

The Best Books about Shakespeare
By Dr Oliver Tearle (Loughborough University)
We thought it was time we offered our pick of the best books about William Shakespeare: the best introductions to his life and his work. The following is not designed to be an exhaustive list, but many of these books were written by leading Shakespeare scholars and each contains something which every fan of the Bard should know.
Disclaimer: as an Amazon Associate, we get commissions for purchases made through links in this post.
This book, published in 1997, examines the legacy of Shakespeare’s work, the way it has inspired others (from Romantic poets and novelists to twentieth-century postcolonial theorists), and how Shakespeare’s writing is constantly reinvented and recast by each new generation.
It’s a hugely readable book, since Bate is happy to speculate – drawing on what evidence is available – as to many of the great mysteries of Shakespeare’s life and work, such as the identity of the ‘Mr W. H.’ to whom the 1609 printing of the Sonnets was dedicated.
It has been called ‘the best modern book on Shakespeare’ (by RSC founder Sir Peter Hall) and is essential reading for anyone interested in the Bard. Also well worth the read is Bate’s biography of the Bard…
This, from 2008, is a sort of ‘intellectual biography’ of Shakespeare which uses Jaques’ ‘Seven Ages of Man’ speech from As You Like It as a conceit or structure through which to examine some of the widely held assumptions about Shakespeare’s life.
Did Shakespeare really retire from London and return to Stratford-upon-Avon to live out his last years with his family, following his ‘curtain call’ on the London stage, his 1611 play The Tempest ? Bate also suggests a highly plausible candidate for the ‘rival poet’ referred to in the Sonnets; his analysis here is compelling. Another must-read.
Greenblatt’s book (from 2004) forms a valuable companion to Bate’s two books, especially Soul of the Age . Greenblatt is the founder of the school of criticism known as New Historicism, which, put crudely and simply, examines literary works in their original context through particular focus on the network of writings that were being produced at the time the literary text was produced.
New Historicism also uses specific events – including anecdotes – from the period to shed light on the social and political background out of which the literature was written. Greenblatt is especially interested in the idea of Shakespeare as a careful and cautious man, a businessman shoring up his earnings from his share in the theatres he worked for, and his property investments, for his retirement.
But Greenblatt is also frequently brilliant about the plays themselves: his discussion of the shift that took place in Shakespeare’s writing in around 1600 (when he wrote Hamlet ) is fascinating.
In short, in plays such as Hamlet , King Lear , and Othello , Shakespeare draws on existing source material for these stories but removes obvious motives for characters’ actions (e.g. Iago’s motive for making mischief, Lear’s reason for testing his daughters), resulting in more psychologically and morally complex and ambiguous drama.
Caroline Spurgeon, Shakespeare’s Imagery and What It Tells Us .
This landmark work of literary analysis was first published in 1934, and is a fascinating study of Shakespeare’s writing and well worth reading.
Spurgeon examines the images of Shakespeare’s plays in order to find out what sorts of images he most frequently draws on and what this might tell us about him, especially in terms of his relation to his contemporaries. It is a good study of what makes Shakespeare so peculiar alongside his fellow Elizabethan and Jacobean writers.
One of the best books on Shakespeare’s language, and a handy companion volume to Spurgeon’s older, groundbreaking study of the Bard’s imagery. Kermode was often a superb close-reader of poetry and a very clear-headed critic, and this shines through here. Highly readable.
This was one of the first of the recent popular books on Shakespeare written by an academic: although it was published a year after Bate’s The Genius of Shakespeare , in 1998, it purportedly sold 100,000 copies in hardback (perhaps as a result of the success of Shakespeare in Love in cinemas that year) and, despite some contentious claims, showed publishers that lots of readers had an appetite for books on the Bard .
In 1904, this immeasurably influential study of Shakespeare’s tragedies appeared. It is still in print – as an affordable Penguin Classics edition – and although Bradley sometimes treats the characters a little too much as though they were real people rather than imaginary constructions, there’s a raft of lucid insights into the plays to be had.
This is our choice for a popular book on Shakespeare written by a non-Shakespearean. It’s short, light, engaging, humorous, with its distinct approach being to discount as much of the speculation about Shakespeare’s life as possible, and instead focus solely on the facts of his life that we definitely (or at least pretty definitely) know.
Written by one of the greatest living critics, this book is perhaps the best one on the Sonnets. A remarkable close reader of poetry, Vendler provides detailed commentaries on all of the 154 sonnets and, like Spurgeon and Kermode, has some particularly astute things to say about the poems’ language. It’s a little pricier than most of the other books on this list, but it’s big, so it’s worth the extra money.
Of course, any list purporting to select the ‘best books on Shakespeare’ is going to be subjective and even tendentious – so do please leave us your suggestions for other titles below.
If you enjoyed this list, check out our pick of the 10 best books about literature and our interesting facts about the Bard . You might also enjoy our interesting Macbeth facts and our facts about Romeo and Juliet . Fans of language trivia might also like our selection of the best accessible books about the English language .
35 thoughts on “The Best Books about Shakespeare”
Really good information. Learning about the man who wrote the manuals on the human condition has got to be a plus.
Hi there. while not wishing to criticise any on your list, a few others might have made it: Ted Hughes’ Shakespeare and the Goddess of Complete Being; Secret Shakespeare; the Arden edition of Troilus and Cressida (and while not a book my post on this play), and Kermode’s long ago Arden on The Tempest. Also important is the dictionary of sexual imagery of the period in three volumes. Reading this will transform any person’s idea of Shakespeare.
Brysons Book ist a bit superficial and shoudn’t be in a list of “best books”. How about MacGregors “Shakespeares Restless World” as a popular alternative? And I am missing Gary Taylors “Reinventing Shakespeare”, which is a bit older, but still an excellent book on the reception of Shakespeare through the ages.
There is also The Shakespearean Ethic by John Vyvyan – the most original book about Shakespeare acoording to Chrisopher Booker. Ive read most of it and find his thesis compelling.
Don’t know that one; I’ll look it up. Thanks!
The Greenblatt book is the one I rely on most.
Shakespeare by Another Name: The Life of Edward de Vere, Earl of Oxford, the Man who was Shakespeare by Mark Anderson belongs on the list.
It’s book that goes so much further than any other in its ability to link the man who wrote the works with the works themselves. Writers write from experience. There’s a real man with real experiences behind the “Shake-Speeare” allonym.
It’s beyond time to stop smoking from the Disney-upon-Avon tourist industry crack pipe and strip the veil from the most fascinating whodunnit in human history.
Something the Stratford tourist industry won’t tell you – Will Shaksper of Stratford was mocked on the London stage in his own lifetime as an illiterate, braggart, pretender.
This latter is in the realm of fantasy or historical fiction . . .
I agree that the Kermode one about language is excellent! Another good one is by Peter Hall not sure of the exact title – smth like Shakespeare’s Notes to his Players? It is about the poetry of the plays and how actors should speak the lines.
Using ‘Shakespeare by Another Name’ to Study Shakespeare as a dramatist is like using ‘Alice in Wonderland’ to study monarchy as a form of government.
Reblogged this on yllibsomar .
All based on a spurious biography. Read Mark Anderson’s “Shakespeare by Another name” for a truly literary approach to the plays and their author — principally Edward de Vere, the 17th Earl of Oxford.
Whatever you say, Bob.
Thanks for a great list! Any list is open for debate, but you did a fine job here.
What an good idea for a post. I read Will in the World years ago and thought it was really interesting. Haven’t read the others. Oh, gosh, I can’t believe anyone still really thinks that anyone besides Shakespeare wrote Shakespeare. I researched this years ago, and the arguments are nonsense. Edward de Vere was dead for most of the time Shakespeare was alive!
Yes — and we know that de Vere DID write this:
Sitting alone upon my thought in melancholy mood, In sight of sea, and at my back an ancient hoary wood, I saw a fair young lady come, her secret fears to wail, Clad all in colour of a nun, and covered with a veil; Yet (for the day was calm and clear) I might discern her face, As one might see a damask rose hid under crystal glass.
The man who wrote that also wrote Hamlet? I don’t think so.
Yeah, that was the other thing I thought when I did my research, that none of the others proposed sounded anything like Shakespeare. It was as if those proposing the idea were tone deaf.
The Bill Bryson book is brilliant. Great post! Will take a look at the other suggestions.
Anthony Burgess wrote a good one. It’s weird and idiosyncratic but he’s incapable of writing a boring sentence so it rollocks along and has got a lot of beautiful illustrations in it.
I wrote to Burgess once. I admired him as a writer and I’ve read everything he wrote (including both Shakespeare (the biography) and Nothing Like The Sun (the fictional biography) but I couldn’t stand his obsession with Graham Greene, who I thought the better writer. It was as though Burgess was upset that Greene didn’t seem to notice him. After Greene’s death, Burgess wrote what was supposed to be an obituary of Greene but was in fact a paean to himself. I didn’t keep a copy of the letter but I do remember that it ended with the words, “You are, sir, a piece of shit.” He wrote back to me on a BBC postcard — his reply was brief but rather good. As one might expect.
Recently entertained by a one-woman play: The Second Best bed. Lichfield Literary Festival. Brilliant, engaging acting and a well held story line.
Well, the nature of lists is that something always gets left off. Can I just commend you on the breadth of your lists – Bill Bryson is a really solid, non-threatening introduction to Shakespeare, in my opinion:)
Great blog post, there are certainly some good suggestions here for my future reading. I’m glad you put “Will in the World” on your list as it’s one book whose approach I found particularly enlightening. Another one I really enjoyed was “Shakespeare for all time” by Stanley Wells; there’s a little bit of biog at the beginning but mostly it’s about how Shakespeare’s works have been interpreted in subsequent centuries and how he came to be the cultural legend he is today.
There are a couple of wonderful novels which capture the man, and are inventive, and also enhance the reader’s appreciation of Shakespeare’s works : Jude Morgan – The Secret Life of William Shakespeare and Robert Winder – The Final Act of Mr Shakespeare.
Oh, and both of them start from the premise that Shakespeare was in fact – Shakespeare, which I found a big relief!
Reblogged this on desperatelyseekingcymbeline and commented: I’m re-posting this to give myself a nice easy-to-access reading list…
- Pingback: The Best Books about Shakespeare | berkshire literature ideas
So glad you included the Bryson book. It’s the book which introduced me to him and I’ve been a big fan ever since. I like his take because, as you say, he sticks to what is known. Plus, Bryson surprises you with facts which stick in your head long after you’ve finished reading. Down side – you become a terrible bore at parties!
I know the ‘bore at parties’ feeling well, having been that person! Bryson is a marvellous populariser of subjects – I love his A Short History of Nearly Everything, about science, for that reason. But I’ve not read one of his I haven’t liked. (Even his latest, One Summer: America 1927, was a page-turner!) He has an eye for a catchy anecdote and is a great debunker of misconceptions, which we love examining here!
I couldn’t agree more! No wonder I like both Bryson and this blog site so much :)
Reblogged this on Rare Films & TV Classics on DVD .
Reblogged this on Jude’s Threshold and commented: William.
- Pingback: Five Fascinating Facts about Shakespeare | Interesting Literature
- Pingback: Ten Underrated Shakespeare Plays | Interesting Literature
- Pingback: Five Fascinating Facts about Hamlet | Interesting Literature
- Pingback: Five Fascinating Facts about Hamlet | xoxori
Comments are closed.
Discover more from Interesting Literature
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- NONFICTION BOOKS
- BEST NONFICTION 2023
- BEST NONFICTION 2024
- Historical Biographies
- The Best Memoirs and Autobiographies
- Philosophical Biographies
- World War 2
- World History
- American History
- British History
- Chinese History
- Russian History
- Ancient History (up to 500)
- Medieval History (500-1400)
- Military History
- Art History
- Travel Books
- Ancient Philosophy
- Contemporary Philosophy
- Ethics & Moral Philosophy
- Great Philosophers
- Social & Political Philosophy
- Classical Studies
- New Science Books
- Maths & Statistics
- Popular Science
- Physics Books
- Climate Change Books
- How to Write
- English Grammar & Usage
- Books for Learning Languages
- Linguistics
- Political Ideologies
- Foreign Policy & International Relations
- American Politics
- British Politics
- Religious History Books
- Mental Health
- Neuroscience
- Child Psychology
- Film & Cinema
- Opera & Classical Music
- Behavioural Economics
- Development Economics
- Economic History
- Financial Crisis
- World Economies
- How to Invest
- Artificial Intelligence/AI Books
- Data Science Books
- Sex & Sexuality
- Death & Dying
- Food & Cooking
- Sports, Games & Hobbies
- FICTION BOOKS
- BEST FICTION 2023
- NEW Fiction
- World Literature
- Literary Criticism
- Literary Figures
- Classic English Literature
- American Literature
- Comics & Graphic Novels
- Fairy Tales & Mythology
- Historical Fiction
- Crime Novels
- Science Fiction
- Short Stories
- South Africa
- United States
- Arctic & Antarctica
- Afghanistan
- Myanmar (Formerly Burma)
- Netherlands
- Kids Recommend Books for Kids
- High School Teachers Recommendations
- Prizewinning Kids' Books
- Popular Series Books for Kids
- BEST BOOKS FOR KIDS (ALL AGES)
- Ages Baby-2
- Books for Teens and Young Adults
- THE BEST SCIENCE BOOKS FOR KIDS
- BEST KIDS' BOOKS OF 2023
- BEST BOOKS FOR TEENS OF 2023
- Best Audiobooks for Kids
- Environment
- Best Books for Teens of 2023
- Best Kids' Books of 2023
- Political Novels
- New History Books
- New Literary Fiction
- New Historical Fiction
- New Biography
- New Memoirs
- New World Literature
- New Economics Books
- New Climate Books
- New Math Books
- New Philosophy Books
- New Psychology Books
- New Physics Books
- THE BEST AUDIOBOOKS
- Actors Read Great Books
- Books Narrated by Their Authors
- Best Audiobook Thrillers
- Best History Audiobooks
- Nobel Literature Prize
- Booker Prize (fiction)
- Baillie Gifford Prize (nonfiction)
- Financial Times (nonfiction)
- Wolfson Prize (history)
- Royal Society (science)
- Pushkin House Prize (Russia)
- Walter Scott Prize (historical fiction)
- Arthur C Clarke Prize (sci fi)
- The Hugos (sci fi & fantasy)
- Audie Awards (audiobooks)
The Best Shakespeare Books
Most recommended books.
Macbeth by William Shakespeare
“This is going to sound heretical, but I think that—particularly in the theatre—a lot of Shakespeare is too long. I think Act 4 in a lot of Shakespeare plays is a bit of a bum-number, and not much happens. I like to see Shakespeare intelligently cut, often to speed it up. Macbeth is a play that may have been cut. We don’t really understand the provenance of that text. It’s very short by Shakespearean standards and it’s very powerful because of that. There’s no subplot, there’s no parallel plot. Just this really intense journey through a psychological drama. It’s a really punchy play because everything is tightly headed in the same direction: the language, the imagery, the plot, the way the characters work. It’s a really superbly powerful, compact, condensed play.” Emma Smith , Literary Scholar
Twelfth Night by William Shakespeare
” What I really like about this play is its sexual playfulness. It seems very modern in that way. There’s no way to play it straight. You’ve either got Orsino in love with Cesario, or you’ve got Olivia in love with Viola, and you’ve always got Antonio in love with Sebastian. It feels to me as if its subtitle What You Will , is a cheeky way of saying ‘whatever, anything goes’. I like the fact that quite often you see productions where at the end Olivia and Orsino are still mixing up the twin they are with and there’s still playfulness. “ Emma Smith , Literary Scholar
King Lear by William Shakespeare
“ Lear is about all sorts of things but one of the things it’s about is people getting old and not ceding what their kids think they should to them and the kids trying to bully them.” Kathleen Taylor , Science Writer
A Midsummer Night’s Dream by William Shakespeare
“ A Midsummer Night’s Dream has always been a great favourite of mine, ever since my school days. I was introduced to it at school when I was about 11 or 12. I’ve seen many productions of it. It’s the first play I edited, for the New Penguin Shakespeare, in 1967. I very much enjoyed writing about it then. It’s a play about imagination, about Shakespeare’s own heart, in many ways. The Mechanicals’ scenes, as they’re called, in which Shakespeare portrays amateur actors putting on the play of Pyramus and Thisbe, actually tell us an awful lot about Shakespeare’s attitude towards the theatre and the acting profession. They’re also wonderfully playable.It’s a play that appeals very much to young people. I’m speaking now from the Shakespeare Birthplace Trust at Stratford-Upon-Avon and we have what’s called ‘Shakespeare Week,’ when we engage with over 10,000 primary schools. The Royal Shakespeare Company put on a production of A Midsummer Night’s Dream which uses amateur actors, including schoolchildren.” Stanley Wells , Literary Scholar
Antony and Cleopatra by William Shakespeare
“Antony and Cleopatra is, in some ways, the most romantic of Shakespeare’s plays. It takes over, in a way, from Romeo and Juliet. Romeo and Juliet gives a wonderful exploration of young love, of first love, of romantic attitudes to love. Antony and Cleopatra are mature lovers. They are seasoned. They are disillusioned. It’s an extraordinarily rich play, poetically—as Romeo and Juliet is—but the poetry of Antony and Cleopatra is that of a mature person who has gone through a lot of experiences himself and is capable of expressing the disillusionment of middle-aged love as well as the raptures of it. “ Stanley Wells , Literary Scholar
Five Books has a series of interviews with world-leading Shakespeare scholars, recommending books on a variety of aspects of the Bard. Disillusioned when forced to study him at school but ready to engage with Shakespeare's plays again? Or do you already know your Hamlet from your Lear but are keen to explore more about the man? Even if you are completely new to Shakespeare, our interviews with the world’s foremost Shakespeare experts will set you on the right path.
These include:
Sir Stanley Wells , honorary president of the Shakespeare Birthplace Trust in Stratford, and General Editor of The Complete Oxford Shakespeare; Emma Smith , Professor of Shakespeare Studies at Oxford University, and acclaimed expert of Shakespeare's First Folio; and James Shapiro , Professor of English at Columbia University, and award-winning author of Contested Will: Who Wrote Shakespeare? and 1599: A Year in the Life of William Shakespeare , which won the Baillie Gifford 'Winner of Winners' award, for the best nonfiction book of the past 25 years!
Knowing I loved my books, he furnished me From mine own library with volumes that I prize above my dukedom. ( The Tempest , I. 2)
The best books on Shakespeare’s Reception , recommended by Emma Smith

Titus Andronicus (Arden Shakespeare) by Jonathan Bate & William Shakespeare

Reinventing Shakespeare: A Cultural History, from the Restoration to the Present by Gary Taylor

Passing Strange: Shakespeare, Race, and Contemporary America by Ayanna Thompson

Shakespeare on Film by Judith Buchanan

The Palgrave Encyclopedia of Global Shakespeare by Alexa Alice Joubin (editor)
In the years after William Shakespeare died, his plays took on a life of their own. They meant different things to different people at different times as they spread around the world, turning a glover's son from a one-horse town in central England into one of the best-known authors of all time. Emma Smith , Professor of Shakespeare Studies at the University of Oxford, recommends books to better understand 'Shakespeare reception'—the study of Shakespeare since his death.

