

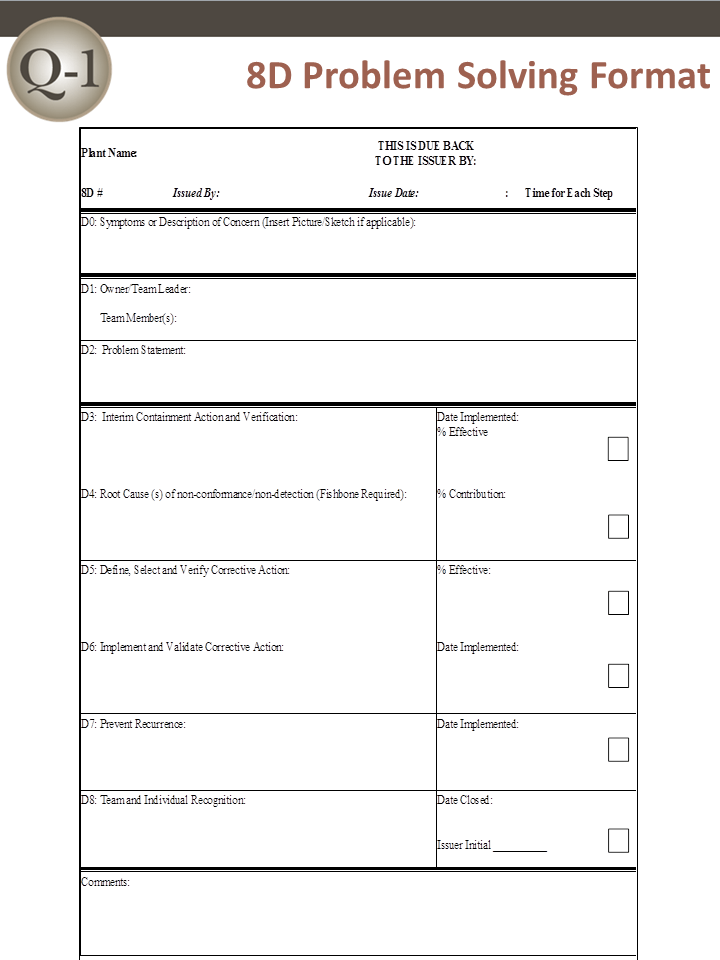
Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
– Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving –
⇓ Introduction to 8D
⇓ What is 8D
⇓ Why Apply 8D
⇓ When to Apply 8D
⇓ How to Apply 8D

Introduction to Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D) is a problem solving methodology designed to find the root cause of a problem, devise a short-term fix and implement a long-term solution to prevent recurring problems. When it’s clear that your product is defective or isn’t satisfying your customers, an 8D is an excellent first step to improving Quality and Reliability.
Ford Motor Company developed this problem solving methodology, then known as Team Oriented Problem Solving (TOPS), in the 1980s. The early usage of 8D proved so effective that it was adopted by Ford as the primary method of documenting problem solving efforts, and the company continues to use 8D today.
8D has become very popular among manufacturers because it is effective and reasonably easy to teach. Below you’ll find the benefits of an 8D, when it is appropriate to perform and how it is performed.
What is Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D problem solving process is a detailed, team oriented approach to solving critical problems in the production process. The goals of this method are to find the root cause of a problem, develop containment actions to protect customers and take corrective action to prevent similar problems in the future.
The strength of the 8D process lies in its structure, discipline and methodology. 8D uses a composite methodology, utilizing best practices from various existing approaches. It is a problem solving method that drives systemic change, improving an entire process in order to avoid not only the problem at hand but also other issues that may stem from a systemic failure.
8D has grown to be one of the most popular problem solving methodologies used for Manufacturing, Assembly and Services around the globe. Read on to learn about the reasons why the Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving may be a good fit for your company.
Why Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D methodology is so popular in part because it offers your engineering team a consistent, easy-to-learn and thorough approach to solving whatever problems might arise at various stages in your production process. When properly applied, you can expect the following benefits:
- Improved team oriented problem solving skills rather than reliance on the individual
- Increased familiarity with a structure for problem solving
- Creation and expansion of a database of past failures and lessons learned to prevent problems in the future
- Better understanding of how to use basic statistical tools required for problem solving
- Improved effectiveness and efficiency at problem solving
- A practical understanding of Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- Problem solving effort may be adopted into the processes and methods of the organization
- Improved skills for implementing corrective action
- Better ability to identify necessary systemic changes and subsequent inputs for change
- More candid and open communication in problem solving discussion, increasing effectiveness
- An improvement in management’s understanding of problems and problem resolution
8D was created to represent the best practices in problem solving. When performed correctly, this methodology not only improves the Quality and Reliability of your products but also prepares your engineering team for future problems.
