
- Book Solutions
- State Boards

Case Study Questions Class 11 Biology Biomolecules
Case study questions class 11 biology chapter 9 biomolecules.
CBSE Class 11 Case Study Questions Biology Biomolecules. Important Case Study Questions for Class 11 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Biomolecules.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 11 Biology Biomolecules
Enzymes are composed of one or several polypeptide chains. However, there are a number of cases in which non-protein constituents called co-factors are bound to the enzyme to make the enzyme catalytically active. In these instances, the protein portion of the enzymes is called the apoenzyme. Three kinds of cofactors may be identified: prosthetic groups, co-enzymes and metal ions. Prosthetic groups are organic compounds and are distinguished from other cofactors in that they are tightly bound to the apoenzyme. For example, in peroxidase and catalase, which catalyze the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen, haem is the prosthetic group and it is a part of the active site of the enzyme. Co-enzymes are also organic compounds but their association with the apoenzyme is only transient, usually occurring during the course of catalysis. Furthermore, co-enzymes serve as co-factors in a number of different enzyme catalyzed reactions. The essential chemical components of many coenzymes are vitamins, e.g., coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and NADP contain the vitamin niacin. A number of enzymes require metal ions for their activity which form coordination bonds with side chains at the active site and at the same time form one or more cordination bonds with the substrate, e.g., zinc is a cofactor for the proteolytic enzyme carboxypeptidase. Catalytic activity is lost when the co-factor is removed from the enzyme which testifies that they play a crucial role in the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
1.) In complex of protein and co-factors, protein is referred as ___________________.
a) Proenzyme
b) Coenzyme
c) Apoenzyme
d.) Proteinase enzyme.
2.) ________________ Co-factor are found very tightly bound to the apoenzyme.
a.) Co-enzyme
b.) Proenzyme
c,) Proteinase
d.) Prosthetic
3.) Enlist the type of co-factor with examples.
4.) Define co-factors.
5.) What result come off if co-factor is removed from the enzyme?
3.) Three kinds of cofactors
- Prosthetic groups – e.g. Haem
- Co-enzymes – e.g. Niacin
- Metal ions – e.g. zinc
4.) Co-factor are the non-protein constituents are bound to the enzyme to make the enzyme catalytically active. Enzymes are composed of one or several polypeptide chains. However, there are a number of cases in which non-protein constituents are bound to the enzyme to make the enzyme catalytically active.
5.) Catalytic activity is lost when the co-factor is removed from the enzyme which testifies that they play a crucial role in the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
The activity of an enzyme can be affected by a change in the conditions which can alter the tertiary structure of the protein. These include temperature, pH, and change in substrate concentration or binding of specific chemicals that regulate its activity. Temperature and pH Enzymes generally function in a narrow range of temperature and pH. Each enzyme shows its highest activity at a particular temperature and pH called the optimum temperature and optimum pH. Activity declines both below and above the optimum value. Low temperature preserves the enzyme in a temporarily inactive state whereas high temperature destroys enzymatic activity because proteins are denatured by heat.
Concentration of Substrate With the increase in substrate concentration, the velocity of the enzymatic reaction rises at first. The reaction ultimately reaches a maximum velocity (Vmax) which is not exceeded by any further rise in concentration of the substrate. This is because the enzyme molecules are fewer than the substrate molecules and after saturation of these molecules, there are no free enzyme molecules to bind with the additional substrate molecules.
The activity of an enzyme is also sensitive to the presence of specific chemicals that bind to the enzyme. When the binding of the chemical shuts off enzyme activity, the process is called inhibition and the chemical is called an inhibitor.
When the inhibitor closely resembles the substrate in its molecular structure and inhibits the activity of the enzyme, it is known as competitive inhibitor. Due to its close structural similarity with the substrate, the inhibitor competes with the substrate for the substrate binding site of the enzyme. Consequently, the substrate cannot bind and as a result, the enzyme action declines, e.g., inhibition of succinic dehydrogenase by malonate which closely resembles the substrate succinate in structure. Such competitive inhibitors are often used in the control of bacterial pathogens.
1.) _______________ is a chemical compound or molecule which is responsible for decrease or stop the enzyme activity by binding to an enzyme.
a.) Catalyser
b) Inhibitor
c) Regulator
d) Controller
2.) _______________ preserve the enzyme and keep them in temporarily inactive state.
a.) Optimum pH
c) Optimum temperature
d) Low temperature
3.) Give reason – why most of the enzymes destroyed in high temperature condition?
4.) Explain the relation between substrate concentration and enzymatic activity?
5.) Explain competitive inhibition and inhibitor.
3.) Enzymes are composed of one or several polypeptide chains. Almost all enzymes are protein. High temperature condition destroys enzymatic activity because proteins are denatured by heat.
4.) Concentration of Substrate With the increase in substrate concentration, the velocity of the enzymatic reaction rises at first. The reaction ultimately reaches a maximum velocity (Vmax) which is not exceeded by any further rise in concentration of the substrate. This is because the enzyme molecules are fewer than the substrate molecules and after saturation of these molecules, there are no free enzyme molecules to bind with the additional substrate molecules.
5.) When the inhibitor closely resembles the substrate in its molecular structure and inhibits the activity of the enzyme, it is known as competitive inhibitor. Due to its close structural similarity with the substrate, the inhibitor competes with the substrate for the substrate binding site of the enzyme. Consequently, the substrate cannot bind and as a result, the enzyme action declines. This phenomenon is called as competitive inhibition.
Almost all enzymes are proteins. There are some nucleic acids that behave like enzymes. These are called ribozymes. An enzyme like any protein has a primary structure, i.e., amino acid sequence of the protein. An enzyme like any protein has the secondary and the tertiary structure. When you look at a tertiary structure you will notice that the backbone of the protein chain folds upon itself, the chain criss-crosses itself and hence, many crevices or pockets are made. One such pocket is the ‘active site’. An active site of an enzyme is a crevice or pocket into which the substrate fits. Thus enzymes, through their active site, catalyse reactions at a high rate. Enzyme catalysts differ from inorganic catalysts in many ways, but one major difference needs mention. Inorganic catalysts work efficiently at high temperatures and high pressures, while enzymes get damaged at high temperatures (say above 40°C). However, enzymes isolated from organisms who normally live under extremely high temperatures (e.g., hot vents and sulphur springs), are stable and retain their catalytic power even at high temperatures (upto 80°-90°C). Thermal stability is thus an important quality of such enzymes isolated from thermophilic organisms.
1.) _____________ is the pocket like region of an enzyme into which substrate molecules bind.
a) Protein site
b) Co-factors
c) Coenzyme
d) Active site
2.) Identify incorrect statement
Statement 1 – Nucleic acids which behave like enzymes are commonly termed as nucliozymes.
Statement 2 – An enzyme like any protein has a primary, secondary and the tertiary structure.
Statement 3 – Enzyme catalysts differ from inorganic catalysts in many ways.
Statement 4 – All enzymes are proteins.
b) Both 1 & 3
d.) None of the above
3.) How active site of enzymes are formed?
4.) Explain how Enzyme catalysts differ from inorganic catalysts?
5.) What is ribozymes?
3.) Enzyme have primary, secondary and tertiary structure like proteins. In tertiary structure, backbone of the protein chain folds upon itself, the chain criss-crosses itself and leads to the formation of many crevices or pockets are made. These pockets are referred as active site of enzyme. An active site of an enzyme is a crevice or pocket into which the substrate fits.
4.) Enzyme catalysts differ from inorganic catalysts in many ways. Inorganic catalysts work efficiently at high temperatures and high pressures, while enzymes get damaged at high temperatures (above 40°C). There are some exceptions such as enzyme isolated from thermophilic organisms.
5.) There are some nucleic acid behave like an enzymes, these nucleic acid is termed as ribozymes.
Metabolic pathways can lead to a more complex structure from a simpler structure (for example, acetic acid becomes cholesterol) or lead to a simpler structure from a complex structure (for example, glucose becomes lactic acid in our skeletal muscle). The former cases are called biosynthetic pathways or anabolic pathways. The latter constitute degradation and hence are called catabolic pathways. Anabolic pathways, as expected, consume energy. Assembly of a protein from amino acids requires energy input. On the other hand, catabolic pathways lead to the release of energy. For example, when glucose is degraded to lactic acid in our skeletal muscle, energy is liberated. This metabolic pathway from glucose to lactic acid which occurs in 10 metabolic steps is called glycolysis. Living organisms have learnt to trap this energy liberated during degradation and store it in the form of chemical bonds. As and when needed, this bond energy is utilised for biosynthetic, osmotic and mechanical work that we perform. The most important form of energy currency in living systems is the bond energy in a chemical called adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
There are thousands of chemical compounds in a living organism, otherwise called as metabolites or biomolecules, are present at concentrations characteristic of each of them. For example, the blood concentration of glucose in a normal healthy individual is 4.2 mmol/L– 6.1 mmol/L, while that of hormones would be nanograms/mL. The most important fact of biological systems is that all living organisms exist in a steady-state characterised by concentrations of each of these biomolecules. These biomolecules are in a metabolic flux. Any chemical or physical process moves spontaneously to equilibrium. The steady state is a non-equilibrium state. Systems at equilibrium cannot perform work. As living organisms work continuously, they cannot afford to reach equilibrium. Hence the living state is a non-equilibrium steady state to be able to perform work; living process is a constant effort to prevent falling into equilibrium. This is achieved by energy input. Metabolism provides a mechanism for the production of energy. Hence the living state and metabolism are synonymous. Without metabolism there cannot be a living state.
1.) ________________ is the destructive process, which involves complex structure breakdown into simple form.
a) Amphibolic pathway
b) Anabolic pathway
c) Catabolic pathway
d) None of the above
2.) ______________ is the normal glucose concentration in normal healthy individual.
a) 9 mmol/L– 6.8 mmol/L
b) 5 mmol/L– 6.5 mmol/L
c) 0 mmol/L– 7.1 mmol/L
d) 2 mmol/L– 6.1 mmol/L
3.) Give any one example of catabolic reaction that take place in human body.
4.) Give the name of chemical bond in which energy liberated during degradation of metabolites, is stored.
5.) Define anabolic pathways and catabolic pathways.
3.) Glucose becomes lactic acid in our skeletal muscle is the catabolic pathway reaction, which constitute degradation of biomolecule and release energy.
4.) In Living organism energy liberated during degradation of metabolites stored in the form of chemical bonds i.e. ATP. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the most important form of energy currency in living systems.
5) Anabolic pathway – Metabolic pathways which leads to a more complex structure from a simpler structure are termed as anabolic pathways or biosynthetic pathways.
Catabolic pathway – Metabolic pathways which leads to a simpler structure from a complex structure are termed as catabolic pathways.
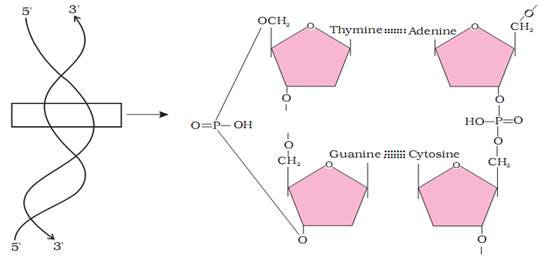
Proteins are heteropolymers containing strings of amino acids. Structure of molecules means different things in different contexts. In inorganic chemistry, the structure invariably refers to the molecular formulae (e.g., NaCl, MgCl2, etc.). Organic chemists always write a two dimensional view of the molecules while representing the structure of the molecules (e.g., benzene, naphthalene, etc.). Physicists conjure up the three dimensional views of molecular structures while biologists describe the protein structure at four levels. The sequence of amino acids i.e., the positional information in a protein – which is the first amino acid, which is second, and so on – is called the primary structure of a protein. A protein is imagined as a line, the left end represented by the first amino acid and the right end represented by the last amino acid. The first amino acid is also called as N-terminal amino acid. The last amino acid is called the C-terminal amino acid. A protein thread does not exist throughout as an extended rigid rod. The thread is folded in the form of a helix, only some portions of the protein thread are arranged in the form of a helix. In proteins, only right handed helices are observed. Other regions of the protein thread are folded into other forms in what is called the secondary structure. In addition, the long protein chain is also folded upon itself like a hollow woollen ball, giving rise to the tertiary structure. This gives us a 3-dimensional view of a protein. Tertiary structure is absolutely necessary for the many biological activities of proteins.
Some proteins are an assembly of more than one polypeptide or subunits. The manner in which these individual folded polypeptides or subunits are arranged with respect to each other (e.g. linear string of spheres, spheres arranged one upon each other in the form of a cube or plate etc.) is the architecture of a protein otherwise called the quaternary structure of a protein (Fig. 9.4 d). Adult human haemoglobin consists of 4 subunits. Two of these are identical to each other. Hence, two subunits of α type and two subunits of β type together constitute the human haemoglobin (Hb).
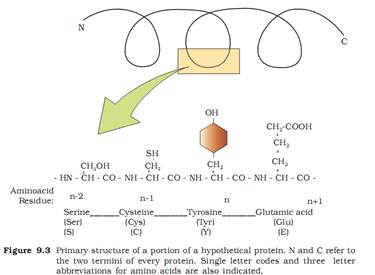
In a polypeptide or a protein, amino acids are linked by a peptide bond which is formed when the carboxyl (-COOH) group of one amino acid reacts with the amino (-NH2 ) group of the next amino acid with the elimination of a water moiety (the process is called dehydration). In a polysaccharide the individual monosaccharides are linked by a Glycosidic bond. This bond is also formed by dehydration. This bond is formed between two carbon atoms of two adjacent monosaccharides. In a nucleic acid a phosphate moiety links the 3’-carbon of one sugar of one nucleotide to the 5’-carbon of the sugar of the succeeding nucleotide. The bond between the phosphate and hydroxyl group of sugar is an ester bond. As there is one such ester bond on either side, it is called phosphodiester bond. Nucleic acids exhibit a wide variety of secondary structures. For example, one of the secondary structures exhibited by DNA is the famous Watson – Crick Model. This model says that DNA exists as a double helix. The two strands of polynucleotides are antiparallel i.e., run in the opposite direction. The backbone is formed by the sugar-phosphate-sugar chain. The nitrogen bases are projected more or less perpendicular to this backbone but face inside. A and G of one strand compulsorily base pairs with T and C, respectively, on the other strand.There are two hydrogen bonds between A and T and three hydrogen bonds between G and C. Each strand appears like a helical staircase.
