

MP8 Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning
Mathematical practice standard #8.
Mathematically proficient students notice if calculations are repeated, and look both for general methods and for shortcuts. Upper elementary students might notice when dividing 25 by 11 that they are repeating the same calculations over and over again, and conclude they have a repeating decimal…. As they work to solve a problem, mathematically proficient students maintain oversight of the process, while attending to the details. They continually evaluate the reasonableness of their intermediate results. —CCSS
The standard in elementary school
A central idea here is that mathematics is open to drawing general results (or at least good conjectures) from trying examples, looking for regularity, and describing the pattern both in what you have done and in the results.
A multiplication fact-practice exercise might, for example, ask children to choose three numbers in a row (e.g., 5, 6, and 7) and compare the middle number times itself to the product of the two outer numbers. In this example, the two products are 36 and 35. After they do this for several triplets of numbers, they are likely to conjecture a pattern that allows them to multiply 29 × 31 mentally because they expect it to be one less than 30 × 30, which they can do easily in their heads. Seeing that regularity is typically easy for fourth graders; expressing it clearly is much harder. Initial attempts are generally inarticulate until students are given the idea of naming the numbers. A simple non-algebraic “naming” scheme was used above to describe the pattern: the numbers were named “middle” and “outer” and that was sufficient. A slightly more sophisticated scheme would distinguish the outer numbers as something like “middle plus 1” and “middle minus 1.” Then children can state (middle – 1) × (middle + 1) = middle 2 – 1. The step from this statement to standard algebra is just a matter of adopting algebraic conventions: naming numbers with a single letter like m instead of a whole word like “middle,” and omitting the × sign.
The recognition that adding 9 can be simplified by treating it as adding 10 and subtracting 1 can be a discovery rather than a taught strategy. In one activity—there are obviously many other ways of doing this—children start, e.g., with 28 and respond as the teacher repeat only the words “ten more” (38), “ten more” (48), “ten more” (58), and so on. They may even be counting, initially, to verify that they are actually adding 10, but they soon hear the pattern in their responses (because no other explanatory or instruction words are interfering) and express that discovery from their repeated reasoning by saying the 68, 78, 88 almost without even the request for “ten more.” When, at some point, the teacher changes and asks for “9 more,” even young students often see it as “almost ten more” and make the correction spontaneously. Describing the discovery then becomes a case of “expressing regularity” that was found through “repeated reasoning.” Young students then find it very exciting to add 99 the same way, first by repeating the experience of getting used to a simple computation, adding 100, and then by coming up with their own adjustment to add 99.
- Learning Framework
- Learning Model
- Research Base
- Our Services
- Articles on Learnership
- Support for Learning at Home
- Downloadable Resources
- Upcoming Presentations
- Presentation Archives
- Professional Learning Books
- Mathematics
- English Language Arts
- Learning at Home Guides
Teach Your Students to Look for and Express Regularity in Repeated Reasoning

Share this article.
In today’s world students who are truly successful in mathematics can not only solve problems, but can explain:
- what each problem is asking,
- how they will solve the problem,
- why their solution plan makes sense, and
- how they know their answer is correct.
In other words, students must be able to think metacognitively about each and every problem and explain their thinking.
The Standards for Mathematical Practice present a helpful framework for this complex and important work. That’s why we’ve provided you with a metacognitive study of each of the mathematical practices—what this thinking looks like at each grade level, a step-by-step approach to teaching each practice, and a reflection guide to support students as they “think about their thinking.”
This article is focused on…
STANDARD FOR MATHEMATICAL PRACTICE 8: Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning.
What this thinking looks like at each grade level.
Because the 8 Standards for Mathematical Practice are the same for all grade levels, they are not specific enough to provide much practical guidance for classroom implementation. So, we’ve provided the standard and its learning progression for every grade from Pre-K through High School to better understand how the thinking builds in tandem with students’ cognitive development and the demands of mathematical content, as shown in the example below.

A Step-By-Step Approach to Teaching Practice 8
Fostering metacognition requires a balance of explicit instruction, teacher modeling, student-centered exploration, and responsive coaching that helps students first learn the kinds of questions and thought processes they can apply, and then grow to use them on their own. These metacognitive skills come naturally to some students but not to others. Teachers must play an active role in teaching them and helping students own their mathematical learning.
Use this process to teach, model, and guide students in mastering Practice 8.
Process to look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning
- Identify the type of problem.
- Identify what operations within this problem you already know how to do.
- Identify what you do over and over again when solving this type of problem.
- Identify which strategies, rules, or patterns you could use to solve this problem.
- Identify other shortcuts you could use based on the patterns you noticed.
- Explain how you can repeat this thinking when solving similar problems.
A Reflection Guide to Support Students as They “Think About Their Thinking”
As we said before, mathematics is much more than just solving the problems and checking to see if the answer is correct. It also involves each student’s understanding of what they are learning, how they can learn it, and what they have learned about their mathematical thinking along the way.
When you’re focusing on Practice 8, teach your students this routine and then encourage them to use it for each and every math problem they solve. In doing so, you will support them in thinking about, reflecting on, and sharing their thoughts as the develop ownership of their mathematics.

Foster Learnership in Mathematics
Owning their mathematics won’t be automatic. On the contrary—most students need a great deal of explicit instruction, modeling, and coaching before they develop the metacognitive habits that allow them to take ownership of their learning. The more students are able to understand their own learning process and articulate it, the easier it will be for them to improve their conceptual understanding, procedural skill and fluency, and applications. In other words, students will own their mathematics with metacognition and develop learnership.
Click here to download a resource with the processes and reflection for the Standard for Mathematical Practice 8: Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Click below to access the same great resources for the other Standards for Mathematical Practices.
- Make Sense of Problems and Persevere in Solving Them
- Reason Abstractly and Quantitatively
- Construct Viable Arguments and Critique the Reasoning of Others
- Model with Mathematics
- Use Appropriate Tools Strategically
- Attend to Precision
- Look for and Make Use of Structure
We hope you check out our resources…use them…share them…continue your learnership.
Continue the Learning
Check out these articles and resources to continue your learning about this topic….
- Our Article, “Building Math Metacognition in Three Easy Steps”
- Our Tools for Teaching the Practices
- Our Posters for Teaching the Mathematical Practices
The Learning Brief
In this article you learned….
- What the metacognitive thinking looks like at each grade level for Mathematical Practice Standard 8.
- A step-by-step approach to teaching Mathematical Practice Standard 8.
- A reflection guide to support students as they “think about their thinking” around Mathematical Practice Standard 8.
Can you imagine building an environment full of motivated, engaged, and eager students who own their learning? We can.
Stay up to date.
Subscribe to The Learnership Review and receive monthly emails so you never miss a thing.
- Name * First Name Last Name
- Email Address *
Elevated Achievement Group
- Our Approach
- Our Resources
- Name * First Last
- Title/Position:
- School/District/Organization:
- Message to Us
©2020 Elevated Achievement Group, Inc. | (562) 852-2975

Engage your students with effective distance learning resources. ACCESS RESOURCES>>
Practice standard - 8, 8 — look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning.
Mathematically proficient students notice if calculations are repeated, and look both for general methods and for shortcuts. As they work to solve a problem, mathematically proficient students maintain oversight of the process, while attending to the details. They continually evaluate the reasonableness of their intermediate results.
Upper elementary students might notice when dividing $25$ by $11$ that they are repeating the same calculations over and over again, and conclude they have a repeating decimal. By paying attention to the calculation of slope as they repeatedly check whether points are on the line through $(1, 2)$ with slope $3$, middle school students might abstract the equation $(y-2)/(x-1) = 3$. Noticing the regularity in the way terms cancel when expanding $(x-1)(x+1)$, $(x-1)(x^2+x+1)$, and $(x-1)(x^3+x^2+x+1)$ might lead them to the general formula for the sum of a geometric series.
New: Vignettes and videos
Kindergarten: double compare.
Double Compare is a card game played with numeral cards, usually in pairs. In the classroom example below, the teacher notices that in some rounds of the game students add or count to find the sums on their numeral cards, while in other rounds some students do not add or count-they have other ways to reason about the two pairs of numbers. Read more (PDF)
Grade 1: Equivalent Addition Problems
As young students learn about addition and subtraction, they naturally begin to notice regularities across problems. Sometimes students point out what they are noticing-especially if being alert for patterns and regularities is expected in math class. Read more (PDF)
Grade 2: Related Story Problems
Although students may have methods to calculate and to solve different kinds of story problems, it is a different skill to look across related problems to notice generalizations about the behavior of the operations involved. Read more (PDF)
See the related videos:
- Related Problems, Part 1
Grade 2: How Do You Know That 23 + 2 = 2 + 23?
What does it mean to use “properties of operations” in the primary grades? The focus is not learning names for the properties, but on understanding how each operation behaves-for example, that the numbers in an addition expression can be rearranged without changing the sum. Read more (PDF)
- How Do You Know That 23 + 2 = 2 + 23?
Grade 3: Adding 1 to an Addend, Adding 1 to a Factor
This extended example presents a sequence of eight lessons in which students 1) identify regularities they notice in pairs of related problems, 2) articulate a generalization about the behavior of an operation, 3) explore that generalization, and 4) develop arguments to prove that the generalization is true for all whole numbers. Read more (PDF)
- Adding 1 to an Addend, Adding 1 to a Factor Part 1
Grade 5: Today’s Number
There are many variations of a task that some teachers call “Number of the Day” or “Today’s Number.” Typically, teachers provide a target number, and students are challenged to write expressions equivalent to that number. Read more (PDF)
Illustrations
- 4.OA Double Plus One
- 6.NS Adding Multiples
- 6.EE The Djinni’s Offer
- 8.EE Extending the Definitions of Exponents, Variation 1
High School
- F-LE Equal Differences over Equal Intervals 1
In this video students use geometric structure in different ways to solve a problem that aligns with 6.G.1.
Search form


CME Project
Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning (practice 8).
Mathematically proficient students notice if calculations are repeated, and look both for general methods and for shortcuts. Upper elementary students might notice when dividing 25 by 11 that they are repeating the same calculations over and over again, and conclude they have a repeating decimal. By paying attention to the calculation of slope as they repeatedly check whether points are on the line through (1, 2) with slope 3, middle school students might abstract the equation (y – 2)/(x – 1) = 3. Noticing the regularity in the way terms cancel when expanding (x – 1)(x + 1), (x – 1)(x2 + x + 1), and (x – 1)(x3 + x2 + x + 1) might lead them to the general formula for the sum of a geometric series. As they work to solve a problem, mathematically proficient students maintain oversight of the process, while attending to the details. They continually evaluate the reasonableness of their intermediate results.
"Common Core State Standards Initiative | Mathematics | Introduction | Standards for Mathematical Practice." < http://corestandards.org/the-standards/mathematics/introduction/standards-for-mathematical-practice/ >.
Click Here for a list of CME Project lesson's that use this practice
Mathematical practice terms: .
- Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning

