
- International Marketing

Apple’s Global Strategy: Simplicity, Innovation, and Adaptability
- January 19, 2024
- LinkedIn 57
Table of Contents
Delving into apple’s global strategy, apple’s core values and the simplicity mantra, apple’s global branding strategy, apple’s global marketing strategy, case studies, apple’s global tax strategy.
- The Cornerstones of Apple’s Global Strateg
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, Apple stands as a beacon of innovation and design, captivating consumers worldwide with its sleek products and user-centric approach. With a global presence spanning over 150 countries and an estimated $383.29 billion in revenue in 2023, according to Statista , Apple’s success is a testament to its astute global strategy , a harmonious blend of differentiation, adaptability, and unwavering commitment to quality.
Apple’s global strategy is rooted in the concept of “differentiation,” a strategic approach that sets it apart from its competitors. By consistently pushing the boundaries of innovation, Apple has carved a niche for itself, offering products that are not only technologically advanced but also aesthetically pleasing and user-friendly . This differentiation has allowed Apple to capture a loyal customer base and establish a strong brand identity across the globe .
Apple’s global strategy has evolved over time, adapting to the changing dynamics of the international market. In its early days, the company focused heavily on innovation, relentlessly pursuing cutting-edge technologies and groundbreaking designs. However, as the company matured, it recognized the importance of customer experience and began placing a greater emphasis on this aspect . Today, Apple’s global strategy is a seamless blend of innovation and customer focus, ensuring that its products and services align with the needs and preferences of consumers worldwide.
At the heart of Apple’s global success lies a set of core values that permeate every aspect of the company’s operations , from product design to marketing campaigns. These values, deeply rooted in the company’s identity, guide Apple’s approach to innovation, customer experience, and global expansion.
- Accessibility: Apple strives to make its products and services accessible to everyone, regardless of their physical or cognitive abilities. This commitment is evident in features like VoiceOver , which provides spoken feedback for visually impaired users, and AssistiveTouch , which allows users with limited mobility to control devices with gestures.
- Educational Support: Apple recognizes the transformative power of technology in education and actively supports initiatives that promote digital literacy and learning. The company’s initiatives include Apple Teacher certification programs, curriculum resources, and educational apps that enhance teaching and learning.
- Carbon Neutrality: Apple is committed to reducing its environmental impact and is working towards becoming carbon neutral by 2030 . The company has implemented numerous initiatives to minimize its carbon footprint, including transitioning to renewable energy sources, designing energy-efficient products, and recycling materials.
- Inclusive Work Environment: Apple is committed to creating a diverse and inclusive workplace where everyone is valued and respected. The company has implemented policies and programs that promote diversity hiring, provide equal opportunities for advancement, and foster a culture of inclusion.
- Privacy: Apple is a staunch advocate for user privacy and believes that individuals should have control over their personal data. The company has implemented robust privacy protections in its products and services, including encryption, data minimization, and transparency.
- Equity and Justice: Apple is committed to promoting equity and justice in its operations and throughout the world. The company supports initiatives that address social and economic inequalities, promotes human rights, and advocates for environmental sustainability.
- Supplier Responsibility: Apple is committed to ensuring that its suppliers adhere to high ethical standards and treat their workers with respect. The company has established stringent supplier codes of conduct and conducts regular audits to monitor compliance.
These core values, collectively, form the foundation of Apple’s global strategy. They guide the company’s product design, marketing campaigns, and customer service interactions , ensuring that Apple delivers products and experiences that are not only technologically advanced but also aligned with its values of simplicity, accessibility, and inclusivity.
Simplicity is a cornerstone of Apple’s design philosophy, evident in the clean aesthetics, intuitive interfaces, and user-friendly features of its products. This emphasis on simplicity has resonated with consumers worldwide , making Apple products accessible to a broad audience and fostering a loyal customer base.
By upholding its core values and embracing simplicity, Apple has not only achieved global success but also established itself as a role model for other companies seeking to build a sustainable and ethical business model.
Apple’s global branding strategy is a delicate balance of standardization and adaptation, ensuring that the company maintains a consistent brand identity while also resonating with consumers in diverse cultures and markets. On the one hand, Apple strives to project a unified brand image, conveying its core values of innovation, simplicity, and elegance across all its products, marketing campaigns, and customer interactions. This standardization helps reinforce Apple’s reputation for quality and consistency, fostering brand loyalty and recognition worldwide.
On the other hand, Apple recognizes the need to adapt its branding to local markets and cultures. This adaptability is evident in the company’s product offerings, marketing messages, and customer support. For instance, Apple has developed localized versions of its products with features and specifications tailored to specific regions . Additionally, the company’s marketing campaigns often incorporate cultural nuances and local references to connect with consumers on a deeper level.
Apple’s ability to balance standardization and adaptation has been a key factor in its global success. By maintaining a consistent brand identity, the company has built a strong foundation of brand recognition and loyalty . However, by adapting to local markets, Apple has been able to cater to the needs and preferences of consumers in different parts of the world, expanding its reach and deepening its customer base.
Examples of Apple’s Standardization
- Unifying Brand Elements: Apple employs a consistent design language across its products, including clean aesthetics, minimalist interfaces, and sleek silhouettes. This consistent visual language helps establish a cohesive brand identity.
- Global Marketing Campaigns: Apple’s marketing campaigns often feature universal themes of innovation, creativity, and personal empowerment, appealing to a global audience.
- Seamless Customer Experience: Apple’s customer support is available in multiple languages, and the company’s online store can be accessed in over 40 countries, ensuring a consistent experience for customers worldwide.
Examples of Apple’s Adaptation
- Localization of Products: Apple offers localized versions of its products, such as the iPhone and iPad, with features and specifications tailored to specific regions. For instance, the iPhone SE 2020 is optimized for Indian consumers with support for two SIM cards and regional cellular bands.