In the years after William Shakespeare died, his plays took on a life of their own. They meant different things to different people at different times as they spread around the world, turning a glover’s son from a one-horse town in central England into one of the best-known authors of all time. Emma Smith, Professor of Shakespeare Studies at the University of Oxford, recommends books to better understand ‘Shakespeare reception’—the study of Shakespeare since his death.
Shakespeare’s Best Plays , recommended by Emma Smith

Measure for Measure by William Shakespeare

Pericles by William Shakespeare

Richard II by William Shakespeare
Shakespearean scholar Emma Smith picks her five favourite plays of the Bard, and controversially argues that not only are some of his plays just too long, but also that the most moving moments in Shakespeare's oeuvre are where we might not expect them

Shakespearean scholar Emma Smith picks her five favourite plays of the Bard, and controversially argues that not only are some of his plays just too long, but also that the most moving moments in Shakespeare’s oeuvre are where we might not expect them
The best books on Shakespeare’s Life , recommended by James Shapiro

Outlines of the Life of Shakespeare by James Orchard Halliwell-Phillipps

William Shakespeare by E K Chambers

Shakespeare’s Lives by S Schoenbaum

The Lodger by Charles Nicholl

William Shakespeare by Peter Holland
Though many scholars have done meticulous work and brought to life slices of his life, writing a traditional, cradle-to-grave biography of Shakespeare is impossible, says Shakespeare scholar James Shapiro . Here he selects some of his favourite books tackling aspects of Shakespeare's life, including the one he most wishes he had written himself.

Though many scholars have done meticulous work and brought to life slices of his life, writing a traditional, cradle-to-grave biography of Shakespeare is impossible, says Shakespeare scholar James Shapiro. Here he selects some of his favourite books tackling aspects of Shakespeare’s life, including the one he most wishes he had written himself.
Robert S Miola on Shakespeare’s Sources

Metamorphoses Ovid (translated by A D Melville)

Roman Lives Plutarch (trans. Robin Waterfield)

Four Comedies Plautus (ed. Erich Segal)

Six Tragedies Seneca (translated by Emily Wilson)

Holinshed's Chronicles by Raphael Holinshed
William Shakespeare has a strong claim to be the most influential writer of all time. But whose works influenced him? And how? Robert S Miola discusses the breadth of Shakespeare’s reading, the vexed question of how we can reconstruct what he read, and the staggeringly innovative ways that Shakespeare shaped his sources

The best books on Shakespeare’s Sonnets , recommended by Scott Newstok

Shakespeare's Sonnets by Katherine Duncan-Jones & William Shakespeare

The Art of Shakespeare's Sonnets by Helen Vendler & William Shakespeare

All the Sonnets of Shakespeare by Paul Edmonson, Stanley Wells & William Shakespeare

The Afterlife of Shakespeare's Sonnets by Jane Kingsley-Smith

Nets by Jen Bervin

Lucy Negro, Redux by Caroline Randall Williams
The beauty of Shakespeare's sonnets speaks to us down the centuries, their lines peaking out at us from the titles of famous books or enjoying outings at weddings or other romantic occasions. But they were not always regarded as perfectly-formed jewels, and the relationships they portray not as conventional as many of us presume. Here, Shakespeare scholar Scott Newstok talks us through books that help us learn more about Shakespeare's sonnets, from the best introduction to the poems for students through to their afterlife and recent creative interpretations.

The beauty of Shakespeare’s sonnets speaks to us down the centuries, their lines peaking out at us from the titles of famous books or enjoying outings at weddings or other romantic occasions. But they were not always regarded as perfectly-formed jewels, and the relationships they portray not as conventional as many of us presume. Here, Shakespeare scholar Scott Newstok talks us through books that help us learn more about Shakespeare’s sonnets, from the best introduction to the poems for students through to their afterlife and recent creative interpretations.
Stanley Wells recommends the best of Shakespeare’s Plays

The Winter's Tale by William Shakespeare

In our Shakespeare series , we ask experts to select their favourite plays from the Bard's oeuvre. Here, preeminent Shakespearean scholar Sir Stanley Wells chooses five plays that best chart the evolution of the Bard of Avon during his 25-year career.

In our Shakespeare series , we ask experts to select their favourite plays from the Bard’s oeuvre. Here, preeminent Shakespearean scholar Sir Stanley Wells chooses five plays that best chart the evolution of the Bard of Avon during his 25-year career.
René Weis on The Best Plays of Shakespeare

Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare

In the second of a Five Books series marking the 400th year since the world's most popular playwright's death, eminent Shakespearean René Weis picks his five favourite plays, and explains why King Lear will change your life.

In the second of a Five Books series marking the 400th year since the world’s most popular playwright’s death, eminent Shakespearean René Weis picks his five favourite plays, and explains why King Lear will change your life.
Best Shakespeare Books for Kids , recommended by Natasha

Illustrated Stories from Shakespeare by Anna Claybourne, Rosie Dickins & William Shakespeare

The Shakespeare Stories by Andrew Matthews

To Wee or Not to Wee by Pamela Butchart

Macbeth by Conrad Mason

Twelfth Night by Rosie Dickins
Are you longing to get your children as excited about Shakespeare as you are? There's a lot of books out there to introduce kids to the Bard. Here, Natasha , a 10-year old living in Oxfordshire, recommends some of her favourite retellings of Shakespeare stories.

Are you longing to get your children as excited about Shakespeare as you are? There’s a lot of books out there to introduce kids to the Bard. Here, Natasha, a 10-year old living in Oxfordshire, recommends some of her favourite retellings of Shakespeare stories.
We ask experts to recommend the five best books in their subject and explain their selection in an interview.
This site has an archive of more than one thousand seven hundred interviews, or eight thousand book recommendations. We publish at least two new interviews per week.
Five Books participates in the Amazon Associate program and earns money from qualifying purchases.
© Five Books 2024
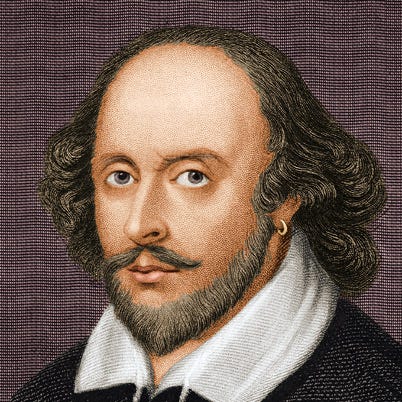
William Shakespeare
Poet and playwright William Shakespeare is considered the greatest dramatist of all time. His works are loved throughout the world, but Shakespeare’s personal life is shrouded in mystery.

Quick Facts
Wife and children, shakespeare’s lost years, poetry and sonnets, the king’s men: life as an actor and playwright, globe theater, william shakespeare’s plays, later years and death, legacy and controversies, who was william shakespeare.
William Shakespeare was an English poet, playwright, and actor of the Renaissance era. He was an important member of the King’s Men theatrical company from roughly 1594 onward. Known throughout the world, Shakespeare’s works—at least 37 plays, 154 sonnets, and 2 narrative poems—capture the range of human emotion and conflict and have been celebrated for more than 400 years. Details about his personal life are limited, though some believe he was born and died on the same day, April 23, 52 years apart.
FULL NAME: William Shakespeare BORN: c. April 23, 1564 DIED: c. April 23, 1616 BIRTHPLACE: Stratford-upon-Avon, England, United Kingdom SPOUSE: Anne Hathaway (1582-1616) CHILDREN: Susanna, Judith, and Hamnet ASTROLOGICAL SIGN: Taurus
The personal life of William Shakespeare is somewhat of a mystery . There are two primary sources that provide historians with an outline of his life. One is his work, and the other is official documentation such as church and court records. However, these provide only brief sketches of specific events in his life and yield little insight into the man himself.
When Was Shakespeare Born?
No birth records exist, but an old church record indicates that William Shakespeare was baptized at Holy Trinity Church in Stratford-upon-Avon on April 26, 1564. From this, it is believed he was born on or near April 23, 1564, and this is the date scholars acknowledge as Shakespeare’s birthday. Located about 100 miles northwest of London, Stratford-upon-Avon was a bustling market town along the River Avon and bisected by a country road during Shakespeare’s time.
Parents and Siblings
Shakespeare was the third child of John Shakespeare, a glove-maker and leather merchant, and Mary Arden, a local heiress to land. John held official positions as alderman and bailiff, an office resembling a mayor. However, records indicate John’s fortunes declined sometime in the late 1570s. Eventually, he recovered somewhat and was granted a coat of arms in 1596, which made him and his sons official gentleman.
John and Mary had eight children together, though three of them did not live past childhood. Their first two children—daughters Joan and Margaret—died in infancy, so William was the oldest surviving offspring. He had three younger brothers and two younger sisters: Gilbert, Joan, Anne, Richard, and Edmund. Anne died at age 7, and Joan was the only sibling to outlive William.
Childhood and Education
Scant records exist of Shakespeare’s childhood and virtually none regarding his education. Scholars have surmised that he most likely attended the King’s New School, in Stratford, which taught reading, writing, and the classics, including Latin. He attended until he was 14 or 15 and did not continue to university. The uncertainty regarding his education has led some people question the authorship of his work.
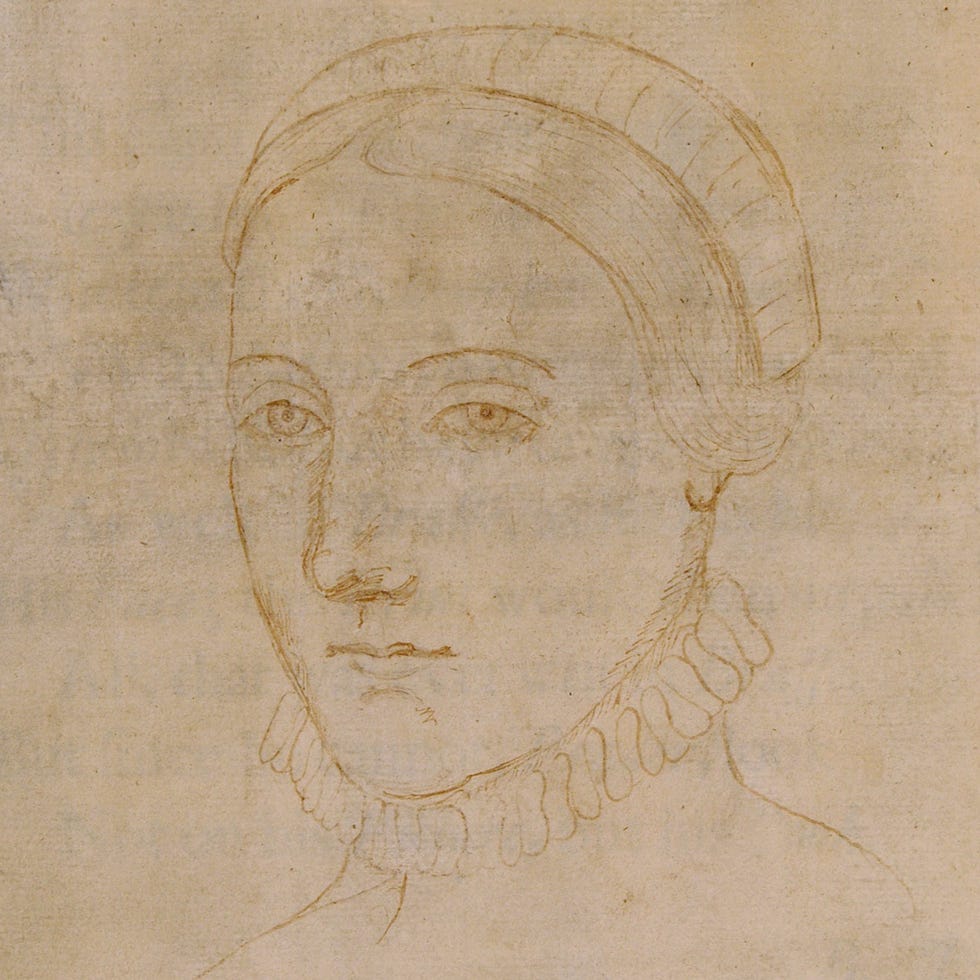

