How to Write Limitations of the Study (with examples)
This blog emphasizes the importance of recognizing and effectively writing about limitations in research. It discusses the types of limitations, their significance, and provides guidelines for writing about them, highlighting their role in advancing scholarly research.
Updated on August 24, 2023

No matter how well thought out, every research endeavor encounters challenges. There is simply no way to predict all possible variances throughout the process.
These uncharted boundaries and abrupt constraints are known as limitations in research . Identifying and acknowledging limitations is crucial for conducting rigorous studies. Limitations provide context and shed light on gaps in the prevailing inquiry and literature.
This article explores the importance of recognizing limitations and discusses how to write them effectively. By interpreting limitations in research and considering prevalent examples, we aim to reframe the perception from shameful mistakes to respectable revelations.

What are limitations in research?
In the clearest terms, research limitations are the practical or theoretical shortcomings of a study that are often outside of the researcher’s control . While these weaknesses limit the generalizability of a study’s conclusions, they also present a foundation for future research.
Sometimes limitations arise from tangible circumstances like time and funding constraints, or equipment and participant availability. Other times the rationale is more obscure and buried within the research design. Common types of limitations and their ramifications include:
- Theoretical: limits the scope, depth, or applicability of a study.
- Methodological: limits the quality, quantity, or diversity of the data.
- Empirical: limits the representativeness, validity, or reliability of the data.
- Analytical: limits the accuracy, completeness, or significance of the findings.
- Ethical: limits the access, consent, or confidentiality of the data.
Regardless of how, when, or why they arise, limitations are a natural part of the research process and should never be ignored . Like all other aspects, they are vital in their own purpose.
Why is identifying limitations important?
Whether to seek acceptance or avoid struggle, humans often instinctively hide flaws and mistakes. Merging this thought process into research by attempting to hide limitations, however, is a bad idea. It has the potential to negate the validity of outcomes and damage the reputation of scholars.
By identifying and addressing limitations throughout a project, researchers strengthen their arguments and curtail the chance of peer censure based on overlooked mistakes. Pointing out these flaws shows an understanding of variable limits and a scrupulous research process.
Showing awareness of and taking responsibility for a project’s boundaries and challenges validates the integrity and transparency of a researcher. It further demonstrates the researchers understand the applicable literature and have thoroughly evaluated their chosen research methods.
Presenting limitations also benefits the readers by providing context for research findings. It guides them to interpret the project’s conclusions only within the scope of very specific conditions. By allowing for an appropriate generalization of the findings that is accurately confined by research boundaries and is not too broad, limitations boost a study’s credibility .
Limitations are true assets to the research process. They highlight opportunities for future research. When researchers identify the limitations of their particular approach to a study question, they enable precise transferability and improve chances for reproducibility.
Simply stating a project’s limitations is not adequate for spurring further research, though. To spark the interest of other researchers, these acknowledgements must come with thorough explanations regarding how the limitations affected the current study and how they can potentially be overcome with amended methods.
How to write limitations
Typically, the information about a study’s limitations is situated either at the beginning of the discussion section to provide context for readers or at the conclusion of the discussion section to acknowledge the need for further research. However, it varies depending upon the target journal or publication guidelines.
Don’t hide your limitations
It is also important to not bury a limitation in the body of the paper unless it has a unique connection to a topic in that section. If so, it needs to be reiterated with the other limitations or at the conclusion of the discussion section. Wherever it is included in the manuscript, ensure that the limitations section is prominently positioned and clearly introduced.
While maintaining transparency by disclosing limitations means taking a comprehensive approach, it is not necessary to discuss everything that could have potentially gone wrong during the research study. If there is no commitment to investigation in the introduction, it is unnecessary to consider the issue a limitation to the research. Wholly consider the term ‘limitations’ and ask, “Did it significantly change or limit the possible outcomes?” Then, qualify the occurrence as either a limitation to include in the current manuscript or as an idea to note for other projects.
Writing limitations
Once the limitations are concretely identified and it is decided where they will be included in the paper, researchers are ready for the writing task. Including only what is pertinent, keeping explanations detailed but concise, and employing the following guidelines is key for crafting valuable limitations:
1) Identify and describe the limitations : Clearly introduce the limitation by classifying its form and specifying its origin. For example:
- An unintentional bias encountered during data collection
- An intentional use of unplanned post-hoc data analysis
2) Explain the implications : Describe how the limitation potentially influences the study’s findings and how the validity and generalizability are subsequently impacted. Provide examples and evidence to support claims of the limitations’ effects without making excuses or exaggerating their impact. Overall, be transparent and objective in presenting the limitations, without undermining the significance of the research.
3) Provide alternative approaches for future studies : Offer specific suggestions for potential improvements or avenues for further investigation. Demonstrate a proactive approach by encouraging future research that addresses the identified gaps and, therefore, expands the knowledge base.
Whether presenting limitations as an individual section within the manuscript or as a subtopic in the discussion area, authors should use clear headings and straightforward language to facilitate readability. There is no need to complicate limitations with jargon, computations, or complex datasets.
Examples of common limitations
Limitations are generally grouped into two categories , methodology and research process .
Methodology limitations
Methodology may include limitations due to:
- Sample size
- Lack of available or reliable data
- Lack of prior research studies on the topic
- Measure used to collect the data
- Self-reported data

The researcher is addressing how the large sample size requires a reassessment of the measures used to collect and analyze the data.
Research process limitations
Limitations during the research process may arise from:
- Access to information
- Longitudinal effects
- Cultural and other biases
- Language fluency
- Time constraints

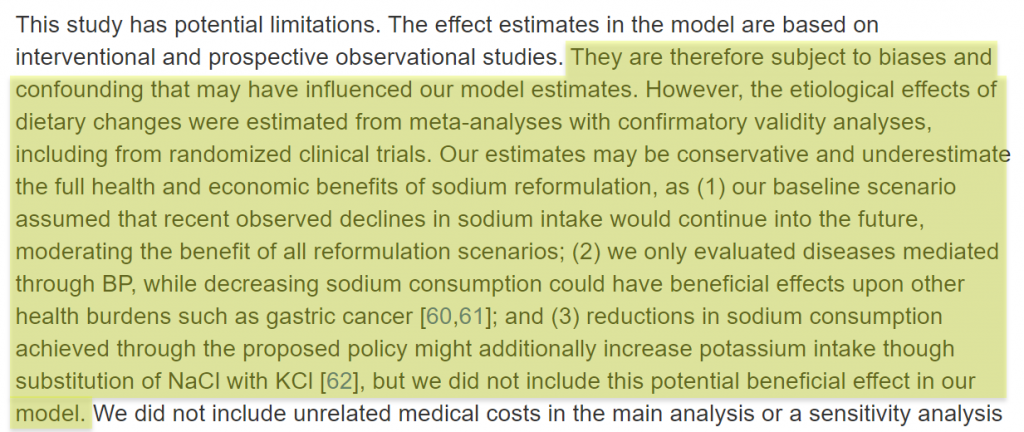
The author is pointing out that the model’s estimates are based on potentially biased observational studies.
Final thoughts
Successfully proving theories and touting great achievements are only two very narrow goals of scholarly research. The true passion and greatest efforts of researchers comes more in the form of confronting assumptions and exploring the obscure.
In many ways, recognizing and sharing the limitations of a research study both allows for and encourages this type of discovery that continuously pushes research forward. By using limitations to provide a transparent account of the project's boundaries and to contextualize the findings, researchers pave the way for even more robust and impactful research in the future.
Charla Viera, MS
See our "Privacy Policy"
Ensure your structure and ideas are consistent and clearly communicated
Pair your Premium Editing with our add-on service Presubmission Review for an overall assessment of your manuscript.
- Write my thesis
- Thesis writers
- Buy thesis papers
- Bachelor thesis
- Master's thesis
- Thesis editing services
- Thesis proofreading services
- Buy a thesis online
- Write my dissertation
- Dissertation proposal help
- Pay for dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help online
- Buy dissertation online
- Cheap dissertation
- Dissertation editing services
- Write my research paper
- Buy research paper online
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper help
- Order research paper
- Custom research paper
- Cheap research paper
- Research papers for sale
- Thesis subjects
- How It Works
Limitations Of the Study Example and Tips For Students

We are all subject to imperfections. This means that while we may excel at something, it’ll always have some flaws. On that note, every study, no matter how proficient the writer may be, has study limitations. Therefore, while you want your academic work to be viewed as exemplary and worthy of premium grades, it’s also essential that you accept it’ll always be subject to the limitations of a study. The sooner you do, the better your work will be, and the better your professor will view you. To put it simply, a little humility goes a long way not only in life but also in research. Described herein is all you need to know about limitations to a study.
What are Limitations in a Study?
Why should you include limitations of a study in your paper, examples of limitations of study in research proposal.
Study limitations refer to those characteristics or constraints that hinder or influence the interpretation of the writer’s findings from research. To put it simply, a limitation is any shortcoming that impacts a study and its outcomes. They are a normal part of any study, observational, or cross-sectional study. In most cases, they are often a result of flawed methodology, insufficient academic resources, or a lack of previous research studies on the topic. These limitations are usually part of the discussion section of the survey, just before the conclusion.
Before we even head over to the examples of study limitations in various papers, take time to see why it’s essential you first understand why you should acknowledge your study limitations below
- They Acknowledge Your Study’s Flaws before Anyone Does. As noted, every study is subject to limitations of the study. Therefore, regardless of how experienced a writer you may be, your work will always have flaws. So it’s wiser to openly acknowledge them rather than wait for your professor to point them out, and give you a lower grade because you appear ignorant.
- They are Proof You’ve Done Enough Research. Limitations of a research study also prove to the reader that you did serious research on the subject. They also show you took time to think critically of the subject questions, understood what was needed, and correctly assessed the various methods available for solving the problem. As a result, they have a reason to believe you did your best with the available findings, hence resulting in greater grades even on a subject with limited research.
- Study Limitations Create Room for Further Research. Study limitations also create room for you to propose further research on a particular topic in the future. This, in turn, keeps the reader tuned for any developments that may come up in the future.
Now that you know study limitations are normal and help make your grade stronger, what are the various limitations of a research study that you should mention? Here are a few to study limitation examples to get you started.
- Language Barrier: Some studies will require you to use a different language other than your native one. In such instances, you might need to use a translator or translation app. Even so, you might not get accurate information or some data might get lost during the translation. An example of this is when you study the effectiveness of a certain model of study on students who are learning English. In such a case, you might deal with language-related issues. If so, make sure you have highlighted it in your discussion. Explain how the language barrier affected the finding.
- Culture Bias: Another factor that can impact your research is cultural bias. Unfortunately, most people are not conscious when it comes to cultural bias. Though you might get positive cultural bias, in most cases, this is a negative issue. So, you should be alert when proofreading your work so that you can take notes of bias. It could be in the samples you offer or any other detail in your research. If the sources you are using for your report have any form of bias, acknowledge it and explain the effort you used to avoid it.
- Timing Study: At times, your resort might need you to investigate a certain phenomenon long after it took place. In such situations, you might be late in your data collection. If so, you might not have the right respondents, and that will affect your study’s outcome. Thus, the timing of your study might represent a strong limitation. Highlight this fact when presenting your research and discuss ways that your study’s poor timing might have influenced the outcome.
- Financial Resource: Some studies might need you to buy certain tools to help. In some incidents, you might have to hire people to assist you with the data collection process. Some studies will need you to buy specific statistical software or reward those who participate in products and giveaways. If you do not have enough financial resources, you will not carry out your research as required. Since such limitations will impact the results of your study, include them in your report. Discuss how lack of financial resources has impacted your outcome.
- Limited Access to Data: Limited access to data is one of the most common limitations of research studies, and one you will face more regularly. For instance, if your subject topic involves researching specific government organizations, then you may lack access to vital information. Also, you may have no respondents. This often limits the scope of your analysis, leaving you no option but to restructure your study based on the findings. In such a case, you must state this as the limitation of the study. But don’t just list it as “limited data access.” Make sure you explain the reasons for limited data access, so the reader doesn’t question the validity of your research.
- Sample Size: This is one of the most common limitations of a cross-sectional study. It often comes about because the nature of the problem dictates the sample size. For instance, if your study seeks to explain the perception of teenage consumers towards a particular product, but you only conduct your study with 50 respondents, your results will be inaccurate. This is because the number of teenagers in a country like the US is incredibly high; hence, the opinion of only 50 respondents doesn’t adequately represent the opinion of the rest. Therefore, if this is your limitation, be sure to state your study is based on a smaller sample size and that you could have generated many accurate results on a larger one.
- Lack of Previous Research on the Subject: In other cases, you might have unlimited access to data, but if there is no research done on the subject matter, then this will also impact the interpretation of your findings. For instance, if the research subject is whether a cryptocurrency will replace fiat currencies as a future currency, then you may not find enough studies on the subject. But if you chose to explore the impact of crypto on the finance industry, then you’ll find tons of information. On that note, if you’re researching a particular subject and find that there it lacks prior research studies, ensure you acknowledge this study limitation and propose further research.
- Data Collection Methodology: Very often, the method used to collect data usually affects the results of the study. For instance, your professor might have assigned you the topic ” is the impact of mobile phones on teenagers negative or positive?” Now, there are various to find out. If you choose only to interview teenagers for answers, there is a high chance of your results being flawed as they will only provide the positives. The data collection method is common among limitations of case-control and observational studies. Contact professional writers to learn more about it.
- Equipment: The type of equipment used to carry out a study can also hinder the findings. This is usually a regular limitation of observational studies. For example, if you’re surveying the effectiveness of smartphones, it’s important to note there is a vast array in the market. Therefore, you may use a high-quality one means your results will be positive, but low-quality ones mean your findings will render smartphones ineffective. That said, you have to consider such a limitation during your research, and if it’s unavoidable, ensure you not only list it but also explain it in your discussion.
As you’ve seen, the limitations of a research study are normal and are quite many. The above are just a few examples. So next time you’re doing research and lack access to data, make sure you include this fact in your work. Honest is a virtue, and admitting as well as explaining why your findings may be flawed will impress your readers.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
APA Citation Generator
MLA Citation Generator
Chicago Citation Generator
Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Present the Limitations of the Study Examples
What are the limitations of a study?
The limitations of a study are the elements of methodology or study design that impact the interpretation of your research results. The limitations essentially detail any flaws or shortcomings in your study. Study limitations can exist due to constraints on research design, methodology, materials, etc., and these factors may impact the findings of your study. However, researchers are often reluctant to discuss the limitations of their study in their papers, feeling that bringing up limitations may undermine its research value in the eyes of readers and reviewers.
In spite of the impact it might have (and perhaps because of it) you should clearly acknowledge any limitations in your research paper in order to show readers—whether journal editors, other researchers, or the general public—that you are aware of these limitations and to explain how they affect the conclusions that can be drawn from the research.
In this article, we provide some guidelines for writing about research limitations, show examples of some frequently seen study limitations, and recommend techniques for presenting this information. And after you have finished drafting and have received manuscript editing for your work, you still might want to follow this up with academic editing before submitting your work to your target journal.
Why do I need to include limitations of research in my paper?
Although limitations address the potential weaknesses of a study, writing about them toward the end of your paper actually strengthens your study by identifying any problems before other researchers or reviewers find them.
Furthermore, pointing out study limitations shows that you’ve considered the impact of research weakness thoroughly and have an in-depth understanding of your research topic. Since all studies face limitations, being honest and detailing these limitations will impress researchers and reviewers more than ignoring them.

Where should I put the limitations of the study in my paper?
Some limitations might be evident to researchers before the start of the study, while others might become clear while you are conducting the research. Whether these limitations are anticipated or not, and whether they are due to research design or to methodology, they should be clearly identified and discussed in the discussion section —the final section of your paper. Most journals now require you to include a discussion of potential limitations of your work, and many journals now ask you to place this “limitations section” at the very end of your article.
Some journals ask you to also discuss the strengths of your work in this section, and some allow you to freely choose where to include that information in your discussion section—make sure to always check the author instructions of your target journal before you finalize a manuscript and submit it for peer review .
Limitations of the Study Examples
There are several reasons why limitations of research might exist. The two main categories of limitations are those that result from the methodology and those that result from issues with the researcher(s).
Common Methodological Limitations of Studies
Limitations of research due to methodological problems can be addressed by clearly and directly identifying the potential problem and suggesting ways in which this could have been addressed—and SHOULD be addressed in future studies. The following are some major potential methodological issues that can impact the conclusions researchers can draw from the research.
Issues with research samples and selection
Sampling errors occur when a probability sampling method is used to select a sample, but that sample does not reflect the general population or appropriate population concerned. This results in limitations of your study known as “sample bias” or “selection bias.”
For example, if you conducted a survey to obtain your research results, your samples (participants) were asked to respond to the survey questions. However, you might have had limited ability to gain access to the appropriate type or geographic scope of participants. In this case, the people who responded to your survey questions may not truly be a random sample.
Insufficient sample size for statistical measurements
When conducting a study, it is important to have a sufficient sample size in order to draw valid conclusions. The larger the sample, the more precise your results will be. If your sample size is too small, it will be difficult to identify significant relationships in the data.
Normally, statistical tests require a larger sample size to ensure that the sample is considered representative of a population and that the statistical result can be generalized to a larger population. It is a good idea to understand how to choose an appropriate sample size before you conduct your research by using scientific calculation tools—in fact, many journals now require such estimation to be included in every manuscript that is sent out for review.
Lack of previous research studies on the topic
Citing and referencing prior research studies constitutes the basis of the literature review for your thesis or study, and these prior studies provide the theoretical foundations for the research question you are investigating. However, depending on the scope of your research topic, prior research studies that are relevant to your thesis might be limited.
When there is very little or no prior research on a specific topic, you may need to develop an entirely new research typology. In this case, discovering a limitation can be considered an important opportunity to identify literature gaps and to present the need for further development in the area of study.
Methods/instruments/techniques used to collect the data
After you complete your analysis of the research findings (in the discussion section), you might realize that the manner in which you have collected the data or the ways in which you have measured variables has limited your ability to conduct a thorough analysis of the results.
For example, you might realize that you should have addressed your survey questions from another viable perspective, or that you were not able to include an important question in the survey. In these cases, you should acknowledge the deficiency or deficiencies by stating a need for future researchers to revise their specific methods for collecting data that includes these missing elements.
Common Limitations of the Researcher(s)
Study limitations that arise from situations relating to the researcher or researchers (whether the direct fault of the individuals or not) should also be addressed and dealt with, and remedies to decrease these limitations—both hypothetically in your study, and practically in future studies—should be proposed.
Limited access to data
If your research involved surveying certain people or organizations, you might have faced the problem of having limited access to these respondents. Due to this limited access, you might need to redesign or restructure your research in a different way. In this case, explain the reasons for limited access and be sure that your finding is still reliable and valid despite this limitation.
Time constraints
Just as students have deadlines to turn in their class papers, academic researchers might also have to meet deadlines for submitting a manuscript to a journal or face other time constraints related to their research (e.g., participants are only available during a certain period; funding runs out; collaborators move to a new institution). The time available to study a research problem and to measure change over time might be constrained by such practical issues. If time constraints negatively impacted your study in any way, acknowledge this impact by mentioning a need for a future study (e.g., a longitudinal study) to answer this research problem.
Conflicts arising from cultural bias and other personal issues
Researchers might hold biased views due to their cultural backgrounds or perspectives of certain phenomena, and this can affect a study’s legitimacy. Also, it is possible that researchers will have biases toward data and results that only support their hypotheses or arguments. In order to avoid these problems, the author(s) of a study should examine whether the way the research problem was stated and the data-gathering process was carried out appropriately.
Steps for Organizing Your Study Limitations Section
When you discuss the limitations of your study, don’t simply list and describe your limitations—explain how these limitations have influenced your research findings. There might be multiple limitations in your study, but you only need to point out and explain those that directly relate to and impact how you address your research questions.
We suggest that you divide your limitations section into three steps: (1) identify the study limitations; (2) explain how they impact your study in detail; and (3) propose a direction for future studies and present alternatives. By following this sequence when discussing your study’s limitations, you will be able to clearly demonstrate your study’s weakness without undermining the quality and integrity of your research.
Step 1. Identify the limitation(s) of the study
- This part should comprise around 10%-20% of your discussion of study limitations.
The first step is to identify the particular limitation(s) that affected your study. There are many possible limitations of research that can affect your study, but you don’t need to write a long review of all possible study limitations. A 200-500 word critique is an appropriate length for a research limitations section. In the beginning of this section, identify what limitations your study has faced and how important these limitations are.
You only need to identify limitations that had the greatest potential impact on: (1) the quality of your findings, and (2) your ability to answer your research question.