When to Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D problem solving process is typically required when:
- Safety or Regulatory issues has been discovered
- Customer complaints are received
- Warranty Concerns have indicated greater-than-expected failure rates
- Internal rejects, waste, scrap, poor performance or test failures are present at unacceptable levels
How to Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D process alternates inductive and deductive problem solving tools to relentlessly move forward toward a solution. The Quality-One approach uses a core team of three individuals for inductive activities with data driven tools and then a larger Subject Matter Expert (SME) group for the deductive activities through brainstorming, data-gathering and experimentation.
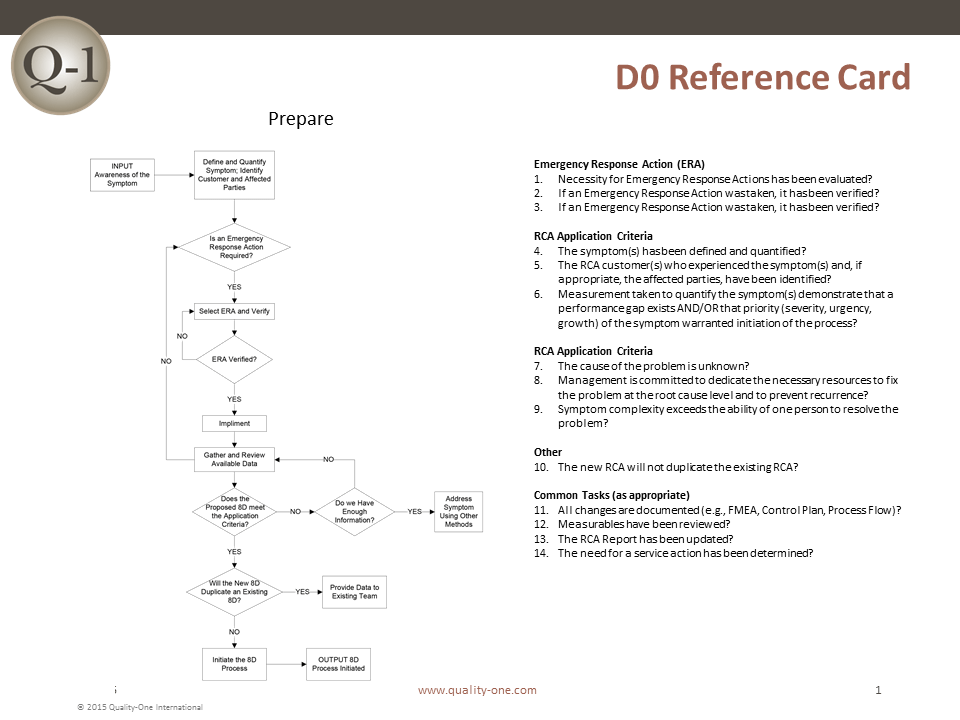
D0: Prepare and Plan for the 8D
Proper planning will always translate to a better start. Thus, before 8D analysis begins, it is always a good idea to ask an expert first for their impressions. After receiving feedback, the following criterion should be applied prior to forming a team:
Collect information on the symptoms
Use a Symptoms Checklist to ask the correct questions
Identify the need for an Emergency Response Action (ERA), which protects the customer from further exposure to the undesired symptoms
D1: Form a Team
A Cross Functional Team (CFT) is made up of members from many disciplines. Quality-One takes this principle one step further by having two levels of CFT:
- The Core Team Structure should involve three people on the respective subjects: product, process and data
- Additional Subject Matter Experts are brought in at various times to assist with brainstorming, data collection and analysis
Teams require proper preparation. Setting the ground rules is paramount. Implementation of disciplines like checklists, forms and techniques will ensure steady progress. 8D must always have two key members: a Leader and a Champion / Sponsor:
- The Leader is the person who knows the 8D process and can lead the team through it (although not always the most knowledgeable about the problem being studied)
- The Champion or Sponsor is the one person who can affect change by agreeing with the findings and can provide final approval on such changes
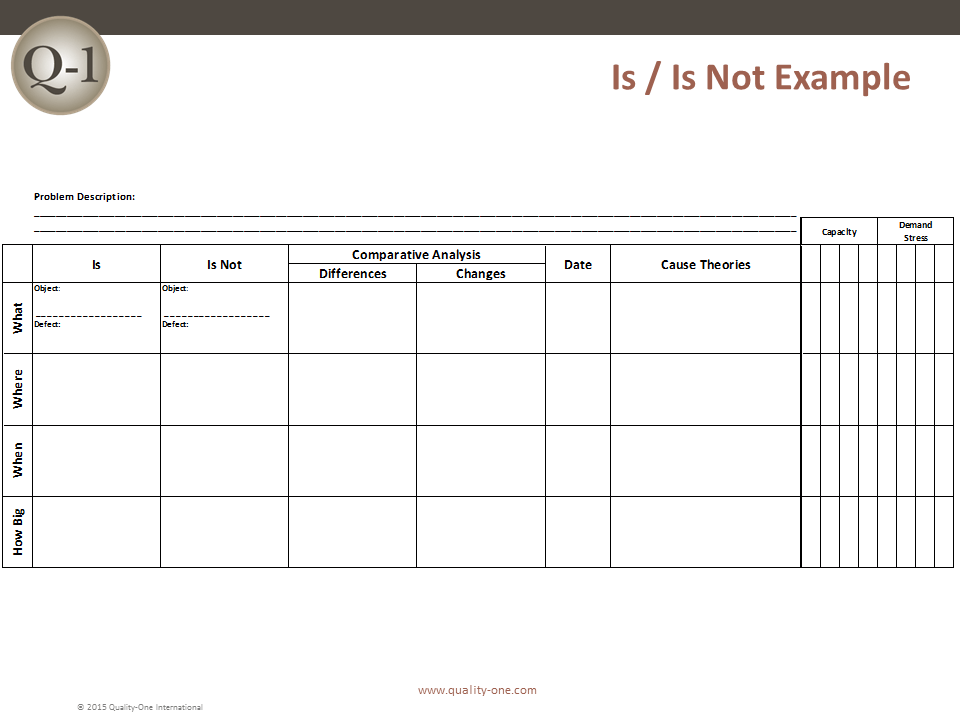
D2: Describe the Problem
The 8D method’s initial focus is to properly describe the problem utilizing the known data and placing it into specific categories for future comparisons. The “Is” data supports the facts whereas the “Is Not” data does not. As the “Is Not” data is collected, many possible reasons for failure are able to be eliminated. This approach utilizes the following tools:
- Problem Statement
- Affinity Diagram (Deductive tool)
- Fishbone/Ishikawa Diagram (Deductive tool)
- Problem Description
D3: Interim Containment Action
In the interim, before the permanent corrective action has been determined, an action to protect the customer can be taken. The Interim Containment Action (ICA) is temporary and is typically removed after the Permanent Correct Action (PCA) is taken.