Shakespeare married Anne Hathaway on November 28, 1582, in Worcester, in Canterbury Province. Hathaway was from Shottery, a small village a mile west of Stratford. Shakespeare was 18, and Anne was 26 and, as it turns out, pregnant.
Their first child, a daughter they named Susanna, was born on May 26, 1583. Two years later, on February 2, 1585, twins Hamnet and Judith were born. Hamnet died of unknown causes at age 11.
There are seven years of Shakespeare’s life where no records exist: after the birth of his twins in 1585 until 1592. Scholars call this period Shakespeare’s lost years, and there is wide speculation about what he was doing during this period.
One theory is that he might have gone into hiding for poaching game from local landlord Sir Thomas Lucy. Another possibility is that he might have been working as an assistant schoolmaster in Lancashire. Some scholars believe he was in London, working as a horse attendant at some of London’s finer theaters before breaking on the scene.
By 1592, there is evidence Shakespeare earned a living as an actor and a playwright in London and possibly had several plays produced. The September 20, 1592, edition of the Stationers’ Register , a guild publication, includes an article by London playwright Robert Greene that takes a few jabs at Shakespeare:
“...There is an upstart Crow, beautified with our feathers, that with his Tiger’s heart wrapped in a Player’s hide, supposes he is as well able to bombast out a blank verse as the best of you: and being an absolute Johannes factotum, is in his own conceit the only Shake-scene in a country.”
Scholars differ on the interpretation of this criticism, but most agree that it was Greene’s way of saying Shakespeare was reaching above his rank, trying to match better known and educated playwrights like Christopher Marlowe , Thomas Nashe, or Greene himself.
Early in his career, Shakespeare was able to attract the attention and patronage of Henry Wriothesley, the Earl of Southampton, to whom he dedicated his first and second published poems: Venus and Adonis (1593) and The Rape of Lucrece (1594). In fact, these long narrative poems—1,194 and 1,855 lines, respectively—were Shakespeare’s first published works. Wriothesley’s financial support was a helpful source of income at a time when the theaters were shuttered due to a plague outbreak.
Shakespeare’s most well-known poetry are his 154 sonnets, which were first published as a collection in 1609 and likely written as early as the 1590s. Scholars broadly categorize the sonnets in groups based on two unknown subjects that Shakespeare addresses: the Fair Youth sonnets (the first 126) and the Dark Lady sonnets (the last 28). The identities of the aristocratic young man and vexing woman continue to be a source of speculation.
In 1594, Shakespeare joined Lord Chamberlain’s Men, the London acting company that he worked with for the duration of his career. Later called the King’s Men, it was considered the most important troupe of its time and was very popular by all accounts. Some sources describe Shakespeare as a founding member of the company, but whatever the case, he became central to its success. Initially, he was an actor and eventually devoted more and more time to writing.
Records show that Shakespeare, who was also a company shareholder, had works published and sold as popular literature. Although The Taming of the Shrew is believed to be the first play that Shakespeare wrote, his first published plays were Titus Andronicus and Henry VI Part 2 . They were printed in 1594 in quarto, an eight-page pamphlet-like book. By the end of 1597, Shakespeare had likely written 16 of his 37 plays and amassed some wealth.
At this time, civil records show Shakespeare purchased one of the largest houses in Stratford, called New Place, for his family. It was a four-day ride by horse from Stratford to London, so it’s believed that Shakespeare spent most of his time in the city writing and acting and came home once a year during the 40-day Lenten period, when the theaters were closed. However, Shakespeare expert and professor Sir Stanley Wells posits that the playwright might have spent more time at home in Stratford than previously believed, only commuting to London when he needed to for work.
Although the theater culture in 16 th century England was not greatly admired by people of high rank, some of the nobility were good patrons of the performing arts and friends of the actors. Two notable exceptions were Queen Elizabeth I , who was a fan of Lord Chamberlain’s Men by the late 1590s after first watching a performance in 1594, and her successor King James I. Following his crowning in 1603, the company changed its name to the King’s Men.
By 1599, Shakespeare and several fellow actors built their own theater on the south bank of the Thames River, which they called the Globe Theater. Julius Caesar is thought to be the first production at the new open-air theater. Owning the playhouse proved to be a financial boon for Shakespeare and the other investors.
In 1613, the Globe caught fire during a performance of Henry VII I and burned to the ground. The company quickly rebuilt it, and it reopened the next year. In 1642, Puritans outlawed all theaters, including the Globe, which was demolished two years later. Centuries passed until American actor Sam Wanamaker began working to resurrect the theater once more. The third Globe Theater opened in 1997, and today, more than 1.25 million people visit it every year.
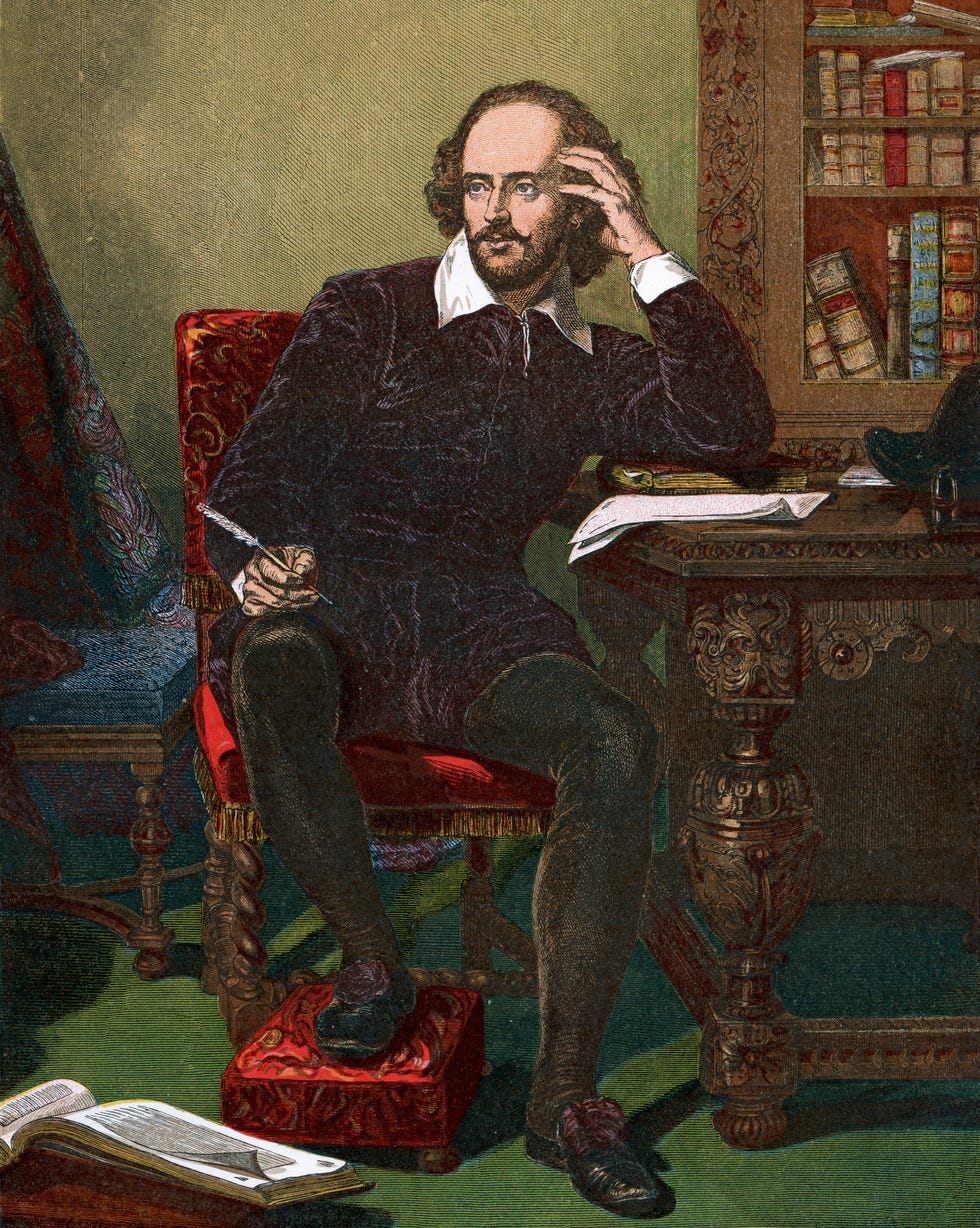

It’s difficult to determine the exact chronology of Shakespeare’s plays, but over the course of two decades, from about 1590 to 1613, he wrote 37 plays revolving around three main themes: history, tragedy, and comedy. Some plays blur these lines, and over time, our interpretation of them has changed, too.
Shakespeare’s early plays were written in the conventional style of the day, with elaborate metaphors and rhetorical phrases that didn’t always align naturally with the story’s plot or characters. However, Shakespeare was very innovative, adapting the traditional style to his own purposes and creating a freer flow of words.
With only small degrees of variation, Shakespeare primarily used a metrical pattern consisting of lines of unrhymed iambic pentameter, or blank verse, to compose his plays. At the same time, there are passages in all the plays that deviate from this and use forms of poetry or simple prose.
Many of Shakespeare’s first plays were histories. All three Henry VI plays, Richard II , and Henry V dramatize the destructive results of weak or corrupt rulers and have been interpreted by drama historians as Shakespeare’s way of justifying the origins of the Tudor Dynasty. Other histories include Richard III , King John , the two Henry IV plays, and Henry VIII . With exception of Henry VIII , which was Shakespeare’s last play, these works were likely written by 1599.
Although Shakespeare wrote three tragedies, including Romeo and Juliet , before 1600, it wasn’t until after the turn of the century that he truly explored the genre. Character in Othello , King Lear , and Macbeth present vivid impressions of human temperament that are timeless and universal.
Possibly the best known of these plays is Hamlet , which explores betrayal, retribution, incest, and moral failure. These moral failures often drive the twists and turns of Shakespeare’s plots, destroying the hero and those he loves.
Julius Caesar , written in circa 1599, portrays upheaval in Roman politics that might have resonated with viewers at a time when England’s aging monarch, Queen Elizabeth I, had no legitimate heir, thus creating the potential for future power struggles.
Titus Andronicus , Anthony and Cleopatra , Timon of Athens , and Coriolanus are Shakespeare’s other tragic plays.
Shakespeare wrote comedies throughout his career, including his first play The Taming of the Shrew . Some of his other early comedies, written before 1600 or so, are: the whimsical A Midsummer Night’s Dream , the romantic Merchant of Venice , the wit and wordplay of Much Ado About Nothing , and the charming As You Like It .
Some of his comedies might be better described as tragicomedies. Among these are Pericles , Cymbeline , The Winter’s Tale, and The Tempest . Although graver in tone than the comedies, they are not the dark tragedies of King Lear or Macbeth because they end with reconciliation and forgiveness.
Additional Shakespeare comedies include:
- The Two Gentlemen of Verona ,
- The Comedy of Errors ,
- Love’s Labour’s Lost ,
- The Merry Wives of Windsor ,
- Twelfth Night ,
- Measure for Measure , and
- All’s Well That Ends Well
Troilus and Cressida is emblematic of the Shakespearean “problem play,” which defies genres. Some of Shakespeare’s contemporaries classified it as a history or a comedy, though the original name of the play was The Tragedie of Troylus and Cressida .
Collaborations and Lost Play
Shakespeare is known to have created plays with other writers, such as John Fletcher. They co-wrote The Two Noble Kinsmen around 1613–14, making it Shakespeare’s last known dramatic work. They also collaborated on Cardenio , a play which was not preserved. Shakespeare’s other jointly written plays are Sir Thomas More and The Raigne of King Edward the Third . When including these works, Shakespeare has 41 plays to his name.
Around the turn of the 17 th century, Shakespeare became a more extensive property owner in Stratford. When his father, John, died in 1601, he inherited the family home. Then, in 1602, he purchased about 107 acres for 320 pounds.
In 1605, Shakespeare purchased leases of real estate near Stratford for 440 pounds, which doubled in value and earned him 60 pounds a year. This made him an entrepreneur as well as an artist, and scholars believe these investments gave him uninterrupted time to write his plays.
A couple years prior, around 1603, Shakespeare is believed to have stopped acting in the King’s Men productions, instead focusing on his playwriting work. He likely spent the last three years of his life in Stratford.
When Did Shakespeare Die?
Tradition holds that Shakespeare died on his 52 nd birthday, April 23, 1616, but some scholars believe this is a myth. Church records show he was interred at Holy Trinity Church on April 25, 1616. The exact cause of Shakespeare’s death is unknown, though many people believe he died following a brief illness.
In his will, he left the bulk of his possessions to his eldest daughter, Susanna, who by then was married. Although entitled to a third of his estate, little seems to have gone to his wife, Anne, whom he bequeathed his “second-best bed.” This has drawn speculation that she had fallen out of favor or that the couple was not close.
However, there is very little evidence the two had a difficult marriage. Other scholars note that the term “second-best bed” often refers to the bed belonging to the household’s master and mistress, the marital bed, and the “first-best bed” was reserved for guests.
The Bard of Avon has gone down in history as the greatest dramatist of all time and is sometimes called England’s national poet. He is credited with inventing or introducing more than 1,700 words to the English language, often as a result of combining words, changing usages, or blending in foreign root words. If you’ve used the words “downstairs,” “egregious,” “kissing,” “zany,” or “skim milk,” you can thank Shakespeare. He is also responsible for many common phrases, such as “love is blind” and “wild goose chase.”
First Folio

Although some of Shakespeare’s works were printed in his lifetime, not all were. It is because of the First Folio that we know about 18 of Shakespeare’s plays, including Macbeth , Twelfth Night , and Julius Caesar . John Heminge and Henry Condell, two of Shakespeare’s friends and fellow actors in the King’s Men, created the 36-play collection, which celebrates its 400 th anniversary this year. It was published with the title Mr. William Shakespeare’s Comedies, Histories and Tragedies in 1623, seven years after Shakespeare died.
In addition to its literary importance, the First Folio contains an original portrait of Shakespeare on the title page. Engraved by Martin Droeshout, it’s considered one of the two authentic portraits of the writer. The other is a memorial bust at Holy Trinity Church in Stratford.
Today, there are 235 surviving copies of the First Folio that date back to 1623, but experts estimate roughly 750 First Folios were printed. Three subsequent editions of Shakespeare’s Folio, with text updates and additional plays, were published between 1632 and 1685.
Did Shakespeare Write His Own Plays?
About 150 years after his death, questions arose about the authorship of Shakespeare’s plays. Scholars and literary critics began to float names like Christopher Marlowe, Edward de Vere, and Francis Bacon —men of more known backgrounds, literary accreditation, or inspiration—as the true authors of the plays.
Much of this stemmed from the sketchy details of Shakespeare’s life and the dearth of contemporary primary sources. Official records from the Holy Trinity Church and the Stratford government record the existence of Shakespeare, but none of these attest to him being an actor or playwright.
Skeptics also questioned how anyone of such modest education could write with the intellectual perceptiveness and poetic power that is displayed in Shakespeare’s works. Over the centuries, several groups have emerged that question the authorship of Shakespeare’s plays.
The most serious and intense skepticism began in the 19 th century when adoration for Shakespeare was at its highest. The detractors believed that the only hard evidence surrounding Shakespeare from Stratford-upon-Avon described a man from modest beginnings who married young and became successful in real estate.
Members of the Shakespeare Oxford Society, founded in 1957, put forth arguments that English aristocrat and poet Edward de Vere, the 17 th Earl of Oxford, was the true author of the poems and plays of “William Shakespeare.” The Oxfordians cite de Vere’s extensive knowledge of aristocratic society, his education, and the structural similarities between his poetry and that found in the works attributed to Shakespeare. They contend that Shakespeare had neither the education nor the literary training to write such eloquent prose and create such rich characters.
However, the vast majority of Shakespearean scholars contend that Shakespeare wrote all his own plays. They point out that other playwrights of the time also had sketchy histories and came from modest backgrounds.
They contend that King’s New School in Stratford had a curriculum of Latin and the classics could have provided a good foundation for literary writers. Supporters of Shakespeare’s authorship argue that the lack of evidence about Shakespeare’s life doesn’t mean his life didn’t exist. They point to evidence that displays his name on the title pages of published poems and plays.
Examples exist of authors and critics of the time acknowledging Shakespeare as the author of plays such as The Two Gentlemen of Verona , The Comedy of Errors , and King John .
Royal records from 1601 show that Shakespeare was recognized as a member of the King’s Men theater company and a Groom of the Chamber by the court of King James I, where the company performed seven of Shakespeare’s plays.
There is also strong circumstantial evidence of personal relationships by contemporaries who interacted with Shakespeare as an actor and a playwright.
Literary Legacy
What seems to be true is that Shakespeare was a respected man of the dramatic arts who wrote plays and acted in the late 16 th and early 17 th centuries. But his reputation as a dramatic genius wasn’t recognized until the 19 th century.
Beginning with the Romantic period of the early 1800s and continuing through the Victorian period, acclaim and reverence for Shakespeare and his work reached its height. In the 20 th century, new movements in scholarship and performance rediscovered and adopted his works.
Today, his plays remain highly popular and are constantly studied and reinterpreted in performances with diverse cultural and political contexts. The genius of Shakespeare’s characters and plots are that they present real human beings in a wide range of emotions and conflicts that transcend their origins in Elizabethan England.
- The fool doth think he is wise, but the wise man knows himself to be a fool.
- This above all: to thine own self be true, and it must follow, as the night the day, thou canst not then be false to any man.
- There is nothing either good or bad, but thinking makes it so.
- Cowards die many times before their deaths; the valiant never taste of death but once.
- Lord, what fools these mortals be!
- To weep is to make less the depth of grief.
- In time we hate that which we often fear.
- Men at some time are masters of their fates: the fault, dear Brutus, is not in our stars, but in ourselves, that we are underlings.
- What’s done cannot be undone.
- We are such stuff as dreams are made on, and our little life is rounded with a sleep.
- Madness in great ones must not unwatched go.
- The first thing we do, let’s kill all the lawyers.
- All the world’s a stage, and all the men and women merely players.
- Give every man thy ear, but few thy voice.
- I say there is no darkness but ignorance.
- I wasted time, and now doth time waste me.
- Some are born great, some achieve greatness, and some have greatness thrust upon them.
Fact Check: We strive for accuracy and fairness. If you see something that doesn’t look right, contact us !
The Biography.com staff is a team of people-obsessed and news-hungry editors with decades of collective experience. We have worked as daily newspaper reporters, major national magazine editors, and as editors-in-chief of regional media publications. Among our ranks are book authors and award-winning journalists. Our staff also works with freelance writers, researchers, and other contributors to produce the smart, compelling profiles and articles you see on our site. To meet the team, visit our About Us page: https://www.biography.com/about/a43602329/about-us
Adrienne directs the daily news operation and content production for Biography.com. She joined the staff in October 2022 and most recently worked as an editor for Popular Mechanics , Runner’s World , and Bicycling . Adrienne has served as editor-in-chief of two regional print magazines, and her work has won several awards, including the Best Explanatory Journalism award from the Alliance of Area Business Publishers. Her current working theory is that people are the point of life, and she’s fascinated by everyone who (and every system that) creates our societal norms. When she’s not behind the news desk, find her hiking, working on her latest cocktail project, or eating mint chocolate chip ice cream.
Playwrights

