- Climate Change Essay Topics Topics: 311
- Climate Essay Topics Topics: 239
- Deforestation Paper Topics Topics: 60
- Water Pollution Research Topics Topics: 54
- Air Pollution Essay Topics Topics: 117
- Recycling Topics Topics: 122
- Biodiversity Paper Topics Topics: 58
- Pollution Research Topics Topics: 231
- Earthquake Essay Topics Topics: 107
- Renewable Energy Paper Topics Topics: 117
- Solar Energy Paper Topics Topics: 55
- Dump Research Topics Topics: 47
- Ecosystem Essay Topics Topics: 71
- Alternative Energy Paper Topics Topics: 91
- Water Quality Essay Topics Topics: 49

178 Global Warming Essay Topics
NASA named July 2023 as the hottest month ever since 1880. This news cannot be ignored, and we suggest delving into this urgent issue that is reshaping our planet. In this compilation of global warming essay topics, you will find title ideas about how human activities impact the environment, what collective actions are required to battle it, and others.
🌡️ TOP 7 Global Warming Topics
🔥 hottest global warming titles for research papers, 🏆 best global warming essay topics, 🎓 interesting global warming essay titles, 🤩 catchy titles for global warming essays, 👍 debate topics on global warming, 💡 simple global warming essay topics, 🌶️ catchy global warming topics, 📌 easy global warming essay titles, ❓ global warming research questions.
- The Problem of Global Warming and Ways of Its Solution
- Al Gore’s Speech on Global Warming
Global Warming and Ozone Depletion
- Global Warming is Not a Myth
- Global Warming: Myth or Reality?
- How Global Warming Affects Wildlife
- Fast Fashion and Its Impacts on Global Warming
Technology’s Influence on Climate Change
The Earth’s climate started going through significant changes after the Industrial Revolution. In your essay, you can study how technology can affect climate change in positive and negative ways. Write about the technological advancements that can help us reduce pollution and reverse global warming, starting with renewable energy sources replacing fossil fuels.
Climate Change in Abu Dhabi
Due to its location, Abu Dhabi is very susceptible to the adverse effects of climate change. Droughts, hotter summers, and higher sea levels are hitting it harder than any other city. Is there anything that can be done to improve the situation? In a paper on this topic, you can analyze the climate change strategy Abu Dhabi adopted and suggest how to improve it.
Car Emissions and Global Warming
Fossil fuels are blamed for the greenhouse effect that causes devastating harm to our planet. It’s believed that car emissions are among the primary air pollutants. What does data say about it? How can car owners reduce emissions? Think these questions through and write a paper about it. Remember to include sufficient sources to support your ideas.
Society and Climate
Climate change affects so much more than just our environment. Everyone feels its impact, but some social groups suffer more than others. How is inequality related to climate change? Why are vulnerable groups at greater risk? You can discuss these issues in your paper and suggest some solutions.
Global warming and ozone depletion are two sides of the same coin: when the ozone layer gets depleted, it causes climate change, which involves global warming. But what are the causes of these changes? What are ozone holes, and why are they dangerous? Explore these issues to write a relevant research paper.
- Climate Change and Global Warming Global warming is a subject that has elicited a heated debate for a long time. This debate is commonplace among scholars and policy makers.
- Global Warming Effects on the Environment and Animals Global warming is a threat to the survival and well-being of human and animal life. This discussion aims to provide the effects of the current global warming threats.
- Car Emission Effects on Global Warming Car emissions are expected to aid policy makers in national governments, automobile manufacturers, fuel industry CEOs and city planners.
- Effects of Global Warming: Essay Example According to environmentalists and other nature conservatives, Africa would be the worst hit continent by the effects of global warming despite emitting less greenhouse gases.
- Global Warming and Business Ethics Business ethics is significant in promoting effective industrial activities that promote environmental conservation and reduce global warming.
- Global Warming From a Social Studies Perspective The inability to find a balance between human needs and the consequences of their realization for the environment leads to conflict resulting in global warming.
- Global Warming as a Humanity’s Fault: Activities Triggering Disasters World leaders were forced to hold discussions in Kigali, Rwanda, in late 2016 to establish a deal addressing mechanisms to be adopted to curb global warming.
- Climate Change and Global Warming Awareness If people continue to have misconceptions about global warming, climate change will negatively impact weather, food security, and biodiversity.
- Global Warming: “Hopeful Lessons From the Battle to Save Rainforests” The “Hopeful lessons from the battle to save rainforests” video proposes several solutions to deforestation and global warming.
- Global Warming: Issue Analysis Global warming is a term commonly used to describe the consequences of man- made pollutants overloading the naturally-occurring greenhouse gases causing an increase of the average global temperature.
- Global Warming: Causes and Consequences Global warming is the result of high levels of greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, and ozone) in the earth’s atmosphere.
- Global Warming Challenges Solving in General Electric Environmental solutions that favor the growth of the company rather than social responsibility drive the decisions and policies of the company.
- Extreme Weather and Global Warming The Global warming is a bad phenomenon that is causing to see level raise, change weather pattern, and create alteration in animal life.
- The Effect of Global Warming and the Future Global warming effects are the social and environmental changes brought-about by the increase in global temperatures.
- Questions on Information Revolution and Global Warming The information revolution characterizes the period of change propelled by the development of computer technology. Technological advancements impact people’s lives.
- Global Warming: Understanding Causes of Event Global warming is a phenomenon characterized by the gradual increase of the temperature of the earth’s atmosphere.
- Global Warming and Climate Change and Their Impact on Humans Climate change and global warming are significant issues with negative impacts on all aspects of human life; for example, they disrupt the food web, hurting humans and wildlife.
- Global Warming Causes and Impacts This paper endeavors to delineate the history of global warming, the causality and every potential revelation towards diminution of the impacts of global warming.
- Is the Threat of Global Warming Real? Increases in Earth’s average temperature over an extended period are called global warming. Greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere have recently increased.
- The History of Climate Change and Global Warming Issue The paper states that the history of climate change and the solutions communities opted for are critical to tackling the current global warming issue.
- Worldwide Effects of Global Warming The article conveys Trenberth’s message about the far-reaching implications of global warming on climate and the urgent need for collective action to address its consequences.
- Devastating Effects of Global Warming The incapacitating consequences of a changing climate have resulted in significant distress among vulnerable populations as they face various challenges.
- Endogenous Substitution Among Energy Resources and Global Warming
- Global Warming and Developing Countries: The Possibility of a Solution by Accelerating Development
- Can Nuclear Power Solve the Global Warming Problem
- The Kyoto Protocol and the Causes and Effects of Global Warming
- Anthropogenic Global Warming Hypothesis: Testing Its Robustness by Granger Causality Analysis
- Using Hydropower Help Stop Global Warming
- Global Warming and Risk of Resources War
- Environmental Issues That Impact the Tourism Industry: Global Warming Causes
- Global Warming Atmosphere Heat Gases
- The Paris Agreement: Solutions to the Issue of Global Warming
- Each Citizen Should Aim to Reduce Their Carbon Footprint to Halt Global Warming
- Atmospheric Pollution the Atmospheric Issues and Global Warming
- Combating Global Warming and Other Problems Associated With Fossil Fuels
- Global Warming and Its Effect on Human Society
- Global Warming and Its Threat to the Future of Wildlife and Its Habitat
- Anthropogenic Global Warming: Man’s Influence in the Environment Critical Thinking
- Global Warming and Planetary Dangers
- Global Warming and Endogenous Technological Change: Revisiting the Green Paradox
- The Global Warming Potential Paradox: Implications for the Design of Climate Policy
- Does Increased Carbon Dioxide Emissions Cause Global Warming
- Global Warming: Cause and Mitigation
- America Should Take the Lead in Stopping Global Warming
- Deforestation: Global Warming and Percent Grass
- Are Global Warming and Economic Growth Compatible? Evidence From Five OPEC Countries
- Did Global Warming and Climate Change Cause the Degradation of Lake Chad, Africa’s Most Important ‘Ecological Catastrophe’
- Global warming vs. climate change: what is happening? Some studies show that climate change isn’t as bad as alarmists believe. One theory states that global warming might be a regular part of our planet’s temperature cycle. Where’s the truth? Do some research and write an essay about your findings.
- The future of global warming: what do the forecasters say? With all the technological advancements and data available, people should be able to make some predictions on what our planet’s climate will look like in the future. Analyze all the information you can find and draw some conclusions.
- Nuclear power plants and the future without global warming. Nuclear power is a fantastic energy source that could fully replace burning fossil fuels. Will we ever make atomic power into a primary source of energy? Discuss whether it can be a possible solution to excess emissions that lead to global warming.
- Buy eBooks – save the planet! Cutting forests for paper and book production is not the biggest reason for climate change, but it’s also not the least. If all people stop buying paper books, would it be impactful enough? Brainstorm this idea and write down your thoughts.
- Climate activists: who is making the most significant change? In climate activism, some public figures are more influential than others. Which influencers inspired the most action? Who had the biggest impact on reducing the adverse effects of global warming, and how did they achieve it?
- Global Warming and Crop Production in Africa Many people are aware of the current and future negative effects of global warming. Global warming will cause severe reductions in the crop in Africa, particularly in Ethiopia.
- Consequences of Global Warming Although the opinions about the causes of climate change are diverse, the effects of human activities and natural elements are similar and lead to global warming.
- Global Warming Effects on Earth Global warming presents a considerable threat by having an enormous influence on humanity’s social, economic, and physical state.
- Global Warming and Economics Discussion The article discusses that at the international level, the carbon tax is not always conducive to climate change regulation.
- Global Warming: The Importance of Addressing the Climate Crisis The paper states that global warming has many consequences. Multiple scientific discoveries emphasize the importance of addressing the climate crisis urgently.
- Examining the Potential of Digital Earth Services in Connection to Global Warming In this work, the primary characteristics of global warming will be discussed with the implementation of digital Earth tools, examining the data from these sources.
- Greenhouse Effect as a Cause of Global Warming The report serves an informative function and is designed to explore the nature of global warming through the greenhouse effect.
- Global Warming in Relation to Human Population Size The density of the world population in the future is a crucial component of climate policy to safeguard the vulnerable future generation.
- Iron Fertilization: Solving Global Warming The discussion in this paper considers some of the international as well as maritime laws that deal with the application of iron fertilization as a method of mitigating global warming.
- How Car Emissions Affect Global Warming This paper examines the concept of global warming with a focal point on the emissions of gases by cars and other automobiles.
- Economic Model for Global Warming The adoption of various economic models is a superior strategy that appears promising and capable of guiding policymakers and nations to tackle the predicament of climate change.
- Climate and Social Change in Global Warming Crisis People in the community should be encouraged to change their behaviors and make better personal choices to mitigate the global warming crisis.
- Global Warming and Climate Change Climate change is caused by greenhouse gas emissions resulting from human activities, mainly through the energy and transport sectors.
- Global Warming, Climate Change and Ozone Depletion Global warming refers to an increase in the Earth’s average temperature that is characterized by rising global surface temperatures and the accumulation of pollutants in the atmosphere.
- Climate Change: The Leading Cause of Global Warming The chosen issue is climate change because it is a social dilemma triggered by human activity and will need joint efforts to reduce or alleviate its adverse effects.
- It’s Not My Fault: Global Warming and Moral Responsibility The work of the American professor of ethical sciences Sinnott-Armstrong approaches the phenomenon of global warming in terms of individual and collective responsibility.
- Climate Change Skepticism in Relation to Global Warming The researcher has used the most appropriate research design that enables her to take a closer look at climate change skepticism.
- The Issue of Global Warming in the Community To effectively mitigate the effects of global warming in the community, the team will be made up of three experts in different disciplines closely related to the environment.
- Global Warming: Do Human Activities Threaten to Change Climate? The greenhouse gases that cause global warming can only be present in the atmosphere if they are emitted and their emission can only come out of the activities of human beings.
- Global Warming and Mitigation Strategies The paper outlines causes of global warming and possible impact on human beings. There is also an evaluation of strategies applied in realization of environmental sustainability.
- Controversy About Global Warming: Skepticism and Reality There are two different points of view on global change. Skeptics believe that global warming is a natural process. Another thinks that it is the result of an exclusive human activity.
- Global Warming and Other Ecology Issues The results of global warming will always remain a topic of controversy. Most scientists will always agree and disagree on the real effects of global warming on human life.
- Global Warming: Harmful Impact on the Polar Bears The natural existence of Polar bears directly depends on the global warming process due to numerous reasons. Global warming fosters the spread of poisoned substances.
- Oil and Gas Industry Response to Global Warming Global warming is a contemporary serious threat to our planet for the combustion of oil, coal, and natural gas contributes in changing the atmospheric balance of carbon dioxide.
- Global Warming: Causes and Solutions Climate change has started to develop since the 20th century and is still in a progressive state of continuation. The true causes of the greenhouse effect are still open to discussion.
- Global Warming and the Effect on Plant Diversity
- Global Warming and Its Effects on Coastal Cities
- Weakening Dust Storm Intensity in Arid Central Asia Due to Global Warming Over the Past 160 Years
- Can Earth End Because of Global Warming?
- Global Warming and Its Effect on the Marine Ecosystem
- The Greenhouse Effect and Its Relationship to Global Warming
- Global Warming and the Need for Energy-Efficient Lighting
- Global Agricultural Trade Pattern in a Warming World: Regional Realities
- Global Warming and Its Effect on Earth’s Surface, Oceans
- Accounting for Global Warming Risks: Resource Management Under Event Uncertainty
- Global Warming and Its Effect on Natural Disasters
- The Global Warming Phenomenon: Is It Real or Not
- Global Warming and Its Effect on the Quality of Life on Earth
- Global Warming and Its Effects on the Human Body
- Global Warming and Electricity Demand: A Study of California
- Global Warming and Climate Change: Melting the Marine Life
- The Multiple Climate Change Indicators of Global Warming
- Adaptation Behaviors Across Ecosystems Under Global Warming: A Spatial Micro-Econometric Model of the Rural Economy in South America
- Global Warming and Extreme Events: Rethinking the Timing and Intensity of Environmental Policy
- Global Warming and the Changes of Temperature on Earth
- Counteracting Global Warming With Artificial Leaves
- Global Warming and Ice Age
- What Role Can Nuclear Power Play in Mitigating Global Warming
- Global Warming and Climate Change: Impacts on Hurricanes and Cyclones Worldwide
- The Long Term Effects of Global Warming and Climate Change
- The Kyoto Protocol: First Framework for Fighting Global Warming The UN Conference, held in Kyoto, in 1997 focussed on creating an international agreement to fight global warming, by reducing greenhouse gases in developed countries.
- Global Warming as Not a New-Fangled Issue Analytical research and an explanatory research have been seen to be helpful in many ways in order to increase the awareness that an audience has about the issues as global warming.
- Journal and Newspaper Collection on Global Warming This paper comments on Journal/ newspaper article on global warming from major newspapers and journals around the world
- The Issue of Unstoppable Global Warming and Its Effects Drought levels shall increase if the temperatures remain high, evaporation shall increase too, mostly at summer and fall, could worsen famine, and the danger of wildfires.
- Car Emissions and Global Warming The emissions problem that is caused by the excessive use of cars is an issue that affects most of the modern world and needs to be addressed as soon as possible to prevent further adverse impact.
- Global Warming and Its Various Consequences The slowly overheating planet may carry a wide variety of repercussions for humanity as one of the species living on its surface.
- Global Warming Leads Climate Change This paper aims to research scholarly literature in order to prove that the human race is largely responsible for global warming and climate change rather than considering it to be a natural course of existence.
- The Paris Accord: Macroeconomics and Global Warming The 21st century has been characterized by the unstoppable emergence of industries due to diverse demands of the ever-increasing world population.
- Virtue Ethics: Altering Testimony on Global Warming The paper discusses an important issue of censorship in regards to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention testimony on global warming.
- Global Warming and Its Health Implications This paper reports on the possible effects of global warming on health, complexities associated with it and the significant general implication of the same around the globe.
- Global Warming and Its Threats: Debates As human civilization continues to expand it brings with it an ever-increasing demand for resources such as food, raw materials, and space.
- The Issue of Global Warming Investigating the issue of global warming keenly would increase the understanding on whether it is a naturally occurring phenomenon or one that has been caused by human activities.
- Global Warming Problems due to Economic Growth This paper investigates if it is possible to deal with global warming by reducing CO2 emissions and energy consumption without any threats to economic development.
- Global Warming and the Free Rider Problem This paper will examine the issue of global warming from an economic standpoint, as well as cover the free rider problem and how it affects the fight against global warming.
- Iron Seeding Oceans: Global Warming Solution The principle behind iron seeding is the reduction of carbon dioxide through photosynthesis. One of the major raw materials needed in photosynthesis is carbon dioxide.
- Biodiversity, Global Warming, Environmental Conservation Several pertinent issues manifest themselves in the discussion of nature. These issues include biodiversity, global warming, and environmental conservation.
- The Problem of Global Warming and Its Effects Global warming is a problem that concerns everyone, and it is necessary to take action personally in order to prevent the development of the problem.
- Global Warming With an Emphasis on the Arctic This paper presents the impact of global warming with a focus on the Arctic region. It also provides key solutions that can be implemented to reduce its effects.
- Global Warming: Impacts and Consequences on Ecology and Society One of the most troubling ecological issues of the contemporary world is global warming. It is defined as an increase of global average surface temperature at an alarming rate.
- Car Emissions and Global Warming: Understanding the Impact The paper will answer the question on how the car emissions affect the global warming. It has been noted that in the UK, cause various health problems to the people.
- Global Warming and Melting Glaciers: A Growing Concern The world’s society turn to new researches directed to find the causes of the warming and possible ways to stop or reverse it because future our planet will face a serious threat.
- Environmental Studies: Causes of Global Warming and Mitigation Strategies Natural climate changes occur in cycles in world, and they are caused by natural interaction with different forces, whereas human activities cause anthropogenic climate changes.
- Environmental Studies: The Global Warming Holocaust Global climate change is a social issue that has captured the imagination of the world’s population. This issue is discussed in mass media and social media platforms.
- Global Warming: Analyzing Causes and Effects on the Environment The Global Warming is a process which points out an increase of approximate temperature in different spots of Earth. Causes and effects of global warming bear in present days an equivocal character.
- Climate Change and the Future of Research on Global Warming According to Feygina, Jost, and Goldsmith
- Global Warming Affects Polar Bears
- Global Warming and How It Will Affect Soil Carbon
- Will Global Warming Lead to Mass Extinction of the World’s Species
- Global Warming and Changes in Marine Ecosystems: Economic Consequences and Adjustment Issues
- Global Warming and Decreased Crop Production
- Global Warming and Its Effect on Our Environment
- Eliciting Public Preference for Nuclear Energy Against the Backdrop of Global Warming
- Could Slowing the Effects of Global Warming Save Our World
- Waste Prevention and Its Effects on Global Warming
- Global Warming and Its Effect on Ecosystems by Stimulating
- Global Warming: Polar Bears Are Endangered
- Global Warming and Its Effects on Water Storage Systems
- Global Warming and Its Effect on Earth’s Atmosphere
- Counterarguing Coleman’s Allegations That Global Warming Is a Scam
- Acid Rain, Global Warming, and Air Quality
- The Three Reasons Why Public Transportation Won’t Solve the Global Warming Problem
- U.S. Climate Report Says Global Warming Impact Already Severe by Darryl Fears
- The Past, Present, and Future of Global Warming and Climate Change
- Global Warming: Could Things Get Better Before They Get Worse
- Global Warming and Electricity Demand in the Rapidly Growing City of Delhi: A Semi-parametric Variable Coefficient Approach
- Global Warming Effects: Scientific Consensus on Temperature Changes
- Environment: Global Warming and Current Carbon Dioxide
- Will Biofuels Solve Global Warming?
- Are Global Warming and Economic Growth Compatible?
- Can Subsidizing Alternative Energy Technology Development Lead to Faster Global Warming?
- How Global Warming Is Changing the World?
- What Is the Economics of Hurricanes and Implications of Global Warming?
- How Global Warming Can Trigger Infectious Diseases Development?
- What Are the Economic Fundamentals of Global Warming?
- How Much More Rain Will Global Warming Bring?
- What Are the National Contributions to Observed Global Warming?
- What Are the Biological Consequences of Global Warming?
- What Is the “Damages Function” for Global Warming?
- How Effective Are Public Policies Against Global Warming?
- How Does Global Warming Benefit the Small in Aquatic Ecosystems?
- What Are the Alternative Mechanisms to Control Global Warming?
- What Is the Planetary Emergency of Global Warming and What We Can Do About It?
- What Is the Spatial Economic Impact of Global Warming?
- What Are the Effects of Global Warming and Urbanization in Cities?
- What Are the Public Perceptions of Global Warming Issues?
- Do People “Personally Experience” Global Warming?
- What Are the Robust Responses of the Hydrological Cycle to Global Warming?
- What Is the Status and Prospects of Renewable Energy for Combating Global Warming?
- How Warm Days Increase Belief in Global Warming?
- Can China Contribute More to the Fight Against Global Warming?
- Can Advances in Science and Technology Prevent Global Warming?
- How the Public Engages With Global Warming?
- What We Think About When We Try Not To Think About Global Warming?
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2021, September 9). 178 Global Warming Essay Topics. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/global-warming-essay-topics/
"178 Global Warming Essay Topics." StudyCorgi , 9 Sept. 2021, studycorgi.com/ideas/global-warming-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2021) '178 Global Warming Essay Topics'. 9 September.
1. StudyCorgi . "178 Global Warming Essay Topics." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/global-warming-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "178 Global Warming Essay Topics." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/global-warming-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2021. "178 Global Warming Essay Topics." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/global-warming-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Global Warming were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on November 3, 2024 .
359 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples
You will notice that there are many climate change research topics you can discuss. Our team has prepared this compilation of brilliant ideas that you can use in your work.
🔝 Top-10 Climate Change Titles
🏆 best climate change title ideas & essay examples, ✨ creative climate change topics for presentation, 🥇 most interesting climate change topics to write about, 🔥 hottest climate change topics for essay, 🎓 simple & easy research titles about climate change, ♻️ renewable energy options and climate change: essay topics, 🌎 titles for climate change and global health essay, 👍 good research topics about climate change, 🌿 climate change argumentative essay topics, 🔍 interesting topics to write about climate change, 🧐 anthropogenic climate change: argument topics, ⭐ good essay topics on climate change, 📚 corporate responsibility and climate change: essay titles, ❓ climate change essay questions, 🤩 how to craft a great title for a climate change essay, 📝 key points to use to write an outstanding climate change essay.
- Climate Change – Problems and Solutions
- Causes and Effects of Climate Changes
- Is Climate Change a Real Threat?
- Climate Change Causes and Predictions
- The Role of Technology in Climate Change
- Global Warming as Serious Threat to Humanity
- Climate Change: Human Impact on the Environment
Climate Change and Extreme Weather Conditions
- Global Warming and Human Impact: Pros and Cons
- Technology Influence on Climate Change
- Climate Change: The Day After Tomorrow In the beginning of the film “The Day After Tomorrow”, the main character, Professor Jack Hall, is trying to warn the world of the drastic consequences of a changing climate being caused by the polluting […]
- The Climate Change Articles Comparison In a broader sense, both articles address the concept of sustainability and the means of reinforcing its significance in the context of modern global society to prevent further deterioration of the environment from happening.
- Climate Change: Mitigation Strategies To address the latter views, the current essay will show that the temperature issue exists and poses a serious threat to the planet.
- Desert, Glaciers, and Climate Change When the wind blows in a relatively flat area with no vegetation, this wind moves loose and fine particles to erode a vast area of the landscape continuously in a process called deflation.
- Climate Change Definition and Description The wind patterns, the temperature and the amount of rainfall are used to determine the changes in temperature. Usually, the atmosphere changes in a way that the energy of the sun absorbed by the atmosphere […]
- Evidence of Climate Change The primary reason for the matter is the melting of ice sheets, which adds water to the ocean. The Republic of Maldives is already starting to feel the effects of global sea-level rise now.