MathCircles.org
Mathematical practice: mp8 - look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning..
- 1st - 2nd (12)
- 3rd - 5th (30)
- 6th - 8th (83)
- 9th - 12th (85)
- College Level (72)
- For Teachers (81)
- Algebra / Arithmetic (33)
- Combinatorics (31)
- Geometry (36)
- Mathematical Games (26)
- Mathematical Modeling (15)
- Number Theory (25)
- Parity / Invariants (2)
- Probability and Statistics (3)
- Problem Solving / General (39)
- Social Justice Mathematics (5)
- Facilitator Guides (88)
- Featured in MCircular (25)
- Handouts (38)
- Lesson Plan (10)
- Photos & Videos (28)
- References (36)
- Virtual Tools (17)
- Manipulatives (33)
- Multiple Representations (33)
- Problem Posing (45)
- Problem Sets (51)
- Try a Smaller Problem (40)
- Work Backwards (21)
- Integrates Technology (17)
- Kinesthetic Element (11)
- MP1 - Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. (83)
- MP2 - Reason abstractly and quantitatively. (53)
- MP3 - Construct viable arguments and critique others' reasoning. (58)
- MP4 - Model with mathematics. (58)
- MP5 - Use appropriate tools strategically. (40)
- MP6 - Attend to precision. (40)
- MP7 - Look for and make use of structure. (72)
- MP8 - Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. (61)
Cup Stacking

Making Connections Between Forms of Quadratic Equations

Solving Linear Equations: An M&M Mystery

Rational Numbers

Trigonometric Ratios in Right Triangles

Liar’s Bingo

Locked Out: A Breakout Box Session for Your Circle

Lockers: An Open-and-Shut Case

Mathemagical Card Tricks
There are many card tricks based on simple mathematics as opposed to sleight of hand. In this session, participants will play with a number of such tricks, test them out and work on discovering the math underneath, with a goal to formalize the mathematics that makes the trick work.

Mathematical Games
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy
Big Ideas Math Answers Grade 8 Chapter 3 Angles and Triangles
The students of middle school can get the Solution Key for Big Ideas Math Grade 8 Chapter 3 Angles and Triangles on this page. With the help of this Big Ideas Math Book 8th Grade Answer Key Chapter 3 Angles and Triangles you can finish your homework in time and also improve your performance in the exams. Get free step by step solutions for all the questions in Big Ideas Math Answers Grade 8 Chapter 3 Angles and Triangles.
Big Ideas Math Book 8th Grade Answer Key Chapter 3 Angles and Triangles
Download Big Ideas Math Answers Grade 8 Chapter 3 Angles and Triangles pdf for free of cost. The solutions for each and every question is prepared in an easy manner. Go through the table of contents shown in the below section to know the topics covered in Big Ideas Math Answers Grade 8 Chapter 3 Angles and Triangles.
Performance
Angles and Triangles STEAM Video/Performance
Angles and triangles getting ready for chapter 3.
Lesson: 1 Parallel Lines and Transversals
Lesson 3.1 Parallel Lines and Transversals
Parallel lines and transversals homework & practice 3.1.
Lesson: 2 Angles of Triangles
Lesson 3.2 Angles of Triangles
Angles of triangles homework & practice 3.2.
Lesson: 3 Angles of Polygons
Lesson 3.3 Angles of Polygons
Angles of polygons homework & practice 3.3.
Lesson: 4 Using Similar Triangles
Lesson 3.4 Using Similar Triangles
Using similar triangles homework & practice 3.4.
Chapter 3 – Angles and Triangles
Angles and Triangles Connecting Concepts
Angles and triangles chapter review, angles and triangles practice test, angles and triangles cumulative practice.
STEAM Video

Watch the STEAM Video “Honeycombs.” Then answer the following questions.
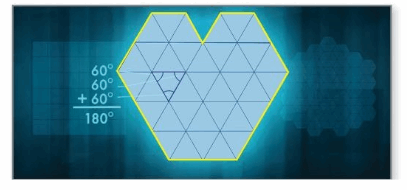
Answer: The sum of interior angles of the equilateral triangle = 180° x + x + x = 180° 3x° = 180° x = 180/3 x° = 60°
Performance Task
Turtle Shells
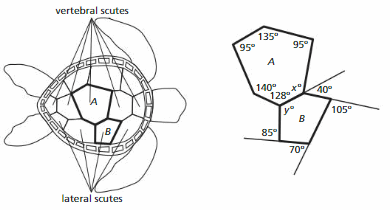
Chapter Exploration
Answer: 8 angles are formed by the parallel lines and the transversal b. Which of these angles have equal measures? Explain your reasoning.

EXPLORATION 1
Use the figure to find the measure of the angle. Explain your reasoning
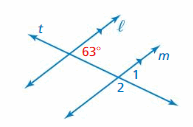
Question 1. ∠1
Answer: 63°
Question 2. ∠2
Answer: 117°
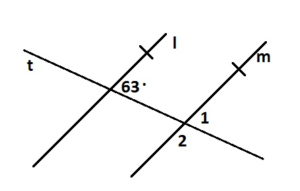
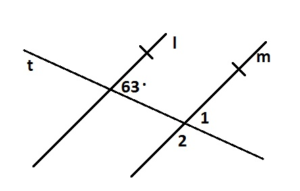
Answer: ∠1 and 59° are the supplementary angles ∠1 + 59° = 180° ∠1 = 180° – 59° ∠1 = 121° ∠2 and 59° are vertical angles. They are congruent. So, the measure of ∠1 is 121° ∠3 and 59° are supplementary angles. ∠3 + 59° = 180° ∠3 = 180° – 59° ∠3 = 121° ∠4, ∠5, ∠6, ∠7 corresponding angles are congruent because they are formed by a transversal intersecting parallel side. the measure of ∠4 is 121° the measure of ∠5 is 59° the measure of ∠6 is 121° the measure of ∠7 is 59°
In Example 3, the measure of ∠4 is 84°. Find the measure of the angle. Explain your reasoning.
Question 4. ∠3
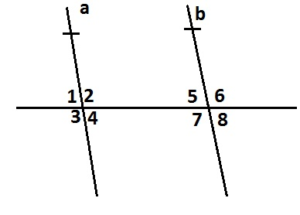
Question 5. ∠5
Answer: ∠4 and ∠5 are alternate interior angles formed by transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. So, the measure of ∠5 is 84°
Question 6. ∠6
Answer: ∠3 and ∠6 are alternate exterior angles formed by transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. So, the measure of ∠6 is 96°
Self-Assessment for Concepts & Skills Solve each exercise. Then rate your understanding of the success criteria in your journal.
FINDING ANGLE MEASURES Use the figure to find the measures of the numbered angles.
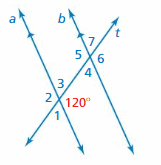
Answer: ∠1 and 120° are the supplementary angles. ∠1 + 120° = 180° ∠1 = 180 – 120 ∠1 = 60° Thus the measure of ∠1 is 60° ∠2 and 120° are the vertical angles. They are congruent. Thus the measure of ∠2 is 120° ∠3 and 120° are the supplementary angles. ∠3 + 120° = 180° ∠3 = 180 – 120 ∠3 = 60° ∠4, ∠5, ∠6, ∠7 are corresponding angles are formed by transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. Thus the measure of ∠4 is 60° Thus the measure of ∠5 is 120° Thus the measure of ∠6 is 120° Thus the measure of ∠7 is 60°
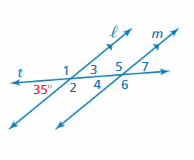
Answer: ∠1 and 35° are the supplementary angles. ∠1 + 35° = 180° ∠1 = 180 – 35 ∠1 = 145° Thus the measure of ∠1 is 145° ∠2 and 35° are the supplementary angles. ∠2 + 35° = 180° ∠2 = 180 – 35 ∠2 = 145° Thus the measure of ∠2 is 145° ∠3 and 35° are the vertical angles. They are congruent. Thus the measure of ∠3 is 35° ∠4, ∠5, ∠6, ∠7 are corresponding angles are formed by transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. Thus the measure of ∠4 is 35° Thus the measure of ∠5 is 145° Thus the measure of ∠6 is 145° Thus the measure of ∠7 is 35°

Answer: ∠2, ∠6 are corresponding angles are formed by transversal intersecting parallel lines. ∠6, ∠8 are vertical angles are formed by transversal intersecting parallel lines. ∠5 does not belong to the other three because all the other three measure are equal.
Self-Assessment for Problem Solving
Solve each exercise. Then rate your understanding of the success criteria in your journal.
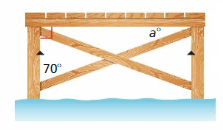
Answer: The angle a and the angle of 70 degrees are complementary angles because they belong to a right triangle, where the third angle is the right angle. ∠a + 70 = 90 ∠a = 90 – 70 ∠a = 20°
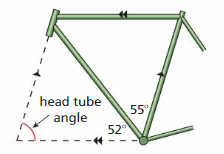
Answer: The lines AB and CD are parallel. ABC and BCD are the corresponding angles formed by transversal intersecting parallel lines. ∠BCD = 55° ∠BAC + ∠ABC + ∠ACB = 180° The sum of the angles in a triangle is 180° ∠BAC + 55°+ 52° = 180° ∠BAC + 107° = 180° ∠BAC = 180° – 107° ∠BAC = 73° So, the head tube angle of a bike is 73°
Review & Refresh
Find the values of the ratios (red to blue) of the perimeters and areas of the similar figures.
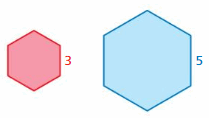
Answer: perimeter of red hexagon/perimeter of blue hexagon = \(\frac{3}{5}\) The values of the ratios of the perimeter is \(\frac{3}{5}\) Area of red hexagon/Area of blue hexagon = (\(\frac{3}{5}\))² = \(\frac{9}{25}\) The values of the ratios of the area is \(\frac{9}{25}\)
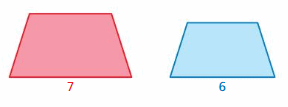
Answer: perimeter of red trapezium /perimeter of blue trapezium = \(\frac{7}{6}\) The values of the ratios of the perimeter is \(\frac{7}{6}\) Area of red hexagon/Area of blue hexagon = (\(\frac{7}{6}\))² = \(\frac{49}{36}\) The values of the ratios of the area is \(\frac{49}{36}\)
Evaluate the expression.
Question 3. 4 + 3 2
Answer: 4 + 9 = 13
Question 4. 5(2) 2 – 6
Answer: 5(4) – 6 20 – 6 = 14
Question 5. 11 + (-7) 2 – 9
Answer: 11 + 49 – 9 11 + 40 = 50
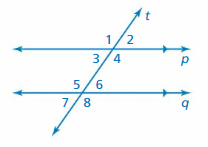
Concepts, Skills, & Problem Solving EXPLORING INTERSECTIONS OF LINES Use a protractor to determine whether lines a and b are parallel. ( See Exploration 1, p. 103.)
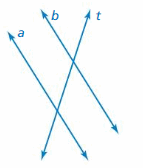
Answer: Use a protractor to measure ∠1 and ∠2 ∠1 ≈ 60° ∠2 ≈ 60° ∠1 and ∠2, it means the two angles are congruent. The angles are exterior alternate angles. According to the converse of the exterior alternate angles theorem, the two lines are parallel. a || b
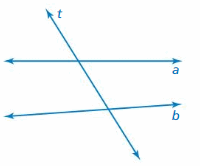
Answer: Use a protractor to measure ∠1 and ∠2 ∠1 ≈ 50° ∠2 ≈ 60° ∠1 and ∠2, it means the two angles are not congruent. The angles are exterior alternate angles. According to the converse of the exterior alternate angles theorem, the two lines are not parallel.
FINDING ANGLE MEASURES Use the figure to find the measures of the numbered angles. Explain your reasoning.
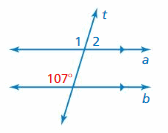
Answer: ∠1 and 107° are corresponding angles. They are congruent. So, the measure of ∠1 is 107°. ∠1 and ∠2 are supplementary angles. ∠1 + ∠2 = 180° 107° + ∠2 = 180° ∠2 = 180° – 107° ∠2 = 73° So, the measure of ∠2 is 73°
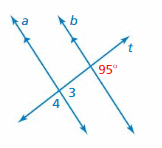
Answer: ∠3 and 95° are corresponding angles. They are congruent. Thus the measure of ∠3 is 95° ∠3 and ∠4 are supplementary angles. ∠3 + ∠4 = 180° 95° + ∠4 = 180° ∠4 = 180 – 95 ∠4 = 85° So the measure of ∠4 is 85°
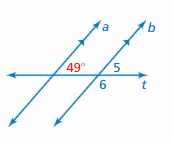
Answer: ∠5 and 49° are corresponding angles. They are congruent. So, the measure of ∠5 is 49° ∠5 and ∠6 are supplementary angles. ∠5 + ∠6 = 180° 49° + ∠6 = 180° ∠6 = 180° – 49° ∠6 = 131° So, the measure of ∠6 is 131°

