- Skip to main content
India’s Largest Career Transformation Portal

Environment Vs Growth Essay for UPSC Mains Preparation
October 15, 2019 by Sandeep
The space inhabited by ecosystems to dwell, survive and thrive, put together is called their respective environment. Environment is typically the place around us, where we dwell in order to make a living and get ourselves adapted to the surroundings and their variations.
Whether we live in a good or a bad environment totally depends on us, as it’s in our hands to keep our surroundings clean and hygienic. Living systems inhabit environments around them and become natural reasons for them to grow and develop beyond boundaries. When this limit is unreasonably crossed by man-made effects of globalised industrialisation cum rapid urbanisation factors, the environment slowly becomes a prey in the hands of human exploitation.
Growth and Expansion
The last four to five decades have seen the world changing rapidly in terms of economic growth, expansion of urban landscapes, industries churning out more global prospects etc. The pace at which our modern ways of living have impacted the environment is unaccounted for. Serious damages to the environment have resulted on account of this unchecked human behavior causing changes in global climate, temperature and mass destruction of species.
Ever wondered why rainfall is becoming so unseasonal and even if it’s in the right season, it may either be scanty or a flood causing trigger, such scenes becoming more common these days. Shortage of drinking water is a global crisis today.
The depletion of ground water has reached unimaginable levels and the supply of fresh and natural air itself is going to become scarce some day in the future. The prospects of growth have multiplied in countless folds on a global scale, ignoring the environment around us, thus creating a big gap between human economic growth and environmental degradation.
Adverse effects of growth on the environment
When man sought expansion of his industries and establishments, he did not fetch even a second glance at the environment. Today with the increase in high rise buildings, our cities have turned into what we call as concrete jungles. This has led to various at-sight problems for citizens. Drinking water facilities are poor and food adulteration is at an all time high.
Sparrows were a common sight in front of every house a while ago, but now they have almost disappeared from everywhere. This is due to all spaces taken over by concrete structures and high intensity mobile radiations. So, we easily lost a species for our irresponsible growth intentions. This is a very good example of our growth having an impact on the environment.
Not just this, if we see the many trees being uprooted in forests, forest fires creating havoc and taking away entire forest ranges in their fumes, we can very easily predict the extent of damage that would be created on the environment in coming years. Soil getting depleted of its vital nutrients has badly affected crop rotation cycles.
This has in turn caused soil to become infertile to an extent that vast lands on earth are becoming barren day by day. This has caused crop failures and inflation rates of essential vegetables to steeply rise.
On the other hand, the excessive use of chloro flouro carbons have created gaping holes in the ozone layer due to which harmful UV radiation are penetrating the earth’s surface more than ever. Also, the depletion of ozone layer has created more deadly chemical reactions leading to incurable cancers etc on earth.
Greenhouse gases responsible to create a sustainable environment on earth are turning into poisonous gases, capable enough of wiping out lives of millions. This has do far weakened the ancient symbiotic relationship between society and the environment on earth. On account of development and population growth, the environment is seeing mass destruction that cannot be set right at least in the years to come.
Creating a sustainable environment
Due to pollution, the early morning fog is now becoming a thick blanket of smog, which is fog, combined with smoke. Smoke that is emitting out from factories and industries causing air pollution. The chemicals that are let out from factories, after mixing with sewage adversely combine with drinking water set ups polluting primary and important water resources. This is how the environment is becoming a store house of air-borne and water-borne diseases.
To come out of these ill effects and create a sustainable environment for the future, we have to first work on increasing the greenery in our environment by pledging to not cut down trees unnecessarily. Cutting down trees on roads to make way for infrastructure growth in cities is common sight, but leads to far stretching ill effects. Urbanisation has brought along with it, hidden adverse effects of environment. Worse, we do not think about the bad we are doing to the environment when we know it very well that it may have disastrous effects on us later on.
Remedies and Solutions
The solution to set the situation right is to think about the environment and show concern towards the apathy we have so far created. Introducing greater scientific rigor about our environment may impact serious assessment of projects.
Government policies and regulations should be strengthened and given more power to check irregularities. The law of the land should be responsible enough to enforce penalties on units that misuse the environment for their selfish needs. Corruption should be ruled out from the place to bring in a better perspective about the environment.
Lack of policy enthusiasm towards environment is as good as taking our environment for granted. This is happening at all places. Illegal mining and quarry units are given permission by governmental agencies after taking Crores of rupees as bribes from prospective money laundering individuals and agencies.
Thus, a deep insight is needed to root out the issue of environmental exploitation, in terms of corruption and bribery cases. The occupation of lake bed areas and converting them into sites for construction is another example where government apathy towards environment is highlighted.
Solutions and remedies are many to tackle such situations. But we can see progress only when initiatives are taken in the right direction by capable authorities who have interest in environmental issues and have concerns on the current plight of our surroundings.
An efficient system to tackle the issue and help it rise from the roots to brighten the haphazard to the society is needed. Citizen initiatives and participation is a much needed effort after all. It is still the biggest way to tackle the problem and we have to join hands with the right governmental agencies to act in the right direction.
Ecological considerations are the need of the hour so that they do not hamper development in the name of modernisation of society. Extensive protection of ecology and environment is essential for sustained economic development. Only if the environment around us is sustainable and friendly can we thrive and make our goals achievable.
It is a false perception that economic growth can lead independently of environmental considerations. We have to live and thrive within our boundaries and not forge ahead leaving out environmental considerations.
Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now

ECONOMIC GROWTH VS ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION

Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
- The Union Coal Ministry has sought to rush through the forest diversion process for proposed opencast coal mining in Angul district of Odisha.
- This would require the felling of more than one lakh standing trees in a reserve forest and cause significant disturbance to the elephant herds.
Economic Growth and the Environment
- The issue of economic growth and the environment essentially concerns the kinds of pressures that economic growth, at the national and international level, places on the environment over time.
- The relationship between ecology and the economy has become increasingly significant as humans gradually understand the impact that economic decisions have on the sustainability and quality of the planet.
Economic growth
- Economic growth is commonly defined as increases in total output from new resources or better use of existing resources; it is measured by increased real incomes per capita.
- All economic growth involves transforming the natural world, and it can effect environmental quality in one of three ways. Environmental quality can increase with growth.
Environment with growth
- Increased incomes, for example, provide the resources for public services such as sanitation and rural electricity.
- With these services widely available, individuals need to worry less about day-to-day survival and can devote more resources to conservation.
- Second, environmental quality can initially worsen but then improve as the growth rate rises.
- In the cases of air pollution , water pollution , and deforestation and encroachment there is little incentive for any individual to invest in maintaining the quality of the environment.
- These problems can only improve when countries deliberately introduce long-range policies to ensure that additional resources are devoted to dealing with them.
- Third, environmental quality can decrease when the rate of growth increases.
- In the cases of emissions generated by the disposal of municipal solid waste , for example, abatement is relatively expensive and the costs associated with the emissions and wastes are not perceived as high because they are often borne by someone else.
