

Class 9 Science Case Study Questions Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 9th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Case study Questions in Class 9 Science Chapter 2 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving Class 9 Science Case Study Questions Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure?
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Is Matter Around Us Pure? Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure?
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1: Akshita wants to separate the mixture of dyes constituting a sample of ink. She marked a line by the ink on the filter paper and placed the filter paper in a glass containing water as shown in the figure. The filter paper was removed when the water moved near the top of the filter paper.

(i) Identify the technique used by the Akshita. (a) Sedimentation (b) Filtration (c) Chromatography (d) Distillation
Answer: (c) Chromatography.
(ii) What would you expect to see, if the ink contains three different coloured components? (a) We will not see any band on the filter paper. (b) We would see three bands on the filter paper at various lengths. (c) We would see infinite bands on the filter paper. (d) We would see the single band on the filter paper.
Answer: (b) The components of the ink will travel with water and we would see three bands on the filter paper at various lengths.
(iii) An application where you can use this technique is: (a) To separate salt from sand (b) To separate the wheat from the husk (c) To separate oil from water (d) To separate drugs from the blood.
Answer: (d) To separate drugs from blood.
(iv) The above process is used for the separation of : (a) insoluble substances (b) single solute that dissolves in the soluble solvent. (c) solutes that dissolve in the same solvent. (d) solutes that dissolve in the different solvents.
Answer: (c) For the separation of those solutes that dissolve in the same solvent.
(v) What is chromatography? (a) It is an agricultural method to separate grains (b) A method to separate magnetic impurities from non-magnetic impurities
(c) The process of separating the suspended particles of an insoluble substance (d) Method of separating and identifying various components in a mixture, which are present in small trace quantities.
Answer: (d) Method of separating and identifying various components in a mixture, which are present in small trace quantities.
Case Study 2: A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances is called a true solution. it consists of solute and solvent. The particle size of the true solution is less than 1 nanometer. A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture in which the solute particle does not dissolve but remains suspended throughout the bulk of the medium. A colloid is a mixture that is actually heterogeneous but appears to be homogeneous as the particles are uniformly spread throughout the solution.
(i) which one of the following is most stable?
A)True solution
B)Suspensions
D) both A and B
Answer: A)True solution
ii) which type of mixture can be separated by filtration?
D)All of these
Answer: B)Suspensions
iii) which statement is incorrect about the Tyndall effect. *
A)True solution shows Tyndall effect
B)Suspensions show the Tyndall effect
C)Colloid show Tyndall effect
D)Both B and C show the Tyndall effect
Answer: A)True solution shows Tyndall effect
iv) Which is the correct order of stability of solution *
A) True < Colloid<Suspension
B)Colloid<Suspension<True
C)Colloid<True<Suspension
D)Suspension<Colloid<True
Answer: D)Suspension Case Study 3: Matter can be classified into two categories: pure substances and mixtures. Pure substances are made up of a single type of particle and cannot be separated into other substances by physical methods. They have definite and constant properties. On the other hand, mixtures are made up of two or more substances that are physically combined and can be separated into their individual components. Mixtures can be further classified into homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures. Homogeneous mixtures are uniform in composition, meaning the components are evenly distributed throughout the mixture. Heterogeneous mixtures, on the other hand, have non-uniform composition with visible different parts. It is important to understand the nature of matter around us and differentiate between pure substances and mixtures to comprehend their properties and behavior. What is the main characteristic of a pure substance? a) Made up of two or more substances b) Cannot be separated into other substances c) Has non-uniform composition d) Components are evenly distributed Answer: b) Cannot be separated into other substances Which of the following is an example of a pure substance? a) Air b) Saltwater c) Gold d) Soil Answer: c) Gold How are mixtures different from pure substances? a) Mixtures have definite and constant properties b) Mixtures are made up of a single type of particle c) Mixtures cannot be separated into other substances d) Mixtures are physically combined and can be separated Answer: d) Mixtures are physically combined and can be separated Which type of mixture has a non-uniform composition? a) Homogeneous mixture b) Heterogeneous mixture Answer: b) Heterogeneous mixture What is the primary reason for understanding the nature of matter around us? a) To separate mixtures into pure substances b) To comprehend the properties and behavior of matter c) To classify mixtures into homogeneous and heterogeneous d) To identify the components in pure substances Answer: b) To comprehend the properties and behavior of matter Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure? with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 9 Science Is Matter Around Us Pure? Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible By Team Study Rate Rs aggarwal class 9 pdf with solutions, mcq class 9 social science civics what is democracy why democracy quiz with answers, class 9 geography case study questions chapter 5 natural vegetation and wildlife, leave a reply cancel reply. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.You Might Also Like

