

Think Like a Researcher: Instruction Resources: #6 Developing Successful Research Questions
- Guide Organization
- Overall Summary
- #1 Think Like a Researcher!
- #2 How to Read a Scholarly Article
- #3 Reading for Keywords (CREDO)
- #4 Using Google for Academic Research
- #4 Using Google for Academic Research (Alternate)
- #5 Integrating Sources
- Research Question Discussion
- #7 Avoiding Researcher Bias
- #8 Understanding the Information Cycle
- #9 Exploring Databases
- #10 Library Session
- #11 Post Library Session Activities
- Summary - Readings
- Summary - Research Journal Prompts
- Summary - Key Assignments
- Jigsaw Readings
- Permission Form
Course Learning Outcome: Develop ability to synthesize and express complex ideas; demonstrate information literacy and be able to work with evidence
Goal: Develop students’ ability to recognize and create successful research questions
Specifically, students will be able to
- identify the components of a successful research question.
- create a viable research question.
What Makes a Good Research Topic Handout
These handouts are intended to be used as a discussion generator that will help students develop a solid research topic or question. Many students start with topics that are poorly articulated, too broad, unarguable, or are socially insignificant. Each of these problems may result in a topic that is virtually un-researchable. Starting with a researchable topic is critical to writing an effective paper.
Research shows that students are much more invested in writing when they are able to choose their own topics. However, there is also research to support the notion that students are completely overwhelmed and frustrated when they are given complete freedom to write about whatever they choose. Providing some structure or topic themes that allow students to make bounded choices may be a way mitigate these competing realities.
These handouts can be modified or edited for your purposes. One can be used as a handout for students while the other can serve as a sample answer key. The document is best used as part of a process. For instance, perhaps starting with discussing the issues and potential research questions, moving on to problems and social significance but returning to proposals/solutions at a later date.
- Research Questions - Handout Key (2 pgs) This document is a condensed version of "What Makes a Good Research Topic". It serves as a key.
- Research Questions - Handout for Students (2 pgs) This document could be used with a class to discuss sample research questions (are they suitable?) and to have them start thinking about problems, social significance, and solutions for additional sample research questions.
- Research Question Discussion This tab includes materials for introduction students to research question criteria for a problem/solution essay.
Additional Resources
These documents have similarities to those above. They represent original documents and conversations about research questions from previous TRAIL trainings.
- What Makes a Good Research Topic? - Original Handout (4 pgs)
- What Makes a Good Research Topic? Revised Jan. 2016 (4 pgs)
- What Makes a Good Research Topic? Revised Jan 2016 with comments
Topic Selection (NCSU Libraries)
Howard, Rebecca Moore, Tricia Serviss, and Tanya K. Rodrigues. " Writing from sources, writing from sentences ." Writing & Pedagogy 2.2 (2010): 177-192.
Research Journal
Assign after students have participated in the Developing Successful Research Topics/Questions Lesson OR have drafted a Research Proposal.
Think about your potential research question.
- What is the problem that underlies your question?
- Is the problem of social significance? Explain.
- Is your proposed solution to the problem feasible? Explain.
- Do you think there is evidence to support your solution?
Keys for Writers - Additional Resource
Keys for Writers (Raimes and Miller-Cochran) includes a section to guide students in the formation of an arguable claim (thesis). The authors advise students to avoid the following since they are not debatable.
- "a neutral statement, which gives no hint of the writer's position"
- "an announcement of the paper's broad subject"
- "a fact, which is not arguable"
- "a truism (statement that is obviously true)"
- "a personal or religious conviction that cannot be logically debated"
- "an opinion based only on your feelings"
- "a sweeping generalization" (Section 4C, pg. 52)
The book also provides examples and key points (pg. 53) for a good working thesis.
- << Previous: #5 Integrating Sources
- Next: Research Question Discussion >>
- Last Updated: Sep 29, 2023 2:51 PM
- URL: https://libguides.ucmerced.edu/think_like_a_researcher

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Published on October 26, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A research question pinpoints exactly what you want to find out in your work. A good research question is essential to guide your research paper , dissertation , or thesis .
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
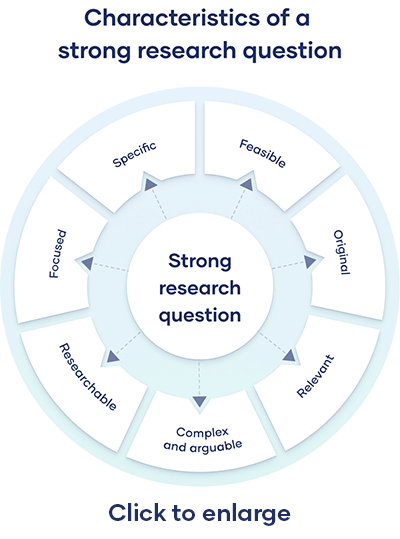
Table of contents
How to write a research question, what makes a strong research question, using sub-questions to strengthen your main research question, research questions quiz, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research questions.
You can follow these steps to develop a strong research question:
- Choose your topic
- Do some preliminary reading about the current state of the field
- Narrow your focus to a specific niche
- Identify the research problem that you will address
The way you frame your question depends on what your research aims to achieve. The table below shows some examples of how you might formulate questions for different purposes.
Using your research problem to develop your research question
Note that while most research questions can be answered with various types of research , the way you frame your question should help determine your choices.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them. The criteria below can help you evaluate the strength of your research question.
Focused and researchable
Feasible and specific, complex and arguable, relevant and original.
Chances are that your main research question likely can’t be answered all at once. That’s why sub-questions are important: they allow you to answer your main question in a step-by-step manner.
Good sub-questions should be:
- Less complex than the main question
- Focused only on 1 type of research
- Presented in a logical order
Here are a few examples of descriptive and framing questions:
- Descriptive: According to current government arguments, how should a European bank tax be implemented?
- Descriptive: Which countries have a bank tax/levy on financial transactions?
- Framing: How should a bank tax/levy on financial transactions look at a European level?
Keep in mind that sub-questions are by no means mandatory. They should only be asked if you need the findings to answer your main question. If your main question is simple enough to stand on its own, it’s okay to skip the sub-question part. As a rule of thumb, the more complex your subject, the more sub-questions you’ll need.
Try to limit yourself to 4 or 5 sub-questions, maximum. If you feel you need more than this, it may be indication that your main research question is not sufficiently specific. In this case, it’s is better to revisit your problem statement and try to tighten your main question up.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
As you cannot possibly read every source related to your topic, it’s important to evaluate sources to assess their relevance. Use preliminary evaluation to determine whether a source is worth examining in more depth.
This involves:
- Reading abstracts , prefaces, introductions , and conclusions
- Looking at the table of contents to determine the scope of the work
- Consulting the index for key terms or the names of important scholars
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (“ x affects y because …”).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses . In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.

Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 21). Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 26, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-questions/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to define a research problem | ideas & examples, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, 10 research question examples to guide your research project, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Secondary menu
- International
Digital Learning Commons
You are here, developing a research question + worksheet.

Time Commitment
Description.
Learn how to take a broad topic and develop it into a research question that will define the scope of your project.
Your research guides your project from beginning to completion. Unlike your topic, which may be fairly general, your research question will define the specific scope of your project. In other words, the research question tells readers what you're trying to find out.
Develop your Research Question
- Define the topic area: In a sentence or two, describe your broad topic or area of research. (Example: Smoking cessation.)
- Describe the problem: In a sentence or two, describe a problem that could be addressed in your topic or area of research. (Example: "Smokers often relapse because of complex physical and psychological factors.)
- Specify the gap and justify the investigation: What is unknown or unresolved? Why should we bother investigating it? (Example: We don't know what combination of physical and pscyological factors is most often associated with smoking relapse.)
- Brainstorm as many questions as you can think of that relate to your research topic/problem/gap. Try starting questions with what, why, where, who, and how; in general, avoid questions that will result in only "yes" or "no" answers.
- Draft a primary question: Do you see one main question emerging from the list above? If not, try doing some additional reading or thinking, or talk to your supervisor or instructor (Example: How do the physiological and psychological effects of smoking make it difficult for young adults to quit smoking?)
- Draft a secondary research questions: What information do you need to gather to answer you primary question? (Example: Before we can answer the question of "how" physiological and psychological effects make it difficult to quit smoking, we need to identify what the key effects are.)
Assess & Refine
Evaluate your research question. Ask yourself the following questions: will readers understand it on first reading? Is it feasible given your time and resources? Does it contribute to a wider academic conversation?
Talk it over: Use this worksheet to talk with your supervisor or instructor about the scope and direction of your research plan.
Tighten your Focus. Look at every word in your question. Replace as many as you can with more specific language or ideas (e.g., instead of "students," say "Grade 9 students in Ontario").
Revisit often! Keep your research question in mind throughout the research and writing process.
You may find that you need to adapt your research question as you learn more.
- Assignment Help
Creative Commons Information

Recommended
5 questions to strengthen your thesis statement.

Asking Questions to Explore Your Topic

Search Modifiers Cheat Sheet

Search form
- Where Is It?

We use cookies and similar technologies to improve your website experience and help us understand how you use our website. By continuing to use this website, you consent to the usage of cookies. Learn more about our Privacy Statement and Cookie Policy .
- Our Mission
- Code of Conduct
- The Consultants
- Hours and Locations
- Apply to Become a Consultant
- Make an Appointment
- Face-to-Face Appointments
- Zoom Appointments
- Written Feedback Appointments
- Support for Writers with Disabilities
- Policies and Restrictions
- Upcoming Workshops
- Class Workshops
- Meet the Consultants
- Writing Guides and Tools
- Schedule an appointment! Login or Register
- Graduate Students
- ESOL Students
How to Write a Research Question
What is a research question? A research question is the question around which you center your research. It should be:
- clear : it provides enough specifics that one’s audience can easily understand its purpose without needing additional explanation.
- focused : it is narrow enough that it can be answered thoroughly in the space the writing task allows.
- concise : it is expressed in the fewest possible words.
- complex : it is not answerable with a simple “yes” or “no,” but rather requires synthesis and analysis of ideas and sources prior to composition of an answer.
- arguable : its potential answers are open to debate rather than accepted facts.
You should ask a question about an issue that you are genuinely curious and/or passionate about.
The question you ask should be developed for the discipline you are studying. A question appropriate for Biology, for instance, is different from an appropriate one in Political Science or Sociology. If you are developing your question for a course other than first-year composition, you may want to discuss your ideas for a research question with your professor.
Why is a research question essential to the research process? Research questions help writers focus their research by providing a path through the research and writing process. The specificity of a well-developed research question helps writers avoid the “all-about” paper and work toward supporting a specific, arguable thesis.
Steps to developing a research question:
- Choose an interesting general topic. Most professional researchers focus on topics they are genuinely interested in studying. Writers should choose a broad topic about which they genuinely would like to know more. An example of a general topic might be “Slavery in the American South” or “Films of the 1930s.”
- Do some preliminary research on your general topic. Do a few quick searches in current periodicals and journals on your topic to see what’s already been done and to help you narrow your focus. What issues are scholars and researchers discussing, when it comes to your topic? What questions occur to you as you read these articles?
- Consider your audience. For most college papers, your audience will be academic, but always keep your audience in mind when narrowing your topic and developing your question. Would that particular audience be interested in the question you are developing?
- Start asking questions. Taking into consideration all of the above, start asking yourself open-ended “how” and “why” questions about your general topic. For example, “Why were slave narratives effective tools in working toward the abolishment of slavery?” or “How did the films of the 1930s reflect or respond to the conditions of the Great Depression?”
- Is your research question clear? With so much research available on any given topic, research questions must be as clear as possible in order to be effective in helping the writer direct his or her research.
- Is your research question focused? Research questions must be specific enough to be well covered in the space available.
- Is your research question complex? Research questions should not be answerable with a simple “yes” or “no” or by easily-found facts. They should, instead, require both research and analysis on the part of the writer. They often begin with “How” or “Why.”
- Begin your research . After you’ve come up with a question, think about the possible paths your research could take. What sources should you consult as you seek answers to your question? What research process will ensure that you find a variety of perspectives and responses to your question?
Sample Research Questions
Unclear: How should social networking sites address the harm they cause? Clear: What action should social networking sites like MySpace and Facebook take to protect users’ personal information and privacy? The unclear version of this question doesn’t specify which social networking sites or suggest what kind of harm the sites might be causing. It also assumes that this “harm” is proven and/or accepted. The clearer version specifies sites (MySpace and Facebook), the type of potential harm (privacy issues), and who may be experiencing that harm (users). A strong research question should never leave room for ambiguity or interpretation. Unfocused: What is the effect on the environment from global warming? Focused: What is the most significant effect of glacial melting on the lives of penguins in Antarctica?
The unfocused research question is so broad that it couldn’t be adequately answered in a book-length piece, let alone a standard college-level paper. The focused version narrows down to a specific effect of global warming (glacial melting), a specific place (Antarctica), and a specific animal that is affected (penguins). It also requires the writer to take a stance on which effect has the greatest impact on the affected animal. When in doubt, make a research question as narrow and focused as possible.
Too simple: How are doctors addressing diabetes in the U.S.? Appropriately Complex: What main environmental, behavioral, and genetic factors predict whether Americans will develop diabetes, and how can these commonalities be used to aid the medical community in prevention of the disease?
The simple version of this question can be looked up online and answered in a few factual sentences; it leaves no room for analysis. The more complex version is written in two parts; it is thought provoking and requires both significant investigation and evaluation from the writer. As a general rule of thumb, if a quick Google search can answer a research question, it’s likely not very effective.
Last updated 8/8/2018

