Essay vs Research Paper: What Sets Them Apart?
Table of contents
- 1.1 What Is an Essay?
- 1.2 What Is a Research Paper?
- 2.1 Purpose and Objective
- 2.2 Structure and Organization
- 2.3 Length and Depth
- 2.4 Sources and Evidence
- 2.5 Voice and Style
- 2.6 Audience and Presentation
- 3 Essay vs Research Paper: 10 Points of Difference
- 4 What Is the Difference Between Research Paper and Different Types of Papers
- 5 Let’s Sum Up
Every student needs to write some academic papers for the university. However, even young people with experience can’t determine the difference between an essay and a research paper. Although these two areas of academic writing have many similarities, the requirements are still significantly different.
- We will outline the key differences between these two types of academic writing.
- In this article, you will get a clear definition of an essay and research paper.
- You will learn more about the organization, structure, essay, and research paper requirements.
Before we dive into the detailed definitions, let’s first explore the key differences between an essay and a research paper.

Definitions and Overview
What is an essay.
An essay is a short piece of writing that presents a personal opinion on a specific topic. Essays can be formal or informal, but in an academic setting, they are usually formal. The main purpose of an essay is to inform the reader or argue a particular perspective.
Essays do not always aim to be scientific but require a clear structure. This structure typically includes an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Following this format lets you organize your thoughts and communicate them effectively.
With their versatility, essays can cover various topics, from complex ideas to everyday subjects. What makes your essay unique is the creativity and originality of your ideas. Before you begin, it is important to drafting an essay carefully. This process involves brainstorming fresh ideas and planning how to present them. Although your classmates might use the same basic structure, your writing skills and unique perspective will help your essay stand out. Focus on making your ideas compelling, rather than just sticking to the format.
What Is a Research Paper?
A research paper explores a specific scientific topic in detail. It provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on careful study. Unlike essays, research papers focus less on personal opinions and more on thorough examination of the subject. They require you to use different sources and add new insights to the academic discussion.
In a research paper, it is not enough to just present facts or share personal views. You need to study the topic in depth, understand what others have said about it, and clearly outline your approach. This type of assignment involves more than just collecting information. You must also evaluate the information to build a strong argument.
Teachers expect you to show your ability to analyze information, choose reliable sources, and have a deep understanding of the topic. Research papers require you to go beyond basic knowledge and present your findings in a clear and organized way.
A typical research paper consists of several key elements that are crucial for presenting your argument and findings clearly:
- Introduction: The paper begins with an introduction that sets the stage and includes a thesis statement.
- Body: The body follows, providing detailed analysis and evidence to support the thesis, using information from reliable sources.
- Research Paper Outline: Creating an outline helps organize these sections, ensuring a logical flow of ideas throughout the paper.
- Conclusion: This part ends with a summary of the main points and a restatement of the thesis.
Whether writing a research paper or a term paper, maintaining this clear structure is essential for demonstrating a thorough understanding of your topic.
Key Differences Between Essay and Research Paper
The central difference is the goal of these academic assignments. The essay aims to express an individual point of view and find a creative, fresh approach to an existing topic. A good research paper seeks to introduce scientific novelty by examining existing data and conducting new experiments to analyze the information obtained.
Purpose and Objective
The first and main difference between an essay and a research paper is the purpose of writing . An essay as an academic task has the goal of developing students’ creative thinking. It also teaches us a structured presentation of thoughts regarding a certain topic. The student is required to have a non-standard approach, fresh thoughts, and reasoned conclusions on the given topic.
The purpose of the research work is to study a scientific topic in detail. This academic assignment is aimed at assessing the student’s analytical abilities and competence to determine cause-and-effect relationships, filter sources, and formulate logical conclusions. Such work requires theoretical knowledge, preliminary study of existing scientific works, and the ability to formulate goals and research methods.
Moreover, a student is supposed to show the capacity to draw comprehensive conclusions based on available data and information obtained during independent research. This task may seem complicated to students, so they opt for resorting to the help of PapersOwl writing service to save time.
Structure and Organization
To start with, the basic structure of any college essay involves a text consisting of five paragraphs, divided into three main factions: introduction, body part, and conclusion. When students lack time to compose a nicely structured academic essay, they can always pay to write a research paper and have their tasks done by a professional. The introduction presents the topic, sets the main direction for further text, and also works as a bait to motivate the reader to study further work. The introduction is followed by three body paragraphs. Each of the three body paragraphs presents a separate idea.
The last paragraph of any essay is a conclusion. In this paragraph, the college or university student must resume the arguments and ideas presented in the text, summarizing them into the main message of the essay. Often, the idea that you present in your conclusions will be most memorable to the reader.
Consequently, let’s overview the structure of a research paper. Compared to the structure of an essay, the organization of a research paper is much more ornate. This type of work requires a title page and abstract that go before the main body of text. On the title page, the student describes his topic of work, as well as gives contact details. An abstract is a short description of the main ideas and research methods of your work. The research work itself consists of an introduction, background, main part, and conclusions. Also, at the very end, they often add acknowledgments and a list of references, which must be formatted following the required international format.
Length and Depth
The length and depth of analysis between these two academic assignments also differ significantly. As for the essay, it is often a short prose piece whose length does not exceed 1000 words. You are faced with the task of fitting a large array of ideas into a small amount of text. The essay format itself rarely requires rigorous and thorough research of the topic, but you should work on creativity and the presence of a message in your essay. Most academic papers fall in the 300 to 600-word range.
On the other hand, a research paper is a scientific project that includes many theoretical aspects that require analysis and clarification. Thus, the volume is significantly bigger. Basic research paper lengths range from 4,000 to 6,000 words. In this case, you will no doubt have to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the selected sources, formulate a research vector, and spend time conducting your experiments, or ask PapersOwl to do a research paper for you . A research paper is a scientific project that includes many theoretical aspects that require analysis and clarification.
Sources and Evidence
The presence of theoretical sources and references is not a mandatory requirement for an essay. You can state your own thoughts on a given topic without resorting to the help of existing sources. Present your ideas on the topic, giving arguments that seem logical to you. If you do decide to base your paper on existing works, you must be sure to indicate where the information was taken from. And yet, the teacher needs to see your own thoughts rather than a dry listing of existing ideas.
Unlike an essay, a quality research paper must include primary and secondary sources, as well as a specific citation format. Surely, you are not the first person to study this scientific topic. In order not to repeat existing thoughts, you need to conduct a search to form a reliable basis for your study. If you skip this step, you risk basing your paper on misleading scientific findings.
Voice and Style
The very specificity of the essay as an academic paper is the subjective presentation of information. A large percentage of your essay should consist of your perspective and vision of the chosen topic. For this reason, essays often use a less formal and more subjective tone. However, you can still use a large amount of colloquial vocabulary, completely disregarding the norms of formal style. Students often have trouble figuring out the right style for their university assignments. In such cases, a reasonable solution is to seek help from a specialist. When you buy custom-written essays from PapersOwl, you’ll always get a perfectly balanced academic paper.
On the other hand, a research paper is a serious scientific work. The student must maintain a formal tone while complying with all structural requirements. Also, in investigative work, there is little room for subjectivity and a personal approach since an objective style is required. At the same time, do not oversaturate your research work with formalism and standard clichés.
Audience and Presentation
The essay format can be used both in the educational process and in an independent literary style. Therefore, the audience for such a written assignment can be wide and varied. When you’re writing an essay, make sure it’s understandable in academia and for a wide audience.
Research work, on the contrary, is aimed at a range of professionals in the chosen field. Written in scientific language, the goal of this work is to attract the attention of scientists and students of certain majors. Your scientific work should be rich in theory and related terms.
Essay vs Research Paper: 10 Points of Difference
As you may have noticed, research papers and essays have many differences, both global and specific. These two types of academic assignments differ in the purpose of writing, have different structures and formats, and are aimed at testing different skills. And yet, every day, students face difficulties in understanding the basic requirements, which leads to incorrect execution of the task. To summarize the main differences, let’s look at the table below.