Class 9th Science - Is Matter Around Us Pure Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
By QB365 on 09 Sep, 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 9th Science Subject - Is Matter Around Us Pure, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Is matter around us pure case study questions with answer key.
9th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
(ii) What would you expect to see, if the ink contains three different coloured components? (a) We will not see any band on the filter paper. (b) We would see three bands on the filter paper at various lengths. (c) We would see infinite bands on the filter paper. (d) We would see single band on the filter paper. iii) Give one application where you can use this technique. (a) To separate salt from sand (b) To separate wheat from husk (c) To separate oil from water (d) To separate drugs from blood. (iv) For the separation of what kind of substances is the above process used ? (a) For the separation of insoluble substances (b) For the separation of single solute that dissolves in single solvent. (c) For the separation of those solutes that dissolve in the same solvent. (d) For the separation of those solutes that dissolve in the different solvents. (v) What is chromatography ? (a) It is an agricultural method to separate grains (b) A method to separate magnetic impurities from non-magnetic impurities (c) The process of separating the suspended particles of an insoluble substance (d) Method of separating and identifying various components in a mixture, which are present in small trace quantities.
(ii) Oil from water.
(iii) Sodium chloride from its solution in water.
(iv) Camphor from salt.
(v) Cream from milk
(ii) Which type of substance can be separated by this method ? (a) Any solvent from its non-volatile solute. (b) The volatile solvent from its non-volatile solute. (c) The non-volatile solvent from its non-volatile solute. (d) The volatile solvent from its volatile solute. (iii) What can we interpret about the nature of ink ?
(iv) Name the component which gets evaporated. ( a) Heating leads to the evaporation of water. (b) Heating leads to the evaporation of dyes. (c) Heating leads to the filtration of water. (d) Heating leads to the distillation of dyes. (v) Define the process shown in the diagram (a) It is the process of conversion of a liquid into its vapours. (b) It is a process of separating insoluble component by filtering the solution (c) It is a process that separates a pure solid in the form of its crystals (d) It is a technique to separate two miscible liquids
(ii) One of the following does not undergo sublimation. This one is :
(iii) The conversion of a solid into vapours without passing through the liquid state is called :
(iv) When heat is constantly supplied by a burner to boiling water, then the temperature of water during vaporisation :
(v) During summer days, water kept in an earthen pot (pitcher) becomes cool because of the phenomenon of :
*****************************************
Is matter around us pure case study questions with answer key answer keys.
(i) (c) Chromatography (ii) (b) We would see three bands on the filter paper at various lengths. (iii) (d) To separate drugs from blood. (iv) (c) For the separation of those solutes that dissolve in the same solvent. (v) (d) Method of separating and identifying various components in a mixture, which are present in small trace quantities.
(i) (b) Sedimentation and Decantation. (ii) (c) Separating funnel (iii) (d) Evaporation (iv) (c) Sublimation (v) (d) Centrifugation.
(i) (a) Boiling (ii) (b) The volatile solvent from its non-volatile solute. (iii) (d) Ink is a mixture of dyes in water. (iv) (a) Heating leads to the evaporation of water. (v) (a) It is the process of conversion of a liquid into its vapours.
(i) (c) sublimation (ii) (b) sodium chloride (iii) (c) sublimation (iv) (d) does not rise at all (v) (d) evaporation.
Related 9th Standard CBSE Science Materials
9th standard cbse syllabus & materials, class 10th social science - pastoralists case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 9th social science - forest society and colonialism case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 9th social science - nazism and the rise of hitler case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 9th social science - socialism in europe and the russian revolution case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 9th social science - the french revolution case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 9th maths - probability case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 9th maths - statistics case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 9th maths - surface case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 9th maths - linear equations in two variables case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 9th maths - coordinate geometry case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, rs aggarwal 9th standard maths ncert solutions for probability, rs aggarwal 9th standard maths ncert solutions for statistics, rs aggarwal 9th standard maths ncert solutions for surface areas volumes, rs aggarwal 9th standard maths ncert solutions for heron's formula, rs aggarwal 9th standard maths ncert solutions for constructions.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

9th Standard CBSE Study Materials

9th Standard CBSE Subjects

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure?
- Last modified on: 2 years ago
- Reading Time: 4 Minutes
Case Study Questions:
Question 1:
Akshita wants to separate the mixture of dyes constituting a sample of ink. She marked a line by the ink on the filter paper and placed the filter paper in a glass containing water as shown in figure. The filter paper was removed when the water moved near the top of the filter paper.

(i) Identify the technique used by the Akshita. (a) Sedimentation (b) Filtration (c) Chromatography (d) Distillation
(ii) What would you expect to see, if the ink contains three different coloured components? (a) We will not see any band on the filter paper. (b) We would see three bands on the filter paper at various lengths. (c) We would see infinite bands on the filter paper. (d) We would see single band on the filter paper.
(iii) An application where you can use this technique is: (a) To separate salt from sand (b) To separate wheat from husk (c) To separate oil from water (d) To separate drugs from blood.
(iv) The above process is used for the separation of : (a) insoluble substances (b) single solute that dissolves in soluble solvent. (c) solutes that dissolve in the same solvent. (d) solutes that dissolve in the different solvents.
(v) What is chromatography ? (a) It is an agricultural method to separate grains (b) A method to separate magnetic impurities from non-magnetic impurities (c) The process of separating the suspended particles of an insoluble substance (d) Method of separating and identifying various components in a mixture, which are present in small trace quantities.
You may also like:
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:5MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then…
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure of Atom
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:4MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure of Atom In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then…
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:4MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then questions based…
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:4MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then…
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:4MinutesCase Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given,…
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
CBSE Expert
Case Study Questions of Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure? PDF Download
Case study Questions on Class 9 Science Chapter 2 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure?

In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Is Matter Around Us Pure? Case Study Questions With answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure?
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
Akshita wants to separate the mixture of dyes constituting a sample of ink. She marked a line by the ink on the filter paper and placed the filter paper in a glass containing water as shown in the figure. The filter paper was removed when the water moved near the top of the filter paper.