- Culturally Sensitive Marketing: Apple’s marketing campaigns often incorporate cultural nuances and local references to connect with consumers on a deeper level. For example, the company’s “ Shot on iPhone ” campaign features images captured by photographers from around the world, showcasing the diversity of visual storytelling.
- Localized Customer Support: Apple provides customer support in multiple languages and offers localized resources, such as online FAQs and tutorials, tailored to specific regions. The company also partners with local businesses to offer personalized support services.
Apple’s success in balancing standardization and adaptation is a testament to its understanding of the complexities of global branding. By striking this delicate balance, the company has been able to maintain a strong brand identity while also resonating with consumers in diverse markets , solidifying its position as one of the world’s most recognizable brands.
Apple’s global marketing strategy is a multifaceted approach that revolves around four key pillars: wide acceptance, brand value, competitive advantage, and low imitation . These pillars are intertwined, working together to propel Apple’s success in the global marketplace.
Wide Acceptance
Apple’s products have achieved widespread acceptance worldwide, attracting a loyal customer base across diverse demographics and regions . This widespread appeal is attributed to several factors, including:
- Innovative Designs: Apple consistently pushes the boundaries of design, creating products that are both aesthetically pleasing and user-friendly. The company’s sleek, minimalist aesthetic has become synonymous with Apple’s brand identity.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Apple’s products are renowned for their intuitive interfaces, making them easy to navigate and use for people of all technical backgrounds.
- Effective Marketing Campaigns: Apple’s marketing campaigns are known for their creativity and emotional appeal, resonating with consumers on a personal level. The company often uses storytelling and cultural references to connect with diverse audiences.
Brand Value
Apple has built a strong brand value over the years, characterized by perceptions of quality, innovation, and premium craftsmanship . This brand value has been instrumental in attracting consumers and fostering brand loyalty.
- Reputation for Quality: Apple is consistently rated among the most reliable and durable consumer electronics brands. This reputation for quality has earned the company a loyal following among consumers who value long-lasting products.
- Innovation: Apple is renowned for its pioneering spirit, consistently introducing innovative products that redefine the technological landscape. This focus on innovation has helped maintain Apple’s cutting-edge reputation and attract early adopters.
- Premium Branding: Apple’s products are positioned in the premium segment of the market , commanding higher prices than its competitors. This premium positioning contributes to the company’s brand value and reinforces its image as a luxury brand.
Competitive Advantage
Apple maintains a competitive advantage in the global market through a combination of factors, including:
- Strategic Product Differentiation: Apple differentiates its products from competitors through unique features, design elements, and user experiences. This differentiation strategy has helped the company carve out a distinct niche in the market.
- Focus on Customer Experience: Apple prioritizes customer satisfaction, creating a seamless and personalized experience for its users. This focus on customer experience has helped foster brand loyalty and attract new customers.
- Global Retail Presence: Apple has a strong global retail presence, with over 500 stores in 23 countries, as per Statista . This extensive retail network provides consumers with easy access to Apple products and services.
Low Imitation
Despite facing intense competition from numerous technology giants, Apple has been able to maintain a relatively low level of imitation . This is due to several factors, including:
- Continuous Innovation: Apple’s relentless pursuit of innovation makes it difficult for competitors to replicate its products and services.
- Strengthened Intellectual Property Protection: Apple has a robust intellectual property portfolio, providing legal protection for its innovative designs and technologies.
- Brand Loyalty: Apple’s loyal customer base is less susceptible to imitation, as they are often willing to pay a premium for Apple products due to their brand loyalty and trust in the company.
Apple’s successful global marketing strategy is a testament to its ability to balance innovation, brand value, competitive advantage, and low imitation. By consistently delivering high-quality products, cultivating a strong brand reputation, and prioritizing customer experience, Apple has cemented its position as one of the world’s leading technology companies .
Apple’s remarkable global success is evident in its ability to penetrate and dominate markets as diverse as China and India. These two countries represent two of the world’s most populous and rapidly growing economies, offering significant opportunities for technology companies. Apple’s success in these markets is a testament to its ability to adapt its global strategy to local conditions and preferences .
China has become Apple’s second-largest market , with over 190 million active iPhones in use as of 2023 ( Statista , 2023). Apple’s success in China can be attributed to several factors, including:
- Pricing Strategy: Apple has adopted a tiered pricing strategy in China, offering a wider range of products at lower price points to cater to a broader range of consumers.
- Distribution Channels: Apple has established a strong network of authorized resellers and retail stores in China, making its products readily available to consumers across the country.
- Partnerships with Local Businesses: Apple has partnered with Chinese telecommunications companies, e-commerce platforms, and content providers to expand its reach and customer base.
- Localization: Apple has made sure to localize its products , marketing campaigns, and customer support for the Chinese market, ensuring that they resonate with local consumers.
Despite facing challenges such as piracy and counterfeiting, Apple has successfully established itself as a premium brand in China . The company’s commitment to innovation, design, and customer experience has resonated with Chinese consumers, who are increasingly embracing technology.
India is another key market for Apple, with a growing middle class and increasing smartphone penetration. Apple’s strategy in India has focused on tailoring its products and services to the specific needs and preferences of Indian consumers .
- Price Sensitivity: Apple has introduced more affordable iPhone models in India, such as the iPhone SE, to attract price-conscious consumers.
- Online Sales: Apple has heavily invested in its online presence in India, making it easier for consumers to purchase its products online.
- Partnerships with Local Businesses: Apple has partnered with Indian e-commerce platforms, mobile carriers, and banks to expand its distribution reach and payment options.
- Localization: Apple’s localization strategy for the Indian market has included the adaptation of its products, marketing campaigns, and customer support, including the development of Hindi-language versions of its software.
Apple’s success in India has been gradual but steady. The company has faced challenges such as competition from local smartphone brands and a lack of brand recognition in rural areas. However, Apple’s commitment to innovation and adaptation has helped it gain traction in this emerging market .
