- Human Development Report 2023-24
- The paths to equal
- 2023 Global Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI)
- 2023 Gender Social Norms Index Publication
- Human Development Index
- Country Insights
- Human Climate Horizons data and insights platform
- Thematic Composite Indices
- Documentation and downloads
- What is Human development?
- NHDR/RHDR Report preparation toolkit

What is Human Development?
While the expression “human development” is widely used, it is understood in different ways around..

HDRO Outreach
2015 marks 25 years since the first Human Development Report introduced a new approach for advancing human flourishing. And while the expression “human development” is widely used, it is understood in different ways around the world. So on the occasion of the 25th anniversary year of human development reporting, we’d like to highlight how the Human Development Report Office (HDRO) presents human development.
Credit: UNDP Kosovo’s animation "What is Human Development?" explains and promotes sustainable human development.
Human development grew out of global discussions on the links between economic growth and development during the second half of the 20th Century. By the early 1960s there were increasingly loud calls to “dethrone” GDP: economic growth had emerged as both a leading objective, and indicator, of national progress in many countries i , even though GDP was never intended to be used as a measure of wellbeing ii . In the 1970s and 80s development debate considered using alternative focuses to go beyond GDP, including putting greater emphasis on employment, followed by redistribution with growth, and then whether people had their basic needs met.
These ideas helped pave the way for the human development approach, which is about expanding the richness of human life, rather than simply the richness of the economy in which human beings live. It is an approach that is focused on creating fair opportunities and choices for all people. So how do these ideas come together in the human development approach?
- People: the human development approach focuses on improving the lives people lead rather than assuming that economic growth will lead, automatically, to greater opportunities for all. Income growth is an important means to development, rather than an end in itself.
- Choices: human development is, fundamentally, about more choice. It is about providing people with opportunities, not insisting that they make use of them. No one can guarantee human happiness, and the choices people make are their own concern. The process of development – human development - should at least create an environment for people, individually and collectively, to develop to their full potential and to have a reasonable chance of leading productive and creative lives that they value.
The human development approach, developed by the economist Mahbub Ul Haq, is anchored in Amartya Sen’s work on human capabilities, often framed in terms of whether people are able to “be” and “do” desirable things in life iii . Examples include
Beings: well fed, sheltered, healthy
Doings: work, education, voting, participating in community life.
Freedom of choice is central: someone choosing to be hungry (during a religious fast say) is quite different to someone who is hungry because they cannot afford to buy food.
As the international community seeks to define a new development agenda post-2015, the human development approach remains useful to articulating the objectives of development and improving people’s well-being by ensuring an equitable, sustainable and stable planet.
i Kennedy, Robert. (1968). Address to the University of Kansas, Lawrence, Kansas on March 18, 1968. www.informationclearinghouse.info/article27718.htm ii Simon Kuznets, who created GDP, warned expressly against using it as a measure of wellbeing. Kuznets, Simon. “National Income, 1929–1932.” U.S. Congress, Senate Doc. No. 124–73, at 7 (1934) iii Professor Sen was awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1998 for his work in welfare economics.
Photo credit: UNDP Mongolia's #GivingTuesday
More on human development
Related News

Announcement: 2021/22 Human Development Report set to be released on 8 September 2022

Two steps forward, one step back - where are we heading with gender equality?

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
What is Development?
Human Development or Lifespan Development is the scientific study of the ways in which people change, as well as remain the same, from conception to death. You will discover that the field, known more broadly as developmental science , examines changes and stability across multiple domains of psychological and social functioning. These include physical and neurophysiological processes, cognition, language, emotion, personality, moral, and psychosocial development, including our relationships with others.

Originally concerned with infants and children, the field has expanded to include adolescence and more recently, aging and the entire life span. Previously, the message was once you are 25, your development is essentially completed. Our academic knowledge of the lifespan has changed, and although there is still less research on adulthood than on childhood, adulthood is gaining increasing attention. This is particularly true now that the large cohort known as the “baby boomers” are beginning to enter late adulthood. The assumption that early childhood experiences dictate our future is also being called into question. Instead, we have come to appreciate that growth and change continues throughout life and experience continues to have an impact on who we are and how we relate to others. We now recognize that adulthood is a dynamic period of life marked by continued cognitive, social, and psychological development.
You will also discover that developmental psychologists investigate key questions, such as whether children are qualitatively different from adults or simply lack the experience that adults draw upon. Other issues they consider include the question of whether development occurs through the gradual accumulation of knowledge or through qualitative shifts from one stage of thinking to another, or if children are born with innate knowledge or figure things out through experience, and whether development is driven by the social context or something inside each child. From these questions, you may already be thinking that developmental psychology is related to other applied fields. You are right. Developmental science informs many applied fields, including, educational psychology, developmental psychopathology, and intervention science. It also complements several other basic research fields in psychology including social psychology, cognitive psychology, and cross-cultural psychology. Lastly, it draws from the theories and research of several scientific fields including biology, sociology, health care, nutrition, and anthropology.
Learning Objectives: Lifespan Perspective
- Explain the lifespan perspective and its assumptions about development
- Differentiate periods of human development
- Identify key assumptions and major meta-theories underlying lifespan development
- Identify major historical and contemporary theories focusing on lifespan development
Lifespan Perspective
Paul Baltes identified several underlying principles of the lifespan perspective (Baltes, 1987; Baltes, Lindenberger, & Staudinger, 2006).
- Development is lifelong . Lifespan theorists believe that development is life-long, and change is apparent across the lifespan. No single age period is more crucial, characterizes, or dominates human development. Consequently, the term lifespan development will be used throughout the textbook.
- Development is multidirectional and multidimensional. Lifespan researchers hold that different people follow different developmental pathways, and proceed along pathways at different rates. Even within the same person, different dimensions or domains of development can change in different ways.
- Development includes both gains and losses . Lifespan theorists do not agree with the traditional view of development that childhood is a period characterized by developmental gains, whereas old age is a time of loss. Instead, the lifespan approach holds that at every age, we may show gains in some areas of development, while showing losses in other areas. Every change, whether it is finishing high school, getting married, or becoming a parent, entails both growth and loss.
- Development is characterized by plasticity. Plasticity is about malleability , or our potential to change and to follow a wide range of developmental pathways. For instance, plasticity is illustrated in the brain’s ability to learn from experience and the many ways it can recover from injury.
- Development is embedded in historical and cultural contexts. Lifespan researchers believe that d evelopment is influenced by the many social contexts in which it unfolds. How people develop will depend on their societal and cultural contexts, and on the historical period during which their development takes place.
- Development is multiply determined. Lifespan theorists argue that development is caused by multiple factors, and is always shaped by both biological and environmental factors. In addition, the individual plays an active role in their own development.
- Development is multidisciplinary. As mentioned at the start of the chapter, human development is such a vast topic of study that it requires the theories, research methods, and knowledge bases of many academic disciplines.
Contextualism as paradigm. Baltes (1987) identified three specific developmental systems of influence, all of which include biological and environmental forces.
- Normative age-graded influences: An age-grade is a specific age group, such as toddler, adolescent, or senior . Humans experience particular age-graded social experiences (e.g., starting school) and biological changes (e.g., puberty).
- Normative history-graded influences: The time period in which you are born (see Table 1.1) shapes your experiences. A cohort is a group of people who are born at roughly the same period in a particular society. These people travel through life often experiencing similar historical changes at similar ages. History-graded influences include both environmental determinants (e.g., historical changes in the job market) and biological determinants (e.g., historical changes in life expectancy).
- Non-normative influences : People’s development is also shaped by specific influences that are not organized by age or historical time, such as immigration, accidents, or the death of a parent. These can be environmental (e.g., parental mental health issues) or biological (e.g., life threatening illness).
Table 1.1. Which generation (cohort) are you?
adapted from Lally & Valentine-French, 2019
Domains of development. We change across three general domains/dimensions; physical, cognitive, and psychosocial. The physical domain includes changes in height and weight, sensory capabilities, the nervous system, as well as the propensity for disease and illness . The cognitive domain encompasses the changes in intelligence, wisdom, perception, problem-solving, memory, and language. The psychosocial domain focuses on changes in emotion, self-perception and interpersonal relationships with families, peers, and friends. All three domains influence each other. It is also important to note that a change in one domain may cascade and prompt changes in the other domains. For instance, an infant who has started to crawl or walk will encounter more objects and people, thus fostering developmental change in the child’s understanding of the physical and social world.
Contextual perspectives , like the lifespan approach, highlight societal contexts that influence our development. An important societal factor is our social standing, socioeconomic status, or social class. Socioeconomic status (SES) is a way to identify families and households based on their shared levels of education, income, and occupation. While there is certainly individual variation, members of a social class tend to share similar privileges, opportunities, lifestyles, patterns of consumption, parenting styles, stressors, religious preferences, and other aspects of daily life. All of us born into a class system are socially located, and we may move up or down depending on a combination of both socially and individually created limits and opportunities.
Families with higher socioeconomic status usually are in occupations (e.g., attorneys, physicians, executives) that not only pay better, but also grant them a certain degree of freedom and control over their job. Having a sense of autonomy or control is a key factor in experiencing job satisfaction, personal happiness, and ultimately health and well-being (Weitz, 2007). Those families with lower socioeconomic status are typically in occupations that are more routine, more heavily supervised, and require less formal education. These occupations are also more subject to job disruptions, including lay-offs and lower wages.
Poverty level is an income amount established by the federal government that is based on a set of thresholds that vary by family size (United States Census Bureau, 2016). If a family’s income is less than the government threshold, that family is considered in poverty. Those living at or near poverty level may find it extremely difficult to sustain a household with this amount of income. Poverty is associated with poorer health and a lower life expectancy due to poorer diet, less healthcare, greater stress, working in more dangerous occupations, higher infant mortality rates, poorer prenatal care, greater iron deficiencies, greater difficulty in school, and many other problems. Members of higher income status may fear losing that status, but the poor may have greater concerns over losing housing.
Today we are more aware of the variations in development and the impact that culture and the environment have on shaping our lives. Culture is the totality of our shared language, knowledge, material objects, and behavior. It includes ideas about what is right and wrong, what to strive for, what to eat, how to speak, what is valued, as well as what kinds of emotions are called for in certain situations. Culture teaches us how to live in a society and allows us to advance because each new generation can benefit from the solutions found and passed down from previous generations. Culture is learned from parents, schools, houses of worship, media, friends and others throughout a lifetime. The kinds of traditions and values that evolve in a particular culture serve to help members function and value their own society. We tend to believe that our own culture’s practices and expectations are the right ones. This belief that our own culture is superior is called ethnocentrism and is a normal by-product of growing up in a culture. It becomes a roadblock, however, when it inhibits understanding of cultural practices from other societies. Cultural relativity is an appreciation for cultural differences and the understanding that cultural practices are best understood from the standpoint of that particular culture.
Culture is an extremely important context for human development and understanding development requires being able to identify which features of development are culturally based. This understanding is somewhat new and still being explored. Much of what developmental theorists have described in the past has been culturally bound and difficult to apply to various cultural contexts. The reader should keep this in mind and realize that there is still much that is unknown when comparing development across cultures.
Lifespan vs. Life expectancy: At this point you must be wondering what the difference between lifespan and life expectancy is, according to developmentalists. Lifespan , or longevity, refers to the maximum age any member of a species can reach under optimal conditions . For instance, the grey wolf can live up to 20 years in captivity, the bald eagle up to 50 years, and the Galapagos tortoise over 150 years (Smithsonian National Zoo, 2016). The longest recorded lifespan for a human was Jean Calment who died in 1994 at the age of 122 years, 5 months, and 14 days (Guinness World Records, 2016). Life expectancy is the average number of years a person born in a particular time period can typically expect to live (Vogt & Johnson, 2016).
Conceptions of Age
How old are you? Chances are you would answer that question based on the number of years since your birth, or what is called your chronological age . Ever felt older than your chronological age? Some days we might “feel” like we are older, especially if we are not feeling well, are tired, or are stressed out. We might notice that a peer seems more emotionally mature than we are, or that they are physically more capable. So years since birth is not the only way we can conceptualize age.
Biological age: Another way developmental researchers can think about the concept of age is to examine how quickly the body is aging , this is your biological age . Several factors determine the rate at which our body ages. Our nutrition, level of physical activity, sleeping habits, smoking, alcohol consumption, how we mentally handle stress, and the genetic history of our ancestors, to name but a few.
Psychological age: Our psychologically adaptive capacity compared to others of our chronological age is our psychological age . This includes our cognitive capacity along with our emotional beliefs about how old we are. An individual who has cognitive impairments might be 20 years of age, yet has the mental capacity of an 8-year-old. A 70- year-old might be travelling to new countries, taking courses at college, or starting a new business. Compared to others of our age group, we may be more or less active and excited to meet new challenges. Remember you are as young or old as you feel.
Social age: Our social age is based on the social norms of our culture and the expectations our culture has for people of our age group . Our culture often reminds us whether we are “on target” or “off target” for reaching certain social milestones, such as completing our education, moving away from home, having children, or retiring from work. However, there have been arguments that social age is becoming less relevant in the 21st century (Neugarten, 1979; 1996). If you look around at your fellow students at college you might notice more people who are older than traditional aged college students, those 18 to 25. Similarly, the age at which people are moving away from the home of their parents, starting their careers, getting married or having children, or even whether they get married or have children at all, is changing.
Those who study lifespan development recognize that chronological age does not completely capture a person’s age. Our age profile is much more complex than this. A person may be physically more competent than others in their age group, while being psychologically immature. So, how old are you?
Table 1.2 Age Periods of Development
Table 1.2 shows the developmental periods that will be explored in this book, starting with prenatal development and continuing thought late adulthood to death. Both childhood and adulthood are divided into multiple developmental periods. So, while both an 8-month old and an 8-year-old are considered children, they have very different motor abilities, social relationships, and cognitive skills. Their nutritional needs are different and their primary psychological concerns are also distinctive. The same is true of an 18-year-old and an 80-year-old, even though both are considered adults.
Prenatal Development : Conception occurs and development begins. All of the major structures of the body are forming, and the health of the mother is of primary concern. Understanding nutrition, teratogens , or environmental factors that can lead to birth defects , and labor and delivery are primary concerns.