The Writing Center
4400 University Drive, 2G8 Fairfax, VA 22030
- Johnson Center, Room 227E
- +1-703-993-1200
- [email protected]
Quick Links
- Register with us
© Copyright 2024 George Mason University . All Rights Reserved. Privacy Statement | Accessibility
Developing Research Questions
- Author By Troy Mikanovich
- Publication date April 8, 2022
- Categories: Research Writing , Writing Tips
- Categories: proposal , prospectus , research , research questions
Developing a research question, like every other aspect of a research project—working with sources, the interpretation of data, the writing, the editing—takes work, and is a skill that you can practice, refine, and personalize. Here’s a short primer on how to come up with a workable research question, references included.
Whether you’re just beginning, or already have a research question in mind, consider starting at the beginning of the worksheet and jotting down answers to each section. I’ve also included a completed worksheet as a example to follow if you are finding it hard to get started.

- UConn Library
- Research Now
- Get Started
- Forming a Research Question
Get Started — Forming a Research Question
- Reading (and Understanding) Your Assignment
- Background Research
- Initial Searching
- Help & Other Resources
- Research Now Homepage
Writing out your research question will help you articulate (to yourself and others) the direction of your research – what you need to be looking for as you prepare to gather specific information.
Forming the Research Question
Performing Background Research and Initial Searching develops your general area of interest so that you can form a more focused topic.
As you review the information you've found from these steps and the ideas you've encountered, these questions may help you to form a focus for your research:
- What am I trying to accomplish?
- How interested am I in this idea?
- How much time do I have?
- What information and resources are available?
(From Guided Inquiry: Learning in the 21st Century by Carol Kuhlthau, Leslie Maniotes, and Ann Caspari)
Your Research Log helps you to keep track of and think about your research. Look back through your log and consider:
What have you found? How does the information and ideas you've encountered fit together? What themes have emerged ? What important question do you want to develop from the ideas and information you have found? What do you want to explore in more detail? What do you want your research to focus on?
And - does your research question answer the assignment?
You'll want to make sure that you're not trying to answer too many questions - think about the time you have available. You'll want to focus on one aspect of your topic.
- Research Questions - The Good and the Not So Good
(Credit: William Badke)
How do I Know if My Topic is Sustainable?
You will not really know if your topic will work until you start searching for information. The information you found while exploring your topic doing background research should give you an idea of whether or not your topic is sustainable.
Test your topic in a few databases by searching for the key concepts or terms.
- Are you finding too much information? Perhaps your topic is too general . Add a few more terms to your search and explore (for example, you might feel like you're finding too much on "College Students." Looking for information about "Freshmen," though, will give you fewer and more specific results).
- Are you finding too little information? Perhaps your topic is too specific . Try searching again using broader synonyms for your search terms (for example, you might not find much on the topic "UConn Students." "College Students" will give you more information).
As you develop your research question, you might find that you need to ask a broader or narrower question, depending upon the resources available and the time you have to complete your assignment.
Sometimes it's hard to determine if a topic is too broad or specific. Try checking in with your instructor (who has a good idea of the field of research!) or a librarian (who has a good idea of the available resources!).
- Ask a Librarian Chat with a UConn librarian.
Developing a Research Question
(Credit: Wilfrid Laurier University Library)
Now apply what you've learned! These tools will help you write out your research question.
- Research Question Generator Worksheet A tool to help you develop your research question.

Test Your Knowledge: Forming a Research Question
- Test your knowledge: Too Broad, Too Narrow Get some practice evaluating a research question.
Does Your Research Question Actually Answer a Question?
Sometimes this is referred to as the "so what" - what makes your project interesting and important.
What makes your question important? What makes your question interesting or exciting? Does your question require anything more of you than just repeating the information you've found? (If you find you're just repeating the information found, you probably don't have a very good question).
- << Previous: Initial Searching
- Next: Help & Other Resources >>
- Last Updated: Mar 27, 2024 3:43 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/getstarted

