CodeFatherTech
Learn to Code. Shape Your Future


Tuple Object Does Not Support Item Assignment. Why?
Have you ever seen the error “tuple object does not support item assignment” when working with tuples in Python? In this article we will learn why this error occurs and how to solve it.
The error “tuple object does not support item assignment” is raised in Python when you try to modify an element of a tuple. This error occurs because tuples are immutable data types. It’s possible to avoid this error by converting tuples to lists or by using the tuple slicing operator.
Let’s go through few examples that will show you in which circumstances this error occurs and what to do about it.
Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Explanation of the Error “Tuple Object Does Not Support Item Assignment”
Define a tuple called cities as shown below:
If you had a list you would be able to update any elements in the list .
But, here is what happens if we try to update one element of a tuple:
Tuples are immutable and that’s why we see this error.
There is a workaround to this, we can:
- Convert the tuple into a list.
- Update any elements in the list.
- Convert the final list back to a tuple.
To convert the tuple into a list we will use the list() function :
Now, let’s update the element at index 1 in the same way we have tried to do before with the tuple:
You can see that the second element of the list has been updated.
Finally, let’s convert the list back to a tuple using the tuple() function :
Makes sense?
Avoid the “Tuple Object Does Not Support Item Assignment” Error with Slicing
The slicing operator also allows to avoid this error.
Let’s see how we can use slicing to create a tuple from our original tuple where only one element is updated.
We will use the following tuple and we will update the value of the element at index 2 to ‘Rome’.
Here is the result we want:
We can use slicing and concatenate the first two elements of the original tuple, the new value and the last two elements of the original tuple.
Here is the generic syntax of the slicing operator (in this case applied to a tuple).
This takes a slice of the tuple including the element at index n and excluding the element at index m .
Firstly, let’s see how to print the first two and last two elements of the tuple using slicing…
First two elements
We can also omit the first zero considering that the slice starts from the beginning of the tuple.
Last two elements
Notice that we have omitted index m considering that the slice includes up to the last element of the tuple.
Now we can create the new tuple starting from the original one using the following code:
(‘Rome’,) is a tuple with one element of type string.
Does “Tuple Object Does Not Support Item Assignment” Apply to a List inside a Tuple?
Let’s see what happens when one of the elements of a tuple is a list.
If we try to update the second element of the tuple we get the expected error:
If we try to assign a new list to the third element…
…once again we get back the error “‘ tuple’ object does not support item assignment “.
But if we append another number to the list inside the tuple, here is what happens:
The Python interpreter doesn’t raise any exceptions because the list is a mutable data type.
This concept is important for you to know when you work with data types in Python:
In Python, lists are mutable and tuples are immutable.
How to Solve This Error with a List of Tuples
Do we see this error also with a list of tuples?
Let’s say we have a list of tuples that is used in a game to store name and score for each user:
The user John has gained additional points and I want to update the points associated to his user:
When I try to update his points we get back the same error we have seen before when updating a tuple.
How can we get around this error?
Tuples are immutable but lists are mutable and we could use this concept to assign the new score to a new tuple in the list, at the same position of the original tuple in the list.
So, instead of updating the tuple at index 0 we will assign a new tuple to it.
Let’s see if it works…
It does work! Once again because a list is mutable .
And here is how we can make this code more generic?
Ok, this is a bit more generic because we didn’t have to provide the name of the user when updating his records.
This is just an example to show you how to address this TypeError , but in reality in this scenario I would prefer to use a dictionary instead.
It would allow us to access the details of each user from the name and to update the score without any issues.
Tuple Object Does Not Support Item Assignment Error With Values Returned by a Function
This error can also occur when a function returns multiple values and you try to directly modify the values returned by the function.
I create a function that returns two values: the number of users registered in our application and the number of users who have accessed our application in the last 30 days.
As you can see the two values are returned by the function as a tuple.
So, let’s assume there is a new registered user and because of that I try to update the value returned by the function directly.
I get the following error…
This can happen especially if I know that two values are returned by the function but I’m not aware that they are returned in a tuple.
Why Using Tuples If We Get This Error?
You might be thinking…
What is the point of using tuples if we get this error every time we try to update them?
Wouldn’t be a lot easier to always use lists instead?
We can see the fact that tuples are immutable as an added value for tuples when we have some data in our application that should never be modified.
Let’s say, for example, that our application integrates with an external system and it needs some configuration properties to connect to that system.
The tuple above contains two values: the API endpoint of the system we connect to and the port for their API.
We want to make sure this configuration is not modified by mistake in our application because it would break the integration with the external system.
So, if our code inadvertently updates one of the values, the following happens:
Remember, it’s not always good to have data structures you can update in your code whenever you want.
In this article we have seen when the error “tuple object does not support item assignment” occurs and how to avoid it.
You have learned how differently the tuple and list data types behave in Python and how you can use that in your programs.
If you have any questions feel free to post them in the comment below 🙂

Claudio Sabato is an IT expert with over 15 years of professional experience in Python programming, Linux Systems Administration, Bash programming, and IT Systems Design. He is a professional certified by the Linux Professional Institute .
With a Master’s degree in Computer Science, he has a strong foundation in Software Engineering and a passion for robotics with Raspberry Pi.
Related posts:
- Unhashable Type Python Error Explained: How To Fix It
- Python TypeError: Object is Not Callable. Why This Error?
- Python AttributeError: Fix This Built-in Exception
- Understand the “str object is not callable” Python Error and Fix It!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.