What Is the Difference Between Research Paper and Different Types of Papers
There are many types of papers, each focusing on different topics, serving different purposes, and requiring a specific structure. Those are different types of essays that share a common ground but differ in the way they present information and arguments.
Analytical paper. The purpose of such an essay is an in-depth analysis of the chosen topic, studying different approaches and points of view, and formulating one’s own conclusions based on the information studied and scientific evidence.
Argumentative paper. This type of essay takes as a basis an ambiguous topic; the author must take a certain position and provide a number of arguments.
Informative paper. It has an informative purpose — a presentation of information to the reader, preceded by careful analysis and selection of data.
Persuasive paper . The purpose of this paper is to present convincing arguments, using chosen writing techniques, confirming the author’s position regarding the selected scientific topic.
To get a high grade, you need to understand the requirements of academic requirements. No matter how informatively rich your work is, if it does not meet the requirements, it cannot be highly appreciated. Each type of academic assignment has its own clearly defined, unique format. It’s necessary to know the difference between a research paper vs argumentative essay so as not to get confused while completing a college assignment. So before you start writing an assignment, make sure you understand the type of academic writing required of you.
Let’s Sum Up
Research papers and essays are aimed at testing various skills of the student, following different structures, and having several requirements. An essay is a more creative writing task, which involves showing originality and expressing a personal opinion on a certain topic. At the same time, a research paper is a type of scientific writing that adheres to a strict structure and uses a formal tone. Understanding the main differences will make your writing process easier, saving you time researching the requirements. Remember that knowing the essence of the assignment is a key factor in writing a decent paper.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
Essay vs. Research Paper
What's the difference.
An essay and a research paper are both academic writing assignments that require students to explore a specific topic and present their findings in a structured manner. However, there are some key differences between the two. An essay is typically shorter in length and focuses on presenting the writer's perspective or argument on a particular subject. It often includes personal opinions and experiences, and the writer's voice is more prominent. On the other hand, a research paper is more extensive and involves in-depth research and analysis of various sources. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the topic and often requires the use of citations and references to support the writer's claims. Additionally, a research paper is usually more formal and objective in tone compared to an essay.
Further Detail
Introduction.
When it comes to academic writing, two common forms of assignments that students often encounter are essays and research papers. While both serve as means of evaluating a student's understanding of a particular topic, they differ in several aspects. This article aims to explore and compare the attributes of essays and research papers, shedding light on their unique characteristics and purposes.
Structure and Organization
One of the primary distinctions between essays and research papers lies in their structure and organization. Essays typically follow a more flexible and fluid structure, allowing the writer to present their ideas in a creative and engaging manner. They often consist of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. In contrast, research papers adhere to a more rigid structure, often requiring specific sections such as an abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. The structure of a research paper is designed to provide a comprehensive and systematic analysis of a particular topic.
Purpose and Focus
Essays and research papers also differ in terms of their purpose and focus. Essays are generally shorter in length and aim to present a concise argument or viewpoint on a specific topic. They often require critical thinking and analysis, allowing the writer to express their own opinions and interpretations. On the other hand, research papers are more extensive and focus on investigating a particular research question or problem. They require in-depth research, data collection, and analysis to provide evidence-based conclusions. Research papers aim to contribute to the existing body of knowledge on a given subject.
Research Requirements
As the name suggests, research papers heavily rely on extensive research to support their claims and arguments. They require the writer to gather information from various sources such as scholarly articles, books, and reputable websites. Research papers often involve conducting experiments, surveys, or interviews to collect primary data. On the other hand, while essays may also require some research, they typically rely more on the writer's existing knowledge and understanding of the topic. Essays often prioritize critical thinking and analysis of the available information rather than extensive research.
Writing Style and Tone
The writing style and tone of essays and research papers can also differ significantly. Essays often allow for a more personal and subjective writing style, enabling the writer to express their thoughts and emotions. The tone of an essay can vary depending on the topic and purpose, ranging from formal and academic to more conversational and informal. In contrast, research papers require a more objective and formal writing style. They should be written in the third person and avoid personal opinions or biases. The tone of a research paper is typically neutral and focused on presenting factual information and analysis.
Citation and Referencing
Both essays and research papers require proper citation and referencing of sources used. However, the extent and complexity of citation may differ between the two. Essays often require the use of in-text citations and a reference list or bibliography at the end of the document. The citation style may vary depending on the academic discipline or the instructor's requirements. Research papers, on the other hand, typically follow a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, and require more detailed and comprehensive referencing. They often include in-text citations, footnotes or endnotes, and a detailed bibliography or works cited page.
Evaluation and Assessment
Essays and research papers are evaluated and assessed based on different criteria. Essays are often graded on the writer's ability to present a coherent argument, critical thinking skills, and the clarity of their writing. The focus is on the writer's ability to convey their ideas effectively. Research papers, on the other hand, are evaluated based on the depth of research, the quality of data analysis, and the validity of the conclusions drawn. The assessment of research papers often considers the writer's ability to contribute to the existing knowledge on the topic and their understanding of research methodologies.
In conclusion, while essays and research papers share the common goal of evaluating a student's understanding of a particular topic, they differ in various aspects. Essays offer more flexibility in structure and allow for personal opinions and interpretations, while research papers adhere to a more rigid structure and require extensive research and analysis. The purpose, focus, writing style, citation requirements, and evaluation criteria also set them apart. Understanding these differences can help students approach each assignment appropriately and effectively meet the expectations of their instructors.
Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or facts. Please report any issues.