Future estimates
- The World Bank estimated that, under present productivity trends and given projected population increases, the output of developing countries would be about five times higher by the year 2030 than it is today.
- The output of industrial countries would rise more slowly, but it would still triple over the same period.
- If environmental pollution were to rise at the same pace, severe environmental hardships would occur.
- Tens of millions of people would become sick or die from environmental causes, and the planet would be significantly and irreparably harmed.
- Yet economic growth and sound environmental management are not incompatible. Economic growth will be undermined without adequate environmental safeguards, and environmental protection will fail without economic growth.
Limited Resources
- The earth's natural resources place limits on economic growth. These limits vary with the extent of resource substitution, technical progress, and structural changes.
- For example, in the late 1960s many feared that the world's supply of useful metals would run out. Yet, today, there is a glut of useful metals and prices have fallen dramatically.
- The demand for other natural resources such as water, however, often exceeds supply.
- In arid regions such as the Middle East and in non-arid regions such as northern China, aquifers have been depleted and rivers so extensively drained that not only irrigation and agriculture are threatened but the local ecosystems.
- Some resources such as water, forests, and clean air are under attack, while others such as metals, minerals, and energy are not threatened.
- This is because the scarcity of metals and similar resources is reflected in market prices. Here, the forces of resource substitution, technical progress, and structural change have a strong influence .
- But resources such as water are characterized by open access, and there are therefore no incentives to conserve.
- Effective policies designed to sustain the environment are most necessary because society must be made to take account of the value of natural resources and governments must create incentives to protect the environment.
- Economic and political institutions have failed to provide these necessary incentives for four separate yet interrelated reasons:
1) short time horizons;
2) failures in property rights;
3) concentration of economic and political power; and
4) immeasurability and institutional uncertainty.
Sustainability
- Although economists and environmentalists disagree on the definition of sustainability, the essence of the idea is that current decisions should not impair the prospects for maintaining or improving future living standards .
- The economic systems of the world should be managed so that societies live off the dividends of the natural resources, always maintaining and improving the asset base.
- Promoting growth, alleviating poverty, and protecting the environment may be mutually supportive objectives in the long run, but they are not always compatible in the short run.
- Poverty is a major cause of environmental degradation , and economic growth is thus necessary to improve the environment. Yet, ill-managed economic growth can also destroy the environment and further jeopardize the lives of the poor.
- In many poor but still forested countries, timber is a good short-run source of foreign exchange.
- When demand for Indonesia's traditional commodity export—petroleum—fell and its foreign exchange income slowed, Indonesia began depleting its hardwood forests at non-sustainable rates in order to earn export income.
- In developed countries, it is competition that can shorten time horizons.
- Competitive forces in agricultural markets, for example, induce farmers to take short-term perspectives for financial survival.
- Farmers must maintain cash flow to satisfy bankers and make a sufficient return on their land investment.
- They therefore adopt high-yield crops, monoculture farming, increased fertilizer and pesticide use, salinizing irrigation methods, and more intensive tillage practices which cause erosion .
Little incentive to reduce damage to the global environment
- " The Tragedy of the Commons " is the classic example of property rights failure. When access to a grazing area, or commons is unlimited, each herdsman knows that grass not eaten today will not be there tomorrow.
- As a rational economic being, each herdsman seeks to maximize his gain and adds more animals to his herd.
- No herdsman has an incentive to prevent his livestock from grazing the area. Degradation follows and the loss of a common resource. In a society without clearly defined property rights, those who pursue their own interests ruin the public good.
- The cheapest methods of avoiding loss of mineral revenues has been to hurry the development of oil and gas in areas which might revert to open water, thereby, hastening erosion and saltwater intrusion, or putting up levies around the property to maintain it as private property, thus interfering with normal estuarine processes.
- Global or transnational problems such as ozone layer depletion or acid rain produce a similar problem.
- Countries have little incentive to reduce damage to the global environment unilaterally when doing so will not reduce the damaging behavior of others or when reduced fossil fuel use would leave that country at a competitive disadvantage.
- International agreements are thus needed to impose order on the world's nations that would be analogous to property rights.
Concentration of wealth
- Concentration of wealth of wealth within the industrialized countries allows for the exploitation and destruction of ecosystems in less developed countries (LDC) through, for example, timber harvests and mineral extraction.
- The concentration of wealth inside a less developed country skews public policy toward benefiting the wealthy and politically powerful, often at the expense of the ecosystem on which the poor depend.
- Local sustainability is dependent upon the goals of those who have power—goals which may or may not be in line with a healthy, sustainable ecosystem. Furthermore, when an exploiting party has substitute ecosystems available, it can exploit one and then move to the next.
- Japanese lumber firms harvest one country and then move on to another. Here the benefits of sustainability are low and exploiters have shorter time horizons than local interests. This is also an example of how the high discount rates in developed countries are imposed on the management of developing countries' assets.
Environmental policy-making
- Policy-makers and institutions are often unable to grasp the direct and indirect effects of policies on ecological sustainability, nor do they know how their actions will affect other areas not under their control.
- Many contemporary economists and environmentalists argue that the value of the environment should nonetheless be factored into the economic policy decision-making process.
- The goal is not necessarily to put monetary values on environmental resources ; it is rather to determine how much environmental quality is being given up in the name of economic growth , and how much growth is being given up in the name of the environment.
- A danger always exists that too much income growth may be given up in the future because of a failure to clarify and minimize tradeoffs and to take advantage of policies that are good for both economic growth and the environment.
Economic development is often put ahead of environmental sustainability as it involves people’s standards of living. However, quality of life can decline if people live in an economic place with a poor environmental quality because of economic development.
- Economic growth means an increase in real output (real GDP). Therefore, with increased output and consumption we are likely to see costs imposed on the environment. The environmental impact of economic growth includes the increased consumption of non-renewable resources, higher levels of pollution, global warming and the potential loss of environmental habitats.
- However, not all forms of economic growth cause damage to the environment. With rising real incomes, individuals have a greater ability to devote resources to protecting the environment and mitigate the harmful effects of pollution. Also, economic growth caused by improved technology can enable higher output with less pollution.
Classic trade-off between economic growth and environmental resources
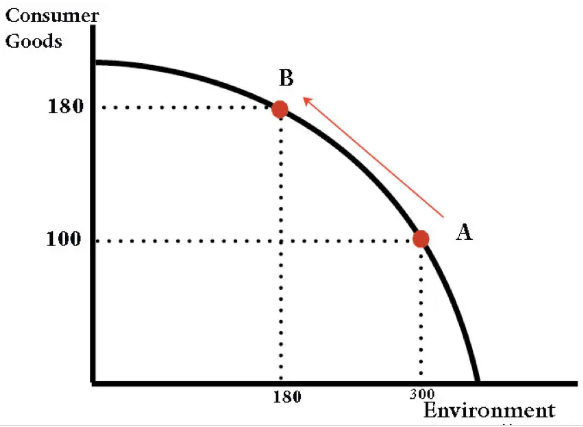
This PPF curve shows a trade-off between non-renewable resources and consumption. As we increase consumption, the opportunity cost implies a lower stock of non-renewable resources.
