
- Ask a Librarian

Locating and Using Images for Presentations and Coursework
- Free & Open Source Images
- How to Cite Images
- Alt Text Image Descriptions
Copyright Resources
- Copyright Term and the Public Domain in the United States from Cornell University Library
- Copyright Overview from Purdue University
- U.S. Copyright Office
- Fair Use Evaluator
- Visual Resources Association's Statement of Fair Use of Images for Teaching, Research, and Study
- Creative Commons Licenses
Attribution
Again, the majority of images you find are under copyright and cannot be used without permission from the creator. There are exceptions with Fair Use, but this Libguide is intended to help you locate images you can use with attribution (and in some case, the images are free to use without attribution when stated, such as with stock images from pixabay). ***Please read about public domain . These images aren't under copyright, but it's still good practice to include attribution if the information is available. Attribution : the act of attributing something, especially the ascribing of a work (as of literature or art) to a particular author or artist. When you have given proper attribution, it means you have given the information necessary for people to know who the creator of the work is.
Citation General Guidelines
Include as much of the information below when citing images in a paper and formal presentations. Apply the appropriate citation style (see below for APA, MLA examples).
- Image creator's name (artist, photographer, etc.)
- Title of the image
- Date the image (or work represented by the image) was created
- Date the image was posted online
- Date of access (the date you accessed the online image)
- Institution (gallery, museum) where the image is located/owned (if applicable)
- Website and/or Database name
Citing Images in MLA, APA, Chicago, and IEEE
- Directions for citing in MLA, APA, and Chicago MLA: Citing images in-text, incorporating images into the text of your paper, works cited APA 6th ed.: Citing images in-text and reference list Chicago 17th ed.: Citing images footnotes and endnotes and bibliography from Simon Fraser University
- How to Cite Images Using IEEE from the SAIT Reg Erhardt Library
- Image, Photograph, or Related Artwork (IEEE) from the Rochester Institute of Technology Library
Citing Images in Your PPT
Currently, citing images in PPT is a bit of the Wild West. If details aren't provided by an instructor, there are a number of ways to cite. What's most important is that if the image is not a free stock image, you give credit to the author for the work. Here are some options:
1. Some sites, such as Creative Commons and Wikimedia, include the citation information with the image. Use that citation when available. Copy the citation and add under the image. For example, an image of a lake from Creative Commons has this citation next to it: "lake" by barnyz is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0 .
2. Include a marker, such as Image 1. or Figure 1., and in the reference section, include full citation information with the corresponding number
3. Include a complete citation (whatever the required format, such as APA) below the image
4. Below the image, include the link to the online image location
5. Hyperlink the title of the image with the online image location
- << Previous: Free & Open Source Images
- Next: Alt Text Image Descriptions >>
- Last Edited: Jun 8, 2023 3:28 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.purdue.edu/images
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How to cite images and graphs in your research paper

Table of Contents
If you are confused about whether you should include pictures, images, charts, and other non-textual elements in your research paper or not, I would suggest you must insert such elements in your research paper. Including non-textual elements like images and charts in the research paper helps extract a higher acceptance of your proposed theories.
An image or chart will make your research paper more attractive, interesting, explanatory, and understandable for the audience. In addition, when you cite an image or chart, it helps you describe your research and its parts with far more precision than simple, long paragraphs.
There are plenty of reasons why you should cite images in your research paper. However, most scholars and academicians avoid it altogether, losing the opportunity to make their research papers more interesting and garner higher readership.
Additionally, it has been observed that there are many misconceptions around the use or citation of images in research papers. For example, it is widely believed and practiced that using pictures or any graphics in the research papers will render it unprofessional or non-academic. However, in reality, no such legit rules or regulations prohibit citing images or any graphic elements in the research papers.
You will find it much easier once you know the appropriate way to cite images or non-textual elements in your research paper. But, it’s important to keep in mind some rules and regulations for using different non-textual elements in your research paper. You can easily upgrade your academic/ research writing skills by leveraging various guides in our repository.
In this guide, you will find clear explanations and guidelines that will teach you how to identify appropriate images and other non-textual elements and cite them in your research paper. So, cut the clutter; let’s start.
Importance of citing images in a research paper
Although it’s not mandatory to cite images in a research paper, however, if you choose to include them, it will help showcase your deep understanding of the research topic. It can even represent the clarity you carry for your research topic and help the audience navigate your paper easily.

There are several reasons why you must cite images in your research paper like:
(i) A better explanation for the various phenomenon
While writing your research paper, certain topics will be comparatively more complex than others. In such a scenario where you find out that words are not providing the necessary explanation, you can always switch to illustrating the process using images. For example, you can write paragraphs describing climate change and its associated factors and/or cite a single illustration to describe the complete process with its embedded factors.
(ii) To simplify examples
To create an impeccable research paper, you need to include evidence and examples supporting your argument for the research topic. Rather than always explaining the supporting evidence and examples through words, it will be better to depict them through images. For example, to demonstrate climate change's effects on a region, you can always showcase and cite the “before and after” images.
(iii) Easy Classification
If your research topic requires segregation into various sub-topics and further, you can easily group and classify them in the form of a classification tree or a chart. Providing such massive information in the format of a classification tree will save you a lot of words and present the information in a more straightforward and understandable form to your audience.
(iv) Acquire greater attention from the audience
Including images in your research paper, theses, and dissertations will help you garner the audience's greater attention. If you add or cite images in the paper, it will provide a better understanding and clarification of the topics covered in your research. Additionally, it will make your research paper visually attractive.
Types of Images that you can use or cite in your research paper
Using and citing images in a research paper as already explained can make your research paper more understanding and structured in appearance. For this, you can use photos, drawings, charts, graphs, infographics, etc. However, there are no mandatory regulations to use or cite images in a research paper, but there are some recommendations as per the journal style.
Before including any images in your research paper, you need to ensure that it fits the research topic and syncs with your writing style. As already mentioned, there are no strict regulations around the usage of images. However, you should make sure that it satisfies certain parameters like:
- Try using HD quality images for better picture clarity in both print and electronic formats
- It should not be copyrighted, and if it is, you must obtain the license to use it. In short cite the image properly by providing necessary credits to its owner
- The image should satisfy the context of the research topic
You can cite images in your research paper either at the end, in between the topics, or in a separate section for all the non-textual elements used in the paper. You can choose to insert images in between texts, but you need to provide the in-text citations for every image that has been used.
Additionally, you need to attach the name, description and image number so that your research paper stays structured. Moreover, you must cite or add the copyright details of the image if you borrow images from other platforms to avoid any copyright infringement.
Graphs and Charts
You can earn an advantage by providing better and simple explanations through graphs and charts rather than wordy descriptions. There are several reasons why you must cite or include graphs and charts in your research paper:
- To draw a comparison between two events, phenomena, or any two random parameters
- Illustration of statistics through charts and graphs are most significant in drawing audience attention towards your research topic
- Classification tree or pie charts goes best to show off the degree of influence of a specific event, or phenomenon in your research paper
With the usage of graphs and charts, you can answer several questions of your readers without them even questioning. With charts and graphs, you can provide an immense amount of information in a brief yet attractive manner to your readers, as these elements keep them interested in your research topic.
Providing these non-textual elements in your research paper increases its readability. Moreover, the graphs and charts will drive the reader’s attention compared to text-heavy paragraphs.
You can easily use the graphs or charts of some previously done research in your chosen domain, provided that you cite them appropriately, or else you can create your graphs through different tools like Canva, Excel, or MS PowerPoint. Additionally, you must provide supporting statements for the graphs and charts so that readers can understand the meaning of these illustrations easily.
Similarly, like pictures or images, you can choose one of the three possible methods of placement in your research paper, i.e., either after the text or on a different page right after the corresponding paragraph or inside the paragraph itself.
How to Cite Images and Graphs in a Research Paper?
Once you have decided the type of images you will be using in your paper, understand the rules of various journals for the fair usage of these elements. Using pictures or graphs as per these rules will help your reader navigate and understand your research paper easily. If you borrow or cite previously used pictures or images, you need to follow the correct procedure for that citation.
Usage or citation of pictures or graphs is not prohibited in any academic writing style, and it just differs from each other due to their respective formats.
Cite an Image/Graphs in APA (American Psychological Association) style
Most of the scientific works, society, and media-based research topics are presented in the APA style. It is usually followed by museums, exhibitions, galleries, libraries, etc. If you create your research paper in APA style and cite already used images or graphics, you need to provide complete information about the source.
In APA style, the list of the information that you must provide while citing an element is as follows:
- Owner of the image (artist, designer, photographer, etc.)
- Complete Date of the Image: Follow the simple DD/MM/YYYY to provide the details about the date of the image. If you have chosen a certain historical image, you can choose to provide the year only, as the exact date or month may be unknown
- Country or City where the Image was first published
- A Name or Title of the Image (Optional: Means If it is not available, you can skip it)
- Publisher Name: Organization, association, or the person to whom the image was first submitted
If you want to cite some images from the internet, try providing its source link rather than the name or webpage.
Format/Example of Image Citation:
Johanson, M. (Photographer). (2017, September, Vienna, Austria. Rescued bird. National gallery.
Cite an Image/Graphs in MLA (Modern Language Association) style
MLA style is again one of the most preferred styles worldwide for research paper publication. You can easily use or cite images in this style provided no rights of the image owner get violated. Additionally, the format or the information required for citation or usage is very brief yet precise.
In the MLA style, the following are the details that a used image or graph must carry:
- Name of the creator of the owner
- Title, Name, or the Description of the Image
- Website Or the Source were first published
- Contributors Name (if any)
- Version or Serial Number (if any)
- Publisher’s Details; at least Name must be provided
- Full Date (DD:MM: YYYY) of the first published Image
- Link to the original image
Auteur, Henry. “Abandoned gardens, Potawatomi, Ontario.” Historical Museum, Reproduction no. QW-YUJ78-1503141, 1989, www.flickr.com/pictures/item/609168336/
Final Words
It is easy to cite images in your research paper, and you should add different forms of non-textual elements in the paper. There are different rules for using or citing images in research papers depending on writing styles to ensure that your paper doesn’t fall for copyright infringement or the owner's rights get violated.
No matter which writing style you choose to write your paper, make sure that you provide all the details in the appropriate format. Once you have all the details and understanding of the format of usage or citation, feel free to use as many images that make your research paper intriguing and interesting enough.
If you still have doubts about how to use or cite images, join our SciSpace (Formerly Typeset) Community and post your questions there. Our experts will address your queries at the earliest. Explore the community to know what's buzzing and be a part of hot discussion topics in the academic domain.
Learn more about SciSpace's dedicated research solutions by heading to our product page. Our suite of products can simplify your research workflows so that you can focus more on what you do best: advance science.
With a best-in-class solution, you can handle everything from literature search and discovery to profile management, research writing, and formatting.
But Before You Go,
You might also like.

