Understanding Prose in Literature: A Comprehensive Guide
Defining prose, types of prose, prose vs. verse, prose styles, narrative style, descriptive style, expository style, argumentative style, literary devices in prose, foreshadowing, analyzing prose, close reading, theme and message, notable authors and their prose, jane austen, ernest hemingway, toni morrison, prose in different cultures, greek prose, indian prose, japanese prose.
Prose in literature is a fascinating topic that has captured the attention of readers and writers for centuries. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different aspects of prose and how it shapes the world of literature. By understanding prose, you will be able to appreciate the beauty of written language and enhance your own writing skills. So, let's dive into the captivating world of prose in literature!
Prose is a form of written language that follows a natural, everyday speech pattern. It is the way we communicate in writing without adhering to the strict rules of poetry or verse. In literature, prose encompasses a wide range of written works, from novels and short stories to essays and articles. To better understand prose in literature, let's look at the different types of prose and how it compares to verse.
There are several types of prose in literature, each serving a unique purpose and offering a different reading experience:
- Fiction: Imaginative works, such as novels and short stories, that tell a story.
- Non-fiction: Informative works, such as essays, articles, and biographies, that present facts and real-life experiences.
- Drama: Plays and scripts written in prose form, often featuring dialogue and stage directions.
- Prose poetry: A hybrid form that combines elements of prose and poetry, creating a more fluid and expressive style.
By exploring these types of prose, you can better appreciate the versatility and depth of prose in literature.
Prose and verse are two distinct forms of written language, each with its own characteristics and purposes. Here's a quick comparison:
- Prose: Written in a natural, conversational style, prose uses sentences and paragraphs to convey meaning. It is the most common form of writing and can be found in novels, essays, articles, and other forms of literature.
- Verse: Written in a structured, rhythmic pattern, verse often uses stanzas, rhyme, and meter to create a more musical quality. It is most commonly found in poetry and song lyrics.
Understanding the differences between prose and verse can help you appreciate the unique qualities of each form and how they contribute to the richness of literature.
Just as there are different types of prose, there are also various prose styles that authors use to convey their ideas and stories. These styles can be categorized into four main groups:
The narrative style tells a story by presenting events in a sequence, typically involving characters and a plot. This style is commonly used in novels, short stories, and biographies. Some key features of the narrative style include:
- Chronological or non-chronological structure
- Use of dialogue and description
- Focus on characters, their actions, and motivations
- Development of a plot, consisting of a beginning, middle, and end
By using the narrative style, authors can create engaging stories that draw readers in and make them feel a part of the experience.
The descriptive style focuses on painting a vivid picture of a person, place, or thing. This style is used to provide detailed information and create a strong sensory experience for the reader. Some key features of the descriptive style include:
- Use of sensory language, such as sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch
- Adjectives and adverbs to enhance descriptions
- Figurative language, such as similes and metaphors, to create vivid imagery
- Attention to detail and setting
By mastering the descriptive style, authors can transport readers to new worlds and enrich their understanding of the subject matter.
The expository style is used to explain, inform, or describe a topic. This style is commonly found in textbooks, essays, and articles. Some key features of the expository style include:
- Clear, concise language
- Logical organization of information
- Use of examples, facts, and statistics to support the main idea
- An objective, unbiased tone
By employing the expository style, authors can effectively convey information and help readers gain a deeper understanding of a subject.
The argumentative style is used to persuade or convince the reader of a certain viewpoint. This style is often found in opinion pieces, essays, and debates. Some key features of the argumentative style include:
- A clear, well-defined thesis statement
- Logical organization of arguments and evidence
- Use of facts, statistics, and examples to support the thesis
- Addressing and refuting opposing viewpoints
- A persuasive, confident tone
By mastering the argumentative style, authors can effectively present their opinions and persuade readers to consider their perspective.
Understanding these different prose styles can help you appreciate the diverse ways authors use language to convey their ideas and enhance your own writing abilities.
Authors use various literary devices to enrich their prose and make it more engaging for the reader. These devices help create an emotional connection, build suspense, or bring out deeper meanings in the text. Let's explore some of the most commonly used literary devices in prose:
Imagery is the use of vivid and descriptive language to create a picture in the reader's mind. This technique appeals to the five senses and can make a piece of writing more immersive and memorable. Some examples of imagery include:
- Visual imagery: describing the appearance of a character or setting
- Auditory imagery: describing sounds, such as the rustling of leaves or the roar of a crowd
- Olfactory imagery: describing smells, such as the scent of fresh-baked cookies or the aroma of a garden
- Gustatory imagery: describing tastes, such as the sweetness of a ripe fruit or the bitterness of a cup of coffee
- Tactile imagery: describing textures and physical sensations, such as the softness of a blanket or the warmth of the sun
By using imagery, authors can create a richer, more engaging experience for the reader.
Foreshadowing is a technique used to hint at events that will occur later in the story. This can create suspense, build anticipation, and keep the reader engaged. Foreshadowing can be subtle or more direct and can take various forms, such as:
- Character dialogue or thoughts
- Symbolism or motifs
- Setting or atmosphere
- Actions or events that mirror or prefigure future events
By incorporating foreshadowing, authors can create a sense of mystery and intrigue that keeps readers turning the pages.
Allusion is a reference to a well-known person, event, or work of art, literature, or music. This technique allows authors to make connections and add depth to their writing without explicitly stating the reference. Allusions can serve various purposes, such as:
- Creating a shared understanding between the author and the reader
- Establishing a cultural, historical, or literary context
- Adding layers of meaning or symbolism
- Providing a subtle commentary or critique
By using allusion, authors can enhance their prose and engage readers with shared knowledge and cultural references.
These are just a few examples of the many literary devices that authors use to enrich their prose in literature. By understanding and recognizing these techniques, you can deepen your appreciation of the written word and perhaps even add some of these tools to your own writing repertoire.
Analyzing prose in literature involves closely examining the text to gain a deeper understanding of the author's intentions, themes, and techniques. This process can help you appreciate the nuances of the writing and uncover new insights. Let's explore some approaches to analyzing prose:
Close reading is a method of carefully examining the text to identify its structure, themes, and literary devices. This approach involves paying attention to details such as:
- Word choice and diction
- Sentence structure and syntax
- Imagery and figurative language
- Characterization and dialogue
- Setting and atmosphere
By closely examining these elements, you can gain a deeper understanding of the author's intentions and the text's overall meaning.
Identifying the theme or central message of a piece of prose is another important aspect of analysis. A theme is a recurring idea, topic, or subject that runs through the text. Some common themes in literature include:
- Love and relationships
- Identity and self-discovery
- Power and authority
- Conflict and resolution
- Nature and the environment
To identify the theme of a piece of prose, consider the overall message or lesson that the author is trying to convey. Look for patterns, motifs, and symbols that support this message. Understanding the theme can help you better appreciate the author's intentions and the text's significance.
By employing these approaches to analyzing prose in literature, you can deepen your understanding of the text and enhance your appreciation of the author's craft. Whether you're studying a classic novel or a contemporary short story, these skills will help you unlock the richness and complexity of the written word.
Throughout history, numerous authors have made significant contributions to the world of prose in literature. Their unique writing styles and innovative approaches to storytelling have left an indelible mark on the literary landscape. Let's take a closer look at some notable authors and their distinctive prose:
Jane Austen, an English author from the early 19th century, is well-known for her witty and satirical prose. Her novels often center on themes of love, marriage, and social class in the Georgian era. Examples of her work include Pride and Prejudice , Sense and Sensibility , and Emma . Austen's prose is characterized by:
- Sharp wit and humor
- Observant descriptions of characters and their social interactions
- Realistic dialogue that reveals the personalities and motivations of her characters
- Insightful commentary on societal norms and expectations of her time
Ernest Hemingway, an American author from the 20th century, is celebrated for his distinctive writing style that has had a lasting impact on prose in literature. His works often explore themes of war, love, and the human condition, such as in A Farewell to Arms , The Old Man and the Sea , and For Whom the Bell Tolls . Hemingway's prose is characterized by:
- Simple, direct language and short sentences
- An emphasis on action and external events
- Understated emotions and a focus on the physical world
- A "less is more" approach that leaves room for reader interpretation
Toni Morrison, an American author and Nobel laureate, is renowned for her powerful, evocative prose that delves into the complexities of human relationships and the African American experience. Notable works include Beloved , Song of Solomon , and The Bluest Eye . Morrison's prose is characterized by:
- Rich, lyrical language and vivid imagery
- Complex characters and multi-layered narratives
- Explorations of race, gender, and identity
- A strong sense of voice and emotional intensity
These authors, among many others, have each left their unique imprint on the realm of prose in literature. By studying their works and understanding their techniques, we can better appreciate the diverse ways in which writers can use prose to convey their stories and ideas.
Prose in literature is a global phenomenon, with each culture bringing its own distinctive style, themes, and literary traditions to the table. Let's explore how prose has developed and evolved in some cultures around the world:
Ancient Greek prose has had a profound influence on Western literature. Spanning various genres such as philosophy, history, and drama, Greek prose is known for its intellectual depth and stylistic sophistication. Key features of Greek prose include:
- Rhetorical devices like repetition, parallelism, and antithesis
- Emphasis on logic, reason, and argumentation
- Rich vocabulary and complex sentence structures
- Notable authors like Plato, Aristotle, and Herodotus
Indian prose in literature spans thousands of years and numerous languages, with each region and time period contributing its own flavor to the mix. Indian prose is often characterized by:
- Epic tales and religious texts, such as the Mahabharata and the Ramayana
- Folk tales, fables, and parables that convey moral lessons
- Ornate and poetic language, with a focus on imagery and symbolism
- Notable authors like Rabindranath Tagore, R. K. Narayan, and Arundhati Roy
Japanese prose in literature is known for its elegance, subtlety, and attention to detail. Spanning various genres such as poetry, drama, and fiction, Japanese prose often explores themes of nature, human emotion, and the passage of time. Key features of Japanese prose include:
- Haiku and other poetic forms that emphasize simplicity and precision
- Descriptions of the natural world and the changing seasons
- Understated emotions and a focus on the inner lives of characters
- Notable authors like Yasunari Kawabata, Yukio Mishima, and Haruki Murakami
By examining the diverse range of prose in literature from various cultures, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the many ways in which authors use language to tell stories, express ideas, and convey the human experience.
If you found this blog post intriguing and want to delve deeper into writing from your memories, be sure to check out Charlie Brogan's workshop, ' Writing From Memory - Part 1 .' This workshop will guide you through the process of tapping into your memories and transforming them into captivating stories. Don't miss this opportunity to enhance your writing skills and unleash your creativity!