For example, the pace of global economic growth in the past century has led to a decline in the availability of natural resources such as forests (cut down for agriculture/demand for wood)
- A decline in sources of oil/coal/gas
- Loss of fishing stocks – due to overfishing
- Loss of species diversity – damage to natural resources has led to species extinction.
External costs of economic growth
Increased consumption of fossil fuels can lead to immediate problems such as poor air quality and soot, (London smogs of the 1950s). Some of the worst problems of burning fossil fuels have been mitigated by Clean Air Acts – which limit the burning of coal in city centres. Showing that economic growth can be consistent with reducing a certain type of pollution.
Less visible more diffuse pollution
While smogs were a very clear and obvious danger, the effects of increased CO2 emissions are less immediately obvious and therefore there is less incentive for policymakers to tackle. Scientists state the accumulation of CO2 emissions have contributed to global warming and more volatile weather. All this suggests economic growth is increasing long-term environmental costs – not just for the present moment, but future generations.
Damage to nature
Air/land/water pollution causes health problems and can damage the productivity of land and seas.
Global warming and volatile weather
Global warming leads to rising sea levels, volatile weather patterns and could cause significant economic costs
Soil erosion
Deforestation resulting from economic development damages soil and makes areas more prone to drought.
Loss of biodiversity
Economic growth leads to resource depletion and loss of biodiversity. This could harm future ‘carrying capacity of ecological systems’ for the economy. Though there is uncertainty about the extent of this cost as the benefit of lost genetic maps may never be known.
Long-term toxins
Economic growth creates long-term waste and toxins, which may have unknown consequences. For example, economic growth has led to increased use of plastic, which when disposed of do not degrade. So there is an ever-increasing stock of plastic in the seas and environment – which is both unsightly but also damaging to wildlife.
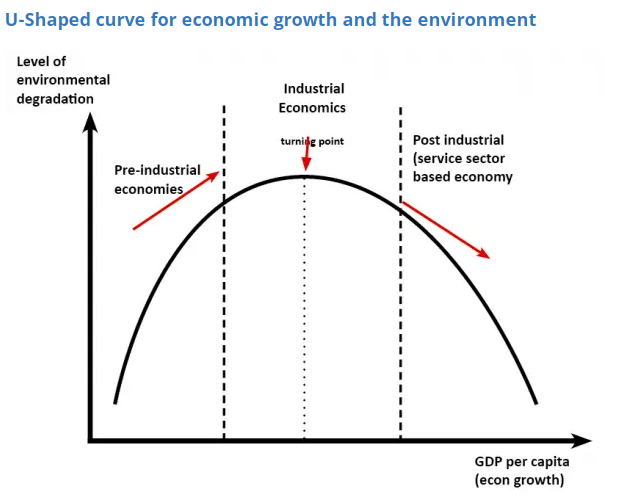
One theory of economic growth and the environment is that up to a certain point economic growth worsens the environment, but after that the move to a post-industrial economy – it leads to a better environment.
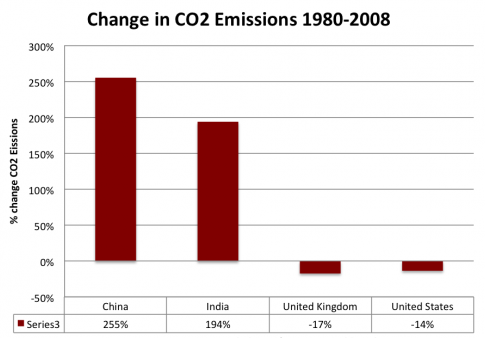
For example – since 1980, the UK and the US have reduced CO2 emission. The global growth in emissions is coming from developing economies.
Another example – In early days of growth, economies tend to burn coal/wood – which cause obvious pollution. But, with higher incomes, an economy can promote cleaner technology which limits this air pollution. However, in a paper “Economic growth and carrying capacity” by Kenneth Arrow et al. they caution about this simplistic u-shape. As the authors state:
“Where the environmental costs of economic activity are home by the poor, by future generation, or by other countries, the incentives to correct the problem are likely to be weak”
- It may be true there is a Kuznets curve for some types of visible pollutants, but it is less true of more diffuse and less visible pollutants. (like CO2)
- The U-shaped maybe true of pollutants, but not the stock of natural resources; economic growth does not reverse the trend to consume and reduce the quantity of non-renewable resources.
- Reducing pollution in one country may lead to the outsourcing of pollution to another, e.g. we import coal from developing economies, effectively exporting our rubbish for recycling and disposal elsewhere.
- Environmental policies tend to deal with pressing issues at hand but ignore future intergenerational problems.
Other models of a link between economic growth and environment
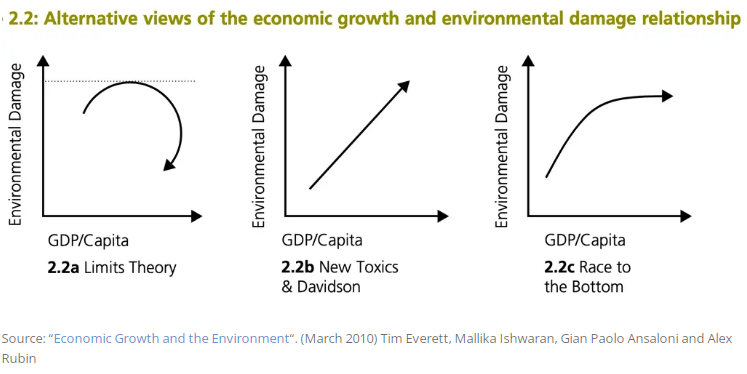
Limits Theory
- This suggests that economic growth will damage the environment, and damage will itself start to act as a brake on growth and will force economies to deal with economic damage.
- In other words, the environment will force us to look after it. For example, if we run down natural resources, their price will rise and this will create an incentive to find alternatives.
- This is more pessimistic suggesting that economic growth leads to an ever-increasing range of toxic output and problems, some issues may get solved, but they are outweighed by newer and more pressing problems which are difficult if impossible to overturn.
- This model has no faith that the free-market will solve the problem because there is no ownership of air quality and many of the effects are piling up on future generations; these future effects cannot be dealt with by the current price mechanism.
Race to the bottom
- This suggests that in the early stages of economic growth, there is little concern about the environment and often countries undermined environmental standards to gain a competitive advantage – the incentive to free-ride on others’ efforts. However, as the environment increasingly worsens, it will reluctantly force economies to reduce the worst effects of environmental damage. This will slow down environmental degradation but not reverse past trends.