HatchJS.com
Cracking the Shell of Mystery
TypeError: Type object does not support item assignment: How to fix it?
TypeError: Type object does not support item assignment
Have you ever tried to assign a value to a property of a type object and received a TypeError? If so, you’re not alone. This error is a common one, and it can be frustrating to figure out what went wrong.
In this article, we’ll take a look at what a type object is, why you can’t assign values to its properties, and how to avoid this error. We’ll also provide some examples of how to work with type objects correctly.
So, if you’re ready to learn more about TypeErrors and type objects, read on!
What is a type object?
A type object is a special kind of object that represents a data type. For example, the `int` type object represents the integer data type, and the `str` type object represents the string data type.
Type objects are created when you use the `type()` function. For example, the following code creates a type object for the integer data type:
python int_type = type(1)
Type objects have a number of properties that you can use to get information about them. For example, the `__name__` property returns the name of the type, and the `__bases__` property returns a list of the type’s base classes.
Why can’t you assign values to type objects?
Type objects are immutable, which means that their values cannot be changed. This is because type objects are used to represent the abstract concept of a data type, and their values are not meant to be changed.
If you try to assign a value to a property of a type object, you’ll receive a TypeError. For example, the following code will raise a TypeError:
python int_type.name = “New name”
How to avoid TypeErrors
To avoid TypeErrors, you should never try to assign values to properties of type objects. If you need to change the value of a property, you should create a new object with the desired value.
For example, the following code correctly changes the value of the `name` property of an integer object:
python new_int = int(1) new_int.name = “New name”
TypeErrors can be frustrating, but they can usually be avoided by understanding what type objects are and how they work. By following the tips in this article, you can avoid these errors and write more robust code.
| Header 1 | Header 2 | Header 3 | |—|—|—| | TypeError: type object does not support item assignment | Definition | Cause | | An error that occurs when you try to assign a value to an element of a type object that does not support item assignment. | The type object is immutable, which means that its values cannot be changed. | Trying to assign a value to an element of a type object will result in a TypeError. |
A TypeError is a type of error that occurs when an operation or function is applied to an object of an inappropriate type. For example, trying to assign a value to an attribute of a type object will result in a TypeError.
TypeErrors can be difficult to debug, because they can occur in a variety of situations. However, by understanding what causes a TypeError, you can be better equipped to avoid them.
What causes a TypeError?
There are a few different things that can cause a TypeError:
- Using an incompatible data type: One of the most common causes of a TypeError is using an incompatible data type. For example, trying to add a string to a number will result in a TypeError.
- Using an invalid operator: Another common cause of a TypeError is using an invalid operator. For example, trying to divide a number by zero will result in a TypeError.
- Calling a method on an object that doesn’t support it: Finally, trying to call a method on an object that doesn’t support it can also result in a TypeError. For example, trying to call the `.sort()` method on a string will result in a TypeError.
There are a few things you can do to avoid TypeErrors:
- Be careful about the data types you use: Make sure that you are using the correct data types for your operations. For example, if you are adding two numbers, make sure that both numbers are numbers.
- Use the correct operators: Make sure that you are using the correct operators for your operations. For example, if you are dividing two numbers, use the `/` operator.
- Read the documentation: If you are not sure whether a method is supported by an object, read the documentation to find out.
By following these tips, you can help to avoid TypeErrors in your code.
TypeErrors can be a frustrating experience, but they can also be a learning opportunity. By understanding what causes a TypeError, you can be better equipped to avoid them. And by following the tips in this article, you can help to reduce the number of TypeErrors in your code.
Additional resources
- [Python TypeError documentation](https://docs.python.org/3/library/exceptions.htmlTypeError)
- [Stack Overflow: TypeError questions](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/typeerror)
- [Real Python: How to avoid TypeErrors in Python](https://realpython.com/python-typeerror/)
3. How to fix a TypeError?
To fix a TypeError, you need to identify the cause of the error and then take steps to correct it. Some common fixes include:
Using the correct data type
Using the correct operator
Calling the correct method on the object
Let’s take a look at some examples of how to fix each of these types of errors.
One of the most common causes of TypeErrors is using the wrong data type. For example, if you try to add a string to an integer, you will get a TypeError because strings and integers are different data types. To fix this error, you need to convert the string to an integer or the integer to a string.
x = ‘123’ y = 456
This will raise a TypeError because you cannot add a string to an integer z = x + y
To fix this error, you can convert the string to an integer z = int(x) + y
Another common cause of TypeErrors is using the wrong operator. For example, if you try to divide an integer by a string, you will get a TypeError because you cannot divide an integer by a string. To fix this error, you need to use the correct operator.
x = 123 y = ‘456’
This will raise a TypeError because you cannot divide an integer by a string z = x / y
To fix this error, you can use the `str()` function to convert the string to an integer z = x / int(y)
Finally, another common cause of TypeErrors is calling the wrong method on an object. For example, if you try to call the `len()` method on a string, you will get a TypeError because the `len()` method is not defined for strings. To fix this error, you need to call the correct method on the object.
x = ‘hello’
This will raise a TypeError because the `len()` method is not defined for strings y = len(x)
To fix this error, you can use the `str()` function to convert the string to an integer y = len(str(x))
By following these tips, you can help to avoid TypeErrors in your Python code.
4. Examples of TypeErrors
Here are some examples of TypeErrors:
x = ‘hello’ x[0] = ‘a’
This will result in a TypeError because strings are immutable and cannot be changed.
print(int(‘123’))
This will also result in a TypeError because the string ‘123’ cannot be converted to an integer.
class MyClass: def __init__(self, name): self.name = name
my_class = MyClass(‘John’) my_class.name = ‘Jane’
This will also result in a TypeError because the method `name` is not defined on the `MyClass` object.
TypeErrors are a common problem in Python, but they can be easily avoided by following the tips in this article. By using the correct data types, operators, and methods, you can help to ensure that your Python code is free of errors.
Q: What does the error “TypeError: type object does not support item assignment” mean?
A: This error occurs when you try to assign a value to a property of a type object. For example, the following code will raise an error:
>>> type = type(‘MyType’, (object,), {}) >>> type.name = ‘MyType’ Traceback (most recent call last): File “ “, line 1, in TypeError: type object does not support item assignment
The reason for this error is that type objects are immutable, which means that their properties cannot be changed after they are created. If you need to change the value of a property of a type object, you can create a new type object with the desired value.
Q: How can I fix the error “TypeError: type object does not support item assignment”?
A: There are two ways to fix this error. The first way is to create a new type object with the desired value. For example, the following code will fix the error in the example above:
>>> type = type(‘MyType’, (object,), {‘name’: ‘MyType’}) >>> type.name ‘MyType’
The second way to fix this error is to use a dictionary to store the properties of the type object. For example, the following code will also fix the error in the example above:
>>> type = type(‘MyType’, (object,), {}) >>> type.__dict__[‘name’] = ‘MyType’ >>> type.name ‘MyType’
Q: What are some common causes of the error “TypeError: type object does not support item assignment”?
A: There are a few common causes of this error. The first is trying to assign a value to a property of a type object that does not exist. For example, the following code will raise an error:
>>> type = type(‘MyType’, (object,), {}) >>> type.foo = ‘bar’ Traceback (most recent call last): File “ “, line 1, in AttributeError: type object has no attribute ‘foo’
The second is trying to assign a value to a property of a type object that is read-only. For example, the following code will also raise an error:
>>> type = type(‘MyType’, (object,), {}) >>> type.name = ‘MyType’ Traceback (most recent call last): File “ “, line 1, in TypeError: can’t set attribute ‘name’ of type object
The third is trying to assign a value to a property of a type object that is not a valid type. For example, the following code will also raise an error:
>>> type = type(‘MyType’, (object,), {}) >>> type.name = 123 Traceback (most recent call last): File “ “, line 1, in TypeError: can’t assign int to str object
Q: How can I avoid the error “TypeError: type object does not support item assignment”?
A: There are a few things you can do to avoid this error. First, make sure that you are trying to assign a value to a property of a type object that exists. Second, make sure that you are not trying to assign a value to a property of a type object that is read-only. Third, make sure that you are not trying to assign a value to a property of a type object that is not a valid type.
Here are some specific examples of how to avoid this error:
- Instead of trying to assign a value to the `name` property of a type object, you can create a new type object with the desired value. For example:
>>> type = type(‘MyType’, (object,), {‘name’: ‘MyType’})
- Instead of trying to assign a value to the `name` property of a type object, you can use a dictionary to store the properties of the type object. For example:
>>> type = type(‘MyType’, (object,), {}) >>> type.__dict__[‘name’] = ‘MyType’
- Instead of trying to assign a value to the `name` property of a type object, you can use a getter and setter method to access the property. For example:
In this blog post, we discussed the TypeError: type object does not support item assignment error. We first explained what the error is and then provided several ways to fix it. We also discussed some common causes of the error and how to avoid them.
We hope that this blog post has been helpful and that you now have a better understanding of the TypeError: type object does not support item assignment error. If you have any other questions or comments, please feel free to leave them below.
Author Profile