Live classes every day
Learn from industry-leading creators
Get useful feedback from experts and peers
Best deal of the year
* billed annually after the trial ends.
*Billed monthly after the trial ends.
- Literary Terms
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Write a Prose

I. What is a Prose?
Prose is just non-verse writing. Pretty much anything other than poetry counts as prose: this article, that textbook in your backpack, the U.S. Constitution, Harry Potter – it’s all prose. The basic defining feature of prose is its lack of line breaks:
In verse, the line ends
when the writer wants it to, but in prose
you just write until you run out of room and then start a new line.
Unlike most other literary devices , prose has a negative definition : in other words, it’s defined by what it isn’t rather than by what it is . (It isn’t verse.) As a result, we have to look pretty closely at verse in order to understand what prose is.
II. Types of Prose
Prose usually appears in one of these three forms.
You’re probably familiar with essays . An essay makes some kind of argument about a specific question or topic. Essays are written in prose because it’s what modern readers are accustomed to.
b. Novels/short stories
When you set out to tell a story in prose, it’s called a novel or short story (depending on length). Stories can also be told through verse, but it’s less common nowadays. Books like Harry Potter and the Fault in Our Stars are written in prose.
c. Nonfiction books
If it’s true, it’s nonfiction. Essays are a kind of nonfiction, but not the only kind. Sometimes, a nonfiction book is just written for entertainment (e.g. David Sedaris’s nonfiction comedy books), or to inform (e.g. a textbook), but not to argue. Again, there’s plenty of nonfiction verse, too, but most nonfiction is written in prose.
III. Examples of Prose
The Bible is usually printed in prose form, unlike the Islamic Qur’an, which is printed in verse. This difference suggests one of the differences between the two ancient cultures that produced these texts: the classical Arabs who first wrote down the Qur’an were a community of poets, and their literature was much more focused on verse than on stories. The ancient Hebrews, by contrast, were more a community of storytellers than poets, so their holy book was written in a more narrative prose form.
Although poetry is almost always written in verse, there is such a thing as “prose poetry.” Prose poetry lacks line breaks, but still has the rhythms of verse poetry and focuses on the sound of the words as well as their meaning. It’s the same as other kinds of poetry except for its lack of line breaks.
IV. The Importance of Prose
Prose is ever-present in our lives, and we pretty much always take it for granted. It seems like the most obvious, natural way to write. But if you stop and think, it’s not totally obvious. After all, people often speak in short phrases with pauses in between – more like lines of poetry than the long, unbroken lines of prose. It’s also easier to read verse, since it’s easier for the eye to follow a short line than a long, unbroken one.
For all of these reasons, it might seem like verse is actually a more natural way of writing! And indeed, we know from archaeological digs that early cultures usually wrote in verse rather than prose. The dominance of prose is a relatively modern trend.
So why do we moderns prefer prose? The answer is probably just that it’s more efficient! Without line breaks, you can fill the entire page with words, meaning it takes less paper to write the same number of words. Before the industrial revolution, paper was very expensive, and early writers may have given up on poetry because it was cheaper to write prose.
V. Examples of Prose in Literature
Although Shakespeare was a poet, his plays are primarily written in prose. He loved to play around with the difference between prose and verse, and if you look closely you can see the purpose behind it: the “regular people” in his plays usually speak in prose – their words are “prosaic” and therefore don’t need to be elevated. Heroic and noble characters , by contrast, speak in verse to highlight the beauty and importance of what they have to say.
Flip open Moby-Dick to a random page, and you’ll probably find a lot of prose. But there are a few exceptions: short sections written in verse. There are many theories as to why Herman Melville chose to write his book this way, but it probably was due in large part to Shakespeare. Melville was very interested in Shakespeare and other classic authors who used verse more extensively, and he may have decided to imitate them by including a few verse sections in his prose novel.
VI. Examples of Prose in Pop Culture
Philosophy has been written in prose since the time of Plato and Aristotle. If you look at a standard philosophy book, you’ll find that it has a regular paragraph structure, but no creative line breaks like you’d see in poetry. No one is exactly sure why this should be true – after all, couldn’t you write a philosophical argument with line breaks in it? Some philosophers, like Nietzsche, have actually experimented with this. But it hasn’t really caught on, and the vast majority of philosophy is still written in prose form.
In the Internet age, we’re very familiar with prose – nearly all blogs and emails are written in prose form. In fact, it would look pretty strange if this were not the case!
Imagine if you had a professor
who wrote class emails
in verse form, with odd
line breaks in the middle
of the email.
VII. Related Terms
Verse is the opposite of prose: it’s the style of writing
that has line breaks.
Most commonly used in poetry, it tends to have rhythm and rhyme but doesn’t necessarily have these features. Anything with artistic line breaks counts as verse.
18 th -century authors saw poetry as a more elevated form of writing – it was a way of reaching for the mysterious and the heavenly. In contrast, prose was for writing about ordinary, everyday topics. As a result, the adjective “prosaic” (meaning prose-like) came to mean “ordinary, unremarkable.”
Prosody is the pleasing sound of words when they come together. Verse and prose can both benefit from having better prosody, since this makes the writing more enjoyable to a reader.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
Definition of Prose
Prose is a literary device referring to writing that is structured in a grammatical way, with words and phrases that build sentences and paragraphs. Works wrote in prose feature language that flows in natural patterns of everyday speech. Prose is the most common and popular form of writing in fiction and non-fiction works.
As a literary device, prose is a way for writers to communicate with readers in a straightforward, even conversational manner and tone . This creates a level of familiarity that allows the reader to connect with the writer’s expression, narrative , and characters. An example of the effective familiarity of prose is J.D. Salinger’s The Catcher in The Rye :
What really knocks me out is a book that, when you’re all done reading it, you wish the author that wrote it was a terrific friend of yours and you could call him up on the phone whenever you felt like it.
Salinger’s prose is presented as first-person narration as if Holden Caulfield’s character is speaking to and conversing directly with the reader. This style of prose establishes familiarity and intimacy between the narrator and the reader that maintains its connection throughout the novel .
Common Examples of First Prose Lines in Well-Known Novels
The first prose line of a novel is significant for the writer and reader. This opening allows the writer to grab the attention of the reader, set the tone and style of the work, and establish elements of setting , character, point of view , and/or plot . For the reader, the first prose line of a novel can be memorable and inspire them to continue reading. Here are some common examples of first prose lines in well-known novels:
- Call me Ishmael. ( moby dick )
- It was the best of times, it was the worst of times ( A Tale of Two Cities )
- It is a truth universally acknowledged, that a single man in possession of a good fortune, must be in want of a wife. ( Pride and Prejudice )
- It was love at first sight. ( catch 22 )
- In my younger and more vulnerable years my father gave me some advice that I’ve been turning over in my mind ever since. ( The Great Gatsby )
- It was a bright cold day in April, and the clocks were striking thirteen. ( 1984 )
- i am an invisible man . ( Invisible Man )
- Mother died today. ( the stranger )
- They shoot the white girl first, but the rest they can take their time. ( Paradise )
- All this happened, more or less. ( Slaughterhouse-Five )
Examples of Famous Lines of Prose
Prose is a powerful literary device in that certain lines in literary works can have a great effect on readers in revealing human truths or resonating as art through language. Well-crafted, memorable prose evokes thought and feeling in readers. Here are some examples of famous lines of prose:
- Shoot all the blue jays you want, if you can hit ‘em, but remember it’s a sin to kill a mockingbird . ( To Kill a Mockingbird )
- In spite of everything, I still believe that people are good at heart. ( Anne Frank : The Diary of a Young Girl )
- All Animals are Equal , but some animals are more equal than others. ( Animal Farm)
- It is easier to start a war than to end it. ( One Hundred Years of Solitude )
- It is not often that someone comes along who is a true friend and a good writer. Charlotte was both. ( Charlotte’s Web )
- I think it pisses God off if you walk by the color purple in a field somewhere and don’t notice it. ( The Color Purple )
- There is no greater agony than bearing an untold story inside you, ( I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings )
- The answer to the ultimate question of life, the universe and everything is 42. ( The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy )
- The only thing worse than a boy who hates you: a boy that loves you. ( The Book Thief )
- Just remember: If one bird carried every grain of sand, grain by grain, across the ocean, by the time he got them all on the other side, that would only be the beginning of eternity. ( In Cold Blood )
Types of Prose
Writers use different types of prose as a literary device depending on the style and purpose of their work. Here are the different types of prose:
- Nonfiction: prose that recounts a true story, provides information, or gives a factual account of something (such as manuals, newspaper articles, textbooks, etc.)
- Heroic: prose usually in the form of a legend or fable that is intended to be recited and has been passed down through oral or written tradition
- Fiction : most familiar form of prose used in novels and short stories and featuring elements such as plot, setting, characters, dialogue , etc.
- Poetic Prose: poetry written in the form of prose, creating a literary hybrid with occasional rhythm and/or rhyme patterns
Difference Between Prose and Poetry
Many people consider prose and poetry to be opposites as literary devices . While that’s not quite the case, there are significant differences between them. Prose typically features natural patterns of speech and communication with grammatical structure in the form of sentences and paragraphs that continue across the lines of a page rather than breaking. In most instances, prose features everyday language.
Poetry, traditionally, features intentional and deliberate patterns, usually in the form of rhythm and rhyme. Many poems also feature a metrical structure in which patterns of beats repeat themselves. In addition, poetry often includes elevated, figurative language rather than everyday verbiage. Unlike prose, poems typically include line breaks and are not presented as or formed into continuous sentences or paragraphs.
Writing a Prose Poem
A prose poem is written in prose form without a metrical pattern and without a proper rhyme scheme . However, other poetic elements such as symbols metaphors , and figurative language are used extensively to make the language poetic. Writing a prose poem involves using all these poetic elements, including many others that a poet could think about.
It is not difficult to write a prose poem. It, however, involves a step-by-step approach.
- Think about an idea related to a specific theme , or a choose topic.
- Think poetically and write as prose is written but insert notes, beats, and patterns where necessary.
- Use repetitions , metaphors, and similes extensively.
- Revise, revise and revise to make it melodious.
Prose Edda vs. Poetic Edda
Prose Edda refers to a collection of stories collected in Iceland, or what they are called the Icelandic Saga. Most of the Prose Edda stories have been written by Snorri Sturluson while has compiled the rest written by several other writers. On the other hand, most of the poems about the Norse gods and goddesses are called the Poetic Edda. It is stated that almost all of these poems have been derived from the Codex Regius written around the 13 th century though they could have been composed much earlier. Such poems are also referred to as Eddaic poetry. In other words, these poetic outputs and writings are classical poetic pieces mostly woven around religious themes.
Examples of Prose in Literature
Prose is an essential literary device in literature and the foundation for storytelling. The prose in literary works functions to convey ideas, present information, and create a narrative for the reader through the intricate combinations of plot, conflict , characters, setting, and resolution . Here are some examples of prose in literature:
Example 1: The Grapes of Wrath by John Steinbeck
A large drop of sun lingered on the horizon and then dripped over and was gone, and the sky was brilliant over the spot where it had gone, and a torn cloud, like a bloody rag, hung over the spot of its going. And dusk crept over the sky from the eastern horizon, and darkness crept over the land from the east.
Steinbeck’s gifted prose in this novel is evident in this passage as he describes the last moment of sunset and the onset of darkness. Steinbeck demonstrates the manner in which a writer can incorporate figurative language into a prose passage without undermining the effect of being straightforward with the reader. The novel’s narrator utilizes figurative language by creating a metaphor comparing the sun to a drop of liquid, as well as through personifying dusk and darkness as they “crept.” This enhances the novel’s setting, tone, and mood in this portion of the story.
However, though Steinbeck incorporates such imagery and poetic phrasing in this descriptive passage, the writing is still accessible to the reader in terms of prose. This demonstrates the value of this literary device in fictional works of literature. Writers can still master and offer everyday language and natural speech patterns without compromising or leaving out the effective descriptions and use of figurative language for readers.
Example 2: This Is Just to Say by William Carlos Williams
I have eaten the plums that were in the icebox and which you were probably saving for breakfast Forgive me they were delicious so sweet and so cold
In this poem by Williams, he utilizes poetic prose to create a hybrid work of literature. The poem is structured in appearances like a poetic work with line breaks and stanzas . However, the wording of the work flows as prose writing in its everyday language and conversational tone. There is an absence of figurative language in the poem, and instead, the expression is direct and straightforward.
By incorporating prose as a literary device in his poem, Williams creates an interesting tension for the reader between the work’s visual representation as a poem and the familiar, literal language making up each individual line. However, rather than undermine the literary beauty of the poem, the prose wording enhances its meaning and impact.
Example 3: Harrison Bergeron by Kurt Vonnegut, Jr.
The year was 2081, and everybody was finally equal. They weren’t only equal before God and the law. They were equal every which way. Nobody was smarter than anybody else. Nobody was better looking than anybody else. Nobody was stronger or quicker than anybody else. All this equality was due to the 211th, 212th, and 213th Amendments to the Constitution, and to the unceasing vigilance of agents of the United States Handicapper General.
This passage introduces Vonnegut’s work of short fiction. The narrator’s prose immediately sets the tone of the story as well as foreshadows the impending conflict. The certainty and finality of the narrator’s statements regarding equality in the story establish a voice that is direct and unequivocal. This unambiguous voice set forth by Vonnegut encourages trust in the narration on behalf of the reader. As a result, when the events and conflict in the story turn to science fiction and even defy the laws of physics, the reader continues to “believe” the narrator’s depiction of the plot and characters.
This suspension of disbelief on the part of the reader demonstrates the power of prose as a literary device and method of storytelling. By utilizing the direct and straightforward nature of prose, the writer invites the reader to become a participant in the story by accepting what they are told and presented through the narrator. This enhances the connection between the writer as a storyteller and a receptive reader.
Synonyms of Prose
Prose has a few close synonyms but cannot be used interchangeably. Some of the words coming near in meanings are unlyrical, unpoetic, factual, literal, antipoetic, writing, prosaic and factual.
Post navigation