- Verification of effectiveness of the ICA is always recommended to prevent any additional customer dissatisfaction calls
D4: Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and Escape Point
The root cause must be identified to take permanent action to eliminate it. The root cause definition requires that it can be turned on or off, at will. Activities in D4 include:
- Comparative Analysis listing differences and changes between “Is” and “Is Not”
- Development of Root Cause Theories based on remaining items
- Verification of the Root Cause through data collection
- Review Process Flow Diagram for location of the root cause
- Determine Escape Point, which is the closest point in the process where the root cause could have been found but was not
D5: Permanent Corrective Action (PCA)
The PCA is directed toward the root cause and removes / changes the conditions of the product or process that was responsible for the problem. Activities in D5 include:
- Establish the Acceptance Criteria which include Mandatory Requirements and Wants
- Perform a Risk Assessment / Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) on the PCA choices
- Based on risk assessment, make a balanced choice for PCA
- Select control-point improvement for the Escape Point
- Verification of Effectiveness for both the PCA and the Escape Point are required
D6: Implement and Validate the Permanent Corrective Action
To successfully implement a permanent change, proper planning is essential. A project plan should encompass: communication, steps to complete, measurement of success and lessons learned. Activities in D6 include:
- Develop Project Plan for Implementation
- Communicate the plan to all stakeholders
- Validation of improvements using measurement
D7: Prevent Recurrence
D7 affords the opportunity to preserve and share the knowledge, preventing problems on similar products, processes, locations or families. Updating documents and procedures / work instructions are expected at this step to improve future use. Activities in D7 include:
- Review Similar Products and Processes for problem prevention
- Develop / Update Procedures and Work Instructions for Systems Prevention
- Capture Standard Work / Practice and reuse
- Assure FMEA updates have been completed
- Assure Control Plans have been updated
D8: Closure and Team Celebration
Teams require feedback to allow for satisfactory closure. Recognizing both team and individual efforts and allowing the team to see the previous and new state solidifies the value of the 8D process. Activities in D8 include:
- Archive the 8D Documents for future reference
- Document Lessons Learned on how to make problem solving better
- Before and After Comparison of issue
- Celebrate Successful Completion
8D and Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
The 8D process has Root Cause Analysis (RCA) imbedded within it. All problem solving techniques include RCA within their structure. The steps and techniques within 8D which correspond to Root Cause Analysis are as follows:
- Problem Symptom is quantified and converted to “Object and Defect”
- Problem Symptom is converted to Problem Statement using Repeated Whys
- Possible and Potential Causes are collected using deductive tools (i.e. Fishbone or Affinity Diagram)
- Problem Statement is converted into Problem Description using Is / Is Not
- Problem Description reduces the number of items on the deductive tool (from step 3)
- Comparative Analysis between the Is and Is Not items (note changes and time)
- Root Cause theories are developed from remaining possible causes on deductive tool and coupled with changes from Is / Is Not
- Compare theories with current data and develop experiments for Root Cause Verification
- Test and confirm the Root Causes
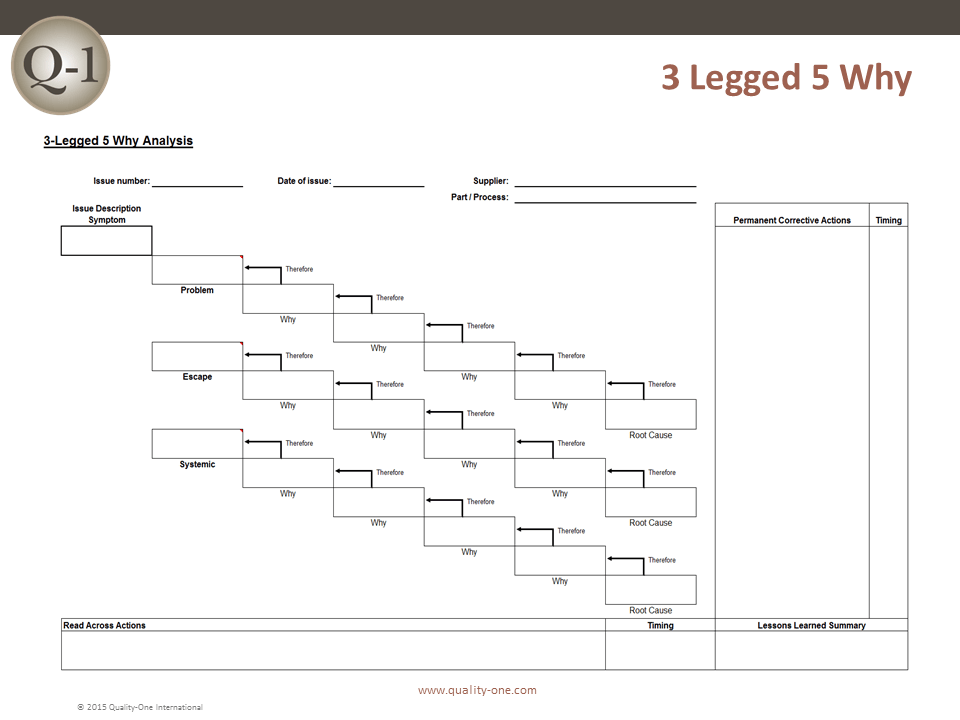
Example: Multiple Why Technique
The Multiple / Repeated Why (Similar to 5 Why) is an inductive tool, which means facts are required to proceed to a more detailed level. The steps required to determine problem statement are:
- Problem Symptom is defined as an Object and Defect i.e. “Passenger Injury”
- Why? In every case “SUV’s Roll Over”
- Why? In every case, it was preceded by a “Blown Tire”
- Why? Many explanations may be applied, therefore the team cannot continue with another repeated why past “Blown Tire”
- Therefore, the Problem Statement is “Blown Tire”
- Why? Low (Air) Pressure, Tire Defect (Degradation of an Interface) and High (Ambient) Temperature
- Counter measures assigned to low pressure and tire defect
This example uses only 4 of the 5 Whys to determine the root causes without going further into the systemic reasons that supported the failure. The Repeated Why is one way to depict this failure chain. Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) could also be used.
Learn More About Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
Quality-One offers Quality and Reliability Support for Product and Process Development through Consulting, Training and Project Support. Quality-One provides Knowledge, Guidance and Direction in Quality and Reliability activities, tailored to your unique wants, needs and desires. Let us help you Discover the Value of 8D Consulting , 8D Training or 8D Project Support .
Contact Us | Discover the Value!
(248) 280-4800 | [email protected]
Remember Me
- Don't have an account? Register
- Lost your password? Click here
- Already have an account? Log in

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 8 min read
8D Problem Solving Process
Solving major problems in a disciplined way.
By the Mind Tools Content Team
(Also known as Global 8D Problem Solving)

When your company runs into a major problem, you need to address it quickly. However, you also need to deal with it thoroughly and ensure that it doesn't recur – and this can take a lot of effort and elapsed time.
The 8D Problem Solving Process helps you do both of these seemingly-contradictory things, in a professional and controlled way. In this article, we'll look at the 8D Problem Solving Process, and we'll discuss how you can use it to help your team solve major problems.