Infancy and Toddlerhood : The first two years of life are ones of dramatic growth and change. A newborn, with a keen sense of hearing but very poor vision, is transformed into a walking, talking toddler within a relatively short period of time. Caregivers are also transformed from someone who manages feeding and sleep schedules to a constantly moving guide and safety inspector for a mobile, energetic child.
Early Childhood: This period is also referred to as the preschool years and consists of the years that follow toddlerhood and precede formal schooling. As a two to six-year-old, the child is busy learning language, gaining a sense of self and greater independence, and beginning to understand the workings of the physical world.
Middle and Late Childhood: The ages of six to the onset of puberty comprise middle and late childhood, and much of what children experience at this age is connected to their involvement in the early grades of school. Now the world becomes one of learning and testing new academic skills, and assessing one’s abilities and accomplishments by making comparisons between self and others.
Adolescence : Adolescence is a period of dramatic physical change marked by an overall growth spurt and sexual maturation, known as puberty . It is also a time of cognitive change as the adolescent begins to think of new possibilities and to consider abstract concepts such as love, fear, and freedom. At the same time, adolescents have a sense of invincibility that puts them at greater risk of accidents or contracting sexually transmitted infections that can have lifelong consequences.
Emerging Adulthood: The period of emerging adulthood is a transitional time between the end of adolescence and before individuals acquire all the benchmarks of adulthood. Continued identity exploration and preparation for full independence from parents are negotiated. Although at one’s physiological peak, emerging adults are most at risk for involvement in violent crimes and substance abuse.
Early Adulthood : The twenties and thirties are identified as early adulthood. Intimate relationships, establishing families (of all shapes and sizes), and work are primary concerns at this stage of life. For adults with children, developmental changes can become organized around the family life cycle.

Middle Adulthood : The forties through the mid-sixties are referred to as middle adulthood. This is a period in which aging becomes more noticeable and when many people are at their peak of productivity in love and work. At this age, some people are negotiating adolescent children and aging parents at the same time.
Late Adulthood : Late adulthood is sometimes subdivided into two categories: The young-old who are from 65-84 years and the oldest-old who are 85 years and older. One of the primary differences between these groups is that the young-old are still relatively healthy, productive, active, and the majority continue to live independently. With both age groups the risks of diseases such as arteriosclerosis, cancer, and cerebral vascular disease increase substantially.
Meta-theories of Human Development
The study of development is guided by the assumptions researchers hold about the nature of humans and their development. These assumptions are called meta-theories . “Meta” means “above” or “beyond,” like “meta-physics.” Other terms used to describe meta-theories are “world views,” “cosmologies,” “perspectives,” or “paradigms,” as in “paradigm shifts.” Explicit discussions of meta-theories are found most often in philosophy.
What are meta-theories of human development?
Meta-theories (or world views or paradigms) of human development are sets of assumptions people hold about the nature of humans and the meaning of development — what it looks like, how it happens, what causes it. These assumptions are important because everyone has them, including researchers, but they are often implicit, meaning we are not always consciously aware of them. In the study of development, such assumptions influence everything about how research is conducted: the questions we ask, the measures and methods that are used, and the interpretation of data. For example, if researchers assume that development ends at 18, they do not look for developmental changes after that age. Or, if researchers assume that aging is a process of decline, then they never look for characteristics that might improve as people get older.
All researchers have meta-theories, since assumptions are baked into the theories and methodologies they use. But researchers are often unaware of them, and so these assumptions are rarely acknowledged. It is important to note that meta-theories are not just cold cognitions. They are often deeply held convictions that researchers will fiercely defend. Typically researchers think that their assumptions are self-evident truths. They are often convinced that their assumptions are right and everyone else’s are wrong.
Researchers holding different meta-theories can have difficulty communicating with each other. Since they are asking different questions and using different truth criteria for research, they often argue past each other or misunderstand each other. One group of researchers will offer what they consider to be irrefutable proof of their ideas, which other researchers then dismiss as irrelevant. Discrepancies, inconsistencies, arguments, and furor often characterize an area of study in which researchers from multiple meta-theories are working.
What kinds of assumptions guide the study of human development?
We consider six key assumptions. You may have heard of many of them, since they are perennial issues in the study of development. They include:
- Assumptions about human nature : whether people are born as blank slates ( tabula rasa ) or whether people are inherently good or inherently bad.
- Assumptions about the causes of development : whether development is determined by nature (genes, biology) or determined by nurture (environment, learning).
- Assumptions about the role of the individual in his or her own development: whether people are passive participants, reacting to external forces or whether they are active in choosing and shaping their own development.
- Assumptions about stability vs. change : whether traits, characteristics, and experiences early in life have permanent effects or whether people are malleable and open to change throughout life.
- Assumptions about continuity vs. discontinuity : whether development involves quantitative incremental change or qualitative shifts.
- Assumptions about universality vs. context specificity : whether development follows a universal pathway or depends more on specific experiences and environmental contexts.
Nature of humans. What is the nature of humans? These assumptions refer to beliefs about the underlying qualities of our species– whether humans are born as blank slates ( tabula rasa ) or whether we all bring intrinsic human characteristics with us into the world. For example, these different assumptions are readily apparent in alternative conceptualizations of motivation—some theories assume that motives and motivation are all acquired, whereas others assume that all humans come with intrinsic motivations.
Nature and Nurture: Why are you the way you are? As you consider some of your features (height, weight, personality, being diabetic, etc.), ask yourself whether these features are a result of heredity or environmental factors, or both. Chances are, you can see the ways in which both heredity and environmental factors (such as lifestyle, diet, and so on) have contributed to these features. For decades, scholars have carried on the “nature/nurture” debate. For any particular feature, those on the side of nature would argue that heredity plays the most important role in bringing about that feature. Those on the side of nurture would argue that one’s environment is most significant in shaping the way we are. This debate continues in all aspects of human development, and most scholars agree that there is a constant interplay between the two forces. It is difficult to isolate the root of any single behavior as a result solely of nature or nurture.
Active versus Passive: How much do you play a role in your own developmental path? Are you at the whim of your genetic inheritance or the environment that surrounds you? Some theorists see humans as playing a much more active role in their own development. Piaget, for instance believed that children actively explore their world and construct new ways of thinking to explain the things they experience. In contrast, many behaviorists view humans as being more passive in the developmental process.
Stability versus Change: How similar are you to how you were as a child? Were you always as out-going or reserved as you are now? Some theorists argue that the personality traits of adults are rooted in the behavioral and emotional tendencies of the infant and young child. Others disagree, and believe that these initial tendencies are modified by social and cultural forces over time.
Continuity versus Discontinuity: Is human development best characterized as a slow, gradual process, or is it best viewed as one of more abrupt change? The answer to that question often depends on which developmental theorist you ask and what topic is being studied. The theories of Freud, Erikson, Piaget, and Kohlberg are called stage theories. Stage theories or discontinuous development assume that developmental change occurs in distinct stages that are qualitatively different from each other, and that unfold in a set, universal sequence . At each stage of development, children and adults have different qualities and characteristics. Thus, stage theorists assume development is discontinuous. Others, such as the behaviorists, Vygotsky, and information processing theorists, assume development is a more slow and gradual process known as continuous development . For instance, they would see the adult as not possessing new skills, but as using more advanced skills that were already present in some form in the child. Brain development and environmental experiences contribute to the acquisition of more developed skills.
Universal vs. context specific . A final assumption focuses on whether pathways of development are presumed to be (1) normative and universal, meaning that all people pass through them in the same sequence, or (2) differential and specific, meaning that a variety of different patterns and pathways of developmental change are possible depending on the individual and the context. Some theorists, like Piaget or Erickson, assume that everyone progresses through the same stages of cognitive development in the same order, or that everyone negotiates the same set of developmental tasks at about the same ages. Other theorists, who endorse lifespan or ecological systems approaches, believe that development can take on a wide variety of patterns and pathways, depending on the specific cultural, historical, and societal under which it unfolds.
What are the guiding meta-theories in human development?
These six basic assumptions are clustered into “packages” that go together. Clusters are organized around metaphors, which are at the root of meta-theories of humans and their development. We consider four meta-theories, each with its own metaphor: (1) humans as seeds , as depicted by Maturational meta-theories; (2) humans as machines , as depicted in Mechanistic meta-theories (3) humans as butterflies , as depicted in Organismic meta-theories; and (4) humans as participants in a tennis game, conversation, or dance , as depicted by Contextualist meta-theories. For an overview of these guiding meta-theories, see this chart [pdf] .
- Maturational meta-theory : Maturational meta-theories can be understood using the plant as a metaphor. It is as if humans develop the same way as plants. The important thing to study is people’s “seeds,” that is, their genetic make-up. People are assumed to be passive, the product of their genes. The environment can provide support and nutrition (rain, sun, and soil), but can’t change a person’s nature (poppy seeds will always produce poppies). The role of the person is to be reactive—to their genes. The course of development will be continuous or discontinuous depending on the genetic program, although acorns always grow into oak trees.
- Mechanistic meta-theory : Mechanistic meta-theories can be understood using the machine as a metaphor. It is as if humans change the same way as machines. People are assumed to be made up of pieces that can be studied apart from the rest of them. They are passive, with the energy coming from outside (like gasoline for a car). Development is continuous and people do not develop into something else (a car stays a car). The person can only react to the environment that is controlling them (like a car responding to the gas pedal or the brake). All causes for development come from the outside, from environmental forces.
- Organismic meta-theory : Organismic meta-theories can be understood using the butterfly as a metaphor. It is as if humans develop the same way as butterflies. People are assumed to be made up of structured wholes. Their nature is to be curious, interested, and open to growth. They are active and develop through discontinuous qualitatively different stages (like the caterpillar, chrysalis, and butterfly). People construct their own next steps in development based on the affordances and opportunities provided by the environment. Development is caused by imbalances that lead to structural reorganizations. Development is progressive (gets better) and only goes in one direction (from caterpillar toward butterfly) and not the reverse.
- Contextual meta-theory : Contextual meta-theories can be understood using the tennis game (or dance) as a metaphor. It is as if humans’ development is like a game of tennis or a dance. The important thing to study is the back and forth between the person and his or her context, both of which are assumed to be proactive and acting on their own agendas. Development can be continuous or discontinuous depending on how the game is played. Both person and environment are active partners in the system, which can lead to transformations in both.
What are examples of theories that fall within each meta-theory?
Nested within each higher-order meta-theory are sets of lower-level approaches or theories called “families” of perspectives or theories to denote that they share common properties, based on their similarity to the root metaphors and characteristics of the guiding meta-theories. This table contains several examples of “big” theories of development and provides an analysis of their defining features according to the meta-theoretical assumptions we have been discussing [pdf]. Based on this analysis, we indicate the higher-order family to which we think each big theory or approach belongs.
Although maturational meta-theories were prevalent in the beginning of the 20th century, their popularity has waxed and waned since then, and they have taken on many different forms. These include some formulations of behavioral genetics, sociobiology, evolutionary, ethological, neuroscience, temperament, and personality theories. Maturational assumptions are signaled by concepts such as “trait,” the search for “the aggression gene,” the discovery of the brain system, hormone, or neurotransmitter responsible for a specific condition, or any other terms that suggest development is solely the product of innate or immutable characteristics of individuals. Although they are not typically referred to as “maturational,” there are many kinds of theories that place all the active ingredients of behavior or development inside the head (or more specifically the social cognitions) of the person. Even if they are not direct descendants, these theories can be considered cousins of Maturational meta-theories because they are exclusively focused on the role of the individual.
The prototypic Mechanistic theories are behaviorist, operant, and classical conditioning learning theories, like social learning theory. This family of theories dominated psychology from the early to the mid-20th century, but Mechanistic theories are still alive and well in many areas, such as learning and motivation, and especially in many theories that have been adapted for use in educational systems. New kinds of machines serve as prototypes for mechanistic theories of memory, learning, and automatic functioning—focusing on the computer, the robot, and the automaton. Such assumptions have even pervaded our understanding of biological systems, as seen in metaphors like “the brain is a computer.” And although the “cognitive revolution” was supposed to have overthrown behaviorist assumptions, some cognitivistic theories treat humans as if they were information processing machines.
Perhaps surprisingly, there are also mechanistic assumptions embedded in certain progressive analyses of the effects of societal and social conditions, such as poverty, oppression, racism, and discrimination, which sometimes seem to imply that these external forces are the sole determinants of the development of stereotypes or implicit attitudes. In this case, because all people are presumed to passively internalize these societal prejudices, psychological phenomena are modeled after the metaphor of the “Xerox machine.” Just as in Maturational meta-theories, where humans could be seen as “hosts” to their genes, who were really running the show, in Mechanistic meta-theories, humans can be seen as “hosts” to their own behaviors, which are automatically reflexively produced based on previous social programming.
The prototypical Organismic theory is Piaget’s constructivist theory of cognitive and affective development, and the several neo-constructivist theories that were inspired by Piaget, for example, Kohlberg’s theory of the development of moral reasoning. Other theories living under the Organismic umbrella include Werner’s comparative psychology, focusing on the orthogenetic principle of differentiation and integration, and Erikson, who posited universal age-graded developmental tasks. Other theories that claim kinship with Organismic meta-theories (e.g., theories of intrinsic motivation) do not typically include notions of universal stages or tasks, but focus instead on Organismic assumptions about the nature of humans, specifically, that humans are innately active, curious, and interested, and inherently desire to explore, understand, and fit in with their social and physical environments. With the rise of radical contextualism and cultural relativism in psychology, theories of “universal” anything (e.g., psychological needs, stages, developmental tasks) have come increasingly under attack.
Some of the better-known members of the Contextualist family include Bronfenbrenner’s bio-ecological model and the lifespan approach, both of which arose in reaction to dominant meta-theories of their day (experimental child psychology and Piagetian psychology, respectively), with their almost exclusive focus on the child as a developing individual. The “contextualist” moniker reflects these perspectives’ insistence that development unfolds within and is shaped by higher-order multi-level ecological or contextual forces outside the individual, such as microsystem settings, and societal, cultural, and historical contexts.
Does the field of psychology have meta-theories?
During different historical periods, specific meta-theories dominated the field of psychology. For example, during the 1940s and 1950s, behaviorism held sway. In the 1960s, Piaget’s theories were introduced to the United States and captured the field’s attention. Some fierce theoretical and empirical battles were fought between behaviorists and Piagetians.
When a specific meta-theory governs the field, it becomes very difficult for researchers from opposing meta-theories to work—they have trouble getting funding, they have trouble getting their research findings published, and they are marginalized by other researchers. For example, when the area of motivation was dominated by behaviorists (who believed that all behavior was motivated by rewards and punishments), it was very difficult for researchers to study and publish research on intrinsic motivation.
What is the dominant meta-theory in the field today?
“Cognitivism” is a guiding meta-theory in the field of psychology today. “Cognitivism” is the assumption that all the causal factors that shape human behavior and development are inside the mind or belief system of the person. You can hear the assumptions in the theories of the field: self-efficacy, self-esteem, attributions, perceived social support, values, sense of purpose, goal orientations, internal working model, identity, and so on.
The paradigm that is currently taking over the field of psychology is neuroscience . That is, the brain is in charge of behavior, and neurobiology is destiny. Some branches of neuroscience are predominantly Maturational , as seen in discussions of the brain systems responsible for certain actions, predilections, and characteristics. Other branches are more Contextual , for example, research on neuroplasticity, which examines the way that social contexts and interactions shape the developing brain.
News flash : In the field of psychology outside developmental, most researchers assume that people don’t develop. In personality, social, cognitive, and industrial-organizational psychology, researchers largely examine individual differences as indicators of people’s permanent characteristics.
Who else has meta-theories?
Everyone has meta-theories about human nature and development: parents, teachers, nurses, social workers, doctors, business people, artists, politicians, and so on.
For example,
- doctors assume that weight loss is all about diet and exercise (nurture), so no one can do research on physiological differences in metabolism (nature).
- teachers have assumptions about whether students come with motivation (nature) or have to be motivated from the outside (nurture), and organize their classrooms accordingly.
- parents often argue about the nature of children’s development, whether it’s just the child’s personality (maturational), or the child is going through a normal stage (organismic), or if they are rewarding the wrong behavior (mechanistic).
What is the meta-theory that guides our class and this book?
Our class endorses a life-span perspective on human development, a contextualist perspective that fought its way through the dominant perspectives in child psychology (e.g., development ends at age 18), starting in the 1980s to become one of the dominant meta-theories governing the field of developmental science today. Note that your instructors chose your book, so their meta-theory is influencing the meta-theoretical filter through which you are learning about development.
What is the correct meta-theory?
There is no single correct definition of development or meta-theory. Really. Even the lifespan approach has its drawbacks.
However, as research accumulates, many theories derived from certain meta-theories have been found to be incomplete—so far researchers have not found any significant aspect of development that is caused only by nature or only by nurture. Therefore, most researchers currently say they favor interactionist metatheories, like contextualist or systems meta-theories. However, it is important to look carefully at researchers’ actual work, because sometimes they say that they have one meta-theory, but their work seems to be guided by assumptions from a different meta-theory.
Do I have a meta-theory about development?
Yes, you do. And you can figure out what it is. Although it’s not easy, you can discern your own assumptions about development—by thinking about which assumptions make the most sense to you. You can also see which kinds of theories you prefer and what kinds of recommendations you would make about how to structure development, like how people should parent, teach, or make policies. The hardest part about discovering your own meta-theory is realizing that it is made up of assumptions you have (based on your experiences and messages from society)—that aren’t necessarily true. Our meta-theories sure seem true to each of us!
How do I get rid of my meta-theory?
It’s not really possible to get rid of all of our assumptions. It is our goal to be aware of our own assumptions or meta-theories, to realize that they are not the truth but are our current working models of how the world operates and people develop. The most important thing is to be explicit about our assumptions and to be cognizant of how they are guiding our actions. It is a goal of this class to help students figure out their own assumptions and to help them become (or remain) open to alternative viewpoints.
Adapted from : Ellen Skinner, Glen Richardson, Jennifer Pitzer, and Cynthia Taylor. Portland State University. July 2011.
Historical Theories of Development
Preformationist View : Well into the 18th century, children were merely thought of as little adults. Preformationism , or the belief that a tiny, fully formed human is implanted in the sperm or egg at conception and then grows in size until birth, was the predominant early theory. Children were believed to possess all their sensory capabilities, emotions, and mental aptitude at birth, and as they developed these abilities unfolded on a predetermined schedule (Thomas, 1979). The environment was thought to play no role in determining development .
John Locke (1632-1704): Locke, a British philosopher, refuted the idea of innate knowledge and instead proposed that children are largely shaped by their social environments, especially their education as adults teach them important knowledge. He believed that through education a child learns socialization, or what is needed to be an appropriate member of society. Locke advocated thinking of a child’s mind as a tabula rasa or blank slate , and whatever comes into the child’s mind comes from the environment. Locke emphasized that the environment is especially powerful in the child’s early life because he considered the mind the most pliable then. Locke indicated that the environment exerts its effects through associations between thoughts and feelings, behavioral repetition, imitation, and rewards and punishments (Crain, 2005). Locke’s ideas laid the groundwork for the behavioral perspective and subsequent learning theories of Pavlov, Skinner and Bandura.
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712-1778): Like Locke, Rousseau also believed that children were not just little adults. However, he did not believe they were blank slates, but instead developed according to a natural plan which unfolded in different stages (Crain, 2005). He did not believe in teaching them the correct way to think, but believed children should be allowed to think by themselves according to their own ways and an inner, biological timetable. This focus on biological maturation resulted in Rousseau being considered the father of developmental psychology. Followers of Rousseau’s developmental perspective include Gesell, Montessori, and Piaget.
Arnold Gesell (1880-1961): Gesell spent 50 years at the Yale Clinic of Child Development, and with his colleagues he studied the neuromotor development of children. Gesell believed that the child’s development was activated by genes and he called this process maturation (Crain, 2005). Further, he believed that development unfolded in fixed sequences, and he opposed efforts to teach children ahead of schedule as he believed they will engage in behaviors when their nervous systems had sufficiently matured.