Prose Type: What are 10 Different Prose Types in Creative Writing?
1. biography, 2. autobiography, 3. folktale.
- 6. Fable
9. Short Story
When discussing the eminent components of literature , we do take into consideration the mode through which a piece of work is presented. While doing so, one gets introduced to terms like Prose and Poetry which later become the center of the talk. These are two such forms through which almost all of the literature encompass.
To elucidate and encounter the difference between the two, one can easily understand Prose as being the writing that we see in our daily lives that does not follow any metrical structure and is written in the form of sentences and paragraphs. Poetry, on the other hand, can be seen as a literary work that caters to aesthetics, follows a certain style and rhythm , and is expressed in stanzas.
Continue reading this article to develop a deeper understanding of the 10 Prose type with examples .
What is a Prose?
Prose can simply be defined as the form of writing which is specifically of pragmatic nature , following a proper grammatical structure. Unlike Poetry it does not follow any fixed metrical parameters and is expressed in the form of sentences and paragraphs in a lucid manner. It often aims at conveying the message by following a narrative structure. Prose can be of various types like biography, folktale, autobiography, fables , and many more. 10 of its types are discussed below.
A thorough description of a person’s life is referred to as his/her Biography.
It is a kind of prose that is full of basic information about all the highs and lows in a person’s life, including anecdotes and memoirs. A biography tells the tale of the person’s personal experiences with life, relationships , work, and all other things. You are the major lead of your biography and it tells your truth to the world. Biographies fall under the category of non- fiction . When written in-depth, we know it as legacy writing.
A biography can also be portrayed or presented in various forms of media, from literature to film. An accredited biography can only be written with the permission, cooperation, and participation of the person or the person’s family or successors. It is the story of a person’s life narrated and drafted by him or her but perfected and written by another person.
Biography Example: The Life of Samuel Johnson (By James Boswell)

This is a perfect example of the English language . Boswell was well acquainted with Samuel Johnson and has created a masterpiece of biography for the late writer and the readers.
Autobiography is also a kind of prose and as the term suggests, it is the self-written account of one’s life.
It is very similar to a biography, except it is written by the same person whose story it is about. For example, if I write the story of my life by myself completely, then it will be referred to as an autobiography. The person can also seek guidance or help from another writer or hire a ghostwriter if required.
Autobiography Example: The Story of My Life by Helen Keller is the best example of an autobiography as it captures it all and that too perfectly.

Folktale is a popular or legendary story, familiar to a specific group or culture reflecting their values and ideas. They are usually passed down verbally from one generation to another. These stories carry a moral or lesson to be absorbed by the audience. Folktales have many types like fables, tall tales, ghost stories, or religious tales.
Folktale Example: The Pied Piper and The Frog King are popular folktales both impart valuable lessons. The Frog King is one of the oldest German folk tales. In the story, a princess promises a frog that she will make him her companion if he retrieves her favourite toy from the bottom of the deep spring . The moral of The Frog King is that one should honour their promises and will be rewarded. The frog honoured his promise to retrieve the ball and the princess (unwillingly) honoured her promise to the frog. His curse was broken, and she got a fancy new husband.

Myth is a traditional story or tale full of symbols. These superficially relate to reality or actual events and are especially associated with religious beliefs and traditions. The key figures in myths are gods, demigods, or supernatural humans with unrealistic powers and talents entangled in extraordinary events or circumstances in an unknown period.
Myth Example: Pandora’s Box is an artifact in Greek mythology connected with the myth of Pandora in Hesiod’s Works and Days.

Legend stories are a subgenre of folktales. The legend may be a traditional story or a group of stories with a sound message for the audience. Also, legends are about a person or a place. Earlier, the term Legend was used for telling a tale about a saint. These are quite similar to folktales in content. They may include supernatural beings, elements of mythology, or explanations of natural phenomena, but they are linked with a particular locality or person and are told as a matter of antiquity.
Legend Example: Some well-known legends are
- The tales of Odysseus from Ancient Greece,
- Beowulf from the Norse lands,
- King Arthur from Old England,
- The famous Robin Hood,
- The Bigfoot .

6 . Fable
A fictional work of literature featuring inanimate objects or forces of nature, animals , plants , or legendary creatures having humanlike attributes. A fable is written in prose or verse, to highlight human foolishness and flaws or mistakes. These have a moral or lesson weaved into the story and are often explicitly planned at the end as a concise maxim or saying.
Fable Example: A splendid example is The Panchatantra, a Sanskrit compilation of beast fables. Animal Farm by George Orwell is an excellent novel depicting the situation of Russia post-war through animals in a satirical form.

A parable is a brief, educational story, written in the form of prose or verse, that explains one or more informative lessons or teachings. It differs from a fable as fables employ animals, plants, inanimate objects, or forces of nature as key figures, whereas parables have human characters. A parable is a kind of metaphorical analogy. Parables in literature impart a moral lesson to the readers. It is excellent for teaching because stories are easier to recall with clarity and interest.
Prose Type Parable Example: “The Boy Who Cried Wolf” warns against lying because of its impending consequences.

A novel is a long literary fictional work, usually written in the form of prose. A novel is a book telling a single tale penned creatively with human experience and exposure. The novel has several chapters, each chapter is connected or linked to the other through a sequence of events and has a specific setting and tone. We have a large number of genres of novels available which have encompassed various styles and types, some of them are picaresque, comedy , drama , romance, gothic, epistolary, and many more.
Prose Type Novel Example: The Harry Potter series by J.K. Rowling.