1.) To form polypeptide molecules, number of amino acids joined together by _______________ bond.
a.) Covalent bond
b) Glycosidic bond
c) Peptide bond
d) Phosphodiester bond
2.) Number of monosaccharides are joined together by _____________ to form polysaccharide.
a.) Phosphodiester bond
c) Hydrogen bond
d) Ester bond
3.) Define N-terminal amino acid and c-terminal amino acid.
4.) Explain how amino acid chain formed in the formation of polypeptide molecule.
5.) Name the bond present between nitrogen bases ( A and G / T and C ) of nucleic acid.
3) The first amino acid present in amino acid chain is also called as N-terminal amino acid. The last amino acid is called the C-terminal amino acid.
4) When the carboxyl (-COOH) group of one amino acid reacts with the amino (-NH2) group of the next amino acid, they form peptide bond between them. This way formation of amino acid chain continuous which leads to the polypeptide.
5) The nitrogen bases A and G of one strand compulsorily base pairs with T and C, respectively, there are two hydrogen bonds between A and T and three hydrogen bonds between G and C.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Odisha board class 8 english music helps plants grow question answers solution, sikkim scert class 5 evs chapter 2 kuku … haaaaaa solution, sikkim scert class 5 english chapter 5e turn off the tv solution, sikkim scert class 5 english chapter 5f the journey of communication solution.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
myCBSEguide
- Class 11 Biology Case...
Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
If you are finding it difficult to solve Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions, you are not alone. Many students face difficulties in solving such questions, as they require in-depth knowledge of the subject. However, with the right resources and guidance, it is possible to overcome these difficulties. One of the best resources for Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions is the myCBSEguide app.
myCBSEguide provides detailed information and Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions that can help you understand the concepts better. Class 11 Biology students can also find several practice questions at the end of each chapter that can help Class 11 Biology students in understanding the concept better.
Biology: The study of living organisms
Biology is the study of life and all living things. It is a natural science that covers a wide range of topics, from the structure and function of the human body to the behavior of plants and animals. Class 11 biology students learn about the various branches of biology, such as anatomy, physiology, ecology, and evolution. In addition, they also study the cell, the building block of all living things. By understanding how cells work, students can better understand how the body works as a whole.
Class 11 students entering the world of Biology
For Class 11 students, biology is the foundation for Class 12 CBSE students. It is a vital topic that helps students grasp the fundamental notions of life and living beings. Cell structure and function, genetics, evolution, ecology, and plant and animal physiology are all themes addressed in biology. Biology is a fascinating topic that teaches students about the natural world around them. Biology is an excellent foundation for Class 11 CBSE students who want to pursue a career in medicine. Biology is critical for understanding the human body and its processes, as well as developing medical remedies.
Significance of Biology for class 11 students
- Biology encourages students to learn the fundamentals of biology.
- It promotes a rational/scientific attitude toward issues such as population, environment, and development by encouraging the acquisition of new information and its application to individuals and society.
- It raises public knowledge of environmental issues, problems, and remedies.
- It raises students’ understanding of the diversity of living species and fosters respect for other living beings.
- It understands that even the most complicated biological phenomena are based on fundamentally simple processes.
Case study questions in Class 11 Biology
Case studies are a part of to Class 11 biology examination paper pattern. These case studies can be used to assess a student’s understanding of a subject as well as their ability to apply that understanding in a real-world context. Incorporating case study questions into Class 11 Biology can provide students with a more hands-on and realistic experience with the subject. Class 11 Biology students can better learn how chemical concepts are utilized in the real world by going through real-life problems. Class 11 Biology Case study questions can also aid in the development of critical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
Examples of Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
We must solve a range of Class 11 Biology case study questions in order to achieve high grades in Biology. Class 11 Biology students must be seeking some examples of case study questions in order to improve their grades. myCBSEguide has prepared a variety of Class 11 Biology case study questions that will undoubtedly assist all students studying the subject. We have compiled a selection of Class 11 Biology case study questions for you. Have a look at the following Class 11 Biology case study question examples.
Class 11 Biology case study questions 1
Read the following and answer any four questions: The detailed structure of the membrane was studied only after the advent of the electron microscope in the 1950s. Meanwhile, chemical studies on the cell membrane, especially in human red blood cells (RBCs), enabled the scientists to deduce the possible structure of the plasma membrane. These studies showed that the cell membrane is composed of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates.
- Nucleic acid
- Carbohydrate
- Phosphoglycerides
- Glycoproteins
- Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
- Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
- Assertion is true but reason is false.
- Both assertion and reason are false.
Answer Key:
- (b) The lipids are arranged in a bilayer in the plasma membrane with the polar head towards the outer sides and the hydrophobic tails towards the inner part.
- (a) The lipid component of the membrane mainly consists of phosphoglycerides.
- (c) In human beings, the membrane of the erythrocyte has approximately 52 percent protein and 40 percent lipids.
- (b) Depending on the ease of extraction, membrane proteins can be classified into two types – integral or peripheral.
- (b) The plasma membrane is selectively permeable to some molecules present on either side of it. Neutral solutes may move across the membrane by the process of simple diffusion along the concentration gradient, i.e., from higher concentration to the lower. Hence, both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Class 11 Biology case study questions 2
Read the following and answer any four questions: Plastids are found in all plant cells and in euglenoids. These are easily observed under the microscope as they are large. They bear some specific pigments, thus imparting specific colours to the plants. Plastids consist of numerous membrane layers embedded in a material called the stroma. They have their own genome and ribosomes.
- Leucoplasts
- Chloroplasts
- Chromoplasts
- Carotenoids
- Amyloplasts
- Aleuroplasts
- Elaioplasts
- (a) The leucoplasts are the colourless plastids of varied shapes and sizes with stored nutrients.
- (b) The aleuroplasts store proteins in grains.
- (a) Amyloplasts are leucoplasts store carbohydrates (starch) in potato.
- (c) The space limited by the inner membrane of the chloroplast is called the stroma.
- (c) The chloroplasts contain chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments which are responsible for trapping light energy essential for photosynthesis. The chromoplasts impart colours to the parts of the plant as yellow, orange or red colour. Hence, Assertion is true but reason is false.
Class 11 Biology case study questions 3
Read the following and answer any four questions: In human beings, the lungs are situated in the thoracic chamber which is formed dorsally by the vertebral column, ventrally by the sternum, laterally by the ribs, and on the lower side by the dome-shaped diaphragm. The anatomical setup of the lungs in the thorax is such that any change in the volume of the thoracic cavity will be reflected in the lung (pulmonary) cavity. Such an arrangement is essential for breathing. Breathing involves two stages – inspiration and expiration. During inspiration, the atmospheric air is drawn in and during expiration, the alveolar air is released out.
- 12 – 16
- 70 – 72
- Ribs lift up
- Diaphragm flattens
- Ribs flatten
- Both ribs lift up and diaphragm flattens
- Tidal volume
- Inspiratory Reserve Volume
- Residual Volume
- Vital Capacity
- 6000 to 8000 mL
- 2500 mL to 3000 mL
- 1000 mL to 1100 mL
- 1100 mL to 1200 mL
- The movement of air into and out of the lungs is carried out by creating a pressure gradient.
- Expiration can occur if the pressure within the lungs (intra-pulmonary pressure) is less than the atmospheric pressure.
- The diaphragm and a specialised set of muscles help in generation of pressure gradients.
- Expiration is initiated by the contraction of diaphragm which increases the volume of thoracic chamber in the antero-posterior axis.
Choose from below the correct alternative.
- a. Only I is true
- b. I and IV are true
- c. III and II are true
- d. I and III are true
- (a) On an average, a healthy human breathes 12-16 times/minute.
- (d) When we breathe in, the ribs are lifted up and the diaphragm flattens which increases the size of the chest cavity. Because of this, the air is sucked into the lungs and fills the expanded alveoli.
- (a) Volume of air inspired or expired during normal respiration is called tidal volume.
- (d) Residual volume of air is the remaining air in the lungs even after a forcible expiration. This averages 1100 mL to 1200 mL.
- (d) The movement of air into and out of the lungs is carried out by creating a pressure gradient between the lungs and the atmosphere. Inspiration can occur if the pressure within the lungs (intra-pulmonary pressure) is less than the atmospheric pressure. The diaphragm and a specialized set of muscles – external and internal intercostals between the ribs, help in the generation of pressure gradients. Inspiration is initiated by the contraction of the diaphragm which increases the volume of thoracic chamber in the antero-posterior axis. Hence, statements I and III are true.
Class 11 Biology case study questions 4
Read the following and answer any four questions: Exchange of gases also occurs between blood and tissues. O 2 and CO 2 are exchanged in these sites by simple diffusion mainly based on pressure/concentration gradient. The solubility of the gases, as well as the thickness of the membranes involved in diffusion, are also some important factors that can affect the rate of diffusion.
- Atmospheric pressure
- Partial pressure
- Differential pressure
- Capillary pressure
- pO 2 – 104 mm Hg, pCO 2 – 40 mm Hg
- pO 2 – 104 mm Hg, pCO 2 – 140 mm Hg
- pO 2 – 95 mm Hg, pCO 2 – 40 mm Hg
- pO 2 – 40 mm Hg, pCO 2 – 45 mm Hg
- The given diagram represents the exchange of gases at the alveolus and the body tissues with blood and the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- The amount of CO 2 that can diffuse through the diffusion membrane per unit difference in partial pressure is much lesser compared to that of O 2 .
- All the factors in our body are favourable for the diffusion of O 2 from tissues to alveoli and that of CO 2 from alveoli to tissues.
- The total thickness of the diffusion membrane is much less than a millimetre.
- Only I is true
- I and IV are true
- III and II are true
- I and III are true
- (b) Pressure contributed by an individual gas in a mixture of gases is called partial pressure.
- (a) Alveoli are the primary sites of exchange of gases.
- (c) The diffusion membrane is made up of three major layers.
- (d) The values of pO 2 and pCO 2 in the body tissues is: pO 2 – 104 mm Hg, pCO 2 – 40 mm Hg.
- (b) The given diagram represents the exchange of gases at the alveolus and the body tissues with blood and the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide. The amount of CO 2 that can diffuse through the diffusion membrane per unit difference in partial pressure is much higher compared to that of O 2 . All the factors in our body are favourable for the diffusion of O 2 from alveoli to tissues and that of CO 2 from tissues to alveoli. The total thickness of diffusion membrane is much less than a millimetre.
Dealing with Class 11 Biology case study questions
There are a number of different ways to approach Class 11 Biology case study questions, but the most important thing is to make sure that Class 11 Biology students answer all parts of the question and provide as much detail as possible. In some cases, you may need to research the topic further in order to be able to answer the Class 11 Biology case study questions fully.
When dealing with Class 11 Biology case study questions, it is also important to think about the different perspectives that might be involved. For example, if you are asked to evaluate a particular decision made by a scientist, you will need to consider the impact of that decision from both the scientist’s perspective and the perspective of those affected by the decision.
Answering case study questions can be challenging, but it is an important skill to develop if you want to pursue a career in fields such as business or law. With practice, Class 11 Biology students will be able to approach these questions with confidence and provide well-reasoned, detailed answers.
Class 11 Biology curriculum: As fascinating as Biology itself
The current curriculum of Class 11 Biology provides students with up-to-date principles as well as more extensive exposure to current topics in the discipline. Class 11 Biology curriculum also strives to emphasize the basic concepts that are shared by animals, plants, and microbes, as well as the link between Biology and other fields of study. Class 11 Biology structure provides for a straightforward, sequential flow of ideas. It connects the science of biology to actual life through technological advancements. It connects biological discoveries and breakthroughs to everyday issues including the environment, industry, health, and agriculture. The new curriculum of Class 11 Biology also emphasizes scientific ideas and their application, while ensuring that enough chances and opportunities for mastering and recognizing fundamental concepts remain within its framework.
CBSE Class 11 Biology (Code No. 044)
COURSE STRUCTURE
myCBSEguide: An app as intriguing as biology
If you’re looking for an app that’s as intriguing as biology, myCBSEguide is a perfect choice. With millions of downloads, it’s one of the most popular apps on the App Store, and for good reason. myCBSEguide offers extensive coverage of the CBSE curriculum, with detailed explanations of concepts, thousands of practice questions, case study questions and much more. Whether you’re a student, teacher, or parent, myCBSEguide is an essential tool for anyone wanting to learn more about biology.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Computer Science Case Study Questions
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Neet Online Test Pack
12th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் subjects.