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing
Works-Cited-List Entries
How to cite an image.
To create a basic works-cited-list entry for an image, list the creator of the image, the title of the image, the date of composition, and the location of the image, which would be a physical location if you viewed the image in person. If you viewed the image online, provide the name of the website containing the image and the URL. If you viewed the image in a print work, provide the publication information for the print work, including a page number. Below are sample entries for images along with links to posts containing many other examples.
A Photograph Viewed in Person
Cameron, Julia Margaret. Alfred, Lord Tennyson . 1866, Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York City.
A Painting Viewed Online
Bearden, Romare. The Train . 1975. MOMA , www.moma.org/collection/works/65232?locale=en.
An Untitled Image from a Print Magazine
Karasik, Paul. Cartoon. The New Yorker , 14 Apr. 2008, p. 49.
More Examples
Advertisements
Photographs
Slide Presentations
- Previous Example
- Works Cited: A Quick Guide
APA Citation Style, 7th edition: Figures/Images
- General Style Guidelines
- One Author or Editor
- Two Authors or Editors
- Three to Five Authors or Editors
- Article or Chapter in an Edited Book
- Article in a Reference Book
- Edition other than the First
- Translation
- Government Publication
- Journal Article with 1 Author
- Journal Article with 2 Authors
- Journal Article with 3–20 Authors
- Journal Article 21 or more Authors
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Basic Web Page
- Web page from a University site
- Web Page with No Author
- Entry in a Reference Work
- Government Document
- Film and Television
- Youtube Video
- Audio Podcast
- Electronic Image
- Twitter/Instagram
- Lecture/PPT
- Conferences
- Secondary Sources
- Citation Support
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Formatting Your Paper
Helpful Tip!
If you are unable to find the author/artist then use the title in your signal phrase or the first word or two of the title in the parentheses.
If there is no date available then use the abbreviation "n.d." (for "no date").
When possible, include the year, month, and date in references. If the month and date are not available, you may use the year of publication.
Situations this Section Covers
There are are many different types of figures, however, APA uses certain basic principles for all figure types.
Types of figures:
- photographs/images
This section will cover the following examples:
- Image from an Electronic Source
For more examples and information, consult the following publications:
Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.)
Call Number: BF76.7 .P83 2020
Locations: Main Reference Collection 1st Floor (1 copy); Book Stacks (5 copies)
About Citing Works of Art
Online Map: Title of work [Map]. (Date or date of latest update {Year, Month Day }). Site name (if needed). URL
Online Image/Web site; Artist's last name, artist’s initials. (Year). Title of work [Online image]. Site name (if needed). URL
For each type of source in this guide, both the general form and an example will be provided.
The following format will be used:
In-Text Citation (Paraphrase) - entry that appears in the body of your paper when you express the ideas of a researcher or author using your own words. For more tips on paraphrasing check out The OWL at Purdue .
In-Text Citation (Quotation) - entry that appears in the body of your paper after a direct quote.
References - entry that appears at the end of your paper.
Information on citing and several of the examples were drawn from the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.).
Subject Guide

- << Previous: Episodes
- Next: Electronic Image >>

- Last Updated: Feb 6, 2024 11:45 AM
- URL: https://guides.himmelfarb.gwu.edu/APA

- Himmelfarb Intranet
- Privacy Notice
- Terms of Use
- GW is committed to digital accessibility. If you experience a barrier that affects your ability to access content on this page, let us know via the Accessibility Feedback Form .
- Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library
- 2300 Eye St., NW, Washington, DC 20037
- Phone: (202) 994-2850
- [email protected]
- https://himmelfarb.gwu.edu
Images: Referencing & Captioning in APA 7th
This page provides information on referencing images in the APA 7th referencing style . For help referencing images in other referencing styles, ask a librarian.
If you are using Indigenous content or works, please note there are additional sensitivities and legal/cultural issues and care should be taken in reusing or repurposing Indigenous work in your studies. Please check with the Library for assistance.
Referencing images in APA 7th
When you mention, describe or analyse an image or artwork in the text of your work, you are referring to the image and therefore you will need to reference it .
If you are copying an image and placing it in your work, then the rules can vary, depending on whether you are a student submitting an assignment or whether you are writing for publication, for example writing a PHD dissertation or a journal article. If you are submitting a work for publication, then you will have to write a copyright note beneath the image you are reproducing. You can find more information on how to do this on pp164-167. of the Library's APA 7th Referencing Guide (linked below this box)
Rules for Copying/Reproducing an image in your work:
- APA 7th Guide
- Referencing & captioning your own work
If you created an image and used it in your assessment, you are required to caption it, even though it’s your own creation.
Your caption should include:
- A Figure number
- A title or description
You do NOT need to include a copyright attribution.
However, you should make it clear in the text of your assessment that the image was created by you.

Images referencing: Hints & tips
- For photographs or images taken of an artwork or other creative work, reference the date of the work depicted in the image (e.g. for a photograph of the Mona Lisa, the date referenced should be the date the Mona Lisa was created, NOT the date the Mona Lisa was photographed).
- When including images in your work, these can go either in the body of your work, or after the reference list but before any Appendices.
- << Previous: Evaluating Images
- How to Find Images (Planning)
- Where to Find Images
- Evaluating Images
- Referencing Images in APA 7th
- Images referencing: Hints & Tips
Related Guides
- Animation Guide
- Design Studies Guide
- Visual Communication Guide
- Data Science
- Architecture Study Guide
- Interior Architecture Guide
Need more help?

- Last Updated: Feb 12, 2024 5:01 PM
- URL: https://studyguides.lib.uts.edu.au/images

TODAY'S HOURS:
Using Images in Research and Presentations
- Finding Images
- Using Images
Why Do I Need to Cite Images?
Creative commons attribution.
Citing all your sources of information and creative work you use is part of academic integrity. You are giving credit where credit is due.
In academic work, images should be followed by and attribution or in text citation whether that be in a note or caption immediately following the image or at the bottom of a presentation slide. A full citation should be found in your Works Cited or Reference List, though you might separate them out into an Image Credit List, depending on the style of citation you are using.
The 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association expended their explanations and examples of how to cite multimedia sources including multimedia materials. Examples of reference are found in Chapter 10 of the Manual and the following sections focus on multimedia sources
- 10.12 Audiovisual works (films, streaming videos, television series, etc.)
- 10.13 Audio works (music, podcast, radio broadcast, etc.)
- 10.14 Visual works (fine art, clip art, infographics, photographs, maps, etc.)
- 10.15 Social media (including Instagram posts).
A related section of the Manual is Chapter 7 which deals with the presentation of tables and figures, so the Manual shows you how images should be incorporated into your work in addition to how they should be cited; see Sample Figure 7.3 for how to include an attribution in the figure note.
Here is an example of how the following photograph (found through Pixabay) should be cited using the APA style.
stokpic. (2015, February 10). Blonde Girl Taking Photo [Photograph]. Pixabay. https://pixabay.com/photos/blonde-girl-taking-photo-629726/

Remember, the library has a copy of the Manual at the Reference Desk if you need to use it.
The 9th edition of the MLA Handbook Appendix 2 has several examples of works-cited-list entries and the examples of citing fine art and still images can be found on pages 331 - 333. The online MLA Style Center also has examples of image citations.
- Citations by Format | MLA Style Center Are you using any other types of information sources in your project? Find more examples of MLA citation styles here.
Here is an example of how the following photograph (found through Pixabay) should be cited using the MLA style.
stokpic. Blonde Girl Taking Photo. 10 February 2015. Pixabay . pixabay.com/photos/blonde-girl-taking-photo-629726/
Remember, the library has a copy of the Handbook at the Reference Desk if you need to use it.
- Use & Remix - Creative Commons The "Use & remix" section of the Creative Commons website details how to properly attribute content licensed under a CC license. Attribution is a condition of all CC licenses. more info... less info... Creative Commons is a nonprofit organization dedicated to building a globally-accessible public commons of knowledge and culture. They provide Creative Commons licenses and public domain tools that give every person and organization in the world a free, simple, and standardized way to grant copyright permissions for creative and academic works; ensure proper attribution; and allow others to copy, distribute, and make use of those works.
- << Previous: Using Images
- Last Updated: Mar 21, 2024 3:46 PM
- URL: https://libguides.umflint.edu/images
Your browser does not support javascript. Some site functionality may not work as expected.
- Images from UW Libraries
- Open Images
- Image Analysis
- Citing Images
- University of Washington Libraries
- Library Guides
- Images Research Guide
Images Research Guide: Citing Images
How to cite images.
There are many ways to cite images. Most important is to include all relevant information so others can locate, understand and evaluate any images you use.
Academic Styles of Citing Images:
APA Style (7th Edition)
MLA Style (9th Edition)
Non-Academic Style:
Image Credits
Reference List
General Format:
Creator, C. (Year of Production or publication). Title of work [Description, Medium, or other relevant information]. Source. Retrieval information or location of work.
Image Found on the Web Euloth, G. (2012). Sleepy Kitty, Purr, Purr, Purr [Photograph]. Flickr. https://flic.kr/p/bD838X
Image from a Database Sharkstar, A.J. (2014). Two Cats Bound Together By A Snake [Sticker]. A rtstor . https://library.artstor.org/public/SS7730635_7730635_12095826
Image from a Book O’Keeffe, G. (1923). Alligator Pears in a Basket [Charcoal drawing]. In Sayre, H.M., Writing about art (6 th ed., pp. 39). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2009.
Image from a Museum or Archive Website Lawrence, J. (1977). The Studio [Painting]. Seattle Art Museum, Seattle, WA, United States. https://art.seattleartmuseum.org/objects/10605/the-studio
Image in a Museum Mirra, H. (2016). Standard Incomparable [Textile]. Pasadena, CA: Armory Center for the Arts.
In-text Citations
(Creator Last Name, Year)
If there is no creator, use (Title, Year)
(Amero, 1951)
Figure Captions
Figure 1. Author, A. A. (Year). Title of material . [Description of material]. Retrieved from http://www.xxxx
Figure 1. Amero, E. (1951). Fiesta. [Print]. Retrieved from Artstor.
Image Credits (Non-Academic Style)
A credit statement can be an alternative to a full academic citation, and especially useful when writing for the Web. Provide a link to the image if you can.
Title by Creator, date (if available), via source (Creative Common License Type, if applicable).
Sleep Kitty, Purr, Purr, Purr by Glenn Euloth, 2012, via Flickr (CC BY-NC-ND 2.0).
Open Attribution Builder:
If you are using an openly licensed image, try generating an image credit with the Open Attribution Builder .