Answer: Since the two lines are not parallel. Hence ∠5 is not congruent to ∠6. By this, we can say that your friend is not correct.
Answer: ∠1 and ∠2 are corresponding angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. The measure of ∠1 is 60° so the measure of ∠2 is 60°
Question 13. OPEN-ENDED Describe two real-life situations that use parallel lines.
Answer: Example 1: The railroad tracks and the tram tracks are parallel lines. Example 2: The shelves of a bookcase.
USING CORRESPONDING ANGLES Use the figure to find the measures of the numbered angles.
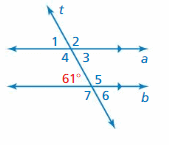
Answer: ∠1 and 60° are corresponding angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. ∠1 and ∠2 are supplementary angles. ∠1 + ∠2 = 180° 60° + ∠2 = 180° ∠2 = 180° – 60° ∠2 = 119° So, the measure of ∠2 is 119° ∠3 and ∠1 are vertical angles. They are congruent. So, the measure of ∠3 is 61° ∠4 and ∠2 are vertical angles. They are congruent. ∠5, ∠6, ∠7 corresponding angles are congruent because they are formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines. So, the measure of ∠5 is 119° So, the measure of ∠6 is 61° So, the measure of ∠7 is 119°
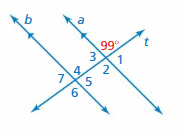
Answer: ∠1 and 99° are supplementary angles. ∠1 + 99° = 180° ∠1 = 180° – 99° ∠1 = 81° Thus the measure of ∠1 is 81° ∠2 and 99° are vertical angles. They are congruent. The measure of ∠2 is 99° ∠3 and ∠1 are vertical angles. They are congruent. So, the measure of ∠3 is 81° ∠4, ∠5, ∠6, ∠7 corresponding angles are congruent because they are formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines. So, the measure of ∠4 is 99° So, the measure of ∠5 is 81° So, the measure of ∠6 is 99° So, the measure of ∠7 is 81°
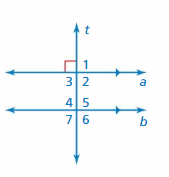
Answer: ∠1 and 90° are supplementary angles. ∠1 + 90° = 180° ∠1 = 180° – 90° ∠1 = 90° Thus the measure of ∠1 is 90° ∠2 and 90° are vertical angles. They are congruent. Thus the measure of ∠2 is 90° ∠3 and ∠1 are vertical angles. They are congruent. So, the measure of ∠3 is 90° ∠4, ∠5, ∠6, ∠7 corresponding angles are congruent because they are formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines. So, the measure of ∠4 is 90° So, the measure of ∠5 is 90° So, the measure of ∠6 is 90° So, the measure of ∠7 is 90°
USING CORRESPONDING ANGLES Complete the statement. Explain your reasoning.
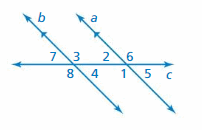
Answer: ∠1 and ∠8 are corresponding angles. They are congruent. The measure of ∠1 = 124°, then the measure of ∠8 is 124° ∠8 and ∠4 are supplementary angles. ∠8 + ∠4 = 180° 124° + ∠4 = 180° ∠4 = 180° – 124° ∠4 = 56° So, the measure of ∠4 is 56°
Answer: ∠2 and ∠7 are corresponding angles. They are congruent. The measure of ∠2 = 48°, then the measure of ∠7 is 48° ∠7 and ∠3 are supplementary angles. ∠7 + ∠3 = 180° 48° + ∠3 = 180° ∠3 = 180° – 48° ∠3 = 132° Thus the measure of ∠3 = 132°
Answer: ∠4 and ∠2 are alternate interior angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. So, the measure of ∠2 is 55°
Answer: ∠6 and ∠8 are alternate exterior angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. So, the measure of ∠8 is 120°
Answer: ∠7 and ∠2 are corresponding angles. They are congruent. The measure of ∠7 is 50.5°, so the measure of ∠2 is 50.5° ∠2 and ∠6 are supplementary angle. ∠2 + ∠6 = 180° 50.5° + ∠6 = 180° ∠6 = 180° – 50.5° ∠6 = 129.5° So, the measure of ∠6 is 129.5°
Answer: ∠3 and ∠6 are corresponding angles. They are congruent. The measure of ∠3 is 118.7° So, the measure of ∠6 is 118.7° ∠6 and ∠2 are supplementary angles. ∠6 + ∠2 = 180° 118.7° + ∠2 = 180° ∠2 = 180° – 118.7° ∠2 = 61.3° So, the measure of ∠2 is 61.3°
Answer: ∠4 and ∠5 are alternate interior angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. So, the measure of ∠1 is 40°
Question 24. REASONING Is there a relationship between exterior angles that lie on the same side of a transversal? interior angles that lie on the same side of a transversal? Explain.
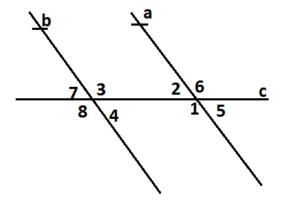
Question 25. REASONING When a transversal is perpendicular to two parallel lines, all the angles formed measure 90°. Explain why.
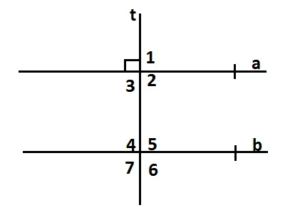
Question 26. REASONING Two horizontal lines are cut by a transversal. What is the least number of angle measures you need to know to find the measure of every angle? Explain your reasoning.
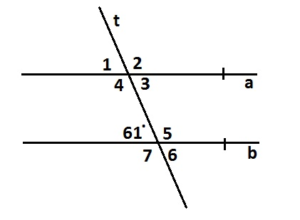
Answer: ∠1 and ∠7 are alternate exterior angles formed by a transeversal intersecting parallel lines. So, ∠1 and ∠7 are congruent. ∠1 and ∠5 are corresponding angles formed by a transeversal intersecting parallel lines. So, ∠1 and ∠5 are congruent. ∠5 and ∠7 are vertical angles so they are congruent. Hence ∠1 and ∠7 are congruent.
FINDING A VALUE Find the value of x.
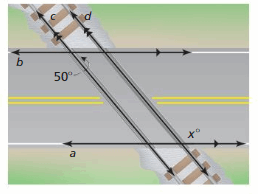
Answer: ∠1 and 50° are alternate interior angles. They are congruent. So, the measure of ∠1 is 50° ∠2 and ∠1 are corresponding angles. They are congruent. So, the measure of ∠2 is 50° ∠2 and x are supplementary angle. ∠2 + x = 180° 50° + x = 180° x = 180° – 50° x = 130° So, the measure of x is 130°
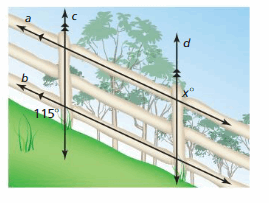
Answer: ∠1 and 115° are corresponding angles. They are congruent. So, the measure of ∠1 is 115° ∠1 and x are alternate exterior angles. They are congruent. So, the measure of x is 115°
Answer: 180° rotation, translation about line t.
Question 31. OPEN-ENDED Refer to the figure. a. Do the horizontal lines appear to be parallel? Explain.
Answer: The three horizontal lines seem to spread apart, even though in reality they are parallel.
Answer: As the lines AB and CD are parallel and ∠BCD are alternate interior angles transversal BC, they are congruent. ∠ABC ≅ ∠BCD x = 64 b. How does the angle the puck hits the edge of the table relate to the angle it leaves the edge of the table?
Answer: m∠MBA + m∠ABC + m∠CBN = 180° 58 ° + 64° + m∠CBN = 180° 122 ° + m∠CBN = 180° m∠CBN = 180° – 122 ° m∠CBN = 58°
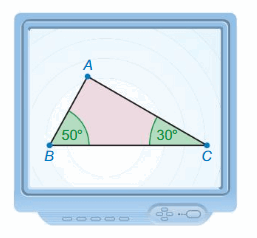
Find the measures of the interior angles of the triangle.
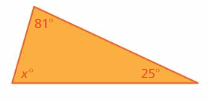
Answer: 81°, 25°, 74°
Explanation: Sum of all the angles in a triangle = 180° x° + 81° + 25° = 180° x° = 180° – 81° – 25° x = 74° Thus the measure of the interior angle is 74°
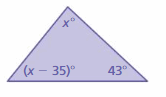
Answer: 43°, 51°, 86°
Explanation: Sum of all the angles in a triangle = 180° x° + (x – 35)° + 43° = 180° x° + x° – 35° + 43° = 180° 2x° + 8° = 180° 2x° = 180° – 8° 2x° = 172° x° = 172°/2 x° = 86° The measure of the interior angle of the triangle (x – 35)° = 86 – 35 (x – 35)° = 51° x° = 51° + 35° x° = 86°
Self-Assessment for Concepts & Skills
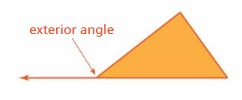
Question 4. VOCABULARY How many exterior angles does a triangle have at each vertex? Explain.
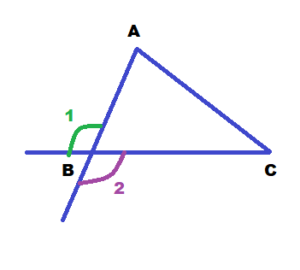
FINDING ANGLE MEASURES Find the value of x.
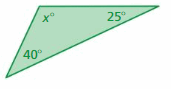
Answer: Sum of all the angles in a triangle = 180° x° + 25° + 40° = 180° x° + 65° = 180° x° = 180° x° = 180° – 65° x° = 115° Thus the value of x is 115°
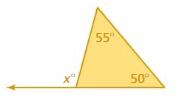
Answer: x° = 50° + 55° x° = 105° Thus the value of x is 105°
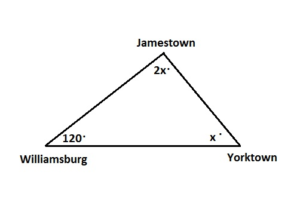
Question 7. The Historic Triangle in Virginia connects Jamestown, Williamsburg, and Yorktown. The interior angle at Williamsburg is 120°. The interior angle at Jamestown is twice the measure of the interior angle at Yorktown. Find the measures of the interior angles at Jamestown and Yorktown. Explain your reasoning.
Answer: Given, A helicopter travels from point C to point A to perform a medical supply drop. The helicopter then needs to land at point B. A = 90° + 32° A = 122° Thus the helicopter should turn 122° at point A to travel towards point B.
Use the figure to find the measure of the angle. Explain your reasoning.
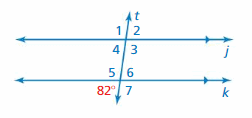
Question 1. ∠2
Answer: 82°
∠2 and 82° are alternate exterior angles formed by transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. Thus the measure of ∠2 is 82°
Question 2. ∠6
∠6 and 82° are vertical angles formed by transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. Thus the measure of ∠6 is 82°
Question 3. ∠4
∠4 and 82° are corresponding angles formed by transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. Thus the measure of ∠4 is 82°
Question 4. ∠1
Answer: 98°
∠4 and 82° are corresponding angles formed by transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. Thus the measure of ∠4 is 82° ∠4 and ∠1 are supplementary angles ∠4 + ∠1 = 180° 82° + ∠1 = 180° ∠1 = 180° – 82° ∠1 = 98°
You spin the spinner shown.
Question 5. What are the favorable outcomes of spinning a number less than 4?
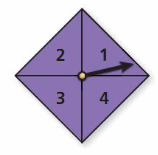
Answer: 1, 2, 3
Explanation: The favorable outcome of spinning a number less than 4 is 1, 2, and 3.
Question 6. In how many ways can spinning an odd number occur?
Answer: two ways Odd numbers = 1 and 3 So, in two ways spinning an odd number can occur.
Concepts, Skills, & Problem Solving
USING PARALLEL LINES AND TRANSVERSALS Consider the figure below. (See Exploration 2, p. 111.)
Question 7. Use a protractor to find the measures of the labeled angles.
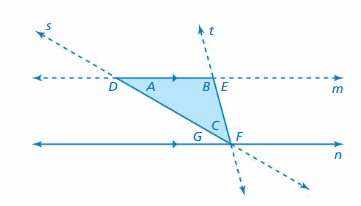
Answer: Use a protractor to determine the measures of the angles A, B, C. m∠A = 30° m∠B = 105° m∠C = 45° m∠D = 150° m∠E = 75° m∠F = 105° m∠G = 30°
Question 8. Is ∠F an exterior angle of Triangle ABC ? Justify your answer.
Answer: An exterior angle is the angle between one side of a triangle and the extension of an adjacent side. ∠F is not an exterior angle of triangle ABC because it has a side of triangle ABC, but not the extension of the adjacent side DF.
USING INTERIOR ANGLE MEASURES Find the measures of the interior angles of the triangle.
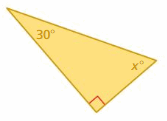
Answer: Sum of all the angles in a triangle = 180° x° + 90° + 30° = 180° x° + 120° = 180° x° = 180° – 120° x° = 60°
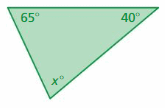
Answer: Sum of all the angles in a triangle = 180° x° + 65° + 40° = 180° x° + 105° = 180° x° = 180° – 105° x° = 75°
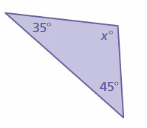
Answer: Sum of all the angles in a triangle = 180° x° + 35° + 45° = 180° x° + 80° = 180° x° = 180° – 80° x° = 100°
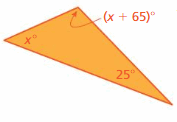
Answer: Sum of all the angles in a triangle = 180° x° + (x + 65)° + 25° = 180° x° + x° + 65° + 25° = 180° 2x° + 90° = 180° 2x° = 180° – 90° 2x° = 90° x° = 90°/2 x° = 45° (x + 65)° = 45 + 65 = 110 x° = 25°