Apple’s global success has been accompanied by scrutiny over its tax practices, particularly its use of a subsidiary company in Ireland to minimize its global tax liability. This strategy, known as “ Double Irish with a Dutch Sandwich ,” has allowed Apple to shift profits offshore, effectively reducing its tax payments in the United States and other countries .
While Apple has defended its tax strategy, arguing that it complies with all applicable laws, it has faced criticism from governments, tax experts, and consumer advocacy groups . Critics argue that Apple’s tax practices amount to corporate tax avoidance, depriving governments of revenue that could be used for public services.
Advantages of Apple’s Tax Strategy
Apple’s tax strategy has several potential advantages for the company, including:
- Reduced Tax Burden: By shifting profits offshore, Apple can effectively reduce its tax payments, which can boost its profitability and financial returns to shareholders.
- Increased Competitiveness: Lowering tax costs can give Apple a competitive advantage over other companies, allowing it to invest more in research and development, marketing, and product development.
- Enhanced Shareholder Value: By reducing its tax burden and increasing profitability, Apple can improve its financial performance and boost shareholder value.
Disadvantages of Apple’s Tax Strategy
Apple’s tax strategy has also been criticized for several potential disadvantages, including:
- Public Image Concerns: Apple’s tax practices have tarnished its public image, raising concerns about corporate social responsibility and ethical behavior.
- Legal Challenges: Governments and tax authorities around the world have been investigating Apple’s tax strategy, and the company faces potential legal challenges that could lead to fines and penalties.
- Political Fallout: Apple’s tax practices have created political tensions, with some countries considering imposing stricter tax laws to prevent multinational corporations from shifting profits offshore.
A Balancing Act
Apple’s global tax strategy has been a source of controversy, highlighting the delicate balance between corporate profitability and societal responsibility . While the company may benefit financially from its tax practices, it also faces reputational risks and potential legal repercussions. Apple must carefully navigate this complex landscape to maintain its global success while addressing concerns about its ethical conduct.
The Cornerstones of Apple’s Global Strategy
Apple’s journey to becoming one of the world’s most recognizable and successful companies is a testament to its ability to balance simplicity, innovation, and adaptability. From its early days as a niche computer manufacturer to its current status as a global technology powerhouse, Apple has consistently demonstrated its knack for understanding and meeting the evolving needs of consumers worldwide .
Apple’s core values, particularly its emphasis on simplicity, have permeated every aspect of its business. The company’s products are renowned for their user-friendly interfaces and intuitive designs , making them accessible to a wide range of users, regardless of their technical expertise. This commitment to simplicity extends to Apple’s marketing campaigns, which often use storytelling and emotional appeals to resonate with consumers on a personal level.
Apple’s unwavering focus on innovation has been another driving force behind its global success. The company has consistently pushed the boundaries of technology, introducing groundbreaking products that have transformed the way people interact with the digital world . From the revolutionary iPhone to the sleek AirPods, Apple has consistently redefined the standards for innovation in the technology industry.
Alongside innovation and simplicity, Apple has also demonstrated remarkable adaptability in its global expansion . The company has successfully tailored its products, marketing strategies, and customer support to suit the unique needs and preferences of different cultures. This adaptability has been crucial in Apple’s ability to penetrate and dominate markets as diverse as China and India, where local competitors pose significant challenges.
Apple’s approach to globalization is not without its critics. The company’s tax strategy, which has been the subject of intense scrutiny, has raised concerns about corporate social responsibility and ethical behavior. As Apple continues to expand its global footprint, it will need to address these concerns and demonstrate its commitment to operating responsibly and ethically in all the markets it serves.
Looking to the future, Apple faces a number of challenges and opportunities. The company will need to continue to innovate and adapt to the ever-changing technological landscape . It will also need to navigate the complexities of global markets, ensuring that its products and services remain relevant and appealing to consumers worldwide.
Apple’s journey to global success is a compelling case study in how a company can build a strong brand and establish a lasting presence in the international arena. By embracing simplicity, innovation, and adaptability, Apple has demonstrated that it has the vision and resilience to continue to thrive in an increasingly competitive and interconnected world .
As Apple embarks on the next chapter of its global journey, it remains to be seen how the company will navigate the evolving landscape of technology, consumerism, and globalization. However, one thing is certain: Apple’s commitment to innovation and its ability to understand the needs of consumers worldwide will continue to be key drivers of its success in the years to come.

Privacy Preferences
When you visit our website, it may store information through your browser from specific services, usually in the form of cookies. Here you can change your Privacy preferences. It is worth noting that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our website and the services we are able to offer.
- Apple Inc.’s Strategic Management Case Study Words: 3587
- Apple, Inc. As an Electronic Companies Words: 2264
- Apple Incorporation’s Strategic Plan Words: 1714
- Apple Company’s Business Ethics Words: 1778
- Apple and Technology Adoption Model Words: 620
- Apple Inc.: History, Vision, Mission, and Strategies Words: 3393
- Apple Inc.’s Strategic Management Recommendations Words: 2856
- Apple Inc.’s Innovation and Simplicity Words: 565
- Apple Computer Inc.: Maintaining the Music Business Words: 1446
- Operations Management: Apple Case Study Words: 3933
- Apple: Future Employment Opportunities Words: 1274
- Apple: Organizational Theory Words: 4153
- Apple Company’s Strategic Analysis Words: 1733
- Apple Inc.: Marketing Principles and Practice Words: 3088
- Aspects of Apple Inc. Analysis Words: 3371
- Apple: Marketing Communication and Branding Words: 3477
- Apple Organizational Behavior, Structure, & Culture Words: 2544
- Apple and Samsung Firms’ Technology Innovation Words: 1774
Apple Inc. Affected by Globalization and Technology
Globalization, industrial organization model, resource-based model, stakeholders.
