Thesis Writing: What to Write in Chapter 5
Table of contents, introduction.
This article tells what a budding researcher must include in Chapter 5-the Summary. It also includes the tense of the verb and the semantic markers, which are predominantly used in writing the summary, conclusions, and recommendations.
For others, writing Chapter 5 is the easiest part of thesis writing, but there are groups of students who would like to know more about it. If you are one of them, this article on how to write chapter 5 of your thesis is purposely written for you.

What to Write in Chapter 5
1. write the summary.
Your summary in Chapter 5 may include:
- objectives of the study.
- statement of the problem.
- respondents.
- sampling procedures.
- method/s of research employed.
- statistical treatment/s applied, or hypotheses tested, if there is any; and
If you notice, all the parts mentioned above are already included in your Chapters 1- 4. So, the challenge is on how you are going to write and present it in Chapter 5 briefly.
First, you must go directly to the point of highlighting the main points. There is no need to explain the details thoroughly. You must avoid copying and pasting what you have written in the previous chapters. Just KISS (keep it short and simple)!
Then, write sentences in simple past and always use passive voice construction rather than the active voice. You must also be familiar with the different semantic markers.
When I was enrolled in Academic Writing in my master’s degree, I learned that there are semantic markers which can be used in order not to repeat the same words or phrases such as additionally, also, further, in addition to, moreover, contrary to, with regard to, as regards, however, finally, during the past ___ years, from 1996 to 2006, after 10 years, as shown in, as presented in, consequently, nevertheless, in fact, on the other hand, subsequently and nonetheless.
Next, you may use the following guide questions to check that you have not missed anything in writing the summary:
- What is the objective of the study?;
- Who/what is the focus of the study?;
- Where and when was the investigation conducted?;
- What method of research was used?;
- How were the research data gathered?;
- How were the respondents chosen?;
- What were the statistical tools applied to treat the collected data?; and
- Based on the data presented and analyzed, what findings can you summarize?
Finally, organize the summary of the results of your study according to the way the questions are sequenced in the statement of the problem.
2. Write the Conclusion or Conclusions

Once you have written the summary in Chapter 5, draw out a conclusion from each finding or result. It can be done per question, or you may arrange the questions per topic or sub-topic if there is any. But if your research is quantitative, answer the research question directly and tell if the hypothesis is rejected or accepted based on the findings.
As to grammar, make sure that you use the present tense of the verb because it comprises a general statement of the theory or the principle newly derived from the present study. So, don’t be confused because, in your summary, you use past tense, while in conclusion; you use the present tense.
3. Write the Recommendations
The recommendations must contain practical suggestions that will improve the situation or solve the problem investigated in the study.
First, it must be logical, specific, attainable, and relevant. Second, it should be addressed to persons, organizations, or agencies directly concerned with the issues or to those who can immediately implement the recommended solutions. Third, present another topic which is very relevant to the present study that can be further investigated by future researchers.
But never recommend anything that is not part of your study or not being mentioned in your findings.
First, it must be logical, specific, attainable, and relevant. Second, it should be addressed to persons, organizations, or agencies directly concerned with the issues or to those who can immediately implement the recommended solutions. Third, present another topic that is very relevant to the present study that can be further investigated by future researchers.
Recommend nothing that is not part of your research or not being mentioned in your findings.
However, there are universities, especially in the Philippines, that require a specific thesis format to be followed by students. Thus, as a student, you must conform to the prescribed form of your college or university.
Nordquist, R. n.d. Imperative Mood. Retrieved July 29, 2014, from https://www.thoughtco.com/imperative-mood-grammar-1691151
© 2014 July 29 M. G. Alvior | Updated 2024 January 10
Related Posts

Three Tips on How to Write a Good Statistical Question
5 ways on how to generate ideas even when you are not inspired, analyzing the macro and microstructures of editorial texts, about the author, mary g. alvior, phd.
Dr. Mary Gillesania Alvior has PhD in Curriculum Development from West Visayas State University. She earned her Master of Arts in Teaching English from De La Salle University, Manila as Commission on Higher Education (CHED) scholar. As academic advisor, she helps learners succeed in their academic careers by providing them the necessary skills and tips in order to survive in this wobbling financial environment. In 2014, she got involved in the establishment of a language institute in the Middle East, particularly in the use of Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR). Then she went to Thailand and became a lecturer in the international college and handled English and Graduate Education courses. From 2017 to 2021, she became the Focal Person for the Establishment of a Medical School, Director of Curriculum and Instructional Materials Development Office (CIMDO), Head of BAC Secretariat, Quality Management System (QMS) Leader, and TWG member of the Procurement for Medical Equipment. Currently, she is the coordinator of the Project Management Committee for the Establishment of the Medical School. In spite of numerous tasks, she is into data privacy, quality management system, and space industry.
100 Comments
can you please make a summary about “Centella Asiatica with virgin Coconut Oil as Ointment”?
I am still having problem in organizing my summary and conclusion (my topic is dress code in public schools. to be more specific, at the Voinjama Public School. Can you help me with a sample?
This is very helpful especially the grammar part. It really jumped start my writing effort… really want to finish my study with style.
I just pray you are okay. Thanks for responding to the questions, I have also learnt a lot.
Hello, Daryl. Thank you so much. About your request, I will find time to write about it. I got so busy the past months.
Precise and direct to the point ,, Thanks maam Mary.
Thanks very much for this all importing information on how to write chapter five in thesis writing. It gives me more insight as to how to develop the chapter five perfectly.
Hello maam my PhD research purely a qualitative study on community based organization of slum ..i used 3 tool case study , participant observation and FGDs to analyse role, impact, challenge and aspiration of CBOs . i used tabular form (matrix to analyse ) did not use any software..
PLEASE HELP/GUIDE ME WHAT SHOULD I WRITE in my Chapter 5 .. your help is very much crucial as i have to submit thesis this weekend KULDEEP
I’m so sorry, Kuldeep. I wish you are done with your doctorate research. It is been a year then. I got sick and had a lot of work to do. God bless!
Hello ma’am, can I ask about in what part the recommendation in chapter 1 reflect the recommendation in chapter5? Thanks.
Sorry, Aly. This is very late. Take your statement of the problem. the results for the statement of the problem will be the basis for your recommendation.
You are welcome, Prince. God bless to your research endeavor.
Thank you very much very insightful.
Eric, you are welcome. I wish you are able to finish your work.
how to write a recommendation, my title is common causes of financial problem. Hope you can help me…
Hello, Jolven. Your recommendation must be based on your findings. So, if that is your title, and you found that the common causes are the ——-, then write a recommendation based on the causes.
Thanks a lot, Mimimi.
Research Guide
Chapter 5 sections of a paper.
Now that you have identified your research question, have compiled the data you need, and have a clear argument and roadmap, it is time for you to write. In this Module, I will briefly explain how to develop different sections of your research paper. I devote a different chapter to the empirical section. Please take into account that these are guidelines to follow in the different section, but you need to adapt them to the specific context of your paper.
5.1 The Abstract
The abstract of a research paper contains the most critical aspects of the paper: your research question, the context (country/population/subjects and period) analyzed, the findings, and the main conclusion. You have about 250 characters to attract the attention of the readers. Many times (in fact, most of the time), readers will only read the abstract. You need to “sell” your argument and entice them to continue reading. Thus, abstracts require good and direct writing. Use journalistic style. Go straight to the point.
There are two ways in which an abstract can start:
By introducing what motivates the research question. This is relevant when some context may be needed. When there is ‘something superior’ motivating your project. Use this strategy with care, as you may confuse the reader who may have a hard time understanding your research question.
By introducing your research question. This is the best way to attract the attention of your readers, as they can understand the main objective of the paper from the beginning. When the question is clear and straightforward this is the best method to follow.
Regardless of the path you follow, make sure that the abstract only includes short sentences written in active voice and present tense. Remember: Readers are very impatient. They will only skim the papers. You should make it simple for readers to find all the necessary information.
5.2 The Introduction
The introduction represents the most important section of your research paper. Whereas your title and abstract guide the readers towards the paper, the introduction should convince them to stay and read the rest of it. This section represents your opportunity to state your research question and link it to the bigger issue (why does your research matter?), how will you respond it (your empirical methods and the theory behind), your findings, and your contribution to the literature on that issue.
I reviewed the “Introduction Formulas” guidelines by Keith Head , David Evans and Jessica B. Hoel and compiled their ideas in this document, based on what my I have seen is used in papers in political economy, and development economics.
This is not a set of rules, as papers may differ depending on the methods and specific characteristics of the field, but it can work as a guideline. An important takeaway is that the introduction will be the section that deserves most of the attention in your paper. You can write it first, but you need to go back to it as you make progress in the rest of teh paper. Keith Head puts it excellent by saying that this exercise (going back and forth) is mostly useful to remind you what are you doing in the paper and why.
5.2.1 Outline
What are the sections generally included in well-written introductions? According to the analysis of what different authors suggest, a well-written introduction includes the following sections:
- Hook: Motivation, puzzle. (1-2 paragraphs)
- Research Question: What is the paper doing? (1 paragraph)
- Antecedents: (optional) How your paper is linked to the bigger issue. Theory. (1-2 paragraphs)
- Empirical approach: Method X, country Y, dataset Z. (1-2 paragraphs)
- Detailed results: Don’t make the readers wait. (2-3 paragraphs)
- Mechanisms, robustness and limitations: (optional) Your results are valid and important (1 paragraph)
- Value added: Why is your paper important? How is it contributing to the field? (1-3 paragraphs)
- Roadmap A convention (1 paragraph)
Now, let’s describe the different sections with more detail.
5.2.1.1 1. The Hook
Your first paragraph(s) should attract the attention of the readers, showing them why your research topic is important. Some attributes here are:
- Big issue, specific angle: This is the big problem, here is this aspect of the problem (that your research tackles)
- Big puzzle: There is no single explanation of the problem (you will address that)
- Major policy implemented: Here is the issue and the policy implemented (you will test if if worked)
- Controversial debate: some argue X, others argue Y
5.2.1.2 2. Research Question
After the issue has been introduced, you need to clearly state your research question; tell the reader what does the paper researches. Some words that may work here are:
- I (We) focus on
- This paper asks whether
- In this paper,
- Given the gaps in knoweldge, this paper
- This paper investigates
5.2.1.3 3. Antecedents (Optional section)
I included this section as optional as it is not always included, but it may help to center the paper in the literature on the field.
However, an important warning needs to be placed here. Remember that the introduction is limited and you need to use it to highlight your work and not someone else’s. So, when the section is included, it is important to:
- Avoid discussing paper that are not part of the larger narrative that surrounds your work
- Use it to notice the gaps that exist in the current literature and that your paper is covering
In this section, you may also want to include a description of theoretical framework of your paper and/or a short description of a story example that frames your work.
5.2.1.4 4. Empirical Approach
One of the most important sections of the paper, particularly if you are trying to infer causality. Here, you need to explain how you are going to answer the research question you introduced earlier. This section of the introduction needs to be succint but clear and indicate your methodology, case selection, and the data used.
5.2.1.5 5. Overview of the Results
Let’s be honest. A large proportion of the readers will not go over the whole article. Readers need to understand what you’re doing, how and what did you obtain in the (brief) time they will allocate to read your paper (some eager readers may go back to some sections of the paper). So, you want to introduce your results early on (another reason you may want to go back to the introduction multiple times). Highlight the results that are more interesting and link them to the context.
According to David Evans , some authors prefer to alternate between the introduction of one of the empirical strategies, to those results, and then they introduce another empirical strategy and the results. This strategy may be useful if different empirical methodologies are used.
5.2.1.6 6. Mechanisms, Robustness and Limitations (Optional Section)
If you have some ideas about what drives your results (the mechanisms involved), you may want to indicate that here. Some of the current critiques towards economics (and probably social sciences in general) has been the strong focus on establishing causation, with little regard to the context surrounding this (if you want to hear more, there is this thread from Dani Rodrick ). Agency matters and if the paper can say something about this (sometimes this goes beyond our research), you should indicate it in the introduction.
You may also want to briefly indicate how your results are valid after trying different specifications or sources of data (this is called Robustness checks). But you also want to be honest about the limitations of your research. But here, do not diminish the importance of your project. After you indicate the limitations, finish the paragraph restating the importance of your findings.
5.2.1.7 7. Value Added
A very important section in the introduction, these paragraphs help readers (and reviewers) to show why is your work important. What are the specific contributions of your paper?
This section is different from section 3 in that it points out the detailed additions you are making to the field with your research. Both sections can be connected if that fits your paper, but it is quite important that you keep the focus on the contributions of your paper, even if you discuss some literature connected to it, but always with the focus of showing what your paper adds. References (literature review) should come after in the paper.
5.2.1.8 8. Roadmap
A convention for the papers, this section needs to be kept short and outline the organization of the paper. To make it more useful, you can highlight some details that might be important in certain sections. But you want to keep this section succint (most readers skip this paragraph altogether).
5.2.2 In summary
The introduction of your paper will play a huge role in defining the future of your paper. Do not waste this opportunity and use it as well as your North Star guiding your path throughout the rest of the paper.
5.3 Context (Literature Review)
Do you need a literature review section?
5.4 Conclusion
- Welcome to Chapter Five
Chapter 5 Webinars
- Alignment of Dissertation Components for DIS-9904ABC
- Dissertation Title Tips
- Proofreading Service in the ASC This link opens in a new window
- Dissertation Publishing: ProQuest
Jump to DSE Guide
Need help ask us.

