard to say why so many believe this very common misconception,” she says. “If these individuals are all living together, they may experience overlap in the timing of their periods. I imagine that this is where the misconception stems from.”
Menstrual synchrony can provide a form of gendered solidarity for some — a sense of sisterhood — for an experience traditionally regarded as shameful and stigmatizing, says Breanne Fahs, professor of women and gender studies at Arizona State University and author of two studies that explore the sociological implications of many women’s belief in menstrual synchrony.
“For some women, there’s also the notion that menstrual synchrony is somehow magical, and they become very upset when you tell them it probably isn’t true,” Fahs says.
Read more from Well+Being
Well+Being shares news and advice for living well every day. Sign up for our newsletter to get tips directly in your inbox.
Are you taking your meds wrong ? Many patients make these common mistakes.
Centenarians give their advice about everything.
The wall sit is a simple exercise that can lower your blood pressure.
Tart cherries — more specifically, tart cherry juice — may help with inflammation and pain.
Do you self-sabotage ? Here’s how to stop.

Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
2023 saw some of the biggest, hardest-fought labor disputes in recent decades

The nearly four-month actors’ strike against major Hollywood production studios in 2023 was the second-largest labor dispute in the United States in at least three decades, according to a Pew Research Center analysis of federal data through Nov. 30.
By the time the strike by the Screen Actors Guild-American Federation of Television and Radio Artists (SAG-AFTRA) ended on Nov. 8, it had idled 160,000 workers for 82 workdays. That resulted in 13,120,000 “days idle,” a metric that the federal Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) uses to describe the impact of work stoppages.
Given the spate of high-profile labor disputes in 2023 and what’s been reported as unions’ greater willingness to confront management , we wanted to take a closer look at the history of labor actions in the United States.
Our source for this analysis was the federal Bureau of Labor Statistics’ database of “major work stoppages,” which has summary figures starting in 1947 and detailed monthly information about individual stoppages since 1993. The agency defines as “major” any work stoppage that involves at least 1,000 workers and lasts at least one full shift during the work week. (The term “work stoppage” encompasses both strikes by workers and lockouts by management. The workers involved may or may not be unionized.)
Unless the context indicates otherwise, all of the analyses in this post are based on stoppages beginning in a given calendar year, rather than all stoppages in effect during a calendar year.
When calculating total days idled, the BLS counts only days that employees are normally scheduled to work (Monday through Friday, excluding federal holidays) but don’t work due to a stoppage. The agency adjusts its calculations if the number of workers involved changes during a stoppage.
Since 1993, when the BLS began keeping detailed monthly statistics on major work stoppages, the only labor dispute to have a greater impact was a strike over actors’ pay for appearing in commercials by the then-separate SAG and AFTRA in 2000. (The two unions merged in 2012.) That strike, against the American Association of Advertising Agencies and the Association of National Advertisers, lasted nearly six months, resulting in 17.3 million days idle and, reportedly, considerable bitterness and division among union members .
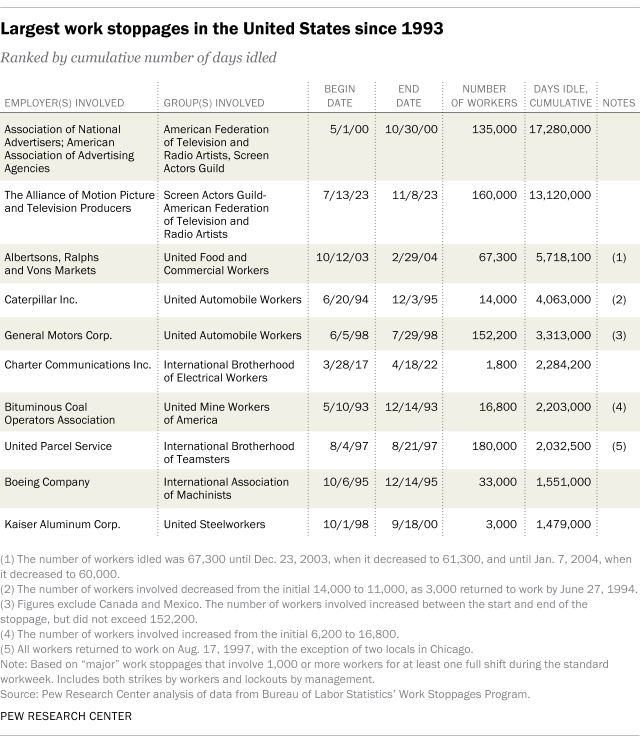
Beyond the SAG-AFTRA strike, 2023 was the most active year overall for major labor disputes in more than two decades, according to our analysis of BLS data on major work stoppages. The BLS defines major stoppages as those involving 1,000 or more workers and lasting at least one full shift during the Monday-Friday work week.