Step 2. Explain these study limitations in detail
- This part should comprise around 60-70% of your discussion of limitations.
After identifying your research limitations, it’s time to explain the nature of the limitations and how they potentially impacted your study. For example, when you conduct quantitative research, a lack of probability sampling is an important issue that you should mention. On the other hand, when you conduct qualitative research, the inability to generalize the research findings could be an issue that deserves mention.
Explain the role these limitations played on the results and implications of the research and justify the choice you made in using this “limiting” methodology or other action in your research. Also, make sure that these limitations didn’t undermine the quality of your dissertation .
Step 3. Propose a direction for future studies and present alternatives (optional)
- This part should comprise around 10-20% of your discussion of limitations.
After acknowledging the limitations of the research, you need to discuss some possible ways to overcome these limitations in future studies. One way to do this is to present alternative methodologies and ways to avoid issues with, or “fill in the gaps of” the limitations of this study you have presented. Discuss both the pros and cons of these alternatives and clearly explain why researchers should choose these approaches.
Make sure you are current on approaches used by prior studies and the impacts they have had on their findings. Cite review articles or scientific bodies that have recommended these approaches and why. This might be evidence in support of the approach you chose, or it might be the reason you consider your choices to be included as limitations. This process can act as a justification for your approach and a defense of your decision to take it while acknowledging the feasibility of other approaches.
P hrases and Tips for Introducing Your Study Limitations in the Discussion Section
The following phrases are frequently used to introduce the limitations of the study:
- “There may be some possible limitations in this study.”
- “The findings of this study have to be seen in light of some limitations.”
- “The first is the…The second limitation concerns the…”
- “The empirical results reported herein should be considered in the light of some limitations.”
- “This research, however, is subject to several limitations.”
- “The primary limitation to the generalization of these results is…”
- “Nonetheless, these results must be interpreted with caution and a number of limitations should be borne in mind.”
- “As with the majority of studies, the design of the current study is subject to limitations.”
- “There are two major limitations in this study that could be addressed in future research. First, the study focused on …. Second ….”
For more articles on research writing and the journal submissions and publication process, visit Wordvice’s Academic Resources page.
And be sure to receive professional English editing and proofreading services , including paper editing services , for your journal manuscript before submitting it to journal editors.
Wordvice Resources
Proofreading & Editing Guide
Writing the Results Section for a Research Paper
How to Write a Literature Review
Research Writing Tips: How to Draft a Powerful Discussion Section
How to Captivate Journal Readers with a Strong Introduction
Tips That Will Make Your Abstract a Success!
APA In-Text Citation Guide for Research Writing
Additional Resources
- Diving Deeper into Limitations and Delimitations (PhD student)
- Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: Limitations of the Study (USC Library)
- Research Limitations (Research Methodology)
- How to Present Limitations and Alternatives (UMASS)
Article References
Pearson-Stuttard, J., Kypridemos, C., Collins, B., Mozaffarian, D., Huang, Y., Bandosz, P.,…Micha, R. (2018). Estimating the health and economic effects of the proposed US Food and Drug Administration voluntary sodium reformulation: Microsimulation cost-effectiveness analysis. PLOS. https://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1002551
Xu, W.L, Pedersen, N.L., Keller, L., Kalpouzos, G., Wang, H.X., Graff, C,. Fratiglioni, L. (2015). HHEX_23 AA Genotype Exacerbates Effect of Diabetes on Dementia and Alzheimer Disease: A Population-Based Longitudinal Study. PLOS. Retrieved from https://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1001853
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Limitations of the Study
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The limitations of the study are those characteristics of design or methodology that impacted or influenced the interpretation of the findings from your research. Study limitations are the constraints placed on the ability to generalize from the results, to further describe applications to practice, and/or related to the utility of findings that are the result of the ways in which you initially chose to design the study or the method used to establish internal and external validity or the result of unanticipated challenges that emerged during the study.
Price, James H. and Judy Murnan. “Research Limitations and the Necessity of Reporting Them.” American Journal of Health Education 35 (2004): 66-67; Theofanidis, Dimitrios and Antigoni Fountouki. "Limitations and Delimitations in the Research Process." Perioperative Nursing 7 (September-December 2018): 155-163. .
Importance of...
Always acknowledge a study's limitations. It is far better that you identify and acknowledge your study’s limitations than to have them pointed out by your professor and have your grade lowered because you appeared to have ignored them or didn't realize they existed.
Keep in mind that acknowledgment of a study's limitations is an opportunity to make suggestions for further research. If you do connect your study's limitations to suggestions for further research, be sure to explain the ways in which these unanswered questions may become more focused because of your study.
Acknowledgment of a study's limitations also provides you with opportunities to demonstrate that you have thought critically about the research problem, understood the relevant literature published about it, and correctly assessed the methods chosen for studying the problem. A key objective of the research process is not only discovering new knowledge but also to confront assumptions and explore what we don't know.
Claiming limitations is a subjective process because you must evaluate the impact of those limitations . Don't just list key weaknesses and the magnitude of a study's limitations. To do so diminishes the validity of your research because it leaves the reader wondering whether, or in what ways, limitation(s) in your study may have impacted the results and conclusions. Limitations require a critical, overall appraisal and interpretation of their impact. You should answer the question: do these problems with errors, methods, validity, etc. eventually matter and, if so, to what extent?
Price, James H. and Judy Murnan. “Research Limitations and the Necessity of Reporting Them.” American Journal of Health Education 35 (2004): 66-67; Structure: How to Structure the Research Limitations Section of Your Dissertation. Dissertations and Theses: An Online Textbook. Laerd.com.
Descriptions of Possible Limitations
All studies have limitations . However, it is important that you restrict your discussion to limitations related to the research problem under investigation. For example, if a meta-analysis of existing literature is not a stated purpose of your research, it should not be discussed as a limitation. Do not apologize for not addressing issues that you did not promise to investigate in the introduction of your paper.
Here are examples of limitations related to methodology and the research process you may need to describe and discuss how they possibly impacted your results. Note that descriptions of limitations should be stated in the past tense because they were discovered after you completed your research.
Possible Methodological Limitations
- Sample size -- the number of the units of analysis you use in your study is dictated by the type of research problem you are investigating. Note that, if your sample size is too small, it will be difficult to find significant relationships from the data, as statistical tests normally require a larger sample size to ensure a representative distribution of the population and to be considered representative of groups of people to whom results will be generalized or transferred. Note that sample size is generally less relevant in qualitative research if explained in the context of the research problem.
- Lack of available and/or reliable data -- a lack of data or of reliable data will likely require you to limit the scope of your analysis, the size of your sample, or it can be a significant obstacle in finding a trend and a meaningful relationship. You need to not only describe these limitations but provide cogent reasons why you believe data is missing or is unreliable. However, don’t just throw up your hands in frustration; use this as an opportunity to describe a need for future research based on designing a different method for gathering data.
- Lack of prior research studies on the topic -- citing prior research studies forms the basis of your literature review and helps lay a foundation for understanding the research problem you are investigating. Depending on the currency or scope of your research topic, there may be little, if any, prior research on your topic. Before assuming this to be true, though, consult with a librarian! In cases when a librarian has confirmed that there is little or no prior research, you may be required to develop an entirely new research typology [for example, using an exploratory rather than an explanatory research design ]. Note again that discovering a limitation can serve as an important opportunity to identify new gaps in the literature and to describe the need for further research.
- Measure used to collect the data -- sometimes it is the case that, after completing your interpretation of the findings, you discover that the way in which you gathered data inhibited your ability to conduct a thorough analysis of the results. For example, you regret not including a specific question in a survey that, in retrospect, could have helped address a particular issue that emerged later in the study. Acknowledge the deficiency by stating a need for future researchers to revise the specific method for gathering data.
- Self-reported data -- whether you are relying on pre-existing data or you are conducting a qualitative research study and gathering the data yourself, self-reported data is limited by the fact that it rarely can be independently verified. In other words, you have to the accuracy of what people say, whether in interviews, focus groups, or on questionnaires, at face value. However, self-reported data can contain several potential sources of bias that you should be alert to and note as limitations. These biases become apparent if they are incongruent with data from other sources. These are: (1) selective memory [remembering or not remembering experiences or events that occurred at some point in the past]; (2) telescoping [recalling events that occurred at one time as if they occurred at another time]; (3) attribution [the act of attributing positive events and outcomes to one's own agency, but attributing negative events and outcomes to external forces]; and, (4) exaggeration [the act of representing outcomes or embellishing events as more significant than is actually suggested from other data].
Possible Limitations of the Researcher
- Access -- if your study depends on having access to people, organizations, data, or documents and, for whatever reason, access is denied or limited in some way, the reasons for this needs to be described. Also, include an explanation why being denied or limited access did not prevent you from following through on your study.
- Longitudinal effects -- unlike your professor, who can literally devote years [even a lifetime] to studying a single topic, the time available to investigate a research problem and to measure change or stability over time is constrained by the due date of your assignment. Be sure to choose a research problem that does not require an excessive amount of time to complete the literature review, apply the methodology, and gather and interpret the results. If you're unsure whether you can complete your research within the confines of the assignment's due date, talk to your professor.
- Cultural and other type of bias -- we all have biases, whether we are conscience of them or not. Bias is when a person, place, event, or thing is viewed or shown in a consistently inaccurate way. Bias is usually negative, though one can have a positive bias as well, especially if that bias reflects your reliance on research that only support your hypothesis. When proof-reading your paper, be especially critical in reviewing how you have stated a problem, selected the data to be studied, what may have been omitted, the manner in which you have ordered events, people, or places, how you have chosen to represent a person, place, or thing, to name a phenomenon, or to use possible words with a positive or negative connotation. NOTE : If you detect bias in prior research, it must be acknowledged and you should explain what measures were taken to avoid perpetuating that bias. For example, if a previous study only used boys to examine how music education supports effective math skills, describe how your research expands the study to include girls.
- Fluency in a language -- if your research focuses , for example, on measuring the perceived value of after-school tutoring among Mexican-American ESL [English as a Second Language] students and you are not fluent in Spanish, you are limited in being able to read and interpret Spanish language research studies on the topic or to speak with these students in their primary language. This deficiency should be acknowledged.
Aguinis, Hermam and Jeffrey R. Edwards. “Methodological Wishes for the Next Decade and How to Make Wishes Come True.” Journal of Management Studies 51 (January 2014): 143-174; Brutus, Stéphane et al. "Self-Reported Limitations and Future Directions in Scholarly Reports: Analysis and Recommendations." Journal of Management 39 (January 2013): 48-75; Senunyeme, Emmanuel K. Business Research Methods. Powerpoint Presentation. Regent University of Science and Technology; ter Riet, Gerben et al. “All That Glitters Isn't Gold: A Survey on Acknowledgment of Limitations in Biomedical Studies.” PLOS One 8 (November 2013): 1-6.
Structure and Writing Style
Information about the limitations of your study are generally placed either at the beginning of the discussion section of your paper so the reader knows and understands the limitations before reading the rest of your analysis of the findings, or, the limitations are outlined at the conclusion of the discussion section as an acknowledgement of the need for further study. Statements about a study's limitations should not be buried in the body [middle] of the discussion section unless a limitation is specific to something covered in that part of the paper. If this is the case, though, the limitation should be reiterated at the conclusion of the section.
If you determine that your study is seriously flawed due to important limitations , such as, an inability to acquire critical data, consider reframing it as an exploratory study intended to lay the groundwork for a more complete research study in the future. Be sure, though, to specifically explain the ways that these flaws can be successfully overcome in a new study.
But, do not use this as an excuse for not developing a thorough research paper! Review the tab in this guide for developing a research topic . If serious limitations exist, it generally indicates a likelihood that your research problem is too narrowly defined or that the issue or event under study is too recent and, thus, very little research has been written about it. If serious limitations do emerge, consult with your professor about possible ways to overcome them or how to revise your study.
When discussing the limitations of your research, be sure to:
- Describe each limitation in detailed but concise terms;
- Explain why each limitation exists;
- Provide the reasons why each limitation could not be overcome using the method(s) chosen to acquire or gather the data [cite to other studies that had similar problems when possible];
- Assess the impact of each limitation in relation to the overall findings and conclusions of your study; and,
- If appropriate, describe how these limitations could point to the need for further research.
Remember that the method you chose may be the source of a significant limitation that has emerged during your interpretation of the results [for example, you didn't interview a group of people that you later wish you had]. If this is the case, don't panic. Acknowledge it, and explain how applying a different or more robust methodology might address the research problem more effectively in a future study. A underlying goal of scholarly research is not only to show what works, but to demonstrate what doesn't work or what needs further clarification.
Aguinis, Hermam and Jeffrey R. Edwards. “Methodological Wishes for the Next Decade and How to Make Wishes Come True.” Journal of Management Studies 51 (January 2014): 143-174; Brutus, Stéphane et al. "Self-Reported Limitations and Future Directions in Scholarly Reports: Analysis and Recommendations." Journal of Management 39 (January 2013): 48-75; Ioannidis, John P.A. "Limitations are not Properly Acknowledged in the Scientific Literature." Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 60 (2007): 324-329; Pasek, Josh. Writing the Empirical Social Science Research Paper: A Guide for the Perplexed. January 24, 2012. Academia.edu; Structure: How to Structure the Research Limitations Section of Your Dissertation. Dissertations and Theses: An Online Textbook. Laerd.com; What Is an Academic Paper? Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College; Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Writing Tip
Don't Inflate the Importance of Your Findings!
After all the hard work and long hours devoted to writing your research paper, it is easy to get carried away with attributing unwarranted importance to what you’ve done. We all want our academic work to be viewed as excellent and worthy of a good grade, but it is important that you understand and openly acknowledge the limitations of your study. Inflating the importance of your study's findings could be perceived by your readers as an attempt hide its flaws or encourage a biased interpretation of the results. A small measure of humility goes a long way!
Another Writing Tip
Negative Results are Not a Limitation!
Negative evidence refers to findings that unexpectedly challenge rather than support your hypothesis. If you didn't get the results you anticipated, it may mean your hypothesis was incorrect and needs to be reformulated. Or, perhaps you have stumbled onto something unexpected that warrants further study. Moreover, the absence of an effect may be very telling in many situations, particularly in experimental research designs. In any case, your results may very well be of importance to others even though they did not support your hypothesis. Do not fall into the trap of thinking that results contrary to what you expected is a limitation to your study. If you carried out the research well, they are simply your results and only require additional interpretation.
Lewis, George H. and Jonathan F. Lewis. “The Dog in the Night-Time: Negative Evidence in Social Research.” The British Journal of Sociology 31 (December 1980): 544-558.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Sample Size Limitations in Qualitative Research
Sample sizes are typically smaller in qualitative research because, as the study goes on, acquiring more data does not necessarily lead to more information. This is because one occurrence of a piece of data, or a code, is all that is necessary to ensure that it becomes part of the analysis framework. However, it remains true that sample sizes that are too small cannot adequately support claims of having achieved valid conclusions and sample sizes that are too large do not permit the deep, naturalistic, and inductive analysis that defines qualitative inquiry. Determining adequate sample size in qualitative research is ultimately a matter of judgment and experience in evaluating the quality of the information collected against the uses to which it will be applied and the particular research method and purposeful sampling strategy employed. If the sample size is found to be a limitation, it may reflect your judgment about the methodological technique chosen [e.g., single life history study versus focus group interviews] rather than the number of respondents used.
Boddy, Clive Roland. "Sample Size for Qualitative Research." Qualitative Market Research: An International Journal 19 (2016): 426-432; Huberman, A. Michael and Matthew B. Miles. "Data Management and Analysis Methods." In Handbook of Qualitative Research . Norman K. Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, eds. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1994), pp. 428-444; Blaikie, Norman. "Confounding Issues Related to Determining Sample Size in Qualitative Research." International Journal of Social Research Methodology 21 (2018): 635-641; Oppong, Steward Harrison. "The Problem of Sampling in qualitative Research." Asian Journal of Management Sciences and Education 2 (2013): 202-210.
- << Previous: 8. The Discussion
- Next: 9. The Conclusion >>
- Last Updated: Apr 1, 2024 9:56 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Limitations in Research – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Limitations in Research – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Limitations in Research
Limitations in research refer to the factors that may affect the results, conclusions , and generalizability of a study. These limitations can arise from various sources, such as the design of the study, the sampling methods used, the measurement tools employed, and the limitations of the data analysis techniques.
Types of Limitations in Research
Types of Limitations in Research are as follows:
Sample Size Limitations
This refers to the size of the group of people or subjects that are being studied. If the sample size is too small, then the results may not be representative of the population being studied. This can lead to a lack of generalizability of the results.
Time Limitations
Time limitations can be a constraint on the research process . This could mean that the study is unable to be conducted for a long enough period of time to observe the long-term effects of an intervention, or to collect enough data to draw accurate conclusions.
Selection Bias
This refers to a type of bias that can occur when the selection of participants in a study is not random. This can lead to a biased sample that is not representative of the population being studied.
Confounding Variables
Confounding variables are factors that can influence the outcome of a study, but are not being measured or controlled for. These can lead to inaccurate conclusions or a lack of clarity in the results.
Measurement Error
This refers to inaccuracies in the measurement of variables, such as using a faulty instrument or scale. This can lead to inaccurate results or a lack of validity in the study.
Ethical Limitations
Ethical limitations refer to the ethical constraints placed on research studies. For example, certain studies may not be allowed to be conducted due to ethical concerns, such as studies that involve harm to participants.
Examples of Limitations in Research
Some Examples of Limitations in Research are as follows:
Research Title: “The Effectiveness of Machine Learning Algorithms in Predicting Customer Behavior”
Limitations:
- The study only considered a limited number of machine learning algorithms and did not explore the effectiveness of other algorithms.
- The study used a specific dataset, which may not be representative of all customer behaviors or demographics.
- The study did not consider the potential ethical implications of using machine learning algorithms in predicting customer behavior.
Research Title: “The Impact of Online Learning on Student Performance in Computer Science Courses”
- The study was conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic, which may have affected the results due to the unique circumstances of remote learning.
- The study only included students from a single university, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other institutions.
- The study did not consider the impact of individual differences, such as prior knowledge or motivation, on student performance in online learning environments.
Research Title: “The Effect of Gamification on User Engagement in Mobile Health Applications”
- The study only tested a specific gamification strategy and did not explore the effectiveness of other gamification techniques.
- The study relied on self-reported measures of user engagement, which may be subject to social desirability bias or measurement errors.
- The study only included a specific demographic group (e.g., young adults) and may not be generalizable to other populations with different preferences or needs.
How to Write Limitations in Research
When writing about the limitations of a research study, it is important to be honest and clear about the potential weaknesses of your work. Here are some tips for writing about limitations in research:
- Identify the limitations: Start by identifying the potential limitations of your research. These may include sample size, selection bias, measurement error, or other issues that could affect the validity and reliability of your findings.
- Be honest and objective: When describing the limitations of your research, be honest and objective. Do not try to minimize or downplay the limitations, but also do not exaggerate them. Be clear and concise in your description of the limitations.
- Provide context: It is important to provide context for the limitations of your research. For example, if your sample size was small, explain why this was the case and how it may have affected your results. Providing context can help readers understand the limitations in a broader context.
- Discuss implications : Discuss the implications of the limitations for your research findings. For example, if there was a selection bias in your sample, explain how this may have affected the generalizability of your findings. This can help readers understand the limitations in terms of their impact on the overall validity of your research.
- Provide suggestions for future research : Finally, provide suggestions for future research that can address the limitations of your study. This can help readers understand how your research fits into the broader field and can provide a roadmap for future studies.
Purpose of Limitations in Research
There are several purposes of limitations in research. Here are some of the most important ones:
- To acknowledge the boundaries of the study : Limitations help to define the scope of the research project and set realistic expectations for the findings. They can help to clarify what the study is not intended to address.
- To identify potential sources of bias: Limitations can help researchers identify potential sources of bias in their research design, data collection, or analysis. This can help to improve the validity and reliability of the findings.
- To provide opportunities for future research: Limitations can highlight areas for future research and suggest avenues for further exploration. This can help to advance knowledge in a particular field.
- To demonstrate transparency and accountability: By acknowledging the limitations of their research, researchers can demonstrate transparency and accountability to their readers, peers, and funders. This can help to build trust and credibility in the research community.
- To encourage critical thinking: Limitations can encourage readers to critically evaluate the study’s findings and consider alternative explanations or interpretations. This can help to promote a more nuanced and sophisticated understanding of the topic under investigation.
When to Write Limitations in Research
Limitations should be included in research when they help to provide a more complete understanding of the study’s results and implications. A limitation is any factor that could potentially impact the accuracy, reliability, or generalizability of the study’s findings.
It is important to identify and discuss limitations in research because doing so helps to ensure that the results are interpreted appropriately and that any conclusions drawn are supported by the available evidence. Limitations can also suggest areas for future research, highlight potential biases or confounding factors that may have affected the results, and provide context for the study’s findings.
Generally, limitations should be discussed in the conclusion section of a research paper or thesis, although they may also be mentioned in other sections, such as the introduction or methods. The specific limitations that are discussed will depend on the nature of the study, the research question being investigated, and the data that was collected.
Examples of limitations that might be discussed in research include sample size limitations, data collection methods, the validity and reliability of measures used, and potential biases or confounding factors that could have affected the results. It is important to note that limitations should not be used as a justification for poor research design or methodology, but rather as a way to enhance the understanding and interpretation of the study’s findings.
Importance of Limitations in Research
Here are some reasons why limitations are important in research:
- Enhances the credibility of research: Limitations highlight the potential weaknesses and threats to validity, which helps readers to understand the scope and boundaries of the study. This improves the credibility of research by acknowledging its limitations and providing a clear picture of what can and cannot be concluded from the study.
- Facilitates replication: By highlighting the limitations, researchers can provide detailed information about the study’s methodology, data collection, and analysis. This information helps other researchers to replicate the study and test the validity of the findings, which enhances the reliability of research.
- Guides future research : Limitations provide insights into areas for future research by identifying gaps or areas that require further investigation. This can help researchers to design more comprehensive and effective studies that build on existing knowledge.
- Provides a balanced view: Limitations help to provide a balanced view of the research by highlighting both strengths and weaknesses. This ensures that readers have a clear understanding of the study’s limitations and can make informed decisions about the generalizability and applicability of the findings.
Advantages of Limitations in Research
Here are some potential advantages of limitations in research:
- Focus : Limitations can help researchers focus their study on a specific area or population, which can make the research more relevant and useful.
- Realism : Limitations can make a study more realistic by reflecting the practical constraints and challenges of conducting research in the real world.
- Innovation : Limitations can spur researchers to be more innovative and creative in their research design and methodology, as they search for ways to work around the limitations.
- Rigor : Limitations can actually increase the rigor and credibility of a study, as researchers are forced to carefully consider the potential sources of bias and error, and address them to the best of their abilities.
- Generalizability : Limitations can actually improve the generalizability of a study by ensuring that it is not overly focused on a specific sample or situation, and that the results can be applied more broadly.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
- The role of limitations in research: why they are important
- How to Organize Limitations of a Research Study