Answer: Sum of all the angles in a triangle = 180° x° + (x – 44)° + 48° = 180° x° + x° – 44° + 48° = 180° 2x° + 4° = 180° 2x° = 180° – 4° 2x° = 176° x° = 176°/2 x° = 88° (x – 44)° = 88 – 44 = 44 x° = 44°
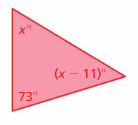
Answer: Sum of all the angles in a triangle = 180° x° + (x – 11)° + 73° = 180° x° + x° – 11° + 73° = 180° 2x° + 62° = 180° 2x° = 180° – 62° 2x° = 118° x° = 118°/2 x° = 59° (x – 11)° = 59 – 11 = 48 x° = 48°
FINDING EXTERIOR ANGLE MEASURES Find the measure of the exterior angle.
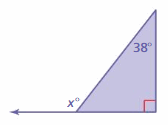
Answer: x° = 38° + 90° x° = 128° The measure of exterior angle is 128°
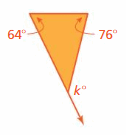
Answer: k° = 64° + 76° k° = 140° The measure of an exterior angle is 140°
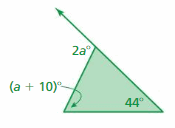
Answer: 2a° = (a + 10°) + 44° 2a° = a + 54° 2a° – a° = 54 a° = 54 The measure of the exterior angle = 2a = 2(54°) = 108°
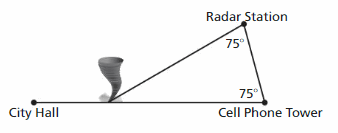
Answer: Sum of all the angles in a triangle = 180° x° + 75° + 75° = 180° x° + 150° – 150° = 180° – 150° x° = 30° Thus the angle that tornado direction needs to change is 30°.
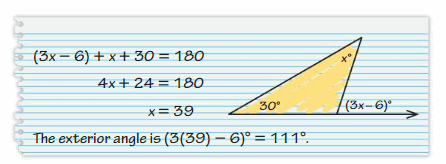
Answer: Your friend is not correct because the measure of the exterior angle is equal to the sum of two non-adjacent interior angles.
Question 20. REASONING The ratio of the interior angle measures of a triangle is 2 : 3 : 5. What are the angle measures?
Answer: Sum of all the angles in a triangle = 180° 2x° + 3x° + 5x° = 180° 10x° = 180° x = 180/10 x = 18° 2x° = 2(18°) = 36° 3x° = 3(18) = 54° 5x° = 5(18) = 90°
Question 21. PROBLEM SOLVING The support for a window air-conditioning unit forms a triangle and an exterior angle. What is the measure of the exterior angle?
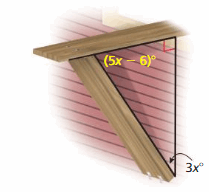
Answer: The measure of the exterior angle DBC is m∠DBC = m∠ABC + m∠ACB m∠ABC + m∠ACB = 90° 5x – 6 + 3x = 90 8x – 6 = 90 8x = 90 + 6 8x = 96 x = 96/8 x = 12 m∠DBC = m∠BAC+ m∠ACB = 90° + 3(12)° = 126°
Question 22. REASONING A triangle has an exterior angle with a measure of 120°. Can you determine the measures of the interior angles? Explain.
Answer: A triangle has an exterior angle with a measure of 120° m∠ACB = m∠A + m∠B m∠A + m∠B = 120° According to the exterior angles We have m∠C + m∠ACD = 180° m∠C + 120° = 180° m∠C = 180° – 120° m∠C = 60°
ANGLES OF TRIANGLES
Determine whether the statement is always, sometimes, or never true. Explain your reasoning.
Question 23. Given three angle measures, you can construct a triangle.
Answer: We can construct a triangle if the sum of the measure of the 3 angles is 180°. As a matter of fact, if the sum of the measures of the 3 angles is 180° We can build an infinity of triangles that are similar.
Question 24. The acute interior angles of a right triangle are complementary.
Answer: Let A, B, C be the angles of a right triangle with m∠A = 90° m∠A + m∠B + m∠C = 180° 90° + m∠B + m∠C = 180° m∠B + m∠C = 180° – 90° m∠B + m∠C = 90° This means ∠B and ∠C are complementary.
Question 25. A triangle has more than one vertex with an acute exterior angle.
Answer: An exterior angle of a triangle and the adjacent triangle’s angle are complementary. If an exterior angle is acute, it means the adjacent triangle’s angle is obtuse. Since we are given that more than one exterior angle is acute, it means the triangle would have more than one obtuse angle, which is impossible. The statement is never true.
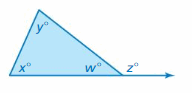
Answer: The angles z and w are supplementary z + w = 180° The sum of a triangle is 180° x + y + w = 180° z = 180° – w x + y = 180° – w z = x + y
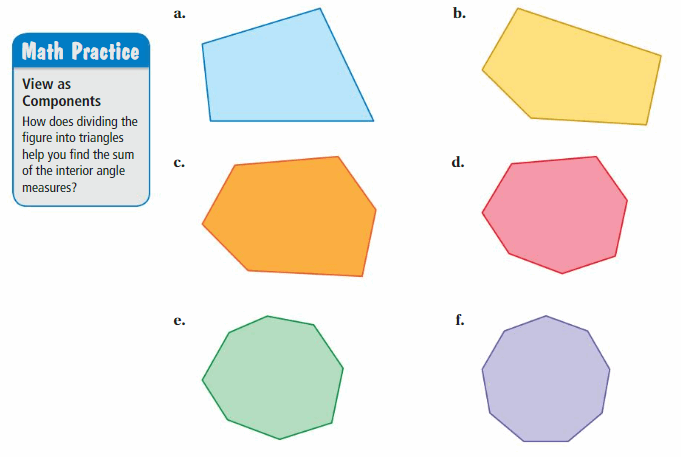
Find the sum of the interior angle measures of the green polygon.

