

Paytm Case Study: The Journey of India's Leading FinTech Company

Devashish Shrivastava
Paytm is India's one of the biggest fintech startups founded in August 2010 by Vijay Shekhar Sharma. The startup offers versatile instalments, e-wallet, and business stages. Even though it began as an energizing stage in 2010, Paytm has changed its plan of action to become a commercial centre and a virtual bank model. It is likewise one of the pioneers of the cashback plan of action.
Paytm has changed itself into an Indian mammoth managing versatile instalments, banking administrations, commercial centre, Paytm gold, energize and charge installments, Paytm wallet and many other provisions which serve around 100 million enlisted clients.
The areas served by Paytm are India, Canada, and Japan, it is also accessible in 11 Indian dialects . It offers online use-cases as versatile energizes, service charge installments, travel, motion pictures, and occasions appointments. In-store instalments at markets, leafy foods shops, cafés, stopping, tolls, drug stores and instructive establishments can be accessed through the Paytm QR code.
One 97 Communications, the parent company of Paytm, is all set to raise its capital target of over ₹16,600 crores ($2.2 billion) through an IPO that it had filed earlier in July 2021. Paytm is seeking to raise $25 billion to $30 billion valuation post this IPO.
According to the organization, more than 7 million traders crosswise over India utilize its QR code to acknowledge instalments straightforwardly into their bank account. The organization uses commercials and pays a special substance to produce income. Let's look at this detailed case study on Paytm to know more about its growth and future plans.
Paytm - Latest News Origin of Paytm Business Model of Paytm Business Growth of Paytm Expected Future Growth of Paytm Why was Paytm Removed from Google Play Store?
Paytm - Latest News
1st November 2021 - The much-awaited Paytm IPO was launched with a price band of ₹ ₹2,080-2,150 per share.
13th October 2021 - Paytm users can now store Aadhaar, driving license, vehicle RC, insurance via Digilocker. Digilocker Mini App on Paytm offers access to these documents to users even when they're offline or in a low connectivity zone.
8th October 2021 - Paytm is looking forward to bringing in sovereign wealth funds as anchor investors in the company's pre-IPO placement.
5th October 2021 - Switzerland-based insurance giant, Swiss RE might join Paytm's insurance business' board.
3rd October 2021 - Paytm has acquired 100% stakes in CreditMate, a Mumbai-based digital lending startup.
Origin of Paytm
The saga and the emergence of Paytm are discussed in this section of the case study of Paytm. It was established in August 2010 with underlying speculation of $2 million by its originator Vijay Shekhar Sharma in Noida, an area nearby India's capital New Delhi .
It began as a prepaid portable and DTH energize stage, and later included information card, postpaid versatile and landline charge installments in 2013. By January 2014, the organization propelled the Paytm pocketbook, and the Indian Railways and Uber included it as an installment option.

It propelled into web-based business with online arrangements and transport ticketing.
In 2015, it disclosed more use-cases like instruction expenses, metro energizes power, gas, and water charge installments. Paytm likewise began driving the installment passage for the Indian Railways.
In 2016, Paytm propelled motion pictures, occasions, and entertainment meccas ticketing just as flight ticket appointments and Paytm QR. Later that year, it propelled rail bookings and gift vouchers . Paytm's enrolled client base developed from 11.8 million in August 2014 to 104 million in August 2015. Its movement business crossed $500 million in annualized GMV run rate, booking two million tickets for each month.
In 2017, Paytm became India's first installment application to traverse 100 million application downloads. That year, it propelled Paytm Gold, an item that enables clients to purchase as meagre as ₹1 of unadulterated gold on the web . It additionally propelled the Paytm Payments Bank and 'Inbox', and informing stage with in-talk installments among other products.
By 2018, it began enabling dealers to acknowledge Paytm UPI and card installments straightforwardly into their financial balances at 0% charge. It likewise propelled the 'Paytm for Business' application, enabling traders to follow their installments and everyday settlements instantly. This drove Paytm's shopper base to more than 7 million by March 2018.
The organization propelled two new riches—Paytm Gold Savings Plan and Gold Gifting—to rearrange long haul savings. It propelled into diversion and speculations, and stripe alongside AGTech to dispatch the stage of a transportable game Gamepind, and putting in Paytm cash with a venture of ₹9 large integers to bring venture and riches as board items for Indians. In May 2019, Paytm joined forces with Citibank to dispatch credit cards .
Business Model of Paytm
Paytm or "Payment Through Mobile" is India's biggest installment, trade, and e-wallet undertaking. It began in 2010 and is a brand of the parent organization One97 Communications, established by Vijay Shekhar Sharma. It was propelled as an online portable energize site and proceeded to change its plan of action to a virtual and commercial centre bank model.
The organization stands today as one of India's biggest online portable administrations that incorporates banking administrations, commercial centres, versatile installments, charge installments, and energize. It has so far given administrations to more than 100 million clients.
Paytm's enhancement has built a solid reputation and has turned out to be praiseworthy for some in the online installment industry. One of its increasingly vital accomplishments is in its joint effort with the Chinese web-based business Goliath, Alibaba for immense measures of subsidizing.
Aside from being a pioneer of the cashback plan of action, the organization has been commended for its introduction as a new business able to build huge partnerships in a limited time period.
Clients of Paytm Business
Paytm's core focus is on serving its Indian client base, especially the cell phone clients. Numerous Indian clients saw the computerized world as an opportunity to open a financial balance. Accessing simple online installments missed the mark, and clients wound up with only poor experience. Paytm presented itself as a superior option to deal with such situations.
Paytm Offers
A portion of Paytm's increasingly conspicuous suggestions was reviving the business which was the organization's underlying administration recommendation.
At that point, it proceeded to differentiate and progressed to creating more current administrations from any semblance of Paytm Wallet, E-business vertical to Digital Gold.
These improvements were appreciated in the form of the Chinese mammoth Alibaba's favours. Immense totals of cash were pumped into Paytm by Alibaba, expanding Paytm's speculation potential. Paytm used cricket and TV promotion to capture more clients.
Relationship with Clients

Paytm has a 24*7 client care focus to interface with its clients. Simultaneously, the vast majority of Paytm administrations are self-served in nature and are open through their foundation straightforward.
Paytm's Channel for Business
Paytm utilizes numerous channels to draw in clients. Aside from its very own site which drives clicks, Paytm has shaped associations with numerous customers and seller destinations that support its endeavour. Demonetization in India enabled the organization to succeed altogether and arrive at new clients too. Disconnected advertising is likewise a piece of their client procurement process.
Distinct Advantages
The RBI (Reserve Bank of India) permit fills in as Paytm's fundamental asset. It should be explicit to Paytm. Different assets like the plan/programming society make it simpler for lower-pay Indians to use Paytm.
Paytm, being an innovation stage, dangers perils, for example, security and misrepresentation which is the reason it needs to take viable measures in ensuring its buyer's cash by improving its security. It is likewise rolling out new improvements inside its foundation to draw in new clients and access their computerized wallets.
Partners of Paytm
Paytm accomplices with the banks that give it installment excursions into the financial framework just as escrow administrations. It works together with a heap of associations that accumulate bills and installments from its customers for its administration.
Structure of Costing
Paytm serves numerous clients which is the motivation behind why it is so cost-driven. The vast majority of its costs are identified with its foundation and client obtaining. It's a typical cost-shared by numerous organizations over the reality where client securing cost is significant.
The cash utilized in this procedure is higher than the income it makes in its underlying buys. Most of its financial limit is to put resources into sloping up of its security and stay away from the danger of misrepresentation, particularly when it needs to deal with more than 65 million clients in its foundation. It incorporates a framework that empowers clients to avoid any tax evasion hazard .
Revenue Model of Paytm
The Paytm revenue models come in two structures. Paytm makes commissions from the client exchanges through their utilization of its foundation. Escrow Accounts are the accounts from where it creates their income. Inferable from the non-appearance of its hidden capital, it offers clients no intrigue. Starting in 2018 Paytm has aggregated 3314.8 crore INR in income.
Paytm Wallet

Paytm wallet is one of Paytm's best benefits that structures a connection between the bank and the retailers. This semi-shut wallet empowers you to take care of your tabs, pay for your tickets, or pay anyone concerned.
Paytm wallet separated from its profit, as approved by the RBI, has the advantage of accepting enthusiasm for a purchaser store, much the same as some other Payment Gateways .
When you store a specific measure of cash in your Paytm wallet, it will at that point set aside that cash in another bank from which it will win enthusiasm eventually.
It is the Paytm wallet's fundamental capacity. For instance, suppose you make an installment of Rs. 1000 to a merchant and the vendor makes 10 exchanges to increase Rs. 10,000. If the installment of that sum is made through the Paytm wallet, the Paytm wallet will take a portion of about 1% of the aggregate sum. So the merchant will get around Rs. 9715.
Mobile Recharge Business

Since its origin in 2010, Paytm's underlying intention was to give online portable energizing administrations. Its capacity to create income was constantly shortsighted. Paytm's administration guidelines are as praiseworthy and proficient as those of other telecom specialist co-ops running from Vodafone to Telecom.
The administrations are without shortcomings and give solace to their clients. As of now, Paytm increases a commission of 2-3% per energize. It is because Paytm, attributable to its support to its client to keep reviving through its foundation, has more grounded power in dealing than different merchants. That is the reason the commission it obtains is so high. This commission from its revive administration fills in as its income.
These administrations have supported the organization essentially in extending its base and thus, developing exponentially. When the client is fulfilled by the administration or item, he makes an arrival to a similar undertaking in this manner. This way Paytm does client maintenance and produces more traffic . Paytm has used this methodology to further its potential benefit and keeps on reaping positive results.
Paytm Digital Gold Paytm Digital Gold

Inferable from its organization with MMTC-PAMP, the outstanding gold purifier, Paytm has propelled "Computerized Gold". This model enables clients to sell, purchase, or store gold in an advanced stage. Presently, clients need to pay at a rate just to get their gold conveyed to their families.
Paytm is very much aware of how much gold is put as a resource in India and is completely arranged to develop from this chance. The organization has made eminent arrangements to urge its clients to get their own Gold Bank Accounts individually. This record separated from empowering clients to purchase their gold will likewise furnish clients with simple access to other Paytm administrations.
In February 2017, Paytm propelled its Paytm Mall application which enables purchasers to shop from 1.4 lakh enrolled sellers. Paytm Mall is a B2C model enlivened by the model of China's biggest B2C retail stage, TMall. For 1.4 lakh merchants enlisted, items need to go through Paytm-guaranteed stockrooms and channels to guarantee buyer trust.
Paytm Mall has set up 17 satisfaction focuses crosswise over India and joined forces with 40+ messengers. Paytm Mall raised $200 million from Alibaba Cluster and SAIF Partners in March 2018. In May 2018, it posted losses of roughly Rs 1,800 crore with an income of Rs 774 crore for money related to the year 2018. Moreover, the piece of the pie in Paytm Mall dropped to 3% in 2018 from 5.6% in 2017.

