

Essential Linear Algebra with Applications
A Problem-Solving Approach
- © 2014
- Titu Andreescu 0
Natural Sciences and Mathematics, University of Texas at Dallas, Richardson, USA
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
- Numerous applications are treated in fields such as computer science, engineering, and the social sciences
- Over 500 problems (roughly half solved), often presenting two or more solutions; one more fundamental and elementary, the second more conceptual and sophisticated
- Can serve as an introductory or advanced undergraduate textbook, a supplementary problem book, a reference work for professionals, and a resource for independent study
- Includes supplementary material: sn.pub/extras
66k Accesses
1 Citations
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this book
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Other ways to access
Licence this eBook for your library
Institutional subscriptions
Table of contents (11 chapters)
Front matter, matrix algebra.
Titu Andreescu
Square Matrices of Order 2
Matrices and linear equations, vector spaces and subspaces, linear transformations, determinants, polynomial expressions of linear transformations and matrices, diagonalizability, appendix: algebraic prerequisites, back matter.
- Cayley-Hamilton theorem
- Determinant
- Diagonalizable
- Linear maps
- Linear systems
- Minimal polynomial
- Quadratic form
- Vector space
- matrix theory
About this book
Rooted in a pedagogically successful problem-solving approach to linear algebra, this work fills a gap in the literature that is sharply divided between, on the one end, elementary texts with only limited exercises and examples, and, at the other end, books too advanced in prerequisites and too specialized in focus to appeal to a wide audience. Instead, it clearly develops the theoretical foundations of vector spaces, linear equations, matrix algebra, eigenvectors, and orthogonality, while simultaneously emphasizing applications to fields such as biology, economics, computer graphics, electrical engineering, cryptography, and political science.
Key features:
* Intertwined discussion of linear algebra and geometry
* Example-driven exposition; each section starts with a concise overview of important concepts, followed by a selection of fully-solved problems
* Over 500 problems are carefully selected for instructive appeal, elegance, and theoretical importance; roughly half include complete solutions
* Two or more solutions provided to many of the problems; paired solutions range from step-by-step, elementary methods whose purpose is to strengthen basic comprehension to more sophisticated, powerful proofs to challenge advanced readers
* Appendices with review material on complex variables
Ideal as an introduction to linear algebra, the extensive exercises and well-chosen applications also make this text suitable for advanced courses a
“This book gives a rigorous introduction to linear algebra from a mathematical point of view. … The book presents a ‘problem-based’ approach, i.e., the author gives the precise theory to permit the reader to solve many different problems. … The book contains many well-chosen examples and exercises. Also, many problems are completely solved.” (Julio Benítez, Mathematical Reviews, June, 2015)
“The present book, as its title indicates, introduces the essential concepts of linear algebra and considers some of its applications. … the book is very suitable for students who are going to prepare for competitions and Olympiads. Moreover, the solved problems make it a very good problem book, with nice ideas, for anybody working with linear algebra. I recommend this book for students, and also for classroom use by teachers.” (Mehdi Hassani, MAA Reviews, April, 2015)
“The present book is a wellcomed addition at the present literature. The approach is elementray, however still rigorous and detailed. It covers the standard topics on linear algebra taught in a two-semester course, from elementray matrix theory to canonical forms and bilinear forms. … I would be happy to teach linear algebra from this book and ask students to work on problems from it.” (A. Arvanitoyeorgos, zbMATH 1309.15001, 2015)
Authors and Affiliations
About the author, bibliographic information.
Book Title : Essential Linear Algebra with Applications
Book Subtitle : A Problem-Solving Approach
Authors : Titu Andreescu
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-8176-4636-3
Publisher : Birkhäuser New York, NY
eBook Packages : Mathematics and Statistics , Mathematics and Statistics (R0)
Copyright Information : Springer Science+Business Media New York 2014
Hardcover ISBN : 978-0-8176-4360-7
Softcover ISBN : 978-1-4939-3853-7
eBook ISBN : 978-0-8176-4636-3
Edition Number : 1
Number of Pages : X, 491
Number of Illustrations : 2 illustrations in colour
Topics : Linear and Multilinear Algebras, Matrix Theory , Algebra , Applications of Mathematics , Game Theory, Economics, Social and Behav. Sciences , Mathematical and Computational Engineering , Math Applications in Computer Science
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
We will keep fighting for all libraries - stand with us!
Internet Archive Audio

- This Just In
- Grateful Dead
- Old Time Radio
- 78 RPMs and Cylinder Recordings
- Audio Books & Poetry
- Computers, Technology and Science
- Music, Arts & Culture
- News & Public Affairs
- Spirituality & Religion
- Radio News Archive

- Flickr Commons
- Occupy Wall Street Flickr
- NASA Images
- Solar System Collection
- Ames Research Center

- All Software
- Old School Emulation
- MS-DOS Games
- Historical Software
- Classic PC Games
- Software Library
- Kodi Archive and Support File
- Vintage Software
- CD-ROM Software
- CD-ROM Software Library
- Software Sites
- Tucows Software Library
- Shareware CD-ROMs
- Software Capsules Compilation
- CD-ROM Images
- ZX Spectrum
- DOOM Level CD

- Smithsonian Libraries
- FEDLINK (US)
- Lincoln Collection
- American Libraries
- Canadian Libraries
- Universal Library
- Project Gutenberg
- Children's Library
- Biodiversity Heritage Library
- Books by Language
- Additional Collections

- Prelinger Archives
- Democracy Now!
- Occupy Wall Street
- TV NSA Clip Library
- Animation & Cartoons
- Arts & Music
- Computers & Technology
- Cultural & Academic Films
- Ephemeral Films
- Sports Videos
- Videogame Videos
- Youth Media
Search the history of over 866 billion web pages on the Internet.
Mobile Apps
- Wayback Machine (iOS)
- Wayback Machine (Android)
Browser Extensions
Archive-it subscription.
- Explore the Collections
- Build Collections
Save Page Now
Capture a web page as it appears now for use as a trusted citation in the future.
Please enter a valid web address
- Donate Donate icon An illustration of a heart shape
Essential linear algebra with applications : a problem-solving approach
Bookreader item preview, share or embed this item, flag this item for.
- Graphic Violence
- Explicit Sexual Content
- Hate Speech
- Misinformation/Disinformation
- Marketing/Phishing/Advertising
- Misleading/Inaccurate/Missing Metadata
![[WorldCat (this item)] [WorldCat (this item)]](https://archive.org/images/worldcat-small.png)
plus-circle Add Review comment Reviews
107 Previews
5 Favorites
Better World Books
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
No suitable files to display here.
PDF access not available for this item.
IN COLLECTIONS
Uploaded by station40.cebu on April 28, 2023
SIMILAR ITEMS (based on metadata)
Essential Linear Algebra with Applications: A Problem-Solving Approach
4 citations
2 citations
Related Papers (5)
Ask Copilot
Related papers
Related topics
Items related to Essential Linear Algebra with Applications: A Problem-Solvin...
Essential linear algebra with applications: a problem-solving approach - hardcover, andreescu, titu.
- 4.57 7 ratings by Goodreads

