
Quantitative Data Analysis 101
The lingo, methods and techniques, explained simply.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) and Kerryn Warren (PhD) | December 2020
Quantitative data analysis is one of those things that often strikes fear in students. It’s totally understandable – quantitative analysis is a complex topic, full of daunting lingo , like medians, modes, correlation and regression. Suddenly we’re all wishing we’d paid a little more attention in math class…
The good news is that while quantitative data analysis is a mammoth topic, gaining a working understanding of the basics isn’t that hard , even for those of us who avoid numbers and math . In this post, we’ll break quantitative analysis down into simple , bite-sized chunks so you can approach your research with confidence.

Overview: Quantitative Data Analysis 101
- What (exactly) is quantitative data analysis?
- When to use quantitative analysis
- How quantitative analysis works
The two “branches” of quantitative analysis
- Descriptive statistics 101
- Inferential statistics 101
- How to choose the right quantitative methods
- Recap & summary
What is quantitative data analysis?
Despite being a mouthful, quantitative data analysis simply means analysing data that is numbers-based – or data that can be easily “converted” into numbers without losing any meaning.
For example, category-based variables like gender, ethnicity, or native language could all be “converted” into numbers without losing meaning – for example, English could equal 1, French 2, etc.
This contrasts against qualitative data analysis, where the focus is on words, phrases and expressions that can’t be reduced to numbers. If you’re interested in learning about qualitative analysis, check out our post and video here .
What is quantitative analysis used for?
Quantitative analysis is generally used for three purposes.
- Firstly, it’s used to measure differences between groups . For example, the popularity of different clothing colours or brands.
- Secondly, it’s used to assess relationships between variables . For example, the relationship between weather temperature and voter turnout.
- And third, it’s used to test hypotheses in a scientifically rigorous way. For example, a hypothesis about the impact of a certain vaccine.
Again, this contrasts with qualitative analysis , which can be used to analyse people’s perceptions and feelings about an event or situation. In other words, things that can’t be reduced to numbers.
How does quantitative analysis work?
Well, since quantitative data analysis is all about analysing numbers , it’s no surprise that it involves statistics . Statistical analysis methods form the engine that powers quantitative analysis, and these methods can vary from pretty basic calculations (for example, averages and medians) to more sophisticated analyses (for example, correlations and regressions).
Sounds like gibberish? Don’t worry. We’ll explain all of that in this post. Importantly, you don’t need to be a statistician or math wiz to pull off a good quantitative analysis. We’ll break down all the technical mumbo jumbo in this post.
Need a helping hand?
As I mentioned, quantitative analysis is powered by statistical analysis methods . There are two main “branches” of statistical methods that are used – descriptive statistics and inferential statistics . In your research, you might only use descriptive statistics, or you might use a mix of both , depending on what you’re trying to figure out. In other words, depending on your research questions, aims and objectives . I’ll explain how to choose your methods later.
So, what are descriptive and inferential statistics?
Well, before I can explain that, we need to take a quick detour to explain some lingo. To understand the difference between these two branches of statistics, you need to understand two important words. These words are population and sample .
First up, population . In statistics, the population is the entire group of people (or animals or organisations or whatever) that you’re interested in researching. For example, if you were interested in researching Tesla owners in the US, then the population would be all Tesla owners in the US.
However, it’s extremely unlikely that you’re going to be able to interview or survey every single Tesla owner in the US. Realistically, you’ll likely only get access to a few hundred, or maybe a few thousand owners using an online survey. This smaller group of accessible people whose data you actually collect is called your sample .
So, to recap – the population is the entire group of people you’re interested in, and the sample is the subset of the population that you can actually get access to. In other words, the population is the full chocolate cake , whereas the sample is a slice of that cake.
So, why is this sample-population thing important?
Well, descriptive statistics focus on describing the sample , while inferential statistics aim to make predictions about the population, based on the findings within the sample. In other words, we use one group of statistical methods – descriptive statistics – to investigate the slice of cake, and another group of methods – inferential statistics – to draw conclusions about the entire cake. There I go with the cake analogy again…
With that out the way, let’s take a closer look at each of these branches in more detail.
Branch 1: Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics serve a simple but critically important role in your research – to describe your data set – hence the name. In other words, they help you understand the details of your sample . Unlike inferential statistics (which we’ll get to soon), descriptive statistics don’t aim to make inferences or predictions about the entire population – they’re purely interested in the details of your specific sample .
When you’re writing up your analysis, descriptive statistics are the first set of stats you’ll cover, before moving on to inferential statistics. But, that said, depending on your research objectives and research questions , they may be the only type of statistics you use. We’ll explore that a little later.
So, what kind of statistics are usually covered in this section?
Some common statistical tests used in this branch include the following:
- Mean – this is simply the mathematical average of a range of numbers.
- Median – this is the midpoint in a range of numbers when the numbers are arranged in numerical order. If the data set makes up an odd number, then the median is the number right in the middle of the set. If the data set makes up an even number, then the median is the midpoint between the two middle numbers.
- Mode – this is simply the most commonly occurring number in the data set.
- In cases where most of the numbers are quite close to the average, the standard deviation will be relatively low.
- Conversely, in cases where the numbers are scattered all over the place, the standard deviation will be relatively high.
- Skewness . As the name suggests, skewness indicates how symmetrical a range of numbers is. In other words, do they tend to cluster into a smooth bell curve shape in the middle of the graph, or do they skew to the left or right?
Feeling a bit confused? Let’s look at a practical example using a small data set.
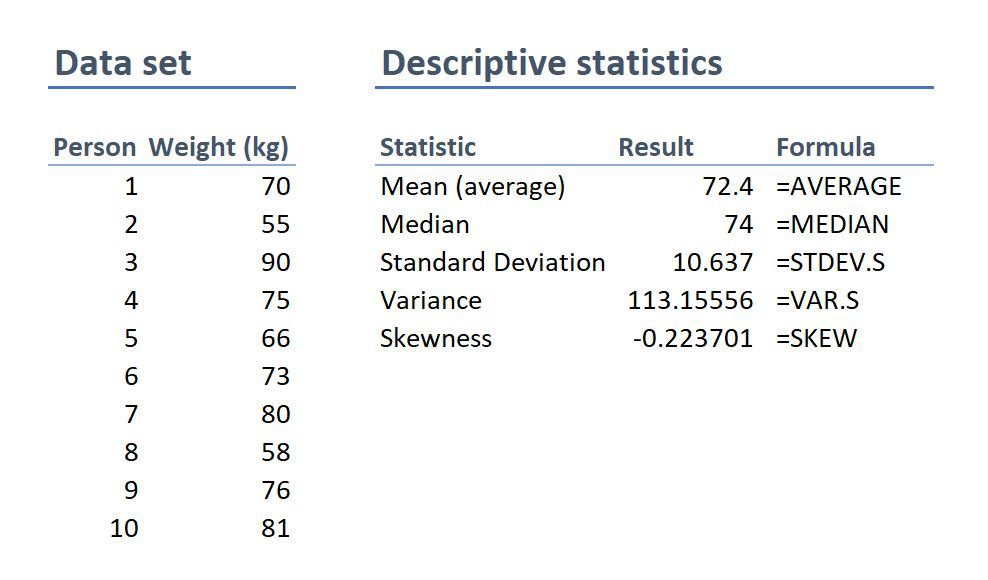
On the left-hand side is the data set. This details the bodyweight of a sample of 10 people. On the right-hand side, we have the descriptive statistics. Let’s take a look at each of them.
First, we can see that the mean weight is 72.4 kilograms. In other words, the average weight across the sample is 72.4 kilograms. Straightforward.
Next, we can see that the median is very similar to the mean (the average). This suggests that this data set has a reasonably symmetrical distribution (in other words, a relatively smooth, centred distribution of weights, clustered towards the centre).
In terms of the mode , there is no mode in this data set. This is because each number is present only once and so there cannot be a “most common number”. If there were two people who were both 65 kilograms, for example, then the mode would be 65.
Next up is the standard deviation . 10.6 indicates that there’s quite a wide spread of numbers. We can see this quite easily by looking at the numbers themselves, which range from 55 to 90, which is quite a stretch from the mean of 72.4.
And lastly, the skewness of -0.2 tells us that the data is very slightly negatively skewed. This makes sense since the mean and the median are slightly different.
As you can see, these descriptive statistics give us some useful insight into the data set. Of course, this is a very small data set (only 10 records), so we can’t read into these statistics too much. Also, keep in mind that this is not a list of all possible descriptive statistics – just the most common ones.
But why do all of these numbers matter?
While these descriptive statistics are all fairly basic, they’re important for a few reasons:
- Firstly, they help you get both a macro and micro-level view of your data. In other words, they help you understand both the big picture and the finer details.
- Secondly, they help you spot potential errors in the data – for example, if an average is way higher than you’d expect, or responses to a question are highly varied, this can act as a warning sign that you need to double-check the data.
- And lastly, these descriptive statistics help inform which inferential statistical techniques you can use, as those techniques depend on the skewness (in other words, the symmetry and normality) of the data.
Simply put, descriptive statistics are really important , even though the statistical techniques used are fairly basic. All too often at Grad Coach, we see students skimming over the descriptives in their eagerness to get to the more exciting inferential methods, and then landing up with some very flawed results.
Don’t be a sucker – give your descriptive statistics the love and attention they deserve!
Branch 2: Inferential Statistics
As I mentioned, while descriptive statistics are all about the details of your specific data set – your sample – inferential statistics aim to make inferences about the population . In other words, you’ll use inferential statistics to make predictions about what you’d expect to find in the full population.
What kind of predictions, you ask? Well, there are two common types of predictions that researchers try to make using inferential stats:
- Firstly, predictions about differences between groups – for example, height differences between children grouped by their favourite meal or gender.
- And secondly, relationships between variables – for example, the relationship between body weight and the number of hours a week a person does yoga.
In other words, inferential statistics (when done correctly), allow you to connect the dots and make predictions about what you expect to see in the real world population, based on what you observe in your sample data. For this reason, inferential statistics are used for hypothesis testing – in other words, to test hypotheses that predict changes or differences.

Of course, when you’re working with inferential statistics, the composition of your sample is really important. In other words, if your sample doesn’t accurately represent the population you’re researching, then your findings won’t necessarily be very useful.
For example, if your population of interest is a mix of 50% male and 50% female , but your sample is 80% male , you can’t make inferences about the population based on your sample, since it’s not representative. This area of statistics is called sampling, but we won’t go down that rabbit hole here (it’s a deep one!) – we’ll save that for another post .
What statistics are usually used in this branch?
There are many, many different statistical analysis methods within the inferential branch and it’d be impossible for us to discuss them all here. So we’ll just take a look at some of the most common inferential statistical methods so that you have a solid starting point.
First up are T-Tests . T-tests compare the means (the averages) of two groups of data to assess whether they’re statistically significantly different. In other words, do they have significantly different means, standard deviations and skewness.
This type of testing is very useful for understanding just how similar or different two groups of data are. For example, you might want to compare the mean blood pressure between two groups of people – one that has taken a new medication and one that hasn’t – to assess whether they are significantly different.
Kicking things up a level, we have ANOVA, which stands for “analysis of variance”. This test is similar to a T-test in that it compares the means of various groups, but ANOVA allows you to analyse multiple groups , not just two groups So it’s basically a t-test on steroids…
Next, we have correlation analysis . This type of analysis assesses the relationship between two variables. In other words, if one variable increases, does the other variable also increase, decrease or stay the same. For example, if the average temperature goes up, do average ice creams sales increase too? We’d expect some sort of relationship between these two variables intuitively , but correlation analysis allows us to measure that relationship scientifically .
Lastly, we have regression analysis – this is quite similar to correlation in that it assesses the relationship between variables, but it goes a step further to understand cause and effect between variables, not just whether they move together. In other words, does the one variable actually cause the other one to move, or do they just happen to move together naturally thanks to another force? Just because two variables correlate doesn’t necessarily mean that one causes the other.
Stats overload…
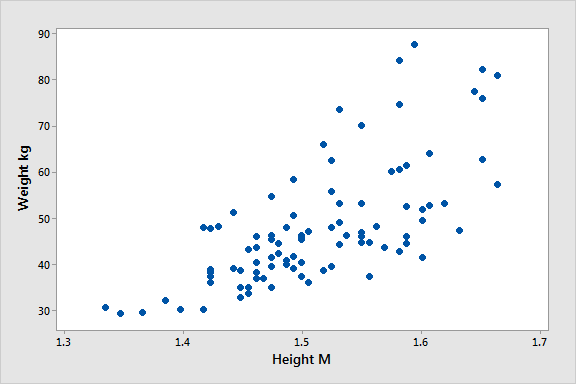
I hear you. To make this all a little more tangible, let’s take a look at an example of a correlation in action.
Here’s a scatter plot demonstrating the correlation (relationship) between weight and height. Intuitively, we’d expect there to be some relationship between these two variables, which is what we see in this scatter plot. In other words, the results tend to cluster together in a diagonal line from bottom left to top right.
As I mentioned, these are are just a handful of inferential techniques – there are many, many more. Importantly, each statistical method has its own assumptions and limitations.
For example, some methods only work with normally distributed (parametric) data, while other methods are designed specifically for non-parametric data. And that’s exactly why descriptive statistics are so important – they’re the first step to knowing which inferential techniques you can and can’t use.

