Can you pass the Citizenship Test? Visit this page to test your civics knowledge!
- AP US History Study Guide
- History U: Courses for High School Students
- History School: Summer Enrichment
- Lesson Plans
- Classroom Resources
- Spotlights on Primary Sources
- Professional Development (Academic Year)
- Professional Development (Summer)
- Book Breaks
- Inside the Vault
- Self-Paced Courses
- Browse All Resources
- Search by Issue
- Search by Essay
- Become a Member (Free)
- Monthly Offer (Free for Members)
- Program Information
- Scholarships and Financial Aid
- Applying and Enrolling
- Eligibility (In-Person)
- EduHam Online
- Hamilton Cast Read Alongs
- Official Website
- Press Coverage
- Veterans Legacy Program
- The Declaration at 250
- Black Lives in the Founding Era
- Celebrating American Historical Holidays
- Browse All Programs
- Donate Items to the Collection
- Search Our Catalog
- Research Guides
- Rights and Reproductions
- See Our Documents on Display
- Bring an Exhibition to Your Organization
- Interactive Exhibitions Online
- About the Transcription Program
- Civil War Letters
- Founding Era Newspapers
- College Fellowships in American History
- Scholarly Fellowship Program
- Richard Gilder History Prize
- David McCullough Essay Prize
- Affiliate School Scholarships
- Nominate a Teacher
- State Winners
- National Winners
- Gilder Lehrman Lincoln Prize
- Gilder Lehrman Military History Prize
- George Washington Prize
- Frederick Douglass Book Prize
- Our Mission and History
- Annual Report
- Contact Information
- Student Advisory Council
- Teacher Advisory Council
- Board of Trustees
- Remembering Richard Gilder
- President's Council
- Scholarly Advisory Board
- Internships
- Our Partners
- Press Releases
History Resources


Selected Essays about Frederick Douglass
Many essays about Frederick Douglass and his times have been published on the Gilder Lehrman Institute website and in History Now , the online journal of the Gilder Lehrman Institute. The selected essays listed below provide historical perspective for teachers, students, and general readers.
The first essay is open to everyone for free. The rest of the essays are available by subscription to History Resources or History Now (both free for K–12 teachers and students in the free Gilder Lehrman Affiliate School Program; to join visit this page: Affiliate School Program ).
Frederick Douglass: An Example for the Twenty-First Century by Noelle N. Trent (National Civil Rights Museum)
Director of Interpretation, Collections, and Education at the National Civil Rights Museum at the Lorraine Motel, Noelle N. Trent writes about Frederick Douglass’s legacy and influence on the present day in this essay.
“The Merits of This Fearful Conflict”: Douglass on the Causes of the Civil War by David Blight (Yale University)
Historian David Blight discusses Douglass’s reflection on the Civil War and his fear that Americans were forgetting about the root causes of the war in their efforts to reconcile the North and the South.
Frederick Douglass: From Slavery to Freedom by Steven Mintz (University of Texas at Austin)
Historian Steven Mintz writes about Douglass’s journey from being enslaved to becoming one of the most prominent Black activists of his time.
The Lion of All Occasions: The Great Black Abolitionist Frederick Douglass by Manisha Sinha (University of Connecticut)
Historian Manisha Sinha writes about Douglass’s work as an abolitionist in this essay from the Winter 2018 issue of History Now, “Frederick Douglass at 200.”
Douglass the Autobiographer by Robert S. Levine (University of Maryland, College Park)
Professor Robert S. Levine discusses Frederick Douglass’s autobiographies and writing in this essay from the Winter 2018 issue of History Now, “Frederick Douglass at 200.”
Frederick Douglass, Orator by Sarah Meer (University of Cambridge)
Sarah Meer, a professor of nineteenth-century literature, explores Douglass’s work through his speeches.
Stay up to date, and subscribe to our quarterly newsletter.
Learn how the Institute impacts history education through our work guiding teachers, energizing students, and supporting research.