Economic growth without environmental damage
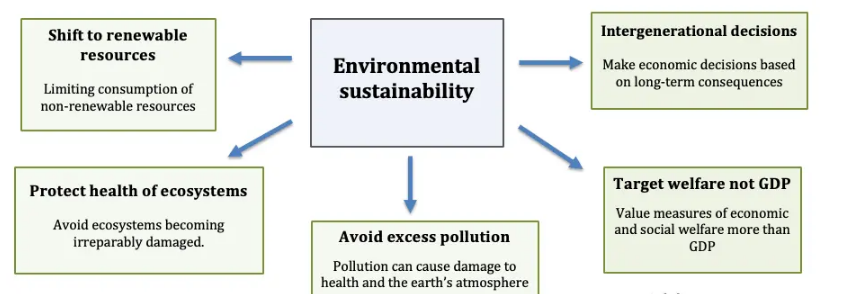
Some ecologists argue economic growth invariably leads to environmental damage. However, there are economists who rightly argue that economic growth can be consistent with a stable environment and even improvement in the environmental impact. This will involve
A shift from non-renewables to renewables
- A recent report suggests that renewable energy is becoming cheaper than more damaging forms of energy production such as burning coal and in 2018 – this has led to a 39% drop in new construction starts from 2017, and an 84% drop since 2015.
Social cost pricing.
- If economic growth causes external costs, economists state it is socially efficient to include the external cost in the price (e.g. carbon tax).
- If the tax equals the full external cost, it will lead to a socially efficient outcome and create a strong incentive to promote growth that minimises external costs.
Treat the environment as a public good
- Environmental policy which protects the environment, through regulations, government ownership and limits on external costs can, in theory, enable economic growth to be based on protection of the environmental resource.
Technological development
- It is possible to replace cars running on petrol with cars running on electricity from renewable sources. This enables an increase in output, but also a reduction in the environmental impact.
- There are numerous possible technological developments which can enable greater efficiency, lower costs and less environmental damage.
- Include quality of life and environmental indicators in economic statistics.
- Rather than targetting GDP, environmental economists argue we should target a wider range of living standards + living standards + environmental indicators. (e.g. Genuine Progress Indicators GPI)
https://epaper.thehindu.com/Home/ShareArticle?OrgId=GUF9PIM30.1&imageview=0
Related Articles
Free access to e-paper and WhatsApp updates

Let's Get In Touch!
© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved
- UPSC Mains PYQ (1979 to 2023)
- UPSC Exam Notes PDF
- UPSC Result
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Interview
- Art and Culture UPSC PDF
- Environment
- International Relation
- Previous Year Paper’s
- Science & Tech
- Toppers Copy
- Agriculture Optional Notes
- Anthropology Optional Notes
- Chemistry Optional Notes
- Commerce Optional Notes
- Economics Optional Notes
- Geography Optional Notes
- History Optional Notes
- Law Optional Notes
- Mathematics Optional Notes
- Philosophy Optional Notes
- Public Administration Optional Notes
- Political Science Optional Notes
- Physics Optional Notes
- Sociology Optional Notes
- GS Score Prelims Test
- Only IAS Prelims Test
- Rau’s IAS Prelims Test
- Shankar IAS Prelims Test
- Vision IAS Prelims Test – English
- Vision IAS Prelims Test – Hindi
- Insight IAS – English
- Insight IAS – Hindi
- Next IAs Prelims Test
- Vision Ias Mains Test – English
- Vision Ias Mains Test – Hindi
- Next IAS Mains Test
- Rau’s IAS Mains Test
- GS Score Mains Test
- Insight IAS Mains Test – English
- Insight IAS Mains Test – Hindi
- Anthropology Optional Test
- Geography Optional Test
- Geology Optional Notes
- History Optional Test
- Mathematics Optional Test
- Optional Test Series
- PSIR Optional Test
- Public Administration Optional Test
- Sociology Optional Test
- Vision IAS Monthly – English
- Vision IAS Monthly – Hindi
- GS Score Monthly
- GS Score Weekly
- Kurukshetra – English
- Kurukshetra – Hindi
- Rau’s IAS Monthly
- Rau’s Prelims Compass
- Rau’s Mains Compass
- Yojana English
- Yojana Hindi
- Insight IAS Magazine – English
- Insights IAS Magazine – Hindi
- Vision IAS – English
- Vision IAS – Hindi
- Shankar IAS
- Standard Books
- NCERT Books
- IGNOU Books
- Current Affairs

Essay UPSC Topic wise Previous Year Questions (1993-2023)
The importance of practicing Essay Papers from previous year questions (PYQ) topic-wise, with the aim of achieving high marks for a better rank in the UPSC Civil Services Examination, cannot be overstated.
The Essay Paper in UPSC CSE Mains carries a weightage of 250 marks. Therefore, the percentage of total marks covered by the Essay Paper is ≈14.29%Percentage.
1. India: Democracy, Administration, Society, Culture
1.1 India Since Independence
- My vision of India in 2001 a.d. -1993
- Whither Indian democracy? -1995
- What we have not learnt during fifty years of independence. -1997
- Why should we be proud of being Indians? -2000
- What have we gained from our democratic set-up? -2001
- How far has democracy in India delivered the goods? -2003
- In the context of Gandhiji’s views on the matter, explore, on an evolutionary scale, the terms ‘Swadhinata’, ‘Swaraj’ and ‘Dharmarajya’. Critically comment on their contemporary relevance to Indian democracy -2012
- Is the Colonial mentality hindering India’s Success? -2013
- Dreams which should not let India sleep. -2015
1.2Federalism, Decentralization
- The language problem in India: its past, present and prospects. -1998
- Water resources should be under the control of the central government. -2004
- Evaluation of panchayati raj system in India from the point of view of eradication of power to people. -2007
- Creation of smaller states and the consequent administrative, economic and developmental implication -2011
- Water disputes between States in federal India. -2016
- Cooperative federalism : Myth or reality. -2016
- Impact of the new economic measures on fiscal ties between the union and states in India. -2017
1.3 Administration
- Politics, bureaucracy and business – fatal triangle. -1994
- Politics without ethics is a disaster. -1995
- The VIP cult is a bane of Indian democracy -1996
- Need for transparency in public administration -1996
- The country’s need for a better disaster management system. -2000
- How should a civil servant conduct himself? -2003
1.4 Judiciary
- Judicial activism. -1997
- Judicial activism and Indian democracy. -2004
- Justice must reach the poor -2005
- We may brave human laws but cannot resist natural laws. -2017
1.5 Poverty, Social Justice
- Reservation, politics and empowerment. -1999
- Food security for sustainable national development -2005
- The focus of health care is increasingly getting skewed towards the ‘haves’ of our society. -2009
- Neglect of primary health care and education in India are reasons for its backwardness. -2019
- There can be no social justice without economic prosperity but economic prosperity without social justice is meaningless -2020
1.6 Indian Society, Culture and Values
- The Indian society at the crossroads. -1994
- New cults and godmen: a threat to traditional religion -1996
- The composite culture of India. -1998
- Indian culture today: a myth or a reality? -2000
- Modernism and our traditional socio-ethical values. -2000
- Culture is what we are, civilization is what we have -2020
- From traditional Indian philanthropy to the gates-buffet model-a natural progression or a paradigm shift? -2010
- A society that has more justice is a society that needs less charity. 2023
1.7 Media, TV & Cinema
- The misinterpretation and misuse of freedom in India. -1998
- Mass media and cultural invasion. -1999
- Responsibility of media in a democracy. -2002
- How has satellite television brought about cultural change in Indian mindsets? -2007
- Role of media in good governance -2008
- Does Indian cinema shape our popular culture or merely reflect it? -2011
- Biased media is a real threat to Indian democracy. -2019
- Is sting operation an invasion on privacy? -2014
2. Economy, Development
2.1 Growth vs Development
- Economic growth without distributive justice is bound to breed violence. -1993
- Resource management in the Indian context. -1999
- GDP (Gross Domestic Product) along with GDH (Gross Domestic Happiness) would be the right indices for judging the wellbeing of a country-2013