- CSI Library Home
- CSI Library
English 151
- Pick a Topic & Develop a Research Question
- Getting Started
- Gather Background Information (or topic browsing)
- Use Databases to Find Articles
- Databases for Current Affairs/ Issues
- OneSearch for E-Books
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Cite Sources: MLA Style
- Off-Campus Access
- Information Literacy and Research Online
- Full Collection of Videos for Library Research
- Test Your Knowledge (Assessments)
- Reach out to a librarian! (Reference Desk Online)
Pick a topic and develop a good research question
The first step in writing a research paper is choosing a good topic. Your topic will have to be something that falls within the guidelines provided by your instructor, and should also be something that you find interesting and would like to learn more about. However, a good research paper involves more than choosing an interesting topic and reporting information on it. A research paper should attempt to critically analyze a complex problem, and that means you need to develop a focused research question, which is essential to the research process. By defining exactly what you are trying to find out, your research question influences most of the rest of the steps taken to conduct your research. Follow the guides below to help you choose a topic and develop a good research question:
- Choosing a Topic A worksheet designed to help students brainstorm a topic for a research paper.
- Crafting a Research Question This is a worksheet designed to help students move from their chosen topic to a more focused research question.
Video: from topic to research question to keywords
Creating Research Questions
This section will help you consider a topic for your research paper that is interesting to you, and that is researchable using library resources. When you select a topic and focused research question, you’ll want to consider a few things:
- Does your section of ENG 151 have a theme? Does your professor want your research topic to correspond to that theme?
- What do YOU find interesting? You are going to spend hours reading information, thinking about how the information fits together, and then writing pages of critical analysis about your topic. This will be a more pleasant experience for you if you are genuinely interested in the topic you choose.
- Keep in mind that when you are searching for information about your topic, you can only find information that has been published This means you’re looking for a topic that other people are talking about, thinking about, and writing about. So, it needs to be interesting to you, but also to others.
- Don’t forget that you already know things! Many research papers start from the spark of an idea from something we hear or witness in the world around us.
Remember, your research question is NOT your thesis statement; it’s exploratory. If you start doing research and discover that people are writing articles about a more interesting (or easier to research) question, you can always adjust your question as you collect information.
The tools collected here will help you think about a topic that genuinely interests you, and develop a clear, concise, and researchable question based on that topic.
From Topic to Research Question
Your topic is the general, overarching area that you’re interested in, while the research question is a focused, smaller sliver of information you’re questioning within that topic. Topics are broad, while research questions are focused.
Topic: Urban Transportation
Research Questions could be…. “Why do some neighborhoods/communities oppose or advocate against creating bike lanes in their neighborhoods?” or “What factors increase or decrease the likelihood of electronic car adoption in urban environments?”
Topic: Immigration
Research Questions could be… “How has the United States’ handling of immigration changed from the Obama White House to the Trump White House?” and if that question ends up being too large or unwieldy, you can adjust it to something like, “What does living in a ‘Sanctuary City’ actually mean for undocumented students attending college in New York?” or “How have immigration policies affected families that live on either side of the Texas/Mexico border?” You can adjust your question based on what (and how much) information comes up in your searches.
What Makes a Research Question "Researchable"?
Good question! Coming up with a research question that leads you to a manageable paper is challenging and gets easier with practice. It’s a delicate balance between a few variables.
- OPEN questions versus SHUT questions: You want to ask a question that doesn’t have an obvious answer, something you can really grapple with. Your topic should have multiple points of view, aspects of it that people don’t all agree on. When the question is open-ended, you have more to investigate. If your question leads to a single point of view, or an obvious answer, you’re going to have a challenging time writing 10 or so pages about it. Shut question: why are vaccines bad? Open question: Where did the debate around vaccines start and why are some convinced vaccines are harmful? What does the science say about the efficacy of vaccines?
- SPECIFIC , rather than VAGUE . A good question tells you where to start your research right there in the question. A vague one will make you feel like you don’t know where to start, like you could be writing about almost anything. A question like “What does living in a ‘Sanctuary City’ actually mean for undocumented students attending college in New York?” gives you all the terms of the question: sanctuary cities, undocumented people, students, college, NYC. These are your search terms in the library databases! A vague question gives you nothing to hold onto. Vague version: How do folks feel about immigration. AHHHHHHHHH where do I start? Who are the folks? Why might they have feelings? Where are they coming from? Where do they live now?
- FOCUSED , rather than BROAD . The paper your professor wants you to write is not a report. (But you can use reports in your research!) You are not writing an overview of a huge topic, but rather a focused critical essay of close analysis. Your research question needs to be focused too. A broad question will leave you drowning in a sea of information that you can’t possibly synthesize in a few pages. Too broad: what is the history of slavery in the US? Focused: An exploratory analysis of the arguments (pro and con) around removing statues of southern civil war generals. This second question relates to slavery, but cuts the topic down to a focused (and researchable) issue.
- ANSWERABLE , but not OBVIOUS . Some of the universe’s interesting questions are not answerable in a research paper you’re writing in a few weeks (or perhaps at all). Why are there so many vampire movies? (Instead, analyze social themes brought up by one of them.) What makes men attack women? (Instead, investigate strategies people use to break the pattern of domestic abuse in relationships.)
Need ideas for topics? Check out these 2 databases
If you are still not sure what topic you would like to explore, the following 2 databases might help. Click the Browse Issues button in the database to see an alphabetical list of issues:
- Gale in Context: Opposing Viewpoints Provides access to full text literature about current controversial issues such as abortion, capital punishment, climate change, cloning, gun control, immigration, and more. Available material on each topic includes viewpoint essays, topic overviews, newspaper and magazine articles, statistics, and links to related web sites.
- CQ Researcher This link opens in a new window Full text reports written by seasoned journalists about current social, political, and economic issues. Includes topics in health, education, international affairs, public policy, the environment, technology, and the economy. Each report includes a concise overview of an issue, historical background, opposing arguments, statistics and polls, and suggestions for further reading. Great place to begin research on current affairs issues. Coverage Dates: 1991 to present
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Gather Background Information (or topic browsing) >>

Facebook Twitter Instagram
- URL: https://library.csi.cuny.edu/eng151
- Last Updated: Mar 12, 2024 2:59 PM