(i) Identify the technique used by the Akshita. (a) Sedimentation (b) Filtration (c) Chromatography (d) Distillation
Answer: (c) Chromatography.
(ii) What would you expect to see, if the ink contains three different coloured components? (a) We will not see any band on the filter paper. (b) We would see three bands on the filter paper at various lengths. (c) We would see infinite bands on the filter paper. (d) We would see the single band on the filter paper.
Answer: (b) The components of the ink will travel with water and we would see three bands on the filter paper at various lengths.
(iii) An application where you can use this technique is: (a) To separate salt from sand (b) To separate the wheat from the husk (c) To separate oil from water (d) To separate drugs from the blood.
Answer: (d) To separate drugs from blood.
(iv) The above process is used for the separation of : (a) insoluble substances (b) single solute that dissolves in the soluble solvent. (c) solutes that dissolve in the same solvent. (d) solutes that dissolve in the different solvents.
Answer: (c) For the separation of those solutes that dissolve in the same solvent.
(v) What is chromatography? (a) It is an agricultural method to separate grains (b) A method to separate magnetic impurities from non-magnetic impurities
(c) The process of separating the suspended particles of an insoluble substance (d) Method of separating and identifying various components in a mixture, which are present in small trace quantities.
Answer: (d) Method of separating and identifying various components in a mixture, which are present in small trace quantities.
Question 2:
A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances is called a true solution. it consists of solute and solvent. The particle size of the true solution is less than 1 nanometer. A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture in which the solute particle does not dissolve but remains suspended throughout the bulk of the medium. A colloid is a mixture that is actually heterogeneous but appears to be homogeneous as the particles are uniformly spread throughout the solution.
(i) which one of the following is most stable?
A)True solution
B)Suspensions
D) both A and B
Answer: A)True solution
ii) which type of mixture can be separated by filtration?
D)All of these
Answer: B)Suspensions
iii) which statement is incorrect about the Tyndall effect. *
A)True solution shows Tyndall effect
B)Suspensions show the Tyndall effect
C)Colloid show Tyndall effect
D)Both B and C show the Tyndall effect
Answer: A)True solution shows Tyndall effect
iv) Which is the correct order of stability of solution *
A) True < Colloid<Suspension
B)Colloid<Suspension<True
C)Colloid<True<Suspension
D)Suspension<Colloid<True
Answer: D)Suspension Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure? with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 9 Science Is Matter Around Us Pure? Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Key Features No thanks, I’m not interested! (I) Read the given passage and answer the questions that follow based on the passage and related studied concepts. A pure substance consist of single type of particles. Mixture consist of more than one kind of pure form of matter. Mixtures can be separated by physical methods but pure substances especially compounds cannot be separated into chemical constituents by physical methods. Pure substance has same composition throughout. Soil and soft drinks are mixtures. Mixtures can be separated by various methods depending upon nature of substance present in it. Solution is a homogeneous mixture. Q1: Name the process by which pure NaCl can be obtained from salt solution. Ans: Crystallisation Q2: What are alloys-compounds or mixtures? Ans: Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of two or more metals or a metal and a non-metal e.g. Brass is alloy of Cu and Zn Q3: What is size of particles in solution? Ans: The size of particles in solutions are less than 1nm (10 –9 m). Q4: What is solute and solvent in cold drinks? Ans: CO 2 gas, sugar, preservative are solute and water is solvent in cold drinks.Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Case Based Questions - Is Matter Around Us Pure??
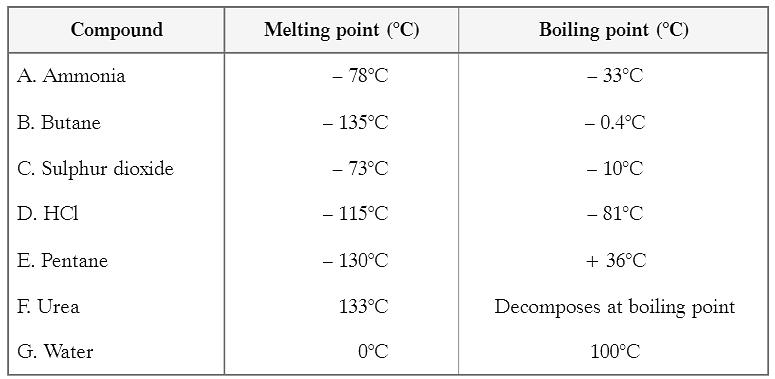
Q2: How can gases be separated that are present in air? Ans: By fractional distillation of liquid air.
Q3: If sample of urea has melting point 129°C, then: (a) It is impure (b) It is pure (c) It can not be predicted (d) The compound is not urea Ans: (a) It is impure
Q4: Which of the following will have boiling point 100°C? (a) Distilled water (b) Sea water (c) River water (d) Well water Ans: (a) Distilled water will have boiling point 100°C.
Top Courses for Class 9
Previous year questions with solutions, important questions, viva questions, mock tests for examination, study material, practice quizzes, extra questions, past year papers, objective type questions, shortcuts and tricks, semester notes, sample paper, video lectures.

Case Based Question Answer: Is Matter Around Us Pure? Free PDF Download
Importance of case based question answer: is matter around us pure, case based question answer: is matter around us pure notes, case based question answer: is matter around us pure class 9 questions, study case based question answer: is matter around us pure on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country.

MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science: Ch 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure

Contact Form

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- DK Goel Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam

CBSE Class 9th Science Value Based Questions Chapter 02 – Is Matter Around us Pure PDF Download
CBSE Class 9th Science Value Based Questions Chapter 02 – Is Matter Around us Pure are the easiest questions which you see in your question paper and the scoring one all student who attempt it surely get they are just little bit difficult and examine your basic knowledge regarding the particular chapter. Science Value Based Questions for Class 9th are available here at Free of cost. These questions are expected to be asked in the Class 9th board examination. These Science Value Based Questions are from complete CBSE Syllabus.
CBSE Class 9th Science Value Based Questions Chapter 02 – Is Matter Around us Pure

Most of these Science Value Based Questions are quite easy and students need only a basic knowledge of the chapter to answer these questions. Download CBSE Science Value Based Questions for board examinations. These Science Value Based Questions are prepared by Directorate of Education, Delhi.
CBSE Science Value Based Questions Class 9th Chapter 02 – Is Matter Around us Pure PDF
The purpose of the Science Value Based Questions is to make students aware of how basic values are needed in the analysis of different situations and how students require to recognize those values in their daily lives. Some questions are subject related. But even if they are not, that one-minute awareness of what we write about value without any specific preparation is a good step indeed.
CBSE Science Value Based Questions for Class 9th Chapter 02 – Is Matter Around us Pure download here in PDF format. The most CBSE Science Value Based Questions for annual examination are given here for free of cost. The additional questions for practice the Class 9th exam are collected from various sources. It covers questions asked in previous year examinations.
CBSE Science Value Based Questions for Class 9th Chapter 02 – Is Matter Around us Pure Free PDF
Class 9th books have many questions. These questions are regularly asked in exams in one or other way. Practising such most CBSE Science Value Based Questions Chapter 02 – Is Matter Around us Pure certainly help students to obtain good marks in the examinations.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Class 9 Chemistry (India)
Course: class 9 chemistry (india) > unit 1.
- Unit test Is Matter Around Us Pure?
- NCERT SOLUTIONS
- CHAPTER NOTES
- PRIVACY POLICY