- Was it the policy paralysis or the paralysis of implementation which slowed the growth of our country? -2014
- Crisis faced in India – moral or economic. -2015
- Can capitalism bring inclusive growth? -2015
- Digital economy: A leveller or a source of economic inequality. -2016
- Innovation is the key determinant of economic growth and social welfare. -2016
- Near jobless growth in India: An anomaly or an outcome of economic reforms. -2016
- Poverty anywhere is a threat to prosperity everywhere. -2018
2.2 Environment vs Development
- Ecological considerations need not hamper development. -1993
- Urbanization is a blessing in disguise. -1997
- Protection of ecology and environment is essential for sustained economic development. -2006
- Urbanisation and its hazards -2008
- Should a moratorium be imposed on all fresh mining in tribal areas of the country? -2010
- Alternative technologies for a climate change resilient India. -2018
- Forests are the best case studies for economic excellence.-2022
- Multinational corporations – saviours or saboteurs -1994
- Globalization would finish small-scale industries in India. -2006
- Special economic zone: boon or bane -2008
- Is the criticism that the ‘Public-Private-Partnership’ (PPP) model for development is more of a bane than a boon in the Indian context, justified ?-2012
2.4 Sectors of Economy
- BPO boom in India. -2007
- Are our traditional handicrafts doomed to a slow death? -2009
- Tourism: Can this be the next big thing for India? -2014
- Farming has lost the ability to be a source of subsistence for majority of farmers in India. -2017
3. Education
3.1 Values in Education
- Literacy is growing very fast, but there is no corresponding growth in education. -1996
- Irrelevance of the classroom. -2001
- Independent thinking should be encouraged right form the childhood. -2007
- Is an egalitarian society possible by educating the masses ? -2008
- What is real education? -2005
- Are the standardized tests good measure of academic ability or progress? -2014
- Is the growing level of competition good for the youth? -2014
- Education without values, as useful as it is, seems rather to make a man more clever devil-2015
- Destiny of a nation is shaped in its classrooms. -2017
- Education is what remains after one has forgotten what one has learned in school. 2023
- Mathematics is the music of reason. 2023
3.2 Scheme implementation
- Restructuring of Indian education system. -1995
- “Education for all” campaign in India: myth or reality. -2006
3.3 Higher education
- Privatization of higher education in India. -2002
- Credit – based higher education system – status, opportunities and challenges -2011
4. Quote based, Philosophy, Ethics
4.1 Character, Honesty, Ethics
- He would reigns within himself and folds his passions and desires and fears is more than a king. -1993
- Attitude makes, habit makes character and character makes a man. -2007
- With greater power comes greater responsibility. -2014
- Words are sharper than the two-edged sword. -2014
- Character of an institution is reflected in its leader. -2015
- Need brings greed, if greed increases it spoils breed. -2016
- A people that values its privileges above its principles loses both. -2018
- Customary morality cannot be a guide to modem file. -2018
- Values are not what humanity is, but what humanity ought to be -2019
- Best for an individual is not necessarily best for the society -2019
- Courage to accept and dedication to improve are two keys to success -2019
- Wisdom finds truth -2019
- Simplicity is the ultimate sophistication -2020
- Ships don’t sink because of water around them ships sink because of water that gets into them -2020
- Life is a long journey between human being and being humane.- 2020
- Philosophy of wantlessness is Utopian, while materialism is a chimera. – 2021
- Your perception of me is a reflection of you; my reaction to you is an awareness of me.- 2021
- The real is rational and the rational is real. – 2021
- History repeats itself, first as a tragedy, second as a farce. – 2021
- A ship in the harbour is safe but that is not what a ship is for. -2022
- Just because you have a choice, it does not mean that any of them has to be right. -2022
- Not all who wander are lost. 2023
4.2 Knowledge
- Disinterested intellectual curiosity is the lifeblood of civilisation. -1995
- There is nothing either good or bad but thinking makes it so. -2003
- ‘The past’ is a permanent dimension of human consciousness and values. -2018
- A good life is one inspired by love and guided by knowledge. -2018
- Mindful manifesto is the catalyst to a tranquil self.- 2020
- Poets are the unacknowledged legislators of the world. -2022
- What is research, but a blind date with knowledge! – 2021
- Visionary decision-making happens at the intersection of intuition and logic. 2023
4.3 Compassion
- Compassion is the basic of all morality of the world -1993
- Be the change you want to see in others (Gandhi)-2013
- Lending hands to someone is better than giving a dole. -2015
- Joy is the simplest form of gratitude. -2017
- Hand that rocks the cradle rules the world. – 2021
- You cannot step twice in the same river. -2022
- Inspiration for creativity springs from the effort to look for the magical in the mundane. 2023
4.4 Truth and reality
- When money speaks, the truth is silent. -1995
- Truth is lived, not taught -1996
- Search for truth can only be a spiritual problem. -2002
- Reality does not conform to the ideal, but confirms it. -2018
4.5 Youth, Discipline
- Youth is a blunder, manhood a struggle, old age a regret -1994
- Youth culture today. -1999
- If youth knew, if age could. -2002
- Discipline means success, anarchy means ruin -2008
- Fifty Golds in Olympics: Can this be a reality for India? -2014
4.6 Towards excellence
- Useless life is an early death. -1994
- Our deeds determine us, as much as we determine our deeds. -1995
- The pursuit of excellence. -2001
- The paths of glory lead but to the grave. -2002
- Quick but steady wins the race. -2015
- There are better practices to “best practices” – 2021
- The time to repair the roof is when the sun is shining. -2022
- Smile is the chosen vehicle for all ambiguities. -2022
- Thinking is like a game, it does not begin unless there is an opposite team. 2023
5. Women Empowerment
5.1 National Politics
- The new emerging women power: the ground realities. -1995
- Greater political power alone will not improve women’s plight. -1997
- Women’s reservation bill would usher in empowerment for women in India. -2006
5.2 World / Quote type
- If women ruled the world -2005
- The hand that rocks the cradle -2005
5.3 Empowerment overall
- Women empowerment: challenges and prospects. -1999
- Empowerment alone cannot help our women. -2001
- Whither women’s emancipation? -2004
- If development is not engendered, it is endangered. -2016
- Fulfilment of ‘new woman’ in India is a myth. -2017
- Patriarchy is the least noticed yet the most significant structure of social inequality. -2020

5.4 Compared to men
- Men have failed: let women take over. -1993
- Woman is god’s best creation. -1998
- Managing work and home – is the Indian working woman getting a fair deal ?-2012
- History is a series of victories won by the scientific man over the romantic man. -2022
- Girls are weighed down by restrictions, boys with demands – two equally harmful disciplines. 2023
6. International issues, Internal Security
6.1 Globalization
- Modernisation and westernisation are not identical concepts. -1994
- India’s contribution to world wisdom. -1998
- The world of the twenty-first century. -1998
- The implications of globalization for India. -2000
- My vision of an ideal world order. -2001
- The masks of new imperialism. -2003
- As civilization advances culture declines. -2003
- Globalizations and its impact on Indian culture. -2004
- National identity and patriotism -2008
- ‘globalization’ vs. ‘nationalism’ -2009