- Developing a Research Question
by acburton | Mar 22, 2024 | Resources for Students , Writing Resources
Selecting your research question and creating a clear goal and structure for your writing can be challenging – whether you are doing it for the first time or if you’ve done it many times before. It can be especially difficult when your research question starts to look and feel a little different somewhere between your first and final draft. Don’t panic! It’s normal for your research question to change a little (or even quite a bit) as you move through and engage with the writing process. Anticipating this can remind you to stay on track while you work and that it’ll be okay even if the literature takes you in a different direction.
What Makes an Effective Research Question?
The most effective research question will usually be a critical thinking question and should use “how” or “why” to ensure it can move beyond a yes/no or one-word type of answer. Consider how your research question can aim to reveal something new, fill in a gap, even if small, and contribute to the field in a meaningful way; How might the proposed project move knowledge forward about a particular place or process? This should be specific and achievable!
The CEWC’s Grad Writing Consultant Tariq says, “I definitely concentrated on those aspects of what I saw in the field where I believed there was an opportunity to move the discipline forward.”
General Tips
Do your research.
Utilize the librarians at your university and take the time to research your topic first. Try looking at very general sources to get an idea of what could be interesting to you before you move to more academic articles that support your rough idea of the topic. It is important that research is grounded in what you see or experience regarding the topic you have chosen and what is already known in the literature. Spend time researching articles, books, etc. that supports your thesis. Once you have a number of sources that you know support what you want to write about, formulate a research question that serves as the interrogative form of your thesis statement.
Grad Writing Consultant Deni advises, “Delineate your intervention in the literature (i.e., be strategic about the literature you discuss and clear about your contributions to it).”
Start Broadly…. then Narrow Your Topic Down to Something Manageable
When brainstorming your research question, let your mind veer toward connections or associations that you might have already considered or that seem to make sense and consider if new research terms, language or concepts come to mind that may be interesting or exciting for you as a researcher. Sometimes testing out a research question while doing some preliminary researching is also useful to see if the language you are using or the direction you are heading toward is fruitful when trying to search strategically in academic databases. Be prepared to focus on a specific area of a broad topic.
Writing Consultant Jessie recommends outlining: “I think some rough outlining with a research question in mind can be helpful for me. I’ll have a research question and maybe a working thesis that I feel may be my claim to the research question based on some preliminary materials, brainstorming, etc.” — Jessie, CEWC Writing Consultant
Try an Exercise
In the earliest phase of brainstorming, try an exercise suggested by CEWC Writing Specialist, Percival! While it is normally used in classroom or workshop settings, this exercise can easily be modified for someone working alone. The flow of the activity, if done within a group setting, is 1) someone starts with an idea, 2) three other people share their idea, and 3) the starting person picks two of these new ideas they like best and combines their original idea with those. The activity then begins again with the idea that was not chosen. The solo version of this exercise substitutes a ‘word bank,’ created using words, topics, or ideas similar to your broad, overarching theme. Pick two words or phrases from your word bank, combine it with your original idea or topic, and ‘start again’ with two different words. This serves as a replacement for different people’s suggestions. Ideas for your ‘word bank’ can range from vague prompts about mapping or webbing (e.g., where your topic falls within the discipline and others like it), to more specific concepts that come from tracing the history of an idea (its past, present, future) or mapping the idea’s related ideas, influences, etc. Care for a physics analogy? There is a particle (your topic) that you can describe, a wave that the particle traces, and a field that the particle is mapped on.

Get Feedback and Affirm Your Confidence!
Creating a few different versions of your research question (they may be the same topic/issue/theme or differ slightly) can be useful during this process. Sharing these with trusted friends, colleagues, mentors, (or tutors!) and having conversations about your questions and ideas with other people can help you decide which version you may feel most confident or interested in. Ask colleagues and mentors to share their research questions with you to get a lot of examples. Once you have done the work of developing an effective research question, do not forget to affirm your confidence! Based on your working thesis, think about how you might organize your chapters or paragraphs and what resources you have for supporting this structure and organization. This can help boost your confidence that the research question you have created is effective and fruitful.
Be Open to Change
Remember, your research question may change from your first to final draft. For questions along the way, make an appointment with the Writing Center. We are here to help you develop an effective and engaging research question and build the foundation for a solid research paper!
Example 1: In my field developing a research question involves navigating the relationship between 1) what one sees/experiences at their field site and 2) what is already known in the literature. During my preliminary research, I found that the financial value of land was often a matter of precisely these cultural factors. So, my research question ended up being: How do the social and material qualities of land entangle with processes of financialization in the city of Lahore. Regarding point #1, this question was absolutely informed by what I saw in the field. But regarding point #2, the question was also heavily shaped by the literature. – Tariq
Example 2: A research question should not be a yes/no question like “Is pollution bad?”; but an open-ended question where the answer has to be supported with reasons and explanation. The question also has to be narrowed down to a specific topic—using the same example as before—”Is pollution bad?” can be revised to “How does pollution affect people?” I would encourage students to be more specific then; e.g., what area of pollution do you want to talk about: water, air, plastic, climate change… what type of people or demographic can we focus on? …how does this affect marginalized communities, minorities, or specific areas in California? After researching and deciding on a focus, your question might sound something like: How does government policy affect water pollution and how does it affect the marginalized communities in the state of California? -Janella
Our Newest Resources!
- Transitioning to Long-form Writing
- Integrating Direct Quotations into Your Writing
- Nurturing a Growth Mindset to Overcome Writing Challenges and Develop Confidence in College Level Writing
- An Introduction to Paraphrasing, Summarizing, and Quoting
Additional Resources
- Graduate Writing Consultants
- Instructor Resources
- Student Resources
- Quick Guides and Handouts
- Self-Guided and Directed Learning Activities
2020 Learning Objects
Worksheet: Compose a Research Question
Elayyan, Mona
This worksheet is a useful tool as you start developing your research question. It is based on the strategy discussed in the handout 'Compose a Research Question'.
- Library research
- Academic libraries

More About This Work
Related items.
- DOI Copy DOI to clipboard

Research Topics: How to Select & Develop: Developing a Research Question
- Understanding the Assignment
- Choosing a Research Topic
- Refining a Research Topic
- Developing a Research Question
- Deciding What Types of Sources You Will Need
- Research Help
Ask a Librarian
Chat with a Librarian
Lisle: (630) 829-6057 Mesa: (480) 878-7514 Toll Free: (877) 575-6050 Email: [email protected]
Book a Research Consultation Library Hours