How to choose the right analysis method
To choose the right statistical methods, you need to think about two important factors :
- The type of quantitative data you have (specifically, level of measurement and the shape of the data). And,
- Your research questions and hypotheses
Let’s take a closer look at each of these.
Factor 1 – Data type
The first thing you need to consider is the type of data you’ve collected (or the type of data you will collect). By data types, I’m referring to the four levels of measurement – namely, nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio. If you’re not familiar with this lingo, check out the video below.
Why does this matter?
Well, because different statistical methods and techniques require different types of data. This is one of the “assumptions” I mentioned earlier – every method has its assumptions regarding the type of data.
For example, some techniques work with categorical data (for example, yes/no type questions, or gender or ethnicity), while others work with continuous numerical data (for example, age, weight or income) – and, of course, some work with multiple data types.
If you try to use a statistical method that doesn’t support the data type you have, your results will be largely meaningless . So, make sure that you have a clear understanding of what types of data you’ve collected (or will collect). Once you have this, you can then check which statistical methods would support your data types here .
If you haven’t collected your data yet, you can work in reverse and look at which statistical method would give you the most useful insights, and then design your data collection strategy to collect the correct data types.
Another important factor to consider is the shape of your data . Specifically, does it have a normal distribution (in other words, is it a bell-shaped curve, centred in the middle) or is it very skewed to the left or the right? Again, different statistical techniques work for different shapes of data – some are designed for symmetrical data while others are designed for skewed data.
This is another reminder of why descriptive statistics are so important – they tell you all about the shape of your data.
Factor 2: Your research questions
The next thing you need to consider is your specific research questions, as well as your hypotheses (if you have some). The nature of your research questions and research hypotheses will heavily influence which statistical methods and techniques you should use.
If you’re just interested in understanding the attributes of your sample (as opposed to the entire population), then descriptive statistics are probably all you need. For example, if you just want to assess the means (averages) and medians (centre points) of variables in a group of people.
On the other hand, if you aim to understand differences between groups or relationships between variables and to infer or predict outcomes in the population, then you’ll likely need both descriptive statistics and inferential statistics.
So, it’s really important to get very clear about your research aims and research questions, as well your hypotheses – before you start looking at which statistical techniques to use.
Never shoehorn a specific statistical technique into your research just because you like it or have some experience with it. Your choice of methods must align with all the factors we’ve covered here.
Time to recap…
You’re still with me? That’s impressive. We’ve covered a lot of ground here, so let’s recap on the key points:
- Quantitative data analysis is all about analysing number-based data (which includes categorical and numerical data) using various statistical techniques.
- The two main branches of statistics are descriptive statistics and inferential statistics . Descriptives describe your sample, whereas inferentials make predictions about what you’ll find in the population.
- Common descriptive statistical methods include mean (average), median , standard deviation and skewness .
- Common inferential statistical methods include t-tests , ANOVA , correlation and regression analysis.
- To choose the right statistical methods and techniques, you need to consider the type of data you’re working with , as well as your research questions and hypotheses.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

74 Comments
Hi, I have read your article. Such a brilliant post you have created.
Thank you for the feedback. Good luck with your quantitative analysis.
Thank you so much.
Thank you so much. I learnt much well. I love your summaries of the concepts. I had love you to explain how to input data using SPSS
Amazing and simple way of breaking down quantitative methods.
This is beautiful….especially for non-statisticians. I have skimmed through but I wish to read again. and please include me in other articles of the same nature when you do post. I am interested. I am sure, I could easily learn from you and get off the fear that I have had in the past. Thank you sincerely.
Send me every new information you might have.
i need every new information
Thank you for the blog. It is quite informative. Dr Peter Nemaenzhe PhD
It is wonderful. l’ve understood some of the concepts in a more compréhensive manner
Your article is so good! However, I am still a bit lost. I am doing a secondary research on Gun control in the US and increase in crime rates and I am not sure which analysis method I should use?
Based on the given learning points, this is inferential analysis, thus, use ‘t-tests, ANOVA, correlation and regression analysis’
Well explained notes. Am an MPH student and currently working on my thesis proposal, this has really helped me understand some of the things I didn’t know.
I like your page..helpful
wonderful i got my concept crystal clear. thankyou!!
This is really helpful , thank you
Thank you so much this helped
Wonderfully explained
thank u so much, it was so informative
THANKYOU, this was very informative and very helpful
This is great GRADACOACH I am not a statistician but I require more of this in my thesis
Include me in your posts.
This is so great and fully useful. I would like to thank you again and again.
Glad to read this article. I’ve read lot of articles but this article is clear on all concepts. Thanks for sharing.
Thank you so much. This is a very good foundation and intro into quantitative data analysis. Appreciate!
You have a very impressive, simple but concise explanation of data analysis for Quantitative Research here. This is a God-send link for me to appreciate research more. Thank you so much!
Avery good presentation followed by the write up. yes you simplified statistics to make sense even to a layman like me. Thank so much keep it up. The presenter did ell too. i would like more of this for Qualitative and exhaust more of the test example like the Anova.
This is a very helpful article, couldn’t have been clearer. Thank you.
Awesome and phenomenal information.Well done
The video with the accompanying article is super helpful to demystify this topic. Very well done. Thank you so much.
thank you so much, your presentation helped me a lot
I don’t know how should I express that ur article is saviour for me 🥺😍
It is well defined information and thanks for sharing. It helps me a lot in understanding the statistical data.
I gain a lot and thanks for sharing brilliant ideas, so wish to be linked on your email update.
Very helpful and clear .Thank you Gradcoach.
Thank for sharing this article, well organized and information presented are very clear.
VERY INTERESTING AND SUPPORTIVE TO NEW RESEARCHERS LIKE ME. AT LEAST SOME BASICS ABOUT QUANTITATIVE.
An outstanding, well explained and helpful article. This will help me so much with my data analysis for my research project. Thank you!
wow this has just simplified everything i was scared of how i am gonna analyse my data but thanks to you i will be able to do so
simple and constant direction to research. thanks
This is helpful
Great writing!! Comprehensive and very helpful.
Do you provide any assistance for other steps of research methodology like making research problem testing hypothesis report and thesis writing?
Thank you so much for such useful article!
Amazing article. So nicely explained. Wow
Very insightfull. Thanks
I am doing a quality improvement project to determine if the implementation of a protocol will change prescribing habits. Would this be a t-test?
The is a very helpful blog, however, I’m still not sure how to analyze my data collected. I’m doing a research on “Free Education at the University of Guyana”
tnx. fruitful blog!
So I am writing exams and would like to know how do establish which method of data analysis to use from the below research questions: I am a bit lost as to how I determine the data analysis method from the research questions.
Do female employees report higher job satisfaction than male employees with similar job descriptions across the South African telecommunications sector? – I though that maybe Chi Square could be used here. – Is there a gender difference in talented employees’ actual turnover decisions across the South African telecommunications sector? T-tests or Correlation in this one. – Is there a gender difference in the cost of actual turnover decisions across the South African telecommunications sector? T-tests or Correlation in this one. – What practical recommendations can be made to the management of South African telecommunications companies on leveraging gender to mitigate employee turnover decisions?
Your assistance will be appreciated if I could get a response as early as possible tomorrow
This was quite helpful. Thank you so much.
wow I got a lot from this article, thank you very much, keep it up
Thanks for yhe guidance. Can you send me this guidance on my email? To enable offline reading?
Thank you very much, this service is very helpful.
Every novice researcher needs to read this article as it puts things so clear and easy to follow. Its been very helpful.
Wonderful!!!! you explained everything in a way that anyone can learn. Thank you!!
I really enjoyed reading though this. Very easy to follow. Thank you
Many thanks for your useful lecture, I would be really appreciated if you could possibly share with me the PPT of presentation related to Data type?
Thank you very much for sharing, I got much from this article
This is a very informative write-up. Kindly include me in your latest posts.
Very interesting mostly for social scientists
Thank you so much, very helpfull
You’re welcome 🙂
woow, its great, its very informative and well understood because of your way of writing like teaching in front of me in simple languages.
I have been struggling to understand a lot of these concepts. Thank you for the informative piece which is written with outstanding clarity.
very informative article. Easy to understand
Beautiful read, much needed.
Always greet intro and summary. I learn so much from GradCoach
Quite informative. Simple and clear summary.
I thoroughly enjoyed reading your informative and inspiring piece. Your profound insights into this topic truly provide a better understanding of its complexity. I agree with the points you raised, especially when you delved into the specifics of the article. In my opinion, that aspect is often overlooked and deserves further attention.
Absolutely!!! Thank you
Thank you very much for this post. It made me to understand how to do my data analysis.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is Quantitative Research? | Definition & Methods
What Is Quantitative Research? | Definition & Methods
Published on 4 April 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 10 October 2022.
Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analysing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalise results to wider populations.
Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research , which involves collecting and analysing non-numerical data (e.g. text, video, or audio).
Quantitative research is widely used in the natural and social sciences: biology, chemistry, psychology, economics, sociology, marketing, etc.
- What is the demographic makeup of Singapore in 2020?
- How has the average temperature changed globally over the last century?
- Does environmental pollution affect the prevalence of honey bees?
- Does working from home increase productivity for people with long commutes?
Table of contents
Quantitative research methods, quantitative data analysis, advantages of quantitative research, disadvantages of quantitative research, frequently asked questions about quantitative research.
You can use quantitative research methods for descriptive, correlational or experimental research.
- In descriptive research , you simply seek an overall summary of your study variables.
- In correlational research , you investigate relationships between your study variables.
- In experimental research , you systematically examine whether there is a cause-and-effect relationship between variables.
Correlational and experimental research can both be used to formally test hypotheses , or predictions, using statistics. The results may be generalised to broader populations based on the sampling method used.
To collect quantitative data, you will often need to use operational definitions that translate abstract concepts (e.g., mood) into observable and quantifiable measures (e.g., self-ratings of feelings and energy levels).
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once data is collected, you may need to process it before it can be analysed. For example, survey and test data may need to be transformed from words to numbers. Then, you can use statistical analysis to answer your research questions .
Descriptive statistics will give you a summary of your data and include measures of averages and variability. You can also use graphs, scatter plots and frequency tables to visualise your data and check for any trends or outliers.
Using inferential statistics , you can make predictions or generalisations based on your data. You can test your hypothesis or use your sample data to estimate the population parameter .
You can also assess the reliability and validity of your data collection methods to indicate how consistently and accurately your methods actually measured what you wanted them to.
Quantitative research is often used to standardise data collection and generalise findings . Strengths of this approach include:
- Replication
Repeating the study is possible because of standardised data collection protocols and tangible definitions of abstract concepts.
- Direct comparisons of results
The study can be reproduced in other cultural settings, times or with different groups of participants. Results can be compared statistically.
- Large samples
Data from large samples can be processed and analysed using reliable and consistent procedures through quantitative data analysis.
- Hypothesis testing
Using formalised and established hypothesis testing procedures means that you have to carefully consider and report your research variables, predictions, data collection and testing methods before coming to a conclusion.
Despite the benefits of quantitative research, it is sometimes inadequate in explaining complex research topics. Its limitations include:
- Superficiality
Using precise and restrictive operational definitions may inadequately represent complex concepts. For example, the concept of mood may be represented with just a number in quantitative research, but explained with elaboration in qualitative research.
- Narrow focus
Predetermined variables and measurement procedures can mean that you ignore other relevant observations.
- Structural bias
Despite standardised procedures, structural biases can still affect quantitative research. Missing data , imprecise measurements or inappropriate sampling methods are biases that can lead to the wrong conclusions.
- Lack of context
Quantitative research often uses unnatural settings like laboratories or fails to consider historical and cultural contexts that may affect data collection and results.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
In mixed methods research , you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question .
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organisations.
Operationalisation means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations.
For example, the concept of social anxiety isn’t directly observable, but it can be operationally defined in terms of self-rating scores, behavioural avoidance of crowded places, or physical anxiety symptoms in social situations.
Before collecting data , it’s important to consider how you will operationalise the variables that you want to measure.
Reliability and validity are both about how well a method measures something:
- Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure (whether the results can be reproduced under the same conditions).
- Validity refers to the accuracy of a measure (whether the results really do represent what they are supposed to measure).
If you are doing experimental research , you also have to consider the internal and external validity of your experiment.
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2022, October 10). What Is Quantitative Research? | Definition & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 22 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/introduction-to-quantitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Quantitative Research
Try Qualtrics for free
Your ultimate guide to quantitative research.
12 min read You may be already using quantitative research and want to check your understanding, or you may be starting from the beginning. Here’s an exploration of this research method and how you can best use it for maximum effect for your business.
You may be already using quantitative research and want to check your understanding, or you may be starting from the beginning. Here’s an exploration of this research method and how you can best use it for maximum effect for your business.
What is quantitative research?
Quantitative is the research method of collecting quantitative data – this is data that can be converted into numbers or numerical data, which can be easily quantified, compared, and analyzed.
Quantitative research deals with primary and secondary sources where data is represented in numerical form. This can include closed-question poll results, statistics, and census information or demographic data .
Quantitative data tends to be used when researchers are interested in understanding a particular moment in time and examining data sets over time to find trends and patterns.
To collect numerical data, surveys are often employed as one of the main research methods to source first-hand information in primary research . Quantitative research can also come from third-party research studies .
Quantitative research is widely used in the realms of social sciences, such as biology, chemistry, psychology, economics, sociology, and marketing .
Research teams collect data that is significant to proving or disproving a hypothesis research question – known as the research objective. When they collect quantitative data, researchers will aim to use a sample size that is representative of the total population of the target market they’re interested in.
Then the data collected will be manually or automatically stored and compared for insights.
Free eBook: The ultimate guide to conducting market research
Quantitative vs qualitative research
While the quantitative research definition focuses on numerical data, qualitative research is defined as data that supplies non-numerical information.
Quantitative research focuses on the thoughts, feelings, and values of a participant , to understand why people act in the way they do . They result in data types like quotes, symbols, images, and written testimonials.
These data types tell researchers subjective information, which can help us assign people into categories, such as a participant’s religion, gender , social class, political alignment, likely favored products to buy, or their preferred training learning style.
For this reason, qualitative research is often used in social research, as this gives a window into the behavior and actions of people.
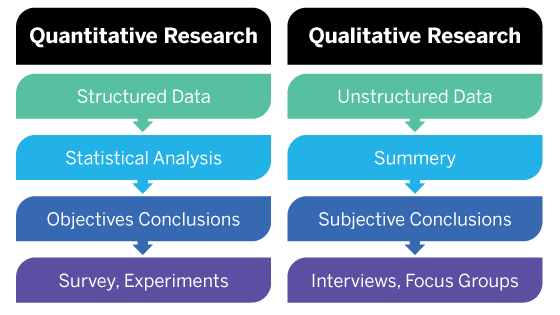
In general, if you’re interested in measuring something or testing a hypothesis, use quantitative methods. If you want to explore ideas, thoughts, and meanings, use qualitative methods.
However, quantitative and qualitative research methods are both recommended when you’re looking to understand a point in time, while also finding out the reason behind the facts.
Quantitative research data collection methods
Quantitative research methods can use structured research instruments like:
- Surveys : A survey is a simple-to-create and easy-to-distribute research method , which helps gather information from large groups of participants quickly. Traditionally, paper-based surveys can now be made online, so costs can stay quite low.
Quantitative questions tend to be closed questions that ask for a numerical result, based on a range of options, or a yes/no answer that can be tallied quickly.
- Face-to-face or phone interviews: Interviews are a great way to connect with participants , though they require time from the research team to set up and conduct.
Researchers may also have issues connecting with participants in different geographical regions . The researcher uses a set of predefined close-ended questions, which ask for yes/no or numerical values.
- Polls: Polls can be a shorter version of surveys , used to get a ‘flavor’ of what the current situation is with participants. Online polls can be shared easily, though polls are best used with simple questions that request a range or a yes/no answer.
Quantitative data is the opposite of qualitative research, another dominant framework for research in the social sciences, explored further below.
Quantitative data types
Quantitative research methods often deliver the following data types:
- Test Scores
- Percent of training course completed
- Performance score out of 100
- Number of support calls active
- Customer Net Promoter Score (NPS)
When gathering numerical data, the emphasis is on how specific the data is, and whether they can provide an indication of what ‘is’ at the time of collection. Pre-existing statistical data can tell us what ‘was’ for the date and time range that it represented
Quantitative research design methods (with examples)
Quantitative research has a number of quantitative research designs you can choose from:
Descriptive
This design type describes the state of a data type is telling researchers, in its native environment. There won’t normally be a clearly defined research question to start with. Instead, data analysis will suggest a conclusion , which can become the hypothesis to investigate further.
Examples of descriptive quantitative design include:
- A description of child’s Christmas gifts they received that year
- A description of what businesses sell the most of during Black Friday
- A description of a product issue being experienced by a customer
Correlational
This design type looks at two or more data types, the relationship between them, and the extent that they differ or align. This does not look at the causal links deeper – instead statistical analysis looks at the variables in a natural environment.
Examples of correlational quantitative design include:
- The relationship between a child’s Christmas gifts and their perceived happiness level
- The relationship between a business’ sales during Black Friday and the total revenue generated over the year
- The relationship between a customer’s product issue and the reputation of the product
Causal-Comparative/Quasi-Experimental
This design type looks at two or more data types and tries to explain any relationship and differences between them, using a cause-effect analysis. The research is carried out in a near-natural environment, where information is gathered from two groups – a naturally occurring group that matches the original natural environment, and one that is not naturally present.
This allows for causal links to be made, though they might not be correct, as other variables may have an impact on results.
Examples of causal-comparative/quasi-experimental quantitative design include:
- The effect of children’s Christmas gifts on happiness
- The effect of Black Friday sales figures on the productivity of company yearly sales
- The effect of product issues on the public perception of a product
Experimental Research
This design type looks to make a controlled environment in which two or more variables are observed to understand the exact cause and effect they have. This becomes a quantitative research study, where data types are manipulated to assess the effect they have. The participants are not naturally occurring groups, as the setting is no longer natural. A quantitative research study can help pinpoint the exact conditions in which variables impact one another.
Examples of experimental quantitative design include:
- The effect of children’s Christmas gifts on a child’s dopamine (happiness) levels
- The effect of Black Friday sales on the success of the company
- The effect of product issues on the perceived reliability of the product
Quantitative research methods need to be carefully considered, as your data collection of a data type can be used to different effects. For example, statistics can be descriptive or correlational (or inferential). Descriptive statistics help us to summarize our data, while inferential statistics help infer conclusions about significant differences.
Advantages of quantitative research
- Easy to do : Doing quantitative research is more straightforward, as the results come in numerical format, which can be more easily interpreted.
- Less interpretation : Due to the factual nature of the results, you will be able to accept or reject your hypothesis based on the numerical data collected.
- Less bias : There are higher levels of control that can be applied to the research, so bias can be reduced , making your data more reliable and precise.
Disadvantages of quantitative research
- Can’t understand reasons: Quantitative research doesn’t always tell you the full story, meaning you won’t understand the context – or the why, of the data you see, why do you see the results you have uncovered?
- Useful for simpler situations: Quantitative research on its own is not great when dealing with complex issues. In these cases, quantitative research may not be enough.
How to use quantitative research to your business’s advantage
Quantitative research methods may help in areas such as:
- Identifying which advert or landing page performs better
- Identifying how satisfied your customers are
- How many customers are likely to recommend you
- Tracking how your brand ranks in awareness and customer purchase intent
- Learn what consumers are likely to buy from your brand.
6 steps to conducting good quantitative research
Businesses can benefit from quantitative research by using it to evaluate the impact of data types. There are several steps to this:
- Define your problem or interest area : What do you observe is happening and is it frequent? Identify the data type/s you’re observing.
- Create a hypothesis : Ask yourself what could be the causes for the situation with those data types.
- Plan your quantitative research : Use structured research instruments like surveys or polls to ask questions that test your hypothesis.
- Data Collection : Collect quantitative data and understand what your data types are telling you. Using data collected on different types over long time periods can give you information on patterns.
- Data analysis : Does your information support your hypothesis? (You may need to redo the research with other variables to see if the results improve)
- Effectively present data : Communicate the results in a clear and concise way to help other people understand the findings.
How Qualtrics products can enhance & simplify the quantitative research process
The Qualtrics XM system gives you an all-in-one, integrated solution to help you all the way through conducting quantitative research. From survey creation and data collection to statistical analysis and data reporting, it can help all your internal teams gain insights from your numerical data.
Quantitative methods are catered to your business through templates or advanced survey designs. While you can manually collect data and conduct data analysis in a spreadsheet program, this solution helps you automate the process of quantitative research, saving you time and administration work.
Using computational techniques helps you to avoid human errors, and participant results come in are already incorporated into the analysis in real-time.
Our key tools, Stats IQ™ and Driver IQ™ make analyzing numerical data easy and simple. Choose to highlight key findings based on variables or highlight statistically insignificant findings. The choice is yours.
Some examples of your workspace in action, using drag and drop to create fast data visualizations quickly:
Related resources
Market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, qualitative vs quantitative research 13 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
Quantitative Research
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 13 January 2019
- Cite this reference work entry