கணினி பயன்பாடுகள்

கணினி அறிவியல்
வணிகக் கணிதம் மற்றும் புள்ளியியல்.

கணினி தொழில்நுட்பம்

கணக்குப்பதிவியல்

English Subjects

Computer Science

Business Maths and Statistics

Accountancy

Computer Applications

Computer Technology

11th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

9th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

Social Science

சமூக அறிவியல்
6th standard stateboard question papers & study material.

10th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

7th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

8th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

கணிதம் - old

12th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

Introductory Micro and Macroeconomics

Business Studies

Indian Society

Physical Education

Bio Technology

Engineering Graphics

Entrepreneurship

Hindi Elective

Home Science

Legal Studies

Political Science

11th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

Mathematics

Enterprenership

Applied Mathematics
10th standard cbse subject question paper & study material.

9th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

8th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

7th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

6th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

School Exams

Tamil Nadu State Board Exams

Scholarship Exams

Study Materials , News and Scholarships

Stateboard Tamil Nadu

Free Online Tests

Educational News

Scholarships

Entrance Exams India

Video Materials

11th Standard CBSE
Class 11th Biology - Biomolecules Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023

Class 11th Biology - Biomolecules Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023 Study Materials Sep-09 , 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 11 Biology Subject - Biomolecules, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.

A PHP Error was encountered
Severity: Warning
Message: in_array() expects parameter 2 to be array, null given
Filename: material/details.php
Line Number: 1436
Message: Use of undefined constant EXAM - assumed 'EXAM' (this will throw an Error in a future version of PHP)
Line Number: 1438

QB365 - Question Bank Software
Biomolecules case study questions with answer key.
Final Semester - June 2015
All the chemical elements found in a sample of earth's crust are also present in a sample of living tissue. But a critical chemical analysis shows that the relative abundance of carbon and hydrogen with respect to other elements is higher in the living organisms. (a) Name the most abundant chemical compound in living organisms. (b) What term is given to the carbon compounds in living cells? (c) Name any two functional groups of such compounds. (d) Name any two elements present in the 'ash' of plants.
The tens and thousands of chemical compounds, called metabolites in a living organism are in a flux and the living state is a non-equilibrium steady-state. Metabolic inputs of energy prevent an equilibrium to be reached. (a) Why is living state considered a non-equilibrium state? (b) Living state and metabolism are considered synonymous. Justify the statement.
All enzymes (except ribozymes) are proteins. An enzyme, like any other protein, has a primary, secondary and tertiary structure. The protein functions as enzyme in its tertiary structure, where active sites are formed. (a) What is active site of an enzyme? (b) How are active sites formed? (e) Mention one major difference between inorganic catalysts and enzyme catalysts.
*****************************************
- Previous Class 11th Biology - Chemical Coordination and Integration Case Study Questions ...
- Next Class 11th Biology - Neural Control and Coordination Case Study Questions and An...
Reviews & Comments about Class 11th Biology - Biomolecules Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023

Write your Comment

11th Standard CBSE Biology Videos
CBSE 11th Biology Sample Model Question Paper with Answer Key 2023
11th Standard CBSE Biology Usefull Links

- 10th Standard
Other 11th Standard CBSE Subjects

Other 11th Standard CBSE Biology Study material
Class 11th biology - chemical coordination and ... click to view, class 11th biology - neural control and ... click to view, class 11th biology - locomotion and movement ... click to view, class 11th biology - excretory products and ... click to view, class 11th biology - body fluids and ... click to view, class 11th biology - breathing and exchange ... click to view, class 11th biology - digestion and absorption ... click to view, class 11th biology - plant growth and ... click to view, class 11th biology - respiration in plants ... click to view, class 11th biology - photosynthesis in higher ... click to view, class 11th biology - mineral nutrition case ... click to view, class 11th biology - transport in plants ... click to view, class 11th biology - cell cycle and ... click to view, class 11th biology - biomolecules case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023 click to view, class 11th biology - cell: the unit ... click to view, register & get the solution for class 11th biology - biomolecules case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 8: Biomolecules
About this unit.
What are living organisms made up of? Learn about biomolecules like lipids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and how special proteins called enzymes help with metabolism. This unit is aligned to the Class 11 NCERT curriculum.
Introduction to biomolecules
- Introduction to biomolecules (Opens a modal)
- Introduction to macromolecules (Opens a modal)
- Biological macromolecules 4 questions Practice
- Lipid overview (Opens a modal)
- Lipids (Opens a modal)
- Lipids 4 questions Practice
- Introduction to proteins and amino acids (Opens a modal)
- Overview of protein structure (Opens a modal)
- Proteins 4 questions Practice
Polysaccharides (Carbohydrates)
- Introduction to carbohydrates (Opens a modal)
- Carbohydrates (Opens a modal)
- Carbohydrates 4 questions Practice
Nucleic acids
- Nucleic acids (Opens a modal)
- Introduction to nucleic acids and nucleotides (Opens a modal)
- DNA (Opens a modal)
- Antiparallel structure of DNA strands (Opens a modal)
- DNA structure 4 questions Practice
- Identifying the nature of bond linking the monomers and the process involved. 4 questions Practice
Metabolism and the living state
- Introduction to metabolism: Anabolism and catabolism (Opens a modal)
- Overview of metabolism (Opens a modal)
- ATP: Adenosine triphosphate (Opens a modal)
- Metabolism 4 questions Practice
- Introduction to kinetics (Opens a modal)
- Activation energy (Opens a modal)
- Enzymes (Opens a modal)
- Enzymes and the active site (Opens a modal)
- Classification of enzymes (Opens a modal)
- Enzymes 4 questions Practice
Regulation of enzymes
- Competitive inhibition (Opens a modal)
- Noncompetitive inhibition (Opens a modal)
- Enzyme cofactors and coenzymes (Opens a modal)
- Basics of enzyme kinetics graphs (Opens a modal)
- Enzyme regulation and inhibition 4 questions Practice
CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules Study Materials
NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology Sample Papers Past Years Papers
Biomolecules : Notes and Study Materials -pdf
- Concepts of Biomolecules
- Biomolecules Master File
- Biomolecules Revision Notes
- Biomolecules NCERT Book
- NCERT Solution Biomolecules
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Biomolecules
- Biomolecules : Solved Example 1
- Biomolecules: Solved Example 2
Biomolecules Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 9
Topics and Subtopics in for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules :
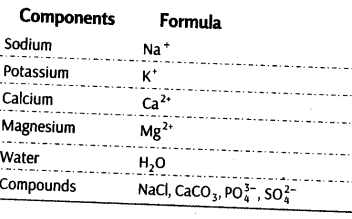
A cell is composed of variety of molecules (like carbon, hydrogen, oxygen) which perform various functions. Other than these basic elements, some metals and non-metals are also present as cellular materials, thence, all these materials combines in different ways in order to form various biomolecules, which are found in cells of organisms. These molecules are not living, but perform various living functions. Thus, biomolecules are the organic substances (e.g., Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, etc.) that play a major role in the structure and function of the living organism. Water is also an important and most abundant chemical compound present in the body of living organism.
Topic 1 Analysis of Basic
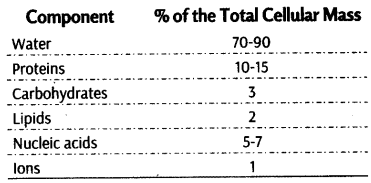
Topic 2 Biomacromolecules
CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter-9 Important Questions
1 Marks Questions
1. Which is the important energy carrier in the cell?
Ans. Adenosine tri phosphate (ATP)
2. Name the monomer subunits which form Nucleic acids?
Ans . Nucleotide.
3. What are macromolecules? Give example.
Ans. Macromolecules are large complex molecules formed by polymerization of micromolecules & have high molecular weight.
4. Identify the polymer which makes exoskeleton of insects.
Ans. Chitin a polymer of glucosamine that forms exoskeleton of insects,
5.Name the following:- i) sugar present is DNA ii) Base not found in DNA
Ans.( i) Deoxyribose sugar (ii) Uracil
6. Why proteins are called biological polymer?
Ans. As proteins are able to perform multiple functions eg. Protection mechanical support, transportation, movement etc, they are called as biological polymers.
7. Which molecule has the capacity to duplicate?
Ans. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
8.Name the abundant proteins in biosphere?
Ans. RUBISCO
9.Lipids are not biomacromolecules why?
Ans. Lipids are not biomacromolecule because their molecular weight does not exceed 800.
10.Which lipid can cause heart ailment?
Ans. Cholesterol.
11. What are micro- nutrients?
Ans. Minerals required by plants in trace quantity eg. Mn, Co, Zn, B, etc. are called micronutrients.
12.Why do oils generally remain in liquid state even in winters?
Ans. Oils are unsaturated lipids, hence have lower melting points.
13. Name an element found in proteins but not in lipids and carbohydrates.
Ans. Nitrogen.
14. What is the difference between RNA and DNA in terms of nitrogenous base?
Ans. RNA has uracil instead of thymine.
15. What does an enzyme do in terms of energy requirement of a reaction?
Ans. Lowers the activation energy of reaction.
16. What is the function of ATP in cell metabolism?
Ans. Are the energy currency of cell.
17. Name the protein which form the intercellular ground substance.
Ans. Collagen.
2 Marks Questions
1.Differentiate between nucleotide & nucleoside?
2.How are glycosidic bonds formed?
Ans. The glycosidic or ketone group of a monosaccharide can react & bind with an alcoholic group of another organic compound to join the two compounds together. This bond is known as glycosidic bond.
3.What do you mean by steady state?
Ans. An open system always remains in steady state i.e. the rate of in put of energy & matter is always equal to the output of energy & matter.
4.What is metabolism? Mention the role of enzymes is metabolism ?
Ans. Metabolism is defined as the sum total of the living processes in the body. Enzymes direct metabolic pathways. Enzymes act as catalysts. Enzymes are highly specialized organic catalysts produced by living cell. Biochemical pathways refer to the reactions occurring in the cells in sequences. Enzymes guide the biochemical pathways along desired directions. They have active site. The substrate binds at active site of enzyme & form enzyme substrate complex.
5.Why are enzymes called as biocatalyst?
Ans. The substances which changes the rate of chemical reaction without altering the equilibrium point of reaction is called catalyst. The catalysts of the organism are called enzymes & they are synthesized in the living cell. Hence called as Biocatalysts.
6.Give the functions of carbohydrates?
(i) Carbohydrates play role in all metabolic reactions of body & formed as intermediate compounds in pathways of the processes.
(ii) Ribose & deoxyribose sugar are found in nucleic acids.
(iii) Glucose is oxidised in respiration to yield energy.
(iv) Glucose is used in synthesis of fats as well as proteins.
7.What do you meant by activation energy?
Ans. Activation energy is the energy required to initiate a chemical or biochemical reaction. Activation energy overcomes the energy barriers of the reactants which occurs amongst the reactants due to i) presence of electrons over their surface ii) Absence of precise & forceful collisions essential for bringing the reactive sites of the chemical together.
8.List the different types of lipids .
Ans. Lipids are of three types:-
(i) Simple lipids:- they are of alcohols or triglycerides containing fatty acid & glycerol.
(ii) Compound lipids:- They are simple lipids with a biologically active compound in them eg. glycolipids ( carbohydrate lipid) lipoprotein ( protein + lipids)
(iii) Derived lipids:- They are hydrolysed products of simple lipids such as fatty acids & alcohol.
9.Enlist three properties of enzymes?
Ans. (i) An enzyme is specific for a substrate & catalyses only a particular reaction. because of the specific shape of active site & substrate.
(ii) Every enzyme requires an optimum temperature for its functioning.
(iii) The enzymes are sensitive to PH & each enzyme shows its maximum activity at a specific PH called optimum PH.
10.Enumerate differences between DNA & RNA?
11.Why are monosaccharide’s sugars are are known as reducing sugars?
Ans. Monosaccharides sugars are called reducing sugars because they have a free aldehyde or ketone group & can reduce Cu 2+ to Cu + . Disaccharides like sucrose does not reduce Cu 2+ to Cu+ so, it not a reducing sugar.
12.How does temperature affects enzyme catalysed reaction?
Ans. The temperature affects the velocity of enzyme action. When the temperature is high, there is a sudden decrease in enzyme action due to denaturation. Mostly enzymatic reactions occur below 45 0 c
13.What is enzymatic competitive inhibition? Give one example?
Ans. Some chemicals prevent the enzyme to function, are known as inhibitors. Enzymatic competitive inhibition is done by the substrate which very closely resembles the substrate in its molecular structure.