Business Growth of Paytm
Advanced installments organization Paytm has professed to arrive at gross exchange esteem (GTV) of over $50 billion, while checking 5.5 billion exchanges in FY19. The Delhi NCR-based organization credited this development to the rising appropriation of Paytm over numerous utilization cases, for example, retail installments, expenses, utility installments, travel booking , excitement, games among others. It has as of late propelled membership-based prizes program (Paytm First) to aid development alongside expanding the client maintenance.
Discussing the feasible arrangements, senior VP of Paytm, Deepak Abbot stated, "We are centred around creating tech-driven arrangements, incorporated client lifecycle the board, upgrading the client experience and growing to Tier 4-5 urban communities. We are certain to accomplish 12 Bn exchanges before the part of the bargain year." Before a month ago, the Ministry Of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) had solicited Paytm to help its objective of encouraging 40 Bn advanced exchanges in FY20.
The organization shared designs to incorporate man-made brainpower in its model and achieve 2x development this year. Paytm professed to possess half piece of the installment entryway industry in India, with 400 Mn month to month exchanges on the stage.
Established by Vijay Shekhar Sharma in 2010, Paytm furnishes various new companies and huge organizations with arrangements running from a shareable PaytmQR code to profound coordination.
It empowers clients to process computerized installments through any favoured installment mode including credit and check cards, net banking, Paytm wallet, and UPI (bound together installment interface). Paytm had likewise propelled its very own installments bank in 2017.
Paytm Payments Bank is versatile first keep money with zero charges on every online exchange, (for example, IMPS, NEFT, RTGS) and no base equalization prerequisite. For investment accounts, the bank right now offers a loan cost of 4% per annum.
Expected Future Growth of Paytm
Computerized installments organization Paytm said it is looking to dramatically increase its exchange volume to 12 billion by part of the arrangement, from 5.5 billion out of 2018-19.
Paytm checked 2.5 billion exchanges in 2017-18. Paytm said it accomplished gross exchange esteem (GTV) of $50 billion out of 2018-19, as contrasted and $25 billion every year prior. GTV is the estimation of all-out exchanges done on the stage.
"This expansion is a consequence of the fast development in the reception of Paytm's computerized installments arrangements crosswise over on the web and disconnected for different use cases including retail installments, charges, utility installments, travel booking, amusement, games and that's only the tip of the iceberg,"
The organization said in an announcement. Its membership-based program Paytm First was propelled in March has pulled into equal parts a million supporters, the organization added.
Paytm has 350 million enrolled clients starting on 5 June, an organization authority said. Paytm offers a variety of installment alternatives that incorporate installment through portable wallets, just like ongoing installment framework Unified Payments Interface (UPI) and web banking.
The organization has been centred around structure instruments for dealers to streamline their everyday business needs. This has brought about enormous dealers obtaining who are very much furnished with innovation to acknowledge all installment modes (cards, wallet, and UPI). Paytm now intends to concentrate on embracing computerized reasoning and improving the UI .
Why was Paytm Removed from Google Play Store?
Paytm India app was removed from Google Play Store because it violated Google guidelines. While other apps like Paytm for Business, Paytm mall , Paytm Money, and a few more were still available. But after a few hours of being taken down, the Paytm app was back on Google Play Store.
#Paytm out of Google Play Store. Google: We don’t allow online casinos/support any unregulated gambling apps that facilitate sports betting. It includes if app leads consumers to an external website that allows them to participate in paid tournaments to win real money/cash prizes pic.twitter.com/poeZzXw5nA — CNBC-TV18 (@CNBCTV18Live) September 18, 2020
“We have these policies to protect users from potential harm. When an app violates these policies, we notify the developer of the violation and remove the app from Google Play until the developer brings the app into compliance. And in the case where there are repeated policy violations, we may take more serious action which may include terminating Google Play Developer accounts. Our policies are applied and enforced on all developers consistently,” Google Added.
Is Paytm a fintech company?
Yes, Paytm is India's leading and one of the most valued fintech startups founded by Vijay Shekar Sharma in 2010.
What are the areas served by Paytm?
Paytm is a leading fintech startup that not only operates in India but it also serves Canada and Japan.
When was Paytm established?
Paytm was founded in 2010 by Vijay Shekar Sharma.
What is Paytm and how does it work?
Paytm is a leading financial service and bill payments app that offers financial solutions to its customers, offline merchants and online platforms. All you need to do is open the Paytm app on your phone, click on 'Pay', and select 'QR code'. Scan the QR code of the receiver and enter the amount to be paid. The money will be transferred in a few seconds.
How much does Vijay Shekhar Sharma own in Paytm?
Vijay Shekhar Sharma currently owns 14.61% of the company.
Must have tools for startups - Recommended by StartupTalky
- Convert Visitors into Leads- SeizeLead
- Payment Gateway- Razorpay
- Spy on your Competitors- Adspyder
- Manage your business smoothly- Google Workspace
Most Valuable IPL Teams 2024
The Indian Premier League (IPL) is one of the most high-profile cricket leagues in the world, known for its star-studded lineups, and thrilling matches. However, the league's significance goes beyond just sporting entertainment. With teams representing significant cities and corporate giants, the IPL has evolved into a massive business venture,
Reddit’s IPO Fever Is Rising High
The year 2005 saw the launch of Reddit, an online community and message board. Over 100,000 distinct neighborhoods/communities (Subreddits) make up Reddit's infrastructure; each has its own lingo, culture, customs, and set of rules—written and unwritten alike. In these communities, people build their own neighborhoods and also
The Economic Impact: How IPL Is Shaping BCCI's Finances
Since its start, the 17th edition of the Indian Premier League (IPL), an idea of the Board of Control for Cricket in India (BCCI), has captivated spectators. The value of the Indian Premier League (IPL), one of the world's most popular sports competitions, increased by nearly 28 percent to a
Navigating the Storm: Mental Health Challenges in the Startup World
In the fast-paced and ever-evolving landscape of startups, where innovation meets ambition, lies a silent struggle often overlooked - the mental health of entrepreneurs. At StartupTalky, we're diving into a crucial yet often overlooked issue: the mental health hurdles faced by startup founders. The relentless pressure to succeed, coupled with
- Revolutionizing Digital Communication: The Power of Olly and AI
- AI-Powered Video Editing with Snapy.ai: The Future of Content Creation is Here
- Dawn of AI-Powered Video Editing: Transform Your Videos with Silence Remover Online
- The Dawn of Generative AI: Why and How to Adopt it for your Business
- Harnessing the Power of Generative AI for Business Innovation: An Exclusive Consultancy Approach
Original content with a single minded focus on value addition.

Case study: The Journey of Paytm
With this piece, we’ll try to understand the case study of Paytm, which will explain how the brand went from being a mere recharge app back in 2010, to hosting everything as of today. This case study also explains the current difficulties of Paytm given the increasing competition and the loss of interest of the investors.
Started by Vijay Shekhar Sharma, as a Recharge platform in 2010, Paytm (One 97 Communications Ltd) became the most successful mobile payment and money transfer app used in India a few years back. For a country which had 95% of monetary transactions made in cash prior to demonetization , it was difficult for Paytm to make customers believe in digital money. But, Paytm did the drill, they tapped the un-served/under-served lots of India and enabled them to do cashless transactions. And, by the means of cashbacks and offers, Paytm raced ahead of its then rivals – Freecharge, PayU, Mobikwik, etc.

However, the picture seems to be changing today. After the entry of players like Google Pay & PhonePe, the brand is starting to fall behind in the race . And given the poised release of WhatsApp Pay somewhere this month (June, 2020), things are only going to be tougher for the company. Let us understand the journey of Paytm to essentially understand their position today.
Business Aspects and Expansion:
Paytm has always focused on the customer-centric approach. This is evident from that fact that, even before Paytm started with wallet services, the company built a 24×7 customer care service. It understood that digital payments were still new in India and so, it had to ensure their customers get all the right support. This enabled people to get their queries solved and trust their money with Paytm. It has spent nearly Rs.14,500 crore to convince Indians to substitute cash with digital payments . One can clearly understand how Paytm must have pivotal role in our Hon. Prime Ministers’ Digital India dream.
In 2014, the company did one of their major launches – that is the Paytm Wallet. This enabled the users to directly pay without entering an OTP again and again. Which was again new for the customers, given they thought using OTP kept their money safe. Now, one might think this to be the wrong move. However, this was one of the features that gave Paytm the best results. When a user kept its money in the Paytm wallet, they were not charged. However, Paytm kept the money with Escrow accounts which fetched Paytm interests.
Demonetization – An opportunity for Paytm:
Anyway. Let’s continue, and understand when the future actually started to look fortunate for Paytm. We’d all remember Demonetization, don’t we? Ah, those long ATM hours, lots of money with not value. Those were the days.
While demonetization spelled doom for most of us, it was actually a fortune for Paytm, and we don’t need to tell you why. Or do we? Okay. So, our Hon. Prime Minister had a vision to turn the economy digital. Digital could help the Government track the money and essentially reduce the influx of black money in the economy.
Now, Paytm was the biggest digital payments app back then. And so, when the demonetization happened, it went through the roofs! It extended services to retail stores, Kiranas, Vegetable shops, Saloons, even Pan shops! It was everywhere! Paytm grabbed the biggest piece of all the online payments happening during that period.
Given the progress Paytm was making and the amount of Government support they were enjoying, it got into aggressive marketing which showcased the involvement of retail shop owners.
Anyway, that was a time to be remembered both for us and Paytm, alike.
The pain-points:
All the good stuff probably ended in the paragraph above, let us now try to understand the challenges the brand has faced in the recent past.
Paytm vs PayPal:
While Paytm was busy counting its profits after Demonetization, a US-based payments company PayPal filed a case against Paytm for using a logo similar to its own. They look pretty similar, PayPal was probably right.