Origins of the Tool
The Ford Motor Company® developed the 8D (8 Disciplines) Problem Solving Process, and published it in their 1987 manual, "Team Oriented Problem Solving (TOPS)." In the mid-90s, Ford added an additional discipline, D0: Plan. The process is now Ford's global standard, and is called Global 8D.
Ford created the 8D Process to help teams deal with quality control and safety issues; develop customized, permanent solutions to problems; and prevent problems from recurring. Although the 8D Process was initially applied in the manufacturing, engineering, and aerospace industries, it's useful and relevant in any industry.
The eight disciplines are shown in figure 1, below:
Figure 1: The 8D Problem Solving Process

The 8D Process works best in teams tasked with solving a complex problem with identifiable symptoms. However, you can also use this process on an individual level, as well.
Applying the Tool
To use the 8D Process, address each of the disciplines listed below, in order. Take care not to skip steps, even when time is limited; the process is only effective when you follow every step.
Discipline 0: Plan
Before you begin to assemble a team to address the problem, you need to plan your approach. This means thinking about who will be on the team, what your time frame is, and what resources you'll need to address the problem at hand.
Discipline 1: Build the Team
You should aim to put together a team that has the skills needed to solve the problem, and that has the time and energy to commit to the problem solving process.
Keep in mind that a diverse team is more likely to find a creative solution than a team of people with the same outlook (although if outlooks are too diverse, people can spend so much time disagreeing that nothing gets done).
Create a team charter that outlines the team's goal and identifies each person's role. Then, do what you can to build trust and get everyone involved in the process that's about to happen.
If your team is made up of professionals who haven't worked together before, consider beginning with team-building activities to ensure that everyone is comfortable working with one another.
Discipline 2: Describe the Problem
Once your team has settled in, describe the problem in detail. Specify the who, what, when, where, why, how, and how many; and use techniques like CATWOE and the Problem-Definition Process to ensure that you're focusing on the right problem.
Start by doing a Risk Analysis – if the problem is causing serious risks, for example, to people's health or life, then you need to take appropriate action. (This may include stopping people using a product or process until the problem is resolved.)
If the problem is with a process, use a Flow Chart , Swim Lane Diagram , or Storyboard to map each step out; these tools will help your team members understand how the process works, and, later on, think about how they can best fix it.
Discovering the root cause of the problem comes later in the process, so don't spend time on this here. Right now, your goal is to look at what's going wrong and to make sure that your team understands the full extent of the problem.
Discipline 3: Implement a Temporary Fix
Once your team understands the problem, come up with a temporary fix. This is particularly important if the problem is affecting customers, reducing product quality, or slowing down work processes.
Harness the knowledge of everyone on the team. To ensure that each person's ideas are heard, consider using brainstorming techniques such as Round Robin Brainstorming or Crawford's Slip Writing Method , alongside more traditional team problem solving discussions.
Once the group has identified possible temporary fixes, address issues such as cost, implementation time, and relevancy. The short-term solution should be quick, easy to implement, and worth the effort.
Discipline 4: Identify and Eliminate the Root Cause
Once your temporary fix is in place, it's time to discover the root cause of the problem.
Conduct a Cause and Effect Analysis to identify the likely causes of the problem. This tool is useful because it helps you uncover many possible causes, and it can highlight other problems that you might not have been aware of. Next, apply Root Cause Analysis to find the root causes of the problems you've identified.
Once you identify the source of the problem, develop several permanent solutions to it.
If your team members are having trouble coming up with viable permanent solutions, use the Straw Man Concept to generate prototype solutions that you can then discuss, tear apart, and rebuild into stronger solutions.
Discipline 5: Verify the Solution
Once your team agrees on a permanent solution, make sure that you test it thoroughly before you fully implement it, in the next step.
- Conducting a Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) to spot any potential problems.
- Using Impact Analysis to make sure that there will be no unexpected future consequences.
- Using Six Thinking Hats to examine the fix from several different emotional perspectives.
Last, conduct a Blind Spot Analysis to confirm that you and your team haven't overlooked a key factor, or made an incorrect assumption about this solution.

Discipline 6: Implement a Permanent Solution
Once your team reaches a consensus on the solution, roll your fix out. Monitor this new solution closely for an appropriate period of time to make sure that it's working correctly, and ensure that there are no unexpected side effects.
Discipline 7: Prevent the Problem From Recurring
When you're sure that the permanent solution has solved the problem, gather your team together again to identify how you'll prevent the problem from recurring in the future.
You might need to update your organization's standards, policies, procedures, or training manual to reflect the new fix. You'll likely also need to train others on the new process or standard. Finally, you'll need to consider whether to change your management practices or procedures to prevent a recurrence.
Discipline 8: Celebrate Team Success
The last step in the process is to celebrate and reward your team's success . Say "thank you" to everyone involved, and be specific about how each person's hard work has made a difference. If appropriate, plan a party or celebration to communicate your appreciation.