Through the end of November, 30 major stoppages had begun in 2023 – the most of any year since 2000. The 2023 stoppages involved a total of 464,410 workers, the second-most since 1986. And several of last year’s stoppages lasted long enough to generate 16.7 million total days idle, more than any year since 2000.
Besides the SAG-AFTRA strike, other significant stoppages last year included:
- The Writers Guild strike against the same group of production companies (11,500 workers idled for 102 workdays; 1,173,000 days idle)
- The United Auto Workers strike against Ford, General Motors, Mack Trucks and Stellantis (53,700 workers, 43 workdays, 925,900 days idle)
- A strike by a coalition of unions against health care company Kaiser Permanente (75,600 workers, three workdays, 226,800 days idle)
While 2023 stands out against the past few decades for its labor strife, it appears less turbulent if one goes back further in U.S. history.
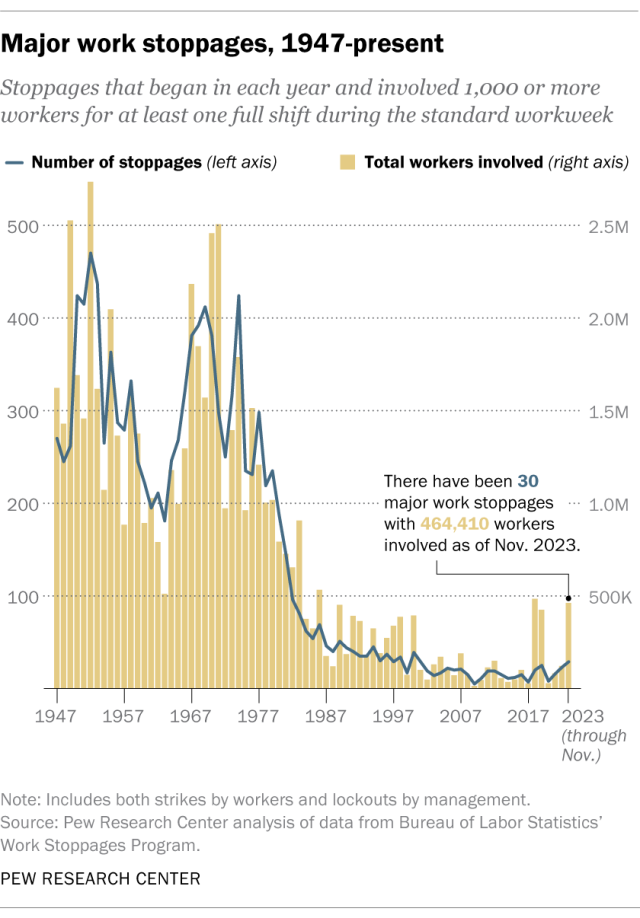
From 1947, the earliest year for which the BLS provides comparable annual data on major work stoppages, through the 1970s, the U.S. routinely experienced hundreds of stoppages a year. Hundreds of thousands or even millions of workers were involved.
The peak was arguably in 1952, when there were 470 major work stoppages involving more than 2.7 million workers. Those stoppages created 48.8 million days idle, the third-most on record. (The top year for days idle was 1959, with 60.9 million, but there were fewer major stoppages that year and fewer workers were involved.)
Whether measured by raw numbers, workers involved or days idle, major work stoppages generally became less common after about 1980 – though not without occasional upsurges. The U.S. economy grew away from its heavily unionized manufacturing sectors , and the federal government under then-President Ronald Reagan turned hostile to organized labor . In 2009, for instance, only five major work stoppages took place, involving a total of just 12,500 workers.