For more than forty decades since its creation, Apple has continued to change the world with a string of products that have upended industries, reshaped society, and revolutionized computing. The company’s success is partly attributed to its ability to leverage technology. This paper will assess how globalization and technology changes have impacted Apple. It will also apply industrial and resource-based models to determine how the company could earn above-average returns and assess the influence of its vision and mission statements on its overall success. The paper will also assess its stakeholders’ categories and their roles in its success.
Globalization encompasses several interrelated processes, such as trade and finance internationalization. It is the incorporation and interaction between people, entities, and governments from across the globe. The entire globalization process influences political stability, information technology, and economic progression. Today, the world is interlinked in every aspect, making it a global village. In business operations, globalization has ensured that goods and services can be produced and used anywhere in the world. Over the last few years, Apple has drastically transformed how businesses are operated across the world. On top of its 43,000 employees in the United States, the company also has 20,000 additional workers overseas. Furthermore, Apple has contractors that employ more than 700,000 people. Interestingly, all of these 700,000 people work outside the United States, particularly in Asia and Europe (Hanson et al., 2). It is cheaper for Apple to produce from outside the US due to low labor costs. For instance, in 2011, the company paid its 13,920 American employees approximately $750 million compared to $320 million paid to 27,250 overseas employees (Hanson et al., 2). This is an indication that it is cheaper for Apple to manufacture overseas.
The significant success that Apple has had in the market over the years has been partly attributed to globalization. It has used the phenomenon to carve a competitive edge over its rivals. China, where more than half of Apple’s products are manufactured, boasts of low cost and a disciplined labor force. The company has managed to exploit this situation to maximize its profits. In addition, Apple has taken most of its manufacturing operations overseas to improve efficiencies and reduce costs. Southeast Asia and China play host to many of Apple’s subassemblies and upstream components. This implies that carrying out the final assembly in the United States presents a myriad of logistical challenges to the organization. As compared to the US, China has more agile and much larger factories.
Technology is increasingly changing the way many businesses are run today. Apple recognizes the fact that technology keeps developing every day. Machine learning, big data, and artificial intelligence are some of the most significant technological advances that have gained popularity within the company over the years. These technological inventions have narrowed the gap between the company and its customers. In June 2020, when Apple announced the iPad OS, macOS, and iOS, it alluded to the fact that several updates and features had machine learning and artificial intelligence.
Artificial intelligence has indeed had significant impacts on the company’s products and services. It allows facial recognition for Homekit, which is a smart home solution that enables users to communicate and control accessories connected through an app. The HomeKit framework allows users to create action controls and configure accessories. Users also have the liberty to cluster their actions together and use Siri to trigger them. Apple has also allowed security cameras that are Homekit enabled to use photos tagged on the phone of a user to identify people at the door. The technology can even call out the name of the person standing at the door. Apple has also used artificial intelligence to help users track their sleep. Through Apple Watch, machine learning can classify a user’s movements and detect if he or she is asleep and for how long. The watch also uses microphone and motion sensors to detect if a user is washing his hands.
The technology of big data analytics is considerably driving Apple’s decision-making processes. The data is primarily used by the company to establish the best way to approach consumers with its technologically advanced products and services. Big data analytics benefits the company in its application design. This helps it to discover how customers are using its many apps in real life. The information helps in altering the app’s future design to fit with various tendencies of customers. Big data analytics also helps the company to keep track of the health of its customers to improve their lifestyles. Through partnerships with mobile applications that are related to health, Apple collects this vital information and utilizes it to treat sicknesses, offer protection against preventable diseases, and prevent the rapid spread of diseases.
Social media is another significant technology frontier that Apple has leveraged over the years. Although the company cannot be said to have a large social media presence, it uses the sites to create much buzz during its launching events. People queue for days outside Apple stores to wait to purchase their new products after the launch. The absence of Apple on Twitter and Facebook is not accidental but a strategic move. In a way, it helps to prevent users from flooding the company’s official social media pages with negative messages. However, the tech giant uses social media platforms like Twitter, Instagram, and Facebook to promote its products. It does so by pushing ads that encourage users to gift their loved ones with Apple products.
Apple uses the industrial organization model to assist it in maintaining a huge stake in a market that is highly segmented. Through this model, the company narrows its pool of competition and creates entry barriers to maintain its foothold in the phone tech industry. Apple operates in a market that has very big competition. There are many players within the industry vying for its market share. Some of its competitors are Samsung, Huawei, LG, and Sony. However, all these competitors use the android operating system, which is an open platform for all (Hitt et al., 3). Apple, on the other hand, uses a closed system that is an end-to-end user platform. This makes it stand out from its competition, a factor that makes it easy to control its market segment.
The highly segmented market that Apple operates in makes it difficult for new entrants to thrive. Several political, technological, sociological, and political barriers imply that for one to enter the market, one will encounter a lot of stakes to surmount. Apple has struck a deal with the Chinese government to necessitate its operations there. This way, it has managed to gain a strong footing in the economic and political infrastructure of the country. In addition, Apple has managed to accurately its competitors’ next possible moves and make relevant and strategic moves to beat them. It did this with Sony and launched the iPod music, which penetrated Sony’s market segment.
Apple considers its resources as the key pillars of its performance that enable it to gain and maintain a competitive advantage. In the middle of its competitive environment, Apple relies on its internal resources to carve a competitive edge. Thus, it utilizes its internal resources to exploit external opportunities and deal with threats. The company’s resources are either tangible or intangible. The company’s headquartering in California is one of its key tangible resources where all its operations are engineered and executed. This is in addition to its labs and workshops in San Francisco and other outlets spread across the world. On the other hand, intangible resources are those that have no physical presence. They include Apple’s trademarks, intellectual property, and brand reputation. Indeed, the company has massively benefited from its brand reputation, which it has built over time. Its OS is one of its strongest intellectual property resources that has also separated it from its competitors.
Both the tangible and intangible resources rely on each other for effectiveness in performance. Although Apple operates in a very competitive industry, it can only achieve its competitive advantage if it uses its unique bundle of resources. Compared to Samsung Electronics, for instance, which also makes the same products (smartphones and tablets), Apple’s products are sold at much higher prices, giving it bigger profit margins. Samsung cannot do the same because it lacks the brand recognition that Apple boasts of. Besides, it does not have the capability to design products that are user-friendly the same way Apple does.