Before the team disbands, conduct a Post-Implementation Review to analyze whether your solution is working as you thought, and to improve the way that you solve problems in the future.
In the late 1980s, Ford Motor Company developed the 8D (8 Disciplines) Problem Solving Process to help manufacturing and engineering teams diagnose, treat, and eliminate quality problems. However, teams in any industry can use this problem solving process.
The eight disciplines are:
- Build the Team.
- Describe the Problem.
- Implement a Temporary Fix.
- Identify and Eliminate the Root Cause.
- Verify the Solution.
- Implement a Permanent Solution.
- Prevent the Problem From Recurring.
- Celebrate Team Success.
The 8D Problem Solving Process is best used with a team solving complex problems; however, individuals can also use it to solve problems on their own.
Ford is a registered trademark of the Ford Motor Company: https://www.ford.com/
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Expert Interviews
The Leadership Code
Kate Sweetman
8 Ways to Improve Your Powers of Observation
Paying Attention and Thinking Critically
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Try Mind Tools for FREE
Get unlimited access to all our career-boosting content and member benefits with our 7-day free trial.
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

What Is Gibbs' Reflective Cycle?

Team Briefings
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Onboarding with steps.
Helping New Employees to Thrive
NEW! Pain Points Podcast - Perfectionism
Why Am I Such a Perfectionist?
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Amazon Prime includes:
Fast, FREE Delivery is available to Prime members. To join, select "Try Amazon Prime and start saving today with Fast, FREE Delivery" below the Add to Cart button.
- Cardmembers earn 5% Back at Amazon.com with a Prime Credit Card.
- Unlimited Free Two-Day Delivery
- Streaming of thousands of movies and TV shows with limited ads on Prime Video.
- A Kindle book to borrow for free each month - with no due dates
- Listen to over 2 million songs and hundreds of playlists
- Unlimited photo storage with anywhere access
Important: Your credit card will NOT be charged when you start your free trial or if you cancel during the trial period. If you're happy with Amazon Prime, do nothing. At the end of the free trial, your membership will automatically upgrade to a monthly membership.
Buy new: $35.00
Return this item for free.
Free returns are available for the shipping address you chose. You can return the item for any reason in new and unused condition: no shipping charges
- Go to your orders and start the return
- Select the return method

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player

Introduction to 8D Problem Solving: Including Practical Applications and Examples Paperback – April 21, 2017
Purchase options and add-ons.
- Print length 62 pages
- Language English
- Publisher ASQ Quality Press
- Publication date April 21, 2017
- Dimensions 8.5 x 0.13 x 11 inches
- ISBN-10 1636941362
- ISBN-13 978-1636941363
- See all details

Customers who bought this item also bought

Product details
- Publisher : ASQ Quality Press (April 21, 2017)
- Language : English
- Paperback : 62 pages
- ISBN-10 : 1636941362
- ISBN-13 : 978-1636941363
- Item Weight : 5.9 ounces
- Dimensions : 8.5 x 0.13 x 11 inches
- #498 in Quality Control (Books)
- #2,088 in Business Decision Making
- #2,957 in Decision-Making & Problem Solving
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
Top review from the United States
There was a problem filtering reviews right now. please try again later..
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

8D (EIGHT DISCIPLINES) PROBLEM-SOLVING METHODOLOGY

Related Papers
Deepak Dhounchak
In the manufacturing organizations the process management and quality management is most important functions. Todays, in a competitive environment to stable organization for long time the organizations want to be successful they must quickly acclimate to changing conditions. If the problems are occurring in the organization related to the product and process the organization should be able to solve occurring problems with the flexibility towards conditions. In the organization there are various tools and methods are used for solving the occurring problems. But, there are one of these methods is 8D (Eight Disciplines). It is a structured process to solving the problems. The 8D methodology allows to solve the problems on time and correctly. Due to that fact, the 8D methodology is one of the best usable approaches for improving the quality of product, process and sort out the complaints of customer. In this research, the 8D methodology has been applied to solve the problems in the automotive industries. The subject area will yield a large value to implementing the 8D methodology for academics, advisers, researcher, and practitioners.
Today the quality is the big challenge for the automotive manufactures. By means of large and mass production of the many types of products in different lines of gathering and manufacturing. The 8D methodology is used to sort out and ameliorate the problems and errors in production. It can be followed out on product as well as system and process as well. The 8D method is used as tool for regular improvement and corrective measure to rectify the minor and major conformities. The primary use of 8D method for client complaints as well as inter plant complaints. 8D also applied for better understanding the problem and finding solutions, the primary advantage of this method, it is an easy and legitimate method to find out problems according to occur. It takes into tools and technique of the various attacks on the PDCA (PLAN-DO-CHEACK-ACT) cycle. The 8D is a team oriented problem solving (TOPS) methodology. The present work offers a direction to examine the 8D philosophy with the utilization of quality improvement thinking in producing high quality products, increase earnings and reducing defects too.