Comparing and Contrasting
What this handout is about.
This handout will help you first to determine whether a particular assignment is asking for comparison/contrast and then to generate a list of similarities and differences, decide which similarities and differences to focus on, and organize your paper so that it will be clear and effective. It will also explain how you can (and why you should) develop a thesis that goes beyond “Thing A and Thing B are similar in many ways but different in others.”
Introduction
In your career as a student, you’ll encounter many different kinds of writing assignments, each with its own requirements. One of the most common is the comparison/contrast essay, in which you focus on the ways in which certain things or ideas—usually two of them—are similar to (this is the comparison) and/or different from (this is the contrast) one another. By assigning such essays, your instructors are encouraging you to make connections between texts or ideas, engage in critical thinking, and go beyond mere description or summary to generate interesting analysis: when you reflect on similarities and differences, you gain a deeper understanding of the items you are comparing, their relationship to each other, and what is most important about them.
Recognizing comparison/contrast in assignments
Some assignments use words—like compare, contrast, similarities, and differences—that make it easy for you to see that they are asking you to compare and/or contrast. Here are a few hypothetical examples:
- Compare and contrast Frye’s and Bartky’s accounts of oppression.
- Compare WWI to WWII, identifying similarities in the causes, development, and outcomes of the wars.
- Contrast Wordsworth and Coleridge; what are the major differences in their poetry?
Notice that some topics ask only for comparison, others only for contrast, and others for both.
But it’s not always so easy to tell whether an assignment is asking you to include comparison/contrast. And in some cases, comparison/contrast is only part of the essay—you begin by comparing and/or contrasting two or more things and then use what you’ve learned to construct an argument or evaluation. Consider these examples, noticing the language that is used to ask for the comparison/contrast and whether the comparison/contrast is only one part of a larger assignment:
- Choose a particular idea or theme, such as romantic love, death, or nature, and consider how it is treated in two Romantic poems.
- How do the different authors we have studied so far define and describe oppression?
- Compare Frye’s and Bartky’s accounts of oppression. What does each imply about women’s collusion in their own oppression? Which is more accurate?
- In the texts we’ve studied, soldiers who served in different wars offer differing accounts of their experiences and feelings both during and after the fighting. What commonalities are there in these accounts? What factors do you think are responsible for their differences?
You may want to check out our handout on understanding assignments for additional tips.
Using comparison/contrast for all kinds of writing projects
Sometimes you may want to use comparison/contrast techniques in your own pre-writing work to get ideas that you can later use for an argument, even if comparison/contrast isn’t an official requirement for the paper you’re writing. For example, if you wanted to argue that Frye’s account of oppression is better than both de Beauvoir’s and Bartky’s, comparing and contrasting the main arguments of those three authors might help you construct your evaluation—even though the topic may not have asked for comparison/contrast and the lists of similarities and differences you generate may not appear anywhere in the final draft of your paper.
Discovering similarities and differences
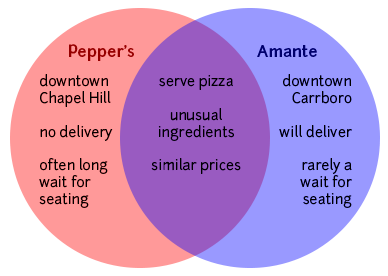
Making a Venn diagram or a chart can help you quickly and efficiently compare and contrast two or more things or ideas. To make a Venn diagram, simply draw some overlapping circles, one circle for each item you’re considering. In the central area where they overlap, list the traits the two items have in common. Assign each one of the areas that doesn’t overlap; in those areas, you can list the traits that make the things different. Here’s a very simple example, using two pizza places:
To make a chart, figure out what criteria you want to focus on in comparing the items. Along the left side of the page, list each of the criteria. Across the top, list the names of the items. You should then have a box per item for each criterion; you can fill the boxes in and then survey what you’ve discovered.
Here’s an example, this time using three pizza places:
As you generate points of comparison, consider the purpose and content of the assignment and the focus of the class. What do you think the professor wants you to learn by doing this comparison/contrast? How does it fit with what you have been studying so far and with the other assignments in the course? Are there any clues about what to focus on in the assignment itself?
Here are some general questions about different types of things you might have to compare. These are by no means complete or definitive lists; they’re just here to give you some ideas—you can generate your own questions for these and other types of comparison. You may want to begin by using the questions reporters traditionally ask: Who? What? Where? When? Why? How? If you’re talking about objects, you might also consider general properties like size, shape, color, sound, weight, taste, texture, smell, number, duration, and location.
Two historical periods or events
- When did they occur—do you know the date(s) and duration? What happened or changed during each? Why are they significant?
- What kinds of work did people do? What kinds of relationships did they have? What did they value?
- What kinds of governments were there? Who were important people involved?
- What caused events in these periods, and what consequences did they have later on?
Two ideas or theories
- What are they about?
- Did they originate at some particular time?
- Who created them? Who uses or defends them?
- What is the central focus, claim, or goal of each? What conclusions do they offer?
- How are they applied to situations/people/things/etc.?
- Which seems more plausible to you, and why? How broad is their scope?
- What kind of evidence is usually offered for them?
Two pieces of writing or art
- What are their titles? What do they describe or depict?
- What is their tone or mood? What is their form?
- Who created them? When were they created? Why do you think they were created as they were? What themes do they address?
- Do you think one is of higher quality or greater merit than the other(s)—and if so, why?
- For writing: what plot, characterization, setting, theme, tone, and type of narration are used?
- Where are they from? How old are they? What is the gender, race, class, etc. of each?
- What, if anything, are they known for? Do they have any relationship to each other?
- What are they like? What did/do they do? What do they believe? Why are they interesting?
- What stands out most about each of them?
Deciding what to focus on
By now you have probably generated a huge list of similarities and differences—congratulations! Next you must decide which of them are interesting, important, and relevant enough to be included in your paper. Ask yourself these questions:
- What’s relevant to the assignment?
- What’s relevant to the course?
- What’s interesting and informative?
- What matters to the argument you are going to make?
- What’s basic or central (and needs to be mentioned even if obvious)?
- Overall, what’s more important—the similarities or the differences?
Suppose that you are writing a paper comparing two novels. For most literature classes, the fact that they both use Caslon type (a kind of typeface, like the fonts you may use in your writing) is not going to be relevant, nor is the fact that one of them has a few illustrations and the other has none; literature classes are more likely to focus on subjects like characterization, plot, setting, the writer’s style and intentions, language, central themes, and so forth. However, if you were writing a paper for a class on typesetting or on how illustrations are used to enhance novels, the typeface and presence or absence of illustrations might be absolutely critical to include in your final paper.
Sometimes a particular point of comparison or contrast might be relevant but not terribly revealing or interesting. For example, if you are writing a paper about Wordsworth’s “Tintern Abbey” and Coleridge’s “Frost at Midnight,” pointing out that they both have nature as a central theme is relevant (comparisons of poetry often talk about themes) but not terribly interesting; your class has probably already had many discussions about the Romantic poets’ fondness for nature. Talking about the different ways nature is depicted or the different aspects of nature that are emphasized might be more interesting and show a more sophisticated understanding of the poems.
Your thesis
The thesis of your comparison/contrast paper is very important: it can help you create a focused argument and give your reader a road map so they don’t get lost in the sea of points you are about to make. As in any paper, you will want to replace vague reports of your general topic (for example, “This paper will compare and contrast two pizza places,” or “Pepper’s and Amante are similar in some ways and different in others,” or “Pepper’s and Amante are similar in many ways, but they have one major difference”) with something more detailed and specific. For example, you might say, “Pepper’s and Amante have similar prices and ingredients, but their atmospheres and willingness to deliver set them apart.”
Be careful, though—although this thesis is fairly specific and does propose a simple argument (that atmosphere and delivery make the two pizza places different), your instructor will often be looking for a bit more analysis. In this case, the obvious question is “So what? Why should anyone care that Pepper’s and Amante are different in this way?” One might also wonder why the writer chose those two particular pizza places to compare—why not Papa John’s, Dominos, or Pizza Hut? Again, thinking about the context the class provides may help you answer such questions and make a stronger argument. Here’s a revision of the thesis mentioned earlier:
Pepper’s and Amante both offer a greater variety of ingredients than other Chapel Hill/Carrboro pizza places (and than any of the national chains), but the funky, lively atmosphere at Pepper’s makes it a better place to give visiting friends and family a taste of local culture.
You may find our handout on constructing thesis statements useful at this stage.
Organizing your paper
There are many different ways to organize a comparison/contrast essay. Here are two:
Subject-by-subject
Begin by saying everything you have to say about the first subject you are discussing, then move on and make all the points you want to make about the second subject (and after that, the third, and so on, if you’re comparing/contrasting more than two things). If the paper is short, you might be able to fit all of your points about each item into a single paragraph, but it’s more likely that you’d have several paragraphs per item. Using our pizza place comparison/contrast as an example, after the introduction, you might have a paragraph about the ingredients available at Pepper’s, a paragraph about its location, and a paragraph about its ambience. Then you’d have three similar paragraphs about Amante, followed by your conclusion.
The danger of this subject-by-subject organization is that your paper will simply be a list of points: a certain number of points (in my example, three) about one subject, then a certain number of points about another. This is usually not what college instructors are looking for in a paper—generally they want you to compare or contrast two or more things very directly, rather than just listing the traits the things have and leaving it up to the reader to reflect on how those traits are similar or different and why those similarities or differences matter. Thus, if you use the subject-by-subject form, you will probably want to have a very strong, analytical thesis and at least one body paragraph that ties all of your different points together.
A subject-by-subject structure can be a logical choice if you are writing what is sometimes called a “lens” comparison, in which you use one subject or item (which isn’t really your main topic) to better understand another item (which is). For example, you might be asked to compare a poem you’ve already covered thoroughly in class with one you are reading on your own. It might make sense to give a brief summary of your main ideas about the first poem (this would be your first subject, the “lens”), and then spend most of your paper discussing how those points are similar to or different from your ideas about the second.
Point-by-point
Rather than addressing things one subject at a time, you may wish to talk about one point of comparison at a time. There are two main ways this might play out, depending on how much you have to say about each of the things you are comparing. If you have just a little, you might, in a single paragraph, discuss how a certain point of comparison/contrast relates to all the items you are discussing. For example, I might describe, in one paragraph, what the prices are like at both Pepper’s and Amante; in the next paragraph, I might compare the ingredients available; in a third, I might contrast the atmospheres of the two restaurants.
If I had a bit more to say about the items I was comparing/contrasting, I might devote a whole paragraph to how each point relates to each item. For example, I might have a whole paragraph about the clientele at Pepper’s, followed by a whole paragraph about the clientele at Amante; then I would move on and do two more paragraphs discussing my next point of comparison/contrast—like the ingredients available at each restaurant.
There are no hard and fast rules about organizing a comparison/contrast paper, of course. Just be sure that your reader can easily tell what’s going on! Be aware, too, of the placement of your different points. If you are writing a comparison/contrast in service of an argument, keep in mind that the last point you make is the one you are leaving your reader with. For example, if I am trying to argue that Amante is better than Pepper’s, I should end with a contrast that leaves Amante sounding good, rather than with a point of comparison that I have to admit makes Pepper’s look better. If you’ve decided that the differences between the items you’re comparing/contrasting are most important, you’ll want to end with the differences—and vice versa, if the similarities seem most important to you.
Our handout on organization can help you write good topic sentences and transitions and make sure that you have a good overall structure in place for your paper.
Cue words and other tips
To help your reader keep track of where you are in the comparison/contrast, you’ll want to be sure that your transitions and topic sentences are especially strong. Your thesis should already have given the reader an idea of the points you’ll be making and the organization you’ll be using, but you can help them out with some extra cues. The following words may be helpful to you in signaling your intentions:
- like, similar to, also, unlike, similarly, in the same way, likewise, again, compared to, in contrast, in like manner, contrasted with, on the contrary, however, although, yet, even though, still, but, nevertheless, conversely, at the same time, regardless, despite, while, on the one hand … on the other hand.
For example, you might have a topic sentence like one of these:
- Compared to Pepper’s, Amante is quiet.
- Like Amante, Pepper’s offers fresh garlic as a topping.
- Despite their different locations (downtown Chapel Hill and downtown Carrboro), Pepper’s and Amante are both fairly easy to get to.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Comparative Essay Writing: Methods and Examples
| Danielle McLeod
Danielle McLeod
Danielle McLeod is a highly qualified secondary English Language Arts Instructor who brings a diverse educational background to her classroom. With degrees in science, English, and literacy, she has worked to create cross-curricular materials to bridge learning gaps and help students focus on effective writing and speech techniques. Currently working as a dual credit technical writing instructor at a Career and Technical Education Center, her curriculum development surrounds student focus on effective communication for future career choices.
Writing effective comparative essays requires strategic techniques and thoughtful consideration of common pitfalls. A comparative essay explores the similarities and differences between subjects, allowing the writer to draw conclusions related to the topics of the material.
This article outlines key strategies, such as using transitions, incorporating evidence, and maintaining a formal tone. It also identifies mistakes to avoid, like failing to establish a clear basis for comparison or providing a superficial analysis.
The article emphasizes the importance of revising your comparative essay. This process enables you to refine your analysis, strengthen your arguments, and enhance the overall quality of your work. Incorporating feedback from peers or instructors can elevate your comparative essay and communicate your unique insights more effectively.
Whether you are a student or a professional writer, this guidance can help you craft comparative essays that captivate and inform your audience. Let’s explore the essentials of comparative analysis to enhance your writing prowess.
What is a Comparative Essay?