- Next: Alignment of Dissertation Components for DIS-9904ABC >>
- Last Updated: Apr 19, 2023 12:55 PM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/c.php?g=1007181

Main navigation
- Current Projects
- Past Projects
- Publications
- News & Events
- Student Research
- List of theses (with abstracts)
- Le droit au logement en France
- Neighborhood Regeneration in Beijing
- Segregation of Women in Islamic Societies of South Asia...
- Practice of Community Architecture
- Alternatives to Home Ownership
- Lilong Housing, A Traditional Settlement Form
- Improving Sanitation in Coastal Communities...
- Settlement Patterns in Unplanned Areas
- Contents and introduction
- Chapter 3 (part 2)
- Urban Renewal in Beijing, Observation and Analysis
Chapter 5: Conclusion, Interpretation and Discussion
Introduction.
The following chapter concludes this report. A summary of the research is presented, and findings of the study are discussed and interpreted. The significance of this research in the immediate context of El Gallo and in the field of low-income housing is examined. Recommendations for further research end the chapter.
The scope of the following conclusions is limited to the context and historical characteristics of El Gallo. Thus, applied to other situations, these conclusions may yield incorrect assumptions. Still, these conclusions are relevant to the process of dwelling evolution in progressive development projects.
5.1 Summary of Research
This study observed the process of dwelling evolution in progressive development projects. The literature review was concentrated on the process of progressive development occurring in planned sponsored projects. It was found that, based on observations of the informal settlement process, progressive development under different contextual conditions was not questioned, and its benefits were taken for granted. Studies in the area were reduced to the period of improvement up to the time when the dwelling was physically consolidated. Longer term evaluation of progressive development projects were not found.
Research was undertaken on a 27-year-old progressive development project in Venezuela. The intention was to observe the process of dwelling evolution and the kind of housing that was being produced under progressive urban development projects on a long-term basis. The case study showed dwellings built with different initial levels of user-participation. Dwelling evolution was observed in a survey sample using parameters relevant to the case study (i.e., area increase, dwelling spatial growth and plot occupation, and changes in the functional structure).
Survey dwellings followed identifiable patterns of evolution in size, spatial structure and use-layout. Patterns were affected by aspects of the surrounding context and by aspects inherent to characteristics of the initial dwelling. Consequently, different dwelling groups showed different processes of progressive development.
5.2 Discussion and Interpretation of Findings.
As progressive developments, dwellings at El Gallo were able to adopt new and diverse roles along their whole process of evolution. In this section, relevant issues of the process of dwelling evolution observed at El Gallo are discussed. The first concerns the role of the non-permanent structure in the context of El Gallo as a sponsored progressive development project. The second comments on the process of dwelling evolution that followed the construction of the permanent structure.
In principle, non-permanent structures at El Gallo were similar to ranchos built in informal settlements. Ranchos at El Gallo served as primary shelters while more basic household priorities were met (i.e., services and infrastructure were provided, sources of income were found and generated, and even a favourable social environment was developed among neighbours). However, the majority of tin shacks were neither considerably increased nor upgraded with better materials even when they were used for long periods of time. This fact, together with the sudden change in the pace of development caused by the construction of a very complete permanent dwelling and subsequent removal of the rancho, had no connection with the gradual process of shack replacement observed in invasion settlements of Ciudad Guayana during this study (Portela, M. 1992). Neither did this process have a relationship with the system of "piecemeal construction" described by several housing researchers as characteristic of low-income dwellers.
The shanties were... housing in process of improvement. In particular the piecemeal system of building afforded great advantages to those who, like most of the poor in developing societies, have great variations in income from month to month (Peattie L. 1982:132).
Under El Gallo conditions of land security, ranchos did not show consolidation, and revealed their transient character because they were eventually substituted by permanent structures. The non-permanent structure revealed the primary household's aspiration for a minimum satisfactory habitable area. However, besides basic shelter during the initial stage, ranchos served to the purposes of capital accumulation that eventually allowed households to buy a basic unit according to official standards, or building a bigger, more complete first permanent structure. The size of ranchos reflected households' aspirations for the permanent dwelling, that is,smaller ranchos were substituted by basic units of the housing programs. Instead larger ranchos were substituted by large self-produced dwellings.
It is difficult to ascertain why ranchos were removed when they could have been kept as part of the dwelling, as in fact did a minority of households (2 cases). Is a fact that the temporary materials of ranchos contributed to their deterioration that ended with the total removal of the rancho. However, an idea that may have contributed to the demolition of the rancho was the household's adoption of the planner's belief that ranchos were a bad but necessary step on the way to obtaining permanent housing. Thus, once the permanent dwelling was built, the price households paid to gain credibility (i.e., that this stage was reached) was the demolition of the rancho itself. This interpretation can be specially true for Ciudad Guayana, where dwellings of certain quality such as those of El Gallo were seen as "casas" or houses. Instead, structures of similar quality in the hills of cities such as Caracas were still considered ranchos. In the long run, informal settlements obtained the largest benefits from this process because they gained far more official tolerance and social credibility (i.e., that shacks were actually temporary means of residence towards good-quality housing).
Those who lived in smaller ranchos improved their spatial conditions by moving to the small basic dwellings. Those who occupied bigger ranchos built bigger dwellings by themselves. Still, some households built their dwellings without going through the rancho stage. Self-produced dwellings followed the formal models either to gain the government's credibility of user commitment to build "good" government-like housing, or because households believed so. Imitation of the formal models, however, varied according to the builder's interpretation. For instance, the pattern of the detached dwelling was adopted, but often one of the side yards was reduced to a physical separation between the dwelling and the plot separation wall. More effective interpretations involved enlarging the front porch or using the central circulation axis to allow easy extension in the future.
The building approach of the permanent structure influenced the process of evolution that followed. Basic units built by the housing agencies had a compact, complete layout with higher standards of construction; however, aspects of the design, such as internal dimensions, were inadequate for household criteria, and the layout was not well adapted. Dwellings built according to provided plans and specificationshad similar problems, but households enlarged spaces and modified layouts when they were building the units. The level of construction standards was also reduced since the lateral façades of some dwellings were unfinished. Dwellings built totally by self-help means were the largest permanent structures. Aspects of the design of the first permanent structure allowed easy extension of the dwelling towards open areas of the plot. More user participation was reflected in straight-forward processes of evolution without internal modifications, and fewer stages to reach the current houseform.
5.3 Significance of the Study
While this study acknowledges again the effectiveness of progressive development in the housing system, it shows how dwelling evolution in progressive development projects can have different characteristics produced by internal and external interventions. Usually, projects are designed and launched to reproduce certain desirable outcomes and meet specific expectations. However, conditions prevailing in these projects and sometimes strategies that are introduced to "improve," "speed up" or make more "efficient" the process of evolution can affect the outcome in many different ways. This study showed how contextual characteristics of El Gallo, as well as the design and level of user participation in the initial permanent dwelling, affected successive stages of progressive development. However, it is important to recognize that are other issues beyond the spatial aspects that are intrinsically related with the evolution of the dwellings and that were not included within the scope of these particular research (i.e., household's changes in income, size, and age or gender structure).
The findings at El Gallo add modestly to the body of knowledge of literature on progressive development. Progressive Urban Development Units, UMUPs , have been the main housing strategy in Ciudad Guayana these last years, and they are likely to keep being used. Simple facts such as knowing the characteristics of the additions and modifications that households make to their dwellings over time can be the basis for more assertive actions supporting or enforcing progressive development activities. Understanding the process of dwelling evolution in low-income developments would be an effective way to help the process that, in the case of Ciudad Guayana, zonings and bylaws have been unable to regulate.