Eg. malonate inhibits the action of succinate dehydrogenase because it shows close resemblance with succinate substrate.
14. Why are aminoacids also known as substituted methane?
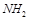
15. Amino acid exist as zwitter ions. Givc its structure. Why is it formed?
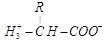
16. Why do starch give blue black colour with iodine?
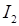
17. Why are starch and glycogen more suitable than glucose as a storage product?
Ans. Occupy lesser space as less bulky and can hydrolysed to glucose when required.
18. What would happed when salivary amylase which acts on starch in mouth and in stomach?
Ans. In mouth, salivary amylase changes starch into maltose. Action of amylase stops in stomach as it cannot act in an acidic medium.
19. Differentiate between homopolysaccharides and heterosaccharides.
20.Why do physicians recommend vegetable oils rich in poly unsaturated fat for persons suffering from cardiovascular diseases?
Ans. Polyunsaturated oils contain fatty acids having one or more double bonds which does not clog arteries due to high proportion of polyunsaturated fatty acids
21. Why does the shelf life of fruits and vegetables increase in a refrigerator?
Ans. Low temperature prevents growth of food spoiling micro organisms and also inhibits the action of enzymes are in the food, because enzymesam inactivated at low temperature.
3 Marks Questions
1.Enumerate the functions of lipids?
Ans . i) Most of the plants & animals fats constitute storage compound. Fat is stored mainly in adipose cells in the animals.
ii) In oil seed plants, oil provides nourishment to developing embryo during seed germination. Oil extracted from these seeds is used in cooking.
iii) Fats provide energy to the body.
iv) Fats serve as insulators & protect body from cold. It gets deposited underneath skin.
v) Phospholipid form an structural component of all bio- membranes in cell.
vi) Cholesterol acts as precursor for synthesis of various hormones, vitamins & bile salts.
vii) The lipid form the white matter, grey matter of brain & myelin sheath of neurons.
2.Describe the lock & key hypothesis of enzyme action?
Ans . According to Fischer’s lock & key hypothesis of enzyme action:- if the right key fits in the right lock, the lock can be opened otherwise not. To explain the above in context with enzyme action it is bedewed that molecules have specific geometric shapes. Proteins are able to act as enzyme because their shape provides space configuration into which other molecules can fit. The molecules which are acted upon by the enzymes are called substrates of the enzymes.
Under the above assumption only those substrate molecule with proper geometric shape can fit into the active site of the enzymes. However, under special circumstances some other molecules which are similar to the substrate can also combine with active site of enzyme. In such cases molecules may compete with substrate & the reaction may either slow down or stop. This is called competitive inhibition.
3.Describe the structure & function of ATP?
Ans. ATP is primary & universal carrier of chemical energy in the cell living cell capture store & transport energy in a chemical form, largely ATP & it is the ATP which is the carrier & intermediate source of chemical energy to those reactions in the cell which do not occur simultaneously. These reactions can take place only if chemical energy is released.
The ATP molecule consists of a nitrogenous base adenine a pentose sugar of ribose type & three inorganic phosphate molecules two phosphate bonds are high energy bonds & one is relatively poor in energy.
Energy released in living cell is thus stored in the chemical bonds of the ATP molecule which then serve as major energy yielding & energy requiring substance in the cell. ATP is broken down into ADP whenever energy is needed.
ATP –> ADP + ip + energy.
4.Differentiate between cofactors, coenzymes & prosthetic group.
5.How does enzymes brings about high rate of chemical conversions?
Ans. A chemical that is converted into a product is known as the substrate. Therefore the enzymes with tertiary structures including an active site convert a substrate into a product. The substrate ‘S’ must bind enzymes at its active site within a given cleft. So an obligatory formation of an ES substrate complex occurs. At a state when the substrate is bound to an enzyme active site, a new structure of substrate is formed.
In the graph, if ‘P’ is at lower level than ‘S’ reaction is exothermic i-e energy is supplied to make product ‘P’. The ‘S’ has to go through much higher energy state known as “transition state. The enzymes brings down energy barrier making transition of ‘S’ to ‘P’ more easy. The difference in average energy content between that of ‘S’ & this transition state is termed as activation energy.
6.What are nucleic acids? Describe the structure of DNA.
Ans. Nucleic acids are found in acid soluble fraction of living tissue. They are linear polymers of deoxyribonucleotides or ribonucleotides A nucleotide has 3 distinct components.
DNA is a double stranded structure & each strand is a polymer of deoxyribonucleotide. The backbone of the nucleic acid is uniformly consisting of alternating pentose sugar & phosphate group
i) The steps composed of nitrogenous bases adenine guanine cytosine & thymine & hydrogen bonds hold two strands together.
ii) Two strands are complementary to each other.
iii) They run in an antiparallel manner.
iv) It is genetic material in all organisms.
v) It has the property to replicate
vi) At one end of strand, 5-c of pentose sugar is free on other end; third carbon of pentose is free.
7. (a) What is anzyme?
(b) Give an example of co-enzyme.
(c) Distinguish between apoenzyme and co-enzyme.
Ans. (a) Are biocatalysts.
(b) NADP, NAD
(c) The enzymes which work only in the presence of co-factors am known as apoenzymes.
An organic non-protein cofactor which is easily separable from the apoenzyme is called co- enzyme.
5 Marks Questions
1. Explain briefly four levels of protein structure?
Ans. FOUR LEVELS OF PROTEIN STRUCTURE:-
a) PRIMARY STRUCTURE:- The protein exists as a long chain of amino acids arranged in a particular sequence such a polypeptide is non- functional
b) SECONDARY STRUCTURE:-first amino acid is N-terminal amino acid & last is known as c-terminal amino acid. There is interaction between every fourth amino acid by formation of hydrogen bond the polypeptide is folded in a helical shape eg. keratin. When two or more polypeptide chains are held together by intermolecular hydrogen bonds the structure is known as pleated sheet.
c) TERTIARY STRUCTURE:- The polypeptide becomes stabilized by folding & coating by the formation of ionic bonds or hydrophobic bonds or disulfide bridges. It is called tertiary structure. It gives a three dimensional view of proteins. Biological activity of protein depends on its tertiary structure.
d) QUATERNARY STRUCTURE:- Such proteins are farmed of more than one polypeptide or subunits each one having primary secondary & tertiary structure. This is called quaternary structure. Each polypeptide chain functions as subunit of the proteins.
NCRT TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS SOLVED
1. What are macromolecules? Give examples. Solution: Macromolecules are large high molecular weight substances with complex molecular structure and occur in colloidal state (being insoluble) in intracellular fluid. These are formed by polymerization of large number of micromolecules. Polysaccharides, proteins and nucleic acids are few examples.
3. What is meant by tertiary structure of proteins? Solution: The helical polypeptide molecule may fold on itself and assume a complex but specific form-spherical, rod-like or any form in between these. These geometrical shapes,are known as tertiary (3°) structure of protein molecules. The coils and folds of the polypeptide molecules are so arranged as to hide the non-polar amino acid chains inside and to expose the polar side chains. The tertiary structure of a protein brings distant amino acid side chains nearer to form active sites of enzymatic proteins. The tertiary structure is maintained by weak bonds such as hydrogen, ionic, disulphide and hydrophilic – hydrophobic bonds, formed between one part of a polypeptide and another. This structure is easily disrupted by pH, temperature and chemicals stopping the function of proteins.
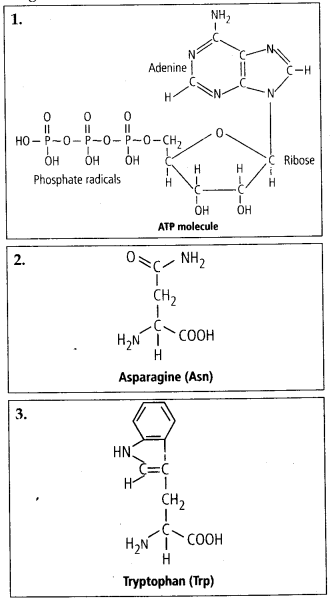
5. Proteins have primary structure. If you are given a method to know which amino acid is at either of two termini (ends) of a protein, can you connect this information to purity or homogeneity of a protein? Solution: There are several methods provided by several scientists to find out the sequence of amino acids. Frederick Sanger proposed Sanger’s reagent to know the amino acid sequence in a polypeptide chain. Sanger used 1-fluoro 2, 4 dinitrobenzene (FD NB) to determine insulin structure. FDNB specifically binds with N-terminal amino acid to form a dinitrophenyl (DNP) derivative of peptide. This DNP- derivative peptide can be identified by chromatography. The identified sequence of amino acids shows the homogeneity of a protein molecule.
6. Find out and make a list of proteins used as therapeutic agents. Find other applications of proteins. Solution: Proteins used as therapeutic agents are: thrombin, fibrinogen, enkephalins, antigens, antibodies, streptokinase, protein tyrosine kinase, diastase, renin, insulin, oxytocin, vasopressin etc. Proteins are also used in cosmetics, dairy industries, textile industries, research techniques, biological buffers etc.
8. Can you describe what happens when milk is converted into curd or yoghurt, from your understanding of proteins. Solution: Milk is converted into curd or yoghurt due to denaturation of proteins. In denaturation, disruption of bonds that maintains secondary and tertiary structure leads to the conversion of globular proteins into fibrous proteins. This involves a change in physical, chemical and biological properties of protein molecules.
9. Can you attempt building models of biomolecules using commercially available atomic models (Ball and stick models). Solution: Yes, models of biomolecules can be prepared using commercially available atomic models. Ball and stick models and space filling models are 3D or spatial molecular models which serve to display the structure of chemical products and substances or biomolecules. With ball and stick models, the centers of the atoms are connected by straight lines which represent the covalent bonds. Double and triple bonds are often represented by springs which form curved connections between the balls. The bond angles and bond lengths reflect the actual relationships, while the space occupied by the atoms is either not represented at all or only denoted essentially by the relative sizes of the spheres.
10. Attempt titrating an amino acid against a weak base and discover the number of dissociating (ionizable) functional groups in the amino acid. Solution: The existence of different ionic forms of amino acids can be easily understood by the titration curves. The number of dissociating functional group is one in case of neutral and basic amino acids and two in case of acidic amino acids.
12. What are gums made of ? Is fevicol different ? Solution: Gums are hetero-polysaccharides (poly-mers) of large number of different monosac-charide units. Yes, fevicol is a different kind of polymer. It is a synthetic sticky substance called resin which is manufactured by esteri-fication of organic compounds.
14. Find out how much cellulose is made by all the plants in the biosphere. Solution: About 100 billion tonnes of cellulose is prepared per year by the plants of the world.
15. Describe the important properties of enzymes. Solution: The important properties of enzymes are as follows: (i) The enzymes are generally proteins which are high molecular weight complex globular proteins. They can associate with non-protein substance for their activity. (ii) The enzymes do not start a chemical reaction but only accelerate it. They combine temporarily with the substrate molecules and are not consumed or changed permanently in the reaction which they catalyse. (iii) The enzyme controlled reactions are reversible. (iv) The enzymes are specific in action. An enzyme catalyses only a particular kind of reaction or acts on a particular substrate only. (v) The enzymes are thermolabile i.e., heat sensitive and can function best at an optimum temperature. Similarly, enzymes show maximum activity at optimum pH. (vi) The enzymes are inactivated by poisons and radiation.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 - Biomolecules
- NCERT Solutions