What are the Limitations of a Study (Research)?
Why and where to include limitations in my research paper, common limitations of the researchers.
- Limited Access to Information
Time Limits
Conflicts on biased views and personal issues, different types, 1. research design limitations, 2. impact limitations, 3. data or statistical limitations, how to structure your research limitations correctly, how to set your research limitations, formulation of your objectives and aims, implementation of your data collection methods, what are sample sizes, lacking previous studies in the same field, scope of discussions, concluding thoughts.
When completing a study or any other important work, there are different details that you should include to present its comprehensive and clear description. Sometimes you might even need to hire a thesis writer to help you with the whole writing process. Don’t underrate the section with limitations in research . It plays a big role in the entire process. Some students find it difficult to write this part, while others are reluctant to include it in their academic papers. Don’t underestimate the significance of limitations in research to provide readers with an accurate context of your work and enough data to evaluate the impact and relevance of your results. What is the best way to go about them? Keep reading to find out more.
Every research has its limitations. These limitations can appear due to constraints on methodology or research design. Needless to say, this may impact your whole study or research paper. Most researchers prefer to not discuss their study limitations because they think it may decrease the value of their paper in the eyes of the audience.
Remember that it’s quite important to show your study limitations to your audience (other researchers, editors of journals, and public readers). You need to notice that you know about these limitations and about the impact they may have. It’s important to give an explanation of how your research limitations can affect the conclusions and thoughts drawn from your research.
In this guide, you can read useful tips on how to write limitations on your future research. Read great techniques on making a proper limitations section and see examples to make sure you have got an idea of writing your qualitative research limitations. You need to understand that even if limitations show the weaknesses of your future research, including them in your study can make your paper strengthen because you show all the problems before your readers will discover them by themselves.
Apart from this, when the author points out the study limitations, it means that you have researched all the weak sides of your study and you understand the topic deeply. Needless to say, all the studies have their limitations even if you know how to make research design properly. When you’re honest with your readers, it can impress people much better than ignoring limitations at all.
Every research has certain limitations, and it’s completely normal, but you need to minimize their range of scope in the process. Provide your acknowledgment of them in the conclusion. Identify and understand potential shortcomings in your work.
When discussing limitations in research, explain how they impact your findings because creating their short list or description isn’t enough. Your research may have many limitations. Your basic goal is to discuss the ones that relate to the research questions that you choose for a specific academic assignment.
Limitations of your qualitative research can become clear to your readers even before they start to read your study. Sometimes, people can see the limitations only when they have viewed the whole document. You have to present your study limitations clearly in the Discussion section of a researh paper . This is the final part of your work where it’s logical to place the limitations section. You should write the limitations at the very beginning of this paragraph, just after you have highlighted the strong sides of the research methodology. When you discuss the limitations before the findings are analyzed, it will help to see how to qualify and apply these findings in future research.
Limitations related to the researcher must also be written and shown to readers. You have to provide suggestions on decreasing these limitations in both your and future studies.
Limited Access to Information
Your study may involve some organizations and people in the research, and sometimes you may get problems with access to these organizations. Due to this, you need to redesign and rewrite your study. You need to explain the cause of limited access to your readers.
Needless to say, all the researchers have their deadlines when they need to complete their studies. Sometimes, time constraints can affect your research negatively. If this happened, you need to acknowledge it and mention a need for future research to solve the main problem.
Some researchers can have biased views because of their cultural background or personal views. Needless to say, it can affect the research. Apart from this, researchers with biased views can choose only those results and data that support their main arguments. If you want to avoid this problem, pay your attention to the problem statement and proper data gathering.
Before you start your study or work, keep in mind that there are specific limitations to what you test or possible research results. What are their types? There are different types that students may encounter and they all have unique features, including:
- Research design limitations,
- Impact limitations,
- Data or statistical limitations.
Specific constraints on your population research or available procedures may affect the final outcomes or results that you obtain.
Even if your research has excellent stats and a strong design, it may suffer from the impact of such factors as:
- The field is conductive to incremental findings,
- Being too population-specific.
- A strong regional focus.
In some cases, it’s impossible to collect enough data or enrollment is very difficult, and all that under-powers your research results. They may stem from your study design. They produce more issues in interpreting your findings.
There are strict rules to structure this section of your academic paper where you need to justify and explain its potential weaknesses. Take these basic steps to end up with a well-structured section:
- Announce to identify your research limitations and explain their importance,
- Reflect to provide the necessary depth, explain their nature, and justify your study choices,
- Look forward to suggest how it’s possible to overcome them in the future.
They walk your readers through this section. You need them to make it clear to your target audience that you recognize potential weaknesses in your work, understand them, and can point effective solutions.
No one is perfect. It means that your work isn’t beyond possible flaws, but you need to use them as a great opportunity to overcome new challenges and improve your knowledge. In a typical academic paper, research limitations can relate to these points:
- Formulation of your objectives and aims,
- Implementation of your data collection methods,
- Sample sizes,
- Lack of previous studies in your chosen area,
- The scope of discussions.
Learn to determine them in each one.
Your work has certain shortcomings if you formulate objectives and aims in a very broad manner. What to do in this case? Specify effective methods or ways to narrow your formulation of objectives and aims to increase the level of your study focus.
If you don’t have a lot of experience in collecting primary data, there’s a certain risk that the implementation of your methods has flaws. It’s necessary to acknowledge that.
They depend on the nature of your chosen problem and their significance is bigger in quantitative studies, unlike the qualitative ones. If your sample size is very small, statistical tests will fail to identify important relationships or connections within a particular data set. How to solve this problem? State that other researchers need to base the same study on a larger sample size to end up with more accurate results. To find more information on how to identify a resesrch problem , check our guide.
Writing a literature review is a key step in any scientific work because it helps students determine the scope of existing studies in the chosen area. Why should you use the literature review findings? They are a basic foundation for any researcher who must use them to achieve a set of specific objectives or aims. What if there are no previous works? You may face this challenge if you choose an evolving or current problem for your study or if it’s very narrow.
Feel free to include this point as a shortcoming of your work, no matter what your chosen area is. Why? The main reason is that you don’t have long years of experience in writing scientific papers or completing complex studies. That’s why the depth and scope of your discussions can be compromised in different levels compared to scholars with a lot of expertise. Include certain points from limitations in research. Use them as suggestions for the future.
Any research suffers from specific limitations that range from common flaws to serious problems in design or methodology dissertation has. The ability to set these shortcomings plays a huge role in writing a successful academic paper and earning good grades. What if you lack it? Turn to our professional thesis writers and get their expert consultation on thesis or research paper.
What comes first, the research design or research problem selection? Read on this guide from our dissertation writing service if you are struggling to answer this question. Any research paper is based on the hypothesis, datum, and methodology. These things though are not written down in the instruct...
The methodology is an important part of your dissertation. It describes a broad philosophical underpinning to your chosen research methods, either quantitative or qualitative, to explain to readers your approach better. Make sure that you’re clear about an academic basis for your choice of research ...
Students have to complete different writing assignments, and some of them are utterly complex. Every assignment has the central idea or problem, which is supposed to be discussed and analyzed during the entire work. It’s called a thesis statement. The main objective of the statement is to explain to...

Writing Limitations of Research Study — 4 Reasons Why It Is Important!
It is not unusual for researchers to come across the term limitations of research during their academic paper writing. More often this is interpreted as something terrible. However, when it comes to research study, limitations can help structure the research study better. Therefore, do not underestimate significance of limitations of research study.
Allow us to take you through the context of how to evaluate the limits of your research and conclude an impactful relevance to your results.
Table of Contents
What Are the Limitations of a Research Study?
Every research has its limit and these limitations arise due to restrictions in methodology or research design. This could impact your entire research or the research paper you wish to publish. Unfortunately, most researchers choose not to discuss their limitations of research fearing it will affect the value of their article in the eyes of readers.
However, it is very important to discuss your study limitations and show it to your target audience (other researchers, journal editors, peer reviewers etc.). It is very important that you provide an explanation of how your research limitations may affect the conclusions and opinions drawn from your research. Moreover, when as an author you state the limitations of research, it shows that you have investigated all the weaknesses of your study and have a deep understanding of the subject. Being honest could impress your readers and mark your study as a sincere effort in research.

Why and Where Should You Include the Research Limitations?
The main goal of your research is to address your research objectives. Conduct experiments, get results and explain those results, and finally justify your research question . It is best to mention the limitations of research in the discussion paragraph of your research article.
At the very beginning of this paragraph, immediately after highlighting the strengths of the research methodology, you should write down your limitations. You can discuss specific points from your research limitations as suggestions for further research in the conclusion of your thesis.
1. Common Limitations of the Researchers
Limitations that are related to the researcher must be mentioned. This will help you gain transparency with your readers. Furthermore, you could provide suggestions on decreasing these limitations in you and your future studies.
2. Limited Access to Information
Your work may involve some institutions and individuals in research, and sometimes you may have problems accessing these institutions. Therefore, you need to redesign and rewrite your work. You must explain your readers the reason for limited access.
3. Limited Time
All researchers are bound by their deadlines when it comes to completing their studies. Sometimes, time constraints can affect your research negatively. However, the best practice is to acknowledge it and mention a requirement for future study to solve the research problem in a better way.
4. Conflict over Biased Views and Personal Issues
Biased views can affect the research. In fact, researchers end up choosing only those results and data that support their main argument, keeping aside the other loose ends of the research.
Types of Limitations of Research
Before beginning your research study, know that there are certain limitations to what you are testing or possible research results. There are different types that researchers may encounter, and they all have unique characteristics, such as:
1. Research Design Limitations
Certain restrictions on your research or available procedures may affect your final results or research outputs. You may have formulated research goals and objectives too broadly. However, this can help you understand how you can narrow down the formulation of research goals and objectives, thereby increasing the focus of your study.
2. Impact Limitations
Even if your research has excellent statistics and a strong design, it can suffer from the influence of the following factors:
- Presence of increasing findings as researched
- Being population specific
- A strong regional focus.
3. Data or statistical limitations
In some cases, it is impossible to collect sufficient data for research or very difficult to get access to the data. This could lead to incomplete conclusion to your study. Moreover, this insufficiency in data could be the outcome of your study design. The unclear, shabby research outline could produce more problems in interpreting your findings.
How to Correctly Structure Your Research Limitations?
There are strict guidelines for narrowing down research questions, wherein you could justify and explain potential weaknesses of your academic paper. You could go through these basic steps to get a well-structured clarity of research limitations:
- Declare that you wish to identify your limitations of research and explain their importance,
- Provide the necessary depth, explain their nature, and justify your study choices.
- Write how you are suggesting that it is possible to overcome them in the future.
In this section, your readers will see that you are aware of the potential weaknesses in your business, understand them and offer effective solutions, and it will positively strengthen your article as you clarify all limitations of research to your target audience.
Know that you cannot be perfect and there is no individual without flaws. You could use the limitations of research as a great opportunity to take on a new challenge and improve the future of research. In a typical academic paper, research limitations may relate to:
1. Formulating your goals and objectives
If you formulate goals and objectives too broadly, your work will have some shortcomings. In this case, specify effective methods or ways to narrow down the formula of goals and aim to increase your level of study focus.
2. Application of your data collection methods in research
If you do not have experience in primary data collection, there is a risk that there will be flaws in the implementation of your methods. It is necessary to accept this, and learn and educate yourself to understand data collection methods.
3. Sample sizes
This depends on the nature of problem you choose. Sample size is of a greater importance in quantitative studies as opposed to qualitative ones. If your sample size is too small, statistical tests cannot identify significant relationships or connections within a given data set.
You could point out that other researchers should base the same study on a larger sample size to get more accurate results.
4. The absence of previous studies in the field you have chosen
Writing a literature review is an important step in any scientific study because it helps researchers determine the scope of current work in the chosen field. It is a major foundation for any researcher who must use them to achieve a set of specific goals or objectives.
However, if you are focused on the most current and evolving research problem or a very narrow research problem, there may be very little prior research on your topic. For example, if you chose to explore the role of Bitcoin as the currency of the future, you may not find tons of scientific papers addressing the research problem as Bitcoins are only a new phenomenon.
It is important that you learn to identify research limitations examples at each step. Whatever field you choose, feel free to add the shortcoming of your work. This is mainly because you do not have many years of experience writing scientific papers or completing complex work. Therefore, the depth and scope of your discussions may be compromised at different levels compared to academics with a lot of expertise. Include specific points from limitations of research. Use them as suggestions for the future.
Have you ever faced a challenge of writing the limitations of research study in your paper? How did you overcome it? What ways did you follow? Were they beneficial? Let us know in the comments below!
Frequently Asked Questions
Setting limitations in our study helps to clarify the outcomes drawn from our research and enhance understanding of the subject. Moreover, it shows that the author has investigated all the weaknesses in the study.
Scope is the range and limitations of a research project which are set to define the boundaries of a project. Limitations are the impacts on the overall study due to the constraints on the research design.
Limitation in research is an impact of a constraint on the research design in the overall study. They are the flaws or weaknesses in the study, which may influence the outcome of the research.
1. Limitations in research can be written as follows: Formulate your goals and objectives 2. Analyze the chosen data collection method and the sample sizes 3. Identify your limitations of research and explain their importance 4. Provide the necessary depth, explain their nature, and justify your study choices 5. Write how you are suggesting that it is possible to overcome them in the future
Excellent article ,,,it has helped me big
This is very helpful information. It has given me an insight on how to go about my study limitations.
Good comments and helpful
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Diversity and Inclusion
- Trending Now
The Silent Struggle: Confronting gender bias in science funding
In the 1990s, Dr. Katalin Kariko’s pioneering mRNA research seemed destined for obscurity, doomed by…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…

Addressing Barriers in Academia: Navigating unconscious biases in the Ph.D. journey
In the journey of academia, a Ph.D. marks a transitional phase, like that of a…

- Manuscripts & Grants
- Reporting Research
Unraveling Research Population and Sample: Understanding their role in statistical inference
Research population and sample serve as the cornerstones of any scientific inquiry. They hold the…

- Manuscript Preparation
- Publishing Research
Research Problem Statement — Find out how to write an impactful one!
What Is a Research Problem Statement? A research problem statement is a clear, concise, and…
How to Develop a Good Research Question? — Types & Examples
5 Effective Ways to Avoid Ghostwriting for Busy Researchers
Top 5 Key Differences Between Methods and Methodology

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?

Diving Deeper into Limitations and Delimitations

If you are working on a thesis, dissertation, or other formal research project, chances are your advisor or committee will ask you to address the delimitations of your study. When faced with this request, many students respond with a puzzled look and then go on to address what are actually the study’s limitations.
In a previous article , we covered what goes into the limitations, delimitations, and assumptions sections of your thesis or dissertation. Here, we will dive a bit deeper into the differences between limitations and delimitations and provide some helpful tips for addressing them in your research project—whether you are working on a quantitative or qualitative study.
Acknowledging Weaknesses vs. Defining Boundaries
These concepts are easy to get confused because both limitations and delimitations restrict (or limit) the questions you’ll be able to answer with your study, most notably in terms of generalizability.
However, the biggest difference between limitations and delimitations is the degree of control you have over them—that is, how much they are based in conscious, intentional choices you made in designing your study.
Limitations occur in all types of research and are, for the most part, outside the researcher’s control (given practical constraints, such as time, funding, and access to populations of interest). They are threats to the study’s internal or external validity.
Limitations may include things such as participant drop-out, a sample that isn’t entirely representative of the desired population, violations to the assumptions of parametric analysis (e.g., normality, homogeneity of variance), the limits of self-report, or the absence of reliability and validity data for some of your survey measures.
Limitations can get in the way of your being able to answer certain questions or draw certain types of inferences from your findings. Therefore, it’s important to acknowledge them upfront and make note of how they restrict the conclusions you’ll be able to draw from your study. Frequently, limitations can get in the way of our ability to generalize our findings to the larger populations or to draw causal conclusions, so be sure to consider these issues when you’re thinking about the potential limitations of your study.
Delimitations are also factors that can restrict the questions you can answer or the inferences you can draw from your findings. However, they are based on intentional choices you make a priori (i.e., as you’re designing the study) about where you’re going to draw the boundaries of your project. In other words, they define the project’s scope.
Like limitations, delimitations are a part of every research project, and this is not a bad thing. In fact, it’s very important! You can’t study everything at once. If you try to do so, your project is bound to get huge and unwieldy, and it will become a lot more difficult to interpret your results or come to meaningful conclusions with so many moving parts. You have to draw the line somewhere, and the delimitations are where you choose to draw these lines.
One of the clearest examples of a delimitation that applies to almost every research project is participant exclusion criteria. In conducting either a quantitative or a qualitative study, you will have to define your population of interest. Defining this population of interest means that you will need to articulate the boundaries of that population (i.e., who is not included). Those boundaries are delimitations.
For example, if you’re interested in understanding the experiences of elementary school teachers who have been implementing a new curriculum into their classrooms, you probably won’t be interviewing or sending a survey to any of the following people: non-teachers, high-school teachers, college professors, principals, parents of elementary school children, or the children themselves. Furthermore, you probably won’t be talking to elementary school teachers who have not yet had the experience of implementing the curriculum in question. You would probably only choose to gather data from elementary school teachers who have had this experience because that is who you’re interested in for the purposes of your study. Perhaps you’ll narrow your focus even more to elementary school teachers in a particular school district who have been teaching for a particular length of time. The possibilities can go on. These are choices you will need to make, both for practical reasons (i.e., the population you have access to) and for the questions you are trying to answer.
Of course, for this particular example, this does not mean that it wouldn’t be interesting to also know what principals think about the new curriculum. Or parents. Or elementary school children. It just means that, for the purposes of your project and your research questions, you’re interested in the experience of the teachers, so you’re excluding anyone who does not meet those criteria. Having delimitations to your population of interest also means that you won’t be able to answer any questions about the experiences of those other populations; this is ok because those populations are outside of the scope of your project . As interesting as their experiences might be, you can save these questions for another study. That is the part of the beauty of research: there will always be more studies to do, more questions to ask. You don’t have to (and can’t) do it all in one project.
Continuing with the previous example, for instance, let’s suppose that the problem you are most interested in addressing is the fact that we know relatively little about elementary school teachers’ experiences of implementing a new curriculum. Perhaps you believe that knowing more about teachers’ experiences could inform their training or help administrators know more about how to support their teachers. If the identified problem is our lack of knowledge about teachers’ experiences, and your research questions focus on better understanding these experiences, that means that you are choosing not to focus on other problems or questions, even those that may seem closely related. For instance, you are not asking how effective the new curriculum is in improving student test scores or graduation rates. You might think that would be a very interesting question, but it will have to wait for another study. In narrowing the focus of your research questions, you limit your ability to answer other questions, and again, that’s ok. These other questions may be interesting and important, but, again, they are beyond the scope of your project .
Common Examples of Limitations
While each study will have its own unique set of limitations, some limitations are more common in quantitative research, and others are more common in qualitative research.
In quantitative research, common limitations include the following:
– Participant dropout
– Small sample size, low power
– Non-representative sample
– Violations of statistical assumptions
– Non-experimental design, lack of manipulation of variables, lack of controls
– Potential confounding variables
– Measures with low (or unknown) reliability or validity
– Limits of an instrument to measure the construct of interest
– Data collection methods (e.g., self-report)
– Anything else that might limit the study’s internal or external validity
In qualitative research, common limitations include the following:
– Lack of generalizability of findings (not the goal of qualitative research, but still worth mentioning as a limitation)
– Inability to draw causal conclusions (again, not the goal of qualitative research, but still worth mentioning)
– Researcher bias/subjectivity (especially if there is only one coder)
– Limitations in participants’ ability/willingness to share or describe their experiences
– Any factors that might limit the rigor of data collection or analysis procedures
Common Examples of Delimitations
As noted above, the two most common sources of delimitations in both quantitative and qualitative research include the following:
– Inclusion/exclusion criteria (or how you define your population of interest)
– Research questions or problems you’ve chosen to examine
Several other common sources of delimitations include the following:
– Theoretical framework or perspective adopted
– Methodological framework or paradigm chosen (e.g., quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods)
– In quantitative research, the variables you’ve chosen to measure or manipulate (as opposed to others)
Whether you’re conducting a quantitative or qualitative study, you will (hopefully!) have chosen your research design because it is well suited to the questions you’re hoping to answer. Because these questions define the boundaries or scope of your project and thus point to its delimitations, your research design itself will also be related to these delimitations.
Questions to Ask Yourself
As you are considering the limitations and delimitations of your project, it can be helpful to ask yourself a few different questions.
Questions to help point out your study’s limitations :
1. If I had an unlimited budget, unlimited amounts of time, access to all possible populations, and the ability to manipulate as many variables as I wanted, how would I design my study differently to be better able to answer the questions I want to answer? (The ways in which your study falls short of this will point to its limitations.)
2. Are there design issues that get in the way of my being able to draw causal conclusions?
3. Are there sampling issues that get in the way of my being able to generalize my findings?
4. Are there issues related to the measures I’m using or the methods I’m using to collect data? Do I have concerns about participants telling the truth or being able to provide accurate responses to my questions?
5. Are there any other factors that might limit my study’s internal or external validity?
Questions that help point out your study’s delimitations :
1. What are my exclusion criteria? Who did I not include in my study, and why did I make this choice?
2. What questions did I choose not to address in my study? (Of course, the possibilities are endless here, but consider related questions that you chose not to address.)
3. In what ways did I narrow the scope of my study in order to hone in on a particular issue or question?
4. What other methodologies did I not use that might have allowed me to answer slightly different questions about the same topic?
How to Write About Limitations and Delimitations
Remember, having limitations and delimitations is not a bad thing. They’re present in even the most rigorous research. The important thing is to be aware of them and to acknowledge how they may impact your findings or the conclusions you can draw.
In fact, writing about them and acknowledging them gives you an opportunity to demonstrate that you can think critically about these aspects of your study and how they impact your findings, even if they were out of your control.
Keep in mind that your study’s limitations will likely point to important directions for future research. Therefore, when you’re getting ready to write about your recommendations for future research in your discussion, remember to refer back to your limitations section!
As you write about your delimitations in particular, remember that they are not weaknesses, and you don’t have to apologize for them. Good, strong research projects have clear boundaries. Also, keep in mind that you are the researcher and you can choose whatever delimitations you want for your study. You’re in control of the delimitations. You just have to be prepared—both in your discussion section and in your dissertation defense itself—to justify the choices you make and acknowledge how these choices impact your findings.
Browse More on PhDStudent

Everything You Need to Know About References and Citations: Part 1
When you conduct your research, it is important to record the details of all the information you find to provide accurate references, …

How to Write a Proposal: For a Master’s Thesis or Dissertation
Note: Many thanks to fellow PhDStudent blogger Ryan Krone for his contributions and insight to this post. Your thesis/dissertation proposal provides an …

How to Find Free Money for Graduate School Part 2
Getting into graduate school is already a challenge on its own, and funding the program once admitted is even harder. Graduate studies …

How to Find Free Money for Graduate School
You’ve finally earned your Bachelor’s degree and have made it into graduate school. Whether you already have massive student loans from undergrad …

Part 3 of How to Pick Your Defense Committee
What strategies can a doctoral student employ to maneuver the trials and tribulations of a dissertation committee? In Part 2, we …
Best Dissertation Proofreading and Editing Tips to Make Your Work Spotless
You’ve heard this statement many times before: “the dissertation is the most important project you’ve ever worked on.” That may sound like …

Part 2 of How to Pick Your Defense Committee
Choosing a committee can be a daunting task for a doctoral student. We’ve already covered two strategies that can help you through this …

Part 1 of How to Pick Your Defense Committee
So you’re ready to pick your committee members; there are a few things to keep in mind first—after all, it is a …

Intro To Series on How to Pick Your Defense Committee
Choosing the right defense committee can potentially be the difference between a smooth transition of receiving your doctoral degree or dodging bullets …

On Babies and Dissertations: Part 3
I recently had the experience of expecting my first baby a month before I graduated. Throughout the process, I accidentally learned several …

On Babies and Dissertations: Part 2

On Babies and Dissertations: Part 1
I recently had the experience of expecting my first baby a month before I graduated and accidentally learned tips on graduating on time with a …
Click here to cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Copyright © 2024 PhDStudent.com. All rights reserved. Designed by Divergent Web Solutions, LLC .
- Cookies & Privacy
- GETTING STARTED
- Introduction
- FUNDAMENTALS
- Acknowledgements
- Research questions & hypotheses
- Concepts, constructs & variables
- Research limitations
- Getting started
- Sampling Strategy
- Research Quality
- Research Ethics
- Data Analysis
EXPECTATIONS
What the reader expects from the research limitations section of your dissertation.
All research suffers from limitations , whether it is performed by undergraduate and master's level dissertation students, or seasoned academics. These research limitations range from flaws in the research design, which can be quite serious, to more common problems, such as the challenge of justifying how and why your findings answer the research questions and/or hypotheses that were set. This article explains some of the broader rules to think about when writing the Research Limitations section of your dissertation. In particular, your Research Limitations section should be: (a) well structured; (b) properly weighted; (c) honest; and (d) pragmatic. Each of these is discussed in turn.
Well structured
There is no "one best way" to structure this Research Limitations section of your dissertation. However, like the dissertation abstract, structure is important because you typically only have around 200 to 500 words to explain and justify all the potential weaknesses and/or limitations in your dissertation. In producing a Research Limitations section that is well structured, we recommend a structure based on three moves (i.e., the announcing , reflecting and forward looking move):
The announcing move immediately allows you to identify the limitations of your dissertation and explain how important each of these limitations is.
The reflecting move provides greater depth, helping to explain the nature of the limitations and justify the choices that you made during the research process.
Finally, the forward looking move enables you to suggest how such limitations could be overcome in future.
The collective aim of these three moves is to help you walk the reader through your Research Limitations section in a succinct and structured way. This will make it clear to the reader that you (a) recognise the limitations of your own research, (b) understand why such factors are limitations, and (c) can point to ways of combating these limitations if future research was carried out.
To understand more about each of these moves and how to clearly structure the Research Limitations section of your dissertation, read the section: How to structure the Research Limitations section of your dissertation .
Properly weighted
You should consider dedicating around 10-20% of the total word count of the Research Limitations section to the announcing move , 60-70% to the reflecting move and 10-20% to the final, forward looking move . Certainly, it is important to acknowledge the potential limitations of your dissertation in the announcing move , as well as suggest how future research could overcome such limitations. However, the focus of the Research Limitations section should be on explaining the nature of your limitations, the degree to which these were a problem, as well as justifying the reasons why you conducted the research the way you did. Since this section of the dissertation is generally only 200-500 words, the section should focus on those limitations that you feel had the greatest impact on your findings, as well as your ability to effectively answer your research questions and/or hypotheses. You are not writing a 2000 word critical review of the limitations of your dissertation.
Acknowledging the limitations of your research is not a way of highlighting to the reader where (and why) they should reduce the marks you receive for your dissertation. Instead, the Research Limitations section provides the right balance to the final chapter of your dissertation (often Chapter Five: Discussion/Conclusions ). It makes it clear to the reader that you recognise the limitations of your own research, that you understand why such factors are limitations, and can point to ways of combating these limitations if future research was carried out. Communicating such an understanding to the reader demonstrates the command that you have over your research, which should help in improving the marks you receive for your dissertation. Added to this, the person reading your dissertation can easily identify potential weaknesses, even if you have not spelt these out. This comes with years of experience in teaching and research, which many academics have. Trying to hide potential limitations to your dissertation is not advised.
There are many ideals in research. For the researcher that prefers to adopt a quantitative research design [see the section on Research Designs for more information about research designs], a probability sampling technique is viewed as the ideal because it enables the researcher to make generalisations (i.e., statistical inferences ) from the sample to the population being studied [see the articles on Sampling: The basics and Probability sampling to learn more about sampling and probability sampling techniques].
For example: If the researcher was investigating the career choices of students at a university of 20,000 students (the population in question), only a small number of these students (e.g., a sample of 400 students), may need to be surveyed. It may then be possible to make generalisations about the career choices of the population of 20,000 students based on the data collected from the sample of 400 students [see the article, Probability sampling , if you want to know more about this example].
However, as all of the articles on types of probability sampling technique illustrate (e.g., simple random sampling , stratified random sampling ), using a probability sampling technique can be very difficult. In fact, there are many reasons why it may be impossible (or near on impossible) to use a probability sampling technique. In such cases, researchers are forced to use non-probability sampling techniques , where is it no longer possible to make generalisations (i.e., statistical inferences) from the sample to the population being studied. However, this does not mean that any study that uses a quantitative research design, but fails to use a probability sampling technique, is of low quality or flawed. It simply means that some things that are limitations in theory are not necessarily weaknesses in practice . It means that you need to adopt a pragmatic approach to your research, whilst acknowledging potential limitations.
If you know the limitations in your dissertation, you may find the next section, How to structure the Research Limitations section of your dissertation , helpful.