Why Cite Images?
There are many important reasons to cite images you use:
- Give credit to the creator of the image.
- Provide information so others can find and reuse the image
- Participate in ongoing scholarly conversations about images
MLA Style (Ninth Edition, 2021)
Works Cited List
Previously, researchers made citations by following the MLA’s instructions for the source’s publication format (book, DVD, Web page, etc.). Now, there is one standard, universal format that researchers can use to create their citations:
Author. Title of source. Title of container, Other contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Publication date, Location.
Note: Containers are the elements that “hold” the source. For example, if a photo is posted on Flickr, Flickr is the container. Sometimes a source is nested inside of two separate containers, like an image found in a book read on an ebook platform like Ebook Library (EBL). Both the title of the source and its container (or multiple containers) are included in a citation.
Image Found on the Web Euloth, Glenn. Sleepy Kitty, Purr, Purr, Purr. 2012. Flickr , flic.kr/p/bD838X .
Image from a Database Amero, Emilio. Fiesta . 1951. National Gallery of Art, Washington, D.C. Artstor , https://library.artstor.org/#/asset/external/8D5Jcj0oMloyLyw%2Ffzx%2FRHsp
Image from a Book O’Keeffe, Georgia. Alligator Pears in a Basket . 1923. Writing about Art by Henry M. Sayre, 6 th ed., Pearson Prentice Hall, 2009, pp. 39.
Image from a Museum or Archive Website Lawrence, Jacob. The Studio . 1977. Seattle Art Museum, Seattle. Seattle Art Museum, www1.seattleartmuseum.org/eMuseum/code/emuseum.asp?style=browse¤trecord=1&page=search&profile=objects&searchdesc=90.27&quicksearch=90.27&newvalues=1&newstyle=single&newcurrentrecord=1.
Image in a Museum Mirra, Helen. Standard Incomparable . 2016, Armory Center for the Arts, Pasadena, CA.
In-text citations
(Creator Last Name, Page Number)
If there is no creator, use (“Title", Page Number)
For images found online, do not list a page number.
Fig 1. Ann Author, Title of Work , Museum and/or Publication information.
Fig 1. Emilio Amero, Fiesta , National Gallery of Art, 1951, Washington, D.C.
- << Previous: Image Analysis
- Last Updated: Nov 15, 2023 12:45 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uw.edu/newimages

Quick Links:

- Citation Generator
- Style Guides
- Chicago/Turabian Format
How to Cite a Picture in MLA
Images and photographs add diversity and visual information that sometimes just isn’t possible with words alone. But, how do you cite a picture and add it to your MLA 8 works cited list? Learn the ins and outs of citing an image in your MLA work and a little about the legalities.

How to Cite a Reproduced Image in Text MLA
Sometimes, it makes sense to reference images visually to prove a point. This is especially true if you’re writing a paper about art or paintings. It can also be true of other humanities type work. Therefore, it’s a good idea to know how to add the picture to your text and then cite it correctly in your MLA paper. Adding original images is a good way to strengthen your primary sources .
Step 1: Discussing the Image in Text
When including the image in the text, refer to the figure through the abbreviation and number: fig. #. For example, if this is your first image, it will be fig. 1. Your 19th image will be fig. 19. This will look something like:
How to Cite an Image In Text MLA
To understand the difference between the contrast, see fig. 1.

Step 2: Picture Caption
For the reproduced image, you include a caption that discusses the picture. This will be followed by the citation information:
How to Cite a Picture In Text MLA
Artist’s name, Work title (italicized), Date, Complete publication information of the source, including page, figure, or plate numbers.
Works that are cited under the image don’t need an additional reference on the works cited page.
Step 3: Works Cited MLA Citation
There is some vitally important information that you need to include about images. It doesn’t matter if they are scanned or online. The important information to cite the picture is the same, but it might come in a different order for your MLA works cited entry. If available, you need:
- Artist’s name
- Date created
- Publisher’s information
Now that you know what you need, breaking down the formatting is a snap.
How to Cite a Scanned Image MLA
For a scanned image, you need to include where you pulled the scan from.
Format for MLA Scanned Image Citation
Creator’s last name, first name. Title of work in italics. Date. Location. Book title in italics . Author(s), Publisher, Page, figure, or plate numbers.
MLA Scanned Image Citation Example
Raine, Mary. Juvisy France . 1947. Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York City. Modern Art, by Jason Daley, Hillsbrook, p. 268.
Online Photograph of Physical Work in MLA
An online photograph of a physical work in MLA includes the URL in addition to the gallery information.
Format for MLA Online Photograph Citation
Creator’s last name, first name. Title of Photograph or Description of the image. Year of creation. Gallery or museum where the image is physically located . URL of the website.
MLA Online Photograph Citation Example
Raine, Mary. Juvisy France . 1947. Metropolitan Museum of Art , New York City, https://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/photograph/juvisyfrance.
How to Cite an Online Image in MLA
When you cite an online image, you need the website and the URL.
Format for MLA Online Image Citation
Creator’s last name, first name. Title in italics. Date of creation. Website name in italics, URL of the website.
MLA Online Image Citation Example
Kahlo, Freida. Self Portrait With Monkey . 1938. Detroit Institute of Arts, https://www.dia.org/kahlodalimediakit.

Reference to an Image or Photograph
There may come a time when you reference an image that you do not include as a figure. In this situation, you want to italicize the work title and cite it with the first element in your works cited for online images. For those from books, you want to include page numbers, if available. For example:
The Dance (Rosseau) shows…
Scanned Image:
The Dance (Rosseau 22)
Legalities for Citing Pictures
Plagiarism is bad. We all know this to be true. Therefore, if you are going to use an image in your work, you must cite it correctly. This can ensure that you are giving credit where credit is due. It will also ensure that you don’t violate copyright laws by using the image in your writing. However, professional writing that is deemed for publication might need to ensure that using the image will be okay, even with appropriate citing.
How MLA Stands Out
MLA format is designed for writing about the arts. The way MLA formats in-text citations for figures within papers is designed to make it easy by using the container system. It focuses on the author or creator in the citations to really highlight them. But it is pretty similar to the other styles. MLA 8 says that including access dates to websites is optional. Add an access date to an undated article or image, only if you feel it’s helpful to the reader.
Adding Images and Photographs
Adding images, photographs, and pictures to your paper can be fun. Not only will it break up the monotony, but they make great sources of information. Now that you have mastered how to add them, follow the steps and give it a try.
MLA Works Cited
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 3.4 / 5. Vote count: 50
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Arranging Numbers in Works Cited List
Mla book citation examples, difference between mla and apa citation pages, how to format your mla cover page.
Visual Resources: Image Citation
- Search Strategies
- Online Image Databases
- Using ARTstor
- Resources by Subject
- CCA Collections
- Copyright Free Images
Image Citation
- Copyright & Fair Use
- Editing & Presentation Tools
- Information and Resources for Faculty