A comparative essay is a form of academic writing that examines and analyzes two or more subjects, identifying their similarities and differences. This type of essay allows students to develop critical thinking skills by evaluating and contrasting various topic elements.
For example, a comparative analysis of the Roman Empire and the Aztec Empire might make a good history class topic. In contrast, a comparative study of the Harlem Renaissance and the Chicano Art Movement would make a good art class focus.
Types of Comparative Methods
There are two main methods of structuring a comparative essay: the block method and the point-by-point method.
Block Method
- In the block method , you discuss each subject separately.
- You spend one or more paragraphs focusing on the first subject, then move on to the second subject.
- This allows you to go into more detail about each subject before comparing.
- The block method is good when the subjects you’re comparing have many differences or when you want to establish a strong foundation for your comparison.
Point-by-Point Method
- The point-by-point method jumps back and forth between the two subjects.
- In each paragraph, you address a specific point of comparison or contrast between the subjects.
- This structure encourages you to compare the subjects directly, clearly highlighting their similarities and differences.
- The point-by-point method works well when the subjects share clear, significant points of comparison, allowing you to explore their differences and similarities efficiently.
Why are Comparative Essays Important?
Comparative essays are an important part of academic writing because they encourage students to engage in deeper analysis, identify meaningful connections, and better understand the subjects being explored.

By comparing and contrasting different concepts, ideas, or phenomena, students can develop a well-rounded perspective and strengthen their ability to think critically.
What Should You Consider When Selecting Topics for Comparison?
When choosing topics for a comparative essay, it’s important to select subjects with some common ground but distinct differences. This will allow you to conduct a meaningful analysis and draw insightful conclusions. Consider factors such as the subjects’ historical context, cultural influences, or underlying themes to ensure a productive comparison.
For example, using the Block Method, you might do the following;
- Comparing the education systems in the United States and Canada
- Analyzing the differences between classic literature and modern young adult novels
- Contrasting the architectural styles of Gothic cathedrals and Renaissance palaces
In a block method essay on these topics, the writer would devote one or more paragraphs to thoroughly describing and analyzing the first subject (e.g., the US education system, classic literature, Gothic cathedrals) before moving on to discuss the second subject (e.g., the Canadian education system, young adult novels, Renaissance palaces). This would allow the reader to fully understand each topic before the comparative analysis is presented.
Using the Point-by-Point Method might be best used with these topics:
- Comparing the use of symbolism in Ernest Hemingway’s “The Old Man and the Sea” and F. Scott Fitzgerald’s “The Great Gatsby.”
- Contrasting the political ideologies of Abraham Lincoln and Theodore Roosevelt
- Analyzing the similarities and differences in the marketing strategies of Coca-Cola and Pepsi
In a point-by-point comparative essay, the writer would alternate between the two subjects in each paragraph, directly comparing and contrasting specific elements (e.g., how symbolism is used, political views, and marketing tactics). This would encourage a more integrated analysis of the similarities and differences between the subjects.
How Can You Brainstorm for a Comparative Essay?
To begin brainstorming for a comparative essay, start by creating a Venn diagram to visually organize the similarities and differences between your chosen topics. This can help you identify key points of comparison and contrast, which will form the foundation of your essay.
Additionally, consider writing down any questions or observations that arise during this process, as they may guide your subsequent research and analysis.
How Should You Formulate a Thesis Statement for a Comparative Essay?
A thesis statement is a one- or two-sentence summary that conveys a comparative essay’s main argument, focus, or purpose. It provides the reader with an overview of the essay’s central claim, which the rest of the paper will work to develop and support.
Your comparative essay’s thesis statement should clearly explain the central argument or insight that your analysis will explore. This statement should go beyond simply identifying the subjects being compared and instead make a substantive claim about the relationship between them. A strong comparative essay thesis will establish the basis for your comparative analysis and provide a roadmap for the rest of your essay.
For example, using the examples mentioned above, consider these options:
- “Classic literature and modern young adult novels differ greatly in their thematic depth, complexity of characterization, and use of literary devices, though both genres can provide valuable insights into the human experience.”
- “Gothic cathedrals and Renaissance palaces represent vastly contrasting architectural styles, with Gothic structures emphasizing verticality, pointed arches, and religious symbolism, while Renaissance palaces showcase classical proportions, ornate facades, and secular grandeur.”
- “Ernest Hemingway’s ‘The Old Man and the Sea’ and F. Scott Fitzgerald’s ‘The Great Gatsby’ both employ symbolic imagery to explore themes of the human condition, but they do so in strikingly different ways that reflect the author’s distinct writing styles and philosophical perspectives.”
- “Though Abraham Lincoln and Theodore Roosevelt held vastly different political ideologies, with Lincoln championing a strong federal government and Roosevelt advocating for a more progressive, regulatory approach, both presidents played pivotal roles in shaping the course of American history.”
What Strategies Should You Employ When Writing Comparative Essays?

When writing a comparative essay, it’s important to employ various strategies to effectively communicate your analysis. This may include using transition words and phrases to establish connections between ideas, incorporating relevant examples or evidence to support your claims, and maintaining a formal, academic tone throughout your writing.
Additionally, consider incorporating a Venn diagram or other visual aids to enhance your comparative analysis.
Strategies for Comparative Essays
To recap, use the following strategies in your work to help organize and structure your essay:
Use Effective Transitions
- Words/phrases like “in contrast,” “on the other hand,” “similarly,” “conversely,” etc.
- Help establish clear connections between ideas and comparisons.
Provide Relevant Examples and Evidence
- Draw from the subjects being compared to support your claims
- Use specific details, quotes, or data to strengthen your analysis
Maintain a Formal, Academic Tone
- Avoid casual or conversational language
- Focus on objective, analytical writing
Incorporate Visual Aids (if appropriate)
- Venn diagrams, tables, or other graphics can effectively illustrate comparisons
- Help the reader visualize the relationships between the subjects
Structure Logically
- Use either the block method or point-by-point organization
- Ensure a clear, coherent flow of ideas
Address Counterarguments or Limitations
- Acknowledge and respond to potential objections or alternative perspectives.
- Demonstrates depth of understanding
Which Mistakes Should You Be Careful of in Comparative Essay Writing?
Here are some examples to illustrate the common mistakes to avoid when writing comparative essays:
Failing to establish a clear basis for comparison
- Attempting to compare the plot of a novel to the musical score of an opera without explaining the relevance of that comparison
- Contrasting two political ideologies without defining the key criteria being used to evaluate them
Neglecting to address significant differences or similarities
- Comparing the leadership styles of two presidents but failing to discuss their differing approaches to domestic or foreign policy
- Analyzing the architectural features of Gothic cathedrals and Renaissance palaces without acknowledging their shared use of symmetry and classical proportions
Providing a superficial or unbalanced analysis
- Dedicating a single paragraph to analyzing the complex socioeconomic factors that shaped the development of two education systems
- The majority of the essay focused on the differences between the two subjects while only briefly mentioning their similarities.
Relying too heavily on plot summary or description
- Retelling the narratives of two novels in detail without delving into a comparative analysis of their themes, character development, or stylistic elements
- Extensively describing the physical attributes of two historical buildings without explaining how those features reflect the broader architectural movements.
Lacking a cohesive and logical organizational structure
- Jumping back and forth between discussing the two subjects without a clear basis for the order or flow of ideas
- Using the block method but failing to create a smooth transition between the sections devoted to each subject
Incorporating specific, relevant examples for each of these potential pitfalls can help illustrate the importance of avoiding them in comparative essay writing. These tips can help you when you just wish you could ask something to “ write my essay for me .”
Why is Revising Your Comparative Essay Crucial?