This specific ISBN edition is currently not available.
- About this title
- About this edition
Rooted in a pedagogically successful problem-solving approach to linear algebra, the present work fills a gap in the literature that is sharply divided between elementary texts and books that are too advanced to appeal to a wide audience. It clearly develops the theoretical foundations of vector spaces, linear equations, matrix algebra, eigenvectors, and orthogonality, while simultaneously emphasizing applications and connections to fields such as biology, economics, computer graphics, electrical engineering, cryptography, and political science.
Ideal as an introduction to linear algebra, the extensive exercises and well-chosen applications also make this text suitable for advanced courses at the junior or senior undergraduate level. Furthermore, it can serve as a colorful supplementary problem book, reference, or self-study manual for professional scientists and mathematicians. Complete with bibliography and index, "Essential Linear Algebra with Applications" is a natural bridge between pure and applied mathematics and the natural and social sciences, appropriate for any student or researcher who needs a strong footing in the theory, problem-solving, and model-building that are the subject’s hallmark.
"synopsis" may belong to another edition of this title.
This textbook provides a rigorous introduction to linear algebra in addition to material suitable for a more advanced course while emphasizing the subject’s interactions with other topics in mathematics such as calculus and geometry. A problem-based approach is used to develop the theoretical foundations of vector spaces, linear equations, matrix algebra, eigenvectors, and orthogonality.
Key features include:
� a thorough presentation of the main results in linear algebra along with numerous examples to illustrate the theory;
� over 500 problems (half with complete solutions) carefully selected for their elegance and theoretical significance;
� an interleaved discussion of geometry and linear algebra, giving readers a solid understanding of both topics and the relationship between them.
Numerous exercises and well-chosen examples make this text suitable for advanced courses at the junior or senior levels. It can also serve as a source of supplementary problems for a sophomore-level course.
"About this title" may belong to another edition of this title.
- Publisher Birkh�user
- Publication date 2014
- ISBN 10 0817643605
- ISBN 13 9780817643607
- Binding Hardcover
- Number of pages 501
Convert currency
Shipping: US$ 2.64 Within U.S.A.
Add to Basket
Other Popular Editions of the Same Title
Featured edition.
ISBN 10: 1493938533 ISBN 13: 9781493938537 Publisher: Birkh�user, 2016 Softcover
Birkh�..., 2014 Softcover
Top Search Results from the AbeBooks Marketplace
Essential linear algebra with applications : a problem-solving approach.
Book Description Condition: New. Seller Inventory # 4926881-n
More information about this seller | Contact seller
Essential Linear Algebra with Applications: A Problem-Solving Approach by Andreescu, Titu [Hardcover ]
Book Description Hardcover. Condition: new. Seller Inventory # 9780817643607
Essential Linear Algebra with Applications: A Problem-Solving Approach
Book Description Condition: New. Seller Inventory # ABLIING23Feb2416190237666
Essential Linear Algebra with Applications : A Problem-Solving Approach
Book Description Condition: New. PRINT ON DEMAND Book; New; Fast Shipping from the UK. No. book. Seller Inventory # ria9780817643607_lsuk
Book Description Condition: New. Seller Inventory # I-9780817643607
Essential Linear Algebra with Applications
Book Description Buch. Condition: Neu. This item is printed on demand - it takes 3-4 days longer - Neuware -Rooted in a pedagogically successful problem-solving approach to linear algebra, the present work fills a gap in the literature that is sharply divided between elementary texts and books that are too advanced to appeal to a wide audience. It clearly develops the theoretical foundations of vector spaces, linear equations, matrix algebra, eigenvectors, and orthogonality, while simultaneously emphasizing applications and connections to fields such as biology, economics, computer graphics, electrical engineering, cryptography, and political science.Ideal as an introduction to linear algebra, the extensive exercises and well-chosen applications also make this text suitable for advanced courses at the junior or senior undergraduate level. Furthermore, it can serve as a colorful supplementary problem book, reference, or self-study manual for professional scientists and mathematicians. Complete with bibliography and index, 'Essential Linear Algebra with Applications' is a natural bridge between pure and applied mathematics and the natural and social sciences, appropriate for any student or researcher who needs a strong footing in the theory, problem-solving, and model-building that are the subject's hallmark. 504 pp. Englisch. Seller Inventory # 9780817643607
Book Description Hardcover. Condition: new. New. Fast Shipping and good customer service. Seller Inventory # Holz_New_0817643605
Book Description Hardcover. Condition: new. New. Seller Inventory # Wizard0817643605
Book Description Condition: new. Seller Inventory # FrontCover0817643605
There are more copies of this book

- Math Careers
Search form
- MAA Centennial
- Spotlight: Archives of American Mathematics
- MAA Officers
- MAA to the Power of New
- Council and Committees
- MAA Code of Conduct
- Policy on Conflict of Interest
- Statement about Conflict of Interest
- Recording or Broadcasting of MAA Events
- Policy for Establishing Endowments and Funds
- Avoiding Implicit Bias
- Copyright Agreement
- Principal Investigator's Manual
- Planned Giving
- The Icosahedron Society
- Our Partners
- Advertise with MAA
- Employment Opportunities
- Staff Directory
- 2022 Impact Report
- In Memoriam
- Membership Categories
- Become a Member
- Membership Renewal
- MERCER Insurance
- MAA Member Directories
- New Member Benefits
- The American Mathematical Monthly
- Mathematics Magazine
- The College Mathematics Journal
- How to Cite
- Communications in Visual Mathematics
- About Convergence
- What's in Convergence?
- Convergence Articles
- Mathematical Treasures
- Portrait Gallery
- Paul R. Halmos Photograph Collection
- Other Images
- Critics Corner
- Problems from Another Time
- Conference Calendar
- Guidelines for Convergence Authors
- Math Horizons
- Submissions to MAA Periodicals
- Guide for Referees
- Scatterplot
- Math Values
- MAA Book Series
- MAA Press (an imprint of the AMS)
- MAA Library Recommendations
- Additional Sources for Math Book Reviews
- About MAA Reviews
- Mathematical Communication
- Information for Libraries
- Author Resources
- Proposal and Abstract Deadlines
- MAA Policies
- Invited Paper Session Proposals
- Contributed Paper Session Proposals
- Panel, Poster, Town Hall, and Workshop Proposals
- Minicourse Proposals
- MAA Section Meetings
- Virtual Programming
- Joint Mathematics Meetings
- Calendar of Events
- MathFest Programs Archive
- MathFest Abstract Archive
- Historical Speakers
- Information for School Administrators
- Information for Students and Parents
- Registration
- Getting Started with the AMC
- AMC Policies
- AMC Administration Policies
- Important AMC Dates
- Competition Locations
- Invitational Competitions
- Putnam Competition Archive
- AMC International
- Curriculum Inspirations
- Sliffe Award
- MAA K-12 Benefits
- Mailing List Requests
- Statistics & Awards
- Submit an NSF Proposal with MAA
- MAA Distinguished Lecture Series
- Common Vision
- CUPM Curriculum Guide
- Instructional Practices Guide
- Möbius MAA Placement Test Suite
- META Math Webinar May 2020
- Progress through Calculus
- Survey and Reports
- "Camp" of Mathematical Queeries
- DMEG Awardees
- National Research Experience for Undergraduates Program (NREUP)
- Neff Outreach Fund Awardees
- Tensor SUMMA Grants
- Tensor Women & Mathematics Grants
- Grantee Highlight Stories
- "Best Practices" Statements
- CoMInDS Summer Workshop 2023
- MAA Travel Grants for Project ACCCESS
- 2024 Summer Workshops
- Minority Serving Institutions Leadership Summit
- Previous Workshops
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Course Resources
- Industrial Math Case Studies
- Participating Faculty
- 2020 PIC Math Student Showcase
- Previous PIC Math Workshops on Data Science
- Dates and Locations
- Past Programs
- Leadership Team
- Support Project NExT
- Section NExT
- Section Officers Meeting History
- Preparations for Section Meetings
- Bylaws Template
- Editor Lectures Program
- MAA Section Lecturer Series
- Officer Election Support
- Section Awards
- Section Liaison Programs
- Section Visitors Program
- Expense Reimbursement
- Guidelines for Bylaw Revisions
- Guidelines for Local Arrangement Chair and/or Committee
- Guidelines for Section Webmasters
- MAA Logo Guidelines
- MAA Section Email Policy
- Section Newsletter Guidelines
- Statement on Federal Tax ID and 501(c)3 Status
- Communication Support
- Guidelines for the Section Secretary and Treasurer
- Legal & Liability Support for Section Officers
- Section Marketing Services
- Section in a Box
- Subventions and Section Finances
- Web Services
- Joining a SIGMAA
- Forming a SIGMAA
- History of SIGMAA
- SIGMAA Officer Handbook
- MAA Connect
- Meetings and Conferences for Students
- Opportunities to Present
- Information and Resources
- MAA Undergraduate Student Poster Session
- Undergraduate Research Resources
- MathFest Student Paper Sessions
- Research Experiences for Undergraduates
- Student Poster Session FAQs
- High School
- A Graduate School Primer
- Reading List
- Student Chapters
- Awards Booklets
- Carl B. Allendoerfer Awards
- Regulations Governing the Association's Award of The Chauvenet Prize
- Trevor Evans Awards
- Paul R. Halmos - Lester R. Ford Awards
- Merten M. Hasse Prize
- George Pólya Awards
- David P. Robbins Prize
- Beckenbach Book Prize
- Euler Book Prize
- Daniel Solow Author’s Award
- Henry L. Alder Award
- Deborah and Franklin Tepper Haimo Award
- Certificate of Merit
- Gung and Hu Distinguished Service
- JPBM Communications Award
- Meritorious Service
- MAA Award for Inclusivity
- T. Christine Stevens Award
- Dolciani Award Guidelines
- Morgan Prize Information
- Selden Award Eligibility and Guidelines for Nomination
- Selden Award Nomination Form
- AMS-MAA-SIAM Gerald and Judith Porter Public Lecture
- Etta Zuber Falconer
- Hedrick Lectures
- James R. C. Leitzel Lecture
- Pólya Lecturer Information
- Putnam Competition Individual and Team Winners
- D. E. Shaw Group AMC 8 Awards & Certificates
- Maryam Mirzakhani AMC 10 A Awards & Certificates
- Two Sigma AMC 10 B Awards & Certificates
- Jane Street AMC 12 A Awards & Certificates
- Akamai AMC 12 B Awards & Certificates
- High School Teachers
- MAA Social Media
You are here
Essential linear algebra with applications.