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
Frederick Douglass
Frederick Douglass (c. 1817–1895) is a central figure in U.S. and African American history. [ 1 ] He was born into slavery circa 1817; his mother was an enslaved black woman, while his father was reputed to be his white master. Douglass escaped from slavery in 1838 and rose to become a principal leader and spokesperson for the U.S. Abolition movement. [ 2 ] He would eventually develop into a towering figure for the U.S. Civil Rights Movement and American politics, and his legacy would be claimed by a diverse span of groups, from liberals and integrationists to conservatives to nationalists, within and without black America.
He wrote three autobiographies, each one expanding on the details of his life. The first was Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written By Himself (1845); the second was My Bondage and My Freedom (1855); and the third was Life and Times of Frederick Douglass (1881/1893). [ 3 ] They are now foremost examples of the American slave narrative. In addition to being autobiographical, they are also, as is standard, explicitly works of political and social criticism and moral suasion; they aim at the hearts and minds of the readers. Their greater purpose was to attack slavery, contribute to its abolition in the United States, and argue for black Americans’ full inclusion into the nation.
Shortly after escaping from slavery, Douglass began operating as a spokesperson, giving numerous speeches about his life and experiences for William Lloyd Garrison’s American Anti-Slavery Society. To spread his story and assist the abolitionist cause and counter early charges that someone so eloquent as he could not have been a slave, Douglass wrote and published his first autobiography, The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written By Himself . It brought Douglass fame throughout the United States and the United Kingdom, and it provided the funds to purchase his freedom. Douglass eventually broke with Garrison and founded his first paper, the North Star . He served as its chief editor and authored a considerable body of letters, editorials, and speeches from then on. These writings are collected in Philip Foner’s multi-volume, The Life and Writings of Frederick Douglass (1950–1975), and John W. Blassingame and John R. McKivigan’s multi-volume, The Frederick Douglass Papers (1979–1992). [ 4 ]
Douglass’s advocacy in the abolition movement and his continued work after the U.S. Civil War, and his writings and participation in national discussions about the nature and future of the American Republic, made him a significant figure in American history and the history of American political ideas. His writings, speeches, and his national and international work have inspired many lines of discussion in debate within the fields of American and African American history and political science. Moreover, political thinkers representing different ideological positions, including liberals, libertarians, and economic and social conservatives, claim his legacy.
But what does anything about this have to do with philosophy? The connections between Douglass’s legacy and social and political philosophy are numerous and ongoing. His ideas about humanity, liberty, equality, property, democracy, and individual and social development addressed immediately pressing concerns, but they were also theoretical—he self-consciously addressed their moral and theological foundations. Furthermore, his work is connected to academic philosophy through the uptake of his political and social legacy and writings by later African American philosophers such as W.E.B. Du Bois (1868–1963) and Alain Locke (1884–1954). [ 5 ] In contemporary philosophy, Douglass’s work is usually taken up within American philosophy, Africana philosophy, black political philosophy, and moral, social, and political philosophy more broadly. In particular, the discussions that involve Douglass focus on his views concerning some of the topics reviewed in this entry: slavery and racial segregation; natural law and the U.S. constitution; liberalism and republicanism; violence, self-respect, and dignity; racial integration versus emigration or separation; cultural assimilation and racial amalgamation; democratic action; and women’s suffrage. Additionally, just as there is a rich discussion about Douglass in philosophy and political theory, there is a related discussion about Douglass’s rhetoric, particularly the structure and meaning of his political rhetoric as displayed in his speeches, autobiographies, and other writings. [ 6 ]
For students and teachers first learning about Douglass, there is no better place to start than his first autobiography, The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass (1845). Next, read some of his speeches and writings referenced in this entry, especially “What To the Slave Is The Fourth of July?” (1852 [SFD: 55–92]). Then dive into the historical, political, literary, and philosophical literature about Douglass.
2. Natural Law
3. on liberty, 4. the u.s. constitution, 5. violence and self-defense, 6. respect and dignity, 7. universal human brotherhood, 8. amalgamation and assimilation, 9. integration versus emigration, 10. leadership, 11. women’s suffrage, 12. at the dawn of jim crow, a.1 collections and abbreviations, a.2 works by douglass, b. secondary literature, other internet resources, related entries.
In his narratives, speeches, and articles leading up to the U.S. Civil War, Douglass vigorously argued against slavery. He sought to demonstrate that it was cruel, unnatural, ungodly, immoral, and unjust. Douglass laid out his arguments, first in his speeches while allied with William Lloyd Garrison’s American Anti-Slavery Society, and then in his first autobiography, the Narrative . As the U.S. Civil War drew closer, he expanded his arguments in many speeches, editorials, and his second autobiography, My Bondage and My Freedom. [ 7 ]
His definition of slavery identified its immorality and injustice by pinpointing its core wrong in the brutalization and the literal commodification of another human being and the stripping of them of their natural rights:
Slavery in the United States is the granting of that power by which on man exercises and enforces a right of property in the body and soul of another. The condition of a slave is simply that of the brute beast . He is a piece of property—a marketable commodity in the language of the law, to be bought and sold at the will and caprice of the master who claims him to be his property; he is spoken of, thought of, and treated as property. His own good, his conscience, his intellect, his affections are all set aside by the master. The will and the wishes of the master are the law of the slave. He is as much a piece of property as a horse. (1846 [SFD: 23]; my emphasis) [ 8 ]
In his own words, he worked to pour out “scorching irony” to expose the evil of slavery (1852 [SFD: 71]). His rebellion against slavery began, as he recounted, while he was enslaved. In his narratives, the depiction of his early recognition and general recognition among blacks and some whites of the injustice, unnaturalness, and cruelty of slavery was a significant element of his argument. It marks his first argument against slavery. Some of the apologists for slavery claimed that blacks were beasts, subhuman, or at least a degenerated form of the human species, drawing on a racial ideology that went back to at least the fifteenth century and that was common in the British American Colonies and then the United States. [ 9 ] Thomas Jefferson, for example, infamously intimates this racist view in his Notes on the State of Virginia (1785: Query 14). Against such racist ideology, Douglass argued that blacks were human, rational, and capable of the full range of human emotions and sensitivity. He mocked slavery’s apologists for their hypocrisies and contradictions when they claimed otherwise. In “The Meaning of July Fourth for the Negro”, he is derisive of the idea that he would even need to argue this point (1852 [SFD: 55–92]). [ 10 ]
Against the claim that blacks were beasts, he argued that instead, slavery had brutalized them. He pointed to the obviousness of blacks’ humanity and mocked the hypocrisy of slavery’s apologists. He rhetorically asked: Why should there be special laws prohibiting the free actions of blacks, such as rebelling against slave masters, or any other white person, if slaves were merely bestial and incapable of independent, responsible behavior? Indeed, why had slave masters encouraged their slaves’ Christianization and then forbade their religious gatherings? Along with this hypocrisy, American slaveholders feared and banned the education of blacks while demanding and profiting from their learning and development in the skilled trades. Thus, Douglass argued the accusation that blacks were beasts was predicated on the guilty knowledge that they were humans. Additionally, it subverted not only the natural goodness of blacks by brutalizing them, but it also did so to white slaveholders and those otherwise innocent whites affected by this wicked institution. Slavery, Douglass pointed out, consistent with Jefferson’s anxieties in Query 18 of the Notes on the State of Virginia (1785), was a poison in the body of the republic.
Second, since blacks were humans, Douglass argued they were entitled to the natural rights that natural law mandated ( §2 and §3 ) and that the United States recognized in the Declaration of Independence and Constitution ( §4 ). Slavery subverted the natural rights of blacks by subjugating and brutalizing them: taking men and turning them, against God’s will and nature, into beasts. Third, as an affront to natural law, slavery contradicted God’s laws and corresponding moral duties to others. As a witness and participant of the second Great Awakening, he took the politicized rhetoric of Christian redemption—personal and social liberation from sin—seriously. Douglass viewed redemption as intrinsically wrapped up with freedom from slavery and national liberation like other abolitionists. Fourth, he argued that slavery was inconsistent with the idea of America, with its national narrative and highest ideals, and not just with its founding documents. Fifth, drawing on theories of providential historical development (echoing common American views of manifest destiny), he argued that slavery was inconsistent with moral, political, economic, and social progress. Insofar as it propagated and protected slave power, America was on the wrong side of history on the question of slavery.
The apologists of slavery drew on the same ideological vein of historical progress to offer the defense that slavery was a benevolent and paternal system for the mutual benefit of whites and blacks. Douglass countered that calumny by drawing on his experiences, and the experiences of other enslaved black Americans, that American slavery was in no way benevolent. It brutalized black people. Slavery subjected them to debilitating, murderous violence, sexual violence and exploitation, split up families, denied them education, exploited their labor, and denied their natural property rights. Slavery, as Douglass’s relentlessly argued, was a deep and enduring injustice and evil. Enslaved black people were not happy slaves benefiting from the largess of kind, gentile white masters. Neither were they lacking in agency, self-esteem, self-respect, or a sense of dignity. They were moral beings, fully aware of the rights and capabilities they were unjustly deprived of. As Douglass proclaimed to the nation and world, black Americans wanted freedom, independence, the recognition of their full personhood, moral equality, and their rights as U.S. citizens (McGary and Lawson, 1992). [ 11 ]
The ideas that Douglass drew on in his arguments against slavery originate from natural law theory and Christian theology. Douglass was an Enlightenment thinker, a nineteenth-century modernist, and a Protestant, so natural law in his view was a combination of the prescriptions of reason and revelation evident in the historical and civilizational progress of humanity. One of his clearest articulations of this combined view is from a 1853 speech, “The Present Condition And Future Prospects of the Negro People” (1853b [FDSW: 250–259]), where condemns declares,
Slavery has no means within itself of perpetuation or permanence. It is a huge lie. It is of the Devil, and it will go to its place. It is against nature, against progress, against improvement, and against the Government of God. It cannot stand. It has an enemy in every bar of railroad iron, in every electric wire, in every improvement in navigation, in the growing intercourse of nations, in cheap postage, in the relaxation of tariffs, in common schools, in the progress of education, the spread of knowledge, in the steam engine, and in the World’s Fair…and in everything that will be exhibited there. (1853b [FDSW: 259]) [ 12 ]
The sources for his driving belief in natural law and its moral implications were many: the founding documents of the United States; popular intellectuals, such as Ralph Waldo Emerson and his colleagues and acquaintances in the American Abolition movement; the allies he encountered abroad; and his appreciation of George Combe’s The Constitution of Man , from 1834 (Van Wyhe 2004). However, given the numerous religious references in his speeches and writings, a primary source for his employment of the idea of natural law was his adaptation of the American Protestantism of the Second Great Awakening, with its democratic and republican values and generally independent spirit. All of this is on prominent display at the conclusion of his famous speech, “The Meaning of July Fourth for the Negro”:
The arm of the Lord is not shortened“, and the doom of slavery is certain. I, therefore, leave off where I began, with hope. While drawing encouragement from the Declaration of Independence, the great principles it contains, and the genius of American Institutions, my spirit is also cheered by the obvious tendencies of the age. (1852 [SFD: 90])
Relying on the deus ex machina was not enough for Douglass. His vision of natural rights involved action; his image of civic republicanism emphasized the need for active participation to claim or earn one’s rights and status as a citizen (Davis 1971; Pettit 1997; Myers 2008; Gooding-Williams 2009). As Douglass scathingly pointed out, the slave-holding states resisted the abolition of slavery, and many Americans were apathetic about its cruel injustices—humans resist providential justice. Therefore, he argued, the end of slavery required agitation, protest, and, if needed, military intervention.
Douglass longed for God to cast his thunderbolts of judgment at American slave power, but he knew that human action was needed to abolish slavery in America (Blight 1989: 26–58). His view of, if you will, enacted providence is on full display at the end of his famous Fourth of July speech of 1852, where he cited Psalm 68:31 and paired the idea of God’s fiat with the image of Africa and Asia rising:
The far off and almost fabulous Pacific rolls in grandeur at our feet. The Celestial Empire, the mystery of ages, is being solved. The fiat of the Almighty, ”Let there be Light“, has not yet spent its force. No abuse, no outrage whether in taste, sport or avarice, can now hide itself from the all-pervading light. The iron shoe, and crippled foot of China must be seen, in contrast with nature. Africa must rise and put on her yet unwoven garment. ”Ethiopia shall stretch out her hand unto God“. (1852 [SFD: 91]) [ 13 ]
There are many possible concerns about Douglass’s view of natural law, manifest destiny, and providence, which we can discern from a careful reading of the passage above; they involve a belief in historical teleological development and the human costs of that assumption. These costs include affirming nineteenth-century conceptions of civilizational backwardness of non-European societies or peoples. Thus, he is relatively silent about the United States’ destructive actions against indigenous peoples.
This aspect of Douglass’s views led Wilson Jeremiah Moses to characterize him and other early black political figures as ”Moses“ figures: exodus leaders, recipients of natural law for a chosen people. The chosen people, in this case, are African Americans in their travail for freedom, as well as the American Republic as a whole. Douglass—twinned eternally with Abraham Lincoln—is a lawgiver in the American civil religion (Moses 1978). This monumental, world-historical vita aside, Douglass’s faith in progress, although tested to its breaking point, resulted in his putting too much belief in the inevitability of progress. Nonetheless, his faith had a moral, social, and political purpose. He had no time for political pessimism, which is either a narcotizing sentiment for those who have surrendered to despair or a performative luxury whose decadence only those secure in their liberty can afford.
Instead of surrendering to despair, he joined the abolition movement after escaping slavery. And for that grand purpose, natural law and rights were ideas he believed in and used to significant effect. Thus, in his writings, his writings he repeatedly makes clear and direct references to concepts that flow from liberalism: liberty; moral and social equality; individuality; property rights, self-defense, and speech; the moral and instrumental value of labor; democracy; and composite (what we would call multiethnic or multiracial) nationality. This is why he is rightly associated with liberalism (Myers 2008; Buccola 2012). The relation between Douglass’s works and those ideas is apparent; however, three merit highlighting because they are not typically emphasized in the theoretical literature about Douglass: free speech, property, and composite nationality.
Douglass’s life after abolition speaks to the importance of the freedoms of speech, thought, and opinion and the great value he placed on them. From his efforts to learn how to read and write to his desire to start his own newspaper, his attitude and actions aggressively asserted the indivisible links between equal liberty and the right to think and speak one’s mind. Like the name of his first newspaper, this value was his North Star . So, on 9 December 1860, in response to the violent disruption of a meeting he was participating in, Douglass directly addressed the matter in his speech, ”A Plea for Freedom of Speech in Boston“, wherein he delivered a classic liberal defense of it that still resonates:
There can be no right where any man however, lifted up or humble, however young or however old, is overawed by force, and compelled to suppress his honest sentiments. (1860c [FDP1 v.3: 423])
The silencing of speech squashes thought, opinion, and discussion, and doing so, as Douglass pointed out—consistent with other philosophers on liberty—commits a ”double wrong. It violates the right of the hearer as well as those of the speaker (Ibid.). [ 14 ]
On property, Douglass argues, as expected, against human bondage. That, however, was not the only thing he had to say about it. The positive right to property, the right of black Americans to their bodies, the labor of their bodies, and the wealth generated from their productivity are ideas that feature prominently throughout the narratives. Douglass wrote movingly about the productivity of his labor, the exploitation of it by his enslavers and those in their employ, the theft of his rightfully earned wages, and the anger of some white laborers who resented having to work and compete with free black workers. The right to self-ownership, labor, and property were not just mere things denied to him—they were expressions, products, and symbols of his liberty and liberty in general. In the Narrative , for example, on the theft of his wages by Hugh Auld, his master’s brother, Douglass wrote,
I was now getting, as I have said, one dollar and fifty cents per day. I contracted for it; I earned it; it was paid to me; it was rightfully my own; yet, upon each returning Saturday night, I was compelled to deliver every cent of that money to Master Hugh. And why? Not because he earned it,—not because he had any hand in earning it,—not because I owed it to him, nor because he possessed the slightest shadow of a right to it; but solely because he had the power to compel me to give it up. The right of the grim-visaged pirate upon the high seas is exactly the same. (FDAB: 84)
From the Civil War through Reconstruction and its betrayal, Douglass continued to see the right to property as a necessary part of genuine emancipation. He wrote and frequently spoke about the ennobling, moral, and economic power of labor, private property, and individual productivity in articles before emancipation like, “What Shall be Done with the Slave if Emancipated” from 1862 (FDSW: 470–473) to speeches like “Self-Made Men” from 1893 (SFD: 414–453).
On composite nationality, or what we would call multiethnic democracy, Douglass’s “Our Composite Nationality” from 1869a (SFD: 278–303) is a ringing endorsement of a robust vision of civic belonging and national identification. It is an outlook that reflects his support for organic processes of assimilation and amalgamation and social reform. More on that below ( §§6–8 and §12 ).
Just as he drew on liberal ideas, he repeatedly invoked ideas of American civic republicanism and advocated for democratic reform, action, and, eventually, universal suffrage ( §11 ). This democratic advocacy has led some philosophers to view Douglass as a civic republican as much as he was a liberal (Gooding-Williams 2009). The evidence for that connection naturally arises from the wide variety of his democratic associational activity. It is modeled in his narratives, particularly in My Bondage and My Freedom , in its depictions of social organization, action, solidarity, friendship, and affection among black men and women (FDAB: 305–306).
Whether we understand Douglass as a liberal or civic republican (or even as a type of black nationalist or black radical liberal), the values and ideas he drew on were the foundation of his fierce denunciations of and active resistance to American slavery and his interpretation of the U.S. Constitution.
In 1851 Douglass broke from William Lloyd Garrison’s position that the U.S. Constitution was a pro-slavery document and that the free states should peacefully secede from the Union. In a letter to Gerrit Smith, he reported that he was “sick and tired of arguing on the slaveholder’s side…” (21 January 1851 [FDSW: 171–173]). So, he decided to break with Garrison and side with Smith and the Liberty party’s position that the United States’ founding documents were anti-slavery (Blight 1989: 26–58; Root 2020).
In his famous speech on the topic, “What To the Slave Is The Fourth of July?” (1852 [SFD: 55–92]), he detailed his signature positions on the U.S. Constitution: that slavery is contrary to natural law, that blacks are self-evidently human and entitled to natural rights, and that slavery is inconsistent with the Constitution, American Republicanism, and Christian doctrine, and that it should be forcefully—violently—resisted. [ 15 ] A principal example of this shift is the changes in his second autobiography, My Bondage and My Freedom (1855, FDAB); particularly relevant is the extra and weighty meaning he imparts to the famous scene of his fight with the slave breaker Covey ( §5 ).
Douglass acknowledged that initially, he accepted the view, promoted by William Lloyd Garrison and allies aligned with him, that the framers intended to allow slavery to continue in the slave states and that the Constitution was thereby consistent with the institution of slavery. However, the Garrisonian view of the Constitution resulted in passivity in the face of the Slave-holding states’ threat of succession. That position did not sit well with Douglass because he wanted a more aggressive stance and strategy for abolishing slavery and the emancipation of the enslaved, including in the southern slave-holding states. Plus, he became convinced of the natural law reading of the U.S. Constitution that foregrounded the values outlined in the U.S. Declaration of Independence. What convinced him were the arguments of Gerrit Smith, Lysander Spooner, William Goddell, and Samuel E. Sewall that the Constitution was an anti-slavery document and that the founders were at cross-purposes on the question of slavery. Douglass argued that the general ideas of America’s founding documents supported an interpretation of the U.S. Constitution as an evolving document in tune with the development of civilization. Thus, he intoned the call, “let there be light”, to capture his hope for abolition, emancipation, and universal political and social progress (1852 [SFD: 91]).
Douglass’s view of the Constitution is one of the reasons why he is associated with the assimilationist (or what is better understood as the integrationist tradition) tradition in African American political thought. It sets him up for the criticism that he did not squarely recognize the racialized character of the nation, how deeply embedded race and racism were in its institutions, and that it was in many respects a racial state. [ 16 ] Douglass, however, was not blithe to the nation’s sins—he repeatedly and forcefully condemned them through the end of his life ( §12 ). His reading of the Constitution was reasonable, grounded in his affirmation of natural law theory, and it was an essential part of the history of abolition (Sinha 2016; Delbanco 2018).
Douglass remained active in the years leading up to the U.S. Civil War. He advocated for the abolition of slavery, worked against the expansion of slavery into new U.S. territories, and vigorously protested the Dred Scott decision and related laws that protected the property rights of slaveholders over slaves who escaped to the Free States in the North.
He was a member of the Liberty party, was involved in other political parties, including the Radical and Free Soil parties, and eventually became involved with the Republican party—all for the sake of abolition and the support of equal citizenship for all Americans (Blight 1989 and 2018). Douglass even met the militant abolitionist, John Brown. Although Douglass declined to join Brown’s militia—he sensed the deadly potential of Brown’s zealotry and the likelihood of its failure—he defended Brown’s ideals and denounced claims that Brown was merely mad. Although Douglass distanced himself from Brown’s plans and destructive actions, he appropriated Brown as a symbol of righteous violence against the national sin of slavery and used the raid at Harper’s Ferry to criticize President Lincoln’s reluctance to support abolitionism (1859 [FDSW: 372–376]; 1860b [FDSW: 417–421]; Myers 2008: 63–73; Blight 1989: 95–100).
Douglass’s rejection of pacifism and his support for Federal military intervention to end slavery was a significant turning point in his thought about natural law, divine providence and manifest destiny, and constitutional interpretation. Douglass’s defense of jus ad Bellum greatly affected his contemporaries and the resulting debate on slavery, struggle, and self-respect. The modern debate over violence and self-respect in African American philosophy, critical race theory, and black political theory begins with Douglass’s narratives, particularly his famous fight with the “Negro breaker”, Edward Covey. This incident plays a significant role in all of Douglass’s narratives: Covey represents the brutalizing institution of American slavery, and Douglass’s fight and victory represent the assertion of manhood, self-respect, dignity, and freedom. However, Douglass’s time with Covey and the suffering he endured by Covey’s hand is given a lengthier description in My Bondage and My Freedom than in the Narrative . In the former, the depiction of the fight explicitly draws parallels between Douglass’s battle with Covey and the struggles of black Americans against slavery and racial degradation.
Additionally, his fight has explicit national political connotations (Gooding-Williams 2009; Myers 2008). The scene’s depiction in each autobiography is powerful and indicates its narrative brilliance (literary, rhetorical, and philosophical), so it deserves to be quoted at length. In the Narrative (1845), Douglass wrote:
The battle with Mr. Covey was the turning-point in my career as a slave. It rekindled the few expiring embers of freedom, and revived within me a sense of my own manhood. It recalled the departed self-confidence, and inspired me again with a determination to be free. The gratification afforded by the triumph was a full compensation for whatever else might follow, even death itself. He only can understand the deep satisfaction which I experienced, who has himself repelled by force the bloody arm of slavery. I felt as I never felt before. It was a glorious resurrection, from the tomb of slavery, to the heaven of freedom. My long-crushed spirit rose, cowardice departed, bold defiance took its place; and I now resolved that, however long I might remain a slave in form, the day had passed forever when I could be a slave in fact. I did not hesitate to let it be known of me, that the white man who expected to succeed in whipping, must also succeed in killing me. (FDAB: 65)
In My Bondage and My Freedom (1855), he gives the following expanded interpretation:
Well, my dear reader, this battle with Mr. Covey,—undignified as it was, and as I fear my narration of it is—was the turning point in my “life as a slave”. It rekindled in my breast the smouldering embers of liberty; it brought up my Baltimore dreams, and revived a sense of my own manhood. I was a changed being after that fight. I was nothing before; I WAS A MAN NOW. It recalled to life my crushed self-respect and my self-confidence, and inspired me with a renewed determination to be a FREEMAN. A man, without force, is without the essential dignity of humanity. Human nature is so constituted, that it cannot honor a helpless man, although it can pity him; and even this it cannot do long, if the signs of power do not arise. (FDAB: 286, original emphases)
The first passage displays Douglass’s romantic and religious influences; it swells with the longing for the freedom of the soul. The second passage, written without the demands of Garrison’s pacifist politics directing his pen, screams independence and force. It recommends violence—it advocates for the coming U.S. Civil War—to throw off tyranny and claim, defend, and even fulfill one’s honor and humanity.
The fight with Covey has inspired several philosophical interpretations of Douglass’s intentions and the meaning of his struggle. It is commonly read as an exemplar of the conception of the state of war within liberal political theory (Davis 1971) and the interpersonal, or generally relational, dynamics of respect and recognition. [ 17 ] In particular, Bernard Boxill (1997 and 1998) developed an exceptionally influential deontological account of Douglass’s fight as emblematic of the individual sense of self-respect of oneself as a moral being. [ 18 ] That self-recognition comes with the obligation to defend one’s self-respect and to expect respect from others, which implies that others should recognize one’s inherent dignity. For Douglass, that fight was a parable—like Jacob’s wrestling with an angel (Genesis 32:24–32 [KJV]), [ 19 ] except in this case, the antagonist was more demonic than angelic—about the American and black American fight against slavery and racism.
What is more, Douglass’s evocation of dignity in his narrative of the fight is intellectually and emotionally stunning. “A man, without force”, he intensely asserted, “is without the essential dignity of humanity”. He adds to that the claim that
[h]uman nature is so constituted, that it cannot honor a helpless man, although it can pity him; and even this it cannot do long, if the signs of power do not arise. (FDAB, 286, original emphases)
The moral weightiness of the idea of dignity and his use of it invites us to consider whether it plays a special role in his thought and its relation to his frequently repeated arguments and assertions of the humanity and equal moral personhood of black people. Most of his mentions of dignity in his speeches and writings primarily refer to it as an ordinary sense of respectful comportment and propriety. Nonetheless, everyday assertions of dignity, even passive ones, have morally serious implications for individuals, groups, and societies under conditions of absolute domination, such as faced by black Americans during slavery and Jim Crow segregation. Assertions of everyday dignity could often be met with severe and sometimes violent consequences under those conditions—a fact that Douglass highlighted and condemned throughout his life. When Douglass referred to moral personhood as such (the essential moral worth of persons), he typically used the ideas of “equality”, “perfect human equality”, “manhood”, “brotherhood”, and “universal human brotherhood”.
There are, however, moments, as noted in the passage above from My Bondage and My Freedom , where his usage of “dignity” explicitly points to the idea of equal moral personhood.
The same is true in an editorial he wrote in 1850 responding to slander, verbal assaults, and a physical one:
My crime is, that I have assumed to be a man, entitled to all the rights, privileges and dignity, which belong to human nature —that color is no crime, and that all men are brother. I have acted on this presumption . The very “head and front of my offending hath this extent—no more”. I have not merely talked of human brotherhood and human equality, but have reduced that talk to practice. This I have done in broad open day, scorning concealment. I have walked through the streets of New York, in company with white persons, not as a menial, but as an equal. (1850 [FDSW: 157]; my emphases)
As discussed in the previous sections on slavery, natural law, liberty, the U.S. Constitution, and self-defense, Douglass vigorously defended equal personhood and thus the moral equality of black people. On that basis, he condemned slavery as an affront to natural law, Christianity, and republicanism. Therefore, regardless of the frequency he referred to the term “dignity”, he does get at the idea, and it does play a central role (along with and defined through the constellation of other ideas he drew on) in his political philosophical thought. Perhaps then, a basic account of dignity, as indicative of individual moral worth, is all that is needed to understand Douglass’s view. Stopping with that, however, would impart a sense of passivity to it. Douglass’s view was not simply static.
Dignity, for Douglass, is a natural and innate thing, bequeathed to all humans as humans. It is static or changeless in that limited sense. At the same time, Douglass suggests that willful action, epitomized by self-defense, was a condition of what was otherwise an inherent and essential quality of being a human person. It is something to be practiced. [ 20 ] But if dignity is innate and inherent, why must an individual practice it for it to be said that they have it? If it is an essential quality, then its practice or expression cannot be a condition of its possession. Douglass is not equivocating on this point. An individual’s equal moral status comes with the obligation to inhabit, abide by, and defend that status. [ 21 ] This is how we should understand Douglass’s view of dignity as modeled by his open-air rejection of servility and assertion of equality.
All the same, Douglass does not, nor could he, consistently hold that every enslaved black person needed to have an equivalent “fight with Covey” moment and assertion of “manhood” to secure their dignity and natural right to be treated as a moral equal. Directly related to this concern is the continuing discussion of whether the depiction of the fight with Covey and its meaning and value promote a masculinist vision of anti-slavery resistance, liberty, and autonomy (Wallace 2009 and 2014; Alfaro 2018). Douglass did not think that the attitudes and actions of the enslaved conditioned the immorality of slavery and the imperative of emancipation, so what counts as resistance to indignities of injustice requires careful and charitable consideration that is attentive to the constraints of individual circumstances and social conditions.
The bravado in Douglass’s wonderful affront to racism aside, his vision of self-respect, dignity, and the obligation to defend oneself and one’s dignity is central to his legacy. It plays a vital role in the history of African American political theory, and for that reason, given this nation’s history, it is a valuable contribution to American political philosophy about respect, dignity, and personhood. Its implications are profound, as can be seen in his view of universal human brotherhood.
Douglass’s conception of providence, with its American themes of individualism, anti-supernaturalism, and activism, and his view of natural law influenced his understanding of universal human brotherhood (Sundstrom 2003 and 2008: 11–35). He believed that the idea of universal human brotherhood was consistent with the high ideals of American Republicanism and Christianity. It was a doctrine dearly held by Douglass, and he offered it as a response to the rise in the United States of Samuel Morton’s (1799–1851) racial theory of polygenesis , that Josiah Nott and George Gliddon’s Types of Mankind (1854) popularized (Martin 1984; Myers 2008).
Douglass put considerable effort into countering arguments that blacks were subhuman, intellectually and morally inferior, and fit to be dominated as children, forever to be a race in nonage. To counter these claims, he turned to his natural law arguments. He argued that by the standards of Christian theology, blacks, as humans and creations of the divine, were all equally the children of God, no matter their present condition. One of his slogans, drawn directly from the title of a poem by the Scottish poet Robert Burns, got to the point: “A man’s a man for a’ that” (1795). [ 22 ] Douglass argued that the Christian Bible had to be correct on this score, that the authority of the biblical text relied on the affirmation of the unity of the human family:
What, after all, if they are able to show very good reasons for believing the Negro to have been created precisely as we find him on the Gold Coast—along the Senegal and the Niger—I say, what of all this?—“ A man’s a man for a’ that ”. I sincerely believe, that the weight of the argument is in favor of the unity of origin of the human race, or species—that the arguments on the other side are partial, superficial, utterly subversive of the happiness of man, and insulting to the wisdom of God. Yet, what if we grant they are not so? What, if we grant that the case, on our part, is not made out? Does it follow, that the Negro should be held in contempt? Does it follow, that to enslave and imbrue him is either just or wise ? I think not. Human rights stand upon a common basis; and by all the reason that they are supported, maintained and defended, for one variety of the human family, they are supported, maintained and defended for all the human family; because all mankind have the same wants, arising out of a common nature. A diverse origin does not disprove a common nature, nor does it disprove a united destiny. (1854 [SFD: 147] [FDP1 v.2: 523])
He emphasized that not only was slavery against natural law and Christian morality but that the very arguments concerning the subhuman status of blacks that slavery’s apologists used to justify attempted slavery contradicted the Bible and were heretical. Douglass, in short, leveraged the Bible and America’s reverence for it against the rising tide of polygenesis race theory. He stated:
The unity of the human race—the brotherhood of man—the reciprocal duties of all to each, and of each to all, are too plainly taught in the Bible to admit of cavil.—The credit of the Bible is at stake—and if it be too much to say, that it must stand or fall, by the decision of this question, it is proper to say, that the value of that sacred Book—as a record of the early history of mankind—must be materially affected, by the decision of the question. (1854 [SFD: 126] [FDP1 v.2: 505])
The doctrine of universal human brotherhood for Douglass, and the abolitionists, was based on the Bible’s creation story and Acts 17:26 [KJV]: “And hath made of one blood all nations of men for to dwell on all the face of the earth”.
These words were not mere words for Douglass and the abolitionists; they were not just-so stories. The Christian doctrine of the unity of the human family or human brotherhood contained the world-historical insight of equal human dignity, which implied—unleashed, as seen in several revolutions in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries—an uncompromising demand for moral equality and equal liberty.
Douglass’s affirmation of universal human brotherhood, his belief in providential human development, and his observation of the mixing of racialized groups in the United States led him to directly support racial amalgamation: race-mixing was a sign of progress for Frederick Douglass. It is important to note here that he thought there were races to amalgamate, so he affirmed the basic idea that biologically distinct races existed (1854 [SFD: 116–150]). As his view of universal human brotherhood should be clear, he did not think much followed from that admission. The existence of biological races did not, in his view, negate the theological-philosophical insight of universal human brotherhood.
Douglass understood that the sexual boundaries between the races were thin and that, indeed, the conditions of slavery led to a great deal of mixing. Recall that he maintained that his unacknowledged father was his white master, and, in no uncertain terms, he condemned the rape, sexual violence, and exploitation of black women. Yet, given his commitment to his ideals, Douglass promoted amalgamation between free peoples. He believed that blacks and white ought to be free to intermarry and that they should do so. Why should they marry? Douglass, sensing the transformation of the black and Native American population in the United States, believed this process was a natural and continual process; that a new third race, an American race, would emerge in this land. During his time, such views were highly inflammatory and served, and continued to serve, as a reason against the emancipation of enslaved black people and later as a justification for segregation (Sundstrom 2008: 11–35). Nonetheless, in the 1860s, he boldly advocated for amalgamation between the races. He remarked to a journalist, the day after his second marriage to Helen Pitts, who was white,