Zotero [zoh-TAIR-oh] is a free, easy-to-use tool to help you collect, organize, cite, and share your research sources.
Take a tour of Zotero .
Download Zotero .
Citation Guides Online
American Pschological Association (APA)
- University of Maryland University College APA Citation Examples - Images
Modern Langauges Association (MLA)
- Perdue OWL: MLA Formatting and Style Guide-Sculpture, Paintings and Photographs
Chicago Manual of Style
- Colgate Visual Resources Library-Citing Images-Chicago Style
Citation and Research Manuals
Online access to the full content of the 16th and 15th editions of the Chicago Manual of Style. Tools include manuscripts preparation, proofreading, and the Chicago-Style citation quick guide.
Citing Images
Images must be cited like all other resources. If you use an image you did not create, you must provide a citation. Images should be cited in all cases, even if the image is very small, or in the public domain. The citation should be accessible in the context of the image's use (within a Powerpoint presentation, on a web page, in a paper, etc.).
Image citations should include the following information at a minimum:
- Creator name
- Repository information (museum, library, or other owning institution)
- Image source (database, website, book, postcard, vendor, etc.)
- Date accessed
It is also useful to include date, culture, and rights information, if known. Citations can be formatted according to the citation style you are using.
Image Sources
Remember...
The citation of an original work of art differs from the citation of a reproduction (photograph or scan) from a secondary source, such as a book or a website. If you visited the California State Library in Sacramento to view a historical photograph, then you had access to an Original Work of Visual Art, but not if you gained access to that photograph online. Similarly, if you went to a museum sculpture garden to study an artwork, you could include a photograph you took of the work in a research paper cited as Original Work of Art--but not if you used a photograph provided by the museum. The person, or institutions responsible for creating Reproductions, such as photographs or digital scans of artworks, have ownership of copyright over the reproduction and must be given credit in your citation.
An Original Work of Art
Citing an original work of art in your research means that you had access to the material work in order to study it--rather than using a book, or website.
Artist’s last name, first name. Title of artwork. Year. Medium. Name of institution/collection housing artwork, city where institution/private collection is located. Example: Rembrandt Harmensz van Rijn . Aristotle with a Bust of Homer. 1653. Oil on canvas. Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
Artist's last name, first name, artist’s role (in parentheses i.e. Artist, Architect). Date (in parentheses). Title, the work type [in brackets i.e. Painting, Cathedral]. Country of origin or city, and state: and repository. Example: Rembrandt Harmensz van Rijn (Artist). (1653). Aristotle with a Bust of Homer [Painting]. New York, New York: Metropolitan Museum of Art.
- Chicago
Artist's first name, last name . Title. Date, medium, dimensions. Repository. Example: Rembrandt Harmensz van Rijn. Aristotle with a Bust of Homer. 1653. Oil on canvas. 143.5 cm × 136.5 cm. Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
A Reproduction of a Work of Art in Print
Citing the reproduction of a work of art in print simply means that you had access to work of art through a print resource, such as a book, magazine, or brochure. If you scan an image from a book or magazine in order to include it in your paper, you still must cite the print resource you used to gain access to the artwork.
Artist’s last name, first name. Title of artwork. Year. Name of institution/private collection housing artwork. Title of print source. Author/editor’s first name last name. Publication city: Publisher, year. Page/plate number. Medium of reproduction. Example: Kahlo, Frida. The Two Fridas. 1939. Museo de Art Moderno, Mexico City. Gardner’s Art Through the Ages: The Western Perspective. 12th ed. Ed. Fred S. Kleiner, Christin J. Mamiya. Vol. 2. Belmont: Thomson Wadsworth, 2006. 774. Print.
Artist's last name, first name, artist’s role (in parentheses i.e. Artist). Date (in parentheses). Title, the work type [in brackets i.e. Painting].Country of origin or city, and state, and repository. Reprinted from, Book Title (page number), by Author First Initial. Second Initial. Surname, Year, Place of Publication: Publisher. Copyright [Year] by Copyright Holder. Example: Kahlo, Frida (Artist). (1939). The Two Fridas [Painting]. Mexico City: Museo de Art Moderno. Reprinted from Gardner’s Art Through the Ages: The Western Perspective Twelfth Edition (p 774). F. Kleiner, C. Mamiya (Ed.). 2001, Belmont: Thomson Wadsworth. Copyright 2006 by Art Resource.
Artist's first name, last name. Title. Date, medium, dimensions. Repository. Author's first name, last name. Title of Book . Place of publication: Publisher, Year of publication. Page or Plate Number. Example: Kahlo, Frida. The Two Fridas. 1939, Oil on canvas, 203.2 x 91.4 cm. Museo de Art Moderno, Mexico City. From: F. Kleiner , C. Mamiya (Ed.). Gardner's Art Through the Ages: The Western Perspective, Twelfth Edition. Belmont: Thomas Wadsworth, 2001. Plate 64.
A Reproduction of a Work of Art accessed Online
Citing the reproduction of a work of art in print simply means that you had access to work of art through an online, such as a webpage or database. If you copy or download an image accessed online in order to include it in your paper, you still must cite the web resource you used to gain access to the artwork.
Artist’s last name, first name. Title of artwork. Year. Name of institution/private collection housing artwork. Title of database or website. Publisher/sponsor of database or website. Medium consulted. Date of access. Example: Braun, Adolphe. Flower Study, Rose of Sharon. 1854. Metropolitan Museum of Art. Grove Art Online. Oxford University Press. Web. 2 June 2011.
Artist's last name, first name, artist’s role (in parentheses i.e. Artist). Date (in parentheses). Title, the work type [in brackets i.e. Painting].Country of origin or city, and state, and repository. Retrieved from, Name of the database. Example: Rousseau, Henri (Artist). (1896). The ship in the storm [Painting]. Musee de l’Orangerie, Paris. Retrieved from Grove Art Online database .
Artist's first name, last name. Title. Date, medium, dimensions. Repository. Available from, Name of the database, web address (date of access in parantheses). Example: Rogier van der Weyden, Saint Catherine of Alexandria. 1430-1432, Diptych panel, 18.5 x 12 cm. Kunsthistorisches Museum, Vienna, Austria. Available from: ARTstor, http://www.artstor.org (accessed September 30. 2009).
Do I need to include the URL?
URLs are now an optional component of a citation, but it is still recommended to include this information if the reader will not be able to locate a resource without it, or it is part of an instructor’s requirements.
When providing a URL, enclose the complete address in angle brackets following the date of access, period, and a space. End the entire entry with a period after the closing angle bracket:
Example: Cloix, Emmanuel. BROUSSAI 2 visu . 2007. Wikimedia Commons. Wikimedia Foundation. Web. 1 June 2011. <http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:BROUSSAI_2_visu.jpg>
- << Previous: Copyright Free Images
- Next: Copyright & Fair Use >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2023 3:28 PM
- URL: https://libguides.cca.edu/visual_resources
Simpson Library: 1111 8th St, San Francisco, CA 94107 ( 415.703.9574 )
How to Cite Google Images
Create citations for free.
Website Book Journal Image
They say a picture tells a thousand words—so photographs can serve an important purpose in essays or presentations you’re working on. Google Images, which contains images from thousands of websites at the click of a button, is one of the easiest places to find photos on the Internet. So knowing how to cite an image found on Google Images is pretty helpful.
While you might know how to cite a thousand-word-long journal article, citing an image might seem more difficult, especially if you’ve obtained that image from an online source. Luckily, citing a picture you’ve found on Google Images isn’t all that different from citing a website you found after doing a quick Google search.
Say you’re working on a biographical paper or PowerPoint presentation about President Franklin D. Roosevelt, and you want your title page or opening slide to contain a photograph of the former president, who has the distinction of being the only president to serve more than two terms throughout much of World War II, and who led the country out of the Great Depression.
Google Images has you covered on the picture—the site has pages and pages of images, including this neat one of FDR sitting at his desk in the Oval Office—and if you want to cite the photo in MLA format , APA format , or Chicago style, we’ve got you covered on that.
Copyright Considerations
Before continuing, you should understand that many of the images found through Google and other search engines are copyright protected. This means that you are not allowed to make money from the use of these images. For example, it is illegal to make and sell t-shirts that display this image of Franklin D. Roosevelt. However, according to Chapter 1, Section 107, of the Copyright Law , you are allowed to use images for research and classroom purposes.
Information Needed for the Citation
After finding the image that you’d like to use, to the right of the image, click the button that says, “Visit page.” This is where you’ll find the information you need to cite the image.
Here’s the specific information you’ll need to locate when citing an image you found on Google Images:
- Full name of the image’s creator, such as the name of the photographer or illustrator (if available)
- Formal title of the image (if available) or a description of the image
- Name of the website where the image lives (Do not use Google as the name of the website!)
- Publisher of the website where the image was found on
- Date this information was published on their site
*Please note that if putting these citations in a printed paper, the lines should be double-spaced and indented.
How to cite an image from Google Images in MLA 9:
Last name, First name of creator. “Title” or description of the image. Title of the Website , Publisher, Date of publication, URL or DOI.
- In MLA, if the image has a title, place it in quotation marks and use title case: capitalize the first letter of each important word and pronoun. If the image does not have an official title, create a simple description and use sentence case: only capitalize the first letter in the description and the first letter of any pronoun.
- Only include the name of the publisher if it is different than the name of the author and title of the site.
- For URLs or DOIs, copy them exactly as shown in the address bar or link from your browser.
How to cite the example image in MLA 9:
Photograph of Franklin D. Roosevelt at his desk. The Washington Post , 25 Apr. 2017, www.washingtonpost.com/news/fact-checker/wp/2017/04/25/the-white-house-boo-boo-in-counting-roosevelts-executive-orders/?utm_term=.06cac0ac12e5.
If you need help with in-text and parenthetical citations, CitationMachine.net, can help. Our MLA citation generator is simple and easy to use!
How to cite an image from Google Images in APA:
Image creator’s Last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year published). Title of image [Photograph, Cartoon, Painting, etc.]. Website Name. URL.
The reference list entry for the image consists of its author, year of publication, title, description in brackets, and source (usually the name of the website and the URL).
- In APA, if the image does not have a formal title, describe the image and place the description in brackets.
- In APA, do not place a period at the end of the URL
How to cite the example image in APA:
US National Trust. (2017). Franklin D. Roosevelt at his desk [Photograph] . Google Images. https://www.google.com/images/the-white-house-boo-boo-in-counting-roosevelts-executive-orders/?utm_term=.06cac0ac12e5
How to cite an image from Google Images in Chicago:
Last name, First name Middle initial of creator of image. “Title of image” or Description. Digital Image. Title of Website. Month Day, Year Published. Accessed date. URL.
- If the image does not have an official title, create a description. Do not place the description in quotation marks.
- Only include the date the image was accessed if there is no publication date!
How to cite the example image in Chicago:
Franklin D. Roosevelt at his desk. Digital Image. The Washington Post. April 25, 2017. https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/fact-checker/wp/2017/04/25/the-white-house-boo-boo-in-counting-roosevelts-executive-orders/?utm_term=.8d30c188c74c.
Works Cited
“Chapter 1: Subject Matter and Scope of Copyright.” Copyright Law of the United States , p. 19, www.copyright.gov/title17/chapter1.pdf.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Google Images is an aggregator or search engine for images. It is not a repository of images by itself. Since Google Images is not the original source for the images found there, you cannot cite or mention “Google Images” as the source of your images.
Instead of citing “Google Images,” you must cite the original source of the image. For any image found from Google Images, find the original source of the image by clicking the “Visit page” button. Then, the image should be cited using the following details (if available) as per your class style (APA, MLA, or Chicago):
- Full name of the image’s original creator
- Formal name of the image or description of the image
- Original website source (not Google Images)
- Website’s publisher
- Date of publication of the image
It is easy to search for relevant images using an online search engine like Google Images, but the issue of copyright has to be addressed when using images found online.
Most images are copyright protected. Copyrighted images belong to the original illustrator, agency, or organization that designed and created them. You cannot use these images for your business needs without the permission of the creator. However, you can use these images for your research and class needs, as long you provide a citation to the source of these images.
Cite the original source of the image (not “Google Images”) per your class style (APA, MLA, or Chicago) using the below details:
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / Harvard Referencing / Harvard Referencing Style Examples / How to reference an image in Harvard style
How to reference an image in Harvard style
Referencing images can be confusing. Do you reference the photographer or the subject of the image itself? Do you include where you saw or found the image? What if you took the photograph yourself? This guide will help clear up the confusion!
Below, the guide will cover how to cite images in different scenarios, both as an in-text citation and a reference. For each scenario, you will be given a citation structure, along with examples to illustrate each case.
Online images/photographs
Today, finding and citing a digital or online image is simple. You’ll need the following information:
- Photographer’s name
- (Year published)
- Title of the photograph, italizised
- Available at: URL (Accessed: the date you sourced the image)
In-text citation structure and example:
(Photographer’s name, Year published)
Photographer’s name (Year published)
B.B. King’s beautiful Gibson semi-hollow body ES-355 guitar (Joseph, 2001) ……
Reference list structure and example:
Photographer’s Last Name, Initial. (Year published) Title of the photograph. Available at: URL (Accessed: the date you sourced the image)
Joseph, J. (2001) Lucille. Available at: http://www.jackjoseph.co.uk/photo_23456.html (Accessed: 22 August 2016)
Online images/photographs from a curated collection
As we know, the Internet has a vast repository of curated image collections, especially on sites like Tumblr, Pinterest and Instagram, to name just a few. The rules stay pretty much unchanged in this case, as well.
You will just need to direct the viewer/reader to the source where you viewed or uploaded the image. You may cite relevant information about images sourced from such Internet collections as follows:
- (Year published)
- Title of the photograph/collection, italicized
Photographs by Gustavo Grandissimo (2015) …
Grandissimo, G. (2015) The heights of abstraction. Available at: https://instagram.com/theheightsofabstraction (Accessed: 10 August 2012)
Images without a listed photographer or artist
You may cite information about images without a listed creator. You’ll need the following information:
- Title of the photograph, italicized
As you can see in the image of the controversial protest rally ( Up in arms , 2019) …
Title of the photograph (Year published) Available at: URL (Accessed: the date you sourced the image)
Up in arms (2019) Available at: http://www.therevolutionbeat.com/protests/2019/image_34567.html (Accessed: 10 March 2019)
Prints or slides
A print refers to a printed reproduction of a popular work of art or image. A slide, on the other hand, is a transparent photograph that consists of chromogenic dyes mounted inside a plastic frame to be projected onto a large screen.
Information needed:
- [Photograph]
- Place of publication: Publisher’s name, if available
The expanding mushroom cloud from the resulting blast was captured on that fateful day (Tanaka, 1945)
Tanaka, N. (1945) The day Fat Boy fell to Earth [Photograph]. Hokkaido: Kurosawa Publishers
Images photographed by you
It is not necessary to provide a reference to a photograph or image if you are the creator. However, check with your tutor about the most appropriate way to present original images or photographs in your work.
If you need to reference an original image, you can use the following citation structure:
- Your name (Year published or taken)
…lays emphasis on the fact that the sun doesn’t need to be the focus of a picture (Koenig, 2019)
Your Last Name, Initial. (Year published) Title of the photograph [Photograph]
Koenig, K. (2019) The sunset [Photograph]
Published October 29, 2020.
Harvard Formatting Guide
Harvard Formatting
- et al Usage
- Direct Quotes
- In-text Citations
- Multiple Authors
- Page Numbers
- Writing an Outline
- View Harvard Guide
Reference Examples
- View all Harvard Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Harvard Referencing Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started