- From Amazon
- From the MAA Bookstore
temp hardcoded node--book.tpl.php
Titu Andreescu
- Table of Contents
The concepts and methods of Linear Algebra appear in several branches of mathematics, including advanced calculus, differential equations, analysis, combinatorics, and algebra; it also plays a crucial role in some other branches of science, such as computer science and physics. Apart from its wide applications, the beauty of its concepts and problems usually motivates teachers and students to have a course in linear algebra. In fact, in most universities it is treated as a fundamental course. The present book, as its title indicates, introduces the essential concepts of linear algebra and considers some of its applications.
The topics discussed in this book are standard. The book starts with matrix algebra, dealing with matrices and the operations associated with them. The second chapter is a rather extended study of the square matrices of order two, which is suitable for beginners to become ready for the higher dimensional case. The application of matrices to solve linear systems and the computation of the inverse of a matrix is the subject of third chapter.
The author then studies vector spaces and subspaces, and considers linear maps between them, and also proves Jordan's classification theorem of nilpotent transformations on a vector space with finite dimension. Chapter 7 deals with determinants and their properties, as well as techniques to compute them.
Chapter 8, which is about eigenvalue theory, moves toward a proof of Cayley-Hamilton theorem. To this end, the author applies almost all the topics discussed in previous chapters, together with properties of polynomials. Chapter 9 considers diagonalizable matrices, and ends in a complete proof of Jordan's classification theorem, as well as a clean proof of the Cayley-Hamilton theorem.
In the last chapter, the author discusses on bilinear and quadratic forms, and utilizes them to define Euclidean spaces and to study their main geometric properties. The book ends with an appendix with algebraic prerequisites.
In each chapter, the book gives some of the fundamental information in detail and then several solved problems, mainly related to that concept, are introduced. Many of problems have the flavor of the Mathematics Olympiad, with solutions that require intelligent and surprising tricks. On the other hand, the author sometimes gives some applications of the given subjects to other areas of mathematics. This includes, for example, an application of the powers of square matrices of order two in solving the so-called Pell's equation in Number Theory. Also, at the end of each section various problems for practice are included, without solutions.
I think the book is very suitable for students who are going to prepare for competitions and Olympiads. Moreover, the solved problems make it a very good problem book, with nice ideas, for anybody working with linear algebra. I recommend this book for students, and also for classroom use by teachers.
Mehdi Hassani is a faculty member at the Department of Mathematics, Zanjan University, Iran. His fields of interest are Elementary, Analytic and Probabilistic Number Theory.
Preface.- Linear Phenomena and Euclidean Spaces of Small Dimension.- Concrete Vector Spaces.- Vector Spaces and Subspaces.- Linear Transformations.- More Matrix Algebra and Determinants.- General Theory of Linear Equations.- Eigenvectors.- Orthogonality.- Forms.- Vector Spaces over Finite Fields.- Appendix A: Complex Numbers.- Appendix B: Polynomials over Complex Numbers.- References.- Index.
- Log in to post comments
Dummy View - NOT TO BE DELETED

MAA Publications
- Periodicals
- MAA History
- Policies and Procedures
- Support MAA
- Member Discount Programs
- Propose a Session
- MathFest Archive
- Putnam Competition
- AMC Resources
- Curriculum Resources
- Outreach Initiatives
- Professional Development
- Communities
Connect with MAA
Mathematical Association of America P: (800) 331-1622 F: (240) 396-5647 Email: [email protected]
Copyright © 2024
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Mobile Version
(Stanford users can avoid this Captcha by logging in.)
- Send to text email RefWorks EndNote printer
Essential linear algebra with applications : a problem-solving approach
Available online.
- SpringerLink
At the library