Are you searching for NCERT Solutions of Biology Class 11 Biomolecules? Here, you will find NCERT Solutions of Biomolecules Class 11 which explains the broad range of diversity of living organisms and their chemical compounds.
Note: ➤ Don't Miss Out: Get Your Free NEET Rank Predictor Instantly!
NCERT solutions of Biology Class 11 Biomolecules is a crucial study material for students who aspire to attain excellent marks in their class. Below you will find the Biomolecules Class 11 NCERT Solutions PDF which is absolutely free of cost. Download Now!
Biomolecules Chapter at a Glance - Class 11 NCERT Solutions
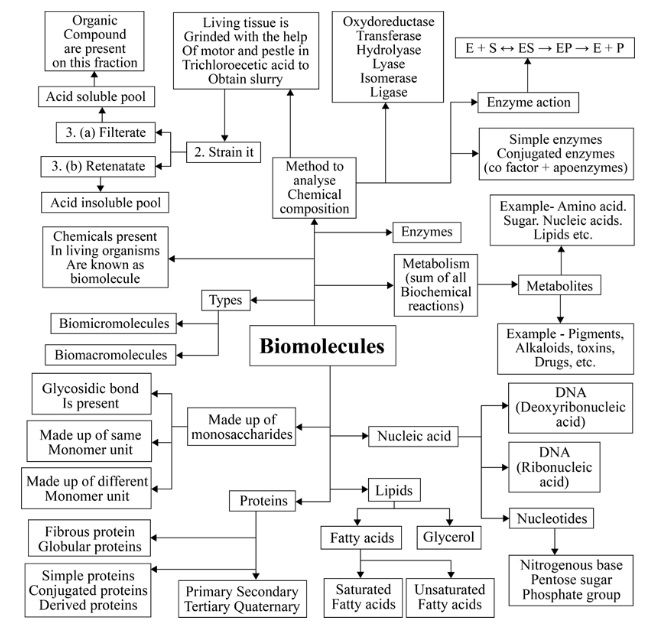
Biomolecules
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology
1. What are macromolecules? Give examples?
Ans: Chemical compounds, which are found in the acid-insoluble fraction are called macromolecules or biomacromolecules. As suggestive of its name, its molecular weights lie above \[1000\] Dalton. Consequently, micro molecules have molecular weights of less than \[1000\] Daltons.
Examples of macromolecules are—proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates, etc. Except for lipids, all the other macromolecules including carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids are polymeric substances.
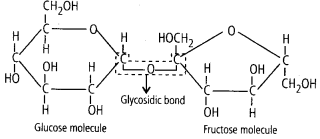
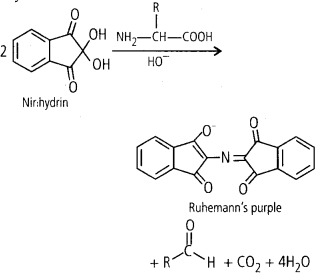
2. Illustrate a peptide, glycosidic, and phosphodiester bond.
Ans: The illustration of peptide, glycosidic and phosphodiester bonds are given below.
Peptide Bond: Amino acids in a protein are linked by Peptide bonds. Correspondingly, the proteins are called a polypeptide. Peptide bonds are formed when the carboxyl group of one amino-acid reacts with the amino group of the next amino acid with the elimination of a water molecule. As water molecule is eliminated so the reaction is that of dehydration.
(Image Will Be Updated Soon)
Figure: Peptide bond
Glycosidic Bond: Glycosidic bonds are bonds linking the individual sugar units (monosaccharides) in a disaccharide or a polysaccharide. When two sugar units join, they join with the help of a glycosidic linkage with the release of a water molecule.
Figure: Glycosidic bond
Phosphodiester Bond: Phosphodiester bonds link individual nucleotides in a nucleic acid. So, we say DNA (a nucleic acid) is a polynucleotide. A phosphodiester linkage is formed due to the linking of carbon of one sugar of a nucleotide with the carbon of the sugar of an adjacent nucleotide by a phosphate moiety. The bond among the phosphate and hydroxyl groups of sugar is an ester bond. It is a phosphodiester bond as there is one such ester bond on either side.
3. Write a short note about the tertiary structure of proteins?
Ans: Tertiary structure specifies the spatial layout of amino acids that are far apart in the linear structure as well as those remains that are adjacent. The arrangement of amino acids specifies the ultimate \[3\] -D structure of any specific protein. The polypeptide chain folds spontaneously so that the majority of its hydrophobic side chains are buried in the interior, and the majority of its polar charged chains are on the surface. The tertiary structure of a protein is stabilized by hydrophobic interactions, electrostatic forces (salt bridges), and disulfide links.
4. Find and write down structures of ten fascinating small molecular weight biomolecules. Find there is any industry that produces the compounds by isolation. Find out who are the buyers.
Ans: The structures of ten different small molecular weight biomolecules are given below.
Cholesterol:
Deoxyribose:
Tryptophan:
Many industries manufacture compounds by the process of isolation. Some examples are given below.
5. Proteins have a primary structure. If you are provided with a method to know which amino acid is at either of the two termini (ends) of a protein, can you link this information to the homogeneity or purity of a protein?
Ans: The series of amino acids, i.e., the positional information in a protein which is the first amino acid, which is second, and so on is known as the primary structure of a protein. The initial amino acid is also known as an N-terminal amino acid. The final amino acid is known as the C-terminal amino acid.
Yes, we can relate this information to the homogeneity or purity of a protein. Based on the number of amino groups and carboxyl groups, there are acidic (e.g., glutamic acid), basic (lysine), and neutral (valine) amino acids, proteins may be acidic, basic, and neutral.
6. Find out and create a list of proteins utilized as therapeutic agents. List additional uses of proteins (e.g., cosmetics, etc.)
Ans: A list of proteins used as therapeutic agents are given below.
Both plants and animals give the appropriate proteinaceous materials for the preparation of cosmetic items. Proteins from algae and fungi, though, are also increasingly being utilized as protein sources.
High-protein plants most widely used as beginning material for making vegetable proteins are wheat and corn gluten, rice, soy, and oat protein concentrates, and defatted oilseeds (almond, peanuts, sunflower). Among the larger variety of vegetable proteins, soy globulins and wheat gluten are by far of the widest use. Wheat gluten (often just known as wheat protein) is a distinctive cereal protein of high elasticity when hydrated. Soy proteins are useful because of their thickening and emulsifying effects.
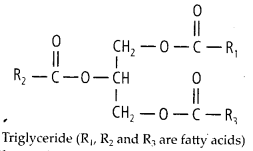
7. Explain the composition of triglyceride.
Ans: Triglycerides are a type of lipids found in living beings, that are synthesised due to the esterification of three fatty acids with a glycerol molecule. These are also called fats and oils based on their melting points.
Oils have lower melting points as compared to fats. The three fatty acids may be different or the same. Therefore, they may be known as simple or mixed.
8. Can you explain what occurs when the milk is converted into yoghurt or curd, from your perception of proteins.
Ans: Milk contains a protein called casein. This protein provides milk with its characteristic white colour. It is of high nutritional value because it contains all the essential amino acids required by the man's body. The curd formation takes place as lactic acid bacteria chemically react to the casein of milk. Lactic acid bacteria present in the curd that is used as the culture, cause coagulation of milk casein and thus, convert it into curd.
9. Can you try the structure of biomolecules utilizing commercially available atomic models (Ball and stick models).
Ans: Yes, we can create models of biomolecules using commercially available atomic models.
10. Attempt titrating an amino acid against a weak base and discover the number of dissociating (ionisable) functional groups in the amino acid.
Ans: Once an amino acid is titrated against a weak base. It dissociates and provides two functional groups: (i) \[{\text{ - COOH}}\] group (carboxylic group) (ii) Amino group ( \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\] ).
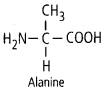
11. Draw the structure of the amino acid alanine.
Ans: The structure of alanine is given below.
12. What are gums made of? Is fevicol different?
Ans: Gums are made up of carbohydrates and chemically they are heteropolysaccharides.
Fevicol is polyvinyl alcohol glue. It is different from natural gums as it is a synthetic product.
13. Find out a qualitative test for proteins, fats and oils, and starch amino acids and test any fruit juice, saliva, sweat, and urine for them.
i. A qualitative test for proteins: Xanthoproteic test
ii. A qualitative test for fats: Emulsification test
iii. A qualitative test for oils: Paper test
iv. A qualitative test for starch : Iodine test
14. Find out exactly how much cellulose is produced by the plants in the biosphere and then compare it to how much paper is produced by human beings and therefore, what is the use of plant material by man each year. What a loss of vegetation?
Ans: Most paper is formed from wood pulp. The major component of wood pulp is cellulose, a polymer made of several glucose molecules linked together. The cellulose molecules and their bonding to each other give the paper its properties. Nearly \[33\% \] of everything in the plant matter is cellulose. The cellulose content of wood is \[40 - 50\% \] and that of cotton is \[90\% \] . For industrial use, cellulose is mostly obtained from cotton and wood pulp. It is used primarily to produce paper and paperboard; to a smaller extent. It is converted into a large variety of derivative products like rayon and cellophane.
15. Describe the important properties of enzymes.
Ans: Enzymes are proteins that catalyse biochemical reactions in cells. So, usually, enzymes are proteins but sometimes RNA also behaves catalytically. Catalytic RNAs are called Ribozymes. Each enzyme works best at its optimum temperature. Subsequently, enzymes are proteins, they are denatured at high temperatures.
Enzymes Work Most Excellent At Their Optimal pH
Graph That Displays The Effect of pH On Enzyme Activity
i. With the rise in substrate concentration, the velocity of the enzymatic reaction increases at first. The reaction ultimately achieves a maximum velocity (v max) which is not exceeded by any additional increase in the concentration of the substrate.
ii. The activity of an enzyme is also sensitive to the presence of particular chemicals (maybe modulators or inhibitors of enzyme action) that bind to the enzyme.
iii. Enzymes are substrate-specific. Due to the three-dimensional folding of the enzyme, it forms pockets or crevices. One such pocket is called the active site. An active site of the enzyme is a crevice or a pocket at which the substrate binds.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 ‘Biomolecules’ - Benefits of Class 11 Ch 9 NCERT Solutions
Class 11 Ch 9 CBSE NCERT Solutions is easy to comprehend so students can attain higher percentages in their final exams. Students can gain the following benefits after going through the NCERT Solution of Biomolecules Class 11.
Specialised subject teachers have formulated the Biomolecules Class 11 questions and answers for students to fetch excellent marks in their exams.
Teachers of a high calibre have described the NCERT solutions in Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 with illustrations for easy understanding.
The NCERT Solution of Biomolecules Class 11 aims to save students valuable time so that they can reap the maximum benefit in less time.
Biology Class 11 NCERT solutions Chapter 9 covers the entire chapter with accuracy.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 ‘Biomolecules’ - Topics Covered in Chapter 9 Biomolecules
Following are the topics covered in the chapter.
Analysis of chemical compounds
Primary and secondary metabolites
Biomacromolecules
Proteins
Structure of Proteins
Polysaccharides
Nucleic Acids
Concept of Metabolism
Metabolic pathways
Class 11 Biology Biomolecules NCERT Solutions - Contents of the Pdf
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter Biomolecules entails solutions to the questions given at the end of the chapter. Students can learn the Class 11 Biomolecules questions and answers from the Biology Biomolecules NCERT Solutions pdf offered by Vedantu on this page. NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules pdf includes questions from the following topics.
Ex 9.1 - How to Analyse Chemical Composition?
Ex 9.2 - Primary and Secondary Metabolites
Ex 9.3 - Biomacromolecules
Ex 9. 4 - Proteins
Ex 9.5 - Polysaccharides
Ex 9.6 - Nucleic Acids
Ex 9.7 - Structure of Protein
Ex 9.8 - Nature of Bond Linking Monomers in a Polymer
Ex 9.9 - Dynamic State of Body Constituents - Concept of Metabolism
Ex 9.10 - Metabolic Basis of Living
Ex 9.11 - The Living State
Ex 9.12 - Enzymes
Class 11 Biology Biomolecules NCERT Solutions - Summary in Points
The Biomolecules chapter is summarised in the following pointers which are as follows:
Biomolecules are chemical substances created by living organisms that range in size from small molecules like metabolites to huge molecules like protein and carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four classifications of macromolecules.
Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, or compounds that yield these when they are hydrolyzed.
Proteins are defined as complex polypeptides which constitute monomeric amino acids. The amino acids are arranged in a specific order.
Based on the structure of the amino acid polypeptide arrangement, the proteins are classified as primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary.
Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) are the genetic content. The nucleic acids are responsible for passing down the hereditary information from one filial generation to another.
Nucleic acids are classified into two classes: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
Transcription and translation are the two key processes that are accomplished by the nucleic acids.
Transcription is defined as the process of formation of m RNA using the genetic code.
The translation is defined as the process of protein formation from the transcribed mRNA.
Lipids are organic compounds that are soluble in organic solvents but insoluble in water, are connected to fatty acids, and are used by living cells.
Fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, mono-, di-, or triglycerides, and phospholipids are examples of lipids.
NCERT Biology Class 11 Biomolecules - Important Questions and Answers (Solved)
1. What do you mean by Hydrolysis?
Ans. While carbohydrates are digested the glycosidic bond between sugar residue is broken with the presence of water and this is termed ‘Hydrolysis’.
2. Name one monosaccharide sugar that is found in the blood plasma of human beings.
Ans. Glucose.
3. How does calcium help our body?
Ans. Calcium helps in making our bones and teeth strong.
NCERT Biology Class 11 Biomolecules Weightage Marks
Students would need to attempt 70 marks in of theory and 30 marks in of practical in the examination. The latest marking scheme suggests that Biology Class 11 Chapter 9, which is a part of Unit III, will carry 12 marks for theory and four marks for practical questions excluding Practical Record and Viva Voce. The students would need to perform one minor experiment under Part A.
Preparation Tips - How Do I Study Biology in CBSE Class 11?
Below are some tips which can be referred to and studied in Biology in CBSE Class 11:
Study the concepts thoroughly and understand the chapters well.
Practice the theories with the diagrams.
Solve NCERT-based questions and answers.
Also, study the previous year’s questions and answers to know the types of questions which might come in the question paper.
NCERT Class 11 Biology Chapter wise Solutions - Free PDF Download
Chapter 1 - The Living World
Chapter 2 - Biological Classification
Chapter 3 - Plant Kingdom
Chapter 4 - Animal Kingdom
Chapter 5 - Morphology of Flowering Plants
Chapter 6 - Anatomy of Flowering Plants
Chapter 7 - Structural Organisation in Animals
Chapter 8 - Cell The Unit of Life
Chapter 9 - Biomolecules
Chapter 10 - Cell Cycle and Cell Division
Chapter 11 - Transport in Plants
Chapter 12 - Mineral Nutrition
Chapter 13 - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
Chapter 14 - Respiration in Plants
Chapter 15 - Plant Growth and Development
Chapter 16 - Digestion and Absorption
Chapter 17 - Breathing and Exchange of Gases
Chapter 18 - Body Fluids and Circulation
Chapter 19 - Excretory Products and their Elimination
Chapter 20 - Locomotion and Movement
Chapter 21 - Neural Control and Coordination
Chapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and integration
Conclusion
Hope this study material was a great help for the students of Class 11 who are studying Biology. NCERT questions and answers must be studied properly by the students so that they can score good marks in their exams.
Download the free pdf and take note of the important chapter coverage covered in this chapter.