- Leigh A. Wilson 2 , 3
4223 Accesses
4 Citations
Quantitative research methods are concerned with the planning, design, and implementation of strategies to collect and analyze data. Descartes, the seventeenth-century philosopher, suggested that how the results are achieved is often more important than the results themselves, as the journey taken along the research path is a journey of discovery. High-quality quantitative research is characterized by the attention given to the methods and the reliability of the tools used to collect the data. The ability to critique research in a systematic way is an essential component of a health professional’s role in order to deliver high quality, evidence-based healthcare. This chapter is intended to provide a simple overview of the way new researchers and health practitioners can understand and employ quantitative methods. The chapter offers practical, realistic guidance in a learner-friendly way and uses a logical sequence to understand the process of hypothesis development, study design, data collection and handling, and finally data analysis and interpretation.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Babbie ER. The practice of social research. 14th ed. Belmont: Wadsworth Cengage; 2016.
Google Scholar
Descartes. Cited in Halverston, W. (1976). In: A concise introduction to philosophy, 3rd ed. New York: Random House; 1637.
Doll R, Hill AB. The mortality of doctors in relation to their smoking habits. BMJ. 1954;328(7455):1529–33. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.328.7455.1529 .
Article Google Scholar
Liamputtong P. Research methods in health: foundations for evidence-based practice. 3rd ed. Melbourne: Oxford University Press; 2017.
McNabb DE. Research methods in public administration and nonprofit management: quantitative and qualitative approaches. 2nd ed. New York: Armonk; 2007.
Merriam-Webster. Dictionary. http://www.merriam-webster.com . Accessed 20th December 2017.
Olesen Larsen P, von Ins M. The rate of growth in scientific publication and the decline in coverage provided by Science Citation Index. Scientometrics. 2010;84(3):575–603.
Pannucci CJ, Wilkins EG. Identifying and avoiding bias in research. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126(2):619–25. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181de24bc .
Petrie A, Sabin C. Medical statistics at a glance. 2nd ed. London: Blackwell Publishing; 2005.
Portney LG, Watkins MP. Foundations of clinical research: applications to practice. 3rd ed. New Jersey: Pearson Publishing; 2009.
Sheehan J. Aspects of research methodology. Nurse Educ Today. 1986;6:193–203.
Wilson LA, Black DA. Health, science research and research methods. Sydney: McGraw Hill; 2013.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Science and Health, Western Sydney University, Penrith, NSW, Australia
Leigh A. Wilson
Faculty of Health Science, Discipline of Behavioural and Social Sciences in Health, University of Sydney, Lidcombe, NSW, Australia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Leigh A. Wilson .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Pranee Liamputtong
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Wilson, L.A. (2019). Quantitative Research. In: Liamputtong, P. (eds) Handbook of Research Methods in Health Social Sciences. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5251-4_54
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5251-4_54
Published : 13 January 2019
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-10-5250-7
Online ISBN : 978-981-10-5251-4
eBook Packages : Social Sciences Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
Quantitative Research
What is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research is the methodology which researchers use to test theories about people’s attitudes and behaviors based on numerical and statistical evidence. Researchers sample a large number of users (e.g., through surveys) to indirectly obtain measurable, bias-free data about users in relevant situations.
“Quantification clarifies issues which qualitative analysis leaves fuzzy. It is more readily contestable and likely to be contested. It sharpens scholarly discussion, sparks off rival hypotheses, and contributes to the dynamics of the research process.” — Angus Maddison, Notable scholar of quantitative macro-economic history
- Transcript loading…
See how quantitative research helps reveal cold, hard facts about users which you can interpret and use to improve your designs.
Use Quantitative Research to Find Mathematical Facts about Users
Quantitative research is a subset of user experience (UX) research . Unlike its softer, more individual-oriented “counterpart”, qualitative research , quantitative research means you collect statistical/numerical data to draw generalized conclusions about users’ attitudes and behaviors . Compare and contrast quantitative with qualitative research, below:
Qualitative Research
You Aim to Determine
The “what”, “where” & “when” of the users’ needs & problems – to help keep your project’s focus on track during development
The “why” – to get behind how users approach their problems in their world
Highly structured (e.g., surveys) – to gather data about what users do & find patterns in large user groups
Loosely structured (e.g., contextual inquiries) – to learn why users behave how they do & explore their opinions
Number of Representative Users
Ideally 30+
Often around 5
Level of Contact with Users
Less direct & more remote (e.g., analytics)
More direct & less remote (e.g., usability testing to examine users’ stress levels when they use your design)
Statistically
Reliable – if you have enough test users
Less reliable, with need for great care with handling non-numerical data (e.g., opinions), as your own opinions might influence findings
Quantitative research is often best done from early on in projects since it helps teams to optimally direct product development and avoid costly design mistakes later. As you typically get user data from a distance—i.e., without close physical contact with users—also applying qualitative research will help you investigate why users think and feel the ways they do. Indeed, in an iterative design process quantitative research helps you test the assumptions you and your design team develop from your qualitative research. Regardless of the method you use, with proper care you can gather objective and unbiased data – information which you can complement with qualitative approaches to build a fuller understanding of your target users. From there, you can work towards firmer conclusions and drive your design process towards a more realistic picture of how target users will ultimately receive your product.