- Geography may remain the same ; history need not. -2010
- Preparedness of our society for India’s global leadership role. 2010
- South Asian societies are woven not around the state, but around their plural cultures and plural identities. -2019
6.2 International Org./ Bilateral
- The global order: political and economic -1993
- Restructuring of UNO reflect present realities -1996
- India’s role in promoting ASEAN co-operation. -2004
- Importance of Indo-US nuclear agreement -2006
- Has the Non-Alignment Movement (NAM) lost its relevance in a multipolar world ? -2017
- Technology as the silent factor in international relations -2020
6.3 Security
- True religion cannot be misused. -1997
- Terrorism and world peace -2005
- Is autonomy the best answer to combat balkanization? -2007
- Are we a ‘soft’ state ? -2009
- Good fences make good neighbours -2009
- In the Indian context , both human intelligence and technical intelligence are crucial in combating terrorism -2011
- Management of Indian border dispute is a complex task. -2018
7. Science-Technology
7.1 Science and Religion
- Spirituality and scientific temper. -2003
- Science and Mysticism : Are they compatible ?-2012
7.2 Science and Education
- Value-based science and education. -1999
- The march of science and the erosion of human values. -2001
- Modern technological education and human values. -2002
7.3 Computer and internet
- Computer: the harbinger of silent revolution. -1993
- The cyberworld: its charms and challenges. -2000
- Increasing computerization would lead to the creation of a dehumanized society. -2006
- Cyberspace and Internet : Blessing or curse to the human civilization in the long run -2016
- ‘Social media’ is inherently a selfish medium. -2017
- Rise of Artificial Intelligence: the threat of jobless future or better job opportunities through reskilling and upskilling. -2019
- Technology as the silent factor in international relations. -2020
7.4 Sci-Tech: others
- The modern doctor and his patients. -1997
- The lure of space. -2004
- Science and technology is the panacea for the growth and security of the nation-2013
- Technology cannot replace manpower. -2015
- The process of self-discovery has now been technologically outsourced. – 2021
Here are several reasons why practice with Essay PYQ’s is crucial:
- Alignment with UPSC Trends: Practicing with PYQs allows candidates to align their preparation with the evolving trends of the UPSC. Understanding the historical context of essay topics helps in anticipating and preparing for potential themes in the upcoming exam.
- Grasp of Exam Expectations: PYQs provide insights into the expectations of the examiners. By analyzing past questions, candidates can discern the depth of analysis, the breadth of knowledge required, and the quality of expression that the UPSC values in essay answers.
- Thematic Coverage: Previous year questions cover a wide array of themes, ranging from socio-economic issues to philosophical concepts. Practicing with these questions ensures that candidates have a comprehensive understanding of the diverse subjects that may be presented in the essay paper.
- Content Refinement: Repeated practice on specific topics from PYQs aids in refining content knowledge. It helps candidates revisit and reinforce their understanding of key concepts, theories, and factual information relevant to different subjects.
- Structural Mastery: Crafting well-structured essays is crucial for effective communication. Practicing with PYQs allows candidates to master the art of structuring their essays, ensuring a logical flow of ideas and a coherent presentation.
- Time Management Skills: The essay paper has a strict time limit. Regular practice with PYQs hones time management skills, enabling candidates to allocate their time wisely between planning, writing, and revising their essays during the actual examination.
- Adaptability to Varied Topics: Since PYQs cover diverse topics, candidates become more adaptable to addressing a broad spectrum of subjects. This adaptability is essential for tackling any unforeseen or unfamiliar topics that may appear in the exam.
- Feedback Incorporation: Practicing essays from PYQs provides candidates with an opportunity to receive feedback on their responses. Constructive feedback helps in identifying areas for improvement, allowing candidates to refine their writing skills and enhance the quality of their answers.
- Holistic Skill Development: The essay paper evaluates a range of skills, including critical analysis, synthesis of information, effective communication, and a nuanced understanding of issues. Practicing with PYQs contributes to the holistic development of these skills.
- Confidence Boost: Regularly practicing essays from PYQs instills confidence in candidates. The familiarity with the exam format, topics, and the ability to produce well-argued essays under timed conditions builds confidence, positively impacting overall performance.
In conclusion, practicing essay papers from PYQs topic-wise is a strategic approach that not only aligns preparation with the expectations of the UPSC but also contributes to comprehensive skill development. This practice enhances a candidate’s chances of securing high marks in the essay paper, ultimately leading to a better rank in the UPSC Civil Services Examination.

Environment vs Development UPSC Notes
One of the toughest challenges modern society faces – environment vs development. The emerging economies and their development push back towards the environment, which perturbs the people worrying about all this growth and development. Protecting natural resources on the one hand v/s developing an economy on the other hand seems to be always different. But in real life somehow both can be achieved together for long-term sustainability. Environmental issues have often come into conflict with development goals. This tug-of-war affects policy decisions, and one side has good arguments against the other. Some points showing the complexity of environment vs development include:
- Development needs natural resources, but overuse can cause irreparable damage to the environment.
- Ecosystem protection is good for biodiversity, but economic growth contributes to the reduction of poverty and a better standard of living.
- Renewable energy could fill the gap between developmental progress and environmental sustainability.
- Long-term environmental impacts are generally not accounted for during short-term development plans.
Table of Contents
The Conflict Between Environment and Development
Central to this argument between an environment and development is the actual basic contradiction between growth and preservation. Once expansion sets in, more and more land, energy, and resources are employed. This might result in deforestation, habitat loss, and resource extraction. Development projects, particularly in terms of infrastructure and industry, often result in exploitation on a large scale. This is most often at the cost of global warming and pollution.
With environmental conservation increasingly becoming known in importance, there is a realization of an urgent need to keep the natural ecosystems in serviceable forms. Ecosystems are considered knowledge banks that aid in the storage of carbon, purifying waters, as well as numerous other critical services crucial to the existence of life on Earth. Sustainable development relates to reducing the negative impact of development while at the same time sustaining economic growth.

Equilibrating Economic Growth with Environmental Sustainability
Balancing the environment vs development calls for adopting sustainable development models. Sustainable development satisfies the needs of the present without making future generations unable to meet their needs. Sustainable development is the integration of economic growth, environmental protection, and social equity.