Apple’s vision statement is “to make the best products on earth, and to leave the world better than we found it” (Apple Mission and Vision Statement Analysis, 1). This vision statement strengthens the company’s strategic management, especially when it comes to decision-making for the future. It sees itself as the global leader when it comes to designing and developing products, hence the “best products” tag. This also challenges the company to always strive to push for novel, innovative products.
Apple’s mission statement is “to bring the best personal computing products and support to students, educators, designers, scientists, engineers, businesspersons, and consumers in over 140 countries around the world” (Apple Mission and Vision Statement Analysis, 1). This mission statement takes into consideration that the business landscape is changing, a factor that influences Apple’s possibilities. The changing trends in consumer tastes inform the development of this mission, which seeks to address the prevailing concerns in the global market.
Apple’s success is partly attributed to its ability to satisfy its various stakeholders who happen to have different concerns. The main stakeholder groups of the company include customers, employees, investors, suppliers, and distributors. Consumers are the people who purchase the company’s products. The company designs efficient and cutting-edge technology products to meet their needs. Employees are the ones who execute the company’s vision and mission. They are the company’s brand ambassadors and help satisfy the concerns of other stakeholders. Investors are mainly focused on maximizing the returns on their investments. To satisfy their interests, Apple always ensures that it registers excellent financial performances. When it comes to suppliers and distributors, the company imposes and monitors requirements on their employment practices to ensure that it does not conflict with its corporate culture.
Apple Mission and Vision Statement Analysis. (n.d). Mission Statements.
Hanson, D., Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., & Hoskisson, R. E. (2016). Strategic management: Competitiveness and globalisation. Cengage Learning.
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., & Hoskiss, R. E. (2016). Strategic Management. Cengage Learning.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, November 7). Apple Inc. Affected by Globalization and Technology. https://studycorgi.com/apple-inc-affected-by-globalization-and-technology/
"Apple Inc. Affected by Globalization and Technology." StudyCorgi , 7 Nov. 2022, studycorgi.com/apple-inc-affected-by-globalization-and-technology/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) 'Apple Inc. Affected by Globalization and Technology'. 7 November.
1. StudyCorgi . "Apple Inc. Affected by Globalization and Technology." November 7, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/apple-inc-affected-by-globalization-and-technology/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Apple Inc. Affected by Globalization and Technology." November 7, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/apple-inc-affected-by-globalization-and-technology/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "Apple Inc. Affected by Globalization and Technology." November 7, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/apple-inc-affected-by-globalization-and-technology/.
This paper, “Apple Inc. Affected by Globalization and Technology”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: December 29, 2022 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.

Technology and Operations Management
Mba student perspectives.
- Assignments
- Assignment: RC TOM Challenge 2017

Globalization with Apple

If the cost of manufacturing continues to increase in China as predicted, will it continue to be the best place to manufacture for Apple products?
Apple Inc has received a lot of bad publicity for using Chinese manufacturing companies to build most of their products. As a consumer would you be willing to pay at least $100 more for an iPhone to know it was designed and manufactured in the United States? (1)
Apple’s role with International Trade
Apple along with other manufacturing companies has taken manufacturing overseas to reduce costs and improve efficiencies. Many of the upstream components and subassemblies are also manufactured in China and Southeast Asia, so to do final assembly in the United States would create huge logistical challenges. China also has much larger and more nimble factories than in the United States. (2) Labor is starting to become an issue during peak seasons, usually over the summer due to the large number of manufacturing companies looking for labor. Companies are competing for moderately “skilled” labor to meet the demands of product launches. During an iPhone launch contract manufacturers need to hire or re-allocate around 250,000 people to work on finally assembly of the new iPhone. There are also all of the upstream suppliers who are also in need of employees to work on their sub-assemblies and components that go into the finished good. Apple now pays a premium on top of minimum wage to their contract manufacturers to ensure that they receive the labor needed to not delay production. Even with China’s population it is still a challenge to meet the demands of labor when so many companies are competing for the labor. Apple is currently heavily weighted in China for final assembly manufacturing, but if there were any changes in government regulations or tariff rates as stated by President Trump, it could put Apple at a significant disadvantage to getting product to customers in a timely manner and take an enormous hit to margins. (3)
Apple’s current strategy
Pathways to Just Digital Future
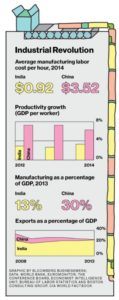
For the mid term, Apple has started to look at other countries to do their final assembly production. Apple is looking to produce in other countries, not just to reduce costs but to also increase revenues. IPhone market share in India isn’t in the top five smartphones so there is a large opportunity to establish its brand with the worlds 2nd largest populated country. (5) India is a strong candidate because the labor wages are approximately 25% the cost of labor in China, they have the experience and skill to quickly learn the manufacturing process for iPhones, and they have the ability to keep up with labor demands during peak seasons. (6)
President Donald Trump and Apple CEO Tim Cook met to discuss Apple’s future of manufacturing overseas. President Trump claims that Tim Cook has promised to build three large plants in the United States. Apple continues to explore its options of where to manufacture based off of costs, complexity, potential and capability. Producing in the United States poses other risks such as speed to market, increased costs, and manufacturing flexibility.
Recommendations for Apple
I think the Apple management team should make a bigger effort to explain the benefits of manufacturing overseas other than costs. Benefits include international opportunities to its employees, speed to market for its customers to have the latest and greatest technology, and efficiencies in the supply chain with the sub-component suppliers. Apple should also promote the number of foreign workers they have sponsored to work in the United States to add to the country’s diversity and accomplished population.