Sigmund Freud (1856-1939): Freud was a very influential figure in the area of development. Freud emphasized the importance of early childhood experiences in shaping our personality and behavior. In our natural state, we are biological beings and are driven primarily by instincts. During childhood, however, we begin to become social beings as we learn how to manage our instincts and transform them into socially acceptable behaviors. His assumptions were that personality formed during the first few years of life. The ways in which parents or other caregivers interacted with children were assumed to have a long-lasting impact on children’s emotional states. His beliefs formed the psychodynamic perspective and his theories of psychosexual development and psychopathology dominated the field of psychiatry until the growth of behaviorism in the 1950s.
However, Freud’s theory has been heavily criticized for several reasons. One is that it is very difficult to test scientifically (Crews, 1998). Freud suggested that much of what determines our actions were unknown to us, and as scientists we cannot measure these unconscious concepts. A second criticism is that Freud’s case studies were not validated and cannot be used as evidence for his theories. Many later theories, particularly behaviorism and humanism, came about as challenges to Freud’s views.
Contemporary Theories on Development

Erikson (1902-1994) and Psychosocial Theory: Now, let’s turn to a less controversial psychodynamic theorist, Erik Erikson. Erikson presents eight developmental stages that encompass the entire lifespan. For that reason, Erikson’s psychosocial theory forms the foundation for much of our discussion of psychosocial development.
Erikson (1950) proposed a model of lifespan development that provides a useful guideline for thinking about the changes we experience throughout life. Erikson broke with Freud’s emphasis on sexuality as the cornerstone of social-emotional development and instead suggested that social relationships fostered development. Erikson proposed that each period of life has a unique challenge or crisis that the person who reaches it must face, referred to as psychosocial crises . According to Erikson, successful development involves dealing with and resolving the goals and demands of each of these psychosocial crises in a positive way. These crises are usually called stages, although that is not the term Erikson used. If a person does not resolve a stage successfully, it may hinder their ability to deal with later stages. For example, the person who does not develop a sense of trust (Erikson’s first stage) may find it challenging as an adult to form a positive intimate relationship (Erikson’s sixth stage). Or an individual who does not develop a clear sense of purpose and identity (Erikson’s fifth stage) may become self-absorbed and stagnate rather than work toward the betterment of others (Erikson’s seventh stage).
However, most individuals are able to successfully complete the eight stages of his theory (See Table 1.3).
Table 1.3 Erikson's Psychosocial Stages
Erikson’s theory has been criticized for focusing so heavily on crises and assuming that the completion of one crisis is a prerequisite for the next crisis of development. His theory also focused on the social expectations that are found in certain cultures, but not in all. For instance, the idea that adolescence is a time of searching for identity might translate well in the middle-class culture of the United States, but not as well in cultures where the transition into adulthood coincides with puberty through rites of passage and where adult roles offer fewer choices.
Learning Theory: Also known as Behaviorism , is based on the premise that it is not possible to objectively study the mind, and therefore psychologists should limit their attention to the study of behavior itself. The most famous behaviorist was Burrhus Frederick (B. F.) Skinner (1904–1990), who expanded the principles of behaviorism and also brought them to the attention of the public at large. Skinner used the ideas of stimulus and response, along with the application of rewards or reinforcements, to train pigeons and other animals. In addition, he used the general principles of behaviorism to develop theories about how best to teach children and how to create societies that were peaceful and productive (Skinner, 1957, 1968, 1972).
The behaviorists made substantial contributions to psychology by identifying the principles of learning. Although the behaviorists were incorrect in their beliefs that it was not possible to measure thoughts and feelings, their ideas provided new insights that helped further our understanding regarding the nature-nurture debate as well as the question of free will. The ideas of behaviorism are fundamental to psychology and have been developed to help us better understand the role of prior experiences in a variety of areas of psychology.
Social Learning Theory , or learning by watching others , was developed by Albert Bandura (1977). His theory calls our attention to the ways in which many of our actions are not learned through conditioning, as suggested by Skinner . Young children frequently learn behaviors through imitation. Especially when children do not know what else to do, they learn by modeling or copying the behavior of others.
Bandura (1986) suggests that there is interplay between the environment and the individual. We are not just the product of our surroundings, rather we influence our surroundings. There is interplay between our personality and the way we interpret events and how they influence us. This concept is called reciprocal determinism . An example of this might be the interplay between parents and children. Parents not only influence their child’s environment, perhaps intentionally through the use of reinforcement, etc., but children influence parents as well. Parents may respond differently with their first child than with their fourth. Perhaps they try to be the perfect parents with their firstborn, but by the time their last child comes along they have very different expectations, both of themselves and their child. Our environment creates us and we create our environment.
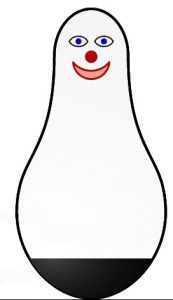
Other social influences: TV or not TV? Bandura, Ross and Ross (1963) began a series of studies to look at the impact of television on the behavior of children. Bandura began by conducting an experiment in which he showed children a film of a woman hitting an inflatable clown or “bobo” doll. Then the children were allowed in the room, where they found the doll and during their play they began to hit it. The children also demonstrated novel ways of being aggressive toward the doll that were not demonstrated by those children who did not see the aggressive model. Bandura’s research raised concerns about the impact of violence on young children. Since then, considerable research has been conducted on the impact of violent media on children’s aggression including playing video games.
Cognitive Theory: The cognitive theories focus on how our mental processes or cognitions change over time . Three important theories are Jean Piaget’s, Lev Vygotsky’s, and Information-processing.
Jean Piaget (1896-1980) was one of the most influential cognitive theorists in development. He was inspired to explore children’s ability to think and reason by watching his own children’s development. He was one of the first to recognize and map out the ways in which children’s intelligence differs from that of adults (Piaget, 1929). He became interested in this area when he was asked to test the IQ of children and began to notice that there was a pattern in their wrong answers. He believed that children’s intellectual skills change over time and that maturation, rather than training, brings about that change. Children of differing ages interpret the world differently. Piaget theorized that children progressed through four stages of cognitive development (see Table 1.4).
Table 1.4 Piaget's Stages of Cognitive Development
Piaget has been criticized for overemphasizing the role that physical maturation plays in cognitive development and in underestimating the role that culture and experience plays. Looking across cultures reveals considerable variation in what children are able to do at various ages. Research has shown considerable overlap among the four stages and that development is more continuous.
Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was a Russian psychologist who wrote in the early 1900s, but whose work was not discovered by researchers in the United States until the 1960s and became more widely known in the 1980s (Crain, 2005). His sociocultural theory emphasizes the importance of culture and interaction in the development of cognitive abilities . Vygotsky differed with Piaget in that he believed that a person not only has a set of abilities, but also a set of potential abilities that can be realized if given the proper guidance from others. Vygotsky developed theories on teaching that have been adopted by educators today.
Information Processing is not the work of a single theorist, but based on the ideas and research of several cognitive scientists studying how individuals perceive, analyze, manipulate, use, and remember information . This approach assumes that humans gradually improve in their processing skills; that is, cognitive development is continuous rather than stage-like. The more complex mental skills of adults are built from the primitive abilities of children. We are born with the ability to notice stimuli, store, and retrieve information. Brain maturation enables advancements in our information processing system. At the same time, interactions with the environment also aid in our development of more effective strategies for processing information.
Urie Bronfenbrenner (1917-2005) developed the Ecological Systems Theory , which provides a framework for understanding and studying the many influences on human development (Bronfenbrenner, 1979). Bronfenbrenner recognized that human interaction is influenced by larger social forces and that an understanding of these forces is essential for understanding an individual. The individual is impacted by several systems including:
- Microsystem includes the individual’s setting and those who have direct, significant contact with the person, such as parents or siblings . The input of those is modified by the cognitive and biological state of the individual as well. These influence the person’s actions, which in turn influence systems operating on him or her.
- Mesosystem includes the larger organizational structures, such as school, the family, or religion. These institutions impact the microsystems just described. The philosophy of the school system, daily routine, assessment methods, and other characteristics can affect the child’s self-image, growth, sense of accomplishment, and schedule thereby impacting the child, physically, cognitively, and emotionally.
- Exosystem includes the larger contexts of community . A community’s values, history, and economy can impact the organizational structures it houses. Mesosystems both influence and are influenced by the exosystem.
- Macrosystem includes the cultural elements, such as global economic conditions, war, technological trends, values, philosophies, and a society’s responses to the global community.
- Chronosystem is the historical context in which these experiences occur. This relates to the different generational time periods previously discussed, such as the baby boomers and millennials.
In sum, a child’s experiences are shaped by larger forces, such as the family, schools, religion, culture, and time period. Bronfenbrenner’s model helps us understand all of the different environments that impact each one of us simultaneously. Despite its comprehensiveness, Bronfenbrenner’s ecological system’s theory is not easy to use. Taking into consideration all the different influences makes it difficult to research and determine the impact of all the different variables (Dixon, 2003). Consequently, psychologists have not fully adopted this approach, although they recognize the importance of the ecology of the individual. Figure 1.9 is a model of Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems Theory.
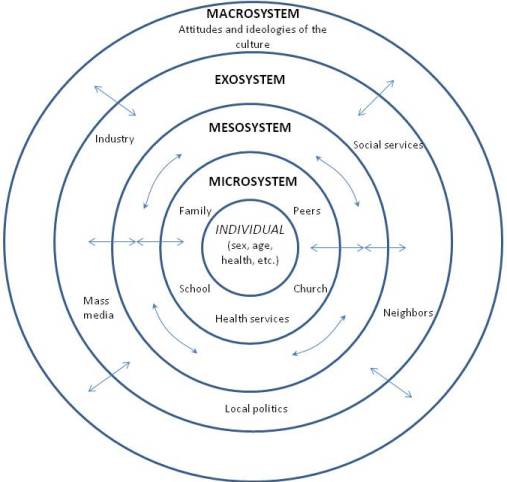
Figure 1.9. Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems Theory
Supplemental Materials
- This article discusses the importance of critical reflection on the underlying assumptions of developmental psychology as a science.
Teo, T. (1997). Developmental Psychology and the Relevance of a Critical Metatheoretical Reflection. Human Development, 40 (4), 195–210. https://doi.org/10.1159/000278723
Baltes, P. B. (1987). Theoretical propositions of life span developmental psychology: On the dynamics between growth and decline. Developmental Psychology, 23, 611-626.
Baltes, P. B., Lindenberger, U., & Staudinger, U. M. (2006). Life span theory in developmental psychology. In W. Damon, & R. M. Lerner (Eds.), Handbook of child psychology , 6th edition (pp. 569-664). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
Bandura, A. (1977). Social learning theory . New York: General Learning Press.
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social-cognitive theory . Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Bandura, A, Ross, D. &. Ross S. (1963). Imitation of film-mediated aggressive models. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 66 , 3-11.
Bronfenbrenner, U. (1979). The ecology of human development: Experiments by nature and design . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Crain, W. (2005). Theories of development concepts and applications (5th ed.). New Jersey: Pearson.
Crews, F. C. (1998). Unauthorized Freud: Doubters confront a legend . New York, NY: Viking Press.
Dixon, W. E. (2003). Twenty studies that revolutionized child psy chology. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Erikson, E. H. (1950). Childhood and society . New York: Norton.
Guinness World Records. (2016). Oldest person (ever). Retrieved from http://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/search?term=oldest+person+%28ever%29
Neugarten, B. L. (1979). Policy for the 1980s: Age or need entitlement? In J. P. Hubbard (Ed.), Aging: Agenda for the eighties, a national journal issues book (pp. 48-52). Washington, DC: Government Research Corporation.
Neugarten, D. A. (Ed.) (1996). The meanings of age . Chicago, IL: The University of Chicago Press.
Piaget, J. (1929). The child’s conception of the world . NY: Harcourt, Brace Jovanovich.
Smithsonian National Zoo. (2016). Retrieved from http://nationalzoo.si.edu/