PayPal accused Paytm of using the similar logo which it had been using since 2007. This would create confusion in Indian customers about the platform. The case is still in court and if Paypal wins, Paytm would have to pay heavy charges for trademark infringement.
UPI (Unified Payments Interface):
With the launch of Unified Payments Interface, two major giants – Google Pay and PhonePe entered the market and people preferred UPI transactions over Paytm wallet transactions. To keep up the race, Paytm also launched BHIM UPI transaction mode but recorded lower transactions than its rivals.
Do you know why?
FMA. The first mover advantage. Paytm probably thought that their wallets will sustain them against these players, which was nice, in theory. We all would remember, right? Google Pay actually went rogue with the middle class of the country, do you remember your friends telling you to send some cash just to gain some extra bucks in the transaction?
Little did you understand that you were actually getting used to using Google Pay, smart. Use less money in marketing and instead give that away to the customers!
Current picture:
Paytm has been losing ground to its competitors with bigger pockets. To add salt to the injury, the Jio-Facebook deal is posing enormous threat to the company. Jio has already started on-boarding local shops on their platform. Who will then essentially host motivate these owners to use Facebook’s WhatsApp Pay, poised to launch in June, 2020.
Given that WhatsApp has around 400 million users in India, integrating payment here would make it convenient for the users to just send money. And, essentially, inconvenient for Paytm. This has raised concerns amongst investors about Paytm’s total valuation and business model. With the losses mounting up, it would be difficult for Paytm to keep its head above the water and continue the trust of its investors.
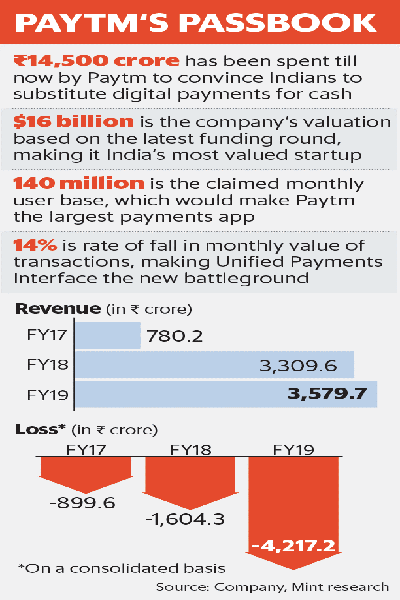
Classic example of why you must choose your niche. If you have ever used Paytm, you will realize that the company actually tried to expand into a lot of spaces. It tried to have movie bookings, travel, bill payments, shopping deals, banking and finance (Paytm banks) and what not! Maintaining so much requires equal amount of capital, and having concerned investors on board will not make that happen for you.
Anyway, that’s it for this piece. This brilliant piece was penned down by Geeta Belani , go drop her a thank. Share this piece with your best friend, and share your thoughts as to what Paytm can do to improve their stance as of right now?
Have a good one!
- Trump vs Twitter: The Content Moderation Game
- BCG Matrix with examples of 4 popular brands
You May Also Like

The Power of Packaging ft. Coca Cola packaging

MTV Case study: India’s beloved youth channel

Indian Deodorant Industry: How FOGG changed the game?
8 thoughts on “ case study: the journey of paytm ”.
Pingback: COVID-19: Bane for the World, Boon for EdTech in India | CaseReads
Pingback: Concepts at ease: What are Neobanks? | www.casereads.com
Pingback: Neobanks In India: Understanding What Are Neobanks?
Pingback: Wirecard Scandal Explained: A Modern-day Hera Pheri
Pingback: The Resurgence Against The App Store Monopoly
Pingback: FinTech In India And The World: Evolution, Impact, And Uses
Pingback: Idea Cellular Case Study: From Idea To Vi
Pingback: The 101 Of Consumer Promotions With Examples
Comments are closed.

Charteredpedia
Home Blog Finance Paytm: A Case Study
Paytm: A Case Study
- By CA Aman Rajput
- Published February 7, 2024

Paytm, the name synonymous with digital payments in India, isn’t simply a platform, it’s a saga woven into the fabric of the nation’s remarkable fintech revolution.
In this article, we delve into the intricate details of Paytm’s journey, from its humble beginnings as a mobile recharge platform to its current multifaceted identity as a “super app.” We dissect its strategic triumphs, market challenges, and enduring impact on the Indian financial landscape, unveiling a story that inspires, intrigues, and challenges.
A Vision to Recharge a Nation
2010: Birth of an Idea: To change the picture of India’s nascent mobile market in 2010, highlighting the pain points faced by users – cumbersome and unreliable methods for recharging prepaid accounts, Vijay Shekhar Sharma, a visionary entrepreneur identified this gap and entered into fintech industry and launched Paytm, a simple yet revolutionary mobile recharge platform.
Early Growth and Marketing: Paytm’s initial growth trajectory, fueled by its user-friendly interface, aggressive marketing campaigns (remember the jingle? Paytm karo), and the burgeoning smartphone penetration in India. The key decisions and strategies that catapulted Paytm to become a household name, capturing a significant share of the mobile recharge market.
Beyond Recharge: Expanding Horizons: Sooner Paytm’s moved beyond mere recharge, venturing into bill payments, online movie tickets, and e-commerce. We delve into the rationale behind these strategic expansions, the challenges encountered, and the impact on user adoption and brand perception.
Demonetization – A Catalyst for Transformation
2016: The Cash Crunch and Opportunity Knocks: The game-changing demonetization move by the Indian government, highlighted the immediate cash shortage and ensuing chaos which impacted traditional payment methods and the sudden surge in demand for digital alternatives.
Paytm’s Rise to Prominence: Let’s delve into Paytm’s strategic response to demonetization, focusing on its aggressive offline merchant onboarding strategy through innovative technologies like QR codes and Soundbox devices. It quantified the surge in user adoption, transaction volume, and Paytm’s market dominance during this period.
Financial Inclusion Champion: Paytm’s impact on financial inclusion, brings millions of unbanked and underbanked individuals into the formal financial system. Even Haward showcases case studies, statistics, and testimonials to illustrate how Paytm empowered rural populations and contributed to economic growth.
From Payments to a Super App – The Evolution Continues
Beyond Transactional: The Super App Vision: Paytm’s ambitions beyond mere payments, and its strategy to evolve into a “super app” offering a comprehensive suite of financial services like wealth management, insurance, and credit. The motivations behind this diversification, the value proposition for users, and the operational challenges encountered.
Partnerships and Acquisitions: Paytm’s strategic partnerships with industry giants like Alibaba and Walmart, explore the access to resources, expertise, and market reach these collaborations facilitated. Also, key acquisitions were undertaken by Paytm and their impact on its super app vision.
Navigating Regulatory Landscape: The complex regulatory environment surrounding digital payments in India, the evolving compliance requirements, and Paytm’s efforts to navigate this landscape many instances of regulatory scrutiny faced by Paytm, will discuss the recent Paytm payments Bank Ltd case soon along with its mitigation strategies.
The Competitive Arena – Challenges and Battles for Supremacy
Emerging Rivals: Today intense competition Paytm faces from players like PhonePe, Google Pay, and Amazon Pay, analyzing their strengths, weaknesses, and market strategies. delving into the ongoing battle for market share and the innovative tactics employed by each player.
Data Privacy Concerns: addressing the data privacy concerns raised against Paytm, understanding the nature of the allegations, the impact on user trust, and Paytm’s initiatives to address these concerns, the discussions on the evolving data privacy regulations in India and their potential impact on Paytm’s operations.
Merchant Onboarding Practices: Let’s analyze the criticism directed towards Paytm’s merchant onboarding practices, including allegations of unfair terms and aggressive tactics. Exploring the impact on merchant relationships and Paytm’s efforts to improve its practices.
The Road Ahead – Innovation, Data Security, and Regulatory Harmony
Emerging Technologies: analyzing the impact of emerging technologies like blockchain on the future of digital payments and exploring how Paytm can leverage these technologies to maintain its competitive edge along with the potential challenges and opportunities associated with blockchain
Data Security and User Trust: emphasizing the crucial role of data security in maintaining user trust and exploring the advanced security measures Paytm can implement to ensure data privacy and protection and the importance of transparency and user education in building trust within the digital payments ecosystem.
Regulatory Harmony: The need for a balanced regulatory environment that fosters innovation while ensuring financial stability exploring the potential collaborative efforts between fintech players, regulators, and policymakers to create a conducive environment for growth.
Sustainable Growth and Financial Inclusion: Paytm’s future roadmap focuses on its continued commitment to financial inclusion for underserved populations with potential strategies like micro-loans, savings instruments, and partnerships with financial institutions to expand financial access.
Paytm Payments Bank and the RBI Crackdown
On January 31, 2024, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) imposed significant restrictions on Paytm Payments Bank Ltd. (PPBL), effectively halting most of its operations. This action resulted in:
- Suspension of deposits: PPBL cannot accept any new deposits from customers.
- Halt on credit transactions: The bank cannot provide loans or engage in any other credit-related activities.
- Restriction on top-ups: Existing customers cannot add money to their wallets, prepaid instruments, or cards used for road toll payments.
- Other impacted services: Services like bill payments and certain types of fund transfers are also affected.
This action by the RBI stemmed from concerns about money laundering and non-compliance with KYC (Know Your Customer) norms .
Reports indicate:
- Millions of wallets linked to PPBL were inactive, raising concerns about their legitimacy.
- Thousands of accounts were linked to single PAN cards, violating regulations.
- The bank reportedly mishandled KYC compliance and submitted false information to the RBI.
Following these findings, the RBI took progressive actions:
- March 2022: RBI barred PPBL from onboarding new customers and mandated an IT audit.
- October 2023: A fine of ₹5.39 crore was imposed for continued KYC non-compliance.
- January 2024: The final restrictions were imposed, essentially halting most banking operations.
Current Status:
- PPBL is appealing the RBI’s decision and attempting to rectify the identified issues.
- Existing customers can still access their existing funds but cannot add more money.
- The future of PPBL remains uncertain, and its ability to resume full operations depends on addressing the RBI’s concerns to their satisfaction.
Points to Remember:
- This case highlights the importance of KYC compliance and adherence to regulations in the financial sector.
- The RBI takes financial irregularities seriously and will act to protect consumers and the integrity of the financial system.
- The future of PPBL remains unclear, and the situation is developing.
Conclusion – A Legacy of Inspiration and Transformation
We paint a hopeful picture of Paytm’s future by reviving soon, drawing upon its learnings, strengths, and commitment to innovation. We express optimism for its continued contribution to shaping a more inclusive and empowered financial ecosystem for India and beyond.
Source: Paytm annual report and RBI website
SHARE THIS POST

Anticipated Changes in the Indian Interi...
Tax tribunal approves registration for c....

Everything About Budget 2024

Best Book to read for every CA Student
Join the newslatter, you willl receive your updates and post in your mailbox.
CA Aman Rajput
Phonepe launches indus appstore developer platform, offering developers a localized alternative to google play.
About PhonePe and Indus Appstore: PhonePe is India’s largest payments…
Clarifying Taxation on Corporate Expenditure: Analysis
Introduction Taxation laws often present complex scenarios, especially concerning corporate…
Income Tax Department Identifies Discrepancies in ITRs: Analysis
The Income Tax Department of India has identified discrepancies between…
Add a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Charteredpedia – The finance professional’s portal
Quick Links
Subscribe To Our Email
For latest news & updates.
©2022 Charteredpedia – All Rights Reserved
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Condition

Paytm Case Study: The Journey of India’s Leading FinTech Company
- Post author: StockPe
- Post published: May 26, 2023
- Post category: Uncategorized
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Financial Technology popularly termed as Fintech sector has flourished exponentially after the demonetization in 2016. According to a report, India’s Fintech industry was valued at US $50 billion in 2021 and is expected to reach the value of US $150 billion by 2025 . And if we talk about the leading players in the industry, Paytm comes to the top of the list unarguably.
Paytm is India’s leading financial services platform offering digital payments ranging from mobile recharge to bill payments (credit cards, DTH, electricity and utility bills). Along with traditional mobile banking, Paytm also acts as a gateway for ticket booking (IRCTC, IPL, etc.) and offers e-commerce services as well. Along with India, Paytm is operable in Japan and Canada and is also available in 11 Indian languages, serving more than 350 million registered users.
In this Paytm case study, we have covered the growth story of Paytm from being just one of the online platforms for recharge payments to becoming a lead disruptor of India’s fintech sector.