Source: Wilfrid Laurier University Library
- Video Transcript
- Supplemental Worksheet
List What You Already Know
Write down what you already know or don't know about the topic
List Questions that Interest You
Develop a list of relevant questions that interest you about the topic. Being interested in what you write about will make writing the paper less tedious. Use probing questions such as why? how? what if? should? Avoid questions that can be answered with yes or no.
If you're not very familiar with your general topic, do a little background reading to get an idea of the issues that relate to it.
Narrow Your List of Questions
Narrow down your list of questions to topics that aren't too narrow or general, depending on the length requirement of your paper. You won't be able to find enough information on a question that is too specific. A very broad topic will yield way too much information to work with.
Refine Your Question
Conduct a preliminary search for information relating to your question. Use search engines, library databases, and the library catalog to be sure that there are enough resources available to you in order to research this question.
Refine your research question to give it a clear, direct focus based on your preliminary research. For example, "How did the U.S. get involved in the Vietnam War?" is better than "What role did the U.S. play in the Vietnam War?" because it is focused on a specific part of a very broad issue. You'll have an easier time writing your paper if your research questions are specific, because you'll use your research question(s) to guide you in writing a thesis for your paper.
Ask your instructor to look over your research questions to be sure you are focused in the right direction.
- << Previous: Refining a Research Topic
- Next: Deciding What Types of Sources You Will Need >>
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 9:55 AM
- URL: https://researchguides.ben.edu/topics
Kindlon Hall 5700 College Rd. Lisle, IL 60532 (630) 829-6050
Gillett Hall 225 E. Main St. Mesa, AZ 85201 (480) 878-7514

Guide to Research
- Background Research
- Write a research question
- Find Books and Articles
- Search strategies
- Evaluate sources
- Cite sources This link opens in a new window
- Developing a research question An interactive, self-guided tutorial from DePaul University
- NYU Abu Dhabi First-Year Writing Seminar This guide covers the fundamentals of academic research and writing, including developing a research question, finding and evaluating sources, and avoiding plagiarism.
- Brown University Library's Guide to Searching An introduction to choosing a topic and developing a research question, with follow up practice exercises.
RESEARCH QUESTIONS
After watching this tutorial, practice developing your research question with the worksheet attached below:
- << Previous: Background Research
- Next: Find Books and Articles >>
- Last Updated: Jun 27, 2023 1:55 PM
- URL: https://libguides.citytech.cuny.edu/researchintro

- Request new password
- Create a new account
Writing a Research Paper in Political Science: A Practical Guide to Inquiry, Structure, and Methods
Student resources.
Worksheets to help students through the process of writing a research paper.
- AB Resources
Jump to navigation
- Learning Commons
College of DuPage Library
- Chat loading... Chat With Us -->
Go back to the Library's homepage
Catalog --> Catalog
Use the Catalog to find books, videos, e-books, and other media
Search for online journal and newspaper articles, e-books, and streaming video
Guides for finding and citing sources in many different subject areas
Learn about the Library's spaces and services
The COD Library and campus are closed Friday (Feb. 9) and Saturday (Feb. 10) due to weather conditions.
Coronavirus Updates & Closings
For the safety of the COD community, the Library will be closed from March 16 through April 19 . However, we are committed to supporting your learning and information needs through remote access to Library services and electronic collections . We are also compiling useful COVID-19 information sources to help keep you informed. You can keep up with COD's response to the coronavirus outbreak through the COD Coronavirus Information page . Last updated: March 15, 5:00 pm
Research Worksheets and Handouts
- Getting Started
- Evaluating Sources
- General Research
Getting Started Having trouble getting your research rolling? These handouts and worksheets can get you past that initial hurdle.
Topic Identification worksheet (pdf) This graphic organizer will help you understand your assignment, identify and focus your topic, create a search strategy and find sources in 6 easy steps! For more information about research topics, visit www.codlrc.org/research101/topics
Developing Your Research Question (pdf) An infographic of journalistic questions that can help you brainstorm potential research questions.
Finding Evidence worksheet (pdf) Before you start your research, consider what evidence you’ll need to support your claims and think about how to find it.
Subject vs. Keyword Searching (pdf) Learn how to use keyword searching and subject searching together to find what you're looking for in the Library catalog and article databases.
Boolean Logic, Truncation, and Nesting (pdf) An introduction to advanced search techniques you can use to help you find information efficiently and effectively.
Advanced Research Search Strategies and Techniques (pdf) A quick reference for the types of advanced searching techniques you can use in databases, the Library catalog and in search engines.
Tips for Evaluating Information (pdf) Whether a resource is print or electronic, text-based or image-based, researchers must carefully evaluate the quality of the source and the information found within. When evaluating the quality of resources, here are some things to consider.
CRAAP Test (pdf) Do your sources pass the CRAAP Test? Use this guide to help you consider whether a source is appropriate for your research needs.
Source Evaluation Worksheet (pdf) Use this form to help you determine if a source is appropriate for your research. For more information about evaluating sources, visit www.codlrc.org/evaluating/sources
Research Article Anatomy (pdf) Reading research gets easier once you understand and recognize the pieces and purposes of research studies, from abstract to references.
Reading (and Understanding) Research (pdf) Adapted from How to Read and Understand a Scientific Paper: A Guide for Non-Scientists by J. Raff.
Introduction to College Research (pdf) Helpful resources for every stage of the research process.
- E-mail page
- Send to phone
- Skip to main content
- Skip to ChatBot Assistant
- Academic Writing
- What is a Research Paper?
- Steps in Writing a Research Paper
- Critical Reading and Writing
- Punctuation
- Writing Exercises
- ELL/ESL Resources
Worksheet: Evaluate Your Own Research Question
Ask the following 8 questions to evaluate the quality of your research question and the ease with which you should be able to answer it:
- Does the question deal with a topic or issue that interests me enough to spark my own thoughts and opinions?
- Is the question easily and fully researchable?
- statistics on airline crashes before and after
- statistics on other safety problems before and after
- information about maintenance practices before and after
- information about government safety requirements before and after
- Is the scope of this information reasonable (e.g., can I really research 30 online writing programs developed over a span of 10 years?)
- Given the type and scope of the information that I need, is my question too broad, too narrow, or okay?
- What sources will have the type of information that I need to answer the research question (journals, books, Internet resources, government documents, people)?
- Can I access these sources?
- Given my answers to the above questions, do I have a good quality research question that I actually will be able to answer by doing research?
Need Assistance?
If you would like assistance with any type of writing assignment, learning coaches are available to assist you. Please contact Academic Support by emailing [email protected].
Questions or feedback about SUNY Empire's Writing Support?
Contact us at [email protected] .
Smart Cookies
They're not just in our classes – they help power our website. Cookies and similar tools allow us to better understand the experience of our visitors. By continuing to use this website, you consent to SUNY Empire State University's usage of cookies and similar technologies in accordance with the university's Privacy Notice and Cookies Policy .
Research Topics & Questions
Main navigation, exquisite corpse topic narrowing activity.
In this activity, students engage in an "exquisite corpse"-style activity, where they will get to pass around their research topic idea and see how other students in the room understand, interpret, illustrate, and expand upon it.
Crafting Insightful Research Questions
Through this activity, students examine what constitutes a strong research question and then, through peer workshopping, start to develop a question to guide their own project.
Crowdsourcing Research Topics and Paths
This discussion-board-based activity helps students narrow down their final RBA research topic by encouraging students to collaborate with each other at the initial stage of conceiving of their RBA projects.
Metonyms and Lenses - Focusing Your Research
This topic helps students narrow and focus their research topics by having them consider them in reference to the idea of the metonym.
The Reflexivity Memo: Developing Student Researcher Identity through Writing
This writing activity asks students to understand their various positionalities as researchers/writers and to recognize how their embodied socialized practices shape their research questions and practices.
Jumbo ‘Spectra’ Worksheets for Narrowing Topics and Locating Positions
In this activity, students use a pair of worksheets to create a visual mapping of research questions to help them focus their topic and their inquiry and identify positions beyond "yes" and "no."
Accordion Pre-Write
Students create an "accordion" of these questions to see the full spectrum of possibilities for their research, developing greater insight into the pitfalls of overly-specific or overly-general questions and the advantages of carefully-focused inquiry.
Research Topic Brainstorm
This asynchronous activity follows a class discussion in which students brainstorm different topics; it asks students to submit their own ideas to Canvas and receive instructor feedback.
Research Question Generator with Padlet
This asynchronous activity uses Padlet to help students generate research questions with a rhetorical approach. Students not only craft research questions with different emphases, they also critically reflect on critical rhetorical concepts and the purpose of their research.
Research Question Framing
This asynchronous activity helps students think through the process of framing their research questions at the early stage of their RBA by asking them to consider different ways of framing their research questions. It also encourages students to work with each other in the process of finalizing their research questions.
Research Proposal Planning Table
This asynchronous activity helps students thoroughly examine their research proposals with a rhetorical approach. Students not only look at different components of the research question itself, but also critically reflect on their audience and the purpose of their research to prepare for an excellent oral delivery of their research proposals.
Online Research Mixer
Instructors designed a 60-minute online workshop (research mixer) between freshmen composition students two different universities. During the session, students have the opportunity to introduce their research projects and provide and receive feedback on their drafts.
Collaborative invention: working with research topics
This collaborative activity invites students to help their classmates to narrow and focus their research topics by taking turns contributing to a shared worksheet that asks them to engage with the topic in different ways.
These activities are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 . Please remember to attribute all activities to their original authors (even if with an “adapted from”) on any handouts, webtexts, slides, or assignments sheets you generate from them.
If you have any activities of your own that you’d like to share, please send them here .