Quantitative analysis helps you test your assumptions and establish clearer views of your users in their various contexts.
Quantitative Research Methods You Can Use to Guide Optimal Designs
There are many quantitative research methods, and they help uncover different types of information on users. Some methods, such as A/B testing, are typically done on finished products, while others such as surveys could be done throughout a project’s design process. Here are some of the most helpful methods:
A/B testing – You test two or more versions of your design on users to find the most effective. Each variation differs by just one feature and may or may not affect how users respond. A/B testing is especially valuable for testing assumptions you’ve drawn from qualitative research. The only potential concerns here are scale—in that you’ll typically need to conduct it on thousands of users—and arguably more complexity in terms of considering the statistical significance involved.
Analytics – With tools such as Google Analytics, you measure metrics (e.g., page views, click-through rates) to build a picture (e.g., “How many users take how long to complete a task?”).
Desirability Studies – You measure an aspect of your product (e.g., aesthetic appeal) by typically showing it to participants and asking them to select from a menu of descriptive words. Their responses can reveal powerful insights (e.g., 78% associate the product/brand with “fashionable”).
Surveys and Questionnaires – When you ask for many users’ opinions, you will gain massive amounts of information. Keep in mind that you’ll have data about what users say they do, as opposed to insights into what they do . You can get more reliable results if you incentivize your participants well and use the right format.
Tree Testing – You remove the user interface so users must navigate the site and complete tasks using links alone. This helps you see if an issue is related to the user interface or information architecture.
Another powerful benefit of conducting quantitative research is that you can keep your stakeholders’ support with hard facts and statistics about your design’s performance—which can show what works well and what needs improvement—and prove a good return on investment. You can also produce reports to check statistics against different versions of your product and your competitors’ products.
Most quantitative research methods are relatively cheap. Since no single research method can help you answer all your questions, it’s vital to judge which method suits your project at the time/stage. Remember, it’s best to spend appropriately on a combination of quantitative and qualitative research from early on in development. Design improvements can be costly, and so you can estimate the value of implementing changes when you get the statistics to suggest that these changes will improve usability. Overall, you want to gather measurements objectively, where your personality, presence and theories won’t create bias.
Learn More about Quantitative Research
Take our User Research course to see how to get the most from quantitative research.
See how quantitative research methods fit into your design research landscape .
This insightful piece shows the value of pairing quantitative with qualitative research .
Find helpful tips on combining quantitative research methods in mixed methods research .
Questions related to Quantitative Research
Qualitative and quantitative research differ primarily in the data they produce. Quantitative research yields numerical data to test hypotheses and quantify patterns. It's precise and generalizable. Qualitative research, on the other hand, generates non-numerical data and explores meanings, interpretations, and deeper insights. Watch our video featuring Professor Alan Dix on different types of research methods.
This video elucidates the nuances and applications of both research types in the design field.
In quantitative research, determining a good sample size is crucial for the reliability of the results. William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm, emphasizes the importance of statistical significance with an example in our video.
He illustrates that even with varying results between design choices, we need to discern whether the differences are statistically significant or products of chance. This ensures the validity of the results, allowing for more accurate interpretations. Statistical tools like chi-square tests can aid in analyzing the results effectively. To delve deeper into these concepts, take William Hudson’s Data-Driven Design: Quantitative UX Research Course .
Quantitative research is crucial as it provides precise, numerical data that allows for high levels of statistical inference. Our video from William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm, highlights the importance of analytics in examining existing solutions.
Quantitative methods, like analytics and A/B testing, are pivotal for identifying areas for improvement, understanding user behaviors, and optimizing user experiences based on solid, empirical evidence. This empirical nature ensures that the insights derived are reliable, allowing for practical improvements and innovations. Perhaps most importantly, numerical data is useful to secure stakeholder buy-in and defend design decisions and proposals. Explore this approach in our Data-Driven Design: Quantitative Research for UX Research course and learn from William Hudson’s detailed explanations of when and why to use analytics in the research process.
After establishing initial requirements, statistical data is crucial for informed decisions through quantitative research. William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm, sheds light on the role of quantitative research throughout a typical project lifecycle in this video:
During the analysis and design phases, quantitative research helps validate user requirements and understand user behaviors. Surveys and analytics are standard tools, offering insights into user preferences and design efficacy. Quantitative research can also be used in early design testing, allowing for optimal design modifications based on user interactions and feedback, and it’s fundamental for A/B and multivariate testing once live solutions are available.
To write a compelling quantitative research question:
Create clear, concise, and unambiguous questions that address one aspect at a time.
Use common, short terms and provide explanations for unusual words.
Avoid leading, compound, and overlapping queries and ensure that questions are not vague or broad.
According to our video by William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm, quality and respondent understanding are vital in forming good questions.
He emphasizes the importance of addressing specific aspects and avoiding intimidating and confusing elements, such as extensive question grids or ranking questions, to ensure participant engagement and accurate responses. For more insights, see the article Writing Good Questions for Surveys .
Survey research is typically quantitative, collecting numerical data and statistical analysis to make generalizable conclusions. However, it can also have qualitative elements, mainly when it includes open-ended questions, allowing for expressive responses. Our video featuring the CEO of Syntagm, William Hudson, provides in-depth insights into when and how to effectively utilize surveys in the product or service lifecycle, focusing on user satisfaction and potential improvements.
He emphasizes the importance of surveys in triangulating data to back up qualitative research findings, ensuring we have a complete understanding of the user's requirements and preferences.
Descriptive research focuses on describing the subject being studied and getting answers to questions like what, where, when, and who of the research question. However, it doesn’t include the answers to the underlying reasons, or the “why” behind the answers obtained from the research. We can use both f qualitative and quantitative methods to conduct descriptive research. Descriptive research does not describe the methods, but rather the data gathered through the research (regardless of the methods used).
When we use quantitative research and gather numerical data, we can use statistical analysis to understand relationships between different variables. Here’s William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm with more on correlation and how we can apply tests such as Pearson’s r and Spearman Rank Coefficient to our data.
This helps interpret phenomena such as user experience by analyzing session lengths and conversion values, revealing whether variables like time spent on a page affect checkout values, for example.
Random Sampling: Each individual in the population has an equitable opportunity to be chosen, which minimizes biases and simplifies analysis.
Systematic Sampling: Selecting every k-th item from a list after a random start. It's simpler and faster than random sampling when dealing with large populations.
Stratified Sampling: Segregate the population into subgroups or strata according to comparable characteristics. Then, samples are taken randomly from each stratum.
Cluster Sampling: Divide the population into clusters and choose a random sample.
Multistage Sampling: Various sampling techniques are used at different stages to collect detailed information from diverse populations.
Convenience Sampling: The researcher selects the sample based on availability and willingness to participate, which may only represent part of the population.
Quota Sampling: Segment the population into subgroups, and samples are non-randomly selected to fulfill a predetermined quota from each subset.
These are just a few techniques, and choosing the right one depends on your research question, discipline, resource availability, and the level of accuracy required. In quantitative research, there isn't a one-size-fits-all sampling technique; choosing a method that aligns with your research goals and population is critical. However, a well-planned strategy is essential to avoid wasting resources and time, as highlighted in our video featuring William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm.
He emphasizes the importance of recruiting participants meticulously, ensuring their engagement and the quality of their responses. Accurate and thoughtful participant responses are crucial for obtaining reliable results. William also sheds light on dealing with failing participants and scrutinizing response quality to refine the outcomes.
The 4 types of quantitative research are Descriptive, Correlational, Causal-Comparative/Quasi-Experimental, and Experimental Research. Descriptive research aims to depict ‘what exists’ clearly and precisely. Correlational research examines relationships between variables. Causal-comparative research investigates the cause-effect relationship between variables. Experimental research explores causal relationships by manipulating independent variables. To gain deeper insights into quantitative research methods in UX, consider enrolling in our Data-Driven Design: Quantitative Research for UX course.
The strength of quantitative research is its ability to provide precise numerical data for analyzing target variables.This allows for generalized conclusions and predictions about future occurrences, proving invaluable in various fields, including user experience. William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm, discusses the role of surveys, analytics, and testing in providing objective insights in our video on quantitative research methods, highlighting the significance of structured methodologies in eliciting reliable results.
To master quantitative research methods, enroll in our comprehensive course, Data-Driven Design: Quantitative Research for UX .
This course empowers you to leverage quantitative data to make informed design decisions, providing a deep dive into methods like surveys and analytics. Whether you’re a novice or a seasoned professional, this course at Interaction Design Foundation offers valuable insights and practical knowledge, ensuring you acquire the skills necessary to excel in user experience research. Explore our diverse topics to elevate your understanding of quantitative research methods.
Literature on Quantitative Research
Here’s the entire UX literature on Quantitative Research by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about Quantitative Research
Take a deep dive into Quantitative Research with our course User Research – Methods and Best Practices .
How do you plan to design a product or service that your users will love , if you don't know what they want in the first place? As a user experience designer, you shouldn't leave it to chance to design something outstanding; you should make the effort to understand your users and build on that knowledge from the outset. User research is the way to do this, and it can therefore be thought of as the largest part of user experience design .
In fact, user research is often the first step of a UX design process—after all, you cannot begin to design a product or service without first understanding what your users want! As you gain the skills required, and learn about the best practices in user research, you’ll get first-hand knowledge of your users and be able to design the optimal product—one that’s truly relevant for your users and, subsequently, outperforms your competitors’ .
This course will give you insights into the most essential qualitative research methods around and will teach you how to put them into practice in your design work. You’ll also have the opportunity to embark on three practical projects where you can apply what you’ve learned to carry out user research in the real world . You’ll learn details about how to plan user research projects and fit them into your own work processes in a way that maximizes the impact your research can have on your designs. On top of that, you’ll gain practice with different methods that will help you analyze the results of your research and communicate your findings to your clients and stakeholders—workshops, user journeys and personas, just to name a few!
By the end of the course, you’ll have not only a Course Certificate but also three case studies to add to your portfolio. And remember, a portfolio with engaging case studies is invaluable if you are looking to break into a career in UX design or user research!
We believe you should learn from the best, so we’ve gathered a team of experts to help teach this course alongside our own course instructors. That means you’ll meet a new instructor in each of the lessons on research methods who is an expert in their field—we hope you enjoy what they have in store for you!
All open-source articles on Quantitative Research
Best practices for qualitative user research.