Latest entries
- December 26, 2023 Error Fixing User: Anonymous is not authorized to perform: execute-api:invoke on resource: How to fix this error
- December 26, 2023 How To Guides Valid Intents Must Be Provided for the Client: Why It’s Important and How to Do It
- December 26, 2023 Error Fixing How to Fix the The Root Filesystem Requires a Manual fsck Error
- December 26, 2023 Troubleshooting How to Fix the `sed unterminated s` Command
Similar Posts
Attributeerror: module numpy has no attribute asscalar.
AttributeError: module numpy has no attribute asscalar If you’re a Python programmer, you’ve probably encountered the dreaded AttributeError at some point. This error occurs when you try to access a property or method that doesn’t exist on an object. In the case of numpy, the asscalar attribute doesn’t exist, so you’ll get an AttributeError if…
TensorRT not found: How to fix this error?
TensorRT Warning: Could Not Find TensorRT TensorRT is a high-performance deep learning inference engine that can be used to deploy models on a variety of hardware platforms. However, sometimes you may encounter the error message “Could not find TensorRT.” This error can occur for a variety of reasons, but it is usually due to a…
Axios get is not a function: How to fix this error
Axios.get is not a function? If you’re a JavaScript developer, you’ve probably heard of Axios. It’s a popular library for making HTTP requests. But what if I told you that `axios.get` is not a function? That’s right, `axios.get` is not a function. It’s actually a method. And this has some important implications for how you…
Error 03000086: Digital Envelope Routines Initialization Error
Have you ever encountered the error message error:03000086: digital envelope routines::initialization error? If so, youre not alone. This error is a common one that can occur when youre trying to send or receive encrypted email. In this article, well take a closer look at what this error means and what you can do to fix…
3 Ways to Fix the ‘No Module Named OpenPyXL’ Error
No module named openpyxl: A guide to fixing the error If you’re a Python developer, you’ve probably encountered the error “No module named openpyxl” at some point. This error can be caused by a number of factors, but it’s usually pretty easy to fix. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to troubleshoot…
How to Fix Torch.cuda.outOfMemoryError: CUDA Out of Memory
Torch.cuda.outOfMemoryError: CUDA out of memory One of the most common errors encountered by PyTorch users is the `torch.cuda.outOfMemoryError`. This error occurs when a PyTorch operation runs out of memory on the GPU. This can be a frustrating problem, as it can often be difficult to track down the source of the error. In this article,…
Explore your training options in 10 minutes Get Started
- Graduate Stories
- Partner Spotlights
- Bootcamp Prep
- Bootcamp Admissions
- University Bootcamps
- Coding Tools
- Software Engineering
- Web Development
- Data Science
- Tech Guides
- Tech Resources
- Career Advice
- Online Learning
- Internships
- Apprenticeships
- Tech Salaries
- Associate Degree
- Bachelor's Degree
- Master's Degree
- University Admissions
- Best Schools
- Certifications
- Bootcamp Financing
- Higher Ed Financing
- Scholarships
- Financial Aid
- Best Coding Bootcamps
- Best Online Bootcamps
- Best Web Design Bootcamps
- Best Data Science Bootcamps
- Best Technology Sales Bootcamps
- Best Data Analytics Bootcamps
- Best Cybersecurity Bootcamps
- Best Digital Marketing Bootcamps
- Los Angeles
- San Francisco
- Browse All Locations
- Digital Marketing
- Machine Learning
- See All Subjects
- Bootcamps 101
- Full-Stack Development
- Career Changes
- View all Career Discussions
- Mobile App Development
- Cybersecurity
- Product Management
- UX/UI Design
- What is a Coding Bootcamp?
- Are Coding Bootcamps Worth It?
- How to Choose a Coding Bootcamp
- Best Online Coding Bootcamps and Courses
- Best Free Bootcamps and Coding Training
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Community College
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Self-Learning
- Bootcamps vs. Certifications: Compared
- What Is a Coding Bootcamp Job Guarantee?
- How to Pay for Coding Bootcamp
- Ultimate Guide to Coding Bootcamp Loans
- Best Coding Bootcamp Scholarships and Grants
- Education Stipends for Coding Bootcamps
- Get Your Coding Bootcamp Sponsored by Your Employer
- GI Bill and Coding Bootcamps
- Tech Intevriews
- Our Enterprise Solution
- Connect With Us
- Publication
- Reskill America
- Partner With Us
- Resource Center
- Bachelor’s Degree
- Master’s Degree
Python typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment Solution
Tuples are immutable objects . “Immutable” means you cannot change the values inside a tuple. You can only remove them. If you try to assign a new value to an item in a variable, you’ll encounter the “typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment” error.
In this guide, we discuss what this error means and why you may experience it. We’ll walk through an example of this error so you can learn how to solve it in your code.
Find your bootcamp match
Typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment.
While tuples and lists both store sequences of data, they have a few distinctions. Whereas you can change the values in a list, the values inside a tuple cannot be changed. Also, tuples are stored within parenthesis whereas lists are declared between square brackets.
Because you cannot change values in a tuple, item assignment does not work.
Consider the following code snippet:
This code snippet lets us change the first value in the “honor_roll” list to Holly. This works because lists are mutable. You can change their values. The same code does not work with data that is stored in a tuple.
An Example Scenario
Let’s build a program that tracks the courses offered by a high school. Students in their senior year are allowed to choose from a class but a few classes are being replaced.
Start by creating a collection of class names:
We’ve created a tuple that stores the names of each class being offered.
The science department has notified the school that psychology is no longer being offered due to a lack of numbers in the class. We’re going to replace psychology with philosophy as the philosophy class has just opened up a few spaces.
To do this, we use the assignment operator:
This code will replace the value at the index position 3 in our list of classes with “Philosophy”. Next, we print our list of classes to the console so that the user can see what classes are being actively offered:
Use a for loop to print out each class in our tuple to the console. Let’s run our code and see what happens:
Our code returns an error.
The Solution
We’ve tried to use the assignment operator to change a subject in our list. Tuples are immutable so we cannot change their values. This is why our code returns an error.
To solve this problem, we convert our “classes” tuple into a list . This will let us change the values in our sequence of class names.
Do this using the list() method:
We use the list() method to convert the value of “classes” to a list. We assign this new list to the variable “as_list”. Now that we have our list of classes stored as a list, we can change existing classes in the list.
Let’s run our code:
Our code successfully changes the “Psychology” class to “Philosophy”. Our code then prints out the list of classes to the console.
If we need to store our data as a tuple, we can always convert our list back to a tuple once we have changed the values we want to change. We can do this using the tuple() method:
This code converts “as_list” to a tuple and prints the value of our tuple to the console:
We could use this tuple later in our code if we needed our class names stored as a tuple.
The “typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment” error is raised when you try to change a value in a tuple using item assignment.
To solve this error, convert a tuple to a list before you change the values in a sequence. Optionally, you can then convert the list back to a tuple.
Now you’re ready to fix this error in your code like a pro !
About us: Career Karma is a platform designed to help job seekers find, research, and connect with job training programs to advance their careers. Learn about the CK publication .