How to write the ‘limitations or shortcomings of the study’ in a research paper?
‘Limitations or shortcomings of the study’ is the last stage of a thesis. After the study is completed, as a researcher, you may have identified shortcomings. Enlisting those areas in the thesis serves many purposes.
Identifying limitations or shortcomings in a study means that you have carefully considered their potential impact on your findings. So, when readers frame an opinion about your study, they know the conditions under which your findings are valid. Secondly, it establishes the credibility of your research. No study is complete without its set of limitations. Therefore identifying these limitations formally acknowledges that your research was carried out ethically. Finally, it establishes the validity of the research.
Researcher versus methodology
Researcher’s limitation occurs due to the researcher’s shortcomings. This may include sampling errors such as using a cluster random sampling instead of simple random sampling. Another type of it is the inability of the researcher to cover a wide range of respondents from a large geographical location. Another researcher based shortcoming is while conducting research that has poor literature support. The research may lack direction of the study, which leads to poor methodology implementation. On the other hand methodology, related limitations include poor methods of data collection.
For example, including fewer questions or irrelevant questions in the survey or interview questionnaire to collect data. In addition, methodological limitations also involve using wrong or irrelevant data analysis methods to present the findings or address the aim of the study. In this case, the limitation is an inadequate questionnaire for data collection to address the aim of the study.
Impact and data related shortcomings
Impact related shortcomings are those where the research suffers from poor impact by the causal factors that do not show a variation of the findings. This mainly occurs when you use manipulated data or have poorly planned the methodology. As a result, the findings may seem to be a too obvious or small positive or negative change in a variable quantity or function. On the other hand, data limitations are almost the same as methodological limitations mentioned in the previous type. Poor data collection methods and lack of large sample size for survey make for poor data.
Pre-research and post-research shortcomings
Pre-research shortcomings are the ones that you are aware of or expect during the conduction of the study. Usually, pre-research shortcomings are presented in the proposal or synopsis of the main research. However, there are no solutions to these problems. On the other hand, post-research limitations are the ones that are identified after the study was conducted. For instance, biased findings or contradictory findings comes under post-research limitations. This may also occur while conducting triangulation, and the findings of quantitative and qualitative do not match the secondary literature findings.
Steps to follow
There are many ways to write this section, but the three-step formula is popular.

Step 1: Announcement
In this step clearly mention the shortcomings that were faced in the study. List out all the shortcomings faced starting from methods to the statistical findings, such as bias in sampling, lack of respondent participation, etc. This section of the limitation should be only 10% of the total content.
Step 2: Reflection
In this step, justify and elaborate on the limitations. Justify why the limitations occurred. This should have the maximum content, of about 60%.
For instance, the biases of the responses may have occurred from poor knowledge of the participants or the participants were not aware of the importance of the study. Another possibility of biases of the responses is that they did not want to display the negative aspects and responded positively for the sake of the study. In addition, research limitation may also be possible as the study chose only one case for the collection of data.
Step 3: Look forward
This mainly comprises of the future scope of the study. Suggest what should be done in the future by researchers looking to conduct similar studies. This section should comprise the remaining 30% of the total content.
For instance, since, the study found the limitation of response biases; it is suggested that future researchers must choose more than one organization for distribution and collection of the survey or interview. In addition, a pilot study can be conducted well before the collection of final data.

What not to write?
- Do not apologize for writing the limitations of the study or never apologize for the occurrence of the limitations. Without it, the research is never complete, and the study will never move in the right direction.
- Avoid referring to personal limitations such as poor data collection due to lack of time. Do not mention points that will show negative impression your due diligence in the research. Avoid statements that will lead to the lack of your credibility. This may include statements such as ‘since the study was on secondary data gathered, many missing variables were discovered. Since the variables are important and cannot be ignored; there was a manipulation of the missing data’.
- Never mention shortcomings that have already been mentioned in the previous studies. Research is initiated by identifying the limitations of past research published in the same field. Do not use sentences like, ‘we found similar limitations as were mentioned by ABD, (2018) in the study ‘how to write limitations’? Or ‘the current study tried to avoid the limitations as mentioned in ABD, (2018), but the same still occurred.’
- Do not over-write or paraphrase just for the sake of filling up words. Never repeat the same points over and over again. For instance, once spoken of the sample size limitations, do not write that, ‘the study also saw the limitation of less number of people turning up for the survey questionnaire fill-ins.’
Sample of ‘limitations of the study’
The following is a classic example of how to write the limitations in a thesis.
The main aim of the study was to assess the factors that lead to poor limitations writing in a research paper by research scholars. Although the study conducted a thorough survey, there were certain limitations while exploring the aim of the study. It is expected that these points will help future researchers to avoid facing the same shortcomings.
- While conducting the pilot study it was expected that the number of participants will be a minimum of 200. However, after the final data collection and compilation of data, there were only 129 participants for the study. This might be from the fact that the participants were not interested in participating or did not have the time to completely fill in the questionnaire. Since the sample populations were mainly research scholars from a tertiary institute, maybe they did not have enough time to fill in the questionnaires. Therefore, in future studies that use research scholars as a sample population but consider providing questionnaires or collect data from a much larger group or choose more than one institutions for the collection of data.
- It was found from the study that, the current findings contradict the findings of previous studies on factors that lead to poor limitations writing in a research paper by research scholars. This may be from the fact that the studies conducted previously were based on European countries and America. Therefore, the perspective of the research scholars may have varied. Again, the methods of research differ from one place to another and the challenges faced by researchers also differ. This may have led to the limitation of contradictory findings. Therefore, it is suggested that the researchers must consider the factors found from different regions and assess them or make a comparative study to find the factors and how they differ.
Concluding note
Limitations of the study is a very important part of the research. It helps future studies and researches to focus on more innovative ways to conduct research and ignore the issues faced. Be honest, pragmatic and structured while writing this section. Go through ample examples from different authors before writing your own. I suggest you using pointers to specifically write or inform the limitations as indicated in the limitation example. Be specific about the limitations and try not to make up to the limitations.
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
3 thoughts on “How to write the ‘limitations or shortcomings of the study’ in a research paper?”
Proofreading.
How To Write A Dissertation Introduction Chapter:
The 7 essential ingredients of an a-grade introduction.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA). Reviewed By Dr Eunice Rautenbach (D. Tech) | March 2020
If you’re reading this, you’re probably at the daunting early phases of writing up the introduction chapter of your dissertation or thesis. It can be intimidating, I know.
In this post, we’ll look at the 7 essential ingredients of a strong dissertation or thesis introduction chapter, as well as the essential things you need to keep in mind as you craft each section. We’ll also share some useful tips to help you optimize your approach.
Overview: How To Write An Introduction Chapter
- Understand the purpose and function of the intro chapter
- Craft an enticing and engaging opening section
- Provide a background and context to the study
- Clearly define the research problem
- State your research aims, objectives and questions
- Explain the significance of your study
- Identify the limitations of your research
- Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis

A quick sidenote:
You’ll notice that I’ve used the words dissertation and thesis interchangeably. While these terms reflect different levels of research – for example, Masters vs PhD-level research – the introduction chapter generally contains the same 7 essential ingredients regardless of level. So, in this post, dissertation introduction equals thesis introduction.
Start with why.
To craft a high-quality dissertation or thesis introduction chapter, you need to understand exactly what this chapter needs to achieve. In other words, what’s its purpose ? As the name suggests, the introduction chapter needs to introduce the reader to your research so that they understand what you’re trying to figure out, or what problem you’re trying to solve. More specifically, you need to answer four important questions in your introduction chapter.
These questions are:
- What will you be researching? (in other words, your research topic)
- Why is that worthwhile? (in other words, your justification)
- What will the scope of your research be? (in other words, what will you cover and what won’t you cover)
- What will the limitations of your research be? (in other words, what will the potential shortcomings of your research be?)
Simply put, your dissertation’s introduction chapter needs to provide an overview of your planned research , as well as a clear rationale for it. In other words, this chapter has to explain the “what” and the “why” of your research – what’s it all about and why’s that important.
Simple enough, right?
Well, the trick is finding the appropriate depth of information. As the researcher, you’ll be extremely close to your topic and this makes it easy to get caught up in the minor details. While these intricate details might be interesting, you need to write your introduction chapter on more of a “need-to-know” type basis, or it will end up way too lengthy and dense. You need to balance painting a clear picture with keeping things concise. Don’t worry though – you’ll be able to explore all the intricate details in later chapters.

Now that you understand what you need to achieve from your introduction chapter, we can get into the details. While the exact requirements for this chapter can vary from university to university, there are seven core components that most universities will require. We call these the seven essential ingredients .
The 7 Essential Ingredients
- The opening section – where you’ll introduce the reader to your research in high-level terms
- The background to the study – where you’ll explain the context of your project
- The research problem – where you’ll explain the “gap” that exists in the current research
- The research aims , objectives and questions – where you’ll clearly state what your research will aim to achieve
- The significance (or justification) – where you’ll explain why your research is worth doing and the value it will provide to the world
- The limitations – where you’ll acknowledge the potential limitations of your project and approach
- The structure – where you’ll briefly outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis to help orient the reader
By incorporating these seven essential ingredients into your introduction chapter, you’ll comprehensively cover both the “ what ” and the “ why ” I mentioned earlier – in other words, you’ll achieve the purpose of the chapter.
Side note – you can also use these 7 ingredients in this order as the structure for your chapter to ensure a smooth, logical flow. This isn’t essential, but, generally speaking, it helps create an engaging narrative that’s easy for your reader to understand. If you’d like, you can also download our free introduction chapter template here.
Alright – let’s look at each of the ingredients now.

#1 – The Opening Section
The very first essential ingredient for your dissertation introduction is, well, an introduction or opening section. Just like every other chapter, your introduction chapter needs to start by providing a brief overview of what you’ll be covering in the chapter.
This section needs to engage the reader with clear, concise language that can be easily understood and digested. If the reader (your marker!) has to struggle through it, they’ll lose interest, which will make it harder for you to earn marks. Just because you’re writing an academic paper doesn’t mean you can ignore the basic principles of engaging writing used by marketers, bloggers, and journalists. At the end of the day, you’re all trying to sell an idea – yours is just a research idea.
So, what goes into this opening section?
Well, while there’s no set formula, it’s a good idea to include the following four foundational sentences in your opening section:
1 – A sentence or two introducing the overall field of your research.
For example:
“Organisational skills development involves identifying current or potential skills gaps within a business and developing programs to resolve these gaps. Management research, including X, Y and Z, has clearly established that organisational skills development is an essential contributor to business growth.”
2 – A sentence introducing your specific research problem.
“However, there are conflicting views and an overall lack of research regarding how best to manage skills development initiatives in highly dynamic environments where subject knowledge is rapidly and continuously evolving – for example, in the website development industry.”
3 – A sentence stating your research aims and objectives.
“This research aims to identify and evaluate skills development approaches and strategies for highly dynamic industries in which subject knowledge is continuously evolving.”.
4 – A sentence outlining the layout of the chapter.
“This chapter will provide an introduction to the study by first discussing the background and context, followed by the research problem, the research aims, objectives and questions, the significance and finally, the limitations.”
As I mentioned, this opening section of your introduction chapter shouldn’t be lengthy . Typically, these four sentences should fit neatly into one or two paragraphs, max. What you’re aiming for here is a clear, concise introduction to your research – not a detailed account.
PS – If some of this terminology sounds unfamiliar, don’t stress – I’ll explain each of the concepts later in this post.

#2 – Background to the study
Now that you’ve provided a high-level overview of your dissertation or thesis, it’s time to go a little deeper and lay a foundation for your research topic. This foundation is what the second ingredient is all about – the background to your study.
So, what is the background section all about?
Well, this section of your introduction chapter should provide a broad overview of the topic area that you’ll be researching, as well as the current contextual factors . This could include, for example, a brief history of the topic, recent developments in the area, key pieces of research in the area and so on. In other words, in this section, you need to provide the relevant background information to give the reader a decent foundational understanding of your research area.
Let’s look at an example to make this a little more concrete.
If we stick with the skills development topic I mentioned earlier, the background to the study section would start by providing an overview of the skills development area and outline the key existing research. Then, it would go on to discuss how the modern-day context has created a new challenge for traditional skills development strategies and approaches. Specifically, that in many industries, technical knowledge is constantly and rapidly evolving, and traditional education providers struggle to keep up with the pace of new technologies.
Importantly, you need to write this section with the assumption that the reader is not an expert in your topic area. So, if there are industry-specific jargon and complex terminology, you should briefly explain that here , so that the reader can understand the rest of your document.
Don’t make assumptions about the reader’s knowledge – in most cases, your markers will not be able to ask you questions if they don’t understand something. So, always err on the safe side and explain anything that’s not common knowledge.

#3 – The research problem
Now that you’ve given your reader an overview of your research area, it’s time to get specific about the research problem that you’ll address in your dissertation or thesis. While the background section would have alluded to a potential research problem (or even multiple research problems), the purpose of this section is to narrow the focus and highlight the specific research problem you’ll focus on.
But, what exactly is a research problem, you ask?
Well, a research problem can be any issue or question for which there isn’t already a well-established and agreed-upon answer in the existing research. In other words, a research problem exists when there’s a need to answer a question (or set of questions), but there’s a gap in the existing literature , or the existing research is conflicting and/or inconsistent.
So, to present your research problem, you need to make it clear what exactly is missing in the current literature and why this is a problem . It’s usually a good idea to structure this discussion into three sections – specifically:
- What’s already well-established in the literature (in other words, the current state of research)
- What’s missing in the literature (in other words, the literature gap)
- Why this is a problem (in other words, why it’s important to fill this gap)
Let’s look at an example of this structure using the skills development topic.
Organisational skills development is critically important for employee satisfaction and company performance (reference). Numerous studies have investigated strategies and approaches to manage skills development programs within organisations (reference).
(this paragraph explains what’s already well-established in the literature)
However, these studies have traditionally focused on relatively slow-paced industries where key skills and knowledge do not change particularly often. This body of theory presents a problem for industries that face a rapidly changing skills landscape – for example, the website development industry – where new platforms, languages and best practices emerge on an extremely frequent basis.
(this paragraph explains what’s missing from the literature)
As a result, the existing research is inadequate for industries in which essential knowledge and skills are constantly and rapidly evolving, as it assumes a slow pace of knowledge development. Industries in such environments, therefore, find themselves ill-equipped in terms of skills development strategies and approaches.
(this paragraph explains why the research gap is problematic)
As you can see in this example, in a few lines, we’ve explained (1) the current state of research, (2) the literature gap and (3) why that gap is problematic. By doing this, the research problem is made crystal clear, which lays the foundation for the next ingredient.
#4 – The research aims, objectives and questions
Now that you’ve clearly identified your research problem, it’s time to identify your research aims and objectives , as well as your research questions . In other words, it’s time to explain what you’re going to do about the research problem.
So, what do you need to do here?
Well, the starting point is to clearly state your research aim (or aims) . The research aim is the main goal or the overarching purpose of your dissertation or thesis. In other words, it’s a high-level statement of what you’re aiming to achieve.
Let’s look at an example, sticking with the skills development topic:
“Given the lack of research regarding organisational skills development in fast-moving industries, this study will aim to identify and evaluate the skills development approaches utilised by web development companies in the UK”.
As you can see in this example, the research aim is clearly outlined, as well as the specific context in which the research will be undertaken (in other words, web development companies in the UK).
Next up is the research objective (or objectives) . While the research aims cover the high-level “what”, the research objectives are a bit more practically oriented, looking at specific things you’ll be doing to achieve those research aims.
Let’s take a look at an example of some research objectives (ROs) to fit the research aim.
- RO1 – To identify common skills development strategies and approaches utilised by web development companies in the UK.
- RO2 – To evaluate the effectiveness of these strategies and approaches.
- RO3 – To compare and contrast these strategies and approaches in terms of their strengths and weaknesses.
As you can see from this example, these objectives describe the actions you’ll take and the specific things you’ll investigate in order to achieve your research aims. They break down the research aims into more specific, actionable objectives.
The final step is to state your research questions . Your research questions bring the aims and objectives another level “down to earth”. These are the specific questions that your dissertation or theses will seek to answer. They’re not fluffy, ambiguous or conceptual – they’re very specific and you’ll need to directly answer them in your conclusions chapter .
The research questions typically relate directly to the research objectives and sometimes can look a bit obvious, but they are still extremely important. Let’s take a look at an example of the research questions (RQs) that would flow from the research objectives I mentioned earlier.
- RQ1 – What skills development strategies and approaches are currently being used by web development companies in the UK?
- RQ2 – How effective are each of these strategies and approaches?
- RQ3 – What are the strengths and weaknesses of each of these strategies and approaches?
As you can see, the research questions mimic the research objectives , but they are presented in question format. These questions will act as the driving force throughout your dissertation or thesis – from the literature review to the methodology and onward – so they’re really important.
A final note about this section – it’s really important to be clear about the scope of your study (more technically, the delimitations ). In other words, what you WILL cover and what you WON’T cover. If your research aims, objectives and questions are too broad, you’ll risk losing focus or investigating a problem that is too big to solve within a single dissertation.
Simply put, you need to establish clear boundaries in your research. You can do this, for example, by limiting it to a specific industry, country or time period. That way, you’ll ringfence your research, which will allow you to investigate your topic deeply and thoroughly – which is what earns marks!
Need a helping hand?
#5 – Significance
Now that you’ve made it clear what you’ll be researching, it’s time to make a strong argument regarding your study’s importance and significance . In other words, now that you’ve covered the what, it’s time to cover the why – enter essential ingredient number 5 – significance.
Of course, by this stage, you’ve already briefly alluded to the importance of your study in your background and research problem sections, but you haven’t explicitly stated how your research findings will benefit the world . So, now’s your chance to clearly state how your study will benefit either industry , academia , or – ideally – both . In other words, you need to explain how your research will make a difference and what implications it will have.
Let’s take a look at an example.
“This study will contribute to the body of knowledge on skills development by incorporating skills development strategies and approaches for industries in which knowledge and skills are rapidly and constantly changing. This will help address the current shortage of research in this area and provide real-world value to organisations operating in such dynamic environments.”
As you can see in this example, the paragraph clearly explains how the research will help fill a gap in the literature and also provide practical real-world value to organisations.
This section doesn’t need to be particularly lengthy, but it does need to be convincing . You need to “sell” the value of your research here so that the reader understands why it’s worth committing an entire dissertation or thesis to it. This section needs to be the salesman of your research. So, spend some time thinking about the ways in which your research will make a unique contribution to the world and how the knowledge you create could benefit both academia and industry – and then “sell it” in this section.

#6 – The limitations
Now that you’ve “sold” your research to the reader and hopefully got them excited about what’s coming up in the rest of your dissertation, it’s time to briefly discuss the potential limitations of your research.
But you’re probably thinking, hold up – what limitations? My research is well thought out and carefully designed – why would there be limitations?
Well, no piece of research is perfect . This is especially true for a dissertation or thesis – which typically has a very low or zero budget, tight time constraints and limited researcher experience. Generally, your dissertation will be the first or second formal research project you’ve ever undertaken, so it’s unlikely to win any research awards…
Simply put, your research will invariably have limitations. Don’t stress yourself out though – this is completely acceptable (and expected). Even “professional” research has limitations – as I said, no piece of research is perfect. The key is to recognise the limitations upfront and be completely transparent about them, so that future researchers are aware of them and can improve the study’s design to minimise the limitations and strengthen the findings.
Generally, you’ll want to consider at least the following four common limitations. These are:
- Your scope – for example, perhaps your focus is very narrow and doesn’t consider how certain variables interact with each other.
- Your research methodology – for example, a qualitative methodology could be criticised for being overly subjective, or a quantitative methodology could be criticised for oversimplifying the situation (learn more about methodologies here ).
- Your resources – for example, a lack of time, money, equipment and your own research experience.
- The generalisability of your findings – for example, the findings from the study of a specific industry or country can’t necessarily be generalised to other industries or countries.
Don’t be shy here. There’s no use trying to hide the limitations or weaknesses of your research. In fact, the more critical you can be of your study, the better. The markers want to see that you are aware of the limitations as this demonstrates your understanding of research design – so be brutal.
#7 – The structural outline
Now that you’ve clearly communicated what your research is going to be about, why it’s important and what the limitations of your research will be, the final ingredient is the structural outline.The purpose of this section is simply to provide your reader with a roadmap of what to expect in terms of the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
In this section, you’ll need to provide a brief summary of each chapter’s purpose and contents (including the introduction chapter). A sentence or two explaining what you’ll do in each chapter is generally enough to orient the reader. You don’t want to get too detailed here – it’s purely an outline, not a summary of your research.
Let’s look at an example:
In Chapter One, the context of the study has been introduced. The research objectives and questions have been identified, and the value of such research argued. The limitations of the study have also been discussed.
In Chapter Two, the existing literature will be reviewed and a foundation of theory will be laid out to identify key skills development approaches and strategies within the context of fast-moving industries, especially technology-intensive industries.
In Chapter Three, the methodological choices will be explored. Specifically, the adoption of a qualitative, inductive research approach will be justified, and the broader research design will be discussed, including the limitations thereof.
So, as you can see from the example, this section is simply an outline of the chapter structure, allocating a short paragraph to each chapter. Done correctly, the outline will help your reader understand what to expect and reassure them that you’ll address the multiple facets of the study.
By the way – if you’re unsure of how to structure your dissertation or thesis, be sure to check out our video post which explains dissertation structure .
Keep calm and carry on.
Hopefully you feel a bit more prepared for this challenge of crafting your dissertation or thesis introduction chapter now. Take a deep breath and remember that Rome wasn’t built in a day – conquer one ingredient at a time and you’ll be firmly on the path to success.
Let’s quickly recap – the 7 ingredients are:
- The opening section – where you give a brief, high-level overview of what your research will be about.
- The study background – where you introduce the reader to key theory, concepts and terminology, as well as the context of your study.
- The research problem – where you explain what the problem with the current research is. In other words, the research gap.
- The research aims , objectives and questions – where you clearly state what your dissertation will investigate.
- The significance – where you explain what value your research will provide to the world.
- The limitations – where you explain what the potential shortcomings and limitations of your research may be.
- The structural outline – where you provide a high-level overview of the structure of your document
If you bake these ingredients into your dissertation introduction chapter, you’ll be well on your way to building an engaging introduction chapter that lays a rock-solid foundation for the rest of your document.
Remember, while we’ve covered the essential ingredients here, there may be some additional components that your university requires, so be sure to double-check your project brief!