IEEE Enacts Ban on 'Lenna' Image from Playboy in Research Papers to Foster Inclusivity
T he IEEE Computer Society announced to its members on Wednesday that, effective April 1, it will no longer accept papers containing the commonly used image of Lena Forsén, a Playboy model from 1972. Known as the “Lenna image,” this image has been utilized in image processing research since 1973 but has faced criticism for contributing to a sense of exclusion among women in the field.
In an email sent to members, Terry Benzel, the Vice President of Technical & Conference Activities at the IEEE Computer Society, stated, “IEEE’s diversity statement and supporting policies such as the IEEE Code of Ethics speak to IEEE’s commitment to promoting an including and equitable culture that welcomes all. In alignment with this culture and with respect to the wishes of the subject of the image, Lena Forsén, IEEE will no longer accept submitted papers which include the ‘Lena image.'”
Originally appearing as a 512×512-pixel test image in the December 1972 issue of Playboy Magazine, the uncropped version served as the centerfold picture. The use of the Lenna image in image processing began around June or July 1973, when Alexander Sawchuck, an assistant professor, and a graduate student at the University of Southern California Signal and Image Processing Institute scanned a square portion of the centerfold image using a primitive drum scanner, excluding nudity. This scan was initially done for a colleague’s conference paper, subsequently leading to widespread adoption of the image by others in the field.
Throughout the 1970s, 80s, and 90s, the image gained traction in various papers, drawing the attention of Playboy, though the company chose to overlook copyright violations. In 1997, Playboy facilitated the location of Forsén, who made an appearance at the 50th Annual Conference of the Society for Imaging Science and Technology, signing autographs for admirers. “They must be so tired of me … looking at the same picture for all these years!” she quipped at the time. Playboy’s Vice President of new media, Eileen Kent, told Wired, “We decided we should exploit this, because it is a phenomenon.”
The image, featuring Forsén’s visage and a bare shoulder adorned with a hat sporting a purple feather, reportedly served as an excellent test subject for early digital image technology due to its high contrast and intricate detail. However, it also presented a sexually suggestive portrayal of an attractive woman. Its persistent use by men in the computing domain has faced critique over the years, particularly from female scientists and engineers. They argue that the image, especially its association with the Playboy brand, objectifies women and fosters an academic environment where they feel unwelcome.
In response to longstanding criticism, dating back to at least 1996, the journal Nature took the step to prohibit the use of the Lena image in paper submissions in 2018.
According to the comp.compression Usenet newsgroup FAQ document, in 1988, a Swedish publication approached Forsén to inquire about her thoughts on her image being used in computer science, to which she reportedly reacted with amusement. However, in a 2019 Wired article by Linda Kinstler, Forsén expressed no resentment toward the image but voiced regret over not being fairly compensated initially. “I’m really proud of that picture,” she told Kinstler at the time.
However, it appears Forsén has since changed her stance. In 2019, Creatable and Code Like a Girl produced an advertising documentary titled “Losing Lena” as part of a campaign aimed at eliminating the use of the Lena image in technology and image processing fields. In a press release for the campaign and film, Forsén is quoted as saying, “I retired from modelling a long time ago. It’s time I retired from tech, too. We can make a simple change today that creates a lasting change for tomorrow. Let’s commit to losing me.”
Relevant articles:
– Playboy image from 1972 gets ban from IEEE computer journals
– Journal publisher bans Playboy centerfold Lena’s image from research papers , NewsBytes, Fri, 29 Mar 2024 09:50:18 GMT
– It’s time to retire Lena from computer science , Pursuit, Fri, 13 Dec 2019 08:00:00 GMT
– The Playboy Centerfold That Helped Create the JPEG , The Atlantic, Tue, 09 Feb 2016 08:00:00 GMT
![The IEEE Computer Society announced to its members on W […] The IEEE Computer Society announced to its members on W […]](https://img-s-msn-com.akamaized.net/tenant/amp/entityid/BB1kS8lB.img?w=768&h=512&m=6)
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- 27 March 2024
Tweeting your research paper boosts engagement but not citations
- Bianca Nogrady
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Even before complaints about X’s declining quality, posting a paper on the social-media platform did not lead to a boost in citations. Credit: Matt Cardy/Getty
Posting about a research paper on social-media platform X (formerly known as Twitter) doesn’t translate into a bump in citations, according to a study that looked at 550 papers.
The finding comes as scientists are moving away from the platform in the wake of changes after its 2022 purchase by entrepreneur Elon Musk.
An international group of 11 researchers, who by the end of the experiment had between them nearly 230,000 followers on X, examined whether there was evidence that posting about a paper would increase its citation rate.
“There certainly is a correlation, and that’s been found in a lot of papers. But very few people have ever looked to see whether there’s any experimental causation,” says Trevor Branch, a marine ecologist at the University of Washington in Seattle and lead author on the paper, published in PLoS ONE last week 1 .
Every month for ten months, each researcher was allocated a randomly selected primary research article or review from a journal of their choice to post about on their personal account. Four randomly chosen articles from the same edition of the journal served as controls, which the researchers did not post about. They conducted the experiment in the period before Elon Musk took ownership of what was then known as Twitter and complaints of its declining quality increased.
‘Nail in the coffin’
Three years after the initial posts, the team compared the citation rates for the 110 posted articles with those of the 440 control articles, and found no significant difference. The researchers did acknowledge that their followers might not have been numerous enough to detect a statistically significant effect on citations.
The rate of daily downloads for the posted papers was nearly fourfold higher on the day that they were shared, compared with controls. Shared papers also had significantly higher accumulated Altmetric scores both 30 days and three years after the initial post. Calculated by London-based technology company Digital Science, an Altmetric score, says Branch, is a measure of how many people have looked at a paper and are talking about it, but it’s not a reliable indicator of a paper’s scientific worth. “It’s thoroughly biased by how many people with large followings tweet about it,” he says.
The findings echo those of information scientist Stefanie Haustein at the University of Ottawa, whose 2013 study 2 found a low correlation between posts and citations.
Haustein says the problem with using posts as a metric is that, even a decade ago, there was a lot of noise in the signal.
“We actually showed that a lot of the counts on Twitter you would get were bots, it wasn’t even humans,” says Haustein, who wasn’t involved in the new study.
She says the more recent departure of scientists from the platform has been the final nail in the coffin of the idea that posting could increase citations.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-00922-y
Branch, T. A. et al. PLoS ONE 19 , e0292201 (2024).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Haustein, S., Peters, I., Sugimoto, C. R., Thelwall, M. & Larivière, V. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 65, 656–669 (2014).
Article Google Scholar
Download references
Reprints and permissions
Related Articles

- Communication
- Scientific community

Divas, captains, ghosts, ants and bumble-bees: collaborator attitudes explained
Career Column 15 MAR 24

Three actions PhD-holders should take to land their next job
Career Column 13 MAR 24

This geologist communicates science from the ski slopes
Career Q&A 11 MAR 24

The corpse of an exploded star and more — March’s best science images
News 28 MAR 24

How OpenAI’s text-to-video tool Sora could change science – and society
News 12 MAR 24

Giant plume of plasma on the Sun’s surface and more — February’s best science images
News 01 MAR 24

How scientists are making the most of Reddit
Career Feature 01 APR 24

Overcoming low vision to prove my abilities under pressure
Career Q&A 28 MAR 24

How a spreadsheet helped me to land my dream job
Career Column 28 MAR 24
Postdoctoral positions in the integrative structural biology of cancer and immunity
Postdoctoral positions in the integrative structural biology study of signaling complexes important in cancer and the immune system
Farmington, Connecticut (US)
University of Connecticut Health Center (UCHC)
Faculty Positions & Postdocs at Institute of Physics (IOP), Chinese Academy of Sciences
IOP is the leading research institute in China in condensed matter physics and related fields. Through the steadfast efforts of generations of scie...
Beijing, China
Institute of Physics (IOP), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS)
Postdoctoral Scholar - PHAST Alzheimer
Memphis, Tennessee
The University of Tennessee Health Science Center (UTHSC)
Postdoctoral Associate- Neurodevelopmental Disease
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Supervisory Bioinformatics Specialist, CTG Program Head
National Institutes of Health (NIH) National Library of Medicine (NLM) National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Information Engineering...
Washington D.C. (US)
National Library of Medicine, National Center for Biotechnology Information
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Plagiarism Checker
Compare your paper to billions of pages and articles with Scribbr’s Turnitin-powered plagiarism checker.
Run a free check

AI Proofreader
Correct your document in minutes.
Upload my document

Proofreading & Editing
Have a human editor polish your writing to ensure your arguments are judged on merit, not grammar errors.
Get expert writing help

Check your Citations
Improve your in-text citations and references for errors and inconsistencies using Scribbr's AI technology or human experts.

Paraphraser
Rewrite and paraphrase texts instantly with our AI-powered paraphrasing tool.
Try for free