- Research Guides
- UCBA Library
English Composition
Developing a research question.
- Choosing Keywords
- Searching for Sources
- Identifying Types of Sources
- Reading & Evaluating Sources
- Recast/Remix/Multimodal Assignment
- Citing Sources
- Contact Guide Owners
Introduction to Research Questions
Inquiry-based research is an ongoing process. Once you've chosen a topic and explored it through various sources, the next step is to develop your research question. This is a critical part of inquiry-based research and is an open-ended question that hasn't been answered before.
- Talk with your professor to determine if your inqury research question is appropriate given the scope and scale of the assignment
- Make sure you go through the research question approval process if required by your professor
- Developing a Research Question Worksheet Use this worksheet to develop your research topic into a research question.
- Developing a Research Question (Video) This video (2:31 minutes) reviews the difference between a research topic and research question.
The following resources can help you discover a topic for research and/or start a deeper exploration into your research question.These are just starting points and other resources will be needed to further investigate your argument or point of analysis.
- 300 Questions & Images to Inspire Argument Writing (The New York Times)
- << Previous: Guide Home
- Next: Choosing Keywords >>
- Last Updated: Mar 11, 2024 11:25 AM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.uc.edu/engl-comp
University of Cincinnati Libraries
PO Box 210033 Cincinnati, Ohio 45221-0033
Phone: 513-556-1424
Contact Us | Staff Directory
University of Cincinnati
Alerts | Clery and HEOA Notice | Notice of Non-Discrimination | eAccessibility Concern | Privacy Statement | Copyright Information
© 2021 University of Cincinnati