Psst… there’s more (for free)
This post is part of our dissertation mini-course, which covers everything you need to get started with your dissertation, thesis or research project.
You Might Also Like:

42 Comments
Thanks very much for such an insight. I feel confident enough in undertaking my thesis on the survey;The future of facial recognition and learning non verbal interaction
Glad to hear that. Good luck with your thesis!
Thanks very much for such an insight. I feel confident now undertaking my thesis; The future of facial recognition and learning non verbal interaction.
Thanks so much for this article. I found myself struggling and wasting a lot of time in my thesis writing but after reading this article and watching some of your youtube videos, I now have a clear understanding of what is required for a thesis.
Thank you Derek, i find your each post so useful. Keep it up.
Thank you so much Derek ,for shedding the light and making it easier for me to handle the daunting task of academic writing .
Thanks do much Dereck for the comprehensive guide. It will assist me queit a lot in my thesis.
thanks a lot for helping
i LOVE the gifs, such a fun way to engage readers. thanks for the advice, much appreciated
Thanks a lot Derek! It will be really useful to the beginner in research!
You’re welcome
This is a well written, easily comprehensible, simple introduction to the basics of a Research Dissertation../the need to keep the reader in mind while writing the dissertation is an important point that is covered../ I appreciate the efforts of the author../
The instruction given are perfect and clear. I was supposed to take the course , unfortunately in Nepal the service is not avaialble.However, I am much more hopeful that you will provide require documents whatever you have produced so far.
Thank you very much
Thanks so much ❤️😘 I feel am ready to start writing my research methodology
This is genuinely the most effective advice I have ever been given regarding academia. Thank you so much!
This is one of the best write up I have seen in my road to PhD thesis. regards, this write up update my knowledge of research
I was looking for some good blogs related to Education hopefully your article will help. Thanks for sharing.
This is an awesome masterpiece. It is one of the most comprehensive guides to writing a Dissertation/Thesis I have seen and read.
You just saved me from going astray in writing a Dissertation for my undergraduate studies. I could not be more grateful for such a relevant guide like this. Thank you so much.
Thank you so much Derek, this has been extremely helpful!!
I do have one question though, in the limitations part do you refer to the scope as the focus of the research on a specific industry/country/chronological period? I assume that in order to talk about whether or not the research could be generalized, the above would need to be already presented and described in the introduction.
Thank you again!
Phew! You have genuinely rescued me. I was stuck how to go about my thesis. Now l have started. Thank you.
This is the very best guide in anything that has to do with thesis or dissertation writing. The numerous blends of examples and detailed insights make it worth a read and in fact, a treasure that is worthy to be bookmarked.
Thanks a lot for this masterpiece!
Powerful insight. I can now take a step
Thank you very much for these valuable introductions to thesis chapters. I saw all your videos about writing the introduction, discussion, and conclusion chapter. Then, I am wondering if we need to explain our research limitations in all three chapters, introduction, discussion, and conclusion? Isn’t it a bit redundant? If not, could you please explain how can we write in different ways? Thank you.
Excellent!!! Thank you…
Thanks for this informative content. I have a question. The research gap is mentioned in both the introduction and literature section. I would like to know how can I demonstrate the research gap in both sections without repeating the contents?
I’m incredibly grateful for this invaluable content. I’ve been dreading compiling my postgrad thesis but breaking each chapter down into sections has made it so much easier for me to engage with the material without feeling overwhelmed. After relying on your guidance, I’m really happy with how I’ve laid out my introduction.
Thank you for the informative content you provided
Hi Derrick and Team, thank you so much for the comprehensive guide on how to write a dissertation or a thesis introduction section. For some of us first-timers, it is a daunting task. However, the instruction with relevant examples makes it clear and easy to follow through. Much appreciated.
It was so helpful. God Bless you. Thanks very much
I thank you Grad coach for your priceless help. I have two questions I have learned from your video the limitations of the research presented in chapter one. but in another video also presented in chapter five. which chapter limitation should be included? If possible, I need your answer since I am doing my thesis. how can I explain If I am asked what is my motivation for this research?
Thank you guys for the great work you are doing. Honestly, you have made the research to be interesting and simplified. Even a novice will easily grasp the ideas you put forward, Thank you once again.
Excellent piece!
I feel like just settling for a good topic is usually the hardest part.
Thank you so much. My confidence has been completely destroyed during my first year of PhD and you have helped me pull myself together again
Happy to help 🙂
I am so glad I ran into your resources and did not waste time doing the wrong this. Research is now making so much sense now.
Gratitude to Derrick and the team I was looking for a solid article that would aid me in drafting the thesis’ introduction. I felt quite happy when I came across the piece you wrote because it was so well-written and insightful. I wish you success in the future.
thank you so much. God Bless you
Thank you so much Grad Coach for these helpful insights. Now I can get started, with a great deal of confidence.
It’s ‘alluded to’ not ‘eluded to’.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

How to Write a Bachelor’s Thesis: A Step-by-Step Guide

The bachelor’s degree is an important milestone in your academic life, and creating a successful bachelor’s thesis is an essential part of this process.
Although it can be a challenge, with a structured approach and a clear timetable, a well-researched, informed, and organized bachelor’s thesis can be created.
In this article, we explain how to write a bachelor’s thesis.
11 Facts About Bachelor’s Theses
- The average length of a bachelor’s thesis is about 30-60 pages.
- Most bachelor’s theses are written in the field of economics.
- The average processing time for a bachelor’s thesis is 3-6 months.
- Typically, bachelor’s theses are supervised by a professor or lecturer.
- Most bachelor’s theses are still written and submitted on paper.
- A bachelor’s thesis is always written within the framework of a study program and is an important part of the degree completion.
- The topic selection for a bachelor’s thesis is usually free, as long as it falls within the field of study.
- Adherence to citation rules and source references is an important part of a bachelor’s thesis.
- Submission of a bachelor’s thesis is usually combined with an oral examination.
- The bachelor’s thesis is the first longer scientific work that a student writes during their studies and therefore represents an important hurdle.
- In 2021, approximately 260,000 students achieved their bachelor’s degree.
Scientific Formulations in Minutes Seconds
11 Tips for Academic Writing (Bachelor’s Theses)
- Start your bachelor’s thesis early to have enough time for research, writing, and revision.
- Choose an interesting and relevant topic that fits well with your field of study.
- Create a detailed work plan to keep track of your steps and deadlines.
- Use trustworthy and current sources to underpin your work.
- Write clearly and precisely, avoid using unnecessarily complicated sentences.
- Use a consistent citation style and pay attention to the correct source citation.
- Logically structure your bachelor’s thesis and ensure that the common thread is recognizable.
- Revise and polish your work multiple times to ensure that it is free from spelling and grammar errors.
- Have your work read by others and seek feedback to recognize areas for improvement.
- Consider publishing your bachelor’s thesis to make it accessible to others and to present your work.
- Have your text scientifically rephrased by Mimir. Sample input : Potatoes are healthy… ➔ Result : Potatoes are rich in vitamins and minerals and can contribute to a balanced diet.
The Process of Writing a Bachelor’s Thesis: Step by Step Guide
The writing process of a bachelor’s thesis is a challenge for many students. In this section, we give an overview of the most important steps and tips to successfully master the process.
- Determine the topic of the bachelor’s thesis and discuss it with the supervisor.
- Conduct comprehensive research and collect relevant sources.
- Create an outline and divide the topic into individual sections.
- Write the main part of the paper by processing and summarizing the insights gained from the research.
- Compose the concluding part, summarizing the main findings of the work and outlining possible further steps or implications.
- Proofread the work and check for formal requirements.
- Submit and defend the bachelor’s thesis.
Choosing a Topic: How to Find the Perfect Topic for Your Bachelor’s Thesis
The first step in creating a bachelor’s thesis is selecting the topic. It’s important that your topic is specific and answers a clear research question. If your topic is too general, it will be harder to achieve meaningful results.
Why is the topic important?
An interesting and relevant topic not only captivates your readers but also gives you the motivation to successfully complete the work.
The topic of your bachelor’s thesis is crucial for the success of your work.
A difficult or boring topic, on the other hand, can lead to you finding the writing process frustrating and ultimately not successfully completing the work. Therefore, it’s important to think carefully about which topic you choose for your bachelor’s thesis.
If you have difficulty finding a topic, you can turn to your supervisors and present your ideas to them.
Research & Study: The Right Way to the Perfect Bachelor’s Thesis
Once the topic is set, it’s time to collect the necessary information. This can be done by searching through libraries and databases, reading specialist literature, and interviewing experts. It’s important to carefully organize and document the collected information so that it’s easily accessible when writing the work.
It’s also important that your sources are current, as research and opinions in your subject area are constantly changing.
Possible Sources
- Academic Publications
- Professional Journals
- Reputable Websites (you should consult your supervisor beforehand)
Structure: Setup and Organization of the Bachelor Thesis
It is important to have a clear structure for your bachelor thesis. This should include an introduction, a main part, and a conclusion. Within the main part, you can divide your arguments into different sections. This helps you to structure your thought process and ensure a smooth and logical flow.
Introduction
- Summary of the research thesis
- Definition of the main terms
- Explanation of the research question and area of interest
- Conduct literature research
- Develop arguments and hypotheses
- Draw conclusions and results
- Cite sources
- Summary of the results
- Comparison of hypotheses and results
- Explanation of the implications of the results
- Recommendations for further research
Writing: Tips and Tricks for the Writing Process
After you have completed your research and established your structure, it is time to write.
It is important that you write your work in simple, academic German/English.
Avoid using too many technical terms and ensure that each sentence conveys a clear thought.
Compose a clear introduction that explains your topic and presents your argumentation. In the main part of your work, you should provide your arguments and examples to prove your thesis. Make sure that your arguments are logical and understandable.
- Write a simple and clear introduction
- Compose the main part of your work
- Ensure that each sentence conveys a clear thought
- Provide your arguments and examples to prove your thesis
- Ensure logical and understandable argumentation
- Avoid too many technical terms
- Avoid vague formulations
- Avoid subjective opinions
Tip: Let Mimir formulate your bullet point ( Example input : Running is great ➔ Result (1/3) : Running is a healthy and effective form of physical activity that can contribute to improving cardiovascular fitness, mobility, and mental health.)
Formatting: How to Properly Format Your Bachelor Thesis
It is important that you adhere to your university’s guidelines when formatting your bachelor thesis. Check the requirements for margins, line spacing, font size, and font type prescribed by your university.
It is also important to format your work consistently to achieve a professional look.
- Adhere to your university’s guidelines
- Check margins, line spacing, font size, and font type
- Consistently format your work
- Create a professional layout
Citing and Referencing: Rules for Citing and Referencing in the Bachelor Thesis
When referring to the ideas of other authors in your work, it is important to cite and reference them correctly. There are various citation styles you can use, but most universities use the Harvard or APA style.
Make sure to properly cite and reference all sources you refer to, to avoid plagiarism.
- Use the Harvard or APA style
- Cite and reference all sources you refer to
- Avoid plagiarism
Proofreading: Error Sources and Tips for a Flawless Bachelor Thesis
After you have written your bachelor thesis, it is important to thoroughly review it. Check the content for correct grammar, spelling, and structure. Also ensure that your arguments are clear and logical and that your statements are supported by your research.
It is important to proofread and edit your work several times. Make sure to correct all spelling and grammar errors so that your work looks professional.
- Read your work aloud to detect errors in grammar, sentence structure, and pronunciation.
- Use a dictionary or an online proofreading program to find errors in spelling and punctuation.
- Have someone else read your work and ask for feedback to gain additional perspectives and suggestions for improvement.
- Carefully review and revise your work to improve its quality and content. This can be done by adding examples, removing unnecessary information, or refining arguments.
Tip: Have your text checked by Mimir (Unscientific words, gender conformity, and more…)
Submission: How to Safely Submit and Defend Your Bachelor Thesis
Writing a bachelor thesis can be a challenging task, but if you follow the steps mentioned above, you will complete your work in a professional manner.
Don’t forget to adhere to the guidelines of your university.
Once you have reviewed and revised your bachelor’s thesis, it’s time to submit it. Make sure your work meets the requirements of your examiner and contains the correct information. If possible, have a friend or family member review it before you submit it.
Earning a bachelor’s degree is a great achievement, and creating a successful bachelor’s thesis is an essential part of this process. Remember, choosing a topic, conducting research, and writing a bachelor’s thesis can be a laborious process. However, if you have a clear schedule and follow the steps mentioned above, you can create a well-researched, informed, and organized bachelor’s thesis.
And last but not least: Congratulations!
Two Practical Examples of the Process
To better understand the steps and tips mentioned above, here are two examples from different academic areas:
- A psychology student writes a bachelor’s thesis on the effects of social media on the mental health of adolescents. She chooses this topic because it combines her personal interest and her expertise in psychology. She gathers information by reading textbooks and conducting interviews with adolescents and experts. She creates an outline consisting of an introduction, three main chapters, and a conclusion, and writes her paper accordingly. She makes sure to use quotes and references and to adhere to the APA formatting requirements. Finally, she carefully corrects her work and has it read by her teacher and a fellow student for improvement suggestions.
- A computer science student writes a bachelor’s thesis on the development of a new algorithm for machine learning. He chooses this topic because it reflects his expertise in computer science and his curiosity about new technologies. He gathers information by reading academic articles and communicating with other experts in his field. He creates an outline consisting of an introduction, three main chapters, a section on results, and a conclusion, and writes his paper accordingly. He makes sure to use citations and references and to adhere to the IEEE formatting requirements. Finally, he carefully corrects his work and has it read by his supervisor and a reviewer from a professional journal for improvement suggestions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you start writing a bachelor’s thesis.
Before you start writing your bachelor’s thesis, you should first plan the topic and structure of the paper. This also includes researching relevant sources and creating an outline. Once you have an overview of the structure of the paper, you can start writing.
How quickly can you write a bachelor’s thesis?
The duration of writing a bachelor’s thesis can vary greatly and depends on various factors, such as the complexity of the topic, the size of the paper, and the time spent on research. However, you should generally plan several weeks or even months for the actual writing of a bachelor’s thesis.
How do you properly write a bachelor’s thesis?
1. Start by selecting an interesting and relevant topic for your bachelor’s thesis. 2. Create a clear and detailed research plan that outlines the goals, methods, and timeline for your work. 3. Gather comprehensive and reliable sources to support your arguments and substantiate your theses. 4. Compose a clear and structured introduction that highlights the topic and significance of your work. 5. Develop your arguments in the main chapters of your bachelor’s thesis and use examples and evidence to support your statements. 6. Conclude your findings and conclusion in a conclusive and detailed section that summarizes the significance and implications of your work. 7. Thoroughly correct and revise your bachelor’s thesis to ensure it is logical, coherent, and error-free.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post Comment
Kostenlose Rechtschreibprüfung
Kostenlose plagiatsprüfung, korrektur deiner bachelorarbeit.
- Wissensdatenbank
- Aufbau und Gliederung
- Limitationen deiner Bachelorarbeit
Limitationen in der Diskussion deiner Bachelorarbeit
Veröffentlicht am 13. August 2020 von Hannah Bachmann . Aktualisiert am 23. Oktober 2023.
Im Rahmen der Forschung deiner Bachelorarbeit stößt du meist auf Limitationen oder auch Begrenzungen, die Auswirkungen auf deine Ergebnisse haben.
Die aufgetretenen Limitationen beschreibst du in einem eigenen Abschnitt im Diskussionsteil deiner Bachelorarbeit.
Scribbrs kostenlose Rechtschreibprüfung
Fehler kostenlos beheben
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Limitationen erkennen und beschreiben, beispielformulierungen limitationen in deiner bachelorarbeit, vollständiges beispiel zu limitationen, identifiziere die limitationen deiner bachelorarbeit mithilfe von chatgpt, häufig gestellte fragen.
Der Begriff ‚Limitationen‘ kommt von dem englischen Begriff ‚limitations‘.
Beim Durchführen deiner Forschung für deine Bachelorarbeit wirst du verschiedenen Limitationen begegnen.
In deinem Diskussionsteil solltest du reflektieren und erläutern, auf welche Limitationen du gestoßen bist und inwiefern diese Auswirkungen auf deine Ergebnisse haben.
Je nach Forschungsvorhaben können mögliche Limitationen vielfältig sein. So kann es z. B. vorkommen, dass bei deiner gewählten Methodik Nachteile deutlich werden oder die Verlässlichkeit beeinträchtigt wird.
Basierend auf der Erklärung der Limitationen gibst du anschließend Empfehlungen für weiterführende Untersuchungen. Du erläuterst, wie an deine eigenen Ergebnisse angeknüpft werden kann oder inwiefern Fragen offen geblieben sind.
Wusstest du schon, dass ...
Scribbr durchschnittlich 150 Fehler pro 1000 Wörter korrigiert?
Unsere Sprachexperten verbessern vor Abgabe deiner Abschlussarbeit den akademischen Ausdruck, die Interpunktion und sprachliche Fehler.
Erfahre mehr zur Korrektur
Um zu verdeutlichen, wie du die Limitationen deiner Bachelorarbeit beschreiben kannst, haben wir dir Beispielformulierungen zusammengetragen.
- Eine Limitation der Arbeit ist zum einen der Mangel an aktueller, deutschsprachiger Literatur.
- Es soll beachtet werden, dass sich die Arbeit ausschließlich auf die Faktoren A und B konzentriert und der Faktor C somit nicht behandelt wurde.
- Als eine Limitation dieser Arbeit kann die gewählte Methodik des Experteninterviews angesehen werden, da …
- Die Arbeit behandelt nicht A, deshalb …
- Begrenzungen ergaben sich beim Durchführen der Interviews, da …
- Da sich die vorliegende Arbeit mit den Auswirkungen von A auf B befasst, können keine verlässlichen Aussagen über die Beziehung zwischen A und C getroffen werden.
- In diesem Zusammenhang wäre es lohnenswert, in zukünftiger Forschung zu untersuchen, wie …
- Weiterer Forschungsbedarf ergibt sich aus …
- Die gewonnenen Ergebnisse werfen weitere Fragen auf, die durch weitere Untersuchungen, beispielsweise … ergänzt werden könnten.
Schau dir das vollständige Beispiel an, um ein Gefühl dafür zu entwickeln, wie der Abschnitt zu den Limitationen deiner Bachelorarbeit aussehen kann.
Limitationen und Begrenzungen der Untersuchung
Die zentralen Limitationen der vorliegenden Arbeit ergeben sich aus dem Mangel an verlässlichen Unternehmensdaten sowie aus der theoretischen Natur der Einzelfallstudie. Zum einen mangelt es allgemein an vollständigem, verlässlichem Material und Aufzeichnungen seitens des Unternehmens. Da das Unternehmen noch vergleichsweise jung ist, sind Prozesse zur Datenerfassung noch nicht ausgereift bzw. fehlen gänzlich. Die Menge an verfügbarem Material wurde weiterhin eingeschränkt, da auf die Verwendung von vertraulichen und sensiblen Unternehmensdaten verzichtet wurde. Vom Unternehmen selbst zur Verfügung gestellte Daten können unter Umständen manipuliert oder fehlerhaft sein. Eine unabhängige Verifizierung war nicht möglich. Über die Verlässlichkeit der Unternehmensdaten kann deshalb keine Aussage getroffen werden. Eine weitere Limitation ergibt sich aus der theoretischen Natur dieser Einzelfallstudie. Obgleich die vorliegende Arbeit darauf abzielt, potenzielle langfristige Ergebnisse zu prognostizieren, soll beachtet werden, dass der Mangel an longitudinaler Methodik eine verlässliche Vorhersage nur bedingt zulässt. Es war nicht Ziel dieser Arbeit, andere Faktoren als die genannten in die Untersuchung miteinzubeziehen. Es lässt sich nicht ausschließen, dass in Zukunft weitere Faktoren relevant werden. Inwiefern verschiedene Faktoren langfristig an Relevanz gewinnen oder verlieren, kann Gegenstand weiterführender Forschung sein.
Im Folgenden findest du einige gute ChatGPT-Prompts, die dir dabei helfen können, präzise Abschnitte zu den Limitationen deiner Bachelorarbeit zu verfassen.
Beispiel: ChatGPT-Prompt für die Limitationen deiner Bachelorarbeit
- Ich möchte im Diskussionsteil meiner Bachelorarbeit die Limitationen meiner Forschung über [Das Leben und Werk von Vincent van Gogh]* erläutern. Hilf mir dabei, die Limitationen zu identifizieren und mache Vorschläge für weiterführende Untersuchungen.
- Begrenzte Verfügbarkeit von Primärquellen: Wenn Sie Schwierigkeiten hatten, Zugang zu ausreichenden Primärquellen wie Briefen, Tagebüchern oder Originalwerken von van Gogh zu erhalten, könnte dies die Genauigkeit Ihrer Forschung beeinträchtigen. In diesem Fall könnten Sie vorschlagen, dass zukünftige Forschungsbemühungen den Zugang zu diesen Quellen verbessern, möglicherweise durch Digitalisierung oder verstärkte Kooperation mit Museen und Archiven.
- Einschränkungen bei der Interpretation von Kunstwerken: Die Interpretation von Kunstwerken ist oft subjektiv und kann von Forscher zu Forscher variieren. Dies kann zu Unsicherheiten in Ihrer Analyse führen. Sie könnten vorschlagen, dass weitere Studien die Anwendung verschiedener kunsthistorischer Methoden und Theorien auf van Goghs Werke untersuchen, um ein umfassenderes Verständnis zu gewinnen.
* Füge in die eckigen Klammern deine eigenen Themen ein. Da ChatGPT Grenzen hat ist es wichtig, dass du die mit ChatGPT erstellten Texte nachträglich kritisch prüfst und anpasst. Zum Beispiel wurde im obigen Beispiel nicht gegendert , obwohl dies an vielen Universitäten verlangt wird.
Limitationen , oder auch Begrenzungen treten bei jeder Forschung auf. Auch bei der Forschung für deine Bachelorarbeit kannst du auf bestimmte Begrenzungen stoßen, die Auswirkungen auf deine Ergebnisse haben.
Limitationen können vielfältiger Art sein. In der Regel hängen die Begrenzungen mit dem jeweiligen Forschungsvorhaben zusammen.
Oftmals stößt du z. B. auf Begrenzungen beim Durchführen der gewählten Methodik.
Die aufgetretenen Limitationen solltest du in deinem Diskussionsteil in einem eigenen Abschnitt beschreiben. Du erläuterst ebenfalls, welche Auswirkungen die Begrenzungen auf deine eigenen Forschungsergebnisse haben, und gibst Empfehlungen, wie weiterführende Untersuchungen anknüpfen können.
Diesen Scribbr-Artikel zitieren
Wenn du diese Quelle zitieren möchtest, kannst du die Quellenangabe kopieren und einfügen oder auf die Schaltfläche „Diesen Artikel zitieren“ klicken, um die Quellenangabe automatisch zu unserem kostenlosen Zitier-Generator hinzuzufügen.
Bachmann, H. (2023, 23. Oktober). Limitationen in der Diskussion deiner Bachelorarbeit. Scribbr. Abgerufen am 2. April 2024, von https://www.scribbr.de/aufbau-und-gliederung/limitationen/
War dieser Artikel hilfreich?
Hannah Bachmann
Das hat anderen studierenden noch gefallen, die diskussion deiner bachelorarbeit schreiben, diskussion beispiel einer bachelorarbeit, das fazit einer bachelorarbeit schreiben, aus versehen plagiiert finde kostenlos heraus.
Enjoy a completely custom, expertly-written dissertation. Choose from hundreds of writers, all of whom are career specialists in your subject.
Limitations of a Study: The Complete Guide