Paytm – O rigin & Journey
Although Paytm was founded by Vijay Shekhar Sharma in 2010 in the NCR region of New Delhi, Noida, in actual terms, it started way before. Vijay Shekhar Sharma launched One97 Communications, the parent company of Paytm back in 2000. Paytm started as a normal mobile recharge website and over time it also introduced DTH recharges and landline bill payments.
A quick timeline of Paytm’s journey is given:
2010 : Paytm was launched as a mobile recharge platform
2013 : Paytm added DTH Recharge, Data Card, and Landline bill payments
2014 : Paytm launched Gateway Payments for IRCTC and Uber
2015 : Paytm became India’s first Fintech unicorn after funding from Alibaba Group and Ratan Tata
2016 : Paytm introduced the Payments Bank
2017 : After demonetisation, Paytm rolled out UPI (Unified Payments Interface)-based payments
2018 : Paytm First Games owned by Paytm and Alibaba-backed AG Tech Holdings was launched
2019 : Paytm launched QR/POS/Gateway combined services
2021 : One97 Communications enters Indian Stock Market by launching its IPO
2023 : Paytm Payments Bank launches UPI Lite
Major Paytm Services
As we move further with the Paytm case study, let us look at some of the popular products & service offerings by Paytm –
Paytm Insider
Paytm Insider is an online ticket booking platform co-owned by Paytm and Insider.in. It is the one-stop ticketing solution for popular events, concerts, cricket matches, and product fests happening in the city.
Paytm Mall is an e-commerce store launched by Paytm in 2017. It is a B2C platform intended to provide a Bazaar-like feel to the customers by choosing from over 1.4 lakh listed items. Paytm Mall takes inspiration from China’s biggest B2C company, Tmall. It raised over $200 million from Alibaba and SAIF partners in a highly anticipated funding round in March 2018.
Paytm Payments Bank
Paytm Payments Bank, after payments bank by Airtel and India Post, is the third payments bank in India. Payments Bank by Paytm received approval from the Reserve Bank of India in 2015 but was officially launched in November 2017. It provides complete banking services ranging from Savings Accounts to Loaning facilities. It also offers Paytm Wallet, which can be used as a mobile payment method while paying at any QR, online merchant or any digital transaction.
Paytm Money
Paytm Money is a SEBI-registered stock brokerage and advisory platform offered by Paytm. It was launched in 2017 and provides free demat account opening, trading and investment in Mutual Funds, the Stock market and also NPS retirement funds.
Revenue Model of Paytm
This Paytm case study highlights the major revenue sources of Paytm, which are as follows:
Interests from Escrow Account: Paytm secures the wallet money of its users in an escrow account linked with a nationalised bank. With this, Paytm makes around 4-6% of interest easily.
Commission from Merchants: Paytm charges nominal commissions from users as well as the merchants while making payments, purchasing digital gold or investing in stocks.
Advertisements: We often see pop-ups of offers and deals when we open the app, Paytm charges the companies and businesses for running those ads.
Marketplace: Paytm has a dedicated e-commerce store which brings a fine chunk of their revenue. Paytm Mall has a commission linked with the sellers.
Gateway Fees: Many platforms like IRCTC have a separate payment gateway linked with Paytm. In such cases, a gateway payment is applied.
Paytm Stats
*All values in Cr
Paytm has generated a revenue of around Rs. 7990 Cr in 2022-2023, which is a growth of over 3000Cr from its previous year’s earnings. After its listing on the NSE, it has given a CAGR of around 69% in its revenue.
PROFIT/LOSS
So, we can see that Paytm has been making significant losses over the years. High Operation costs and Customer acquisition costs are the main reasons for the above losses. Additionally, Paytm is often struggling with Government regulations as well which inhibits their income.
Major Acquisitions
Paytm acquired a majority stake in event booking and ticketing platform, Insider.in owned by OML Entertainment in June 2017. The deal was finalised for an amount of $5.42 million (44 crores).
NightStay is a hotel-booking startup based out of Noida. Paytm acquired Nighstay in a $20 million (160 Crores) deal in 2019.
Paytm acquired complete stakes in CreditMate, a Mumbai-based digital lending startup in October 2021, a few days before its stock market inaugural. The amount of acquisition was however undeclared.
Paytm is one of the biggest fintech companies in India with a wide range of services on board. Since its inception in 2010, Paytm has been delivering high-end digital banking solutions. As a result, it is among the top 3 companies with maximum UPI transaction volumes in India. Additionally, Paytm is working on improving the infrastructure of digital payments in the country and making it even more robust.So, we hope you find this Paytm case study helpful and informative.
You Might Also Like

Best Monopoly stocks to invest in India

What is Long and Short Position in Future

Best Dividend Paying Penny Stocks To Buy
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Looking to try stock market fantasy game?
Play on StockPe now to win big rewards with secured withdrawals.
Today, Paytm stands as a one-stop-shop for consumers, offering a plethora of financial and other services that include e-commerce, banking, investments, loans, bus tickets, money transfers, etc.
Total revenue has grown from ₹2,802 Cr in FY 2021 to ₹7,990 Cr in FY 2023, growing at a CAGR of 69%
In 2017, Paytm piloted bill payment services in Canada and in the year 2018, Paytm partnered with Softbank and Yahoo Japan Corporation to launch PayPay, a leading digital payments and financial services company in Japan.
Paytm went public with its IPO on NSE & BSE in November 2021 and raised INR 18,300 crs via IPO. The IPO was one of the largest in India, although Paytm’s debut in the stock market faced mixed reactions.
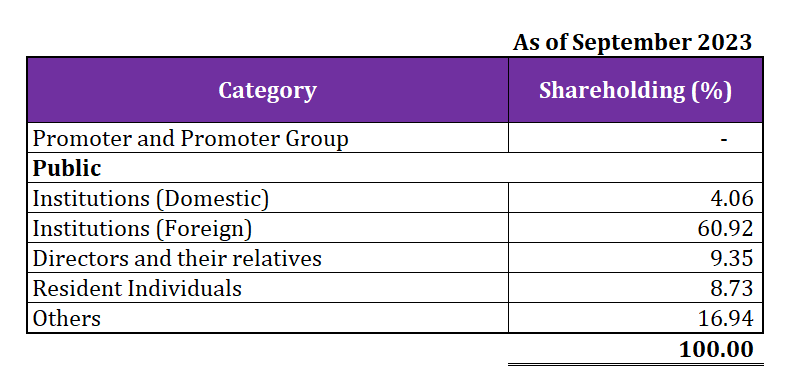
As of September 2023, there is no identifiable Promoter of Paytm. Have a look at the shareholding pattern of Paytm:
Products and Services
Paytm offers a variety of products and services, such as payment services, financial services, cloud, etc.
Payment Services
Payment Services are meant for both consumers and merchants and enable them to make and receive payments seamlessly both online and in-store. Paytm has an overall market share of 40% in payment transactions. Paytm also launched the Paytm Wallet in 2014 and QR code services in 2015. QR Code was later upgraded to an All-in-One QR code in 2020 so that consumers and merchants can have a seamless payment experience while accepting payments from third-party UPI platforms.
Further, in 2020, Paytm launched soundbox service that gives real-time payment audio confirmation for payment completion. With Paytm’s payment services, consumers can make online bill payments, recharge, and transfer money through the app.
Commerce & Cloud Services
Paytm allow consumers to avail of lifestyle commerce services that include booking online tickets, entertainment, gaming, and food delivery within the Paytm app. Merchants can also connect with consumers to improve their business operations. Paytm provides merchants with services such as billing, ledger, vendor management, inventory management, catalogues, etc.
Paytm also provides software and cloud services to enterprises, telecom companies, digital and fintech platforms.
Financial Services
Paytm provide the following financial services to consumers and merchants:
Mobile Banking Services – Paytm provides mobile banking services through Paytm Payments Bank that includes digital banking products such as current accounts, savings accounts, salary accounts, fixed deposit accounts, and debit cards for individuals, SMEs and corporates.
Lending – Paytm collaborates with financial institutions to improve distribution, underwriting and collections and provide seamless access to loans to consumers and merchants. Paytm also launched the Paytm Postpaid, which is a buy now pay later (BNPL) product.
Insurance and Attachment Products – Paytm in collaboration with its insurance partners, provides attachment products like movie and travel ticket cancellations protection. Paytm’s subsidiary company, Paytm Insurance Broking Private Limited provides insurance services that include auto insurance, life insurance and health insurance.
Wealth Management – Paytm provides wealth management services to consumers through the Paytm app and Paytm Money App. It also launched Paytm Gold, which allows customers to buy digital gold on their platform. Paytm Money app offers investment in mutual funds, equities, and derivatives trading.
Awards & Recognitions

Paytm has received multiple awards and recognitions. Some of the major recognitions are:
- BrandWagon Ace Award for best social media campaign in 2020.
- ET BFSI Excellence Award for Best Digital Bank of the Year in 2020.
- India Digital Award by IAMAI for Best Fintech Growth Story and Best Data-Driven Marketing Strategy in 2021.
- FinTech India Innovation Awards 2023 for Best Fintech Company of the Year in 2022.
- 8th CFO Vision and Innovation Summit & Awards 2023 for Best Fintech Company of the Year.
- Quantic 4th Annual BFSI Excellence Awards 2023 for best Wealth Management Company of India.
Advertising Campaigns
- “Kar De Paytm” in the year 2010.
- “Zindagi jeene ka naya tarika shuru karo – Paytm Karo” in the year 2015.
- “ATM nahi, Paytm Karo” in the year 2016.
- “Dimag Khul ke Jee” in the year 2017.
- “India Kahe Paytm Karo” in the year 2022.
Competitive Advantages of Paytm
- Paytm was an early entrant into the digital payments landscape and had a first-mover advantage.
- Paytm has a wide market of payment services across India with a brand value of US $6.3 billion.
- Paytm builds and innovates its technology which helps it to launch products and services rapidly with a high success rate. Paytm has a technology team of over 2,500 members that continuously works to improve the user experience.
- Paytm tries to understand the needs of its users and innovates products accordingly.
- To engage with customers, Paytm invests in marketing campaigns and other promotional offers.
Growth Trajectory of Paytm