- Climate Change and Its Impacts on the UAE Currently, the rise in temperature in the Arctic is contributing to the melting of the ice sheets. The long-range weather forecast indicates that the majority of the coastal areas in the UAE are at the […]
- Transportation Impact on Climate Change It is apparent that the number of motor vehicles in the world is increasing by the day, and this translates to an increase in the amount of pollutants produced by the transportation industry annually.
- The Way Climate Change Affects the Planet It can help analyze past events such as the Pleistocene ice ages, but the current climate change does not fit the criteria. It demonstrates how slower the change was when compared to the current climate […]
- Climate Change and Renewable Energy Options The existence of various classes of world economies in the rural setting and the rise of the middle class economies has put more pressure on environmental services that are highly demanded and the use of […]
- Climate Change: Impact of Carbon Emissions to the Atmosphere There is also the problem on the management of operations that would ensure minimization of green house gas emissions to the atmosphere.
- Climate Change Impact on Bangladesh Today, there are a lot of scientists from the fields of ecology and meteorology who are monitoring the changes of climate in various regions of the world.
- Climate Change – Global Warming For instance, in the last one century, scientists have directly linked the concentration of these gases in the atmosphere with the increase in temperature of the earth.
- Climate Change’s Impact on Crop Production I will address the inefficiencies of water use in our food production systems, food waste, and the impact of temperature on crop yield.
- Global Warming and Climate Change The author shows the tragedy of the situation with climate change by the example of birds that arrived too early from the South, as the buds begin to bloom, although it is still icy.
- The Impact of Climate Change on Food Security Currently, the world is beginning to encounter the effects of the continuous warming of the Earth. Some of the heat must be reflected in space to ensure that there is a temperature balance in the […]
- Moral Obligations to Climate Change and Animal Life To be able to become a rational person, it is essential to think critically about the concepts and domains that the individual faces and the way it will be sensible to react to them.
- Climate Change in Abu Dhabi Abu Dhabi is an emirate in the country and it could suffer some of the worst effects of climate change in the UAE.
- CO2 Emission and Climate Change Misconceptions However, people start to recognize the pernicious effect their actions might have on the state of our planet and want to know more about the processes that occur due to these very actions.
- Climate Change Impacts on Ocean Life The destruction of the ozone layer has led to the exposure of the earth to harmful radiation from the sun. The rising temperatures in the oceans hinder the upward flow of nutrients from the seabed […]
- Organisational Sustainability and Climate Change Strategy Porter and Kramer are of the opinion that an organisation has to create a set of effective share values between the society and the firm in order to enhance organisational performance.
- Climate Change, Development and Disaster Risk Reduction However, the increased cases of droughts, storms, and very high rainfalls in different places are indicative of the culmination of the effects of climate change, and major disasters are yet to follow in the future.
- Threat to Biodiversity Is Just as Important as Climate Change This paper shall articulate the truth of this statement by demonstrating that threats to biodiversity pose significant threat to the sustainability of human life on earth and are therefore the protection of biodiversity is as […]
- Starbucks: Corporate Social Responsibility and Global Climate Change Then in the 90s and onwards to the 21st century, Starbucks coffee can be seen almost anywhere and in places where one least expects to see a Starbucks store.
- Neolithic Revolution and Climate Change At the primary stage of the evolution of human civilization, the rise of agriculture in the later part of stone age, also known as the Neolithic Revolution, was ultimately necessary to keep pace with the […]
- Impact of Glacier Melting on Biodiversity, Water Levels, and Climate Change The summer surface melting of the ice, which enters the bed through fissures or tunnels similar to chimneys and then flows under the pressure of the ice sheet, is the most critical process.
- Climate Change and Interdisciplinary Approach Natural sciences such as physics, chemistry, and biology are essential in understanding the physical and chemical processes contributing to climate change.
- Climate Change Crisis: The Role of Responsibility McKibben is trying to make the point that people are responsible for their actions and therefore have a responsibility to act.
- Climate Change and Alternative Ways to Address It Climate change, which includes anomalies like droughts, severe storms, and floods, is the observed and anticipated long-term changes in the average climate and climate variability brought on by human activity.
- Climate Change: KWL Analysis and Reflection From the natural science lens, I have learned that the major distinctive trait of climate change is identified by the 1.
- Climate Change and Baseball: Bidirectional Relationship For example, in the case of baseball, the effect is bidirectional since global warming may affect the players, and this industry can impact the environment.
- Climate Change’s Impact on Winter Sports The difficulty of climate change for companies in the responsibility of large sports facilities is positioned within a broader framework of advancements.
- Climate Change Affecting Snow Management in Ski Resorts Among the challenges might be the detection of snow accumulation in forested areas and the adaptation of the techniques to frequent, large-scale computation.
- Climate Change Through Four Lenses of Thinking Natural science is rooted in the study of the natural and physical world. Social science studies the past and the present, but history concerns only the past.
- Integrated Remote Sensing System for Climate Change Mitigation Climate change presents a complicated global problem that requires a thorough understanding of society’s impact on the climate and the internal mechanisms in the process of climate change.
- The Climate Change Legislation In the remarks made on his official White House website, the President touted the law to be the biggest commitment that the country has demonstrated in tackling the issue of climate change.
- Human Health: Impact of Climate Change According to the International Panel on Climate Change, in order to avert catastrophic health impacts and prevent millions of climate change-related deaths, the world must limit the rise in temperature.
- Climate Change’s Impact on Ocean: Finding Solutions According to the diagram by Gattuso et al, the most successful and fast method of saving the ocean will be the protection of biota and ecosystems.
- Climate Change: Offering a Solution to the Problem We can contribute toward a sustainable future that benefits the environment and our economy by making individual decisions and supporting group initiatives.
- Impact of Food Waste on Climate Change In conclusion, I believe that some of the measures that can be taken to prevent food waste are calculating the population and their needs.
Climate change is believed to cause frequent and intense weather events. Floods, wildfires, extreme heat, and hurricanes occur more often than ever before. As the planet warms, the sea level rises, affecting the patterns of coastal storms. The severity of weather conditions is predicted to become stronger with time.
Climate Change Effect on Agriculture
While slight warming can help crops grow faster, the extreme conditions farmers have faced in recent years have reduced yields. Regular heat waves, droughts, and floods cause erosion and soil depletion. Climate change also puts livestock at risk by causing droughts and decreased feed quality.
Economic Impact of Climate Change
Climate change affects the cost of raw materials. Moreover, severe meteorological conditions will likely disrupt supply chains by delaying transportation and damaging factories. All this causes businesses to lose money. In addition, new regulations pose additional costs. Companies that don’t follow environmentally friendly practices may get a bad reputation and leave business.
Climate Change Impact on Bangladesh
Bangladesh was ranked among the top 10 countries at risk from climate change. In the next few decades, the sea level will rise enough to flood almost one-third of the country’s lands used for agriculture. As the coastal areas become inhabitable, people will be forced to move to the cities.
Polar Ice Cap Melting
Polar ice caps are an integral part of the planet’s ecosystem. Their slightest changes affect the climate worldwide. Melting ice caps means less surface area that can reflect solar radiation. In turn, water and land absorb more heat and raise the temperature, causing more ice to melt.
- Climate Change and Resource Sustainability in Balkan: How Quickly the Impact is Happening In addition, regarding the relief of the Balkans, their territory is dominated by a large number of mountains and hills, especially in the west, among which the northern boundary extends to the Julian Alps and […]
- Climate Change: Renewable Energy Sources Climate change is the biggest threat to humanity, and deforestation and “oil dependency” only exacerbate the situation and rapidly kill people. Therefore it is important to invest in the development of renewable energy sources.
- Climate Change and the Allegory of the Cave Plato’s allegory of the cave reflects well our current relationship with the environment and ways to find a better way to live in the world and live with it.
- Climate Change, Economy, and Environment Central to the sociological approach to climate change is studying the relationship between the economy and the environment. Another critical area of sociologists ‘ attention is the relationship between inequality and the environment.
- The Three Myths of Climate Change In the video, Linda Mortsch debunks three fundamental misconceptions people have regarding climate change and sets the record straight that the phenomenon is happening now, affects everyone, and is not easy to adapt.
- Terrorism, Corruption, and Climate Change as Threats Therefore, threats affecting countries around the globe include terrorism, corruption, and climate change that can be mitigated through integrated counter-terror mechanisms, severe punishment for dishonest practices, and creating awareness of safe practices.
- Climate Change’s Impact on Hendra Virus Transmission to humans occurs once people are exposed to an infected horse’s body fluids, excretions, and tissues. Land clearing in giant fruit bats’ habitats has exacerbated food shortages due to climate change, which has led […]
- Global Climate Change and Environmental Conservation There may be a significantly lesser possibility that skeptics will acknowledge the facts and implications of climate change, which may result in a lower desire on their part to adopt adaptation. The climate of Minnesota […]
- Beef Production’s Impact on Climate Change This industry is detrimental to the state of the planet and, in the long term, can lead to irreversible consequences. It is important to monitor the possible consequences and reduce the consumption of beef.
- Cities and Climate Change: Articles Summary The exponential population growth in the United States of America and the energy demands put the nation in a dilemma. Climate change challenges are experienced as a result of an increase in greenhouse gas emissions […]
- The Impact of Climate Change on Vulnerable Human Populations The fact that the rise in temperatures caused by the greenhouse effect is a threat to humans development has focused global attention on the “emissions generated from the combustion” of fossil fuels.
- How Aviation Impacts Climate Change A measurement of the earth’s radiation budget imbalance brought on by changes in the quantities of gases and aerosols or cloudiness is known as radiative forcing.
- Food Waste Management: Impact on Sustainability and Climate Change How effective is composting food waste in enhancing sustainability and reducing the effects of climate change? The following key terms are used to identify and scrutinize references and study materials.”Food waste” and sustain* “Food waste” […]
- Protecting the Environment Against Climate Change The destruction of the ozone layer, which helps in filtering the excessive ray of light and heat from the sun, expose people to some skin cancer and causes drought.
- The Global Warming Problem and Solution Therefore, it is essential to make radical decisions, first of all, to reduce the use of fossil fuels such as oil, carbon, and natural gas. One of the ways of struggle is to protest in […]
- Climate Change and Immigration Issues Due to its extensive coverage of the aspects of climate migration, the article will be significant to the research process in acquiring a better understanding of the effects of climate change on different people from […]
- Global Warming: Speculation and Biased Information For example, people or organizations that deny the extent or existence of global warming may finance the creation and dissemination of incorrect information.
- Impacts of Climate Change on Ocean The development of phytoplankton is sensitive to the temperature of the ocean. Some marine life is leaving the ocean due to the rising water temperature.
- Impact of Climate Change on the Mining Sector After studying the necessary information on the topic of sustainability and Sustainability reports, the organization was allocated one of the activities that it performs to maintain it.
- Climate Change: Historical Background and Social Values The Presidential and Congress elections in the US were usually accompanied by the increased interest in the issue of climate change in the 2010s.
- Communities and Climate Change Article by Kehoe In the article, he describes the stringent living conditions of the First Nations communities and estimates the dangers of climate change for these remote areas.
- Discussion: Reverting Climate Change Undertaking some of these activities requires a lot of finances that have seen governments setting aside funds to help in the budgeting and planning of the institutions.
- Was Climate Change Affecting Species? It was used because it helps establish the significance of the research topic and describes the specific effects of climate change on species.
- Climate Change Attitudes and Counteractions The argument is constructed around the assumption that the deteriorating conditions of climate will soon become one of the main reasons why many people decide to migrate to other places.
- How Climate Change Could Impact the Global Economy In “This is How Climate Change Could Affect the World Economy,” Natalie Marchand draws attention to the fact that over the next 30 years, global GDP will shrink by up to 18% if global temperatures […]
- Effective Policy Sets to Curb Climate Change A low population and economic growth significantly reduce climate change while reducing deforestation and methane gas, further slowing climate change. The world should adopt this model and effectively increase renewable use to fight climate change.
- Climate Change: Social-Ecological Systems Framework One of the ways to understand and assess the technogenic impact on various ecological systems is to apply the Social-Ecological Systems Framework.
- The Climate Change Mitigation Issues Indeed, from the utilitarian perspective, the current state of affairs is beneficial only for the small percentage of the world population that mostly resides in developed countries.
- The Dangers of Global Warming: Environmental and Economic Collapse Global warming is caused by the so-called ‘Greenhouse effect’, when gases in Earth’s atmosphere, such as water vapor or methane, let the Sun’s light enter the planet but keep some of its heat in.
- Wildfires and Impact of Climate Change Climate change has played a significant role in raise the likelihood and size of wildfires around the world. Climate change causes more moisture to evaporate from the earth, drying up the soil and making vegetation […]
- Aviation, Climate Change, and Better Engine Designs: Reducing CO2 Emissions The presence of increasing levels of CO2 and other oxides led to the deterioration of the ozone layer. More clients and partners in the industry were becoming aware and willing to pursue the issue of […]
- Climate Change as a Problem for Businesses and How to Manage It Additionally, some businesses are directly contributing to climate change due to a lack of measures that will minimise the emission of carbon.
- Climate Change and Disease-Carrying Insects In order to prevent the spreading of the viruses through insects, the governments should implement policies against the emissions which contribute to the growth of the insects’ populations.
- Aspects of Global Warming Global warming refers to the steadily increasing temperature of the Earth, while climate change is how global warming changes the weather and climate of the planet.
- David Lammy on Climate Change and Racial Justice However, Lammy argues that people of color living in the global south and urban areas are the ones who are most affected by the climate emergency.
- Moral Aspects of Climate Change Addresses However, these approaches are anthropocentric because they intend to alleviate the level of human destruction to the environment, but place human beings and their economic development at the center of all initiatives.
- Feminism: A Road Map to Overcoming COVID-19 and Climate Change By exposing how individuals relate to one another as humans, institutions, and organizations, feminism aids in the identification of these frequent dimensions of suffering.
- Global Warming: Moral and Political Challenge That is, if the politicians were to advocate the preservation of the environment, they would encourage businesses completely to adopt alternative methods and careful usage of resources.
- Climate Change: Inconsistencies in Reporting An alternative route that may be taken is to engage in honest debates about the issue, which will reduce alarmism and defeatism.
- Climate Change: The Chornobyl Nuclear Accident Also, I want to investigate the reasons behind the decision of the USSR government to conceal the truth and not let people save their lives.
Causes of Climate Change
Some experts claim that the current climate change might be a natural part of the cycle. However, it’s impossible to deny that greenhouse gas production has increased since the Industrial Revolution, speeding up the warming. The primary source of emissions is burning fossil fuels. Manufacturing goods, producing food, and using transportation are additional causes.
Climate Change Impacts on Ocean Life
Global warming is raising the average ocean temperature. This creates a cascading effect, starting with ice caps melting and raising sea levels, which means the planet absorbs more heat. In addition, warming leads to acidification that impacts ocean life. Unfortunately, this results in the loss of marine biodiversity.
Is Climate Change Affecting Animal Migrations?
Extreme weather conditions and unpredictable events affect animal migration patterns. Since over half of all species migrate, this phenomenon significantly impacts fauna. Due to the increased occurrence of hurricanes and floods, most animals go north and try to find higher ground. This puts some slower-moving species at risk.
Climate Change and the Role of Government
Implementing carbon taxes is one of the most popular methods of fighting climate change that governments use worldwide. It makes the most significant greenhouse gas producers pay for the damage they cause. Other ways of stopping climate change include international agreements, policies, and clean energy standards regarding renewable energy.
The Climate Change Mitigation Issues
The world’s dependence on fossil fuels is the biggest issue in fighting climate change. Another challenge is the increasing demand for minerals and metals, such as lithium. In addition, food systems need significant improvement, especially practices like recycling and regulating production to reduce food waste. These challenges are an opportunity for development.
- “World on the Edge”: Managing the Causes of Climate Change Brown’s main idea is to show the possibility of an extremely unfortunate outcome in the future as a result of the development of local agricultural problems – China, Iran, Mexico, Saudi Arabia, and others – […]
- The Straw Man Fallacy in the Topic of Climate Change The straw man fallacy is a type of logical fallacy whereby one person misrepresents their opponent’s question or argument to make it easier to respond.
- Gendering Climate Change: Geographical Insights In the given article, the author discusses the implications of climate change on gender and social relations and encourages scholars and activists to think critically and engage in debates on a global scale.
- Climate Change and Its Consequences for Oklahoma This concept can be defined as a rise in the Earth’s temperature due to anthropogenic activity, resulting in alteration of usual weather in various parts of the planet.
- Climate Change Impacts in Sub-Saharan Africa This is why I believe it is necessary to conduct careful, thorough research on why climate change is a threat to our planet and how to stop it.
- Climate Change: Global Warming Intensity Average temperatures on Earth are rising faster than at any time in the past 2,000 years, and the last five of them have been the hottest in the history of meteorological observations since 1850.
- The Negative Results of Climate Change Climate change refers to the rise of the sea due to hot oceans expanding and the melting of ice sheets and glaciers.
- Addressing Climate Change: The Collective Action Problem While all the nations agree that climate change is a source of substantial harm to the economy, the environment, and public health, not all countries have similar incentives for addressing the problem. Addressing the problem […]
- Health Issues on the Climate Change However, the mortality rate of air pollution in the United States is relatively low compared to the rest of the world.
- Collective Climate Change Responsibility The fact is that individuals are not the most critical contributors to the climate crisis, and while ditching the plastic straw might feel good on a personal level, it will not solve the situation.
- Climate Change and Challenges in Miami, Florida The issue of poor environment maintenance in Miami, Florida, has led to climate change, resulting in sea-level rise, an increase of flood levels, and droughts, and warmer temperatures in the area.
- Global Perspectives in the Climate Change Strategy It is required to provide an overview of those programs and schemes of actions that were used in the local, federal and global policies of the countries of the world to combat air pollution.
- Climate Change and Role of Government He considers that the forest’s preservation is vital, as it is the wellspring of our human well-being. As such, the legislature can pass policies that would contribute to safeguarding our nation’s well-being, but they do […]
- Climate Change as Systemic Risk of Globalization However, the integration became more complex and rapid over the years, making it systemic due to the higher number of internal connections.
- Impact of Climate Change on Increased Wildfires Over the past decades, America has experienced the most severe fires in its history regarding the coverage of affected areas and the cost of damage.
- Creating a Policy Briefing Book: Climate Change in China After that, a necessary step included the evaluation of the data gathered and the development of a summary that perfectly demonstrated the crucial points of this complication.
- Natural Climate Solutions for Climate Change in China The social system and its response to climate change are directly related to the well-being, economic status, and quality of life of the population.
- Climate Change and Limiting the Fuel-Powered Transportation When considering the options for limiting the extent of the usage of fuel-powered vehicles, one should pay attention to the use of personal vehicles and the propensity among most citizens to prefer diesel cars as […]
- Climate Change Laboratory Report To determine the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere causing global warming in the next ten decades, if the estimated rate of deforestation is maintained.
- Climate Change: Causes, Impact on People and the Environment Climate change is the alteration of the normal climatic conditions in the earth, and it occurs over some time. In as much as there are arguments based around the subject, it is mainly caused by […]
- Climate Change and Stabilization Wages The more the annual road activity indicates that more cars traversed throughout a fiscal year, the higher the size of the annual fuel consumption. The Carbon Capture and Storage technology can also reduce carbon emissions […]
- UK Climate Change Act 2008 The aim of the UK is to balance the levels of greenhouse gases to circumvent the perilous issue of climate change, as well as make it probable for people to acclimatize to an inevitable climate […]
- Sustainability, Climate Change Impact on Supply Chains & Circular Economy With recycling, reusing of materials, and collecting waste, industries help to fight ecological issues, which are the cause of climate change by saving nature’s integrity.
- Climate Change Indicators and Media Interference There is no certainty in the bright future for the Earth in the long-term perspective considering the devastating aftereffects that the phenomenon might bring. The indicators are essential to evaluate the scale of the growing […]
- Research Driven Critique: Steven Maher and Climate Change The ravaging effects of Covid-19 must not distract the world from the impending ramifications of severe environmental and climatic events that shaped the lives of a significant portion of the population in the past year.
- Climate Change: Sustainability Development and Environmental Law The media significantly contributes to the creation of awareness, thus the importance of integrating the role of the news press with sustainability practices.
- How Climate Change Affects Conflict and Peace The review looks at various works from different years on the environment, connections to conflict, and the impact of climate change.
- Toyota Corporation: The Effects of Climate Change on the Word’s Automobile Sector Considering the broad nature of the sector, the study has taken into account the case of Toyota Motor Corporation which is one of the firms operating within the sector.
- The Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture However, the move to introduce foreign species of grass such as Bermuda grass in the region while maintaining the native grass has been faced by challenges related to the fiscal importance of the production.
- Health and Climate Change Climate change, which is a universal problem, is thought to have devastating effects on human and animal health. However, the precise health effects are not known.
- The Issue of Climate Change The only confirmed facts are the impact of one’s culture and community on willingness to participate in environmental projects, and some people can refuse to join, thereby demonstrating their individuality.
- Climate Change as a Battle of Generation Z These issues have attracted the attention of the generation who they have identified climate change as the most challenging problem the world is facing today.
- Climate Change and Health in Nunavut, Canada Then, the authors tend to use strict and formal language while delivering their findings and ideas, which, again, is due to the scholarly character of the article. Thus, the article seems to have a good […]
- Climate Change: Anticipating Drastic Consequences Modern scientists focus on the problem of the climate change because of expecting the dramatic consequences of the process in the future.
- The Analysis of Process of Climate Change Dietz is the head of the Division of Nutrition and Physical Activity at the federal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta.
- Polar Bear Decline: Climate Change From Pole to Pole In comparison to 2005 where five of the populations were stable, it shows that there was a decline in stability of polar bear population.
- Preparing for the Impacts of Climate Change The three areas of interest that this report discusses are the impacts of climate change on social, economic and environmental fronts which are the key areas that have created a lot of debate and discussion […]
- Climate Change and Threat to Animals In the coming years, the increase in the global temperatures will make many living populations less able to adapt to the emergent conditions or to migrate to other regions that are suitable for their survival.
- Strategy for Garnering Effective Action on Climate Change Mitigation The approach should be participatory in that every member of the community is aware of ways that leads to climate change in order to take the necessary precaution measures. Many member nations have failed to […]
- Impact of Global Climate Change on Malaria There will be a comparison of the intensity of the changes to the magnitude of the impacts on malaria endemicity proposed within the future scenarios of the climate.
Check out the following essay ideas that will spark everyone’s interest:
- The difference between renewable and clean energy. Energy sources can be green but not renewable. For example, nuclear power doesn’t spread harmful waste if stored properly but doesn’t replenish itself. Compare different sources of energy regarding their type.
- What happens when fossil fuels are out? In the near future, some energy sources like oil and coal will run out. It’s inevitable, but people can prepare for it. What would be the best strategy? How fast can humanity switch to renewable energy sources?
- Radical changes to reduce carbon footprint. The energy sector contributes almost three-quarters of the total amount of emissions. This issue must be addressed as soon as possible to slow global warming. What would be the most significant change all countries in the world need to make?
- Solar panels in the deserts to power the whole planet: crazy idea or possible reality? Installing a field of solar panels big enough to power the entire planet seems unrealistic. However, it would require only a tiny part of the uninhabited land in Africa. Discuss this project from the perspective of physics and math
If you would like to write a paper about the effects of climate change on humanity, here are top-4 title ideas:
- People experiencing homelessness as a vulnerable group during the extreme heat waves. Climate change causes intense heat waves, especially in big cities. What does the government do to protect vulnerable groups, such as people without housing, in these conditions?
- Increased risk of allergies due to climate change. Climate change causes carbon dioxide levels to grow and temperatures to rise. In turn, this promotes airborne allergens, like ragweed pollen. Discuss what people with asthma can do to reduce risks to their health.
- Intestinal issues caused by power outages due to severe weather conditions. Weather patterns intensified by climate change trigger disruptions such as power outages. In addition, people often report intestinal and stomach illnesses after such events. Look into this issue using reliable sources.