Grammar Checker
Eliminate grammar errors and improve your writing with our free AI-powered grammar checker.
universalSourceForm.defaults.intro.title
universalSourceForm.overwrites.image.intro.text,universalSourceForm.defaults.intro.text
Read our research on: Abortion | Podcasts | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
What the data says about abortion in the u.s..
Pew Research Center has conducted many surveys about abortion over the years, providing a lens into Americans’ views on whether the procedure should be legal, among a host of other questions.
In a Center survey conducted nearly a year after the Supreme Court’s June 2022 decision that ended the constitutional right to abortion , 62% of U.S. adults said the practice should be legal in all or most cases, while 36% said it should be illegal in all or most cases. Another survey conducted a few months before the decision showed that relatively few Americans take an absolutist view on the issue .
Find answers to common questions about abortion in America, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Guttmacher Institute, which have tracked these patterns for several decades:
How many abortions are there in the U.S. each year?
How has the number of abortions in the u.s. changed over time, what is the abortion rate among women in the u.s. how has it changed over time, what are the most common types of abortion, how many abortion providers are there in the u.s., and how has that number changed, what percentage of abortions are for women who live in a different state from the abortion provider, what are the demographics of women who have had abortions, when during pregnancy do most abortions occur, how often are there medical complications from abortion.
This compilation of data on abortion in the United States draws mainly from two sources: the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Guttmacher Institute, both of which have regularly compiled national abortion data for approximately half a century, and which collect their data in different ways.
The CDC data that is highlighted in this post comes from the agency’s “abortion surveillance” reports, which have been published annually since 1974 (and which have included data from 1969). Its figures from 1973 through 1996 include data from all 50 states, the District of Columbia and New York City – 52 “reporting areas” in all. Since 1997, the CDC’s totals have lacked data from some states (most notably California) for the years that those states did not report data to the agency. The four reporting areas that did not submit data to the CDC in 2021 – California, Maryland, New Hampshire and New Jersey – accounted for approximately 25% of all legal induced abortions in the U.S. in 2020, according to Guttmacher’s data. Most states, though, do have data in the reports, and the figures for the vast majority of them came from each state’s central health agency, while for some states, the figures came from hospitals and other medical facilities.
Discussion of CDC abortion data involving women’s state of residence, marital status, race, ethnicity, age, abortion history and the number of previous live births excludes the low share of abortions where that information was not supplied. Read the methodology for the CDC’s latest abortion surveillance report , which includes data from 2021, for more details. Previous reports can be found at stacks.cdc.gov by entering “abortion surveillance” into the search box.
For the numbers of deaths caused by induced abortions in 1963 and 1965, this analysis looks at reports by the then-U.S. Department of Health, Education and Welfare, a precursor to the Department of Health and Human Services. In computing those figures, we excluded abortions listed in the report under the categories “spontaneous or unspecified” or as “other.” (“Spontaneous abortion” is another way of referring to miscarriages.)
Guttmacher data in this post comes from national surveys of abortion providers that Guttmacher has conducted 19 times since 1973. Guttmacher compiles its figures after contacting every known provider of abortions – clinics, hospitals and physicians’ offices – in the country. It uses questionnaires and health department data, and it provides estimates for abortion providers that don’t respond to its inquiries. (In 2020, the last year for which it has released data on the number of abortions in the U.S., it used estimates for 12% of abortions.) For most of the 2000s, Guttmacher has conducted these national surveys every three years, each time getting abortion data for the prior two years. For each interim year, Guttmacher has calculated estimates based on trends from its own figures and from other data.
The latest full summary of Guttmacher data came in the institute’s report titled “Abortion Incidence and Service Availability in the United States, 2020.” It includes figures for 2020 and 2019 and estimates for 2018. The report includes a methods section.
In addition, this post uses data from StatPearls, an online health care resource, on complications from abortion.
An exact answer is hard to come by. The CDC and the Guttmacher Institute have each tried to measure this for around half a century, but they use different methods and publish different figures.
The last year for which the CDC reported a yearly national total for abortions is 2021. It found there were 625,978 abortions in the District of Columbia and the 46 states with available data that year, up from 597,355 in those states and D.C. in 2020. The corresponding figure for 2019 was 607,720.
The last year for which Guttmacher reported a yearly national total was 2020. It said there were 930,160 abortions that year in all 50 states and the District of Columbia, compared with 916,460 in 2019.
- How the CDC gets its data: It compiles figures that are voluntarily reported by states’ central health agencies, including separate figures for New York City and the District of Columbia. Its latest totals do not include figures from California, Maryland, New Hampshire or New Jersey, which did not report data to the CDC. ( Read the methodology from the latest CDC report .)
- How Guttmacher gets its data: It compiles its figures after contacting every known abortion provider – clinics, hospitals and physicians’ offices – in the country. It uses questionnaires and health department data, then provides estimates for abortion providers that don’t respond. Guttmacher’s figures are higher than the CDC’s in part because they include data (and in some instances, estimates) from all 50 states. ( Read the institute’s latest full report and methodology .)
While the Guttmacher Institute supports abortion rights, its empirical data on abortions in the U.S. has been widely cited by groups and publications across the political spectrum, including by a number of those that disagree with its positions .
These estimates from Guttmacher and the CDC are results of multiyear efforts to collect data on abortion across the U.S. Last year, Guttmacher also began publishing less precise estimates every few months , based on a much smaller sample of providers.
The figures reported by these organizations include only legal induced abortions conducted by clinics, hospitals or physicians’ offices, or those that make use of abortion pills dispensed from certified facilities such as clinics or physicians’ offices. They do not account for the use of abortion pills that were obtained outside of clinical settings .
(Back to top)
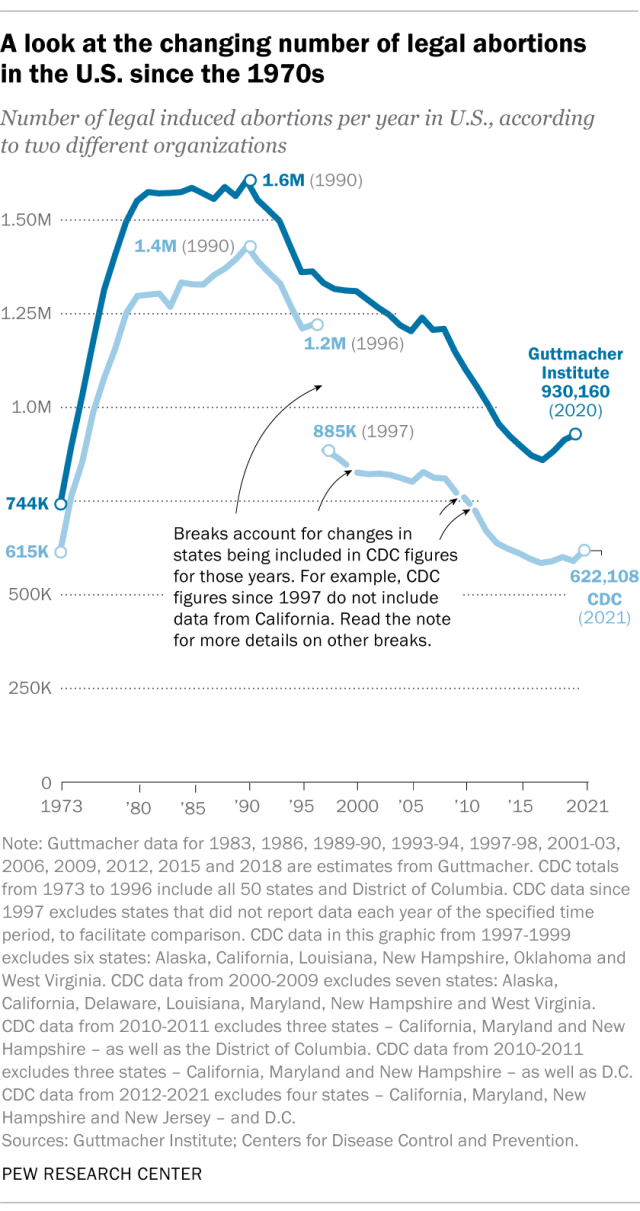
The annual number of U.S. abortions rose for years after Roe v. Wade legalized the procedure in 1973, reaching its highest levels around the late 1980s and early 1990s, according to both the CDC and Guttmacher. Since then, abortions have generally decreased at what a CDC analysis called “a slow yet steady pace.”
Guttmacher says the number of abortions occurring in the U.S. in 2020 was 40% lower than it was in 1991. According to the CDC, the number was 36% lower in 2021 than in 1991, looking just at the District of Columbia and the 46 states that reported both of those years.
(The corresponding line graph shows the long-term trend in the number of legal abortions reported by both organizations. To allow for consistent comparisons over time, the CDC figures in the chart have been adjusted to ensure that the same states are counted from one year to the next. Using that approach, the CDC figure for 2021 is 622,108 legal abortions.)
There have been occasional breaks in this long-term pattern of decline – during the middle of the first decade of the 2000s, and then again in the late 2010s. The CDC reported modest 1% and 2% increases in abortions in 2018 and 2019, and then, after a 2% decrease in 2020, a 5% increase in 2021. Guttmacher reported an 8% increase over the three-year period from 2017 to 2020.
As noted above, these figures do not include abortions that use pills obtained outside of clinical settings.
Guttmacher says that in 2020 there were 14.4 abortions in the U.S. per 1,000 women ages 15 to 44. Its data shows that the rate of abortions among women has generally been declining in the U.S. since 1981, when it reported there were 29.3 abortions per 1,000 women in that age range.
The CDC says that in 2021, there were 11.6 abortions in the U.S. per 1,000 women ages 15 to 44. (That figure excludes data from California, the District of Columbia, Maryland, New Hampshire and New Jersey.) Like Guttmacher’s data, the CDC’s figures also suggest a general decline in the abortion rate over time. In 1980, when the CDC reported on all 50 states and D.C., it said there were 25 abortions per 1,000 women ages 15 to 44.
That said, both Guttmacher and the CDC say there were slight increases in the rate of abortions during the late 2010s and early 2020s. Guttmacher says the abortion rate per 1,000 women ages 15 to 44 rose from 13.5 in 2017 to 14.4 in 2020. The CDC says it rose from 11.2 per 1,000 in 2017 to 11.4 in 2019, before falling back to 11.1 in 2020 and then rising again to 11.6 in 2021. (The CDC’s figures for those years exclude data from California, D.C., Maryland, New Hampshire and New Jersey.)
The CDC broadly divides abortions into two categories: surgical abortions and medication abortions, which involve pills. Since the Food and Drug Administration first approved abortion pills in 2000, their use has increased over time as a share of abortions nationally, according to both the CDC and Guttmacher.
The majority of abortions in the U.S. now involve pills, according to both the CDC and Guttmacher. The CDC says 56% of U.S. abortions in 2021 involved pills, up from 53% in 2020 and 44% in 2019. Its figures for 2021 include the District of Columbia and 44 states that provided this data; its figures for 2020 include D.C. and 44 states (though not all of the same states as in 2021), and its figures for 2019 include D.C. and 45 states.
Guttmacher, which measures this every three years, says 53% of U.S. abortions involved pills in 2020, up from 39% in 2017.
Two pills commonly used together for medication abortions are mifepristone, which, taken first, blocks hormones that support a pregnancy, and misoprostol, which then causes the uterus to empty. According to the FDA, medication abortions are safe until 10 weeks into pregnancy.
Surgical abortions conducted during the first trimester of pregnancy typically use a suction process, while the relatively few surgical abortions that occur during the second trimester of a pregnancy typically use a process called dilation and evacuation, according to the UCLA School of Medicine.
In 2020, there were 1,603 facilities in the U.S. that provided abortions, according to Guttmacher . This included 807 clinics, 530 hospitals and 266 physicians’ offices.
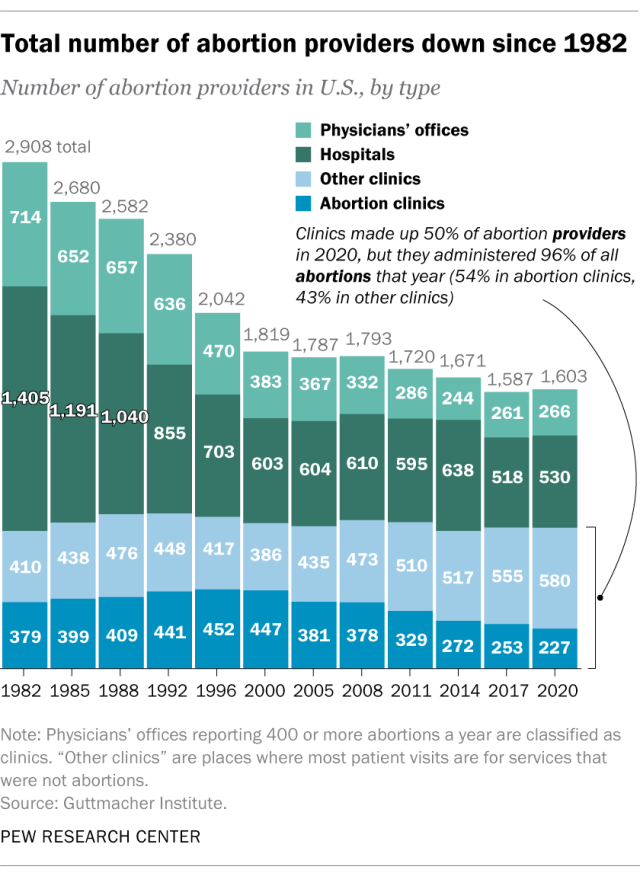
While clinics make up half of the facilities that provide abortions, they are the sites where the vast majority (96%) of abortions are administered, either through procedures or the distribution of pills, according to Guttmacher’s 2020 data. (This includes 54% of abortions that are administered at specialized abortion clinics and 43% at nonspecialized clinics.) Hospitals made up 33% of the facilities that provided abortions in 2020 but accounted for only 3% of abortions that year, while just 1% of abortions were conducted by physicians’ offices.
Looking just at clinics – that is, the total number of specialized abortion clinics and nonspecialized clinics in the U.S. – Guttmacher found the total virtually unchanged between 2017 (808 clinics) and 2020 (807 clinics). However, there were regional differences. In the Midwest, the number of clinics that provide abortions increased by 11% during those years, and in the West by 6%. The number of clinics decreased during those years by 9% in the Northeast and 3% in the South.
The total number of abortion providers has declined dramatically since the 1980s. In 1982, according to Guttmacher, there were 2,908 facilities providing abortions in the U.S., including 789 clinics, 1,405 hospitals and 714 physicians’ offices.
The CDC does not track the number of abortion providers.
In the District of Columbia and the 46 states that provided abortion and residency information to the CDC in 2021, 10.9% of all abortions were performed on women known to live outside the state where the abortion occurred – slightly higher than the percentage in 2020 (9.7%). That year, D.C. and 46 states (though not the same ones as in 2021) reported abortion and residency data. (The total number of abortions used in these calculations included figures for women with both known and unknown residential status.)
The share of reported abortions performed on women outside their state of residence was much higher before the 1973 Roe decision that stopped states from banning abortion. In 1972, 41% of all abortions in D.C. and the 20 states that provided this information to the CDC that year were performed on women outside their state of residence. In 1973, the corresponding figure was 21% in the District of Columbia and the 41 states that provided this information, and in 1974 it was 11% in D.C. and the 43 states that provided data.
In the District of Columbia and the 46 states that reported age data to the CDC in 2021, the majority of women who had abortions (57%) were in their 20s, while about three-in-ten (31%) were in their 30s. Teens ages 13 to 19 accounted for 8% of those who had abortions, while women ages 40 to 44 accounted for about 4%.
The vast majority of women who had abortions in 2021 were unmarried (87%), while married women accounted for 13%, according to the CDC , which had data on this from 37 states.
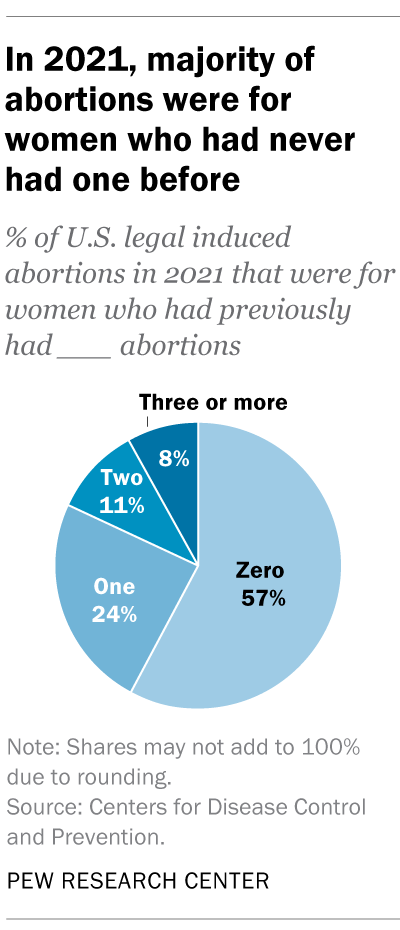
In the District of Columbia, New York City (but not the rest of New York) and the 31 states that reported racial and ethnic data on abortion to the CDC , 42% of all women who had abortions in 2021 were non-Hispanic Black, while 30% were non-Hispanic White, 22% were Hispanic and 6% were of other races.
Looking at abortion rates among those ages 15 to 44, there were 28.6 abortions per 1,000 non-Hispanic Black women in 2021; 12.3 abortions per 1,000 Hispanic women; 6.4 abortions per 1,000 non-Hispanic White women; and 9.2 abortions per 1,000 women of other races, the CDC reported from those same 31 states, D.C. and New York City.
For 57% of U.S. women who had induced abortions in 2021, it was the first time they had ever had one, according to the CDC. For nearly a quarter (24%), it was their second abortion. For 11% of women who had an abortion that year, it was their third, and for 8% it was their fourth or more. These CDC figures include data from 41 states and New York City, but not the rest of New York.
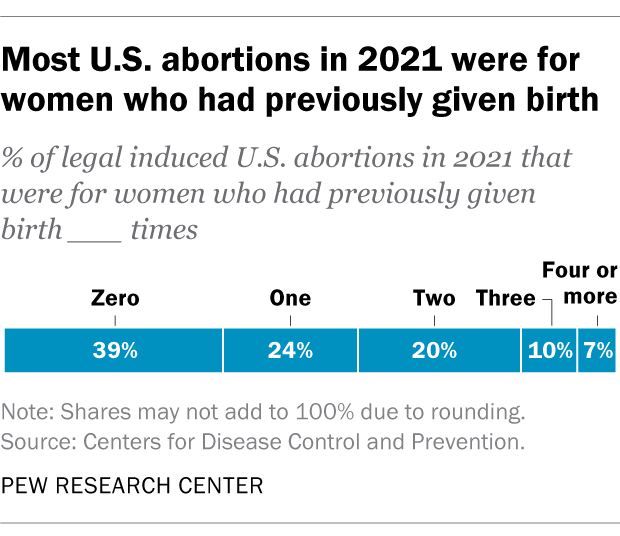
Nearly four-in-ten women who had abortions in 2021 (39%) had no previous live births at the time they had an abortion, according to the CDC . Almost a quarter (24%) of women who had abortions in 2021 had one previous live birth, 20% had two previous live births, 10% had three, and 7% had four or more previous live births. These CDC figures include data from 41 states and New York City, but not the rest of New York.
The vast majority of abortions occur during the first trimester of a pregnancy. In 2021, 93% of abortions occurred during the first trimester – that is, at or before 13 weeks of gestation, according to the CDC . An additional 6% occurred between 14 and 20 weeks of pregnancy, and about 1% were performed at 21 weeks or more of gestation. These CDC figures include data from 40 states and New York City, but not the rest of New York.
About 2% of all abortions in the U.S. involve some type of complication for the woman , according to an article in StatPearls, an online health care resource. “Most complications are considered minor such as pain, bleeding, infection and post-anesthesia complications,” according to the article.
The CDC calculates case-fatality rates for women from induced abortions – that is, how many women die from abortion-related complications, for every 100,000 legal abortions that occur in the U.S . The rate was lowest during the most recent period examined by the agency (2013 to 2020), when there were 0.45 deaths to women per 100,000 legal induced abortions. The case-fatality rate reported by the CDC was highest during the first period examined by the agency (1973 to 1977), when it was 2.09 deaths to women per 100,000 legal induced abortions. During the five-year periods in between, the figure ranged from 0.52 (from 1993 to 1997) to 0.78 (from 1978 to 1982).
The CDC calculates death rates by five-year and seven-year periods because of year-to-year fluctuation in the numbers and due to the relatively low number of women who die from legal induced abortions.
In 2020, the last year for which the CDC has information , six women in the U.S. died due to complications from induced abortions. Four women died in this way in 2019, two in 2018, and three in 2017. (These deaths all followed legal abortions.) Since 1990, the annual number of deaths among women due to legal induced abortion has ranged from two to 12.
The annual number of reported deaths from induced abortions (legal and illegal) tended to be higher in the 1980s, when it ranged from nine to 16, and from 1972 to 1979, when it ranged from 13 to 63. One driver of the decline was the drop in deaths from illegal abortions. There were 39 deaths from illegal abortions in 1972, the last full year before Roe v. Wade. The total fell to 19 in 1973 and to single digits or zero every year after that. (The number of deaths from legal abortions has also declined since then, though with some slight variation over time.)
The number of deaths from induced abortions was considerably higher in the 1960s than afterward. For instance, there were 119 deaths from induced abortions in 1963 and 99 in 1965 , according to reports by the then-U.S. Department of Health, Education and Welfare, a precursor to the Department of Health and Human Services. The CDC is a division of Health and Human Services.
Note: This is an update of a post originally published May 27, 2022, and first updated June 24, 2022.

Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
Key facts about the abortion debate in America
Public opinion on abortion, three-in-ten or more democrats and republicans don’t agree with their party on abortion, partisanship a bigger factor than geography in views of abortion access locally, do state laws on abortion reflect public opinion, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
- Mobile Site
- Staff Directory
- Advertise with Ars
Filter by topic
- Biz & IT
- Gaming & Culture
Front page layout
image processing —
Playboy image from 1972 gets ban from ieee computer journals, use of "lenna" image in computer image processing research stretches back to the 1970s..
Benj Edwards - Mar 29, 2024 9:16 pm UTC

On Wednesday, the IEEE Computer Society announced to members that, after April 1, it would no longer accept papers that include a frequently used image of a 1972 Playboy model named Lena Forsén. The so-called " Lenna image ," (Forsén added an extra "n" to her name in her Playboy appearance to aid pronunciation) has been used in image processing research since 1973 and has attracted criticism for making some women feel unwelcome in the field.
Further Reading
In an email from the IEEE Computer Society sent to members on Wednesday, Technical & Conference Activities Vice President Terry Benzel wrote , "IEEE's diversity statement and supporting policies such as the IEEE Code of Ethics speak to IEEE's commitment to promoting an including and equitable culture that welcomes all. In alignment with this culture and with respect to the wishes of the subject of the image, Lena Forsén, IEEE will no longer accept submitted papers which include the 'Lena image.'"
An uncropped version of the 512×512-pixel test image originally appeared as the centerfold picture for the December 1972 issue of Playboy Magazine. Usage of the Lenna image in image processing began in June or July 1973 when an assistant professor named Alexander Sawchuck and a graduate student at the University of Southern California Signal and Image Processing Institute scanned a square portion of the centerfold image with a primitive drum scanner, omitting nudity present in the original image. They scanned it for a colleague's conference paper, and after that, others began to use the image as well.
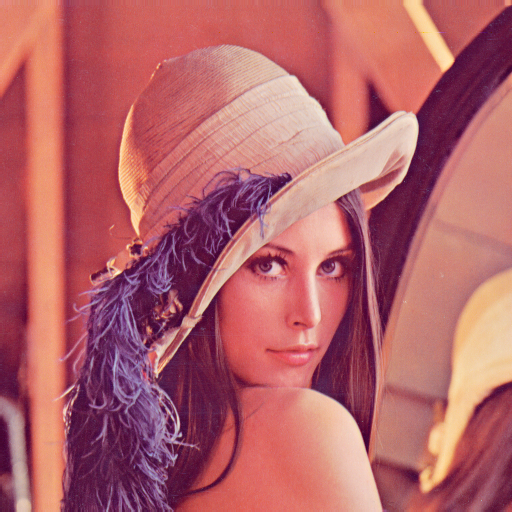