As the name suggests, a short story is a fictional prose narrative that is shorter than a novel. A short story has only one or few events and passages, has few characters and few to no chapters. The form encourages conservation of setting, concise narrative, and the omission of a complex plot ; character is disclosed in action and dramatic encounters but is seldom fully developed.
Prose Type Short Story Example: “ A Christmas Carol ” by Charles Dickens and “The Lottery” by Shirley Jackson.

A piece of writing that lets the author present his/her ideas and feelings or argument. An essay doesn’t necessarily have to be formal or have a system to follow, it usually deals with its topic in a more personal manner, putting out its point of view .
Some of the popular essays are :
- David Sedaris
- Kookaburra,
- Zadie Smith – Fail Better
- Virginia Woolf – Death of the Moth.

Hope you enjoyed knowing about these prose types. Check out 9 genres of Poetry to learn about different poetry genres .
Share with your friends
Related Posts:

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

The difference between prose and poetry seems easy to explain: one has blocks of text and fully-fleshed characters, the other has line breaks and pretty words. That’s it, right?
Despite their visual quirks, prose and poetry share many similarities: prose can be musical, poetry can have plots and characters, and both are millennia-old traditions. As such, it would be wrong to prescribe a rigid decision tree for writing prose vs. poetry—many writers have both in their toolkits, relying on each form to communicate different truths.
“Poetry creates the myth, the prose writer draws its portrait.” —Jean-Paul Sartre
So what is the difference between poetry and prose? And which should you write for which occasions? Again, we won’t give hard-and-fast rules, but we can explore their differences in depth and discuss their possibilities.
First, we’ll discuss the features of prose and poetry independently, then we’ll loop back to examine both their differences and their areas of overlap.
Prose vs. Poetry: Defining Prose
Prose is the more common writing form that everyone is comfortable reading and writing. This article relies on prose—as do most ( but not all! ) novels, and just about all news stories, instruction manuals, scientific papers, and so on.
Prose Versus Verse: Line Breaks
The most straightforward rule of thumb for knowing that you’re reading prose (as opposed to its counterpart, verse ) is that there are no defined line breaks: words go all the way to the edge of the page without “turning back” early.
A rule of thumb for prose (as opposed to its counterpart, verse ) is that there are no defined line breaks.
Again, that’s how this blog article works, along with most other writing, from tweets to short stories to scientific papers.
So why would you stop writing prose, and move over to the with-line-breaks type of writing known as verse? The line breaks aren’t arbitrary, but reflect an underlying difference in how prose and verse tend to be structured. To quote the always-helpful Wikipedia:
“Where the common unit of verse is based on meter or rhyme, the common unit of prose is purely grammatical, such as a sentence or paragraph.”
So is verse (writing with line breaks) always poetry? While two are often used synonymously, defining poetry requires more than just scanning for line breaks: as we’ll discuss below, poetry is also about the rich and musical use of language.
Prose is not the counterpart of poetry, but the counterpart of verse.
So prose is not the counterpart of poetry, but rather the counterpart of verse. So verse is not what strictly defines poetry. In fact, not all poetry is in verse—specifically, prose poetry isn’t. In other words, prose and poetry do overlap, whereas prose and verse don’t.
Most poetry is in verse, but some poetry is in prose.
We go into more detail on line breaks, stanzas, and the use of page space in the sections below.
Prose is More Functional than Poetry
A helpful pattern in understanding prose vs. poetry is as follows: prose tends to work in clearer meanings, and to be less musical (that is, working with the inherent rhythms and sonic properties of language) and less densely packed with meanings, literary devices , and associations, than poetry.
As such, prose writing tends to be linear: while a prosaic sentence can twist and turn, it tends to share clear information, generally in a logical order.
Prose tends to work in clearer meanings, and to be less musical and dense, than poetry.
Again, exceptions exist, notably prose poetry : prose writing—writing with no line endings or defined rhythmic meter—that is highly musical and dense, and that is generally more impressionistic and multifaceted than most prose in the meanings it conveys.
And then there’s prose writing that is enigmatic and dreamlike rather than clear and orderly, such as the stream-of-consciousness prose writing in James Joyce’s Ulysses .
These exceptions prove the rule, though: most other prose, from this blog article your friend’s next Facebook post to Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein , tends to follow the delineation described here.
We’ll allow Hemingway a last word with a slightly macho, not-applicable-to-every-prose-work, but still helpful description of prose: “Prose is architecture, not interior decoration.”
Sound good? To get a stronger feel for prose and further acquaint yourself with prose writing, take a look at the readings below.
How to Read Prose
This article gives close reading strategies for prose writing.
How to Read Prose: Close Reading Strategies for Prose Writers
Further Readings in Fiction and Nonfiction
The articles below outline helpful practices for numerous kinds of prose writing, from flash fiction to the novel, focusing especially on the common ingredients of storytelling.
- Crafting a Story Outline
- Freytag’s Pyramid
- Literary Devices in Prose
- Writing Flash Fiction
- Writing the Short Story
- Writing the Novella
- Writing the Novel
Prose vs. Poetry: Defining Poetry
Poetry is the oldest literary form, predating the written word (and therefore, prose) by several millennia. Up until the printing press revolutionized the distribution of literature, poetry was the main form for storytellers, who used meter and rhythm to perform oral retellings of their work.
So, what is poetry? As we’ve seen in our introduction to prose above, most—but not all—poetry is written in verse: writing with line breaks, organized around rhythm or meter rather than grammar. Still, we’ve also seen that verse is not what defines poetry, nor is all poetry based in verse.
So it’s not simply another word for verse. Is there an agreed-upon artistic definition of poetry as a literary form? (Spoiler: No.)
Artistic Definitions of Poetry Vary
Artistic definitions of poetry change from poetic movement to poetic movement—and from poet to poet.
For example, William Wordsworth said that poetry is “the spontaneous overflow of powerful feelings… recollected in tranquility.” This sentiment—largely reflective of the Romantic era—certainly rings true for some poetry. However, New Formalist poets work with poetry to distill and reflect emotion through form and meter: in other words, structure over emotion.
The point is, there’s no singular way to define or understand the artistic aims of poetry. Rather, all poets must define these aims for themselves and write accordingly.
Poets must define the artistic aims of poetry for themselves and write accordingly.
Learning about poetry requires familiarizing yourself with what other poets have already done. This list of poetry movements can jumpstart your understanding of poetry’s complex and various histories.

Poetry Uses Language Richly
Good poetry, from any tradition, sings and resonates beyond the merely “prosaic.”
Whatever literary tradition you ascribe to, poetry has a clear job to be rich, musical, evocative. Good poetry, from any tradition, sings and resonates in a way that goes beyond the merely “prosaic,” as in the following poem excerpt by Derek Walcott:
You will love again the stranger who was your self. Give wine. Give bread. Give back your heart to itself, to the stranger who has loved you
all your life, whom you ignored for another, who knows you by heart.
So poetry, in any tradition, is the “cheesecake of language”: packed to the brim with sonic and expressive power. In poetry, it’s not enough to make a rational point straightforwardly, like the prosaic sentence you’re reading is doing.
Samuel Taylor Coleridge said this beautifully, and we can give him the last word in defining poetry.
“Poetry: the best words in the best order.” —Samuel Taylor Coleridge
Cool, right? If you’d like to learn more, check out our guides for reading and understanding poetry.
How to Read Poetry
This article gives close reading strategies for poetry writing.
How to Read Poetry Like a Poet
Further Readings in Poetry
The articles below outline helpful practices poetry writing, including deep dives on common literary devices in poetry and established poetry forms.
- Poetry Forms
- Writing and Publishing a Poetry Book
Poetry vs. Prose: A Clear Example of Each
Let’s cap the definitions of poetry and prose above by simply giving a clear example of each.
Here is some beautiful fiction writing that is definitely prose:
They were nearly born on a bus, Estha and Rahel. The car in which Baba, their father, was taking Ammu, their mother, to hospital in Shillong to have them, broke down on the winding tea-estate road in Assam. They abandoned the car and flagged down a crowded State Transport bus. With the queer compassion of the very poor for the comparatively well off, or perhaps only because they saw how hugely pregnant Ammu was, seated passengers made room for the couple, and for the rest of the journey Estha and Rahel’s father had to hold their mother’s stomach (with them in it) to prevent it from wobbling. That was before they were divorced and Ammu came back to live in Kerala.
—Arundhati Roy, The God of Small Things
And here is some writing that is definitely poetry:
We are such stuff As dreams are made on; and our little life Is rounded with a sleep.
—Shakespeare, The Tempest
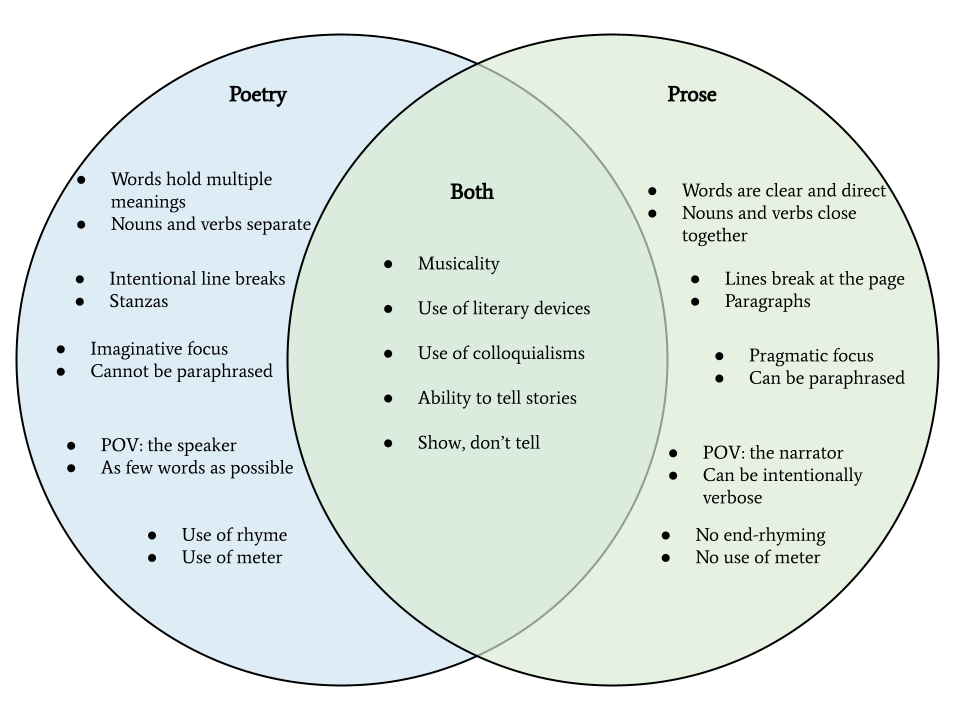
5 Similar Features of Prose and Poetry
Having defined prose and poetry above, the reality is that they can be more similar than you might imagine. We’ll discuss their differences in a moment, but first, it’s important to understand the shared potential that each form holds:
- Musicality and rhythm
- Use of colloquial speech
- Use of literary devices
- Ability to tell stories
- Show, don’t tell
1. Musicality and Rhythm
It’s a common misconception that only poetry can be musical. While rhythm and meter are important aspects of a poem’s construction, musicality begins with language, not with structure.
An immediate example of “musical prose” is The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald. Susan Bell, writer of The Artful Edit , argues that Gatsby finds its success precisely because of the story’s musical, elegant storytelling—certainly, the book has a charged poeticism that feels just as decadent and tasteful as the high society of the Roaring Twenties. Below is some undeniably musical prose:
2. Use of Literary Devices
Things are like other things, which is the essence of literary devices. While some devices are unique to each form—poems have enjambment, prose can begin in media res —a successful piece of writing requires literary devices .
3. Use of Colloquial Speech
Yes, some writing uses lofty and erudite language. However, contemporary prose and poetry writers, from all eras, recognize the importance of speaking to their audience.
Colloquial speech is one way of speaking to your audience. A colloquialism is a turn of phrase with a specific social and temporal context. For example, “groovy” belongs to the American 1970s, Victorian Brits called a brave person “bricky,” and Gen Z’ers “stan” on Twitter.
In literature, Jay Gatsby’s “old sport” is just as colloquial as the poem “A Study of Reading Habits ,” which uses phrases like “right hook” and “load of crap.”
4. Storytelling
Another common misconception is that poetry doesn’t tell stories. While fiction and nonfiction are the genres of prose, poetry also possesses a powerful narrative voice.
Singular poems can tell grand stories, especially poetry in antiquity. The Epic of Gilgamesh , The Odyssey , and Beowulf are all stories in verse, as are novel-poems like Autobiography of Red .
Additionally, contemporary poetry collections often tell stories, just with less linearity. Louise Gluck’s collection Wild Iris is told from the perspective of a flower, and as the seasons change, the flower observes the infinite singularity of mankind, God, and the Universe.
5. Show, Don’t Tell Writing
It’s important for storytellers to demonstrate their ideas without spoon feeding the reader. In other words, writers should Show instead of Tell.
Don’t tell me the moon is shining; show me the glint of light on broken glass. —Anton Chekhov
We consider “Show, Don’t Tell” a golden rule of writing. Brush up on it here !
10 Differences Between Prose and Poetry
We’ve discussed their similarities, but the difference between poetry and prose is usually fairly clear in practice. The following ten items distinguish the two. To help demonstrate our point, we represent each form with a well known piece of literature. Poetry examples were pulled from Dylan Thomas’ “ Do Not Go Gentle Into That Good Night ,” and prose examples come from “ The Cask of Amontillado ” by Edgar Allan Poe.
1. Prose vs. Poetry: Use of Page Space
In prose, a line of text begins and ends at the margins of the page. In poetry, the author uses shorter lines, broken before the page margins to introduce multiple meanings. Line breaks are an enduring feature of what differentiates prose and poetry, adding extra emphasis to certain words and sounds.
You’ll notice in prose that a partial line occurs only before a new paragraph.