August Wilson

Langston Hughes

7 Facts About Literary Icon Langston Hughes

11 Notable Artists from the Harlem Renaissance
Robert Browning

Christopher Marlowe

Eugene O'Neill

J.M. Barrie

Oscar Wilde

Lorraine Hansberry
Share this page
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
William Shakespeare Biography
Who was william shakespeare.
- In this section
An Introduction
William Shakespeare was a renowned English poet, playwright, and actor born in 1564 in Stratford-upon-Avon . His birthday is most commonly celebrated on 23 April (see When was Shakespeare born ), which is also believed to be the date he died in 1616.
Shakespeare was a prolific writer during the Elizabethan and Jacobean ages of British theatre (sometimes called the English Renaissance or the Early Modern Period). Shakespeare’s plays are perhaps his most enduring legacy, but they are not all he wrote. Shakespeare’s poems also remain popular to this day.
Shakespeare's Family Life
Records survive relating to William Shakespeare’s family that offer an understanding of the context of Shakespeare's early life and the lives of his family members. John Shakespeare married Mary Arden , and together they had eight children. John and Mary lost two daughters as infants, so William became their eldest child. John Shakespeare worked as a glove-maker, but he also became an important figure in the town of Stratford by fulfilling civic positions. His elevated status meant that he was even more likely to have sent his children, including William, to the local grammar school .
William Shakespeare would have lived with his family in their house on Henley Street until he turned eighteen. When he was eighteen, Shakespeare married Anne Hathaway , who was twenty-six. It was a rushed marriage because Anne was already pregnant at the time of the ceremony. Together they had three children. Their first daughter, Susanna , was born six months after the wedding and was later followed by twins Hamnet and Judith . Hamnet died when he was just 11 years old.
- For an overview of William Shakespeare's life, see Shakespeare's Life: A Timeline
Shakespeare in London
Shakespeare's career jump-started in London, but when did he go there? We know Shakespeare's twins were baptised in 1585, and that by 1592 his reputation was established in London, but the intervening years are considered a mystery. Scholars generally refer to these years as ‘ The Lost Years ’.
During his time in London, Shakespeare’s first printed works were published. They were two long poems, 'Venus and Adonis' (1593) and 'The Rape of Lucrece' (1594). He also became a founding member of The Lord Chamberlain’s Men, a company of actors. Shakespeare was the company's regular dramatist, producing on average two plays a year, for almost twenty years.
He remained with the company for the rest of his career, during which time it evolved into The King’s Men under the patronage of King James I (from 1603). During his time in the company Shakespeare wrote many of his most famous tragedies, such as King Lear and Macbeth , as well as great romances, like The Winter’s Tale and The Tempest .
- For more about Shakespeare's patrons and his work in London see; Shakespeare's Career
Shakespeare's Works
Altogether Shakespeare's works include 38 plays, 2 narrative poems, 154 sonnets, and a variety of other poems. No original manuscripts of Shakespeare's plays are known to exist today. It is actually thanks to a group of actors from Shakespeare's company that we have about half of the plays at all. They collected them for publication after Shakespeare died, preserving the plays. These writings were brought together in what is known as the First Folio ('Folio' refers to the size of the paper used). It contained 36 of his plays, but none of his poetry.
Shakespeare’s legacy is as rich and diverse as his work; his plays have spawned countless adaptations across multiple genres and cultures. His plays have had an enduring presence on stage and film. His writings have been compiled in various iterations of The Complete Works of William Shakespeare, which include all of his plays, sonnets, and other poems. William Shakespeare continues to be one of the most important literary figures of the English language.
New Place; a home in Stratford-upon-Avon
Shakespeare’s success in the London theatres made him considerably wealthy, and by 1597 he was able to purchase New Place , the largest house in the borough of Stratford-upon-Avon . Although his professional career was spent in London, he maintained close links with his native town.
Recent archaeological evidence discovered on the site of Shakespeare’s New Place shows that Shakespeare was only ever an intermittent lodger in London. This suggests he divided his time between Stratford and London (a two or three-day commute). In his later years, he may have spent more time in Stratford-upon-Avon than scholars previously thought.
- Watch our video for more about Shakespeare as a literary commuter:
On his father's death in 1601, William Shakespeare inherited the old family home in Henley Street part of which was then leased to tenants. Further property investments in Stratford followed, including the purchase of 107 acres of land in 1602.
Shakespeare died in Stratford-upon-Avon on 23 April 1616 at the age of 52. He is buried in the sanctuary of the parish church, Holy Trinity.
All the world's a stage /And all the men and women merely players. / They have their exits and their entrances, / And one man in his time plays many parts. — As You Like It, Act 2 Scene 7
Help keep Shakespeare's story alive
More like this, go behind the scenes, shakespeare's birthplace, anne hathaway's cottage, shakespeare's new place.
We use essential and non-essential cookies that improve the functionality and experience of the website. For more information, see our Cookies Policy.
Necessary cookies
Necessary cookies ensure the smooth running of the website, including core functionality and security. The website cannot function properly without these cookies.
Analytics cookies
Analytical cookies are used to determine how visitors are using a website, enabling us to enhance performance and functionality of the website. These are non-essential cookies but are not used for advertising purposes.
Advertising cookies
Advertising cookies help us monitor the effectiveness of our recruitment campaigns as well as enabling advertising to be tailored to you through retargeting advertising services. This means there is the possibility of you seeing more adverts from the Shakespeare Birthplace Trust on other websites that you visit.
- Save settings Minimise
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
William Shakespeare
By: History.com Editors
Updated: June 7, 2019 | Original: October 3, 2011

Considered the greatest English-speaking writer in history and known as England’s national poet, William Shakespeare (1564-1616) has had more theatrical works performed than any other playwright. To this day, countless theater festivals around the world honor his work, students memorize his eloquent poems and scholars reinterpret the million words of text he composed. They also hunt for clues about the life of the man who inspires such “bardolatry” (as George Bernard Shaw derisively called it), much of which remains shrouded in mystery. Born into a family of modest means in Elizabethan England, the “Bard of Avon” wrote at least 37 plays and a collection of sonnets, established the legendary Globe theater and helped transform the English language.

Shakespeare’s Childhood and Family Life
William Shakespeare was born in Stratford-upon-Avon, a bustling market town 100 miles northwest of London, and baptized there on April 26, 1564. His birthday is traditionally celebrated on April 23, which was the date of his death in 1616 and is the feast day of St. George, the patron saint of England. Shakespeare’s father, John, dabbled in farming, wood trading, tanning, leatherwork, money lending and other occupations; he also held a series of municipal positions before falling into debt in the late 1580s. The ambitious son of a tenant farmer, John boosted his social status by marrying Mary Arden, the daughter of an aristocratic landowner. Like John, she may have been a practicing Catholic at a time when those who rejected the newly established Church of England faced persecution.
Did you know? Sources from William Shakespeare's lifetime spell his last name in more than 80 different ways, ranging from “Shappere” to “Shaxberd.” In the handful of signatures that have survived, he himself never spelled his name “William Shakespeare,” using variations such as “Willm Shakspere” and “William Shakspeare” instead.
William was the third of eight Shakespeare children, of whom three died in childhood. Though no records of his education survive, it is likely that he attended the well-regarded local grammar school, where he would have studied Latin grammar and classics. It is unknown whether he completed his studies or abandoned them as an adolescent to apprentice with his father.
At 18 Shakespeare married Anne Hathaway (1556-1616), a woman eight years his senior, in a ceremony thought to have been hastily arranged due to her pregnancy. A daughter, Susanna, was born less than seven months later in May 1583. Twins Hamnet and Judith followed in February 1585. Susanna and Judith would live to old age, while Hamnet, Shakespeare’s only son, died at 11. As for William and Anne, it is believed that the couple lived apart for most of the year while the bard pursued his writing and theater career in London. It was not until the end of his life that Shakespeare moved back in with Anne in their Stratford home.
Shakespeare’s Lost Years and Early Career
To the dismay of his biographers, Shakespeare disappears from the historical record between 1585, when his twins’ baptism was recorded, and 1592, when the playwright Robert Greene denounced him in a pamphlet as an “upstart crow” (evidence that he had already made a name for himself on the London stage). What did the newly married father and future literary icon do during those seven “lost” years? Historians have speculated that he worked as a schoolteacher, studied law, traveled across continental Europe or joined an acting troupe that was passing through Stratford. According to one 17th-century account, he fled his hometown after poaching deer from a local politician’s estate.
Whatever the answer, by 1592 Shakespeare had begun working as an actor, penned several plays and spent enough time in London to write about its geography, culture and diverse personalities with great authority. Even his earliest works evince knowledge of European affairs and foreign countries, familiarity with the royal court and general erudition that might seem unattainable to a young man raised in the provinces by parents who were probably illiterate. For this reason, some theorists have suggested that one or several authors wishing to conceal their true identity used the person of William Shakespeare as a front. (Most scholars and literary historians dismiss this hypothesis, although many suspect Shakespeare sometimes collaborated with other playwrights.)
Shakespeare’s Plays and Poems
Shakespeare’s first plays, believed to have been written before or around 1592, encompass all three of the main dramatic genres in the bard’s oeuvre: tragedy (“Titus Andronicus”); comedy (“The Two Gentlemen of Verona,” “The Comedy of Errors” and “The Taming of the Shrew”); and history (the “Henry VI” trilogy and “Richard III”). Shakespeare was likely affiliated with several different theater companies when these early works debuted on the London stage. In 1594 he began writing and acting for a troupe known as the Lord Chamberlain’s Men (renamed the King’s Men when James I appointed himself its patron), ultimately becoming its house playwright and partnering with other members to establish the legendary Globe theater in 1599.
Between the mid-1590s and his retirement around 1612, Shakespeare penned the most famous of his 37-plus plays, including “Romeo and Juliet,” “A Midsummer Night’s Dream,” “Hamlet,” “King Lear,” “Macbeth” and “The Tempest.” As a dramatist, he is known for his frequent use of iambic pentameter, meditative soliloquies (such as Hamlet’s ubiquitous “To be, or not to be” speech) and ingenious wordplay. His works weave together and reinvent theatrical conventions dating back to ancient Greece, featuring assorted casts of characters with complex psyches and profoundly human interpersonal conflicts. Some of his plays—notably “All’s Well That Ends Well,” “Measure for Measure” and “Troilus and Cressida”—are characterized by moral ambiguity and jarring shifts in tone, defying, much like life itself, classification as purely tragic or comic.
Also remembered for his non-dramatic contributions, Shakespeare published his first narrative poem—the erotic “Venus and Adonis,” intriguingly dedicated to his close friend Henry Wriothesley, Earl of Southampton—while London theaters were closed due to a plague outbreak in 1593. The many reprints of this piece and a second poem, “The Rape of Lucrece,” hint that during his lifetime the bard was chiefly renowned for his poetry. Shakespeare’s famed collection of sonnets, which address themes ranging from love and sensuality to truth and beauty, was printed in 1609, possibly without its writer’s consent. (It has been suggested that he intended them for his intimate circle only, not the general public.) Perhaps because of their explicit sexual references or dark emotional character, the sonnets did not enjoy the same success as Shakespeare’s earlier lyrical works.
Shakespeare’s Death and Legacy
Shakespeare died at age 52 of unknown causes on April 23, 1616, leaving the bulk of his estate to his daughter Susanna. (Anne Hathaway, who outlived her husband by seven years, famously received his “second-best bed.”) The slabstone over Shakespeare’s tomb, located inside a Stratford church, bears an epitaph—written, some say, by the bard himself—warding off grave robbers with a curse: “Blessed be the man that spares these stones, / And cursed be he that moves my bones.” His remains have yet to be disturbed, despite requests by archaeologists keen to reveal what killed him.
In 1623, two of Shakespeare’s former colleagues published a collection of his plays, commonly known as the First Folio. In its preface, the dramatist Ben Jonson wrote of his late contemporary, “He was not of an age, but for all time.” Indeed, Shakespeare’s plays continue to grace stages and resonate with audiences around the world, and have yielded a vast array of film, television and theatrical adaptations. Furthermore, Shakespeare is believed to have influenced the English language more than any other writer in history, coining—or, at the very least, popularizing—terms and phrases that still regularly crop up in everyday conversation. Examples include the words “fashionable” (“Troilus and Cressida”), “sanctimonious” (“Measure for Measure”), “eyeball” (“A Midsummer Night’s Dream”) and “lackluster” (“As You Like It”); and the expressions “foregone conclusion” (“Othello”), “in a pickle” (“The Tempest”), “wild goose chase” (“Romeo and Juliet”) and “one fell swoop” (“Macbeth”).