- Can the spread of climate-sensitive diseases be reversed? Vector-borne diseases are linked to changes in humidity and temperature, which causes more drastic and widespread epidemics of illnesses, such as Lyme disease. Can preventative measures reverse this epidemic?
- Climate Change Economics: A Review of Greenstone and Oliver’s Analysis The article by Greenstone and Oliver indicates that the problem of global warming is one of the most perilous disasters whose effects are seen in low agricultural output, poor economic wellbeing of people, and high […]
- Rainforests of Victoria: Potential Effects of Climate Change The results of the research by Brooke in the year 2005 was examined to establish the actual impacts of climate change on the East Gippsland forest, especially for the fern specie.
- Pygmy-Possum Burramys Parvus: The Effects of Climate Change The study will be guided by the following research question: In what ways will the predicted loss of snow cover due to climate change influence the density and habitat use of the mountain pygmy-possum populations […]
- Climate Change and the Occurrence of Infectious Diseases This paper seeks to explore the nature of two vector-borne diseases, malaria, and dengue fever, in regards to the characteristics that would make them prone to effects of climate change, and to highlight some of […]
- Links Between Methane, Plants, and Climate Change According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, it is the anthropogenic activities that has increased the load of greenhouse gases since the mid-20th century that has resulted in global warming. It is only the […]
- United Nations Climate Change Conference In the Kyoto protocol, members agreed that nations needed to reduce the carbon emissions to levels that could not threaten the planet’s livelihoods.
- The Involve of Black People in the Seeking of Climate Change Whereas some researchers use the magnitude of pollution release as opposed to closeness to a hazardous site to define exposure, others utilize the dispersion of pollutants model to comprehend the link between exposure and population.
- Climate Change Dynamics: Are We Ready for the Future? One of the critical challenges of preparedness for future environmental changes is the uncertainty of how the climate system will change in several decades.
- How Climate Change Impacts Ocean Temperature and Marine Life The ocean’s surface consumes the excess heat from the air, which leads to significant issues in all of the planet’s ecosystems.
- Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation Plan for Abu Dhabi City, UAE Abu Dhabi is the capital city of the UAE and the Abu Dhabi Emirate and is located on a triangular island in the Persian Gulf.
- Climate Change in Communication Moreover, environmental reporting is not accurate and useful since profits influence and political interference affect the attainment of truthful, objective, and fair facts that would promote efficiency in newsrooms on environmental reporting.
- Global Pollution and Climate Change Both of these works address the topic of Global pollution, Global warming, and Climate change, which are relevant to the current situation in the world.
- Climate Change: The Key Issues An analysis of world literature indicates the emergence in recent years of a number of scientific publications on the medical and environmental consequences of global climate change.
- Climate Change Is a Scientific Fallacy Even in the worst-case scenario whereby the earth gives in and fails to support human activities, there can always be a way out.
- Climate Change: Change Up Your Approach People are becoming aware of the relevance of things and different aspects of their life, which is a positive trend. However, the share of this kind of energy will be reduced dramatically which is favorable […]
- Climate Change: The Broken Ozone Layer It explains the effects of climate change and the adaptation methods used. Vulnerability is basically the level of exposure and weakness of an aspect with regard to climate change.
- Climate Change and Economic Growth The graph displays the levels of the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and the years before our time with the number 0 being the year 1950.
- Tropic of Chaos: Climate Change and the New Geography of Violence The point of confluence in the cattle raids in East Africa and the planting of opium in the poor communities is the struggle to beat the effects of climatic changes.
- Personal Insight: Climate Change To my mind, economic implications are one of the most concerning because the economy is one of the pillars of modern society.
- A Shift From Climate Change Awareness Under New President Such statements raised concerns among American journalists and general population about the future of the organization as one of the main forces who advocated for the safe and healthy environment of Americans and the global […]
- Human Influence on Climate Change Climate changes are dangerous because they influence all the living creatures in the world. Thus, it is hard to overestimate the threat for humankind the climate changes represent.
- Environmental Studies: Climate Changes Ozone hole is related to forest loss in that the hole is caused by reaction of different chemicals that are found in the atmosphere and some of these gases, for example, the carbon dioxide gas […]
- Global Warming: Negative Effects to the Environment The effect was the greening of the environment and its transformation into habitable zones for humans The second system has been a consequence of the first, storage.
- Global Warming Problem Overview: Significantly Changing the Climate Patterns The government is not in a position to come up with specific costs that are attached to the extent of environmental pollution neither are the polluters aware about the costs that are attached to the […]
- Global Change Biology in Terms of Global Warming A risk assessment method showed that the current population could persist for at least 2000 years at hatchling sex ratios of up to 75% male.
- The Politics of Climate Change, Saving the Environment In the first article, the author expresses his concern with the problem of data utilization on climate change and negative consequences arising from this.
- Maize Production and Climate Change in South Africa Maize farming covers 58% of the crop area in South Africa and 60% of this is in drier areas of the country.
- Global Warming Issues Review and Environmental Sustainability Whether it is the melt down of Arctic ice, the damage of the Ozone layer, extra pollution in developing countries; all sums up to one thing in common and that is global warming.
- Global Warming: Ways to Help End Global Warming An innovative understanding of global warming has included it in the agenda of firms and governments. 5 trillion dollars are shouldering the responsibility of collecting and distributing information on the firms’ exposure to carbon emission-related […]
- Biofuels and Climate Change Developed countries are in the forefront to promote biofuels as a solution to the oil crisis and to a broader sense, the food crisis.
- The Influence of Global Warming and Pollution on the Environment This essay is going to address global warming from a psychological point of view with an emphasis on the psychological and social reasons that make it important to tackle this problem which is threatening the […]
- How Global Warming Has an Effect on Wildlife? According to one of the most detailed ecological studies of climate change, global warming is already directly affecting the lives of animals and plants living in various habitats across the world.
- Climate Change Risks in South Eastern Australia Some of the risks for agribusinesses in southeastern Australia are as discussed below Impacts on Australian agriculture of anticipated climate change are likely to be spatially and chronologically diverse, with many areas likely to experience […]
- The Politics and Economics of International Action on Climate Change The most important question is not whether nations can afford the cost and the risks incurred in reducing the emissions, but whether they can fail to act on the problem of emissions by way of […]
- Climate Change: Influence on Lifestyle in the Future My driving habits will change when the climate changes, and I will have to drive less, even though it can be avoided if environment-friendly cars are used.
- Global Warming and Effects Within 50 Years Global warming by few Scientists is often known as “climate change” the reason being is that according to the global warming is not the warming of earth it basically is the misbalance in climate.
- Climate Change During Socialism and Capitalistic Epochs The exclusion of utopian component of the first epoch socialism leading to capitalistic epoch is responsible for the current state of affairs in climate change hence creating the need for second epoch socialism Climate change […]
- Climate Change and Public Health Policies The US is one of the front emitters of carbon dioxide in the world and the current policies of the federal government that led to withdrawal from the Paris Agreement only worsen the situation.
- Climate Changes: Cause and Effect This, therefore, calls for appropriate discussions on the relationship between agroforestry and the improvement of climate conditions in arid and semi-arid regions of the world Urbanization also leads to the creation of the urban microclimate.
- Global Warming: Causes and Consequences Other definitions of global warming are “the increase in the average temperature of the Earth’s near-surface air and oceans since the mid-twentieth century and its projected continuation”.
Is Climate Change a Scientific Deception?
Despite the growing scientific evidence that global warming is real, some people still don’t believe it. They try to create controversy by bringing up unsupported arguments. For example, this community denies the role of humans in climate change and diminishes its adverse effects. The phenomenon is called climate change denial.
Wildfires and the Impact of Climate Change
Global warming leads to more heat waves, which dry out the soil and leaves and cause longer wildfire seasons. A lack of moisture and earlier spring melting also contribute to the issue because they reduce the amount of water available during summer.
How Does Overpopulation Influence Climate Change?
The main way overpopulation contributes to climate change is through resource demand. An increasing population means the need for more food, water, and energy. Agriculture expansion requires more land, which means deforestation. At the same time, vehicles and factories need fossil fuels that release carbon dioxide. All this contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and climate crisis.
Communication and Climate Change
Climate change communication aims to educate people about environmental issues and prompt them to take action. It is a field that raises discussion about the causes and effects of global warming. The experts’ primary concern is the barriers to understanding and creating change. Climate communication is developing new ways of talking to the audience.
Can People Lower the Global Temperature?
The biggest change people can make to help global warming is to switch to green and renewable energy sources. Burning fossil fuels is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, so using solar power would help. Reducing waste and planting more trees is something everyone can try to achieve.
- World Trade as the Adjustment Mechanism of Agriculture to Climate Change by Julia & Duchin
- Chad Frischmann: The Young Minds Solving Climate Change
- Public Health Education on Climate Change Effects
- Research Plan “Climate Change”
- Diets and Climate Change
- The Role of Human Activities on the Climate Change
- Climate Change Factors and Countermeasures
- Climate Change Effects on Population Health
- Climate Change: Who Is at Fault?
- Technological and Policy Solutions to Prevent Climate Change
- Climate Change: Reducing Industrial Air Pollution
- Global Climate Change and Biological Implications
- Weather Abnormalities and Climate Change
- Global Warming, Its Consequences and Prevention
- Climate Change and Risks for Business in Australia
- Climate Change Solutions for Australia
- “Climate Change May Destroy Alaskan Towns” Video
- Climate Change Effects on Kenya’s Tea Industry
- Environmental Perils: Climate Change Issue
- Technologically Produced Emissions Impact on Climate Change
- Climate Change and American National Security
- Climate Change, Air Pollution, Soil Degradation
- Climate Change in Canada
- Polar Transformations as a Global Warming Issue
- Technology’s Impact on Climate Change
- Global Warming and Climate Change: Fighting and Solutions
- Climate Change Debates and Scientific Opinion
- Earth’s Geologic History and Global Climate Change
- Geoengineering as a Possible Response to Climate Change
- Global Warming: People Impact on the Environment
- Climate Change Probability and Predictions
- Climate Change as International Issue
- Climate Change for Australian Magpie-Lark Birds
- Climate Change Effects on Ocean Acidification
- Climate Change Governance: Concepts and Theories
- Climate Change Impacts on the Aviation Industry
- Climate Change’s Negative Impact on Biodiversity
- United Nation and Climate Change
- Human Rights and Climate Change Policy-Making
- Climate Change: Anthropological Concepts and Perspectives
- Climate Change Impacts on Business in Bangladesh
- Pollution & Climate Change as Environmental Risks
- Climate Change: Nicholas Stern and Ross Garnaut Views
- Challenges Facing Humanity: Technology and Climate Change
- Climate Change Potential Consequences
- Climate Change in United Kingdom
- Climate Change From International Relations Perspective
- Climate Change and International Collaboration
- International Security and Climate Change
- Climate Change Effects on World Economy
- Energy Conservation for Solving Climate Change Problem
- Global Warming and Climate Change
- Responsible Factors for Climate Change
- The Role of Science and Technology in International Relations Regarding Climate Change
- The Effect of Science on Climate Change
- “Climate Change: Turning Up the Heat” by Barrie Pittock
- Vulnerability of World Countries to Climate Change
- Anthropogenic Climate Change
If you’re struggling to come up with new ideas for climate change essay topics, here’s a list of ideas for your inspiration:
- Policies related to climate change aren’t strict enough. Large businesses keep up with large amounts of emissions despite all the fees and policies against them. Will more restrictions help them switch to more environmentally friendly methods?
- Science has more arguments against climate change deniers. Many people believe global warming is a faux. However, the growing base of evidence proves them wrong. Compare the arguments of both sides.
- Reversing climate change: positive changes in the ozone hole. The worst state of the ozone hole was registered at the beginning of the 21st century. 20 years later, the hole has shrunk after many changes towards environmentally friendly practices. What should we do to keep up with the positive changes? How long will it take to reverse the damages from climate change completely?
- Teaching individual responsibility from kindergarten age . Significant changes start from every person individually. People should understand it and learn responsibility for the planet’s well-being from a young age. What should children learn about climate change in kindergarten and school?
- The Implementation of MOOCs on Climate Change
- The Climate Change and the Asset-Based Community Development
- Global Warming and Its Effects on the Environment
- Climate Change Research Studies
- Environmental Issue – Climate Change
- Climate Change Negative Health Impacts
- Early Climate Change Science
- Climate Change and Corporate World
- Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA) in Reducing the Effects of Climate Change
- Climate Change Affecting Coral Triangle Turtles
- Introduction to Climate Change: Major Threats and the Means to Avoid Them
- Climate Change and Its Effects on Indigenous Peoples
- Asian Drivers of Global Change
- The Causes and Effects of Climate Change in the US
- Metholdogy for Economic Discourse Analysis in Climate Change
- The Impact of Climate Change on New Hampshire Business
- Climate Change Effects on an Individual’s Life in the Future
- The Role of Behavioural Economics in Energy and Climate Policy
- The Economic Cost of Climate Change Effects
- Climate Change: Is Capitalism the Problem or the Solution?
- Climate Change: Floods in Queensland Australia
- Climate Change as a Global Security Threat
- Climate Change and Its Effects on Tourism in Coastal Areas
- Impact of Climate Change and Solutions
- Climate Change and Its Global Implications in Hospitality and Tourism
- Climate Change Needs Human Behavior Change
- The Negative Effects of Climate Change in Cities
- Negative Impacts of Climate Change in the Urban Areas and Possible Strategies to Address Them
- The United Nation’s Response to Climate Change
- Critical Review: “Food’s Footprint: Agriculture and Climate Change” by Jennifer Burney
- Global Warming: Justing Gillis Discussing Studies on Climate Change
- The Key Drivers of Climate Change
- Economics and Human Induced Climate Change
- Biology of Climate Change
- Business & Climate Change
- Global Warming Causes and Unfavorable Climatic Changes
- Spin, Science and Climate Change
- Climate Change, Coming Home: Global Warming’s Effects on Populations
- Social Concepts and Climate Change
- Climate Change and Human Health
- Climate Change: The Complex Issue of Global Warming
- Climate Changes: Human Activities and Global Warming
- Tourism and Climate Change Problem
- Public Awareness of Climate Changes and Carbon Footprints
- Problems of Climate Change
- Solving the Climate Change Crisis Through Development of Renewable Energy
- Climate Change Is the Biggest Challenge in the World That Affects the Flexibility of Individual Specie
- Climate Changes
- Ways to Reduce Global Warming
- Saving the Forest and Climate Changes
- Climate Change Definition and Causes
- Climate Change: Nearing a Mini Ice Age
- Global Warming Outcomes and Sea-Level Changes
- Climate Change: Causes and Effects
- China Climate Change
- Protecting Forests to Prevent Climate Change
- Climate Change in Saudi Arabia and Miami
- Effects of Global Warming on the Environment
You can use the following titles as examples if you’re out of ideas:
- Clean energy and business: can environmentally-friendly practices be profitable? Big corporations stick to the old-fashioned ways of powering their factories because it’s cheap. But can clean and green energy be profitable? Can people build businesses and save the planet at the same time?
- How do big corporations handle environmental regulations? Decision-making is already a difficult task for corporations controlling the market, and climate change regulations are adding extra work. What changes do they make? How does it affect the business?
- Environmentally friendly investors are the new climate activists. More and more investors are implementing eco-friendly ideas in corporations. Discuss how they can help change global warming issues by investing.
- Should people cancel greenwashing corporations? Greenwashing has become a new way for big corporations to follow climate change regulations while still gaining new customers. Talk about why it’s not the same as being environmentally friendly.
- Does Climate Change Affect Entrepreneurs?
- Does Climate Change Information Affect Stated Risks of Pine Beetle Impacts on Forests
- Does Energy Consumption Contribute to Climate Change?
- Does Forced Solidarity Hinder Adaptation to Climate Change?
- Does Risk Communication Really Decrease Cooperation in Climate Change Mitigation?
- Does Risk Perception Limit the Climate Change Mitigation Behaviors?
- What Are the Differences Between Climate Change and Global Warming?
- What Are the Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture in North East Central Europe?
- What Are the Policy Challenges That National Governments Face in Addressing Climate Change?
- What Are the Primary Causes of Climate Change?
- What Are the Risks of Climate Change and Global Warming?
- What Does Climate Change Mean for Agriculture in Developing Countries?
- What Drives the International Transfer of Climate Change Mitigation Technologies?
- What Economic Impacts Are Expected to Result From Climate Change?
- What Motivates Farmers’ Adaptation to Climate Change?
- What Natural Forces Have Caused Climate Change?
- What Problems Are Involved With Establishing an International Climate Change?
- What Role Has Human Activity Played in Causing Climate Change?
- Which Incentives Does Regulation Give to Adapt Network Infrastructure to Climate Change?
- Why Climate Change Affects Us?
- Why Does Climate Change Present Potential Dangers for the African Continent?
- Why Economic Analysis Supports Strong Action on Climate Change?
- Why Should People Care For the Perceived Event of Climate Change?
- Why the Climate Change Debate Has Not Created More Cleantech Funds in Sweden?
- Why Worry About Climate Change?
- Will African Agriculture Survive Climate Change?
- Will Carbon Tax Mitigate the Effects of Climate Change?
- Will Climate Change Affect Agriculture?
- Will Climate Change Cause Enormous Social Costs for Poor Asian Cities?
- Will Religion and Faith Be the Answer to Climate Change?
Here’s some advice on how to create a good title:
- Write your essay first. Building an argument and thesis statement are the steps that make the foundation for your title, so it’s best to take your time.
- Use your thesis as the basis for the title. It will better reflect your main idea.
- Take popular phrases as inspiration. Your title is the hook for your readers, so consider using idiomatic phrases they can relate to and get interested in your essay.
- Choose the appropriate tone. Serious scientific essays don’t go well with the informal style of the title and vice versa.
Here are some model essay titles you can use as inspiration:
- The Biggest Challenges of Adapting to Climate Change.
- What Renewable Energy Solutions Can We Expect in the Next 100 Years?
- Politics vs. Climate Change: How International Negotiations Get in the Way of Global Warming Solutions.
- Solutions to the Declining Biodiversity Due to Climate Change.
A climate change essay is familiar to most students who learn biology, ecology, and politics. In order to write a great essay on climate change, you need to explore the topic in great detail and show your understanding of it.
This article will provide you with some key points that you could use in your paper to make it engaging and compelling.
First of all, explore the factors contributing to climate change. Most people know that climate change is associated with pollution, but it is essential to examine the bigger picture. Consider the following questions:
- What is the mechanism by which climate change occurs?
- How do the activities of large corporations contribute to climate change?
- Why is the issue of deforestation essential to climate change?
- How do people’s daily activities promote climate change?
Secondly, you can focus on solutions to the problems outlined above.
Climate change essay topics often provide recommendations on how individuals and corporations could reduce their environmental impact. These questions may help to guide you through this section:
- How can large corporations decrease the influence of their operations on the environment?
- Can you think of any examples of corporations who have successfully decreased their environmental footprint?
- What steps can people take to reduce pollution and waste as part of their daily routine?
- Do you believe that trends such as reforestation and renewable energy will help to stop climate change? Why or why not?
- Can climate change be reversed at all, or is it an inescapable trend?
In connection with these topics, you could also discuss various government policies to address climate change. Over the past decades, many countries enacted laws to reduce environmental damage. There are plenty of ideas that you could address here:
- What are some famous national policies for environmental protection?
- Are laws and regulations effective in protecting the environment? Why or why not?
- How do environmentally-friendly policies affect individuals and businesses?
- Are there any climate change graphs that show the effectiveness of national policies for reducing environmental damage?
- How could government policies on climate change be improved?
Despite the fact that there is definite proof of climate change, the concept is opposed by certain politicians, business persons, and even scientists.
You could address the opposition to climate change in your essay and consider the following:
- Why do some people think that climate change is not real?
- What is the ultimate proof of climate change?
- Why is it beneficial for politicians and business persons to argue against climate change?
- Do you think that climate change is a real issue? Why or why not?
The impact of ecological damage on people, animals, and plants is the focus of most essay titles on global warming and climate change. Indeed, describing climate change effects in detail could earn you some extra marks. Use scholarly resources to research these climate change essay questions:
- How has climate change impacted wildlife already?
- If climate change advances at the same pace, what will be the consequences for people?
- Besides climate change, what are the impacts of water and air pollution? What does the recent United Nations report on climate change say about its effects?
- In your opinion, could climate change lead to the end of life on Earth? Why or why not?
Covering at least some of the points discussed in this post will help you write an excellent climate change paper! Don’t forget to search our website for more useful materials, including a climate change essay outline, sample papers, and much more!
- Flood Essay Topics
- Ecosystem Essay Topics
- Atmosphere Questions
- Extinction Research Topics
- Desert Research Ideas
- Greenhouse Gases Research Ideas
- Recycling Research Ideas
- Water Issues Research Ideas
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, November 20). 359 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/climate-change-essay-examples/
"359 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples." IvyPanda , 20 Nov. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/climate-change-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '359 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples'. 20 November.
IvyPanda . 2024. "359 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples." November 20, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/climate-change-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "359 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples." November 20, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/climate-change-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "359 Climate Change Research Topics & Examples." November 20, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/climate-change-essay-examples/.
Climate change, energy, environment and sustainability topics research guide
What is climate change.
Climate change refers to long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns. The world is now warming faster than at any point in recorded history, which disrupts the usual balance of nature and is a threat to human beings and other forms of life on Earth. This topic guide includes sample keywords and search terms, databases to find sources, and samples of online books.
Example keywords and subtopics
Example keywords or search terms:
- Climate change
- global warming
- greenhouse effect or greenhouse gas
- climate crisis
- environmental change
- clean energy
- alternative energy or renewable energy
- green energy or renewable energy or clean energy
- Low carbon or carbon neutral
- Carbon offsetting
- sustainability environment or sustainability
- environmental protection
- pollution or contamination
- impact or effect or influence
- cost or price or expense or money or financial
- fossil fuels or coal or oil or gas
Tip: This is a big topic with lots written so you can often focus on one or two subtopics. This will help to find more relevant sources, more quickly and be a better fit for an assignment.
Possible subtopics ideas: Pick one or two subtopics and then add those words to your search.
- Health impacts of climate changes (e.g. air pollution, water pollution, etc.)
- impacts on a specific city, state, region or country
- political impacts (e.g. voting, government policy, etc.)
- impact on specific population or culture (e.g. children, elderly, racial or ethic group, country, etc.)
- specific types of renewable or alternative energy (e.g. solar, wind, bio, etc.)
- example of new technology (e.g. electric cars or electric vehicles or hybrid vehicles
- economic impacts (e.g. business, employment, industry (e.g. oil, coal, etc.)
- weather and impacts (e.g. rising sea levels, flooding, droughts or heat waves, etc.)
- media aspects (e.g. news coverage, advertising, misinformation, movies, music, etc.)
- Tutorial: Creating an effective search strategy
- Use meaningful keywords to find the best sources
- Apply search strategies like AND and OR to connect keywords
- Tutorial: What is a library database and why should I use one?
- Identify what a library database is
- Recognize the two main types of library databases
- Know why you should use them
- Understand why searching a library database is different than searching the general internet
Databases for finding sources
Article Databases -
Use articles to find new research, specific information and evidence to support or refute a claim. You can also look at the bibliography or works cited to find additional sources. Some articles give an overview of a specific topic -- sometimes called "review articles" or "meta-analyses" or "systematic review." Databases are like mini-search engines for finding articles (e.g. Business Source Premier database searches business journals, business magazines and business newspapers). Pick a database that searches the subject of articles you want to find.
- Agricultural & Environmental Science Database Search journals and literature on agriculture, pollution, animals, environment, policy, natural resources, water issues and more. Searches tools like AGRICOLA, Environmental Sciences & Pollution Management (ESPM), and Digests of Environmental Impact Statements (EIS) databases.
- GreenFILE Collection of scholarly, government and general-interest titles. Multidisciplinary by nature, GreenFILE draws on the connections between the environment and agriculture, education, law, health and technology. Topics covered include global climate change, green building, pollution, sustainable agriculture, renewable energy, recycling, and more.