In poetry, the line breaks mean something more intentional. The ending words can help uphold meter and rhyme schemes, and it also emphasizes important words: “night” and “light” are repeatedly pit against each other in Thomas’ villanelle .

2. Prose vs. Poetry: Paragraphs vs. Stanzas
Prose passages divide single ideas into sentences, and those sentences go on to form paragraphs. A new paragraph signifies the introduction of new ideas or the continuation of relevant information.

The equivalent of a paragraph in poetry is the stanza. Stanzas are groupings of lines which act as units of meaning, with different stanzas containing different ideas and images.

3. Prose vs. Poetry: Single vs. Multiple Meanings
In prose, the meaning of each word is usually straightforward, with double meanings (like puns and irony) clearly expressed. Most prose relies on clear meanings to deliver clear, linear messages.
By contrast, the language of poetry contains multitudes. One word can hold many different meanings, and ideas can be broken into both sentences and lines.
Take the line “old age should burn and rave at close of day.” The word rave can mean multiple things: it can mean to rant and rave as old people (stereotypically) do, or it can mean to rage and fight against. The pun here is intended to energize the reader,
4. Prose vs. Poetry: Noun-Verb Placements
In Standard English , which is the common (but not default) language of prose, nouns and verbs are found close to each other. This is a facet of “clear communication”—it’s important to know who is doing what as efficiently as possible.
We have bolded the noun-verb pairs in an excerpt from both the poem and prose piece.

Notice how the noun-verb pairs can stray from each other much more easily in poetry. Dylan Thomas inserts a noun-verb pair between a noun-verb pair in each stanza—which is much harder to use effectively in prose.