The image's use spread in other papers throughout the 1970s, '80s, and '90s , and it caught Playboy's attention, but the company decided to overlook the copyright violations. In 1997, Playboy helped track down Forsén, who appeared at the 50th Annual Conference of the Society for Imaging Science in Technology, signing autographs for fans. "They must be so tired of me... looking at the same picture for all these years!" she said at the time. VP of new media at Playboy Eileen Kent told Wired , "We decided we should exploit this, because it is a phenomenon."
The image, which features Forsén's face and bare shoulder as she wears a hat with a purple feather, was reportedly ideal for testing image processing systems in the early years of digital image technology due to its high contrast and varied detail. It is also a sexually suggestive photo of an attractive woman, and its use by men in the computer field has garnered criticism over the decades, especially from female scientists and engineers who felt that the image (especially related to its association with the Playboy brand) objectified women and created an academic climate where they did not feel entirely welcome.
Due to some of this criticism, which dates back to at least 1996 , the journal Nature banned the use of the Lena image in paper submissions in 2018.
The comp.compression Usenet newsgroup FAQ document claims that in 1988, a Swedish publication asked Forsén if she minded her image being used in computer science, and she was reportedly pleasantly amused. In a 2019 Wired article , Linda Kinstler wrote that Forsén did not harbor resentment about the image, but she regretted that she wasn't paid better for it originally. "I’m really proud of that picture," she told Kinstler at the time.
Since then, Forsén has apparently changed her mind. In 2019, Creatable and Code Like a Girl created an advertising documentary titled Losing Lena , which was part of a promotional campaign aimed at removing the Lena image from use in tech and the image processing field. In a press release for the campaign and film, Forsén is quoted as saying, "I retired from modelling a long time ago. It’s time I retired from tech, too. We can make a simple change today that creates a lasting change for tomorrow. Let’s commit to losing me."
It seems like that commitment is now being granted. The ban in IEEE publications, which have been historically important journals for computer imaging development, will likely further set a precedent toward removing the Lenna image from common use. In the email, IEEE's Benzel recommended wider sensitivity about the issue, writing, "In order to raise awareness of and increase author compliance with this new policy, program committee members and reviewers should look for inclusion of this image, and if present, should ask authors to replace the Lena image with an alternative."
reader comments
Channel ars technica.
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Title: remamber: referring image segmentation with mamba twister.
Abstract: Referring Image Segmentation (RIS) leveraging transformers has achieved great success on the interpretation of complex visual-language tasks. However, the quadratic computation cost makes it resource-consuming in capturing long-range visual-language dependencies. Fortunately, Mamba addresses this with efficient linear complexity in processing. However, directly applying Mamba to multi-modal interactions presents challenges, primarily due to inadequate channel interactions for the effective fusion of multi-modal data. In this paper, we propose ReMamber, a novel RIS architecture that integrates the power of Mamba with a multi-modal Mamba Twister block. The Mamba Twister explicitly models image-text interaction, and fuses textual and visual features through its unique channel and spatial twisting mechanism. We achieve the state-of-the-art on three challenging benchmarks. Moreover, we conduct thorough analyses of ReMamber and discuss other fusion designs using Mamba. These provide valuable perspectives for future research.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Citing an image in APA Style. In an APA Style reference entry for an image found on a website, write the image title in italics, followed by a description of its format in square brackets. Include the name of the site and the URL. The APA in-text citation just includes the photographer's name and the year. APA format. Author last name, Initials.
Citing vs. 'reproducing' This guide provides information on how to cite images and photographs. However, reproducing the image inside of your essay or research paper might require additional permissions and/or attributions. Section 12.15 of the Publication Manual provides more information on reproducing images and graphics.
Include as much of the information below when citing images in a paper and formal presentations. Apply the appropriate citation style (see below for APA, MLA examples). Image creator's name (artist, photographer, etc.) Title of the image; Date the image (or work represented by the image) was created; Date the image was posted online
If you include an image directly in your paper, it should be labeled "Fig." (short for "Figure"), given a number, and presented in the MLA figure format. Directly below the image, place a centered caption starting with the figure label and number (e.g. "Fig. 2"), then a period. For the rest of the caption, you have two options:
You can cite images in your research paper either at the end, in between the topics, or in a separate section for all the non-textual elements used in the paper. You can choose to insert images in between texts, but you need to provide the in-text citations for every image that has been used. Additionally, you need to attach the name ...
Here's the standard structure for a digital image citation found on a website. It follows guidance found in the MLA Style Center. Works Cited. Structure. Image Creator's Last Name, First Name. "Image Title.". Website Name, Day Month Year Published, URL. Example. de Jong, Sidsel.
How to Cite an Image. To create a basic works-cited-list entry for an image, list the creator of the image, the title of the image, the date of composition, and the location of the image, which would be a physical location if you viewed the image in person. If you viewed the image online, provide the name of the website containing the image and ...
drawings. photographs/images. This section will cover the following examples: Image from an Electronic Source. Figures. For more examples and information, consult the following publications: Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.) Call Number: BF76.7 .P83 2020.
To cite an image found through Google using the image-search function or through searching Google Images, identify the website where the image was originally posted. Cite the image as though you found it on the original website where it was posted. To find the publisher's details, this means clicking through to the site with the image.
For photographs or images taken of an artwork or other creative work, reference the date of the work depicted in the image (e.g. for a photograph of the Mona Lisa, the date referenced should be the date the Mona Lisa was created, NOT the date the Mona Lisa was photographed). When including images in your work, these can go either in the body of your work, or after the reference list but before ...
APA 7 Format for Image Citations. Photo and image citations follow the APA basic format . Use the artist or photographer's name, if known, as the first element. Include the URL as the last element. Basic Format. Artist Last Name, First Initial. Second Initial. (Year). Title of the artwork [Format].
The only official, authorized book on MLA style. The new, ninth edition builds on the MLA's unique approach to documenting sources using a template of core elements facts, common to most sources, like author, title, and publication date that allows writers to cite any type of work, from books, e-books, and journal articles in databases to song lyrics, online images, social media posts ...
For example, if a photo is posted on Flickr, Flickr is the container. Sometimes a source is nested inside of two separate containers, like an image found in a book read on an ebook platform like Ebook Library (EBL). Both the title of the source and its container (or multiple containers) are included in a citation. Examples: Image Found on the Web
Step 1: Discussing the Image in Text. When including the image in the text, refer to the figure through the abbreviation and number: fig. #. For example, if this is your first image, it will be fig. 1. Your 19th image will be fig. 19. This will look something like: How to Cite an Image In Text MLA.
Images should be cited in all cases, even if the image is very small, or in the public domain. The citation should be accessible in the context of the image's use (within a Powerpoint presentation, on a web page, in a paper, etc.). Image citations should include the following information at a minimum: Title. Creator name.
How to cite an image from Google Images in APA: Image creator's Last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year published). Title of image [Photograph, Cartoon, Painting, etc.]. Website Name. URL. The reference list entry for the image consists of its author, year of publication, title, description in brackets, and source (usually the name of ...
Today, finding and citing a digital or online image is simple. You'll need the following information: Photographer's name. (Year published) Title of the photograph, italizised. Available at: URL (Accessed: the date you sourced the image) In-text citation structure and example: (Photographer's name, Year published) OR.
Either Imagetwin or the authors' visual scrutiny flagged 112 — almost 20% — of the 588 image-containing papers. ... Publishers unite to tackle doctored images in research papers
In this work, we discuss building performant Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). In particular, we study the importance of various architecture components and data choices. Through careful and comprehensive ablations of the image encoder, the vision language connector, and various pre-training data choices, we identified several crucial design lessons. For example, we demonstrate that ...
Citing an image from a book. An image you encountered in a book, journal article, or other print source should be cited by first listing information about the image itself, then listing information about the source it was contained in, including the page number where the image can be found.. Use italics for the title an image originally created outside the context of the book or article (e.g ...
- Journal publisher bans Playboy centerfold Lena's image from research papers, NewsBytes, Fri, 29 Mar 2024 09:50:18 GMT - It's time to retire Lena from computer science , Pursuit, Fri, 13 ...
Posting about a research paper on social-media platform X (formerly known as Twitter) doesn't translate into a bump in citations, according to a study that looked at 550 papers. The finding ...
We present Stable Video 3D (SV3D) -- a latent video diffusion model for high-resolution, image-to-multi-view generation of orbital videos around a 3D object. Recent work on 3D generation propose techniques to adapt 2D generative models for novel view synthesis (NVS) and 3D optimization. However, these methods have several disadvantages due to either limited views or inconsistent NVS, thereby ...
This work presents FlashFace, a practical tool with which users can easily personalize their own photos on the fly by providing one or a few reference face images and a text prompt. Our approach is distinguishable from existing human photo customization methods by higher-fidelity identity preservation and better instruction following, benefiting from two subtle designs. First, we encode the ...
Citation Tools. Citation Generator ... Plagiarism Checker. Compare your paper to billions of pages and articles with Scribbr's Turnitin-powered plagiarism checker. Run a free check. AI Proofreader. Correct your document in minutes. Upload my document. ... universalSourceForm.overwrites.image.intro.text,universalSourceForm.defaults.intro.text.
Pew Research Center has conducted many surveys about abortion over the years, providing a lens into Americans' views on whether the procedure should be legal, among a host of other questions. ... While the Guttmacher Institute supports abortion rights, its empirical data on abortions in the U.S. has been widely cited by groups and ...
Synthetic image data generation represents a promising avenue for training deep learning models, particularly in the realm of transfer learning, where obtaining real images within a specific domain can be prohibitively expensive due to privacy and intellectual property considerations. This work delves into the generation and utilization of synthetic images derived from text-to-image generative ...
On Wednesday, the IEEE Computer Society announced to members that, after April 1, it would no longer accept papers that include a frequently used image of a 1972 Playboy model named Lena Forsén ...
Referring Image Segmentation (RIS) leveraging transformers has achieved great success on the interpretation of complex visual-language tasks. However, the quadratic computation cost makes it resource-consuming in capturing long-range visual-language dependencies. Fortunately, Mamba addresses this with efficient linear complexity in processing. However, directly applying Mamba to multi-modal ...