Revising your comparative essay is always considered an important step in the writing process, as it allows you to refine your analysis, strengthen your arguments, and ensure the overall explanation of connections and effectiveness of your essay.
During the revision stage, consider seeking feedback from peers or instructors. Their perspectives can help you identify areas for improvement and enhance the quality of your comparative essay.
Reasons to Revise Comparative Essays
Refine Your Analysis
- Example: Upon revision, you realize your comparison of two political ideologies lacks nuance and fails to acknowledge the complexities within each position. You then expand your analysis to provide a more nuanced and balanced perspective.
Strengthen Your Arguments
- Example: During revision, you identify gaps in your supporting evidence for a key point contrasting the marketing strategies of two rival companies. You then incorporate additional data and examples to bolster your comparative claims.
Ensure Coherence and Organization
- Example: In reviewing your essay, you recognize that your use of the point-by-point method is causing your comparisons to feel disjointed. You then reorganize your essay to follow a more cohesive block structure, improving the overall flow of ideas.
Incorporate Peer/Instructor Feedback
- Example: After receiving feedback from your instructor, you realize your comparison of two literary works does not adequately address a significant thematic similarity. You then revise the essay to incorporate this overlooked element into your analysis.
Enhance the Overall Quality
- Example: During the revision process, you identify opportunities to improve the clarity and precision of your language, ensuring your comparative essay communicates your insights effectively to the reader.
A comparative essay is a valuable academic writing exercise that encourages critical thinking, in-depth analysis, and the development of essential written communication skills. By mastering the structure, thesis formulation, and writing strategies associated with comparative essays, students can enhance their ability to engage in thoughtful, well-reasoned comparisons and effectively convey their research, discoveries, and opinions to their audience.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
Welcome to the new OASIS website! We have academic skills, library skills, math and statistics support, and writing resources all together in one new home.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Comparing & Contrasting
A compare and contrast paper discusses the similarities and differences between two or more topics. The paper should contain an introduction with a thesis statement, a body where the comparisons and contrasts are discussed, and a conclusion.
Address Both Similarities and Differences
Because this is a compare and contrast paper, both the similarities and differences should be discussed. This will require analysis on your part, as some topics will appear to be quite similar, and you will have to work to find the differing elements.
Make Sure You Have a Clear Thesis Statement
Just like any other essay, a compare and contrast essay needs a thesis statement. The thesis statement should not only tell your reader what you will do, but it should also address the purpose and importance of comparing and contrasting the material.
Use Clear Transitions
Transitions are important in compare and contrast essays, where you will be moving frequently between different topics or perspectives.
- Examples of transitions and phrases for comparisons: as well, similar to, consistent with, likewise, too
- Examples of transitions and phrases for contrasts: on the other hand, however, although, differs, conversely, rather than.
For more information, check out our transitions page.
Structure Your Paper
Consider how you will present the information. You could present all of the similarities first and then present all of the differences. Or you could go point by point and show the similarity and difference of one point, then the similarity and difference for another point, and so on.
Include Analysis
It is tempting to just provide summary for this type of paper, but analysis will show the importance of the comparisons and contrasts. For instance, if you are comparing two articles on the topic of the nursing shortage, help us understand what this will achieve. Did you find consensus between the articles that will support a certain action step for people in the field? Did you find discrepancies between the two that point to the need for further investigation?
Make Analogous Comparisons
When drawing comparisons or making contrasts, be sure you are dealing with similar aspects of each item. To use an old cliché, are you comparing apples to apples?
- Example of poor comparisons: Kubista studied the effects of a later start time on high school students, but Cook used a mixed methods approach. (This example does not compare similar items. It is not a clear contrast because the sentence does not discuss the same element of the articles. It is like comparing apples to oranges.)
- Example of analogous comparisons: Cook used a mixed methods approach, whereas Kubista used only quantitative methods. (Here, methods are clearly being compared, allowing the reader to understand the distinction.
Related Webinar
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Developing Arguments
- Next Page: Avoiding Logical Fallacies
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Cost of Attendance
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

Research Papers Vs. Essays (Differences and Similarities)

In high school, college, university, and even professional life, you will write many assignments, including research papers and essays. In school, instructors and professors use essays and research papers to test your understanding of concepts taught in class. It is, therefore, imperative to know the difference between essays and research papers.
You came to the right place if you struggle to get the facts right about essays vs. research papers. This guide guides you through the similarities and differences between the two common papers written at all academic levels.
In a nutshell, research papers focus on facts to argue a point, while essays focus on an individual's understanding of a topic. Understanding the difference between these two pieces of writing will help you succeed in school.
With that said, here is an overview of essays and research papers.