…there is no division of races. God Almighty made but one race. I adopt the theory that in time the varieties of races will be blended into one. Let us look back when the black and the white people were distinct in this country. In two hundred and fifty years there has grown up a million of intermediate. And this will continue. You may say that Frederick Douglass considers himself a member of the one race which exists. (1884 [FDP1 v.5: 147])
Douglass’s amalgamation is easy to confuse with his support for assimilation. Amalgamation is conceptually distinct from assimilation; one does not have to accept amalgamation to support assimilation. Assimilation concerns various degrees of acculturation. It can theoretically go in either direction, from black to white or white to black, and it can involve the subtle blending of both and many groups (Sundstrom 2008). His support for amalgamation and assimilation could not be any clearer than what he proclaimed in “On Composite Nationality”, in which he called for the molding of all in the land into a common Americanness (1869a [SFD: 278–303]; §12 ). In his enthusiasm for this molding, he is distinct, but he was not exceptional in his support of assimilation; several of his contemporaries and leaders who followed him supported some degree of assimilation. Even some of Douglass’s early critics, such as Edward Blyden (1832–1912), Martin Delany (1812–1885), and Alexander Crummell (1819–1898), who did not support amalgamation, still believed in the assimilation of black Americans to the standards and values Western civilization (Moses 1978).
Douglas advocated assimilation and amalgamation, so, understandably, he supported the right of black Americans to remain in the United States and thought they ought to do so. Rather than leave the country to find homes and start lives abroad in places that they imagined might provide friendlier quarters, Douglass urged black Americans to stay and support abolition efforts and then, in the postbellum years, to fight for equal rights and citizenship. He can be considered a primary example of the political ideal of racial integration as distinct from racial separatism. Douglass’s amalgamation-assimilationist views of the 1860s are not the desegregationist and integrationist ideas associated with the U.S. Civil Rights movement that began around the mid-1950s. Other thinkers and movements influenced those views, which advocated for equal rights, protection, citizenship, and equal access to schools, colleges and universities, and neighborhoods. Yet, Douglass is a fitting icon for the American integrationist impulse.
In his essay from 1848, “The Folly of Racially Exclusive Organization”, Douglass criticized the creation of separate societies, with distinct “negro pews, negro berths in steamboats, negro cars, Sabbath or week-day schools or churches”, and in other social spaces and institutions (FDP1 v.2: 110–111). Formal racial segregation and informal separatism generally served the interests of the defenders of slavery; thus, after the U.S. Civil War, Douglass regarded ongoing racial separatism as a counter to the ideals of the abolition movement. It was a message he frequently repeated (1848a [FDSW: 117–122]).
He opposed plans for black American emigration to Africa, the Caribbean, Mexico, or Latin America for similar reasons. He criticized the emigrationist visions of the American Colonization Society, founded by whites, and the African Civilization Society, founded by blacks. He had four reasons to oppose emigration schemes: First, for slavery to end, Douglass argued that black Americans needed to struggle against it in America. Second, Americans had no other home but the United States; they were uniquely American and products of American history. Third, black Americans had a right to the property their labor had produced. By abandoning the United States, they would leave the land they had built. In his 1894 speech, “Lessons of the Hour” (SFD: 454–497), he wrote,
The native land of the American Negro in America. His bones, his muscles, his sinews, are all American. His ancestors for two hundred and seventy years have lived and laboured and died, on American soil, and millions of his posterity have inherited Caucasian blood. It is competent, therefore, to ask, in view of this admixture, as well as in view of other facts, where the people of this mixed-race are to go, for their ancestors are white and black, and it will be difficult to find their native land anywhere outside of the United States. (1894 [SFD: 485]).
Fourth, according to Douglass, emigration and separation were contrary to historical development and the emergence of a composite nation comprised of a blended people. All the same, Douglass was not opposed to blacks collectively acting in self-help and self-defense. Nonetheless, his opposition to emigration displayed a downside of his commitment to his natural law and manifest destiny-inspired principles. He did not appreciate enough how immigration might be more than a reasonable act of self-preservation and self-determination—in the face of anti-black life-crushing oppression and murderous violence—much like his own escape from slavery. [ 23 ] Initially, Douglass even opposed the internal migration of black Americans from the southern states to the northern ones (Myers 2008). However, he moderated his position nearer the end of his life (1879 [FDP1 v.4: 510–533]; 357 [FDP1 v.5: 357–373]); 1894 [SFD: 454–497]).
Douglass was a leader among the Americans involved in the abolition movement, and after the Civil War, although unelected into any office, he remained a leading voice for black Americans. [ 24 ] Garrison presented Douglass as a victim of and witness to slavery and as a spokesperson for Garrisonian abolitionism, but he freed himself from their restraints, just as he freed himself from slavery. To speak for himself, be his own man, and be a leader among men. That is what Douglass wanted. Thus, he shaped his own story, insisted on speaking his mind free from the control of handlers like Garrison, and strove to represent the interests of black Americans.
His example of leadership was quick to be seized and claimed by other prospective black leaders and spokespersons. The most significant example of this was the conflicting claim between W.E.B. Du Bois and Booker T. Washington (1856–1915) over Douglass’s legacy. Both men competed for the opportunity to publish a biography of Douglass with the publishers George W. Jacobs & Company in their series The American Crisis Biographies (Sundstrom 2008: 11–35). The press rejected Du Bois’s bid for this task in favor of Washington’s (1907) and granted Du Bois the project of writing a biography of John Brown instead—but he included within it an extensive discussion on Douglass (Du Bois 1909).
After the death of Douglass, Du Bois penned an unpublished elegiac poem, “The Passing of Douglass” (Du Bois 1999: ix), and he incorporated elements of Douglass’s narrative in The Souls of Black Folk (1903 [1999: xxii]), John Brown (1909), and Black Reconstruction in America (1935 [2021]). Du Bois presented Douglass as a self-assertive freedom fighter and a leader of an activist community that demanded full social and political liberty, equality, and inclusion. Du Bois’s Douglass was not an accommodationist: He was not the sort of black leader who paid obeisance to white leaders and consented to an oppressive status quo, all for a token pittance or self-aggrandizement. Du Bois made this pointed interpretation very clear in his The Souls of Black Folks . In the third chapter (“Of Mr. Booker T. Washington and Others”) of Souls , Du Bois argues against Booker T. Washington’s accommodationism in favor of his and Douglass’s demand for, and assertion of, black political and social equality and rights. Economic liberty is not enough, and any gains in the economic sphere would be hampered and vulnerable without the protections and opportunities provided by social and political liberty and rights. And, of course, economic considerations aside, the fight for equal rights and liberty is not solely about economic opportunity—it is about equal dignity and one’s full humanity.
However, it is essential to note that Du Bois took on Douglass’s mantle of leadership after he argued against Douglass’s view of assimilation and amalgamation. In “The Conservation of Races”, Du Bois rejected amalgamation, which Douglass supported, and advocated for conserving a distinct black identity and community (1897 [1992]). Here is his critical reduction of the amalgamation position:
It may, however, be objected here that the situation of our race in America renders this attitude impossible; that our sole hope of salvation lies in our being able to lose our race identity in the commingled blood of the nation; and that nay other course would merely increase the friction of races which we call race prejudice, and against which we have so long and so earnestly fought. (Du Bois 1897 [1992: 488])
Du Bois, in opposition to amalgamation, argued that black Americans ought to embrace a “stalwart originality” that follows “Negro Ideals” and not dissolve into a general American identity (Ibid.). It is a view associated with cultural pluralism that expresses an early version of black cultural nationalism. And as such, it is a historical conceptual landmark in debates in African social and political thought over racial separation versus assimilation and the conservation of race (Boxill 1992a: 173–85; 1992b; 1999; McGary 1999a; 1999b: 43–61; Pittman 1999). [ 25 ]
Because of his cultural pluralism, it is tempting to think that Du Bois rejected Douglass’s view of assimilation and integration, but that would be a mistake. He turned away from Douglass’s vision of total assimilation in favor of retaining some black ideals, which he too quickly assumed that all blacks qua blacks share. Still, his cultural pluralism has at its end the creation of a community that is a “co-worker” in the “kingdom of culture” (Du Bois 1903 [1999: 11]). What results from Du Bois’s rejection of amalgamation and acceptance of some elements of assimilation is the brilliant idea of double consciousness, especially the double consciousness brought on by the black American experience. As is evident from the rhetorical questions at the end of the following passage, Du Bois argued against Douglass’s hopes of amalgamation and presaged his view of black political, social, and cultural solidarity:
No Negro who has given earnest thought to the situation of his people in America has failed, at some time in life, to find himself at these cross-roads; has failed to ask himself at some time: What, after all, am I? Am I an American or am I a Negro? Can I be both? Or is it my duty to cease to be a Negro as soon as possible and be an American? If I strive as a Negro, am I not perpetuating the very cleft that threatens and separates Black and White America? Is not my only possible aim the subduction of all that is Negro in me to the American? Does my black blood place upon me any more obligation to assert my nationality than German, or Irish or Italian blood would? (Du Bois 1897 [1992: 488])
Du Bois’s answers to these questions directly contradict Douglass’s view about amalgamation. However, their opinions about assimilation share similarities, such as the co-production and enjoyment of a shared American culture. In the end, however, Du Bois’s image of Douglass is skewed toward his political projects of elite leadership, racial solidarity, and uplift.
Likewise, Booker T. Washington’s Douglass is equally a work of art that reflects the artist’s image. His The Life of Frederick Douglass (1907) presents a picture of Douglass contrary to Du Bois’s and is incompatible with many of Douglass’s views. It is, in part, a work of self-promotion. Although Washington accurately pointed out the similarities between Douglass and himself, he failed to mention Douglass’s assertions of equal personhood, his uncompromising demands for equal social and political rights, and that Douglass fully expected that black Americans would fully integrate into a “composite nation”. Washington’s claim over Douglass’s legacy of leadership falls short of the facts. Douglass was a radical Republican and demanded full inclusion of black Americans in the nation’s life and the opening of all opportunities for education and advancement for blacks, and Washington did not.
Du Bois’s claims over Douglass, however, also fall short. Despite Du Bois’s assumption that he had inherited the mantle of black political, social, and (he would add) cultural leadership from Douglass, Douglass’s leadership style and politics were markedly more democratic than Du Bois’s. Although Douglass likely saw himself as an instance of what Ralph Waldo Emerson called a “representative man” (Emerson 1850 [2004]) and as a self-made man to boot (1893 [SFD: 414–453]; 1860d [FDP1 v.3: 289–300]), he did not envision himself as the embodiment of the spirit or culture of his people Gooding-Williams 2009: 19–65).
Douglass’s political activities provide a model of democratic politics in action (Gooding-Williams 2009). He worked with various groups, some underground, while he was enslaved. For example, unbeknownst to his master, he participated in at least one Sabbath School and helped other slaves learn to read and write. And, of course, he worked with several other black and racially integrated advocacy groups after his escape and emancipation. These groups had cross-cutting interests that he had to navigate. He pushed them to reach a consensus on different issues, such as in his work with the American Equal Rights Association, an organization devoted to universal suffrage. So, he did not pose as a singular spokesman for movements, groups, or his race, although he never shied away from pushing or arguing his opinions and promoting democratic action (1848 [FDSW: 117–122]).
Indeed, his liberal and civic republican ideas influenced his thoughts about leadership and his vision of the work and role of “heroes” and so-called “representative men” (1883b [SFD: 374–400]; 1893 [SFD: 414–453]; 1860d [FDP1 v.3: 289–300]). For Douglass, they were invaluable in their stance against tyranny and defense of equal rights and liberty. On John Brown, for example, Douglass wrote, putting him into heroic terms (with overtones of Thomas Carlyle and Ralph Waldo Emerson),
He believes the Declaration of Independence to be true, and the Bible to be a guide to human conduct, and acting upon the doctrines of both, he threw himself against the serried ranks of American oppression, and translated into heroic deeds the love of liberty and hatred of tyrants, with which he was inspired from both these forces acting upon his philanthropic and heroic soul. (1859 [FDSW: 375])
Thus, in his elegies to John Brown and Abraham Lincoln, we see the value he places on Emersonian representative men and the ideal of the statesman guided by liberal and civic republican principles (1859 [FDSW: 372–376]; 1860b [FDSW: 417–421]; 1876 [FDSW: 616–624]).
After the Civil War, Douglass remained active in Republican Party. He was a staunch supporter of uncompromising Reconstruction of the Union and advocated for economic and education investment in free and newly-freed black Americans. Douglass pressed for the expansion of and guarantee of civil rights for blacks, particularly for the defense of the Civil Rights Act of 1875, which the Supreme Court declared unconstitutional in 1883 (1883a [FDSW: 685–693]). Additionally, in keeping with his civil rights efforts and his view of natural rights and the development of the United States into a just Republic, he was an advocate, although a complicated one, of women’s suffrage (Douglass 1976). He joined other prominent leaders in the abolition movement, such as Sojourner Truth, and emerging leaders in the suffrage movement, such as Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton, in these efforts.
The American Equal Rights Association was the principal national organization working on behalf of women’s right to vote. At least in rhetoric, it had a dual platform of racial and sexual equality (DuBois 1978). Middle-class and wealthy white women primarily led it, and Douglass supported its platform but clashed with its leaders over conflicting interests and its latent racism. The tensions within the American Equal Rights Association, and the suffrage movement generally, erupted over the passing of the fifteenth amendment to the U.S. Constitution. The fifteenth amendment franchised all male citizens, although, as U.S. history so brutally revealed, it did so in word but not in deed. Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Susan B. Anthony opposed the fifteenth amendment because they demanded that black men and all women (particularly white women) should be enfranchised simultaneously. Some within the suffrage movement based their arguments for women’s suffrage and against blacks’ enfranchisement on racist grounds. Although the white women who led the association were abolitionists, they also, and not inconsequentially, held that blacks, particularly black men, were inferior to white women and neither as ready for nor deserving of the vote as they were (Stanton 1868 [2000: 194–199] and 1869 [2000: 236–238]).
Douglass was sympathetic to the cause of the universal franchise; however, he condemned arguments for women’s suffrage that were predicated on the supposed racial superiority of white women. He roundly condemned Stanton’s racist claims that black and “Oriental” men, and by extension black and Asian women—i.e., Stanton’s nasty references to “Sambo” and “Yung Tung”—were not as deserving as white women (1869b [FDP1 v.4: 213–219]; Stanton 1868 [2000: 194–199]). Douglass did not want to delay the franchise for black males to resolve the question of women’s right to vote. He believed it a practical matter to quickly get some protections for black Americans while the fight for suffrage for black and white women continued. Moreover, he argued it was imperative to obtain some measure of blacks’ political, legal, and social rights to confront the rising level of horrific anti-black violence sweeping the United States. Douglass firmly made this claim in his speech at an American Equal Rights Association meeting in 1869:
I must say that I do not see how any one can pretend that there is the same urgency in giving the ballot to women as to the negro. With us, the matter is a question of life and death. It is a matter of existence, at least in fifteen states of the Union. When women, because they are women, are hunted down through the cities of New York and New Orleans; when they are dragged from their houses and hung upon lamp-posts; when their children are torn from their arms, and their brains dashed out upon the pavement; when they are objects of insult and outrage at every turn; when they are in danger of having their homes burnt down over their heads; when their children are not allowed to enter schools; then they will have an urgency to obtain the ballot equal to our own. (1869b [FDP1 v.4: 216] [SFD: 271])
When asked if this did not apply to black women, Douglass replied that it did, but because they were black and not women (Ibid.). He did not have ready answers, however, to concerns about how well black men, including elite black men, represented and protected the rights and interests of black women. Generations of black male leaders repeated his shortsightedness, which black women leaders, like Anna Julia Cooper (c. 1859–1964), criticized while also struggling against the racism of first-wave feminism (Cooper 1998).
During and after the Reconstruction, Douglass remained deeply concerned about the prospect that the U.S. would compromise on black Americans’ civil and human rights. He became increasingly worried about the denial of black civil rights and the rising waves of anti-black violence and criticized the growing practice of black peonage in agriculture. And over time, his sympathy for black individuals and families fleeing the American South grew. He did not support internal mass migration as a policy because he judged it a poor option for black labor since it did not address the institutional problems that caused the flight: peonage and exploitation, unequal justice, unrestrained violence, lack of resources and opportunities, and in particular, education. For taking that position, Douglass received a great deal of criticism for failing to support the individual choices of black Americans who sought to flee the inhospitable, degrading, and deadly conditions in the American South. It compelled him to rethink his views on the question ( §9 ).
Related to the conditions causing the flight of black Americans from the southern states, Douglass criticized the inequitable and unfair treatment of blacks in state criminal justice systems, particularly criticizing the Convict-Lease system (Davis 1999). And he joined with Ida B. Wells-Barnett (1862–1931) in raising the alarm over the growing practice of anti-black lynching in the United States (Giddings 2008; Wells-Barnett et al. 2014). Douglass saw America’s failure to support civil rights and equal citizenship for black Americans as indicative of its moral and political failure. He even went so far as to provocatively claim that emancipation was a stupendous fraud (1888a [FDSW: 712–724]).
Douglass’s later-day activities are an essential part of his record and life; indeed, they are a part of the evolving discussions on various subjects in African American philosophy, political theory, and critical theories in several disciplines. He was part of several movements that helped to mold the nation; they took their confidence in providential historical development in hand—as he did when he first committed to seizing his liberty in his “soul’s complaint”, an “apostrophe” to ships on the Chesapeake Bay:
You are loosed from your mooring, and are free; I am fast in my chains, and am a slave! You move merrily before the gentle gale, and I sadly before the bloody whip! You are freedom’s swift-winged angels, that fly round the world; I am confined in bands of iron! O that I were free! O, that I were on one of your gallant decks, and under your protecting wing! Alas! Betwixt me and you, the turbid waters roll. Go on, go on. O that I could also go! Could I but swim! If I could fly! O, why was I born a man, of whom to make a brute! The glad ship is gone; she hides in the dim distance. I am left in the hottest hell of unending slavery. O God, save me! God, deliver me! Let me be free! Is there any God? Why am I a slave? (1845 [FDAB: 59])
The historian David Blight called Douglass a prophet of freedom, perfectly capturing Douglass’s enduring appeal (2018). His ideas, values, and rhetoric defending equal liberty continue to cry out to us in celebration and defense of equality and liberty. There is no better summation of all that he stood for than what he proclaimed in 1869 at the end of “On Composite Nationality”:
If our action shall be in accordance with the principles of justice, liberty, and perfect human equality, no eloquence can adequately portray the greatness and grandeur of the Republic. We shall spread the network of our science and our civilization over all who seek their shelter, whether from Asia, Africa, or the Isles of the Sea. We shall mould them all, each after his kind, into Americans; Indian and Celt, negro and Saxon, Latin and Teuton, Mongolian and Caucasian, Jew and gentile, all shall bow to the same law, speak the same language, support the same government, enjoy the same liberty, vibrate with the same national enthusiasm, and seek the same national ends. (1869 [SFD: 302–303])
Those inspiring and challenging words stand as an invitation to us to closely study Douglass’s works and legacy and to achieve our nation.
A. Primary Sources
- [FDAB] Autobiographies: Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave ; My Bondage and My Freedom ; Life and Times of Frederick Douglass , Henry Louis Gates (ed.), (The Library of America 68), New York: Literary Classics of the United States, 1994.
- [FDP1] Series One, Speeches, Debates, and Interviews , John W. Blassingame and John R. McKivigan (eds.), 5 volumes, 1979–1992.
- [FDP2] Series Two, Autobiographical Writings , John W. Blassingame (ed.), 3 volumes, 1999–2012.
- [FDP3] Series Three, Correspondence , 2 volumes (3 more forthcoming), John R. McKivigan (ed.), 2009–.
- [FDSW] Frederick Douglass: Selected Speeches and Writings , Philip Sheldon Foner and Yuval Taylor (eds.), (Library of Black America), Chicago: Lawrence Hill Books, 1999.
- [SFD] The Speeches of Frederick Douglass: A Critical Edition , John R. McKivigan, Julie Husband, and Heather L. Kaufman (eds.), New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 2018.
- 1950, Early years, 1817–1849 , volume 1
- 1950, Pre-Civil War decade, 1850–1860 , volume 2
- 1952, The Civil War, 1861–1865 , volume 3
- 1955, Reconstruction and After , volume 4
- 1975, Supplementary volume, 1844–1860 , volume 5
- 1976, Frederick Douglass on Women’s Rights , Philip Sheldon Foner (ed.), (Contributions in Afro-American and African Studies 25), Westport, CT: Greenwood Press.
- 2016, The Essential Douglass: Selected Writings & Speeches , Nicholas Buccola (ed.), Indianapolis. IN: Hackett Publishing Company.
- Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave , David W. Blight (ed.), second edition, (Bedford Books in American History), Boston: Bedford Books of St. Martin’s Press, 2003.
- Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself: A New Critical Edition , (Open Media Series), Angela Y. Davis (ed.), San Francisco, CA: City Lights Books, 2010; includes Angela Y. Davis, “Lectures on Liberation”.
- 1846, “American Slavery, American Religion, and the Free Church of Scotland”, London, England, 22 May; in SFD: 17–54
- 1848a “An Address to the Colored People of the United States”, The North Star , 29 September; in FDSW: 117–122
- 1848b, “The Folly of Racially Exclusive Organization”, Rochester, New York, 6 March; in FDP1: v.2: 109–112.
- 1850, “At Home Again”, The North Star , 30 May; in FDSW: 156–157
- 1852, “What To the Slave Is The Fourth of July?”, Rochester, NY, 5 July; in SFD: 55–92
- 1853a [2015], “The Heroic Slave”, in Autographs for Freedom , Julia Griffiths (ed.), Boston: John P. Jewett and Company, 174–239. Reprinted, 2015, as The Heroic Slave: A Cultural and Critical Edition , Robert S. Levine, John Stauffer, and John R. McKivigan (eds.), New Haven, CT/London: Yale University Press.
- 1853b, “The Present Condition And Future Prospects of the Negro People”, annual meeting of the American and Foreign Anti-Slavery Society, New York City, 11 May; FDSW: 250–259.
- 1854, “The Claims of the Negro Ethnologically Considered”, Hudson, Ohio, 12 July; in SFD: 116–150
- 1855, My Bondage and My Freedom , New York: Miller, Orton & Mulligan. Reprinted David W. Blight (ed.), New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 2014. Also in FDAB: 103–452.
- 1857, “The Significance of Emancipation in the West Indies”, Canandaigua, New York, 3 August.
- 1859, “Capt. John Brown Not Insane”, Douglass’ Monthly , November; FDSW: 374–375/6.
- 1860a, “The American Constitution and the Slaves”, Glasgow, Scotland, 26 March; in SFD: 151–185.
- 1860b, “Speech on John Brown”, Tremont Temple, Boston, 3 December; FDSW: 417–421.
- 1860c, “A Plea for Freedom of Speech in Boston”, Boston, Massachusetts, 9 December; in FDP1 v.3: 420–424.
- 1860d, “The Trials and Triumphs of Self-Made Men”, Halifax, England: in FDP1 v.3: 289–300.
- 1862, “What Shall be Done with the Slave if Emancipated”, Douglass’ Monthly , January; FDSW: 470–473.
- 1869a, “Our Composite Nationality”, Boston, Massachusetts, 7 December; in SFD: 278–303.
- 1869b, “We Welcome the Fifteenth Amendment”, Addresses delivered to the American Equal Rights Association, New York, 12–13 May; in SFD: 267–277; in FDP1 v.4: 213–219.
- 1876, “Oration in Memory of Abraham Lincoln”, unveiling of Freedmen’s Monument in Memory of Abraham Lincoln, Lincoln Park, Washington, DC, 14 April; FDSW: 616–624.
- 1879, “The Negro Exodus From the Gulf States”, New York, September: in FDP1 v.4: 510–533.
- 1881/1893, Life and Times of Frederick Douglass , new revised edition, Boston: De Wolfe & Fiske; earlier shorter version, 1881. Reprinted in FDP2: volume 3, John R. McKivigan (ed.), 2012.
- 1883a, “The Civil Rights Case”, Civil Rights Mass-Meeting, Lincoln Hall, Washington, DC, 22 October; FDSW: 685–693.
- 1883b, “‘It Moves’, Or the Philosophy of Reform”, Washington, DC, 20 November; in SFD: 374–400.
- 1884, “Mr. Douglass Interviewed”, Washington Post , 26 January, page 1; in FDP1 v.5: 147.
- 1888a, “Denounce the So-Called Emancipation as a Stupendous Fraud”, speech on the occasion of the Twenty-Sixth Anniversary of Emancipation in the District of Columbia, Washington, DC, 16 April; FDSW: 712–724.
- 1888b, “In Law Free: In Fact, A Slave”, Washington, DC, 16 May: FDP1 v.5: 357–373.
- 1893, “Self-Made Men”, Carlisle, Pennsylvania, March; in SFD: 414–453.
- 1894, “Lessons of the Hour”, Washington, DC, 9 January; in SFD: 454–497.
- Alfaro, Ange-Marie Hancock, 2018, “Black Masculinity Achieves Nothing without Restorative Care: An Intersectional Rearticulation of Frederick Douglass”, in Roberts 2018: 236–251 (ch. 7).
- Appiah, Anthony, 1985 [1986], “The Uncompleted Argument: Du Bois and the Illusion of Race”, Critical Inquiry , 12(1): 21–37. Reprinted in “Race”, Writing and Difference , Henry Louis Gates Jr. (ed.), Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 21–37.
- Bernasconi, Robert, 1991, “The Constitution Of The People: Frederick Douglass And The Dred Scott Decision”, Cardozo Law Review , 13(4): 1281–1296.
- Blight, David W., 1989, Frederick Douglass’ Civil War: Keeping Faith in Jubilee , Baton Rouge, LA: Louisiana State University Press.
- –––, 2018, Frederick Douglass: Prophet of Freedom , New York: Simon & Schuster.
- Boxill, Bernard R., 1976, “Self-Respect and Protest”, Philosophy & Public Affairs , 6(1): 58–69.
- –––, 1992a, Blacks and Social Justice , revised edition, Savage, MD: Rowman & Littlefield.
- –––, 1992b, “Two Traditions in African American Political Philosophy”, Philosophical Forum , 24: 119–135.
- –––, 1997, “The Fight with Covey”, in Existence in Black: An Anthology of Black Existential Philosophy , Lewis R. Gordon (ed.), New York: Routledge, 273–290.
- –––, 1998, “Radical Implications of Locke’s Moral Theory: The Views of Frederick Douglass”, in Lott 1998: 29–48.
- –––, 1999, “Douglass against the Emigrationists”, in Lawson and Kirkland 1999: 21–49 (ch. 1).
- Bromell, Nicholas Knowles, 2021, The Powers of Dignity: The Black Political Philosophy of Frederick Douglass , Durham, NC: Duke University Press.
- Brotz, Howard, 1992, African-American Social and Political Thought, 1850–1920 , New Brunswick, NJ: Transaction Publishers.
- Buccola, Nicholas, 2012, The Political Thought of Frederick Douglass: In Pursuit of American Liberty , New York: New York University Press.
- Burns, Robert, 1795, “A Man’s a Man for a’ That”. Collected in multiple places including in Burns: Poems , Gerard Carruthers (ed.), New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 2007, 131–132.[ Burn 1795 available online ]
- Combe, George, 1828, The Constitution of Man Considered in Relation to External Objects , Edinburgh.
- Cooper, Anna J., 1998, The Voice of Anna Julia Cooper: Including A Voice from the South and Other Important Essays, Papers, and Letters , Charles C. Lemert and Esme Bhan (eds.), Lanham, MD: Rowan & Littlefield.
- Cruse, Harold, 1967 [2005], The Crisis of the Negro Intellectual , New York: Morrow. Reprinted as The Crisis of the Negro Intellectual: A Historical Analysis of the Failure of Black Leadership , (New York Review Books Classics), New York: New York Review Books, 2005.
- Davis, Angela Y., 1971, Lectures on Liberation , New York: New York Committee to Free Angela Davis. Reprinted in the 2010 edition of Douglass 1845 which she edited.
- –––, 1971 [1983], “Unfinished Lecture on Liberation-II”, in Philosophy Born of Struggle: Anthology of Afro-American Philosophy from 1917 , Leonard Harris (ed.), Dubuque: Kendall/Hunt Publishing, 130–136.
- –––, 1999, “From the Prison of Slavery to the Slavery of Prison: Frederick Douglass and the Convict Lease System”, in Lawson and Kirkland 1999: 339–362 (ch. 12).
- –––, 2005, Abolition Democracy: Beyond Empire, Prisons, and Torture , New York: Seven Stories Press.
- Delany, Martin Robison, 1852 [1968], The Condition, Elevation, Emigration, and Destiny of the Colored People of the United States. Politically Considered , Philadelphia. Reprinted, 1968, (American Negro, His History and Literature), New York: Arno Press.
- Delbanco, Andrew, 2018, The War before the War: Fugitive Slaves and the Struggle for America’s Soul from the Revolution to the Civil War , New York: Penguin Press.
- Du Bois, W.E.B. 1897 [1992], “The Conservation of Races”, speech to the American Negro Academy, March 1897. Reprinted in Brotz 1992: 483–492.
- –––, 1903 [1999], The Souls of Black Folk , Chicago: A.C. McClurg & Co. Reprinted, 1999, Henry Louis Gates and Terri Hume Oliver (eds), (A Norton Critical Edition) New York: W.W. Norton.
- –––, 1909, John Brown , (American Crisis Biographies), Philadelphia: G. W. Jacobs & company.
- –––, 1935 [2021], Black Reconstruction: An Essay toward a History of the Part Which Black Folk Played in the Attempt to Reconstruct Democracy in America, 1860–1880 , New York: Harcourt, Brace and Co. Reprinted, 2021, Eric Foner and Henry Louis Gates, Jr., (eds.), (Library of America 350), New York, NY: The Library of America.
- DuBois, Ellen Carol, 1978, Feminism and Suffrage: The Emergence of an Independent Women’s Movement in America, 1848–1869 , Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
- Dworkin, Ronald, 2006, Is Democracy Possible Here? Principles for a New Political Debate , Princeton, N.J: Princeton University Press.
- Emerson, Ralph Waldo, 1850 [2004], Representative Men: Seven Lectures , Boston: Phillips, Sampson & Co. Reprinted, 2004, Brenda Wineapple (ed.), New York: Modern Library.
- Foner, Philip Sheldon, 1964, Frederick Douglass: A Biography , New York: Citadel Press.
- Fredrickson, George M., 2002, Racism: A Short History , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Giddings, Paula, 2008, Ida: A Sword among Lions: Ida B. Wells and the Campaign against Lynching , New York: Amistad.
- Gooding-Williams, Robert, 2009, In the Shadow of Du Bois: Afro-Modern Political Thought in America , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Gordon, Ann D. (ed.), 2000, The Selected Papers of Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Susan B. Anthony, Volume 2: Against an Aristocracy of Sex, 1866 to 1873 , New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press.
- Gordon, Lewis R. 1999. “Douglass as an Existentialist”, in Lawson and Kirkland 1999: 207–226 (ch. 8).
- Hobbes, Thomas, 1651/1668 [1994], Leviathan , London; revised Latin edition, 1668. Reprinted as Leviathan: With Selected Variants from the Latin Edition of 1668 , E. M. Curley (ed.), Indianapolis, IN: Hackett.
- Jefferson, Thomas, 1785 [1999], Notes on the State of Virginia , Paris; reprinted, 1999, Frank Shuffelton (ed.), New York: Penguin Books.
- Lawson, Bill E. and Frank M. Kirkland (eds.), 1999, Frederick Douglass: A Critical Reader (Blackwell Critical Readers), Malden, MA/Oxford: Blackwell Publishers.
- Lee, Maurice S. (ed.), 2009, The Cambridge Companion to Frederick Douglass (Cambridge Companions to American Studies), Cambridge/New York: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CCOL9780521889230
- Levine, Robert S., 1997, Martin Delany, Frederick Douglass, and the Politics of Representative Identity , Chapel Hill, NC: The University of North Carolina Press.
- –––, 2016, The Lives of Frederick Douglass , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Lott, Tommy Lee (ed.), 1998, Subjugation and Bondage: Critical Essays on Slavery and Social Philosophy , Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers.
- Martin, Waldo E., Jr., 1984, The Mind of Frederick Douglass , Chapel Hill, NC: The University of North Carolina Press.
- Mazzini, Giuseppe [Joseph], 1860 [1862], Doveri dell’uomo , London; translated as The Duties of Man , London: Chapman & Hall, 1862; re-translated by Ella Noyes in The Duties of Man And Other Essays , introduced by Thomas Jones, London: J.M. Dent & Sons, 1907.
- McFeely, William S., 1991, Frederick Douglass , New York: Norton.
- McGary, Howard, 1999a, “Douglass on Racial Assimilation and Racial Institutions”, in Lawson and Kirkland 1999: 50–63 (ch. 2).
- –––, 1999b, Race and Social Justice , Malden, MA: Blackwell.
- McGary, Howard and Bill E. Lawson, 1992, Between Slavery and Freedom: Philosophy and American Slavery , (Blacks in the Diaspora), Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press.
- Mills, Charles W., 1997, The Racial Contract , Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
- –––, 1999, “Whose Fourth of July? Frederick Douglass and ‘Original Intent’”, in Lawson and Kirkland 1999: 100–142 (ch. 5).
- Moses, Wilson Jeremiah, 1978, The Golden Age of Black Nationalism, 1850–1925 , Hamden, CT: Archon Books.
- Myers, Peter C., 2008, Frederick Douglass: Race and the Rebirth of American Liberalism , (American Political Thought), Lawrence, KS: University Press of Kansas.
- Nott, Josiah C. and George R. Gliddon, 1854, Types of Mankind or, Ethnological Researches: Based upon the Ancient Monuments, Paintings, Sculptures, and Crania of Races, and upon Their Natural, Geographical, Philological and Biblical History, Illustrated by Selections from the Inedited Papers of Samuel George Morton and by Additional Contributions from L. Agassiz; W. Usher; and H. S. Patterson , Philadelphia, PA: J.B. Lippincott, Grambo & co.
- Outlaw, Lucius, 1992 [1996], “Against the Grain of Modernity: The Politics of Difference and the Conservation of ‘Race’”, Man and World , 25(3–4): 443–468. Reprinted in his On Race and Philosophy , New York: Routledge, 1996, 135–157. doi:10.1007/BF01252429
- Patterson, Orlando, 1982, Slavery and Social Death: A Comparative Study , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Pettit, Philip, 1997, Republicanism: A Theory of Freedom and Government , Oxford: Clarendon Press. doi:10.1093/0198296428.001.0001
- Pittman, John, 1999, “Douglass’s Assimilationism and Antislavery”, in Lawson and Kirkland 1999: 64–81 (ch. 3).
- Preston, Dickson J., 1980, Young Frederick Douglass: The Maryland Years , Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press.
- Roberts, Neil (ed.), 2018, A Political Companion to Frederick Douglass , (Political Companions to Great American Authors), Lexington, KY: University Press of Kentucky.
- Root, Damon, 2020, A Glorious Liberty: Frederick Douglass and the Fight for an Antislavery Constitution , Lincoln, NE: Potomac Books, an imprint of the University of Nebraska Press.
- Schrader, David E., 1999, “Natural Law in the Constitutional Thought of Frederick Douglass”, in Lawson and Kirkland 1999: 85–99 (ch. 4).
- Stanton, Elizabeth Cady, 1868 [2000], “Manhood Suffrage”, 24 December 1868. Collected in A. Gordon 2000: 194–199 (§71).
- –––, 1869 [2000], “Sixteenth Amendment”, 29 April 1869. Collected in A. Gordon 2000: 236–238 (§84).
- Sinha, Manisha, 2016, The Slave’s Cause: A History of Abolition , New Haven: Yale University Press.
- Sundquist, Eric J. (ed.), 1990, Frederick Douglass: New Literary and Historical Essays (Cambridge Studies in American Literature and Culture), Cambridge, New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Sundstrom, Ronald Robles, 2003, “Douglass & Du Bois’s Der Schwarze Volksgeist ”, in Race and Racism in Continental Philosophy , Robert Bernasconi (ed.), Indianapolis, IN: Indiana University Press, 32–53 (ch. 3).
- –––, 2008, The Browning of America and the Evasion of Social Justice , (SUNY Series, Philosophy and Race), Albany, NY: SUNY Press.
- Taylor, Paul C., 2022, Race: A Philosophical Introduction , third revised edition, Cambridge: Polity Press.
- Van Wyhe, John, 2004, Combe’s “Constitution of Man”, and Nineteenth-Century Responses , Bristol: Thoemmes Continuum.
- Wallace, Maurice O., 2009, “Violence, Manhood, and War in Douglass”, in Lee 2009: 73–88. doi:10.1017/CCOL9780521889230.006
- –––, 2014, “‘I Rose a Freeman’: Power, Property, and the Performance of Manhood in Slave Narratives”, in The Oxford Handbook of the African American Slave Narrative , John Ernest (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, 260–276.
- Washington, Booker T., 1907, Frederick Douglass , (American Crisis Biographies), Philadelphia/London: G.W. Jacobs & Company.
- Waldron, Jeremy, 2012, Dignity, Rank, and Rights , Meir Dan-Cohen (ed.), (Berkeley Tanner Lectures), New York: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199915439.001.0001
- –––, 2017, One Another’s Equals: The Basis of Human Equality , Cambridge, MA: The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press.
- Wells-Barnett, Ida B., 2014, The Light of Truth: Writings of an Anti-Lynching Crusader , Mia Bay and Henry Louis Jr. Gates (eds.), (Penguin Classics), New York: Penguin Books.
- Willett, Cynthia, 1998, “The Master-Slave Dialectic: Hegel vs. Douglass”, in Lott 1998: 151–170.
- –––, 2001, “The Genealogy of Freedom in Slave America: Frederick Douglass”, in her The Soul of Justice: Social Bonds and Racial Hubris , Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 188–202 (ch. 8).
- Yancy, George, 2008, “Exploring the Serious World of Whiteness through Frederick Douglass’s Autobiographical Reflections”, in his Black Bodies, White Gazes: The Continuing Significance of Race , Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield, 141–181.
- Yaure, Philip, 2018, “Deliberation and Emancipation: Some Critical Remarks”, Ethics , 129(1): 8–38. doi:10.1086/698731
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- Frederick Douglass Papers, at the Library of Congress
- Frederick Douglass Papers, at the National Archives
- Frederick Douglass National Historic Site
Emerson, Ralph Waldo | ethics: natural law tradition | liberalism | Locke, John | Locke, John: political philosophy | republicanism W.E.B. Du Bois |
Copyright © 2023 by Ronald Sundstrom < rrsundstrom @ usfca . edu >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2023 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
Frederick Douglass
By: History.com Editors
Updated: March 8, 2024 | Original: October 27, 2009