- RD SHARMA SOLUTIONS
- IIT JEE SOLVED QUESTIONS
Class 9 Science Is Matter Around Us Pure

- A solution is a homogeneous mixture.
- Particles of a solution are smaller than 1 nm and cannot be seen by naked eyes.
- Do not scatter beam of light.
- Solute particles cannot be separated from the mixture by the process of filtration and thus, solution is stable.
- Suspension is a heterogeneous mixture having particle size greater than 100 nm.
- The particles of a suspension can be seen by naked eyes.
- Particles can scatter a beam of light.
- It is unstable.
- It is a heterogeneous mixture having particle size between 1 nm to 100 nm.
- Size of particles is very small, cannot be seen with naked eyes.
- It scatters a beam of light.
- They are stable as the particles do not settle when left undisturbed.
- Used in diagnostic laboratories for blood and urine test.
- Used in dairies and home to separate butter from cream.
- Used in a washing machines to squeeze out water from wet clothes.
- To separate colours in a dye.
- To separate pigments from natural colours.
- To separate drugs from blood.
- Some solids decompose or some, like sugar may get charred on heating to dryness.
- Some impurities may remain dissolved in the solution even after filtration which on evaporation contaminates the solid.

- Each component present in air retains its properties.
- Each component can be separated by simple physical processes.
- The components do not have any fixed proportion. All gases are present in different amount. Example, in greener area—more oxygen and water vapour is present; near industrial area—air consists of lot of impurities and smoke suspended in it.
- The properties of oxygen and hydrogen gases sire entirely different from that of liquid water.
- The ratio of oxygen: hydrogen combination is always constant i.e., 1: 2 by volume.
- To separate the components of water, we need electrolytic cell, and it is not a simple process.

About STUDYGUIDE360 STUDYGUIDE360 is a student centric educational web portal which provides quality test papers and study materials for the students preparing for CBSE or targeting various entrance exams. During past few years, a number of surveys on students were made to better understand their problems regarding their studies and their basic requirement.
LIKE US ON FACEBOOK
Contact form.

Case Study Questions Class 9 Science Matter in our Surroundings
Case study questions class 9 science chapter 1 matter in our surroundings.
CBSE Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Matter in our Surroundings. Important Case Study Questions for Class 9 Exam. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Matter in our Surroundings.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks or 4 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science – Matter in our Surroundings
Case study 1:.
1.) A matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Pen, paper, clips, sand, air, ice, etc. are different forms of matter. Every matter is made up of small particles. These particles are so tiny that they can’t be seen with naked eyes. Let’s see about the different characteristics of particles of matter.
- All matter is made up of very small particles.
- .Particles of matter has spaces between them.
- Particles of matter are continuously moving.
- Particles of matter attract each other.
Answer the following questions by referring above paragraph.
i.) Which of following is not matter?
c.) smell of perfume
d.) None of these
ii.) Thoughts coming in our mind are example of matter. True or false
c.) None of these
iii.) Which of the following is true about particles of matter?
a.) Particles of matter has spaces between them
b.) Particles of matter are continuously moving
c.) Particles of matter attract each other
d.) All of these
iv.) Give 5 examples of matter in our surroundings
v.) Enlist all properties of particles of matter
Answer key-1
iv.) pen, pencil, notebook, ice and water
v.) Different characteristics of particles of matter are
Case Study 2:
2.) There are three states of matter – solid, liquid and gas.
Solids have a definite shape, distinct boundaries and fixed volumes, that is, have negligible compressibility. Solids have a tendency to maintain their shape when subjected to outside force. Solids may break under force but it is difficult to change their shape, so they are rigid.
Liquids have no fixed shape but have a fixed volume. They take up the shape of the container in which they are kept. Liquids flow and change shape, so they are not rigid but can be called fluid.
Gas as has indefinite shape, no fixed volume. Gas gets the shape and volume of container.
Gas has very low density hence are light. Gas can flow easily and hence are called fluid.
i.) Which of the following state of matter takes shape of container in which it is filled?
d.) Both b and c
ii.) Distance between particles of matter least in
iii.) Compressibility is least in case of
iv.) Give properties of solids.
v.) Give properties of Gases.
Answer key-2
iv.) properties of solid are given below
- Solid has fixed volume.
- Solid has fixed shape.
- Solid has high density.
- Solids are heavy.
- Solid does not flow.
v.) Properties of gases are
- Gas has indefinite shape
- Gas has no fixed volume.
- Gas gets the shape and volume of container.
- Gas fills the container completely.
- Gas has very low density.
- Because of low density gas are light.
- Gas can flow easily and hence are called fluid.
Case Study 3:
3.) What happens inside the matter during change of state? On increasing the temperature of solids, the kinetic energy of the particles increases. Due to the increase in kinetic energy, the
Particles start vibrating with greater speed. The energy supplied by heat overcomes the forces of attraction between the particles. The particles leave their fixed positions and start moving more freely. A stage is reached when the solid melts and is converted to a liquid. The minimum temperature at which a solid melts to become a liquid at the atmospheric pressure is called its melting point.
The temperature of the system does not change after the melting point is reached, till all the ice melts. This happens even though we continue to heat the beaker, that is, we continue to supply heat. This heat gets used up in changing the state by overcoming the forces of attraction between the particles. The amount of heat energy that is required to change 1 kg of a solid into liquid at atmospheric pressure at its melting point is known as the latent heat of fusion. So, particles in water at 0 0 C (273 K) have more energy as compared to particles in ice at the same temperature.
The temperature at which a liquid starts boiling at the atmospheric pressure is known as its boiling point. Boiling is a bulk phenomenon. Particles from the bulk of the liquid gain enough energy to change into the vapour state. A change of state directly from solid to gas without changing into liquid state is called sublimation and the direct change of gas to solid without changing into liquid is called deposition.
i.) A change of state directly from solid to gas without changing into liquid state is called
a.) Sublimation
b.) Deposition
c.) Boiling point
ii.) The direct change of gas to solid without changing into liquid is called
iii.) The energy supplied by heat to solid is used to overcome the forces of attraction between the particles. True or false
iv.) Define melting point and boiling point
v.) Define latent heat of fusion
Answer key-3
iv.) The minimum temperature at which a solid melts to become a liquid at the atmospheric pressure is called its melting point.
The temperature at which a liquid starts boiling at the atmospheric pressure is known as its boiling point.
v.) The amount of heat energy that is required to change 1 kg of a solid into liquid at atmospheric pressure at its melting point is known as the latent heat of fusion.
Case Study 4:
4 .) Do we always need to heat or change pressure for changing the state of matter? Can you quote some examples from everyday life where change of state from liquid to vapour takes place without the liquid reaching the boiling point? In the case of liquids, a small fraction of particles at the surface, having higher kinetic energy, is able to break away from the forces of attraction of other particles and gets converted into vapour. This phenomenon of change of a liquid into vapors at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation.
i.) Evaporation of liquid takes place at
a.) Boiling point
b.) Above boiling point
c.) Below boiling point
ii.) Evaporation takes place at surface of liquid because
a.) They are heavy as compare to other particles
b.) They have sufficient kinetic energy to break the force
c.) They are light weight as compare to other particles
iii.) During evaporation particles of liquid change into vapour
a.) From the surface
b.) From the bottom
c.) From all over the liquid
iv.) Define evaporation.
v.) Explain process of evaporation
Answer key-4
iv.) The phenomenon of change of a liquid into vapors at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation.
v.) In the case of liquids, a small fraction of particles at the surface, having higher kinetic energy, is able to break away from the forces of attraction of other particles and gets converted into vapour. This phenomenon of change of a liquid into vapors at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation.
Case Study 5:
5.) You must have observed that the rate of evaporation increases with–
- an increase of surface area:
- We know that evaporation is a surface phenomenon. If the surface area is increased, the rate of evaporation increases. For example, while putting clothes for drying up we spread them out.
- an increase of temperature:
With the increase of temperature, more number of particles get enough kinetic energy to go into the vapour state.
In an open vessel, the liquid keeps on evaporating. The particles of liquid absorb energy from the surrounding to regain the energy lost during evaporation. This absorption of energy from the surroundings makes the surroundings cold. What happens when you pour some acetone (nail polish remover) on your palm? The particles gain energy from your palm or surroundings and evaporate causing the palm to feel cool. After a hot sunny day, people sprinkle water on the roof or open ground because the large latent heat of vaporization of water helps to cool the hot surface.
i.) Evaporation is surface phenomenon. True or false
ii.) As temperature increases the rate of evaporation is
a.) increases
b.) decreases
c.) remains constant
iii.) The rate of evaporation increases with
a.) Increase in wind speed
b.) Decrease in wind speed
c.) Does not have any effect from wind speed
iv.) What happens when you pour some acetone (nail polish remover) on your palm?
v.) We are able to sip hot tea from saucer than from cup. Why?
Answer key-5
iv.) The particles gain energy from your palm or surroundings and evaporate causing the palm to feel cool.
v.) We are able to sip hot tea from saucer than from cup. This is because saucer has large surface area, due to large surface area as compare to cut area tea evaporates at faster rate.
Thank you It helped me a lot
Why smell of Perfume is not a matter?
Because there is no particle
Because their are perfume particles suspended in air
These all case study questions are really helpful . Thanks
This is my first I was so nervous but these questions help me alot thank you
Smell of perfume is a matter because it have gas particles means perfume particles
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
The Site is down as we are performing important server maintenance, during which time the server will be unavailable for approximately 24 hours. Please hold off on any critical actions until we are finished. As always your feedback is appreciated.