Science Library (Li and Ma)
More options.
- Find it at other libraries via WorldCat
- Contributors
Description
Creators/contributors, contents/summary.
- Preface.- Linear Phenomena and Euclidean Spaces of Small Dimension.- Concrete Vector Spaces.- Vector Spaces and Subspaces.- Linear Transformations.- More Matrix Algebra and Determinants.- General Theory of Linear Equations.- Eigenvectors.- Orthogonality.- Forms.- Vector Spaces over Finite Fields.- Appendix A: Complex Numbers.- Appendix B: Polynomials over Complex Numbers.- References.- Index.
- (source: Nielsen Book Data)
Bibliographic information
Browse related items.
- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
4.2 Modeling with Linear Functions
Learning objectives.
In this section, you will:
- Build linear models from verbal descriptions.
- Model a set of data with a linear function.
Elan is a college student who plans to spend a summer in Seattle. Elan has saved $3,500 for their trip and anticipates spending $400 each week on rent, food, and activities. How can we write a linear model to represent this situation? What would be the x -intercept, and what can Elan learn from it? To answer these and related questions, we can create a model using a linear function. Models such as this one can be extremely useful for analyzing relationships and making predictions based on those relationships. In this section, we will explore examples of linear function models.
Building Linear Models from Verbal Descriptions
When building linear models to solve problems involving quantities with a constant rate of change, we typically follow the same problem strategies that we would use for any type of function. Let’s briefly review them:
- Identify changing quantities, and then define descriptive variables to represent those quantities. When appropriate, sketch a picture or define a coordinate system.
- Carefully read the problem to identify important information. Look for information that provides values for the variables or values for parts of the functional model, such as slope and initial value.
- Carefully read the problem to determine what we are trying to find, identify, solve, or interpret.
- Identify a solution pathway from the provided information to what we are trying to find. Often this will involve checking and tracking units, building a table, or even finding a formula for the function being used to model the problem.
- When needed, write a formula for the function.
- Solve or evaluate the function using the formula.
- Reflect on whether your answer is reasonable for the given situation and whether it makes sense mathematically.
- Clearly convey your result using appropriate units, and answer in full sentences when necessary.
Now let’s take a look at the student in Seattle. In Elan’s situation, there are two changing quantities: time and money. The amount of money they have remaining while on vacation depends on how long they stay. We can use this information to define our variables, including units.
So, the amount of money remaining depends on the number of weeks: M ( t ) M ( t ) .
Notice that the unit of dollars per week matches the unit of our output variable divided by our input variable. Also, because the slope is negative, the linear function is decreasing. This should make sense because she is spending money each week.
The rate of change is constant, so we can start with the linear model M ( t ) = m t + b . M ( t ) = m t + b . Then we can substitute the intercept and slope provided.
To find the t- intercept (horizontal axis intercept), we set the output to zero, and solve for the input.
The t -intercept (horizontal axis intercept) is 8.75 weeks. Because this represents the input value when the output will be zero, we could say that Elan will have no money left after 8.75 weeks.
When modeling any real-life scenario with functions, there is typically a limited domain over which that model will be valid—almost no trend continues indefinitely. Here the domain refers to the number of weeks. In this case, it doesn’t make sense to talk about input values less than zero. A negative input value could refer to a number of weeks before Elan saved $3,500, but the scenario discussed poses the question once they saved $3,500 because this is when the trip and subsequent spending starts. It is also likely that this model is not valid after the t -intercept (horizontal axis intercept), unless Elan uses a credit card and goes into debt. The domain represents the set of input values, so the reasonable domain for this function is 0 ≤ t ≤ 8.75. 0 ≤ t ≤ 8.75.
In this example, we were given a written description of the situation. We followed the steps of modeling a problem to analyze the information. However, the information provided may not always be the same. Sometimes we might be provided with an intercept. Other times we might be provided with an output value. We must be careful to analyze the information we are given, and use it appropriately to build a linear model.
Using a Given Intercept to Build a Model
Some real-world problems provide the vertical axis intercept, which is the constant or initial value. Once the vertical axis intercept is known, the t -intercept (horizontal axis intercept) can be calculated. Suppose, for example, that Hannah plans to pay off a no-interest loan from her parents. Her loan balance is $1,000. She plans to pay $250 per month until her balance is $0. The y -intercept is the initial amount of her debt, or $1,000. The rate of change, or slope, is -$250 per month. We can then use the slope-intercept form and the given information to develop a linear model.
Now we can set the function equal to 0, and solve for x x to find the x -intercept.
The x -intercept is the number of months it takes her to reach a balance of $0. The x -intercept is 4 months, so it will take Hannah four months to pay off her loan.
Using a Given Input and Output to Build a Model
Many real-world applications are not as direct as the ones we just considered. Instead they require us to identify some aspect of a linear function. We might sometimes instead be asked to evaluate the linear model at a given input or set the equation of the linear model equal to a specified output.
Given a word problem that includes two pairs of input and output values, use the linear function to solve a problem.
- Identify the input and output values.
- Convert the data to two coordinate pairs.
- Find the slope.
- Write the linear model.
- Use the model to make a prediction by evaluating the function at a given x -value.
- Use the model to identify an x -value that results in a given y -value.
- Answer the question posed.
Using a Linear Model to Investigate a Town’s Population
A town’s population has been growing linearly. In 2004, the population was 6,200. By 2009, the population had grown to 8,100. Assume this trend continues.
- ⓐ Predict the population in 2013.
- ⓑ Identify the year in which the population will reach 15,000.
The two changing quantities are the population size and time. While we could use the actual year value as the input quantity, doing so tends to lead to very cumbersome equations because the y -intercept would correspond to the year 0, more than 2000 years ago!
To make computation a little nicer, we will define our input as the number of years since 2004.
To predict the population in 2013 ( t = 9 t = 9 ), we would first need an equation for the population. Likewise, to find when the population would reach 15,000, we would need to solve for the input that would provide an output of 15,000. To write an equation, we need the initial value and the rate of change, or slope.
To determine the rate of change, we will use the change in output per change in input.
The problem gives us two input-output pairs. Converting them to match our defined variables, the year 2004 would correspond to t = 0 , t = 0 , giving the point ( 0 , 6200 ) . ( 0 , 6200 ) . Notice that through our clever choice of variable definition, we have “given” ourselves the y -intercept of the function. The year 2009 would correspond to t = 5, t = 5, giving the point ( 5 , 8100 ) . ( 5 , 8100 ) .
The two coordinate pairs are ( 0 , 6200 ) ( 0 , 6200 ) and ( 5 , 8100 ) . ( 5 , 8100 ) . Recall that we encountered examples in which we were provided two points earlier in the chapter. We can use these values to calculate the slope.
We already know the y -intercept of the line, so we can immediately write the equation:
To predict the population in 2013, we evaluate our function at t = 9. t = 9.
If the trend continues, our model predicts a population of 9,620 in 2013.
To find when the population will reach 15,000, we can set P ( t ) = 15000 P ( t ) = 15000 and solve for t . t .
Our model predicts the population will reach 15,000 in a little more than 23 years after 2004, or somewhere around the year 2027.
A company sells doughnuts. They incur a fixed cost of $25,000 for rent, insurance, and other expenses. It costs $0.25 to produce each doughnut.
ⓐ Write a linear model to represent the cost C C of the company as a function of x , x , the number of doughnuts produced. ⓑ Find and interpret the y -intercept.
A city’s population has been growing linearly. In 2008, the population was 28,200. By 2012, the population was 36,800. Assume this trend continues.
- ⓐ Predict the population in 2014.
- ⓑ Identify the year in which the population will reach 54,000.
Using a Diagram to Build a Model
It is useful for many real-world applications to draw a picture to gain a sense of how the variables representing the input and output may be used to answer a question. To draw the picture, first consider what the problem is asking for. Then, determine the input and the output. The diagram should relate the variables. Often, geometrical shapes or figures are drawn. Distances are often traced out. If a right triangle is sketched, the Pythagorean Theorem relates the sides. If a rectangle is sketched, labeling width and height is helpful.
Using a Diagram to Model Distance Walked
Anna and Emanuel start at the same intersection. Anna walks east at 4 miles per hour while Emanuel walks south at 3 miles per hour. They are communicating with a two-way radio that has a range of 2 miles. How long after they start walking will they fall out of radio contact?
In essence, we can partially answer this question by saying they will fall out of radio contact when they are 2 miles apart, which leads us to ask a new question:
"How long will it take them to be 2 miles apart"?
In this problem, our changing quantities are time and position, but ultimately we need to know how long will it take for them to be 2 miles apart. We can see that time will be our input variable, so we’ll define our input and output variables.
Because it is not obvious how to define our output variable, we’ll start by drawing a picture such as Figure 2 .
Initial Value: They both start at the same intersection so when t = 0 , t = 0 , the distance traveled by each person should also be 0. Thus the initial value for each is 0.
Rate of Change: Anna is walking 4 miles per hour and Emanuel is walking 3 miles per hour, which are both rates of change. The slope for A A is 4 and the slope for E E is 3.
Using those values, we can write formulas for the distance each person has walked.
For this problem, the distances from the starting point are important. To notate these, we can define a coordinate system, identifying the “starting point” at the intersection where they both started. Then we can use the variable, A , A , which we introduced above, to represent Anna’s position, and define it to be a measurement from the starting point in the eastward direction. Likewise, can use the variable, E , E , to represent Emanuel’s position, measured from the starting point in the southward direction. Note that in defining the coordinate system, we specified both the starting point of the measurement and the direction of measure.
We can then define a third variable, D , D , to be the measurement of the distance between Anna and Emanuel. Showing the variables on the diagram is often helpful, as we can see from Figure 3 .
Recall that we need to know how long it takes for D , D , the distance between them, to equal 2 miles. Notice that for any given input t , t , the outputs A ( t ) , E ( t ) , A ( t ) , E ( t ) , and D ( t ) D ( t ) represent distances.
Figure 2 shows us that we can use the Pythagorean Theorem because we have drawn a right angle.
Using the Pythagorean Theorem, we get:
In this scenario we are considering only positive values of t , t , so our distance D ( t ) D ( t ) will always be positive. We can simplify this answer to D ( t ) = 5 t . D ( t ) = 5 t . This means that the distance between Anna and Emanuel is also a linear function. Because D D is a linear function, we can now answer the question of when the distance between them will reach 2 miles. We will set the output D ( t ) = 2 D ( t ) = 2 and solve for t . t .
They will fall out of radio contact in 0.4 hour, or 24 minutes.
Should I draw diagrams when given information based on a geometric shape?
Yes. Sketch the figure and label the quantities and unknowns on the sketch.
Using a Diagram to Model Distance Between Cities
There is a straight road leading from the town of Westborough to Agritown 30 miles east and 10 miles north. Partway down this road, it junctions with a second road, perpendicular to the first, leading to the town of Eastborough. If the town of Eastborough is located 20 miles directly east of the town of Westborough, how far is the road junction from Westborough?
It might help here to draw a picture of the situation. See Figure 4 . It would then be helpful to introduce a coordinate system. While we could place the origin anywhere, placing it at Westborough seems convenient. This puts Agritown at coordinates ( 3 0 , 1 0 ) , ( 3 0 , 1 0 ) , and Eastborough at ( 2 0 , 0 ) . ( 2 0 , 0 ) .
Using this point along with the origin, we can find the slope of the line from Westborough to Agritown.
Now we can write an equation to describe the road from Westborough to Agritown.
From this, we can determine the perpendicular road to Eastborough will have slope m = – 3. m = – 3. Because the town of Eastborough is at the point (20, 0), we can find the equation.
We can now find the coordinates of the junction of the roads by finding the intersection of these lines. Setting them equal,
The roads intersect at the point (18, 6). Using the distance formula, we can now find the distance from Westborough to the junction.
One nice use of linear models is to take advantage of the fact that the graphs of these functions are lines. This means real-world applications discussing maps need linear functions to model the distances between reference points.
There is a straight road leading from the town of Timpson to Ashburn 60 miles east and 12 miles north. Partway down the road, it junctions with a second road, perpendicular to the first, leading to the town of Garrison. If the town of Garrison is located 22 miles directly east of the town of Timpson, how far is the road junction from Timpson?
Modeling a Set of Data with Linear Functions
Real-world situations including two or more linear functions may be modeled with a system of linear equations . Remember, when solving a system of linear equations, we are looking for points the two lines have in common. Typically, there are three types of answers possible, as shown in Figure 5 .
Given a situation that represents a system of linear equations, write the system of equations and identify the solution.
- Identify the input and output of each linear model.
- Identify the slope and y -intercept of each linear model.
- Find the solution by setting the two linear functions equal to another and solving for x , x , or find the point of intersection on a graph.
Building a System of Linear Models to Choose a Truck Rental Company
Jamal is choosing between two truck-rental companies. The first, Keep on Trucking, Inc., charges an up-front fee of $20, then 59 cents a mile. The second, Move It Your Way, charges an up-front fee of $16, then 63 cents a mile 4 . When will Keep on Trucking, Inc. be the better choice for Jamal?
The two important quantities in this problem are the cost and the number of miles driven. Because we have two companies to consider, we will define two functions in Table 1 .
A linear function is of the form f ( x ) = m x + b . f ( x ) = m x + b . Using the rates of change and initial charges, we can write the equations
Using these equations, we can determine when Keep on Trucking, Inc., will be the better choice. Because all we have to make that decision from is the costs, we are looking for when Move It Your Way, will cost less, or when K ( d ) < M ( d ) . K ( d ) < M ( d ) . The solution pathway will lead us to find the equations for the two functions, find the intersection, and then see where the K ( d ) K ( d ) function is smaller.
These graphs are sketched in Figure 6 , with K ( d ) K ( d ) in blue.
To find the intersection, we set the equations equal and solve:
This tells us that the cost from the two companies will be the same if 100 miles are driven. Either by looking at the graph, or noting that K ( d ) K ( d ) is growing at a slower rate, we can conclude that Keep on Trucking, Inc. will be the cheaper price when more than 100 miles are driven, that is d > 100 d > 100 .
Access this online resource for additional instruction and practice with linear function models.
- Interpreting a Linear Function