Notice that, in prose, a noun can have multiple verbs attached to it, but the first verb is almost always next to the noun.
5. Prose vs. Poetry: Rhyme (Sometimes)
There are two types of rhyme: internal and external rhyme. External rhyme occurs at the ends of lines, such as the many “-ight” words in Thomas’ poem.
Internal rhyme refers to words that rhyme with each other inside the same beat. These rhymes are not always intentional or charged with meaning, but they occur, such as in this sentence from Poe’s story:
“We had passed through walls of piled bones , with casks and puncheons intermingling, into the inmost recesses of the catacombs.”
Bones and catacombs aptly rhyme with each other. Note, rhyme is not a necessary feature of any prose and many poems. Though some poetry forms do require rhyme schemes, contemporary poets tend to eschew rhyming.
6. Prose vs. Poetry: Meter (Sometimes)
Like rhyme, meter is an (often) optional component of poetry writing. Meter refers to the stress patterns of syllables and the number of syllables per line. Well-executed meter can give poetry a certain musical quality.
Thomas’ poem is written in iambic pentameter, a requirement of the traditional villanelle form. This means there are 10 syllables in each line, following an unstressed-stressed pattern. To understand syllable stress, read Thomas’ poem out loud, and note how every second syllable is emphasized harder than the first.
Prose does not rely on meter to tell a story.
Prose does not have any metrical requirements, and thank goodness for that. Meter can be extraordinarily tough to impose on a poem, but it also affects how the reader interprets the piece. However, prose does not rely on meter to tell a story, as these poetry devices often instill multiple meanings in a piece.
7. Prose vs. Poetry: Pragmatic vs. Imaginative Focus
On a macro-level, the vision of poets and prose writers tends to differ. Prose has a pragmatic focus, meaning that each word should clearly advance a specific idea or narrative. The focus of prose is storytelling, so the author has a duty to use words diligently.
While poetry can tell stories, a poem rarely focuses on plot points, settings, and characters.
While poetry can tell stories, a poem rarely focuses on plot points, settings, and characters. Rather, poetry has an imaginative focus. Words are allowed to break their conventional bounds in the goal of expressing emotions, and ideas can stack upon each other like grains of sand in a sand castle.
So, what’s pragmatic about Poe, and what’s imaginative about Thomas? Every word in Poe’s piece describes details and events that push the reader towards the climax. At no point does the reader jump out of the narrative to speculate or stargaze.
In Thomas’ poem, the words don’t point the reader towards a specific event, but they do encourage the reader to think deeply about abstract ideas. Old or young, the reader will contend with ideas of life, death, justice, goodness, and the judgment against our souls. In 19 lines of mostly concrete images, the poet asks us to read imaginatively—and in the process, to learn what we believe.
8. Prose vs. Poetry: Paraphrasability
A piece of prose can be summarized. If you ask “what is ‘The Cask of Amontillado’ about?”, it is possible to paraphrase the story and get the gist of its deeper meaning. In short, Poe’s story observes a man desperate for revenge, only to find that revenge often hurts both the punisher and the punished.
Poetry is generally harder to summarize than prose, because it tends to include greater multiplicities of meaning.
Poetry is generally harder to summarize than prose, because it tends to include greater multiplicities of meaning. No one can tell you what a certain poem means. They can tell you what it isn’t —for example, “Do Not Go Gentle” is not about heartbreak, war, or the summertime—but deciding what a poem means requires a reader’s own attention.
For example, one could summarize Thomas’ poem as “an ode to Thomas’ dying father, with a vengeful bent against mankind’s eventual death.” But, does saying that invoke Thomas’ juxtaposition of light and dark? His use of rhyme to draw a conceit? His need to believe in the transience of the soul? By the time you’ve summarized the poem, you’ve written something as long as the poem itself. Poetry cannot be paraphrased.
9. Prose vs. Poetry: Point of View
Prose and poetry treat “point of view” in very different ways. A point of view (POV) refers to who is telling the story. The storyteller doesn’t always have a name or a face, but they do inevitably change how a story is read.
In prose, there are 4 main POVs:
- First Person (I): The story is told in the first person, from a character who is either the protagonist or adjacent to the protagonist. The Cask of Amontillado uses the first person POV.
- Second Person (You): The story is told in the second person. Often, the writer will substitute “the protagonist” for “you,” making the story’s actions feel more intimate and personal. Second Person storytelling is rare, but not unheard of.
- Third Person Limited (He/She/They): The story is told in the third person, and it focuses on the perspective of the protagonist. We have access to most of their thoughts and feelings, but our access to other people is limited by the protagonist’s perspective.
- Third Person Omniscient (He/She/They): The story is told in the third person, and the narrator has access to everyone’s thoughts, feelings, and actions. We can jump from person to person with ease, interweaving webs of complex narratives together.
Some stories will also take a Third Person Mixed approach, meaning the meat of the story is told from the protagonist’s perspective, but the reader occasionally jumps to someone else’s POV or to a historical time period.
While poetry can use the same pronouns (I/You/He/She/They), it uses POV differently. A poem is always told from the perspective of “the speaker.” The speaker can be the poet themselves—Dylan Thomas is certainly the voice behind his poem, and he is certainly talking to his father. However, the correct approach is to always call the poem’s POV “the speaker,” as a poem can inhibit many different voices at once. Finally, poetry is much easier to apply to yourself when the speaker isn’t anyone in particular.
10. Prose vs. Poetry: Concision
Prose and poetry writers should both write concisely. Concise writing eschews redundancies and makes every word count. However, concision means something different for the two forms.
In prose, concision generally means that not a word is wasted in conveying information. Concise prose expresses its meaning clearly.
Concise prose expresses its meaning clearly.
Of course, good prose can still be long-winded, as long as this heightens the effect of the work. Take this sentence from Poe’s story:
“It must be understood that neither by word nor deed had I given Fortunato cause to doubt my good-will. I continued, as was my wont, to smile in his face, and he did not perceive that my smile now was at the thought of his immolation.”
These sentences are 19 and 27 words long, respectively. They can also be summarized as follows: “Fortunato thought my smile bore good-will, not the desire to immolate him.”
What does Poe’s long-windedness afford him? Despite being easily paraphrased, every word does count in these two sentences, because they are a part of the narrator’s characterization. He is a long-winded schemer, and that affects how the story must be told, since Poe has chosen the first person to make us intimate with the narrator’s internal conflict.
Poetry is a different situation. Because poetry has line breaks, stanzas, and (sometimes) rhyme and meter, its concision takes a different form. In a poem, it’s great if every word contains heavy meaning; it’s even greater when words contain multiplicities and challenge the reader’s ideas. Economy in poetry is maximizing its impact, musicality, and richness—not necessarily its clear, single meaning.
Economy in poetry is maximizing its impact, musicality, and richness—not necessarily its clear, single meaning.
If you stretched a poem into prose, it would read like a terrible short story, because the concision afforded to poetry is different than that of prose. Concise prose focuses more on clarity of meaning, and poetry more on maximizing the richness and impact of every syllable.
Poetry vs. Prose Venn Diagram
Prose vs. Poetry: A Final Note On Literary Binaries
Any article like this risks making literature seem binary, as though prose and poetry were totally discrete entities; so in closing, it’s good to note again that writers, especially contemporary writers, often work at the intersection of prose and poetry, resulting in genres like the prose poem , the lyrical essay or the poetry novel . (And we haven’t even touched on scriptwriting, which is a different form of communication altogether.)
There is much to explore outside of poetry and prose; this article simply covers the basics. As you advance on your writing journey, don’t be afraid to experiment with words outside of the traditional “prose vs. poetry” binary. You might be shocked by what you can accomplish!
Explore both Prose and Poetry at Writers.com
Whether you’re experimenting with poetry, fiction, or creative nonfiction, Writers.com has the classes to help you succeed. Take a look at our upcoming courses —and gain valuable insights from our instructors and writing community .
Sean Glatch
Great summary. I write poetry, prose poems, flash fiction and short stories so I’m using the grab bag of everything you said here! Never taught about line breaks, though. I see some poets going willy nilly all over the page. Maybe there just aren’t any rules where this is concerned…
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Frequently asked questions
What’s the difference between an expository essay and an argumentative essay.
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
Frequently asked questions: Writing an essay
For a stronger conclusion paragraph, avoid including:
- Important evidence or analysis that wasn’t mentioned in the main body
- Generic concluding phrases (e.g. “In conclusion…”)
- Weak statements that undermine your argument (e.g. “There are good points on both sides of this issue.”)
Your conclusion should leave the reader with a strong, decisive impression of your work.
Your essay’s conclusion should contain:
- A rephrased version of your overall thesis
- A brief review of the key points you made in the main body
- An indication of why your argument matters
The conclusion may also reflect on the broader implications of your argument, showing how your ideas could applied to other contexts or debates.
The conclusion paragraph of an essay is usually shorter than the introduction . As a rule, it shouldn’t take up more than 10–15% of the text.
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates.
In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills.
Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence, analysis and interpretation.
The “hook” is the first sentence of your essay introduction . It should lead the reader into your essay, giving a sense of why it’s interesting.
To write a good hook, avoid overly broad statements or long, dense sentences. Try to start with something clear, concise and catchy that will spark your reader’s curiosity.
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
Let’s say you’re writing a five-paragraph essay about the environmental impacts of dietary choices. Here are three examples of topic sentences you could use for each of the three body paragraphs :
- Research has shown that the meat industry has severe environmental impacts.
- However, many plant-based foods are also produced in environmentally damaging ways.
- It’s important to consider not only what type of diet we eat, but where our food comes from and how it is produced.
Each of these sentences expresses one main idea – by listing them in order, we can see the overall structure of the essay at a glance. Each paragraph will expand on the topic sentence with relevant detail, evidence, and arguments.
The topic sentence usually comes at the very start of the paragraph .
However, sometimes you might start with a transition sentence to summarize what was discussed in previous paragraphs, followed by the topic sentence that expresses the focus of the current paragraph.
Topic sentences help keep your writing focused and guide the reader through your argument.
In an essay or paper , each paragraph should focus on a single idea. By stating the main idea in the topic sentence, you clarify what the paragraph is about for both yourself and your reader.
A topic sentence is a sentence that expresses the main point of a paragraph . Everything else in the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
An essay isn’t just a loose collection of facts and ideas. Instead, it should be centered on an overarching argument (summarized in your thesis statement ) that every part of the essay relates to.
The way you structure your essay is crucial to presenting your argument coherently. A well-structured essay helps your reader follow the logic of your ideas and understand your overall point.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
The vast majority of essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Almost all academic writing involves building up an argument, though other types of essay might be assigned in composition classes.
Essays can present arguments about all kinds of different topics. For example:
- In a literary analysis essay, you might make an argument for a specific interpretation of a text
- In a history essay, you might present an argument for the importance of a particular event
- In a politics essay, you might argue for the validity of a certain political theory
At high school and in composition classes at university, you’ll often be told to write a specific type of essay , but you might also just be given prompts.
Look for keywords in these prompts that suggest a certain approach: The word “explain” suggests you should write an expository essay , while the word “describe” implies a descriptive essay . An argumentative essay might be prompted with the word “assess” or “argue.”