Writing Research Papers
- Information Literacy Goals
- Why Write Research Papers?
- Inquiry Process
- Research Topic / Question
- Developing Research Questions & Search Terms
- Source Types - Part 1
- Source Types - Part 2
- Finding Sources - OneSearch & Databases
- Evaluating Information
- Synthesis / Writing
- Citing Sources & Bibliographies
Tutorial on Search Terms from UCLA
To do an effective search using the library's databases or OneSearch, you have to use keywords -- search terms related to your topic or research questions.
Before you go any further, click on the following link and complete the tutorial on Developing Research Questions and Creating Search Terms. Then watch the additional videos that follow.
- Developing Research Questions and Creating Keywords
Developing Keywords
Analysis – breaking the “big picture” into its proper parts; dividing a topic into subtopics of inquiry; dividing a problem into its sub-problems.
Breaking the "big picture" into its proper parts.
- Identifying Keywords & Synonyms - Worksheet Use this worksheet to start developing your search terms after you've completed the tutorial below and watched the following videos.
Searching Databases With Keywords
How To Develop Keywords
Search Tips
- Phrase Searching 1 min. video
Refining Your Topic / Picking Search Terms
Tips on selecting search terms:, 1. find your "ideal" article on your topic using several keywords you have thought of. look at the subject words that are used by the database to describe this article. try another search using some of these subject words., 2. use the "lingo" of the discipline you are interested in. look at the thesaurus of subject terms list in the database to select terms. there is usually a tab indicating this list on the search page of the database..
- << Previous: Research Topic / Question
- Next: Background >>
- Last Updated: Jan 24, 2024 1:02 PM
- URL: https://libguides.lehman.edu/writing-research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Worksheet #1: Developing a Research Question Developing a Meaningful, Feasible, and Focused Research Question A Good Research Question . . . Is meaningful and significant to you. Is possible to research with the time, resources, and students you work with. Is deliberate, narrow and focused, so that your project will adequately answer the research
Course Learning Outcome: Develop ability to synthesize and express complex ideas; demonstrate information literacy and be able to work with evidence Goal: Develop students' ability to recognize and create successful research questions Specifically, students will be able to. identify the components of a successful research question. create a viable research question.
- Is your research question clear? - Is your research question focused? (Research questions must be specific enough to be well covered in the space available.) - Is your research question complex? (Questions shouldn't have a simple yes/no answer and should require research and analysis.) • Hypothesize. After you've come up with a question ...
Worksheet: Research Question Starters The sentence starters below can help you to write your own research questions. Starting questions are in each box. Pick the questions that fit the best - and edit them to make them specific to your topic. It's okay to start with only a few of the questions in each box.
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
Part II: Remember, a good historical question will help you investigate your topic's cause and effect, multiple perspectives, and the short- and long-term impacts. Brainstorm some questions to about your topic. Use two or three of these questions to help guide your further research. Category Example: The Fugitive Slave Act of 1850 Research Questions for Your Topic
Developing a Research Question + Worksheet Skip to transcript. Time Commitment. 2 - 5 Minutes. Description. Learn how to take a broad topic and develop it into a research question that will define the scope of your project. Transcript Downloads. Download Developing_a_Research_Question.pdf (60.32 ...
Research questions should not be answerable with a simple "yes" or "no" or by easily-found facts. They should, instead, require both research and analysis on the part of the writer. They often begin with "How" or "Why.". Begin your research. After you've come up with a question, think about the possible paths your research ...
Developing a research question, like every other aspect of a research project—working with sources, the interpretation of data, the writing, the editing—takes work, and is a skill that you can practice, refine, and personalize. Here's a short primer on how to come up with a workable research question, references included. Whether you're ...
Forming the Research Question. Performing Background Research and Initial Searching develops your general area of interest so that you can form a more focused topic. As you review the information you've found from these steps and the ideas you've encountered, these questions may help you to form a focus for your research:
If you start doing research and discover that people are writing articles about a more interesting (or easier to research) question, you can always adjust your question as you collect information. The tools collected here will help you think about a topic that genuinely interests you, and develop a clear, concise, and researchable question ...
When brainstorming your research question, let your mind veer toward connections or associations that you might have already considered or that seem to make sense and consider if new research terms, language or concepts come to mind that may be interesting or exciting for you as a researcher. Sometimes testing out a research question while ...
2020 Learning Objects. Worksheet: Compose a Research Question. Elayyan, Mona. This worksheet is a useful tool as you start developing your research question. It is based on the strategy discussed in the handout 'Compose a Research Question'.
Supplemental Worksheet. List What You Already Know. Write down what you already know or don't know about the topic. List Questions that Interest You. ... You'll have an easier time writing your paper if your research questions are specific, because you'll use your research question(s) to guide you in writing a thesis for your paper. ...
Before writing research questions, you will need to do some pre-research. The answers to these ... You can't write research questions until you have done your pre-research. WORKSHEET: WRITING RESEARCH QUESTIONS Part of Project Sample: Rosa Parks Your Topic Long Before What issues or problems were the main players involved with your topic ...
After watching this tutorial, practice developing your research question with the worksheet attached below: Research Question Worksheet Need help writing a research question? Fill out the steps in this worksheet to reach your question! Be sure to save the file to your computer to keep track of any changes.
Worksheets. Making Sense of the Scholarly Answers to Your Research Questions: Writing the Literature Review. Effectively Distilling Your Argument: The Thesis, Model, and Hypothesis. Revising and Editing Your Work: The Research-Writing-Thinking Spiral. Making Your Plan and Protecting Yourself from Criticism: The Research Design.
These handouts and worksheets can get you past that initial hurdle. This graphic organizer will help you understand your assignment, identify and focus your topic, create a search strategy and find sources in 6 easy steps! An infographic of journalistic questions that can help you brainstorm potential research questions.
Worksheet: Evaluate Your Own Research Question. Ask the following 8 questions to evaluate the quality of your research question and the ease with which you should be able to answer it: Does the question deal with a topic or issue that interests me enough to spark my own thoughts and opinions?
Research Question Framing. This asynchronous activity helps students think through the process of framing their research questions at the early stage of their RBA by asking them to consider different ways of framing their research questions. It also encourages students to work with each other in the process of finalizing their research questions.
Research writing worksheets help children build the skills necessary to succeed at all levels of schooling. Designed by educators for children from first to fifth grade, research writing worksheets combine whimsical themes with real assignments to make learning enjoyable. Your child can write an animal report on camels, discover information ...
Talk with your professor to determine if your inqury research question is appropriate given the scope and scale of the assignment. Make sure you go through the research question approval process if required by your professor. Developing a Research Question Worksheet. Use this worksheet to develop your research topic into a research question.
Worksheet. Print Worksheet. 1. A student is writing a research question. What should his/her first step be? Specifying what the question is about. Indicating where the research funding is coming ...
To do an effective search using the library's databases or OneSearch, you have to use keywords-- search terms related to your topic or research questions. Before you go any further, click on the following link and complete the tutorial on Developing Research Questions and Creating Search Terms. Then watch the additional videos that follow.