Frederick Douglass was a formerly enslaved man who became a prominent activist, author and public speaker. He became a leader in the abolitionist movement , which sought to end the practice of slavery, before and during the Civil War . After that conflict and the Emancipation Proclamation of 1862, he continued to push for equality and human rights until his death in 1895.
Douglass’ 1845 autobiography, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave , described his time as an enslaved worker in Maryland . It was one of three autobiographies he penned, along with dozens of noteworthy speeches, despite receiving minimal formal education.
An advocate for women’s rights, and specifically the right of women to vote , Douglass’ legacy as an author and leader lives on. His work served as an inspiration to the civil rights movement of the 1960s and beyond.
Who Was Frederick Douglass?
Frederick Douglass was born into slavery in or around 1818 in Talbot County, Maryland. Douglass himself was never sure of his exact birth date.
His mother was an enslaved Black women and his father was white and of European descent. He was actually born Frederick Bailey (his mother’s name), and took the name Douglass only after he escaped. His full name at birth was “Frederick Augustus Washington Bailey.”
After he was separated from his mother as an infant, Douglass lived for a time with his maternal grandmother, Betty Bailey. However, at the age of six, he was moved away from her to live and work on the Wye House plantation in Maryland.
From there, Douglass was “given” to Lucretia Auld, whose husband, Thomas, sent him to work with his brother Hugh in Baltimore. Douglass credits Hugh’s wife Sophia with first teaching him the alphabet. With that foundation, Douglass then taught himself to read and write. By the time he was hired out to work under William Freeland, he was teaching other enslaved people to read using the Bible .
As word spread of his efforts to educate fellow enslaved people, Thomas Auld took him back and transferred him to Edward Covey, a farmer who was known for his brutal treatment of the enslaved people in his charge. Roughly 16 at this time, Douglass was regularly whipped by Covey.
Frederick Douglass Escapes from Slavery
After several failed attempts at escape, Douglass finally left Covey’s farm in 1838, first boarding a train to Havre de Grace, Maryland. From there he traveled through Delaware , another slave state, before arriving in New York and the safe house of abolitionist David Ruggles.
Once settled in New York, he sent for Anna Murray, a free Black woman from Baltimore he met while in captivity with the Aulds. She joined him, and the two were married in September 1838. They had five children together.
From Slavery to Abolitionist Leader
After their marriage, the young couple moved to New Bedford, Massachusetts , where they met Nathan and Mary Johnson, a married couple who were born “free persons of color.” It was the Johnsons who inspired the couple to take the surname Douglass, after the character in the Sir Walter Scott poem, “The Lady of the Lake.”
In New Bedford, Douglass began attending meetings of the abolitionist movement . During these meetings, he was exposed to the writings of abolitionist and journalist William Lloyd Garrison.
The two men eventually met when both were asked to speak at an abolitionist meeting, during which Douglass shared his story of slavery and escape. It was Garrison who encouraged Douglass to become a speaker and leader in the abolitionist movement.
By 1843, Douglass had become part of the American Anti-Slavery Society’s “Hundred Conventions” project, a six-month tour through the United States. Douglass was physically assaulted several times during the tour by those opposed to the abolitionist movement.
In one particularly brutal attack, in Pendleton, Indiana , Douglass’ hand was broken. The injuries never fully healed, and he never regained full use of his hand.
In 1858, radical abolitionist John Brown stayed with Frederick Douglass in Rochester, New York, as he planned his raid on the U.S. military arsenal at Harper’s Ferry , part of his attempt to establish a stronghold of formerly enslaved people in the mountains of Maryland and Virginia. Brown was caught and hanged for masterminding the attack, offering the following prophetic words as his final statement: “I, John Brown, am now quite certain that the crimes of this guilty land will never be purged away but with blood.”
'Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass'
Two years later, Douglass published the first and most famous of his autobiographies, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave . (He also authored My Bondage and My Freedom and Life and Times of Frederick Douglass).
In it Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass , he wrote: “From my earliest recollection, I date the entertainment of a deep conviction that slavery would not always be able to hold me within its foul embrace; and in the darkest hours of my career in slavery, this living word of faith and spirit of hope departed not from me, but remained like ministering angels to cheer me through the gloom.”
He also noted, “Thus is slavery the enemy of both the slave and the slaveholder.”
Frederick Douglass in Ireland and Great Britain
Later that same year, Douglass would travel to Ireland and Great Britain. At the time, the former country was just entering the early stages of the Irish Potato Famine , or the Great Hunger.
While overseas, he was impressed by the relative freedom he had as a man of color, compared to what he had experienced in the United States. During his time in Ireland, he met the Irish nationalist Daniel O’Connell , who became an inspiration for his later work.
In England, Douglass also delivered what would later be viewed as one of his most famous speeches, the so-called “London Reception Speech.”
In the speech, he said, “What is to be thought of a nation boasting of its liberty, boasting of its humanity, boasting of its Christianity , boasting of its love of justice and purity, and yet having within its own borders three millions of persons denied by law the right of marriage?… I need not lift up the veil by giving you any experience of my own. Every one that can put two ideas together, must see the most fearful results from such a state of things…”
Frederick Douglass’ Abolitionist Paper
When he returned to the United States in 1847, Douglass began publishing his own abolitionist newsletter, the North Star . He also became involved in the movement for women’s rights .
He was the only African American to attend the Seneca Falls Convention , a gathering of women’s rights activists in New York, in 1848.
He spoke forcefully during the meeting and said, “In this denial of the right to participate in government, not merely the degradation of woman and the perpetuation of a great injustice happens, but the maiming and repudiation of one-half of the moral and intellectual power of the government of the world.”
He later included coverage of women’s rights issues in the pages of the North Star . The newsletter’s name was changed to Frederick Douglass’ Paper in 1851, and was published until 1860, just before the start of the Civil War .
Frederick Douglass Quotes
In 1852, he delivered another of his more famous speeches, one that later came to be called “What to a slave is the 4th of July?”
In one section of the speech, Douglass noted, “What, to the American slave, is your 4th of July? I answer: a day that reveals to him, more than all other days in the year, the gross injustice and cruelty to which he is the constant victim. To him, your celebration is a sham; your boasted liberty, an unholy license; your national greatness, swelling vanity; your sounds of rejoicing are empty and heartless; your denunciations of tyrants, brass fronted impudence; your shouts of liberty and equality, hollow mockery; your prayers and hymns, your sermons and thanksgivings, with all your religious parade, and solemnity, are, to him, mere bombast, fraud, deception, impiety, and hypocrisy—a thin veil to cover up crimes which would disgrace a nation of savages.”
For the 24th anniversary of the Emancipation Proclamation , in 1886, Douglass delivered a rousing address in Washington, D.C., during which he said, “where justice is denied, where poverty is enforced, where ignorance prevails, and where any one class is made to feel that society is an organized conspiracy to oppress, rob and degrade them, neither persons nor property will be safe.”
Frederick Douglass During the Civil War
During the brutal conflict that divided the still-young United States, Douglass continued to speak and worked tirelessly for the end of slavery and the right of newly freed Black Americans to vote.
Although he supported President Abraham Lincoln in the early years of the Civil War, Douglass fell into disagreement with the politician after the Emancipation Proclamation of 1863, which effectively ended the practice of slavery. Douglass was disappointed that Lincoln didn’t use the proclamation to grant formerly enslaved people the right to vote, particularly after they had fought bravely alongside soldiers for the Union army.
It is said, though, that Douglass and Lincoln later reconciled and, following Lincoln’s assassination in 1865, and the passage of the 13th amendment , 14th amendment , and 15th amendment to the U.S. Constitution (which, respectively, outlawed slavery, granted formerly enslaved people citizenship and equal protection under the law, and protected all citizens from racial discrimination in voting), Douglass was asked to speak at the dedication of the Emancipation Memorial in Washington, D.C.’s Lincoln Park in 1876.
Historians, in fact, suggest that Lincoln’s widow, Mary Todd Lincoln , bequeathed the late-president’s favorite walking stick to Douglass after that speech.
In the post-war Reconstruction era, Douglass served in many official positions in government, including as an ambassador to the Dominican Republic, thereby becoming the first Black man to hold high office. He also continued speaking and advocating for African American and women’s rights.
In the 1868 presidential election, he supported the candidacy of former Union general Ulysses S. Grant , who promised to take a hard line against white supremacist-led insurgencies in the post-war South. Grant notably also oversaw passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1871 , which was designed to suppress the growing Ku Klux Klan movement.
Frederick Douglass: Later Life and Death
In 1877, Douglass met with Thomas Auld , the man who once “owned” him, and the two reportedly reconciled.
Douglass’ wife Anna died in 1882, and he married white activist Helen Pitts in 1884.
In 1888, he became the first African American to receive a vote for President of the United States, during the Republican National Convention. Ultimately, though, Benjamin Harrison received the party nomination.
Douglass remained an active speaker, writer and activist until his death in 1895. He died after suffering a heart attack at home after arriving back from a meeting of the National Council of Women , a women’s rights group still in its infancy at the time, in Washington, D.C.
His life’s work still serves as an inspiration to those who seek equality and a more just society.