I also think that Apple needs to ban together with other manufacturing companies such as Microsoft, Alphabet, and Amazon to contest the current President’s goals of bringing all manufacturing back to the United States and “making America great again”. To bring that much manufacturing back to the United States would be a drastic change that would cause the companies to invest a significant amount and money and resources toward the move back and the country may not be able to keep up with the high demands of skills and labor needed to produce all hardware products.
Key Outstanding Questions
- With the rising labor costs in China and the competition for labor should Apple consider moving back to the United States or to another country? If so, which country?
- Do you think the United States can handle bringing back all manufacturing jobs in the medium term?
(Word Count 798)
- Swearingen, Jake. “Apple Isn’t Building 3 Factories in the U.S., No Matter What Trump Says.” Nymag.com, 25 July 2017, nymag.com/selectall/2017/07/despite-trump-claims-apple-wont-build-3-factories-in-u-s.html.
- Blodget, Henry. This Article Explains Why Apple Makes iPhones In China And Why The US Is Screwed. Business Insider, 22 Jan. 2012, businessinsider.com/you-simply-must-read-this-article-that-explains-why-apple-makes-iphones-in-china-and-why-the-us-is-screwed-2012-1 .
- Kharpal, Arjun. Apple is exploring moving iPhone production to the US: Report. CNBC, 18 Nov. 2016, cnbc.com/2016/11/18/apple-is-exploring-moving-iphone-production-to-the-us-report.html .
- Apple CEO Promised to Build 3 ‘Big’ Plants in U.S., Trump Says. Fortune, 25 July 2017, fortune.com/2017/07/25/apple-ceo-big-plants-trump/.
- Vincent, James. Apple has started assembling iPhones in India. The Verge, 17 May 2017, theverge.com/2017/5/17/15651842/apple-iphone-india-assembling-begun .
- Zhu, William. Comparison of Manufacturing Between India vs. China. LinkedIn, 9 Sept. 2016, www.linkedin.com/pulse/comparison-manufacturing-between-india-vs-china-william-zhu/.
Student comments on Globalization with Apple
I agree that it is not viable to bring a great deal of labor-intensive manufacturing back to America. The cost seems too high for most companies and would ultimately be passed through to the consumer. I think a better approach is understanding the root causes that are driving companies to manufacture abroad (e.g., is it purely cost of labor or other factors). The New Yorker posted an interesting article about Trump’s manufacturing policies (see link below). I believe the labor content required for manufacturer is going to decrease while the need for skilled workers who can operate specialized manufacturing equipment will grow. Both the US government as well as US based companies like Apple should evaluate how they are positioning American workers to shift to the changing environment and help these employees receive the requisite training they need to handle the shift to the modern factory.
https://www.newyorker.com/business/currency/why-donald-trump-is-wrong-about-manufacturing-jobs-and-china
Although the future of unskilled or low-skill labor seems very much in question, this article also brings into question the very long-term implications of new technology and the effect on capital and labor investment. If machines/capital are able to replace more and more human labor, will the production shift back to the countries where the final goods will be sold? Or will it still make sense to manufacture those items in certain countries based on the labor base and the price of the labor in those countries? Furthermore, what affect will the shift from human labor to capital for production have on those countries that have relied heavily on manufacturing jobs to boost the middle class?
Very interesting topic!
There were two things that came to my mind as to how apple can combat wage inflation. 1. Automation: How much will Apple invest in automation and work with their suppliers to reduce dependency on labor, especially eliminating the low to medium skill jobs. However, this is not easy and will take time. 2. Diversification of supplier base: Given the need to expand the manufacturing footprint and move to cheaper locations, India is a potential destination for apple with one of the solutions being to manufacture the older iPhones in Bangalore [1]. Yet, developing new suppliers and maintaining quality and scale in India is a whole new challenge.
However, on the isolationist policy and moving manufacturing back to US, Apple could potentially move manufacturing of some of the low volume high complexity items to US, employing few workers as a show of good faith. But with regards to scale and cost, I am unable to see how they would ever be able to manufacture a large portion of their demand in the US.
[1] http://mashable.com/2017/03/24/apple-iphone-india-6-6s-se/#Q9i1Fz2vCsq2
Thanks for sharing your insights on Apple and the implications protectionists policies will have on the company moving forward. To answer your first question regarding Apple’s response to rising labor costs in China, I do think that in the short term Apple should consider diversifying its geographic footprint to expand into neighboring countries with lower labor costs. That being said, I believe increasing dependence on automation will have a tremendous impact on Apple’s strategy moving forward as it considers labor costs management. As more and more workers are replaced with machines, Apple prospects of moving manufacturing back to the US in line with Trump’s protectionists agenda may increase. I think the central question to answer here is what type of labor Apple will need from a manufacturing prospective in the automated landscape of the future.
Lastly, I think one other element that will figure into Apple’s decision to invest more in US manufacturing is where its key partners and suppliers are going. Foxxconn, one of Apple’s largest manufacturing partners, already has plans to build new factories in the US [1], and if this trend continues I believe that Apple may consider increasing their US investment as well.
[1] https://www.cnbc.com/2017/05/09/foxconn-us-factory-likely-may-be-used-for-iphone-and-ipad-displays.html
Leave a comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Harvard Business School →
- Faculty & Research →
- November 2023
- HBS Case Collection
Apple Inc. in 2023
- Format: Print
- | Language: English
- | Pages: 26
About The Author
David B. Yoffie
Related work.
- January 2024
- Faculty Research
- Apple Inc. in 2023 By: David B. Yoffie
- High School
- You don't have any recent items yet.
- You don't have any courses yet.
- You don't have any books yet.
- You don't have any Studylists yet.
- Information
Apple case (globalization)
North south university, recommended for you, students also viewed.
- Factors Influencing Eating Behavior
- International Financial Management
- Nova accesories
- Mgt 314 group 2 project
- Value Stream Mapping - scm
- Updated Report on Procurement
Related documents
- Logistics - scm
- Aggregate Planning - scm
- MGT 210 Group project report on Ecstasy
- MGT 314 Case study 1 Fall 2021
- Productivity math - Practice papers
- Ch-1 Tfmcq - The is MCQ of MGT314 course
Preview text
Who makes the apple iphone.