Paytm has shown an impressive growth and expansion journey over the years. It has evolved from a mobile recharge platform to a financial services powerhouse. It claims to have more than 300 million active users. Paytm’s strategic partnerships with HDFC Bank, Uber, Indian Railways, and major E-commerce platforms have helped the company to grow over the years. Cashback and Promotional offers still attract new customers and hold the existing ones. Paytm has moved beyond payment services and has ventured into travel, wealth, credit cards, loans, etc.
SWOT Analysis

- Paytm is a leading player in the payment sector and enjoys a large user base.
- Paytm has strong brand recognition in the fintech sector of India.
- Paytm has a diversified product portfolio such as financial services, loans, broking, credit cards, travel, etc.
- The lack of profits in the company has raised financial sustainability issues for the company.
- Paytm heavily depends on the Indian market for its revenue and any kind of regulatory changes can impact the company’s business operations.
- The company faces tough competition from other fintech startups like PhonePe, Google Pay, etc.
Opportunities
- Penetration in the rural area to provide digital payment services can help Paytm grow its business further.
- A comprehensive app for seamless user experience can drive the revenue growth of the company.
- Tapping into the International markets can help Paytm provide services outside of India, which boosts the company’s revenue growth.
- Digital payment systems like Paytm are often prone to cyber security risks. Such risks have the potential to significantly alter the user base of Paytm.
- Economic downturns can affect consumer spending. This will eventually reduce the user base and revenue growth of the company.
- Innovative Competitors and Big Giants like Google Pay and PhonePe could challenge Paytm’s growth.
Paytm’s case study provides useful insights into the dynamics of the fintech landscape and cashless economy in India. Paytm’s diversification of services and first-mover advantage have allowed it to create a strong and loyal user base in India. The company should continue to innovate and explore the emerging digital landscape of India for better market positioning and customer engagement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Who founded Paytm?
Ans. Vijay Shekhar Sharma founded Paytm in 2010.
2. What is the shareholding percentage of promoters in Paytm?
Ans. As of September 2023, holding of promoters is nil.
3. Paytm faces tough competition from which companies?
Ans. PhonePe, Google Pay, etc..
4. When was Paytm listed on NSE & BSE?
Ans. November, 2021.
5. What financial services are offered by Paytm?
Ans. Mobile Banking Services, Loans, Mutual funds, Equity Investments, Credit Cards, etc.
Disclaimer: The securities, funds, and strategies mentioned in this blog are purely for informational purposes and are not recommendations.

Related Posts

BAT Stake Sale in ITC: Overview, Reasons, and Impact on Shareholders Explained

Punjab National Bank (PNB) Case Study: Overview, Financials, and SWOT Analysis

Patanjali Foods Case Study: Business Model, Financials, KPIs, and SWOT Analysis
We are a concern of pace group. pocketful is an investing platform that helps people be better investors. pocketful unlocks the discoverability of new investment and trading ideas., quick links.
- Open an Account
- Pocketful Web
- Pocketful App
- Investment Tool
- Trading Tool
- Support Portal
- Referral Program
- Calculators
- Stocks Pages
- Government Schemes
- Index Heat Map
- Stock Screener
- Mutual Funds
- Terms & Conditions
- Policies & Procedures
- Privacy Policy
- Press & Media
- Harvard Business School →
- Faculty & Research →
- January 2017 (Revised May 2019)
- HBS Case Collection
Paytm: Building a Payments Network
- Format: Print
- | Language: English
- | Pages: 21
About The Authors
Sunil Gupta
Das Narayandas
Related work.
- Faculty Research
- Paytm: Building a Payments Network By: Sunil Gupta, Das Narayandas and Rachna Tahilyani

- Case Study , Finance
A Case Study of Paytm: Revolutionizing Digital Payments in India

- December 16, 2023
In recent years, the digital payment landscape in India has witnessed a remarkable transformation. One company that has played a significant role in this revolution is Paytm . This case study delves into the journey of Paytm, highlighting its key milestones, strategies, and impact on the Indian economy.
Paytm was founded in 2010 by Vijay Shekhar Sharma with the aim of making digital payments accessible to all Indians. Initially, it started as a mobile recharge and bill payment platform. However, recognizing the potential of digital wallets, Paytm expanded its services to include peer-to-peer transactions, online shopping, and even banking services.
Key Milestones
Paytm’s journey has been marked by several significant milestones:
1. Demonetization Boost
In 2016, the Indian government’s bold move to demonetize high-value currency notes provided a massive opportunity for digital payment platforms. Paytm capitalized on this by promoting its services as a convenient alternative to cash transactions. This led to a surge in the number of users and transactions on the platform.
2. Strategic Partnerships
Paytm forged strategic partnerships with various stakeholders, including banks, e-commerce platforms, and offline retailers. These collaborations helped expand its user base and acceptance across both online and offline channels.
3. Paytm Payments Bank
In 2017, Paytm became the first digital wallet company to launch a payments bank in India. This move allowed Paytm to offer a wide range of banking services, including savings accounts, debit cards, and digital loans.
4. Diversification into E-commerce
Recognizing the potential of the e-commerce market, Paytm expanded its services to include online shopping. It launched the Paytm Mall platform, offering a wide range of products and attracting millions of customers.
Strategies for Success
Paytm’s success can be attributed to several key strategies:
1. User-Friendly Interface
Paytm’s user-friendly interface made it easy for even non-tech-savvy individuals to adopt digital payments. The app’s intuitive design and simple navigation contributed to its widespread adoption.
2. Cashback and Discounts
Paytm leveraged the power of cashback offers and discounts to attract and retain users. These incentives encouraged users to make more transactions on the platform, further driving its growth.
3. Focus on Merchant Acceptance
Paytm actively focused on increasing its acceptance among merchants, both online and offline. It offered seamless integration options, attractive pricing models, and dedicated support, making it an attractive choice for businesses.
Impact on the Indian Economy
The rise of Paytm has had a profound impact on the Indian economy:
1. Financial Inclusion
Paytm’s services have played a crucial role in bringing financial inclusion to millions of unbanked and underbanked individuals in India. It has provided them with a safe and convenient platform to manage their finances.
2. Boost to Digital Payments
Paytm’s success has significantly contributed to the growth of digital payments in India. It has helped reduce cash dependency, leading to increased transparency and accountability in financial transactions.
3. Job Creation
Paytm’s expansion has created numerous job opportunities, both directly and indirectly. From customer support to technology development and merchant onboarding, Paytm has contributed to employment generation in the country.
4. E-commerce Growth
Paytm’s foray into the e-commerce sector has provided a platform for small and medium-sized businesses to reach a wider customer base. It has contributed to the growth of the Indian e-commerce industry.
Paytm’s journey from a mobile recharge platform to a leading digital payment and e-commerce player is a testament to its innovative strategies and relentless focus on customer experience. Its impact on the Indian economy is undeniable, driving financial inclusion, digital payments, job creation, and e-commerce growth. Paytm continues to evolve and shape the future of digital payments in India.
- Tags : digital payments , India , Paytm
We Do Simple Things To Get More Clients
Marketing | brand building | online advertising | web design & development, knowledge hub: explore & learn.
You’ve been successfully subscribed to our newsletter!
Related posts

The Best Niche Blog Ideas for 2024
Are you thinking about starting a blog in 2024? Congratulations! Blogging is a fantastic way

The Ultimate Guide to WhatsApp Marketing in 2024
WhatsApp has become one of the most popular messaging apps in the world, with over

The Ultimate Guide to Creating a Sales Funnel
Welcome to the ultimate guide to creating a sales funnel! Whether you’re a small business
- © 2024 All Rights Reserved.
- Privacy Policy
- International
- Today’s Paper
- Premium Stories
- Bihar 10th Result
- Express Shorts
- Health & Wellness
- Board Exam Results
RBI action against Paytm: probable causes, effects, and what happens to your money
Given the significant customer base of the paytm, once the poster boy of india’s fintech revolution, the rbi action could impact a large number of customers. we explain what the order means.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on Wednesday (January 31) barred Paytm Payments Bank from offering all its core services — including accounts and wallets — from March, effectively crippling the company’s business.
The action is technically not a cancellation of the licence of Paytm Payments Bank, but it constricts the company’s operations to a very large extent.

However, the central bank has allowed the withdrawal or utilisation of balance amounts by customers “without any restrictions, up to their available balance”.
Paytm, which was once the poster boy of India’s fintech revolution, has a significant customer base. On its website, Paytm Payments Bank says it has more than 100 million know your customer (KYC) verified customers.
“We are also the largest issuer of FASTag with over 8 million FASTag units issued,” the website says.