- 3 years ago
Card Sorting

Understand the User’s Perspective through Research for Mobile UX

- 10 mths ago
7 Simple Ways to Get Better Results From Ethnographic Research

Question Everything


Tree Testing
Adding Quality to Your Design Research with an SSQS Checklist
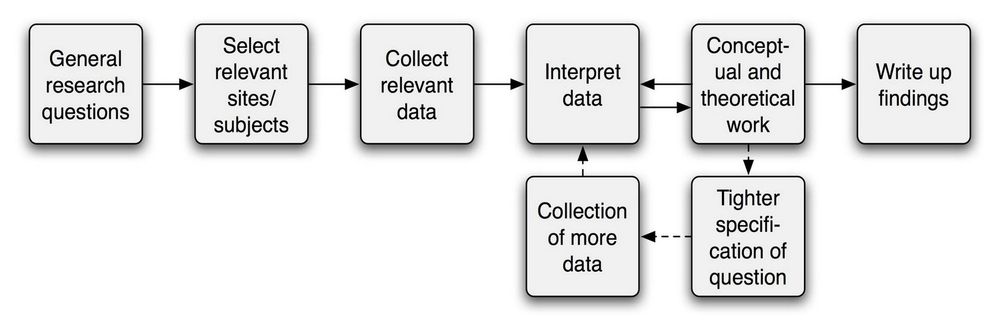
- 8 years ago
How to Fit Quantitative Research into the Project Lifecycle
Why and When to Use Surveys

Correlation in User Experience
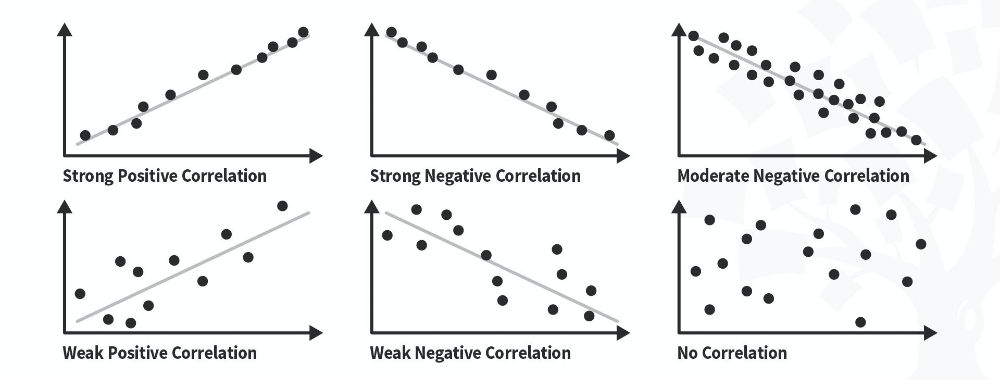
First-Click Testing

What to Test

Rating Scales in UX Research: The Ultimate Guide

Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
- A/B Monadic Test
- A/B Pre-Roll Test
- Key Driver Analysis
- Multiple Implicit
- Penalty Reward
- Price Sensitivity
- Segmentation
- Single Implicit
- Category Exploration
- Competitive Landscape
- Consumer Segmentation
- Innovation & Renovation
- Product Portfolio
- Marketing Creatives
- Advertising
- Shelf Optimization
- Performance Monitoring
- Better Brand Health Tracking
- Ad Tracking
- Trend Tracking
- Satisfaction Tracking
- AI Insights
- Case Studies
quantilope is the Consumer Intelligence Platform for all end-to-end research needs
What Are Quantitative Survey Questions? Types and Examples

Table of contents:
- Types of quantitative survey questions - with examples
- Quantitative question formats
- How to write quantitative survey questions
- Examples of quantitative survey questions
Leveraging quantilope for your quantitative survey
In a quantitative research study brands will gather numeric data for most of their questions through formats like numerical scale questions or ranking questions. However, brands can also include some non-quantitative questions throughout their quantitative study - like open-ended questions, where respondents will type in their own feedback to a question prompt. Even so, open-ended answers can be numerically coded to sift through feedback easily (e.g. anyone who writes in 'Pepsi' in a soda study would be assigned the number '1', to look at Pepsi feedback as a whole). One of the biggest benefits of using a quantitative research approach is that insights around a research topic can undergo statistical analysis; the same can’t be said for qualitative data like focus group feedback or interviews. Another major difference between quantitative and qualitative research methods is that quantitative surveys require respondents to choose from a limited number of choices in a close-ended question - generating clear, actionable takeaways. However, these distinct quantitative takeaways often pair well with freeform qualitative responses - making quant and qual a great team to use together. The rest of this article focuses on quantitative research, taking a closer look at quantitative survey question types and question formats/layouts.
Back to table of contents
Types of dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139745">quantitative survey questions - with examples
Quantitative questions come in many forms, each with different benefits depending on dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139784">your dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139740">market research objectives. Below we’ll explore some of these dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139745">quantitative dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139785">survey question dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-menu-id-param="menu_term_281139785" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139785"> types, which are commonly used together in a single survey to keep things interesting for dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">respondents . The style of questioning used during dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139739">quantitative dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139750">data dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-menu-id-param="menu_term_281139750" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139750"> collection is important, as a good mix of the right types of questions will deliver rich data, limit dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">respondent fatigue, and optimize the dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139757">response rate . dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139742">Questionnaires should be enjoyable - and varying the dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139755">types of dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-menu-id-param="menu_term_281139755" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139755">quantitative research dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139755"> questions used throughout your survey will help achieve that.
Descriptive survey questions
dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139763">Descriptive research questions (also known as usage and attitude, or, U&A questions) seek a general indication or prediction about how a dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139773">group of people behaves or will behave, how that group is characterized, or how a group thinks.
For example, a business might want to know what portion of adult men shave, and how often they do so. To find this out, they will survey men (the dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139743">target audience ) and ask descriptive questions about their frequency of shaving (e.g. daily, a few times a week, once per week, and so on.) Each of these frequencies get assigned a numerical ‘code’ so that it’s simple to chart and analyze the data later on; daily might be assigned ‘5’, a few times a week might be assigned ‘4’, and so on. That way, brands can create charts using the ‘top two’ and ‘bottom two’ values in a descriptive question to view these metrics side by side.
Another business might want to know how important local transit issues are to residents, so dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139745">quantitative survey questions will allow dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">respondents to indicate the degrees of opinion attached to various transit issues. Perhaps the transit business running this survey would use a sliding numeric scale to see how important a particular issue is.
Comparative survey questions
dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139782">Comparative research questions are concerned with comparing individuals or groups of people based on one or more variables. These questions might be posed when a business wants to find out which segment of its dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139743">target audience might be more profitable, or which types of products might appeal to different sets of consumers.
For example, a business might want to know how the popularity of its chocolate bars is spread out across its entire customer base (i.e. do women prefer a certain flavor? Are children drawn to candy bars by certain packaging attributes? etc.). Questions in this case will be designed to profile and ‘compare’ segments of the market.
Other businesses might be looking to compare coffee consumption among older and younger consumers (i.e. dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139741">demographic segments), the difference in smartphone usage between younger men and women, or how women from different regions differ in their approach to skincare.
Relationship-based survey questions
As the name suggests, relationship-based survey questions are concerned with the relationship between two or more variables within one or more dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139741">demographic groups. This might be a dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139759">causal link between one thing and the other - for example, the consumption of caffeine and dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">respondents ’ reported energy levels throughout the day. In this case, a coffee or energy drink brand might be interested in how energy levels differ between those who drink their caffeinated line of beverages and those who drink decaf/non-caffeinated beverages.
Alternatively, it might be a case of two or more factors co-existing, without there necessarily being a dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139759">causal link - for example, a particular type of air freshener being more popular amongst a certain dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139741">demographic (maybe one that is controlled wirelessly via Bluetooth is more popular among younger homeowners than one that’s plugged into the wall with no controls). Knowing that millennials favor air fresheners which have options for swapping out scents and setting up schedules would be valuable information for new product development.
Advanced method survey questions
Aside from descriptive, comparative, and relationship-based survey questions, brands can opt to include advanced methodologies in their quantitative dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139742">questionnaire for richer depth. Though advanced methods are more complex in terms of the insights output, quantilope’s Consumer Intelligence Platform automates the setup and analysis of these methods so that researchers of any background or skillset can leverage them with ease.
With quantilope’s pre-programmed suite of 12 advanced methodologies , including MaxDiff , TURF , Implicit , and more, users can drag and drop any of these into a dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139742">questionnaire and customize for their own dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139740">market research objectives.
For example, consider a beverage company that’s looking to expand its flavor profiles. This brand would benefit from a MaxDiff which forces dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">respondents to make tradeoff decisions between a set of flavors. A dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">respondent might say that coconut is their most-preferred flavor, and lime their least (when in a consideration set with strawberry), yet later on in the MaxDiff that same dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">respondent may say Strawberry is their most-preferred flavor (over black cherry and kiwi). While this is just one example of an advanced method, instantly you can see how much richer and more actionable these quantitative metrics become compared to a standard usage and attitude question .
Advanced methods can be used alongside descriptive, comparison, or relationship questions to add a new layer of context wherever a business sees fit. Back to table of contents
Quantitative question formats
So we’ve covered the kinds of dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139736">quantitative research questions you might want to answer using dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139740">market research , but how do these translate into the actual format of questions that you might include on your dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139742">questionnaire ?
Thinking ahead to your reporting process during your dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139742">questionnaire setup is actually quite important, as the available chart types differ among the types of questions asked; some question data is compatible with bar chart displays, others pie charts, others in trended line graphs, etc. Also consider how well the questions you’re asking will translate onto different devices that your dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">respondents might be using to complete the survey (mobile, PC, or tablet).
Single Select questions
Single select questions are the simplest form of quantitative questioning, as dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">respondents are asked to choose just one answer from a list of items, which tend to be ‘either/or’, ‘yes/no’, or ‘true/false’ questions. These questions are useful when you need to get a clear answer without any qualifying nuances.
Multi-select questions
Multi-select questions (aka, dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139767">multiple choice ) offer more flexibility for responses, allowing for a number of responses on a single question. dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">Respondents can be asked to ‘check all that apply’ or a cap can be applied (e.g. ‘select up to 3 choices’).
For example:
Aside from asking text-based questions like the above examples, a brand could also use a single or multi-select question to ask respondents to select the image they prefer more (like different iterations of a logo design, packaging options, branding colors, etc.).
dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139749">Likert dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139766">scale dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-menu-id-param="menu_term_281139766" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139766"> questions
A dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139749">Likert scale is widely used as a convenient and easy-to-interpret rating method. dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">Respondents find it easy to indicate their degree of feelings by selecting the response they most identify with.
Slider scales
Slider scales are another good interactive way of formatting questions. They allow dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">respondents to customize their level of feeling about a question, with a bit more variance and nuance allowed than a numeric scale:

One particularly common use of a slider scale in a dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139740">market dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139770">research dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-menu-id-param="menu_term_281139770" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139770"> study is known as a NPS (Net Promoter Score) - a way to measure dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139775">customer experience and loyalty . A 0-10 scale is used to ask customers how likely they are to recommend a brand’s product or services to others. The NPS score is calculated by subtracting the percentage of ‘detractors’ (those who respond with a 0-6) from the percentage of promoters (those who respond with a 9-10). dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">Respondents who select 7-8 are known as ‘passives’.
For example:
Drag and drop questions
Drag-and-drop question formats are a more ‘gamified’ approach to survey capture as they ask dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">respondents to do more than simply check boxes or slide a scale. Drag-and-drop question formats are great for ranking exercises - asking dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">respondents to place answer options in a certain order by dragging with their mouse. For example, you could ask survey takers to put pizza toppings in order of preference by dragging options from a list of possible answers to a box displaying their personal preferences:
Matrix questions
Matrix questions are a great way to consolidate a number of questions that ask for the same type of response (e.g. single select yes/no, true/false, or multi-select lists). They are mutually beneficial - making a survey look less daunting for the dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">respondent , and easier for a brand to set up than asking multiple separate questions.
Items in a matrix question are presented one by one, as respondents cycle through the pages selecting one answer for each coffee flavor shown.
-1.png?width=1500&height=800&name=Untitled%20design%20(5)-1.png)
While the above example shows a single-matrix question - meaning a respondent can only select one answer per element (in this case, coffee flavors), a matrix setup can also be used for multiple-choice questions - allowing respondents to choose multiple answers per element shown, or for rating questions - allowing respondents to assign a rating (e.g. 1-5) for a list of elements at once. Back to table of contents
How to write dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139745">quantitative survey questions
We’ve reviewed the types of questions you might ask in a quantitative survey, and how you might format those questions, but now for the actual crafting of the content.
When considering which questions to include in your survey, you’ll first want to establish what your research goals are and how these relate to your business goals. For example, thinking about the three types of dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139745">quantitative survey questions explained above - descriptive, comparative, and relationship-based - which type (or which combination) will best meet your research needs? The questions you ask dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">respondents may be phrased in similar ways no matter what kind of layout you leverage, but you should have a good idea of how you’ll want to analyze the results as that will make it much easier to correctly set up your survey.
Quantitative questions tend to start with words like ‘how much,’ ‘how often,’ ‘to what degree,’ ‘what do you think of,’ ‘which of the following’ - anything that establishes what consumers do or think and that can be assigned a numerical code or value. Be sure to also include ‘other’ or ‘none of the above’ options in your quant questions, accommodating those who don’t feel the pre-set answers reflect their true opinion. As mentioned earlier, you can always include a small number of dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139748">open-ended questions in your quant survey to account for any ideas or expanded feedback that the pre-coded questions don’t (or can’t) cover. Back to table of contents
Examples of dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139745">quantitative survey questions
dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139745">Quantitative survey questions impose limits on the answers that dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">respondents can choose from, and this is a good thing when it comes to measuring consumer opinions on a large scale and comparing across dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">respondents . A large volume of freeform, open-ended answers is interesting when looking for themes from qualitative studies, but impractical to wade through when dealing with a large dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139756">sample size , and impossible to subject to dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139774">statistical analysis .
For example, a quantitative survey might aim to establish consumers' smartphone habits. This could include their frequency of buying a new smartphone, the considerations that drive purchase, which features they use their phone for, and how much they like their smartphone.
Some examples of quantitative survey questions relating to these habits would be:
Q. How often do you buy a new smartphone?
[single select question]
More than once per year
Every 1-2 years
Every 3-5 years
Every 6+ years
Q. Thinking about when you buy a smartphone, please rank the following factors in order of importance:
[drag and drop ranking question]
screen size
storage capacity
Q. How often do you use the following features on your smartphone?
[matrix question]
Q. How do you feel about your current smartphone?
[sliding scale]
I love it <-------> I hate it
Answers from these above questions, and others within the survey, would be analyzed to paint a picture of smartphone usage and attitude trends across a population and its sub-groups. dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139738">Qualitative research might then be carried out to explore those findings further - for example, people’s detailed attitudes towards their smartphones, how they feel about the amount of time they spend on it, and how features could be improved. Back to table of contents
quantilope’s Consumer Intelligence Platform specializes in automated, advanced survey insights so that researchers of any skill level can benefit from quick, high-quality consumer insights. With 12 advanced methods to choose from and a wide variety of quantitative question formats, quantilope is your one-stop-shop for all things dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139740">market research (including its dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139776">in-depth dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139738">qualitative research solution - inColor ).
When it comes to building your survey, you decide how you want to go about it. You can start with a blank slate and drop questions into your survey from a pre-programmed list, or you can get a head start with a survey dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139765">template for a particular business use case (like concept testing ) and customize from there. Once your survey is ready to launch, simply specify your dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139743">target audience , connect any panel (quantilope is panel agnostic), and watch as dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139737">respondents dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139783">answer questions in your survey in real-time by monitoring the fieldwork section of your project. AI-driven dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139764">data analysis takes the raw data and converts it into actionable findings so you never have to worry about manual calculations or statistical testing.
Whether you want to run your quantitative study entirely on your own or with the help of a classically trained research team member, the choice is yours on quantilope’s platform. For more information on how quantilope can help with your next dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139736">quantitative dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139768">research dropdown#toggle" data-dropdown-menu-id-param="menu_term_281139768" data-dropdown-placement-param="top" data-term-id="281139768"> project , get in touch below!
Get in touch to learn more about quantitative research with quantilope!
Related posts, survey results: how to analyze data and report on findings, how florida's natural leveraged better brand health tracking, quirk's virtual event: fab-brew-lous collaboration: product innovations from the melitta group, brand value: what it is, how to build it, and how to measure it.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Writing Survey Questions
Perhaps the most important part of the survey process is the creation of questions that accurately measure the opinions, experiences and behaviors of the public. Accurate random sampling will be wasted if the information gathered is built on a shaky foundation of ambiguous or biased questions. Creating good measures involves both writing good questions and organizing them to form the questionnaire.
Questionnaire design is a multistage process that requires attention to many details at once. Designing the questionnaire is complicated because surveys can ask about topics in varying degrees of detail, questions can be asked in different ways, and questions asked earlier in a survey may influence how people respond to later questions. Researchers are also often interested in measuring change over time and therefore must be attentive to how opinions or behaviors have been measured in prior surveys.
Surveyors may conduct pilot tests or focus groups in the early stages of questionnaire development in order to better understand how people think about an issue or comprehend a question. Pretesting a survey is an essential step in the questionnaire design process to evaluate how people respond to the overall questionnaire and specific questions, especially when questions are being introduced for the first time.
For many years, surveyors approached questionnaire design as an art, but substantial research over the past forty years has demonstrated that there is a lot of science involved in crafting a good survey questionnaire. Here, we discuss the pitfalls and best practices of designing questionnaires.
Question development
There are several steps involved in developing a survey questionnaire. The first is identifying what topics will be covered in the survey. For Pew Research Center surveys, this involves thinking about what is happening in our nation and the world and what will be relevant to the public, policymakers and the media. We also track opinion on a variety of issues over time so we often ensure that we update these trends on a regular basis to better understand whether people’s opinions are changing.
At Pew Research Center, questionnaire development is a collaborative and iterative process where staff meet to discuss drafts of the questionnaire several times over the course of its development. We frequently test new survey questions ahead of time through qualitative research methods such as focus groups , cognitive interviews, pretesting (often using an online, opt-in sample ), or a combination of these approaches. Researchers use insights from this testing to refine questions before they are asked in a production survey, such as on the ATP.
Measuring change over time
Many surveyors want to track changes over time in people’s attitudes, opinions and behaviors. To measure change, questions are asked at two or more points in time. A cross-sectional design surveys different people in the same population at multiple points in time. A panel, such as the ATP, surveys the same people over time. However, it is common for the set of people in survey panels to change over time as new panelists are added and some prior panelists drop out. Many of the questions in Pew Research Center surveys have been asked in prior polls. Asking the same questions at different points in time allows us to report on changes in the overall views of the general public (or a subset of the public, such as registered voters, men or Black Americans), or what we call “trending the data”.
When measuring change over time, it is important to use the same question wording and to be sensitive to where the question is asked in the questionnaire to maintain a similar context as when the question was asked previously (see question wording and question order for further information). All of our survey reports include a topline questionnaire that provides the exact question wording and sequencing, along with results from the current survey and previous surveys in which we asked the question.
The Center’s transition from conducting U.S. surveys by live telephone interviewing to an online panel (around 2014 to 2020) complicated some opinion trends, but not others. Opinion trends that ask about sensitive topics (e.g., personal finances or attending religious services ) or that elicited volunteered answers (e.g., “neither” or “don’t know”) over the phone tended to show larger differences than other trends when shifting from phone polls to the online ATP. The Center adopted several strategies for coping with changes to data trends that may be related to this change in methodology. If there is evidence suggesting that a change in a trend stems from switching from phone to online measurement, Center reports flag that possibility for readers to try to head off confusion or erroneous conclusions.
Open- and closed-ended questions
One of the most significant decisions that can affect how people answer questions is whether the question is posed as an open-ended question, where respondents provide a response in their own words, or a closed-ended question, where they are asked to choose from a list of answer choices.
For example, in a poll conducted after the 2008 presidential election, people responded very differently to two versions of the question: “What one issue mattered most to you in deciding how you voted for president?” One was closed-ended and the other open-ended. In the closed-ended version, respondents were provided five options and could volunteer an option not on the list.
When explicitly offered the economy as a response, more than half of respondents (58%) chose this answer; only 35% of those who responded to the open-ended version volunteered the economy. Moreover, among those asked the closed-ended version, fewer than one-in-ten (8%) provided a response other than the five they were read. By contrast, fully 43% of those asked the open-ended version provided a response not listed in the closed-ended version of the question. All of the other issues were chosen at least slightly more often when explicitly offered in the closed-ended version than in the open-ended version. (Also see “High Marks for the Campaign, a High Bar for Obama” for more information.)
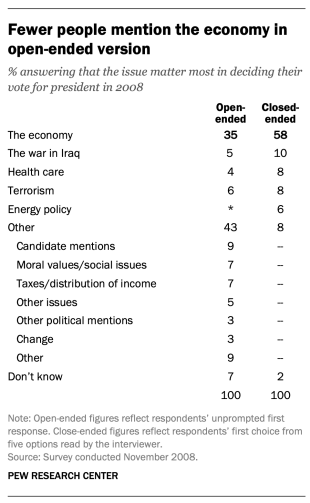
Researchers will sometimes conduct a pilot study using open-ended questions to discover which answers are most common. They will then develop closed-ended questions based off that pilot study that include the most common responses as answer choices. In this way, the questions may better reflect what the public is thinking, how they view a particular issue, or bring certain issues to light that the researchers may not have been aware of.
When asking closed-ended questions, the choice of options provided, how each option is described, the number of response options offered, and the order in which options are read can all influence how people respond. One example of the impact of how categories are defined can be found in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in January 2002. When half of the sample was asked whether it was “more important for President Bush to focus on domestic policy or foreign policy,” 52% chose domestic policy while only 34% said foreign policy. When the category “foreign policy” was narrowed to a specific aspect – “the war on terrorism” – far more people chose it; only 33% chose domestic policy while 52% chose the war on terrorism.
In most circumstances, the number of answer choices should be kept to a relatively small number – just four or perhaps five at most – especially in telephone surveys. Psychological research indicates that people have a hard time keeping more than this number of choices in mind at one time. When the question is asking about an objective fact and/or demographics, such as the religious affiliation of the respondent, more categories can be used. In fact, they are encouraged to ensure inclusivity. For example, Pew Research Center’s standard religion questions include more than 12 different categories, beginning with the most common affiliations (Protestant and Catholic). Most respondents have no trouble with this question because they can expect to see their religious group within that list in a self-administered survey.
In addition to the number and choice of response options offered, the order of answer categories can influence how people respond to closed-ended questions. Research suggests that in telephone surveys respondents more frequently choose items heard later in a list (a “recency effect”), and in self-administered surveys, they tend to choose items at the top of the list (a “primacy” effect).
Because of concerns about the effects of category order on responses to closed-ended questions, many sets of response options in Pew Research Center’s surveys are programmed to be randomized to ensure that the options are not asked in the same order for each respondent. Rotating or randomizing means that questions or items in a list are not asked in the same order to each respondent. Answers to questions are sometimes affected by questions that precede them. By presenting questions in a different order to each respondent, we ensure that each question gets asked in the same context as every other question the same number of times (e.g., first, last or any position in between). This does not eliminate the potential impact of previous questions on the current question, but it does ensure that this bias is spread randomly across all of the questions or items in the list. For instance, in the example discussed above about what issue mattered most in people’s vote, the order of the five issues in the closed-ended version of the question was randomized so that no one issue appeared early or late in the list for all respondents. Randomization of response items does not eliminate order effects, but it does ensure that this type of bias is spread randomly.
Questions with ordinal response categories – those with an underlying order (e.g., excellent, good, only fair, poor OR very favorable, mostly favorable, mostly unfavorable, very unfavorable) – are generally not randomized because the order of the categories conveys important information to help respondents answer the question. Generally, these types of scales should be presented in order so respondents can easily place their responses along the continuum, but the order can be reversed for some respondents. For example, in one of Pew Research Center’s questions about abortion, half of the sample is asked whether abortion should be “legal in all cases, legal in most cases, illegal in most cases, illegal in all cases,” while the other half of the sample is asked the same question with the response categories read in reverse order, starting with “illegal in all cases.” Again, reversing the order does not eliminate the recency effect but distributes it randomly across the population.
Question wording
The choice of words and phrases in a question is critical in expressing the meaning and intent of the question to the respondent and ensuring that all respondents interpret the question the same way. Even small wording differences can substantially affect the answers people provide.
[View more Methods 101 Videos ]
An example of a wording difference that had a significant impact on responses comes from a January 2003 Pew Research Center survey. When people were asked whether they would “favor or oppose taking military action in Iraq to end Saddam Hussein’s rule,” 68% said they favored military action while 25% said they opposed military action. However, when asked whether they would “favor or oppose taking military action in Iraq to end Saddam Hussein’s rule even if it meant that U.S. forces might suffer thousands of casualties, ” responses were dramatically different; only 43% said they favored military action, while 48% said they opposed it. The introduction of U.S. casualties altered the context of the question and influenced whether people favored or opposed military action in Iraq.
There has been a substantial amount of research to gauge the impact of different ways of asking questions and how to minimize differences in the way respondents interpret what is being asked. The issues related to question wording are more numerous than can be treated adequately in this short space, but below are a few of the important things to consider:
First, it is important to ask questions that are clear and specific and that each respondent will be able to answer. If a question is open-ended, it should be evident to respondents that they can answer in their own words and what type of response they should provide (an issue or problem, a month, number of days, etc.). Closed-ended questions should include all reasonable responses (i.e., the list of options is exhaustive) and the response categories should not overlap (i.e., response options should be mutually exclusive). Further, it is important to discern when it is best to use forced-choice close-ended questions (often denoted with a radio button in online surveys) versus “select-all-that-apply” lists (or check-all boxes). A 2019 Center study found that forced-choice questions tend to yield more accurate responses, especially for sensitive questions. Based on that research, the Center generally avoids using select-all-that-apply questions.
It is also important to ask only one question at a time. Questions that ask respondents to evaluate more than one concept (known as double-barreled questions) – such as “How much confidence do you have in President Obama to handle domestic and foreign policy?” – are difficult for respondents to answer and often lead to responses that are difficult to interpret. In this example, it would be more effective to ask two separate questions, one about domestic policy and another about foreign policy.
In general, questions that use simple and concrete language are more easily understood by respondents. It is especially important to consider the education level of the survey population when thinking about how easy it will be for respondents to interpret and answer a question. Double negatives (e.g., do you favor or oppose not allowing gays and lesbians to legally marry) or unfamiliar abbreviations or jargon (e.g., ANWR instead of Arctic National Wildlife Refuge) can result in respondent confusion and should be avoided.
Similarly, it is important to consider whether certain words may be viewed as biased or potentially offensive to some respondents, as well as the emotional reaction that some words may provoke. For example, in a 2005 Pew Research Center survey, 51% of respondents said they favored “making it legal for doctors to give terminally ill patients the means to end their lives,” but only 44% said they favored “making it legal for doctors to assist terminally ill patients in committing suicide.” Although both versions of the question are asking about the same thing, the reaction of respondents was different. In another example, respondents have reacted differently to questions using the word “welfare” as opposed to the more generic “assistance to the poor.” Several experiments have shown that there is much greater public support for expanding “assistance to the poor” than for expanding “welfare.”
We often write two versions of a question and ask half of the survey sample one version of the question and the other half the second version. Thus, we say we have two forms of the questionnaire. Respondents are assigned randomly to receive either form, so we can assume that the two groups of respondents are essentially identical. On questions where two versions are used, significant differences in the answers between the two forms tell us that the difference is a result of the way we worded the two versions.