- Study Packages
- NCERT Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Online Test

- Questions Bank
- Is Matter Around Us Pure
- Test Series
- Ncert Solutions
- Solved Papers
- Current Affairs
- JEE Main & Advanced
- Pre-Primary
- MP State Exams
- UP State Exams
- Rajasthan State Exams
- Jharkhand State Exams
- Chhattisgarh State Exams
- Bihar State Exams
- Haryana State Exams
- Gujarat State Exams
- MH State Exams
- Himachal State Exams
- Delhi State Exams
- Uttarakhand State Exams
- Punjab State Exams
- J&K State Exams
9th Class Science Is Matter Around Us Pure Question Bank
Done mcqs - is matter around us pure total questions - 60.

question_answer 1) Which of following is a pure substance?
A) Air done clear
B) Distilled water done clear
C) Steel done clear
D) Brass done clear
A) I and II done clear
B) I and III done clear
C) III and IV done clear
D) II and III done clear
question_answer 3) Which of the following is considered to be a pure substance?
A) Sodium chloride done clear
B) Muddy water done clear
C) Granite done clear
D) Milk of magnesia done clear
question_answer 4) Which of the following property does not prove that water is a compound?
A) Water is made up of two different elements (H and O). Which chemically combined with one another in a fixed proportion done clear
B) Water has fixed boiling point (b. p.) done clear
C) The constituents of water cannot be separated by simple physical methods done clear
D) Distilled water and tap water have same taste and constituents done clear
question_answer 5) The element 'X' having atomic number 16 is
A) a metal done clear
B) a metalloid done clear
C) a non-metal done clear
D) None of these done clear
question_answer 6) Which of the following element is a non-metal?
A) Fe done clear
B) Na done clear
C) Cu done clear
D) CI done clear
question_answer 7) Which one of following is a metalloid?
A) Na done clear
B) Fe done clear
D) As done clear
question_answer 8) Two elements X and Y combine to give a product Z. The correct statement about Z is
A) Z has more mass than that of X done clear
B) Z has less mass than that of X done clear
C) Z has less mass than that of Y done clear
D) Z show same properties as that of X and Y done clear
A) I, II and III done clear
B) II, III and IV done clear
C) I, III and IV done clear
D) II, III and IV done clear
question_answer 10) Which of the following is not a compound?
B) Germanium done clear
C) Water done clear
D) Methane done clear
A) I and III done clear
B) I, II and IV done clear
C) II, III and IV done clear
D) I, III and IV done clear
question_answer 12) The metal present in quicklime is lithium.
A) True done clear
B) False done clear
C) Can't say done clear
D) Partially true/false done clear
question_answer 13) Which of the following statements is not true about the compound?
A) Elements are combined chemically to form a compound done clear
B) The constituents lose their properties done clear
C) The constituents can be separated by simple physical methods done clear
D) A compound is always homogeneous in nature done clear
question_answer 14) Which of the following compounds contains only non-metals?
A) Ammonia done clear
B) Rust done clear
C) Quicklime done clear
D) Sodium chloride done clear
question_answer 15) In which of the following the constituents are present in any ratio?
A) Compound done clear
B) Mixture done clear
C) Colloid done clear
D) Solution done clear
B) II and IV done clear
C) I and IV done clear
D) III and IV done clear
question_answer 17) Which of the following is an example of a homogeneous mixture?
A) Polluted air done clear
C) Salt solution done clear
question_answer 18) Identify homogeneous mixture from the following
A) soil done clear
B) vinegar done clear
C) unfiltered tea done clear
D) polluted air done clear
question_answer 19) Select the homogenous mixture from the following
A) carbon dioxide gas dissolved in water done clear
B) air containing suspended particles done clear
C) soap bubbles formed by blowing air into soap solution done clear
D) water in milk done clear
question_answer 20) Mixtures are always combination of the same compounds that are in different states.
question_answer 21) ....... is a heterogeneous mixture.
A) Soda water done clear
B) Sodium chloride solution done clear
C) Oil in water done clear
D) Copper sulphate solution done clear
D) Only IV done clear
A) A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4 done clear
B) A-4, B-3, C-1, D-2 done clear
C) A-4, B-1, C-2,D-3 done clear
D) A-2, B-3,C-1,D-4 done clear
question_answer 24) Which of the following statement is correct?
A) A mixture containing two compounds must be heterogeneous done clear
B) A heterogeneous mixture must contain at least three elements done clear
C) A homogeneous mixture must be uniform done clear
D) A pure substance must contain only one type of atom done clear
question_answer 25) When zinc and copper are mixed we get heterogeneous mixture.
question_answer 26) Air is regarded as mixture because
A) its volume changes under different conditions done clear
B) its temperature may change done clear
C) its pressure may vary done clear
D) its composition may vary done clear
question_answer 27) Tincture of iodine has antiseptic properties. This solution is made by dissolving (NCERT Exemplar)
A) iodine in potassium iodide done clear
B) iodine in Vaseline done clear
C) iodine in water done clear
D) iodine in alcohol done clear
question_answer 28) Which of the following is not true regarding properties of a solution?
A) It is a homogeneous mixture done clear
B) The solute particles do not settle down when left undisturbed done clear