- Ethnic NewsWatch Ethnic NewsWatch is a current resource of full-text newspapers, magazines, and journals of the ethnic and minority press from 1990, providing researchers access to essential, often overlooked perspectives.
- Opposing Viewpoints in Context Find articles on current issues, including viewpoint articles, topic overviews, statistics, primary documents, magazine and newspaper articles.
Sample of online books
Below are a selection of online books and readings on the broad topic. We have more online books, journal articles, and sources in our Libraries Search and article databases.
- A climate policy revolution : what the science of complexity reveals about saving our planet by Roland Kupers ISBN: 9780674246812 Publication Date: 2020 "In this book, Roland Kupers argues that the climate crisis is well suited to the bottom-up, rapid, and revolutionary change complexity science theorizes; he succinctly makes the case that complexity science promises policy solutions to address climate change."
Get help from the U Libraries - Online!
- Peer Research Consultants Make an online 30 minute appointment for one-on-one peer assistance with your research. Get help with researching your topic, finding sources, citing sources and more. Peer Research Consultants can also help you get started with faculty-sponsored research.
- Chat 24/7 online with the Libraries Ask us anything! Chat with a librarian, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week with any research or library questions.
- Meet with a librarian Schedule an online consultations for personalized research support primarily for University of Minnesota faculty, instructors, graduate and undergraduate students and staff.
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

A review of the global climate change impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures
Kashif abbass, muhammad zeeshan qasim, huaming song, muntasir murshed, haider mahmood, ijaz younis.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues.
Corresponding author.
Received 2021 Aug 26; Accepted 2022 Mar 10; Issue date 2022.
This article is made available via the PMC Open Access Subset for unrestricted research re-use and secondary analysis in any form or by any means with acknowledgement of the original source. These permissions are granted for the duration of the World Health Organization (WHO) declaration of COVID-19 as a global pandemic.
Climate change is a long-lasting change in the weather arrays across tropics to polls. It is a global threat that has embarked on to put stress on various sectors. This study is aimed to conceptually engineer how climate variability is deteriorating the sustainability of diverse sectors worldwide. Specifically, the agricultural sector’s vulnerability is a globally concerning scenario, as sufficient production and food supplies are threatened due to irreversible weather fluctuations. In turn, it is challenging the global feeding patterns, particularly in countries with agriculture as an integral part of their economy and total productivity. Climate change has also put the integrity and survival of many species at stake due to shifts in optimum temperature ranges, thereby accelerating biodiversity loss by progressively changing the ecosystem structures. Climate variations increase the likelihood of particular food and waterborne and vector-borne diseases, and a recent example is a coronavirus pandemic. Climate change also accelerates the enigma of antimicrobial resistance, another threat to human health due to the increasing incidence of resistant pathogenic infections. Besides, the global tourism industry is devastated as climate change impacts unfavorable tourism spots. The methodology investigates hypothetical scenarios of climate variability and attempts to describe the quality of evidence to facilitate readers’ careful, critical engagement. Secondary data is used to identify sustainability issues such as environmental, social, and economic viability. To better understand the problem, gathered the information in this report from various media outlets, research agencies, policy papers, newspapers, and other sources. This review is a sectorial assessment of climate change mitigation and adaptation approaches worldwide in the aforementioned sectors and the associated economic costs. According to the findings, government involvement is necessary for the country’s long-term development through strict accountability of resources and regulations implemented in the past to generate cutting-edge climate policy. Therefore, mitigating the impacts of climate change must be of the utmost importance, and hence, this global threat requires global commitment to address its dreadful implications to ensure global sustenance.
Keywords: Climate change, COVID-19, Antimicrobial resistance, Biodiversity, Mitigation measures
Introduction
Worldwide observed and anticipated climatic changes for the twenty-first century and global warming are significant global changes that have been encountered during the past 65 years. Climate change (CC) is an inter-governmental complex challenge globally with its influence over various components of the ecological, environmental, socio-political, and socio-economic disciplines (Adger et al. 2005 ; Leal Filho et al. 2021 ; Feliciano et al. 2022 ). Climate change involves heightened temperatures across numerous worlds (Battisti and Naylor 2009 ; Schuurmans 2021 ; Weisheimer and Palmer 2005 ; Yadav et al. 2015 ). With the onset of the industrial revolution, the problem of earth climate was amplified manifold (Leppänen et al. 2014 ). It is reported that the immediate attention and due steps might increase the probability of overcoming its devastating impacts. It is not plausible to interpret the exact consequences of climate change (CC) on a sectoral basis (Izaguirre et al. 2021 ; Jurgilevich et al. 2017 ), which is evident by the emerging level of recognition plus the inclusion of climatic uncertainties at both local and national level of policymaking (Ayers et al. 2014 ).
Climate change is characterized based on the comprehensive long-haul temperature and precipitation trends and other components such as pressure and humidity level in the surrounding environment. Besides, the irregular weather patterns, retreating of global ice sheets, and the corresponding elevated sea level rise are among the most renowned international and domestic effects of climate change (Lipczynska-Kochany 2018 ; Michel et al. 2021 ; Murshed and Dao 2020 ). Before the industrial revolution, natural sources, including volcanoes, forest fires, and seismic activities, were regarded as the distinct sources of greenhouse gases (GHGs) such as CO 2 , CH 4 , N 2 O, and H 2 O into the atmosphere (Murshed et al. 2020 ; Hussain et al. 2020 ; Sovacool et al. 2021 ; Usman and Balsalobre-Lorente 2022 ; Murshed 2022 ). United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) struck a major agreement to tackle climate change and accelerate and intensify the actions and investments required for a sustainable low-carbon future at Conference of the Parties (COP-21) in Paris on December 12, 2015. The Paris Agreement expands on the Convention by bringing all nations together for the first time in a single cause to undertake ambitious measures to prevent climate change and adapt to its impacts, with increased funding to assist developing countries in doing so. As so, it marks a turning point in the global climate fight. The core goal of the Paris Agreement is to improve the global response to the threat of climate change by keeping the global temperature rise this century well below 2 °C over pre-industrial levels and to pursue efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5° C (Sharma et al. 2020 ; Sharif et al. 2020 ; Chien et al. 2021 .
Furthermore, the agreement aspires to strengthen nations’ ability to deal with the effects of climate change and align financing flows with low GHG emissions and climate-resilient paths (Shahbaz et al. 2019 ; Anwar et al. 2021 ; Usman et al. 2022a ). To achieve these lofty goals, adequate financial resources must be mobilized and provided, as well as a new technology framework and expanded capacity building, allowing developing countries and the most vulnerable countries to act under their respective national objectives. The agreement also establishes a more transparent action and support mechanism. All Parties are required by the Paris Agreement to do their best through “nationally determined contributions” (NDCs) and to strengthen these efforts in the coming years (Balsalobre-Lorente et al. 2020 ). It includes obligations that all Parties regularly report on their emissions and implementation activities. A global stock-take will be conducted every five years to review collective progress toward the agreement’s goal and inform the Parties’ future individual actions. The Paris Agreement became available for signature on April 22, 2016, Earth Day, at the United Nations Headquarters in New York. On November 4, 2016, it went into effect 30 days after the so-called double threshold was met (ratification by 55 nations accounting for at least 55% of world emissions). More countries have ratified and continue to ratify the agreement since then, bringing 125 Parties in early 2017. To fully operationalize the Paris Agreement, a work program was initiated in Paris to define mechanisms, processes, and recommendations on a wide range of concerns (Murshed et al. 2021 ). Since 2016, Parties have collaborated in subsidiary bodies (APA, SBSTA, and SBI) and numerous formed entities. The Conference of the Parties functioning as the meeting of the Parties to the Paris Agreement (CMA) convened for the first time in November 2016 in Marrakesh in conjunction with COP22 and made its first two resolutions. The work plan is scheduled to be finished by 2018. Some mitigation and adaptation strategies to reduce the emission in the prospective of Paris agreement are following firstly, a long-term goal of keeping the increase in global average temperature to well below 2 °C above pre-industrial levels, secondly, to aim to limit the rise to 1.5 °C, since this would significantly reduce risks and the impacts of climate change, thirdly, on the need for global emissions to peak as soon as possible, recognizing that this will take longer for developing countries, lastly, to undertake rapid reductions after that under the best available science, to achieve a balance between emissions and removals in the second half of the century. On the other side, some adaptation strategies are; strengthening societies’ ability to deal with the effects of climate change and to continue & expand international assistance for developing nations’ adaptation.
However, anthropogenic activities are currently regarded as most accountable for CC (Murshed et al. 2022 ). Apart from the industrial revolution, other anthropogenic activities include excessive agricultural operations, which further involve the high use of fuel-based mechanization, burning of agricultural residues, burning fossil fuels, deforestation, national and domestic transportation sectors, etc. (Huang et al. 2016 ). Consequently, these anthropogenic activities lead to climatic catastrophes, damaging local and global infrastructure, human health, and total productivity. Energy consumption has mounted GHGs levels concerning warming temperatures as most of the energy production in developing countries comes from fossil fuels (Balsalobre-Lorente et al. 2022 ; Usman et al. 2022b ; Abbass et al. 2021a ; Ishikawa-Ishiwata and Furuya 2022 ).
This review aims to highlight the effects of climate change in a socio-scientific aspect by analyzing the existing literature on various sectorial pieces of evidence globally that influence the environment. Although this review provides a thorough examination of climate change and its severe affected sectors that pose a grave danger for global agriculture, biodiversity, health, economy, forestry, and tourism, and to purpose some practical prophylactic measures and mitigation strategies to be adapted as sound substitutes to survive from climate change (CC) impacts. The societal implications of irregular weather patterns and other effects of climate changes are discussed in detail. Some numerous sustainable mitigation measures and adaptation practices and techniques at the global level are discussed in this review with an in-depth focus on its economic, social, and environmental aspects. Methods of data collection section are included in the supplementary information.
Review methodology
Related study and its objectives.
Today, we live an ordinary life in the beautiful digital, globalized world where climate change has a decisive role. What happens in one country has a massive influence on geographically far apart countries, which points to the current crisis known as COVID-19 (Sarkar et al. 2021 ). The most dangerous disease like COVID-19 has affected the world’s climate changes and economic conditions (Abbass et al. 2022 ; Pirasteh-Anosheh et al. 2021 ). The purpose of the present study is to review the status of research on the subject, which is based on “Global Climate Change Impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures” by systematically reviewing past published and unpublished research work. Furthermore, the current study seeks to comment on research on the same topic and suggest future research on the same topic. Specifically, the present study aims: The first one is, organize publications to make them easy and quick to find. Secondly, to explore issues in this area, propose an outline of research for future work. The third aim of the study is to synthesize the previous literature on climate change, various sectors, and their mitigation measurement. Lastly , classify the articles according to the different methods and procedures that have been adopted.
Review methodology for reviewers
This review-based article followed systematic literature review techniques that have proved the literature review as a rigorous framework (Benita 2021 ; Tranfield et al. 2003 ). Moreover, we illustrate in Fig. 1 the search method that we have started for this research. First, finalized the research theme to search literature (Cooper et al. 2018 ). Second, used numerous research databases to search related articles and download from the database (Web of Science, Google Scholar, Scopus Index Journals, Emerald, Elsevier Science Direct, Springer, and Sciverse). We focused on various articles, with research articles, feedback pieces, short notes, debates, and review articles published in scholarly journals. Reports used to search for multiple keywords such as “Climate Change,” “Mitigation and Adaptation,” “Department of Agriculture and Human Health,” “Department of Biodiversity and Forestry,” etc.; in summary, keyword list and full text have been made. Initially, the search for keywords yielded a large amount of literature.
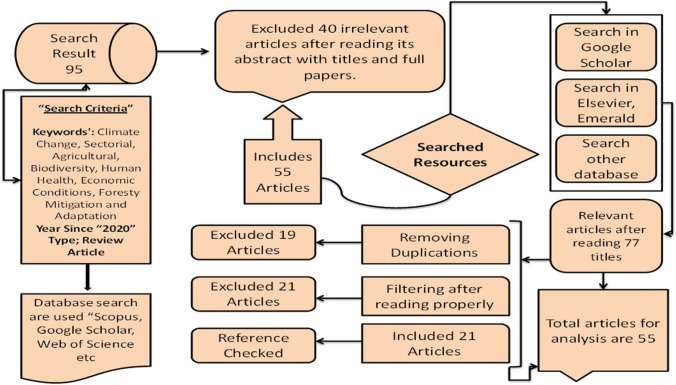
Methodology search for finalized articles for investigations.
Source : constructed by authors
Since 2020, it has been impossible to review all the articles found; some restrictions have been set for the literature exhibition. The study searched 95 articles on a different database mentioned above based on the nature of the study. It excluded 40 irrelevant papers due to copied from a previous search after readings tiles, abstract and full pieces. The criteria for inclusion were: (i) articles focused on “Global Climate Change Impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures,” and (ii) the search key terms related to study requirements. The complete procedure yielded 55 articles for our study. We repeat our search on the “Web of Science and Google Scholars” database to enhance the search results and check the referenced articles.
In this study, 55 articles are reviewed systematically and analyzed for research topics and other aspects, such as the methods, contexts, and theories used in these studies. Furthermore, this study analyzes closely related areas to provide unique research opportunities in the future. The study also discussed future direction opportunities and research questions by understanding the research findings climate changes and other affected sectors. The reviewed paper framework analysis process is outlined in Fig. 2 .
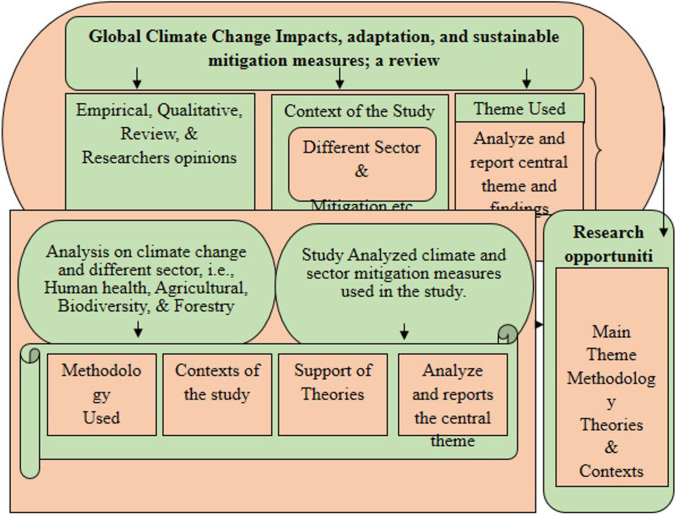
Framework of the analysis Process.
Natural disasters and climate change’s socio-economic consequences
Natural and environmental disasters can be highly variable from year to year; some years pass with very few deaths before a significant disaster event claims many lives (Symanski et al. 2021 ). Approximately 60,000 people globally died from natural disasters each year on average over the past decade (Ritchie and Roser 2014 ; Wiranata and Simbolon 2021 ). So, according to the report, around 0.1% of global deaths. Annual variability in the number and share of deaths from natural disasters in recent decades are shown in Fig. 3 . The number of fatalities can be meager—sometimes less than 10,000, and as few as 0.01% of all deaths. But shock events have a devastating impact: the 1983–1985 famine and drought in Ethiopia; the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami; Cyclone Nargis, which struck Myanmar in 2008; and the 2010 Port-au-Prince earthquake in Haiti and now recent example is COVID-19 pandemic (Erman et al. 2021 ). These events pushed global disaster deaths to over 200,000—more than 0.4% of deaths in these years. Low-frequency, high-impact events such as earthquakes and tsunamis are not preventable, but such high losses of human life are. Historical evidence shows that earlier disaster detection, more robust infrastructure, emergency preparedness, and response programmers have substantially reduced disaster deaths worldwide. Low-income is also the most vulnerable to disasters; improving living conditions, facilities, and response services in these areas would be critical in reducing natural disaster deaths in the coming decades.
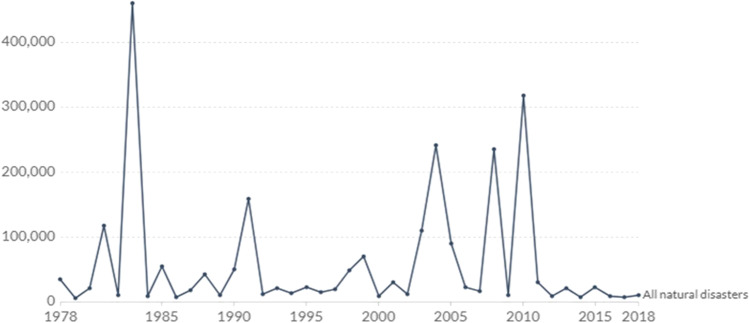
Global deaths from natural disasters, 1978 to 2020.
Source EMDAT ( 2020 )
The interior regions of the continent are likely to be impacted by rising temperatures (Dimri et al. 2018 ; Goes et al. 2020 ; Mannig et al. 2018 ; Schuurmans 2021 ). Weather patterns change due to the shortage of natural resources (water), increase in glacier melting, and rising mercury are likely to cause extinction to many planted species (Gampe et al. 2016 ; Mihiretu et al. 2021 ; Shaffril et al. 2018 ).On the other hand, the coastal ecosystem is on the verge of devastation (Perera et al. 2018 ; Phillips 2018 ). The temperature rises, insect disease outbreaks, health-related problems, and seasonal and lifestyle changes are persistent, with a strong probability of these patterns continuing in the future (Abbass et al. 2021c ; Hussain et al. 2018 ). At the global level, a shortage of good infrastructure and insufficient adaptive capacity are hammering the most (IPCC 2013 ). In addition to the above concerns, a lack of environmental education and knowledge, outdated consumer behavior, a scarcity of incentives, a lack of legislation, and the government’s lack of commitment to climate change contribute to the general public’s concerns. By 2050, a 2 to 3% rise in mercury and a drastic shift in rainfall patterns may have serious consequences (Huang et al. 2022 ; Gorst et al. 2018 ). Natural and environmental calamities caused huge losses globally, such as decreased agriculture outputs, rehabilitation of the system, and rebuilding necessary technologies (Ali and Erenstein 2017 ; Ramankutty et al. 2018 ; Yu et al. 2021 ) (Table 1 ). Furthermore, in the last 3 or 4 years, the world has been plagued by smog-related eye and skin diseases, as well as a rise in road accidents due to poor visibility.
Main natural danger statistics for 1985–2020 at the global level
Source: EM-DAT ( 2020 )
Climate change and agriculture
Global agriculture is the ultimate sector responsible for 30–40% of all greenhouse emissions, which makes it a leading industry predominantly contributing to climate warming and significantly impacted by it (Grieg; Mishra et al. 2021 ; Ortiz et al. 2021 ; Thornton and Lipper 2014 ). Numerous agro-environmental and climatic factors that have a dominant influence on agriculture productivity (Pautasso et al. 2012 ) are significantly impacted in response to precipitation extremes including floods, forest fires, and droughts (Huang 2004 ). Besides, the immense dependency on exhaustible resources also fuels the fire and leads global agriculture to become prone to devastation. Godfray et al. ( 2010 ) mentioned that decline in agriculture challenges the farmer’s quality of life and thus a significant factor to poverty as the food and water supplies are critically impacted by CC (Ortiz et al. 2021 ; Rosenzweig et al. 2014 ). As an essential part of the economic systems, especially in developing countries, agricultural systems affect the overall economy and potentially the well-being of households (Schlenker and Roberts 2009 ). According to the report published by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases, i.e., CH 4, CO 2 , and N 2 O, are increased in the air to extraordinary levels over the last few centuries (Usman and Makhdum 2021 ; Stocker et al. 2013 ). Climate change is the composite outcome of two different factors. The first is the natural causes, and the second is the anthropogenic actions (Karami 2012 ). It is also forecasted that the world may experience a typical rise in temperature stretching from 1 to 3.7 °C at the end of this century (Pachauri et al. 2014 ). The world’s crop production is also highly vulnerable to these global temperature-changing trends as raised temperatures will pose severe negative impacts on crop growth (Reidsma et al. 2009 ). Some of the recent modeling about the fate of global agriculture is briefly described below.
Decline in cereal productivity
Crop productivity will also be affected dramatically in the next few decades due to variations in integral abiotic factors such as temperature, solar radiation, precipitation, and CO 2 . These all factors are included in various regulatory instruments like progress and growth, weather-tempted changes, pest invasions (Cammell and Knight 1992 ), accompanying disease snags (Fand et al. 2012 ), water supplies (Panda et al. 2003 ), high prices of agro-products in world’s agriculture industry, and preeminent quantity of fertilizer consumption. Lobell and field ( 2007 ) claimed that from 1962 to 2002, wheat crop output had condensed significantly due to rising temperatures. Therefore, during 1980–2011, the common wheat productivity trends endorsed extreme temperature events confirmed by Gourdji et al. ( 2013 ) around South Asia, South America, and Central Asia. Various other studies (Asseng, Cao, Zhang, and Ludwig 2009 ; Asseng et al. 2013 ; García et al. 2015 ; Ortiz et al. 2021 ) also proved that wheat output is negatively affected by the rising temperatures and also caused adverse effects on biomass productivity (Calderini et al. 1999 ; Sadras and Slafer 2012 ). Hereafter, the rice crop is also influenced by the high temperatures at night. These difficulties will worsen because the temperature will be rising further in the future owing to CC (Tebaldi et al. 2006 ). Another research conducted in China revealed that a 4.6% of rice production per 1 °C has happened connected with the advancement in night temperatures (Tao et al. 2006 ). Moreover, the average night temperature growth also affected rice indicia cultivar’s output pragmatically during 25 years in the Philippines (Peng et al. 2004 ). It is anticipated that the increase in world average temperature will also cause a substantial reduction in yield (Hatfield et al. 2011 ; Lobell and Gourdji 2012 ). In the southern hemisphere, Parry et al. ( 2007 ) noted a rise of 1–4 °C in average daily temperatures at the end of spring season unti the middle of summers, and this raised temperature reduced crop output by cutting down the time length for phenophases eventually reduce the yield (Hatfield and Prueger 2015 ; R. Ortiz 2008 ). Also, world climate models have recommended that humid and subtropical regions expect to be plentiful prey to the upcoming heat strokes (Battisti and Naylor 2009 ). Grain production is the amalgamation of two constituents: the average weight and the grain output/m 2 , however, in crop production. Crop output is mainly accredited to the grain quantity (Araus et al. 2008 ; Gambín and Borrás 2010 ). In the times of grain set, yield resources are mainly strewn between hitherto defined components, i.e., grain usual weight and grain output, which presents a trade-off between them (Gambín and Borrás 2010 ) beside disparities in per grain integration (B. L. Gambín et al. 2006 ). In addition to this, the maize crop is also susceptible to raised temperatures, principally in the flowering stage (Edreira and Otegui 2013 ). In reality, the lower grain number is associated with insufficient acclimatization due to intense photosynthesis and higher respiration and the high-temperature effect on the reproduction phenomena (Edreira and Otegui 2013 ). During the flowering phase, maize visible to heat (30–36 °C) seemed less anthesis-silking intermissions (Edreira et al. 2011 ). Another research by Dupuis and Dumas ( 1990 ) proved that a drop in spikelet when directly visible to high temperatures above 35 °C in vitro pollination. Abnormalities in kernel number claimed by Vega et al. ( 2001 ) is related to conceded plant development during a flowering phase that is linked with the active ear growth phase and categorized as a critical phase for approximation of kernel number during silking (Otegui and Bonhomme 1998 ).
The retort of rice output to high temperature presents disparities in flowering patterns, and seed set lessens and lessens grain weight (Qasim et al. 2020 ; Qasim, Hammad, Maqsood, Tariq, & Chawla). During the daytime, heat directly impacts flowers which lessens the thesis period and quickens the earlier peak flowering (Tao et al. 2006 ). Antagonistic effect of higher daytime temperature d on pollen sprouting proposed seed set decay, whereas, seed set was lengthily reduced than could be explicated by pollen growing at high temperatures 40◦C (Matsui et al. 2001 ).