In more recent years, relatively few major stoppages have occurred in traditional manufacturing sectors. From January 2018 through November 2023, just 13 out of 122 major stoppages (11%) involved manufacturing. That compares with 77 out of 176 (44%) between 1993 and 1997.
Instead, major work stoppages in recent years have tended to occurr in two service sectors: education and health care. Nearly two-thirds (65%, or 79 out of 122) of all major stoppages that began between January 2018 and November 2023 were in those two sectors.
The information sector has also seen notable labor actions in recent years. For instance, before the SAG-AFTRA strikes, there was a six-week strike against Verizon in 2016 (36,500 workers involved, 1.2 million days idle) and a strike by 1,800 electrical workers against cable-television giant Charter Communications that started in 2017 and lasted over five years .
- Business & Workplace
- Economy & Work
- Employee Benefits

A look at small businesses in the U.S.
Majorities of adults see decline of union membership as bad for the u.s. and working people, a look at black-owned businesses in the u.s., from businesses and banks to colleges and churches: americans’ views of u.s. institutions, older workers are growing in number and earning higher wages, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Kee says funding for a humanities Ph.D. program typically only lasts five years, even though it is uncommon for someone to obtain a Ph.D. degree in a humanities field within that time frame ...
The optimal length of a Ph.D. dissertation is a strategic equilibrium, determined by the intricate interplay of research complexity, disciplinary norms, and institutional guidelines, emphasizing quality over mere quantity. In the intricate tapestry of academia, the length of a dissertation is a nuanced consideration, influenced by a myriad of ...
The length of a full-time PhD is around three to four years in most countries (it's longer in for a PhD in the USA, but you don't spend all that time doing research). Three years may seem like a long time, but researching a PhD is a lot of work and you'll probably spend at least some of your time on other activities like teaching, conference ...
A PhD program typically takes four to seven years, but a variety of factors can impact that timeline. A PhD, or doctorate degree, is the highest degree you can earn in certain disciplines, such as psychology, engineering, education, and mathematics. As a result, it often takes longer to earn than it does for a bachelor's or master's degree.
The typical length of a PhD is three to four years full-time, or five to six years part-time.. Unlike most Masters courses (or all undergraduate programmes), a PhD is a pure research degree. But that doesn't mean you'll just spend years locked away in a library or laboratory.
A full-time PhD in the UK usually takes between three and four years, while a part-time project typically lasts between five and six years. The the length of a PhD depends on a range of factors, such as your funding arrangements, your country and institution of study, and the nature of your research topic. For example, if you're doing a funded PhD you're more likely to face completion ...
In the UK, a full-time PhD will typically take you 3 to 4 years. You will usually spend the first three years on the technical aspects of your doctorate. This includes undertaking independent research, designing your research methodology and collecting and analysing data. You will then spend an additional academic year on writing up your PhD ...
Research methodologies. The approaches and methods used in the research can dramatically affect the length of the dissertation. For example, some dissertations include case studies, which may require lengthy explanations and analyses. Others use quantitative research methods and may include a number of charts and figures. Committee feedback ...
In the rest of the world, students normally have a master's degree before beginning the PhD, so they proceed directly to the research stage and complete a PhD in 3-5 years. Frequently asked questions: Graduate school ... The typical length of a personal statement for graduate school applications is between 500 and 1,000 words.
Interestingly, the PhD dissertation length and content vary significantly based on the field you are studying and the publishing conventions. A PhD can be anywhere from 50 pages to over 450 pages long. This equates to between about 20,000 words to 100,000 words. Most PhD theses are between 60,000 and 80,000 words long excluding contents ...
The heart of a doctoral program is the dissertation, a rigorous research project that demands an in-depth exploration of your chosen field. This phase alone can take several months to years, significantly influencing the overall length of your PhD journey. Beyond the dissertation, coursework, exams, and sometimes teaching responsibilities add ...
An undergraduate dissertation is typically 8,000-15,000 words. A master's dissertation is typically 12,000-50,000 words. A PhD thesis is typically book-length: 70,000-100,000 words. However, none of these are strict guidelines - your word count may be lower or higher than the numbers stated here. Always check the guidelines provided ...