C) The particles of a solution are smaller than 1 nm in diameter done clear
D) The solute particles can be separated from the mixture by the process by filtration done clear
question_answer 29) In a sweetened tea, the sugar is called
A) solvent done clear
B) solute done clear
C) solution done clear
D) None of the above done clear
question_answer 30) The concentration of a solution represents
A) the total quantity of solution done clear
B) the quantity of the solvent present in a solution done clear
C) the quantity of the solute present in a solution done clear
D) the quantity of the impurities present in a solution done clear
question_answer 31) The solutions with low amount of solutes are called ........
A) diluted done clear
B) concentrated done clear
C) solvents done clear
question_answer 32) A solution contains 50 g of common salt in 450 g of water. The concentration of the solution is
A) 500% done clear
B) 50% done clear
C) 10% done clear
D) 80% done clear
question_answer 33) A solution is heterogeneous mixture, which contains non-uniform composition.
question_answer 34) Which of the following is an example of solution?
B) Unfiltered tea done clear
C) Sand and water done clear
D) Milk done clear
question_answer 35) The particles of solution can be seen by naked eye.
question_answer 36) A mixture of chalk powder in water is an example of
A) homogeneous mixture done clear
B) compound done clear
C) colloidal solution done clear
D) suspension done clear
question_answer 37) Which of the following will not show Tyndall effect?
A) Smoke done clear
B) Foam done clear
C) Jelly done clear
D) Salt solution done clear
question_answer 38) Suspensions are .........
A) invisible to naked eye done clear
B) visible to naked eye done clear
C) visible through microscope done clear
D) invisible under electron microscope done clear
question_answer 39) A colloid is a .. .X... mixture and its components can be separated by the technique known as ... Y...
A) X=homogeneous, y=filtration done clear
B) X= heterogeneous, V= filtration done clear
C) X=heterogeneous. y=centrifugation done clear
D) X=homogeneous, y=centrifugation done clear
question_answer 40) A liquid is able to scatter a beam of light but it leaves no residue after passing through a filter paper. A liquid can be a
A) true solution done clear
B) suspension done clear
C) colloidal sol done clear
D) concentrated solution done clear
question_answer 41) The fine particles of an insoluble substance uniformly dispersed throughout a gas or liquid is called
A) precipitate done clear
D) true solution done clear
question_answer 42) Gel is which of the following kind of solution?
A) Mixture done clear
B) True solution done clear
C) Suspension done clear
D) Colloid done clear
question_answer 43) Which of the following is an example of emulsion?
A) Mist done clear
B) Milk done clear
C) Face cream done clear
D) Both [b] and [c] done clear
question_answer 44) A mixture of sulphur and carbon disulphide is (NCERT Exemplar)
A) heterogeneous and shows Tyndall effect done clear
B) homogeneous and shows Tyndall effect done clear
C) heterogeneous and does not show Tyndall effect done clear
D) homogeneous and does not show Tyndall Effect done clear
question_answer 45) Which of the following is not an example of colloid?
A) Sugar syrup done clear
C) Fog done clear
D) Butter done clear
question_answer 46) Which of the following will not form a true solution upon shaking?
A) Alum done clear
B) Starch solution done clear
C) Sucrose done clear
D) Common salt done clear
question_answer 47) Select the false statement about colloids form the following.
A) Colloids are homogeneous done clear
B) Colloids can scatter a beam of light passing through it done clear
C) Colloids show Tyndall effect done clear
D) Colloids are quite stable done clear
question_answer 48) Butter is a colloid which formed when
A) water is dispersed in fat done clear
B) fat is dispersed in milk done clear
C) water is dispersed in milk done clear
D) fat is dispersed in water done clear
question_answer 49) The number of phases in colloidal system are
A) one done clear
B) two done clear
C) three done clear
D) is depends on substances done clear
B) A-4, B-2, C-3, D-1 done clear
C) A-1, B-3, C-4, D-2 done clear
D) A-3, B-4, C-1, D-2 done clear
question_answer 51) Smoke and fog differ from each other because
A) they have different dispersion medium done clear
B) they have different dispersed phase done clear
C) Both [a] and [b] done clear
question_answer 52) Miscible liquids are separated by ........
A) centrifugation done clear
B) fractional distillation done clear
C) filtration done clear
D) sublimation done clear
question_answer 53) The method used to separate a dye from blue ink is
A) evaporation done clear
B) sedimentation done clear
C) crystallisation done clear
D) filtration done clear
question_answer 54) The most suitable technique used to separate mixture of different gases from bulk of air, can be
A) chromatography done clear
B) sublimation done clear
C) fractional distillation done clear
D) centrifugation done clear
question_answer 55) ........ is used when a mixture contains two components, out of which one is soluble.
A) Evaporation done clear
B) Sublimation done clear
C) Chromatography done clear
D) Filtration done clear
question_answer 57) A mixture contains four solid compounds P, Q, R and S. On heating, R changes to vapour state. It can be separated from rest of the solids by
A) sublimation done clear
B) filtration done clear
D) distillation done clear
question_answer 59) During burning of candle, both physical and chemical takes place.
B) II and III done clear
D) I and IV done clear
Study Package