The decline in wheat output is linked with higher temperatures, confirmed in numerous studies (Semenov 2009 ; Stone and Nicolas 1994 ). High temperatures fast-track the arrangements of plant expansion (Blum et al. 2001 ), diminution photosynthetic process (Salvucci and Crafts‐Brandner 2004 ), and also considerably affect the reproductive operations (Farooq et al. 2011 ).
The destructive impacts of CC induced weather extremes to deteriorate the integrity of crops (Chaudhary et al. 2011 ), e.g., Spartan cold and extreme fog cause falling and discoloration of betel leaves (Rosenzweig et al. 2001 ), giving them a somehow reddish appearance, squeezing of lemon leaves (Pautasso et al. 2012 ), as well as root rot of pineapple, have reported (Vedwan and Rhoades 2001 ). Henceforth, in tackling the disruptive effects of CC, several short-term and long-term management approaches are the crucial need of time (Fig. 4 ). Moreover, various studies (Chaudhary et al. 2011 ; Patz et al. 2005 ; Pautasso et al. 2012 ) have demonstrated adapting trends such as ameliorating crop diversity can yield better adaptability towards CC.
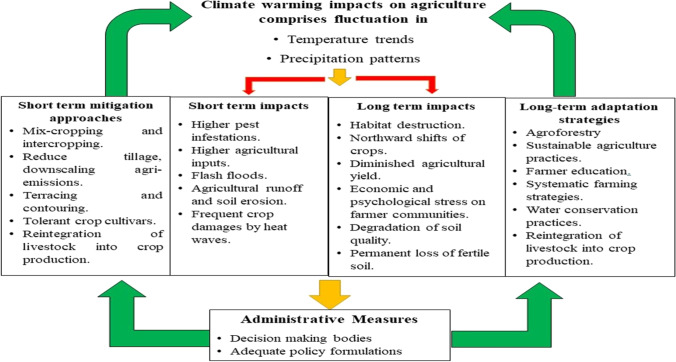
Schematic description of potential impacts of climate change on the agriculture sector and the appropriate mitigation and adaptation measures to overcome its impact.
Climate change impacts on biodiversity
Global biodiversity is among the severe victims of CC because it is the fastest emerging cause of species loss. Studies demonstrated that the massive scale species dynamics are considerably associated with diverse climatic events (Abraham and Chain 1988 ; Manes et al. 2021 ; A. M. D. Ortiz et al. 2021 ). Both the pace and magnitude of CC are altering the compatible habitat ranges for living entities of marine, freshwater, and terrestrial regions. Alterations in general climate regimes influence the integrity of ecosystems in numerous ways, such as variation in the relative abundance of species, range shifts, changes in activity timing, and microhabitat use (Bates et al. 2014 ). The geographic distribution of any species often depends upon its ability to tolerate environmental stresses, biological interactions, and dispersal constraints. Hence, instead of the CC, the local species must only accept, adapt, move, or face extinction (Berg et al. 2010 ). So, the best performer species have a better survival capacity for adjusting to new ecosystems or a decreased perseverance to survive where they are already situated (Bates et al. 2014 ). An important aspect here is the inadequate habitat connectivity and access to microclimates, also crucial in raising the exposure to climate warming and extreme heatwave episodes. For example, the carbon sequestration rates are undergoing fluctuations due to climate-driven expansion in the range of global mangroves (Cavanaugh et al. 2014 ).
Similarly, the loss of kelp-forest ecosystems in various regions and its occupancy by the seaweed turfs has set the track for elevated herbivory by the high influx of tropical fish populations. Not only this, the increased water temperatures have exacerbated the conditions far away from the physiological tolerance level of the kelp communities (Vergés et al. 2016 ; Wernberg et al. 2016 ). Another pertinent danger is the devastation of keystone species, which even has more pervasive effects on the entire communities in that habitat (Zarnetske et al. 2012 ). It is particularly important as CC does not specify specific populations or communities. Eventually, this CC-induced redistribution of species may deteriorate carbon storage and the net ecosystem productivity (Weed et al. 2013 ). Among the typical disruptions, the prominent ones include impacts on marine and terrestrial productivity, marine community assembly, and the extended invasion of toxic cyanobacteria bloom (Fossheim et al. 2015 ).
The CC-impacted species extinction is widely reported in the literature (Beesley et al. 2019 ; Urban 2015 ), and the predictions of demise until the twenty-first century are dreadful (Abbass et al. 2019 ; Pereira et al. 2013 ). In a few cases, northward shifting of species may not be formidable as it allows mountain-dwelling species to find optimum climates. However, the migrant species may be trapped in isolated and incompatible habitats due to losing topography and range (Dullinger et al. 2012 ). For example, a study indicated that the American pika has been extirpated or intensely diminished in some regions, primarily attributed to the CC-impacted extinction or at least local extirpation (Stewart et al. 2015 ). Besides, the anticipation of persistent responses to the impacts of CC often requires data records of several decades to rigorously analyze the critical pre and post CC patterns at species and ecosystem levels (Manes et al. 2021 ; Testa et al. 2018 ).
Nonetheless, the availability of such long-term data records is rare; hence, attempts are needed to focus on these profound aspects. Biodiversity is also vulnerable to the other associated impacts of CC, such as rising temperatures, droughts, and certain invasive pest species. For instance, a study revealed the changes in the composition of plankton communities attributed to rising temperatures. Henceforth, alterations in such aquatic producer communities, i.e., diatoms and calcareous plants, can ultimately lead to variation in the recycling of biological carbon. Moreover, such changes are characterized as a potential contributor to CO 2 differences between the Pleistocene glacial and interglacial periods (Kohfeld et al. 2005 ).
Climate change implications on human health
It is an understood corporality that human health is a significant victim of CC (Costello et al. 2009 ). According to the WHO, CC might be responsible for 250,000 additional deaths per year during 2030–2050 (Watts et al. 2015 ). These deaths are attributed to extreme weather-induced mortality and morbidity and the global expansion of vector-borne diseases (Lemery et al. 2021; Yang and Usman 2021 ; Meierrieks 2021 ; UNEP 2017 ). Here, some of the emerging health issues pertinent to this global problem are briefly described.
Climate change and antimicrobial resistance with corresponding economic costs
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is an up-surging complex global health challenge (Garner et al. 2019 ; Lemery et al. 2021 ). Health professionals across the globe are extremely worried due to this phenomenon that has critical potential to reverse almost all the progress that has been achieved so far in the health discipline (Gosling and Arnell 2016 ). A massive amount of antibiotics is produced by many pharmaceutical industries worldwide, and the pathogenic microorganisms are gradually developing resistance to them, which can be comprehended how strongly this aspect can shake the foundations of national and global economies (UNEP 2017 ). This statement is supported by the fact that AMR is not developing in a particular region or country. Instead, it is flourishing in every continent of the world (WHO 2018 ). This plague is heavily pushing humanity to the post-antibiotic era, in which currently antibiotic-susceptible pathogens will once again lead to certain endemics and pandemics after being resistant(WHO 2018 ). Undesirably, if this statement would become a factuality, there might emerge certain risks in undertaking sophisticated interventions such as chemotherapy, joint replacement cases, and organ transplantation (Su et al. 2018 ). Presently, the amplification of drug resistance cases has made common illnesses like pneumonia, post-surgical infections, HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria, etc., too difficult and costly to be treated or cure well (WHO 2018 ). From a simple example, it can be assumed how easily antibiotic-resistant strains can be transmitted from one person to another and ultimately travel across the boundaries (Berendonk et al. 2015 ). Talking about the second- and third-generation classes of antibiotics, e.g., most renowned generations of cephalosporin antibiotics that are more expensive, broad-spectrum, more toxic, and usually require more extended periods whenever prescribed to patients (Lemery et al. 2021 ; Pärnänen et al. 2019 ). This scenario has also revealed that the abundance of resistant strains of pathogens was also higher in the Southern part (WHO 2018 ). As southern parts are generally warmer than their counterparts, it is evident from this example how CC-induced global warming can augment the spread of antibiotic-resistant strains within the biosphere, eventually putting additional economic burden in the face of developing new and costlier antibiotics. The ARG exchange to susceptible bacteria through one of the potential mechanisms, transformation, transduction, and conjugation; Selection pressure can be caused by certain antibiotics, metals or pesticides, etc., as shown in Fig. 5 .
A typical interaction between the susceptible and resistant strains.
Source: Elsayed et al. ( 2021 ); Karkman et al. ( 2018 )
Certain studies highlighted that conventional urban wastewater treatment plants are typical hotspots where most bacterial strains exchange genetic material through horizontal gene transfer (Fig. 5 ). Although at present, the extent of risks associated with the antibiotic resistance found in wastewater is complicated; environmental scientists and engineers have particular concerns about the potential impacts of these antibiotic resistance genes on human health (Ashbolt 2015 ). At most undesirable and worst case, these antibiotic-resistant genes containing bacteria can make their way to enter into the environment (Pruden et al. 2013 ), irrigation water used for crops and public water supplies and ultimately become a part of food chains and food webs (Ma et al. 2019 ; D. Wu et al. 2019 ). This problem has been reported manifold in several countries (Hendriksen et al. 2019 ), where wastewater as a means of irrigated water is quite common.
Climate change and vector borne-diseases
Temperature is a fundamental factor for the sustenance of living entities regardless of an ecosystem. So, a specific living being, especially a pathogen, requires a sophisticated temperature range to exist on earth. The second essential component of CC is precipitation, which also impacts numerous infectious agents’ transport and dissemination patterns. Global rising temperature is a significant cause of many species extinction. On the one hand, this changing environmental temperature may be causing species extinction, and on the other, this warming temperature might favor the thriving of some new organisms. Here, it was evident that some pathogens may also upraise once non-evident or reported (Patz et al. 2000 ). This concept can be exemplified through certain pathogenic strains of microorganisms that how the likelihood of various diseases increases in response to climate warming-induced environmental changes (Table 2 ).
Examples of how various environmental changes affect various infectious diseases in humans
Source: Aron and Patz ( 2001 )
A recent example is an outburst of coronavirus (COVID-19) in the Republic of China, causing pneumonia and severe acute respiratory complications (Cui et al. 2021 ; Song et al. 2021 ). The large family of viruses is harbored in numerous animals, bats, and snakes in particular (livescience.com) with the subsequent transfer into human beings. Hence, it is worth noting that the thriving of numerous vectors involved in spreading various diseases is influenced by Climate change (Ogden 2018 ; Santos et al. 2021 ).
Psychological impacts of climate change
Climate change (CC) is responsible for the rapid dissemination and exaggeration of certain epidemics and pandemics. In addition to the vast apparent impacts of climate change on health, forestry, agriculture, etc., it may also have psychological implications on vulnerable societies. It can be exemplified through the recent outburst of (COVID-19) in various countries around the world (Pal 2021 ). Besides, the victims of this viral infection have made healthy beings scarier and terrified. In the wake of such epidemics, people with common colds or fever are also frightened and must pass specific regulatory protocols. Living in such situations continuously terrifies the public and makes the stress familiar, which eventually makes them psychologically weak (npr.org).
CC boosts the extent of anxiety, distress, and other issues in public, pushing them to develop various mental-related problems. Besides, frequent exposure to extreme climatic catastrophes such as geological disasters also imprints post-traumatic disorder, and their ubiquitous occurrence paves the way to developing chronic psychological dysfunction. Moreover, repetitive listening from media also causes an increase in the person’s stress level (Association 2020 ). Similarly, communities living in flood-prone areas constantly live in extreme fear of drowning and die by floods. In addition to human lives, the flood-induced destruction of physical infrastructure is a specific reason for putting pressure on these communities (Ogden 2018 ). For instance, Ogden ( 2018 ) comprehensively denoted that Katrina’s Hurricane augmented the mental health issues in the victim communities.
Climate change impacts on the forestry sector
Forests are the global regulators of the world’s climate (FAO 2018 ) and have an indispensable role in regulating global carbon and nitrogen cycles (Rehman et al. 2021 ; Reichstein and Carvalhais 2019 ). Hence, disturbances in forest ecology affect the micro and macro-climates (Ellison et al. 2017 ). Climate warming, in return, has profound impacts on the growth and productivity of transboundary forests by influencing the temperature and precipitation patterns, etc. As CC induces specific changes in the typical structure and functions of ecosystems (Zhang et al. 2017 ) as well impacts forest health, climate change also has several devastating consequences such as forest fires, droughts, pest outbreaks (EPA 2018 ), and last but not the least is the livelihoods of forest-dependent communities. The rising frequency and intensity of another CC product, i.e., droughts, pose plenty of challenges to the well-being of global forests (Diffenbaugh et al. 2017 ), which is further projected to increase soon (Hartmann et al. 2018 ; Lehner et al. 2017 ; Rehman et al. 2021 ). Hence, CC induces storms, with more significant impacts also put extra pressure on the survival of the global forests (Martínez-Alvarado et al. 2018 ), significantly since their influences are augmented during higher winter precipitations with corresponding wetter soils causing weak root anchorage of trees (Brázdil et al. 2018 ). Surging temperature regimes causes alterations in usual precipitation patterns, which is a significant hurdle for the survival of temperate forests (Allen et al. 2010 ; Flannigan et al. 2013 ), letting them encounter severe stress and disturbances which adversely affects the local tree species (Hubbart et al. 2016 ; Millar and Stephenson 2015 ; Rehman et al. 2021 ).
Climate change impacts on forest-dependent communities
Forests are the fundamental livelihood resource for about 1.6 billion people worldwide; out of them, 350 million are distinguished with relatively higher reliance (Bank 2008 ). Agro-forestry-dependent communities comprise 1.2 billion, and 60 million indigenous people solely rely on forests and their products to sustain their lives (Sunderlin et al. 2005 ). For example, in the entire African continent, more than 2/3rd of inhabitants depend on forest resources and woodlands for their alimonies, e.g., food, fuelwood and grazing (Wasiq and Ahmad 2004 ). The livings of these people are more intensely affected by the climatic disruptions making their lives harder (Brown et al. 2014 ). On the one hand, forest communities are incredibly vulnerable to CC due to their livelihoods, cultural and spiritual ties as well as socio-ecological connections, and on the other, they are not familiar with the term “climate change.” (Rahman and Alam 2016 ). Among the destructive impacts of temperature and rainfall, disruption of the agroforestry crops with resultant downscale growth and yield (Macchi et al. 2008 ). Cruz ( 2015 ) ascribed that forest-dependent smallholder farmers in the Philippines face the enigma of delayed fruiting, more severe damages by insect and pest incidences due to unfavorable temperature regimes, and changed rainfall patterns.
Among these series of challenges to forest communities, their well-being is also distinctly vulnerable to CC. Though the detailed climate change impacts on human health have been comprehensively mentioned in the previous section, some studies have listed a few more devastating effects on the prosperity of forest-dependent communities. For instance, the Himalayan people have been experiencing frequent skin-borne diseases such as malaria and other skin diseases due to increasing mosquitoes, wild boar as well, and new wasps species, particularly in higher altitudes that were almost non-existent before last 5–10 years (Xu et al. 2008 ). Similarly, people living at high altitudes in Bangladesh have experienced frequent mosquito-borne calamities (Fardous; Sharma 2012 ). In addition, the pace of other waterborne diseases such as infectious diarrhea, cholera, pathogenic induced abdominal complications and dengue has also been boosted in other distinguished regions of Bangladesh (Cell 2009 ; Gunter et al. 2008 ).
Pest outbreak
Upscaling hotter climate may positively affect the mobile organisms with shorter generation times because they can scurry from harsh conditions than the immobile species (Fettig et al. 2013 ; Schoene and Bernier 2012 ) and are also relatively more capable of adapting to new environments (Jactel et al. 2019 ). It reveals that insects adapt quickly to global warming due to their mobility advantages. Due to past outbreaks, the trees (forests) are relatively more susceptible victims (Kurz et al. 2008 ). Before CC, the influence of factors mentioned earlier, i.e., droughts and storms, was existent and made the forests susceptible to insect pest interventions; however, the global forests remain steadfast, assiduous, and green (Jactel et al. 2019 ). The typical reasons could be the insect herbivores were regulated by several tree defenses and pressures of predation (Wilkinson and Sherratt 2016 ). As climate greatly influences these phenomena, the global forests cannot be so sedulous against such challenges (Jactel et al. 2019 ). Table 3 demonstrates some of the particular considerations with practical examples that are essential while mitigating the impacts of CC in the forestry sector.
Essential considerations while mitigating the climate change impacts on the forestry sector
Source : Fischer ( 2019 )
Climate change impacts on tourism
Tourism is a commercial activity that has roots in multi-dimensions and an efficient tool with adequate job generation potential, revenue creation, earning of spectacular foreign exchange, enhancement in cross-cultural promulgation and cooperation, a business tool for entrepreneurs and eventually for the country’s national development (Arshad et al. 2018 ; Scott 2021 ). Among a plethora of other disciplines, the tourism industry is also a distinct victim of climate warming (Gössling et al. 2012 ; Hall et al. 2015 ) as the climate is among the essential resources that enable tourism in particular regions as most preferred locations. Different places at different times of the year attract tourists both within and across the countries depending upon the feasibility and compatibility of particular weather patterns. Hence, the massive variations in these weather patterns resulting from CC will eventually lead to monumental challenges to the local economy in that specific area’s particular and national economy (Bujosa et al. 2015 ). For instance, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report demonstrated that the global tourism industry had faced a considerable decline in the duration of ski season, including the loss of some ski areas and the dramatic shifts in tourist destinations’ climate warming.
Furthermore, different studies (Neuvonen et al. 2015 ; Scott et al. 2004 ) indicated that various currently perfect tourist spots, e.g., coastal areas, splendid islands, and ski resorts, will suffer consequences of CC. It is also worth noting that the quality and potential of administrative management potential to cope with the influence of CC on the tourism industry is of crucial significance, which renders specific strengths of resiliency to numerous destinations to withstand against it (Füssel and Hildén 2014 ). Similarly, in the partial or complete absence of adequate socio-economic and socio-political capital, the high-demanding tourist sites scurry towards the verge of vulnerability. The susceptibility of tourism is based on different components such as the extent of exposure, sensitivity, life-supporting sectors, and capacity assessment factors (Füssel and Hildén 2014 ). It is obvious corporality that sectors such as health, food, ecosystems, human habitat, infrastructure, water availability, and the accessibility of a particular region are prone to CC. Henceforth, the sensitivity of these critical sectors to CC and, in return, the adaptive measures are a hallmark in determining the composite vulnerability of climate warming (Ionescu et al. 2009 ).
Moreover, the dependence on imported food items, poor hygienic conditions, and inadequate health professionals are dominant aspects affecting the local terrestrial and aquatic biodiversity. Meanwhile, the greater dependency on ecosystem services and its products also makes a destination more fragile to become a prey of CC (Rizvi et al. 2015 ). Some significant non-climatic factors are important indicators of a particular ecosystem’s typical health and functioning, e.g., resource richness and abundance portray the picture of ecosystem stability. Similarly, the species abundance is also a productive tool that ensures that the ecosystem has a higher buffering capacity, which is terrific in terms of resiliency (Roscher et al. 2013 ).
Climate change impacts on the economic sector
Climate plays a significant role in overall productivity and economic growth. Due to its increasingly global existence and its effect on economic growth, CC has become one of the major concerns of both local and international environmental policymakers (Ferreira et al. 2020 ; Gleditsch 2021 ; Abbass et al. 2021b ; Lamperti et al. 2021 ). The adverse effects of CC on the overall productivity factor of the agricultural sector are therefore significant for understanding the creation of local adaptation policies and the composition of productive climate policy contracts. Previous studies on CC in the world have already forecasted its effects on the agricultural sector. Researchers have found that global CC will impact the agricultural sector in different world regions. The study of the impacts of CC on various agrarian activities in other demographic areas and the development of relative strategies to respond to effects has become a focal point for researchers (Chandioet al. 2020 ; Gleditsch 2021 ; Mosavi et al. 2020 ).
With the rapid growth of global warming since the 1980s, the temperature has started increasing globally, which resulted in the incredible transformation of rain and evaporation in the countries. The agricultural development of many countries has been reliant, delicate, and susceptible to CC for a long time, and it is on the development of agriculture total factor productivity (ATFP) influence different crops and yields of farmers (Alhassan 2021 ; Wu 2020 ).
Food security and natural disasters are increasing rapidly in the world. Several major climatic/natural disasters have impacted local crop production in the countries concerned. The effects of these natural disasters have been poorly controlled by the development of the economies and populations and may affect human life as well. One example is China, which is among the world’s most affected countries, vulnerable to natural disasters due to its large population, harsh environmental conditions, rapid CC, low environmental stability, and disaster power. According to the January 2016 statistical survey, China experienced an economic loss of 298.3 billion Yuan, and about 137 million Chinese people were severely affected by various natural disasters (Xie et al. 2018 ).

Mitigation and adaptation strategies of climate changes
Adaptation and mitigation are the crucial factors to address the response to CC (Jahanzad et al. 2020 ). Researchers define mitigation on climate changes, and on the other hand, adaptation directly impacts climate changes like floods. To some extent, mitigation reduces or moderates greenhouse gas emission, and it becomes a critical issue both economically and environmentally (Botzen et al. 2021 ; Jahanzad et al. 2020 ; Kongsager 2018 ; Smit et al. 2000 ; Vale et al. 2021 ; Usman et al. 2021 ; Verheyen 2005 ).
Researchers have deep concern about the adaptation and mitigation methodologies in sectoral and geographical contexts. Agriculture, industry, forestry, transport, and land use are the main sectors to adapt and mitigate policies(Kärkkäinen et al. 2020 ; Waheed et al. 2021 ). Adaptation and mitigation require particular concern both at the national and international levels. The world has faced a significant problem of climate change in the last decades, and adaptation to these effects is compulsory for economic and social development. To adapt and mitigate against CC, one should develop policies and strategies at the international level (Hussain et al. 2020 ). Figure 6 depicts the list of current studies on sectoral impacts of CC with adaptation and mitigation measures globally.
Sectoral impacts of climate change with adaptation and mitigation measures.
Conclusion and future perspectives
Specific socio-agricultural, socio-economic, and physical systems are the cornerstone of psychological well-being, and the alteration in these systems by CC will have disastrous impacts. Climate variability, alongside other anthropogenic and natural stressors, influences human and environmental health sustainability. Food security is another concerning scenario that may lead to compromised food quality, higher food prices, and inadequate food distribution systems. Global forests are challenged by different climatic factors such as storms, droughts, flash floods, and intense precipitation. On the other hand, their anthropogenic wiping is aggrandizing their existence. Undoubtedly, the vulnerability scale of the world’s regions differs; however, appropriate mitigation and adaptation measures can aid the decision-making bodies in developing effective policies to tackle its impacts. Presently, modern life on earth has tailored to consistent climatic patterns, and accordingly, adapting to such considerable variations is of paramount importance. Because the faster changes in climate will make it harder to survive and adjust, this globally-raising enigma calls for immediate attention at every scale ranging from elementary community level to international level. Still, much effort, research, and dedication are required, which is the most critical time. Some policy implications can help us to mitigate the consequences of climate change, especially the most affected sectors like the agriculture sector;
Seasonal variations and cultivation practices
Warming might lengthen the season in frost-prone growing regions (temperate and arctic zones), allowing for longer-maturing seasonal cultivars with better yields (Pfadenhauer 2020 ; Bonacci 2019 ). Extending the planting season may allow additional crops each year; when warming leads to frequent warmer months highs over critical thresholds, a split season with a brief summer fallow may be conceivable for short-period crops such as wheat barley, cereals, and many other vegetable crops. The capacity to prolong the planting season in tropical and subtropical places where the harvest season is constrained by precipitation or agriculture farming occurs after the year may be more limited and dependent on how precipitation patterns vary (Wu et al. 2017 ).
New varieties of crops
The genetic component is comprehensive for many yields, but it is restricted like kiwi fruit for a few. Ali et al. ( 2017 ) investigated how new crops will react to climatic changes (also stated in Mall et al. 2017 ). Hot temperature, drought, insect resistance; salt tolerance; and overall crop production and product quality increases would all be advantageous (Akkari 2016 ). Genetic mapping and engineering can introduce a greater spectrum of features. The adoption of genetically altered cultivars has been slowed, particularly in the early forecasts owing to the complexity in ensuring features are expediently expressed throughout the entire plant, customer concerns, economic profitability, and regulatory impediments (Wirehn 2018 ; Davidson et al. 2016 ).