4.2 Section Exercises
Explain how to find the input variable in a word problem that uses a linear function.
Explain how to find the output variable in a word problem that uses a linear function.
Explain how to interpret the initial value in a word problem that uses a linear function.
Explain how to determine the slope in a word problem that uses a linear function.
Find the area of a parallelogram bounded by the y -axis, the line x = 3 , x = 3 , the line f ( x ) = 1 + 2 x , f ( x ) = 1 + 2 x , and the line parallel to f ( x ) f ( x ) passing through ( 2 , 7 ) . ( 2 , 7 ) .
Find the area of a triangle bounded by the x -axis, the line f ( x ) = 12 – 1 3 x , f ( x ) = 12 – 1 3 x , and the line perpendicular to f ( x ) f ( x ) that passes through the origin.
Find the area of a triangle bounded by the y -axis, the line f ( x ) = 9 – 6 7 x , f ( x ) = 9 – 6 7 x , and the line perpendicular to f ( x ) f ( x ) that passes through the origin.
Find the area of a parallelogram bounded by the x -axis, the line g ( x ) = 2 , g ( x ) = 2 , the line f ( x ) = 3 x , f ( x ) = 3 x , and the line parallel to f ( x ) f ( x ) passing through ( 6 , 1 ) . ( 6 , 1 ) .
For the following exercises, consider this scenario: A town’s population has been decreasing at a constant rate. In 2010 the population was 5,900. By 2012 the population had dropped to 4,700. Assume this trend continues.
Predict the population in 2016.
Identify the year in which the population will reach 0.
For the following exercises, consider this scenario: A town’s population has been increased at a constant rate. In 2010 the population was 46,020. By 2012 the population had increased to 52,070. Assume this trend continues.
Identify the year in which the population will reach 75,000.
For the following exercises, consider this scenario: A town has an initial population of 75,000. It grows at a constant rate of 2,500 per year for 5 years.
Find the linear function that models the town’s population P P as a function of the year, t , t , where t t is the number of years since the model began.
Find a reasonable domain and range for the function P . P .
If the function P P is graphed, find and interpret the x - and y -intercepts.
If the function P P is graphed, find and interpret the slope of the function.
When will the population reach 100,000?
What is the population in the year 12 years from the onset of the model?
For the following exercises, consider this scenario: The weight of a newborn is 7.5 pounds. The baby gained one-half pound a month for its first year.
Find the linear function that models the baby’s weight W W as a function of the age of the baby, in months, t . t .
Find a reasonable domain and range for the function W . W .
If the function W W is graphed, find and interpret the x - and y -intercepts.
If the function W is graphed, find and interpret the slope of the function.
When did the baby weight 10.4 pounds?
What is the output when the input is 6.2?
For the following exercises, consider this scenario: The number of people afflicted with the common cold in the winter months steadily decreased by 205 each year from 2005 until 2010. In 2005, 12,025 people were inflicted.
Find the linear function that models the number of people inflicted with the common cold C C as a function of the year, t . t .
Find a reasonable domain and range for the function C . C .
If the function C C is graphed, find and interpret the x - and y -intercepts.
If the function C C is graphed, find and interpret the slope of the function.
When will the output reach 0?
In what year will the number of people be 9,700?
For the following exercises, use the graph in Figure 7 , which shows the profit, y , y , in thousands of dollars, of a company in a given year, t , t , where t t represents the number of years since 1980.
Find the linear function y , y , where y y depends on t , t , the number of years since 1980.
Find and interpret the y -intercept.
Find and interpret the x -intercept.
Find and interpret the slope.
For the following exercises, use the graph in Figure 8 , which shows the profit, y , y , in thousands of dollars, of a company in a given year, t , t , where t t represents the number of years since 1980.
For the following exercises, use the median home values in Mississippi and Hawaii (adjusted for inflation) shown in Table 2 . Assume that the house values are changing linearly.
In which state have home values increased at a higher rate?
If these trends were to continue, what would be the median home value in Mississippi in 2010?
If we assume the linear trend existed before 1950 and continues after 2000, the two states’ median house values will be (or were) equal in what year? (The answer might be absurd.)
For the following exercises, use the median home values in Indiana and Alabama (adjusted for inflation) shown in Table 3 . Assume that the house values are changing linearly.
If these trends were to continue, what would be the median home value in Indiana in 2010?
Amazon Prime incluye:
Las entregas GRATIS y rápidas están disponibles para los miembros Prime. Para unirte, selecciona "Prueba Amazon Prime y comienza a ahorrar hoy mismo con entregas GRATIS y rápidas" debajo del botón Agregar al Carrito.
- Los tarjetahabientes obtienen un 5% de vuelta en Amazon.com con la Tarjeta de Crédito Prime.
- Entrega gratis en dos días ilimitado
- Streaming de películas y programas de televisión con anuncios limitados en Prime Video.
- Un libro Kindle para tomar prestado cada mes - plazos
- Escucha más de 2 millónes de canciones y cientos de listas de reproducción.
- Almacenamiento de fotos sin límite con acceso desde cualquier lugar
Importante: Tu tarjeta de crédito no será cobrada cuando comiences tu período de prueba gratuito, o si cancelas durante este período. Si estás contento con Amazon Prime, no hagas nada. Al final del período de prueba gratuito, tu membresía se actualizará automáticamente a una membresía mensual.
Nuevo: US$73.03 US$73.03 Entrega GRATIS: mayo 5 - 7 Enviado por: Amazon.com Vendido por: Amazon.com
Devolver gratis este producto.
Las devoluciones gratis están disponibles para la dirección de envío que elegiste. Puedes devolver el producto por cualquier motivo, en estado nuevo y sin usar: no se aplican gastos de envío
- Ve a tus pedidos y empieza el proceso de devolución
- Selecciona el método de devolución
Usado: US$54.87