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
- Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects
How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section William Shakespeare
Introduction.
- Reference Works
- Data Sources
- Overviews and Companions
- Source Materials
- Shakespeare and the Classics
- Tragicomedies and Romances
- Narrative Poems and Sonnets
- Critical History
- Recent Criticism
- Language and Style
- Editorial and Textual Issues
- Psychoanalysis
- Politics and Patronage
- Elizabethan and Jacobean Playhouses
- Cross-dressing and Gender
- Shakespeare and his Contemporaries
- Performance History
- Shakespeare on Film
Related Articles Expand or collapse the "related articles" section about
About related articles close popup.
Lorem Ipsum Sit Dolor Amet
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam ligula odio, euismod ut aliquam et, vestibulum nec risus. Nulla viverra, arcu et iaculis consequat, justo diam ornare tellus, semper ultrices tellus nunc eu tellus.
- Adapting Shakespeare
- George Gascoigne
- Globe Theatre
- Prosody and Meter: Early Modern to 19th Century
Other Subject Areas
Forthcoming articles expand or collapse the "forthcoming articles" section.
- Children's Literature and Young Adult Literature in Ireland
- Shakespeare in Translation
- Find more forthcoming articles...
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
William Shakespeare by Andrew Hadfield , Amy Kenny LAST REVIEWED: 12 April 2019 LAST MODIFIED: 27 November 2013 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780199846719-0085
William Shakespeare (b. 1564–d. 1616) is widely regarded as the greatest writer and dramatist of all time. His poetry, plays, and life continue to fascinate academics, theater practitioners, and the general public over four hundred years after his death. Over the course of his career, he wrote 154 sonnets, forty plays that are known about (not all of which are extant), two narrative poems, and had a major influence on the development of English as a world language. Literary and theater critics, historians, cultural commentators, journalists, major authors, and philosophers have engaged in a variety of ways with his work, studying and analyzing an enormous range of themes: editorial and textual issues, feminism, psychoanalysis, politics, patronage, performance history, and film studies. This selective bibliography aims to provide the reader with an introductory guide through the enormous amount of material available that tries to explain why Shakespeare’s work matters and is relevant in the 21st century. Shakespeare has been analyzed and studied in almost every conceivable way, and there is a massive bibliography of literary criticism, historical contextualization, theater history, theoretical readings, biography, and, of course, speculation.
From his early years in Stratford-upon-Avon to his successful career in the playhouse of London, Shakespeare’s life and art have been profusely studied and analyzed for clues about his work. This section will give a sense of the different approaches to exploring Shakespeare’s life. Shakespeare was thought of as an untutored genius and was regarded with some suspicion by 18th-century men of letters and embraced by the Romantics; however, recent evidence has pointed out that he had a series of entrepreneurial dealings with his company, the Lord Chamberlain’s Men, and this has influenced recent conceptions of him. Instead of merely being thought of as a writer, Shakespeare is now thought to be a shrewd business man who was a shareholder in his company and profited from their success. Schoenbaum 1991 provides an exhaustive list of the stories that have circulated about Shakespeare in order to provide the basis for analyzing the life records. Shapiro 2006 isolates one year of Shakespeare’s life as a microcosm for his biography and as a means of explaining the cultural life of London at the end of Elizabeth’s reign, while Ackroyd 2005 analyze records from various points in his life to create cradle-to-grave biographies. Duncan-Jones 2001 compiles evidence to suggest that Shakespeare was less the untutored genius of romantic legend and more a social climber who was interested in material gain. Bate 2009 uses information about early modern life and theater to create a portrait of Shakespeare’s life based on his own writing techniques and style. Greenblatt 2004 and Potter 2012 analyze his canon for clues about his personal life, drawing data from his characters and plot devices.
Ackroyd, Peter. Shakespeare: The Biography . New York: Nan A. Talese, 2005.
A biography that is keen to show a close relationship between the life and the works and that Shakespeare’s art was rooted in his life experience, suggesting that we can read what he wrote autobiographically.
Bate, Jonathan. Soul of the Age: A Biography of the Mind of William Shakespeare . New York: Random House, 2009.
Explores Shakespeare’s life through the Elizabethan philosophy of the seven ages of man, based on Jacques’s speech in As You Like It , providing historical information about 16th-century life for each of the seven stages.
Bevington, David. Shakespeare and Biography . Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2010.
A useful resource for those interested in the history of Shakespearean biography, which outlines the issues that have been the focus of several biographies of Shakespeare, including politics, religion, and familial relationships.
Duncan-Jones, Katherine. Shakespeare: An Ungentle Life . London: Arden, 2001.
Shows Shakespeare’s life as a playwright who has a shrewd business sense as well as an aptitude for verse, and consequently is the object of envy in late Elizabethan London.
Greenblatt, Stephen. Will in the World: How Shakespeare Became Shakespeare . New York: Norton, 2004.
Like Ackroyd 2005 , this book is eager to relate Shakespeare’s works to his life and, in particular, his experiences. Greenblatt makes much of the death of Shakespeare’s son Hamnet as an inspiration for Hamlet and Shakespeare having witnessed miracle plays as a youth.
Potter, Lois. The Life of William Shakespeare: A Critical Biography . Chichester, UK: Wiley, 2012.
DOI: 10.1002/9781118231746
Considers the role that early modern actors and playwrights had in collaborating, revising, or influencing Shakespeare’s works. Potter explores Shakespeare’s life chronologically through a series of his own words and pays particular attention to the construction of memory in Shakespeare’s works and in their afterlives.
Schoenbaum, Samuel. Shakespeare’s Lives . Oxford: Clarendon, 1991.
A comprehensive study of the various myths and narratives about Shakespeare’s life, including those now-discredited yet imaginative tales introduced by famous authors
Shapiro, James. 1599: A Year in the Life of William Shakespeare . London: Faber and Faber, 2006.
Investigates one year of Shakespeare’s life and the events that took place in that year such as the building of the Globe Theatre, Will Kempe leaving his acting company, and writing Henry V and As You Like It as a turning point in Shakespeare’s career.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About British and Irish Literature »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- Abbey Theatre
- Alfred (King)
- Alliterative Verse
- Ancrene Wisse, and the Katherine and Wooing Groups
- Anglo-Irish Poetry, 1500–1800
- Anglo-Saxon Hagiography
- Arthurian Literature
- Austen, Jane
- Ballard, J. G.
- Barnes, Julian
- Beckett, Samuel
- Behn, Aphra
- Biblical Literature
- Biography and Autobiography
- Blake, William
- Bloomsbury Group
- Bowen, Elizabeth
- Brontë, Anne
- Brooke-Rose, Christine
- Browne, Thomas
- Burgess, Anthony
- Burney, Frances
- Burns, Robert
- Butler, Hubert
- Byron, Lord
- Carroll, Lewis
- Carter, Angela
- Catholic Literature
- Celtic and Irish Revival
- Chatterton, Thomas
- Chaucer, Geoffrey
- Chorographical and Landscape Writing
- Coffeehouse
- Congreve, William
- Conrad, Joseph
- Crime Fiction
- Defoe, Daniel
- Dickens, Charles
- Donne, John
- Drama, Northern Irish
- Drayton, Michael
- Early Modern Prose, 1500-1650
- Eighteenth-Century Novel
- Eliot, George
- English Bible and Literature, The
- English Civil War / War of the Three Kingdoms
- English Reformation Literature
- Epistolatory Novel, The
- Erotic, Obscene, and Pornographic Writing, 1660-1900
- Ferrier, Susan
- Fielding, Henry
- Ford, Ford Madox
- French Revolution, 1789–1799
- Friel, Brian
- Gascoigne, George
- Golding, William
- Goldsmith, Oliver
- Gosse, Edmund
- Gower, John
- Gray, Thomas
- Gunpowder Plot (1605), The
- Hardy, Thomas
- Heaney, Seamus
- Henry Howard, Earl of Surrey
- Herbert, George
- Highlands, The
- Hogg, James
- Holmes, Sherlock
- Hopkins, Gerard Manley
- Hurd, Richard
- Ireland and Memory Studies
- Irish Crime Fiction
- Irish Famine, Writing of the
- Irish Gothic Tradition
- Irish Life Writing
- Irish Literature and the Union with Britain, 1801-1921
- Irish Modernism
- Irish Poetry of the First World War
- Irish Short Story, The
- Irish Travel Writing
- Johnson, B. S.
- Johnson, Samuel
- Jones, David
- Jonson, Ben
- Joyce, James
- Keats, John
- Kelman, James
- Kempe, Margery
- Lamb, Charles and Mary
- Larkin, Philip
- Law, Medieval
- Lawrence, D. H.
- Literature, Neo-Latin
- Literature of the Bardic Revival
- Literature of the Irish Civil War
- Literature of the 'Thirties
- MacDiarmid, Hugh
- MacPherson, James
- Malory, Thomas
- Marlowe, Christopher
- Marvell, Andrew
- Mary Shelley's Frankenstein
- McEwan, Ian
- McGuckian, Medbh
- Medieval Lyrics
- Medieval Manuscripts
- Medieval Scottish Poetry
- Medieval Sermons
- Middleton, Thomas
- Milton, John
- Miéville, China
- Morality Plays
- Morris, William
- Muir, Edwin
- Muldoon, Paul
- Ní Chuilleanáin, Eiléan
- Nonsense Literature
- Novel, Contemporary British
- Novel, The Contemporary Irish
- O’Casey, Sean
- O'Connor, Frank
- O’Faoláin, Seán
- Old English Literature
- Percy, Thomas
- Piers Plowman
- Pope, Alexander
- Postmodernism
- Post-War Irish Drama
- Post-war Irish Writing
- Pre-Raphaelites
- Prosody and Meter: Twentieth Century
- Quincey, Thomas De
- Ralegh (Raleigh), Sir Walter
- Ramsay, Allan and Robert Fergusson
- Revenge Tragedy
- Richardson, Samuel
- Rise of the Novel in Britain, 1660–1780, The
- Robin Hood Literature
- Romance, Medieval English
- Romanticism
- Ruskin, John
- Science Fiction
- Scott, Walter
- Shakespeare, William
- Shaw, George Bernard
- Shelley, Percy Bysshe
- Sidney, Mary, Countess of Pembroke
- Sinclair, Iain
- Sir Gawain and the Green Knight
- Smollett, Tobias
- Sonnet and Sonnet Sequence
- Spenser, Edmund
- Sterne, Laurence
- Swift, Jonathan
- Synge, John Millington
- Thomas, Dylan
- Thomas, R. S.
- Tóibín, Colm
- Travel Writing
- Trollope, Anthony
- Tudor Literature
- Twenty-First-Century Irish Prose
- Urban Literature
- Utopian and Dystopian Literature to 1800
- Vampire Fiction
- Verse Satire from the Renaissance to the Romantic Period
- Webster, John
- Welsh, Irvine
- Welsh Poetry, Medieval
- Welsh Writing Before 1500
- Wilmot, John, Second Earl of Rochester
- Wollstonecraft, Mary
- Wollstonecraft Shelley, Mary
- Wordsworth, William
- Writing and Evolutionary Theory
- Wulfstan, Archbishop of York
- Wyatt, Thomas
- Yeats, W. B.
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [66.249.64.20|185.66.14.133]
- 185.66.14.133
Website navigation
Shakespeare's life.
19th-century portrait of Shakespeare with his family at home in Stratford
William Shakespeare: A biography
Since William Shakespeare lived more than 400 years ago, and many records from that time are lost or never existed in the first place, we don’t know everything about Shakespeare’s life. For example, we know that he was baptized in Stratford-upon-Avon, 100 miles northwest of London, on April 26, 1564. But we don’t know his exact birthdate, which must have been a few days earlier.
We do know that Shakespeare’s life revolved around two locations: Stratford and London. He grew up, had a family, and bought property in Stratford, but he worked in London, the center of English theater. As an actor, a playwright, and a partner in a leading acting company, he became both prosperous and well-known. Even without knowing everything about his life, fans of Shakespeare have imagined and reimagined him according to their own tastes.
Looking for more in-depth information? Need something you can cite? Read an essay about Shakespeare’s life from the Folger Shakespeare Editions. Read essay
Primary sources
Visit Shakespeare Documented to see primary-source materials documenting Shakespeare’s life. This online resource of items from the Folger and other institutions brings together all known manuscript and print references to Shakespeare and his works, as well as additional references to his family, in his lifetime and shortly thereafter.
Early life: Birth and childhood
William Shakespeare was probably born on about April 23, 1564, the date that is traditionally given for his birth. He was John and Mary Shakespeare’s oldest surviving child; their first two children, both girls, did not live beyond infancy. Growing up as the big brother of the family, William had three younger brothers, Gilbert, Richard, and Edmund, and two younger sisters: Anne, who died at seven, and Joan.
Their father, John Shakespeare, was a leatherworker who specialized in the soft white leather used for gloves and similar items. A prosperous businessman, he married Mary Arden, of the prominent Arden family. John rose through local offices in Stratford, becoming an alderman and eventually, when William was five, the town bailiff—much like a mayor. Not long after that, however, John Shakespeare stepped back from public life; we don’t know why.
Shakespeare, as the son of a leading Stratford citizen, almost certainly attended Stratford’s grammar school. Like all such schools, its curriculum consisted of an intense emphasis on the Latin classics, including memorization, writing, and acting classic Latin plays. Shakespeare most likely attended until about age 15.

A horn book in the Folger collection, similar to one that Shakespeare might have learned to read from
Marriage (to Anne Hathaway) and children
A few years after he left school, in late 1582, William Shakespeare married Anne Hathaway. She was already expecting their first-born child, Susanna, which was a fairly common situation at the time. When they married, Anne was 26 and William was 18. Anne grew up just outside Stratford in the village of Shottery. After marrying, she spent the rest of her life in Stratford.
In early 1585, the couple had twins, Judith and Hamnet, completing the family. In the years ahead, Anne and the children lived in Stratford while Shakespeare worked in London, although we don’t know when he moved there. Some later observers have suggested that this separation, and the couple’s relatively few children, were signs of a strained marriage, but we do not know that, either. Someone pursuing a theater career had no choice but to work in London, and many branches of the Shakespeares had small families.
Shakespeare’s only son, Hamnet, died in 1596 at the age of 11. His older daughter Susanna later married a well-to-do Stratford doctor, John Hall. Their daughter Elizabeth, Shakespeare’s first grandchild, was born in 1608. In 1616, just months before his death, Shakespeare’s daughter Judith married Thomas Quiney, a Stratford vintner. The family subsequently died out, leaving no direct descendants of Shakespeare.
London theater
For several years after the birth of Judith and Hamnet in 1585, nothing is known for certain of Shakespeare’s activities: how he earned a living, when he moved from Stratford, or how he got his start in the theater.
Following this gap in the record, the first definite mention of Shakespeare is in 1592 as an established London actor and playwright, mocked by a contemporary as a “Shake-scene.” The same writer alludes to one of Shakespeare’s earliest history plays, Henry VI, Part 3 , which must already have been performed. The next year, in 1593, Shakespeare published a long poem, Venus and Adonis . The first quarto editions of his early plays appeared in 1594.
For more than two decades, Shakespeare had multiple roles in the London theater as an actor, playwright, and, in time, a business partner in a major acting company, the Lord Chamberlain’s Men (renamed the King’s Men in 1603). Over the years, he became steadily more famous in the London theater world; his name, which was not even listed on the first quartos of his plays, became a regular feature—clearly a selling point—on later title pages.
Final years and death
Shakespeare prospered financially from his partnership in the Lord Chamberlain’s Men (later the King’s Men), as well as from his writing and acting. He invested much of his wealth in real-estate purchases in Stratford and bought the second-largest house in town, New Place, in 1597.
Among the last plays that Shakespeare worked on was The Two Noble Kinsmen , which he wrote with a frequent collaborator, John Fletcher, most likely in 1613. He died on April 23, 1616—the traditional date of his birthday, though his precise birthdate is unknown. We also do not know the cause of his death. His brother-in-law had died a week earlier, which could imply infectious disease, but Shakespeare’s health may have had a longer decline.
The memorial bust of Shakespeare at Holy Trinity Church in Stratford is considered one of two authentic likenesses, because it was approved by people who knew him. The other such likeness is the engraving by Martin Droeshout in the 1623 First Folio edition of Shakespeare’s plays, produced seven years after his death by his friends and colleagues from the King’s Men.
View a timeline of Shakespeare’s life with links to key supporting documents on Shakespeare Documented .
View timeline

The bust of Shakespeare in the Folger Reading Room is a copy of the statue at Holy Trinity Church in Stratford.
Frequently asked questions
Why did shakespeare leave his wife his “second best bed”.
William Shakespeare wrote in his last will and testament, dated March 25, 1616, “Item I gyve unto my wife my second best bed with the furniture” (furniture is used to refer to the curtains and bedcover which formed part of the complete bed).
This was not an unusual bequest, nor was it likely to have been intended as a snub. The best bed was usually regarded as an heirloom piece, to be passed to the heir rather than the spouse. It is also probable that the best bed would have been reserved for guests, meaning the “second best” was the bed that William and Anne shared.
What did Shakespeare’s son die of?
We don’t really know how Shakespeare’s young son Hamnet died. He had a twin sister named Judith, who lived to adulthood and married, but Hamnet died at the age of 11 and a half. Child mortality was high in the 16th century; there were no antibiotics and many childhood diseases might therefore prove fatal, such as scarlet fever, whooping cough, diphtheria, and even measles. He was buried on August 11, 1596.
What is the inscription on Shakespeare’s grave?
GOOD FREND FOR JESUS SAKE FORBEARE, TO DIGG THE DUST ENCLOASED HEARE: BLESTE BE Ye [the] MAN Yt [that] SPARES THES STONES, AND CURST BE HE Yt [that] MOVES MY BONES.
Did Shakespeare have a coat of arms?
Yes, William’s father, John Shakespeare, was granted a coat of arms in 1596. It was disputed in 1602 by York Herald, Ralph Brooke, saying that the arms were too similar to existing coats of arms, and that the family was unworthy. However, the challenge was unsuccessful, as the Shakespeare coat of arms appears in later heraldic collections and on William Shakespeare’s funeral monument in Holy Trinity Church, Stratford-upon-Avon.
Does Shakespeare have descendants?
William Shakespeare and Anne Hathaway had three children. The eldest, Susanna, was baptized on May 26, 1583, and married John Hall in 1607. They had one child, Elizabeth, in 1608. Elizabeth was married twice, to Thomas Nash in 1626, and to John Bernard in 1649. However, she had no children by either husband.
William and Anne also had twins, Judith and Hamnet, who were baptized on February 2, 1585. Hamnet died at age 11 and a half. Judith married Thomas Quiney in 1616, and the couple had three sons: Shakespeare Quiney, who died in infancy, and Richard and Thomas, who both died in 1639 within a month of each other. Since neither of the boys married, there is no possibility of any legitimate descendants from Shakespeare’s line.
It is possible, however, to claim a relationship to Shakespeare through his sister, Joan. She married William Hart some time before 1600, and there are many descendants of this marriage alive today, in both the male and female lines.
Stay connected
Find out what’s on, read our latest stories, and learn how you can get involved.

- Literature & Fiction
- History & Criticism

Enjoy fast, free delivery, exclusive deals, and award-winning movies & TV shows with Prime Try Prime and start saving today with fast, free delivery
Amazon Prime includes:
Fast, FREE Delivery is available to Prime members. To join, select "Try Amazon Prime and start saving today with Fast, FREE Delivery" below the Add to Cart button.
- Cardmembers earn 5% Back at Amazon.com with a Prime Credit Card.
- Unlimited Free Two-Day Delivery
- Streaming of thousands of movies and TV shows with limited ads on Prime Video.
- A Kindle book to borrow for free each month - with no due dates
- Listen to over 2 million songs and hundreds of playlists
- Unlimited photo storage with anywhere access
Important: Your credit card will NOT be charged when you start your free trial or if you cancel during the trial period. If you're happy with Amazon Prime, do nothing. At the end of the free trial, your membership will automatically upgrade to a monthly membership.

Buy new: $19.15 $19.15 FREE delivery: Tuesday, April 9 on orders over $35.00 shipped by Amazon. Ships from: Amazon Sold by: numberonestore
Return this item for free.
Free returns are available for the shipping address you chose. You can return the item for any reason in new and unused condition: no shipping charges
- Go to your orders and start the return
- Select the return method
Buy used: $15.25
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is a service we offer sellers that lets them store their products in Amazon's fulfillment centers, and we directly pack, ship, and provide customer service for these products. Something we hope you'll especially enjoy: FBA items qualify for FREE Shipping and Amazon Prime.
If you're a seller, Fulfillment by Amazon can help you grow your business. Learn more about the program.
Other Sellers on Amazon

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player
Follow the author

Shakespeare: The Biography Paperback – Illustrated, November 14, 2006
Purchase options and add-ons.
A TIMES LITERARY SUPPLEMENT BEST BOOK OF THE YEAR Drawing on an exceptional combination of skills as literary biographer, novelist, and chronicler of London history, Peter Ackroyd surely re-creates the world that shaped Shakespeare--and brings the playwright himself into unusually vivid focus. With characteristic narrative panache, Ackroyd immerses us in sixteenth-century Stratford and the rural landscape–the industry, the animals, even the flowers–that would appear in Shakespeare’s plays. He takes us through Shakespeare’s London neighborhood and the fertile, competitive theater world where he worked as actor and writer. He shows us Shakespeare as a businessman, and as a constant reviser of his writing. In joining these intimate details with profound intuitions about the playwright and his work, Ackroyd has produced an altogether engaging masterpiece.
- Print length 572 pages
- Language English
- Publisher Anchor
- Publication date November 14, 2006
- Dimensions 5.22 x 1.33 x 7.87 inches
- ISBN-10 9781400075980
- ISBN-13 978-1400075980
- See all details