5.4 Recommendations for Further Research
Long term assessments are particularly constrained by the availability and reliability of recorded data. The frequency, and often the methodology, in which censuses and surveys are made do not always suit the purposes of this kind of research. Household interviews are very important, but they may become troubled by informant's limited memories and the continuity of the household in the dwelling. Aerial documentation, if available, represents one of the most reliable sources to observe physical change. Nevertheless, a careful and detailed process of observation of aerial data becomes very time consuming. For similar studies, a first phase in which the housing diversity is identified in the aerial data according to the selected criteria, would allow to reduce the number of detailed survey samples needed, thus considerably reducing the time of data collection.
In the context of Ciudad Guayana, further studies of the non-permanent dwelling in recent UMUPs would reveal new insights into the function of these structures in progressive development projects. This would be essential especially if any kind of initial aid is to be provided. On the other hand, following the growth of progressive developments is necessary if services and infrastructure are, as they are now, the responsibility of the local government. Identifying the producers of physical evolution -- i.e., the drivers and catalysts of change -- would be an important step for further research. An interesting step within this trend could be to ascertain the extent in which other household processes -- family growth, income increase and economic stability, household aging, changes in the household composition (single- to multi- family), etc., affect the process of dwelling evolution.
In the context of low-income housing, the process of progressive development needs further understanding. As in Ciudad Guayana, progressive development is likely to be the main housing strategy for other developing countries in the near future. Local authorities would do well to follow the evolution of settlements and to identify real household needs, and the consequences of public and/or private interventions in low-income settlements. Perhaps the most important learning of this study is that the experience of El Gallo acknowledges again the dynamic participation of the low-income households under different conditions, and still leaves wide room for a positive participation for the many other actors in the evolving urban entity.
. Notes for Chapter V
1 Dodge reports that some settlers of Ciudad Guayana kept the rancho and rented it to poorer families (Dodge,C. 1968:220). This attitude has been more common in other progressive development projects. The Dandora site and services also encouraged the construction of temporary shacks while the permanent dwelling was built. However, non-permanent structures remained to be rented or used as storage areas even after the permanent dwelling was built (McCarney, P.L. 1987:90).
Department and University Information
Minimum cost housing group.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 5: The Literature Review
Learning Objectives
- Describe a literature review and explain its purpose.
- Describe the steps in undertaking a literature review.
- Write a literature review.
- Identify acceptable sources to include in your literature review.
- Apply the five ‘C’s of writing a literature review.
- Compare a literature review, an essay and an annotated bibliography.
- Explain the importance of APA referencing and list some of the sources for getting assistance with APA referencing.
In this chapter, we will focus on writing a literature review. As part of this focus we will concentrate on four key aspects, as follows:
- The purpose behind a literature review and where it fits in the research process;
- The difference between a literature review, an essay, and an annotated bibliography;
- The special aspects that distinguish a literature review from other styles of academic writing; and
- The way to conduct a literature review and is the importance of reviewing previous research studies.
If you have never written a literature review, and even if you have, this chapter will provide valuable information for you. Understanding how to write a literature review is important because it is quite likely that you will have to do another one at some point in your academic and/or professional career.
Research Methods, Data Collection and Ethics Copyright © 2020 by Valerie Sheppard is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

How to Write a Research Paper: Parts of the Paper
- Choosing Your Topic
- Citation & Style Guides This link opens in a new window
- Critical Thinking
- Evaluating Information
- Parts of the Paper
- Writing Tips from UNC-Chapel Hill
- Librarian Contact
Parts of the Research Paper Papers should have a beginning, a middle, and an end. Your introductory paragraph should grab the reader's attention, state your main idea, and indicate how you will support it. The body of the paper should expand on what you have stated in the introduction. Finally, the conclusion restates the paper's thesis and should explain what you have learned, giving a wrap up of your main ideas.
1. The Title The title should be specific and indicate the theme of the research and what ideas it addresses. Use keywords that help explain your paper's topic to the reader. Try to avoid abbreviations and jargon. Think about keywords that people would use to search for your paper and include them in your title.
2. The Abstract The abstract is used by readers to get a quick overview of your paper. Typically, they are about 200 words in length (120 words minimum to 250 words maximum). The abstract should introduce the topic and thesis, and should provide a general statement about what you have found in your research. The abstract allows you to mention each major aspect of your topic and helps readers decide whether they want to read the rest of the paper. Because it is a summary of the entire research paper, it is often written last.
3. The Introduction The introduction should be designed to attract the reader's attention and explain the focus of the research. You will introduce your overview of the topic, your main points of information, and why this subject is important. You can introduce the current understanding and background information about the topic. Toward the end of the introduction, you add your thesis statement, and explain how you will provide information to support your research questions. This provides the purpose and focus for the rest of the paper.
4. Thesis Statement Most papers will have a thesis statement or main idea and supporting facts/ideas/arguments. State your main idea (something of interest or something to be proven or argued for or against) as your thesis statement, and then provide your supporting facts and arguments. A thesis statement is a declarative sentence that asserts the position a paper will be taking. It also points toward the paper's development. This statement should be both specific and arguable. Generally, the thesis statement will be placed at the end of the first paragraph of your paper. The remainder of your paper will support this thesis.
Students often learn to write a thesis as a first step in the writing process, but often, after research, a writer's viewpoint may change. Therefore a thesis statement may be one of the final steps in writing.
Examples of Thesis Statements from Purdue OWL
5. The Literature Review The purpose of the literature review is to describe past important research and how it specifically relates to the research thesis. It should be a synthesis of the previous literature and the new idea being researched. The review should examine the major theories related to the topic to date and their contributors. It should include all relevant findings from credible sources, such as academic books and peer-reviewed journal articles. You will want to:
- Explain how the literature helps the researcher understand the topic.
- Try to show connections and any disparities between the literature.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
More about writing a literature review. . .
6. The Discussion The purpose of the discussion is to interpret and describe what you have learned from your research. Make the reader understand why your topic is important. The discussion should always demonstrate what you have learned from your readings (and viewings) and how that learning has made the topic evolve, especially from the short description of main points in the introduction.Explain any new understanding or insights you have had after reading your articles and/or books. Paragraphs should use transitioning sentences to develop how one paragraph idea leads to the next. The discussion will always connect to the introduction, your thesis statement, and the literature you reviewed, but it does not simply repeat or rearrange the introduction. You want to:
- Demonstrate critical thinking, not just reporting back facts that you gathered.
- If possible, tell how the topic has evolved over the past and give it's implications for the future.
- Fully explain your main ideas with supporting information.
- Explain why your thesis is correct giving arguments to counter points.
7. The Conclusion A concluding paragraph is a brief summary of your main ideas and restates the paper's main thesis, giving the reader the sense that the stated goal of the paper has been accomplished. What have you learned by doing this research that you didn't know before? What conclusions have you drawn? You may also want to suggest further areas of study, improvement of research possibilities, etc. to demonstrate your critical thinking regarding your research.
- << Previous: Evaluating Information
- Next: Research >>
- Last Updated: Feb 13, 2024 8:35 AM
- URL: https://libguides.ucc.edu/research_paper
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Chapter 5 SUMMARY, CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS

Related Papers
Human movement science
Peter H . Wilson
Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism
Imran Mushtaq
Linda Isherwood
CLIC Note, to be …
Barbara Dalena , D. Adams
R. Tomás 1 , E. Adli 1 , I. Ahmed 2 , PK Ambatu 3 , D. Angal-Kalinin 4 , R. Barlow 4&6 , JP Baud 5 , ... B. Bolzon 5 , H. Braun 1 , H. Burkhardt 1 , GC Burt 4 , R. Corsini 1 , B. Dalena 1 , AC Dexter 3 , ... V. Dolgashev 7 , K. Elsener 1 , JL Fernandez Hernando 4 , G. Gaillard 5 , N. Geffroy ...
Hormone Research in Paediatrics
Jillian Bryce
Background: Research and audit are vital for the management of Differences/Disorders of Sex Development (DSD). Clinical networks have a strong potential to drive these activities with the development of care standards including patient experience data and peer-observation of clinical care provision. Summary: Following the 2005 Consensus Workshop that stressed the need for the regular collection and sharing of data across geographical boundaries, the current I-DSD registry was initially launched in 2008. Over a decade later, this registry and its associated network play an increasingly important role in supporting research, training, and benchmarking of care and service. Patient registries can also facilitate the development of local circles of patients and parents with similar conditions who can support each other. Key Messages: The case for participating in standardized data collection and exchange for DSD has now been made and should be standard practice in centres that care for p...
Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology
Michael E . Stone
Address given in Sydney in Sept. 2014 to the Australian Friends of the Hebrew University and the Sir Zelman Cowan Universities Fund.
Advances in urology
Juerg C Streuli
Brian Cuthbertson
Tokokasur Busasurabaya3
daftar harga kasur busa olympic, harga kasur busa olympic, harga kasur busa olympic ukuran 180x200, harga kasur busa olympic ukuran 120x200, harga kasur busa olympic ukuran 140x207 Anda Butuh Kasur dan lemari Bermerk dan Bergaransi Hanya di ANEKA JAYA MEBEL Solusinya ANEKA JAYA MEBEL (Pusatnya Mebel Harga Murah) Distributor Pusat Jual Kasur busa,spring bed dan Lemari Di Suabaya Kami Menyediakan Berbagai Macam Kasur busa,Spring bed dan juga lemari produk kami semua bergaransi resmi pabrik Produk Kami Antara lain : ~ kasur Busa Merk Big Foam dan Olympic (GARANSI 5THN) ~ Spring Bed Merk Olympic & Big Land (GARANSI PIR 15THN) ~ Spring Bed Merk Central Deluxe (GARANSI PIR 10THN) ~ Lemari Merk Olympic silahkan lihat testimoni dari pembeli kami Penjualan Kami Pembayaran system COD atau Bayar di tempat/Rumah anda dan tidak menerima ambil di gudang untuk informasi dan pemesanan silahkan hubungi kami tlp/wa 0838-5659-2523 atau klik wa.me/6283856592523 #distributorkasurbusabigfoam, #hargakasurbusabigfoam, #hargakasurbusabigfoam2018, #hargakasurbusabigfoam2019
RELATED PAPERS
Revista Brasileira de Enfermagem
Eliete Maria Silva
Gualtiero Spiro Jaeger
Haifa Tahlawi
Economics and Philosophy
Jelle de Boer
Building Resilience at Universities: Role of Innovation and Entrepreneurship
Mahmoud Syam
Computers & Mathematics with Applications
Saiful R Mondal
Neurologie pro praxi
Marek Peterka
International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Iwona Rzeszutek
Sanjaye Ramgoolam
Revista de Historia - IHNCA
Bradley Hilgert
Logan Murray
Jessica Floyd
African Journal of Plant Science
Ben Chikamai
EXTRA TERITORIAL
Betha El sherra
Noriyuki Nishida
Hormigón y Acero
Antonio Martínez Cutillas
Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data
Revista Mexicana De Fisica
mohamed abatal
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism
Sabrieh Amini
International Review of Finance
Vivek Miranda
Prostate Cancer
eduardo amaral
Integral Equations and Operator Theory
David Natroshvili
Ibnosina Journal of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences
Prakash Katakam
Four Point Bending
Per Ullidtz
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Chapter 5 Summary, Conclusions, Discussions, & Recommendations
Jul 29, 2014
2.15k likes | 6.42k Views
Chapter 5 Summary, Conclusions, Discussions, & Recommendations . Applied Research Center Abraham S. Fischler School of Education Summer Conference 2012. General Information. This session will address the components of Chapter 5 of the Applied Dissertation.
Share Presentation
- straightforward manner
- statistical jargon
- liberal statistics
- health promotion
- education summer conference

Presentation Transcript
Chapter 5 Summary, Conclusions, Discussions, & Recommendations Applied Research Center Abraham S. Fischler School of Education Summer Conference 2012
General Information This session will address the components of Chapter 5 of the Applied Dissertation. The format and style of Chapter 5 should follow the Style Guide for the Applied Dissertationand the sixth edition of the APA manual.
Chapter 5 Purpose of Chapter 5: To provide the readers with a thorough understanding of what the results of your study mean to the research field and to professional practice.
Chapter 5 Chapter 5 allows you to summarize the findings, discuss the importance of the findings, place the research findings in the context of current literature, compare and contrast the research findings with other relevant research, identify the strengths and weaknesses of the research study, discuss the implications of the research findings, and make recommendations for future research.
Summary of Findings Restate the results presented in Chapter 4 using little or no statistical jargon. Write in a clear straightforward manner with no interpretation of the results. Use past tense. Do not include tables and figures. Identify whether the findings of your study supported the hypotheses or research questions. Present unusual findings (e.g., results that you did not expect to be significant but were, and vice versa).
Interpretation of Findings Analyze both significant findings and not significant findings. Were the results what you predicted? Why do you think the results turned out the way they did? Were there any issues related to sampling, measurement, and procedural issues, as well as confounding variables? Provide possible explanations for the results. Link the results to any theoretical framework you used to develop your research question or hypotheses.
Context of Findings Place your findings in perspective to other studies of the topic found in the reviewed literature. How are your findings similar or different from those of other studies? Based on the literature, are the findings what might have been expected? If your results differ from those of other studies, what plausible explanations can account for this?
Implications of Findings • How do the findings expand the understanding of the phenomenon under study? • Identify the implications of the findings for • Theory: Are findings consistent with current theories in the field? Are they consistent with the selected theoretical framework for your study? • Research: Does the study help advance the research methodology in the field? (e.g., understanding of new confounding variables, issues of measurement, issues of design) • Practice: Who may be interested in using these findings in a professional field? Why should they pay attention to the findings? Could the findings lead to changes in the way professionals “do” things?
Discussion on Limitations Review the potential limitations that you initially proposed in the proposal. Discuss the limitations that may have affected—one way or another—your findings. Limitations typically originate in one of two sources: the study’s design and the study’s problems during implementation. Issues of design involve decisions about sampling, assessment, procedures, and choice of research design (poor match). Some of the issues that may have arisen at the time of research implementation relate to low sample size, measurement issues, heterogeneous groups, and so forth.
Discussion on Limitations (Cont.) Think of limitations in four major areas: Internal Validity—Unless the study is a “true experiment” one cannot claim that the IV “caused” changes in the DV. External Validity—Discuss the extent to which findings can be generalized. Measurement—Discuss issues of reliability and validity of assessment instruments. Statistical Analysis—Discuss issues of power, effect size, conservative or liberal statistics, and statistical test chosen.
Discussion on Future Directions Discuss findings in light of questions or issues that suggest future research directions. Extend the study to other populations. Think of other IVs and DVs that ought to be explored in the field; also, think of how to assess those additional variables. This is the section of the paper where most researchers are allowed to dream; think of extending your study to other questions that may add to the understanding of the issues.
Bibliography Cone, J. D., & Foster, S. F. (2006). Dissertations and theses from start to finish: Psychology and related fields. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. Cottrell, R. R., & McKenzie, J. F. (2011). Health Promotion and education research methods: Using the five-chapter thesis/dissertation model (2nd ed.). Sudbury, MA: Jones and Bartlett.
- More by User

Technical Recommendations for Highways No 12 TRH 12
Technical Recommendations for Highways No 12 TRH 12. Technical Recommendations for Highways No 12 TRH 12. 1980 1983 – draft TRH 12: Bituminous pavement rehabilitation design 1983 1989 1990
1.29k views • 53 slides

Chapter 8. Producing Summary Reports. Section 8.1. Introduction to Summary Reports. Objectives. Identify the different report writing procedures. Create one-way and two-way frequency tables using the FREQ procedure. Restrict the variables processed by the FREQ procedure.
1.93k views • 158 slides

Chapter 8 Perfect Competition
Chapter 8 Perfect Competition. Key Concepts Summary Practice Quiz Internet Exercises. ©2000 South-Western College Publishing. In this chapter, you will learn to solve these economic puzzles:. Why is the demand curve horizontal for a firm in a perfectly competitive market?.
1.47k views • 95 slides

Chapter 4 Markets in Action
Chapter 4 Markets in Action. Key Concepts Summary Practice Quiz Internet Exercises. ©2000 South-Western College Publishing. In this chapter, you will learn to solve these economic puzzles:. How does the spotted owl affect the price of homes?.
1.17k views • 76 slides
Lec 3 Sept 2 complete Chapter 1 exercises from Chapter 1 quiz # 1 Chapter 2 st
Lec 3 Sept 2 complete Chapter 1 exercises from Chapter 1 quiz # 1 Chapter 2 start. Performance Summary. Performance depends on Algorithm: affects IC, possibly CPI Programming language: affects IC, CPI Compiler: affects IC, CPI
1.03k views • 28 slides