In its early days, Apple usually didn’t look beyond its own backyard to manufacture its devices. A few years after Apple started to make the Macintosh computer back in 1983, Steve Jobs bragged that it was “a machine that was made in America.” As late as the early 2000s, Apple still manufactured many of its computers at the company’s iMac plant in Elk Grove, California. Jobs often said that he was as proud of the Apple’s manufacturing plants as he was of the devices themselves.
By 2004, however, Apple had largely turned to foreign manufacturing. The shift to offshore manufacturing reached its peak with the iconic iPhone, which Apple first introduced in 2007. All iPhones contain hundreds of parts, an estimated 90 percent of which are manufactured abroad. Advanced semiconductors come from Germany and Taiwan, memory from Korea and Japan, display panels and circuitry from Korea and Taiwan, chipsets from Europe, and rare metals from Africa and Asia. Apple’s major subcontractor, the Taiwanese multinational firm, Foxconn, performs final assembly in China.
Apple still employees some 43,000 people in the United States, and it has kept important activities at home, including product design, software engineering, and marketing. Furthermore, Apple claims that its business supports another 254,000 jobs in the United States in engineering, manufacturing, and transportation. For example, the glass for the iPhone is manufactured at Corning’s U. plants in Kentucky and New York. But an additional 700,000 people are involved in the engineering, building, and final assembly of its products outside of the United States, and most of them work at subcontractors like Foxconn.
When explaining its decision to assemble the iPhone in China, Apple cites a number of factors. While it is true that labor costs are much lower in China, Apple executives point out that labor costs only account for a very small proportion of the total value of its products and are not the main driver of location decisions. Far more important, according to Apple, is the ability of its Chinese subcontractors to respond very quickly to requests from Apple to scale production up and down. In a famous illustration of this capability, back in 2007 Steve Jobs demanded that a glass screen replace the plastic. Jobs didn’t like the look and feel of plastic screens, which at the time were standard in the industry, nor did he like the way they scratched easily. This last minute change in the design of the iPhone put Apple’s market introduction date at risk. Apple had selected Corning to manufacture large panes of strengthened glass, but finding a manufacturer that could cut those panes into millions of iPhone screens wasn’t easy. Then a bid arrived from a Chinese factory. When the Apple team visited the factory, they found that the plant’s owners were already constructing a new wing to cut the glass and installing equipment. “This is in case you give us the contract,” the manager said. The plant also had a warehouse full of glass samples for Apple, and a team of engineers avai lable to work with Apple. They had built on-site dormitories, so that the factory could run three shifts seven days a week in order to meet Apple’s demanding production schedule. The Chinese company got the bid.
Another critical advantage of China for Apple was that it was much easier to hire engineers there. Apple calculated that about 8,700 industrial engineers were needed to oversee and guide the 200,000 assembly-line workers involved in manufacturing the iPhone. The company had estimated that it would take as long as nine months to find that many engineers in the United States. In China it took 15 days.
Also important is the clustering together of factories in China. Many of the factories providing components for the iPhone are located close to Foxconn’s assembly plant. As one executive noted, “The entire supply chain is in China. You need a thousand rubber gaskets? That’s the factory next door. You need a million screws? That factory is a block away? You need a screw made a little bit different? That will take three hours.”
All this being said, there are drawbacks to outsourcing to China. Several of Apple’s subcontractors have been targeted for their poor working conditions. Criticisms include low pay of line workers, long hours, mandatory overtime for little or no additional pay, and poor safety records. Some former Apple executives say that there is an unresolved tension within the company; executives want to improve working conditions within the factories of subcontractors such as Foxconn, but that dedication falters when it conflicts with crucial supplier relationships or the fast delivery of new products.
- What are the benefits to Apple of outsourcing the assembly of the iPhone to foreign countries, and particularly China? What are the potential costs and risks to Apple?
- In addition to Apple, who else benefits from Apple’s decision to outsource assembly to China? Who are the potential losers here?
- What are the potential ethical problems associated with outsourcing assembly jobs to Foxconn in China? How might Apple deal with these?
- On balance, do you think that the kind of outsourcing undertaken by Apple is a good thing or a bad thing for the American economy> Explain your reasoning?
- Multiple Choice
Course : MGT (314)
University : north south university.

- More from: MGT 314 North South University 131 Documents Go to course
International Journal of Frontiers in Sociology , 2021, 3(17); doi: 10.25236/IJFS.2021.031716 .
An Analysis of Apple’s Internationalization Strategy
School of Economics, Shanghai University, Shanghai, China
- Full-Text HTML
- Full-Text XML
- Full-Text Epub
- Download PDF
- Download: 194
With the sustained and rapid growth of the world economy and the gradual increase in the number of consumers of electronic products, Apple Inc has successfully shaped its own brand by means of market positioning, characteristic marketing, etc., improve the recognition and brand recognition of Apple products. Therefore, from the perspective of Apple’s value creation strategy, this paper explores the reasons for Apple’s success, and further analyzes the positive and negative factors of its value creation strategy. Then it carries on the SWOT analysis to the Apple Inc, analyzes the apple company’s strengths and weaknesses as well as meets the opportunity and the challenge, thus further analyzes the apple company’s marketing strategy accuracy and the importance, finally proposes the corresponding improvement measure.
SWOT analysis, internationalization strategy, Apple Inc
Cite This Paper
Li Zeng. An Analysis of Apple’s Internationalization Strategy. International Journal of Frontiers in Sociology (2021), Vol. 3, Issue 17: 105-111. https://doi.org/10.25236/IJFS.2021.031716.
[1] Duan Tao. Apple's enterprise strategic management innovation under the background of "Internet +" [J]. The marketing world, 2019 (02): 34 and 35.