Frequently bought together

Similar items that may ship from close to you

Editorial Reviews
From the back cover, about the author.
PETER ACKROYD is the bestselling writer of both fiction and nonfiction, most notably the definitive history of London, London, The Biography . His most recent books include The Lambs of London and J.M.W. Turner, the second biography in the Ackroyd Brief Lives series. He has also written full-scale biographies of Dickens, Blake, and Thomas More and the novels The Clerkenwell Tales, The Trial of Elizabeth Cree, Milton in America, and The Plato Papers . He has won the Whitbread Award for Biography, the Royal Society of Literature Award under the William Heinemann Bequest (jointly), the Somerset Maugham Award, the South Bank Award for Literature, the James Tait Black Memorial Prize, and The Guardian fiction prize. He lives in London.
Excerpt. © Reprinted by permission. All rights reserved.
Product details.
- ASIN : 140007598X
- Publisher : Anchor (November 14, 2006)
- Language : English
- Paperback : 572 pages
- ISBN-10 : 9781400075980
- ISBN-13 : 978-1400075980
- Item Weight : 1.08 pounds
- Dimensions : 5.22 x 1.33 x 7.87 inches
- #255 in Shakespeare Literary Criticism
- #733 in British & Irish Literary Criticism (Books)
- #3,322 in Author Biographies
About the author
Peter ackroyd.
Peter Ackroyd, (born 5 October 1949) is an English biographer, novelist and critic with a particular interest in the history and culture of London. For his novels about English history and culture and his biographies of, among others, William Blake, Charles Dickens, T. S. Eliot and Sir Thomas More, he won the Somerset Maugham Award and two Whitbread Awards. He is noted for the volume of work he has produced, the range of styles therein, his skill at assuming different voices and the depth of his research.
He was elected a fellow of the Royal Society of Literature in 1984 and appointed a Commander of the Order of the British Empire in 2003.
Bio from Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
Top reviews from the United States
There was a problem filtering reviews right now. please try again later..
Top reviews from other countries
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Start Selling with Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Host an Amazon Hub
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Your Ads Privacy Choices
Biography of William Shakespeare, History's Most Famous Playwright
His plays and sonnets are still studied and performed to this day
fitopardo.com / Moment / Getty Images
- Shakespeare's Life and World
- Best Sellers
- Classic Literature
- Plays & Drama
- Short Stories
- Children's Books
- M.A., Theater Studies, Warwick University
- B.A., Drama and English, DeMontfort University
William Shakespeare (April 23, 1564–April 23, 1616) wrote at least 37 plays and 154 sonnets , which are considered among the most important and enduring ever written. Although the plays have captured the imagination of theatergoers for centuries, some historians claim that Shakespeare didn’t actually write them .
Amazingly, little is known about Shakespeare’s life. Even though he is the world’s most famous and popular playwright , historians have had to fill in the gaps between the handful of surviving records from Elizabethan times .
Fast Facts: William Shakespeare
- Known For : One of history's most famous playwrights, who wrote at least 37 plays, which are still studied and performed to this day, as well as 154 sonnets, which are also highly regarded
- Also Known As : The Bard
- Born : April 23, 1564 in Stratford-upon-Avon, England
- Parents : John Shakespeare, Mary Arden
- Died : April 23, 1616 in Stratford-upon-Avon
- Published Works : " Romeo and Juliet" (1594–1595), "A Midsummer Night’s Dream" (1595–1596), " Much Ado About Nothing " (1598–1599), "Henry V" (1598–1599), " Hamlet " 1600–1601, "King Lear" (1605–1606), "Macbeth" ( 1605–1606), "The Tempest" (1611–1612)
- Awards and Honors : After Shakespeare's death, a funerary monument was erected to honor him at Holy Trinity Church in Stratford-upon-Avon, where he is buried. It depicts a half-effigy of The Bard in the act of writing. Numerous statues and monuments have been erected around the world to honor the playwright.
- Spouse : Anne Hathaway (m. Nov. 28, 1582–April 23, 1616)
- Children : Susanna, Judith and Hamnet (twins)
- Notable Quote : "All the world's a stage, and all the men and women merely players: they have their exits and their entrances; and one man in his time plays many parts, his acts being seven ages."
Early Years
Shakespeare was probably born on April 23, 1564 , but this date is an educated guess because we only have a record of his baptism three days later. His parents, John Shakespeare and Mary Arden, were successful townsfolk who moved to a large house in Henley Street, Stratford-upon-Avon, from the surrounding villages. His father became a wealthy town official and his mother was from an important, respected family.
It is widely assumed that Shakespeare attended the local grammar school where he would have studied Latin, Greek, and classical literature . His early education must have made a huge impact on him because many of his plots draw on the classics.
Shakespeare’s Family
At age 18, on November 28, 1582, Shakespeare married Anne Hathaway from Shottery, who was already pregnant with their first daughter. The wedding would have been arranged quickly to avoid the shame of having a child born out of wedlock. Shakespeare fathered three children, Susanna, born in May 1583 but conceived out of wedlock, and Judith and Hamnet, twins who were born in February 1585.
Hamnet died in 1596 at age 11. Shakespeare was devastated by the death of his only son, and it is argued that "Hamlet," written four years later, is evidence of this.
Theater Career
At some point in the late 1580s, Shakespeare made the four-day ride to London, and by 1592 had established himself as a writer. In 1594, an event occurred that changed the course of literary history: Shakespeare joined Richard Burbage’s acting company and became its chief playwright for the next two decades. Here, Shakespeare was able to hone his craft, writing for a regular group of performers.
Shakespeare also worked as an actor in the theater company , although the lead roles were always reserved for Burbage himself. The company became very successful and often performed in front of the Queen of England, Elizabeth I. In 1603, James I ascended the throne and granted his royal patronage to Shakespeare’s company, which became known as The King’s Men.
Shakespeare the Gentleman
Like his father, Shakespeare had excellent business sense. He bought the largest house in Stratford-upon-Avon by 1597, owned shares in the Globe Theater, and profited from some real estate deals near Stratford-upon-Avon in 1605. Before long, Shakespeare officially became a gentleman, partly due to his own wealth and partly due to inheriting a coat of arms from his father who died in 1601.
Later Years and Death
Shakespeare retired to Stratford in 1611 and lived comfortably off his wealth for the rest of his life. In his will, he bequeathed most of his properties to Susanna, his eldest daughter, and some actors from The King’s Men. Famously, he left his wife his “second-best bed” before he died on April 23, 1616 . (This date is an educated guess because we only have a record of his burial two days later).
If you visit Holy Trinity Church in Stratford-upon-Avon, you can still view his grave and read his epitaph engraved into the stone:
Good friend, for Jesus' sake forbear To dig the dust enclosed here. Blessed be the man that spares these stones, And cursed be he that moves my bones.
More than 400 years after his death, Shakespeare's plays and sonnets still hold a special place in theaters, libraries, and schools around the world. "His plays and sonnets have been performed in nearly every major language on every continent," notes Greg Timmons writing on Biography.com.
In addition to the legacy of his plays and sonnets, many of the words and phrases Shakespeare created infuse dictionaries today and are embedded in modern English, including these sayings from some of his plays:
- All that glitters isn't gold (" The Merchant of Venice ")
- All's well that ends well (" All's Well that Ends Well ")
- To be-all and the end-all (" Macbeth ")
- Break the ice (" The Taming of the Shrew )
- We have seen better days (" As You Like It ")
- Brave new world (" The Tempest ")
- Brevity is the soul of wit (" Hamlet ")
- Cruel to be kind ("Hamlet")
- It's Greek to me (" Julius Caesar ")
- Something wicked this way comes ("Macbeth")
- Star-crossed lovers (" Romeo and Juliet ")
- Wild-goose chase ("Romeo and Juliet")
- The world is my oyster (" The Merry Wives of Windsor ")
Few writers, poets, and playwrights—and Shakespeare was all three—have had the influence on culture and learning that Shakespeare has. With luck, his plays and sonnets may still be revered and studied four centuries from now.
- “ IWonder - William Shakespeare: The Life and Legacy of England's Bard. ” BBC.
- “ Shakespeare's Words & Phrases. ” Shakespeare Birthplace Trust.
- Timmons, Greg. “ William Shakespeare's 400th Anniversary: The Life & Legacy of The Bard. ” Biography.com , A&E Networks Television, 2 Nov. 2018.
- “ Who Was William Shakespeare? Everything You Need to Know. ” Childhood, Life Achievements & Timeline , thefamouspeople.com.
- “ William Shakespeare Quotes. ” BrainyQuote , Xplore.
- Facts About Shakespeare
- A Timeline of William Shakespeare's Life
- Fun and Creative Ways to Celebrate Shakespeare's Birthday
- How Did William Shakespeare Die?
- William Shakespeare's School Life, Childhood, and Education
- Shakespeare's Brothers and Sisters
- Cervantes and Shakespeare: What They Had in Common (and Didn’t)
- The Influence of the Renaissance in Shakespeare's Work
- Was Shakespeare Gay?
- An Introduction to Shakespearean Sonnets
- William Shakespeare's Most Famous Plays
- William Shakespeare's Family
- Everything You Need to Know About Shakespeare's Plays
- Study Shakespeare
- A Complete List of Shakespeare’s Plays
- List of Phrases Shakespeare Invented
Advertisement
Supported by
A Scholarly Analysis of Shakespeare’s Life That Reads Like a Detective Story
- Share full article

- Apple Books
- Barnes and Noble
- Books-A-Million
When you purchase an independently reviewed book through our site, we earn an affiliate commission.
By James Shapiro
- Nov. 23, 2021
THE PRIVATE LIFE OF WILLIAM SHAKESPEARE By Lena Cowen Orlin
Much of the evidence documenting Shakespeare ’s life wasn’t discovered until the late 18th or early 19th century, and comes packaged in the assumptions of those who made these finds. We have been told that his marriage to an older woman was an unhappy one, that Shakespeare’s bequest to his wife of a “second-best bed” confirms how “little he esteemed her,” and that the “Birthplace,” his house on Henley Street, a mecca for literary pilgrims, has remained virtually unchanged since Shakespeare’s infancy. Over the past 200 years these and similar claims have hardened into fact and have become enshrined in popular biographies.
In “The Private Life of William Shakespeare,” Lena Cowen Orlin has re-examined all of the documentary evidence. She reads it afresh, along with thousands of contemporary wills and local records that provide context for those in which Shakespeare is mentioned. Anyone who has ever struggled to decipher Elizabethan “secretary hand” will know how daunting this task has been. The great and lasting result of her labors is how punishingly she demolishes shoddy claims and biased inferences that have distorted our understanding of Shakespeare’s life.
Shakespeare was born and raised in Stratford-upon-Avon, where he married Anne Hathaway at the age of 18, had three children with her and left town — only returning for good late in life. He spent the intervening years, roughly half his lifetime, in London, where he acted and wrote plays. He didn’t travel back and forth much, reportedly once a year, and was unlikely, Orlin writes, to have attended the funeral in Stratford of his son, Hamnet, or of either of his parents.
Biographers confronted with the mystery of “How did Shakespeare become Shakespeare?” split into two groups: those who see his early years in his hometown as formative, and those (myself included) who place greater weight on his experiences in London. Orlin, whose Shakespeare had a “persistent allegiance to his hometown,” and whose choices there, she argues, determined the trajectory of his life, belongs to the Stratford camp. Her title is somewhat misleading: “By ‘private life,’” she writes, “I mean Shakespeare’s family life in Stratford.” Readers eager for revelations about who were Shakespeare’s friends and lovers, or what were his religious and political convictions (what we ordinarily mean when we speak of someone’s private life), will not find answers here.
“Neither a literary biography nor a full biography,” this book looks more narrowly at what surviving documents tell us, and, when their trail runs dry, what documents about his neighbors might reveal about events that defined Shakespeare’s Stratford life: his father’s financial collapse, his marriage, his homes (including the “Birthplace,” likely damaged by fire in the 1590s, then rebuilt), his will and his memorial. Though most of it consists of dense scholarly analysis, it reads like a detective story in which a skilled investigator returns to a cold case.
It amounts to a revisionist portrait of the artist. The transgressive image of Shakespeare circulating in recent years — cosmopolitan, perhaps secretly Catholic, most likely gay or bisexual, eager to flee Stratford — is replaced here by a Shakespeare who is “a family man” in a close economic partnership with his wife. He is especially devoted to his father, whose fall from the height of Stratford’s leadership to a man who was afraid to leave his house for fear of arrest for debt was, for Orlin, “the defining event” of Shakespeare’s private life, from which “all else followed.” She interprets Shakespeare’s marriage at a young age (which would have brought to an end any apprenticeship and precluded as well a university education) as an act that helped restore his family’s fortunes. Most scholars have read Shakespeare’s last will and testament as at best chilly, especially when it came to his family. But Orlin sees it otherwise. While it was not, like many Jacobean wills, an “expressive” one, she shows how each gift that Shakespeare specifies, including apparel, sword, bowl and that notorious bed, shares “the imprint of an unnamed grief.”
She also shows that much of what we take as fact about Shakespeare’s life hangs by the slenderest of archival threads. Anne Hathaway’s baptismal record does not survive, and the only reason for believing she was eight years older than Shakespeare is the number that appears on her memorial brass — often enough, Orlin shows, imprecisely remembered or rendered. In her assiduous research Orlin came upon a baptismal record from 1566 for a Johanna Hathaway, daughter (as Shakespeare’s wife was) to a Richard Hathaway of Shottery. Orlin doesn’t push this possibility too hard, but if this was the woman Shakespeare married — her first name inaccurately transcribed — Anne might have been two years younger than her husband.
Three contemporary images of Shakespeare are widely accepted as authoritative. One is the awkwardly executed woodcut that appears in the 1623 First Folio. Another is the romantic Chandos portrait now in the National Portrait Gallery. These two are endlessly reproduced. Not the third, an effigy in painted limestone in Stratford’s Holy Trinity Church, in which Shakespeare looks like — as the scholar John Dover Wilson put it — a “self-satisfied pork butcher.” Orlin’s account of this monument is definitive. She sends packing the “authorship skeptics” for whom a conspiratorial cover-up accounts for the differences between 17th-century sketches of this memorial and the frequently repaired and looted effigy (from which the actor David Garrick reputedly stole the “right forefinger”). She goes on to suggest that Shakespeare likely commissioned the effigy and had met Nicholas Johnson, the artist who made it. If so, like it or not, this is how Shakespeare wanted to be remembered. Her account, detailed and dazzling, also left me melancholy, for all too soon, given cutbacks in funding and training, this kind of scholarship may no longer be possible.
Shakespeare biography is often marked by overreach, and Orlin is not immune. An academic herself, she can’t help recasting Shakespeare as one, urging us to “picture Shakespeare participating in the intellectual culture of Oxford” and asserting that “Shakespeare is nearly certain to have taken in lectures and sermons in college chapels.” There is no hard evidence given for these claims. And having argued that Shakespeare had a study in New Place, the large house he purchased in Stratford, she can’t resist fantasizing that this is where he wrote his late plays: “How many of his characters and episodes developed out of the scenes that unfolded on the streets below him as he wrote in the western light of the study window?” Her source? The gossip-hunting vicar of Stratford from the early 1660s, John Ward. Orlin’s meticulous handling of archival material fails her here, as her eagerness to encroach upon the London Shakespeare upends her usual accuracy. Ward never wrote that Shakespeare “in his elder days lived at Stratford, and supplied the stage with two plays every year.” He in fact jotted down two separate anecdotes, which Orlin then combines, linking them with a comma (those who are curious can consult a facsimile at the Folger Shakespeare Library’s site, “Shakespeare Documented” ). Orlin knows that late in his career Shakespeare collaborated with other dramatists, working with John Fletcher on his last three: “Henry VIII,” “The Two Noble Kinsmen” and the lost “Cardenio.” You don’t write plays with co-authors who live a three days’ ride away. These are unfortunate missteps in an otherwise impressive and valuable book, a biography that will lead many to revise their classroom lectures.
James Shapiro teaches at Columbia. His book “Shakespeare in a Divided America” was one of the Book Review’s 10 Best Books of 2020.
THE PRIVATE LIFE OF WILLIAM SHAKESPEARE By Lena Cowen Orlin Illustrated. 430 pp. Oxford University Press. $40.
Explore More in Books
Want to know about the best books to read and the latest news start here..
James McBride’s novel sold a million copies, and he isn’t sure how he feels about that, as he considers the critical and commercial success of “The Heaven & Earth Grocery Store.”
How did gender become a scary word? Judith Butler, the theorist who got us talking about the subject , has answers.
You never know what’s going to go wrong in these graphic novels, where Circus tigers, giant spiders, shifting borders and motherhood all threaten to end life as we know it .
When the author Tommy Orange received an impassioned email from a teacher in the Bronx, he dropped everything to visit the students who inspired it.
Do you want to be a better reader? Here’s some helpful advice to show you how to get the most out of your literary endeavor .
Each week, top authors and critics join the Book Review’s podcast to talk about the latest news in the literary world. Listen here .