Research limitations make most studies imperfect. At its core, the research aims to investigate a specific question or questions about a topic. However, some things can hinder your ability to investigate the question or questions extensively. While this can make achieving your goals challenging, it enables you to point areas that require further studies.
That’s why you should demonstrate how future studies can provide answers to your unanswered questions if you encounter study limitations that affect your findings. Presenting the limitations of a study properly shows the readers that you understand your research problem.
After presenting your research findings, your assessment committee wants to see that you did your work professionally. And presenting limitations in a study shows that you carefully thought about your study problem and performed a review of the available literature while analyzing your preferred methods.
What Are Limitations in Research?
Well, limitations mean anything that might affect the generalizability or reliability of the outcomes of an experiment or a study. And this can relate to research design, like your approach or methods. It can also be something to do with how you carried out your research, like running out of resources or time before completing the study.
Either way, students should include their limitations when writing up their studies. In most cases, researchers include limitations in their analysis and discussions. But different schools can provide varying guidelines on how to include limitations in a research paper. Therefore, seek advice from your educator or check your writing style guide to know where to include the limitations of a study when writing a dissertation.
Common Study Limitations
Each study can have unique limitations. However, most students encounter common study limitations when writing academic papers. Here are some of the most common limitations you’re likely to encounter when writing your academic papers.
Sample profile or size: Most researchers encounter sampling as a limitation for their studies. That’s because they have difficulties finding the right sample with the necessary characteristics and size parameters. And this hinders the generalizability of their study results. Also, different sampling techniques are prone to bias and errors. And this can influence the study outcomes. In some cases, researchers have difficulties selecting their samples and opt to pick their participants selectively. Some researchers can even include irrelevant subjects in their general pool to hit their preferred sample size. Availability of previous research or information: Theoretical concepts or previous knowledge form the basis of studies on specific topics. And this provides a sound foundation on which a researcher can develop a research problem for their investigation and a design. However, a topic can be relatively specific or very progressive. In that case, the lack of or inadequate knowledge and previous studies can limit the analysis scope. And this can cause inaccuracies in the arguments or present a significant error margin in several methodologies and research aspects. Methodology errors: Modern research complexity can cause potential methodology limitations. In most cases, these research limitations relate to how the researchers collect and analyze data. That’s because these aspects can influence the outcomes of a study. Researchers use different techniques to gather data. While these techniques may suit a study design, they can present limitations in terms of inappropriate detail levels, distractions, and privacy. Bias: Bias is a potential limitation whose effects can influence the outcome of every study. However, a researcher can avoid this limitation by eliminating prejudiced or emotional attitudes towards their topic and conflict of interest. Researchers should also establish an oversight level by referring to peer-review procedures or an ethics committee. Bias is an inherent trait for human beings. Even the most objective people exhibit a bias to some extent. Nevertheless, a researcher should remain objective while trying to control potential inaccuracies or bias during the research process.
A researcher may not have control over the limitation of study. However, the limitation can be the condition, influence, or shortcoming that places restrictions on their conclusions or methodology. Therefore, researchers should mention all limitations that can influence their results.
Limitations of the Study Example
The purpose of most studies is to confirm or establish facts, reaffirm a previous study’s outcomes, solve current or new issues, develop a new theory, or support theorems. Research should also enable experts to develop knowledge on specific subjects. And people research different subjects, depending on their interests. However, researchers experience limitations of quantitative research and qualitative research. Here are the most common limitations in research.
Lack or inadequate interactions: Researchers might lack adequate interactions with government institutions and businesses. Consequently, they do not tap a substantial data amount. Researchers should arrange interaction programs with other establishments. That way, they can identify issues that warrant investigation and the necessary data for conducting research, as well as, the benefits of their studies. Overlapping studies can lead fritter resources away or duplicate the findings. Appropriate revision and compilation at regular intervals can solve this problem. Costly publishing: After researching a topic, a researcher should find ways to publish their findings. However, international journals cost a lot of money to publish a study. And this can discourage a researcher from publishing their work. For instance, a study involving females only or carried out in a specific town can have limitations like sample size, gender, and location. What’s more, the entire study could be limited to the researcher’s perception. Lack of or inadequate training: The research process doesn’t have a systematic methodology. Many researchers do not understand the research method when carrying out their work. Consequently, most researchers experience methodological limitations. Essentially, most researchers replicate the methodologies of similar studies. Even some research guides don’t explain the methodologies accurately. And this can limit the outcome of some studies. Lack of code of conduct: Researchers don’t have a code of conduct. And this causes inter-university and inter-departmental rivalries. Library functioning and management are not adequate in most places. Consequently, some researchers spend a lot of energy and time tracing the necessary books, reports, and journals for their studies. Such energy and time can be spent tracing relevant materials. Lack of confidence: The lack of confidence is among the most common limitations of research studies because company managers think that a researcher can misuse the data they disclose to them. Consequently, they don’t want to reveal their business information. And this can affect studies, yet data from researchers can help the same institutions. Therefore, organizations and researchers should implement confidence-building strategies to encourage companies to share data, knowing that researchers will use it productively.
Why Write the Limitations of a Study?
When writing a research paper or a thesis, some people think including study limitations is counterintuitive. That’s particularly the case for researchers that experienced something wrong. However, mentioning the limitations of your study is imperative for the following reasons.
- It tells the readers that you understand that no study lacks some limitations, and you took the time to analyze your work critically.
- It provides opportunities for further studies.
- It enables you to discuss the impacts of the limitations on your analysis and how future studies can address the challenges you encountered if granted a chance to do the study again.
- It presents your study as a transparent undertaking, making the results useful and credible for other people.
Most professors spot problems with the students’ work even if they don’t mention them. Consequently, embracing the limitations of your study and including them in your analysis is the best approach. Leaving out the limitations of research or vital aspects of a study can be detrimental to the entire study field. That’s because it can establish a potentially fallacious and incomplete depiction of the study.
In the academic world, players expect researchers to include the limitations of their works. And this includes a section that demonstrates a holistic and comprehensive understanding of a topic and research process by the author. Discussing limitations is a learning process for assessing the magnitude while critically evaluating the extenuating effect of the stated limitations.
Stating the limitations of a study also improves the validity and quality of future studies. And this includes limitations whose basis is the transparency principle in scientific research, whose purpose is to promote further progress while maintaining mutual integrity in similar studies.
How to Write Study Limitations
When writing your research limitations, do it in a way that demonstrates your understanding of the core concepts of confounding, analytical self-criticism, and bias. Highlighting every limitation might not be necessary. However, include every limitation with a direct impact on your research problem or study results.
Present your thought process as a researcher and explain the pros and cons of your decisions. Also, explain circumstances that may have led to a research limitation. Here’s how you should structure your limitations.
- Identification and description of the limitation: Use professional terminology to identify and describe the limitation. Also, include all necessary accompanying definitions. The limitation explanation should be precise and brief to ensure that the audience can easily understand the issue. Additionally, make sure that your audience can follow your thought pattern.
- Outline the possible impact or influence of the limitation: Explain to your readers how the limitation may have affected or influenced your study. And this comprises elements like the impact’s magnitude, occurrence likelihood, and the general direction the specific limitation could have driven your findings. Researchers generally accept that a limitation can have a more profound influence on a study than others. Therefore, highlight the effect or influence of a limitation to help readers decide on the issues to consider while examining your topic. And this is vital because a limitation whose value bias is null is less dangerous.
- Discuss alternative approaches to limitations: You can also discuss alternative ways to approach the limitations of your research question. However, the researcher should support the methodology or approach they selected in their study. Also, a research paper should explain why the study context warranted the methodology or approach, regardless of the limitation’s nature. Some researchers even provide persuasive evidence while discussing alternative decisions to some extent. And this shows thought transparency while reassuring readers that the researcher chose the best approach, despite the possible laminations.
- Description of the techniques for minimizing risks: Any limitation in research comes with some risks. Therefore, a researcher should describe possible techniques for minimizing the potential risk from the stated limitations. Such techniques can include a reference of previous studies and suggestions for improving data analysis and research design.
Don’t forget that acknowledging your study limitations provides a chance to suggest the direction for further studies. Therefore, connect the limitations of your study to the suggestions you make for further research. Also, explain how your study can make the unanswered questions more focused.
Also, acknowledging the limitation of the study enables you to demonstrate to the professor that you have critically thought about your research problem and understood the importance of the already-published literature. What’s more, it shows that you’ve carefully assessed the methods for studying your study problem. In research, a key objective is to discover new knowledge while confronting assumptions as you explore what others might not know.
Writing limitations should be a subjective process. That’s because you must analyze the impacts of the limitations and include them in your paper. In this section, don’t include the key weaknesses only. Instead, highlight the magnitude of the limitations of your research. And doing this requires you to demonstrate your study’s validity. Show the readers how the limitations have impacted your study outcomes and conclusions. Thus, writing the limitations section of your paper requires an overall, critical interpretation and appraisal of the impact. Essentially, this section should tell the readers why the problems with methods, errors, validity, and other limitations matter and to what extent.
Practical Tips for Writing Research Limitations
When writing a research paper, include information about your study’s limitations at the beginning of the discussion section. That way, your readers can understand your study limitations before delving into the deeper analysis. In some cases, authors bring out limitations when concluding their research discussion and highlighting the essence of further study on the subject. Here are practical tips to help you write the limitations of your study more effectively.
- Check some examples of limitations in research first: To understand the best way to include or present the limitations of your study, check how other authors do it. The internet is awash with good sample papers with a section for limitations. Checking such samples can help you write a limitations section for your academic paper.
- Include essential limitations only: Don’t come up with a list of limitations in your research paper. That’s because doing so can discredit the entire research project. Instead, highlight up to 3 limitations whose influence on your work was the highest. Also, explain how each of the limitations affected your work and research findings.
- Be brief and direct to the point: Identify the limitation, what caused it, and its impact on your research. Don’t expound on the limitation beyond this because the limitation section should be a small part of your paper.
- Be sincere: Don’t make up some lies or disguise your research limitations. That’s because doing so could prove you aren’t prepared. Therefore, be true and sincere with the audience. As you might see in good examples of study limitations, this section tells the audience what could be different or better.
- Explain what caused the limitations of your study: Your audience should have an easy time identifying the reason for the limitations. Therefore, make sure that you have explained everything correctly. Telling the readers about a limiting factor without explaining it can give them the impression that you’re outside your research project.
- Make suggestions for further studies: An ideal way for reversing points that other researchers can explore is to suggest future research paths. Your study could have failed in certain aspects. Maybe you didn’t achieve your expected results. However, it can prompt other researchers to take different directions in their future studies. Also, explain how other researchers can overcome the limitations you encountered in your study. You can even demonstrate why additional studies on the topic or subject are essential.
- Don’t confuse negative results with limitations: If your study brings out negative results, don’t confuse them for limitations. What negative outcomes mean is that you should support your hypothesis instead of opposing it. Perhaps, you can check sample limitations to understand what qualifies as a limitation. However, you can reformulate your hypothesis if you get negative results. Even when you stumble onto something you didn’t expect, don’t highlight it as a limitation.
Final Thoughts
When working on the limitations section of a research paper, be precise and clear. If writing this section becomes challenging, follow the tips shared in this article or seek assistance. That way, you can impress your educator by highlighting the limitations of your study properly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Richard Ginger is a dissertation writer and freelance columnist with a wealth of knowledge and expertise in the writing industry. He handles every project he works on with precision while keeping attention to details and ensuring that every work he does is unique.

Succeed With A Perfect Dissertation

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
Training videos | Faqs

Academic Phrases for Writing Results & Discussion Sections of a Research Paper
Overview | Abstract | Introduction | Literature Review | Materials & Methods | Results & Discussion | Conclusion & Future Work | Acknowledgements & Appendix
The results and discussion sections are one of the challenging sections to write. It is important to plan this section carefully as it may contain a large amount of scientific data that needs to be presented in a clear and concise fashion. The purpose of a Results section is to present the key results of your research. Results and discussions can either be combined into one section or organized as separate sections depending on the requirements of the journal to which you are submitting your research paper. Use subsections and subheadings to improve readability and clarity. Number all tables and figures with descriptive titles. Present your results as figures and tables and point the reader to relevant items while discussing the results. This section should highlight significant or interesting findings along with P values for statistical tests. Be sure to include negative results and highlight potential limitations of the paper. You will be criticised by the reviewers if you don’t discuss the shortcomings of your research. This often makes up for a great discussion section, so do not be afraid to highlight them.
The results and discussion section of your research paper should include the following:
- Comparison with prior studies
- Limitations of your work
- Casual arguments
- Speculations
- Deductive arguments
1. Findings
From the short review above, key findings emerge: __ We describe the results of __, which show __ This suggests that __ We showed that __ Our findings on __ at least hint that __ This is an important finding in the understanding of the __ The present study confirmed the findings about __ Another promising finding was that __ Our results demonstrated that __ This result highlights that little is known about the __ A further novel finding is that __ Together, the present findings confirm __ The implications of these findings are discussed in __ The results demonstrate two things. First, __. Second, __ The results of the experiment found clear support for the __ This analysis found evidence for __ Planned comparisons revealed that __ Our results casts a new light on __ This section summarises the findings and contributions made. It performs well, giving good results. This gives clearly better results than __ The results confirm that this a good choice for __ From the results, it is clear that __ In this section, we will illustrate some experimental results. This delivers significantly better results due to __ The result now provides evidence to __ It leads to good results, even if the improvement is negligible. This yields increasingly good results on data. The result of this analysis is then compared with the __ The applicability of these new results are then tested on __ This is important to correctly interpret the results. The results are substantially better than __ The results lead to similar conclusion where __ Superior results are seen for __ From these results it is clear that __ Extensive results carried out show that this method improves __ We obtain good results with this simple method. However, even better results are achieved when using our algorithm. It is worth discussing these interesting facts revealed by the results of __ Overall, our method was the one that obtained the most robust results. Slightly superior results are achieved with our algorithm. The result is equal to or better than a result that is currently accepted.
2. Comparison with prior studies
The results demonstrated in this chapter match state of the art methods. Here we compare the results of the proposed method with those of the traditional methods. These results go beyond previous reports, showing that __ In line with previous studies __ This result ties well with previous studies wherein __ Contrary to the findings of __ we did not find __ They have demonstrated that __ Others have shown that __ improves __ By comparing the results from __, we hope to determine __ However, in line with the ideas of __, it can be concluded that __ When comparing our results to those of older studies, it must be pointed out that __ We have verified that using __ produces similar results Overall these findings are in accordance with findings reported by __ Even though we did not replicate the previously reported __, our results suggest that __ A similar conclusion was reached by __ However, when comparing our results to those of older studies, it must be pointed out __ This is consistent with what has been found in previous __ A similar pattern of results was obtained in __ The findings are directly in line with previous findings These basic findings are consistent with research showing that __ Other results were broadly in line with __
3. Limitations of your work
Because of the lack of __ we decided to not investigate __ One concern about the findings of __ was that __ Because of this potential limitation, we treat __ The limitations of the present studies naturally include __ Regarding the limitations of __, it could be argued that __ Another limitation of this __ This limitation is apparent in many __ Another limitation in __ involves the issue of __ The main limitation is the lack of __ One limitation is found in this case. One limitation of these methods however is that they __ It presents some limitations such as __ Although widely accepted, it suffers from some limitations due to __ An apparent limitation of the method is __ There are several limitations to this approach. One limitation of our implementation is that it is __ A major source of limitation is due to __ The approach utilised suffers from the limitation that __ The limitations are becoming clear __ It suffers from the same limitations associated with a __
4. Casual arguments
A popular explanation of __ is that __ It is by now generally accepted that __ A popular explanation is that __ As it is not generally agreed that __ These are very small and difficult to observe. It is important to highlight the fact that __ It is notable that __ An important question associated with __ is __ This did not impair the __ This is important because there is __ This implies that __ is associated with __ This is indicative for lack of __ This will not be biased by __ There were also some important differences in __ It is interesting to note that, __ It is unlikely that __ This may alter or improve aspects of __ In contrast, this makes it possible to __ This is particularly important when investigating __ This has been used to successfully account for __ This introduces a possible confound in __ This was included to verify that __
5. Speculations
However, we acknowledge that there are considerable discussions among researchers as to __ We speculate that this might be due to __ There are reasons to doubt this explanation of __ It remains unclear to which degree __ are attributed to __ However, __ does seem to improve __ This does seem to depend on __ It is important to note, that the present evidence relies on __ The results show that __ does not seem to impact the __ However, the extent to which it is possible to __ is unknown Alternatively, it could simply mean that __ It is difficult to explain such results within the context of __ It is unclear whether this is a suitable for __ This appears to be a case of __ From this standpoint, __ can be considered as __ To date, __remain unknown Under certain assumptions, this can be construed as __ Because of this potential limitation, we treat __ In addition, several questions remain unanswered. At this stage of understanding, we believe__ Therefore, it remains unclear whether __ This may explain why __
6. Deductive arguments
A difference between these __ can only be attributable to __ Nonetheless, we believe that it is well justified to __ This may raise concerns about __ which can be addressed by __ As discussed, this is due to the fact that __ Results demonstrate that this is not necessarily true. These findings support the notion that __ is not influenced by __ This may be the reason why we did not find __ In order to test whether this is equivalent across __, we __ Therefore, __ can be considered to be equivalent for __
Similar Posts

Academic Phrases for Writing Conclusion Section of a Research Paper
In this blog, we discuss phrases related to conclusion section such as summary of results and future work.

Academic Phrases for Writing Acknowledgements & Appendix Sections of a Research Paper
In this blog, we discuss phrases related to thanking colleagues, acknowledging funders and writing the appendix section.

How to Write a Research Paper? A Beginners Guide with Useful Academic Phrases
This blog explains how to write a research paper and provides writing ideas in the form of academic phrases.

Academic Phrases for Writing Introduction Section of a Research Paper
In this blog, we discuss phrases related to introduction section such as opening statement, problem definition and research aims.

Academic Writing Resources – Academic PhraseBank | Academic Vocabulary & Word Lists
In this blog, we review various academic writing resources such as academic phrasebank, academic wordlists, academic vocabulary training sites.