Skinner, B. (1957). Verbal behavior . Acton, MA: Copley.
Skinner, B. (1968). The technology of teaching . New York, NY: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
Skinner, B. (1972). Beyond freedom and dignity . New York, NY: Vintage Books.
Thomas, R. M. (1979). Comparing theories of child development . Santa Barbara, CA: Wadsworth.
United States Census Bureau. (2016). Povert y. Retrieved from http://www.census.gov/topics/income-poverty/poverty/about/glossary.html
Vogt, W.P., & Johnson, R.B. (2016). The SAGE dictionary of statistics and methodology . Los Angeles, CA: Sage
Webb, S. J., Dawson, G., Bernier, R., & Panagiotides, H. (2006). ERP evidence of atypical face processing in young children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 36 , 884-890. doi: 10.1007/s10803-006-0126-x
Weitz, R. (2007). The sociology of health, illness, and health care: A critical approach, (4th ed.). Belmont, CA: Thomson.
OER Attribution: “Lifespan Development: A Psychological Perspective, Second Edition” by Martha Lally and Suzanne Valentine-French is licensed under a CC-BY-NC-SA-3.0
Additional written material (Meta-theories of Human Development) by Ellen Skinner, Glen Richardson, Jennifer Pitzer, and Cynthia Taylor, Portland State University is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 .
Media Attributions
- Private: jana-sabeth-snDUMdYF7o8-unsplash © Jana Sabeth is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- Private: garrett-jackson-oOnJWBMlb5A-unsplash © Garrett Jackson is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Private: 6152423507_009b2626cd_o © Woody Hibbard is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Private: original © Noba Project is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA (Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike) license
- Private: Preformation is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Private: Sigmund_Freud,_by_Max_Halberstadt_(cropped) © Max Halberstadt is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Private: Erik_Erikson © Unknown is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Private: original © Semhur is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Private: Bronfenbrenner’s_Ecological_Theory_of_Development_(English) © Hchokr at English Wikipedia is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
Human Development Copyright © 2020 by Human Development Teaching & Learning Group is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Essay on Human Development
Students are often asked to write an essay on Human Development in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Human Development
The concept of human development.
Human development is a process of enlarging people’s freedoms and improving their well-being. It involves increasing the choices and opportunities for all people.
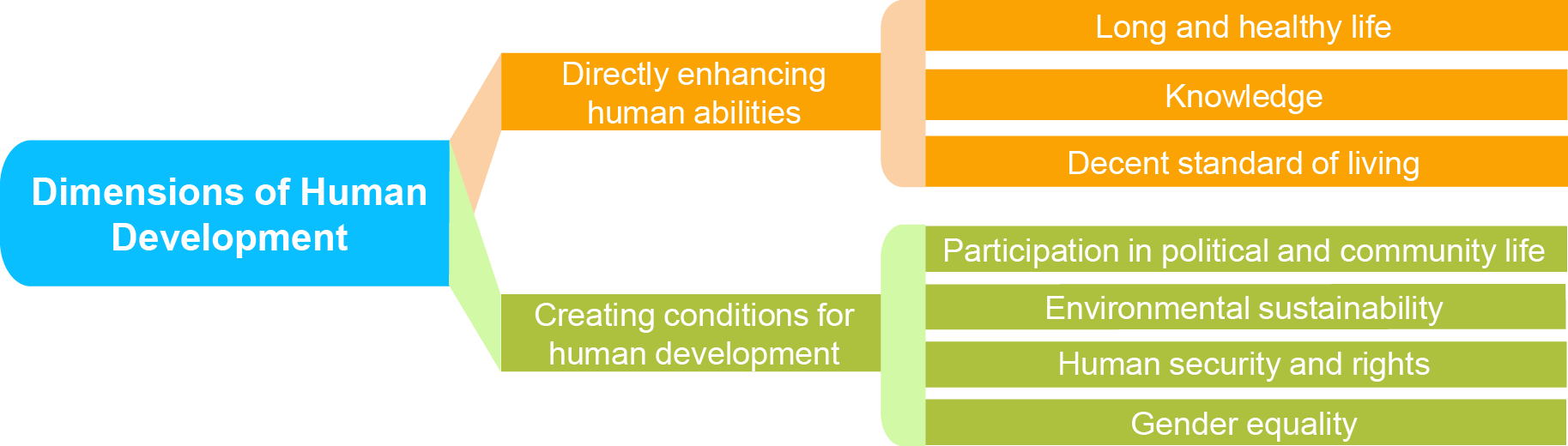
Dimensions of Human Development
There are three main dimensions: health, education, and living standards. Health is measured by life expectancy, education by years of schooling, and living standards by income.
The Importance of Human Development
Human development is crucial. It helps societies to progress, reduces poverty, and promotes equality. It’s a way to help everyone live a productive and fulfilling life.
Challenges in Human Development
Despite its importance, many challenges exist, like inequality, environmental degradation, and political instability. Overcoming these challenges is vital for sustainable human development.
250 Words Essay on Human Development
Introduction.
Human development, a multidimensional concept, is a process of enlarging people’s freedoms and improving their well-being. It encompasses the enhancement of both individual potential and societal growth, focusing on aspects such as education, health, standard of living, and participation in societal activities.
Theoretical Framework
The Human Development Index (HDI), introduced by the United Nations Development Programme, quantifies human development. It emphasizes three fundamental dimensions: knowledge, longevity, and decent standard of living. However, human development is not merely a function of these quantifiable elements; it also involves intangible aspects such as freedom, dignity, and autonomy.
Role of Education
Education plays a central role in human development. It equips individuals with knowledge and skills, empowering them to contribute to societal progress. Education fosters creativity and innovation, driving technological advancements and economic growth.
Health and Living Standards
Health is another crucial component. A healthy population is more productive, contributing to economic growth and societal development. Additionally, a decent standard of living, characterized by access to basic needs and services, is vital for human development.
Societal Participation
Active societal participation promotes inclusivity and equality, essential elements of human development. It enables individuals to contribute to and benefit from societal progress, fostering a sense of belonging and mutual respect.
In conclusion, human development is a comprehensive and nuanced concept. It encompasses not only economic growth but also aspects such as education, health, living standards, and societal participation. It is about creating an environment where individuals can develop their full potential and lead productive, creative lives in accord with their needs and interests.
500 Words Essay on Human Development
Human development is an intricate interplay of biological, psychological, and sociocultural processes that begin at conception and continue throughout the lifespan. It encompasses the growth and maturation of the human being, including physical, cognitive, emotional, and social changes.
The Biological Perspective
From the biological standpoint, human development begins with genetics. Our genetic makeup, coupled with environmental influences, guides our physical growth and maturation. This includes the development of the brain, motor skills, and health. Understanding the biological aspects of human development allows us to grasp why we are the way we are, and how our physical attributes and health conditions may influence our life experiences.
The Psychological Perspective
The psychological perspective focuses on the development of mental processes, behaviors, and emotions. Cognitive development theory, proposed by Jean Piaget, suggests that individuals pass through different stages of cognitive growth as they mature. This theory underscores the importance of experiences and interactions in shaping our cognitive abilities, personality, and emotional well-being.
The Sociocultural Perspective
The sociocultural perspective emphasizes the impact of social and cultural factors on human development. According to Lev Vygotsky’s sociocultural theory, our cognitive development is heavily influenced by our social interactions and cultural context. This perspective highlights the importance of understanding the cultural and social norms, values, and expectations that shape our behaviors and identities.
Interplay of Factors
It is important to recognize that these perspectives do not exist in isolation. They interact in complex ways to shape human development. For instance, our biological makeup may influence our cognitive abilities, which in turn can be shaped by our sociocultural environment. Similarly, our sociocultural context may impact our physical health through factors such as diet, lifestyle, and access to healthcare.
Human Development Index
To measure human development, the United Nations uses the Human Development Index (HDI). The HDI is a summary measure of average achievement in key dimensions of human development: a long and healthy life, being knowledgeable, and having a decent standard of living. It is a standard means of measuring well-being, especially child welfare.
In conclusion, human development is a multifaceted process influenced by biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors. It is a continuous journey that shapes our physical attributes, cognitive abilities, emotional well-being, and social interactions. Understanding these factors and their interplay can provide valuable insights into human behavior and well-being, and guide efforts to promote healthy development and improve quality of life. The HDI, while not perfect, gives us a tool to measure and compare human development across different contexts.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Development of Rural Areas
- Essay on Development
- Essay on Determination
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Module 1: Lifespan Development
Defining human development, learning outcomes.
- Describe human development and its three domains: physical, cognitive, and psychosocial development
- Explain key human development issues about the nature of change: continuous/discontinuous, one course/multiple courses, and nature/nurture
Domains in Human Development

Figure 1 . Human development encompasses the physical, cognitive, and psychosocial changes that occur throughout a lifetime.
Physical Domain
Many of us are familiar with the height and weight charts that pediatricians consult to estimate if babies, children, and teens are growing within normative ranges of physical development. We may also be aware of changes in children’s fine and gross motor skills, as well as their increasing coordination, particularly in terms of playing sports. But we may not realize that physical development also involves brain development, which not only enables childhood motor coordination but also greater coordination between emotions and planning in adulthood, as our brains are not done developing in infancy or childhood. Physical development also includes puberty, sexual health, fertility, menopause, changes in our senses, and primary versus secondary aging. Healthy habits with nutrition and exercise are also important at every age and stage across the lifespan.
Cognitive Domain
If we watch and listen to infants and toddlers, we can’t help but wonder how they learn so much so fast, particularly when it comes to language development. Then as we compare young children to those in middle childhood, there appear to be huge differences in their ability to think logically about the concrete world around them. Cognitive development includes mental processes, thinking, learning, and understanding, and it doesn’t stop in childhood. Adolescents develop the ability to think logically about the abstract world (and may like to debate matters with adults as they exercise their new cognitive skills!). Moral reasoning develops further, as does practical intelligence—wisdom may develop with experience over time. Memory abilities and different forms of intelligence tend to change with age. Brain development and the brain’s ability to change and compensate for losses is significant to cognitive functions across the lifespan, too.
Psychosocial Domain
Development in this domain involves what’s going on both psychologically and socially. Early on, the focus is on infants and caregivers, as temperament and attachment are significant. As the social world expands and the child grows psychologically, different types of play and interactions with other children and teachers become important. Psychosocial development involves emotions, personality, self-esteem, and relationships. Peers become more important for adolescents, who are exploring new roles and forming their own identities. Dating, romance, cohabitation, marriage, having children, and finding work or a career are all parts of the transition into adulthood. Psychosocial development continues across adulthood with similar (and some different) developmental issues of family, friends, parenting, romance, divorce, remarriage, blended families, caregiving for elders, becoming grandparents and great grandparents, retirement, new careers, coping with losses, and death and dying.
As you may have already noticed, physical, cognitive, and psychosocial development are often interrelated, as with the example of brain development. We will be examining human development in these three domains in detail throughout the modules in this course, as we learn about infancy/toddlerhood, early childhood, middle childhood, adolescence, young adulthood, middle adulthood, and late adulthood development, as well as death and dying.
Who Studies Human Development and Why?
Many academic disciplines contribute to the study of development and this type of course is offered in some schools as psychology (particularly as developmental psychology); in other schools, it is taught under sociology, human development, or family studies. This multidisciplinary course is made up of contributions from researchers in the areas of health care, anthropology, nutrition, child development, biology, gerontology, psychology, and sociology, among others. Consequently, the stories provided are rich and well-rounded and the theories and findings can be part of a collaborative effort to understand human lives.
The main goals of those involved in studying human development are to describe and explain changes. Throughout this course, we will describe observations during development, then examine how theories provide explanations for why these changes occur. For example, you may observe two-year-old children to be particularly temperamental, and researchers offer theories to explain why that is. We’ll learn a lot more about theories, especially developmental theories, in the next module.
Key Issues in Human Development
- Is the change smooth or uneven (continuous versus discontinuous)?
- Is this pattern of change the same for everyone, or are there different patterns of change (one course of development versus many courses)?
- How do genetics and environment interact to influence development (nature versus nurture)?
Is Development Continuous or Discontinuous?
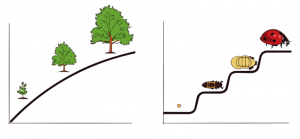
Continuous development views development as a cumulative process, gradually improving on existing skills (Figure 2). With this type of development, there is a gradual change. Consider, for example, a child’s physical growth: adding inches to their height year by year. In contrast, theorists who view development as discontinuous believe that development takes place in unique stages and that it occurs at specific times or ages. With this type of development, the change is more sudden, such as an infant’s ability to demonstrate awareness of object permanence (which is a cognitive skill that develops toward the end of infancy, according to Piaget’s cognitive theory—more on that theory in the next module).