Chapter 14 Environmental Economics
Chapter 14 Environmental Economics. Key Concepts Summary Practice Quiz Internet Exercises. ©2000 South-Western College Publishing. In this chapter, you will learn to solve these economic puzzles:.
1.15k views • 77 slides

Chapter 8 Biosocial Approaches
Chapter 8 Biosocial Approaches. Chapter Summary. Chapter Eight discusses the importance of both genetic and hereditary influences on criminal behavior as well as the environmental interaction with those genetic & biological mechanisms.
1.05k views • 50 slides


The Word Is Alive 1 Corinthians
The Word Is Alive 1 Corinthians. Chapter Five Narrated by Tony Gillon. Chapter Five. Summary of Chapter Five This brief chapter deals with a specific instance of gross sexual immorality that Paul clearly states must be dealt with.
1.22k views • 102 slides

The Word Is Alive 1 John
The Word Is Alive 1 John. Chapter One Narrated by Tony Gillon. Chapter One. Summary of Chapter One The most eloquent introduction. Chapter One. Summary of Chapter One The most eloquent introduction. God is light. Chapter One. Summary of Chapter One The most eloquent introduction.
1.58k views • 143 slides

The Word Is Alive Galatians
The Word Is Alive Galatians. Chapter Three Narrated by Tony Gillon. Chapter Three. Summary of Chapter Three The theme of justification by faith alone continues. Chapter Three. Summary of Chapter Three The theme of justification by faith alone continues. The promise precedes the law.
2.27k views • 216 slides

The Word Is Alive The Book of Acts
The Word Is Alive The Book of Acts. Chapter Twelve Narrated by Tony Gillon. Chapter Twelve. Summary of Chapter Twelve The martyrdom of James Zebedee. Chapter Twelve. Summary of Chapter Twelve The martyrdom of James Zebedee. King Agrippa arrests Peter. Chapter Twelve.
1.65k views • 126 slides

The Word Is Alive The Gospel of Matthew
The Word Is Alive The Gospel of Matthew. Chapter Four Narrated by Tony Gillon. Chapter Four. Summary of Chapter Four Forty days of testing by the devil. Chapter Four. Summary of Chapter Four Forty days of testing by the devil. Jesus’ teaching ministry commences. Chapter Four.
2.13k views • 203 slides

Unit 1 Overview
Unit 1 Overview. Significance – How strong is the evidence of an effect? (Chapter 1 ) Estimation – How large is the effect? (Chapter 2 ) Generalization – How broadly do the conclusions apply? (Chapter 3 ) Causation – Can we say what caused the observed difference? (Chapter 4).
1.19k views • 94 slides

Chapter 13 Flyweight
Chapter 13 Flyweight. Summary prepared by Kirk Scott. Design Patterns in Java Chapter 13 Flyweight. Summary prepared by Kirk Scott. That animal is known as a couscous A trip to Wikipedia will allow you to determine whether it is related to the food named couscous…. Introduction.
1.3k views • 114 slides

The Word Is Alive 1 Timothy
The Word Is Alive 1 Timothy. Chapter Five Narrated by Tony Gillon. Chapter Five. Summary of Chapter Five The need to show respect in church. Chapter Five. Summary of Chapter Five The need to show respect in church. Honouring widows. Chapter Five. Summary of Chapter Five
2.06k views • 191 slides

Chapter 8: IP Addressing
Chapter 8: IP Addressing. Introduction to Networks. Chapter 8. 8 .0 Introduction 8.1 IPv4 Network Addresses 8 .2 IPv6 Network Addresses 8 .3 Connectivity Verification 8.4 Summary. IP Addressing Chapter 8: Objectives. In this chapter, you will be able to:
1.04k views • 88 slides
Audit Engagement Overview
Audit Engagement Overview. Plan. Perform. Communicate. Monitor. Research and apply Standards. Maintain fraud awareness. Assess risk. Collect, evaluate, analyze, interpret data. Report findings, conclusions, recommendations. Monitor engagement outcomes. Develop workpapers.
1.8k views • 69 slides

The Word Is Alive The Gospel of Luke
The Word Is Alive The Gospel of Luke. Chapter Twenty Four Presented by Tony Gillon. Chapter Twenty Four. Summary of Chapter Twenty Four The empty tomb. Chapter Twenty Four. Summary of Chapter Twenty Four The empty tomb. The Emmaus Road. Chapter Twenty Four.
2.39k views • 212 slides

The Word Is Alive 1 Timothy. Chapter Two Narrated by Tony Gillon. Chapter Two. Summary of Chapter Two The requirements for corporate worship. Chapter Two. Summary of Chapter Two The requirements for corporate worship Paul addresses the behaviour in gatherings. Chapter Two.
2.41k views • 225 slides

Chapter 2. THE RELATIONAL MODEL OF DATA. Chapter 2 The Relational Model of Data. 2.1 An Overview of Data Models 2.2 Basics of Relational Model 2.3 Defining a Relation Schema in SQL 2.4 An Algebraic Query Language 2.5 Constraints on Relations 2.6 Summary of Chapter 2
1.36k views • 105 slides

Electralink Customer Survey Presentation 3 rd December 2007
R. Electralink Customer Survey Presentation 3 rd December 2007. Presentation Coverage. Introduction Overview Quantitative Survey Results Focus On DTS Focus On SPAA Focus On DCUSA Qualitative Research Summary & Conclusions Recommendations For 2008 Research. R. Introduction.
1.29k views • 113 slides

Chapter 12. Advanced Genetics. 11.3 Section Summary 6.3 – pages 296 - 301. Mutations. Mutation: a change in __. May involve : an entire __ a specific __ may take place in __ cell.
996 views • 87 slides
Experimental Research
- First Online: 25 February 2021
Cite this chapter