Changes in management and other input factors
To get the full benefit of the CO 2 would certainly require additional nitrogen and other fertilizers. Nitrogen not consumed by the plants may be excreted into groundwater, discharged into water surface, or emitted from the land, soil nitrous oxide when large doses of fertilizer are sprayed. Increased nitrogen levels in groundwater sources have been related to human chronic illnesses and impact marine ecosystems. Cultivation, grain drying, and other field activities have all been examined in depth in the studies (Barua et al. 2018 ).
The technological and socio-economic adaptation
The policy consequence of the causative conclusion is that as a source of alternative energy, biofuel production is one of the routes that explain oil price volatility separate from international macroeconomic factors. Even though biofuel production has just begun in a few sample nations, there is still a tremendous worldwide need for feedstock to satisfy industrial expansion in China and the USA, which explains the food price relationship to the global oil price. Essentially, oil-exporting countries may create incentives in their economies to increase food production. It may accomplish by giving farmers financing, seedlings, fertilizers, and farming equipment. Because of the declining global oil price and, as a result, their earnings from oil export, oil-producing nations may be unable to subsidize food imports even in the near term. As a result, these countries can boost the agricultural value chain for export. It may be accomplished through R&D and adding value to their food products to increase income by correcting exchange rate misalignment and adverse trade terms. These nations may also diversify their economies away from oil, as dependence on oil exports alone is no longer economically viable given the extreme volatility of global oil prices. Finally, resource-rich and oil-exporting countries can convert to non-food renewable energy sources such as solar, hydro, coal, wind, wave, and tidal energy. By doing so, both world food and oil supplies would be maintained rather than harmed.
IRENA’s modeling work shows that, if a comprehensive policy framework is in place, efforts toward decarbonizing the energy future will benefit economic activity, jobs (outweighing losses in the fossil fuel industry), and welfare. Countries with weak domestic supply chains and a large reliance on fossil fuel income, in particular, must undertake structural reforms to capitalize on the opportunities inherent in the energy transition. Governments continue to give major policy assistance to extract fossil fuels, including tax incentives, financing, direct infrastructure expenditures, exemptions from environmental regulations, and other measures. The majority of major oil and gas producing countries intend to increase output. Some countries intend to cut coal output, while others plan to maintain or expand it. While some nations are beginning to explore and execute policies aimed at a just and equitable transition away from fossil fuel production, these efforts have yet to impact major producing countries’ plans and goals. Verifiable and comparable data on fossil fuel output and assistance from governments and industries are critical to closing the production gap. Governments could increase openness by declaring their production intentions in their climate obligations under the Paris Agreement.
It is firmly believed that achieving the Paris Agreement commitments is doubtlful without undergoing renewable energy transition across the globe (Murshed 2020 ; Zhao et al. 2022 ). Policy instruments play the most important role in determining the degree of investment in renewable energy technology. This study examines the efficacy of various policy strategies in the renewable energy industry of multiple nations. Although its impact is more visible in established renewable energy markets, a renewable portfolio standard is also a useful policy instrument. The cost of producing renewable energy is still greater than other traditional energy sources. Furthermore, government incentives in the R&D sector can foster innovation in this field, resulting in cost reductions in the renewable energy industry. These nations may export their technologies and share their policy experiences by forming networks among their renewable energy-focused organizations. All policy measures aim to reduce production costs while increasing the proportion of renewables to a country’s energy system. Meanwhile, long-term contracts with renewable energy providers, government commitment and control, and the establishment of long-term goals can assist developing nations in deploying renewable energy technology in their energy sector.
Author contribution
KA: Writing the original manuscript, data collection, data analysis, Study design, Formal analysis, Visualization, Revised draft, Writing-review, and editing. MZQ: Writing the original manuscript, data collection, data analysis, Writing-review, and editing. HS: Contribution to the contextualization of the theme, Conceptualization, Validation, Supervision, literature review, Revised drapt, and writing review and editing. MM: Writing review and editing, compiling the literature review, language editing. HM: Writing review and editing, compiling the literature review, language editing. IY: Contribution to the contextualization of the theme, literature review, and writing review and editing.
Availability of data and material
Data sources and relevant links are provided in the paper to access data.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Kashif Abbass, Email: [email protected].
Muhammad Zeeshan Qasim, Email: [email protected].
Huaming Song, Email: [email protected].
Muntasir Murshed, Email: [email protected].
Haider Mahmood, Email: [email protected].
Ijaz Younis, Email: [email protected].
- Abbass K, Begum H, Alam ASA, Awang AH, Abdelsalam MK, Egdair IMM, Wahid R (2022) Fresh Insight through a Keynesian Theory Approach to Investigate the Economic Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Pakistan. Sustain 14(3):1054
- Abbass K, Niazi AAK, Qazi TF, Basit A, Song H (2021a) The aftermath of COVID-19 pandemic period: barriers in implementation of social distancing at workplace. Library Hi Tech
- Abbass K, Song H, Khan F, Begum H, Asif M (2021b) Fresh insight through the VAR approach to investigate the effects of fiscal policy on environmental pollution in Pakistan. Environ Scie Poll Res 1–14 [ DOI ] [ PubMed ]
- Abbass K, Song H, Shah SM, Aziz B. Determinants of Stock Return for Non-Financial Sector: Evidence from Energy Sector of Pakistan. J Bus Fin Aff. 2019;8(370):2167–0234. [ Google Scholar ]
- Abbass K, Tanveer A, Huaming S, Khatiya AA (2021c) Impact of financial resources utilization on firm performance: a case of SMEs working in Pakistan
- Abraham E, Chain E. An enzyme from bacteria able to destroy penicillin. 1940. Rev Infect Dis. 1988;10(4):677. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Adger WN, Arnell NW, Tompkins EL. Successful adaptation to climate change across scales. Glob Environ Chang. 2005;15(2):77–86. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2004.12.005. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Akkari C, Bryant CR. The co-construction approach as approach to developing adaptation strategies in the face of climate change and variability: A conceptual framework. Agricultural Research. 2016;5(2):162–173. doi: 10.1007/s40003-016-0208-8. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Alhassan H (2021) The effect of agricultural total factor productivity on environmental degradation in sub-Saharan Africa. Sci Afr 12:e00740
- Ali A, Erenstein O. Assessing farmer use of climate change adaptation practices and impacts on food security and poverty in Pakistan. Clim Risk Manag. 2017;16:183–194. doi: 10.1016/j.crm.2016.12.001. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Allen CD, Macalady AK, Chenchouni H, Bachelet D, McDowell N, Vennetier M, Hogg ET. A global overview of drought and heat-induced tree mortality reveals emerging climate change risks for forests. For Ecol Manag. 2010;259(4):660–684. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2009.09.001. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anwar A, Sinha A, Sharif A, Siddique M, Irshad S, Anwar W, Malik S (2021) The nexus between urbanization, renewable energy consumption, financial development, and CO2 emissions: evidence from selected Asian countries. Environ Dev Sust. 10.1007/s10668-021-01716-2
- Araus JL, Slafer GA, Royo C, Serret MD. Breeding for yield potential and stress adaptation in cereals. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 2008;27(6):377–412. doi: 10.1080/07352680802467736. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aron JL, Patz J (2001) Ecosystem change and public health: a global perspective: JHU Press
- Arshad MI, Iqbal MA, Shahbaz M. Pakistan tourism industry and challenges: a review. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research. 2018;23(2):121–132. doi: 10.1080/10941665.2017.1410192. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ashbolt NJ. Microbial contamination of drinking water and human health from community water systems. Current Environmental Health Reports. 2015;2(1):95–106. doi: 10.1007/s40572-014-0037-5. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Asseng S, Cao W, Zhang W, Ludwig F (2009) Crop physiology, modelling and climate change: impact and adaptation strategies. Crop Physiol 511–543
- Asseng S, Ewert F, Rosenzweig C, Jones JW, Hatfield JL, Ruane AC, Cammarano D. Uncertainty in simulating wheat yields under climate change. Nat Clim Chang. 2013;3(9):827–832. doi: 10.1038/nclimate1916. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Association A (2020) Climate change is threatening mental health, American Psychological Association, “Kirsten Weir, . from < https://www.apa.org/monitor/2016/07-08/climate-change >, Accessed on 26 Jan 2020.
- Ayers J, Huq S, Wright H, Faisal A, Hussain S. Mainstreaming climate change adaptation into development in Bangladesh. Clim Dev. 2014;6:293–305. doi: 10.1080/17565529.2014.977761. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Balsalobre-Lorente D, Driha OM, Bekun FV, Sinha A, Adedoyin FF (2020) Consequences of COVID-19 on the social isolation of the Chinese economy: accounting for the role of reduction in carbon emissions. Air Qual Atmos Health 13(12):1439–1451
- Balsalobre-Lorente D, Ibáñez-Luzón L, Usman M, Shahbaz M. The environmental Kuznets curve, based on the economic complexity, and the pollution haven hypothesis in PIIGS countries. Renew Energy. 2022;185:1441–1455. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.10.059. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bank W (2008) Forests sourcebook: practical guidance for sustaining forests in development cooperation: World Bank
- Barua S, Valenzuela E (2018) Climate change impacts on global agricultural trade patterns: evidence from the past 50 years. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Sustainable Development (pp. 26–28)
- Bates AE, Pecl GT, Frusher S, Hobday AJ, Wernberg T, Smale DA, Colwell RK. Defining and observing stages of climate-mediated range shifts in marine systems. Glob Environ Chang. 2014;26:27–38. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2014.03.009. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Battisti DS, Naylor RL. Historical warnings of future food insecurity with unprecedented seasonal heat. Science. 2009;323(5911):240–244. doi: 10.1126/science.1164363. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Beesley L, Close PG, Gwinn DC, Long M, Moroz M, Koster WM, Storer T. Flow-mediated movement of freshwater catfish, Tandanus bostocki, in a regulated semi-urban river, to inform environmental water releases. Ecol Freshw Fish. 2019;28(3):434–445. doi: 10.1111/eff.12466. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Benita F (2021) Human mobility behavior in COVID-19: A systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis. Sustain Cities Soc 70:102916 [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Berendonk TU, Manaia CM, Merlin C, Fatta-Kassinos D, Cytryn E, Walsh F, Pons M-N. Tackling antibiotic resistance: the environmental framework. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015;13(5):310–317. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3439. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Berg MP, Kiers ET, Driessen G, Van DerHEIJDEN M, Kooi BW, Kuenen F, Ellers J. Adapt or disperse: understanding species persistence in a changing world. Glob Change Biol. 2010;16(2):587–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.02014.x. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Blum A, Klueva N, Nguyen H. Wheat cellular thermotolerance is related to yield under heat stress. Euphytica. 2001;117(2):117–123. doi: 10.1023/A:1004083305905. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bonacci O. Air temperature and precipitation analyses on a small Mediterranean island: the case of the remote island of Lastovo (Adriatic Sea, Croatia) Acta Hydrotechnica. 2019;32(57):135–150. doi: 10.15292/acta.hydro.2019.10. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Botzen W, Duijndam S, van Beukering P (2021) Lessons for climate policy from behavioral biases towards COVID-19 and climate change risks. World Dev 137:105214 [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Brázdil R, Stucki P, Szabó P, Řezníčková L, Dolák L, Dobrovolný P, Suchánková S. Windstorms and forest disturbances in the Czech Lands: 1801–2015. Agric for Meteorol. 2018;250:47–63. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2017.11.036. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brown HCP, Smit B, Somorin OA, Sonwa DJ, Nkem JN. Climate change and forest communities: prospects for building institutional adaptive capacity in the Congo Basin forests. Ambio. 2014;43(6):759–769. doi: 10.1007/s13280-014-0493-z. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bujosa A, Riera A, Torres CM. Valuing tourism demand attributes to guide climate change adaptation measures efficiently: the case of the Spanish domestic travel market. Tour Manage. 2015;47:233–239. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2014.09.023. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Calderini D, Abeledo L, Savin R, Slafer GA. Effect of temperature and carpel size during pre-anthesis on potential grain weight in wheat. J Agric Sci. 1999;132(4):453–459. doi: 10.1017/S0021859699006504. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cammell M, Knight J. Effects of climatic change on the population dynamics of crop pests. Adv Ecol Res. 1992;22:117–162. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2504(08)60135-X. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cavanaugh KC, Kellner JR, Forde AJ, Gruner DS, Parker JD, Rodriguez W, Feller IC. Poleward expansion of mangroves is a threshold response to decreased frequency of extreme cold events. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014;111(2):723–727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1315800111. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cell CC (2009) Climate change and health impacts in Bangladesh. Clima Chang Cell DoE MoEF
- Chandio AA, Jiang Y, Rehman A, Rauf A (2020) Short and long-run impacts of climate change on agriculture: an empirical evidence from China. Int J Clim Chang Strat Manag
- Chaudhary P, Rai S, Wangdi S, Mao A, Rehman N, Chettri S, Bawa KS (2011) Consistency of local perceptions of climate change in the Kangchenjunga Himalaya landscape. Curr Sci 504–513
- Chien F, Anwar A, Hsu CC, Sharif A, Razzaq A, Sinha A (2021) The role of information and communication technology in encountering environmental degradation: proposing an SDG framework for the BRICS countries. Technol Soc 65:101587
- Cooper C, Booth A, Varley-Campbell J, Britten N, Garside R. Defining the process to literature searching in systematic reviews: a literature review of guidance and supporting studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018;18(1):1–14. doi: 10.1186/s12874-018-0545-3. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Costello A, Abbas M, Allen A, Ball S, Bell S, Bellamy R, Kett M. Managing the health effects of climate change: lancet and University College London Institute for Global Health Commission. The Lancet. 2009;373(9676):1693–1733. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60935-1. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cruz DLA (2015) Mother Figured. University of Chicago Press. Retrieved from, 10.7208/9780226315072
- Cui W, Ouyang T, Qiu Y, Cui D (2021) Literature Review of the Implications of Exercise Rehabilitation Strategies for SARS Patients on the Recovery of COVID-19 Patients. Paper presented at the Healthcare [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Davidson D. Gaps in agricultural climate adaptation research. Nat Clim Chang. 2016;6(5):433–435. doi: 10.1038/nclimate3007. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Diffenbaugh NS, Singh D, Mankin JS, Horton DE, Swain DL, Touma D, Tsiang M. Quantifying the influence of global warming on unprecedented extreme climate events. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2017;114(19):4881–4886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1618082114. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dimri A, Kumar D, Choudhary A, Maharana P. Future changes over the Himalayas: mean temperature. Global Planet Change. 2018;162:235–251. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2018.01.014. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dullinger S, Gattringer A, Thuiller W, Moser D, Zimmermann N, Guisan A. Extinction debt of high-mountain plants under twenty-first-century climate change. Nat Clim Chang: Nature Publishing Group; 2012. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dupuis I, Dumas C. Influence of temperature stress on in vitro fertilization and heat shock protein synthesis in maize (Zea mays L.) reproductive tissues. Plant Physiol. 1990;94(2):665–670. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.2.665. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Edreira JR, Otegui ME. Heat stress in temperate and tropical maize hybrids: a novel approach for assessing sources of kernel loss in field conditions. Field Crop Res. 2013;142:58–67. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2012.11.009. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Edreira JR, Carpici EB, Sammarro D, Otegui M. Heat stress effects around flowering on kernel set of temperate and tropical maize hybrids. Field Crop Res. 2011;123(2):62–73. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2011.04.015. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ellison D, Morris CE, Locatelli B, Sheil D, Cohen J, Murdiyarso D, Pokorny J. Trees, forests and water: Cool insights for a hot world. Glob Environ Chang. 2017;43:51–61. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2017.01.002. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elsayed ZM, Eldehna WM, Abdel-Aziz MM, El Hassab MA, Elkaeed EB, Al-Warhi T, Mohammed ER. Development of novel isatin–nicotinohydrazide hybrids with potent activity against susceptible/resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis and bronchitis causing–bacteria. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021;36(1):384–393. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2020.1868450. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- EM-DAT (2020) EMDAT: OFDA/CRED International Disaster Database, Université catholique de Louvain – Brussels – Belgium. from http://www.emdat.be
- EPA U (2018) United States Environmental Protection Agency, EPA Year in Review
- Erman A, De Vries Robbe SA, Thies SF, Kabir K, Maruo M (2021) Gender Dimensions of Disaster Risk and Resilience
- Fand BB, Kamble AL, Kumar M. Will climate change pose serious threat to crop pest management: a critical review. Int J Sci Res Publ. 2012;2(11):1–14. [ Google Scholar ]
- FAO (2018).The State of the World’s Forests 2018 - Forest Pathways to Sustainable Development.
- Fardous S Perception of climate change in Kaptai National Park. Rural Livelihoods and Protected Landscape: Co-Management in the Wetlands and Forests of Bangladesh, 186–204
- Farooq M, Bramley H, Palta JA, Siddique KH. Heat stress in wheat during reproductive and grain-filling phases. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 2011;30(6):491–507. doi: 10.1080/07352689.2011.615687. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Feliciano D, Recha J, Ambaw G, MacSween K, Solomon D, Wollenberg E (2022) Assessment of agricultural emissions, climate change mitigation and adaptation practices in Ethiopia. Clim Policy 1–18
- Ferreira JJ, Fernandes CI, Ferreira FA (2020) Technology transfer, climate change mitigation, and environmental patent impact on sustainability and economic growth: a comparison of European countries. Technol Forecast Soc Change 150:119770
- Fettig CJ, Reid ML, Bentz BJ, Sevanto S, Spittlehouse DL, Wang T. Changing climates, changing forests: a western North American perspective. J Forest. 2013;111(3):214–228. doi: 10.5849/jof.12-085. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fischer AP. Characterizing behavioral adaptation to climate change in temperate forests. Landsc Urban Plan. 2019;188:72–79. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2018.09.024. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Flannigan M, Cantin AS, De Groot WJ, Wotton M, Newbery A, Gowman LM. Global wildland fire season severity in the 21st century. For Ecol Manage. 2013;294:54–61. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2012.10.022. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fossheim M, Primicerio R, Johannesen E, Ingvaldsen RB, Aschan MM, Dolgov AV. Recent warming leads to a rapid borealization of fish communities in the Arctic. Nat Clim Chang. 2015;5(7):673–677. doi: 10.1038/nclimate2647. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Füssel HM, Hildén M (2014) How is uncertainty addressed in the knowledge base for national adaptation planning? Adapting to an Uncertain Climate (pp. 41–66): Springer
- Gambín BL, Borrás L, Otegui ME. Source–sink relations and kernel weight differences in maize temperate hybrids. Field Crop Res. 2006;95(2–3):316–326. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2005.04.002. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gambín B, Borrás L. Resource distribution and the trade-off between seed number and seed weight: a comparison across crop species. Annals of Applied Biology. 2010;156(1):91–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7348.2009.00367.x. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gampe D, Nikulin G, Ludwig R. Using an ensemble of regional climate models to assess climate change impacts on water scarcity in European river basins. Sci Total Environ. 2016;573:1503–1518. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.08.053. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- García GA, Dreccer MF, Miralles DJ, Serrago RA. High night temperatures during grain number determination reduce wheat and barley grain yield: a field study. Glob Change Biol. 2015;21(11):4153–4164. doi: 10.1111/gcb.13009. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Garner E, Inyang M, Garvey E, Parks J, Glover C, Grimaldi A, Edwards MA. Impact of blending for direct potable reuse on premise plumbing microbial ecology and regrowth of opportunistic pathogens and antibiotic resistant bacteria. Water Res. 2019;151:75–86. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.12.003. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gleditsch NP (2021) This time is different! Or is it? NeoMalthusians and environmental optimists in the age of climate change. J Peace Res 0022343320969785
- Godfray HCJ, Beddington JR, Crute IR, Haddad L, Lawrence D, Muir JF, Toulmin C. Food security: the challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science. 2010;327(5967):812–818. doi: 10.1126/science.1185383. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Goes S, Hasterok D, Schutt DL, Klöcking M (2020) Continental lithospheric temperatures: A review. Phys Earth Planet Inter 106509
- Gorst A, Dehlavi A, Groom B. Crop productivity and adaptation to climate change in Pakistan. Environ Dev Econ. 2018;23(6):679–701. doi: 10.1017/S1355770X18000232. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gosling SN, Arnell NW. A global assessment of the impact of climate change on water scarcity. Clim Change. 2016;134(3):371–385. doi: 10.1007/s10584-013-0853-x. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gössling S, Scott D, Hall CM, Ceron J-P, Dubois G. Consumer behaviour and demand response of tourists to climate change. Ann Tour Res. 2012;39(1):36–58. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2011.11.002. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gourdji SM, Sibley AM, Lobell DB. Global crop exposure to critical high temperatures in the reproductive period: historical trends and future projections. Environ Res Lett. 2013;8(2):024041. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/8/2/024041. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Grieg E Responsible Consumption and Production
- Gunter BG, Rahman A, Rahman A (2008) How Vulnerable are Bangladesh’s Indigenous People to Climate Change? Bangladesh Development Research Center (BDRC)
- Hall CM, Amelung B, Cohen S, Eijgelaar E, Gössling S, Higham J, Scott D. On climate change skepticism and denial in tourism. J Sustain Tour. 2015;23(1):4–25. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2014.953544. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hartmann H, Moura CF, Anderegg WR, Ruehr NK, Salmon Y, Allen CD, Galbraith D. Research frontiers for improving our understanding of drought-induced tree and forest mortality. New Phytol. 2018;218(1):15–28. doi: 10.1111/nph.15048. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hatfield JL, Prueger JH. Temperature extremes: Effect on plant growth and development. Weather and Climate Extremes. 2015;10:4–10. doi: 10.1016/j.wace.2015.08.001. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hatfield JL, Boote KJ, Kimball B, Ziska L, Izaurralde RC, Ort D, Wolfe D. Climate impacts on agriculture: implications for crop production. Agron J. 2011;103(2):351–370. doi: 10.2134/agronj2010.0303. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hendriksen RS, Munk P, Njage P, Van Bunnik B, McNally L, Lukjancenko O, Kjeldgaard J. Global monitoring of antimicrobial resistance based on metagenomics analyses of urban sewage. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1124. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08853-3. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Huang S (2004) Global trade patterns in fruits and vegetables. USDA-ERS Agriculture and Trade Report No. WRS-04–06
- Huang W, Gao Q-X, Cao G-L, Ma Z-Y, Zhang W-D, Chao Q-C. Effect of urban symbiosis development in China on GHG emissions reduction. Adv Clim Chang Res. 2016;7(4):247–252. doi: 10.1016/j.accre.2016.12.003. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Huang Y, Haseeb M, Usman M, Ozturk I (2022) Dynamic association between ICT, renewable energy, economic complexity and ecological footprint: Is there any difference between E-7 (developing) and G-7 (developed) countries? Tech Soc 68:101853
- Hubbart JA, Guyette R, Muzika R-M. More than drought: precipitation variance, excessive wetness, pathogens and the future of the western edge of the eastern deciduous forest. Sci Total Environ. 2016;566:463–467. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.05.108. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hussain M, Butt AR, Uzma F, Ahmed R, Irshad S, Rehman A, Yousaf B. A comprehensive review of climate change impacts, adaptation, and mitigation on environmental and natural calamities in Pakistan. Environ Monit Assess. 2020;192(1):48. doi: 10.1007/s10661-019-7956-4. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hussain M, Liu G, Yousaf B, Ahmed R, Uzma F, Ali MU, Butt AR. Regional and sectoral assessment on climate-change in Pakistan: social norms and indigenous perceptions on climate-change adaptation and mitigation in relation to global context. J Clean Prod. 2018;200:791–808. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.272. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Intergov. Panel Clim Chang 33 from 10.1017/CBO9781107415324
- Ionescu C, Klein RJ, Hinkel J, Kumar KK, Klein R. Towards a formal framework of vulnerability to climate change. Environ Model Assess. 2009;14(1):1–16. doi: 10.1007/s10666-008-9179-x. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- IPCC (2013) Summary for policymakers. Clim Chang Phys Sci Basis Contrib Work Gr I Fifth Assess Rep
- Ishikawa-Ishiwata Y, Furuya J (2022) Economic evaluation and climate change adaptation measures for rice production in vietnam using a supply and demand model: special emphasis on the Mekong River Delta region in Vietnam. In Interlocal Adaptations to Climate Change in East and Southeast Asia (pp. 45–53). Springer, Cham
- Izaguirre C, Losada I, Camus P, Vigh J, Stenek V. Climate change risk to global port operations. Nat Clim Chang. 2021;11(1):14–20. doi: 10.1038/s41558-020-00937-z. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jactel H, Koricheva J, Castagneyrol B (2019) Responses of forest insect pests to climate change: not so simple. Current opinion in insect science [ DOI ] [ PubMed ]
- Jahanzad E, Holtz BA, Zuber CA, Doll D, Brewer KM, Hogan S, Gaudin AC. Orchard recycling improves climate change adaptation and mitigation potential of almond production systems. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(3):e0229588. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229588. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jurgilevich A, Räsänen A, Groundstroem F, Juhola S. A systematic review of dynamics in climate risk and vulnerability assessments. Environ Res Lett. 2017;12(1):013002. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/aa5508. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Karami E (2012) Climate change, resilience and poverty in the developing world. Paper presented at the Culture, Politics and Climate change conference
- Kärkkäinen L, Lehtonen H, Helin J, Lintunen J, Peltonen-Sainio P, Regina K, . . . Packalen T (2020) Evaluation of policy instruments for supporting greenhouse gas mitigation efforts in agricultural and urban land use. Land Use Policy 99:104991
- Karkman A, Do TT, Walsh F, Virta MP. Antibiotic-resistance genes in waste water. Trends Microbiol. 2018;26(3):220–228. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.09.005. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kohfeld KE, Le Quéré C, Harrison SP, Anderson RF. Role of marine biology in glacial-interglacial CO2 cycles. Science. 2005;308(5718):74–78. doi: 10.1126/science.1105375. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kongsager R. Linking climate change adaptation and mitigation: a review with evidence from the land-use sectors. Land. 2018;7(4):158. doi: 10.3390/land7040158. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kurz WA, Dymond C, Stinson G, Rampley G, Neilson E, Carroll A, Safranyik L. Mountain pine beetle and forest carbon feedback to climate change. Nature. 2008;452(7190):987. doi: 10.1038/nature06777. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lamperti F, Bosetti V, Roventini A, Tavoni M, Treibich T (2021) Three green financial policies to address climate risks. J Financial Stab 54:100875