In rhetorical analysis , a claim is something the author wants the audience to believe. A support is the evidence or appeal they use to convince the reader to believe the claim. A warrant is the (often implicit) assumption that links the support with the claim.
Logos appeals to the audience’s reason, building up logical arguments . Ethos appeals to the speaker’s status or authority, making the audience more likely to trust them. Pathos appeals to the emotions, trying to make the audience feel angry or sympathetic, for example.
Collectively, these three appeals are sometimes called the rhetorical triangle . They are central to rhetorical analysis , though a piece of rhetoric might not necessarily use all of them.
The term “text” in a rhetorical analysis essay refers to whatever object you’re analyzing. It’s frequently a piece of writing or a speech, but it doesn’t have to be. For example, you could also treat an advertisement or political cartoon as a text.
The goal of a rhetorical analysis is to explain the effect a piece of writing or oratory has on its audience, how successful it is, and the devices and appeals it uses to achieve its goals.
Unlike a standard argumentative essay , it’s less about taking a position on the arguments presented, and more about exploring how they are constructed.
You should try to follow your outline as you write your essay . However, if your ideas change or it becomes clear that your structure could be better, it’s okay to depart from your essay outline . Just make sure you know why you’re doing so.
If you have to hand in your essay outline , you may be given specific guidelines stating whether you have to use full sentences. If you’re not sure, ask your supervisor.
When writing an essay outline for yourself, the choice is yours. Some students find it helpful to write out their ideas in full sentences, while others prefer to summarize them in short phrases.
You will sometimes be asked to hand in an essay outline before you start writing your essay . Your supervisor wants to see that you have a clear idea of your structure so that writing will go smoothly.
Even when you do not have to hand it in, writing an essay outline is an important part of the writing process . It’s a good idea to write one (as informally as you like) to clarify your structure for yourself whenever you are working on an essay.
Comparisons in essays are generally structured in one of two ways:
- The alternating method, where you compare your subjects side by side according to one specific aspect at a time.
- The block method, where you cover each subject separately in its entirety.
It’s also possible to combine both methods, for example by writing a full paragraph on each of your topics and then a final paragraph contrasting the two according to a specific metric.
Your subjects might be very different or quite similar, but it’s important that there be meaningful grounds for comparison . You can probably describe many differences between a cat and a bicycle, but there isn’t really any connection between them to justify the comparison.
You’ll have to write a thesis statement explaining the central point you want to make in your essay , so be sure to know in advance what connects your subjects and makes them worth comparing.
Some essay prompts include the keywords “compare” and/or “contrast.” In these cases, an essay structured around comparing and contrasting is the appropriate response.
Comparing and contrasting is also a useful approach in all kinds of academic writing : You might compare different studies in a literature review , weigh up different arguments in an argumentative essay , or consider different theoretical approaches in a theoretical framework .
The key difference is that a narrative essay is designed to tell a complete story, while a descriptive essay is meant to convey an intense description of a particular place, object, or concept.
Narrative and descriptive essays both allow you to write more personally and creatively than other kinds of essays , and similar writing skills can apply to both.
If you’re not given a specific prompt for your descriptive essay , think about places and objects you know well, that you can think of interesting ways to describe, or that have strong personal significance for you.
The best kind of object for a descriptive essay is one specific enough that you can describe its particular features in detail—don’t choose something too vague or general.
If you’re not given much guidance on what your narrative essay should be about, consider the context and scope of the assignment. What kind of story is relevant, interesting, and possible to tell within the word count?
The best kind of story for a narrative essay is one you can use to reflect on a particular theme or lesson, or that takes a surprising turn somewhere along the way.
Don’t worry too much if your topic seems unoriginal. The point of a narrative essay is how you tell the story and the point you make with it, not the subject of the story itself.
Narrative essays are usually assigned as writing exercises at high school or in university composition classes. They may also form part of a university application.
When you are prompted to tell a story about your own life or experiences, a narrative essay is usually the right response.
The majority of the essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Unless otherwise specified, you can assume that the goal of any essay you’re asked to write is argumentative: To convince the reader of your position using evidence and reasoning.
In composition classes you might be given assignments that specifically test your ability to write an argumentative essay. Look out for prompts including instructions like “argue,” “assess,” or “discuss” to see if this is the goal.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
An expository essay is a common assignment in high-school and university composition classes. It might be assigned as coursework, in class, or as part of an exam.
Sometimes you might not be told explicitly to write an expository essay. Look out for prompts containing keywords like “explain” and “define.” An expository essay is usually the right response to these prompts.
An expository essay is a broad form that varies in length according to the scope of the assignment.
Expository essays are often assigned as a writing exercise or as part of an exam, in which case a five-paragraph essay of around 800 words may be appropriate.
You’ll usually be given guidelines regarding length; if you’re not sure, ask.
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Our team helps students graduate by offering:
- A world-class citation generator
- Plagiarism Checker software powered by Turnitin
- Innovative Citation Checker software
- Professional proofreading services
- Over 300 helpful articles about academic writing, citing sources, plagiarism, and more
Scribbr specializes in editing study-related documents . We proofread:
- PhD dissertations
- Research proposals
- Personal statements
- Admission essays
- Motivation letters
- Reflection papers
- Journal articles
- Capstone projects
Scribbr’s Plagiarism Checker is powered by elements of Turnitin’s Similarity Checker , namely the plagiarism detection software and the Internet Archive and Premium Scholarly Publications content databases .
The add-on AI detector is powered by Scribbr’s proprietary software.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .
- Prose vs. Verse: Which Form of Writing Should You Choose?
- Literature and writing
Are you someone who loves to express themselves through writing but is unsure which form to choose? Do you struggle with deciding whether prose or verse would be the best way to convey your message?
The prose is a form of language that follows ordinary grammar and natural flow, lacking a specific metrical structure, while the verse is a structured form of language characterized by rhythm, meter, and poetic techniques.
Prose vs. Verse
- Notice vs. Circular
- Journal vs. Magazine
- Newspaper vs. Magazine
What is Prose?
Prose refers to a form of written or spoken language that does not adhere to a specific poetic structure or rhythm. It is the most common and natural way of expressing thoughts, ideas, and narratives in everyday communication.
The prose is characterized by its typical sentence and paragraph structure, lacking the formal metrical or rhyming patterns found in poetry. It allows for the use of complete sentences, paragraphs, and ordinary language, enabling a more straightforward and conventional mode of expression in literature, essays, novels, speeches, and everyday writing.
What is Verse?
The verse refers to a form of written or spoken language that follows a specific metrical and rhythmic pattern. It is commonly associated with poetry, where lines of verse are arranged in stanzas and often utilize rhyme, meter, and other poetic devices to create a structured and musical quality.
The verse can vary in its form, including traditional forms such as sonnets or haikus, as well as free verse that does not adhere to a specific pattern. Unlike prose, the verse emphasizes the artistic and aesthetic aspects of language, utilizing rhythm, meter, and poetic techniques to evoke emotions and create a distinct artistic expression followed by lines of iambic trimeter.
Similarities between Prose and Verse
- Language: Both prose and verse use language as a means of communication and expression.
- Meaning and Content: Both prose and verse convey meaning and content through the use of words, sentences, and paragraphs.
- Literary Elements: Both prose and verse can incorporate literary elements such as imagery, symbolism, metaphors, and themes to enhance the depth and richness of the writing.
- Narrative Structure: Both prose and verse can be used to tell stories, present ideas, or convey information in a structured manner.
- Creativity and Artistry: While verse is more commonly associated with artistic expression, prose can also be crafted with creativity and artistry, utilizing literary techniques and stylistic choices to engage the reader.
Pros and cons of each form of writing
Pros of Prose:
- Clarity: Prose allows for clear and straightforward communication, making it suitable for conveying information, narratives, and ideas in a direct and accessible manner.
- Versatility: Prose can be used in a wide range of writing forms, including novels, essays, articles, and everyday communication, providing flexibility in expressing various topics and styles.
- Natural Expression: Prose reflects the natural flow of spoken language, making it easy to read, understand, and connect with for the reader.
Cons of Prose:
- Lack of Musicality: Prose lacks the inherent musicality and rhythmic patterns found in verse, which can limit its ability to evoke a specific emotional or aesthetic response through sound and rhythm.
- Limited Poetic Techniques: Prose does not typically employ poetic devices such as rhyme, meter, or specific poetic structures, which can restrict its use for creating certain artistic effects.
Pros of Verse:
- Aesthetic Appeal: Verse offers a heightened sense of rhythm, meter, and musicality, which can create a more captivating and aesthetically pleasing reading experience.
- Poetic Techniques: Verse allows for the use of poetic devices such as rhyme, alliteration, repetition, and meter, enabling writers to convey meaning and emotions in a more vivid and memorable way.
- Emotional Impact: The rhythmic patterns and poetic techniques in verse can evoke powerful emotions, adding depth and resonance to the content being expressed.
Cons of Verse:
- Complexity: Writing in verse requires a good understanding of poetic techniques, meter, and rhyme schemes, making it more challenging to craft effectively.
- Limited Accessibility: The structured nature of the verse can sometimes create a barrier for readers who are less familiar with poetic conventions, potentially limiting its reach and appeal.
- Expressive Constraints: The adherence to specific metrical and rhyme patterns in verse may restrict the writer’s ability to express certain ideas or narratives freely.
How to choose the right form of writing for your project
Prose is the standard form of writing, and is typically used for things like novels, short stories, and essays. It is characterized by its use of complete sentences and paragraphs and its focus on narrative.
The verse is often seen as more poetic and lyrical. It can be used for things like poetry, song lyrics, and plays. It is often shorter and less formal than prose and makes use of rhythm and rhyme.
If you’re looking to write something that is longer and more complex, then prose may be the better option. But if you want something that is shorter and more lyrical, then verse may be a better fit.
Key differences between Prose and Verse
- Structure: Prose is characterized by its natural flow of sentences and paragraphs, lacking a specific rhythmic or metrical pattern. The verse follows a structured arrangement of lines, often with a specific meter, rhyme, or poetic form.
- Rhythm and Meter: Prose does not adhere to a specific rhythmic or metrical pattern, while verse utilizes rhythmic patterns, such as syllabic count, stressed and unstressed syllables, or specific poetic meters, to create a musical quality.
- Language and Expression: Prose typically uses ordinary language and focuses on clarity and directness in communication. Verse often employs heightened and more imaginative language, utilizing poetic devices and techniques to create artistic effects and evoke emotions.
- Difference between Management and Administration
- Difference between Morals and Ethics
- Difference between Link and URL
Prose offers a natural and direct communication style, suitable for conveying information and narratives with clarity. It is versatile and accessible to a wide range of readers. Verse adds a layer of musicality and poetic techniques, enhancing the aesthetic appeal and emotional impact of the writing. While verse requires a deeper understanding of poetic conventions, it allows for a more expressive and artistic exploration.
They are the communicators. They truly understand the value of crafting content that resonates with our readers.