- C. George Thomas 2
4280 Accesses
Experiments are part of the scientific method that helps to decide the fate of two or more competing hypotheses or explanations on a phenomenon. The term ‘experiment’ arises from Latin, Experiri, which means, ‘to try’. The knowledge accrues from experiments differs from other types of knowledge in that it is always shaped upon observation or experience. In other words, experiments generate empirical knowledge. In fact, the emphasis on experimentation in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries for establishing causal relationships for various phenomena happening in nature heralded the resurgence of modern science from its roots in ancient philosophy spearheaded by great Greek philosophers such as Aristotle.
The strongest arguments prove nothing so long as the conclusions are not verified by experience. Experimental science is the queen of sciences and the goal of all speculation . Roger Bacon (1214–1294)
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Bibliography
Best, J.W. and Kahn, J.V. 1993. Research in Education (7th Ed., Indian Reprint, 2004). Prentice–Hall of India, New Delhi, 435p.
Google Scholar
Campbell, D. and Stanley, J. 1963. Experimental and quasi-experimental designs for research. In: Gage, N.L., Handbook of Research on Teaching. Rand McNally, Chicago, pp. 171–247.
Chandel, S.R.S. 1991. A Handbook of Agricultural Statistics. Achal Prakashan Mandir, Kanpur, 560p.
Cox, D.R. 1958. Planning of Experiments. John Wiley & Sons, New York, 308p.
Fathalla, M.F. and Fathalla, M.M.F. 2004. A Practical Guide for Health Researchers. WHO Regional Publications Eastern Mediterranean Series 30. World Health Organization Regional Office for the Eastern Mediterranean, Cairo, 232p.
Fowkes, F.G.R., and Fulton, P.M. 1991. Critical appraisal of published research: Introductory guidelines. Br. Med. J. 302: 1136–1140.
Gall, M.D., Borg, W.R., and Gall, J.P. 1996. Education Research: An Introduction (6th Ed.). Longman, New York, 788p.
Gomez, K.A. 1972. Techniques for Field Experiments with Rice. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines, 46p.
Gomez, K.A. and Gomez, A.A. 1984. Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research (2nd Ed.). John Wiley & Sons, New York, 680p.
Hill, A.B. 1971. Principles of Medical Statistics (9th Ed.). Oxford University Press, New York, 390p.
Holmes, D., Moody, P., and Dine, D. 2010. Research Methods for the Bioscience (2nd Ed.). Oxford University Press, Oxford, 457p.
Kerlinger, F.N. 1986. Foundations of Behavioural Research (3rd Ed.). Holt, Rinehart and Winston, USA. 667p.
Kirk, R.E. 2012. Experimental Design: Procedures for the Behavioural Sciences (4th Ed.). Sage Publications, 1072p.
Kothari, C.R. 2004. Research Methodology: Methods and Techniques (2nd Ed.). New Age International, New Delhi, 401p.
Kumar, R. 2011. Research Methodology: A Step-by step Guide for Beginners (3rd Ed.). Sage Publications India, New Delhi, 415p.
Leedy, P.D. and Ormrod, J.L. 2010. Practical Research: Planning and Design (9th Ed.), Pearson Education, New Jersey, 360p.
Marder, M.P. 2011. Research Methods for Science. Cambridge University Press, 227p.
Panse, V.G. and Sukhatme, P.V. 1985. Statistical Methods for Agricultural Workers (4th Ed., revised: Sukhatme, P.V. and Amble, V. N.). ICAR, New Delhi, 359p.
Ross, S.M. and Morrison, G.R. 2004. Experimental research methods. In: Jonassen, D.H. (ed.), Handbook of Research for Educational Communications and Technology (2nd Ed.). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, New Jersey, pp. 10211043.
Snedecor, G.W. and Cochran, W.G. 1980. Statistical Methods (7th Ed.). Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa, 507p.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Kerala Agricultural University, Thrissur, Kerala, India
C. George Thomas
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to C. George Thomas .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Thomas, C.G. (2021). Experimental Research. In: Research Methodology and Scientific Writing . Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64865-7_5
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64865-7_5
Published : 25 February 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-64864-0
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-64865-7
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Fortnite: Best Chapter 5 Season 2 Landing Spots
- Charon's Crossing offers beginner players plenty of loot and easy access to rotating to other POIs for quick engagements.
- Summit Temple on the edge of the map provides high rarity loot and natural resources while linking to nearby POIs for rotation.
- Research Rock in the corner of the map is underrated but a goldmine for loot with 22 chests and farming opportunities.
Fortnite ’s Chapter 5 Season 2 is in full swing, and players are excited to explore the Greek mythology-inspired map. The map is filled with secret corners, cabins, and spots awaiting a player’s discovery. While all these locations have valuable items players can loot, some have more potential than others. This makes picking the best landing spot crucial to surviving the match and claiming a Victory Royale. Players who want to excel should pick locations on the map that suit individual playstyles while providing solid loot.
Fortnite: All Chapter 5 Season 2 Battle Pass Skins
The best landing spots in Fortnite have sufficient loot spawn, are out of the way, and are close to POIs (points of interest). Since there’s no shortage of fantastic landing spots, picking the ideal locations boils down to the player’s preferences. Here’s a list of the best landing spots in Chapter 5 Season 2.
Charon’s Crossing
Optimal location with multiple loot routes.
Charon’s Crossing is located in the Underworld biome, and it's a lowkey landing spot with a good amount of loot. Players can find up to five chests in this location with reliable weapons and shields. The beauty of Charon’s Crossing is that it’s close to other high POIs like Grim’s Gate. So, players can drop, loot chests, and rotate to these POIs quickly and easily .
Charon’s Crossing is ideal for beginner Fortnite players who want a chill landing spot where they can grab sufficient loot. It’s not too contested and is right next to the water, which players can use to get more loot, activate the Underworld Dash, and rotate.
Summit Temple
A good amount of valuable loot and natural resources.
Summit Temple is located near the Mount Olympus POI at the edge of the map. The landing spot has up to eight chests for players to loot and plenty of natural resources for farming. Summit’s Temple is one of the few Fortnite locations with Olympus chests , which contain blue or higher rarity weapons alongside the Wings of Icarus item.
Fortnite: Chapter 5 Season 2 Kickstart Quests
Although Summit Temple is at the edge of the map, it’s close to other POIs, where players can rotate. Players should consider landing at the base camp to obtain loot before branching out towards the building on the slope with 11 slurp barrels and more chests. There are also more chests at the top of the hill in a tent camp, plus a Launch Pad for rotation.
Cliffside Lodge
A deadside region with valuable loot.
Cliffside Lodge is located in Brawler’s Battleground at the south corner of the map. It’s a deadside location, meaning players land here after missing other POI spots near Mount Olympus. So, there’s a chance players may run into a few opponents, but for the most part, it's uncontested.
Cliffside Lodge has plenty of weapon chests for players to loot and several slurp barrels and kegs for shields. Players should know that Cliffside Lodge isn’t close to water, so rotation may be a challenge if they can't find the Wings of Icarus , but it’s close to POIs like Brawler’s Battleground and Mount Olympus. When dropping into this location, land at the top of the house since most chests are on top floors, then work your way down.
Research Rock
Riddled with loot.
Research Rock is located east of Brawler's Battleground, and it’s one of the greatest Fortnite POIs with tons of loot. The region has up to 22 chests with weapons of blue and higher rarities . Many players often underrate Research Rock since it's at the corner of the map, and it's relatively small compared to other POIs in this biome.
Fortnite: Chapter 5 Season 2 Milestone Quests
However, it has large amounts of chests and tons of metal for farming. Players who want locations with sufficient loot should consider landing at Research Rock. Here, they can find enough to loot, eliminating the need to visit other POIs for better weapons and more shields.
Central Location with a Large Amount of Loot
Grim Gate is located in the Underworld biome, and it's a central location with a lot of loot . Players can loot up to 36 chests in this area and farm plenty of materials, including brick. The central location of Grim Gate offers players access to various POIs for rotation, but this means it may be contested, so players should be ready for enemy encounters.
Grim Gate is one of the few Fortnite locations containing Underworld Chests, so players should consider landing here to acquire the Wings of Icarus or Cerberus's Aspect of Agility medallion . Players can also find several slurp barrels and kegs for shields. Even though Grim Gate is a smaller and more concentrated version of Underworld, it’s one of the best landing spots in Fortnite .
Platform(s) Xbox Series S, Xbox Series X, Switch, PS5, PC, iOS, Android, Mobile, Xbox One
Released July 25, 2017
Developer(s) Epic Games
Genre(s) Survival, Battle Royale
Multiplayer Online Multiplayer

- World of Warcraft
- Baldur's Gate
- League of Legends
- Counter-Strike
- Ethics Policy
- Ownership Policy
- Fact Checking Policy
- Corrections Policy
- Affiliate Policy

All Perseus level-up quests in Fortnite Chapter 5, season 2
The end of Fortnite Chapter Five, season two is on the horizon, and if you’re lagging behind in the race to complete the battle pass, the Perseus level-up quests can provide a huge boost.
Every quest completed from the Perseus level-up pack increases your Fortnite battle pass ranking by one level. You can earn 28 levels through this method—but it comes at a cost. The Perseus level-up pack in Fortnite costs 1,200 V-Bucks, and once purchased, you unlock the quests associated with the pack. We’ve got details on how to complete all the quests below.
How to complete all Perseus level-up quests in Fortnite
There are four stages to the Perseus level-up quests in Fortnite, with a new part released every week.
All part one Perseus level-up quests
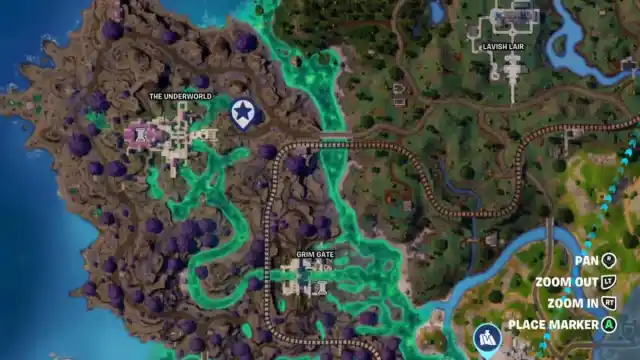
In part one of the Perseus level-up quests, you must collect parts of the Mirrorscale Tokens on the map. Track this quest, and you will be directed to a location on the map near The Underworld, shown in the image above.
Immediately after collecting the first Mirrorscale Token, you will be directed to the next a short distance away. This trend continues until you have collected all the Mirrorscale Tokens and unlock the Mirror Aegis Back Bling.
You should be able to collect all the Mirrorscale Tokens in one game, but if you get eliminated, return to The Underworld and continue your search.
All part two Perseus level-up quests
Part two of the Perseus level-up quests in Fortnite will be available from April 30. Completing the quests unlocks the Mortal’s Myth Item Wrap.
All part three Perseus level-up quests
Part three of the Perseus level-up quests in Fortnite will be available from May 7. Completing the quests unlocks the Shattered Harpe Pickaxe.
All part four Perseus level-up quests
Part four of the Perseus level-up quests in Fortnite will be available from May 14. Completing the quests unlocks the Storied Hero Perseus Style for the Perseus Outfit.