"Career Karma entered my life when I needed it most and quickly helped me match with a bootcamp. Two months after graduating, I found my dream job that aligned with my values and goals in life!"
Venus, Software Engineer at Rockbot
What's Next?
Get matched with top bootcamps
Ask a question to our community, take our careers quiz.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

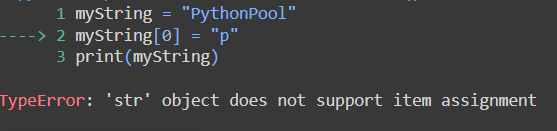
[Solved] TypeError: ‘str’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment

In this article, we will be discussing the TypeError:’str’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment exception . We will also be going through solutions to this problem with example programs.
Why is This Error Raised?
When you attempt to change a character within a string using the assignment operator, you will receive the Python error TypeError: ‘str’ object does not support item assignment.
As we know, strings are immutable. If you attempt to change the content of a string, you will receive the error TypeError: ‘str’ object does not support item assignment .
There are four other similar variations based on immutable data types :
- TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
- TypeError: 'int' object does not support item assignment
- TypeError: 'float' object does not support item assignment
- TypeError: 'bool' object does not support item assignment
Replacing String Characters using Assignment Operators
Replicate these errors yourself online to get a better idea here .
In this code, we will attempt to replace characters in a string.
Strings are an immutable data type. However, we can change the memory to a different set of characters like so:
TypeError: ‘str’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in JSON
Let’s review the following code, which retrieves data from a JSON file.
In line 5, we are assigning data['sample'] to a string instead of an actual dictionary. This causes the interpreter to believe we are reassigning the value for an immutable string type.
TypeError: ‘str’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in PySpark
The following program reads files from a folder in a loop and creates data frames.
This occurs when a PySpark function is overwritten with a string. You can try directly importing the functions like so:
TypeError: ‘str’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in PyMongo
The following program writes decoded messages in a MongoDB collection. The decoded message is in a Python Dictionary.
At the 10th visible line, the variable x is converted as a string.
It’s better to use:
Please note that msg are a dictionary and NOT an object of context.
TypeError: ‘str’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in Random Shuffle
The below implementation takes an input main and the value is shuffled. The shuffled value is placed into Second .
random.shuffle is being called on a string, which is not supported. Convert the string type into a list and back to a string as an output in Second
TypeError: ‘str’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in Pandas Data Frame
The following program attempts to add a new column into the data frame
The iteration statement for dataset in df: loops through all the column names of “sample.csv”. To add an extra column, remove the iteration and simply pass dataset['Column'] = 1 .
![item assignment with class 'list' not supported [Solved] runtimeerror: cuda error: invalid device ordinal](https://www.pythonpool.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Solved-runtimeerror-cuda-error-invalid-device-ordinal-300x157.webp)
These are the causes for TypeErrors : – Incompatible operations between 2 operands: – Passing a non-callable identifier – Incorrect list index type – Iterating a non-iterable identifier.
The data types that support item assignment are: – Lists – Dictionaries – and Sets These data types are mutable and support item assignment
As we know, TypeErrors occur due to unsupported operations between operands. To avoid facing such errors, we must: – Learn Proper Python syntax for all Data Types. – Establish the mutable and immutable Data Types. – Figure how list indexing works and other data types that support indexing. – Explore how function calls work in Python and various ways to call a function. – Establish the difference between an iterable and non-iterable identifier. – Learn the properties of Python Data Types.
We have looked at various error cases in TypeError:’str’ Object Does Not Support Item Assignment. Solutions for these cases have been provided. We have also mentioned similar variations of this exception.
Trending Python Articles
![item assignment with class 'list' not supported [Fixed] typeerror can’t compare datetime.datetime to datetime.date](https://www.pythonpool.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/typeerror-cant-compare-datetime.datetime-to-datetime.date_-300x157.webp)
TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024 Reading time · 4 min

# TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
The Python "TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment" occurs when we try to change the value of an item in a tuple.
To solve the error, convert the tuple to a list, change the item at the specific index and convert the list back to a tuple.
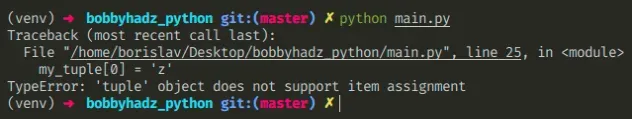
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
We tried to update an element in a tuple, but tuple objects are immutable which caused the error.
# Convert the tuple to a list to solve the error
We cannot assign a value to an individual item of a tuple.
Instead, we have to convert the tuple to a list.
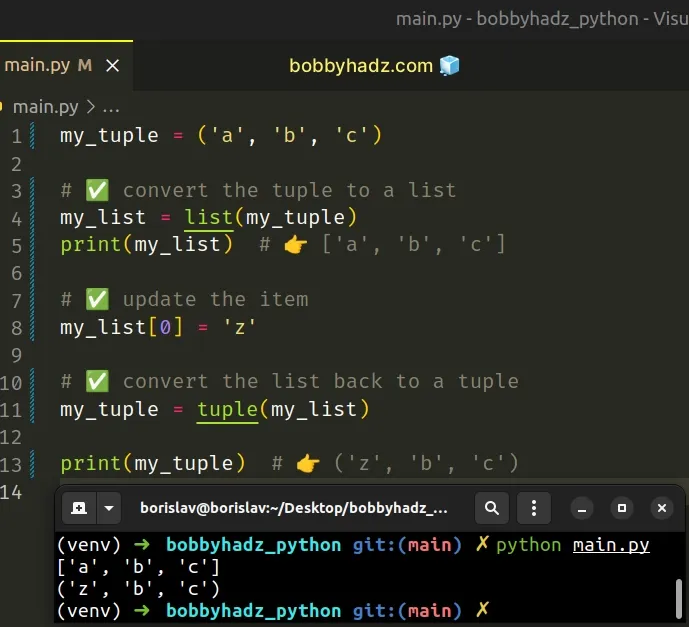
This is a three-step process:
- Use the list() class to convert the tuple to a list.
- Update the item at the specified index.
- Use the tuple() class to convert the list back to a tuple.
Once we have a list, we can update the item at the specified index and optionally convert the result back to a tuple.
Python indexes are zero-based, so the first item in a tuple has an index of 0 , and the last item has an index of -1 or len(my_tuple) - 1 .
# Constructing a new tuple with the updated element
Alternatively, you can construct a new tuple that contains the updated element at the specified index.
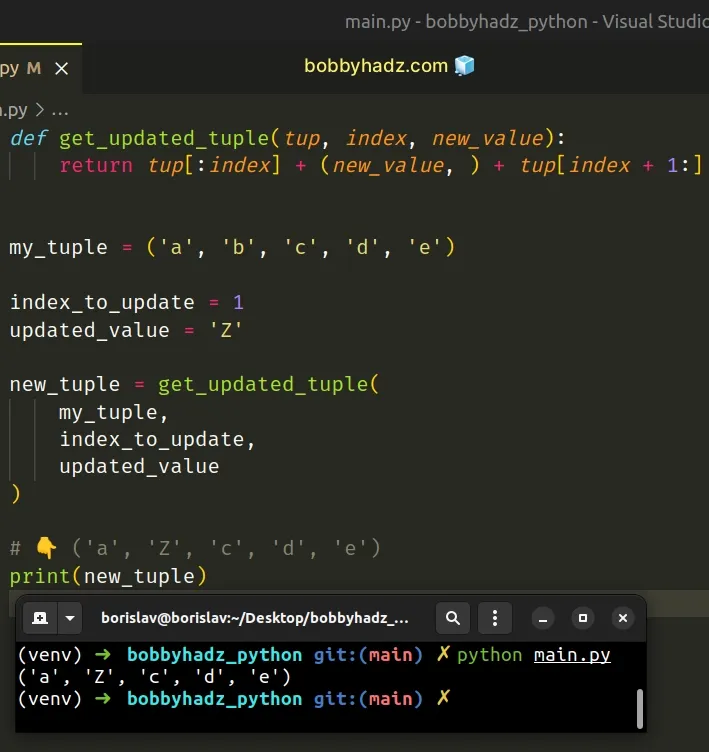
The get_updated_tuple function takes a tuple, an index and a new value and returns a new tuple with the updated value at the specified index.
The original tuple remains unchanged because tuples are immutable.
We updated the tuple element at index 1 , setting it to Z .
If you only have to do this once, you don't have to define a function.
The code sample achieves the same result without using a reusable function.
The values on the left and right-hand sides of the addition (+) operator have to all be tuples.
The syntax for tuple slicing is my_tuple[start:stop:step] .
The start index is inclusive and the stop index is exclusive (up to, but not including).
If the start index is omitted, it is considered to be 0 , if the stop index is omitted, the slice goes to the end of the tuple.
# Using a list instead of a tuple
Alternatively, you can declare a list from the beginning by wrapping the elements in square brackets (not parentheses).
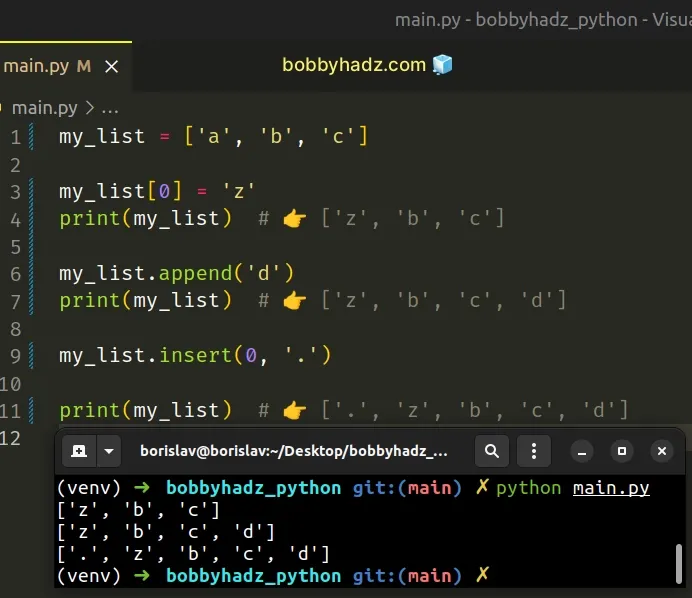
Declaring a list from the beginning is much more efficient if you have to change the values in the collection often.
Tuples are intended to store values that never change.
# How tuples are constructed in Python
In case you declared a tuple by mistake, tuples are constructed in multiple ways:
- Using a pair of parentheses () creates an empty tuple
- Using a trailing comma - a, or (a,)
- Separating items with commas - a, b or (a, b)
- Using the tuple() constructor

# Checking if the value is a tuple
You can also handle the error by checking if the value is a tuple before the assignment.
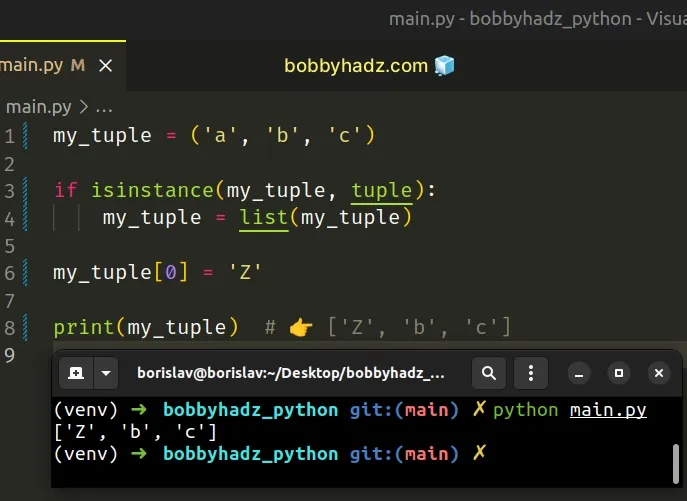
If the variable stores a tuple, we set it to a list to be able to update the value at the specified index.
The isinstance() function returns True if the passed-in object is an instance or a subclass of the passed-in class.
If you aren't sure what type a variable stores, use the built-in type() class.
The type class returns the type of an object.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- How to convert a Tuple to an Integer in Python
- How to convert a Tuple to JSON in Python
- Find Min and Max values in Tuple or List of Tuples in Python
- Get the Nth element of a Tuple or List of Tuples in Python
- Creating a Tuple or a Set from user Input in Python
- How to Iterate through a List of Tuples in Python
- Write a List of Tuples to a File in Python
- AttributeError: 'tuple' object has no attribute X in Python
- TypeError: 'tuple' object is not callable in Python [Fixed]

Borislav Hadzhiev
Web Developer

Copyright © 2024 Borislav Hadzhiev

How to Fix the Error “Cannot Set Headers After They are Sent to the Client” in JavaScript?