What is an Essay?
An essay is a short piece of writing demonstrating your comprehension, critical thinking, analytical skills, creativity, and awareness of a given topic. The length of the essay will determine the citations it should have and how long it takes to write it. So for a 500 words essay, the instructor will require at least five verifiable sources. Since they are short in length, they usually have five paragraphs starting with an introduction, followed by the body, and then a conclusion.
The main objectives of an essay are to:
- Inform the reader by providing accurate and proven information about a particular topic
- Convince the audience of a specific headline using researched evidence
- Explain a topic by providing in-depth information with flowing content
- Entertain the readers through humor and other funny statements
Check out our comprehensive guide on how to write a good essay .
Format and Structure
The basic format of an essay is an introduction, body, and conclusion. You must fashion all the ideas- one at a time - in the order that makes sense. To successfully deliver the content to the readers, you must attend to their logic. You have to introduce the arguments, analyze all the data, provide counterarguments and conclude the topic.
You should consider every part of the essay answering basic questions the reader is probably asking. These questions are: what, how, why.
The "what" explains what evidence leads you to your thesis statement, and you must therefore examine all the evidence demonstrating the truth of your fact.
The "how" explains how other arguments can counter your thesis statements. In other words, how does another way of looking at things affect your claims?
The "why" shows why the readers should care about your statements and allows them to learn more about what you are saying in a larger context.
An essay follows different formats depending on the academic style of writing requested; it could be MLA, APA, or Chicago format. For example, the APA style is used in social and health sciences, MLA in liberal arts, Language, Literature, and humanities, and the Chicago style in literature, history, and arts.
However, the structure is as follows:
Introduction
The introduction paragraph sets the stage for what is to come. It has three main parts:
- Background information
- Thesis statement
The first sentence of the introduction should grab the reader's attention . Next, you should arouse curiosity through an eye-catching statement for the reader to continue reading the essay. You can achieve this by using a joke, statistics, or research findings.
Background Information
Give the readers the context of the essay by providing some background information depending on the essay's subject. Don't give too much information — mention just a few points you will divulge later in the text. Just make sure you save the evidence for the body of the essay. The length of this information will depend on the scope of your essay.
Thesis Statement
A thesis statement sums up the main ideas of your topic and helps control the essay's narrative. Therefore, the statement should state clearly the main idea you want readers to grasp.
Body (Arguments)
The body is the longest part of the essay, which is organized into different paragraphs. Each paragraph elaborates on one idea and contains between four to five sentences. Every paragraph contains three sections starting with the topic sentence, followed by a supporting sentence and a concluding sentence.
The topic sentence informs the reader about the paragraph, and the supporting sentence expounds on the central idea. And the concluding sentence summarizes what you have talked about.
The conclusion is the last paragraph of the essay. It aims to summarize the essay's main parts, show the essence of your argument, and leave the reader with a sense of closure.
When writing the conclusion paragraph of an essay , you should restate the thesis statement to remind the reader what you talked about, followed by a summary of your arguments and counterarguments. Finally, the last sentence of the paragraph should state your concluding thought.
Types of Essays
There are different types of essays, each with its own objectives. They include:
- Descriptive
- Argumentative
Narrative Essays
Narrative essays are mostly personal, and they tell a story. This essay is written from a first-person perspective.
Descriptive Essays
Descriptive essays describe something— object, person, place, emotion, or situation from your own perspective.
Expository Essays
Expository essays aim at explaining a topic with facts. This is where you analyze a given piece of information and explain in detail how you have reached your conclusion.
Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay presents both sides of an argument to inform the reader. An instructor will give this type of essay to gauge your debating skills.
Persuasive Essay
The persuasive essay aims to convince the reader. The writing presents logical information with an emotional appeal to the reader to believe your point of view.
What is a Research Paper?
A research paper is academic writing that involves supportive evidence about a given topic. It provides a perspective on a given topic using various sources supported by qualitative and quantitative research methods.
Research papers are usually similar to essays, but they are much longer and involve in-depth research conducted independently. In addition, you must spend time investigating and evaluating multiple sources to offer an interpretation of a given text.
Since the main aim of a research paper is to develop a new argument, you must include a literature review. A literature review is a foundation and support for your research, and it is a survey of academic sources on a given topic that helps you identify theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
They are more formal as they involve rigorous and thorough research resulting in a central idea. Only when a paper meets this requirement will the instructor give a good grade. Their aim is to differentiate between opinions and facts, provide a detailed understanding of a given topic, and critique previously written work.
To effectively write a research paper, you must clearly define your research question. If your instructor has already assigned you a topic, there is no need. If not, try to choose an interesting research question.
Choose a research strategy by analyzing the materials you will use for your research. Then evaluate all the sources by focusing on their credibility and whether they support your research question.
Like essays, research papers also have paragraphs and follow the same academic writing formats, but their structure is much different. Their structure is as follows:
- Materials/methods
Acknowledgments
A title page contains all the vital information about the paper you are writing. The page is usually placed in front of the research paper. It contains your name, the name of the project, and your learning institution. Since it's the first page the reader will see, it should be well formatted. The title on the page should clearly display your thesis statement.
The abstract highlights the main points of your projects to help inform the readers what the paper is about. They are recorded along with keywords to help readers find your content more easily. The abstract should be clear and accurate.
An introduction part allows you to define the topic and establish your voice. The introduction should be interesting enough to get the reader hooked. It usually aims at:
- Presenting the problem statement, topic, and research investigation in the first part of the introduction
- Establish the aim and focus of your research in the second part
- Present the summary of your arguments in the third part
Research papers also have a thesis statement, like essays mostly found at the end of the introduction. It aims to explain what you are trying to prove and provide the main points in the research.
Materials/ Methods
The material/ methods section clearly defines what materials you used to perform your research. The aim is to direct readers to specialized materials, general procedures, and methods to weigh the value of your project. For example, these materials could be questionnaires that provide information about your paper. The materials should be specific and relevant to your field of study.
You should describe in detail how you conducted the analysis in their personal narrative and briefly list the methods used.
The results section is where you report what your findings are based on all the information you gathered with the materials you had. You should state the findings without biases or interpretation, allowing the reader to do that themselves. The findings should only be from your study, and they could be:
- Quantitative information - is data that can be measured and is presented in graphs, tables, or charts.
- Qualitative information - which is brief descriptions or explanations and is often presented as lists or essay like form
The discussion section shows the results and outcomes of your paper. It reviews and interprets the findings of the research and allows the readers to see the connection between all the parts of the paper. The discussion should include the following:
- Results you gathered from the research
- Discussion of related research
- Comparison between the research and your initial hypothesis
You must demonstrate your critical thinking skills when developing your arguments and establishing the relationship between each part the same way you would in an essay.
The conclusion section outlines why the research is important to the reader and why they should care. It summarizes all the parts mentioned in the paper and demonstrates the implications of your research. The writing should be on point to deliver your message to the readers.
The acknowledgment section appreciates all the contributors for their efforts in the research. You should mention all the contributors directly involved in your research. They could be:
- Funding Organization/ Donor
- Administrative personnel
- Your professors
- Work supervisors
The reference section is the last part of your research paper. This section shows that you have clearly and carefully conducted your research. It demonstrates that your work is credible, and readers can rely on it. You should list all the research material used. The average number of references in most research papers is 45.
Types of Research Papers
Like essays, there are different research papers, each requiring different preparation. These are argumentative and analytical research papers:
Argumentative Research Paper
When writing an argumentative research paper, you discuss your topic and then choose the stand you will be taking. The hope is to persuade the reader to take your stand.
Analytical Research Paper
You state your topic in an analytical research paper and take a neutral stance. You will then provide your arguments and facts, leaving the reader to choose their stance. The aim is not to persuade the reader but to present a well-supported analysis of a given topic.
Survey Research Paper
Survey research involves collecting data from a group of people through quantitative and qualitative research methods.
Experimental Research Paper
Based on experimental research or empirical research, this type of paper provides information about the procedures you have used in your research. It is mainly written as a scientific or empirical paper following the IMRAD format.
Definition Paper
In definition papers, you will describe an argument's facts without sharing personal emotions and only provide a list of facts without analyzing them.
What is the Aim of the Research Paper?
Learning how to write a research paper is to:
Provide Knowledge
Through research, you will gain new insights about a particular topic making you more knowledgeable.
Boost the Success, Not Business
The findings of a research paper will influence decision-makers to take positive action. For instance, if you wrote a paper about the importance of using laptops in schools, more laptops will be provided even to learners.
Enhance Public Awareness
By writing compelling research about a given headline and sharing it with the public, you give them an understanding of your ideas. Providing detailed and well-researched information will help the readers see the relevance of your conclusion.
What Are the Differences Between an Essay and a Research Paper?
After looking at each of them individually, what are the differences between them?
They Have Different Purposes
Even though they are both academic writings, they have different purposes. When an instructor assigns you a research paper, they want to know your deep understanding of a given topic by sharing how you have come to that realization. In other words, it demonstrates your opinions and those of other scientists. On the other hand, an essay shows your opinion about something even though you will research your information, and your point of view about the topic should be unique.
A Research Paper is More Formal
A research paper involves in-depth research from reputable sources, which you should prove in the form of references. On the other hand, an essay doesn't need in-depth research; it mainly relies on your thoughts and opinion. They are also not as complex as a research paper in terms of headings and subheadings.
More Time and Effort Are Needed in Writing a Research Paper Than an Essay
A research paper is a long piece of academic writing that requires multiple sources and a deeper understanding of information to reach a conclusion. Since there is tons of information to find and go through, more time is taken to do the research.
So while an essay can be completed in a few hours, a research paper can take days or even weeks to complete.
Differences in Length
Both essays and research papers are organized the same way. An essay has three parts: an introduction which includes a thesis statement, a body, and a supportive conclusion. You will need to hook your readers when writing the introduction for them to proceed with writing. The body usually has between four to five paragraphs which must be arranged systematically to make sense to the reader. Their word count ranges between 500 and 1000 words with about 5 citations.
Because research papers require in-depth research, they are much longer than essays and are usually referred to as multipage writing. A research paper typically has nine parts arranged in order with between 8 to 100 references. Regardless, both forms of academic writing follow the same organizational structure.
Here is a table that shows the similarities and differences between the two.
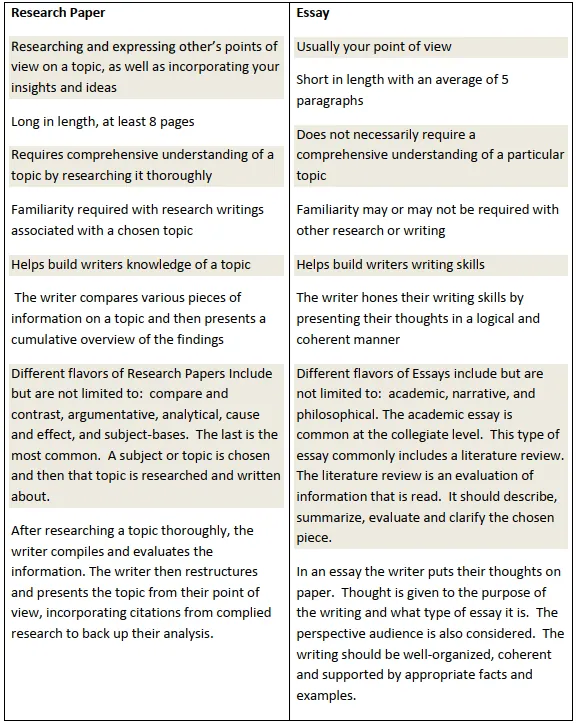
More differences and similarities between essays and research papers ( source )
Final Words
An essay and research paper are common types of academic writing assigned to high school, college, and university students. Essays are the shortest pieces of writing which show your understanding of a given topic during a research paper. The above difference will help you in your academic writing journey.
Life is full of demands, and you will juggle work, home duties, family responsibilities, and social life. When you add studies and writing papers to the packed schedule, you might break down mentally.
Do you need help with a research paper or an essay ? GradeCrest is the most preferred place for students and professionals who want their research papers done. We have expert paper writers who can handle papers on various topics and almost all subjects; no subject lacks an expert or is too hard to crack for us. You can order your essay or research paper by filling out the order form on our home page.