HISTORY Vault: Black History
Watch acclaimed Black History documentaries on HISTORY Vault.
Frederick Douglas, PBS.org . Frederick Douglas, National Parks Service, nps.gov . Frederick Douglas, 1818-1895, Documenting the South, University of North Carolina , docsouth.unc.edu . Frederick Douglass Quotes, brainyquote.com . “Reception Speech. At Finsbury Chapel, Moorfields, England, May 12, 1846.” USF.edu . “What to the slave is the 4th of July?” TeachingAmericanHistory.org . Graham, D.A. (2017). “Donald Trump’s Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass.” The Atlantic .
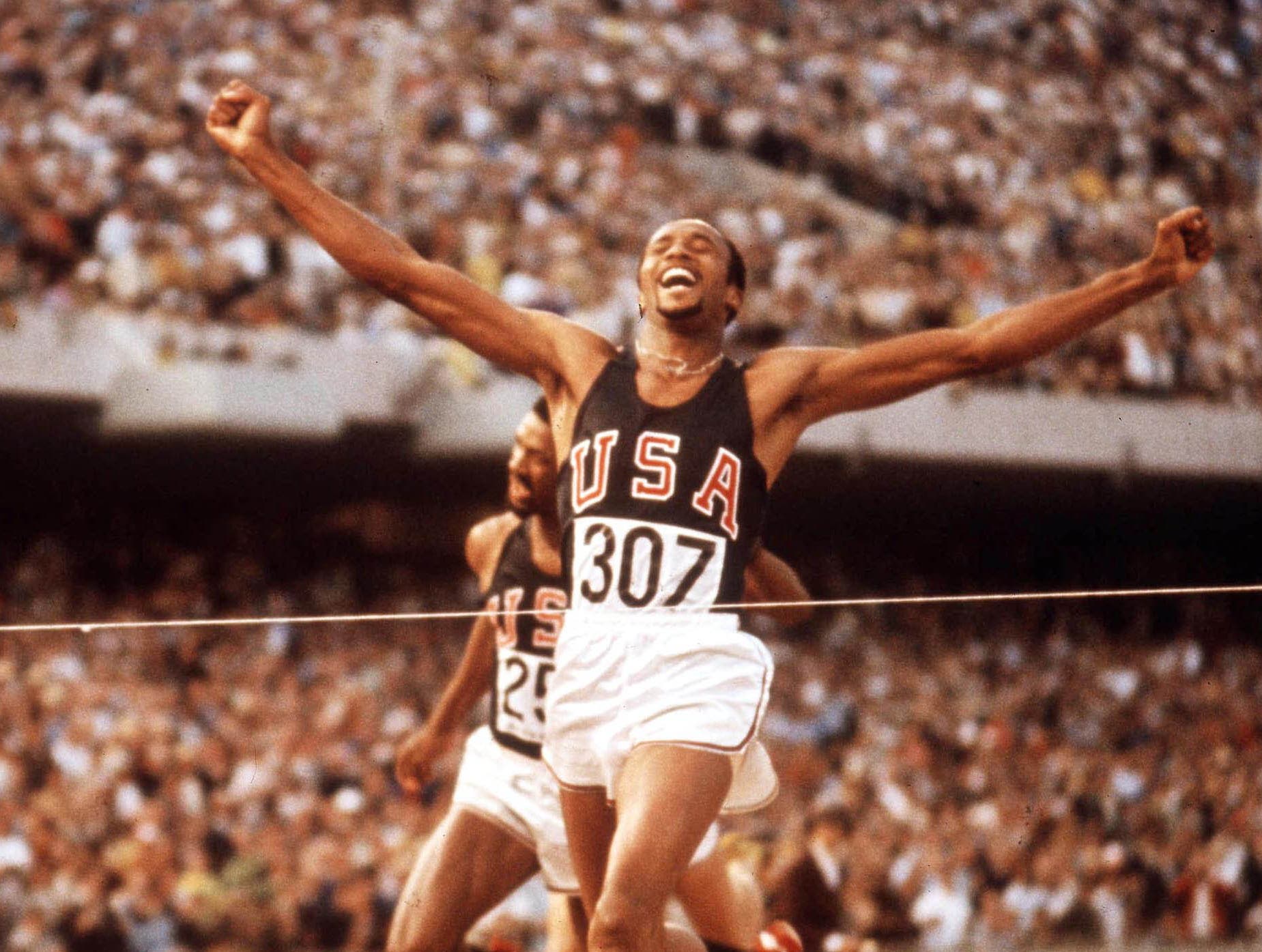