Answer: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (7 – 2) . 180° S = 5 . 180° S = 900° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 900°
Answer: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (6 – 2) . 180° S = 4 . 180° S = 720° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 720°
Question 5. WRITING Explain how to find the sum of the interior measures of a polygon.

Answer: Steps to find the sum of the interior measurements of the polygon: 1. Count the number of sides of the polygon. 2. Subtract the number of sides by 2. 3. Multiply the result of the subtraction by 180°
Question 6. FINDING THE SUM OF INTERIOR ANGLE MEASURES Find the sum of the interior angle measures of the green polygon.
Answer: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (4 – 2) . 180° S = 2 . 180° S = 360° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 360°
FINDING AN INTERIOR ANGLE MEASURE
Find the value of x.
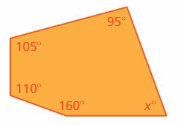
Answer: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (5 – 2) . 180° S = 3 . 180° S = 540° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 540° x° + 160° + 110° + 105° + 95° = 540° x° + 470° = 540° x° = 540° – 470° x° = 70° Thus the value of x is 70°.
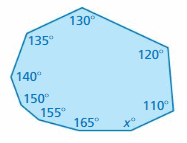
Answer: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (9 – 2) . 180° S = 7 . 180° S = 1260° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 1260° x° + 165° + 155° + 150° + 140° + 135° + 130° + 125° + 110° = 1260° x° + 1105° = 1260° x° = 1260° – 1105° x° = 155° Thus the value of x is 155°
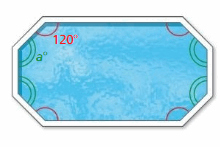
Question 9. A company installs an octagonal swimming pool. a. Find the value of a for the pool shown at the left.
Answer: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (8 – 2) . 180° S = 6 . 180° S = 1080° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 1080° a° + 120° + a° + 120° + a° + 120° + a° + 120° = 1080° 4a° + 480° = 1080° 4a° = 1080° – 480° 4a° = 600° a° = 600/4 a° = 150° Thus the value of x is 150°.
Answer: No for any octagon the sum of the interior angles is 1080 degrees.
Question 10. DIG DEEPER! A Bronze Star Medal A is shown. a. How many interior angles are there?
Answer: 10 interior angles are there

Answer: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (10 – 2) . 180° S = 8 . 180° S = 1440° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 1440°
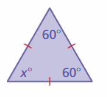
Answer: 60°
Explanation: Sum of all the angles = 180° x° + 60° + 60° = 180° x° + 120° = 180° x° = 180° – 120° x° = 60°
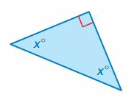
Answer: 45°
Explanation: Sum of all the angles = 180° x° + x° + 90° = 180° 2x° + 90° = 180° 2x° = 180° – 90° 2x° = 90° x° = 45°
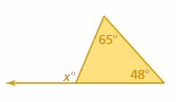
Answer: 113°
Explanation: x° = 65° + 48° x° = 113° Thus the measure of an exterior angle is 113°
Solve the proportion.
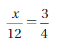
Explanation: \(\frac{x}{12}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) 12 . \(\frac{x}{12}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\) . 12 x = 3 . 3 x = 9
Explanation: \(\frac{14}{21}\) = \(\frac{x}{3}\) 3 . \(\frac{14}{21}\) = \(\frac{x}{3}\) . 3 x = 2
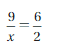
Explanation: \(\frac{9}{x}\) = \(\frac{6}{2}\) 2. \(\frac{9}{x}\) = 6 18 = 6x x = 3
Concepts, Skills, & Problem Solving EXPLORING INTERIOR ANGLES OF POLYGONS Use triangles to find the sum of the interior angle measures of the polygon. (See Exploration 1, p. 117.)
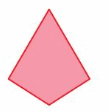
Answer: 360°
Explanation: Number of sides = 4 Number of interior triangles in the given figure = 2 The Sum of the measures of the interior angles using triangle = 2 . 180° = 360°
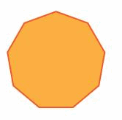
Answer: 1260°
Explanation: Number of sides = 9 Number of interior triangles in the given figure = 7 The Sum of the measures of the interior angles using triangle = 7 . 180° = 1260°
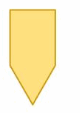
Answer: 540°
Explanation: Number of sides = 5 Number of interior triangles in the given figure = 3 The Sum of the measures of the interior angles using triangle = 3 . 180° = 540°
FINDING THE SUM OF INTERIOR ANGLE MEASURES Find the sum of the interior angle measures of the polygon.
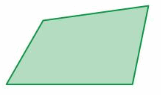
Explanation: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (4- 2) . 180° S = 2 . 180° S = 360° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 360°
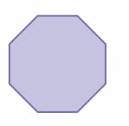
Answer: 1080°
Explanation: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (8- 2) . 180° S = 6 . 180° S = 1080° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 1080°
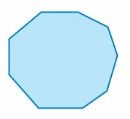
Explanation: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (9- 2) . 180° S = 7 . 180° S = 1260° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 1260°
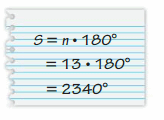
Answer: To find the sum of the interior angle measures he should subtract 2 from the number of sides of the polygon and then multiply by 180° S = (n – 2) . 180° By this, we can say that your friend is not correct.
FINDING AN INTERIOR ANGLE MEASURE Find the value of x.
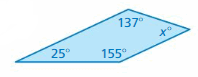
Answer: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (4- 2) . 180° S = 2 . 180° S = 360° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 360° x° + 155° + 25° + 137° = 360° x° + 317° = 360° x° = 360° – 317° x° = 43°
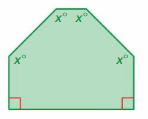
Answer: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (6- 2) . 180° S = 4 . 180° S = 720° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 720° x° + x° + x° + x° + 90° + 90° = 720° 4x° + 180° = 720° 4x° = 720° – 180° 4x° = 540° x° = 540/4 x° = 135°
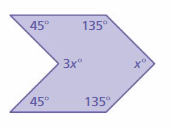
Answer: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (6- 2) . 180° S = 4 . 180° S = 720° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 720° 3x° + 45° + 135° + x° + 135° + 45° = 720° 4x° + 360° = 720° 4x° = 720° – 360° 4x° = 360° x° = 360/4 x° = 90°
FINDING A MEASURE Find the measure of each interior angle of the regular polygon.

Answer: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (3- 2) . 180° S = 1 . 180° S = 180° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 180° In a regular polygon, each interior angle is congruent. So, divide the sum of the interior angle measures by the number of interior angles, 3. 180 ÷ 3 = 60°
S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (9 – 2) . 180° S = 7 . 180° S = 1260° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 1260° In a regular polygon, each interior angle is congruent. So, divide the sum of the interior angle measures by the number of interior angles, 9. 1260 ÷ 9 = 140°

S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (12 – 2) . 180° S = 10 . 180° S = 1800° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 1800° In a regular polygon, each interior angle is congruent. So, divide the sum of the interior angle measures by the number of interior angles, 12. 1800 ÷ 12 = 150°
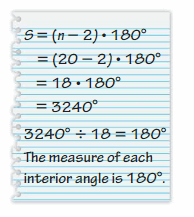
Answer: No, my friend is not correct because to find the measure of each interior angle of a regular 20-gon, he should divide the sum of the measured interior angles by the number of interior angles, in this case, 20 but your friend divide it by 18 so he is not correct.

Answer: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (5- 2) . 180° S = 3 . 180° S = 540° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 540° In a regular polygon, each interior angle is congruent. So, divide the sum of the interior angle measures by the number of interior angles, 5. 540÷ 5 = 108°
b. RESEARCH Why are firehydrants made this way?
Question 22. PROBLEM SOLVING The interior angles of a regular polygon each measure 165°. How many sides does the polygon have?
Answer: (n – 2) . 180 = 165 . n 180n – 360 = 165n 180n – 360 + 360 – 165n = 165n + 360 – 165n 15n = 360 n = 360/15 n = 24 Therefore the polygon has 24 sides
Question 23. STRUCTURE A molecule can be represented by a polygon with interior angles that each measure 120°. What polygon represents the molecule? Does the polygon have to be regular? Justify your answers.
Answer: (n – 2) . 180 = 120 . n 180n – 360 = 120n 180n – 120n = 360 60n = 360 n = 6
Question 24. PROBLEM SOLVING The border of a Susan B. Anthony dollar is in the shape of a regular polygon. a. How many sides does the polygon have?
Answer: The polygon has 11 sides.

Answer: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (11 – 2) . 180° S = 9 . 180° S = 1620° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 1620° In a regular polygon, each interior angle is congruent. So, divide the sum of the interior angle measures by the number of interior angles, 11. 1620 ÷ 11 = 147°
Question 25. REASONING The center of the stained glass window is in the shape of a regular polygon. What are the measures of the interior angles of the green triangle?
Answer: (n-2)180°/n = (8-2)180°/8 = 135° m∠OAB = m∠OBA = 135/2 = 67.5° m∠AOB + m∠OAB + m∠OBA = 180° m∠AOB + 67.5° + 67.5° = 180° m∠AOB + 135° = 180° m∠AOB = 180° – 135° m∠AOB = 45°