William Shakespeare Biography
This page offers a complete biography of Shakespeare, from birth to death. Read the whole William Shakespeare biography , or skip to the section of Shakespeare’s life you’re most interested in:
Shakespeare’s Birth and Family Shakespeare’s Childhood & Education Shakespeare’s Marriage & Children Shakespeare’s Lost Years Shakespeare’s London Years Shakespeare’s Retirement Shakespeare’s Death
A Very Brief William Shakespeare Biography
- Parents: John Shakespeare & Mary Shakespeare (nee Arden).
- Date of Birth: Generally accepted as 23rd April 1564. Shakespeare was baptised on 26th April, 1564.
- Wife: Anne Hathaway (married 1582).
- Children : Susanna (born 1583), Hamnet and Judith (twins, born 1585).
- Resided: Born and raised in Stratford-Upon-Avon. Prime working years spent away from family in London. Returned to family in Stratford-Upon-Avon upon retirement.
- Career: Writer, actor, theatre owner and producer.
- Body of Work : 37 plays. 149 sonnets. 2 long narrative poems.
- Died: 23 April 1616, aged 52. Buried at Holy Trinity Church in Stratford-upon-Avon . Read 50 fun facts about Shakespeare

The Chandos portrait of William Shakespeare
Shakespeare’s Birth and Family
Shakespeare was the third of the eight children born to John and Mary Shakespeare of Stratford-upon-Avon on April 23rd 1564.
John Shakespeare ran his own business as a glove maker and a wool dealer. He held local public positions and was a bailiff (like a mayor) in the town council. After 1567 it is alleged that he was in financial difficulties. In 1557 John married Mary Arden who had no formal education at all. John and Mary had lost two daughters prior to William’s birth, leaving him as their oldest surviving child. William’s younger siblings were Gilbert (born in 1566), Joan (1569), Anne (1571), Richard (1574) and Edmund (1580). Anne died at the age of eight, but William’s four other younger siblings lived into adulthoods.
Shakespeare’s family lived in a townhouse on Henley Street in the centre of Stratford-Upon-Avon. John used one of his downstairs rooms as a workshop for his glove business, displaying his gloves on his house windowsill for passers-by to peruse and buy. Read more about Shakespeare’s birthplace .
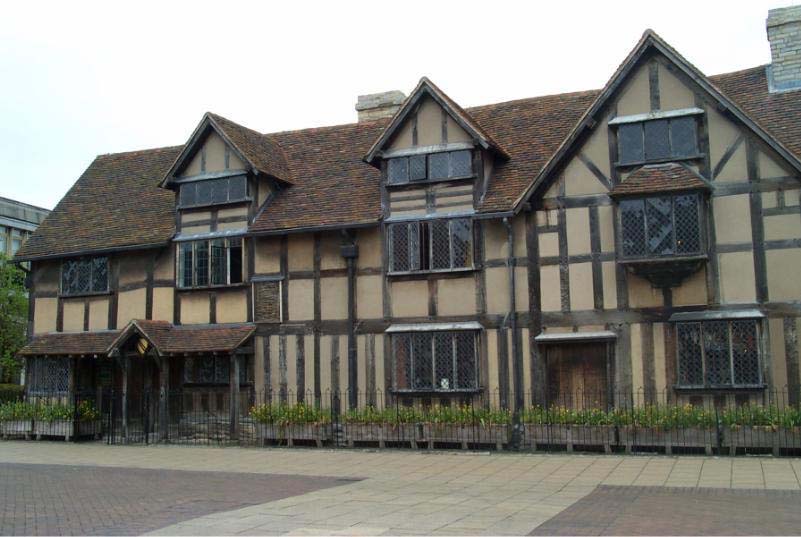

Shakespeare’s family home on Henley Street, Stratford-upon-Avon
Shakespeare’s Childhood and Education
During Shakespeare’s time it was typical for boys to start their education at grammar school at seven and be taught a curriculum with Latin at is centre. Children would be expected to learn long passages of prose and poetry. In addition, children were drilled in grammar, logic, rhetoric, arithmetic and astronomy. Children of public officials received free tuition. Girls did not receive a school education.
It is likely that William lived with his family and was taught according to the above principles at his local grammar school. This was called The King’s New School , and was just a five-minute walk from his home on Henley Street. When William was fourteen his father lost his public position, so it’s probable that William left school and joined his father in business, making and selling gloves. There is no record of Shakespeare going to university. His contemporary Christopher Marlowe did go to Cambridge, but most playwrights, including Ben Johnson , did not.
To get a feel for Shakespeare’s childhood it’s interesting to note that when Shakespeare was a child water was not clean enough to drink. Attitudes towards hygiene differed hugley to our modern understanding of cleanliness., and tt’s believed that in Tudor times bathing occurred only once a year – probably in May. After the water had been fetched it would be boiled and poured into a large barrel or tub. The father bathed first, followed by any other men who lived in the house, then the women, and finally the children, in order of their age. Talking of such issues, the toilet facilities were quite basic with a simple pewter chamber-pot (a wide jug with a handle) serving as a toilet to be used indoors. Outside, garden privies would consist of a wooden seat with a hole cut in it, sitting over a cess-pit or open sewer.
Read more about Shakespeare’s early childhood >>
Read more about Shakespeare’s teen & school years >>

Shakespeare’s likely classroom at The King’s New School
Shakespeare’s Marriage and Children
Parish records show that when Shakespeare was 18 years old he married Anne Hathaway, a 26 year old, wealthy farmer’s daughter , in Canterbury Province, Worcester.
Anne was three months pregnant when they married, with their first daughter, Susanna, born on the 26th May 1583. William and Anne went on to have twins Hamnet (a boy) and Judith (a girl), born on the 2nd February 1585. Hamnet died of unknown causes at 11 years old, but William’s daughters and wife outlived him. Judith went on to marry Thomas Quinney in 1616 and had three sons: Shakespeare, Richard, and Thomas. Shakespeare died in infancy and Richard and Thomas both died bachelors in 1639 leaving behind no legitimate descendants. There are legitimate descendants stemming from Shakespeare’s sister Joan who married William Hart some time before 1600.

Portrait of Anne Hathaway, Shakespeare’s wife
Shakespeare’s Lost Years
The seven year period after the birth of Hamnet and Judith is known as Shakespeare’s ‘lost years’ as there are no recordings about him, other than one mention of him visiting London in 1616 to see his son-in-law, John Hall.
Speculation about this time is rife. One prominent speculative theory is that Shakespeare fled from Stratford to avoid prosecution as a poacher. This theory could explain why he left his wife and children in Stratford and reappeared 90 miles away in London. Other theories are that Shakespeare toured with an acting troupe possibly in Italy. This latter theory is given weight as 14 plus of his plays include Italian settings, and a 16th Century guest book in Rome signed by pilgrims includes three cryptic signings that some attribute to Shakespeare. This is not a watertight argument though because Italian literature would have been widely read at the time. In addition, there is speculation that Shakespeare met John Florio , an apostle of Italian culture in England and tutor to Shakespeare’s patron; Henry Wriothesley, the Earl of Southampton . The possibility that Shakespeare was a soldier has also been debated widely but there is no proof to support this claim.
The truth is though that no one actually knows where Shakespeare lived or worked. What historians are certain of is that during this time Shakespeare left behind the image of a country youth and re-emerged as a playwright and businessman, so at some point during this time he learned his trade as a writer in London.
Shakespeare in London
The late sixteenth century and early seventeenth century is referred to as the golden age of English drama, due to the popularity of theatre, and volume of plays produced at that time. There was fierce competition among the twenty or so theatres in London, keeping scores of writers busy churning out new plays. Shakespeare became one of those writers, though we are not sure exactly how this occurred.
It seems that Shakespeare did not maintain a London household, but lived in several lodgings with landlords and other lodgers during his London years. He was always within walking distance of the theatre zone, so we can imagine him walking to work every day.
By the early 1590s, court records show Shakespeare was living somewhere in Bishopsgate, London. By then he had written Two Gentlemen of Verona , Love’s Labours Lost and A Midsummer Night’s Dream , Romeo and Julie t, Richard II , and The Merchant of Venice . He seems to have been interested in writing poems: in addition to his day job of writing plays – he also wrote his two long poems, Venus and Adonis and The Rape of Lucrece . Not only that, but this is the period when he started work on his sonnets .
In 1595 documents show that Shakespeare was a shareholder in the Lord Chamberlain’s Men , along with William Kempe and Richard Burbage . Shakespeare was involved with this company of actors in London for most of his career, as actor, producer, theatre owner and, of course, a very popular playwright.
It’s evident that Shakespeare was earning good money from his theatre business, as civil records show that in 1597 he bought New Place, one of Stratford’s biggest houses, and moved his family into it. In this same year, his son Hamnet died of unknown causes, aged eleven.
By 1599 Shakespeare was living in Bankside, on the south side of The Thames near the infamous Clink Prison. It was in this area Shakespeare and his business partners Kempe and Burbage built their own theater on the south bank of The Thames river, which they called the Globe Theater . and tt’s likely Shakespeare moved to Bankside to be near to the building site. Shakespeare’s playwriting would have been a necessity to provide material to fill his company’s new theatre every day. Between 1599 and 1604 he wrote at least seven plays, including Henry IV Parts 1 and 2 , The Merry Wives of Windsor , As You Like It , Much Ado About Nothing , Henry V and Julius Caesar .
Records show that in 1604 Shakespeare moved back to the City of London and rented a room in the house in Cripplegate, near St Paul’s Cathedral. In 1605, Shakespeare purchased leases of real estate near Stratford for 440 pounds, which doubled in value and earned him an income of 60 pounds a year. This made him an entrepreneur as well as an artist, and scholars believe these investments gave him the time to write his plays uninterrupted.
Shakespeare lived in Cripplegate for about eight years writing many plays, including Twelfth Night , Hamlet , Troilus and Cressida , Alls Well That Ends Well , Measure for Measure , Othello , King Lear , Macbeth , Antony and Cleopatra , Coriolanus , Timon of Athens , Pericles , Cymbeline , The Winter’s Tale , and The Tempest .
In 1607 his older daughter, Susanna, married and his mother died the following year. His sonnets were published in 1609.
It was a four-day ride by horse from Stratford to London, so it’s believed that Shakespeare spent all of his time in London writing and acting except for the 40-day Lenten period when theatres were closed when he travelled back to stay in Stratford-upon-Avon.
A map of London in Shakespeare’s time
Shakespeare’s Retirement
After a glittering career as an actor, playwright, and theatre proprietor in London, Shakespeare ‘retired’ to Stratford sometime after 1611 whilst in his late 40s. He rejoined his wife and two surviving children. By this time he also had a granddaughter, Elizabeth, daughter of Judith.
Retirement for Shakespeare was not a matter of sitting around in slippers and letting the world pass him by. He had a portfolio of properties and many business interests, including some in the corn and malt trades. He also continued to make the occasional long journey to London. Before leaving London Shakespeare had built up a selection of plays that hadn’t yet been performed. These included The Winter’s Tale, Macbeth, The Tempest, and Cymbeline. It is likely that he visited London for some of these first performances, most probably those of The Tempest and The Winter’s Tale, which were performed to King James.
On June 29th, 1613 Shakespeare’s Globe Theatre was burnt down. It is likely that this event meant more time spent in London for Shakespeare. Shakespeare was definitely in Westminster on 11th May 1612 where he appeared as a witness in the case of Bellot v. Mountjoy . At one time Shakespeare had been a lodger in Christopher Mountjoy’s house in Cripplegate, and now Mountjoy was being sued by his son-in-law, Stephen Bellott for defaulting on a promised marriage settlement. Shakespeare had been involved in the dowry negotiations and so was called to give evidence in the case.
Shakespeare enjoyed visits from his many friends in the world of theatre, arts, and letters to his home in Stratford-upon-Avon. He continued to collaborate with younger playwrights , participating in the writing of Henry VIII , Two Noble Kinsmen , and also the lost play, Cardenio , with his friend John Webster .
Shakespeare’s Death
We aren’t sure of the exact date of his death but it is assumed, from a record of his burial two days later at Holy Trinity Church, Stratford-Upon-Avon that he died on his 52nd birthday on 23rd April 1616. His gravestone remains there and bears the following engraving:
Good frend for Jesus sake forbeare To digg the dust enclosed heare; Blese be ye man yt spares these stones And curst be he yt moves my bones
It is believed that Shakespeare’s death occurred in New House, where he would have been attended by his son-in-law, Dr John Hall, the local physician.
Most historians agree that in the 17th Century Stratford-Upon-Avon had a reputation for scandalous stories and rumours with no basis in fact. This means that we must be cautious in believing for certain the commonly held theory about the cause of Shakespeare’s death:
in 1661, many years after Shakespeare’s death John Ward, the vicar of Holy Trinity Church noted in his diary : “Shakespeare, Drayton, and Ben Jonson had a merry meeting, and it seems drank too hard; for Shakespeare died of a fever there contracted.” It is therefore often stated that Shakespeare died from a fever after a drinking binge with fellow playwrights Ben Jonson and Michael Drayton . There are other reports that Michael Drayton and Ben Johnson visited Shakespeare a week before he died and spent the evening eating and drinking together.
This may be true, but there is a further theory that Shakespeare was sick for over a month before he died. The evidence comes from the fact that on 25th March 1616 (just 4 weeks before his death) Shakespeare dictated his will – in keeping with the 17th Century tradition of drawing up wills on one’s deathbed. This points to the fact that Shakespeare was aware his life was coming to an end. Some scholars also point to his signature on his will being somewhat shaky, suggesting his frailty at the time. As an aside, there is lots of historical discussion and exploration about whether bequeathing his second-best bed to his wife Anne Hathaway was a slight against her or not. It probably wasn’t but we don’t know for sure.
Despite all of the theories, the cause of Shakespeare’s death at the age of just 52 will likely remain a mystery. Shakespeare died a grandfather after living a relatively long and healthy life where the average life expectancy was just 35.
Shakespeare was buried on 25th April, 1616, in Holy Trinity Church in Stratford.

William Shakespeare’s grave in Holy Trinity Church, complete with curse and flowers

Buy Peter Ackroyd’s “Shakespeare The Biography” on Amazon

Buy Michael Wood’s “In Search of Shakespeare” on Amazon

Buy Harold Bloom’s “Shakespeare, The Invention of Human” on Amazon

Buy Bill Bryson’s “Shakespeare” on Amazon
Read Our Favourite Shakespeare Biographies in Print
There are so many books out there about Shakespeare and his life, but these four below are our all-time favourites. Each one is readable, informative and well worth relaxing with for a few hours to get a deeper understanding about the man himself:
Author’s Notes
Despite William Shakespeare’s fame as a historical figure, there are very few hard facts known about him. Historians use the following primary sources to piece together his life:
- Shakespeare’s works — the plays, poems and sonnets.
- Official records such as church and court records ( available here ).
- Written commentary about Shakespeare and his work from contemporaries such as Robert Green and Ben Johnson.
Biographers over the years have amassed an immense amount of knowledge and information Some fact, some opinion. A key purpose of this biography of William Shakespeare has been to make clear what is supposition or assumption rather than fact. We acknowledge here our reference to the following established secondary sources:
Bill Bryson. Shakespeare. London. Wilkie Collins. 2016 Peter Ackroyd. Shakespeare the biography. London. Vintage 2006. https://www.shakespeare.org.uk/ https://www.rsc.org.uk/ https://www.folger.edu/ https://www.britannica.com/biography/William-Shakespeare/ http://theshakespeareblog.com/http://www.william-shakespeare.info/ https://www.gutenberg.org/files/ http://www.literarygenius.info/education-of-william-shakespeare.htm http://www.william-shakespeare.info/ http://www.shakespeare-online.com/biography/shakespeareeducation.html
As an Amazon Associate, we may earn a commission from qualifying purchases, at no additional cost to you.
Read More About Shakespeare’s Life
Shakespeare’s life | Shakespeare timeline | Shakespeare biography | Shakespeare’s early childhood | Shakespeare’s teenage years | Shakespeare’s lost years | Shakespeare’s London years | Shakespeare’s final years | Shakespeare’s death
Read More About Shakespeare’s Family
Shakespeare’s family | Shakespeare’s family tree | Shakespeare’s grandparents | Shakespeare’s parents | Mary Arden, Shakespeare’s mother | John Shakespeare, Shakespeare’s father | Anne Hathaway, Shakespeare wife | Shakespeare’s children | Judith Quiney | Hamnet Shakespeare | Shakespeare’s grandchildren
- Pinterest 0
thanks this biography helped me with a school project!
Same Here!! lol :D
this will help me with my school project for history and i have probably gone beyond what we have learent in school
WoW! Thanks alot!! I actually had to do reasearch on william shakesphere for school!!! :)
you spelled it wrong
More process information and knowledge in terms of facts and his plays is needed otherwise, this is one of the few websites helping me to do my presentation on Shakey! Thanks for the help!
You guys can add some more stuff to it. Although this proved to be helpful for me yet I’d say that more points about Shakespeare’s life can be added.
can’t find quiz
I have very recently discovered that my Great+ grandfather, Thomas Ffoxe, Jr. lived on Silver Street, which was only a block long, and on which Shakespeare lived 1602-1612. Thomas was baptized at St. Olave’s Church, which was Hugenot, or Scandinavian, in 1618. I am still researching to see if Thomas’ father of the same name lived there before him. This church was catecorner to the Mountjoy House, a headdress maker and shop, where Shakespeare lived as a lodger during this period.
Enjoyed reading this and thank you .
Leave a Reply
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Shakespeare biographies: the good, the Bard and the ugly
James Shapiro's Contested Will concentrates on the lunatic fringe of Shakespeare authorship theories – a fascinating topic, to be sure, if you admire snobbery, philistinism and ignorance.
But as it happens, Shakespeare biography is now (at least) 300 years old, and there have been plenty of bemusing, eccentric or downright surreal contributions to the field, even among those biographers who don't think Shakespeare was the Earl of Oxford. Crackpot theorising, outright fantasising and expressions of superimposed vanity (Shakespeare, c'est moi!) are all part of the fun. Take the following examples, for example: attempts at writing the ultimate writer's life, good, bad, indifferent, ugly, or just plain delusional. Further suggestions/angry objections welcome.
John Aubrey
According to Aubrey's Brief Lives , that fine blend of antiquarian notes and 17th-century table talk, Shakespeare's father was a butcher. When he was a boy, "he exercised his father's trade, but when he killed a calf he would do it in a high style, and make a speech". Shakespeare was a schoolteacher for a while and taught Latin (no doubts there about Shakespeare's linguistic abilities). "His comedies will remain wit as long as the English tongue is understood."
Nicholas Rowe
The business of Shakespeare biography gets going with Rowe , the poet laureate and playwright who (correct me if I'm wrong) gave the English language the word "Lothario". Rowe prefaced his 1709 edition of Shakespeare's Works with a short biography that was reissued last year to mark its 300th anniversary. Marvellously wide of the mark on most matters of fact, it's full of praise for the plays. Rowe sees Shylock in The Merchant of Venice as a serious rather than a buffoonish part, which is how it was acted at the time, and defends Shakespeare against general critical prejudices. The young Shakespeare was a deer-poacher. Getting caught led directly to his move – his escape – into the theatre business.
John Payne Collier
The great 19th-century scholar was also a great forger. Some of his inventions were simply single words added to existing documents; on other occasions, he simply made up evidence and presented it, humbly declining to take credit for the discovery, as material for scholarly consideration. Did a ballad that happened to mention King Priam, "False Cressid" and "loving Troylus" refer to Shakespeare's play Troilus and Cressida? With mock cautiousness, Collier conceded that it could allude to "a different play on the same subject". Another ballad had Marlowe breaking his leg while acting on the stage of the Curtain theatre. Collier later came to repent it all bitterly.
Frank Harris " Frank Harris is upstairs, thinking about Shakespeare at the top of his voice." Oscar Wilde (who died in 1900) wouldn't have been surprised by The Man Shakespeare and His Tragic Life-Story (1909), his friend Harris's masterpiece of unfounded assertion and biographical melodrama. For Harris ("Liar, libertine, and blackmailer", as one critic calls him), it was the humble Shakespeare's doomed passion for one of the Queen's Maid of Honour, Mary Fitton, that brought the playwright to "self-knowledge and knowledge of life, and turned him from a light-hearted writer of comedies and histories into the author of the greatest tragedies that have ever been conceived" (shades of Shakespeare in Love there). Plays aren't plays – they're exercises in autobiography – which makes Harris a prime example of the literal-minded tendency derided by James Shapiro in Contested Will.
Perhaps Rowse , the Oxford historian who wrote several books relating to Shakespeare, is not so remarkable for what he thought as for the attitude that carried him along, brushing aside all objections to his "decoding" of Shakespeare's Sonnets. He told a newspaper in 1963: "I am prepared to stake my reputation as an Elizabethan scholar on the claim that all the problems of the Sonnets save one – the identity of Shakespeare's mistress, the Dark Lady – are susceptible of solution, and that I have solved them". Ten years later, he'd solved the one remaining problem, too: the Dark Lady was the poet Emilia Lanier. "This is she! This is the Lady!" Never mind that it's not even clear that Lanier was a dark lady, let alone the Dark Lady – or indeed, whether or not there was a real Dark Lady at all. My goodness, what if Shakespeare actually made the whole thing up?
- William Shakespeare
- Theatre blog
- Biography books
Comments (…)
Most viewed.
William Shakespeare Biography