Governments, firms, and societies increasingly use green energy, green infrastructure, and responsible consumption to regulate resources. For example, investment in renewable sources of energy like solar and wind power reduces dependence on fossil fuels, one of the key causes of environmental degradation. Some environment vs development considerations are as follows.
- Green sources of energy : Green energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydro can be utilized to power industries, thereby reducing the impacts of greenhouse gases in the environment.
- Sustainable agriculture : Eco-friendly farming practices thus prevent land degradation and enhance biodiversity
- Responsible urban planning : Smart cities and green spaces help in reducing pollution while promoting economic growth.
- Circular economy models : Reducing, reusing, and recycling supports resource efficiency.
Environmental Impact of Rapid Industrialization
Many economic developments have been brought about by rapid industrialization, though such developments come along with price packages against the environment. These include countries such as China and India, which, in the not-too-distant past, have witnessed unbelievable economic development, as it were. Economic development in such countries has resulted in resultant severities both in air and water pollution. Here, environment vs development becomes an important debate.
Consuming industries are energy and raw material-intensive. Factory emissions and chemical release into rivers and air worsen climate change and biodiversity. In response to these challenges, industries seek cleaner technologies, waste reduction, and improved energy efficiency.
Is Development the Solution to Poverty?
Development plays a significant role in better living, especially in developing countries. Economic growth improves health, education, and infrastructural development, and increases employment opportunities. These stimulate less poor development in these nations. However, if the case of this development is not environmentally friendly, it would significantly lead to the depletion of natural resources on which these populations depend.
There should be environmental safeguards in every development project. In fact, most development can strive for both sustainability and the environment to ensure that benefits from development are accrued across many generations.
Solutions to Sustainable Development
Finding a middle ground between environment vs development is the key to having a future where both economic growth and environmental health blend together. Now, many governments, as well as organizations, preach policies that enhance sustainable growth by tallying both development and the environment in the plan. This end ensures that economic growth can continue without exhausting the resources on Earth or harming the ecosystems on which life depends. Here are some of the ways to enhance sustainable development:
- Investment in renewable energy : from fossil fuels to clean energy sources, which include solar, wind, and hydropower.
- Environmental education : raising awareness about the environmental impacts of unbridled development.
- Government policies : regulation policies that insist on applying sustainable principles in industrial and urban planning
- Green Technologies : technology innovation that reduces carbon footprints, waste, and resource consumption.

The Role of International Cooperation
This is a very central challenge of the environment versus development where international cooperation becomes essential. A few examples of things that cannot be dealt with by one country alone are climate change, deforestation, and pollution. International agreements are in place such as the Paris Agreement that set out frameworks concerning the reduction of carbon emissions by countries and sustainable development.
Balancing development with environmental protection is much more difficult for developing countries as they suffer from the lack of adequate financial resources and access to technology. Developed countries may play a positive role in technology transfer, funding sustainable projects, and capacity-building programs.
The environment versus development debate is complex and not an either-or choice. While on the surface, apparently, development and the protection of the environment are mutually conflicting choices, it is indeed possible to marry the two with careful planning, innovative technologies, and positive practices. It’s time to find an appropriate balance whereby economic growth runs in tandem with environmental sustainability for the good of this planet.
Post navigation
Previous post.


Mastering Essays on Environmental Issues for UPSC: A Comprehensive Approach
Essays on environmental issues have become increasingly significant in the UPSC Civil Services Examination (CSE). These topics not only test your understanding of current global and national environmental challenges but also assess your ability to present solutions with a balanced perspective. Writing on environmental issues for UPSC requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining knowledge from geography, ecology, governance, and ethics. In this blog, we’ll explore how to effectively approach such essays and share tips on resources to enhance your preparation.
1. Understand the Broader Context of Environmental Issues
The first step to mastering essays on environmental issues for UPSC is developing a strong foundational understanding. Topics related to climate change, biodiversity loss, pollution, sustainable development, and environmental policies are commonly asked. When approaching these essays, you need to be aware of both the scientific causes and socio-economic impacts of environmental challenges. This can help you provide a well-rounded analysis.
For example, if you are writing about climate change , discuss the greenhouse gas effect, its impact on global temperatures, and how it exacerbates socio-economic issues such as food insecurity and migration. This would help you write more about Environmental Issues for UPSC.
Where to Study:
- NCERT Geography textbooks (Class 11 and 12) for foundational knowledge.
- Environment by Shankar IAS for a detailed overview of various environmental issues for upsc.
- Sleepy Classes’ General Studies Foundation Course provides up-to-date insights on environmental topics for essay preparation.
2. Incorporate Key Statistics and Reports
Data-driven arguments always make an essay more compelling. For essays on environmental issues for UPSC , it’s important to integrate statistics, official reports, and international agreements to support your points. For example, when writing on biodiversity loss, citing the Global Biodiversity Outlook Report or the Living Planet Report gives your essay credibility.
Similarly, while discussing air pollution, you can quote from WHO air quality guidelines or India’s National Clean Air Programme (NCAP). These details demonstrate not only your understanding but also that you are well-versed with current developments.
- Government sources like the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) for updates on Indian environmental policies.
- Reports by UNEP, IPCC , and WWF for global data and perspectives on environmental challenges.
- Sleepy Classes’ Current Affairs modules often include summaries of key environmental reports, which can be directly used in essays.
3. Structure Your Essay Effectively
The structure of your essay is critical. An essay on environmental issues for UPSC should follow a logical flow, from introducing the problem to presenting solutions. Here’s a suggested structure:
- Introduction : Start with a thought-provoking fact, quote, or a general observation about the current state of the environment. You could reference key events like the Paris Agreement or India’s role in COP (Conference of Parties) .
- Causes : Discuss the scientific and human-driven causes of environmental degradation. Explain how industrialization, urbanization, and overpopulation contribute to issues like deforestation, pollution, and climate change.
- Impact : Highlight the social, economic, and political impacts of these environmental challenges. Discuss how marginalized communities are often the worst affected and how environmental degradation can fuel resource conflicts.
- Government Policies and Global Initiatives : Present the steps taken by India and the international community to address environmental issues, such as NDCs (Nationally Determined Contributions) under the Paris Agreement or India’s National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) .
- Conclusion : End with a forward-looking solution, focusing on sustainable development. Mention concepts like eco-restoration , the importance of individual responsibility, and international cooperation.
Practice Resources:
- Yojana and Kurukshetra magazines , which often cover topics related to environmental policies and initiatives in India.
- Sleepy Classes’ Essay Writing Course for practical tips on structuring and content delivery.
4. Incorporate Case Studies and Examples
Examples and case studies bring authenticity to your essay. When preparing for environmental issues for UPSC , make a habit of collecting case studies, both from India and abroad. These real-world examples can provide depth to your essays and make them more relatable.
For instance:
- The Chipko Movement or Silent Valley Movement in India can be discussed under forest conservation efforts.
- The Ken-Betwa River Linking Project can be explored for issues related to water management and biodiversity loss.