An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Fifth National Climate Assessment - Read the Report
Authors Selected for the First National Nature Assessment
The U.S. Global Change Research Program is pleased to announce the selection of authors for the first-ever National Nature Assessment (NNA1). The diverse team that will number over 150 experts was selected by the 11 NNA1 chapter leads in consultation with federal leadership, based in part on a public call for author nominations. The authors come to NNA1 from a range of organizations across the country—from universities to federal, and state government, national laboratories, businesses, and nonprofits. They bring deep experience and expertise in fields like ecology, health, economics, nature-based solutions, urban systems, environmental justice, agriculture, engineering, and much more. The author team also includes Indigenous Knowledge holders with place-based knowledge reflecting local experiences with nature.
“We have an amazing author team of truly interdisciplinary thinkers, ready to collaborate in a way that’s integral to this effort. As the team drafts the report over the next two years, the authors will draw on insights from our consultations with Tribal communities and listening sessions with people across the country to understand how nature supports them and how NNA1 could make a difference in their lives—building a report that reflects diverse experiences with nature and the many benefits it provides.” - Phil Levin, NNA Director
With extensive consultations conducted and the full author team in place, the writing phase of the assessment is now kicking off.
Over the next two years, NNA1 authors will take stock of what nature provides to us in terms of its inherent worth, our culture, health, and well-being, jobs and livelihoods, safety, and more, while looking ahead to understand how these benefits might change in the future. The final report is expected in late 2026.
“The NNA will provide a comprehensive understanding of nature, enriched by diverse scientific expertise, Indigenous knowledge, and lived experience of authors from across the United States. The NNA is an opportunity to integrate and assess information—from multiple sources and through a diversity of voices—to capture and communicate what nature means to different people, and to explore the future of nature in this Nation.” - Jane Lubchenco, Deputy Director for Climate and Environment, White House Office of Science and Technology Policy
NNA1 authors will have many opportunities to hear from the public throughout their work—including calls for public comment on the report outline and draft, expected in summer 2024 and fall 2025, respectively. Opportunities to participate in NNA1 will be made available on the USGCRP website .
Read a blog by NNA1 Director Phil Levin, “ A Nature Imperative on Earth Day ,” for the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy
NNA1 is also mentioned in the Presidential Proclamation on National Park Week, 2024
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Changing Partisan Coalitions in a Politically Divided Nation
5. party identification among religious groups and religiously unaffiliated voters, table of contents.
- What this report tells us – and what it doesn’t
- Partisans and partisan leaners in the U.S. electorate
- Party identification and ideology
- Education and partisanship
- Education, race and partisanship
- Partisanship by race and gender
- Partisanship across educational and gender groups by race and ethnicity
- Gender and partisanship
- Parents are more Republican than voters without children
- Partisanship among men and women within age groups
- Race, age and partisanship
- The partisanship of generational cohorts
- Religion, race and ethnicity, and partisanship
- Party identification among atheists, agnostics and ‘nothing in particular’
- Partisanship and religious service attendance
- Partisanship by income groups
- The relationship between income and partisanship differs by education
- Union members remain more Democratic than Republican
- Homeowners are more Republican than renters
- Partisanship of military veterans
- Demographic differences in partisanship by community type
- Race and ethnicity
- Age and the U.S. electorate
- Education by race and ethnicity
- Religious affiliation
- Ideological composition of voters
- Acknowledgments
- Overview of survey methodologies
- The 2023 American Trends Panel profile survey methodology
- Measuring party identification across survey modes
- Adjusting telephone survey trends
- Appendix B: Religious category definitions
- Appendix C: Age cohort definitions
The relationship between partisanship and voters’ religious affiliation continues to be strong – especially when it comes to whether they belong to any organized religion at all.
The gap between voters who identify with an organized religion and those who do not has grown much wider in recent years.
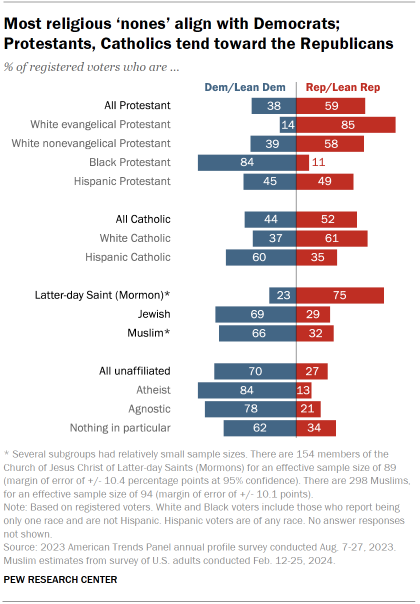
Protestants mostly align with the Republican Party. Protestants remain the largest single religious group in the United States. As they have for most of the past 15 years, a majority of Protestant registered voters (59%) associate with the GOP, though as recently as 2009 they were split nearly equally between the two parties.
Partisan identity among Catholics had been closely divided, but the GOP now has a modest advantage among Catholics. About half of Catholic voters identify as Republicans or lean toward the Republican Party, compared with 44% who identify as Democrats or lean Democratic.
Members of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints remain overwhelmingly Republican. Three-quarters of voters in this group, widely known as Mormons, identify as Republicans or lean Republican. Only about a quarter (23%) associate with the Democratic Party.
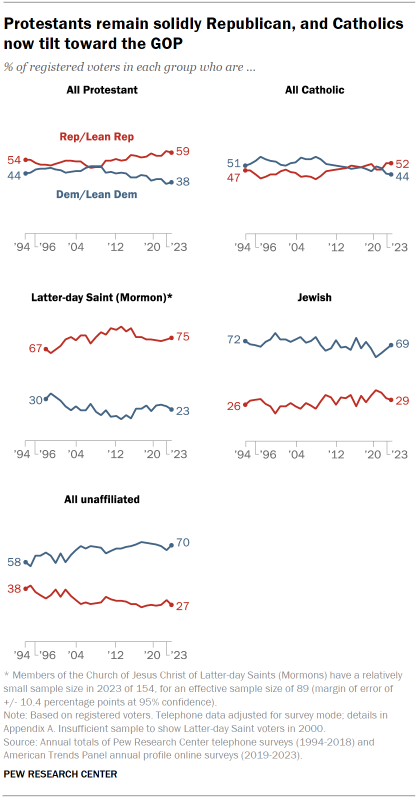
Jewish voters continue to mostly align with the Democrats. About seven-in-ten Jewish voters (69%) associate with the Democratic Party, while 29% affiliate with the Republican Party. The share of Jewish voters who align with the Democrats has increased 8 percentage points since 2020.
Muslims associate with Democrats over Republicans by a wide margin. Currently, 66% of Muslim voters say they are Democrats or independents who lean Democratic, compared with 32% who are Republicans or lean Republican. (Data for Muslim voters is not available for earlier years because of small sample sizes.)
Democrats maintain a wide advantage among religiously unaffiliated voters. Religious “nones” have become more Democratic over the past few decades as their size in the U.S. population overall and in the electorate has grown significantly. While 70% of religiously unaffiliated voters align with the Democratic Party, just 27% identify as Republicans or lean Republican.
Related: Religious “nones” in America: Who they are and what they believe
Over the past few decades, White evangelical Protestant voters have moved increasingly toward the GOP.
- Today, 85% of White evangelical voters identify with or lean toward the GOP; just 14% align with the Democrats.
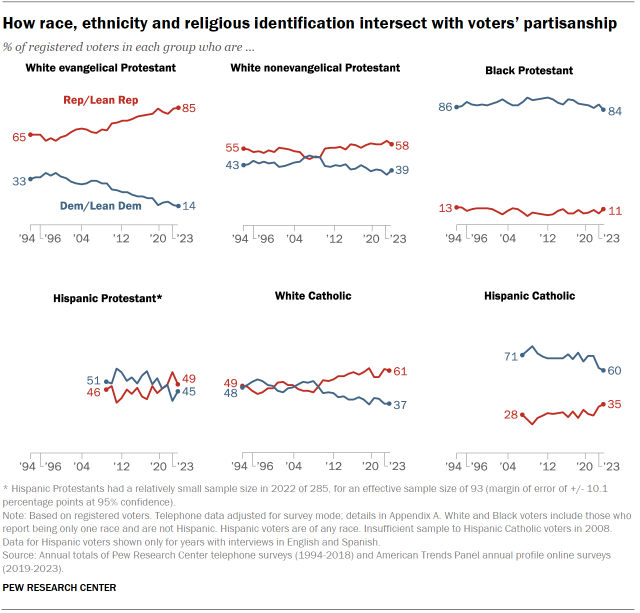
- Over the past three decades, there has been a 20 percentage point rise in the share of White evangelicals who associate with the GOP – and a 20-point decline in the share identifying as or leaning Democratic.
Over the past 15 years, the GOP also has made gains among White nonevangelical and White Catholic voters.
About six-in-ten White nonevangelicals (58%) and White Catholics (61%) align with the GOP. Voters in both groups were equally divided between the two parties in 2009.
Partisanship among Hispanic voters varies widely among Catholics and Protestants.
- 60% of Hispanic Catholic voters identify as Democrats or lean Democratic, but that share has declined over the past 15 years.
- Hispanic Protestant voters are evenly divided: 49% associate with the Republican Party, while 45% identify as Democrats or lean Democratic.
A large majority of Black Protestants identify with the Democrats (84%), but that share is down 9 points from where it was 15 years ago (93%).
Atheists and agnostics, who make up relatively small shares of all religiously unaffiliated voters, are heavily Democratic.
Among those who identify their religion as “nothing in particular” – and who comprise a majority of all religious “nones” – Democrats hold a smaller advantage in party identification.
- More than eight-in-ten atheists (84%) align with the Democratic Party, as do 78% of agnostics.
- 62% of voters who describe themselves as “nothing in particular” identify as Democrats or lean Democratic, while 34% align with the GOP.
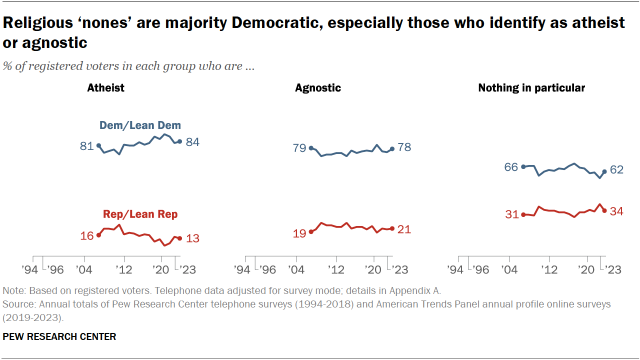
Voters who regularly attend religious services are more likely to identify with or lean toward the Republican Party than voters who attend less regularly.
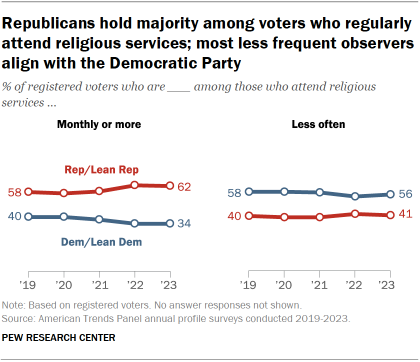
In 2023, 62% of registered voters who attended religious services once a month or more aligned with Republicans, compared with 41% of those who attend services less often.
This pattern has been evident for many years. However, the share of voters who identify as Republicans or lean Republican has edged up in recent years.
For White, Hispanic and Asian voters, regular attendance at religious services is linked to an increase in association with the Republican Party.
However, this is not the case among Black voters.
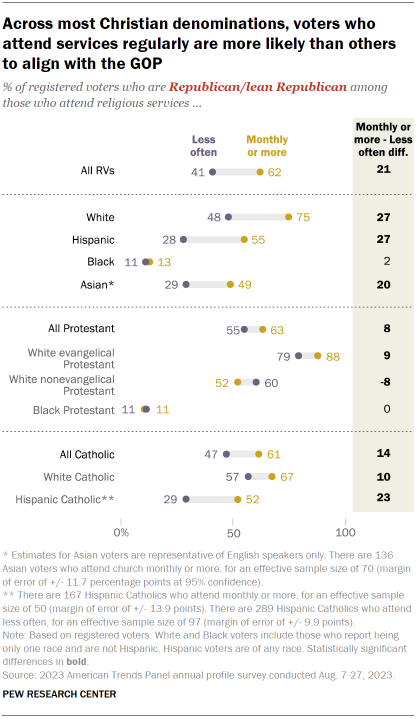
Only about one-in-ten Black voters who are regular attenders (13%) and a similar share (11%) of those who attend less often identify as Republicans or Republican leaners.
Higher GOP association among regular attenders of religious services is seen across most denominations.
For example, among Catholic voters who attend services monthly or more often, 61% identify as Republicans or lean toward the Republican Party.
Among less frequent attenders, 47% align with the GOP.