Paytm founder and Chairman Vijay Shekhar Sharma is part-time chairman of the bank.
What does the RBI direction say?
Paytm Payments Bank has been barred from offering almost all of its key services — accepting deposits or top-ups in any customer account, prepaid instruments, wallets, FASTags, National Common Mobility Card (NCMC), etc., after February 29 in the wake of “persistent non-compliances and material supervisory concerns”.
“No other banking services…like fund transfers (irrespective of name and nature of services like AEPS, IMPS, etc.), BBPOU and UPI facility should be provided by the bank after February 29, 2024,” the RBI has said.
It has directed that the nodal accounts of the parent company One97 Communications and Paytm Payments Services should be terminated at the earliest, and not later than February 29.
The settlement of all pipeline transactions and nodal accounts — in respect of all transactions initiated on or before February 29 — should be completed by March 15, and no transactions shall be permitted thereafter, the central bank has said.
Can customers use or withdraw their stored balances in various Paytm instruments?
As per the RBI, withdrawal or utilisation of balances by customers from their Paytm accounts including savings bank accounts, current accounts, prepaid instruments, FASTags, NCMC, etc. are permitted without any restrictions, “up to their available balance”.
The RBI statement, however, does not mention a number of other services like loans, mutual funds, bill payments, digital gold, and credit cards.
What has Paytm said in response to the RBI action?
As Paytm shares fell 20 per cent on the exchanges on Thursday (February 1), One97 Communications Ltd said it was “taking immediate steps to comply with RBI directions”, including working with the regulator to address their concerns as quickly as possible.
Depending on the nature of the resolution, the company expects the RBI action to have a worst-case impact of Rs 300-500 crore on its annual EBITDA (earnings before interest, tax, depreciation and amortisation) going forward.
Also, going forward, One97 Communications will be working only with other banks, and not with Paytm Payments Bank, it said in an exchange filing.
“We offer acquiring services to merchants in partnership with several leading banks in the country and will continue to expand third-party bank partnerships. The Paytm Payment Gateway business (online merchants) will continue to offer payment solutions to its existing merchants,” it said.
OCL’s offline merchant payment network offerings like Paytm QR, Paytm Soundbox, Paytm Card Machine, will continue as usual, where it can onboard new offline merchants as well, Paytm said.
What led to the RBI’s action against Paytm?
The central bank gave no reasons for its action. However, Paytm Payments Bank has been facing scrutiny from RBI since 2018.
Sources said the RBI’s action could be due to concerns on KYC compliance and IT-related issues. The central bank is concerned about allowing any institution or banking entity to expose depositors’ money to such risks.
It is learnt that Paytm Payments Bank and its parent OCL also came under RBI scrutiny for purported lack of requisite information barriers within the group, and data access to China-based entities that were indirect shareholders in the payments bank through their stake in the parent company.
The failure to address these concerns at multiple levels over an extended period led to the latest action by the RBI, it is learnt.
Antfin, an affiliate of the Chinese conglomerate Alibaba, is a shareholder in One97 Communications — as of December 31, 2023, Antfin held 9.89% stake in the company, stock exchange data show. Given the frosty relationship between India and China over the past few years, Chinese investments in Indian companies have attracted intense scrutiny by Indian regulators.
What other actions has RBI taken against Paytm earlier?
In October 2023, the RBI had fined Paytm Payments Bank Rs 5.39 crore due to deficiencies in regulatory compliance. According to the regulator, the payments bank had failed to identify the beneficial owner in respect of entities onboarded by it for providing payout services; did not monitor payout transactions and failed to carry out risk profiling of entities availing payout services; had breached the regulatory ceiling of end-of-the-day balance in certain customer advance accounts; and had delayed reporting a cyber security incident.
In March 2022, the RBI directed Paytm Payments Bank to stop the onboarding of new customers with immediate effect. The Comprehensive System Audit report and subsequent compliance validation report of the external auditors revealed “persistent non-compliances and continued material supervisory concerns in the bank”, warranting further supervisory action, the RBI said on January 31.
Even before 2022, the central bank had made certain observations in 2018 about the processes the company followed to acquire new users, especially on KYC norms.
The RBI also had concerns over the close relationship between Paytm Payments Bank and its parent One97 Communications. Payments banks are required to maintain an arm’s length distance from promoter group entities. OCL held 49% stake in Paytm Payments Bank, while 51% was held by Paytm founder Vijay Shekhar Sharma.
There were also allegations that the payments bank had failed to meet the Rs 100-crore net worth criteria, and had exceeded the Rs 1-lakh deposit limit allowed per account for payments banks at the time.
Sukalp Sharma is a Senior Assistant Editor with The Indian Express and writes on a host of subjects and sectors, notably energy and aviation. He has over 13 years of experience in journalism with a body of work spanning areas like politics, development, equity markets, corporates, trade, and economic policy. Before joining The Indian Express, Sukalp had long and enriching stints at financial newswire Informist and the Express Group’s pink paper The Financial Express. He considers himself an above-average photographer, which goes well with his love for travel. ... Read More
- Express Explained

PSEB announces Class 5 exam results on April 1 at 3 pm. Girls outshine boys with a pass percentage of 99.74%. Transgender students achieve a perfect 100% pass rate. Marksheet includes student's name, roll number, parents' names, school name, total score, and subject-wise marks. Overall pass percentage increases slightly from 2022 to 2023.

More Explained

Best of Express

EXPRESS OPINION

Apr 01: Latest News
- 01 11 hours ago Vintage Dhoni, almost: MSD ends game with six while batting for 1st time in IPL 2024, but CSK fall short
- 02 11 hours ago Maharashtra keeps ready reckoner rates unchanged
- 03 11 hours ago ‘Prithvi Shaw’s knock came from hurt within’, ‘Let’s hope that hunger stays’: Cricketers react to DC star’s knock
- 04 11 hours ago DRI arrests Sierra Leone man carrying cocaine worth Rs 11 crore in his body
- 05 20 hours ago 2 killed, 3 injured during shootings at separate Houston-area birthday parties
- Elections 2024
- Political Pulse
- Entertainment
- Movie Review
- Newsletters
- Gold Rate Today
- Silver Rate Today
- Petrol Rate Today
- Diesel Rate Today
- Web Stories

Paytm Case Study
Paytm creates a social payment experience with Sendbird
Customer Paytm
Product Chat
Vertical Fintech
Country India

Send notifications that remain accessible in your app
Founded in 2010, Paytm is India’s leading financial services company that offers full-stack payments and solutions to consumers, offline merchants, and online platforms. Paytm’s mission is to bring half a billion Indians into the mainstream economy through payments, commerce, banking, investments, and financial services.
In March 2021 alone, Paytm recorded over 1.4 billion transactions. With over 21 million merchant partners on board, the company currently maintains the highest market share in offline payments in India. In addition, it is the only platform in the country that promotes all digital payments services, including Paytm Wallet, UPI, Paytm Postpaid, cards, and net banking.

Business Challenge
Paytm saw chat as a potential game changer in increasing user engagement and satisfaction. Given this climate, Paytm’s product team sought to further innovate its user experience, and explore how it could better serve the millions of customers using the platform every day.
Traditionally, Paytm has viewed transaction history as simply a chronological list of payment records. However, the company wanted to address three different pillars and bring them to the forefront of the company’s money transfer interface:
- Identity (who users are paying)
- Context (why users are being paid)
- Distribution (a payment ecosystem between users, businesses, partners, etc.)
Why Paytm Chose Sendbird
Paytm understood that building messaging functionality in-house would be an incredibly complex task. Payments would come from multiple service channels such as Paytm UPI, Paytm wallet, Paytm postpaid, Paytm payments bank, and more. According to Paytm Insider Head of Product Abhishek Madan, “all of these are presented in the same user experience. These are completely separate backends that have nothing to do with each other, and our attempt is to bring all of this data and show it in one place. It’s a massive tech complication.”
Furthermore, due to the heavily regulated nature of each product, developing chat in-house would be an immense compliance undertaking as well. Madan emphasizes that PMs would have to additionally oversee chat for the company’s “lending insurance and equity trading businesses, and to have all of these in one UX requires us to work very closely with compliance teams. Three years ago, each of these products was probably a standalone company.”
With the sheer scale of Paytm’s user base paired with its breadth of offerings, the company needed a service that could offload the complexity and resources necessary to stand up a high-functioning chat interface while simultaneously offer the features customers desired. With Sendbird, Paytm could concentrate on developing its core money transfer features and go to market quickly without the burdens that come with developing chat functionality. “The MVP bar for chat is so high that we would have to invest significant resources with this product complexity, this feature complexity of real-time messaging,” Madan explains, “along with our existing complexities, Sendbird really offloaded all of that from us.”

Across its service suite, Paytm supports more than 333 million users , and in partnering with Sendbird, has sent over 1 billion messages to date . This scale is supported by the Sendbird Platform API, which has given Paytm the building blocks necessary to create many of its rich features and interfaces used today. Madan states, “when you think about Paytm, we’re pretty wide… We have all of these apps, and because of these platform APIs, I can build walled gardens that I can deploy into each of these apps. So the work I do once is reusable by every business unit inside Paytm. So Sendbird’s platform is a massive help.”
Within the Paytm main app, users have access to a messages section that Madan refers to as a “chat powered payments and engagement platform… and represents a change in how users look at transaction history.” Here, Paytm has invested in what it calls an “identities-first approach” where users can simply tap on a contact’s profile and instantly see a clear view of who they are, conversations discussed, what payments were made, when they occurred, and for what purpose. These actions link deeply within Paytm’s money transfer suite and allow for a convenient and rich experience for end-users, entirely contained within the company’s ecosystem.
In a survey of Paytm customers, over 85% of the user base was satisfied with both the new functionality and speed of chat within the application.
1) Since day one, Sendbird has partnered with AWS to establish itself as a leading conversations platform that enables a secure, global, and scalable in-app conversation experience. Sendbird is an AWS advanced tier technology partner operating 45+ AWS native services in 9 regions. Thanks to Amazon’s AWS Auto Scaling and Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud services, Sendbird manages massive digital traffic sending billions of messages monthly. Using Elastic Load Balancing and Amazon Route53 geolocation functions, Sendbird ensures reliable global traffic distribution. Sendbird also leverages AWS CloudFormation to automate its servers’ management in each region efficiently. Lastly, AWS Elasticache and Amazon Aurora allow Sendbird to achieve millisecond latency and data storage for over 300 million monthly active users. Sendbird’s world-class conversation platform architecture and technical foundations are certified by AWS.
Related Case Studies
Ready for the next level.

- Consultation
- Done For You!
Paytm Case Study (Detailed Business Model)
lapaasindia
April 23, 2019
Recent Blogs

2 Minute Summary
Paytm one of the biggest Fintech Company of Indian which has become a case study for Harvard University students. Revenue of Paytm was 3579 crores that is 500 million dollars in 2019. Paytm earns throughs varios business like Market Place which it runs by the name of Paytm Mall, and other recharge services, bill payment, Ticket Boking services as well. Paytm also have its Payment Gateway Solution which it charges a decent amount on every transaction. If we fututer go paytm has it wallet services and also they have released a digital gold services by which you can buy gold online.Now, they have launched their paytm payments bank which further increase their valuation. For detail information you can read the blog or watch our video.
People often ask me how do I gather all the data about different business models for my Youtube channel( Intellectual Indies )
So I thought How about I assemble all the details about all the business models on my website lapaas.com.
After reading this blog, I am sure you’ll get all the details about the Business Model of Paytm from Funding to How do they earn.
Paytm is India’s Biggest platform in the e-wallet industry and e-commerce platform.
Started by Vijay Shekhar Sharma in 2010, Paytm changed its business model to a virtual bank model, marketplace and gold e-wallet.
Vijay Shekhar Sharma is an engineer from the Delhi College of Engineering and today he is worth $2.6 Billion.
One97 Communications Ltd of Paytm’s Parent Company got their first institutional investor, venture capital and SAIF Partners in the year of 2007. Berkshire Hathaway confirmed investment of $356 Million for 3% – 4% Stake in Paytm in August 2018 and it was confirmed by Berkshire company that Warren Buffet is not involved in this transaction.

Do you know Paytm serve 100 million users? They offer Payment Solution to over 7 Million Merchants and allow customers to make seamless mobile payments.

According to an article published by Economic Times, Paytm’s success story has become a case study at Harvard University.

According to Wikipedia, Revenue of Paytm is 814 crores INR (US$120 million, 2017)

But How Paytm Makes Money even after 50% to 100% Cashback? It’s a worthy question to ask. Let us first discuss their revenue model one by one.
The revenue model is divided into the following categories:
There was a time when Paytm was into Mobile recharge, bill payments only but today they have 8 Revenue Models.
In this Paytm Case Study, we’ll discuss 8 Revenue Models of Paytm.
How paytm earns money?
Paytm earns throughs varios business like Market Place which it runs by the name of Paytm Mall, and other recharge services, bill payment, Ticket Boking services as well. Paytm also have its Payment Gateway Solution which it charges a decent amount on every transaction. If we fututer go paytm has it wallet services and also they have released a digital gold services by which you can buy gold online.Now, they have launched their paytm payments bank which further increase their valuation. For detail information you can read the blog or watch our video.
Let’s find out.