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction & Top Questions
Early life and enslavement
Escape from slavery, life in new bedford, and work with the american anti-slavery society, narrative of the life of frederick douglass , european travel, and the north star, involvement with john brown, abraham lincoln, elizabeth cady stanton, and susan b. anthony, move to washington, d.c., the freedman’s bank, government office-holding, and later years.

What was Frederick Douglass’s childhood like?
How did frederick douglass become involved in the abolitionist movement, how was frederick douglass involved in the american civil war and reconstruction, what are some of frederick douglass’s most famous writings and speeches.

Frederick Douglass
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy - Biography of Frederick Douglass
- Free Speech Center - Frederick Douglass
- American Battlefield Trust - Frederick Douglass
- National Park Service - Frederick Douglass National Historic Site - Biography of Frederick Douglass
- Library of Congress - Frederick Douglass Timeline
- Social Studies for Kids - Biography of Frederick Douglass
- PBS LearningMedia - The Abolitionists: The Emancipation Proclamation and the Civil War
- NPR - Frederick Douglass On How Slave Owners Used Food As A Weapon Of Control
- HistoryNet - Frederick Douglass
- Humanities Libretexts - Frederick Douglass (1818–1895)
- United States History - Biography of Frederick Douglass
- Frederick Douglass - Children's Encyclopedia (Ages 8-11)
- Frederick Douglass - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)
- Table Of Contents
Frederick Douglass was born in slavery to a Black mother and a white father. At age eight the man who owned him sent him to Baltimore, Maryland, to live in the household of Hugh Auld. There Auld’s wife taught Douglass to read. Douglass attempted to escape slavery at age 15 but was discovered before he could do so.
Frederick Douglass escaped from slavery to New York City in 1838, later settling in New Bedford, Massachusetts. At an 1841 antislavery convention, he was asked to recount his experience as an enslaved person. He so moved his audience that he became an agent for the Massachusetts Anti-Slavery Society. His 1845 autobiography cemented his prominence as an abolitionist .
During the American Civil War Frederick Douglass served as an adviser to Pres. Abraham Lincoln . Douglass played a crucial role in persuading Lincoln to arm enslaved people and prioritize abolition. During Reconstruction Douglass became the highest-ranking Black official of his time and advocated for full civil rights for Black people as well as for women.
Frederick Douglass published three autobiographies. The first autobiography, The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, An American Slave, Written by Himself , catapulted him to fame and invigorated the abolitionist movement. Of Douglass’s many speeches, “What to the Slave Is the Fourth of July?” was perhaps one of the most well-known.
What was Frederick Douglass’s legacy?
Frederick Douglass was a prolific writer and a masterful orator who captivated readers and listeners throughout the U.S. and Great Britain. His talents contributed to the rise of antislavery sentiments in public consciousness.
Frederick Douglass (born February 1818, Talbot county, Maryland , U.S.—died February 20, 1895, Washington, D.C.) was an African American abolitionist, orator, newspaper publisher, and author who is famous for his first autobiography , Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself . He became the first Black U.S. marshal and was the most photographed American man of the 19th century.

Douglass was born enslaved as Frederick Augustus Washington Bailey on Holme Hill Farm in Talbot county, Maryland. Although the date of his birth was not recorded, Douglass estimated that he had been born in February 1818, and he later celebrated his birthday on February 14. (The best source for the events in Douglass’s life is Douglass himself in his oratory and writings, especially his three autobiographies, the details of which have been checked when possible and have largely been confirmed, though his biographers have contributed corrections and clarifications.) Douglass was owned by Capt. Aaron Anthony, who was the clerk and superintendent of overseers for Edward Lloyd V (also known as Colonel Lloyd), a wealthy landowner and slaveholder in eastern Maryland. Like many other enslaved children, Douglass was separated from his mother, Harriet Bailey, when he was very young. He spent his formative years with his maternal grandmother, Betsey Bailey, who had the responsibility of raising young enslaved children.

Harriet Bailey worked as a field hand on a neighbouring plantation and had to walk more than 12 miles (about 19 km) to visit her son, whom she met with only a few times in his life. He described her as “tall and finely proportioned, of dark, glossy complexion, with regular features, and amongst the slaves was remarkably sedate and dignified.” She died when he was about seven years old. As an adult, Douglass learned that his mother had been the only Black person in what was then Talbot county who could read, an extraordinarily rare achievement for a field hand.

When Douglass was age five or six, he was taken to live on Colonel Lloyd’s home plantation, Wye House. Lloyd’s plantation functioned like a small town. Young Douglass found himself among several other enslaved children competing for food and other comforts. In 1826 at approximately age eight, he was sent to live with Hugh and Sophia Auld at Fells Point, Baltimore . Hugh’s brother Capt. Thomas Auld was the son-in-law of Douglass’s owner, Aaron Anthony. Douglass’s responsibility in Baltimore was to care for Hugh and Sophia’s young son, Thomas. Sophia began teaching Douglass how to read, along with her son. The lessons ended abruptly, however, when Hugh discovered what had been going on and informed Sophia that literacy would “spoil” a slave. According to Douglass, Hugh stated that if a slave were given an inch, he would “take an ell [a unit of measure equal to about 45 inches].” In Maryland, as in many other slaveholding states, it was forbidden to teach enslaved people how to read and write. Douglass continued his learning in secret, by exchanging bread for lessons from the poor white boys he played with in the neighbourhood and by tracing the letters in Thomas’s old schoolbooks.
In March 1832 Douglass was sent from Baltimore to St. Michaels, on Maryland’s Eastern Shore. After both Aaron Anthony and his daughter Lucretia died, her husband, Capt. Thomas Auld, became Douglass’s owner. Teenage Douglass experienced harsher living conditions with Auld, who was known for his abusive practices.
In January 1833 Douglass was leased to local farmer Edward Covey. Leasing or hiring out enslaved persons was a common revenue-generating practice. Farmers would pay slaveholders a monthly fee for enslaved people and take responsibility for their care, food, and lodging. Covey was known as a “slave breaker,” someone who abused slaves physically and psychologically in order to make them more compliant . According to Douglass, Covey’s abuse led to a climactic confrontation six months into Douglass’s time with the farmer. One day Covey attacked Douglass, and Douglass fought back. The two men engaged in an epic two-hour-long physical struggle. Douglass ultimately won the fight, and Covey never attacked him again. Douglass emerged from the incident determined to protect himself from any physical assault from anyone in the future.

In January 1834 Douglass was sent to William Freeland’s farm. Living and working conditions were better under Freeland; however, Douglass still desired his freedom. While living with Freeland, he started a Sabbath school at which he taught area Blacks how to read and write. Along with four other enslaved men, Douglass plotted to escape north by taking a large canoe up the coast of Maryland and to proceed to Pennsylvania, but their plot was discovered. Douglass and the other participants were arrested. Captain Auld then sent Douglass back to Baltimore to live again with Hugh and Sophia Auld and to learn a trade.
Hugh Auld hired out Douglass to local shipyards as a ship caulker. Now working as a skilled tradesman, Douglass was paid by the shipyards for his efforts. He would then submit his earnings to Auld, who gave Douglass a small percentage of the wages. Douglass would eventually hire out his own time, which meant that he paid Auld a set amount every week but was responsible for maintaining his own food and clothing. During this time, Douglass became more involved in Baltimore’s Black community , which led him to meet Anna Murray , a freeborn Black woman, whom he would eventually marry.
Douglass moved about Baltimore with few restrictions, but that privilege came to an end when he decided to attend a religious meeting outside of Baltimore on a Saturday evening and postpone paying Auld his weekly fee. The following Monday, when Douglass returned, Auld threatened him. After that encounter, Douglass was determined to escape his bondage. He escaped in September 1838 by dressing as a sailor and traveling from Baltimore to Wilmington , Delaware, by train, then on to Philadelphia by steamboat , and from there to New York City by train. Black sailors in the 19th century traveled with documents granting them protection under the American flag. Douglass used such documents to secure his passage north with the help of Anna, who, according to family lore , had sold her feather bed to help finance his passage.

New York City was a dangerous place for enslaved people seeking freedom. Numerous slave catchers traveled to the city to track down those who had escaped. Many locals, Black and white, were willing, for money, to tell the authorities about people trying to escape enslavement. For his own protection, Douglass (still months from assuming that name) changed his name from Frederick Bailey to Frederick Johnson. A chance meeting with Black abolitionist David Ruggles led Douglass to safety. Anna arrived in New York several days later, and the two were married by the Reverend J.W.C. Pennington.

At Ruggles’s recommendation, the couple quickly left New York City for New Bedford , Massachusetts. Ruggles had determined that New Bedford’s shipping industry would offer Douglass the best chance to find work as a ship caulker. In New Bedford the couple stayed with a local Black married couple, Nathan and Polly Johnson. Because many families in New Bedford had the surname Johnson, Douglass chose to change his name again. Nathan Johnson suggested the name Douglass, which was inspired by the name of an exiled nobleman in Sir Walter Scott ’s poem The Lady of the Lake . The newly minted Frederick Douglass earned money for the first time as a free man. However, despite Douglass’s previous work experience, racial prejudice in New Bedford prevented him from working as a ship caulker (white caulkers refused to work with Black caulkers). Consequently, Douglass spent his first years in Massachusetts working as a common labourer.

Douglass remained an avid reader throughout his adult life. When he escaped to New York, he carried with him a copy of The Columbian Orator . In New Bedford he discovered William Lloyd Garrison ’s abolitionist newspaper, The Liberator . Inspired by it, Douglass attended a Massachusetts Anti-Slavery Society convention in Nantucket in the summer of 1841. At the meeting, abolitionist William C. Coffin, having heard Douglass speak in New Bedford, invited him to address the general body. Douglass’s extemporaneous speech was lauded by the audience, and he was recruited as an agent for the group.
As an agent of both the Massachusetts Anti-Slavery Society and the American Anti-Slavery Society , Douglass traveled the country promoting abolition and the organizations’ agenda. He and other persons who had escaped conditions of enslavement frequently described their own experiences under those conditions. The American Anti-Slavery Society supported “moral suasion” abolition, the belief that slavery was a moral wrong that should be resisted through nonviolent means. Douglass strongly promoted this philosophy during the early years of his abolitionist career. In his speech at the 1843 National Convention of Colored Citizens in Buffalo, New York, Black abolitionist and minister Henry Highland Garnet proposed a resolution that called for enslaved people to rise up against their masters. The controversial resolution ignited a tense debate at the convention, with Douglass rising in firm opposition. His belief in moral suasion would repeatedly place him at odds with other Black abolitionists during this phase of his career. Work as an agent provided Douglass with the means to support his family. He and Anna had five children: Rosetta (born 1839), Lewis (born 1840), Frederick, Jr. (born 1842), Charles (born 1844), and Annie (born 1849).