Figure 2 . The concept of continuous development can be visualized as a smooth slope of progression, whereas discontinuous development sees growth in more discrete stages.
Is There One Course of Development or Many?
Is development essentially the same, or universal, for all children (i.e., there is one course of development) or does development follow a different course for each child, depending on the child’s specific genetics and environment (i.e., there are many courses of development)? Do people across the world share more similarities or more differences in their development? How much do culture and genetics influence a child’s behavior?
Stage theories hold that the sequence of development is universal. For example, in cross-cultural studies of language development, children from around the world reach language milestones in a similar sequence (Gleitman & Newport, 1995). Infants in all cultures coo before they babble. They begin babbling at about the same age and utter their first word around 12 months old. Yet we live in diverse contexts that have a unique effect on each of us. For example, researchers once believed that motor development followed one course for all children regardless of culture. However, childcare practices vary by culture, and different practices have been found to accelerate or inhibit the achievement of developmental milestones such as sitting, crawling, and walking (Karasik, Adolph, Tamis-LeMonda, & Bornstein, 2010).
For instance, let’s look at the Aché society in Paraguay. They spend a significant amount of time foraging in forests. While foraging, Aché mothers carry their young children, rarely putting them down in order to protect them from getting hurt in the forest. Consequently, their children walk much later: They walk around 23–25 months old, in comparison to infants in Western cultures who begin to walk around 12 months old. However, as Aché children become older, they are allowed more freedom to move about, and by about age 9, their motor skills surpass those of U.S. children of the same age: Aché children are able to climb trees up to 25 feet tall and use machetes to chop their way through the forest (Kaplan & Dove, 1987). As you can see, our development is influenced by multiple contexts, so the timing of basic motor functions may vary across cultures. However, the functions are present in all societies.

Figure 3. All children across the world love to play. Whether in (a) Florida or (b) South Africa, children enjoy exploring sand, sunshine, and the sea. (credit a: modification of work by “Visit St. Pete/Clearwater”/Flickr; credit b: modification of work by “stringer_bel”/Flickr)
How Do Nature and Nurture Influence Development?
Are we who we are because of nature (biology and genetics), or are we who we are because of nurture (our environment and culture)? This longstanding question is known in psychology as the nature versus nurture debate. It seeks to understand how our personalities and traits are the product of our genetic makeup and biological factors, and how they are shaped by our environment, including our parents, peers, and culture. For instance, why do biological children sometimes act like their parents—is it because of genetics or because of early childhood environment and what the child has learned from their parents? What about children who are adopted—are they more like their biological families or more like their adoptive families? And how can siblings from the same family be so different?
We are all born with specific genetic traits inherited from our parents, such as eye color, height, and certain personality traits. Beyond our basic genotype, however, there is a deep interaction between our genes and our environment. Our unique experiences in our environment influence whether and how particular traits are expressed, and at the same time, our genes influence how we interact with our environment (Diamond, 2009; Lobo, 2008). There is a reciprocal interaction between nature and nurture as they both shape who we become, but the debate continues as to the relative contributions of each.
Contribute!
Improve this page Learn More
- Psyc 200 Lifespan Psychology. Authored by : Laura Overstreet. Located at : http://opencourselibrary.org/econ-201/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Family picture. Authored by : Wazzle. Provided by : Wikimedia. Located at : https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:African_Family.jpg . License : CC BY: Attribution
- What is Lifespan Development. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : https://opentext.wsu.edu/ospsychrevisions/chapter/what-is-lifespan-development/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Modification, adaptation, and original content. Authored by : Margaret Clark-Plaskie for Lumen Learning. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Key issues in Human Development. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/waymaker-psychology/chapter/what-is-lifespan-development/ . License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- Developmental Psychology. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Developmental_psychology . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Kids running. Authored by : Airman 1st Class Soo c. Kim. Provided by : U.S. Air Force photo. Located at : https://www.army.mil/article/135427/childhood_obesity_a_preventable_disease . License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- Technical Support
- Find My Rep
You are here
An Introduction to Theories of Human Development
- Neil J Salkind
- Description
- Pedagogical features such as chapter opening quotes, boxed highlights, key terms, a glossary, and websites for further reading enhance student understanding of everyday human behavior.
See what’s new to this edition by selecting the Features tab on this page. Should you need additional information or have questions regarding the HEOA information provided for this title, including what is new to this edition, please email [email protected] . Please include your name, contact information, and the name of the title for which you would like more information. For information on the HEOA, please go to http://ed.gov/policy/highered/leg/hea08/index.html .
For assistance with your order: Please email us at [email protected] or connect with your SAGE representative.
SAGE 2455 Teller Road Thousand Oaks, CA 91320 www.sagepub.com
“The book is well written and the theorists and their respective work are well-presented and clearly explained. . . . As a text dealing with the historical overview of major theorists and their work in human development over the last century or so, it is extremely strong and could be widely used in a variety of both undergraduate and graduate courses.”
“In general, I found the websites and references listed at the end of each chapter to be very interesting and useful for taking students beyond what is in the text.”
“A fine choice for a classic theories course, and I believe that the level of presentation would be appropriate for advanced undergraduate or graduate students. . . . The up-to-date web sites at the end of each section are a definite plus. The choice of sites is excellent.”
Overall, An Introduction to Theories of Human Development is an excellent introduction for students who are already grounded – or who at the very least intend to become grounded – in traditional ways of ‘doing science.’ It is clear and well structured, reader-friendly (including summary boxes, illustrations, highlights of important points, and employs jargon only where it is necessary – without oversimplifying or dumbing down), orients to up-to-date additional readings and web sites, and, not irrelevant for students, it is not too expensive
Students found this text beneficial to their research especially for their assessment work that linked to life stage development. It is a full comprehensive text that covers a wide arch of theories from Piaget to Chomsky.
This book is an easy read covering the main theorists of human development - set out in easy to follow sections. Offering further reading at the end of each chapter. A relevant and detailed text - to support the essential reading on my units.
Excellent layout and easy to follow text with up to date theories and web sites. This is an excellent book for learners who want a more advanced insight into human development.
This provides the basic reading for students on the course and has been recommended to the library
this module is not runnig this year due to change in the programm structure.
The book would be more suitable for psychology students rather than social science students. The chapter with theories comparison can be usefull to prepare a review of different approaches in theories.
- A final, integrative chapter compares the various theories presented in the book using Murry Sidman's model of six criteria for judging a theory (introduced in chapter 1), thus helping students develop skills for critically assessing theory, guiding them toward the types of questions one should ask about theories and what kinds of answers one should expect.
- Boxed highlights contain material that focuses on the applied nature of developmental theories to enhance student understanding of everyday human behavior in settings that students in applied majors (education, social work, counseling psychology, etc.) are likely to encounter and appreciate.
- Pedagogical tools reinforce learning and assist in study and review: chapter-opening quotes by famous psychologists, authors, and other historical figures that stimulate student interest; key terms that are boldfaced and defined in text and in a glossary at the end of the book; marginal comments that reiterate and emphasize important points; and in-text references to web sites that guide students to further exploration of a topic.
- Chapters conclude with annotated lists of material to extend students' exploration of topics beyond the text: suggestions of further readings and references to still more web sites on topics covered in each chapter intended to further inform the student about the nature of different theoretical positions.
Sample Materials & Chapters
Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Study of Human Development
For instructors
Select a purchasing option, related products.