Answer: The given polygon has 7 sides. S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (7 – 2) . 180° S = 5 . 180° S = 900° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 900° 4 . 135° + 3 . x° = 900° 540° + 3x° = 900° 3x° = 900° – 540° 3x° = 360° x° = 360/3 x° = 120°
Using Similar Triangles
Tell whether the triangles are similar. Explain.
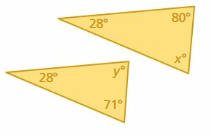
Answer: Yes
Explanation: x° + 66° + 90° = 180° x° + 156° = 180° x° = 180° – 156° x° = 24° y° + 24° + 90° = 180° y° + 114° = 180° y° = 180° – 114° y° = 66° The triangles have two pairs of congruent angles. Thus the triangles are similar.
Explanation: We are not given any information about the lengths of the sides either, therefore with only a pair of congruent angles, we cannot tell whether the triangles are similar.
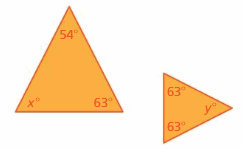
Explanation: x° + 54° + 63° = 180° x° + 107° = 180° x° = 180° – 107° x° = 63°
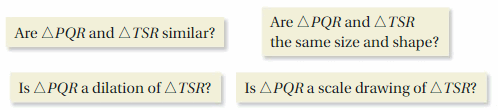
Answer: Option B
Explanation: ΔPQR and ΔTSR are congruent as TS || PQ leads to two pairs of correspondent congruent angles. ΔPQR is a dilation of ΔTSR because their sides are proportional, the constant of proportionality being greater than 1. ΔPQR is a scale drawing of ΔTSR because their sides are proportional. The question that does not fit is “Are ΔPQR and ΔTSR the same size and shape?” because the triangles do not have the same size, but they have the same shape.
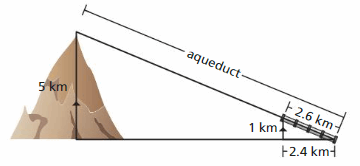
Answer: Aqueduct/2.6 = 5/1 Aqueduct = 5 × 2.6 Aqueduct = 13 Thus the length of the Aqueduct is 13 km.
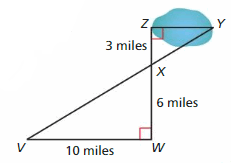
Answer: a/10 = 3/6 6 × a = 3 × 10 6a = 30 a = 30/6 a = 5 The length from point Z to point Y is 5 miles. Time to travel from point Z to point Y = 5/3.5 = 1.56 hour
Find the measure of each interior angle of the regular polygon.
Question 1. octagon
Answer: The measure of each interior angle is 135°
Explanation: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (8- 2) . 180° S = 6 . 180° S = 1080° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 1080° In a regular polygon, each interior angle is congruent. So, divide the sum of the interior angle measures by the number of interior angles, 8. 1080÷ 8= 135°
Question 2. decagon
Answer: The measure of each exterior angle is 144°
Explanation: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (10 – 2) . 180° S = 8 . 180° S = 1440° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 1440° In a regular polygon, each interior angle is congruent. So, divide the sum of the interior angle measures by the number of interior angles, 10. 1440÷ 10= 144°
Question 3. 18-gon
Answer: The measure of each interior angle is 160°
Explanation: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (18- 2) . 180° S = 16 . 180° S = 2880° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 2880° In a regular polygon, each interior angle is congruent. So, divide the sum of the interior angle measures by the number of interior angles, 18. 2880 ÷ 18= 160°
Solve the equation. Check your solution.
Question 4. 3.5 + y = -1
Answer: Given the equation 3.5 + y = -1 y = -1 – 3.5 y = -4.5
Question 5. 9x = 54
Answer: Given the equation 9x = 54 x = 54/9 x = 6
Question 6. -4 = \(\frac{2}{7}\)p
Answer: Given the equation -4 = \(\frac{2}{7}\)p -4 × 7 = 2p 2p = -28 p = -28/2 p = -14
Concepts, Skills, & Problem Solving CREATING SIMILAR TRIANGLES Draw a triangle that is either larger or smaller than the one given and has two of the same angle measures. Explain why the new triangle is similar to the original triangle. (See Exploration 1, p. 123.)
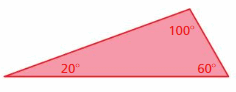
IDENTIFYING SIMILAR TRIANGLES Tell whether the triangles are similar. Explain.
Answer: The triangles have two pairs of congruent angles. So, the third angles are congruent, and the triangles are similar.
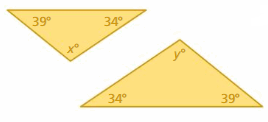
Answer: x° + 36° + 72° = 180° x° + 108° = 180° x° = 180° – 108° x° = 72° y° + 33° + 72° = 180° y° + 105° = 180° y° = 180° – 105° y° = 72° The triangles do not have two pairs of congruent angles. Therefore the triangles are not similar.
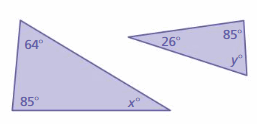
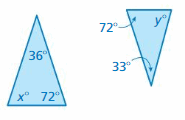
Answer: x° + 64° + 85° = 180° x° + 149° = 180° x° = 180° – 149° x° = 31° y° + 26° + 85° = 180° y° + 111° = 180° y° = 180° – 111° y° = 69° The triangles do not have two pairs of congruent angles. Therefore the triangles are not similar.
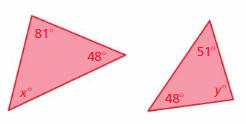
Answer: x° + 48° + 81° = 180° x° + 129° = 180° x° = 180° – 129° x° = 51° y° + 48° + 51° = 180° y° + 99° = 180° y° = 180° – 99° y° = 81° The triangles have two pairs of congruent angles. Therefore the triangles are similar.
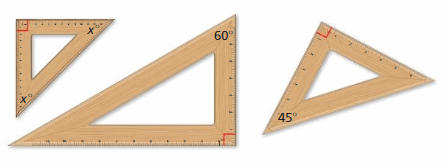
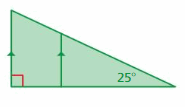
Answer: 2x + 90 = 180° 2x = 180 – 90° 2x = 90° x = 90/2 x = 45° The ruler on the left and the ruler on the right both have the shape of a right triangle with 45° angles, therefore they are similar in shape, while the middle ruler has 60°, 30° angles.
STRUCTURE Tell whether the triangles are similar. Explain.
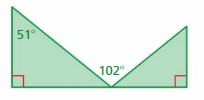
Answer: m∠APB + m∠B = 90° m∠APB + 51° = 90° m∠APB = 90° – 51° m∠APB = 39° m∠APB + m∠BPD + m∠DPC = 180° 39° + 102° + m∠DPC = 180° m∠DPC + 141° = 180 m∠DPC = 180 – 141° m∠DPC = 39° m∠A = m∠C m∠APB = m∠DPC
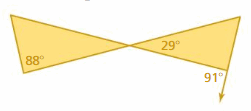
Answer: ∠APB ≅ ∠CPD m∠APB = m∠CPD m∠APB = 29° m∠A + m∠B + m∠APB = 180° m∠A + 88° + 29° = 180° m∠A + 117° = 180° m∠A = 180° – 117° m∠A = 63° m∠PDC + m∠PDE = 180° m∠PDC + 91° = 180° m∠PDC = 180° – 91° m∠PDC = 89°
IDENTIFYING SIMILAR TRIANGLES Can you determine whether the triangles are similar? Explain.
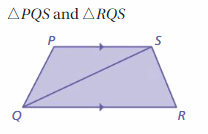
Answer: PS || QR ∠PSQ and ∠SQR are interior angles using the transversal QS, thus they are congruent. ∠PSQ ≅ ∠SQR

Answer: As AB || DE there are two pairs of congruent alternate interior angles, using the transversals AE and BD. ∠A≅ ∠E ∠B≅ ∠D The two pairs of congruent angles are enough to prove that the triangles are similar. ΔABC ∼ ΔEDC
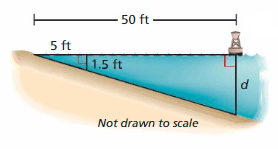
Answer: ΔAMN ∼ ΔABC MN/BC = AM/AB 1.5/d = 5/50 d = 1.5 × 10 d = 15 feet Therefore 15 feet is not an appropriate location.
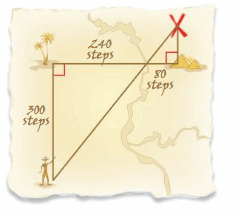
Answer: The two triangles are similar because they are right triangles and ∠AXB ≅ ∠PXQ because they are vertical angles. PQ/300 = 80/240 240PQ = 24000 PQ = 24000/240 PQ = 100 steps
Answer: Given, A person who is 6 feet tall casts a 3-foot-long shadow. A nearby pine tree casts a 15-foot-long shadow. ΔXAB ∼ ΔXPQ AB/PQ = XB/XQ 6/PQ = 3/15 PQ = 30 ft
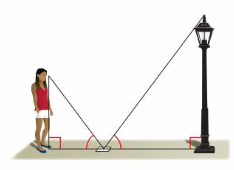
Question 21. OPEN-ENDED You place a mirror on the ground 6 feet from the lamppost. You move back 3 feet and see the top of the lamppost in the mirror. What is the height of the lamppost?
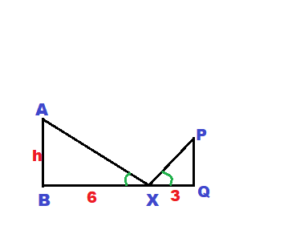
Question 22. DIG DEEPER! In each of two right triangles, one angle measure is two times another angle measure. Can you determine that the triangles are similar? Explain your reasoning.
Answer: We are given the right triangle ABC m∠A = 2m∠B Case 1: m∠A = 90° 90° = 2m∠B m∠B = 45° m∠C = 180° – 90° – 45° = 45° Case 2: m∠B = 90° m∠A = 2 × 90° = 180° Case 3: m∠C = 90° m∠A + m∠B = 180 – m∠C = 180° – 90° = 90° 2m∠B + m∠B = 90° 3m∠B = 90° m∠B = 30° m∠A = 2 . 30° = 60°
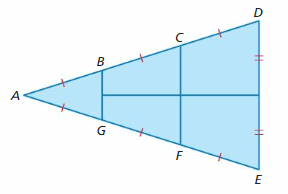
Answer: ΔABG ∼ ΔACF ΔACF ∼ ΔADE ΔABG ∼ ΔADE AB = BC = CD = BD/2 = 6.32/2 = 3.16 AB/CD = BG/DE 3BG = 6 BG = 2 feet ΔACF ∼ ΔADE AC/AD = CF/DE 2/3 = CF/6 3CF = 2(6) CF = 4 feet
Using the Problem-Solving Plan
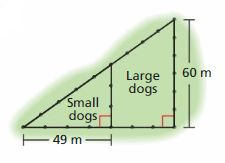
Understand the problem You know two dimensions of a dog park and the ratio of the perimeter of the small dog section to the perimeter of the entire park. You are asked to find the area of each section. Make a plan Verify that the small triangle and the large triangle are similar. Then use the ratio of the perimeters to find the base or the height of each triangle and calculate the areas. Solve and check. Use the plan to solve the problem. Then check your solution.
Review Vocabulary
Choose and complete a graphic organizer to help you study the concept.
- interior angles formed by parallel lines and a transversal
- exterior angles formed by parallel lines and a transversal
- interior angles of a triangle
- exterior angles of a triangle
- similar triangles
Chapter Self-Assessment