1 Marketplace(Paytm Mall)
Do you know Paytm is the first company with a mobile-only marketplace in India?
Paytm gives you the leverage to sell on Paytm Mall.
The process is easy, Just sign up and upload catalogue and that’s it.
Commission %= 2.8 from seller

According to Paytm Mall, sales of 20 lakh is generated every day. Can you imagine?
Also, 90% of payments are prepaid, It has been tested that in Prepaid orders
Possibility of returns is less.

How is your payout from Paytm calculated?

2. Recharge Services
They are linked with all the existing telecom service provider in the market, also metro card can be recharged and a specific commission is fixed. Again Commission 🙂 More user uses Paytm, more Paytm earns.

3. Bill Payments & Ticket Bookings

With the help of Advance technology, the Internet has made our lives simple and Paytm made is simpler. Save more with Paytm, avail exciting deals & cashback offers while paying a postpaid bill online. Be it Water Bills, Electricity Bills Paytm convert them into lifetime customers 🙂 Ticket bookings and any bill payments and what not!! But How do they earn? Commission 🙂
4. Payment Gateway Solutions
Gateway solution is a one-time investment and mode of revenue is the same. Commission 🙂 Although Gateway option setup is free along with maintenance charges but company charges a commission of 1.99% on every transaction.

Top linked accounts

5 Paytm Wallet
Paytm is a semi-closed wallet and it has been approved by RBI (Reserve Bank of India). It can be used to pay for anything and almost everywhere. According to RBI guidelines, Money deposited by users in Paytm Wallet is deposited into an Escrow Account with a partner bank.

And Interest is decided based on an average of the deposited amount in a certain period ( almost 58 weeks)

Whenever we receive a cashback, why does it stored into a wallet and not into our bank account? There is a reason J Whenever you transfer money to the bank account, Paytm charge a little commission.
6. Digital Gold
Paytm has launched Digital Gold in partners with MMTC-PAMP allowing users to buy even gold worth 10 rupees. Yes, 10 Rupees and so on.
Paytm has launched Digital Gold in partners with MMTC-PAMP allowing users to buy even gold worth 10 rupees. Yes, 10 Rupees and so on. How do they earn? Their commission no matter if the price of gold rises or not Also, company main motive of Digital Gold was to create a platform where user can buy gold and store it in a digital form but the user can also use the same gold to buy other services, be it recharge or bill payments.

7. Paytm Payment Bank
With the launch of Paytm Payment Bank, Paytm aim to bring banking and financial services to half-a-billion un-served and under-served Indians. Also, Paytm is linked with financial institutions and banks to sell their products and services like investments, loans etc. They earn a specific commission. QR codes can also be scanned at various points(issues debit cards). You can open a zero deposit digital current and savings bank accounts at an interest of 4%p.a. Balance deposited above ₹1 lakh is shifted to a fixed deposit(FD) at an interest rate of 7% p.a. How do they earn from a Bank?
8. Coupon codes/Voucher cards
They are linked with surplus brands.

Their whole business is based on commission. Let’s have a look at some of the data:
Also, Ratan Tata is involved in investing in Paytm. So have a look at some of their Marketing Campaigns:
Kisi ki life asaan Karo #Paytmkaro
Kisi ki Life ka Paytm Bano Campaign:
URI Surgical Strike Paytm Campaign:
Latest Updates: Rana Kapoor who is the Co-founder of Yes bank is in talks with Vijay Shekhar Sharma – the Founder of Paytm.
Rana Kapoor wishes to sell his own and his family’s stake in yes bank for Rs 1,800-2,000 crore to Paytm. The investment firm, Rana Kapoor and his family members together control a 9.64% stake in Yes Bank.
Still, there is no confirmation about the news, but both the companies are still negotiating on the price and other related issues.
Leading digital payments service Paytm on Wednesday said it is in the process of hiring over 1,000 engineers, data scientists, financial analysts among other positions for tech and non-tech roles. Paytm in April announced to hire over 500 people for multiple roles, aside from continued hiring in product and technology and the current move is to ramp up recruitments for expanding its financial and wealth management services.
Paytm has grabbed 50 per cent share in the payments to merchants (P2M) segment in India and the financial services platform has emerged as the most integrated payments provider in the fintech space.
Paytm has just seen a hit by online scammers where 190 Paytm users duped of Rs 1.13 crore on the pretext of KYC update.
Paytm Money, the wealth management arm of One97 Communications, has softly launched a stockbroking feature within the app. The company has been planning to launch a stockbroking service.

I hope you like this Paytm Case Study , let me know in the comments if I missed out anything. Paytm Website Audit: Lapaas seo audit
UPDATED ON – 26/4/19
FAQ’s
Paytm one of the biggest Fintech Company of Indian which has become a case study for Harvard University students. Revenue of Paytm was 3579 crores that is 500 million dollars in 2019. Paytm earns throughs varios business like Market Place which it runs by the name of Paytm Mall, and other recharge services, bill payment, Ticket Boking services as well.
18 Responses
Very useful content
Detailed case study
Thanks, Do check our other blogs 🙂
This is most informative blog on paytm case study.
Thank you sharing.
Great Sir…
Thank you sharing the revenue model of paytm. Detailed Paytm case study
Great information
Attractive section of content. I just stumbled upon your weblog and in accession capital to assert that I acquire in fact enjoyed account your blog posts. Anyway I’ll be subscribing to your augment and even I achievement you access consistently quickly.
Thank you so much, do check our other blogs.
I came here from your Instagram poster about #paytmcasestudy, I read it its real informative and use and also seo friendly
Thanks brother, do check our other blogs.
Its like you read my mind! You appear to know a lot about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you could do with some pics to drive the message home a bit, but instead of that, this is wonderful blog. A great read. I’ll definitely be back.
Hey There. I found your weblog the usage of msn. This is a really well written article. I’ll be sure to bookmark it and come back to learn more of your helpful information. Thank you for the post. I’ll certainly return.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We don't do BLACK MAGIC No overnight results Guarantee
- Lapaas Learning
- Lapaas Voice
- Privacy & Policy
- Terms Condition
Copyright Lapaas © 2024. All rights reserved

Payment Banks in India – The PayTM Case – Explained Pointwise

The recent case of RBI’s crackdown on Paytm has put the spotlight on the operations of Payment Banks In India. RBI has ordered Paytm Payments Bank Ltd (PPBL) to halt most of its business including taking further deposits, conducting credit transactions and carrying out top-ups on any customer accounts, prepaid instruments, wallets, and cards for paying road tolls after February 29, 2024.
Reasons for RBI Clampdown on Paytm payments Bank

What are Payment Banks? What are their features?
Historical Background- Payment Banks in India were established in 2014 based on the recommendations of the Nachiket Mor Committee . It was set up to operate on a smaller scale with minimal credit risk.
Objective- The main objective is to advance financial inclusion by offering banking and financial services to the unbanked and under-banked areas. It also caters to the needs of uncovered masses in the banking sector like the migrant labour force, low-income households and small entrepreneurs.
Legal Provisions- The legal provisions governing the payment banking operations in India are mentioned below- a. These banks have to register as a Public Limited Company under the Companies Act 2013 and obtain licence as per Banking Regulation Act 1949 . They are also regulated by the RBI Act 1934, Foreign Exchange Management Act 1999 and Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007. b. The minimum capital requirement is 100 crores . For the first five years, the stake of promoters should not be less than 40%. Foreign shareholdings will also be allowed as per FDI rules for private banks in India. c. The voting right of the shareholder is capped to 10% and which can be raised to 26% from the approval of Reserve Bank of India. The banks should be fully networked from the beginning.
Features- These Banks have several distinct features when compared to the conventional Banks. These are mentioned below-
Payment Banks operating in India- Currently only 6 banks are operating in the country- Airtel Payments Bank Limited, India Post Payments Bank Limited, Fino Payments Bank Limited, Paytm Payments Bank Limited, NSDL Payments Bank Limited and Jio Payments Bank Limited.
What is The Significance of these Banks for India?
1. Promotion of Financial inclusion- These banks have promoted financial inclusion by catering to financial services to the unbanked sections of the society like migrant workers, low-income households and small scale entrepreneurs.
2. Expanded Geographical reach- These banks have a wider geographical reach due to its technology oriented services, unlike traditional banks whose geographical outreach is constrained by the requirements of physical infrastructure.
3. Zero balance accounts and No minimum balance accounts- These banks offer a zero balance account or a no minimum balance account without any extra or hidden charge, unlike a commercial bank who levy charges if the customer doesn’t hold a minimum balance in their account.
4. Complements the financial efforts of traditional banks- Payments banks complement the financial efforts of traditional banks by partnering to sell mutual funds , pension products , and insurance products through their platform. For ex- SBI Life Insurance product through Paytm.
5. Low Value, High Volume Transactions- They have provided effective infrastructure to deal with low value, high volume transactions. For Ex- Use of Paytm QR codes by the vegetable Vendors to grocery shop owners .
6. Higher rates of Interest- The rates of interest being offered by these banks is higher in comparison to the traditional banks . For Ex- ROI of Payment Bank is generally around 7% whereas as ROI of commercial bank ~3.5 and 6 per cent.
What are The Challenges with Payment Banks in India?
1. Low avenues of profitability- These banks are not allowed to lend money and earn interest income unlike traditional banks. Further, the stringent SLR requirements of 75% demand liabilities to be invested in G-secs have impinged on the avenues of profitability of these banks. For ex- The operational payments banks showed net losses of Rs 516.5crore for financial year 2018.
2. Low return on equity- The cap on the amount of demand deposits at Rs 2,00,000 and the 15% capital to Risk Weighted Assets ratio , has severely impacted the returns on equities of payment bank in India. Their return on equity is less than 5%.
3. Digital Divide and slow internet connectivity- These banks have no physical presence and their banking operations are solely reliant on internet connectivity. However, the rural-urban divide in internet connectivity has impacted their expansion and penetration .
4. Large number of dormant accounts- The large number of dormant zero balance accounts have impacted the operations of payment bank in India. They have also been used as conduits for personal loan scams and Money Laundering . For ex- Out of the 35 crore Paytm payment bank accounts, 31 cr remained dormant and were misused.
5. Cut-throat Competition- These banks are facing cut-throat competition from the payment wallets like Phone pe, Bharat Pe and conventional commercial banks payment bank services like SBI yono, ICICI i mobile pay.
6. Increasing number of Defunct Payment Bank- The over-regulated functioning and huge losses , have led to increase in the number of banks surrendering their licences and halting their operations. For ex- Cholamandalam Distribution Services , Sun Pharmaceuticals , Tech Mahindra and Aditya Birla Payment Bank have surrendered their licences.
Read More UPSC Topics-
What should be the way forward.
1. Open up more avenues of profit generation- RBI must increase deposit limits of payment bank. Also, a mechanism must be worked out to let these banks transfer the surplus money in the demand deposit accounts to the universal banks.
2. Facilitate Infrastructure sharing- RBI should take measure to facilitate infrastructure sharing among the traditional banks and Payment Bank. For ex- Payment bank desks in traditional bank branches.
3. Increased Internet connectivity- The internet connectivity in rural areas must be increased for the entry of new players in the payment bank market as payment bank sector is dominated by telecom giants like Airtel and Jio which have their own network.
4. Increase the scope of operations- The payment bank should be allowed to offer their own mutual fund and insurance products to enhance their source of revenue generation and profitability.
5. Increase regulatory vigilance- The compliance of e-KYC and no frill accounts must be regularly undertaken by the RBI to prevent future crisis like the Paytm crisis . The recommendations of the Anand Sinha committee must be implemented to ring-fence the banking operations of the payment bank from the ownership structure.