- Leal Filho W, Azeiteiro UM, Balogun AL, Setti AFF, Mucova SA, Ayal D, . . . Oguge NO (2021) The influence of ecosystems services depletion to climate change adaptation efforts in Africa. Sci Total Environ 146414 [ DOI ] [ PubMed ]
- Lehner F, Coats S, Stocker TF, Pendergrass AG, Sanderson BM, Raible CC, Smerdon JE. Projected drought risk in 1.5 C and 2 C warmer climates. Geophys Res Lett. 2017;44(14):7419–7428. doi: 10.1002/2017GL074117. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lemery J, Knowlton K, Sorensen C (2021) Global climate change and human health: from science to practice: John Wiley & Sons
- Leppänen S, Saikkonen L, Ollikainen M (2014) Impact of Climate Change on cereal grain production in Russia: Mimeo
- Lipczynska-Kochany E. Effect of climate change on humic substances and associated impacts on the quality of surface water and groundwater: a review. Sci Total Environ. 2018;640:1548–1565. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.376. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- livescience.com. New coronavirus may have ‘jumped’ to humans from snakes, study finds, live science,. from < https://www.livescience.com/new-coronavirus-origin-snakes.html > accessed on Jan 2020
- Lobell DB, Field CB. Global scale climate–crop yield relationships and the impacts of recent warming. Environ Res Lett. 2007;2(1):014002. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/2/1/014002. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lobell DB, Gourdji SM. The influence of climate change on global crop productivity. Plant Physiol. 2012;160(4):1686–1697. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.208298. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ma L, Li B, Zhang T. New insights into antibiotic resistome in drinking water and management perspectives: a metagenomic based study of small-sized microbes. Water Res. 2019;152:191–201. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.12.069. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Macchi M, Oviedo G, Gotheil S, Cross K, Boedhihartono A, Wolfangel C, Howell M (2008) Indigenous and traditional peoples and climate change. International Union for the Conservation of Nature, Gland, Suiza
- Mall RK, Gupta A, Sonkar G (2017) Effect of climate change on agricultural crops. In Current developments in biotechnology and bioengineering (pp. 23–46). Elsevier
- Manes S, Costello MJ, Beckett H, Debnath A, Devenish-Nelson E, Grey KA, . . . Krause C (2021) Endemism increases species’ climate change risk in areas of global biodiversity importance. Biol Conserv 257:109070
- Mannig B, Pollinger F, Gafurov A, Vorogushyn S, Unger-Shayesteh K (2018) Impacts of climate change in Central Asia Encyclopedia of the Anthropocene (pp. 195–203): Elsevier
- Martínez-Alvarado O, Gray SL, Hart NC, Clark PA, Hodges K, Roberts MJ. Increased wind risk from sting-jet windstorms with climate change. Environ Res Lett. 2018;13(4):044002. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/aaae3a. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Matsui T, Omasa K, Horie T. The difference in sterility due to high temperatures during the flowering period among japonica-rice varieties. Plant Production Science. 2001;4(2):90–93. doi: 10.1626/pps.4.90. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Meierrieks D (2021) Weather shocks, climate change and human health. World Dev 138:105228
- Michel D, Eriksson M, Klimes M (2021) Climate change and (in) security in transboundary river basins Handbook of Security and the Environment: Edward Elgar Publishing
- Mihiretu A, Okoyo EN, Lemma T. Awareness of climate change and its associated risks jointly explain context-specific adaptation in the Arid-tropics. Northeast Ethiopia SN Social Sciences. 2021;1(2):1–18. [ Google Scholar ]
- Millar CI, Stephenson NL. Temperate forest health in an era of emerging megadisturbance. Science. 2015;349(6250):823–826. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa9933. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mishra A, Bruno E, Zilberman D (2021) Compound natural and human disasters: Managing drought and COVID-19 to sustain global agriculture and food sectors. Sci Total Environ 754:142210 [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Mosavi SH, Soltani S, Khalilian S (2020) Coping with climate change in agriculture: Evidence from Hamadan-Bahar plain in Iran. Agric Water Manag 241:106332
- Murshed M (2020) An empirical analysis of the non-linear impacts of ICT-trade openness on renewable energy transition, energy efficiency, clean cooking fuel access and environmental sustainability in South Asia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(29):36254–36281. 10.1007/s11356-020-09497-3 [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Murshed M. Pathways to clean cooking fuel transition in low and middle income Sub-Saharan African countries: the relevance of improving energy use efficiency. Sustainable Production and Consumption. 2022;30:396–412. doi: 10.1016/j.spc.2021.12.016. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murshed M, Dao NTT. Revisiting the CO2 emission-induced EKC hypothesis in South Asia: the role of Export Quality Improvement. GeoJournal. 2020 doi: 10.1007/s10708-020-10270-9. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murshed M, Abbass K, Rashid S. Modelling renewable energy adoption across south Asian economies: Empirical evidence from Bangladesh, India, Pakistan and Sri Lanka. Int J Finan Eco. 2021;26(4):5425–5450. doi: 10.1002/ijfe.2073. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murshed M, Nurmakhanova M, Elheddad M, Ahmed R. Value addition in the services sector and its heterogeneous impacts on CO2 emissions: revisiting the EKC hypothesis for the OPEC using panel spatial estimation techniques. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2020;27(31):38951–38973. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09593-4. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murshed M, Nurmakhanova M, Al-Tal R, Mahmood H, Elheddad M, Ahmed R (2022) Can intra-regional trade, renewable energy use, foreign direct investments, and economic growth reduce ecological footprints in South Asia? Energy Sources, Part B: Economics, Planning, and Policy. 10.1080/15567249.2022.2038730
- Neuvonen M, Sievänen T, Fronzek S, Lahtinen I, Veijalainen N, Carter TR. Vulnerability of cross-country skiing to climate change in Finland–an interactive mapping tool. J Outdoor Recreat Tour. 2015;11:64–79. doi: 10.1016/j.jort.2015.06.010. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- npr.org. Please Help Me.’ What people in China are saying about the outbreak on social media, npr.org, . from < https://www.npr.org/sections/goatsandsoda/2020/01/24/799000379/please-help-me-what-people-in-china-are-saying-about-the-outbreak-on-social-medi >, Accessed on 26 Jan 2020.
- Ogden LE. Climate change, pathogens, and people: the challenges of monitoring a moving target. Bioscience. 2018;68(10):733–739. doi: 10.1093/biosci/biy101. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ortiz AMD, Outhwaite CL, Dalin C, Newbold T. A review of the interactions between biodiversity, agriculture, climate change, and international trade: research and policy priorities. One Earth. 2021;4(1):88–101. doi: 10.1016/j.oneear.2020.12.008. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ortiz R. Crop genetic engineering under global climate change. Ann Arid Zone. 2008;47(3):343. [ Google Scholar ]
- Otegui MAE, Bonhomme R. Grain yield components in maize: I. Ear growth and kernel set. Field Crop Res. 1998;56(3):247–256. doi: 10.1016/S0378-4290(97)00093-2. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pachauri RK, Allen MR, Barros VR, Broome J, Cramer W, Christ R, . . . Dasgupta P (2014) Climate change 2014: synthesis report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the fifth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Ipcc
- Pal JK. Visualizing the knowledge outburst in global research on COVID-19. Scientometrics. 2021;126(5):4173–4193. doi: 10.1007/s11192-021-03912-3. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Panda R, Behera S, Kashyap P. Effective management of irrigation water for wheat under stressed conditions. Agric Water Manag. 2003;63(1):37–56. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3774(03)00099-4. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pärnänen KM, Narciso-da-Rocha C, Kneis D, Berendonk TU, Cacace D, Do TT, Jaeger T. Antibiotic resistance in European wastewater treatment plants mirrors the pattern of clinical antibiotic resistance prevalence. Sci Adv. 2019;5(3):eaau9124. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aau9124. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Parry M, Parry ML, Canziani O, Palutikof J, Van der Linden P, Hanson C (2007) Climate change 2007-impacts, adaptation and vulnerability: Working group II contribution to the fourth assessment report of the IPCC (Vol. 4): Cambridge University Press
- Patz JA, Campbell-Lendrum D, Holloway T, Foley JA. Impact of regional climate change on human health. Nature. 2005;438(7066):310–317. doi: 10.1038/nature04188. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Patz JA, Graczyk TK, Geller N, Vittor AY. Effects of environmental change on emerging parasitic diseases. Int J Parasitol. 2000;30(12–13):1395–1405. doi: 10.1016/S0020-7519(00)00141-7. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pautasso M, Döring TF, Garbelotto M, Pellis L, Jeger MJ. Impacts of climate change on plant diseases—opinions and trends. Eur J Plant Pathol. 2012;133(1):295–313. doi: 10.1007/s10658-012-9936-1. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Peng S, Huang J, Sheehy JE, Laza RC, Visperas RM, Zhong X, Cassman KG. Rice yields decline with higher night temperature from global warming. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2004;101(27):9971–9975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403720101. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pereira HM, Ferrier S, Walters M, Geller GN, Jongman R, Scholes RJ, Cardoso A. Essential biodiversity variables. Science. 2013;339(6117):277–278. doi: 10.1126/science.1229931. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Perera K, De Silva K, Amarasinghe M. Potential impact of predicted sea level rise on carbon sink function of mangrove ecosystems with special reference to Negombo estuary, Sri Lanka. Global Planet Change. 2018;161:162–171. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2017.12.016. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pfadenhauer JS, Klötzli FA (2020) Zonal Vegetation of the Subtropical (Warm–Temperate) Zone with Winter Rain. In Global Vegetation (pp. 455–514). Springer, Cham
- Phillips JD. Environmental gradients and complexity in coastal landscape response to sea level rise. CATENA. 2018;169:107–118. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2018.05.036. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pirasteh-Anosheh H, Parnian A, Spasiano D, Race M, Ashraf M (2021) Haloculture: A system to mitigate the negative impacts of pandemics on the environment, society and economy, emphasizing COVID-19. Environ Res 111228 [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Pruden A, Larsson DJ, Amézquita A, Collignon P, Brandt KK, Graham DW, Snape JR. Management options for reducing the release of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes to the environment. Environ Health Perspect. 2013;121(8):878–885. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1206446. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Qasim MZ, Hammad HM, Abbas F, Saeed S, Bakhat HF, Nasim W, Fahad S. The potential applications of picotechnology in biomedical and environmental sciences. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2020;27(1):133–142. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06554-4. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Qasim MZ, Hammad HM, Maqsood F, Tariq T, Chawla MS Climate Change Implication on Cereal Crop Productivity
- Rahman M, Alam K. Forest dependent indigenous communities’ perception and adaptation to climate change through local knowledge in the protected area—a Bangladesh case study. Climate. 2016;4(1):12. doi: 10.3390/cli4010012. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ramankutty N, Mehrabi Z, Waha K, Jarvis L, Kremen C, Herrero M, Rieseberg LH. Trends in global agricultural land use: implications for environmental health and food security. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2018;69:789–815. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042817-040256. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rehman A, Ma H, Ahmad M, Irfan M, Traore O, Chandio AA (2021) Towards environmental Sustainability: devolving the influence of carbon dioxide emission to population growth, climate change, Forestry, livestock and crops production in Pakistan. Ecol Indic 125:107460
- Reichstein M, Carvalhais N. Aspects of forest biomass in the Earth system: its role and major unknowns. Surv Geophys. 2019;40(4):693–707. doi: 10.1007/s10712-019-09551-x. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reidsma P, Ewert F, Boogaard H, van Diepen K. Regional crop modelling in Europe: the impact of climatic conditions and farm characteristics on maize yields. Agric Syst. 2009;100(1–3):51–60. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2008.12.009. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ritchie H, Roser M (2014) Natural disasters. Our World in Data
- Rizvi AR, Baig S, Verdone M. Ecosystems based adaptation: knowledge gaps in making an economic case for investing in nature based solutions for climate change. Gland, Switzerland: IUCN; 2015. p. 48. [ Google Scholar ]
- Roscher C, Fergus AJ, Petermann JS, Buchmann N, Schmid B, Schulze E-D. What happens to the sown species if a biodiversity experiment is not weeded? Basic Appl Ecol. 2013;14(3):187–198. doi: 10.1016/j.baae.2013.01.003. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenzweig C, Elliott J, Deryng D, Ruane AC, Müller C, Arneth A, Khabarov N. Assessing agricultural risks of climate change in the 21st century in a global gridded crop model intercomparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014;111(9):3268–3273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1222463110. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenzweig C, Iglesius A, Yang XB, Epstein PR, Chivian E (2001) Climate change and extreme weather events-implications for food production, plant diseases, and pests
- Sadras VO, Slafer GA. Environmental modulation of yield components in cereals: heritabilities reveal a hierarchy of phenotypic plasticities. Field Crop Res. 2012;127:215–224. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2011.11.014. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Salvucci ME, Crafts-Brandner SJ. Inhibition of photosynthesis by heat stress: the activation state of Rubisco as a limiting factor in photosynthesis. Physiol Plant. 2004;120(2):179–186. doi: 10.1111/j.0031-9317.2004.0173.x. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Santos WS, Gurgel-Gonçalves R, Garcez LM, Abad-Franch F. Deforestation effects on Attalea palms and their resident Rhodnius, vectors of Chagas disease, in eastern Amazonia. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(5):e0252071. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252071. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sarkar P, Debnath N, Reang D (2021) Coupled human-environment system amid COVID-19 crisis: a conceptual model to understand the nexus. Sci Total Environ 753:141757 [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Schlenker W, Roberts MJ. Nonlinear temperature effects indicate severe damages to US crop yields under climate change. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2009;106(37):15594–15598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906865106. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schoene DH, Bernier PY. Adapting forestry and forests to climate change: a challenge to change the paradigm. Forest Policy Econ. 2012;24:12–19. doi: 10.1016/j.forpol.2011.04.007. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schuurmans C (2021) The world heat budget: expected changes Climate Change (pp. 1–15): CRC Press
- Scott D. Sustainable Tourism and the Grand Challenge of Climate Change. Sustainability. 2021;13(4):1966. doi: 10.3390/su13041966. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Scott D, McBoyle G, Schwartzentruber M. Climate change and the distribution of climatic resources for tourism in North America. Climate Res. 2004;27(2):105–117. doi: 10.3354/cr027105. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Semenov MA. Impacts of climate change on wheat in England and Wales. J R Soc Interface. 2009;6(33):343–350. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2008.0285. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shaffril HAM, Krauss SE, Samsuddin SF. A systematic review on Asian’s farmers’ adaptation practices towards climate change. Sci Total Environ. 2018;644:683–695. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.349. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shahbaz M, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Sinha A (2019) Foreign direct Investment–CO2 emissions nexus in Middle East and North African countries: Importance of biomass energy consumption. J Clean Product 217:603–614
- Sharif A, Mishra S, Sinha A, Jiao Z, Shahbaz M, Afshan S (2020) The renewable energy consumption-environmental degradation nexus in Top-10 polluted countries: Fresh insights from quantile-on-quantile regression approach. Renew Energy 150:670–690
- Sharma R. Impacts on human health of climate and land use change in the Hindu Kush-Himalayan region. Mt Res Dev. 2012;32(4):480–486. doi: 10.1659/MRD-JOURNAL-D-12-00068.1. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sharma R, Sinha A, Kautish P. Examining the impacts of economic and demographic aspects on the ecological footprint in South and Southeast Asian countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2020;27(29):36970–36982. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09659-3. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Smit B, Burton I, Klein RJ, Wandel J (2000) An anatomy of adaptation to climate change and variability Societal adaptation to climate variability and change (pp. 223–251): Springer
- Song Y, Fan H, Tang X, Luo Y, Liu P, Chen Y (2021) The effects of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) on ischemic stroke and the possible underlying mechanisms. Int J Neurosci 1–20 [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Sovacool BK, Griffiths S, Kim J, Bazilian M (2021) Climate change and industrial F-gases: a critical and systematic review of developments, sociotechnical systems and policy options for reducing synthetic greenhouse gas emissions. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 141:110759
- Stewart JA, Perrine JD, Nichols LB, Thorne JH, Millar CI, Goehring KE, Wright DH. Revisiting the past to foretell the future: summer temperature and habitat area predict pika extirpations in California. J Biogeogr. 2015;42(5):880–890. doi: 10.1111/jbi.12466. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stocker T, Qin D, Plattner G, Tignor M, Allen S, Boschung J, . . . Midgley P (2013) Climate change 2013: The physical science basis. Working group I contribution to the IPCC Fifth assessment report: Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 1535p
- Stone P, Nicolas M. Wheat cultivars vary widely in their responses of grain yield and quality to short periods of post-anthesis heat stress. Funct Plant Biol. 1994;21(6):887–900. doi: 10.1071/PP9940887. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Su H-C, Liu Y-S, Pan C-G, Chen J, He L-Y, Ying G-G. Persistence of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community changes in drinking water treatment system: from drinking water source to tap water. Sci Total Environ. 2018;616:453–461. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.318. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sunderlin WD, Angelsen A, Belcher B, Burgers P, Nasi R, Santoso L, Wunder S. Livelihoods, forests, and conservation in developing countries: an overview. World Dev. 2005;33(9):1383–1402. doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2004.10.004. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Symanski E, Han HA, Han I, McDaniel M, Whitworth KW, McCurdy S, . . . Delclos GL (2021) Responding to natural and industrial disasters: partnerships and lessons learned. Disaster medicine and public health preparedness 1–4 [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Tao F, Yokozawa M, Xu Y, Hayashi Y, Zhang Z. Climate changes and trends in phenology and yields of field crops in China, 1981–2000. Agric for Meteorol. 2006;138(1–4):82–92. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2006.03.014. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tebaldi C, Hayhoe K, Arblaster JM, Meehl GA. Going to the extremes. Clim Change. 2006;79(3–4):185–211. doi: 10.1007/s10584-006-9051-4. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Testa G, Koon E, Johannesson L, McKenna G, Anthony T, Klintmalm G, Gunby R (2018) This article has been accepted for publication and undergone full peer review but has not been through the copyediting, typesetting, pagination and proofreading process, which may lead to differences between this version and the Version of Record. Please cite this article as
- Thornton PK, Lipper L (2014) How does climate change alter agricultural strategies to support food security? (Vol. 1340): Intl Food Policy Res Inst
- Tranfield D, Denyer D, Smart P. Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Br J Manag. 2003;14(3):207–222. doi: 10.1111/1467-8551.00375. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- UNEP (2017) United nations environment programme: frontiers 2017. from https://www.unenvironment.org/news-and-stories/press-release/antimicrobial-resistance - environmental-pollution-among-biggest
- Usman M, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2022) Environmental concern in the era of industrialization: Can financial development, renewable energy and natural resources alleviate some load? Ene Policy 162:112780
- Usman M, Makhdum MSA (2021) What abates ecological footprint in BRICS-T region? Exploring the influence of renewable energy, non-renewable energy, agriculture, forest area and financial development. Renew Energy 179:12–28
- Usman M, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Jahanger A, Ahmad P. Pollution concern during globalization mode in financially resource-rich countries: Do financial development, natural resources, and renewable energy consumption matter? Rene. Energy. 2022;183:90–102. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.10.067. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Usman M, Jahanger A, Makhdum MSA, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Bashir A (2022a) How do financial development, energy consumption, natural resources, and globalization affect Arctic countries’ economic growth and environmental quality? An advanced panel data simulation. Energy 241:122515
- Usman M, Khalid K, Mehdi MA. What determines environmental deficit in Asia? Embossing the role of renewable and non-renewable energy utilization. Renew Energy. 2021;168:1165–1176. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2021.01.012. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Urban MC. Accelerating extinction risk from climate change. Science. 2015;348(6234):571–573. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa4984. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vale MM, Arias PA, Ortega G, Cardoso M, Oliveira BF, Loyola R, Scarano FR (2021) Climate change and biodiversity in the Atlantic Forest: best climatic models, predicted changes and impacts, and adaptation options The Atlantic Forest (pp. 253–267): Springer
- Vedwan N, Rhoades RE. Climate change in the Western Himalayas of India: a study of local perception and response. Climate Res. 2001;19(2):109–117. doi: 10.3354/cr019109. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vega CR, Andrade FH, Sadras VO, Uhart SA, Valentinuz OR. Seed number as a function of growth. A comparative study in soybean, sunflower, and maize. Crop Sci. 2001;41(3):748–754. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2001.413748x. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vergés A, Doropoulos C, Malcolm HA, Skye M, Garcia-Pizá M, Marzinelli EM, Vila-Concejo A. Long-term empirical evidence of ocean warming leading to tropicalization of fish communities, increased herbivory, and loss of kelp. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2016;113(48):13791–13796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1610725113. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Verheyen R (2005) Climate change damage and international law: prevention duties and state responsibility (Vol. 54): Martinus Nijhoff Publishers
- Waheed A, Fischer TB, Khan MI. Climate Change Policy Coherence across Policies, Plans, and Strategies in Pakistan—implications for the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor Plan. Environ Manage. 2021;67(5):793–810. doi: 10.1007/s00267-021-01449-y. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wasiq M, Ahmad M (2004) Sustaining forests: a development strategy: The World Bank
- Watts N, Adger WN, Agnolucci P, Blackstock J, Byass P, Cai W, Cooper A. Health and climate change: policy responses to protect public health. The Lancet. 2015;386(10006):1861–1914. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60854-6. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weed AS, Ayres MP, Hicke JA. Consequences of climate change for biotic disturbances in North American forests. Ecol Monogr. 2013;83(4):441–470. doi: 10.1890/13-0160.1. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weisheimer A, Palmer T (2005) Changing frequency of occurrence of extreme seasonal temperatures under global warming. Geophys Res Lett 32(20)
- Wernberg T, Bennett S, Babcock RC, De Bettignies T, Cure K, Depczynski M, Hovey RK. Climate-driven regime shift of a temperate marine ecosystem. Science. 2016;353(6295):169–172. doi: 10.1126/science.aad8745. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- WHO (2018) WHO, 2018. Antimicrobial resistance
- Wilkinson DM, Sherratt TN. Why is the world green? The interactions of top–down and bottom–up processes in terrestrial vegetation ecology. Plant Ecolog Divers. 2016;9(2):127–140. doi: 10.1080/17550874.2016.1178353. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiranata IJ, Simbolon K. Increasing awareness capacity of disaster potential as a support to achieve sustainable development goal (sdg) 13 in lampung province. Jurnal Pir: Power in International Relations. 2021;5(2):129–146. doi: 10.22303/pir.5.2.2021.129-146. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiréhn L. Nordic agriculture under climate change: a systematic review of challenges, opportunities and adaptation strategies for crop production. Land Use Policy. 2018;77:63–74. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.04.059. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wu D, Su Y, Xi H, Chen X, Xie B. Urban and agriculturally influenced water contribute differently to the spread of antibiotic resistance genes in a mega-city river network. Water Res. 2019;158:11–21. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.03.010. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wu HX (2020) Losing Steam?—An industry origin analysis of China’s productivity slowdown Measuring Economic Growth and Productivity (pp. 137–167): Elsevier
- Wu H, Qian H, Chen J, Huo C. Assessment of agricultural drought vulnerability in the Guanzhong Plain. China Water Resources Management. 2017;31(5):1557–1574. doi: 10.1007/s11269-017-1594-9. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Xie W, Huang J, Wang J, Cui Q, Robertson R, Chen K (2018) Climate change impacts on China’s agriculture: the responses from market and trade. China Econ Rev
- Xu J, Sharma R, Fang J, Xu Y. Critical linkages between land-use transition and human health in the Himalayan region. Environ Int. 2008;34(2):239–247. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2007.08.004. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yadav MK, Singh R, Singh K, Mall R, Patel C, Yadav S, Singh M. Assessment of climate change impact on productivity of different cereal crops in Varanasi. India J Agrometeorol. 2015;17(2):179–184. doi: 10.54386/jam.v17i2.1000. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yang B, Usman M. Do industrialization, economic growth and globalization processes influence the ecological footprint and healthcare expenditures? Fresh insights based on the STIRPAT model for countries with the highest healthcare expenditures. Sust Prod Cons. 2021;28:893–910. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yu Z, Razzaq A, Rehman A, Shah A, Jameel K, Mor RS (2021) Disruption in global supply chain and socio-economic shocks: a lesson from COVID-19 for sustainable production and consumption. Oper Manag Res 1–16
- Zarnetske PL, Skelly DK, Urban MC. Biotic multipliers of climate change. Science. 2012;336(6088):1516–1518. doi: 10.1126/science.1222732. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang M, Liu N, Harper R, Li Q, Liu K, Wei X, Liu S. A global review on hydrological responses to forest change across multiple spatial scales: importance of scale, climate, forest type and hydrological regime. J Hydrol. 2017;546:44–59. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.12.040. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhao J, Sinha A, Inuwa N, Wang Y, Murshed M, Abbasi KR (2022) Does Structural Transformation in Economy Impact Inequality in Renewable Energy Productivity? Implications for Sustainable Development. Renew Energy 189:853–864. 10.1016/j.renene.2022.03.050
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
- View on publisher site
- PDF (1.8 MB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections
Yale Program on Climate Change Communication
- About YPCCC
- Yale Climate Connections
- Student Employment
- For The Media
- Past Events
- YPCCC in the News
- Climate Change in the American Mind (CCAM)
- CCAM Politics Report, Spring 2024
- Publications
- Climate Opinion Maps
- Climate Opinion Factsheets
- Six Americas Super Short Survey (SASSY)
- Resources for Educators
- All Tools & Interactives
- Partner with YPCCC
Home / For Educators: Grades 6-12 / Climate Explained: Introductory Essays About Climate Change Topics
Climate Explained: Introductory Essays About Climate Change Topics
Filed under: backgrounders for educators ,.