Descarga la app de Kindle gratis y comienza a leer libros Kindle al instante desde tu smartphone, tablet o computadora, sin necesidad de ningún dispositivo Kindle .
Lee al instante desde tu navegador con Kindle para la web.
Usando la cámara de tu celular escanea el siguiente código y descarga la aplicación Kindle.

Imagen no disponible

- Para ver la descarga de este video Flash Player
- VISTA EN 360º
Seguir al autor

Essential Linear Algebra with Applications: A Problem-Solving Approach 2014th Edición
Opciones de compra y productos add-on.
Rooted in a pedagogically successful problem-solving approach to linear algebra, this work fills a gap in the literature that is sharply divided between, on the one end, elementary texts with only limited exercises and examples, and, at the other end, books too advanced in prerequisites and too specialized in focus to appeal to a wide audience. Instead, it clearly develops the theoretical foundations of vector spaces, linear equations, matrix algebra, eigenvectors, and orthogonality, while simultaneously emphasizing applications to fields such as biology, economics, computer graphics, electrical engineering, cryptography, and political science.
Key features:
* Intertwined discussion of linear algebra and geometry
* Example-driven exposition; each section starts with a concise overview of important concepts, followed by a selection of fully-solved problems
* Over 500 problems are carefully selected for instructive appeal, elegance, and theoretical importance; roughly half include complete solutions
* Two or more solutions provided to many of the problems; paired solutions range from step-by-step, elementary methods whose purpose is to strengthen basic comprehension to more sophisticated, powerful proofs to challenge advanced readers
* Appendices with review material on complex variables
Ideal as an introduction to linear algebra, the extensive exercises and well-chosen applications also make this text suitable for advanced courses a
- ISBN-10 0817643605
- ISBN-13 978-0817643607
- Edición 2014a
- Editorial Birkhäuser
- Fecha de publicación 15 Octubre 2014
- Idioma Inglés
- Dimensiones 6.5 x 1.25 x 9.25 pulgadas
- Número de páginas 501 páginas
- Ver todos los detalles
Títulos populares de este autor