Black Protestants are an exception to this pattern: Black Protestant voters who attend religious services monthly or more often are no more likely to associate with the Republican Party than less frequent attenders.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Education & Politics
- Election 2024
- Gender & Politics
- Political Parties
- Race, Ethnicity & Politics
- Religion & Politics
- Rural, Urban and Suburban Communities
- Voter Demographics
What’s It Like To Be a Teacher in America Today?
Republican gains in 2022 midterms driven mostly by turnout advantage, more americans disapprove than approve of colleges considering race, ethnicity in admissions decisions, partisan divides over k-12 education in 8 charts, school district mission statements highlight a partisan divide over diversity, equity and inclusion in k-12 education, most popular, report materials.
- Party Identification Detailed Tables, 1994-2023
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The conclusions are as stated below: i. Students' use of language in the oral sessions depicted their beliefs and values. based on their intentions. The oral sessions prompted the students to be ...
The Purpose of Chapter 5Topic 2: Chapter 5. The Purpose of Chapter 5. Topic 2: Chapter 5. Learning Goals: Understand the components of Chapter 5. Write the introduction to include the problem, purpose, research questions and brief description of the methodology. Review and verify findings for the study. Write the Summary of Findings.
Overview of Chapter 5. A well-written Chapter 5 should include information about the following: Summary of findings. Interpretation of findings. Context of findings. Implications of findings. Discussion on limitations of study. Discussion on future directions of research/field.
4. A second section in the discussion chapter addresses and explores implications for practice. For the sake of clarity, create separate sections for implications that involve research, professional practice, or policy. 5. When preparing the conclusion section, imagine giving a brief talk to your colleagues. Based
method/s of research employed. statistical treatment/s applied, or hypotheses tested, if there is any; and; results. If you notice, all the parts mentioned above are already included in your Chapters 1- 4. So, the challenge is on how you are going to write and present it in Chapter 5 briefly.
5.1 The Abstract. The abstract of a research paper contains the most critical aspects of the paper: your research question, the context (country/population/subjects and period) analyzed, the findings, and the main conclusion. You have about 250 characters to attract the attention of the readers. Many times (in fact, most of the time), readers ...
Research Study Findings and Conclusions. Chapter 5: Home. Welcome to Chapter Five ; Chapter 5 Webinars; Alignment of Dissertation Components for DIS-9904ABC
Introduction The following chapter concludes this report. A summary of the research is presented, and findings of the study are discussed and interpreted. The significance of this research in the immediate context of El Gallo and in the field of low-income housing is examined. Recommendations for further research end the chapter. The scope of the following conclusions is limited to the context ...
Chapter 5: The Literature Review. Describe a literature review and explain its purpose. Describe the steps in undertaking a literature review. Write a literature review. Identify acceptable sources to include in your literature review. Apply the five 'C's of writing a literature review. Compare a literature review, an essay and an annotated ...
of this report discuss the investigation in three parts: first, a summary of study's research design and results; second, a positing of the implications of those results; and third, a proffering of two kinds of recommendations—(a) for further research, and (b) for future directions in policy making and professional development planning.
5 parts of research paper - Download as a PDF or view online for free. ... ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION OF DATA • CHAPTER 5 SUMMARY, CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS • Others 3. • Background of the Study - includes purpose and reason behind the conduct of the study. (What made you conduct the study?)
1. The Title. The title should be specific and indicate the theme of the research and what ideas it addresses. Use keywords that help explain your paper's topic to the reader. Try to avoid abbreviations and jargon. Think about keywords that people would use to search for your paper and include them in your title. 2.
Dissertation Chapter 5 Sample. be research. CHAPTER V: DISCUSSION be. The purpose of this qualitative grounded theory study was to identify what motivates. Outline the organization. women to stay in or return to STEM professions, leading to a model of motivation. This.
View PDF. Chapter 5 SUMMARY, CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS Chapter 5 contains the research summary, conclusions and recommendations of the whole study. The findings of the study without so much detailed information is written on the summary. Generalizations and other interferences would be seen on the conclusion while the recommendations of ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Restate the problem. Step 2: Sum up the paper. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Research paper conclusion examples. Frequently asked questions about research paper conclusions.
6. This was conducted for the purpose of determining the status of teaching science in the high schools of Province A. The descriptive method is used of research was utilized and the nominative survey technique was used for gathering data.
Chapter 5 Summary, Conclusions, Discussions, & Recommendations Applied Research Center Abraham S. Fischler School of Education Summer Conference 2012 General Information This session will address the components of Chapter 5 of the Applied Dissertation. The format and style of Chapter 5 should follow the Style Guide for the Applied Dissertationand the sixth edition of the APA manual.
This chapter begins with a summary of my thesis in Section 5.2, with each chapter summarised. Section 5.3 addresses the major findings of my study, followed by Section 5.4 that describes three major contributions of my study. The constraints and limitations of my study are summarised in Section 5.5, whereas Section 5.6
Chapter 5 Experimental Research The strongest arguments prove nothing so long as the conclusions are not verified by experience. Experimental science is the queen of sciences and the goal of all speculation. Roger Bacon (1214-1294) Experiments are part of the scientific method that helps to decide the fate of two
PDF | Chapter 5 consists of three parts, namely: (1) Summary of the Problems, Method and Findings; (2) Conclusions; and (3) Recommendations. Part One,... | Find, read and cite all the research you ...
Conclusions Based on the findings of the study, the following conclusions are drawn: 1. The researchers conclude that the Filipino tour guide should have enough skills and knowledge to be an effective leader. 3. 70 EULOGIO "AMANG" RODRIGUEZ INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY COLLEGE OF HOSPITALITY MANAGEMENT 2.
Topic 2: Chapter 5. In this activity, you will draft the introduction for Chapter 5. Provide an overview of your study, keeping in mind throughout this chapter your understanding of the audience and writing in a voice for the audience without distortion. Write from a retrospective vision and the wisdom of hindsight.
took part in this research was 118. Interviews were conducted with 118 respondents using a prepared structured pre-tested interview schedule. The interview schedule was coded for easy analysis and analised using the SPSS computer program. The findings were presented and discussed in chapter 4 by making use of frequency tables, bar and pie graphs.
Research Rock in the corner of the map is underrated but a goldmine for loot with 22 chests and farming opportunities. Fortnite 's Chapter 5 Season 2 is in full swing, and players are excited to ...
The share who are Hispanic has about tripled, from 5% then to 16% today. Asian voters have increased from less than 1% of Democrats' coalition to 6% over the same period. The share of Black voters within the Democratic coalition has remained fairly stable, and they currently make up 18% of Democratic and Democratic-leaning voters.
collect parts of the Mirrorscale Tokens on the map. unlock the Mirror Aegis Back Bling. available from April 30. Mortal's Myth Item Wrap. available from May 7. Shattered Harpe Pickaxe. available ...
Women (66%) are more likely than men (57%) to say abortion should be legal in most or all cases, according to the survey conducted after the court's ruling. More than half of U.S. adults - including 60% of women and 51% of men - said in March that women should have a greater say than men in setting abortion policy.
The U.S. Global Change Research Program is pleased to announce the selection of authors for the first-ever National Nature Assessment (NNA1). The diverse team that will number over 150 experts was selected by the 11 NNA1 chapter leads in consultation with federal leadership, based in part on a public call for author nominations. The authors come to NNA1 from a range of organizations across the ...
Release Copy. Governor Kathy Hochul today announced her plan to transform New York's economy and workforce as part of the FY 2025 Budget. The Budget includes a $500 million capital investment to jumpstart a $10 billion partnership for next-generation chips research; a $200 million investment to support four ON-RAMP advanced manufacturing training centers and prepare New Yorkers for the jobs ...
Protestants mostly align with the Republican Party. Protestants remain the largest single religious group in the United States. As they have for most of the past 15 years, a majority of Protestant registered voters (59%) associate with the GOP, though as recently as 2009 they were split nearly equally between the two parties.