Type your email…
Search Articles
Latest articles.
- UPSC Prelims Marathon 1st April – Environment & Ecology – 2024
- 10 PM Daily UPSC Current Affairs 31st March – 2024 | Revision Test
- UPSC Prelims Marathon 31st March – Revision – 2024
- 10 PM UPSC Current Affairs Quiz 30 March, 2024
- 9 PM UPSC Current Affairs Articles 30 March, 2024
- UPSC Prelims Marathon 30th March – International Economic Organizations – 2024
- 10 PM UPSC Current Affairs Quiz 29 March, 2024
- 9 PM UPSC Current Affairs Articles 29 March, 2024
- Taking on big tech
- Young and the old – lancet report on fertility rate
Prelims 2024 Current Affairs
- Art and Culture
- Indian Economy
- Science and Technology
- Environment & Ecology
- International Relations
- Polity & Nation
- Important Bills and Acts
- International Organizations
- Index, Reports and Summits
- Government Schemes and Programs
- Miscellaneous
- Species in news
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Sign out of AWS Builder ID
- AWS Management Console
- Account Settings
- Billing & Cost Management
- Security Credentials
- AWS Personal Health Dashboard
- Support Center
- Expert Help
- Knowledge Center
- AWS Support Overview
- AWS re:Post

We’ve seen immediate success with our use of Amazon Textract. Our goal is to also develop further capabilities in our tech solution by adding facial recognition and other machine learning capabilities on OCR problems, and gradually replace existing third-party software with AWS solutions.”
Manoj Kumar Senior vice president and head of data platform, Paytm
Empowering Automation for Business Growth
Prakash Anand, senior lead data scientist at Paytm, says Amazon Textract has served Paytm’s rapidly growing business needs well. “We had a limited budget and short timeframe to implement a more efficient user KYC solution. We found Amazon Textract to be the best option—it was cost-effective, had a high accuracy rate, and only took an hour to roll out,” says Anand.
Developing an economical in-house solution using Amazon Textract helped Paytm to avoid investing in expensive third-party independent software solutions and achieve cost savings of up to 75 percent.
According to Manoj Kumar, senior vice president and head of data platform at Paytm, digitizing the user KYC process using Amazon Textract as part of a scalable microservices architecture,has opened new avenues for Paytm to automate data extraction.
“We’ve seen immediate success with our use of Amazon Textract. Our goal is to also develop further capabilities in our tech solution by adding facial recognition and other machine learning capabilities on OCR problems, and gradually replace existing third-party software with AWS solutions,” says Kumar.
Today, Paytm supports 24.4 million merchants and is used by millions of individuals daily to pay for utilities, groceries, movie tickets, and more. The company is on a mission to extend mainstream financial services to half a billion Indian citizens on its platform.
To learn more, visit aws.amazon.com/financial-services/
About Paytm
Paytm is the consumer brand of India’s leading mobile internet company, One97 Communications. The brand is one of India’s largest financial services companies, offering full-stack payments and financial solutions to consumers, offline merchants, and online platforms. Today, the company serves millions of merchants and customers on its platform in India.
Benefits of AWS
- Reduced time required for user KYC from days to minutes
- Deployed KYC solution in one hour
- Reduced costs by 75 percent
- Better customer and merchant experience
AWS Services Used
Amazon textract.
Automatically extract printed text, handwriting, and data from any document.
Learn more »
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) offers the broadest and deepest compute platform, with over 475 instances and choice of the latest processor, storage, networking, operating system, and purchase model to help you best match the needs of your workload.
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is an object storage service offering industry-leading scalability, data availability, security, and performance.
Amazon Cloudwatch
Amazon CloudWatch is a monitoring and observability service built for DevOps engineers, developers, site reliability engineers (SREs), IT managers, and product owners.
Get Started
Companies of all sizes across all industries are transforming their businesses every day using AWS. Contact our experts and start your own AWS Cloud journey today.

Ending Support for Internet Explorer
RBI’s crackdown on Paytm Payments Bank: The inside story
Cnbc-tv18 has learnt that the reserve bank of india had found 31 crore out of 35 crore paytm wallets inoperative in its inspection, cases where a single pan card was linked to thousands of accounts, absence of kyc for lakhs of accounts and violation of kyc-anti money laundering rules, instances of false compliance reports being submitted by the bank, ppbl’s financial and non-financial business co-mingled with its promoter group companies in violation of licensing conditions, and many other red flags, which pushed the regulator to put stringent curbs on the bank, bringing its operations to a standstill..

By Ritu Singh February 5, 2024, 9:31:16 AM IST (Updated)

VIDEO
COMMENTS
The saga and the emergence of Paytm are discussed in this section of the case study of Paytm. It was established in August 2010 with underlying speculation of $2 million by its originator Vijay Shekhar Sharma in Noida, an area nearby India's capital New Delhi. 2013.
This case study also explains the current difficulties of Paytm given the increasing competition and the loss of interest of the investors. Started by Vijay Shekhar Sharma, as a Recharge platform in 2010, Paytm (One 97 Communications Ltd) became the most successful mobile payment and money transfer app used in India a few years back.
Paytm: A Case Study. Paytm, the name synonymous with digital payments in India, isn't simply a platform, it's a saga woven into the fabric of the nation's remarkable fintech revolution. In this article, we delve into the intricate details of Paytm's journey, from its humble beginnings as a mobile recharge platform to its current ...
Paytm Case Study: The Journey of India's Leading FinTech Company. Financial Technology popularly termed as Fintech sector has flourished exponentially after the demonetization in 2016. According to a report, India's Fintech industry was valued at US $50 billion in 2021 and is expected to reach the value of US $150 billion by 2025. And if we ...
This is a company case study paper on the basis of data collected from the official site of Paytm and other websites and it includes the subject areas like Organization, Share-holder competitors ...
Paytm's case study provides useful insights into the dynamics of the fintech landscape and cashless economy in India. Paytm's diversification of services and first-mover advantage have allowed it to create a strong and loyal user base in India. The company should continue to innovate and explore the emerging digital landscape of India for ...
Our entrepreneurial growth into becoming India's leading mobile payments and financial services company has become a case study to be taught to future business leaders at Harvard Business School (HBS). ... Back in 2017, HBS' India Research Centre (IRC) included Paytm in the curriculum. The study titled 'Paytm: Building a Payments Network ...
Paytm's mission statementdeclaresits intentiontobring half a billion people in India into the mainstream economy (Paytm Bank, 2020a). Digital intermediary platforms have the potential to play a significant role in curbing social and financial exclusion by facilitating the widespread adoption of digital financial services. Our case study
By January 2017, Paytm, a mobile payments company that started in 2010, became India's largest mobile payments platform with over 142 million users and $5 billion valuation. Could Paytm become a $100 billion company its founder Vijay Shekhar Sharma envisioned it be? ... Harvard Business School Case 517-091, January 2017. (Revised May 2019 ...
Conclusion. In conclusion, the Paytm case study is a testament to India's fintech revolution. Paytm's journey from inception to becoming a digital finance giant is a remarkable story of vision ...
On January 31st, 2024, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) dealt a severe blow by barring Paytm Payments Bank from offering its core services due to persistent non-compliance issues. This move sent ...
This case study delves into the journey of Paytm, highlighting its key milestones, strategies, and impact on the Indian economy. Background. Paytm was founded in 2010 by Vijay Shekhar Sharma with the aim of making digital payments accessible to all Indians. Initially, it started as a mobile recharge and bill payment platform.
Paytm is a payment app in India providing e‐wallet services; it is also the most prominent mobile e‐commerce app in the world's third‐largest economy. This article uses Paytm as a case ...
Paytm is the consumer brand of India's leading mobile internet company, One97 Communications. The brand is one of India's largest financial services companies, offering full-stack payments and financial solutions to consumers, offline merchants, and online platforms. Today, the company serves millions of merchants and customers on its platform in India.
Examples of Entrepreneurship and Innovation are-IBM, Microsoft, Flipkart, Paytm, Ola etc. This research paper is concerned with the importance of innovation in entrepreneurship with the help of ...
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on Wednesday (January 31) barred Paytm Payments Bank from offering all its core services — including accounts and wallets — from March, effectively crippling the company's business. The action is technically not a cancellation of the licence of Paytm Payments Bank, but it constricts the company's operations to a very large extent.
Sendbird's world-class conversation platform architecture and technical foundations are certified by AWS. Founded in 2010, Paytm is India's leading financial services company that offers full-stack payments and solutions to consumers, offline merchants, and online platforms. Paytm's mission is to bring half a billion Indians into the ...
Paytm—which supports over 20 million merchants and business—is the largest digital payments, commerce, and financial services platform in India, used by more than 300 million Indians. Paytm has been experiencing rapid growth, achieving 76 percent year-on-year revenue growth based on its Q2 FY 2023 results. "Our vision is to serve half a ...
lapaasindia. April 23, 2019. 2 Minute Summary. Paytm one of the biggest Fintech Company of Indian which has become a case study for Harvard University students. Revenue of Paytm was 3579 crores that is 500 million dollars in 2019. Paytm earns throughs varios business like Market Place which it runs by the name of Paytm Mall, and other recharge ...
The recent case of RBI's crackdown on Paytm has put the spotlight on the operations of Payment Banks In India. RBI has ordered Paytm Payments Bank Ltd (PPBL) to halt most of its business including taking further deposits, conducting credit transactions and carrying out top-ups on any customer accounts, prepaid instruments, wallets, and cards for paying road tolls after February 29, 2024.
Paytm is one of India's largest financial services companies, offering solutions ranging from payments, e-commerce, banking, and more, to serve the underbanked population and businesses in India. To keep pace with business growth and a rapidly increasing pool of users and customers, the company adopted Amazon Textract, which instantly and accurately extracts text and data from users ...
CNBC-TV18 has learnt that the Reserve Bank of India had found 31 crore out of 35 crore Paytm Wallets inoperative in its inspection, cases where a single PAN card was linked to thousands of accounts, absence of KYC for lakhs of accounts and violation of KYC-anti money laundering rules, instances of false compliance reports being submitted by the bank, PPBL's financial and non-financial ...