Gradecrest is a professional writing service that provides original model papers. We offer personalized services along with research materials for assistance purposes only. All the materials from our website should be used with proper references. See our Terms of Use Page for proper details.

Get 50% OFF Yearly and Lifetime Plans This Black Friday
Comparing and Contrasting: A Guide to Improve Your Essays

By Walter Akolo

Essays that require you to compare and contrast two or more subjects, ideas, places, or items are common.
They call for you to highlight the key similarities (compare) and differences (contrast) between them.
This guide contains all the information you need to become better at writing comparing and contrasting essays.
This includes: how to structure your essay, how to decide on the content, and some examples of essay questions.
Let’s dive in.

What Is Comparing and Contrasting?
Is compare and contrast the same as similarities and differences, what is the purpose of comparing and contrasting, can you compare and contrast any two items, how do you compare and contrast in writing, what are some comparing and contrasting techniques, how do you compare and contrast in college level writing, the four essentials of compare and contrast essays, what can you learn from a compare and contrast essay.
At their most basic, both comparing and contrasting base their evaluation on two or more subjects that share a connection.
The subjects could have similar characteristics, features, or foundations.
But while a comparison discusses the similarities of the two subjects, e.g. a banana and a watermelon are both fruit, contrasting highlights how the subjects or items differ from each other, e.g. a watermelon is around 10 times larger than a banana.
Any question that you are asked in education will have a variety of interesting comparisons and deductions that you can make.
Compare is the same as similarities.
Contrast is the same as differences.
This is because comparing identifies the likeness between two subjects, items, or categories, while contrasting recognizes disparities between them.
When you compare things, you represent them regarding their similarity, but when you contrast things, you define them in reference to their differences.
As a result, if you are asked to discuss the similarities and differences between two subjects, you can take an identical approach to if you are writing a compare and contrast essay.
In writing, the purpose of comparing and contrasting is to highlight subtle but important differences or similarities that might not be immediately obvious.

By illustrating the differences between elements in a similar category, you help heighten readers’ understanding of the subject or topic of discussion.
For instance, you might choose to compare and contrast red wine and white wine by pointing out the subtle differences. One of these differences is that red wine is best served at room temperature while white is best served chilled.
Also, comparing and contrasting helps to make abstract ideas more definite and minimizes the confusion that might exist between two related concepts.
Can Comparing and Contrasting Be Useful Outside of Academia?
Comparing enables you to see the pros and cons, allowing you to have a better understanding of the things under discussion. In an essay, this helps you demonstrate that you understand the nuances of your topic enough to draw meaningful conclusions from them.
Let's use a real-word example to see the benefits. Imagine you're contrasting two dresses you could buy. You might think:
- Dress A is purple, my favorite color, but it has a difficult zip and is practically impossible to match a jacket to.
- Dress B is more expensive but I already have a suitable pair of shoes and jacket and it is easier to move in.
You're linking the qualities of each dress to the context of the decision you're making. This is the same for your essay. Your comparison and contrast points will be in relation to the question you need to answer.
Comparing and contrasting is only a useful technique when applied to two related concepts.
To effectively compare two or more things, they must feature characteristics similar enough to warrant comparison.
In addition to this they must also feature a similarity that generates an interesting discussion. But what do I mean by “interesting” here?
Let’s look at two concepts, the Magna Carta and my third grade poetry competition entry.
They are both text, written on paper by a person so they fulfil the first requirement, they have a similarity. But this comparison clearly would not fulfil the second requirement, you would not be able to draw any interesting conclusions.
However, if we compare the Magna Carta to the Bill of Rights, you would be able to come to some very interesting conclusions concerning the history of world politics.
To write a good compare and contrast essay, it’s best to pick two or more topics that share a meaningful connection .
The aim of the essay would be to show the subtle differences or unforeseen similarities.
By highlighting the distinctions between elements in a similar category you can increase your readers’ understanding.
Alternatively, you could choose to focus on a comparison between two subjects that initially appear unrelated.
The more dissimilar they seem, the more interesting the comparison essay will turn out.
For instance, you could compare and contrast professional rugby players with marathon runners.
Can You Compare and Contrast in an Essay That Does Not Specifically Require It?
As a writer, you can employ comparing and contrasting techniques in your writing, particularly when looking for ideas you can later apply in your argument.
You can do this even when the comparison or contrast is not a requirement for the topic or argument you are presenting. Doing so could enable you to build your evaluation and develop a stronger argument.
Note that the similarities and differences you come up with might not even show up in the final draft.
While the use of compare and contrast can be neutral, you can also use it to highlight one option under discussion. When used this way, you can influence the perceived advantages of your preferred option.
As a writing style, comparing and contrasting can encompass an entire essay. However, it could also appear in some select paragraphs within the essay, where making some comparisons serves to better illustrate a point.
What Should You Do First?
Before you compare two things, always start by deciding on the reason for your comparison, then outline the criteria you will use to compare them.
Words and phrases commonly used for comparison include:
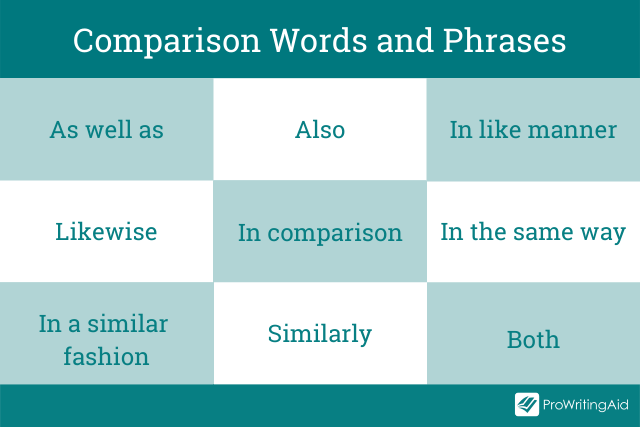
In writing, these words and phrases are called transitions . They help readers to understand or make the connection between sentences, paragraphs, and ideas.
Without transition words writing can feel clumsy and disjointed making it difficult to read. ProWritingAid’s transition report highlights all of a documents transitions and suggests that 25% of any sentences in a piece include a transition.
Sign up for a free ProWritingAid account to use the Transitions Report.
So, how do you form all of this into a coherent essay? It's a good idea to plan first, then decide what your paragraph layout will look like.
Venn diagrams are useful tool to start generating ideas. The, for your essay, you need to choose between going idea by idea and going point by point.
Using a Venn Diagram
A Venn diagram helps you to clearly see the similarities and differences between multiple objects, things, or subjects.
The writing tool comprises two, or more, simple, overlapping circles in which you list down the things that are alike (within the overlapping area) and those that differ (outside the overlapping area).
It’s great for brainstorming ideas and for creating your essay’s outline. You could even use it in an exam setting because it is quick and simple.
Going Subject by Subject
Going subject by subject is a structural choice for your essay.
Start by saying all you have to say on the first subject, then proceed to do the same about the second subject.
Depending on the length of your essay, you can fit the points about each subject into one paragraph or have several sections per each subject, ending with a conclusion.
This method is best for short essays on simple topics. Most university-level essays will go point by point instead.
Going Point by Point
Going point by point, or alternating, is the opposite essay structure from going subject by subject. This is ideal when you want to do more direct comparing and contrasting. It entails discussing one comparison point at a time. It allows you to use a paragraph to talk about how a certain comparing/contrasting point relates to the subjects or items you are discussing.
Alternatively, if you have lots of details about the subject, you might decide to use a paragraph for each point.
An academic compare and contrast essay looks at two or more subjects, ideas, people, or objects, compares their likeness, and contrasts their differences.
It’s an informative essay that provides insights on what is similar and different between the two items.
Depending on the essay’s instructions, you can focus solely on comparing or contrasting, or a combination of the two.
Examples of College Level Compare and Contrast Essay Questions
Here are eleven examples of compare and contrast essay questions that you might encounter at university:

- Archaeology: Compare and contrast the skulls of homo habilis, homo erectus, and homo sapiens.
- Art: Compare and contrast the working styles of any two Neoclassic artists.
- Astrophysics: Compare and contrast the chemical composition of Venus and Neptune.
- Biology: Compare and contrast the theories of Lamarck and Darwin.
- Business: Compare and contrast 2 or more business models within the agricultural industry.
- Creative writing: Compare and contrast free indirect discourse with epistolary styles.
- English Literature: Compare and contrast William Wordsworth with Robert Browning.
- Geography: Compare and contrast the benefit of solar panels with the benefit of wind turbines.
- History: Compare and contrast WWI to WWII with specific reference to the causes and outcomes.
- Medicine: Compare and contrast England’s health service with America’s health service.
- Psychology: Compare and contrast the behaviorist theory with the psychodynamic theory.
So, the key takeaways to keep in mind are:
Have a basis for comparison. The two things need to have enough in common to justify a discussion about their similarities and disparities.
Don’t go back and forth when using the block method. The best way to write your essay is to begin with a paragraph discussing all the facets of the first topic. Then, move on to another paragraph and talk through all the aspects of the second subject.
You can use both alternating and blocking techniques. Combining the two approaches is also an option. You can apply the alternating method in some paragraphs, then switch and use the block method. This method will help you offer a much deeper analysis of the subjects.
Have a reason for comparing the two things. Only select the points of comparison that resonate with your purpose.
Comparing and contrasting are essential analytical skills in academic writing. When your professor issues you with such an essay, their primary goal is to teach you how to:
- Engage in critical thinking
- See and make connections between words or ideas
- Move beyond mere descriptions or summaries to developing interesting analysis
- Get a deeper understanding of the subjects or items under comparison, their key features, and their interrelationships with each other.
Ultimately, your essay should enlighten readers by providing useful information.
Want to use ProWritingAid with your classroom? Download this free book now:

ProWritingAid Teacher’s Manual
Editing technology like prowritingaid provides immediate, personalized feedback that will help students to better understand grammar and writing techniques., in this guide , we walk you through exactly how to use prowritingaid in your classroom and give you tools and templates for creating a rigorous, effective independent writing practice with your students..
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Walter Akolo
Walter Akolo is a freelance writer, internet marketer, trainer, and blogger for hire. He loves helping businesses increase their reach and conversion through excellent and engaging content. He has gotten millions of pageviews on his blog, FreelancerKenya, where he mentors writers. Check out his website walterakolo.com.
Get started with ProWritingAid

All features—half price
Save 50% on yearly and lifetime plans
this Black Friday.
Grab the discount while it lasts.
Visit our Help Center or let's stay in touch via:
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Compare and Contrast Essay

5-minute read
- 9th March 2021
In a compare and contrast essay , you look at the similarities and differences between two subjects. How do you write one, though? Key steps include:
- Pick two things to compare based on the assignment you were given.
- Brainstorm the similarities and differences between your chosen subjects.
- Choose a structure for your essay and plan how you will write it.
- Write up your comparison and use evidence to support your argument.
- Revise and proofread your essay to make sure it is perfect.
For more advice on each stage, check out our guide below.
1. Pick Two Subjects to Compare and Contrast
A compare and contrast assignment will ask you, unsurprisingly, to compare and contrast two things. In some cases, the assignment question will make this clear. For instance, if the assignment says “Compare how Mozart and Beethoven use melody,” you will have a very clear sense of what to write about!
Other times, you will have a choice of what to compare. In this case, you will want to pick two things that are similar enough to make a useful comparison.
For example, comparing Mozart and Beethoven makes sense because both are classical composers. This means there will be lots of points of comparison between them. But comparing Mozart to a Ferrari SF90 Stradale would just be confusing: one is a renowned composer and musician, the other is a high-end sports car, so they have very little in common that we could usefully compare.

At the same time, the things you pick should be different enough that you can find points of contrast. Were you asked to compare the calorific content of two types of fast food, for example, it might not make sense to compare hamburgers and cheeseburgers as they are too similar. But you could compare hamburgers and pizzas since both are forms of fast food but they differ in other respects.
As such, if you need to pick the subjects of your essay, read your assignment question carefully and try to find two things that will produce a helpful comparison.
2. Brainstorm Their Similarities and Differences
The next step is to brainstorm similarities and differences between your chosen subjects. You can do this as a simple list, but you could also use a Venn diagram .
This is a set of overlapping circles, each of which represents one subject. You can then add characteristics to each circle, with anything your subjects have in common going in the overlapping bit in the middle.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.

Once you’ve listed characteristics, you’ll need to pick out the similarities and differences relevant to your essay. If you were assigned a question, use this to guide your choices. Otherwise, look for features that seem surprising or interesting and plan your essay around these. The key is to pick points of comparison that help us to understand each thing better, or where the similarities and differences show us something that we might not have expected or noticed otherwise.
3. Choose a Structure for Your Essay
As with any essay, you will want to start with a short introduction where you introduce your topic and what you will argue. Beyond this, most compare and contrast essays are structured in one of two ways. Decide which approach to take before you write your essay outline :
- Divide by subject – Cover each subject in turn, looking at the key features you’ve identified in the previous step. You can then include a final section where you highlight what comparing the subjects tell us.
- Divide by individual points – Break your essay down into a series of sections. Each section will then focus on one of the key features you’ve identified, explaining the similarities and differences between your chosen subjects.
For instance, if you were comparing two novels, you could write about each novel in turn and then compare them at the end. Alternatively, you could structure your essay so that each section covers an individual idea (e.g., one on structure, one on characters, one on language), looking at how each book uses these things.
In either case, you will want to end on a conclusion where you summarize what the comparison has shown us about the two subjects.
4. Use Supporting Evidence for Your Argument
It is important that you also back up your statements with supporting evidence. In some cases, this will simply involve pointing to the features of each subject that you’re discussing (e.g., citing specific parts of the novels you’re comparing).
However, you can also do extra research to back up your arguments. Were you comparing two countries’ economic performance, for example, you could use statistics from other studies or reports to show the similarities and differences.
5. Proofread Your Compare and Contrast Essay
Once you have a first draft of your compare and contrast essay, take a break. If you have time, leave it overnight. The aim is to come back to it with fresh eyes and reread it, looking for any areas you could improve. After this, you can redraft your essay to make sure your argument is clear, concise, and convincing.
It is also a good idea to have your essay proofread before submitting it. This will ensure your work is error free and help you get the marks you deserve.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
Free email newsletter template.
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

COMMENTS
Although these two areas of academic writing have many similarities, the requirements are still significantly different. ... Research papers and essays are aimed at testing various skills of the student, following different structures, and having several requirements. An essay is a more creative writing task, which involves showing originality ...
It involves taking two or more subjects and analyzing the differences and similarities between them. You might find yourself comparing all kinds of things in an academic essay: historical figures, literary works, policies, research methods, etc. Doing so is an important part of constructing arguments.
similarities and differences: You discuss all the similarities between your subjects and then all the differences, or vice versa (differences first and then similarities). No matter which option you choose, you have to pay particular attention to topic sentences. Paragraphs in compare-and-contrast essays can get complicated, so it's crucial ...
The assessment of research papers often considers the writer's ability to contribute to the existing knowledge on the topic and their understanding of research methodologies. Conclusion. In conclusion, while essays and research papers share the common goal of evaluating a student's understanding of a particular topic, they differ in various ...
By assigning such essays, your instructors are encouraging you to make connections between texts or ideas, engage in critical thinking, and go beyond mere description or summary to generate interesting analysis: when you reflect on similarities and differences, you gain a deeper understanding of the items you are comparing, their relationship ...
A comparative essay explores the similarities and differences between subjects, allowing the writer to draw conclusions related to the topics of the material. This article outlines key strategies, such as using transitions, incorporating evidence, and maintaining a formal tone. ... as they may guide your subsequent research and analysis.
Start Your Research; Find Articles, Dissertations, and Books ; Verify Peer Review; Document Delivery Service (DDS) ... A compare and contrast paper discusses the similarities and differences between two or more topics. The paper should contain an introduction with a thesis statement, a body where the comparisons and contrasts are discussed, and ...
More differences and similarities between essays and research papers . Final Words. An essay and research paper are common types of academic writing assigned to high school, college, and university students. Essays are the shortest pieces of writing which show your understanding of a given topic during a research paper. The above difference ...
This method is best for short essays on simple topics. Most university-level essays will go point by point instead. Going Point by Point. Going point by point, or alternating, is the opposite essay structure from going subject by subject. This is ideal when you want to do more direct comparing and contrasting.
Brainstorm the similarities and differences between your chosen subjects. Choose a structure for your essay and plan how you will write it. Write up your comparison and use evidence to support your argument. Revise and proofread your essay to make sure it is perfect. For more advice on each stage, check out our guide below. 1.