In 1845 Douglass published his first autobiography, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself . Prior to its publication, audiences at Douglass’s lectures had questioned his authenticity as an ex-slave because of his eloquence, refusal to use “plantation speak,” and unwillingness to provide details about his origins. The Narrative settled these disputes by naming people and locations in Douglass’s life. The book also challenged the conventional employment of ghostwriters for slave narratives by boldly acknowledging that Douglass wrote it himself. Douglass would publish two additional autobiographies: My Bondage and My Freedom (1855) and Life and Times of Frederick Douglass (1881). The Narrative quickly became popular, especially in Europe, but the book’s success contributed to Hugh Auld’s determination to return Douglass to the conditions of enslavement.
The threat of capture, as well as the book’s excellent performance in Europe, prompted Douglass to travel abroad from August 1845 to 1847, and he lectured throughout the United Kingdom. His English supporters, led by Ellen and Anna Richardson, purchased Douglass from Hugh Auld, giving him his freedom. In the spring of 1847, Douglass returned to the United States a free man with the funding to start his own newspaper.

Douglass moved to Rochester , New York, to publish his newspaper, The North Star , despite objections from Garrison and others. Basing the newspaper in Rochester ensured that The North Star did not compete with the distribution of The Liberator and the National Anti-Slavery Standard in New England . The North Star ’s first issue appeared on December 3, 1847. In 1851 the paper merged with the Liberty Party Paper to form Frederick Douglass’ Paper , which ran until 1860. Douglass would publish two additional newspapers during his life, Douglass’ Monthly (1859–63) and New National Era (1870–74).
The move to Rochester surrounded Douglass with political abolitionists such as Gerrit Smith . During his first few years in Rochester, Douglass remained loyal to Garrison’s philosophy, which promoted moral suasion, stated that the U.S. Constitution was an invalid document, and discouraged participation in American politics because it was a system corrupted by slavery. In 1851, however, Douglass announced his split from Garrison when he declared that the Constitution was a valid legal document that could be used on behalf of emancipation. Consequently, Douglass became more engaged in American politics and constitutional interpretation.

The country’s tension around slavery rapidly increased in the 1850s. Douglass’s Rochester home was part of the Underground Railroad and hosted numerous fellow abolitionists. In 1859 Douglass met with abolitionist John Brown in a quarry in Chambersburg, Pennsylvania. Brown invited Douglass to participate in the planned raid on the federal arsenal in Harpers Ferry , Virginia (now in West Virginia), which Brown hoped would inspire a massive uprising by enslaved people. Douglass declined the invitation. Shortly after the raid (October 16–19), Douglass received word that the authorities were looking to arrest him as an accomplice . He quickly fled to Canada before heading to Europe for a scheduled lecture tour. Douglass returned home in April 1860 after learning that his youngest daughter, Annie, had died.

With the outbreak of the Civil War , Douglass strongly advocated for inclusion of Black soldiers in the Union army. He became a recruiter for the Massachusetts 54th, an all-Black infantry regiment in which his sons Lewis and Charles served. In 1863 Douglass visited the White House to meet with Pres. Abraham Lincoln to advocate for better pay and conditions for the soldiers. Lincoln then invited Douglass to the White House in 1864 to discuss what could be done for Blacks in the case of a Union loss. Douglass would meet with Lincoln a third time, after the president’s second inauguration and about a month before his assassination.
The Emancipation Proclamation and the Union’s victory presented a new reality: millions of Black people were free. Douglass dedicated himself to securing the community’s rights to this new freedom. He strongly supported the Fourteenth Amendment , which granted Blacks citizenship, but he realized that this new citizenship status needed to be protected by suffrage. Initially Douglass supported a constitutional amendment supporting suffrage for all men and women. Having attended the 1848 women’s rights convention in Seneca Falls , New York, he was a longtime supporter of women’s rights, joining Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Susan B. Anthony in this stance. Reconstruction politics, however, indicated that a universal suffrage amendment would fail. Douglass then supported Black male suffrage with the idea that Black men could help women secure the right to vote later. This placed him at odds with Stanton and Anthony. Douglass hoped that the passage of the Fifteenth Amendment would encourage African Americans to stay in the South to consolidate their power as a voting bloc, but the region’s high levels of violence against African Americans led him to support Black migration to safer areas of the country.

After a fire destroyed his Rochester home, Douglass moved in 1872 to Washington, D.C. , where he published his latest newspaper venture, New National Era . The newspaper folded in 1874 because of its poor fiscal health. That same year Douglass was appointed president of the Freedman’s Savings & Trust, also known as the Freedman’s Bank. The bank failed four months after he became president because of the years of corruption that predated his association with the bank. The bank’s failure harmed his reputation, but Douglass worked with the U.S. Congress to remedy the damage caused by the bank.

After the Freedman’s Bank debacle , Douglass held numerous government appointments. He became the first Black U.S. marshal in 1877 when he was appointed to that post for the District of Columbia by Pres. Rutherford B. Hayes . He served in that capacity until 1881, when Pres. James A. Garfield appointed him to the high-paying position of recorder of deeds for the District of Columbia. In 1889 Pres. Benjamin Harrison selected Douglass as the U.S. minister resident and consul general to the Republic of Haiti . The major controversy during Douglass’s tenure was the quest by the United States to acquire the port town of Môle Saint-Nicolas as a refueling station for the U.S. Navy. Douglass disagreed with the Harrison administration’s approach, preferring to promote the autonomy of the Haitian government. He resigned the position in 1891 and returned to his home in Washington, D.C.

Douglass spent the last 17 years of his life at Cedar Hill, his home in the Anacostia neighbourhood of Washington, D.C., to which he had moved in 1878. On August 4, 1882, Anna Murray Douglass died in the home after suffering a stroke. In 1884 Douglass married Helen Pitts, his white secretary, who was about 20 years younger than her husband. The marriage was controversial for its time, and it resulted in Douglass’s temporary estrangement from some friends and family.

During the latter years of his life, Douglass remained committed to social justice and the African American community. His prominence and work resulted in his being the most photographed American man in the 19th century . His distinguished photographs were deliberate contradictions to the visual stereotypes of African Americans at the time, which often exaggerated their facial features, skin colour, and physical bodies and demeaned their intelligence. He served on Howard University ’s board of trustees from 1871 to 1895. Douglass cultivated relationships with younger activists, most notably Ida B. Wells , who featured his letter to her in her book Southern Horrors: Lynch Law in All Its Phases. He also contributed to her pamphlet protesting the exclusion of exhibits dedicated to African American culture from the 1893 World’s Columbian Exposition , The Reason Why the Colored American Is Not in the World’s Columbian Exposition .

Douglass died in his Cedar Hill home on February 20, 1895. After his death, Helen Pitts Douglass established the Frederick Douglass Memorial and Historical Association to preserve his legacy . She bequeathed the home and its belongings to the organization in her will. Cedar Hill became part of the National Park system in 1962, and it was designated the Frederick Douglass National Historic Site in 1988. The U.S. Library of Congress digitized its holdings of Douglass’s papers , which include letters, speeches, and personal documents.
At the end of his life, Douglass, an American icon who fought for social justice and equity , became known as the “Lion of Anacostia.” Through his writings, speeches, and photographs, he boldly challenged the racial stereotypes of African Americans. Douglass’s contributions to the Black American community and American history were recognized in the early 20th century during Negro History Week, the predecessor of Black History Month , which many communities anchored to the day on which his birthday was celebrated, February 14. Today Douglass is renowned not just for his rise from slavery to the highest levels of American society but also for his dedication to challenging the country to recognize the rights of all people and be consistent with its ideals.
Home — Essay Samples — History — Abolitionism — Frederick Douglass Thesis
Frederick Douglass Thesis
- Categories: Abolitionism Slavery
About this sample

Words: 621 |
Published: Mar 19, 2024
Words: 621 | Page: 1 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, douglass's thesis, personal story as support, critique of slavery, supporting arguments and techniques.

Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Karlyna PhD
Verified writer
- Expert in: History Social Issues

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1592 words
2 pages / 790 words
1 pages / 506 words
7 pages / 3196 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Abolitionism
Frederick Douglass, a prominent African American abolitionist and social reformer, is known for his powerful speeches and writings that challenged the institution of slavery in the United States. In his works, Douglass [...]
The abolitionist movement, which emerged in the 18th and 19th centuries, stands as a testament to the power of collective action, moral conviction, and the unwavering pursuit of justice. This transformative social and political [...]
Introduction to Sojourner Truth's speech "Ain't I a Woman" Mention of its historical context and significance Statement of the essay's purpose: analyzing the effectiveness of rhetorical strategies in the [...]
William Cowper, William Blake, and Anna Barbauld, in their poetry on race and abolitionism, wrote about both the humanity of racialized peoples and the greed and evil of slavery. In post-colonialism, it is important to confront [...]
During 1700s-1865, free African Americans and white abolitionists who were against slavery, developed a secret network of people who helped fugitive slaves in their escape from slavery. The people who aided the slaves were known [...]
Solomon Northup’s book Twelve Year’s a Slave covered the story of Northup himself as he was kidnapped and forced into slavery. He worked as a slave for 12 years before the government was able to locate and free him. Solomon [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
To register on our site and for the best user experience, please enable Javascript in your browser using these instructions .

Products and services
Our innovative products and services for learners, authors and customers are based on world-class research and are relevant, exciting and inspiring.
- Academic Research, Teaching and Learning
- English Language Learning
- English Language Assessment
- International Education
- Educational resources for schools
- Educational Research & Network
- Cambridge Assessment Admissions Testing
- Cambridge CEM
- Partnership for Education
- Cambridge Dictionary
- The Cambridge Mathematics Project
We unlock the potential of millions of people worldwide. Our assessments, publications and research spread knowledge, spark enquiry and aid understanding around the world.
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Environment
- United Nations Global Compact
- Communities
- Anti Slavery and Human Trafficking
- Diversity and inclusion
- Annual Report 2023
- News and insights
- Candidate Privacy Notice
- Conditions of Sale - Consumer
- Conditions of Sale - Business
- Freedom of Information
- Mobile Apps
- Purchase Terms
- Social media comments policy
- Safeguarding policy
- Website Terms of Use
- Accessibility
- Rights and permissions
- Media enquiries
No matter who you are, what you do, or where you come from, you’ll feel proud to work here.
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Arts, theatre and culture
- Classical studies
- Computer science
- Earth and environmental science
- Engineering
- General science
- Languages and linguistics
- Life science
- Mathematics
- Physics and astronomy
- Politics and international relations
- Statistics and probability
- Social science research methods
- Browse all subjects
- Conferences
Unlocking potential with the best learning and research solutions
- Cambridge University Press
- American literature

I want this title to be available as an eBook
Frederick Douglass New Literary and Historical Essays
Part of Cambridge Studies in American Literature and Culture
- Editor: Eric J. Sundquist
- Date Published: February 1993
- availability: Available
- format: Paperback
- isbn: 9780521435901
$ 49.99 (P) Paperback
Other available formats: hardback, looking for an examination copy.
If you are interested in the title for your course we can consider offering an examination copy. To register your interest please contact [email protected] providing details of the course you are teaching.
This is a 1993 collection of fourteen essays by America's leading historians and literary critics which evaluates the importance of Frederick Douglass in his own day and on into the twentieth century. As a result of the research and interpretation in both literary and historical studies, Frederick Douglass has assumed a central place in the revival of interest in the multicultural study of American literature. His autobiographies are fundamental case studies of the slave narratives that form the basis of African-American culture. His remarkable achievements as abolitionist orator, journalist, and writer of fiction and historical essays have made him a pivotal figure in a variety of disciplines. The essays examine Douglass' own views on gender and class, as well as racial issues, and place his thought and writings in the context of debates about slavery and freedom that dominated the intellectual landscape of nineteenth-century America.
Customer reviews
Not yet reviewed.
Be the first to review
Log in to review
Review was not posted due to profanity
, create a review
(If you're not , sign out )
How do you rate this item?
Product details.
- length: 306 pages
- dimensions: 229 x 153 x 21 mm
- weight: 0.36kg
Table of Contents
Introduction 1. 'Ironic tenacity': Frederick Douglass' seizure of the dialectic Sterling Stuckey 2. From Wheatley to Douglass: the politics of displacement Henry Louis Gates, Jr 3. Writing freely? Frederick Douglass and the constraints of racialized writing Wilson J. Moses 4. Faith, doubt, and apostasy: evidence of things unseen in Frederick Douglass' narrative Donald B. Gibson 5. Franklinian Douglass: the Afro-American as representative man Rafia Zafar 6. Reading slavery: the anxiety of ethnicity in Douglass' narrative David Van Leer 7. The punishment of Esther: Frederick Douglass and the construction of the feminine Jenny Franchot 8. Race, violence, and manhood: the masculine ideal in Frederick Douglass' 'The Heroic Slave' Richard Yarborough 9. 'We hold these truths to be self-evident': the rhetoric of Frederick Douglass' journalism Shelley Fisher and Carla L. Peterson 10. The Frederick Douglass-Gerrit Smith friendship and political abolitionism in the 1850s John R. McKivigan 11. The shadow of slavery: Frederick Douglass, the savage South, and the next generation Wayne Mixon 12. Frederick Douglass' life and times: progressive rhetoric and the problem of constituency Kenneth W. Warren 13. Images of Frederick Douglass in the Afro-American mind: the recent Black freedom struggle Waldo E. Martin, Jr. Selected bibliography Notes on contributors Index.
Contributors
Sterling Stuckey, Henry Louis Gates, Jr., Wilson J. Moses, Donald B. Gibson, Rafia Zafar, David Van Lee,; Jenny Franchot, Richard Yarborough, Shelley Fisher, Carla L. Peterson, John R. McKivigan, Wayne Mixon, Kenneth W. Warren, Waldo E. Martin, Jr.
Related Books

Frederick Douglass in Context

The Cambridge Companion to Frederick Douglass
New essays on uncle tom's cabin.

Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass
An American Slave

Melville and the Idea of Blackness
Race and Imperialism in Nineteenth-Century America
also by this author

Writing America Black
Race Rhetoric and the Public Sphere
Browse by related subject
- African and Caribbean literature
- Anglo Saxon and medieval literature
- Asian literature
- Canadian literature
- English literature: general interest
- English literature 1700-1830
- English literature 1830-1900
- English literature 1900-1945
- English literature after 1945
- European and world literature: general interest
- European literature
- Irish literature
- Latin American literature
- Literary texts
- Literary theory
- Printing and publishing history
- Renaissance and early modern literature
Sorry, this resource is locked
Please register or sign in to request access. If you are having problems accessing these resources please email [email protected]
You are now leaving the Cambridge University Press website. Your eBook purchase and download will be completed by our partner www.ebooks.com. Please see the permission section of the www.ebooks.com catalogue page for details of the print & copy limits on our eBooks.
Remove this title from your notification list?

Turn stock notifications on?
You must be signed in to your Cambridge account to turn product stock notifications on or off.