Opiniones editoriales
“This book gives a rigorous introduction to linear algebra from a mathematical point of view. … The book presents a ‘problem-based’ approach, i.e., the author gives the precise theory to permit the reader to solve many different problems. … The book contains many well-chosen examples and exercises. Also, many problems are completely solved.” (Julio Benítez, Mathematical Reviews, June, 2015)
“The present book, as its title indicates, introduces the essential concepts of linear algebra and considers some of its applications. … the book is very suitable for students who are going to prepare for competitions and Olympiads. Moreover, the solved problems make it a very good problem book, with nice ideas, for anybody working with linear algebra. I recommend this book for students, and also for classroom use by teachers.” (Mehdi Hassani, MAA Reviews, April, 2015)
“The present book is a wellcomed addition at the present literature. The approach is elementray, however still rigorous and detailed. It covers the standard topics on linear algebra taught in a two-semester course, from elementray matrix theory to canonical forms and bilinear forms. … I would be happy to teach linear algebra from this book and ask students to work on problems from it.” (A. Arvanitoyeorgos, zbMATH 1309.15001, 2015)
Contraportada
This textbook provides a rigorous introduction to linear algebra in addition to material suitable for a more advanced course while emphasizing the subject’s interactions with other topics in mathematics such as calculus and geometry. A problem-based approach is used to develop the theoretical foundations of vector spaces, linear equations, matrix algebra, eigenvectors, and orthogonality.
Key features include:
• a thorough presentation of the main results in linear algebra along with numerous examples to illustrate the theory;
• over 500 problems (half with complete solutions) carefully selected for their elegance and theoretical significance;
• an interleaved discussion of geometry and linear algebra, giving readers a solid understanding of both topics and the relationship between them.
Numerous exercises and well-chosen examples make this text suitable for advanced courses at the junior or senior levels. It can also serve as a source of supplementary problems for a sophomore-level course.
Biografía del autor
Detalles del producto.
- Editorial : Birkhäuser; 2014a edición (15 Octubre 2014)
- Idioma : Inglés
- Tapa dura : 501 páginas
- ISBN-10 : 0817643605
- ISBN-13 : 978-0817643607
- Dimensiones : 6.5 x 1.25 x 9.25 pulgadas
- nº600 en Teoría de Juegos (Libros)
- nº643 en Algebra Lineal (Libros)
- nº1,521 en Álgebra y Trigonometría
Sobre el autor
Titu andreescu.
Dr. Titu Andreescu is an associate professor of mathematics in the Science and Mathematics Education department at the University of Texas at Dallas (UTD). Much of his career has been devoted to competition math, an efficient medium for teaching creative problem-solving for a wide-range of math topics. With over 30 years of experience teaching, coaching, and mentoring the brightest mathematical minds of our age, Dr. Andreescu's books are essential for every math enthusiast's library. Here are just a few highlights from his distinguished career:
-Authored, co-authored, and edited more than 40 math books and publications
-Head coach and leader of the USA International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO) for 8 years
-Director of the Mathematical Association of American (MAA) American Mathematics -Competitions for 5 years
-Has contributed hundreds of problems to various math competitions including and up to the IMO
-Co-founder of the Purple Comet! Math Meet, the first international team based math competition, http://www.purplecomet.org/
-Founder and Director of AwesomeMath, an organization that provides enriching experiences in mathematics to intellectually curious learners, https://www.awesomemath.org/
Opiniones de clientes
Las opiniones de clientes, incluidas las valoraciones de productos ayudan a que los clientes conozcan más acerca del producto y decidan si es el producto adecuado para ellos.
Para calcular la valoración global y el desglose porcentual por estrella, no utilizamos un promedio simple. En cambio, nuestro sistema considera cosas como la actualidad de la opinión y si el revisor compró el producto en Amazon. También analiza las opiniones para verificar la confiabilidad.
- Ordenar opiniones por Opiniones principales Más recientes Opiniones principales
Opinión destacada de los Estados Unidos
Ha surgido un problema al filtrar las opiniones justo en este momento. vuelva a intentarlo en otro momento..
- Trabaja en Amazon
- Boletín de Amazon
- Acerca de Amazon
- Accesibilidad
- Sostenibilidad
- Notas de Prensa
- Relaciones con los Inversionistas
- Dispositivos Amazon
- Amazon Science
- Vende en Amazon
- Vende tus Apps en Amazon
- Suministrar a Amazon
- Protege y construye tu marca
- Programa de Afiliados
- Únete al Equipo de Transportistas
- Comienza una Empresa Transportista
- Anuncia tus Productos
- Publica tu Libro en Kindle
- Hazte socio de Amazon Hub
- › Ver más Gana Dinero con Nosotros
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Compra con Puntos
- Tarjeta de Crédito
- Recarga tu Saldo
- Tarjetas de Regalo
- Conversor de divisas de Amazon
- Tus Pedidos
- Tarifas de Envío y Políticas
- Amazon Prime
- Devoluciones y Reemplazos
- Administrar Contenido y Dispositivos
- Retiros y alertas de seguridad del producto
- Condiciones de uso
- Aviso de privacidad
- Aviso de Privacidad de Datos de Salud del Consumidor
- Tus opciones de privacidad de los anuncios
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
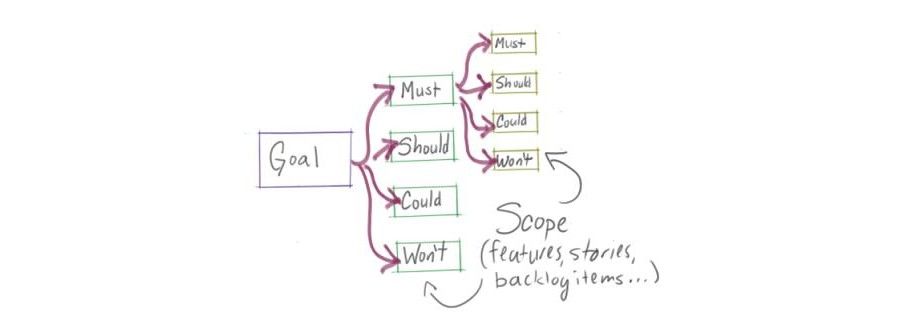
Making Your UX Life Easier with the MoSCoW
If you’re stuck trying to move a project forward because it seems like there are too many things to concentrate on then the MoSCoW method may help you get unstuck. It’s a prioritization technique which is easy to learn and simple to apply. It can also help you decide what’s really valuable for your UX projects before you get started on them.
There are many different prioritization techniques that can be employed on design projects but one of the simplest to use is the MoSCoW method. It’s used across all business disciplines to enable project teams to work with stakeholders to define requirements. It can also be used as a personal prioritization technique.
What Does MoSCoW Stand For?
MoSCoW is an (almost) acronym designed to reflect the four categories used by the technique to determine priorities; Must have, Should have, Could have and Would like but won’t get. The lower case “o’s” are added simply to give the acronym a pronounceable form. Occasionally, you may also see the whole phrase in block capitals MOSCOW to distinguish it from the name of the city but MoSCoW is more common.
What is the MoSCoW Method?

Experts Dai Clegg and Richard Barker proposed the method in their paper “Case Method Fast-Track: A RAD Approach” and while it was initially intended to be used with the Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM) it has long since been adopted throughout many areas of business. In recent times it has become very popular in the Agile and RAD (rapid application development) communities.
The MoSCoW method is most effective when it comes to prioritizing requirements in projects with either fixed or tight deadlines. It works by understanding the idea that all project requirements can be considered important but that they should be prioritized to give the biggest benefits in the fastest possible time frame.
It breaks down the requirements into four categories:
These are the requirements without which a project will fail. They MUST be delivered within the timeframe in order for anyone involved with the project to move on. In essence they make up the MVP ( Minimum Viable Product ) though it can be argued that MUST could stand for Minimum Usable SubseT too.
Should have
Should have requirements aren’t 100% necessary for delivering the project successfully but they are the “most nice to have” out of the list. They may be less time critical than “must have” or might be better held for a future release.

Could have requirements are just “nice to have” they are desirable to provide a nice user experience or customer experience but they’re not that important to the delivery of the project. They will be delivered only if there’s enough time and resources to spare to devote to them. Otherwise, they’re likely to be tabled for future releases and re-reviewed to see if they have become higher or lower priority in the interim.
These are the requirements that everyone agrees aren’t going to happen. It might be because they cost too much to implement or provide too little ROI ( Return on Investment ) for the efforts required to implement them. These are simply left to one side until they are either removed from the requirements list or become a higher priority.
The MoSCoW method provides a simple way of clarifying the priorities involved on a project. It’s most useful in time bound situations and it can be used to prioritize your own workload (usually with the buy in from a supervisor or manager if you work for someone else) as easily as it can be used for project work.
Implementing MoSCoW – A Practical Process