MCQs - Is Matter Around us Pure
Related question.

Reset Password.
OTP has been sent to your mobile number and is valid for one hour
Mobile Number Verified
Your mobile number is verified.
- Chemistry Concept Questions and Answers
- Is Matter Around us Pure Questions
Is Matter around us Pure Questions
Have you ever noticed everything we encounter is made of matter? For example: – Books, paper, pens and even human beings are made of matter. All the matter present around us might or might not be pure.
Is Matter around us Pure Chemistry Questions with Solutions
Q1. Dissolving common salt in water is a
- Physical change
- Chemical change
- Both a and b
- None of these
Answer: Dissolving common salt in water is a physical change.
Q2. Name the technique to separate butter from curd.
- Centrifugation
- Evaporation
- Fractional Distillation
Answer: (a), Centrifugation is used to separate butter from curd.
Q3. What are the constituents of brass?
- Zinc and Carbon
- Copper and Carbon
- Iron and Copper
- Zinc and Copper
Answer: (d), Zinc and Copper are the constituents of the brass.
Q4. State a difference between pure and impure substances.
Answer: The constituents that make a pure substance cannot be separated by physical means. In contrast, the components of an impure substance can be separated by physical means.
Q5. What is the tincture of iodine?
Answer: The tincture of iodine is a weak iodine solution. It is used as an antiseptic used to disinfect wounds.
Q6. How can you change a saturated solution to an unsaturated solution without adding more solvent?
Answer: By heating the saturated solution, we can change a saturated solution to an unsaturated solution without adding more solvent
Q7. Two liquids, ‘A’ and ‘B’, are miscible with each other at room temperature. Which separation method will you apply to separate the mixture of ‘A’ and ‘B’ if the difference in their boiling points is 27°C?
Answer: We can separate two miscible liquids by fractional distillation if they have a difference in boiling points.
Q8. What kind of mixtures can be separated by crystallisation?
Answer: Crystallization is used to separate solids from a liquid solution. It is related to precipitation, but the precipitate is formed in a crystal form that exhibits extremely high purity levels in this process. We can apply the principle of crystallisation to purify impure substances.
Q9. What is the Tyndall effect? Which types of solutions show it?
Answer: The scattering of light on colloidal particles is known as the Tyndall effect. Colloidal solutions and a few suspensions show this effect.
Suspension and colloidal solutions are heterogeneous solutions where the solute is partially dissolved in the solvent. The solute particles remain freely suspended in the solution, and the scatter light shows solute particles.
Q10. What is a suspension? Mention a few properties of suspension?
Answer: A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture of solids dispersed in liquids. The suspended solute particles do not dissolve but remain suspended throughout the medium—for example, Mud water.
Few properties of suspension are mentioned below.
- A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture.
- Suspension shows the Tyndall effect, i.e. if a light beam is scattered on colloidal particles, then the scatter light will show solute particles.
- The naked eye can see the suspension particles.
Q11. Differentiate between elements and compounds.
Q12. Differentiate between compound and mixture.
Q13. Differentiate between sol, solution and suspension.
Q14. Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixture.
Q15. What is chromatography? What are the applications of chromatography?
Answer: Chromatography is an analytical technique to separate components of a mixture. The mixture is dissolved in the movable phase, which carries it through a dual substance called the static phase.
The applications of chromatography are mentioned below.
- It is widely used in the pharmaceutical and food industries.
- It is used in detecting drugs in urine or other body fluid.
- It is used in forensics in witnessing and determining scrap amounts of substances in the contents of the bladder or stomach.
- It is used in monitoring air quality and testing drinking water.
Practise Questions on Is Matter around us Pure
Q1. How will you separate a mixture containing kerosene and petrol, which are miscible with each other (the difference in their boiling points is more than 25°C)?
Q2. Name the methods used to separate the following:
- Butter from curd.
- Salt from seawater
- Camphor from salt
Q3. Give an example of a solution in which solid is a solute and the solvent.
Q4. What is centrifugation? Where is it used?
Q5. Can we separate a mixture of alcohol and water by a separating funnel?
Click the PDF to check the answers for Practice Questions. Download PDF
Recommended Videos
Matter around us 01 – learn how to learn.