One of the most common formats used in survey questions is the “agree-disagree” format. In this type of question, respondents are asked whether they agree or disagree with a particular statement. Research has shown that, compared with the better educated and better informed, less educated and less informed respondents have a greater tendency to agree with such statements. This is sometimes called an “acquiescence bias” (since some kinds of respondents are more likely to acquiesce to the assertion than are others). This behavior is even more pronounced when there’s an interviewer present, rather than when the survey is self-administered. A better practice is to offer respondents a choice between alternative statements. A Pew Research Center experiment with one of its routinely asked values questions illustrates the difference that question format can make. Not only does the forced choice format yield a very different result overall from the agree-disagree format, but the pattern of answers between respondents with more or less formal education also tends to be very different.
One other challenge in developing questionnaires is what is called “social desirability bias.” People have a natural tendency to want to be accepted and liked, and this may lead people to provide inaccurate answers to questions that deal with sensitive subjects. Research has shown that respondents understate alcohol and drug use, tax evasion and racial bias. They also may overstate church attendance, charitable contributions and the likelihood that they will vote in an election. Researchers attempt to account for this potential bias in crafting questions about these topics. For instance, when Pew Research Center surveys ask about past voting behavior, it is important to note that circumstances may have prevented the respondent from voting: “In the 2012 presidential election between Barack Obama and Mitt Romney, did things come up that kept you from voting, or did you happen to vote?” The choice of response options can also make it easier for people to be honest. For example, a question about church attendance might include three of six response options that indicate infrequent attendance. Research has also shown that social desirability bias can be greater when an interviewer is present (e.g., telephone and face-to-face surveys) than when respondents complete the survey themselves (e.g., paper and web surveys).
Lastly, because slight modifications in question wording can affect responses, identical question wording should be used when the intention is to compare results to those from earlier surveys. Similarly, because question wording and responses can vary based on the mode used to survey respondents, researchers should carefully evaluate the likely effects on trend measurements if a different survey mode will be used to assess change in opinion over time.
Question order
Once the survey questions are developed, particular attention should be paid to how they are ordered in the questionnaire. Surveyors must be attentive to how questions early in a questionnaire may have unintended effects on how respondents answer subsequent questions. Researchers have demonstrated that the order in which questions are asked can influence how people respond; earlier questions can unintentionally provide context for the questions that follow (these effects are called “order effects”).
One kind of order effect can be seen in responses to open-ended questions. Pew Research Center surveys generally ask open-ended questions about national problems, opinions about leaders and similar topics near the beginning of the questionnaire. If closed-ended questions that relate to the topic are placed before the open-ended question, respondents are much more likely to mention concepts or considerations raised in those earlier questions when responding to the open-ended question.
For closed-ended opinion questions, there are two main types of order effects: contrast effects ( where the order results in greater differences in responses), and assimilation effects (where responses are more similar as a result of their order).
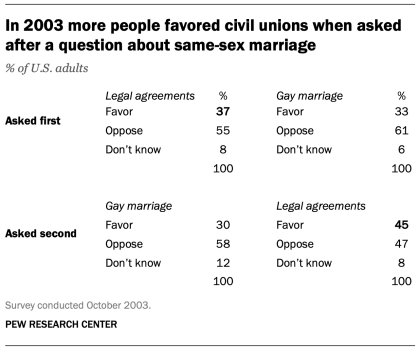
An example of a contrast effect can be seen in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in October 2003, a dozen years before same-sex marriage was legalized in the U.S. That poll found that people were more likely to favor allowing gays and lesbians to enter into legal agreements that give them the same rights as married couples when this question was asked after one about whether they favored or opposed allowing gays and lesbians to marry (45% favored legal agreements when asked after the marriage question, but 37% favored legal agreements without the immediate preceding context of a question about same-sex marriage). Responses to the question about same-sex marriage, meanwhile, were not significantly affected by its placement before or after the legal agreements question.
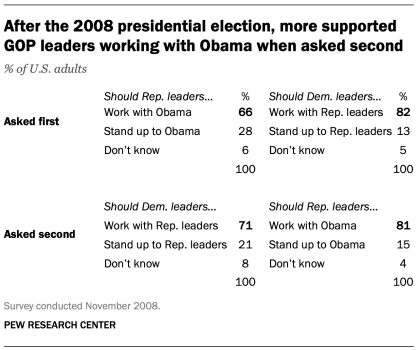
Another experiment embedded in a December 2008 Pew Research Center poll also resulted in a contrast effect. When people were asked “All in all, are you satisfied or dissatisfied with the way things are going in this country today?” immediately after having been asked “Do you approve or disapprove of the way George W. Bush is handling his job as president?”; 88% said they were dissatisfied, compared with only 78% without the context of the prior question.
Responses to presidential approval remained relatively unchanged whether national satisfaction was asked before or after it. A similar finding occurred in December 2004 when both satisfaction and presidential approval were much higher (57% were dissatisfied when Bush approval was asked first vs. 51% when general satisfaction was asked first).
Several studies also have shown that asking a more specific question before a more general question (e.g., asking about happiness with one’s marriage before asking about one’s overall happiness) can result in a contrast effect. Although some exceptions have been found, people tend to avoid redundancy by excluding the more specific question from the general rating.
Assimilation effects occur when responses to two questions are more consistent or closer together because of their placement in the questionnaire. We found an example of an assimilation effect in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in November 2008 when we asked whether Republican leaders should work with Obama or stand up to him on important issues and whether Democratic leaders should work with Republican leaders or stand up to them on important issues. People were more likely to say that Republican leaders should work with Obama when the question was preceded by the one asking what Democratic leaders should do in working with Republican leaders (81% vs. 66%). However, when people were first asked about Republican leaders working with Obama, fewer said that Democratic leaders should work with Republican leaders (71% vs. 82%).
The order questions are asked is of particular importance when tracking trends over time. As a result, care should be taken to ensure that the context is similar each time a question is asked. Modifying the context of the question could call into question any observed changes over time (see measuring change over time for more information).
A questionnaire, like a conversation, should be grouped by topic and unfold in a logical order. It is often helpful to begin the survey with simple questions that respondents will find interesting and engaging. Throughout the survey, an effort should be made to keep the survey interesting and not overburden respondents with several difficult questions right after one another. Demographic questions such as income, education or age should not be asked near the beginning of a survey unless they are needed to determine eligibility for the survey or for routing respondents through particular sections of the questionnaire. Even then, it is best to precede such items with more interesting and engaging questions. One virtue of survey panels like the ATP is that demographic questions usually only need to be asked once a year, not in each survey.
U.S. Surveys
Other research methods, sign up for our weekly newsletter.
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
10 Quantitative Data Analysis Software for Every Data Scientist