The easiest way to use MoSCoW is to bring together all the relevant stakeholders to the project and then:
List the requirements (on a flip chart or on a screen)
Vote on which category each requirement falls into (bearing in mind any hierarchical issues within the company itself – the CEOs vote may count for more than the votes of everyone else in the room)
Then collate the information and ensure that each requirement is presented against the relevant category in written form so that it can be used for reference by the project team
You can repeat this exercise whenever you feel it is necessary. Priorities may change mid-project or between releases. It’s important for everyone to understand what the implications of changing priorities in the middle of a project may be in terms of costs, resources, and time.
Issues with MoSCoW
It’s important to know that the MoSCoW method isn’t without its detractors. The main flaw in the method, as identified by authors Kark Weigers and Joy Beatty in their book Software Requirements, is that the method offers no means for comparing one requirement to another. This can make it difficult for those tasked with prioritizing requirements to know which category to place them in.
The Take Away
The MoSCoW method offers a simple process for prioritizing within project delivery. It can also be used to prioritize your work load. It should be used with some caution in that it may be too simple – particularly for complex projects – but it makes for a good starting point. One of the big advantages to its simplicity is that it should be easy to get buy in from other stakeholders to put it into practice.
Check out this useful study into how the MoSCoW method is used by business analysts .
You can read about the MoSCoW method as it was originally designed in: Clegg, Dai; Barker, Richard (2004-11-09). Case Method Fast-Track: A RAD Approach. Addison-Wesley. ISBN 978-0-201-62432-8.
You can read Weigers and Beatty’s criticism and their suggestion for a more complex method in: Wiegers, Karl; Beatty, Joy (2013). Software Requirements. Washington, USA: Microsoft Press. pp. 320–321. ISBN 978-0-7356-7966-5.
Hero Image: Author/Copyright holder: Agile Connection. Copyright terms and licence: All rights reserved. Img
User Experience: The Beginner’s Guide

Get Weekly Design Insights
Topics in this article, what you should read next, apple’s product development process – inside the world’s greatest design organization.

- 1.4k shares
How to Change Your Career from Graphic Design to UX Design
What is Interaction Design?

Shneiderman’s Eight Golden Rules Will Help You Design Better Interfaces

- 1.3k shares
The Principles of Service Design Thinking - Building Better Services

A Simple Introduction to Lean UX
- 3 years ago
Dieter Rams: 10 Timeless Commandments for Good Design

The 7 Factors that Influence User Experience
- 1.2k shares
Adaptive vs. Responsive Design
The Grid System: Building a Solid Design Layout
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this article , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share the knowledge!
Share this content on:
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this article.
New to UX Design? We’re giving you a free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Rooted in a pedagogically successful problem-solving approach to linear algebra, this work fills a gap in the literature that is sharply divided between, on the one end, elementary texts with only limited exercises and examples, and, at the other end, books too advanced in prerequisites and too specialized in focus to appeal to a wide audience.
Essential linear algebra with applications : a problem-solving approach ... Essential linear algebra with applications : a problem-solving approach by Andreescu, Titu, 1956- author. Publication date 2014 Topics Algebras, Linear, Algebras, Linear -- Problems, exercises, etc Publisher
Complete with bibliography and index, "Essential Linear Algebra with Applications" is a natural bridge between pure and applied mathematics and the natural and social sciences, appropriate for any student or researcher who needs a strong footing in the theory, problem-solving, and model-building that are the subjects hallmark.
Rooted in a pedagogically successful problem-solving approach to linear algebra, the present work fills a gap in the literature that is sharply divided between elementary texts and books that are too advanced to appeal to a wide audience. It clearly develops the theoretical foundations of vector spaces, linear equations, matrix algebra, eigenvectors, and orthogonality, while simultaneously ...
Essential Linear Algebra with Applications: A Problem-Solving Approach by Titu Andreescu. Rooted in a pedagogically successful problem-solving approach to linear algebra, this work fills a gap in the literature that is sharply divided between, on the one end, elementary texts with only limited exercises and examples, and, at the other extreme ...
Titu Andreescu. 4.57. 7 ratings0 reviews. Rooted in a pedagogically successful problem-solving approach to linear algebra, the present work fills a gap in the literature that is sharply divided between elementary texts and books that are too advanced to appeal to a wide audience. It clearly develops the theoretical foundations of vector spaces ...
Buy a copy of Essential Linear Algebra with Applications : A Problem-Solving Approach book by Titu Andreescu. Rooted in a pedagogically successful problem-solving approach to linear algebra, this work fills a gap in the literature that is sharply divided between, on the one end, elementary texts with only limited exercises and examples, and, at the other ext ...
Complete with bibliography and index, "Essential Linear Algebra with Applications" is a natural bridge between pure and applied mathematics and the natural and social sciences, appropriate for any student or researcher who needs a strong footing in the theory, problem-solving, and model-building that are the subject's hallmark.
Rooted in a pedagogically successful problem-solving approach to linear algebra, this work fills a gap in the literature that is sharply divided between, on the one end, elementary texts with only limited exercises and examples, and, at the other extreme, books too advanced in prerequisites and too specialized in focus to appeal to a wide audience.
"Essential Linear Algebra with Applications" is a natural bridge between pure and applied mathematics and the natural and social sciences, appropriate for any student or researcher who needs a strong footing in the theory, problem-solving, and model-building that are the subjects hallmark. Rooted in a pedagogically successful problem-solving approach to linear algebra, the present work fills a ...
AbeBooks.com: Essential Linear Algebra with Applications: A Problem-Solving Approach (9780817643607) by Andreescu, Titu and a great selection of similar New, Used and Collectible Books available now at great prices. ... Rooted in a pedagogically successful problem-solving approach to linear algebra, the present work fills a gap in the ...
Much of his career has been devoted to competition math, an efficient medium for teaching creative problem-solving for a wide-range of math topics. With over 30 years of experience teaching, coaching, and mentoring the brightest mathematical minds of our age, Dr. Andreescu's books are essential for every math enthusiast's library.
The present book, as its title indicates, introduces the essential concepts of linear algebra and considers some of its applications. The topics discussed in this book are standard. The book starts with matrix algebra, dealing with matrices and the operations associated with them. The second chapter is a rather extended study of the square ...
all catalog, articles, website, & more in one search catalog books, media & more in the Stanford Libraries' collections articles+ journal articles & other e-resources
Rooted in a pedagogically successful problem-solving approach to linear algebra, the present work fills a gap in the literature that is sharply divided ... Essential Linear Algebra with Applications: A Problem-Solving Approach. by Titu Andreescu. View More | Read Reviews. Add to Wishlist. ISBN-10: 1493938533. ISBN-13: 9781493938537. Pub. Date:
Paperback. $52.60 3 Used from $52.37 11 New from $46.61. Rooted in a pedagogically successful problem-solving approach to linear algebra, the present work fills a gap in the literature that is sharply divided between elementary texts and books that are too advanced to appeal to a wide audience. It clearly develops the theoretical foundations of ...
Given a word problem that includes two pairs of input and output values, use the linear function to solve a problem. Identify the input and output values. Convert the data to two coordinate pairs. Find the slope. Write the linear model. Use the model to make a prediction by evaluating the function at a given x-value.
In this accessible, comprehensive text, George Luger captures the essence of artificial intelligence-solving the complex problems that arise wherever computer technology is applied. Key representation techniques including logic, semantic and connectionist networks, graphical models, and many more are introduced. Presentation of agent technology and the use of ontologies are added.
Amazon.com: Essential Linear Algebra with Applications: A Problem-Solving Approach: 0000817643605: Andreescu, Titu: Libros ... "Essential Linear Algebra with Applications" is a natural bridge between pure and applied mathematics and the natural and social sciences, appropriate for any student or researcher who needs a strong footing in the ...
Prof. Mohammed K A Kaabar received his undergraduate and graduate degrees both in… · Experience: Frontiers · Education: Massachusetts Institute of Technology · Location: Fort Collins ...
MoSCoW is an (almost) acronym designed to reflect the four categories used by the technique to determine priorities; Must have, Should have, Could have and Would like but won't get. The lower case "o's" are added simply to give the acronym a pronounceable form. Occasionally, you may also see the whole phrase in block capitals MOSCOW to ...