Useful Phrases and Sentences for Academic & Research Paper Writing
In this blog, we explain various sections of a research paper and give you an overview of what these sections should contain.
32 Comments
Awesome vocab given, I am really thankful. keep it up!
Why didn’t I find this earlier? Thank you very much! Bless your soul!
thank you!! very useful!!!
Thank you, thank you thank you!!
I’m currently writing up my PhD thesis and as a non-native English speaker, I find this site extremely useful. Thanks for making it!
Very ve4y resourceful..well done Sam
Plesse add me to your mailing list Email: [email protected]
Hi, would like to clarify if that is “casual” or “causal”? Thanks!
Hi there, it should read “causal.”
Thanx for this. so helpful!
Very helpful. Thanks
thank you so much
- Pingback: Scholarly Paraphrasing Tool and Essay Rewriter for Rewording Academic Papers - Ref-N-Write: Scientific Research Paper Writing Software Tool - Improve Academic English Writing Skills
thankyouuuuuu
thank you very much
wow thanks for the help!!
Quite interesting! Thanks a lot!
This is ammmaazzinggg, too bad im in my last year of university this is very handy!!!
Extremely Useful. Thank-you so much.
This is an excellent collection of phrases for effective writing
Thank you so much, it has been helpful.
I found it extremely important!!!
It is a precise, brief and important guides;
It is a very important which gives a guide;
It is a very important guiding explanation for writing result and discussion;
It is a very important guiding academic phrases for writing;
thank you so much.I was in need of this.
- Pingback: Research Paper Structure – Main Sections and Parts of a Research Paper
Thank you so much!!! They are so helpful!
thank its very important.
This is timely, I needed it. Thanks
This is very helpful. Thanks.
You saved my Bachoelor thesis! Huge thanks
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- 90 Share Facebook
- 66 Share Twitter
- 52 Share LinkedIn
- 0.1K Share Email
Ensuring bachelor’s thesis assessment quality: a case study at one Dutch research university
Higher Education Evaluation and Development
ISSN : 2514-5789
Article publication date: 30 May 2023
In the Netherlands, thesis assessment quality is a growing concern for the national accreditation organization due to increasing student numbers and supervisor workload. However, the accreditation framework lacks guidance on how to meet quality standards. This study aims to address these issues by sharing our experience, identifying problems and proposing guidelines for quality assurance for a thesis assessment system.
Design/methodology/approach
This study has two parts. The first part is a narrative literature review conducted to derive guidelines for thesis assessment based on observations made at four Dutch universities. The second part is a case study conducted in one bachelor’s psychology-related program, where the assessment practitioners and the vice program director analyzed the assessment documents based on the guidelines developed from the literature review.
The findings of this study include a list of guidelines based on the four standards. The case study results showed that the program meets most of the guidelines, as it has a comprehensive set of thesis learning outcomes, peer coaching for novice supervisors, clear and complete assessment information and procedures for both examiners and students, and a concise assessment form.
Originality/value
This study is original in that it demonstrates how to holistically ensure the quality of thesis assessments by considering the context of the program and paying more attention to validity (e.g. program curriculum and assessment design), transparency (e.g. integrating assessment into the supervision process) and the assessment expertise of teaching staff.
- Quality assurance
- Accreditation
- Thesis assessment
Hsiao, Y.-P.(A). , van de Watering, G. , Heitbrink, M. , Vlas, H. and Chiu, M.-S. (2023), "Ensuring bachelor’s thesis assessment quality: a case study at one Dutch research university", Higher Education Evaluation and Development , Vol. ahead-of-print No. ahead-of-print. https://doi.org/10.1108/HEED-08-2022-0033
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2023, Ya-Ping (Amy) Hsiao, Gerard van de Watering, Marthe Heitbrink, Helma Vlas and Mei-Shiu Chiu
Published in Higher Education Evaluation and Development . Published by Emerald Publishing Limited. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) licence. Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial and non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. The full terms of this licence may be seen at http:// creativecommons.org/licences/by/4.0/legalcode
Introduction
According to data from the universities of the Netherlands, the number of bachelor’s students at Dutch research universities has been steadily increasing from 2015 to 2021 [1] , leading to increased workload for teaching staff due to the need for greater supervision of students [2] . This increased supervision is particularly evident in the supervision of students’ final projects. In the Netherlands, students can begin working on their final projects in the final year of their program’s curriculum once they pass the first-year diploma (the so-called Propaedeutic phase based on a positive binding study advice, BSA), earn a required number of European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS) credits and meet other requirements. A bachelor’s degree is awarded when a student has “demonstrated by the results of tests, the final projects, and the performance of graduates in actual practice or in postgraduate programmes” (The Accreditation Organisation of the Netherlands and Flanders [Nederlands-Vlaamse Accreditatieorganisatie], hereinafter abbreviated as the NVAO, 2018 , p. 34).
The Bachelor’s thesis is the culmination of the Bachelor’s programme. A Bachelor’s thesis is carried out in the form of a research project within a department. It is an opportunity to put the knowledge learned during the programme into practice. The Bachelor’s thesis is used to assess the student’s initiative and their ability to plan, report and present a project. The difficulty level of the thesis is described by the attainment targets of the programme and the modules followed up until that moment. Students work independently on a Bachelor’s thesis or Individual Assignment (IOO) under the guidance of a supervisor.
This definition highlights the pedagogical value of the thesis (i.e. the opportunity to carry out an independent project) and the purpose of thesis assessment (i.e. to determine the extent to which the intended learning outcomes have been achieved). While this definition acknowledges the importance of a bachelor’s thesis, relatively little research has been done on examining the quality of undergraduate thesis assessment ( Hand and Clewes, 2000 ; Shay, 2005 ; Webster et al ., 2000 ; Todd et al ., 2004 ), let alone in the Dutch context where thesis supervisors and examiners of bachelor’s students are experiencing an increasing workload.
In recent years, the Dutch government has placed increasing emphasis on assessment quality in higher education ( Inspectorate of Education [Inspectie van het Onderwijs], 2016 ). The NVAO has established the Assessment Framework for the Higher Education Accreditation System of the Netherlands (hereinafter abbreviated as the Framework, NVAO, 2018 ). The standards for the accreditation of initial and existing study programs emphasize whether a program has established an adequate student assessment system that appropriately assesses the intended learning outcomes ( NVAO, 2018 ). According to the quality standards of the Framework, thesis assessment should be valid, reliable, transparent and independent. Assessment literature in the higher education context has defined these criteria as follows (e.g. Biggs and Tang, 2007 ; Bloxham and Boyd, 2007 ). Validity refers to the extent to which an assessment accurately measures what it is intended to measure. Reliability refers to the consistency of the assessment results, or how well they accurately reflect a student’s actual achievement level. Transparency is the clarity and specificity with which assessment information is communicated to both students and examiners. Independency is a necessary condition for ensuring the validity and reliability of an assessment, as it requires that examiners remain objective in the assessment process.
Despite the inclusion of these standards in the Framework ( NVAO, 2008 ), official guidance on establishing a quality system of assessing graduation projects that test achievement of the exit level of a study program at Dutch research universities is limited. As assessment practitioners (the first four authors of this article), we have found that it is often unclear for a program’s curriculum and/or management team to establish appropriate thesis assessment procedures at the undergraduate level that meet the NVAO’s quality standards. We hope that our experience can provide valuable insights and guidance for programs seeking to ensure quality assurance for thesis assessment.
Aims and research questions
The purpose of this study is to share our experience and the challenges we faced during internal and external quality assurance processes of thesis assessment. Based on these challenges, we conducted a narrative literature review to develop a set of guidelines for ensuring thesis assessment quality that aligns with the four standards outlined in the Framework ( NVAO, 2018 ): (1) intended learning outcomes, (2) teaching and learning environment, (3) assessment and (4) achieved learning outcomes. To illustrate the application of these guidelines, we present a case study of bachelor’s thesis assessment practices at one Dutch research university.
What are the guidelines for ensuring the quality of thesis assessment procedures that meet the standards specified in the Framework?
How can these guidelines be applied to evaluate the quality of thesis assessment in a study program?
It is important to note that this study is limited to the context of four Dutch research universities, where we encountered common issues during internal quality assurance processes of thesis assessment. Our goal is to share our experience and offer insights that could be useful to other institutions seeking to ensure the quality of thesis assessment. We do not intend to assume that these problems are present at all Dutch research universities.
Problems and guidelines in meeting the four standards
According to the didactic principle of constructive alignment ( Biggs and Tang, 2007 ), which is commonly used in Dutch higher education, the three education processes, teaching, learning and assessment, should be aligned with the intended learning outcomes. We begin with Standards 1 and 2, which set out the conditions under which thesis assessment takes place, and then we place more emphasis on Standards 3 and 4, which focus on the quality criteria for thesis assessment.
Standard 1: intended learning outcomes
To ensure that a study program meets Standard 1 of the Dutch Qualification Framework ( NLQF, 2008 ), the intended learning outcomes for graduates in specific subject areas and qualifications are typically developed using the Dublin Descriptors ( Bologna Working Group, 2005 ), which provide generic statements of competencies and attributes. However, it is often assumed that a thesis should assess all of these program learning outcomes (PLOs) since it is intended to evaluate the achieved learning outcomes at the exit level. Unfortunately, these PLOs can be global and unclear, which can confuse and hinder students from trying to understand the expectations for thesis assessment. Our observation is that programs often utilize PLOs as thesis learning outcomes (TLOs), although a thesis is not equivalent to the entire program curriculum.
According to Biggs and Tang (2007) , it is important for teachers to first clearly define the learning outcomes before designing instructional activities to guide students toward achieving them. In addition, the outcomes at the program and course levels (i.e. a thesis is also a course) should also be constructively aligned, and the course-level outcomes should be specific to the context of the course. Therefore, to design effective thesis activities (such as supervision) and develop assessment criteria, it would be more pedagogically valuable to formulate thesis-specific learning outcomes and explain how they contribute to the PLOs and Dublin Descriptors, rather than directly using the PLOs for thesis assessment.
In addition, a thesis course often involves most of the teaching staff in the program. Therefore, it is important to establish clear and specific expectations for what students should achieve at the end of a bachelor’s thesis course ( Willison and O'Regan, 2006 ; Todd et al ., 2004 ), such as the scope and type of research (e.g. scaffolded or self-initiated), integrating disciplinary knowledge and research skills from earlier program curriculum, demonstrating critical thinking through well-supported arguments and developing independent learning skills for future work ( Willison and O'Regan, 2006 ).
Standard 2: teaching-learning environment
According to Standard 2 of the Dutch Qualification Framework ( NLQF, 2008 ), the quality of the teaching and learning environment should be designed to help students achieve the intended learning outcomes of the program curriculum. However, our experience has revealed problems in this area. In informal discussions with thesis supervisors, we have found that students often report a lack of preparedness for a bachelor’s thesis, as they have not been adequately taught or practiced certain academic and research skills such as communication, information seeking and methodologies. Conversely, many teachers in the program believe they have covered these skills in their courses. Furthermore, during thesis calibration sessions, we have observed that novice examiners lack expertise due to insufficient experience in research education, a lack of training as thesis examiners, and unclear instructions on thesis assessment procedures.
To meet Standard 2, we recommend the following two guidelines. First, as suggested by research on curriculum alignment ( Wijngaards-de Meij and Merx, 2018 ) and research skills development ( Willison, 2012 ; Reguant et al ., 2018 ), the program-level curriculum design should arrange domain-specific subjects in a logical order and gradually develop students’ research, communication and independent learning skills so that they are well prepared to work on the thesis. At the same time, universities should focus on converting teaching staff’s research experience into research education expertise ( Maxwell and Smyth, 2011 ) for the long term.
Second, the program should ensure the quality of the teaching staff because examiners’ practices are crucial for the quality of thesis assessment ( Golding et al ., 2014 ; Kiley and Mullins, 2004 ; Mullins and Kiley, 2002 ). According to the literature, thesis examiners should receive sufficient instructions and training on how to grade a thesis ( Hand and Clewes, 2000 ; Kiley and Mullins, 2004 ). In addition, the university should provide teaching staff with written instructions to regulate and communicate thesis assessment procedures for supervisors, examiners and students, as well as assessment training on using the assessment forms and holding calibration sessions to achieve consistency in interpreting criteria and grade points. The literature on how supporting teaching staff in assessment practices contributes to consistency is discussed further in the section on Reliability.
Standards 3 and 4: student assessment and achieved learning outcomes
Ensuring validity starts with clearly defining what the assessment is intended to measure. According to the definition of validity and principle of constructive alignment ( Biggs and Tang, 2007 ), thesis assessment should be aligned with learning outcomes.
We have identified two problems in this regard. The first problem is the use of a generic assessment form with a set of uniform criteria across different programs within the same department or school. We believe this practice does not follow the principle of constructive alignment ( Biggs and Tang, 2007 ). In particular, the same assessment form cannot be used directly for different degrees (i.e. Bachelor, Master and PhD) based on the Dublin Descriptors. It would be difficult for a generic assessment form to assess the different levels of cognitive demand and skills required at each degree level. For example, the concept of “originality” is defined very differently at each degree level and this should be reflected in the assessment criteria.
The second problem is the quality of the assessment form itself. We have observed the following issues: (1) some criteria are not always directly relevant to the TLOs, (2) the assessment form only lists the names of criteria without defining them or providing specific indicators for each criterion, (3) it is unclear whether different criteria are given equal weight and (4) it is unclear how the final grade is determined (e.g. whether each criterion must be “sufficient” or “passing”).
To address these problems, we recommend the following guidelines. The assessment criteria listed in the form should align with the TLOs and should describe the characteristics of student work that provide relevant, representative and important evidence of their attainment of the learning outcomes ( Brookhart, 2013 , 2018 ; Walvoord and Anderson, 2011 ). In addition to aligning the criteria with the outcomes, the quality of the criteria also affects what is actually being assessed. The criteria should avoid vagueness that leads to multiple interpretations of quality indicators ( Biggs and Tang, 2007 ; Bloxham et al ., 2011 ; Hand and Clewes, 2000 ; Webster et al ., 2000 ). To ensure that the assessment measures what it is intended to measure, the criteria should meet the following five criteria ( Brookhart, 2013 , 2018 ; Walvoord and Anderson, 2011 ): they should be definable, observable, distinct from one another, complete and able to support descriptions along a continuum of quality.
Another important aspect of validity is the weighting of multiple assessment criteria. The weighting should reflect the relative importance of the criteria based on the disciplinary focus of the study program. For example, the criterion of “method and data analysis” might carry more weight in psychology than it would in philosophy.
Reliability and independency
Reliability is a necessary condition for validity and refers to the consistency of assessment results. Reliability is important because it allows us to confidently interpret and determine students’ true performance on a thesis.
Independency between examiners is necessary to ensure the reliability (or objectivity) of the assessment process, as it helps prevent influence on each other’s judgment. Independent grading is often specified in the Education and Examination Regulations of an institution.
Intra-rater reliability refers to the consistency of a single examiner’s grading process over time. Inconsistencies may occur due to internal influences rather than true differences in student performance. We have observed inconsistencies in completed assessment forms, including discrepancies between comments and scores given by the same examiner across different student theses.
Analytical: Examiners assign a rating to each criterion and then determine a thesis grade based on the grading guidelines.
Analytical and then holistic: Examiners assign a rating to each criterion and then determine a thesis grade based on the grading guidelines. If the thesis grade does not match the holistic judgment, examiners adjust the ratings of the criteria.
Holistic and then analytical: Examiners hold an initial grade (in their mind) based on holistic judgment. Next, examiners assign a rating to each criterion and determine a thesis grade based on the grading guidelines. If the thesis grade is different from the initial grade, examiners adjust the ratings of the criteria to make sure that these two grades are the same.
To ensure intra-rater reliability, it is essential to clearly define each criterion to prevent multiple interpretations by examiners. Additionally, examiners should be provided with bias-reduction training ( Wylie and Szpara, 2004 ) to make them aware of potential biases, such as supervisor bias ( Bettany-Saltikov et al ., 2009 ; McQuade et al ., 2020 ; Nyamapfene, 2012 ), and to take actions to prevent them. During the grading process, examiners should also consistently revisit the established criteria and level descriptors to maintain consistency.
To improve inter-rater reliability, the literature suggests establishing standard assessment procedures and improving examiners’ assessment practices ( Hand and Clewes, 2000 ; Kiley and Mullins, 2004 ; Pathirage et al ., 2007 ). Standard assessment procedures should clearly outline the process for considering the relative importance of multiple criteria and the relative importance of various indicators within a criterion ( Hand and Clewes, 2000 ; Bloxham et al ., 2016a ; Pathirage et al ., 2007 ; Webster et al ., 2000 ). To improve examiners’ assessment practices, common approaches include providing examiners with the following three processes ( Sadler, 2013 ):
Prior to grading, to ensure consistent grading, examiners should have a shared understanding of the expectations for each criterion and score level. This can be achieved through the use of anchor or exemplar theses, which are previously graded theses that illustrate the characteristics of each score level ( Osborn Popp et al ., 2009 ). Examiners can refer to these anchor theses as they grade to ensure that they are accurately distinguishing between the different score levels. It should also be clear to examiners how to complete the grading form and whether they are allowed to discuss with other examiners during the grading process ( Pathirage et al ., 2007 ; Dierick et al ., 2002 ).
During the grading process, moderation refers to the process of two examiners arriving at a collective thesis grade ( Bloxham et al ., 2016b ). It is important to have clear instructions on how to control evaluative judgments and stay within reasonable limits during the moderation process. Examiners should also be informed of score resolution methods in case of large discrepancies between their scores, as averaging the scores may not be sufficient in such cases ( Johnson et al ., 2005 ; Sadler, 2013 ). If a third examiner is involved in the moderation process, it should be clear who is qualified for this task and how their results are used to determine the final thesis grade ( Johnson et al ., 2005 ).
As a “post-judgment” process, calibration is the act of ensuring that examiners grade student work against the agreed quality criteria and “how a particular level of quality should be represented” ( Sadler, 2013 , p. 6). It can be helpful to think of calibration as similar to checking the accuracy of a weighing scale by comparing it to a standard and making adjustments to bring it into alignment. In a similar vein, the thesis assessment form (including criteria and score-level descriptors) and examiners’ assessment practices should be calibrated, particularly when there are significant changes in thesis assessment procedures. As noted by Sadler (2013) , high-quality evaluative judgments also require the development of “calibrated” academics who serve not only as custodians of quality criteria and level standards but also as consultants for novice and short-term examiners. Calibration can be implemented alongside the normal grading period as part of an internal quality assurance system ( Andriessen and Manders, 2013 ; Bergwerff and Klaren, 2016 ).
Transparency
Transparency in assessment has received increasing attention in higher education in recent years ( Bamber, 2015 ; Bell et al ., 2013 ; O'Donovan et al ., 2004 ; Price, 2005 ). It refers to making the perceptions and expectations of assessors, including requirements, standards and assessment criteria, known and understood by all participants, particularly students ( O'Donovan et al ., 2004 ).
To ensure transparency in thesis assessment, it’s not enough to only provide students with assessment forms and instructions on assessment procedures. Our observations indicate that without discussing the deeper meaning of criteria and standards, there is a risk of different interpretations by examiners and students.
To address this issue, it is important to foster shared understanding and promote assessment for learning and feedback on progress. This can be achieved by helping students develop their understanding of the quality criteria and standards through observation, discussion and imitation of good-quality theses ( Malcolm, 2020 ). Using anchor theses ( Orsmond et al ., 2002 ; Sadler, 1987 ) and involving students in peer review and grading of each other’s theses using the criteria ( O'Donovan et al ., 2004 ; Rust et al ., 2003 ) can be effective ways to do this.
To ensure transparency, supervisors should use the assessment form not only for thesis examination but also during supervising activities, and should clearly explain the criteria and score levels to their students using anchor theses for illustration ( O'Donovan et al ., 2004 ; Rust et al ., 2003 ).
Overview of guidelines
Formulate program-specific TLOs.
Thesis assessment should be appropriate for the program curriculum and assessment plan.
The program should ensure examiners’ assessment expertise by providing training or instructions.
Standards 3 and 4 – student assessment and achieved learning outcomes
TLOs, thesis supervision and thesis assessment should be constructively aligned.
The assessment criteria should be clearly defined and meet quality requirements. The weighting of multiple criteria should reflect the relative importance of TLOs.
Intra-rater reliability: Examiners should revisit the established criteria to ensure consistency and strive to prevent any possible assessor bias.
○ The program should make assessment procedures consistent across examiners.
○ The program should improve examiners’ assessment practices through the use of anchor or exemplary theses, moderation prior to and during assessment practices, and calibration after thesis assessment.
The program should inform students of what is expected of them and how their thesis will be assessed.
The program should instruct supervisors to explicitly use the criteria during supervising activities.
To illustrate the application of these guidelines, we present a case study of a psychology-related bachelor’s program at a Dutch research university. We chose to focus on this program because all of the authors have experience in quality assurance at various psychology programs. The documents for this case study were provided by one of the co-authors, who played a significant role in the quality assurance of assessment at the program. These documents include the program’s learning outcomes, a thesis handbook, a thesis assessment form, grading instructions for examiners and a self-assessment report (which includes reflections on the four standards of the Framework and is required to be submitted to the NVAO before a site visit).
Four of the authors and the vice program director (as a self-reflection exercise) examined these documents and answered open-ended questions derived from the guidelines in Box 1 . The findings were then structured based on the guidelines in Box 1 .
Motivation for participating in this study
Improving the quality of the assessment criteria to prevent multiple interpretations by examiners.
Clearly defining the roles, tasks and responsibilities of supervisors (as the first examiner) and the second examiner.
The vice program director indicated that the assessment form is still in development and that it is a dynamic improvement process, based on examiners’ accumulated experience and feedback from supervisors, examiners, students and assessment specialists.
Brief course descriptions of the Bachelor’s thesis
In this thesis course, students perform a study that covers the entire empirical research cycle, from developing a specific research question to using theory to answer the question and testing the theory through data collection. They integrate knowledge from various disciplines and practice conducting research on a technology-related problem. Students may collaborate in groups for literature search or data collection, but they must formulate a specific question to be answered in their individually written bachelor’s thesis.
Standard 1 – intended learning outcomes
PLO1 – Competent in scientific disciplines
PLO2 – Competent in doing research
PLO3 – Competent in designing
PLO4 – Use of a scientific approach
PLO5 – Basic intellectual skills
PLO6 – Competent in cooperating and communicating
PLO7 – Take into account the temporal, technological and social context.
TLO1 – formulate a research question fitted to the problem and relevant scholarly literature (PLO1,2)
TLO2 – conduct a literature search (PLO1,2,3,4,6)
TLO3 – apply and modify relevant scientific theory in order to solve a technology-related problem (PLO1,2,4,5,7)
TLO4 – make an adequate research design for empirical research (PLO2,3,4)
TLO5 – apply relevant scientific methods for empirical research (PLO1,2,3,4,5)
TLO6 – relate interpretation of data to theory and to design and/or policy recommendations (PLO1,2,3,4,5,7)
TLO7 – individually write a scientific report (PLO5,6)
TLO8 – reflect and think systematically (PLO5,6,7)
We conclude that TLOs contribute to the development of all seven competences outlined in the PLOs, as well as the five components of the Dublin Descriptors.
Standard 2 – teaching-learning environment
The bachelor’s thesis builds upon the knowledge and skills developed in previous courses. According to the curriculum and program assessment plan, student skills progress from year 1 to 3 and are assessed through various types of assessment, such as presentations, reports and reflective writing. However, there is no specific learning trajectory for academic and research skills available.
To ensure student readiness for working independently on their thesis, students must have passed the propaedeutic phase and obtained a required number of ECTS upon enrolment in the bachelor’s thesis course. They must also have passed the two methods courses.
Written instructions, including a detailed explanation of assessment procedures, criteria and rubrics, are provided in a thesis handbook for supervisors, examiners and students.
The program requires novice examiners to go through an “examiner internship” with senior examiners (mentors). They are guided and monitored by their mentors when assessing graduation theses in their first year of practice. They can directly approach mentors when encountering problems during supervision and assessment.
C1 – Abstract (TLO7,8)
C2 – Introduction/Theory (TLO1,2,3,8)
C3 – Method and results (TLO2,4,5,6)
C4 – Discussion (TLO1,2,3,6,8)
C5 – Writing style (TLO7)
C6 – Process/Work attitude (TLO7,8)
Each criterion on the assessment form includes a short definition and a number of indicators, which are graded using a five-point rating scale (Poor–Insufficient–Sufficient–Good–Very good). It is required that qualitative comments be added to all of the criteria.
It is not clear how each criterion is weighted.
It is not clear how the ratings of multiple indicators and criteria are aggregated to determine the total grade.
Although a rating scale is provided, score-level descriptors are not available. It is not clear whether the indicators describe the “Very good” or “Sufficient” score level.
These issues correspond to areas that the program is currently working to improve, as mentioned at the beginning of this section.
Reliability
New examiners receive a one-day training, in which they practice assessing theses based on the rubric, and discuss their practice results with senior examiners. They also receive guidance on how to use the criteria during the supervision process.
The first and second examiners assess the thesis independently by using the same rubric and register their initial grading results separately to the administration system.
It is obligatory for both examiners to hold a moderation meeting in order to arrive at collective grading results. In this meeting, they go through each criterion and discuss the differences. Then they register the collective results in the administration system, which generates the thesis grade.
When the discrepancies between two examiners cannot be moderated during the meeting, both examiners register these in the administration system. Next, a subcommittee from the Examination Board is informed, which carries out additional grading. The members of the subcommittee are senior examiners who are often mentors assigned to the novice examiners during the examiner internship.
There are no institution-wide guidelines on the moderation and calibration process. These quality assurance processes are organized by study programs. How they are implemented depends on the available resources, assessment expertise and time per study program.
Although no calibration procedure is established, the subcommittee regularly regrades a sample of the borderline theses around the fail/pass grade, the theses with a resit, and theses for which the two examiners differ substantially in their initial grading. In addition, this subcommittee holds a regular plenary meeting to discuss their assessment practices and report their findings regularly to the Examination Board.
After the assessment, both examiners and students are asked to fill out a survey to evaluate the use of rubric and the assessment procedures. The results are used for improving the quality of rubric.
These procedures are in line with most of our guidelines. Still, we suggest that the subcommittee systematically analyses their findings of regrading practices and acts on the improvements in order to complete the quality assurance cycle. In addition, as lessons learned from one university, we highly recommend the Examination Board or the program to carry out a regular review of the completed assessment forms to detect whether there is any assessor bias in order to safeguard intra-rater reliability.
The program has established clear guidelines on how to ensure transparency. At the beginning of the final project, an information session is organized to explain the supervision and assessment procedures and rules to students. It is made clear what the role tasks and responsibilities of supervisor, examiner and student are, in what way the thesis is assessed, and what is assessed (i.e. the criteria in the rubric). The criteria and indicators per criterion are explained in detail in this information session.
The program also makes it clear that the criteria should be used from the beginning and during the supervision activities, as well as in the assessment process. Supervisors are instructed to formulate feedback based on the criteria.
To sum up, this case study shows that their thesis assessment practices apply most of the guidelines suggested in this study.
Conclusion and discussion
This study presents problems encountered from a practitioner’s perspective and derives guidelines from the literature to address these issues. These guidelines cover the entire education process, taking the context of the program into account. They not only explain how to meet the quality criteria of validity, reliability, transparency and independence but also include the conditions that increase the likelihood of meeting these criteria, such as the importance of examiners’ assessment expertise and how the institution should facilitate their development in this area. The case study demonstrates how these guidelines are applied to examine thesis assessment practices at a bachelor’s psychology-related program at a Dutch academic university.
Our experience highlights the importance of applying the didactic principle of constructive alignment at the exit level, as it is not always clear to teaching staff what this means in the context of thesis assessment (despite its widespread use at the course level for instructional design) and how it can be used to ensure the four standards of the Framework. This has led to a focus on reliability, as noted by Webster et al . (2000) , such as revising thesis assessment forms and ensuring consistency among examiners. Our study aims to draw the attention of program teams to validity by considering the program’s curriculum and assessment design and the didactic purpose of using a thesis as a graduation project.
While other studies have focused on specific thesis assessment quality criteria such as reliability (e.g. Pathirage et al ., 2007 ), transparency (e.g. Malcolm, 2020 ) and independence ( Todd et al ., 2004 ; e.g. Nyamapfene, 2012 ), our case study shows how to ensure all of these criteria and carry out a complete quality assurance process. This does not mean that a program needs to address all of them at the same time. Instead, we want to emphasize the importance of research education in a bachelor’s program and recommend that the program align its thesis assessment design with its curriculum design for research education (i.e. as a learning trajectory) and its overall assessment design. Improving thesis assessment alone is not sufficient for students to achieve the intended learning outcomes of the program.
A final, and perhaps the most important, aspect to consider is how to effectively use limited resources to improve teaching staff’s assessment expertise so that they can continuously contribute to the improvement of thesis assessment practices. The guidelines presented in this study can be further developed or adapted as training materials for teaching staff.
Limitations
We would like to acknowledge two limitations of this study. First, unlike more traditional research methods such as surveys and interviews, the problems we reported here were compiled from various sources at four Dutch research universities. Without a more rigorous synthesis of these sources, it is possible that there may be some subjectivity and selection bias present. Second, the guidelines we derived from a narrative review of these problem topics may not include all relevant references.
It is important to note that our use of only one psychology-related bachelor’s program for the case study does not allow us to generalize our findings to all bachelor’s psychology programs at other Dutch academic universities. Rather, our aim is to share our experience and research-informed guidelines, and to examine thesis assessment quality from a practitioner perspective. In line with the goals of Koris and Pello’s (2022) article, our aim is to gradually find solutions that are appropriate for our context through several subsequent iterations in the future.
https://www.universiteitenvannederland.nl/en_GB/f_c_ingeschreven_studenten.html
https://www.universiteitenvannederland.nl/en_GB/reduce-work-pressure#eerste
Andriessen , D. and Manders , P. ( 2013 ), Beoordelen Is Mensenwerk [Evaluation Is Human Work] , Vereniging Hogescholen , Den Haag .
Bamber , M. ( 2015 ), “ The impact on stakeholder confidence of increased transparency in the examination assessment process ”, Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education , Vol. 40 , pp. 471 - 487 .
Bell , A. , Mladenovic , R. and Price , M. ( 2013 ), “ Students' perceptions of the usefulness of marking guides, grade descriptors and annotated exemplars ”, Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education , Vol. 38 , pp. 769 - 788 .
Bergwerff , M. and Klaren , M. ( 2016 ), Kwaliteitsborging Toetsing: En Handreiking Voor Examencommissies [Quality Assurance of Assessment: A Guide for Examination Boards] , Leiden University , Leiden .
Bettany-Saltikov , J. , Kilinc , S. and Stow , K. ( 2009 ), “ Bones, boys, bombs and booze: an exploratory study of the reliability of marking dissertations across disciplines ”, Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education , Vol. 34 , pp. 621 - 639 .
Biggs , J. and Tang , C. ( 2007 ), Teaching for Quality Learning at University , Open University Press , New York, NY .
Bloxham , S. and Boyd , P. ( 2007 ), Developing Effective Assessment in Higher Education: A Practical Guide , McGraw-Hill Education , New York, NY .
Bloxham , S. , Boyd , P. and Orr , S. ( 2011 ), “ Mark my words: the role of assessment criteria in UK higher education grading practices ”, Studies in Higher Education , Vol. 36 , pp. 655 - 670 .
Bloxham , S. , den-Outer , B. , Hudson , J. and Price , M. ( 2016a ), “ Let's stop the pretence of consistent marking: exploring the multiple limitations of assessment criteria ”, Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education , Vol. 41 , pp. 466 - 481 .
Bloxham , S. , Hughes , C. and Adie , L. ( 2016b ), “ What's the point of moderation? A discussion of the purposes achieved through contemporary moderation practices ”, Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education , Vol. 41 , pp. 638 - 653 .
Bologna Working Group ( 2005 ), A Framework for Qualifications of the European Higher Education Area. Bologna Working Group Report on Qualifications Frameworks , Danish Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation , Copenhagen .
Brookhart , S.M. ( 2013 ), How to Create and Use Rubrics for Formative Assessment and Grading , Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (ASCD) , Alexandria, VA .
Brookhart , S.M. ( 2018 ), “ Appropriate criteria: key to effective rubrics ”, Frontiers in Education , [Online] , Vol. 3 , available at: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/feduc.2018.00022 ( accessed 10 April 2018 ).
Dierick , S. , van de Watering , G.A. and Muijtjens , A. ( 2002 ), “ De actuele kwaliteit van assessment: ontwikkelingen in de edumetrie ”, in Dochy , F. , Heylen , L. and van de Mosselaer , H. (Eds), Assessment in onderwijs: Nieuwe toetsvormen en examinering in studentgericht onderwijs en competentiegericht onderwijs , Boom Lemma Uitgevers , Amsterdam .
Golding , C. , Sharmini , S. and Lazarovitch , A. ( 2014 ), “ What examiners do: what thesis students should know ”, Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education , Vol. 39 , pp. 563 - 576 .
Hand , L. and Clewes , D. ( 2000 ), “ Marking the difference: an investigation of the criteria used for assessing undergraduate dissertations in a business school ”, Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education , Vol. 25 , pp. 5 - 21 .
Hsiao , Y.P. and Verhagen , M. ( 2018 ), “ Examining the quality and use of the grading form to assess undergraduate theses ”, 9th Biennial Conference of EARLI SIG 1: Assessment and Evaluation , Helsinki, Finland .
Inspectorate of Education [Inspectie van het Onderwijs] ( 2016 ), De kwaliteit van de toetsing in het hoger onderwijs [The assessment quality in higher education] , Ministry of Education, Culture and Science [Ministerie van Onderwijs, Cultuur en Wetenschap] , Utrecht .
Johnson , R.L. , Penny , J. , Gordon , B. , Shumate , S.R. and Fisher , S.P. ( 2005 ), “ Resolving score differences in the rating of writing samples: does discussion improve the accuracy of scores? ”, Language Assessment Quarterly , Vol. 2 , pp. 117 - 146 .
Kiley , M. and Mullins , G. ( 2004 ), “ Examining the examiners: how inexperienced examiners approach the assessment of research theses ”, International Journal of Educational Research , Vol. 41 , pp. 121 - 135 .
Koris , R. and Pello , R. ( 2022 ), “ We cannot agree to disagree: ensuring consistency, transparency and fairness across bachelor thesis writing, supervision and evaluation ”, Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education , pp. 1 - 12 .
Malcolm , M. ( 2020 ), “ The challenge of achieving transparency in undergraduate honours-level dissertation supervision ”, Teaching in Higher Education , Vol. 28 No. 1 , pp. 1 - 17 .
Maxwell , T.W. and Smyth , R. ( 2011 ), “ Higher degree research supervision: from practice toward theory ”, Higher Education Research and Development , Vol. 30 , pp. 219 - 231 .
McQuade , R. , Kometa , S. , Brown , J. , Bevitt , D. and Hall , J. ( 2020 ), “ Research project assessments and supervisor marking: maintaining academic rigour through robust reconciliation processes ”, Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education , Vol. 45 , pp. 1181 - 1191 .
Mullins , G. and Kiley , M. ( 2002 ), “ 'It's a PhD, not a Nobel Prize': how experienced examiners assess research theses ”, Studies in Higher Education , Vol. 27 , pp. 369 - 386 .
NLQF ( 2008 ), The Higher Education Qualifications Framework in the Netherlands, a Presentation for Compatibility with the Framework for Qualifications of the European Higher Education Area , Dutch Qualifications Framework (NLQF) , ’s-Hertogenbosch, The Netherlands .
NVAO ( 2008 ), The Higher Education Qualifications Framework in the Netherlands: A Presentation for Compatibility with the Framework for Qualifications of the European Higher Education Area , Accreditation Organisation of the Netherlands and Flanders (NVAO) , Den Haag .
NVAO ( 2018 ), Assessment Framework for the Higher Education Accreditation System of the Netherlands , Accreditation Organisation of the Netherlands and Flanders (NVAO) , Den Haag .
Nyamapfene , A. ( 2012 ), “ Involving supervisors in assessing undergraduate student projects: is double marking robust? ”, Engineering Education , Vol. 7 , pp. 40 - 47 .
O'Donovan , B. , Price , M. and Rust , C. ( 2004 ), “ Know what I mean? Enhancing student understanding of assessment standards and criteria ”, Teaching in Higher Education , Vol. 9 , pp. 325 - 335 .
Orsmond , P. , Merry , S. and Reiling , K. ( 2002 ), “ The use of exemplars and formative feedback when using student derived marking criteria in peer and self-assessment ”, Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education , Vol. 27 , pp. 309 - 323 .
Osborn Popp , S.E. , Ryan , J.M. and Thompson , M.S. ( 2009 ), “ The critical role of anchor paper selection in writing assessment ”, Applied Measurement in Education , Vol. 22 , pp. 255 - 271 .
Pathirage , C. , Haigh , R. , Amaratunga , D. and Baldry , D. ( 2007 ), “ Enhancing the quality and consistency of undergraduate dissertation assessment: a case study ”, Quality Assurance in Education , Vol. 15 , pp. 271 - 286 .
Price , M. ( 2005 ), “ Assessment standards: the role of communities of practice and the scholarship of assessment ”, Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education , Vol. 30 , pp. 215 - 230 .
Reguant , M. , Martínez-Olmo , F. and Contreras-Higuera , W. ( 2018 ), “ Supervisors' perceptions of research competencies in the final-year project ”, Educational Research , Vol. 60 , pp. 113 - 129 .
Rust , C. , Price , M. and O'Donovan , B. ( 2003 ), “ Improving students' learning by developing their understanding of assessment criteria and processes ”, Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education , Vol. 28 , pp. 147 - 164 .
Sadler , D.R. ( 1987 ), “ Specifying and promulgating achievement standards ”, Oxford Review of Education , Vol. 13 , pp. 191 - 209 .
Sadler , D.R. ( 2013 ), “ Assuring academic achievement standards: from moderation to calibration ”, Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy and Practice , Vol. 20 , pp. 5 - 19 .
Shay , S. ( 2005 ), “ The assessment of complex tasks: a double reading ”, Studies in Higher Education , Vol. 30 , pp. 663 - 679 .
Todd , M. , Bannister , P. and Clegg , S. ( 2004 ), “ Independent inquiry and the undergraduate dissertation: perceptions and experiences of final-year social science students ”, Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education , Vol. 29 , pp. 335 - 355 .
University of Twente ( 2019 ), The Bachelor's Thesis [Online] . University of Twente , Enschede, The Netherlands , available at: https://www.utwente.nl/en/bee/programme/thesis/ (accessed 8 September 2019) .
Walvoord , B.E. and Anderson , V.J. ( 2011 ), Effective Grading: A Tool for Learning and Assessment in College , Jossey-Bass , San Francisco, CA .
Webster , F. , Pepper , D. and Jenkins , A. ( 2000 ), “ Assessing the undergraduate dissertation ”, Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education , Vol. 25 , pp. 71 - 80 .
Wijngaards-de Meij , L. and Merx , S. ( 2018 ), “ Improving curriculum alignment and achieving learning goals by making the curriculum visible ”, International Journal for Academic Development , Vol. 23 , pp. 219 - 231 .
Willison , J.W. ( 2012 ), “ When academics integrate research skill development in the curriculum ”, Higher Education Research and Development , Vol. 31 , pp. 905 - 919 .
Willison , J.W. and O'Regan , K. ( 2006 ), Research Skill Development Framework [Online] , The University of Adelaide , Adelaide , available at: https://www.adelaide.edu.au/rsd/ ( accessed 19th November 2019 ).
Wylie , E.C. and Szpara , M.Y. ( 2004 ), National Board for Professional Teaching Standards Bias-Reduction Training: Impact on Assessors’ Awareness , ETS Research Report Series , Princeton, NJ , Vol. 2004 , p. i - 55 .
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the reviewers for their thorough review and valuable feedback, which allowed the authors to improve the quality of the manuscript. The authors appreciate the time and effort they put into the review process.
Funding: This work was supported by National Chengchi University (DZ15-B4). The funder only provides financial support and does not substantially influence the entire research process, from study design to submission. The authors are fully responsible for the content of the paper.
Corresponding author
About the authors.
Ya-Ping (Amy) Hsiao is an assessment specialist and teacher trainer at Tilburg University. Her current research focuses on the reflection, portfolio and performance assessment of the graduation projects.
Gerard van de Watering is a policy advisor at Eindhoven University of Technology. His research and development interest focus on assessment and evaluation, student-centered learning environments, independent learning and study skills. He is also the founder of a network of assessment specialists in academic higher education in the Netherlands.
Marthe Heitbrink is a testing and assessment coordinator at the Psychology department of the University of Amsterdam.
Helma Vlas is an educational consultant, teacher trainer/assessor and assessment specialist at the University of Twente. She is stationed at the Centre of Expertise in Learning and Teaching. She is coordinator of the Senior Examination Qualification trajectory at the University of Twente.
Mei-Shiu Chiu is a full professor of Education at National Chengchi University in Taiwan. Her research interests focus on interactions between emotion/affect, cognition and culture for diverse knowledge domains (e.g. mathematics, science and energy) in relation to teaching, assessment and large-scale databases.
Related articles
We’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
Published on September 7, 2022 by Tegan George and Shona McCombes. Revised on November 21, 2023.
The introduction is the first section of your thesis or dissertation , appearing right after the table of contents . Your introduction draws your reader in, setting the stage for your research with a clear focus, purpose, and direction on a relevant topic .
Your introduction should include:
- Your topic, in context: what does your reader need to know to understand your thesis dissertation?
- Your focus and scope: what specific aspect of the topic will you address?
- The relevance of your research: how does your work fit into existing studies on your topic?
- Your questions and objectives: what does your research aim to find out, and how?
- An overview of your structure: what does each section contribute to the overall aim?
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
How to start your introduction, topic and context, focus and scope, relevance and importance, questions and objectives, overview of the structure, thesis introduction example, introduction checklist, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about introductions.
Although your introduction kicks off your dissertation, it doesn’t have to be the first thing you write — in fact, it’s often one of the very last parts to be completed (just before your abstract ).
It’s a good idea to write a rough draft of your introduction as you begin your research, to help guide you. If you wrote a research proposal , consider using this as a template, as it contains many of the same elements. However, be sure to revise your introduction throughout the writing process, making sure it matches the content of your ensuing sections.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Begin by introducing your dissertation topic and giving any necessary background information. It’s important to contextualize your research and generate interest. Aim to show why your topic is timely or important. You may want to mention a relevant news item, academic debate, or practical problem.
After a brief introduction to your general area of interest, narrow your focus and define the scope of your research.
You can narrow this down in many ways, such as by:
- Geographical area
- Time period
- Demographics or communities
- Themes or aspects of the topic
It’s essential to share your motivation for doing this research, as well as how it relates to existing work on your topic. Further, you should also mention what new insights you expect it will contribute.
Start by giving a brief overview of the current state of research. You should definitely cite the most relevant literature, but remember that you will conduct a more in-depth survey of relevant sources in the literature review section, so there’s no need to go too in-depth in the introduction.
Depending on your field, the importance of your research might focus on its practical application (e.g., in policy or management) or on advancing scholarly understanding of the topic (e.g., by developing theories or adding new empirical data). In many cases, it will do both.
Ultimately, your introduction should explain how your thesis or dissertation:
- Helps solve a practical or theoretical problem
- Addresses a gap in the literature
- Builds on existing research
- Proposes a new understanding of your topic
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
Perhaps the most important part of your introduction is your questions and objectives, as it sets up the expectations for the rest of your thesis or dissertation. How you formulate your research questions and research objectives will depend on your discipline, topic, and focus, but you should always clearly state the central aim of your research.
If your research aims to test hypotheses , you can formulate them here. Your introduction is also a good place for a conceptual framework that suggests relationships between variables .
- Conduct surveys to collect data on students’ levels of knowledge, understanding, and positive/negative perceptions of government policy.
- Determine whether attitudes to climate policy are associated with variables such as age, gender, region, and social class.
- Conduct interviews to gain qualitative insights into students’ perspectives and actions in relation to climate policy.
To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
I. Introduction
Human language consists of a set of vowels and consonants which are combined to form words. During the speech production process, thoughts are converted into spoken utterances to convey a message. The appropriate words and their meanings are selected in the mental lexicon (Dell & Burger, 1997). This pre-verbal message is then grammatically coded, during which a syntactic representation of the utterance is built.
Speech, language, and voice disorders affect the vocal cords, nerves, muscles, and brain structures, which result in a distorted language reception or speech production (Sataloff & Hawkshaw, 2014). The symptoms vary from adding superfluous words and taking pauses to hoarseness of the voice, depending on the type of disorder (Dodd, 2005). However, distortions of the speech may also occur as a result of a disease that seems unrelated to speech, such as multiple sclerosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
This study aims to determine which acoustic parameters are suitable for the automatic detection of exacerbations in patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) by investigating which aspects of speech differ between COPD patients and healthy speakers and which aspects differ between COPD patients in exacerbation and stable COPD patients.
Checklist: Introduction
I have introduced my research topic in an engaging way.
I have provided necessary context to help the reader understand my topic.
I have clearly specified the focus of my research.
I have shown the relevance and importance of the dissertation topic .
I have clearly stated the problem or question that my research addresses.
I have outlined the specific objectives of the research .
I have provided an overview of the dissertation’s structure .
You've written a strong introduction for your thesis or dissertation. Use the other checklists to continue improving your dissertation.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarize the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
Scope of research is determined at the beginning of your research process , prior to the data collection stage. Sometimes called “scope of study,” your scope delineates what will and will not be covered in your project. It helps you focus your work and your time, ensuring that you’ll be able to achieve your goals and outcomes.
Defining a scope can be very useful in any research project, from a research proposal to a thesis or dissertation . A scope is needed for all types of research: quantitative , qualitative , and mixed methods .
To define your scope of research, consider the following:
- Budget constraints or any specifics of grant funding
- Your proposed timeline and duration
- Specifics about your population of study, your proposed sample size , and the research methodology you’ll pursue
- Any inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Any anticipated control , extraneous , or confounding variables that could bias your research if not accounted for properly.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. & McCombes, S. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/introduction-structure/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to write an abstract | steps & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