How to Fix “Type ‘Null’ Is Not Assignable to Type ‘String’” in TypeScript?
How to Fix the Java “Package Does Not Exist” Error?
Recent posts.

How to Fix “ReferenceError: Variable Is Not Defined” in JavaScript?
- WooCommerce
- Webpack warning
How to Fix “TypeError: Tuple Does Not Support Item Assignment” in Python?
Did you assign a tuple to a new value and get the TypeError: tuple does not support item assignment in Python?
If you’re working with Python and you encounter the “TypeError: ‘tuple’ does not support item assignment” error, it means that you are trying to change the value of an element within a tuple, which is not possible.
When we try to update the value of an item in a tuple, Python throws the error TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment . Tuples are immutable data types, hence assigning a tuple to a variable or data causes the TypeError exception . Transforming tuples to lists or slicing them, can be helpful in preventing the TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment .
Furthermore, you can convert the tuple to a list, to make the necessary changes, and then convert the list back to a tuple to fix the problem.
In this article, we’ll discuss the TypeError: tuple object does not support item assignment in Python, why it occurs, and how to fix ⚒️it. So without further ado, let’s dive deep into the topic. Let’s go over a few examples that will show this error’s causes and possible solutions.
Table of Contents
Why does the typeerror: tuple does not support item assignment error occur, how to fix typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment in python, 1. assigning a value to the index, 2. with the use of slice operator, 3. apply list inside a tuple.
As we’ve discussed in Python, when we try to assign a new value to a tuple that causes TypeError: tuple object does not support item assignment. Let’s see an example 👇

See the above example; we have created a tuple Tuple_1 and assigned values. Then we assigned “Kelvin” at index 2 of Tuple and print the tuple that gives the TypeError: tuple does not support item assignment as we are trying to assign a value to an already created tuple.
As we have seen in the above example, we have created a tuple and assigned a value, we can convert the tuple into a list, and then we can assign values to it. To convert a tuple into a list, we utilized the list() class. In the above example, we have assigned 1.
To fix the error first we have to change the tuple to a list: we have three different alternate solutions.
- Assigning a Value to the Index
- With the Use of Slice Operator
- Apply List Inside a Tuple
We have to convert Convert the tuple into a list by using a list function and then assigning a value at any index of a list that will update any elements in the list. The final step is to convert
final list back to a tuple as shown in the following example.
In the above example, we have converted the tuple to a list, assigned “Sofia” at the index on the list, and again converted the list to a tuple and printed it.
This “Type error: tuple object does not support item assignment” can also be avoided using the slicing operator. Let’s look at how we can slice our original tuple to get a new one after omitting some elements of the tuple. You can also add an element to any index after in the tuple using the slice operator.
If one element in a tuple is listed, only on that particular index we can assign another element. But if we assign an element at the index of an element that is not a list it will generate a “Type error: tuple object does not support item assignment.” Let’s see what happens when a tuple has a list as one of its elements.
To summarize the article on how to fix the TypeError: tuple does not support item assignment , we’ve discussed why it occurs and how to fix it. Furthermore, we’ve seen that the three approaches that help fix the TypeError: ‘tuple’ object do not support item assignment , including Assigning a value to the index, With the use of slice Operator, Applying a list inside a tuple
Let’s have a quick recap of the topics discussed in this article.
- Why does the TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment occurs?
- How to fix the TypeError TypeError: tuple does not support item assignment in Python?
- Assigning a value to the index.
- With the use of slice Operator.
- Apply List inside a Tuple.
If you’ve found this article helpful, don’t forget to share and comment below 👇 which solutions have helped you solve the problem.
Happy Coding!

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Posts

How to Fix “AttributeError: ‘Str’ Object Has no Attribute ‘Decode'” in Python?

What is the Revised Simplex Method? – Intro, Python Example
How to Draw or Add a Bounding Box to an Image in Python?
How to Fix Pygame GUI Window Not Opening, Loading, or Working?
Solve Python TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
by Nathan Sebhastian
Posted on Dec 26, 2022
Reading time: 2 minutes

In Python, tuples are immutable sequences that cannot be modified once they are created. This means that you cannot change, add, or delete elements from a tuple.
When you try to modify a tuple using the square brackets and the assignment operator, you will get the “TypeError: ’tuple’ object does not support item assignment” error.
Consider the example below:
The above code tries to change the first element of the tuple from “Orange” to “Mango”.
But since a tuple is immutable, Python will respond with the following error:
There are two solutions you can use to edit a tuple in Python.
Solution #1: Change the tuple to list first
When you need to modify the elements of a tuple, you can convert the tuple to a list first using the list() function.
Lists are mutable sequences that allow you to change, add, and delete elements.
Once you have made the changes to the list, you can convert it back to a tuple using the tuple() function:
By converting a tuple into a list, you can modify its elements. Once done, convert it back to a tuple.
Solution #2: Create a new tuple
When you only need to modify a single element of a tuple, you can create a new tuple with the modified element.
To access a range of elements from a tuple, you can use the slice operator.
For example, the following code creates a new tuple by adding a slice of elements from an existing tuple:
The code fruits[1:] means you are slicing the fruits tuple to return the second element to the last.
Creating a new tuple is more efficient than converting the entire tuple to a list and back as it requires only one line of code.
But this solution doesn’t work when you need a complex modification.
The Python TypeError: tuple object does not support item assignment issue occurs when you try to modify a tuple using the square brackets (i.e., [] ) and the assignment operator (i.e., = ).
A tuple is immutable, so you need a creative way to change, add, or remove its elements.
This tutorial shows you two easy solutions on how to change the tuple object element(s) and avoid the TypeError.
Thanks for reading. I hope this helps! 🙏
Take your skills to the next level ⚡️
I'm sending out an occasional email with the latest tutorials on programming, web development, and statistics. Drop your email in the box below and I'll send new stuff straight into your inbox!
Hello! This website is dedicated to help you learn tech and data science skills with its step-by-step, beginner-friendly tutorials. Learn statistics, JavaScript and other programming languages using clear examples written for people.
Learn more about this website
Connect with me on Twitter
Or LinkedIn
Type the keyword below and hit enter
Click to see all tutorials tagged with:

Typeerror: int object does not support item assignment
Today, we will explore the “typeerror: int object does not support item assignment” error message in Python.
If this error keeps bothering you, don’t worry! We’ve got your back.
In this article, we will explain in detail what this error is all about and why it occurs in your Python script.
Aside from that, we’ll hand you the different solutions that will get rid of this “typeerror: ‘int’ object does not support item assignment” error.
What is “typeerror: ‘int’ object does not support item assignment”?
The “typeerror int object does not support item assignment” is an error message in Python that occurs when you try to assign a value to an integer as if it were a list or dictionary, which is not allowed.
It is mainly because integers are immutable in Python, meaning their value cannot be changed after they are created.
In other words, once an integer is created, its value cannot be changed.
For example:
In this example, the code tries to assign the value 1 to the first element of sample , but sample is an integer, not a list or dictionary, and as a result, it throws an error:
This error message indicates that you need to modify your code to avoid attempting to change an integer’s value using item assignment.
What are the root causes of “typeerror: ‘int’ object does not support item assignment”
Here are the most common root causes of “int object does not support item assignment”, which include the following:
- Attempting to modify an integer directly
- Using an integer where a sequence is expected
- Not converting integer objects to mutable data types before modifying them
- Using an integer as a dictionary key
- Passing an integer to a function that expects a mutable object
- Mixing up variables
- Incorrect syntax
- Using the wrong method or function
How to fix “typeerror: int object does not support item assignment”
Here are the following solutions to fix the “typeerror: ‘int’ object does not support item assignment” error message:
Solution 1: Use a list instead of an integer
Since integers are immutable in Python, we cannot modify them.
Therefore, we can use a mutable data type such as a list instead to modify individual elements within a variable.
Solution 2: Convert the integer to a list first
You have to convert the integer first to a string using the str() function.
Then, convert the string to a list using the list() function.
We can also modify individual elements within the list and join it back into a string using the join() function.
Finally, we convert the string back to an integer using the int() function.
Solution 3: Use a dictionary instead of an integer
This solution is similar to using a list. We can use a dictionary data type to modify individual elements within a variable.
In this example code, we modify the value of the ‘b’ key within the dictionary.
Another example:
Solution 4: Use a different method or function
You can define sample as a list and append items to the list using the append() method .
How to avoid “typeerror: int object does not support item assignment”
- You have to use appropriate data types for the task at hand.
- You must convert immutable data types to mutable types before modifying it.
- You have to use the correct operators and functions for specific data types.
- Avoid modifying objects directly if they are not mutable.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
You can easily resolve the error by converting the integer object to a mutable data type or creating a new integer object with the desired value.
The error occurs when you try to modify an integer object, which is not allowed since integer objects are immutable.
By executing the different solutions that this article has already given, you can definitely resolve the “typeerror: int object does not support item assignment” error message in Python.
We are hoping that this article provides you with sufficient solutions.
You could also check out other “ typeerror ” articles that may help you in the future if you encounter them.
- Uncaught typeerror: illegal invocation
- Typeerror slice none none none 0 is an invalid key
- Typeerror: cannot read property ‘getrange’ of null
Thank you very much for reading to the end of this article.

How to Solve Python TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment
by Suf | Programming , Python , Tips
Tuples are immutable objects, which means you cannot change them once created. If you try to change a tuple in place using the indexing operator [], you will raise the TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment.
To solve this error, you can convert the tuple to a list, perform an index assignment then convert the list back to a tuple.
This tutorial will go through how to solve this error and solve it with the help of code examples.
Table of contents
Typeerror: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment.
Let’s break up the error message to understand what the error means. TypeError occurs whenever you attempt to use an illegal operation for a specific data type.
The part 'tuple' object tells us that the error concerns an illegal operation for tuples.
The part does not support item assignment tells us that item assignment is the illegal operation we are attempting.
Tuples are immutable objects, which means we cannot change them once created. We have to convert the tuple to a list, a mutable data type suitable for item assignment.
Let’s look at an example of assigning items to a list. We will iterate over a list and check if each item is even. If the number is even, we will assign the square of that number in place at that index position.
Let’s run the code to see the result:
We can successfully do item assignments on a list.
Let’s see what happens when we try to change a tuple using item assignment:
We throw the TypeError because the tuple object is immutable.
To solve this error, we need to convert the tuple to a list then perform the item assignment. We will then convert the list back to a tuple. However, you can leave the object as a list if you do not need a tuple.
Let’s run the code to see the updated tuple:
Congratulations on reading to the end of this tutorial. The TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment occurs when you try to change a tuple in-place using the indexing operator [] . You cannot modify a tuple once you create it. To solve this error, you need to convert the tuple to a list, update it, then convert it back to a tuple.
For further reading on TypeErrors, go to the article:
- How to Solve Python TypeError: ‘str’ object does not support item assignment
To learn more about Python for data science and machine learning, go to the online courses page on Python for the most comprehensive courses available.
Have fun and happy researching!
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
Python Tuple does not support item assignment
5 minute read
Introduction
In Python, tuples are immutable, meaning that their elements cannot be modified once they have been assigned. This means that attempting to assign a value to an element in a tuple will result in the following error:
TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment
This error can be frustrating, but there are a few ways to work around it and achieve the desired outcome. In this article, we will explore three different ways to fix this error and give an in-depth explanation of how each method works.
Error and Cause
When attempting to reassign an item in a tuple using the indexing operator, such as:
Python will raise a TypeError, indicating that the tuple object does not support item assignment. This is because, as previously mentioned, tuples are immutable , and their elements cannot be modified once they have been assigned.
Python’s tuple is a built-in data structure that can store multiple values in a single object. This makes it useful for situations where you need to store multiple related values together.
Tuples are defined by enclosing the values in parentheses and separating them with commas. For example, the following code creates a tuple with three integers:
This tuple object, as stated before, is immutable, which means that once it is created, its elements cannot be modified. This means that you cannot add, remove, or change the values of the elements in a tuple.
This is why when you try to reassign a value to an element in the tuple using the indexing operator, such as my_tuple[0] = 4, python will raise a TypeError, indicating that the tuple object does not support item assignment.
Fix 1: Convert Tuple to List
One way to fix this error is to convert the tuple to a list, make the desired changes, and then convert it back to a tuple.
In the above example, we first convert the tuple to a list using the built-in list() function. Once the tuple is converted to a list, we can use the indexing operator to reassign the value at index 0 to 4.
Since lists are mutable, this operation is allowed. Once the desired changes have been made, we convert the list back to a tuple using the built-in tuple() function. The original tuple object is now replaced by the new tuple object which has the desired value at index 0.
It’s important to note that the original tuple remains unchanged, and the new tuple is created with the modified values. This method is useful when you want to make changes to the tuple and need to keep the original tuple object intact.
Fix 2: Using Slicing
Another way to change the values in a tuple is by using slicing. You can create a new tuple with the desired values by slicing the original tuple and concatenating the new values.
In this example, we use slicing to create a new tuple. The my_tuple[:0] slice returns an empty tuple, the (4,) creates a new tuple with the value 4, and the my_tuple[1:] slice returns a new tuple with all elements of the original tuple except the first element.
We then concatenate these three tuples using the + operator to create a new tuple with the desired values.
It’s important to note that the original tuple remains unchanged, and the new tuple is created with the modified values.
This method is useful when you want to make changes to the tuple and need to keep the original tuple object intact.
It is also worth noting that this method is the most efficient one of the three, as it only uses slicing which has O(k) time complexity where k is the number of elements in the slice.
Fix 3: Creating a new Tuple
The last fix is creating a new tuple with the desired values.
This method works similarly to the previous method, but instead of using slicing and concatenation, we create a new tuple with the desired value and concatenate it with the rest of the elements of the original tuple using the + operator.
While tuples are immutable in Python, there are a few ways to work around the ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment error. By converting the tuple to a list, using slicing, or creating a new tuple, you can achieve the desired outcome.
We hope this article was useful.
You may also enjoy
Python’s Default dict explained
4 minute read
In this article, we will explain how to use default dicts in the Python programming language. Find examples and more
C++ Undefined reference to std::cout
3 minute read
How to fix the undefined reference to std::cout in the C++ programming language. This error is usually caused by a dependency problem in the gcc compiler.
C++ Length of an Array With Examples (3 easy ways)
In this article, we will use sizeof() operator, for loop method and the std::size function to determine the length of any C++ array. We will provide examples
C++ Convert Int to String
1 minute read
How to convert an int to a string in C++, we will be using the to_string, stringstream and sprintf functions from the std library. Easiest methods to convert