This title is also available on SAGE Knowledge , the ultimate social sciences online library. If your library doesn’t have access, ask your librarian to start a trial .
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 29 July 2021
The evolution of our understanding of human development over the last 10 years
- Ali H. Brivanlou ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1761-280X 1 &
- Norbert Gleicher ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0202-4167 2 , 3 , 4
Nature Communications volume 12 , Article number: 4615 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
5668 Accesses
4 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Developmental biology
- Embryogenesis
As it fulfills an irresistible need to understand our own origins, research on human development occupies a unique niche in scientific and medical research. In this Comment, we explore the progress in our understanding of human development over the past 10 years. The focus is on basic research, clinical applications, and ethical considerations.
What basic research has taught us about human development
Over the last decade, progress in understanding our own development was mostly driven by the emergence and combination of remarkable new technologies. New molecular biology tools such as single-cell RNA-sequencing (sc-RNA-seq) unveiled the earliest genetic signature of the three cell lineages of the human blastocyst and allowed for the discovery of human-specific signatures 1 , 2 , 3 . CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing has offered further access to in vitro functional studies in human blastocysts 4 . However, as we discuss below, an ethical line was crossed when a group claimed that genetically modified human embryos had been transferred, leading to births 5 when neither public opinion nor a consensus within the scientific community had been reached regarding whether crossing the germline in in vitro fertilization (IVF) was safe and ethically acceptable.
On the embryology side, the development of an in vitro attachment platform for human blastocysts offered a first glance into post-implantation events up to 12 days 1 , 3 , 5 , 6 . This paved the way for several important discoveries, including the observation that the human embryo can self-organize to generate embryonic and extraembryonic germ layers, yolk sac, and amniotic cavities in the absence of maternal influences 5 , 6 ; and the presence of a transient embryonic tissue of trophectodermal lineage, adjacent to the yolk sac, therefore named, yolk-sac trophectoderm ( ysTE ) 5 . The presence of these seemingly human-specific populations was independently confirmed by sc-RNA-seq 1 .
The marriage of stem cell biology with bioengineering gave birth to the field of synthetic embryology 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 . This technology uses human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) cultured on geometrically confined micropatterned substrates to generate 2D in vitro models of human conceptuses, such as models of the gastrula ( gastruloids ) 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , or parts of the embryo, such as cerebroids and neuruloids 14 . Thousands of nearly identical self-organizing human embryonic structures allow for standardization and reproducibility, which cannot be achieved in standard organoid structures 15 . Cells within these structures can be tracked and quantified in real time with sub-cellular resolution, using sophisticated quantification code, including artificial intelligence 14 .
Human gastruloids induce formation of the primitive streak and have enabled the deciphering of the molecular network underlying gastrulation—the most crucial moment of our lives 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 . 3D models of human epiblasts can spontaneously break axial symmetry, thus providing an assay for the elucidation of molecular events underlying the emergence of antero–posterior polarity 11 , 16 . A highly homogenous population of self-organizing 3D models of amniotic ectoderm-like cells can be obtained by combining microfluidic and microculture approaches 17 .
Finally, the development of interspecies chimeras provided the most stringent in vivo validation of human embryo models 9 , 10 , 18 . Unimaginable in human models, inter-species chimeras have become the next best choice to test whether hESC behavior in self-organizing gastruloids , as observed on microchips, would also occur in an embryonic environment 10 , 18 , 19 . Human/bird chimeras generated from transplanting human gastruloids into early chick embryos in ovo unexpectedly proved more efficient than previous methods 9 , 19 . They allowed for the observation of an entire self-organizing embryonic axis in bird eggs 9 . As birds are closer to dinosaurs than to humans, this high rate of success with these chimeras further suggested that these early patterning events must be highly conserved.
Translational clinical applications that arose from basic research
The past 10 years bore witness to significant clinical progress in reproductive medicine, often translated from basic research. Successful human uterus transplantation and the subsequent birth of healthy offspring was, for example, only achieved after years of meticulous laboratory work in animals 10 . Significant improvements in cryopreservation technology for human eggs and ovarian tissue were also preceded by research in model systems 10 , 20 . Practical clinical applications have been developed for women in need of cancer treatment that are toxic to ovaries. In these cases, oocytes and/or ovarian tissue can be cryopreserved for later use in fertility treatments once the patient is cured of her cancer 21 . This ever-evolving technology has already proven to result in live births, and has also become an integral part of routine infertility treatments with IVF, giving rise to the brand-new concept of fertility extension through egg-freezing.
Diagnostic technologies to assess retrieved eggs and preimplantation-stage embryos in the IVF process have been disappointing. For example, tracking extended embryo culture to blastocyst-stage with time-lapse imaging failed to improve embryo selection 22 . That chromosomal-abnormal embryos increase with maternal (but not paternal) age has been interpreted to mean that chromosomal abnormalities were a principal cause for lower implantation chances and higher miscarriage risks among older women. This assumption led to the rapidly growing utilization of chromosomal testing of human embryos prior to embryo transfer in a procedure recently renamed preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A) 23 . The hypothesis behind PGT-A is to exclude chromosomal-abnormal embryos from the transfer, thereby improving implantation potentials of remaining euploid embryos.
Here too, clinical evidence was unable to confirm the hypothesis 24 . Moreover, basic research demonstrated a self-correction mechanism in mouse 25 and human embryos 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 that arose during embryogenesis that was cell lineage-specific to the embryonic cell lineage. In contrast, PGT-A biopsies are obtained from the extraembryonic-derived trophectoderm, rendering any diagnostic procedure at the blastocyst stage ineffective. In addition, mathematical modeling demonstrated that results from a single trophectoderm biopsy could not be extrapolated to the whole embryo 30 . Transfer of PGT-A “chromosomal-abnormal diagnosed embryos” has resulted in the births of over 400 chromosomal-normal offspring 20 , 21 .
In recent years, increasing attention has also been given to the quickly evolving understanding of how interdependent lifestyle and human fertility are 31 , 32 , 33 , including the influence of diet on the microbiome, as in many other areas of medicine.
The ethical significance of understanding human development
Whether in clinical medicine or in the research laboratory, human embryology has remained an ethical minefield, strongly influenced by socio-political and religious considerations. At the core of the controversy resides the special moral value of the human embryo, a subject that has come to the forefront again with the ascent of human embryonic stem cell research 34 . There is, however, little consensus as to how to answer a previously raised question: “ what is an embryo ?” 35 . The term pre-embryo, first introduced in 1986, was defined as the interval up to the appearance of the primitive streak, which marks biological individuation at ~14 days post-fertilization. This definition designated the period beyond 14 days as the time when a pre-embryo attains special moral status 36 , 37 . Paradoxically, the term pre-embryo has been replaced by the indiscriminate use of the term embryo, whether at preimplantation cleavage or blastocyst-stages or post-implantation before day 14. It was suggested that the distinction was important for ethical, moral, and biological relevance. The principal reason is simple: Until a pre-embryo becomes an embryo, there is no way of knowing whether implantation has taken place, whether a pregnancy is developing, whether there is a single pregnancy or twinning, or whether fertilization ended up in a benign (hydatidiform mole) or even in a malignant tumor (choriocarcinoma) 35 . Assigning advanced moral value to embryos at those early stages is, therefore, difficult to defend.
The past 10 years have witnessed innumerous ethical debates related to this subject, each with its own social, historical, and religious justifications, reflecting cultural diversities in human populations. Most are triggered by scientific breakthroughs. We summarize here the major ethical challenges preoccupying reproductive research and clinical practice.
We have already briefly referred to CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing. While the use of sc-RNA-seq to identify the molecular blueprint of human development has not elicited significant controversy, CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing of human embryos has been a topic of intense discussions and is currently permissible only in vitro 38 . An alleged attempt in China of implanting human genome-edited embryos into the uterus supposedly led to two births (one a twin birth). Though widely discussed in the media, neither attempt was published in the medical literature, and therefore cannot be verified 5 , 38 .
The ethical debates surrounding the 14-day rule, quiescent since the early IVF days, experienced a rebirth that was prompted by in vitro human embryo attachment studies and the emergence of synthetic human embryos. Within this context, we note that self-organizing embryo models are nothing more than cells in culture and are certainly not embryos. Regardless of scientific merits, in the U.S., the National Institutes of Health (NIH) currently prohibits the use of public funds for the study of synthetic embryos “for ethical reasons”. After being under an NIH moratorium for more than a year, research on chimeras is now, however, again permitted, though human/non-human primate chimeras remain prohibited.
These ongoing ethical debates mostly also mirror those surrounding the lack of U.S. federal funding for clinical IVF and related research, as well as hESCs-derived model embryos. In this context, the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM)’s Ethics in Embryo Research Task Force recently made an important statement: “ Scientific research using human embryos advances human health and provides vital insights into reproduction and disease ” 39 .
Provided certain guidelines and safeguards are followed, research with already existing embryos or embryos specifically produced for research should be ethically acceptable as a means of obtaining new knowledge that may benefit human health. ASRM also pointed out that scientists and society must understand which research questions necessitate the use of human embryos.
It is gratifying to acknowledge the history and vitality of ongoing debates, especially since they increasingly mimic decision-making processes in the medical field. These debates are meant to be based on cost-benefit and/or risk-benefit assessments. These debates will, unquestionably, continue and, indeed, considering that every intervention has consequences, must be decided based on careful considerations, including all relevant stakeholders and all parts of society.
Zhou, F. et al. Reconstituting the transcriptome and DNA methylome landscapes of human implantation. Nature 572 , 660–664 (2019).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar
Petropoulos, S. et al. Single-cell RNA-Seq reveals lineage and X chromosome dynamics in human preimplantation embryos. Cell 167 , 285 (2016).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Xiang, L. et al. A developmental landscape of 3D-cultured human pre-gastrulation embryos. Nature 577 , 537–542 (2020).
Ma, H. et al. Correction of a pathogenic gene mutation in human embryos. Nature 548 , 413–419 (2017).
Deglincerti, A. et al. Self-organization of the in vitro attached human embryo. Nature 533 , 251–254 (2016).
Shahbazi, M. N. et al. Self-organization of the human embryo in the absence of maternal tissues. Nat. Cell Biol. 18 , 700–708 (2016).
Warmflash, A., Sorre, B., Etoc, F., Siggia, E. D. & Brivanlou, A. H. A method to recapitulate early embryonic spatial patterning in human embryonic stem cells. Nat. Methods 11 , 847–854 (2014).
Etoc, F. et al. A balance between secreted inhibitors and edge sensing controls gastruloid self-organization. Developmental Cell 39 , 302–315 (2016).
Martyn, I., Kanno, T. Y., Ruzo, A., Siggia, E. D. & Brivanlou, A. H. Self-organization of a human organizer by combined Wnt and Nodal signalling. Nature 558 , 132–135 (2018).
Yoney, A. et al. WNT signaling memory is required for ACTIVIN to function as a morphogen in human gastruloids. Elife 7 , e38279 (2018).
Simunovic, M. & Brivanlou, A. H. Embryoids, organoids and gastruloids: new approaches to understanding embryogenesis. Development 144 , 976–985 (2017).
Martyn, I., Brivanlou, A. H. & Siggia, E. D. A wave of WNT signaling balanced by secreted inhibitors controls primitive streak formation in micropattern colonies of human embryonic stem cells. Development 146 , dev172791 (2019).
Deglincerti, A. et al. Self-organization of human embryonic stem cells on micropatterns. Nat. Protoc. 11 , 2223–2232 (2016).
Haremaki, T. et al. Self-organizing neuruloids model developmental aspects of Huntington’s disease in the ectodermal compartment. Nat. Biotechnol. 37 , 1198–1208 (2019).
Lancaster, M. A. et al. Cerebral organoids model human brain development and microcephaly. Nature 501 , 373–379 (2013).
Simunovic, M. et al. A 3D model of a human epiblast reveals BMP4-driven symmetry breaking. Nat. Cell Biol. 21 , 900–910 (2019).
Zheng, Y. et al. Controlled modelling of human epiblast and amnion development using stem cells. Nature 573 , 421–425 (2019).
Levine, S. & Grabel, L. The contribution of human/non-human animal chimeras to stem cell research. Stem. Cell Res. 24 , 128–134 (2017).
Article Google Scholar
James, D., Noggle, S. A., Swigut, T. & Brivanlou, A. H. Contribution of human embryonic stem cells to mouse blastocysts. Dev. Biol. 295 , 90–102 (2006).
ESHRE Working Group on Time-Lapse Technology, et al. Good practice recommendations for the use of time-lapse technology. Hum. Reprod. Open 2020 , hoaa008 (2020).
Homer, H. A. Preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A): the biology, the technology and the clinical outcomes. Aust. N. Z. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 59 , 317–324 (2019).
Castellón, L. A. R. et al. The history behind successful uterine transplantation in humans. JBRA Assist. Reprod. 21 , 126–134 (2017).
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Saragusty, J. & Arav, A. Current progress in oocyte and embryo cryopreservation by slow freezing and vitrification. Reproduction 141 , 1–19 (2011).
Bracewell-Milnes, T., Norman-Taylor, J. & Nikolaou, D. Social egg freezing should be offered to single women approaching their late thirties: AGAINST: Women should be freezing their eggs earlier. BJOG 125 , 1580 (2018).
Rito, T., Naftaly, J., Gleicher, N. & Brivanlou, A. H. Self-correction of aneuploidy in human blastocysts and self-organizing gastruloids. Fertil. Steril. 112 , e127 (2019).
Chu, W. et al. Metagenomic analysis identified microbiome alterations and pathological association between intestinal microbiota and polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil. Steril. 113 , 1286–1298 (2020). e1284.
Hug, K. Therapeutic perspectives of human embryonic stem cell reserach versus the moreal status of a human embryo- does one have to be compromised for the other? Medicina 42 , 107–114 (2006).
PubMed Google Scholar
Jones, H. W. Jr & Veeck, L. What is an embryo? Fertil. Steril. 77 , 658–659 (2002).
American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Ethical considerations of the new reproductive technologies. Ethics Comm. Opin. Fertil. Steril. 46 , 1–93 (1986).
Google Scholar
Loren, A. W. et al. Fertility preservation for patients with cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update. J. Clin. Oncol. 31 , 2500–2510 (2013).
Gleicher, N. et al. The 2019 PGDIS position statement on transfer of mosaic embryos within a context of new information on PGT-A. Reprod. Biol. Endocrin 18 , 57 (2020).
Gleicher, N. et al. A single trophectoderm biopsy at blastocyst stage is mathematically unable to determine embryo ploidy accurately enough for clinical use. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 15 , 33 (2017).
Patrizio, P. et al. Worldwide live births following the transfer of chromosomally “Abnormal” embryos after PGT/A: results of a worldwide web-based survey. J. Assist Reprod. Genet. 36 , 1599–1607 (2019).
Barmat, L. I. et al. Human preembryo development on autologous endometrial coculture versus conventional medium. Fertil. Steril. 70 , 1109–1113 (1998).
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Examining the State of the Science of Mammalian Embryo Model Systems: Proceedings of a Workshop (2020).
Abbott, A. et al. 2016 in news: the science events that shaped the year. Nat. N. 540 , 496 (2016).
Gleicher, N., Kushnir, V. A., Albertini, D. A. & Barad, D. H. First birth following spindle transfer. Reprod. BioMedicine Online 35 , 542–543 (2017).
Research CfBEa. Therapeutic Cloning and Genome Modification (FDA, 2019).
van den Brink, S. C. et al. Symmetry breaking, germ layer specification and axial organisation in aggregates of mouse embryonic stem cells. Development 141 , 4231–4242 (2014).
Download references

Acknowledgements
We like to thank Min Yang, Jean Marx Santel, Adam Souza, and Amir Brivanlou, for data gathering and critical reading of the manuscript, and constructive criticism.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Stem Cell Biology and Molecular Embryology Laboratory, The Rockefeller University, New York, NY, USA
Ali H. Brivanlou
The Center for Human Reproduction, New York, NY, USA
- Norbert Gleicher
The Foundation for Reproductive Medicine, New York, NY, USA
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Both A.H.B. and N.G. have contributed to writing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ali H. Brivanlou .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
A.H.B. and N.G. are co-founders of OvaNova Inc. A.H.B. is a co-founder of Rumi Scientific Inc.
Additional information
Peer review information Nature Communications thanks Alfonso Martinez Arias, Annelien Bredenoord and the other anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Brivanlou, A.H., Gleicher, N. The evolution of our understanding of human development over the last 10 years. Nat Commun 12 , 4615 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24793-3
Download citation
Received : 09 June 2020
Accepted : 29 June 2021
Published : 29 July 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24793-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Revisiting selected ethical aspects of current clinical in vitro fertilization (ivf) practice.
- Anja von Schondorf-Gleicher
- Lyka Mochizuki
Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics (2022)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Home — Essay Samples — Psychology — Childhood Development — Human Growth and Development
Human Growth and Development
- Categories: Childhood Development
About this sample