COMMENTS
Common types of limitations and their ramifications include: Theoretical: limits the scope, depth, or applicability of a study. Methodological: limits the quality, quantity, or diversity of the data. Empirical: limits the representativeness, validity, or reliability of the data. Analytical: limits the accuracy, completeness, or significance of ...
Having identified the most important limitations to your dissertation in the announcing move, the reflecting move focuses on explaining the nature of these limitations and justifying the choices that you made during the research process. This part should be around 60-70% of the total word count of the Research Limitations section.
Limited Access to Data: Limited access to data is one of the most common limitations of research studies, and one you will face more regularly. For instance, if your subject topic involves researching specific government organizations, then you may lack access to vital information. Also, you may have no respondents.
Table of contents. What not to include in your discussion section. Step 1: Summarize your key findings. Step 2: Give your interpretations. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Step 4: Acknowledge the limitations. Step 5: Share your recommendations. Discussion section example. Other interesting articles.
Step 1. Identify the limitation (s) of the study. This part should comprise around 10%-20% of your discussion of study limitations. The first step is to identify the particular limitation (s) that affected your study. There are many possible limitations of research that can affect your study, but you don't need to write a long review of all ...
For each limitation you identify, provide a sentence that refutes the limitation or that provides information to counterbalance or otherwise minimize the limitation's perceived impact. You can cite previous studies to help substantiate your assertions: "However, this small sample represents the largest of its kind to date, which means that our
Claiming limitations is a subjective process because you must evaluate the impact of those limitations. Don't just list key weaknesses and the magnitude of a study's limitations. To do so diminishes the validity of your research because it leaves the reader wondering whether, or in what ways, limitation(s) in your study may have impacted the ...
Generally, limitations should be discussed in the conclusion section of a research paper or thesis, although they may also be mentioned in other sections, such as the introduction or methods. The specific limitations that are discussed will depend on the nature of the study, the research question being investigated, and the data that was collected.
Why and Where to Include Limitations in My Research Paper. Common Limitations of the Researchers. Limited Access to Information. Time Limits. Conflicts on Biased Views and Personal Issues. Different types. 1. Research design limitations. 2.
3. Identify your limitations of research and explain their importance. 4. Provide the necessary depth, explain their nature, and justify your study choices. 5. Write how you are suggesting that it is possible to overcome them in the future. Limitations can help structure the research study better.
While each study will have its own unique set of limitations, some limitations are more common in quantitative research, and others are more common in qualitative research. In quantitative research, common limitations include the following: - Participant dropout. - Small sample size, low power. - Non-representative sample.
EXPECTATIONS What the reader expects from the Research Limitations section of your dissertation. All research suffers from limitations, whether it is performed by undergraduate and master's level dissertation students, or seasoned academics.These research limitations range from flaws in the research design, which can be quite serious, to more common problems, such as the challenge of ...
The following is a classic example of how to write the limitations in a thesis. The main aim of the study was to assess the factors that lead to poor limitations writing in a research paper by research scholars. Although the study conducted a thorough survey, there were certain limitations while exploring the aim of the study.
Step 2: Summarize and reflect on your research. Step 3: Make future recommendations. Step 4: Emphasize your contributions to your field. Step 5: Wrap up your thesis or dissertation. Full conclusion example. Conclusion checklist. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about conclusion sections.
Tip. You can acknowledge limitations or weaknesses in the approach you chose, but justify why these were outweighed by the strengths. Here are a few examples: ... Shona has a bachelor's and two master's degrees, so she's an expert at writing a great thesis. She has also worked as an editor and teacher, working with students at all different ...
Craft an enticing and engaging opening section. Provide a background and context to the study. Clearly define the research problem. State your research aims, objectives and questions. Explain the significance of your study. Identify the limitations of your research. Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
Determine the topic of the bachelor's thesis and discuss it with the supervisor. Conduct comprehensive research and collect relevant sources. Create an outline and divide the topic into individual sections. Write the main part of the paper by processing and summarizing the insights gained from the research.
Limitationen erkennen und beschreiben. Der Begriff ‚Limitationen' kommt von dem englischen Begriff ‚limitations'. Beim Durchführen deiner Forschung für deine Bachelorarbeit wirst du verschiedenen Limitationen begegnen.. In deinem Diskussionsteil solltest du reflektieren und erläutern, auf welche Limitationen du gestoßen bist und inwiefern diese Auswirkungen auf deine Ergebnisse haben.
For instance, a study involving females only or carried out in a specific town can have limitations like sample size, gender, and location. What's more, the entire study could be limited to the researcher's perception. Lack of or inadequate training: The research process doesn't have a systematic methodology.
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
In this blog, we discuss phrases related to results and discussion sections such as findings, limitations, arguments, and comparison to previous studies. The results and discussion sections are one of the challenging sections to write. It is important to plan this section carefully as it may contain a large amount of scientific data that needs to be presented in a clear and concise fashion.
The Bachelor's thesis is used to assess the student's initiative and their ability to plan, report and present a project. The difficulty level of the thesis is described by the attainment targets of the programme and the modules followed up until that moment. ... Limitations. We would like to acknowledge two limitations of this study. First ...
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.