Eduard Shevtshenko
Nature Communications
José Cameselle-teijeiro
Jurnal Penyakit Dalam Indonesia
Pendahuluan. Endokarditis infektif (EI) pada pasien hemodialisis (HD) merupakan salah satu contoh EI yang terkait dengan perawatan kesehatan dan menjadi penyebab kematian kedua pada pasien HD setelah penyakit kardiovaskuler. Penggunaan kateter intravaskuler sebagai akses HD meningkatkan risiko kejadian bakteremia sebesar sepuluh kali lipat serta infeksi “metastatik” seperti EI dan emboli septik pulmoner sebesar 10-40%.Ilustrasi Kasus. Seorang laki-laki berusia 35 tahun datang dengan keluhan dyspnea d’effort, orthopnea, dan post-nocturnal dyspnea, disertai batuk dengan bercak darah dan demam tinggi sejak lima hari sebelum masuk rumah sakit. Pasien menjalani HD kronik selama 15 bulan dengan menggunakan catheter double-lumen (CDL). Dari pemeriksaan fisik didapatkan ronki basah kasar bilateral, murmur pansistolik grade 3/6 pada sela iga keempat linea sternalis sinistra, dan gallop S3. Pada ekokardiografi ditemukan vegetasi di katup trikuspid dan pemeriksaan CT-scan toraks memberikan gam...
Biological Cybernetics
Manuel Pío Portugal
Animals for survival in complex, time-evolving environments can estimate in a “single parallel run” the fitness of different alternatives. Understanding of how the brain makes an effective compact internal representation (CIR) of such dynamic situations is a challenging problem. We propose an artificial neural network capable of creating CIRs of dynamic situations describing the behavior of a mobile agent in
Jaap Timmerman
The brain has a remarkably different lipid composition than other organs; it is highly enriched in poly-unsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) and cholesterol, both major constituents of synaptic membranes. Unlike glial cells, neurons have a poor capacity to synthesize lipids, and specifically astrocytes have been proposed, based on in vitro studies, to actively supply lipids to neurons and thereby regulate synapse formation and function. However, the contribution of astrocyte lipid synthesis to synaptic function in vivo is not clear. To investigate this, we analysed mice in which the sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) cleavage-activating protein (SCAP) was deleted from GFAP-cre expressing cells. Next to astrocytes, also a large population of granular cells in the hippocampus is targeted in these mice and consequently is defective in lipid synthesis. SCAP mutant mice showed strongly reduced hippocampal LTP and impaired contextual fear memory, however, had only small changes i...
arXiv: Populations and Evolution
Marcelo Marchesin
The goal of this work is to analyse the effects of control policies for the coronavirus (COVID-19) epidemic in Brazil. This is done by considering an age-structured SEIR model with a quarantine class and two types of controls. The first one studies the sensitivity with regard to the parameters of the basic reproductive number R0 which is calculated by the next generation method. The second one evaluates different quarantine strategies by comparing their relative total number of deaths.
Vippal Savani
The problem of parameter estimation and statistical inference when fitting an M/G/∞ queuing process to data is considered in the situation where the times of arrival and departure are unknown; instead recurrent events, which occur according to a mixed Poisson process, are observed between the times of arrival and departure.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The 8D objective is to define the problem, implement containment, correct and eliminate the concern, improve quality control sys-tems, and document and report findings. It is important to note that the problem could be product or process related and the 8D process is well equipped to address both.
The eight discipline (8D) problem-solving methodology includes the following:1. Select an appropriate team2. Formulate the problem definition3. Activate interim containment4. Find root cause(s)5. Select and verify correction(s)6. Implement and validate corrective action(s)7. Take preventive steps8. Congratulate the teamThis unique book provides an overview of the 8D process, gives guidance on ...
D2: Problem description D3: Immediate measure(s) D4: Failure cause(s) D5: Planned corrective measure(s) D6: Implemented corrective measure(s) D7: Prevent a repeat of the failure D8: Acknowledge the team's success The problem solving process according to 8D is part of the complaint process and aims to provide quality assurance. 8D reporting
The 8D problem solving process is a detailed, team oriented approach to solving critical problems in the production process. The goals of this method are to find the root cause of a problem, develop containment actions to protect customers and take corrective action to prevent similar problems in the future. The strength of the 8D process lies ...
Global 8D problem solving (G8D) was developed by Ford Motor Company in the mid 1990's and is based upon their original Tops 8D problem solving method. Since then it has become one of the most commonly used structured problem solving methodologies throughout the world, in many industries both inside and outside of automotive.