Words: 481 |
Published: Jan 31, 2024
Words: 481 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Table of contents
Theoretical foundations of human growth and development, physical development, cognitive development, social and emotional development, environmental and genetic influences on human growth and development, lifespan development.
- Freud, S. (1905). Three essays on the theory of sexuality. Standard Edition, 7, 123-255.
- Erikson, E. (1950). Childhood and society. New York: Norton.
- Piaget, J. (1952). The origins of intelligence in children. New York: International Universities Press.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Psychology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 915 words
2 pages / 875 words
6 pages / 2596 words
1 pages / 370 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Childhood Development
Human growth and development involve a variety of complex processes, periods, and theories that contribute to the understanding of how individuals change and develop over time. In this essay, we will explore the developmental [...]
Understanding and managing parents' expectations from their child is a delicate yet crucial aspect of family dynamics. The aspirations parents hold for their offspring often reflect a deep desire for success, happiness, and the [...]
Easterlin, M. C., Chung, P. J., & Leng, M. (2023). Association of Team Sports Participation With Long-term Mental Health Outcomes Among Individuals Exposed to Adverse Childhood Experiences. JAMA Pediatrics.National Public Radio. [...]
Child development is a fascinating and complex journey, shaped by various factors such as genetics, environment, and parenting. To gain deeper insights into this intricate process, I had the opportunity to interview a parent and [...]
The Adverse Childhood Experiences Study provides important education to health care providers that can change the course of children’s lives. Unfortunately, this is not regularly educated to patients within primary care. [...]
The initiative versus guilt stage is a critical period in children's development, where they begin to explore their independence and take on new challenges. The successful resolution of this conflict is important for children's [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
The evolution of our understanding of human development over the last 10 years
Ali h. brivanlou.
1 Stem Cell Biology and Molecular Embryology Laboratory, The Rockefeller University, New York, NY USA
Norbert Gleicher
2 The Center for Human Reproduction, New York, NY USA
3 The Foundation for Reproductive Medicine, New York, NY USA
4 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
As it fulfills an irresistible need to understand our own origins, research on human development occupies a unique niche in scientific and medical research. In this Comment, we explore the progress in our understanding of human development over the past 10 years. The focus is on basic research, clinical applications, and ethical considerations.
What basic research has taught us about human development
Over the last decade, progress in understanding our own development was mostly driven by the emergence and combination of remarkable new technologies. New molecular biology tools such as single-cell RNA-sequencing (sc-RNA-seq) unveiled the earliest genetic signature of the three cell lineages of the human blastocyst and allowed for the discovery of human-specific signatures 1 – 3 . CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing has offered further access to in vitro functional studies in human blastocysts 4 . However, as we discuss below, an ethical line was crossed when a group claimed that genetically modified human embryos had been transferred, leading to births 5 when neither public opinion nor a consensus within the scientific community had been reached regarding whether crossing the germline in in vitro fertilization (IVF) was safe and ethically acceptable.
On the embryology side, the development of an in vitro attachment platform for human blastocysts offered a first glance into post-implantation events up to 12 days 1 , 3 , 5 , 6 . This paved the way for several important discoveries, including the observation that the human embryo can self-organize to generate embryonic and extraembryonic germ layers, yolk sac, and amniotic cavities in the absence of maternal influences 5 , 6 ; and the presence of a transient embryonic tissue of trophectodermal lineage, adjacent to the yolk sac, therefore named, yolk-sac trophectoderm ( ysTE ) 5 . The presence of these seemingly human-specific populations was independently confirmed by sc-RNA-seq 1 .
The marriage of stem cell biology with bioengineering gave birth to the field of synthetic embryology 7 – 13 . This technology uses human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) cultured on geometrically confined micropatterned substrates to generate 2D in vitro models of human conceptuses, such as models of the gastrula ( gastruloids ) 7 – 13 , or parts of the embryo, such as cerebroids and neuruloids 14 . Thousands of nearly identical self-organizing human embryonic structures allow for standardization and reproducibility, which cannot be achieved in standard organoid structures 15 . Cells within these structures can be tracked and quantified in real time with sub-cellular resolution, using sophisticated quantification code, including artificial intelligence 14 .
Human gastruloids induce formation of the primitive streak and have enabled the deciphering of the molecular network underlying gastrulation—the most crucial moment of our lives 7 – 13 . 3D models of human epiblasts can spontaneously break axial symmetry, thus providing an assay for the elucidation of molecular events underlying the emergence of antero–posterior polarity 11 , 16 . A highly homogenous population of self-organizing 3D models of amniotic ectoderm-like cells can be obtained by combining microfluidic and microculture approaches 17 .
Finally, the development of interspecies chimeras provided the most stringent in vivo validation of human embryo models 9 , 10 , 18 . Unimaginable in human models, inter-species chimeras have become the next best choice to test whether hESC behavior in self-organizing gastruloids , as observed on microchips, would also occur in an embryonic environment 10 , 18 , 19 . Human/bird chimeras generated from transplanting human gastruloids into early chick embryos in ovo unexpectedly proved more efficient than previous methods 9 , 19 . They allowed for the observation of an entire self-organizing embryonic axis in bird eggs 9 . As birds are closer to dinosaurs than to humans, this high rate of success with these chimeras further suggested that these early patterning events must be highly conserved.
Translational clinical applications that arose from basic research
The past 10 years bore witness to significant clinical progress in reproductive medicine, often translated from basic research. Successful human uterus transplantation and the subsequent birth of healthy offspring was, for example, only achieved after years of meticulous laboratory work in animals 10 . Significant improvements in cryopreservation technology for human eggs and ovarian tissue were also preceded by research in model systems 10 , 20 . Practical clinical applications have been developed for women in need of cancer treatment that are toxic to ovaries. In these cases, oocytes and/or ovarian tissue can be cryopreserved for later use in fertility treatments once the patient is cured of her cancer 21 . This ever-evolving technology has already proven to result in live births, and has also become an integral part of routine infertility treatments with IVF, giving rise to the brand-new concept of fertility extension through egg-freezing.
Diagnostic technologies to assess retrieved eggs and preimplantation-stage embryos in the IVF process have been disappointing. For example, tracking extended embryo culture to blastocyst-stage with time-lapse imaging failed to improve embryo selection 22 . That chromosomal-abnormal embryos increase with maternal (but not paternal) age has been interpreted to mean that chromosomal abnormalities were a principal cause for lower implantation chances and higher miscarriage risks among older women. This assumption led to the rapidly growing utilization of chromosomal testing of human embryos prior to embryo transfer in a procedure recently renamed preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A) 23 . The hypothesis behind PGT-A is to exclude chromosomal-abnormal embryos from the transfer, thereby improving implantation potentials of remaining euploid embryos.
Here too, clinical evidence was unable to confirm the hypothesis 24 . Moreover, basic research demonstrated a self-correction mechanism in mouse 25 and human embryos 26 – 29 that arose during embryogenesis that was cell lineage-specific to the embryonic cell lineage. In contrast, PGT-A biopsies are obtained from the extraembryonic-derived trophectoderm, rendering any diagnostic procedure at the blastocyst stage ineffective. In addition, mathematical modeling demonstrated that results from a single trophectoderm biopsy could not be extrapolated to the whole embryo 30 . Transfer of PGT-A “chromosomal-abnormal diagnosed embryos” has resulted in the births of over 400 chromosomal-normal offspring 20 , 21 .
In recent years, increasing attention has also been given to the quickly evolving understanding of how interdependent lifestyle and human fertility are 31 – 33 , including the influence of diet on the microbiome, as in many other areas of medicine.
The ethical significance of understanding human development
Whether in clinical medicine or in the research laboratory, human embryology has remained an ethical minefield, strongly influenced by socio-political and religious considerations. At the core of the controversy resides the special moral value of the human embryo, a subject that has come to the forefront again with the ascent of human embryonic stem cell research 34 . There is, however, little consensus as to how to answer a previously raised question: “ what is an embryo ?” 35 . The term pre-embryo, first introduced in 1986, was defined as the interval up to the appearance of the primitive streak, which marks biological individuation at ~14 days post-fertilization. This definition designated the period beyond 14 days as the time when a pre-embryo attains special moral status 36 , 37 . Paradoxically, the term pre-embryo has been replaced by the indiscriminate use of the term embryo, whether at preimplantation cleavage or blastocyst-stages or post-implantation before day 14. It was suggested that the distinction was important for ethical, moral, and biological relevance. The principal reason is simple: Until a pre-embryo becomes an embryo, there is no way of knowing whether implantation has taken place, whether a pregnancy is developing, whether there is a single pregnancy or twinning, or whether fertilization ended up in a benign (hydatidiform mole) or even in a malignant tumor (choriocarcinoma) 35 . Assigning advanced moral value to embryos at those early stages is, therefore, difficult to defend.
The past 10 years have witnessed innumerous ethical debates related to this subject, each with its own social, historical, and religious justifications, reflecting cultural diversities in human populations. Most are triggered by scientific breakthroughs. We summarize here the major ethical challenges preoccupying reproductive research and clinical practice.
We have already briefly referred to CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing. While the use of sc-RNA-seq to identify the molecular blueprint of human development has not elicited significant controversy, CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing of human embryos has been a topic of intense discussions and is currently permissible only in vitro 38 . An alleged attempt in China of implanting human genome-edited embryos into the uterus supposedly led to two births (one a twin birth). Though widely discussed in the media, neither attempt was published in the medical literature, and therefore cannot be verified 5 , 38 .
The ethical debates surrounding the 14-day rule, quiescent since the early IVF days, experienced a rebirth that was prompted by in vitro human embryo attachment studies and the emergence of synthetic human embryos. Within this context, we note that self-organizing embryo models are nothing more than cells in culture and are certainly not embryos. Regardless of scientific merits, in the U.S., the National Institutes of Health (NIH) currently prohibits the use of public funds for the study of synthetic embryos “for ethical reasons”. After being under an NIH moratorium for more than a year, research on chimeras is now, however, again permitted, though human/non-human primate chimeras remain prohibited.
These ongoing ethical debates mostly also mirror those surrounding the lack of U.S. federal funding for clinical IVF and related research, as well as hESCs-derived model embryos. In this context, the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM)’s Ethics in Embryo Research Task Force recently made an important statement: “ Scientific research using human embryos advances human health and provides vital insights into reproduction and disease ” 39 .
Provided certain guidelines and safeguards are followed, research with already existing embryos or embryos specifically produced for research should be ethically acceptable as a means of obtaining new knowledge that may benefit human health. ASRM also pointed out that scientists and society must understand which research questions necessitate the use of human embryos.
It is gratifying to acknowledge the history and vitality of ongoing debates, especially since they increasingly mimic decision-making processes in the medical field. These debates are meant to be based on cost-benefit and/or risk-benefit assessments. These debates will, unquestionably, continue and, indeed, considering that every intervention has consequences, must be decided based on careful considerations, including all relevant stakeholders and all parts of society.
Acknowledgements
We like to thank Min Yang, Jean Marx Santel, Adam Souza, and Amir Brivanlou, for data gathering and critical reading of the manuscript, and constructive criticism.
Author contributions
Both A.H.B. and N.G. have contributed to writing the manuscript.
Competing interests
A.H.B. and N.G. are co-founders of OvaNova Inc. A.H.B. is a co-founder of Rumi Scientific Inc.
Peer review information Nature Communications thanks Alfonso Martinez Arias, Annelien Bredenoord and the other anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
- Human Development: Meaning, Objectives and Components
Let us make an in-depth study of the meaning, objectives and components of human development
Meaning of Human Development:
The term ‘human development’ may be defined as an expansion of human capabilities, a widening of choices, ‘an enhancement of freedom, and a fulfilment of human rights.
At the beginning, the notion of human development incorporates the need for income expansion. However, income growth should consider expansion of human capabilities. Hence development cannot be equated solely to income expansion.
Income is not the sum-total of human life. As income growth is essential, so are health, education, physical environment, and freedom. Human development should embrace human rights, socio-eco-politico freedoms. Based on the notion of human development. Human Development Index (HDI) is constructed. It serves as a more humane measure of development than a strictly .income-based benchmark of per capita GNP.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The first UNDP Human Development Report published in 1990 stated that: “The basic objective of development is to create an enabling environment for people to enjoy long, healthy and creative lives.” It also defined human development as “a process of enlarging people’s choices”, “and strengthen human capabilities” in a way which enables them to lead longer, healthier and fuller lives.
From this broad definition of human development, one gets an idea of three critical issues involved in human development interpretation. These are: to lead a long and healthy life, to be educated, and to enjoy a decent standard of living. Barring these three crucial parameters of human development as a process enlarging people’s choices, there are additional choices that include political freedoms, other guaranteed human rights, and various ingredients of self-respect.
One may conclude unhesistantly that the absence of these essential choices debars or blocks many other opportunities that people should have in widening their choices. Human development is thus a process of widening people’s choices as well as raising the level of well-being achieved.
What emerges from- the above discussion is that economic growth measured in terms of per capita GNP focuses only on one choice that is income. On the other hand, the notion of human development embraces the widening of all human choices—whether economic, social, cultural or political. One may, however, contest GDP/GNP as a useful measure of development since income growth enables persons in expanding their range of choices.
This argument is, however, faulty. Most importantly, human choices go far beyond income expansion. There are so many choices that are not dependent on income. Thus, human development covers all aspects of development. Hence it is a holistic concept. “Economic growth, as such becomes only a subset of human development paradigm.”
Objectives of Human Development:
In the traditional development economics, development meant growth of per capita real income. Later on, a wider definition of development came to be assigned that focused on distributional objectives. Economic development, in other words, came to be redefined in terms of reduction or elimination of poverty and inequality.
These are, after all, ‘a goods-oriented’ view of development. True development has to be ‘people- centred’. When development is defined in terms of human welfare it means that people are put first. This ‘people-oriented’ view of development is to be called human development.
It is thus clear that per capita income does not stand as a true index of development of any country. To overcome this problem and to understand the dynamics of development, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) developed the concept of Human Development Index (HDI) in the 1990s. This index brought in revolutionary changes not only in development, but also in the policy environment in which the government was assigned a major role instead of market forces.
Economic development now refers to expanding capabilities. According to Amartya Sen, the basic objective of development is ‘the expansion of human capabilities’. The capability of a person reflects the various combinations of ‘doings and beings’ that one can achieve. It then reflects that the people are capable of doing or being. Capability thus describes a person’s freedom to choose between different ways of living.
For example:
Can people read and write? Are foodstuffs distributed among people in a universal manner? Do poor students get midday meal in schools? Do the poor children get adequately nourishing diets at home? No one would doubt that an illiterate poor person cannot have the same capabilities that a rich literate one gets. Thus capability failure leads to poverty and deprivation. This perspective of development, as enunciated by A. Sen, suggests why development economists put greater emphasis on education and health.
There are many countries in the world which —despite high levels of per capita GDP growth/ real income—experience high mortality rate, undernourishment rate, poor literacy, and so on. This is a case called ‘growth without development’. M. P Todaro and S. C. Smith assert: “Real income is essential, but to convert the characteristics of commodities into functions…. surely requires health and education as well as income.” In other words, income does not define peoples’ ‘well- being’ adequately.
Well-being, although a diverse notion, should consider health and education, in addition to income. Sen’s intellectual insights and fundamental ideas induced UNDP to formulate HDI as a comprehensive measure of development. It may be reiterated that the HDI as used in the Human Development Reports to compare different countries in the world has been designed as alternative to per capita GDP/GNP. Today, it is the most single commonly used measure to evaluate development outcomes.
Components of Human Development:
The noted Pakistani economist Mahbub ul Haq considered four essential pillars of human development.
i. Equality,
ii. Sustainability,
iii. Productivity, and
iv. Empowerment.
If development is viewed in terms of enhancing people’s basic capabilities, people must enjoy equitable access to opportunities. Such may be called equality-related capabilities. To ensure equality-related capabilities or access to opportunities what is essential is that the societal institutional structure needs to be more favourable or progressive.
In other words, the unfavourable initial asset distribution, like land, can be made more farmer-friendly through land reform and other redistributive measures. In addition, uneven income distribution may be addressed through various tax-expenditure policies. Economic or legislative- measures that interferes with market exchange may enable people to enlarge their capabilities and, hence, well-being.
Further, to ensure basic equality, political opportunities need to be more equal. In the absence of effective political organisation, disadvantaged groups are exploited by the ‘rich’ to further their own interests rather than social goals. However, participatory politics gets a beating by the inequality in opportunities in having basic education.
It is to be added here that basic education serves as a catalyst of social change. Once the access to such opportunity is opened up in an equitable way, women or religious minorities or ethnic minorities would be able to remove socioeconomic obstacles of development. This then surely brings about a change in power relations and makes society more equitable.
Sustainability:
Another important facet of human development is that development should ‘keep going’, should ‘last long’. The concept of sustainable development focuses on the need to maintain the long term protective capacity of the biosphere. This then suggests that growth cannot go on indefinitely; there are, of course, ‘limits to growth.’
Here we assume that environment is an essential factor of production. In 1987, the Bruntland Commission Report (named after the then Prime Minister Go Harlem Bruntland of Norway) defined sustainable development as ‘… development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their basic needs.’ This means that the term sustainability focuses on the desired balance between future economic growth and environ-mental quality. To attain the goal of sustainable development, what is of great importance is the attainment of the goal of both intra- generation and inter-generation equality.
This kind of inequality includes the term ‘social well-being’ not only for the present generation but also for the people who will be on the earth in the future. Any kind of environmental decline is tantamount to violation of distributive justice of the disadvantaged peoples. Social well-being thus, then, depends on environ-mental equality.
Productivity:
Another component of human development is productivity which requires investment in people. This is commonly called investment in human capital. Investment in human capital—in addition to physical capital—can add more productivity.
The improvement in the quality of human resources raises the productivity of existing resources. Theodore W. Schultz—the Nobel Prize-winning economist—articulated its importance: “The decisive factors of production in improving the welfare of poor people are not space, energy, and crop land; the decisive factor is the improvement in population quality.” Empirical evidence from many East Asian countries corroborate this view.
Empowerment:
The empowerment of people—particularly women—is another component of human development. In other words, genuine human development requires empowerment in all aspects of life. Empowerment implies a political democracy in which people themselves make the decisions about their lives. Under it, people enjoy greater political and civil liberties and remain free from excessive controls and regulations. Empowerment refers to decentralisation of power so that the benefits of governance are reaped by all peoples.
It focuses on grassroots participation which promotes democracy by enfranchising the disadvantaged groups. Unfortunately, benefits are cornered by the elites because of lack of empowerment of people. Participation as a goal is a feature of ‘bottom-up’ development strategy rather than ‘top-down’. Further, development policies and strategies male-dominated. But the benefits of development are to be made ‘gender-sensitive’.
Discrimination against women in health and education is very costly from the viewpoint of achieving development goals. Education of women can lead to a virtuous circle of lower fertility, better care of children, more educational opportunity, and higher productivity. Above all, as women’s education rises, women’s independence in making their own choices also increase.
Anyway, decentralization and participation empower people, specially the women and the poor. It then breaks the ‘deprivation trap’. Mahbub ul Haq asserts: “If people can exercise their choices in the political, social and economic spheres, there is a good prospect that growth will be strong, democratic, participatory and durable.”
Related Articles:
- Human Development Index (HDI): Indicators & Shortcomings | Economics
- Essay on Human Development | Economics
- Human Capital Formation: Meaning, Importance and Composition
Human Development and Learning Essay
One of the at-risk behaviors of the seventh grader concerns poor reading and comprehension skills. As a rule, students that lag behind the group feel inferior and can experience emotional stress which can become the reason of other emotional-social problems and gaps in behavior.
The poor reading and comprehension skills can be qualified as unaddressed learning problems or as poor performance in class which can influence a student’s academic progress in other domains. The interventions to cope with this at-risk behavior include the following:
- Clear instructions and more attention can be paid to a student; besides, this individual should be involved into some special programs if other methods turn out to be ineffective.
- Work in groups or with a partner can be effective in terms of improvements to reading and comprehension skills.
- As a student shows interest in drawing, it is possible to visualize instructions to the reading tasks and make the understanding of material more available to this student.
The next at-risk behavior is the daydreaming which can have negative consequences on the student’s social-emotional behavior and academic progress. Such behavior results in lack of attention to the subjects learnt and influence on the overall social-emotional and academic progress of this student.
At the same time, daydreaming can be the result of self-analysis which is considered normal for the age of 13-18 when children start to think about the future and their future roles of adults. As parents of this individual are divorced, it is possible that the student is concerned about becoming an adult and experiencing the same problems as his/her parents. The interventions include the following:
- Removing distractions can be the first step to coping with the problem of not being focused. A student should know the goal and achieve it while a teacher can guide him/her on the way to attaining the goal.
- A teacher might allow movements in class for all students. These would be short breaks for children to think about things that distract them and to get down to learning after that.
- A teacher can make this student responsible for certain activities by assigning a role of a manger in class to this student. So, additional activities can help this student not to be distracted because when a person is responsible for the activities of the entire class, it can change his/her perception of the learning process.
Finally, lack of social skills can be treated as at-risk behavior because it can influence social-emotional behavior and academic progress. A teacher should do everything possible to make a student feel safe in class. Hylen (2008) emphasizes the importance of safe and healthy learning climate for children, especially those with at-risk behavior (pp. 18-20).
Regressive behavior of students can be seen in their academic achievements and their anti-social behavior (Kruger & Maher, 1990, p. 35). Possible interventions to cope with recess and lack of communication skills include the following:
- It is necessary to encourage a student to communicate with classmates. A teacher can introduce more tasks that require a work in team.
- A teacher can structure the class activities in a way that a student should cooperate with classmates before asking for teacher’s help or requiring some additional guidelines.
- A teacher can ask students that lack social skills to monitor the class activities and report about those in the end of every day.
Hylen, M. G. (2008). The impact of a character education based interactive discipline program on at-risk student behavior in an alternative school. (Doctoral dissertation). Retrieved from ProQuest.
Kruger, L. J., & Maher, C. A. (Eds.). (1990). Promoting success with at-risk students: Emerging perspectives and practical approaches . Binghamton, NY: Routledge.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, January 7). Human Development and Learning. https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-development-and-learning/
"Human Development and Learning." IvyPanda , 7 Jan. 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/human-development-and-learning/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Human Development and Learning'. 7 January.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Human Development and Learning." January 7, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-development-and-learning/.
1. IvyPanda . "Human Development and Learning." January 7, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-development-and-learning/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Human Development and Learning." January 7, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-development-and-learning/.
- Experimental Devices in Marcom’s Novel “The Daydreaming Boy”
- Social-Emotional Learning in Human Development
- At-Risk Students Empowerment
- School-Based Interventions for Students With Behavior Problems
- Cognitive Development and Social-Emotional Functioning in Young Foster Children
- COVID-19 Social-Emotional Impact on Young Children
- The Behavior of an At-Risk Student
- Effects of an Intervention Program for at-Risk Males
- The Impact of Entrepreneurship Programs on Children’s Development
- Social-Emotional Learning for Kindergarten Education
- Selection of the gender of correctional officers
- Research Programme for Preschool Students
- Moral Panic from Implementing Stern Security Measures
- The Reggio Emilia and Montessori Approaches Used in Early Childhood Education in the 20th Century
- Struggling Readers vs. Non-Struggling Readers
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
6 Common Leadership Styles — and How to Decide Which to Use When
- Rebecca Knight