Unfortunately, there's no one size fits all answer to this question. However, from the analysis of over 100 PhD theses, the average thesis length is between 80,000 and 100,000 words. A further analysis of 1000 PhD thesis shows the average number of pages to be 204. In reality, the actual word count for each PhD thesis will depend on the ...
The length of time required to complete a PhD or master's degree varies. Unsurprisingly, PhDs take much longer, usually between 3-7 years. ... Foundation Graduate Research Program in the United States) that relieves them of any obligations to be a teaching or research assistant. Doctoral programs in the US tend to be better funded than in ...
A research proposal summarises your intended research. Your research proposal is used to confirm you understand the topic, and that the university has the expertise to support your study. The length of a research proposal varies. It is usually specified by either the programme requirements or the supervisor upon request. 1500 to 3500 words is ...
How the PhD Program Works. Completing your doctorate at Wharton requires 5 years of full-time study. The first 2 years in the program prepare you for admission to candidacy by taking courses, qualifying exams, and starting research projects. In the last few years, you are primarily conducting research full-time including writing and defending ...
Brown University awards more than 200 doctor of philosophy degrees annually. The Brown Ph.D. is primarily a research degree. Teaching is an important part of many doctoral programs, and many departments require candidates for the Ph.D. to have teaching experience. Brown University offers substantial financial support to doctoral students.
Therefore, in a good research proposal you will need to demonstrate two main things: 1. that you are capable of independent critical thinking and analysis. 2. that you are capable of communicating your ideas clearly. Applying for a PhD is like applying for a job, you are not applying for a taught programme.
According to the Survey of Earned Doctorates, a census of recent research doctorate recipients who earned their degree from U.S. institutions, the median amount of time it took individuals who received their doctorates in 2017 to complete their program was 5.8 years. However, there are many types of programs that typically take longer than six ...
The PhD program in psychology with a concentration in quantitative research methods offers an immersive education in advanced statistical techniques and research methodologies that are employed in the conduct of both basic and applied psychological research. A collaborative, interdisciplinary approach to research empowers students to deepen ...
The median BLS salary for psychologists include both graduate and undergraduate level occupations. According to Payscale, of the 25 people reporting in September 2023, the average salary for graduates with a Ph.D. in psychology is $95,000. September Payscale data for 2023 reports the average salary for graduates with a Psy.D. as $92,000.
Students in our PhD programs are encouraged from day one to think of this experience as their first job in business academia—a training ground for a challenging and rewarding career generating rigorous, relevant research that influences practice. Our doctoral students work with faculty and access resources throughout HBS and Harvard University.
School of Medicine offers several master's and PhD-level graduate programs for students interested in pursuing careers in health and biomedical sciences research. Our graduate students conduct their thesis work in faculty labs, where their basic, translational and clinical research advances our understanding of human development and disease. ...
Dylan Meyer. Advisor: Scott Diddams Lab: Frequency Comb & Quantum Metrology Lab Bio: Meyer is a first-year PhD student in the FCQM group.He received his undergraduate degree from the University of Alabama in Electrical Engineering. My research proposal is the development of highly stable and robust millimeter wave time and frequency (T&F) transfer, supporting T&F transfer between atomic clocks.
The researchers tested the telomere length of 175 research participants using data from the start of the CALERIE study, one year into the study and the end of the study after 24 months of caloric ...
Research proposal length. The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor's or master's thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
What research says about the common assumption. By Marlene Cimons. April 22, 2024 at 7:00 a.m. EDT ... "Cycles vary in length, and all this variability will lead to convergence and divergence ...
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to understand what Americans know about their government. For this analysis, we surveyed 5,115 adults from June 5 to 11, 2023. Everyone who took part in the survey is a member of the Center's American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of ...
On average, K-12 public schools will be in session close to 180 days this year, according to a Pew Research Center analysis of data from the ... and D.C. do. In 16 of those states, the requirements vary by grade level. In Pennsylvania, for example, the minimum length for a school day is 2.5 hours for kindergarten, 5 hours for first through ...
Workers in a SAG-AFTRA picket line at Sony Pictures Studios in Culver City, California, on Oct. 11, 2023. (Apu Gomes/Getty Images) The nearly four-month actors' strike against major Hollywood production studios in 2023 was the second-largest labor dispute in the United States in at least three decades, according to a Pew Research Center analysis of federal data through Nov. 30.