0. The Planning Stage: The 8-D method of problem solving is appropriate in "cause unknown" situations and is not the right tool if concerns center solely on decision-making or problem prevention. 8-D is especially useful as it results in not just a problem-solving process, but also a standard and a reporting format.
The eight discipline (8D) problem-solving methodology includes the following: This unique book provides an overview of the 8D process, gives guidance on tools for finding root causes, shows 8D in action in eight case studies, and gives five unsolved problems for readers to apply 8D themselves for practice. Anyone who wants to improve quality ...
Discipline 1 - Build The Team. Assemble a small team of people with the right mix of skills, experience and authority to resolve the problem and implement solutions. Ensure these people have the time and inclination to work towards the common goal. Get your people "on board" by using team building tools such as ice-breakers and team ...
The 8D Problem Solving Process is a no-nonsense, easy-to-use, set of detailed instructions; a practical and comprehensive 8D Process Guidebook. Here's Why: It will save you time, is ready to use and will help you reap maximum benefits from the 8D method. ... As a text book for training teams in the use of the 8 D reporting format you find ...
The Ford Motor Company® developed the 8D (8 Disciplines) Problem Solving Process, and published it in their 1987 manual, "Team Oriented Problem Solving (TOPS)." In the mid-90s, Ford added an additional discipline, D0: Plan. The process is now Ford's global standard, and is called Global 8D. Ford created the 8D Process to help teams deal with ...
Eight Disciplines Methodology (8D) is a method or model developed at Ford Motor Company used to approach and to resolve problems, typically employed by quality engineers or other professionals. Focused on product and process improvement, its purpose is to identify, correct, and eliminate recurring problems. It establishes a permanent corrective action based on statistical analysis of the ...
Root Cause Corrective Action Using the 8D Process Eight Disciplines (8D) Problem Solving is a method developed at Ford Motor Company used to approach and to resolve problems, typically . employed by engineers and quality professionals. Focused on product and process improvement, its purpose is to identify, correct, and
The purpose of using the 8D method is to eliminate problems in products or processes and avoid the recurrence of similar or same problems. Method improves effectiveness and efficiency in problem solving. Create and expand a database of past failures and lessons learned to prevent problems in the future. The 8D method enables you to:
Full Text. This excerpt from the new book describes the 8D problem-solving approach and application. Problem solvers are a very important resource in any organization. These are the people who are able to identify creatively and remove barriers that keep the organization from accomplishing its mission. All personnel should understand that part ...
The eight discipline (8D) problem-solving methodology includes the following: Select an appropriate team Formulate the problem definition Activate interim containment Find root cause(s) Select and verify correction(s) Implement and validate corrective action(s) Take preventive steps Congratulate the team This unique book provides an overview of the 8D process, gives guidance on tools for ...
The eight discipline (8D) problem-solving methodology includes the following: Select an appropriate team Formulate the problem definition Activate interim containment Find root cause(s) Select and verify correction(s) Implement and validate corrective action(s) Take preventive steps Congratulate the team This unique book provides an overview of the 8D process, gives guidance on tools for ...
8D+Methodology+of+Problem+Solving - Free download as Word Doc (.doc), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. 8D process is a problem solving method for product and process improvement. It is structured into 8 steps (the D's) and emphasizes team. By taking this approach we can continuously improve quality by eliminating the causes of problems and prevent their reoccurrence.
An improved model for solving truck vibration problem is established by using the G8D method, and the unbalanced excitation force of the wheel system is analysed, which can improve the sustainability of product manufacturing, provide industry guidance for solving the quality problem of truck vibration, and provide a sustainable guarantee for social public transport safety.
These eight step process of problem solving is known as 8D (Eight disciplines)* and is by far the common disciplines used and accepted by most industries today. It is the basis for all subsequent problem solving technique developments such as 6D, 7D, 9D and 10D. The 8D Problem Solving Process to identify, correct and eliminate the recurrence of ...
A 74FPUR13 PDF | PDF | Business | Evaluation. 8D Work Instructions Rev. A 74FPUR13.pdf - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.
8D Problem Solving 1½ days virtual training PRACTITIONER MODULE 8D is the global problem solving method of choice for business and industry, and a mandatory quality deliverable in many sectors such as aerospace and automotive. The 8D approach focuses on analysing and improving the control systems that allow problems to escape.
8D-Problem Solving Method or Tools - Free download as Word Doc (.doc), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. The 8d problem solving method consists of 7 steps. Each step involves a well rounded team with different skill and intimate knowledge of the processes where the problem has occurred. The final step is to Implement and Verify Interim Actions.
Title: Microsoft Word - 8D Problem Solving training.docx Author: KowalcD1 Created Date: 12/16/2019 6:51:23 PM