[2] Huang Ming. Analysis of Apple's Strategy in China -- Taking iPhone as an example [J]. Shopping Mall Modernization, 2018(10):6-8.
[3] Zhou Yuan, Yang Yi. Strategic cost management innovation of Apple and Xiaomi: Changing with the environment [J]. Tax & Economics, 2017(06):55-59.
[6] Zhang Yaoting, SHA Xiujuan. Apple's financial strategy transformation based on cash [J]. Finance and Accounting, 2017(05):61-62.
[7] Guo Huanqing. Analysis of Apple's enterprise strategic management innovation under the background of "Internet +" [J]. Time’s agricultural machinery, 2017, 44(02):120-121.
[8] Ding Qianmang. Analysis of reasons and Countermeasures for apple's declining Performance in China [J]. Science & Technology Economic Guide, 2016(28):234-235.]
[9] Wang Xinmeng. Analysis of Apple's differentiation strategy [J]. Finance (Academic Edition), 2014(18):141.
[11] Fan LI. Analysis on international Strategy of Apple Inc. [J]. Modern Business, 2013(17):192.
[12] Dai Tianjing, Zhang Ru, Tang Guliang. Corporate profitability driven by financial strategy: a case study of Apple's asset-light Model [J]. Accounting Research, 2012(11):23-32+94.]
[13] Jiang Lizhu, DENG Rui. The interpretation of Apple's brand Strategy [J]. Times Finance, 2012(30):208.
[14] Lv Wenchen, WANG Ronghao. Strategic orientation analysis of multinational companies' global competition: a case study of apple [J]. Technology and innovation management, 2012, 33(01):32-34+40.
Brought to you by:

Apple Inc.: Global Supply Chain Management
By: P. Fraser Johnson
This case focuses on the supply chain strategy of Apple Inc. (Apple). Set in early 2020, it provides a detailed description of the company's supply chain network and capabilities. Data in the case…
- Length: 20 page(s)
- Publication Date: Jun 1, 2020
- Discipline: Operations Management
- Product #: W20472-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Same page, Teaching Note
- Same page, Educator Copy
$4.95 per student
degree granting course
$8.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- World-famous HBS cases and simulations
- Course material from 60+ global publishers
- Teaching Notes from the material's author
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
This case focuses on the supply chain strategy of Apple Inc. (Apple). Set in early 2020, it provides a detailed description of the company's supply chain network and capabilities. Data in the case allows students to develop an understanding of Apple's source of competitiveness and to gain insights into the management of a large, complex global supply chain network that focused on the intersection of services, hardware and software. Students will obtain an understanding of the supply chain challenges faced by Apple, in the context of supporting its corporate strategy and growth objectives.
Learning Objectives
This case can be used in an undergraduate- and graduate-level courses on operations management, supply chain management, logistics, business strategy, or marketing. It provides an opportunity to appreciate the complexities of managing a complex global supply chain. After completing the case, students will be able to do the following: Assess Apple's supply chain, and identify its key competitive advantages. Quantify Apple's ability to generate value from its supply chain. Identify potential opportunities and challenges for Apple in improving its supply chain. Analyze the effects of the opportunities and challenges Apple faces in its growth and evolution.
Jun 1, 2020 (Revised: Nov 13, 2023)
Discipline:
Operations Management
Geographies:
United States
Industries:
Ivey Publishing
W20472-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Apple's journey to global success is a compelling case study in how a company can build a strong brand and establish a lasting presence in the international arena. By embracing simplicity, innovation, and adaptability, Apple has demonstrated that it has the vision and resilience to continue to thrive in an increasingly competitive and ...
Operations Management: Apple Case Study. Words: 3933. Apple: Future Employment Opportunities. Words: 1274. Apple: Organizational Theory. Words: 4153. Apple Company's Strategic Analysis. ... Need an essay on Apple Inc. Affected by Globalization and Technology written from scratch by an expert specifically for you? ...
A case solution (apple goes global) COURSE NAME: Organizational Behavior and ... Jatropha - Global Industry Analysis and Case Study of its Value Chain in Zambia. August 2007. Andrew Chitembo;
Apple's role with International Trade. Apple along with other manufacturing companies has taken manufacturing overseas to reduce costs and improve efficiencies. Many of the upstream components and subassemblies are also manufactured in China and Southeast Asia, so to do final assembly in the United States would create huge logistical challenges.
At the same time, Apple was facing headwinds: smartphones were maturing in developed economies, revenues were dependent on premium pricing for the iPhone, services were closely tied to iPhone sales, and a new wave of regulations in the U.S., China, and Europe were casting a shadow on Apple's future. This case explores the sources of Apple's ...
- A $578m deal signed between Apple and GTAT in November 2013 looked as though it would not only bring sapphire screens to iPhones, but also create thousands of jobs in the US, salving a sore point with legislators critical of Apple's use of foreign assembly for almost all its products, especially the iPhone and iPad.
Mgt 314 case study about apple globalization . Course. MGT (314) 131 Documents. Students shared 131 documents in this course. University North South University. Info More info. Academic year: 2022/2023. Listed books Accounting Operations Management. Uploaded by: Anonymous Student.
Corporate profitability driven by financial strategy: a case study of Apple's asset-light Model [J]. Accounting Research, 2012(11):23-32+94.] [13] Jiang Lizhu, DENG Rui. ... Strategic orientation analysis of multinational companies' global competition: a case study of apple [J]. Technology and innovation management, 2012, 33(01):32-34+40. Links ...
This case focuses on the supply chain strategy of Apple Inc. (Apple). Set in early 2020, it provides a detailed description of the company's supply chain network and capabilities. Data in the case allows students to develop an understanding of Apple's source of competitiveness and to gain insights into the management of a large, complex global supply chain network that focused on the ...
Apple Inc. is a famous information technology firm in the global market. The organization has a wide range of products which consists of MacBook, iPhones, Apple TV, iPad and Apple watch.