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To avoid inheritance from dict, you can make a class inherit from MutableMapping, and then provide methods for __setitem__ and __getitem__. Additionally, the class will need to support methods for __delitem__, __iter__, __len__, and (optionally) other inherited mixin methods, like pop. The documentation has more info on the details.
3. You don't have any code in the class that allows for item assignment. For an object to allow item assignment, it needs to implement __setitem__. You would need something like: class MyList: def __init__(self,list): self.list=list. def __setitem__(self, i, elem): self.list[i] = elem.
Does "Tuple Object Does Not Support Item Assignment" Apply to a List inside a Tuple? Let's see what happens when one of the elements of a tuple is a list. >>> values = (1, '2', [3]) If we try to update the second element of the tuple we get the expected error:
Marcus Greenwood Hatch, established in 2011 by Marcus Greenwood, has evolved significantly over the years. Marcus, a seasoned developer, brought a rich background in developing both B2B and consumer software for a diverse range of organizations, including hedge funds and web agencies.
If the variable stores a None value, we set it to an empty dictionary. # Track down where the variable got assigned a None value You have to figure out where the variable got assigned a None value in your code and correct the assignment to a list or a dictionary.. The most common sources of None values are:. Having a function that doesn't return anything (returns None implicitly).
typeerror: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment. While tuples and lists both store sequences of data, they have a few distinctions. Whereas you can change the values in a list, the values inside a tuple cannot be changed. Also, tuples are stored within parenthesis whereas lists are declared between square brackets.
Python indexes are zero-based, so the first item in a list has an index of 0, and the last item has an index of -1 or len(a_list) - 1. # Checking what type a variable stores. The Python "TypeError: 'float' object does not support item assignment" is caused when we try to mutate the value of a float.
TypeError: 'str' Object Does Not Support Item Assignment in Pandas Data Frame The following program attempts to add a new column into the data frame import numpy as np import pandas as pd import random as rnd df = pd.read_csv('sample.csv') for dataset in df: dataset['Column'] = 1
greet[0] = 'J'. TypeError: 'str' object does not support item assignment. To fix this error, you can create a new string with the desired modifications, instead of trying to modify the original string. This can be done by calling the replace() method from the string. See the example below: old_str = 'Hello, world!'.
Once we have a list, we can update the item at the specified index and optionally convert the result back to a tuple. Python indexes are zero-based, so the first item in a tuple has an index of 0, and the last item has an index of -1 or len(my_tuple) - 1. # Constructing a new tuple with the updated element Alternatively, you can construct a new tuple that contains the updated element at the ...
To convert a tuple into a list, we utilized the list() class. In the above example, we have assigned 1. ... This "Type error: tuple object does not support item assignment" can also be avoided using the slicing operator. Let's look at how we can slice our original tuple to get a new one after omitting some elements of the tuple.
There are two solutions you can use to edit a tuple in Python. Solution #1: Change the tuple to list first. When you need to modify the elements of a tuple, you can convert the tuple to a list first using the list() function.. Lists are mutable sequences that allow you to change, add, and delete elements.. Once you have made the changes to the list, you can convert it back to a tuple using the ...
How to Solve Python TypeError: 'str' object does not support item assignment; How to Solve Python TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment; To learn more about Python for data science and machine learning, go to the online courses page on Python for the most comprehensive courses available. Have fun and happy researching!
The TypeError: 'set' object does not support item assignment occurs when you try to change the elements of a set using indexing. The set data type is not indexable. To perform item assignment you should convert the set to a list, perform the item assignment then convert the list back to a set.
5. Strings in Python are immutable (you cannot change them inplace). What you are trying to do can be done in many ways: Copy the string: foo = 'Hello'. bar = foo. Create a new string by joining all characters of the old string: new_string = ''.join(c for c in oldstring) Slice and copy:
Here are the most common root causes of "int object does not support item assignment", which include the following: Attempting to modify an integer directly. Using an integer where a sequence is expected. Not converting integer objects to mutable data types before modifying them. Using an integer as a dictionary key.
List. List is a collection of objects, represented in square brackets. mylist = [1, 2, "a", True] Lists can be used for storing objects with any data type or a mixture of data types. Lists are mutable. We can add new items to a list or delete the existing ones.
Tuples are immutable objects, which means you cannot change them once created. If you try to change a tuple in place using the indexing operator [], you will raise the TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment. To solve this error, you can convert the tuple to a list, perform an index assignment then…
array[0][0] = 0*0 >> TypeError: 'int' object does not support item assignment Since array[0] is an integer, you can't use the second [0]. There is nothing there to get. So, like Ashalynd said, the array = x*y seems to be the problem. Depending on what you really want to do, there could be many solutions.
Python will raise a TypeError, indicating that the tuple object does not support item assignment. This is because, as previously mentioned, tuples are immutable, and their elements cannot be modified once they have been assigned.. Python's tuple is a built-in data structure that can store multiple values in a single object.
But, I come to know that the feature of mutable arrays are not yet implemented in dask arrays so I am getting NotImplementedError: Item assignment with <class 'tuple'> not supported Is there any workaround for my code below-