Climate Explained, a part of Yale Climate Connections, is an essay collection that addresses an array of climate change questions and topics, including why it’s cold outside if global warming is real, how we know that humans are responsible for global warming, and the relationship between climate change and national security.
More Activities like this

Climate Change Basics: Five Facts, Ten Words
Backgrounders for Educators
To simplify the scientific complexity of climate change, we focus on communicating five key facts about climate change that everyone should know.

Why should we care about climate change?
Having different perspectives about global warming is natural, but the most important thing that anyone should know about climate change is why it matters.

External Resources
Looking for resources to help you and your students build a solid climate change science foundation? We’ve compiled a list of reputable, student-friendly links to help you do just that!
Subscribe to our mailing list
Please select all the ways you would like to hear from Yale Program on Climate Change Communication:
You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the link in the footer of our emails. For information about our privacy practices, please visit our website.
We use Mailchimp as our marketing platform. By clicking below to subscribe, you acknowledge that your information will be transferred to Mailchimp for processing. Learn more about Mailchimp's privacy practices here.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Research articles
Projections of multiple climate-related coastal hazards for the US Southeast Atlantic
Multiple climate-related coastal hazards could impact people, infrastructure and ecosystems, yet previous works often focused on flooding only. By analysing the future exposure to four types of hazard along the US Southeast Atlantic coast, this research emphasizes the risks beyond flooding.
- Patrick L. Barnard
- Kevin M. Befus
- Jamie L. Jones
Increasing aerosol emissions from boreal biomass burning exacerbate Arctic warming
Boreal fires are expected to increase with warming, but how the aerosols emitted in these fires affect the climate is not well understood. Here the authors show that this increase in boreal fire aerosols results in a positive radiative forcing, leading to additional Arctic warming.
- Qirui Zhong
- Nick Schutgens
- Guido R. van der Werf
Internet image search outputs propagate climate change sentiment and impact policy support
The influence of internet search algorithms on users’ beliefs and behaviours remains understudied. This study finds that nationwide climate concern predicted the emotional content of Google Image Search outputs, which subsequently influenced users’ climate concern and support for climate policy.
- Michael Berkebile-Weinberg
- Madalina Vlasceanu
Emergence of a climate oscillation in the Arctic Ocean due to global warming
Abrupt transitions in the climate system are discussed mostly in terms of mean state changes. Here, the authors use simulations to show that a decline in Arctic sea ice can lead to a new multidecadal mode of surface temperatures in the Arctic Ocean.
- Soong-Ki Kim
Mapping the global variation in the efficiency of ocean alkalinity enhancement for carbon dioxide removal
Ocean alkalinity enhancement (OAE) is seen as a promising method for CO 2 removal as it alters the surface carbon equilibrium, driving the transfer of CO 2 into the ocean. Here the authors computationally map the spatiotemporal efficiency of OAE to identify locations and timing for optimal OAE deployment.
- Mengyang Zhou
- Michael D. Tyka
- Matthew C. Long
Conventional agriculture increases global warming while decreasing system sustainability
The authors provide a global, cradle-to-gate quantification of the changes in the global warming potential and sustainability index of conventional agriculture from 1961 to the 2020s. They show an eightfold global warming potential increase and threefold decrease in sustainability index, largely due to tillage, fertilizer use and irrigation.
- Ahmed I. Abdo
- Yakov Kuzyakov
Waning snowfields have transformed into hotspots of greening within the alpine zone
The authors use multidecadal, high-resolution data to investigate the spatial variability of vegetation greening in European mountains. They show that changes in snow cover duration play a more significant role than rising air temperatures alone in driving greening patterns.
- Philippe Choler
- Arthur Bayle
- Simon Gascoin
Global exposure risk of frogs to increasing environmental dryness
The authors consider the future risks of warming and drying to water-sensitive anuran species. They show that increased aridity of anuran habitats and drought exposure under climate change, combined with warming, can substantially reduce anuran activity.
- Nicholas C. Wu
- Rafael Parelli Bovo
- Jacinta D. Kong
Attributing human mortality from fire PM 2.5 to climate change
The authors combine fire–vegetation models, a chemical transport model and a health risk model to link human mortality from fire emissions to climate change. They estimate that 12.8% of mortalities in 2010 were linked to climate change, with South America, Australia, Europe and boreal forests most impacted.
- Chae Yeon Park
- Kiyoshi Takahashi
- Tomoko Hasegawa
Global burned area increasingly explained by climate change
Complex interactions between drivers have hampered efforts to understand observed changes in fire behaviour worldwide. Here fire model ensembles and impact attribution show that climate change increasingly explains changes in global burned area.
- Chantelle Burton
- Seppe Lampe
- Matthias Mengel
Climate justice beliefs related to climate action and policy support around the world
Little is known about public understanding of climate justice, despite its increasing prominence in climate change communication. Here a global survey reveals that, although awareness of climate justice is low, beliefs in climate justice are widely supported across countries.
- Charles A. Ogunbode
- Rouven Doran
- Susan Clayton
Drought and aridity influence internal migration worldwide
Limited comparative evidence exists on the impacts of climatic factors on internal migration. Here, using a harmonized census-based dataset, the authors find that drought and aridity substantially increase internal migration, with considerable heterogeneity across regions, age groups and education levels.
- Roman Hoffmann
- Marco Percoco
Canopy structure regulates autumn phenology by mediating the microclimate in temperate forests
The authors demonstrate a significant influence of canopy structure on autumn phenology in temperate forests, mediated by microclimate regulation. Incorporating this relationship into autumn phenology models enhances their prediction accuracy and reduces previously projected delays in autumn phenology.
- Xiaoyong Wu
- Chunyue Niu
Assessing the impacts of fertility and retirement policies on China’s carbon emissions
Demographic policies to address population aging could have major climate consequences, and such interaction effect is context dependent. This study shows that relaxing the fertility policy and delaying retirement age in China could lead to an increase in total and per capita household carbon footprint.
Maize breeding for smaller tassels threatens yield under a warming climate
By comparing the responses of 323 elite maize lines from different breeding eras, the authors demonstrate that reduced tassel size in newer lines can lead to increased susceptibility to high temperature. This highlights the potential for traits optimized by breeding to lead to climate maladaptation.
- Yingjun Zhang
- Shoubing Huang
Climate-driven global redistribution of an ocean giant predicts increased threat from shipping
The authors use long-term satellite tracking to project climate-induced shifts in whale shark distributions and understand their potential future risk of ship-strike. Under high-emission scenarios, the movement of sharks to current range-edge habitat is linked to 15,000-fold increased co-occurrence with ships.
- Freya C. Womersley
- Lara L. Sousa
- David W. Sims
A multi-model assessment of inequality and climate change
Climate change and economic inequality are critical issues, and we still lack understanding of the interaction between them. Multi-model analysis shows how climate policies compatible with the goals of the Paris Agreement, including revenue-redistribution schemes, can reduce inequality—particularly in the short and medium terms.
- Johannes Emmerling
- Pietro Andreoni
- Massimo Tavoni
Arctic soil carbon trajectories shaped by plant–microbe interactions
Arctic warming is thought to lead to large losses in soil carbon stocks. Here a 35-year-long fertilization experiment in Alaska shows that increased shrub productivity and changes in plant–microbial feedbacks may eventually reverse trends of carbon loss and restore the soil carbon sink.
- Megan B. Machmuller
- Laurel M. Lynch
- Matthew D. Wallenstein
Climate variability shifts the vertical structure of phytoplankton in the Sargasso Sea
The authors reveal distinct trends in surface and subsurface phytoplankton dynamics, highlighting the need for subsurface monitoring. Whereas subsurface phytoplankton respond to recent warming with biomass increases, surface phytoplankton show altered carbon-to-chlorophyll ratios but minimal biomass change.
- Johannes J. Viljoen
- Xuerong Sun
- Robert J. W. Brewin
Using cost–benefit analyses to identify key opportunities in demand-side mitigation
Demand-side mitigation solutions are seen as an essential part for climate actions, yet their adoption is still lower than expected. Cost–benefit analysis shows that the main barriers lie in the non-pecuniary costs of behaviour switching, and highlights opportunities for targeted policy intervention.
- Jie-Sheng Tan-Soo
- Xiaoxi Wang
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
January 4, 2020
These Are the Biggest Climate Questions for the New Decade
The 2010s brought major climate science advances, but researchers still want to pin down estimates of Arctic melt and sea-level rise
By Chelsea Harvey & E&E News

In this aerial view ice lies in a lake formed by meltwater from the Rhone glacier on August 19, 2019 near Obergoms, Switzerland.
Sean Gallup Getty Images
The 2010s were almost certainly the hottest decade on record — and it showed. The world burned, melted and flooded. Heat waves smashed temperature records around the globe. Glaciers lost ice at accelerating rates. Sea levels continued to swell.
At the same time, scientists have diligently worked to untangle the chaos of a rapidly warming planet.
In the past decade, scientists substantially improved their ability to draw connections between climate change and extreme weather events. They made breakthroughs in their understanding of ice sheets. They raised critical questions about the implications of Arctic warming. They honed their predictions about future climate change.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
As another decade begins, scientists say there are more questions to be answered. We asked climate researchers across a variety of disciplines about the biggest priorities and hottest topics for the 2020s. Here's what they said.
Arctic mysteries
The Arctic is warming faster than anywhere else on Earth, with temperatures rising at least twice as fast as the global average. Many scientists believe that understanding the consequences of Arctic warming is essential for making accurate predictions about climate change around the world.
Some of these links are straightforward. Melting Arctic ice pouring into the ocean can raise global sea levels. Thawing permafrost can release large amounts of carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere, potentially accelerating the rate of global warming.
Others are more contentious.
In the last decade, a growing scientific debate has arisen about the influence of Arctic warming on global climate and weather patterns, particularly in the midlatitudes.
Some observational studies have pointed to a statistical connection between Arctic warming and weather events in places like the United States, Europe and parts of Asia — for instance, a link between shrinking sea ice and cold winters in Siberia, or Arctic heat waves and extreme winter weather in the United States.
The trouble is models have a hard time capturing the causes driving these connections.
"No one argues that the Arctic meltdown will affect weather patterns, the question is exactly how," said Arctic climate expert Jennifer Francis, a researcher at Woods Hole Research Center. "So figuring out what's not right in the models will be a major focus. Without realistic models, it's hard to use them to separate Arctic influences from other possible factors."
Resolving the debate will require "a combination of data and modeling," according to NASA climatologist Claire Parkinson. Many scientists are already hard at work on this issue.
One ongoing project known as the Polar Amplification Model Intercomparison Project is conducting a series of coordinated model experiments, all using the same standard methods, to investigate the Arctic climate and its connections to the rest of the globe. Experts say these kinds of projects may help explain why modeling studies conducted by different groups with different methods don't always get the same results.
At the same time, improving the way that physical processes are represented in Arctic climate models is also essential, according to Xiangdong Zhang, an Arctic and atmospheric scientist at the University of Alaska, Fairbanks.
Outside that debate, there are still big questions about the Arctic climate to resolve. Scientists know the Arctic is heating up at breakneck speed — but they're still investigating all the reasons why.
Researchers believe a combination of feedback processes are probably at play. Sea ice and snow help reflect sunlight away from the Earth. As they melt away, they allow more heat to reach the surface, warming the local climate and causing even more melting to occur.
One key question for the coming decade, Zhang said in an email, is "what relative role each of the physical processes plays and how these processes work together" to drive the accelerating warming.
Unraveling these feedbacks will help scientists better predict how fast the Arctic will warm in the future, according to Francis — and how quickly they should expect its consequences to occur. They include vanishing sea ice, thawing permafrost and melting on the Greenland ice sheet.
Oceans and ice
Sea-level rise is one of the most serious consequences of climate change, with the potential to displace millions of people in coastal areas around the world.
At the moment, the world's oceans are rising at an average rate of about 3 millimeters each year. It appears to be speeding up over time. That may not sound like much, but scientists are already documenting an increase in coastal flooding in many places around the world.
Accurately predicting the pace of future sea-level rise is one of the biggest priorities in climate science. And one of the biggest uncertainties about future sea-level rise is the behavior of the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets, both of which are pouring billions of tons of ice into the ocean each year.
Recent satellite studies have found that ice loss in both places is speeding up. Antarctica is losing about three times as much ice as it was in the 1990s, while losses in Greenland may be as much as seven times higher than they were in previous decades.
Investigating the processes driving the accelerations — and then using that knowledge to fine-tune predictions of future sea-level rise — is a key priority for 2020 and beyond, according to Marco Tedesco, an ice sheet expert at Columbia University.
"How do we connect the physical processes that we do understand are creating this acceleration from Greenland and Antarctica, very likely over the next decade, to sea-level rise impacts?" he asked E&E News. "And how do we account for the potential shocks of the things that we cannot anticipate still?"
Some scientists worry that as ice loss continues to speed up in both Greenland and Antarctica, parts of the ice sheets could eventually destabilize and collapse entirely — leading to catastrophic sea-level rise.
In recent years, scientists have discovered that warm ocean currents are helping to melt some glaciers from the bottom up, both in Greenland and particularly in parts of West Antarctica. Better understanding the relationship between oceans and ice is a key priority for glacier experts, Tedesco said.
At the same time, monitoring the way water melts and moves along the top of the ice is also a major priority. In Greenland, climate-driven changes in the behavior of large air currents like the jet stream may be helping to drive more surface melting.
"The important thing is to understand how Greenland mass loss can be connected to the recent changes in the atmospheric circulation that we are witnessing," Tedesco said.
Extreme weather events
The past decade saw leaps and bounds in a field of climate research known as "attribution science" — the connection between climate change and extreme weather events.
It was once thought to be impossible, but scientists are now able to estimate the influence of global warming on individual events, like heat waves or hurricanes. In the past few years alone, scientists have found that some events are now occurring that would have been impossible in a world with no human-caused climate change.
As attribution science has advanced, researchers have been able to tackle increasingly complex events, like hurricanes and wildfires, which were previously too complicated to evaluate with any confidence. They've gotten faster, too — researchers are now able to assess some extreme events nearly in real time.
Some organizations are working to develop sophisticated attribution services, similar to weather services, which would release analyses of extreme events as soon as they occur. The German national weather service; the United Kingdom's Met Office; and the Copernicus program, part of the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts, have all begun exploring these kinds of projects.
At the same time, scientists are working to improve their predictions of future extreme events in a warming world.
So far, climate models predict that many extreme weather events will happen more frequently, or will become more severe, as the climate continues to change. Heat waves will be hotter, hurricanes will intensify, heavy rainfall events may happen more frequently in some places, and droughts may be longer in others.
Continuing to improve these kinds of predictions — and then communicating them in useful ways to communities that will be affected by them — is a major priority, according to Piers Forster, director of the Priestley International Centre for Climate at the University of Leeds.
There's often great uncertainty when it comes to predicting extreme weather events, he noted — different climate models sometimes deliver vastly different results. But it can often be both expensive and time-consuming to run the models enough times, and at high enough resolutions, to investigate and narrow these uncertainties.
Tackling this issue is one of the key challenges for climate modeling in the coming years, Forster said, noting that "we need to get clever about how we use models to make projections and how we test them."
Projecting the future
Predicting how much the Earth will warm, given a certain level of greenhouse gas emissions, may seem like the simplest goal of climate modeling. But it's harder than it sounds.
Climate models don't always agree on the Earth's exact sensitivity to greenhouse gas emissions — although they do tend to fall within a certain range. If global carbon dioxide concentrations were to double, for instance, models from the past decade have tended to predict that the Earth would warm from between 1.5 and 4.5 degrees Celsius.
Scientists around the world are working on a new suite of updated climate models, which will be used to inform future reports produced by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. But there's one issue that's already raising eyebrows, according to Zeke Hausfather, a climate scientist at the University of California, Berkeley — so far, the newer models seem to be predicting a much higher climate sensitivity than the older models.
"The high end is much higher," he told E&E News. "There's a number of models above 4.8 degrees sensitivity and even up to 5.6."
Only about 20 new models have submitted results; far more will come pouring in before the project is complete. And as Hausfather pointed out, other recent studies have suggested that the Earth's climate sensitivity might actually be narrower than the old models suggested.
But it's something to keep in mind at a time when accurate predictions about future warming are more pressing than ever.
"The fact that some of these models are high is interesting but doesn't necessarily mean we should believe them over other lines of evidence," Hausfather said. "It just reflects the fact that climate sensitivity is this huge remaining source of uncertainty in our climate projections."
At the same time, climate modelers are also working to hone their projections in other ways. Models are able to capture increasingly complex processes the more they advance. But there are still a few key areas scientists are focused on improving.
Clouds, for instance, are believed to have a significant influence on the climate system. But they're notoriously difficult to reproduce in climate models. Certain aspects of the carbon cycle are also underrepresented in models, Hausfather noted — for instance, the way that forests and oceans absorb or release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
And scientists are also working to develop more realistic climate scenarios for their modeling projects. In the past, many studies have focused on a "business as usual" climate scenario, which suggests high rates of future greenhouse gas emissions, the continued expansion of coal, and other assumptions about industry and socioeconomics that may no longer be realistic, according to Hausfather.
While global climate action is still significantly lagging when it comes to meeting the goals of the Paris climate agreement, the future may not be as dire as previous business-as-usual climate studies would suggest. Focusing new studies on more realistic scenarios may be more useful to policymakers and communities trying to plan for the future.
"In many ways the range of possible futures is narrowing," Hausfather said. "As we get closer to 2100 and as the world takes more climate action, the worst-case 4 degrees-plus warming scenarios are a lot less likely."
Reprinted from Climatewire with permission from E&E News. E&E provides daily coverage of essential energy and environmental news at www.eenews.net .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this compilation of global warming essay topics, you will find title ideas about how human activities impact the environment, what collective actions are required to battle it, and others. ... Explore these issues to write a relevant research paper. 🏆 Best Global Warming Essay Topics. Global Warming Effects on the Environment and Animals.
☀Top 10 Global Warming Essay Topics. The impact of global warming on physical geography. The benefits and limitations of solar power. Contribution of deforestation to climate change. How successful are international climate agreements? Comparing the average carbon footprint across different countries. How individuals can fight against global ...
The impact of ecological damage on people, animals, and plants is the focus of most essay titles on global warming and climate change. Indeed, describing climate change effects in detail could earn you some extra marks. Use scholarly resources to research these climate change essay questions: How has climate change impacted wildlife already?
The world is now warming faster than at any point in recorded history, which disrupts the usual balance of nature and is a threat to human beings and other forms of life on Earth. This topic guide includes sample keywords and search terms, databases to find sources, and samples of online books.
Worldwide observed and anticipated climatic changes for the twenty-first century and global warming are significant global changes that have been encountered during the past 65 years. ... 55 articles are reviewed systematically and analyzed for research topics and other aspects, such as the methods, contexts, and theories used in these studies ...
Climate Explained, a part of Yale Climate Connections, is an essay collection that addresses an array of climate change questions and topics, including why it's cold outside if global warming is real, how we know that humans are responsible for global warming, and the relationship between climate change and national security.
Global Warming. Long-term warming trends and increases in extreme weather events have the potential to impact all life on Earth. Even though at least 97 percent of climate scientists agree that human activities have contributed to rising global temperatures, the predominance and causes of these phenomena continue to be debated and many Americans deny global warming.
Read the latest Research articles from Nature Climate Change ... cradle-to-gate quantification of the changes in the global warming potential and sustainability index of conventional agriculture ...
global warming, the phenomenon of increasing average air temperatures near the surface of Earth over the past one to two centuries. Climate scientists have since the mid-20th century gathered detailed observations of various weather phenomena (such as temperatures, precipitation, and storms) and of related influences on climate (such as ocean currents and the atmosphere's chemical composition).
We asked climate researchers across a variety of disciplines about the biggest priorities and hottest topics for the 2020s. ... rate of global warming. ... of climate research known as ...