- Global examples like the Great Pacific Garbage Patch can illustrate the global scale of plastic pollution.
- Down to Earth magazine by Centre for Science and Environment for Indian environmental case studies.
- Sleepy Classes’ Case Study compilations for easy access to recent case studies and examples.
5. Include Ethical and Philosophical Dimensions
Environmental issues are not just about policies and science. They also encompass deeper ethical questions about our relationship with nature. In your essay on environmental issues for UPSC , include a discussion on the ethical dimensions of environmental conservation. You can draw upon ideas like deep ecology (which emphasizes intrinsic value in nature) or Gandhian environmentalism , which advocates for minimalism and sustainability.
You can also discuss the ethical responsibilities of developed nations in reducing emissions, given their historical role in climate change, as part of the principle of Common But Differentiated Responsibilities (CBDR) in climate negotiations.
- Ethics, Integrity, and Aptitude textbooks for understanding environmental ethics.
- Sleepy Classes’ Ethics Case Study Course for insights on how to integrate ethics into environmental discussions.
6. Practice Answer Writing Regularly
Finally, no matter how much you read, the key to mastering essays on environmental issues for UPSC is consistent practice. Write at least one essay a week, focusing on a different environmental topic. This will help you develop a clear, concise writing style and learn how to present your arguments in a time-bound manner.
- Previous year’s UPSC Essay papers for environmental topics.
- Sleepy Classes’ UPSC Essay Test Series , which provides personalized feedback and model answers.
Writing essays on environmental issues for UPSC is a skill that requires thorough preparation, structured thinking, and frequent practice. By understanding the core issues, incorporating statistics, using real-world examples, and offering balanced solutions, you can craft high-quality essays that are both informative and engaging. Don’t forget to use the right resources, including textbooks, government reports, and the guidance provided by Sleepy Classes , to keep your preparation on track.
Previous Post Mastering Indian Politics Since Independence: A Comprehensive Strategy for PSIR Optional
Next post mastering social stratification for sociology optional: a step-by-step guide, similar posts, how to study indian art and architecture for upsc mains.
How to Tackle Regionalism in Indian Politics for UPSC
Preparing with a focus on current affairs for upsc prelims.
Comments are closed.
Browse Our Content
Information.
- Disclaimer
- Privacy Policy
- Refund & Cancellation
- General Studies
- Monday – Saturday (9AM – 5PM)
- [email protected]
- 1800-890-3043
- Sleepy Edusolutions Private Limited
- GST No.- 03ABDCS3013L1ZN
- Plot No. E-42, Phase 8, Industrial Area, Sahibzada Ajit Singh Nagar, Punjab 160071
© 2024 Sleepy Classes IAS.
- General Studies 2025
- Sociology 2025
- Political Science & IR 2025
- Political Science & International Relations
- Essay Courses
- Psychological Counselling
- Prelims Courses
- Political Science & IR
- NCERT Batch
- Current Affairs

- Uttar Pradesh PSC Courses
- Jammu & Kashmir PCS Courses
- Punjab PSC Courses
- Bihar PSC Courses
- Haryana PSC Courses
- Himachal Pradesh PSC Courses
- Odisha PSC Courses
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- UPSC Previous Year Papers
- PSIR Optional – Syllabus & PYQs
- Uttar Pradesh PCS
- Haryana PCS
- Rajasthan RPSC
- Himachal Pradesh PCS
- Jammu & Kashmir PCS
- Recommended Books For UPSC
- Yojana & Kurukshetra
- Our Toppers
Fill the Form to Register
Which Year are You Targeting to Crack the UPSC Exam? —Please choose an option— Preparing for UPSC 2024 Preparing for UPSC 2025 Beyond That Preparing for State PSC
Do You Require Coaching? —Please choose an option— Yes No Joined Sleepy Classes Joined Some Other Coaching
Which Optional are You Preparing For? Sociology Political Science & International Relations Others
Which Year are You Targeting to Crack the UPSC Exam? Preparing for UPSC 2024 Preparing for UPSC 2025 Beyond That Preparing for State PSC
Do You Require Coaching? Yes No Joined Sleepy Classes Joined Some Other Coaching
Fill the Form to Get State PYQs
Which State PCS Are You Preparing For? Select Your State Uttar Pradesh Bihar Punjab Haryana Himachal Pradesh Jammu and Kashmir Other
Do You Require Coaching? Looking for Coaching Preparing by Yourself Already Joined Coaching
Fill Your Details to Register
Fill the form to download your files.
What is Your UPSC Optional —Please choose an option— Sociology Political Science & IR Others
Year of Attempt UPSC 2024 UPSC 2025 Beyond that
Are You Preparing On Your Own? —Please choose an option— Yes No Joined Sleepy Classes Joined Some Other Coaching Looking for Mentorship Only
Fill the Form to Download Your File
Are You Preparing On Your Own? Yes I have already joined Coaching I am looking for Coaching I am looking for Mentorship
Fill Your Details to Register for the IGP 2023
Roll Number
What is Your Optional?
Preferred Mode for Mock Interview —Please choose an option— Online Offline – Delhi Offline – Chandigarh
Marks in Previous Interview (if applicable)
Date of UPSC Interview (if applicable)
Home State & Other States (if any)
Academic Qualifications
Upload DAF-I
Upload DAF-II
Upload Passport-Size Photograph

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Introducing greater scientific rigor about our environment may impact serious assessment of projects. Government policies and regulations should be strengthened and given more power to check irregularities.
Today, with rising population, developmental needs, consumerism culture and disasters we confront a critical challenge of our era, which is maintaining the delicate balance between environmental conservation and economic development.
However, the man-made changes and natural exploitation for economic growth are the major contributors to climate change and its effects. This is due to the underlying thought that development policies promote economic well being, while environmental policies have been seen to be restricting it.
The environmental impact of economic growth includes the increased consumption of non-renewable resources, higher levels of pollution, global warming and the potential loss of environmental habitats. However, not all forms of economic growth cause damage to the environment.
The importance of practicing Essay Papers from previous year questions (PYQ) topic-wise, with the aim of achieving high marks for a better rank in the UPSC Civil Services Examination, cannot be overstated. The Essay Paper in UPSC CSE Mains carries a weightage of 250 marks.
Economic growth improves health, education, and infrastructural development, and increases employment opportunities. These stimulate less poor development in these nations. However, if the case of this development is not environmentally friendly, it would significantly lead to the depletion of natural resources on which these populations depend.
Environment vs Development – with focus on the significance of environment, the impact of prioritization of economic growth over Environment and Need for Sustainable Development
Essays on environmental issues have become increasingly significant in the UPSC Civil Services Examination (CSE). These topics not only test your understanding of current global and national environmental challenges but also assess your ability to present solutions with a balanced perspective.
Learn about the complex relationship between development and environment in India, as it navigates economic growth and ecological sustainability.
Achieving a balance between economic growth and natural resource consumption is critical. Development is worthless without an environment. We must conserve energy for future generations and understanding the notion of sustainable development is the only way to do it.