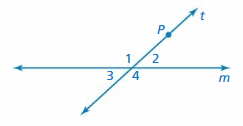
3.1 Parallel Lines and Transversals (pp. 103–110)
Question 1. ∠8
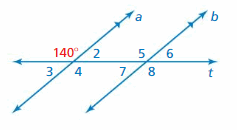
Answer: 140°
Explanation: ∠8 and 140 degrees angle are alternate exterior angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. So, the measure of ∠8 is 140°
Question 2. ∠5
Explanation: ∠5 and 140 degrees angle are corresponding angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. So, the measure of ∠5 is 140°
Question 3. ∠7
Answer: 40°
Explanation: ∠5 and 140 degrees angle are corresponding angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. So, the measure of ∠5 is 140° ∠5 and ∠7 are supplementary angle. ∠5 + ∠7 = 180° 140° + ∠7 = 180° ∠7 = 180° – 140° ∠7 = 40° So, the measure of ∠7 is 40°
Question 4. ∠2
Explanation: 140 and ∠2 are supplementary angle. 140° + ∠2 = 180° ∠2 = 180° – 140° ∠2 = 40° So, the measure of ∠2 is 40°
Question 5. ∠6
Explanation: ∠5 and 140 degrees angle are corresponding angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. So, the measure of ∠5 is 140° ∠5 and ∠6 are supplementary angle. 140° + ∠6 = 180° ∠6 = 180° – 140° ∠6 = 40° So, the measure of ∠6 is 40°
Complete the statement. Explain your reasoning.
Answer: 123°
Explanation: ∠1 and ∠7 are alternate exterior angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. So, the measure of ∠7 is 123°
Answer: 122°
Explanation: ∠2 and ∠6 are corresponding angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. So, the measure of ∠6 is 58° ∠5 and ∠6 are supplementary angle. ∠5 + ∠6 = 180° 58° + ∠5 = 180° ∠5 = 180° – 58° ∠5 = 122° So, the measure of ∠5 is 122°
Answer: 119°
Explanation: ∠3 and ∠5 are alternate interior angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. So, the measure of ∠3 is 119°
Explanation: ∠4 and ∠6 are alternate exterior angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. So, the measure of ∠4 is 60°
Question 10. In Exercises 6–9, describe the relationship between ∠2 and ∠8.
Answer: ∠2 ≅ ∠8
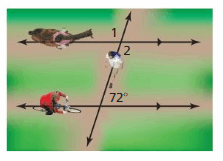
Answer: ∠1 = 108°, ∠2 = 108°
Explanation: ∠3 and 72° are alternate interior angles. They are congruent. So, the measure of ∠3 is 72° ∠3 + ∠1 = 180° 72° + ∠1 = 180° ∠1 = 180° – 72° ∠1 = 108° So, the measure of ∠1 is 108° ∠1 and ∠2 are alternating interior angles. They are congruent.
3.2 Angles of Triangles (pp. 111 – 116)
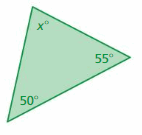
Answer: Sum of all the angles in a triangle = 180° x° + 50° + 55° = 180° x° + 105° = 180° x° = 180° – 105° x° = 75°
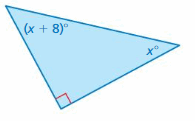
Answer: Sum of all the angles in a triangle = 180° x° + (x + 8)° + 90° = 180° 2x° + 8° + 90° = 180° 2x° + 98° = 180° 2x° = 180° – 98° 2x° = 82 x° = 82/2 x° = 41° (x + 8)° = (41 + 8)° = 49°
Find the measure of the exterior angle.
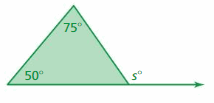
Answer: s° = 50° + 75° s° = 125° Thus the measure of the exterior angle is 125°
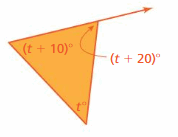
Answer: Sum of all the angles in a triangle = 180° t° + (t + 10)° + (t + 20)° = 180° 3t° + 10° + 20° = 180° 3t° + 30° = 180° 3t° = 180° – 30° 3t° = 150° t° = 150/3 t° = 50° Exterior angle: t° + (t + 10)° t° + t° + 10° 2t° + 10° 2(50)° + 10° = 100° + 10° = 110° Thus the measure of the exterior angle is 110°.
Question 16. What is the measure of each interior angle of an equilateral triangle? Explain.
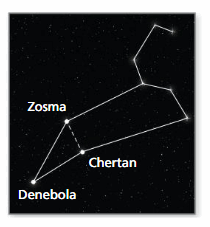
Answer: Sum of all the angles in a triangle = 180° x° + 30° + 56° = 180° x° + 86° = 180° x° = 180° – 86° x° = 94° Thus the measure of the interior angle of the triangle at Chertan = 94°
3.3 Angles of Polygons (pp. 117–122)
Find the sum of the interior angle measures of the polygon.
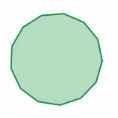
Answer: The polygon has 13 sides S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (13- 2) . 180° S = 11 . 180° S = 1980° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 1980°
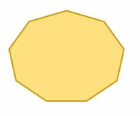
Answer: The polygon has 9 sides S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (9- 2) . 180° S = 7 . 180° S = 1260° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 1260°
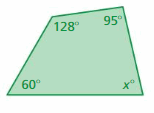
Answer: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (4 – 2) . 180° S = 2 . 180° S = 360° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 360° x° + 60° + 128° + 95° = 360° x° + 283° = 360° x° = 360° – 283° x° = 77° Thus the value of x is 77°.
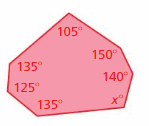
Answer: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (7 – 2) . 180° S = 5 . 180° S = 900° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 900° x° + 135° + 125° + 135° + 105° + 150° + 140° = 900° x° + 790° = 900° x° = 900° – 790° x° = 110°
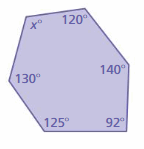
Answer: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (6 – 2) . 180° S = 4 . 180° S = 720° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 720° x° + 120° + 140° + 92° + 125° + 130° = 720° x° + 607° = 720° x° = 720° – 607° x° = 113° The value of x° is 113°

Answer: The given polygon is an octagon. It has 8 sides. S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (8 – 2) . 180° S = 6 . 180° S = 1080° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 1080° In a regular polygon, each interior angle is congruent. So, divide the sum of the interior angle measures by the number of interior angles, 8. 1080 ÷ 3 = 135°
3.4 Using Similar Triangles (pp. 123–128)
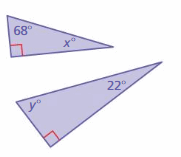
Answer: x° + 68° + 90° = 180° x° = 180° – 158° x° = 22° y° + 22° + 90° = 180° y° + 112° = 180° y° = 180° – 112° y° = 68° The triangles have two pairs of congruent angles. So, the triangles are similar.
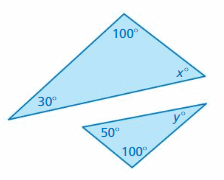
Answer: x° + 100° + 30° = 180° x° + 130° = 180° x° = 180° – 130° x° = 50° y° + 100° + 50° = 180° y° + 150° = 180° y° = 180° – 150° y° = 30° The triangles have two pairs of congruent angles. So, the triangles are similar.
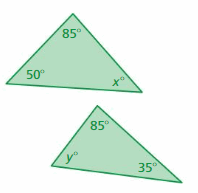
Answer: x° + 50° + 85° = 180° x° + 135° = 180° x° = 180° – 135° x° = 45° y° + 85° + 35° = 180° y° + 120° = 180° y° = 180° – 120° y° = 60° The triangles do not have two pairs of congruent angles. So, the triangles are not similar.
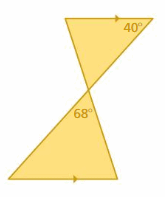
Answer: ∠B ≅ ∠D ∠A ≅ ∠C ∠AXB ≅ ∠CXD ∠AXB and ∠CXD are vertical angles. ΔAXB ∼ ΔCXD
Question 28. A person who is 5 feet tall casts a shadow that is 4 feet long. A nearby building casts a shadow that is 24 feet long. What is the height of the building?
Answer: Given, A person who is 5 feet tall casts a shadow that is 4 feet long. A nearby building casts a shadow that is 24 feet long. Let the height of the building = x ft x/24 = 5/4 24 . x/24 = 5/4 . 24 x = 30 Thus the height of the building is 30 ft.
Practice Test
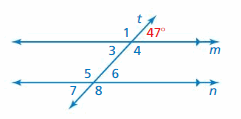
Question 1. ∠7
Answer: 47°
Explanation: ∠7 and 47° angles are alternate exterior angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. Thus the measure of ∠7 is 47°
Explanation: ∠6 and 47° angles are corresponding angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. Thus the measure of ∠6 is 47°
Answer: 133°
Explanation: ∠4 and 47° are supplementary angles. 47° + ∠4 = 180° ∠4 = 180° – 47° ∠4 = 133° Thus the measure of ∠4 = 133°
Question 4. ∠5
Explanation: ∠6 and 47° angles are corresponding angles formed by transversal intersecting parallel lines. The angles are congruent. Thus the measure of ∠6 is 47° ∠6 + ∠5 = 180° 47° + ∠5 = 180° ∠5 = 180° – 47° ∠5 = 133° Thus the measure of ∠5 = 133°
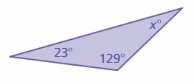
Answer: 28°
Explanation: Sum of all the angles in a triangle = 180° x° + 129° + 23° = 180° x° + 152° = 180° x° = 180° – 152° x° = 28° Thus the value of x° is 28°
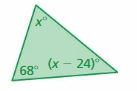
Answer: 68°
Explanation: Sum of all the angles in a triangle = 180° x° + (x – 24)° + 68° = 180° x° + x° – 24° + 68° = 180° 2x° + 44° = 180° 2x° = 180° – 44° 2x° = 136° x° = 68° (x – 24)° = (68 – 24)° = 44°
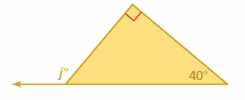
Answer: j° = 40° + 90° j° = 130° The measure of an exterior angle is 130°.