Are you curious about digging into data but not sure where to start? Don’t worry; we’ve got you covered! As a data scientist, you know that having the right tools can make all the difference in the world. When it comes to analyzing quantitative data, having the right quantitative data analysis software can help you extract insights faster and more efficiently.
From spotting trends to making smart decisions, quantitative analysis helps us unlock the secrets hidden within our data and chart a course for success.
In this blog post, we’ll introduce you to 10 quantitative data analysis software that every data scientist should know about.
What is Quantitative Data Analysis?
Quantitative data analysis refers to the process of systematically examining numerical data to uncover patterns, trends, relationships, and insights.
Unlike analyzing qualitative data, which deals with non-numeric data like text or images, quantitative research focuses on data that can be quantified, measured, and analyzed using statistical techniques.
What is Quantitative Data Analysis Software?
Quantitative data analysis software refers to specialized computer programs or tools designed to assist researchers, analysts, and professionals in analyzing numerical data.
These software applications are tailored to handle quantitative data, which consists of measurable quantities, counts, or numerical values. Quantitative data analysis software provides a range of features and functionalities to manage, analyze, visualize, and interpret numerical data effectively.
Key features commonly found in quantitative data analysis software include:
- Data Import and Management: Capability to import data from various sources such as spreadsheets, databases, text files, or online repositories.
- Descriptive Statistics: Tools for computing basic descriptive statistics such as measures of central tendency (e.g., mean, median, mode) and measures of dispersion (e.g., standard deviation, variance).
- Data Visualization: Functionality to create visual representations of data through charts, graphs, histograms, scatter plots, or heatmaps.
- Statistical Analysis: Support for conducting a wide range of statistical tests and analyses to explore relationships, test hypotheses, make predictions, or infer population characteristics from sample data.
- Advanced Analytics: Advanced analytical techniques for more complex data exploration and modeling, such as cluster analysis, principal component analysis (PCA), time series analysis, survival analysis, and structural equation modeling (SEM).
- Automation and Reproducibility: Features for automating analysis workflows, scripting repetitive tasks, and ensuring the reproducibility of results.
- Reporting and Collaboration: Tools for generating customizable reports, summaries, or presentations to communicate analysis results effectively to stakeholders.
Benefits of Quantitative Data Analysis
Quantitative data analysis offers numerous benefits across various fields and disciplines. Here are some of the key advantages:
Making Confident Decisions
Quantitative data analysis provides solid, evidence-based insights that support decision-making. By relying on data rather than intuition, you can reduce the risk of making incorrect decisions. This not only increases confidence in your choices but also fosters buy-in from stakeholders and team members.
Cost Reduction
Analyzing quantitative data helps identify areas where costs can be reduced or optimized. For instance, if certain marketing campaigns yield lower-than-average results, reallocating resources to more effective channels can lead to cost savings and improved ROI.
Personalizing User Experience
Quantitative analysis allows for the mapping of customer journeys and the identification of preferences and behaviors. By understanding these patterns, businesses can tailor their offerings, content, and communication to specific user segments, leading to enhanced user satisfaction and engagement.
Improving User Satisfaction and Delight
Quantitative data analysis highlights areas of success and areas for improvement in products or services. For instance, if a webpage shows high engagement but low conversion rates, further investigation can uncover user pain points or friction in the conversion process. Addressing these issues can lead to improved user satisfaction and increased conversion rates.
Best 10 Quantitative Data Analysis Software
1. questionpro.
Known for its robust survey and research capabilities, QuestionPro is a versatile platform that offers powerful data analysis tools tailored for market research, customer feedback, and academic studies. With features like advanced survey logic, data segmentation, and customizable reports, QuestionPro empowers users to derive actionable insights from their quantitative data.
Features of QuestionPro
- Customizable Surveys
- Advanced Question Types:
- Survey Logic and Branching
- Data Segmentation
- Real-Time Reporting
- Mobile Optimization
- Integration Options
- Multi-Language Support
- Data Export
- User-friendly interface.
- Extensive question types.
- Seamless data export capabilities.
- Limited free version.
Pricing :
Starts at $99 per month per user.
2. SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences
SPSS is a venerable software package widely used in the social sciences for statistical analysis. Its intuitive interface and comprehensive range of statistical techniques make it a favorite among researchers and analysts for hypothesis testing, regression analysis, and data visualization tasks.
- Advanced statistical analysis capabilities.
- Data management and manipulation tools.
- Customizable graphs and charts.
- Syntax-based programming for automation.
- Extensive statistical procedures.
- Flexible data handling.
- Integration with other statistical software package
- High cost for the full version.
- Steep learning curve for beginners.
Pricing:
- Starts at $99 per month.
3. Google Analytics
Primarily used for web analytics, Google Analytics provides invaluable insights into website traffic, user behavior, and conversion metrics. By tracking key performance indicators such as page views, bounce rates, and traffic sources, Google Analytics helps businesses optimize their online presence and maximize their digital marketing efforts.
- Real-time tracking of website visitors.
- Conversion tracking and goal setting.
- Customizable reports and dashboards.
- Integration with Google Ads and other Google products.
- Free version available.
- Easy to set up and use.
- Comprehensive insights into website performance.
- Limited customization options in the free version.
- Free for basic features.
Hotjar is a powerful tool for understanding user behavior on websites and digital platforms. Hotjar enables businesses to visualize how users interact with their websites, identify pain points, and optimize the user experience for better conversion rates and customer satisfaction through features like heatmaps, session recordings, and on-site surveys.
- Heatmaps to visualize user clicks, taps, and scrolling behavior.
- Session recordings for in-depth user interaction analysis.
- Feedback polls and surveys.
- Funnel and form analysis.
- Easy to install and set up.
- Comprehensive insights into user behavior.
- Affordable pricing plans.
- Limited customization options for surveys.
Starts at $39 per month.
While not a dedicated data analysis software, Python is a versatile programming language widely used for data analysis, machine learning, and scientific computing. With libraries such as NumPy, pandas, and matplotlib, Python provides a comprehensive ecosystem for data manipulation, visualization, and statistical analysis, making it a favorite among data scientists and analysts.
- The rich ecosystem of data analysis libraries.
- Flexible and scalable for large datasets.
- Integration with other tools and platforms.
- Open-source with a supportive community.
- Free and open-source.
- High performance and scalability.
- Great for automation and customization.
- Requires programming knowledge.
- It is Free for the beginners.
6. SAS (Statistical Analysis System)
SAS is a comprehensive software suite renowned for its advanced analytics, business intelligence, and data management capabilities. With a wide range of statistical techniques, predictive modeling tools, and data visualization options, SAS is trusted by organizations across industries for complex data analysis tasks and decision support.
- Wide range of statistical procedures.
- Data integration and cleansing tools.
- Advanced analytics and machine learning capabilities.
- Scalable for enterprise-level data analysis.
- Powerful statistical modeling capabilities.
- Excellent support for large datasets.
- Trusted by industries for decades.
- Expensive licensing fees.
- Steep learning curve.
- Contact sales for pricing details.
Despite its simplicity compared to specialized data analysis software, Excel remains popular for basic quantitative analysis and data visualization. With features like pivot tables, functions, and charting tools, Excel provides a familiar and accessible platform for users to perform tasks such as data cleaning, summarization, and exploratory analysis.
- Formulas and functions for calculations.
- Pivot tables and charts for data visualization.
- Data sorting and filtering capabilities.
- Integration with other Microsoft Office applications.
- Widely available and familiar interface.
- Affordable for basic analysis tasks.
- Versatile for various data formats.
- Limited statistical functions compared to specialized software.
- Not suitable for handling large datasets.
- Included in Microsoft 365 subscription plans, starts at $6.99 per month.
8. IBM SPSS Statistics
Building on the foundation of SPSS, IBM SPSS Statistics offers enhanced features and capabilities for advanced statistical analysis and predictive modeling. With modules for data preparation, regression analysis, and survival analysis, IBM SPSS Statistics is well-suited for researchers and analysts tackling complex data analysis challenges.
- Advanced statistical procedures.
- Data preparation and transformation tools.
- Automated model building and deployment.
- Integration with other IBM products.
- Extensive statistical capabilities.
- User-friendly interface for beginners.
- Enterprise-grade security and scalability.
- Limited support for open-source integration.
Minitab is a specialized software package designed for quality improvement and statistical analysis in manufacturing, engineering, and healthcare industries. With tools for experiment design, statistical process control, and reliability analysis, Minitab empowers users to optimize processes, reduce defects, and improve product quality.
- Basic and advanced statistical analysis.
- Graphical analysis tools for data visualization.
- Statistical methods improvement.
- DOE (Design of Experiments) capabilities.
- Streamlined interface for statistical analysis.
- Comprehensive quality improvement tools.
- Excellent customer support.
- Limited flexibility for customization.
Pricing:
- Starts at $29 per month.
JMP is a dynamic data visualization and statistical analysis tool developed by SAS Institute. Known for its interactive graphics and exploratory data analysis capabilities, JMP enables users to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships in their data, facilitating deeper insights and informed decision-making.
- Interactive data visualization.
- Statistical modeling and analysis.
- Predictive analytics and machine learning.
- Integration with SAS and other data sources.
- Intuitive interface for exploratory data analysis.
- Dynamic graphics for better insights.
- Integration with SAS for advanced analytics.
- Limited scripting capabilities.
- Less customizable compared to other SAS products.
QuestionPro is Your Right Quantitative Data Analysis Software?
QuestionPro offers a range of features specifically designed for quantitative data analysis, making it a suitable choice for various research, survey, and data-driven decision-making needs. Here’s why it might be the right fit for you:
Comprehensive Survey Capabilities
QuestionPro provides extensive tools for creating surveys with quantitative questions, allowing you to gather structured data from respondents. Whether you need Likert scale questions, multiple-choice questions, or numerical input fields, QuestionPro offers the flexibility to design surveys tailored to your research objectives.
Real-Time Data Analysis
With QuestionPro’s real-time data collection and analysis features, you can access and analyze survey responses as soon as they are submitted. This enables you to quickly identify trends, patterns, and insights without delay, facilitating agile decision-making based on up-to-date information.
Advanced Statistical Analysis
QuestionPro includes advanced statistical analysis tools that allow you to perform in-depth quantitative analysis of survey data. Whether you need to calculate means, medians, standard deviations, correlations, or conduct regression analysis, QuestionPro offers the functionality to derive meaningful insights from your data.
Data Visualization
Visualizing quantitative data is crucial for understanding trends and communicating findings effectively. QuestionPro offers a variety of visualization options, including charts, graphs, and dashboards, to help you visually represent your survey data and make it easier to interpret and share with stakeholders.
Segmentation and Filtering
QuestionPro enables you to segment and filter survey data based on various criteria, such as demographics, responses to specific questions, or custom variables. This segmentation capability allows you to analyze different subgroups within your dataset separately, gaining deeper insights into specific audience segments or patterns.
Cost-Effective Solutions
QuestionPro offers pricing plans tailored to different user needs and budgets, including options for individuals, businesses, and enterprise-level organizations. Whether conducting a one-time survey or needing ongoing access to advanced features, QuestionPro provides cost-effective solutions to meet your requirements.
Choosing the right quantitative data analysis software depends on your specific needs, budget, and level of expertise. Whether you’re a researcher, marketer, or business analyst, these top 10 software options offer diverse features and capabilities to help you unlock valuable insights from your data.
If you’re looking for a comprehensive, user-friendly, and cost-effective solution for quantitative data analysis, QuestionPro could be the right choice for your research, survey, or data-driven decision-making needs. With its powerful features, intuitive interface, and flexible pricing options, QuestionPro empowers users to derive valuable insights from their survey data efficiently and effectively.
So go ahead, explore QuestionPro, and empower yourself to unlock valuable insights from your data!
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Customer Communication Tool: Types, Methods, Uses, & Tools
Apr 23, 2024

Top 12 Sentiment Analysis Tools for Understanding Emotions

QuestionPro BI: From research data to actionable dashboards within minutes
Apr 22, 2024

21 Best Customer Experience Management Software in 2024
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

Decoding Factors Influencing Mental Health Help-Seeking in Asian International Students: A Correlational Survey Study
Article sidebar.

Main Article Content
This study investigates the effects of gender, age, perceived socioeconomic status, and attitudes toward mental health treatment, alongside the awareness and accessibility of mental health services, on the propensity of Asian international undergraduate and graduate students in U.S. colleges to seek mental health support. Utilizing an online survey, responses from a diverse group of 116 participants, aged 18 and above, from universities across the nation were examined through correlation analysis. Findings indicated no significant gender differences in attitudes toward mental health treatment. However, factors such as higher educational level, superior socioeconomic background, longer U.S. residency, and increased awareness and accessibility of mental health services positively influenced attitudes. This quantitative study extends previous qualitative research addressing similar questions, filling a gap by offering broader empirical insights into this population’s mental health service utilization. The outcome underscores the need for university counseling centers to develop targeted interventions that acknowledge the needs of Asian international students. Future research should explore the longitudinal impacts of these factors on mental health help-seeking behaviors to inform ongoing service improvement.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Revised on June 22, 2023. Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalize results to wider populations. Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research, which involves collecting and analyzing ...
Here are some key characteristics of quantitative research: Numerical data: Quantitative research involves collecting numerical data through standardized methods such as surveys, experiments, and observational studies. This data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify patterns and relationships.
Quantitative data analysis is one of those things that often strikes fear in students. It's totally understandable - quantitative analysis is a complex topic, full of daunting lingo, like medians, modes, correlation and regression.Suddenly we're all wishing we'd paid a little more attention in math class…. The good news is that while quantitative data analysis is a mammoth topic ...
Quantitative Research: Focus: Quantitative research focuses on numerical data, seeking to quantify variables and examine relationships between them. It aims to provide statistical evidence and generalize findings to a larger population. Measurement: Quantitative research involves standardized measurement instruments, such as surveys or questionnaires, to collect data.
Factor analysis is a way to reduce the complexity of your research findings by trading a large number of initial variables for a smaller number of deeper, underlying ones. In performing factor analysis, you uncover "hidden" factors that explain variance (difference from the average) in your findings.
Survey research is defined as "the collection of information from a sample of individuals through their responses to questions" ( Check & Schutt, 2012, p. 160 ). This type of research allows for a variety of methods to recruit participants, collect data, and utilize various methods of instrumentation. Survey research can use quantitative ...
Revised on 10 October 2022. Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analysing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalise results to wider populations. Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research, which involves collecting and ...
The survey is a common technique in quantitative observational research (Creswell 2014); it provides a numeric description of sample characteristics or the whole population under study (Balnaves and Caputi 2001).It is widely used in a variety of fields to generate information.
Historically, surveys have been seen as an exclusively quantitative research method but this is really an outmoded view. ... between experienced and less experienced therapists on a variety of topics and illustrate just how stimulating survey data analysis can be. From a statistical perspective crosstabulations can be analysed using the Chi ...
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. ... In quantitative research, ... and changed during the qualitative study.3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in ...
The survey that was shown at the beginning of the chapter was done on pen and paper, so it had to be manually entered into a spreadsheet for analysis. As we discussed, quantitative research generally means using numbers and statistical techniques, so all those question you asked have to be converted.
Quantitative research focuses on the thoughts, feelings, and values of a participant, to understand why people act in the way they do. They result in data types like quotes, symbols, images, and written testimonials. These data types tell researchers subjective information, which can help us assign people into categories, such as a participant ...
Qualitative data is often very detailed, but the tradeoff is that it takes a very long time to collect and analyze. In contrast, quantitative research data can be captured very quickly, and if you use tools like SurveyMonkey's analysis tools, statistical analysis can be almost immediate. This is very useful if you need insight critically.
Quantitative research methods are concerned with the planning, design, and implementation of strategies to collect and analyze data. Descartes, the seventeenth-century philosopher, suggested that how the results are achieved is often more important than the results themselves, as the journey taken along the research path is a journey of discovery. . High-quality quantitative research is ...
Quantitative research is the methodology which researchers use to test theories about people's attitudes and behaviors based on numerical and statistical evidence. Researchers sample a large number of users (e.g., through surveys) to indirectly obtain measurable, bias-free data about users in relevant situations.
One of the biggest benefits of using a quantitative research approach is that insights around a research topic can undergo statistical analysis; the same can't be said for qualitative data like focus group feedback or interviews. Another major difference between quantitative and qualitative research methods is that quantitative surveys ...
With its many data analysis techniques, SurveyMonkey makes it easy for you to turn your raw data into actionable insights presented in easy-to-grasp formats.Features such as automatic charts and graphs and word clouds help bring data to life. For instance, Sentiment Analysis allows you to get an instant summary of how people feel from thousands or even millions of open text responses.
Quantitative research involves studying a group of people representing a larger population. Researchers use a survey or another quantitative research method to efficiently gather information from these participants, making the process of analyzing the data and identifying patterns faster and more manageable through the use of statistical analysis.
Conclusions. Data cleaning and deduplication preserve survey integrity. Exploratory data analysis provides a chance to detect trends and gain intuition. Composite formation improves both reliability and validity. Hypothesis testing based on expert knowledge.
Quantitative research is used to validate or test a hypothesis through the collection and analysis of data. (Image by Freepik) If you're wondering what is quantitative research and whether this methodology works for your research study, you're not alone. If you want a simple quantitative research definition, then it's enough to say that this is a method undertaken by researchers based on ...
Course Introduction • 4 minutes • Preview module. Introduction to Preparing to Design a Quantitative Survey for Market Research • 1 minute. Identifying Business Objectives • 4 minutes. Assessing Suitability of Quantitative Research • 5 minutes. Building On Qualitative Findings to Inform a Quantitative Survey • 4 minutes.
Writing Survey Questions. Perhaps the most important part of the survey process is the creation of questions that accurately measure the opinions, experiences and behaviors of the public. Accurate random sampling will be wasted if the information gathered is built on a shaky foundation of ambiguous or biased questions.
Best 10 Quantitative Data Analysis Software. 1. QuestionPro. Known for its robust survey and research capabilities, QuestionPro is a versatile platform that offers powerful data analysis tools tailored for market research, customer feedback, and academic studies.
Utilizing an online survey, responses from a diverse group of 116 participants, aged 18 and above, from universities across the nation were examined through correlation analysis. ... This quantitative study extends previous qualitative research addressing similar questions, filling a gap by offering broader empirical insights into this ...
Introduction. Journal clubs are fora where research articles are discussed and criticised [Citation 1].They can be used as a learning activity for developing students' skills in critical appraisal and data analysis and for introducing them to various methodologies and current research [Citation 1].Moreover, journal clubs are perceived as suitable for increasing students' exposure to ...