Matter Around us – Characteristics of Particles of Matter

Is Matter Around us Pure?

Matter Around us 04 – States of Matter | Learn from BYJU’S

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


COMMENTS
d) To identify the components in pure substances. Answer: b) To comprehend the properties and behavior of matter. Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure? with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent.
Case Study. A child wanted to separate the mixture of dyes constituting a sample of ink. He marked a line by the ink on the filter paper and placed the filter paper in a glass containing water as shown in figure. The filter paper was removed when the water moved near the top of the filter paper. (i) Identify the technique used by the child.
Case Study Questions: Question 1: Akshita wants to separate the mixture of dyes constituting a sample of ink. She marked a line by the ink on the filter paper and placed the filter paper in a glass containing water as shown in figure. The filter paper was removed when the water moved near the top … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is ...
Question 1: Akshita wants to separate the mixture of dyes constituting a sample of ink. She marked a line by the ink on the filter paper and placed the filter paper in a glass containing water as shown in the figure. The filter paper was removed when the water moved near the top of the filter paper. (i) Identify the technique used by the ...
Direction: Q. 1 to 5 : Read the following and answer questions from [1] to [5]. Pure substances are classified as elements or compounds. An element is a substance that contains only one type of atom.
CASE STUDY QUESTIONS CLASS IX SCIENCE CHAPTER 2 - IS MATTER AROUND US PURE 1. A solution which can dissolve more of the solute at a given temperature is called unsaturated solution. However, a solution which cannot dissolve any ... Use this information to answer the following questions: i) A 30 % solution of X at 298 K is marked as saturated ...
Free Question Bank for 9th Class Science Is Matter Around Us Pure. Customer Care : 6267349244. Toggle navigation 0 . 0 ... Case Based MCQs - Is Matter Around Practice Now. Assertion and Reason MCQs - Is Matter Practice Now ... Study Packages Question Bank Online Test Rajasthan State Exams ; Videos Sample Papers
The Case Based Question Answer: Is Matter Around Us Pure? is an invaluable resource that delves deep into the core of the Class 9 exam. These study notes are curated by experts and cover all the essential topics and concepts, making your preparation more efficient and effective.
Class 9 Chemistry (India) 4 units · 15 skills. Unit 1 Is Matter Around Us Pure? Unit 2 Matter in Our Surroundings. Unit 3 Atoms and Molecules. Unit 4 Structure of the Atom. Course challenge. Test your knowledge of the skills in this course. Start Course challenge. Science.
2. Which of the following property does not describe a compound? (a) It is composed of two or more elements. (b) It is a pure substance. (c) It cannot be separated into constituents by physical means. (d) It is mixed in any proportion by mass. (d) It is mixed in any proportion by mass. 3.
2. Write the steps you would use for making tea. Use the words solution, solvent, solute, dissolve, soluble, insoluble, filtrate, and residue. Solution: (a) Into a vessel, add a cup of milk, which is the solvent, and supply it with heat. (b) Add tea powder or tea leaves to the boiling milk, which acts as a solute.
Is Matter Around Us Pure Class 9 Extra Questions Short Answer Questions-I. Question 1. 'Sea water can be classified as homogeneous as well as heterogeneous mixture.'. Comment. [NCERT Exemplar] Answer: Sea water is a mixture of salts and water which cannot be separated except by evaporation.
CBSE Science Value Based Questions Class 9th Chapter 02 - Is Matter Around us Pure PDF. The purpose of the Science Value Based Questions is to make students aware of how basic values are needed in the analysis of different situations and how students require to recognize those values in their daily lives. Some questions are subject related.
Class 9 chemistry important questions with answers are provided here for Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure. These important questions are based on the CBSE board curriculum and correspond to the most recent Class 9 chemistry syllabus. By practising these Class 9 important questions, students will be able to quickly review all of the ideas ...
This solution contains questions, answers, images, step by step explanations of the complete Chapter 2 titled Is Matter Around Us Pure of Science taught in class 9. If you are a student of class 9 who is using NCERT Textbook to study Science, then you must come across Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure. After you have studied lesson, you must ...
Course: Class 9 Chemistry (India) >. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere.
Download PDF. Class 9 Is Matter Around Us Pure? MCQs. 1.What is true about homogeneous mixture? (a) Homogeneous mixture is the mixture of two or more than two components. (b) In homogeneous mixture the composition and properties are uniform throughout the mixture. (c) both (a) and (b) are true. (d) none of the above.
About STUDYGUIDE360 STUDYGUIDE360 is a student centric educational web portal which provides quality test papers and study materials for the students preparing for CBSE or targeting various entrance exams. During past few years, a number of surveys on students were made to better understand their problems regarding their studies and their basic ...
Direction: For question given below two statements are given-one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes [a], [b], [c] and [d] as given below
Case Study 1: 1.) A matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Pen, paper, clips, sand, air, ice, etc. are different forms of matter. Every matter is made up of small particles. These particles are so tiny that they can't be seen with naked eyes. Let's see about the different characteristics of particles of matter.
Which of the following statements are true for pure substances? I. Pure substances contain only one kind of particles. II. Pure substances may be compounds or mixtures. III. Pure substances have the same composition throughout. IV. Pure substances can be exemplified by all elements other than nickel. (NCERT Exemplar)
It is considered as a valuable study material while preparing for exam. It helps students in quickly revising important topics of the chapter. Students can download Important Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 2 - Is Matter Around Us Pure by clicking the below-mentioned link.
Is Matter around us Pure Questions and Answers - Practice questions, MCQs, PYQs, NCERT Questions, Question Bank, Class 11 and Class 12 Questions, NCERT Exemplar Questions, and PDF Questions with answers, solutions, explanations, NCERT reference, and difficulty level in Is Matter around us Pure chemistry.