Answer: The coin has 7 sides. S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (7 – 2) . 180° S = 5 . 180° S = 900° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 900°
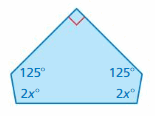
Answer: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (5 – 2) . 180° S = 3 . 180° S = 540° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 540° 2x° + 125° + 90° + 2x° + 125° = 540° 4x° + 340° = 540° 4x° = 540° – 340° 4x° = 200° x° = 200/4 x° = 50° The value of x° is 50°
Answer: S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (6 – 2) . 180° S = 4 . 180° S = 720° Thus the sum of the interior angle measure is 720° In a regular polygon, each interior angle is congruent. So, divide the sum of the interior angle measures by the number of interior angles, 6. 720 ÷ 6 = 120°
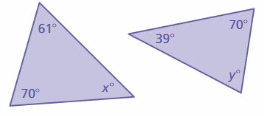
Answer: To find x°: x° + 61° + 70° = 180° x° + 131° = 180° x° = 180° – 131° x° = 49° To find y°: x° + 39° + 70° = 180° x° + 109° = 180° x° = 180° – 109° x° = 71° The triangles do not have two pairs of congruent angles. So, the triangles are not similar.
Answer: ∠A ≅ ∠QPB ∠C ≅ ∠PQB ΔBPQ ∼ ΔBAC
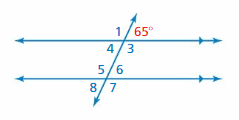
Answer: One way: ∠3 and 65° are supplementary angles. ∠5 and ∠3 are alternate interior angles. Another way: ∠8 and 65° are alternate exterior angles. ∠5 and ∠8 are supplementary angles.
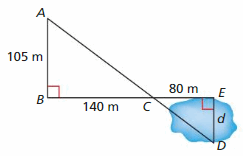
Answer: Given, You swim 3.6 kilometers per hour. d/105 = 80/140 105 . d/105 = 80/140 . 105 d = 60 The length of the pond is 60 m. Speed = 3.6 km per hour = 1 m sec Distance = d = 60m Time it will take to swim across the pond = distance/speed = 60/1 = 60 sec = 1 min

Answer: C = 11 + 1.6t C – 11 = 1.6t 1.6t = C – 11 t = (C – 11)/1.6 Thus the correct answer is option B.
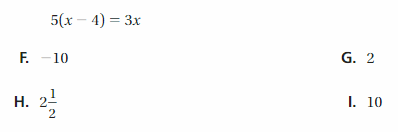
Answer: 5(x – 4) = 3x 5x – 20 = 3x 5x – 3x = 20 2x = 20 x = 20/2 x = 10 Thus the correct answer is option I.
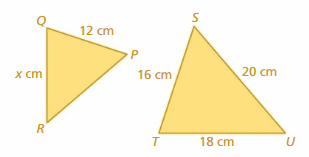
Answer: △PQR is similar to △STU PQ = 12 ST = 16 SU = 20 TU = 18 PQ/ST = QR/TU 12/16 = X/18 16X = 12 × 18 X = 216/16 X = 13.5 cm Thus the correct answer is option C.
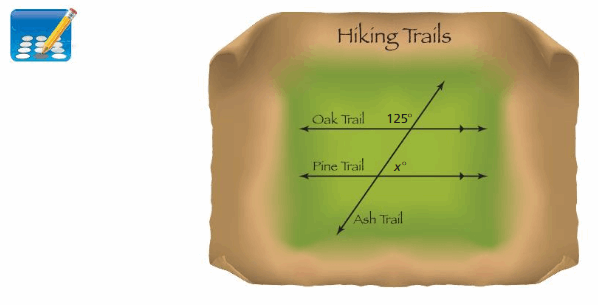
Answer: ∠y and 125° are supplementary angles. 125° + ∠y = 180° ∠y = 180° – 125° ∠y = 55° So, the measure of ∠y = 55° ∠x and ∠y are alternate interior angles. They are congruent. So, the measure of ∠x = 55°
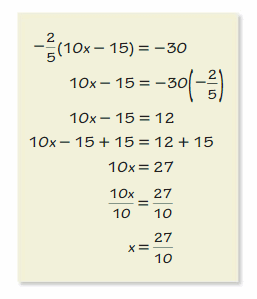
Answer: My friend made the error by multiplying both sides by –\(\frac{2}{5}\). To correct the error she should multiply both sides by –\(\frac{5}{2}\) instead of –\(\frac{2}{5}\) Thus the correct answer is option F.
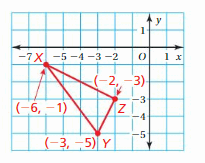
Answer: Given, X(-6,-1) Y(-3,-5) X(-2,-3) Reflecting a point (x,y) in the y-axis. (x, y) = (-x, y) X(-6,-1) = X'(6, -1) Y(-3,-5) = Y'(3, -5) X(-2,-3) = Z'(2, -3) Thus the correct answer is option B.
Answer: S = (n – 2) . 180° Part B A quadrilateral has angles measuring 100°, 90°, and 90°. Find the measure of its fourth angle. Show your work and explain your reasoning.
Answer: The quadrilateral has 4 sides S = (n – 2) . 180° S = (4 – 2) . 180° S = 2 . 180° S = 360 ° Thus the sum of the interior angles is 360 ° x° + 100° + 90° + 90° = 360° x° + 280° = 360° x° = 360° – 280° x° = 80° Thus the value of x° is 80°
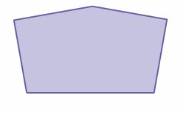
Answer: Number of sides = 3 The number of interior triangles in the given figure = 3 Sum of the interior angles measure using triangle = 3 × 180° = 540
Conclusion:
I wish the details prevailed in the above article is beneficial for all the 8th grade students. Hope our Big Ideas Math Answers Grade 8 Chapter 3 Angles and Triangles helped you a lot to overcome the difficulties in this chapter. Feel free to post your comments in the comment box. Stay tuned to our ccssmathanswers.com to get step by step explanation for all the Grade 8 chapters.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Inside Mathematics
- Math Pathways (DCMP)
- Keywords Search
- common core resources
- mathematical practice standards
- standard 8 look express regularity repeated reasoning
- standard 8 look express regularity repeated reasoning using fractions part 7
Standard 8: Look for & Express Regularity in Repeated Reasoning
Clip 5/8: standard 8: look for & express regularity in repeated reasoning using fractions part 7.
Mathematically proficient students notice if calculations are repeated, and look both for general methods and for shortcuts.
Michelle Kious works with her 5th grade students on understanding multiple representations of mixed numbers. In this clip, her students engage in a final reflection on the lesson, and one observes that the day’s focus, using line segments to understand fractions and mixed numbers is similar to (but more challenging to this particular student) using an area model to represent fractions and mixed numbers.
See this video in the context of an entire lesson.
Materials & Artifacts
Copyright 2024 The Charles A. Dana Center The University of Texas at Austin Site by Mighty Citizen

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This short video goes over the Guided Practice section of Savvas Lesson 3-8 for third grade multiplication. We cover repeated reasoning, using facts you alre...
REPEATED REASONING Consider an integer n. a. Is the opposite of n always less than 0? Explain your reasoning. ... Rational Numbers Homework & Practice 8.3. Review & Refresh. Copy and complete the statement using < or >. Question 1. Answer: 5 < 8. ... Explain your reasoning. Answer: (6,-3) and (6,3) is different from other 3 points.
Expert-verified. Answer 1. Additional Practice 3-7 Repeated Reasoning 6×7=(5×7)+(1×7)= 42 6×5=(5×5)+(1×5)= 30 Tell how you can use repeated reasoning to find multiplication facts. - I can look for repeated calculations. This generalization is a statement based on examplas - I can make generalizations about the and is true about a larger ...
A multiplication fact-practice exercise might, for example, ask children to choose three numbers in a row (e.g., 5, 6, and 7) and compare the middle number times itself to the product of the two outer numbers. ... and express that discovery from their repeated reasoning by saying the 68, 78, 88 almost without even the request for "ten more ...
Lesson 3-6: Practice Multiplication Facts 1. ... Lesson 3-8: Repeated Reasoning 1. Multiply using the distributive property 4 Topic 4 ... Two-step word problems: identify reasonable answers 12 Topic 12. Understand Fractions as Numbers Lesson 12-1 ...
Clip 3/8: Standard 8: Look for & Express Regularity in Repeated Reasoning Discussing Numbers. ... Passeggi challenges her students to look at the relationships between numbers to determine whether or not a given answer can be correct, without calculating the result. In this clip, after initial discussion by the class, Passeggi asks the students ...
This article is focused on Mathematical Practice Standard 8: Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Learn what the metacognitive thinking looks like at each grade level, a step-by-step approach to teaching this practice, and a reflection guide to support students as they "think about their thinking."
Practice Standard - 8. 8 — Look For and Express Regularity in Repeated Reasoning Mathematically proficient students notice if calculations are repeated, and look both for general methods and for shortcuts. As they work to solve a problem, mathematically proficient students maintain oversight of the process, while attending to the details. ...
CCSS.Math.Practice.MP8 Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Mathematically proficient students notice if calculations are repeated, and look both for general methods and for shortcuts. Upper elementary students might notice when dividing 25 by 11 that they are repeating the same calculations over and over again, and conclude ...
2nd Grade (1 clip) Standard 8: Look for & Express Regularity in Repeated Reasoning Using Addition. 3rd Grade (1 clip) 4th Grade (2 clips) 5th Grade (3 clips) 5th/6th Grade (1 clip) Integrating Standard Eight into classroom practice is not only a matter of planning for lessons that occasion students to look for general methods and shortcuts. It ...
Mathematically proficient students notice if calculations are repeated, and look both for general methods and for shortcuts. In this clip, Buljan works with her 3rd-grade students on a number talk, using a mental math approach to multiplying a two-digit number and a one-digit number. She encourages her students to identify regularity among the various approaches identified, and guides them ...
Mathematically proficient students notice if calculations are repeated, and look both for general methods and for shortcuts. Upper elementary students might notice when dividing 25 by 11 that they are repeating the same calculations over and over again, and conclude they have a repeating decimal. By paying attention to the calculation of slope ...
MP1 - Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. (3) MP2 - Reason abstractly and quantitatively. (1) MP5 - Use appropriate tools strategically. (1) MP6 - Attend to precision. (1) MP7 - Look for and make use of structure.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright ...
Overview. As they work to solve a problem, mathematically proficient students maintain oversight of the process, while attending to the details. They continually evaluate the reasonableness of their intermediate results. In Katie Arrillaga's 2nd grade Spanish bilingual classroom, she engages her students in a number talk, discussing whether ...
Common Core and Mathematics: Grades K-5 > Module 3 > Reading: The Eight Standards of Mathematical Practice: Standards 5-8 _____ Standard 8: Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Standard 8 focuses on the ability to see repetition and regularity. Students who master this standard can Notice if calculations are repeated.
Here's the Pythagorean Theorem formula for your quick reference. Problem 1: Find the value of [latex]x [/latex] in the right triangle. Problem 2: Find the value of [latex]x [/latex] in the right triangle. Problem 3: Find the value of [latex]x [/latex] in the right triangle. Problem 4: The legs of a right triangle are [latex]5 [/latex] and ...
As they work to solve a problem, mathematically proficient students maintain oversight of the process, while attending to the details. They continually evaluate the reasonableness of their intermediate results. Michelle Makinson challenges her students to individually select one grouping of representations from their chart, and move those representations over to a poster without the ...
Mathematically proficient students notice if calculations are repeated, and look both for general methods and for shortcuts. Noticing the regularity…might lead them to the general formula…. As they work to solve a problem, mathematically proficient students maintain oversight of the process, while attending to the details. They continually evaluate the reasonableness of their intermediate ...
Question 23. Given three angle measures, you can construct a triangle. Answer: We can construct a triangle if the sum of the measure of the 3 angles is 180°. As a matter of fact, if the sum of the measures of the 3 angles is 180°. We can build an infinity of triangles that are similar. Question 24.
Mathematically proficient students notice if calculations are repeated, and look both for general methods and for shortcuts. Michelle Kious works with her 5th grade students on understanding multiple representations of mixed numbers. In this clip, her students engage in a final reflection on the lesson, and one observes that the day's focus, using line segments to understand fractions and ...