Save 20% off on your next online purchase with Cambridge Alerts
Receive email alerts on new books, offers and news...
Find content that relates to you
Join us online.
What we do What we do
- Author support
- Assessment Research
About us About us
- People and planet
- Accessibillity
- University of Cambridge
© 2024 Cambridge University Press & Assessment
- Modern slavery
Are you sure you want to delete your account?
This cannot be undone.
Thank you for your feedback which will help us improve our service.
If you requested a response, we will make sure to get back to you shortly.
3.4 Annotated Sample Reading: from Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass by Frederick Douglass
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Read in several genres to understand how conventions are shaped by purpose, language, culture, and expectation.
- Use reading for inquiry, learning, critical thinking, and communicating in varying rhetorical and cultural contexts.
- Read a diverse range of texts, attending to relationships among ideas, patterns of organization, and interplay between verbal and nonverbal elements.
Introduction
Frederick Douglass (1818–1895) was born into slavery in Maryland. He never knew his father, barely knew his mother, and was separated from his grandmother at a young age. As a boy, Douglass understood there to be a connection between literacy and freedom. In the excerpt from his autobiography, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave , that follows, you will learn about how Douglass learned to read. By age 12, he was reading texts about the natural rights of human beings. At age 15, he began educating other enslaved people. When Douglass was 20, he met Anna Murray, whom he would later marry. Murray helped Douglass plot his escape from slavery. Dressed as a sailor, Douglass bought a train ticket northward. Within 24 hours, he arrived in New York City and declared himself free. Douglass went on to work as an activist in the abolitionist movement as well as the women’s suffrage movement.
In the portion of the text included here, Douglass chooses to represent the dialogue of Mr. Auld, an enslaver who by the laws of the time owns Douglass. Douglass describes this moment with detail and accuracy, including Mr. Auld’s use of a racial slur. In an interview with the Public Broadcasting Service (PBS), Harvard professor Randall Kennedy (b. 1954), who has traced the historical evolution of the word, notes that one of its first uses, recorded in 1619, appears to have been descriptive rather than derogatory. However, by the mid-1800s, White people had appropriated the term and begun using it with its current negative connotation. In response, over time, Black people have reclaimed the word (or variations of it) for different purposes, including mirroring racism, creating irony, and reclaiming community and personal power—using the word for a contrasting purpose to the way others use it. Despite this evolution, Professor Kennedy explains that the use of the word should be accompanied by a deep understanding of one’s audience and by being clear about the intention. However, even when intention is very clear and malice is not intended, harm can, and likely will, occur. Thus, Professor Kennedy cautions that all people should understand the history of the word, be aware of its potential negative effect on an audience, and therefore use it sparingly, or preferably not at all.
In the case of Mr. Auld and Douglass, Douglass gives an account of Auld’s exact language in order to hold a mirror to the racism of Mr. Auld—and the reading audience of his memoir—and to emphasize the theme that literacy (or education) is one way to combat racism.
Living by Their Own Words
Literacy from unexpected sources.
annotated text From the title and from Douglass’s use of pronoun I, you know this work is autobiographical and therefore written from the first-person point of view. end annotated text
public domain text [excerpt begins with first full paragraph on page 33 and ends on page 34 where the paragraph ends] end public domain text
public domain text Very soon after I went to live with Mr. and Mrs. Auld, she very kindly commenced to teach me the A, B, C. After I had learned this, she assisted me in learning to spell words of three or four letters. Just at this point of my progress, Mr. Auld found out what was going on, and at once forbade Mrs. Auld to instruct me further, telling her, among other things, that it was unlawful, as well as unsafe, to teach a slave to read. end public domain text
annotated text Douglass describes the background situation and the culture of the time, which he will defy in his quest for literacy. The word choice in his narration of events indicates that he is writing for an educated audience. end annotated text
public domain text To use his own words, further, he said, “If you give a nigger an inch, he will take an ell. A nigger should know nothing but to obey his master—to do as he is told to do. Learning would spoil the best nigger in the world. Now,” said he, “if you teach that nigger (speaking of myself) how to read, there would be no keeping him. It would forever unfit him to be a slave. He would at once become unmanageable, and of no value to his master. As to himself, it could do him no good, but a great deal of harm. It would make him discontented and unhappy.” end public domain text
annotated text In sharing this part of the narrative, Douglass underscores the importance of literacy. He provides a description of Mr. Auld, a slaveholder, who seeks to impose illiteracy as a means to oppress others. In this description of Mr. Auld’s reaction, Douglass shows that slaveholders feared the power that enslaved people would have if they could read and write. end annotated text
annotated text Douglass provides the details of Auld’s dialogue not only because it is a convention of narrative genre but also because it demonstrates the purpose and motivation for his forthcoming pursuit of literacy. We have chosen to maintain the authenticity of the original text by using the language that Douglass offers to quote Mr. Auld’s dialogue because it both provides context for the rhetorical situation and underscores the value of the attainment of literacy for Douglass. However, contemporary audiences must understand that this language should be uttered only under very narrow circumstances in any current rhetorical situation. In general, it is best to avoid its use. end annotated text
public domain text These words sank deep into my heart, stirred up sentiments within that lay slumbering, and called into existence an entirely new train of thought. It was a new and special revelation, explaining dark and mysterious things, with which my youthful understanding had struggled, but struggled in vain. I now understood what had been to me a most perplexing difficulty—to wit, the white man’s power to enslave the black man. It was a grand achievement, and I prized it highly. From that moment, I understood the pathway from slavery to freedom. It was just what I wanted, and I got it at a time when I the least expected it. Whilst I was saddened by the thought of losing the aid of my kind mistress, I was gladdened by the invaluable instruction which, by the merest accident, I had gained from my master. end public domain text
annotated text In this reflection, Douglass has a definitive and transformative moment with reading and writing. The moment that sparked a desire for literacy is a common feature in literacy narratives, particularly those of enslaved people. In that moment, he understood the value of literacy and its life-changing possibilities; that transformative moment is a central part of the arc of this literacy narrative. end annotated text
public domain text Though conscious of the difficulty of learning without a teacher, I set out with high hope, and a fixed purpose, at whatever cost of trouble, to learn how to read. The very decided manner with which he spoke, and strove to impress his wife with the evil consequences of giving me instruction, served to convince me that he was deeply sensible of the truths he was uttering. It gave me the best assurance that I might rely with the utmost confidence on the results which, he said, would flow from teaching me to read. What he most dreaded, that I most desired. What he most loved, that I most hated. That which to him was a great evil, to be carefully shunned, was to me a great good, to be diligently sought; and the argument which he so warmly urged, against my learning to read, only served to inspire me with a desire and determination to learn. In learning to read, I owe almost as much to the bitter opposition of my master, as to the kindly aid of my mistress. I acknowledge the benefit of both. end public domain text
annotated text Douglass articulates that this moment changed his relationship to literacy and ignited a purposeful engagement with language and learning that would last throughout his long life. The rhythm, sentence structure, and poetic phrasing in this reflection provide further evidence that Douglass, over the course of his life, actively pursued and mastered language after having this experience with Mr. Auld. end annotated text
public domain text [excerpt continues with the beginning of Chapter 7 on page 36 and ends with the end of the paragraph at the top of page 39] end public domain text
public domain text [In Chapter 7, the narrative continues] I lived in Master Hugh’s family about seven years. During this time, I succeeded in learning to read and write. In accomplishing this, I was compelled to resort to various stratagems. I had no regular teacher. My mistress, who had kindly commenced to instruct me, had, in compliance with the advice and direction of her husband, not only ceased to instruct, but had set her face against my being instructed by any one else. It is due, however, to my mistress to say of her, that she did not adopt this course of treatment immediately. She at first lacked the depravity indispensable to shutting me up in mental darkness. It was at least necessary for her to have some training in the exercise of irresponsible power, to make her equal to the task of treating me as though I were a brute. end public domain text
public domain text My mistress was, as I have said, a kind and tender-hearted woman; and in the simplicity of her soul she commenced, when I first went to live with her, to treat me as she supposed one human being ought to treat another. In entering upon the duties of a slaveholder, she did not seem to perceive that I sustained to her the relation of a mere chattel, and that for her to treat me as a human being was not only wrong, but dangerously so. Slavery proved as injurious to her as it did to me. When I went there, she was a pious, warm, and tender-hearted woman. There was no sorrow or suffering for which she had not a tear. She had bread for the hungry, clothes for the naked, and comfort for every mourner that came within her reach. Slavery soon proved its ability to divest her of these heavenly qualities. Under its influence, the tender heart became stone, and the lamblike disposition gave way to one of tiger-like fierceness. The first step in her downward course was in her ceasing to instruct me. She now commenced to practise her husband’s precepts. She finally became even more violent in her opposition than her husband himself. end public domain text
annotated text Douglass describes in detail a person in his life and his relationship to her. He uses specific diction to describe her kindness and to help readers get to know her—a “tear” for the “suffering”; “bread for the hungry, clothes for the naked, and comfort for every mourner.” end annotated text
public domain text She was not satisfied with simply doing as well as he had commanded; she seemed anxious to do better. Nothing seemed to make her more angry than to see me with a newspaper. She seemed to think that here lay the danger. I have had her rush at me with a face made all up of fury, and snatch from me a newspaper, in a manner that fully revealed her apprehension. She was an apt woman; and a little experience soon demonstrated, to her satisfaction, that education and slavery were incompatible with each other. end public domain text
annotated text The fact that Douglass can understand the harm caused by the institution of slavery to slaveholders as well as to enslaved people shows a level of sophistication in thought, identifies the complexity and detriment of this historical period, and demonstrates an acute awareness of the rhetorical situation, especially for his audience for this text. The way that he articulates compassion for the slaveholders, despite their ill treatment of him, would create empathy in his readers and possibly provide a revelation for his audience. end annotated text
public domain text From this time I was most narrowly watched. If I was in a separate room any considerable length of time, I was sure to be suspected of having a book, and was at once called to give an account of myself. All this, however, was too late. The first step had been taken. Mistress, in teaching me the alphabet, had given me the inch , and no precaution could prevent me from taking the ell . end public domain text
annotated text Once again, Douglass underscores the value that literacy has for transforming the lived experiences of enslaved people. The reference to the inch and the ell circles back to Mr. Auld’s warnings and recalls the impact of that moment on his life. end annotated text
public domain text The plan which I adopted, and the one by which I was most successful, was that of making friends of all the little white boys whom I met in the street. As many of these as I could, I converted into teachers. With their kindly aid, obtained at different times and in different places, I finally succeeded in learning to read. When I was sent of errands, I always took my book with me, and by going one part of my errand quickly, I found time to get a lesson before my return. I used also to carry bread with me, enough of which was always in the house, and to which I was always welcome; for I was much better off in this regard than many of the poor white children in our neighborhood. This bread I used to bestow upon the hungry little urchins, who, in return, would give me that more valuable bread of knowledge. I am strongly tempted to give the names of two or three of those little boys, as a testimonial of the gratitude and affection I bear them; but prudence forbids;—not that it would injure me, but it might embarrass them; for it is almost an unpardonable offence to teach slaves to read in this Christian country. end public domain text
annotated text Douglass comments on the culture of the time, which still permitted slavery; he is sensitive to the fact that these boys might be embarrassed by their participation in unacceptable, though humanitarian, behavior. His audience will also recognize the irony in his tone when he writes that it is “an unpardonable offense to teach slaves . . . in this Christian country.” Such behavior is surely “unchristian.” end annotated text
public domain text It is enough to say of the dear little fellows, that they lived on Philpot Street, very near Durgin and Bailey’s ship-yard. I used to talk this matter of slavery over with them. I would sometimes say to them, I wished I could be as free as they would be when they got to be men. “You will be free as soon as you are twenty-one, but I am a slave for life ! Have not I as good a right to be free as you have?” These words used to trouble them; they would express for me the liveliest sympathy, and console me with the hope that something would occur by which I might be free. end public domain text
annotated text Douglass pursues and attains literacy not only for his own benefit; his knowledge also allows him to begin to instruct, as well as advocate for, those around him. Douglass’s use of language and his understanding of the rhetorical situation give the audience evidence of the power of literacy for all people, round out the arc of his narrative, and provide a resolution. end annotated text
Discussion Questions
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Michelle Bachelor Robinson, Maria Jerskey, featuring Toby Fulwiler
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Writing Guide with Handbook
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/3-4-annotated-sample-reading-from-narrative-of-the-life-of-frederick-douglass-by-frederick-douglass
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Civil Religion in the Discourse of Frederick Douglass
- ALTRALANG Journal 6(1):440-449

- Abou Bakr Belkaid University of Tlemcen
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Frederick Douglass
- Harriet Beecher Stowe
- James H. Evans
- Robert S. Levine
- DAEDALUS-US
- Robert Neelly Bellah
- Robert B. Stepto
- James Arthur
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
Top of page
Collection Frederick Douglass Papers at the Library of Congress
1818 to 1835.
Born Frederick Augustus Washington Bailey, a slave, in Tuckahoe, Talbot County, Maryland. Mother is a slave, Harriet Bailey, and father is a white man, rumored to be his master, Aaron Anthony. He had three older siblings, Perry, Sarah, and Eliza.
Raised by grandmother Betsey Bailey at Holme Hill Farm, where he was born; sees his mother only a few times.
Sister Kitty is born.
Sister Arianna is born.
Moves to plantation on Wye River, where he lives with his siblings Perry, Sarah, and Eliza.
Sees his mother for the last time.
His mother dies.
Sent to Baltimore to live with Hugh Auld and his wife Sophia. His master, Aaron Anthony, dies late in the year; Frederick becomes the property of Thomas Auld, Anthony's son-in-law. Thomas Auld sends him back to Hugh Auld.
Asks Sophia Auld to teach him to read. She does so until Hugh Auld stops them, believing that education makes slaves rebellious.
Works in shipyard as general assistant; practices reading and writing in secret.
Reads newspaper article on John Quincy Adams's antislavery petitions in Congress; learns of the abolitionist movement.
Buys copy of a compilation of speeches, Caleb Bingham's The Columbian Orator , with which he hones his reading and speaking skills.
Sister Sarah is sold to a planter in Mississippi.
Sent to St. Michaels, Maryland, where he works for Thomas Auld. Tries to teach other slaves to read until Auld discovers it and stops him.
Auld rents him out to farmer Edward Covey, known as a "slave breaker." He is beaten several times and finally fights back. Covey never tries to beat him again.
Hired out to work for William Freeland, a Talbot County, Maryland, farmer. Secretly organizes Sunday school and teaches other slaves to read.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
frederick douglass, an american slave by frederick douglass 7^wys`f7taa]e. narrative of the life of frederick douglass, an american slave. w ritten by himself. boston published at the anti-slavery office, no. 25 cornhill 1845 . entered, according to act of congress, in the year 1845,
To understand Frederick Douglass, his struggles, and the times he lived in, one must read about his life in his own words. Below are links to complete online texts of all three Douglass autobiographies. Two have been part of online collections at the Library of Congress; one is provided by the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Libraries.
In His Own Words To understand Frederick Douglass, his struggles, and the times he lived in, one must read about his life in his own words. Below are links to complete online texts of all three Douglass autobiographies. Two have been part of online collections at the Library of Congress; one is provided by the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Libraries.
The papers of nineteenth-century African American abolitionist Frederick Douglass (1818-1895), who escaped from slavery and then risked his freedom by becoming an outspoken antislavery lecturer, writer, and publisher, consist of approximately 7,400 items (38,000 images), most of which were digitized from 34 reels of previously produced microfilm. The collection spans the years 1841-1964, with ...
My Master's Thesis examines Frederick Douglass' definition of American identity by navigating through his struggle between his acknowledgement of American ideals and his
Many essays about Frederick Douglass and his times have been published on the Gilder Lehrman Institute website and in History Now, the online journal of the Gilder Lehrman Institute. The selected essays listed below provide historical perspective for teachers, students, and general readers.
Essays and criticism on Frederick Douglass' Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave - Essays and Criticism
Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave is an 1845 memoir and treatise on abolition written by African-American orator and former slave Frederick Douglass during his time in Lynn, Massachusetts. [1] It is the first of Douglass's three autobiographies, the others being My Bondage and My Freedom (1855) and Life and Times of Frederick Douglass (1881, revised 1892).
Frederick Douglass. Frederick Douglass (c. 1817-1895) is a central figure in U.S. and African American history. [1] He was born into slavery circa 1817; his mother was an enslaved black woman, while his father was reputed to be his white master. Douglass escaped from slavery in 1838 and rose to become a principal leader and spokesperson for ...
Frederick Douglass has received per-haps more scholarly attention since the 1970s than any other nineteenth-century African American writer. Yet these provoc-ative essays urge a return to Douglass's pre-Civil War narratives with an awareness of just how much we have yet to learn.
Life and Times of Frederick Douglass, Written by Himself documents the author's life in the 1800's, a century that includes Douglass's birth in its second decade and his ascension to ...
Frederick Douglass was an escaped slave who became a prominent activist, author and public speaker. He became a leader in the abolitionist movement, which sought to end the practice of slavery ...
Frederick Douglass, African American abolitionist, orator, newspaper publisher, and author who is famous for his first autobiography, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself. He became the first Black U.S. marshal and was the most photographed American man of the 19th century.
In conclusion, Frederick Douglass's central thesis in "Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave" is that slavery dehumanizes both the enslaved and the enslavers. Through his personal narrative, Douglass provides a powerful indictment of the institution of slavery, exposing its moral bankruptcy and intellectual stagnation.
The essays examine Douglass' own views on gender and class, as well as racial issues, and place his thought and writings in the context of debates about slavery and freedom that dominated the intellectual landscape of nineteenth-century America.
As a boy, Douglass understood there to be a connection between literacy and freedom. In the excerpt from his autobiography, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, that follows, you will learn about how Douglass learned to read. By age 12, he was reading texts about the natural rights of human beings.
Born into slavery, American writer and abolitionist Frederick Douglass (1817-1895) bought his freedom with income earned from lecturing abroad after the publication of his autobiography, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass.
It seeks to unravel the religious dimension of Frederick Douglass's discourse in its relation to American civil religion. ... Ja mes Baldwi n's T he F ire Next Time colle ction of essays on ...
1818 Born Frederick Augustus Washington Bailey, a slave, in Tuckahoe, Talbot County, Maryland. Mother is a slave, Harriet Bailey, and father is a white man, rumored to be his master, Aaron Anthony. He had three older siblings, Perry, Sarah, and Eliza.
Get an answer for 'Does the thesis adequately capture Frederick Douglass' influence on American social policies through his autobiographies, advocacy for women, and call for colored Union troops ...