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 - Biomolecules
1. Explain Macromolecules with an Example.
Macromolecules or biomacromolecules are polymerised biomolecules that constitute an array of macromolecules having a high degree of molecular weight. Such formation of significantly large biomolecules is macromolecules. Their molecular weight roughly lies between 18 to 800 daltons (Da). Though macromolecules are comparatively larger than other molecules, you cannot see it with a naked eye. You can find these complex macromolecules in a colloidal state present in the intercellular fluid and are polymeric. Broad macromolecules examples are protein, nucleic acids, polysaccharides, etc. Other macromolecules examples are DNA, RNA, Nylon, Polyester, Keratin in hair, waxes,oil, steroids, grease, hormones, etc.
2. Can you use Protein as a Therapeutic Agent? What are the Other Applications of Protein? List Them.
Yes, protein can be used as therapeutic agents. Scientists have formulated proteins in the laboratory for several pharmaceutical requirements. Such proteins are termed therapeutic proteins, including:
Streptokinase
Vasopressin
Antibody-based drugs
Fc fusion proteins,
Bone morphogenetic proteins,
Engineered protein scaffolds.
Therapeutic proteins with carbohydrate profile affect solubility, cellular interactions, tertiary structural stability, immunogenicity, and pharmacokinetics. Thus, they are considered significant in several serious ailments, such as cancer treatment, HIV, etc. Furthermore, proteins are a useful element in cosmetics, textile industries, textile industries, biological buffers, and research techniques. Therapeutic proteins have transformed the healthcare sector.
3. What are the benefits of NCERT solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules?
There are many benefits of NCERT solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules, which is available on Vedantu for free. The content is given chapter-wise and in an easy-to-understand language. In Chapter 9 Biomolecules, all the topics and questions/answers are given in one place as it is convenient for the students to study. Explanations are given in a detailed as well as a precise manner and written by Biology experts.
4. What are the important topics of NCERT solutions for Class 11 biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules?
For the preparation of class tests and annual exams, Vedantu helps the students to get easy and free access to NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology chapter-wise. The solutions are also available on the Vedantu Mobile app. Some of the important topics that are covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology from Chapter 9 are listed below:
1. Enzymes- Types
2. How is chemical composition analysed
3. Theory of metabolism
4. Primary and Secondary Metabolites
5. Proteins arrangement
6. Nucleic acids.
5. Throw some light on Micro Molecules.
The word ‘micro’ means small. In simple terms, molecules that are mini or small in size are called micro molecules. They are also called ‘monomers,’ which are combined to form ‘polymers’ or large molecules. They have a low molecular weight in comparison to macromolecules. Through metabolic processes, micro molecules are formed.
6. List out the main physical properties of Amino Acids.
The main physical properties of amino acids are given below :
They don’t contain any colour. Hence they are colourless
They are decomposed when they are heated to higher temperatures
They have a high melting point, which is more than 200 degrees celsius,
Their existence is usually in d, and I form
Apart from glycerine, which is perceptibly inactive, all the amino acids are perceptibly active.
7. What is the weightage of marks from Chapter 9 Biomolecules?
The weightage of marks from Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules vary across topics. Questions come in short as well as long types. However, they don't fetch you a lot of marks. Most of the questions are from the NCERT course book only. However, it can be useful. Hence, complete preparation is advised.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Class 11
- NCERT 11 Biology
- Chapter 9: Biomolecules
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 - Biomolecules
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules are important concepts in understanding the chemical composition of matter found in living entities. This chapter is categorised under the latest CBSE Syllabus 2023-24. Students who look forward to making a career in the medical field must know the fundamentals. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 include solved solutions for all the questions appearing in the textbook, answered in the same order for the convenience of students.
Students might be tense before their examinations. But with a deep understanding of concepts, thorough revision and practice, students are assured of performing exceedingly well. Class 11 can be a crucial year, as a substantial number of questions appear in the competitive exams; therefore, analysing and understanding concepts is inevitable. NCERT Solutions steps in right here, sufficing all the academic needs of students.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 – Biomolecules
carouselExampleControls111

Previous Next
Access Answers to NCERT Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 – Biomolecules
1. What are macromolecules? Give examples.
Macromolecules are the biomolecules that are formed by the polymerisation of a huge number of micromolecules possessing higher molecular weight. Micromolecules are found in the colloidal state in the intercellular fluid due to their insoluble nature. Protein is a macromolecule.
2. Illustrate a glycosidic peptide and a phospho-diester bond.
Glycosidic bond – The bond between the individual monosaccharides is called a glycosidic linkage. This bond is formed between two carbon atoms of two adjacent monosaccharide units.

Peptide bond – It is a covalent bond. The amino acids in proteins are linked to one another through peptide bonds. It is formed when the carboxyl group (-COOH) of one amino acid interacts with the amino group (-NH2 ) of the adjacent amino acid when condensed.
Formation of Peptide bond – Example

Phospho-diester bond – That joins successive sugar molecules in a polynucleotide. It is a strong covalent bond formed between two adjacent sugar groups and phosphate. These are the bonds that form the sugar-phosphate backbone of the nucleic acids.

3. What is meant by the tertiary structure of proteins?
It is a structure that forms when the secondary coiled polypeptides are folded to produce a hollow, wollen ball-like structure. It is folded such that the functional side groups appear on the surface while the inactive side groups are found inside.

4. Find and write down structures of 10 interesting small molecular weight biomolecules. Find if there is any industry which manufactures the compounds by isolation. Find out who are the buyers.

5. Proteins have a primary structure. If you are given a method to know which amino acid is at either of the two termini (ends) of a protein, can you connect this information to the purity or homogeneity of a protein?
The positional information of a protein is called the primary structure of the protein. The first amino acid in a protein is called the N-terminal amino acid, and the last amino acid in a protein is called the C-terminal amino acid.
Yes, we can connect this information to check the purity or homogeneity of a protein. On the basis of carboxyl and amino groups, amino acids can be acidic, basic and neutral. Proteins can be acidic, basic and neutral.
6. Find out and make a list of proteins used as therapeutic agents. Find other applications of proteins (e.g., Cosmetics, etc.)
Following is the list of proteins used as therapeutic agents.
Insulin, Oxytocin, Immunoglobin, Antidiuretic Hormone( ADH), Thrombin, Fibrinogen, Renin and streptokinases.
Some other applications are
- They are used as artificial sweeteners. Thaumatin is a low-calorie sweetener.
- Proteins are used as dietary supplements to maintain health.
- They are used in creams and shampoos.
7. Explain the composition of triglyceride.
When glycerol combines with three fatty acids on each of the OH groups through ester bonds, it is known as a triglyceride.

All three fatty acids of triglyceride in pure fat are similar, while in mixed fat, they are dissimilar.
8. Can you describe what happens when milk is converted into curd or yoghurt, from your understanding of proteins
During fermentation, milk protein such as casein is denatured, which transforms globular proteins into fibrous proteins. This change is responsible for the production of curd or yoghurt.
9. Can you attempt building models of biomolecules using commercially available atomic models (Ball and Stick models)?
Yes, Biomolecules can be represented by the ball and stick model. Here, the bonds which hold the molecule are indicated by sticks, while the atoms are represented by balls. The figure below is a model of D-glucose, where atoms of hydrogen are indicated by green balls, oxygen atoms are represented by pink balls, and carbon atoms are represented by grey balls.

10. Attempt titrating an amino acid against a weak base and discover the number of dissociating (ionisable) functional groups in the amino acid.
The pH of the amino acid is recorded, and the weak base is slowly supplemented to the amino acids while continuously noting the pH. The number of changes recorded indicates the number of ionisable functional groups –COOH in the acidic range and –NH 2 in the alkaline range.
11. Draw the structure of the amino acid alanine.
The structure of Alanine is as follows:

12. What are gums made of? Is Fevicol different?
Gums are heteropolysaccharides formed by different monosaccharide units associated with glycosidic bonds. On the other hand, Fevicol is different from gums, as it is made up of synthetic polymers.
13. Find out a qualitative test for proteins, fats and oils, and amino acids and test any fruit juice, saliva, sweat and urine for them.
Qualitative test for proteins
Biuret test: Biuret test identifies the presence of proteins by turning the colour of the solution from light blue to purple.
Qualitative test for fats and oils
Grease test for oils: Certain oils give a translucent stain on blue paper. This test can be used to detect the presence of oils and fats.
Qualitative test for amino acids
Ninhydrin test
Upon adding ninhydrin reagent to the solution, the colour of the solution turns to pink, purple or blue based on the type of amino acid.
14. Find out how much cellulose is made by all the plants in the biosphere and compare it with how much of paper is manufactured by man and hence what is the consumption of plant material by man annually. What a loss of vegetation!
The biosphere produces about 100 billion tonnes of cellulose out of 170 billion tonnes of total organic matter. Production of paper consumes about 0.5 billion tonnes of wood. Trees are also utilised for other purposes, including food, medicines, timber, spices, etc. An approximate estimate of 1.5 billion tonnes of food is required. Wood requirement for various purposes includes 2 billion tonnes. Therefore, it is difficult to gauge the annual consumption of plant material by man. Thus, the use of cellulose led to a great loss of vegetation.
15. Describe the important properties of enzymes.
Almost all enzymes are proteins. Important properties of enzymes are as follows:
- They have a higher molecular weight and are complex macromolecules.
- They catalyse the biochemical reactions involved in the cell, assisting in breaking down larger molecules into simpler molecules or getting together two smaller molecules to form a larger one.
- Enzymes do not initiate but accelerate a reaction.
- They affect the rate of biochemical reaction and do not influence the direction of the reaction.
- They are action-specific.
- A higher turnover of enzymes causes an increase in the efficiency of a reaction. Most of the enzymes have a high turnover number.
- Enzymes are affected by temperature. As the temperature increases, enzymatic activity decreases. Maximum activity is observed at 30-40 degree Celsius.
- Maximum activity is observed at a 6-8 pH level.
- With an increase in substrate concentration, the enzymatic velocity also increases, reaching maximum velocity.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 – Biomolecules are categorised under Unit 3 – Cell: Structure and Functions of the latest CBSE Syllabus 2023-24. This particular unit totals up to 15 marks as per the previous years’ question papers which approximately adds up to 21% of the total weightage of the paper.
Students can revise from previous years’ question papers to get an idea of the typology of questions that can be expected from this chapter. Apart from learning concepts, knowing how to answer is the key to scoring optimum marks, and NCERT Solutions help students with it.
List of subtopics covered in Chapter 9 – Biomolecules
Biomolecules include some important topics which enable students to understand the chemical composition. To be able to analyse a living tissue sample and identify a specific organic compound in higher classes, a fundamental understanding of different types of tissues, anatomy, morphology, the common site at which they are found, different functionalities they carry out, etc., are equally required to comprehend concepts.
Students thus understand different chemical reactions and their conversions, the role of enzymes, the nature of different enzyme actions, various factors affecting the activity of enzymes, and the classification and nomenclature of different enzymes.
Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 – Biomolecules
- Solutions framed by subject-matter experts.
- Solutions are provided as per the expected answering pattern.
- NCERT Solutions are available for free download.
- Simple and easy to understand.
- Efficient and effective study tool.
Disclaimer –
Dropped Topics –
9.8 Nature of Bond Linking Monomers in a Polymer 9.9 Dynamic State of Body Constituents – Concept of Metabolism 9.10 Metabolic Basis for Living 9.11 The Living State Question nos 2, 3, 5, 8, 10
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9
List out the properties of enzymes covered in chapter 9 of ncert solutions for class 11 biology., what are the fundamental concepts i can learn from chapter 9 of ncert solutions for class 11 biology, why should students refer to the ncert solutions for class 11 biology chapter 9, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 11 Biology
Chapter 1: The Living World Chapter 2: Biological Classification Chapter 3: Plant Kingdom Chapter 4: Animal Kingdom Chapter 5: Morphology of Flowering Plants Chapter 6: Anatomy of Flowering Plants Chapter 7: Structural Organisation in Animals Chapter 8: The Unit of Life Chapter 9: Biomolecules Chapter 10: Cell Cycle and Cell Division Chapter 11: Transport in Plants Chapter 12: Mineral Nutrition Chapter 13: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Chapter 14: Respiration in Plants Chapter 15: Plant Growth and Development Chapter 16: Digestion and Absorption Chapter 17: Breathing and Exchange of Gases Chapter 18: Body Fluids and Circulation Chapter 19: Excretory Products and Their Elimination Chapter 20: Locomotion and Movement Chapter 21: Neural Control and Coordination Chapter 22: Chemical Coordination and Integration
Share this:
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs

NCERT Solutions for Class 11th: Ch 9 Biomolecules Biology

Contact Form
CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 – Biomolecules Class 11 Notes
Biomolecules class 11 cbse revision notes.
The chapter of Biomolecules in Class 11th Biology serves of great importance. Furthermore, it introduces students to molecules that are present in living organisms. Thus, this chapter will help you learn about a wide range of sizes and structures. Thus, through biomolecules class 11 notes you will be able to study in detail about these things. It will help students understanding the bodies of living beings in a clear and concise manner.
After that, they will learn about various terms like monomers, enzymes, metabolic basis, nucleic acids, polysaccharides, proteins and more. Furthermore, it will also explain how to analyze chemical compositions. It also discusses primary and secondary metabolites. Most importantly, the concept of metabolism will become very clear to you after this chapter. Thus, biomolecules class 11 notes are great for understanding these concepts.
Download Toppr app for Android and iOS or signup for free.
Sub-topics covered under Biomolecules
- Biomacromolecules – This section will teach students about the molecules which the cells produce in our body.
- Bond linking Monomers – Through this part, students will learn about the smaller units present in macromolecules known as monomers.
- Enzymes – You will learn about the proteins that living organisms produce create metabolic and chemical reactions in our body.
- Metabolic Basis For Living – It will discuss the way our bodies convert the food we eat into energy so as to produce power.
- Nucleic Acids – Students will learn about the biomolecules which are building blocks of an organism known as nucleic acid.
- Polysaccharides – The complex biomacromolecules made up of chains of monosaccharides known as polysaccharides.
- Proteins – The complex biomolecules made up of smaller units called amino acids termed as proteins are taught here.
You can download CBSE Class 11 Biomolecules Revision Notes by clicking on the download button below

Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

CBSE Class 11 Biology Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 22 – Chemical Coordination and Integration Class 11 Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 21 – Neural Control and Coordination Class 11 Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 20 – Locomotion and Movement Class 11 Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 19 – Excretory Products and their Elimination Class 11 Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 – Body Fluids and Circulation Class 11 Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 – Breathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 16 – Digestion and Absorption Class 11 Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 – Anatomy of Flowering Plants Class 11 Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 15 – Plant Growth and Development Class 11 Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 – Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Study Material
.webp)
Home > Class 11 Biology Important Questions
Chapter 9 Biomolecules Class 11 Biology Important Questions
Every year several questions are asked from this chapter in competitive and board examinations. In Biomolecules Important Questions PDF Class 11 , you will study about Lipids, Proteins, Polysaccharides, Enzymes, Regulation of enzymes, Metabolism, Nucleic acids, etc.
PREMIUM EDUCART QUESTIONS
<cta2> Download <cta2>
(Important Questions of this Chapter from our 📕)
In the table given below, we have provided the links to Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules Important Questions PDFs. You can download them without having to share any login info.
📈 Trending: 2024-25 CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
📝 Recommended: Important Questions PDFs for Class 11
📚 Don’t Miss: Class 11 2024-25 Question Banks
We hope that you practice the above Biomolecules Class 11 Important Questions and achieve your dream marks.
All the best!
Extra 10% Discount

CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
Ncert books for class 11, class 11 important questions.
Buy Latest Books
Teacher's Corner

To Download PDF
Please verify your Whatsapp number first, so you can download this pdf immediately
Please type a valid 10 digit whatsapp number

OTP sent, check your whatsapp
Your OTP is incorrect, Please enter valid OTP
- Mathematics (Standard)
- Mathematics (Basic)
- Social Science
- Computer Application
- Information Technology
- English Core
- Mathematics
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political Science
- Science (Hindi )
- Maths (Hindi)
- Social Science (Hindi )
- Applied Maths
- Physical Education
- English Language
- History & Civics
- 10 Year Solved Papers
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 English
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Math Standard
- Computer Applications
- Class 12 PCB Combo
- Class 12 PCM Combo
- Entrance Exam
- K-8 Raspberry Solutions
- K-8 Kiwi Solutions
NCERT Books and Solutions for all classes
Notes And Questions NCERT Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules
Please refer to Biomolecules Class 11 Biology Notes and important questions below. The Class 11 Biology Chapter wise notes have been prepared based on the latest syllabus issued for the current academic year by CBSE. Students should revise these notes and go through important Class 11 Biology examination questions given below to obtain better marks in exams
Biomolecules Class 11 Biology Notes and Questions
The below Class 11 Biomolecules notes have been designed by expert Biology teachers. These will help you a lot to understand all the important topics given in your NCERT Class 11 Biology textbook. Refer to Chapter 9 Biomolecules Notes below which have been designed as per the latest syllabus issued by CBSE and will be very useful for upcoming examinations to help clear your concepts and get better marks in examinations.
• Chemicals or molecules present in the living organism are known as biomolecules. Biomolecules are divided into two types- inorganic and organic. • Inorganic biomolecules includes minerals, gases and water and organic biomolecules includes carbohydrates, fats, proteins, nucleic acids, vitamins, etc. • Different biomolecules can be classified as aldehyde, ketones and aromatic compounds as chemical forms. The amino acids, nucleotides and fatty acids can be classified as biochemical forms.

• Except lipids, macromolecules are formed by polymerization of sub-units called monomers. • Proteins are polymers of amino acids. Amino acids are linked by peptide bond formed by dehydration between COOH group of one amino acids and NH3 group of next with the removal of H2O.
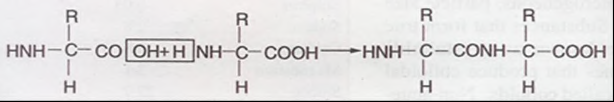
• In nucleic acids, the phosphate molecules links 3’ C of sugar of one nucleoside to the 5’ C of sugar of next nucleosides releasing two water molecules to form 3’-5’
phosphodiester bond. • In polysaccharides, the mono-saccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds formed by dehydration between two carbon atoms of two adjacent monosaccharides.
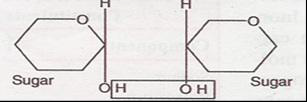
Carbohydrates (Polysaccharides) • Polysaccharides are long chain of sugar containing different monosaccharaides as a building block.
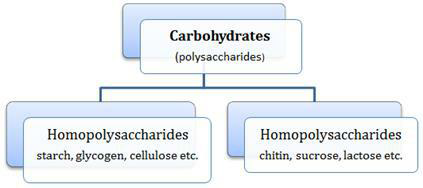
• Starch is present in plants as store house of energy. It forms helical secondary structure. It can hold the I2 molecules in the helical structure. • Cellulose molecules contain glucose molecules joined together by 1-4 β linkage. It is the most abundant organic molecules on earth. • Glycogen is called animal starch as it is the reserve food materials for animals, bacteria and fungi. In this, glucose molecules are arranged in highly branched bush like chain having two types of linkage 1-4 α in straight chain and 1-6 linkage in branching. Proteins are polypeptide chains made up of amino acids. There are 20 types of amino acids joined together by peptide bond between amino and carboxylic group. There are two kinds of amino acids-
1. Essential amino acids are obtained by living organism along with food. 2. Non-essential amino acids can be prepared by our body from raw materials.
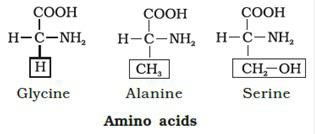
• The main functions of protein in living cell are 1. Transport of nutrient across the membrane. 2. Fight infectious organisms. 3. Produce enzyme and proteins.
• Collagen is the most abundant protein in animal world.

• Primary structure of protein is the basic structure of protein in which a number of polypeptides are involved having sequence of amino acids. The first amino acid of sequence is called N-terminal amino acid and last amino acid of peptide chain is called C-terminal amino acid.
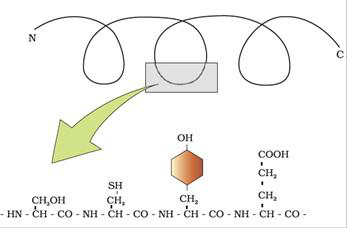
• Secondary structure protein threads forms helix. There are three types of secondary structure- α helix, β pleated and collagen. In α helix, the polypeptide chain is coiled spirally in right handed manner. • In β pleated secondary proteins two or more polypeptide chains are interconnected by hydrogen bonds. In collagen there are three strands or polypeptides coiled around one another by hydrogen bonds. • In Tertiary structure long protein chain is folded upon itself like a hollow woollen ball to give three dimensional view of protein.
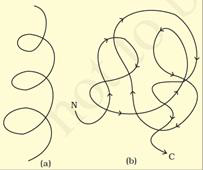
(a) secondary structure (b) Tertiary structure • In Quaternary structure each polypeptide develops its own tertiary structure and function as subunit of protein. Eg. Hemoglobin. In adult human hemoglobin 4 subunits are involved. The two subunits are of α type and two subunits of β types. Nucleic Acid: Nucleic acids are polynucleotides. A nucleic acid has three chemically distinct components- heterocyclic compound ( nitrogenous base), polysaccharides ( ribose/ deoxy- ribose sugar) and phosphate or phosphoric acid.
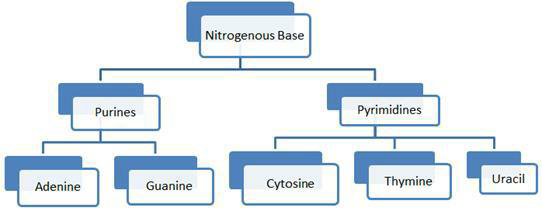
• The sugar found in nucleic acid is either ribose or deoxyribose. Nucleic acid containing deoxyribose sugar is called DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and those containing ribose sugars are called RNA (Ribonucleic acid). • Biomolecules are constantly being changed into some other biomolecules and also made from other biomolecules. This breaking and making is through chemical process called metabolism. • In living organism, all the metabolic reactions are enzyme catalyzed. Catalysts are those substances that alter the rate of reaction. The protein with catalytic power is called enzyme.
Metabolic Basis for living organism • The metabolic pathways that lead to more complex structure from simpler structure are called biosynthetic or anabolic pathways and those pathways that lead to simpler structure from complex structure are called catabolic pathways. • Photosynthesis and protein synthesis are example of anabolic pathway. Respiration and digestion are examples of catabolic pathway. • ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the most important form of energy currency in living world. • All living organism exist in steady state characterized by concentration of each of the metabolites. The living state is a non-equilibrium steady state to be able to perform work.
Enzymes • Enzymes are commonly proteinaceous substances which are capable of catalysing chemical reactions of biological origin without themselves undergoing any change. They are commonly called as biocatalysts. • The nucleic acids that behave like enzymes are called ribozymes.

• The tertiary structure of protein/Enzyme has pockets or crevice into which substrate fit to form ES complex. • The formation of the ES complex is essential for catalysis. E + S ES → EP →E + P • The structure of substrate gets transformed into the structure of product through formation of transient state structure. • The major difference between inorganic and organic catalyst is inorganic catalyst works effectively at high temperature and pressure but enzyme get damaged at high temperature. • The external energy required to start a chemical reaction is called activation energy.
Factors influencing Enzyme Activity
1. Temperature- An enzyme is active within a narrow range of temperature. Temperature ate which enzyme is most active is called optimum temperature. The enzyme activity decrease above and below this temperature.

2. pH – every enzymes has an optimum pH at which it is maximum active. Most of the intracellular enzymes work at neutral pH. 3. Concentration of Substrate – increase in substrate concentration increases the rate of reaction due to occupation of more active sites by substrate
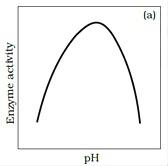
Competitive Inhibitor – when the molecular structure of inhibitor resembles the substrate, it inhibits the function of enzymes.
Enzymes are classified as 1. Oxidoreductases/Dehydrogenases- S reduced + S’ oxidised → S oxidised + S’ reduced
2. Transferases S – G + S’ → S + S’ – G 3. Hydrolases catalyses the hydrolysis of peptide, ester, glycosidic bonds et 4. Lyases remove the groups from substrate.

5. Isomerases – inter conversion of optical, geometrical or positional isomers. 6. Ligases – catalyses the linking together of two compounds. Co-factors are the non-protein constituent of an enzyme which make the enzyme more catalytically active. The protein portions of enzyme are called apoenzyme.
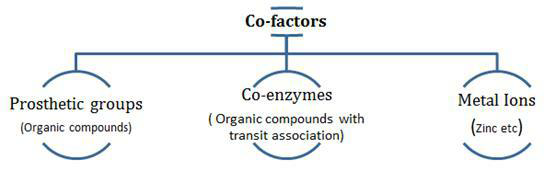
Prosthetic groups are organic compounds and are tightly bound to the apoenzyme. For example, in peroxidase and catalase, which catalyze the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide, haem is the prosthetic group
The essential chemical components of any coenzymes are vitamins. Example, coenzyme NAD and NADP contain the vitamin niacin

Related Posts:

Related Posts

Notes And Questions NCERT Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 9 Dictionary in Python

Notes And Questions NCERT Class 11 Business Studies

Notes And Questions NCERT Class 11 Biology Chapter 21 Neural Control and Coordination

Class 11 Biology: Case Study of Chapter 8 Cell: The Unit of Life PDF Download
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: Class 11
- Post comments: 0 Comments
In Class 11 Final Exams there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Download of CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter8 Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 11 Biology Cell : The Unit of Life to know their preparation level.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 11 Biology Paper, There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Cell: The Unit of Life Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 Cell : The Unit of Life
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1:
The prokaryotic cells are represented by bacteria, blue-green algae, mycoplasma and PPLO (Pleuro Pneumonia like Organisms). They are generally smaller and multiply more rapidly than the eukaryotic cells. They may vary greatly in shape and size. The four basic shapes of bacteria are bacillus (rod like), coccus (spherical), vibrio (comma shaped) and spirillum (spiral).
The organisation of the prokaryotic cell is fundamentally similar even though prokaryotes exhibit a wide variety of shapes and functions. All prokaryotes have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane except in mycoplasma. The fluid matrix filling the cell is the cytoplasm. There is no well-defined nucleus. The genetic material is basically naked, not enveloped by a nuclear membrane. In addition to the genomic DNA (the single chromosome/circular DNA), many bacteria have small circular DNA outside the genomic DNA. These smaller DNA are called plasmids. The plasmid DNA confers certain unique phenotypic characters to such bacteria. One such character is resistance to antibiotics. Nuclear membrane is found in eukaryotes. No organelles, like the ones in eukaryotes, are found in prokaryotic cells except for ribosomes. Prokaryotes have something unique in the form of inclusions. A specialised differentiated form of cell membrane called mesosome is the characteristic of prokaryotes. They are essentially infoldings of cell membrane.
1.) ______________ is the fluid matrix, which fills the prokaryotic cell.
- a.) Cell sap
- b) Cytoplasm
- d.) Both a & b
Ans: b) Cytoplasm
2.) Identify incorrect statement
Statement 1 – In prokaryotic cell nucleus is absent.
Statement 2 – In prokaryotic cells genetic material appears naked.
Statement 3 – In prokaryotic cells genetic material not enveloped by a nuclear membrane.
Statement 4 – prokaryotic cells do not have a cell wall.
- c.) Both 2 & 3
- d.) All of the above
Ans: b) Only 4
3.) Give reason – why genetic material in prokaryotic cell is not enveloped in nuclear membrane?
Ans: In prokaryotic cell well-defined nucleus is absent. Hence all genetic material appears naked and not enveloped by a nuclear membrane.
4.) Define mesosome.
Ans: Mesosome – A specialised differentiated form of cell membrane called mesosome is the characteristic of prokaryotes. They are essentially infoldings of cell membrane
5.) Give the any two characteristic of prokaryotic cells.
Ans: Characteristic of prokaryotic cells;
- There is no well-defined nucleus.
- The genetic material is basically naked, not enveloped by a nuclear membrane.
- Cellulose is the fluid matrix, which fills the prokaryotic cell.
- The prokaryotic cells are generally smaller and multiply more rapidly than the eukaryotic cells.
- All prokaryotes have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane except in mycoplasma.
6.) Enlist the shapes of bacteria are generally occurs.
Ans : The four basic shapes of bacteria are bacillus (rod like), coccus (spherical), vibrio (comma shaped) and spirillum (spiral).
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 Cell: The Unit of Life with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell: The Unit of Life Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate

You Might Also Like
Mcq questions class 11 accountancy chapter 3 recording of transactions 1 with answers, mcq questions class 11 english hornbill chapter 1 the portrait of a lady with answers, mcq questions class 11 english hornbill chapter 4 landscape of the soul with answers, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

The Topper Combo Flashcards
- Contains the Latest NCERT in just 350 flashcards.
- Colourful and Interactive
- Summarised Important reactions according to the latest PYQs of NEET(UG) and JEE
No thanks, I’m not interested!
Not Able To Find Desired Paper or Worksheet SEARCH
Find papers & worksheets search, case study questions class 11 biology chapter 2 biological classifications.
- (0) Comments
- 14 Downloads
Related Papers
Click to view more related papers, display_name = "class 11" && $paper->display_name = "class 12") { // echo $paper->display_name." questions papers and worksheets"; } //else { // echo $paper->display_name." sample papers and previous year papers"; //} //>, cbse class 11 biology chapter wise important questions - free pdf download.
CBSE Important Questions for Class 11 Biology are available in Printable format for Free Download.Here you may find NCERT Important Questions and Extra Questions for Class 11 Biology chapter wise with answers also. These questions will act as chapter wise test papers for Class 11 Biology. These Important Questions for Class 11 Biology are as per latest NCERT and CBSE Pattern syllabus and assure great success in achieving high score in Board Examinations
Total Papers :
Biology Topics to be covered for Class 11 Science
- The Living World
- Biological Classification
- Plant Kingdom
- Animal Kingdom
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Structural Organisation in Animals
- Cell-The Unit of Life
- Biomolecules
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Transport in Plants
- Mineral Nutrition
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Respiration in Plants
- Plant - Growth and Development
- Digestion and Absorption
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Excretory Products and Their Elimination
- Locomotion and Movement
- Neural Control and Coordination
- Chemical Coordination and Integration
Structure of CBSE Biology Sample Paper for Class 12 Science is
For Preparation of exams students can also check out other resource material
CBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Papers
CBSE Class 11 Biology Worksheets
CBSE Class 11 Biology Question Papers
CBSE Class 11 Biology Test Papers
CBSE Class 11 Biology Revision Notes
Question Bank of Other Subjects of Class 11
Importance of Question Bank for Exam Preparation?
There are many ways to ascertain whether a student has understood the important points and topics of a particular chapter and is he or she well prepared for exams and tests of that particular chapter. Apart from reference books and notes, Question Banks are very effective study materials for exam preparation. When a student tries to attempt and solve all the important questions of any particular subject , it becomes very easy to gauge how much well the topics have been understood and what kind of questions are asked in exams related to that chapter.. Some of the other advantaging factors of Question Banks are as follows
- Since Important questions included in question bank are collections of questions that were asked in previous exams and tests thus when a student tries to attempt them they get a complete idea about what type of questions are usually asked and whether they have learned the topics well enough. This gives them an edge to prepare well for the exam.Students get the clear idea whether the questions framed from any particular chapter are mostly either short or long answer type questions or multiple choice based and also marks weightage of any particular chapter in final exams.
- CBSE Question Banks are great tools to help in analysis for Exams. As it has a collection of important questions that were asked previously in exams thereby it covers every question from most of the important topics. Thus solving questions from the question bank helps students in analysing their preparation levels for the exam. However the practice should be done in a way that first the set of questions on any particular chapter are solved and then solutions should be consulted to get an analysis of their strong and weak points. This ensures that they are more clear about what to answer and what can be avoided on the day of the exam.
- Solving a lot of different types of important questions gives students a clear idea of what are the main important topics of any particular chapter that needs to focussed on from examination perspective and should be emphasised on for revision before attempting the final paper. So attempting most frequently asked questions and important questions helps students to prepare well for almost everything in that subject.
- Although students cover up all the chapters included in the course syllabus by the end of the session, sometimes revision becomes a time consuming and difficult process. Thus, practicing important questions from Question Bank allows students to check the preparation status of each and every small topic in a chapter. Doing that ensures quick and easy insight into all the important questions and topics in each and every individual. Solving the important questions also acts as the revision process.
Question Bank of Other Classes
To Prepare better for CBSE paperclass; ?> " title="Download Free CBSE Papers">Ribblu.com brings to you all the previous years papers & worksheets of subject; ?//> for CBSE paperclass; ?>. This CBSE paper and worksheet can be instrumental in students achieving maximum marks in their exams. These Papers and worksheets help students gain confidence and make them ready to face their school examinations. These Papers and worksheets school wise, covers important concepts from an examination perspective. Students and parents can download all the available papers & worksheets directly in the form of PDF. One can use these papers and worksheets to get extensive practice and familiarise themselves with the format of the question paper.
You can help other users
Be the first to write comment .
Upload papers and the more your paper get downloaded the more you earn the points
You may send papers on email [email protected] along with userid
- Downloaded by: Prerna 2020
- Downloaded by: Francisca Fernandes
Rules and regulations for uploads
Write your comment, report this paper, how to earn points.
Upload Papers / Worksheets and Earn 50 Points.
The uploaded material should be original paper or worksheet of any school. Check out some videos on how to upload papers on ribblu
Rate & Review your school and Earn 25 Points.
Review any school that you may be knowing and once your review is approved, you will be credited with 25 points.
Answer on question posted on JustAsk and earn 15 points.
JustAsk is a platform where you can help others to find answers of any question. Share your Knowledge. Answer questions and once approved you will earn 15 points
Complete your profile and earn upto 25 Points.
Edit and complete your user profile and earn points. The more details you submit, the more points you will earn.
Download Ribblu Mobile App and you will (Earn 20 Points) (one time only)
CBSE Schools
- CBSE Schools In Delhi
- CBSE Schools In Noida
- CBSE Schools In Greater Noida
- CBSE Schools In Faridabad
- CBSE Schools In Ghaziabad
- CBSE Schools In Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools In Mumbai
- CBSE Schools In Pune
- CBSE Schools In Bangalore
- CBSE Schools In Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools In Kolkata
- CBSE Schools In Chennai
- CBSE Schools In Patna
- CBSE Schools In Meerut
- CBSE Schools In Kanpur
- CBSE Schools In Indore
- CBSE Schools In Ludhiana
- CBSE Schools In Dehradun
Top Schools
- Schools In Delhi
- Schools In Noida
- Schools In Greater Noida
- Schools In Faridabad
- Schools In Ghaziabad
- Schools In Gurgaon
- Schools In Mumbai
- Schools In Pune
- Schools In Bangalore
- Schools In Hyderabad
- Schools In Kolkata
- Schools In Chennai
- Schools In Patna
- Schools In Meerut
- Schools In Kanpur
- Schools In Indore
- Schools In Ludhiana
- Schools In Dehradun
Other Schools
- Pre Nursery Schools In Noida
- Day Boarding Schools In Noida
- Pre Nursery Schools In Gurgaon
- Pre Nursery Schools In Delhi
- Play Schools In Delhi
- Day Boarding Schools In Delhi
CBSE Papers
- CBSE Class 1 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 2 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 3 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 4 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 5 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 6 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 7 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 8 Sample Papers
Paper Categories
- Question Bank
- Question Papers
- Revision Notes
- Sample Papers
- Test Papers
- CBSE Class 9 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 11 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Sample Papers


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 11 Biology Biomolecules. CASE 1. Enzymes are composed of one or several polypeptide chains. However, there are a number of cases in which non-protein constituents called co-factors are bound to the enzyme to make the enzyme catalytically active. In these instances, the protein portion of the enzymes is called the ...
Class 11 Biology case study questions 1. Read the following and answer any four questions: The detailed structure of the membrane was studied only after the advent of the electron microscope in the 1950s. Meanwhile, chemical studies on the cell membrane, especially in human red blood cells (RBCs), enabled the scientists to deduce the possible ...
Free PDF Download of CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 11 Biology Biomolecules to know their preparation level. Download Books for Boards. Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards ...
Case Study-Based Questions for Class 11 Biology. Chapter 1 : The Living World. Chapter 2 : Biological Classification. Chapter 3 : Plant Kingdom. Chapter 4 : Animal Kingdom. Chapter 5 : Morphology of Flowering Plants. Chapter 6 : Anatomy of Flowering Plants. Chapter 7 : Structural Organisation in Animals.
5. (a) The molecular structures of three amino acids are given above. (a) Identify the amino acids A, Band C. (b) Mention their respective variable group (designated as R-group). 5. (a) Study the changes in the structure of an amino acid shown above and answer the following questions. (a) Mention the specific property of amino acids shown in ...
CLASS -XI BIOLOGY STUDY MATERIAL 2022-23 . FORWARD ... assertion and reasoning questions, case based questions, board previous years ... Chapter 9: Biomolecules Chapter 10: Cell Cycle and Cell Division UNIT-IV PLANT PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 13.Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
Very Short Answer Type Questions. Q.1. Classify the following based on whether they were initially received as a natural product or as a synthetic chemical. a) Penicillin b) Sulfonamide c) Vitamin C d) Growth hormone. A.1. Listed below is the classification. Natural product. Synthetic Chemical.
Hydrolysis is a reaction between lactose and water. So, when lactose combines chemically with water, it breaks up to produce its constituent substances. On hydrolysis of lactose, a smaller sugar molecule is formed. Students of Class 11 will study different types of sugars in Chapter 9 Biomolecules of Class 11 Biology. 2.
Learn about biomolecules like lipids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and how special proteins called enzymes help with metabolism. This unit is aligned to the Class 11 NCERT curriculum. ... Class 11 Biology (India) 20 units · 94 skills. Unit 1. The living world. Unit 2. Biological classification. Unit 3.
In Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Notes, you will learn about different types of biomolecules present in the human body and other living organisms. Also, you will find out how various biomolecules play vital roles in our daily life. Students can download a free PDF of CBSE Class 11 Biology Revision Notes for Chapter 9 Biomolecules through the PDF ...
Solution: Macromolecules are large high molecular weight substances with complex molecular structure and occur in colloidal state (being insoluble) in intracellular fluid. These are formed by polymerization of large number of micromolecules. Polysaccharides, proteins and nucleic acids are few examples. 2.
Class 11 Biology Biomolecules NCERT Solutions - Contents of the Pdf . NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter Biomolecules entails solutions to the questions given at the end of the chapter. Students can learn the Class 11 Biomolecules questions and answers from the Biology Biomolecules NCERT Solutions pdf offered by Vedantu on this page.
The properties of enzymes covered in Chapter 9 of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology are. 1. The enzymes have higher molecular weight and are complex macromolecules. 2. The biochemical reactions involved in the cell are catalysed by the enzymes, assisting in breaking down larger molecules into simpler molecules. 3.
Case Study Questions for Class 11 Biology. Chapter 1: The Living World. Chapter 2: Biological Classification. Chapter 3: Plant Kingdom. Chapter 4: Animal Kingdom. Chapter 5: Morphology of Flowering Plants. Chapter 6: Anatomy of Flowering Plants. Chapter 7: Structural Organisation in Animals. Chapter 8: The Unit of Life.
2. Illustrate a glycosidic, peptide and a phospho-diester bond. Answer. (a) Glycosidic bond is formed normally between carbon atoms, 1 and 4, of neighbouring monosaccharide units. (b) Peptide bond is a covalent bond that joins the two amino acids by - NH - CO linkage. (c) Phosphodiester bond is a strong covalent bond between phosphate and two ...
The chapter of Biomolecules in Class 11th Biology serves of great importance. Furthermore, it introduces students to molecules that are present in living organisms. Thus, this chapter will help you learn about a wide range of sizes and structures. Thus, through biomolecules class 11 notes you will be able to study in detail about these things.
Every year several questions are asked from this chapter in competitive and board examinations. In Biomolecules Important Questions PDF Class 11, you will study about Lipids, Proteins, Polysaccharides, Enzymes, Regulation of enzymes, Metabolism, Nucleic acids, etc. PREMIUM EDUCART QUESTIONS. Download.
1. Transport of nutrient across the membrane. 2. Fight infectious organisms. 3. Produce enzyme and proteins. • Collagen is the most abundant protein in animal world. • Primary structure of protein is the basic structure of protein in which a number of polypeptides are involved having sequence of amino acids.
Answer: During the digestion of carbohydrates, the glycosidic bond between sugar residues is broken by the addition of water and this is called hydrolysis. Question 2. Define fatty acid. Answer: Fatty acids are organic acids with a hydrocarbon chain ending in a carboxyl group. Question 3.
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 Cell : The Unit of Life. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Case Study 1: The prokaryotic cells are represented by bacteria, blue-green algae, mycoplasma and PPLO (Pleuro Pneumonia like Organisms).
14 Downloads. Case Study Questions Class 11 Biology Chapter 2 Biological Classifications Biology Class 11 Important Questions Chapter wise CBSE Class 11 Biology Extra Questions and Answers Assertion Reasoning Questions Class 11 Biology Free PDF Download Class 11 Biology CBSE 2022. Download Paper.