William Shakespeare was indisputably among the top English-language poets and playwrights of all time. He was born in the village of Stratford-upon-Avon in April 1564 and died there in April 1616. His surviving body of work includes 38 plays, 154 sonnets and two narrative poems, the majority of which he penned between 1589 and 1613. While much of Shakespeare's biography is unknown, murky or subject to dispute, historians have managed to verify factual data through his own writings, the works of his contemporaries and historical documents.
Early Years: 1564 to 1585
The Bard of Avon, as William Shakespeare is also known, was the child of a leather merchant and glover, John Shakespeare. His mother was from a family of landed gentry. In the absence of records detailing Shakespeare's early education, historians guess he attended a nearby school where he learned to read and write English as well as Latin.
In 1582, when he was just 18, Shakespeare married Anne Hathaway, a woman eight years his senior. They would have three children, a daughter in 1583 and a set of twins in 1585. They lost their only son, Hamnet, when the boy was 11 years old. Daughters Susanna and Judith would live to be 66 and 77, respectively.
Middle Years: 1586 to 1599
From 1586 until 1592, very little information is available regarding the Shakespeare household or the bard himself. During this period that historians refer to as the writer's lost years, only a scant legal document or two gives evidence of Shakespeare's existence. Over the years, various biographers have speculated that he may have been a poacher on the run from a disgruntled landowner, a horse-minder at a London theater, or more probably, a local schoolmaster.
Also during his lost years, the bard was devoting a good portion of his time to playwriting. By 1592, solid evidence shows that one if not more of his plays was underway on London stages. The first of his plays in production was probably "Henry IV, Part One," an historical work which not only chronicles the active years of the monarch's reign but also introduces his son Hal and Henry Percy, or Hotspur, a rival.
The bard had established himself in London prior to 1592, as evidenced by a mention in the London Times by a fellow playwright. He completed "Henry IV, Part Two" and "Henry V" early in the 1590s. By 1594, he and a group of colleagues had formed an acting troupe they called The Lord Chamberlain's Men, in honor of their patron, which would soon grow to prominence in the London theater scene.
The 1590s were quite a prolific time for Shakespeare. He wrote additional historic plays, including "Richard II," "Richard III," and "Titus Andronicus." He also penned the comedies "Two Gentlemen of Verona," "The Taming of the Shrew" and "A Comedy of Errors," probably early in the decade.
From around 1595 to the end of the century, Shakespeare turned his sights toward more romantic comedies, including "A Midsummer Night's Dream," "The Merchant of Venice," Twelfth Night" and "Much Ado About Nothing." The bard wrote the tragedies "Romeo and Juliet," and "Julius Caesar" during this period of his life as well,
By 1597, Shakespeare had written approximately 15 of his 38 surviving plays. He had achieved enough financial success to purchase one of Stratford's nicest homes for his family. He continued to live principally in London where he wrote and acted in his plays. During periods such as Lent when theaters were closed and when outbreaks of the plague shut down the city, he likely spent time with his family in Stratford..
Shakespeare was not only writing scripts for his company, often based on stories from mythology, literature and historic accounts, but he was also acting in his own plays. The Lord Chamberlain's Men put on performances at such London venues as The Theatre and The Curtain. In 1599, the acting troupe built The Globe from the ruins of The Theater, establishing their own playhouse, which opened in 1599.
Later Years: 1600-1613
Early in the new century, the bard continued to produce great literature, penning such masterworks as "Troilus and Cressida," "Measure for Measure," "All's Well That Ends Well," and some of his most renowned tragedies, including "Hamlet," "Othello" and "King Lear." In 1603, The Lord Chamberlain's Men delivered a command performance of "A Midsummer Night's Dream" at Queen Elizabeth's Hampton court. When the Queen died later that year, the acting troupe changed its name to The King's Men in honor of the newly crowned King James I. Their first performance for the monarch was "As You Like It."
The bard was growing artistically during this era, customizing his mastery of blank verse with wit and intention to enrich his characters' dialogue and enliven the action. He employed such techniques as run-on lines and inflected phrasing to breathe life into a poetic form that tended to the monotone if used within strict parameters of ten syllables per line and alternating stressed and unstressed syllables. The dialogue of his play "Hamlet," for example, seems animated in comparison to the more strictly patterned lines of earlier works such as "Henry V." Shakespeare also provided moments of variation in his plays by inserting bits of rhymed verse in the dialogue, for example in Puck's epilogue in "A Midsummer Night's Dream."
During the first decade of the 17th century, Shakespeare published his "Sonnets," a collection of 154 14-line works that employed the same blank verse format as his plays but with the specific rhyme scheme of three quatrains and a concluding couplet. Released as a printed collection in 1609, Shakespeare's sonnets had likely been written individually over time, and those within his circle of friends were probably already familiar with some of them. The form the bard employed for his verses became known as the Shakespearean sonnet, as opposed to the traditional Petrarchan sonnet, which consists of an octet and a sestet.
In his last plays, "Cymbeline," "A Winter's Tale," and "The Tempest," the bard test-drove a hybrid genre, the tragicomedy, also known as the romance. While they take a more somber, serious tone than such comedies as "Twelfth Night," these tragicomedies end on a positive note, unlike such tragedies as "King Lear." The bard also completed two last works for theater, "Henry VIII" and "The Two Noble Kinsmen," with a collaborator, likely John Fletcher, a contemporary playwright.
Just after the completion of "Henry VIII" in 1613, The King's Men lost the Globe playhouse to a fire. By the time they reopened in 1614, Shakespeare had already retired to his family home in Stratford where he died in 1616 at the age of 52. While no verified version of the manner of his death exists today, one account, written by the vicar of Stratford 50 years later, attributes his untimely demise to drinking too hard with his friends John Drayton and Ben Johnson, and catching a fatal fever as a result.
The Controversy
Due in part to the great gaps in knowledge regarding Shakespeare's early education and the lost years, the bard has always been shrouded in mystery. In addition, not a single manuscript he wrote in his own hand survived the centuries. One scholarly explanation for this lack of historical verification is that "William Shakespeare" was the pen name of some more illustrious, well-educated figure of the Elizabethan era.
The controversy did not see the light of day until more than two centuries after the bard's death. Among the first to question the authorship of such all-time great works as "Macbeth" was a Pennsylvanian Lutheran named Samuel Schmucker, and he was merely drawing an analogy. He likened the scholarly trend of his time in using historic data to raise doubts about the existence of Christ was akin to speculating that Shakespeare never existed. An offhand remark, but that is all it took to sow the seed of controversy.
Some of the fuel for the fire included: 1. The lack of documentation for Shakespeare's existence. 2. The disputed authorship of particular works. 3. The unlikelihood that someone with the bard's background would rise to greatness.
Among the most famous doubters were Mark Twain, Henry James, Sigmund Freud and Orson Wells. Among the candidates people have mentioned as the "real" William Shakespeare are Sir Francis Bacon, Christopher Marlowe, and Earl of Oxford Edward DeVere. The controversy has even found its way into the U.S. Supreme Court as the subject of a moot debate.
The Influence of William Shakespeare Through the Centuries
One of the bard's most enduring influences is on the English language. Not only are many quotes from his plays, such as Polonius' advice to Hamlet, "Neither a borrower nor a lender be," a part of the English lexicon, but the way in which Shakespeare shaped the language to suit his own artistic purposes would influence future writers and poets throughout subsequent history, from Charles Dickens to Maya Angelou. Charles Dickens drew upon the bard's writings for many of his titles as well as numerous quotations he used within his novels.
Shakespeare also enriched the language with the addition of approximately 2,000 new words and numerous new usages of existing vocabulary. Some of the words attributed to the bard include "auspicious," "dwindle" and "sanctimonious." Phrases he originated that are still in the popular lexicon include, "break the ice" from "The Taming of the Shrew" and "in a pickle" from "The Tempest."
The bard's masterful characterizations have become archetypes for social standards. Such larger-than-life characters as Hamlet, King Lear, Othello, Romeo and Juliet, Ophelia and a host of others inform contemporary social standards in ways that are inextricably woven into the fabric of modern society. They not only appear as standard icons in the theater, movies, literature and visual arts, but also have established themselves as cultural norms, particularly in English-speaking societies. It is not even necessary to have read the works of Shakespeare to be familiar with his well-known quotations and characters.
Even the controversy surrounding the authorship of Shakespeare's plays and sonnets serves to keep the bard very much a vital figure in contemporary lore. The probability that the mystery will probably never be resolved, given the lack of hard evidence, means that Shakespearean scholars, school teachers and their students will be reading and discussing the 16th-century master far into the future.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Frank Kermode, Shakespeare's Language. One of the best books on Shakespeare's language, and a handy companion volume to Spurgeon's older, groundbreaking study of the Bard's imagery. Kermode was often a superb close-reader of poetry and a very clear-headed critic, and this shines through here. Highly readable. James Shapiro, 1599: A Year ...
The best books on Shakespeare's Reception, recommended by Emma Smith. In the years after William Shakespeare died, his plays took on a life of their own. They meant different things to different people at different times as they spread around the world, turning a glover's son from a one-horse town in central England into one of the best ...
William Shakespeare was an English poet, playwright, and actor of the Renaissance era. He was an important member of the King's Men theatrical company from roughly 1594 onward. Known throughout ...
William Shakespeare (baptized April 26, 1564, Stratford-upon-Avon, Warwickshire, England—died April 23, 1616, Stratford-upon-Avon) English poet, dramatist, and actor often called the English national poet and considered by many to be the greatest dramatist of all time.. Shakespeare occupies a position unique in world literature.Other poets, such as Homer and Dante, and novelists, such as Leo ...
William Shakespeare. William Shakespeare ( bapt. 26 [a] April 1564 - 23 April 1616) [b] was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. [3] [4] [5] He is often called England's national poet and the " Bard of Avon" (or simply "the Bard").
9. Nothing like the Sun by Anthony Burgess. Burgess's fascination with Shakespeare was a lifetime's obsession. His first foray into Shakespeare's world occurred in 1964 with this exuberant ...
An Introduction. William Shakespeare was a renowned English poet, playwright, and actor born in 1564 in Stratford-upon-Avon. His birthday is most commonly celebrated on 23 April (see When was Shakespeare born ), which is also believed to be the date he died in 1616. Shakespeare was a prolific writer during the Elizabethan and Jacobean ages of ...
William Shakespeare (1564-1616), considered the greatest English-speaking writer in history and England's national poet, has had more theatrical works performed than any other playwright.
William Shakespeare (b. 1564-d. 1616) is widely regarded as the greatest writer and dramatist of all time. His poetry, plays, and life continue to fascinate academics, theater practitioners, and the general public over four hundred years after his death. Over the course of his career, he wrote 154 sonnets, forty plays that are known about ...
William Shakespeare - Poet, Playwright, Bard: Shakespeare lived at a time when ideas and social structures established in the Middle Ages still informed human thought and behaviour. Queen Elizabeth I was God's deputy on earth, and lords and commoners had their due places in society under her, with responsibilities up through her to God and down to those of more humble rank. The order of ...
Life & Times. 1564-1616. In his 52 years of life William Shakespeare transformed himself from the son of a small-town glovemaker to a favorite playwright of Queen Elizabeth and King James. Today he is celebrated as the most popular writer in the English language.
Since William Shakespeare lived more than 400 years ago, and many records from that time are lost or never existed in the first place, we don't know everything about Shakespeare's life. For example, we know that he was baptized in Stratford-upon-Avon, 100 miles northwest of London, on April 26, 1564. But we don't know his exact birthdate ...
A TIMES LITERARY SUPPLEMENT BEST BOOK OF THE YEAR. Drawing on an exceptional combination of skills as literary biographer, novelist, and chronicler of London history, Peter Ackroyd surely re-creates the world that shaped Shakespeare--and brings the playwright himself into unusually vivid focus. With characteristic narrative panache, Ackroyd ...
Best Books About Shakespeare ... Shakespeare: The Biography by. Peter Ackroyd. 4.02 avg rating — 2,161 ratings. score: 1,665, and 17 people voted ... The Mysterious William Shakespeare: The Myth & the Reality by. Charlton Ogburn Jr. 4.19 avg rating — 58 ratings.
A TIMES LITERARY SUPPLEMENT BEST BOOK OF THE YEAR Drawing on an exceptional combination of skills as literary biographer, novelist, and chronicler of London history, Peter Ackroyd surely re-creates the world that shaped Shakespeare--and brings the playwright himself into unusually vivid focus. With characteristic narrative panache, Ackroyd immerses us in sixteenth-century Stratford and the ...
Macbeth, hands down, should be number one as it is the best of Shakespeare's works (at least in my opinion). I have read 5 of the works listed (as I am only in high school and haven't had the vocabulary or analysis skills to read more earlier). The five include: Macbeth, Romeo and Juliet, Hamlet, Julius Caesar, and Othello.
Early Years . Shakespeare was probably born on April 23, 1564, but this date is an educated guess because we only have a record of his baptism three days later.His parents, John Shakespeare and Mary Arden, were successful townsfolk who moved to a large house in Henley Street, Stratford-upon-Avon, from the surrounding villages.
Shakespeare was born and raised in Stratford-upon-Avon, where he married Anne Hathaway at the age of 18, had three children with her and left town — only returning for good late in life. He ...
A Very Brief William Shakespeare Biography. Parents: John Shakespeare & Mary Shakespeare (nee Arden). Date of Birth: Generally accepted as 23rd April 1564. Shakespeare was baptised on 26th April, 1564. Wife: Anne Hathaway (married 1582). Children: Susanna (born 1583), Hamnet and Judith (twins, born 1585).; Resided: Born and raised in Stratford-Upon-Avon. Prime working years spent away from ...
William Shakespeare's Life & Times Early Life. Shakespeare was born in 1564 in Stratford-upon-Avon, a small town in the middle of the English countryside. His father, John Shakespeare, was a glover and public servant with social ambitions, as suggested by his marriage to Mary Arden, the daughter of a well-to-do farmer.
Rowe prefaced his 1709 edition of Shakespeare's Works with a short biography that was reissued last year to mark its 300th anniversary. Marvellously wide of the mark on most matters of fact, it's ...
William Shakespeare Biography. William Shakespeare was indisputably among the top English-language poets and playwrights of all time. He was born in the village of Stratford-upon-Avon in April 1564 and died there in April 1616. His surviving body of work includes 38 plays, 154 sonnets and two narrative poems, the majority of which he penned ...
Interestingly, William Shakespeare's tomb in Trinity Church, located in his hometown of Stratford-upon-Avon, features a poem on its outside. It acts as a warning to anyone who might consider disturbing his final resting place. The poem includes the phrase, "and cursed be he that moves my bones.".