Being a great leader means recognizing that different circumstances call for different approaches.
Research suggests that the most effective leaders adapt their style to different circumstances — be it a change in setting, a shift in organizational dynamics, or a turn in the business cycle. But what if you feel like you’re not equipped to take on a new and different leadership style — let alone more than one? In this article, the author outlines the six leadership styles Daniel Goleman first introduced in his 2000 HBR article, “Leadership That Gets Results,” and explains when to use each one. The good news is that personality is not destiny. Even if you’re naturally introverted or you tend to be driven by data and analysis rather than emotion, you can still learn how to adapt different leadership styles to organize, motivate, and direct your team.
Much has been written about common leadership styles and how to identify the right style for you, whether it’s transactional or transformational, bureaucratic or laissez-faire. But according to Daniel Goleman, a psychologist best known for his work on emotional intelligence, “Being a great leader means recognizing that different circumstances may call for different approaches.”
- RK Rebecca Knight is a journalist who writes about all things related to the changing nature of careers and the workplace. Her essays and reported stories have been featured in The Boston Globe, Business Insider, The New York Times, BBC, and The Christian Science Monitor. She was shortlisted as a Reuters Institute Fellow at Oxford University in 2023. Earlier in her career, she spent a decade as an editor and reporter at the Financial Times in New York, London, and Boston.
Partner Center
AI Index Report
Welcome to the seventh edition of the AI Index report. The 2024 Index is our most comprehensive to date and arrives at an important moment when AI’s influence on society has never been more pronounced. This year, we have broadened our scope to more extensively cover essential trends such as technical advancements in AI, public perceptions of the technology, and the geopolitical dynamics surrounding its development. Featuring more original data than ever before, this edition introduces new estimates on AI training costs, detailed analyses of the responsible AI landscape, and an entirely new chapter dedicated to AI’s impact on science and medicine.
Read the 2024 AI Index Report
The AI Index report tracks, collates, distills, and visualizes data related to artificial intelligence (AI). Our mission is to provide unbiased, rigorously vetted, broadly sourced data in order for policymakers, researchers, executives, journalists, and the general public to develop a more thorough and nuanced understanding of the complex field of AI.
The AI Index is recognized globally as one of the most credible and authoritative sources for data and insights on artificial intelligence. Previous editions have been cited in major newspapers, including the The New York Times, Bloomberg, and The Guardian, have amassed hundreds of academic citations, and been referenced by high-level policymakers in the United States, the United Kingdom, and the European Union, among other places. This year’s edition surpasses all previous ones in size, scale, and scope, reflecting the growing significance that AI is coming to hold in all of our lives.
Steering Committee Co-Directors

Ray Perrault
Steering committee members.

Erik Brynjolfsson

John Etchemendy

Katrina Ligett

Terah Lyons

James Manyika

Juan Carlos Niebles

Vanessa Parli

Yoav Shoham

Russell Wald
Staff members.

Loredana Fattorini

Nestor Maslej
Letter from the co-directors.
A decade ago, the best AI systems in the world were unable to classify objects in images at a human level. AI struggled with language comprehension and could not solve math problems. Today, AI systems routinely exceed human performance on standard benchmarks.
Progress accelerated in 2023. New state-of-the-art systems like GPT-4, Gemini, and Claude 3 are impressively multimodal: They can generate fluent text in dozens of languages, process audio, and even explain memes. As AI has improved, it has increasingly forced its way into our lives. Companies are racing to build AI-based products, and AI is increasingly being used by the general public. But current AI technology still has significant problems. It cannot reliably deal with facts, perform complex reasoning, or explain its conclusions.
AI faces two interrelated futures. First, technology continues to improve and is increasingly used, having major consequences for productivity and employment. It can be put to both good and bad uses. In the second future, the adoption of AI is constrained by the limitations of the technology. Regardless of which future unfolds, governments are increasingly concerned. They are stepping in to encourage the upside, such as funding university R&D and incentivizing private investment. Governments are also aiming to manage the potential downsides, such as impacts on employment, privacy concerns, misinformation, and intellectual property rights.
As AI rapidly evolves, the AI Index aims to help the AI community, policymakers, business leaders, journalists, and the general public navigate this complex landscape. It provides ongoing, objective snapshots tracking several key areas: technical progress in AI capabilities, the community and investments driving AI development and deployment, public opinion on current and potential future impacts, and policy measures taken to stimulate AI innovation while managing its risks and challenges. By comprehensively monitoring the AI ecosystem, the Index serves as an important resource for understanding this transformative technological force.
On the technical front, this year’s AI Index reports that the number of new large language models released worldwide in 2023 doubled over the previous year. Two-thirds were open-source, but the highest-performing models came from industry players with closed systems. Gemini Ultra became the first LLM to reach human-level performance on the Massive Multitask Language Understanding (MMLU) benchmark; performance on the benchmark has improved by 15 percentage points since last year. Additionally, GPT-4 achieved an impressive 0.97 mean win rate score on the comprehensive Holistic Evaluation of Language Models (HELM) benchmark, which includes MMLU among other evaluations.
Although global private investment in AI decreased for the second consecutive year, investment in generative AI skyrocketed. More Fortune 500 earnings calls mentioned AI than ever before, and new studies show that AI tangibly boosts worker productivity. On the policymaking front, global mentions of AI in legislative proceedings have never been higher. U.S. regulators passed more AI-related regulations in 2023 than ever before. Still, many expressed concerns about AI’s ability to generate deepfakes and impact elections. The public became more aware of AI, and studies suggest that they responded with nervousness.
Ray Perrault Co-director, AI Index
Our Supporting Partners

Analytics & Research Partners

Stay up to date on the AI Index by subscribing to the Stanford HAI newsletter.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The human development approach, developed by the economist Mahbub Ul Haq, is anchored in Amartya Sen's work on human capabilities, often framed in terms of whether people are able to "be" and "do" desirable things in life iii. Examples include. Beings: well fed, sheltered, healthy. Doings: work, education, voting, participating in ...
Human Development or Lifespan Development is the scientific study of the ways in which people change, as well as remain the same, from conception to death. You will discover that the field, known more broadly as developmental science, examines changes and stability across multiple domains of psychological and social functioning.
human development, the process of growth and change that takes place between birth and maturity.. Human growth is far from being a simple and uniform process of becoming taller or larger. As a child gets bigger, there are changes in shape and in tissue composition and distribution. In the newborn infant the head represents about a quarter of the total length; in the adult it represents about ...
Discussion of Human Development. Human development refers to individuals' social, psychological, physical, and cognitive development throughout their lifespan, from prenatal development to late adulthood. Physical development includes growth in motor skills and brain, body, sense, and health development.
Human development, a multidimensional concept, is a process of enlarging people's freedoms and improving their well-being. It encompasses the enhancement of both individual potential and societal growth, focusing on aspects such as education, health, standard of living, and participation in societal activities.
Download this Document. Total Length: 1835 words ( 6 double-spaced pages) Total Sources: 5. Page 1 of 6. Human development refers to the psychological and biological growth of a human being throughout life. It starts from infancy all the way to adulthood. The scientific study of the development of a human being, psychologically, is referred to ...
Human development is a branch of psychology that studies—and strives to optimize—the elements that help people live healthy and fulfilling lives. This field aims to understand the various changes individuals and their relationships go through as they continue to learn and grow. The more complex definition of human development in psychology ...
Figure 1. Human development encompasses the physical, cognitive, and psychosocial changes that occur throughout a lifetime. Human development refers to the physical, cognitive, and psychosocial development of humans throughout the lifespan. What types of development are involved in each of these three domains, or areas, of life?
the full meaning of human development as envisioned by its founders, Mahbub ul Haq and Amartya Sen. The last three decades have also brought major advances in science and technology, enabling rapid change along with the emergence of new ideas about the meaning of human flourishing and the scales that make up the different dimensions of human
Overall, An Introduction to Theories of Human Development is an excellent introduction for students who are already grounded - or who at the very least intend to become grounded - in traditional ways of 'doing science.' It is clear and well structured, reader-friendly (including summary boxes, illustrations, highlights of important points, and employs jargon only where it is necessary ...
This is a book about lifespan human development —the ways in which people grow, change, and stay the same throughout their lives, from conception to death. When people use the term development , they often mean the transformation from infant to adult. However, development does not end with adulthood.
This paper and presentation discusses human development, its meaning and purpose. The term. 'human development' is most often loosely defined and difficult to describe. Many individuals, public ...
on childhood development, evolutionary theory, and their applications to education. Hall was a strong believer in . the scientific method and its application to the study of human nature. He supported empirical research in the then emerging area of child development, developing both theories of psychological development and its applica-
As it fulfills an irresistible need to understand our own origins, research on human development occupies a unique niche in scientific and medical research. In this Comment, we explore the ...
Human Growth and Development. Human growth and development is a complex and multi-faceted process that encompasses physical, cognitive, social, emotional, and psychological changes across the lifespan. Understanding human growth and development is crucial for various fields such as education, healthcare, psychology, and sociology, as it ...
Abstract. As it fulfills an irresistible need to understand our own origins, research on human development occupies a unique niche in scientific and medical research. In this Comment, we explore the progress in our understanding of human development over the past 10 years. The focus is on basic research, clinical applications, and ethical ...
This essay provides information about the human development ! The notion of human development essentially addresses the human in development — all those elements which make a person human not only in terms of what she/he needs for basic survival such as food, clothing or shelter, health, etc., but a sense of dignity, what Adam Smith called the ability to mix with others without being ashamed ...
The term 'human development' may be defined as an expansion of human capabilities, a widening of choices, 'an enhancement of freedom, and a fulfilment of human rights. At the beginning, the notion of human development incorporates the need for income expansion. However, income growth should consider expansion of human capabilities.
The definition of human development is the process of expansion of human's potential, an increase of choices and opportunities and fulfillment of human rights. Human development also describes as the growth of humans throughout their lifespan, from conception to death. Changes are ordinary and expected, and yet people still able to pose ...
The human development approach puts equal emphasis on the production and distribution of resources, expansion and use of human capabilities, scope of choice, livelihood security, participatory process, and social, economic and political freedom. All these indeed emphases a paradigm shift in the social development strategy of the State.
This essay, "Human Development and Learning" is published exclusively on IvyPanda's free essay examples database. You can use it for research and reference purposes to write your own paper. However, you must cite it accordingly. Donate a paper. Removal Request.
Human Development: Lifelong, Multifaceted, Dynamic. Development can be defined as the orderly changes of an individual from conception to death. From a biological point of view, development can be Identified as a growth from early life, stablllty In early and middle adulthood, and decline in later life. This is the "gain-stability-loss" model.
Categories: Adult Adulthood. Download. Essay, Pages 7 (1595 words) Views. 2. As time goes by, everything changes and as the world changes, so does the people. Psychology designates human life into few stages as their age gets older. For example, infants become children, children become teenagers, and suddenly a teenager becomes an adult.
Much has been written about common leadership styles and how to identify the right style for you, whether it's transactional or transformational, bureaucratic or laissez-faire. But according to ...
This year's AI Index — a 500-page report tracking 2023's worldwide trends in AI — is out.. The index is an independent initiative at the Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI), led by the AI Index Steering Committee, an interdisciplinary group of experts from across academia and industry. This year's report covers the rise of multimodal foundation models ...
The AI Index report tracks, collates, distills, and visualizes data related to artificial intelligence (AI). Our mission is to provide unbiased, rigorously vetted, broadly sourced data in order for policymakers, researchers, executives, journalists, and the general public to develop a more thorough and nuanced understanding of the complex field ...