Have you ever struggled with the terms “syntax” and “grammar”? Do they seem interchangeable, or do you feel like there’s…

Are you confused about the difference between Gaelic and Celtic? Do you use the terms interchangeably, not really understanding that…

In the world of intellectual property, there are two words that often get thrown around interchangeably: copyright infringement and plagiarism….

Are you confused about the differences between an abstract and an introduction? Don’t worry, you’re not alone! Many writers struggle…

- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Intel Receives $8.5 Billion in Grants to Build Chip Plants
The award, announced by President Biden at a plant in Arizona, is the biggest the government has made under a new program that aims to rebuild the nation’s semiconductor manufacturing industry.

By Zolan Kanno-Youngs , Madeleine Ngo and Don Clark
Zolan Kanno-Youngs reported from Chandler, Ariz., Madeleine Ngo from Washington and Don Clark from San Francisco.
President Biden on Wednesday awarded $8.5 billion in grants to Intel, a major investment to bolster the nation’s semiconductor production, during a tour of battleground states meant to sell his economic agenda.
Speaking from the Intel campus in Chandler, Ariz., Mr. Biden said the award would support thousands of new manufacturing jobs, including ones that do not require a college degree.
“It’s going to transform the semiconductor industry,” Mr. Biden said. “Where the hell is it written saying that we’re not going to be the manufacturing capital of the world again?”
The award, which will go to the construction and expansion of Intel facilities around the United States, is the biggest the federal government has made with funding from the CHIPS Act , which lawmakers passed in 2022 to help re-establish the United States as a leader in semiconductor manufacturing.
The Biden administration, equipped with $39 billion in subsidies to distribute, is spearheading an ambitious effort to ramp up production of the tiny chips that power everything from smartphones to computers and cars. The effort is at the center of Mr. Biden’s goal to reduce America’s reliance on foreign countries: Although semiconductors were invented in the United States, only about 10 percent of the world’s chips are made domestically.
“Nearly all manufacturing of leading-edge chips across the entire industry moved overseas to Asia years ago,” Mr. Biden said. “That’s why today’s investment is such a big deal: We will enable advanced semiconductor manufacturing to make a comeback here in America.”
In addition to the grants, the federal government is planning to award Intel up to $11 billion in loans on what the company characterized as generous terms. Intel is also expected to claim federal tax credits that could cover 25 percent of the expense of its U.S. expansion projects, which are expected to cost more than $100 billion over five years.
The grants are intended to help fund the company’s construction plans in Arizona, Ohio, New Mexico and Oregon. The projects are expected to create more than 10,000 manufacturing jobs and roughly 20,000 construction jobs, according to Biden administration officials.
Commerce Secretary Gina Raimondo, whose department is overseeing the distribution of the grants, said the award would help ramp up the country’s production of the most advanced semiconductors, which are used in artificial intelligence, smartphones, supercomputers and the most sensitive military hardware. The United States currently produces none.
Ms. Raimondo said the Intel award would be the single largest grant to a chipmaker under the new program. The investment will help put the United States on track to produce roughly 20 percent of the world’s leading-edge chips by the end of the decade, she said.
“This investment will enable Intel to produce leading edge, the most sophisticated chips in the world that will power our economic and national security,” Ms. Raimondo said at the Intel campus on Wednesday.
In Arizona, the money will help fund Intel’s recent construction of two advanced plants and the modernization of another facility. The money will also help establish an entirely new site near Columbus, Ohio, starting with two factories, in its first move to a new U.S. region in more than 40 years.
In Rio Rancho, N.M., Intel will use the federal funds to transform two plants into advanced packaging facilities, where chips are assembled together to enhance performance and reduce costs. The company will also expand and modernize an innovation hub in Hillsboro, Ore., which is expected to further the company’s technological leadership and development of new innovations.
Mr. Biden and his Democratic allies view the semiconductor investments as a key way to try to turn around perceptions of the economy among voters in battleground states like Arizona.
“We have not been talking to folks about the issues that President Biden has been delivering on, and that’s what we are determined to do,” Yolanda Bejarano, the Arizona Democratic Party chairwoman, said on Tuesday, adding that Democrats would need to talk more about the effects of the semiconductor investments.
Although Intel will have to meet certain milestones before the money is distributed, senior Biden administration officials said they expected the funds to start flowing to the company by the end of this year.
Patrick Gelsinger, Intel’s chief executive, told reporters in a briefing on Tuesday evening that the government incentives represented a proud moment for his company and a major achievement for politicians of both parties. Though satisfied with the incentives earmarked for Intel, he said officials might need to invest more in the industry to reverse decades of shifting investment from the United States to countries in Asia.
“It doesn’t get fixed in one three- to five-year program,” Mr. Gelsinger said. “I do think we’ll need at least a CHIPS 2 to finish that job.”
Intel is the fourth company to receive a federal award under the new program, and brings the total announced grants to more than $10 billion. The first three grants — to GlobalFoundries, Microchip Technology and BAE Systems — were to makers of legacy chips, which are created with older production processes but are still used in many products like cars and dishwashers.
Biden administration officials are expected to announce more awards in the coming months to other major chipmakers, including the Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Samsung and Micron Technology. Those companies have also made major investments in new or expanded semiconductor manufacturing plants in the United States in recent years.
The United States’ dependence on Asia for its chips has become even more pronounced with the rise of artificial intelligence. Nearly all chips used to power the latest generative A.I. services were manufactured in Taiwan by T.S.M.C., though designed by the Silicon Valley company Nvidia.
Intel has been trying to change that by developing new manufacturing technology, beginning to build chips designed by other companies and lobbying heavily for the legislation. The investment in Intel is intended to help enable U.S. companies to lead in the A.I. industry by ensuring there is a domestic supply of advanced chips.
About $50 million of federal funding will be set aside for Intel to spend on training and developing “a new generation of workers for the semiconductor industry,” Mr. Biden said. Many semiconductor companies and industry groups have voiced concerns about potential shortages of technicians, engineers and other workers to fill all of the positions that will be created once the facilities are constructed.
In total, private companies have announced more than $240 billion in semiconductor and electronic manufacturing investments since Mr. Biden took office, according to administration officials. Some chipmakers, however, have run into obstacles while trying to expand their domestic manufacturing capacity, resulting in delays.
Zolan Kanno-Youngs is a White House correspondent, covering President Biden and his administration. More about Zolan Kanno-Youngs
Madeleine Ngo covers U.S. economic policy and how it affects people across the country. More about Madeleine Ngo

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
As nouns the difference between prose and essay is that prose is language, particularly written language, not intended as poetry while essay is a written composition of moderate length exploring a particular issue or subject. As verbs the difference between prose and essay is that prose is to write or repeat in a dull, tedious, or prosy way while essay is to try.
Fictional prose contains the five features of fiction: mood, point of view, character, setting, and plot. 2 Nonfictional prose. Nonfictional prose is prose that tells a true story or otherwise communicates factual information. Guidebooks, memoirs, analytical essays, editorials, news stories, and textbooks are all examples of nonfictional prose ...
Defining Prose. Prose is a form of written language that follows a natural, everyday speech pattern. It is the way we communicate in writing without adhering to the strict rules of poetry or verse. In literature, prose encompasses a wide range of written works, from novels and short stories to essays and articles.
Essays. You're probably familiar with essays. An essay makes some kind of argument about a specific question or topic. Essays are written in prose because it's what modern readers are accustomed to. ... He loved to play around with the difference between prose and verse, and if you look closely you can see the purpose behind it: the ...
The first prose line of a novel is significant for the writer and reader. This opening allows the writer to grab the attention of the reader, set the tone and style of the work, and establish elements of setting, character, point of view, and/or plot.For the reader, the first prose line of a novel can be memorable and inspire them to continue reading.
The key difference is that a narrative essay is designed to tell a complete story, while a descriptive essay is meant to convey an intense description of a particular place, object, or concept. Narrative and descriptive essays both allow you to write more personally and creatively than other kinds of essays , and similar writing skills can ...
A prose passage of approximately 500 to 700 words and a prompt will be given to guide your analytical essay. Worth about 18% of your total grade, the essay will be graded out of six points depending on the quality of your thesis (0-1 points), evidence and commentary (0-4 points), and sophistication (0-1 points).
In writing, prose refers to any written work that follows a basic grammatical structure (think words and phrases arranged into sentences and paragraphs). This stands out from works of poetry, which follow a metrical structure (think lines and stanzas). Prose simply means language that follows the natural patterns found in everyday speech.
Hope you enjoyed knowing about these prose types. Check out 9 genres of Poetry to learn about different poetry genres. Share with your friends. 10 different prose type in creative writing are biography. autobiography Folktales Myth, Legend, Fable, PARABLE. NOVEL and Short Stories'.
Prose. Prose is a form of language that possesses ordinary syntax and natural speech rather than rhythmic structure; in which regard, along with its measurement in sentences rather than lines, it differs from poetry. [9] On the historical development of prose, Richard Graff notes that " Novel: a long fictional prose narrative.
What's the difference between essay and prose? Essay. Definition: (n.) An effort made, or exertion of body or mind, for the performance of anything; a trial; attempt; as, to make an essay to benefit a friend. ... The present essay gives a brief review of the findings on sex differences in the human brain. (7) Evidence exists in the literature ...
The Difference Between Poetry and Prose. By Martin Earl. Prose is all about accumulation (a morality of work), while poetry as it is practiced today is about the isolation of feelings (an aesthetics of omission). Among other things, prose is principally an ethical project, while poetry is amoral, a tampering with truths which the world of prose ...
In fact, not all poetry is in verse—specifically, prose poetry isn't. In other words, prose and poetry do overlap, whereas prose and verse don't. Most poetry is in verse, but some poetry is in prose. We go into more detail on line breaks, stanzas, and the use of page space in the sections below.
总结来说,"prose"是一种以普通语言书写的文学形式,用于叙述故事或表达思想;而"essay"是一种短文,用于探讨、分析或阐述一个主题。. 这两个词在用法和目的上有所不同,但都是用来表达作者的观点和思想的文学形式。. Ralon17. 7 Jul 2023. English (US) Prose is a ...
Solve the prose vs. poetry debate with our useful guide & examples. ... However, each different type of writing has a unique structure and purpose. Learn the similarities and differences between prose and poetry through a cumulative overview of each. ... types. However, when it comes to their structure and purpose, they are quite different ...
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way. An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn't have to make an original argument.
Poetry uses rhythmic and metaphorical language, while prose follows a natural flow of speech. Poetic language is used to create artistry in the work, while prosaic language is used to communicate information to a specific audience. Poetry is often associated with more artistic or literary genres, while prosaic language is more commonly used in ...
The Difference Between an Article and an Essay. In composition studies, an article is a short work of nonfiction that typically appears in a magazine or newspaper or on a website. Unlike essays, which often highlight the subjective impressions of the author (or narrator ), articles are commonly written from an objective point of view.
Prose is characterized by its straightforward and ordinary language, which is used to convey information or tell a story. Narrative, on the other hand, is a form of writing that tells a story. It can be written in prose or verse and is often used in literature, film, and other forms of storytelling.
Prose Exercise 2: Persuasive essays require a clear argument and supporting evidence. Make sure to use persuasive language and address counterarguments to make your case stronger. ... After exploring the differences between prose and verse, it is clear that both have their own unique characteristics and purposes in writing. Prose is often used ...
The major difference between the two is that poetry is a form of writing that uses rhythm and rhyme to create a musical or chant-like effect, whereas prose, is a form of writing that is more straightforward and doesn't rely on rhyme or meter. Poetry often uses figurative language to create images or expressive ideas, while prose is more ...
Prose is the name of any sort of literary work that follows the basic grammatical structure to form sentences and paragraphs. 1. It is called verse when words are metrically arranged in a sequence, as per a given design or rhythm. 2. Prose is a type of text. 2. Verse is a type of poetic composition.
Of mice and men. Andy Smart, who translated "The Gruffalo" into Arabic with his wife, Nadia Fouda, distilled the pair's modus operandi to: "Keep the mood, keep the rhyme, don't lose the ...
Prose vs. Verse. Prose refers to ordinary language that lacks a formal metrical structure or poetic qualities. It is the most common form of written and spoken language used in everyday communication and literary works such as novels, essays, and non-fiction. Verse refers to a form of language that follows a specific metrical and rhythmic pattern.
The privilege walk is a pedagogical tool used to teach students about often-ignored aspects of privilege. Despite their popularity, privilege walks are under-examined in the scholarship of teaching and learning. This leaves open questions about the efficacy of the walk, and whether, and to what extent, the walk yields different results among students from different backgrounds.
March 20, 2024. President Biden on Wednesday awarded $8.5 billion in grants to Intel, a major investment to bolster the nation's semiconductor production, during a tour of battleground states ...