- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000

Indian Agriculture: Farming Types, Features and Challenges
Last updated on October 31, 2023 by ClearIAS Team
India has one of the largest plain areas of the world-the Indo-Gangetic plain which is immensely fertile.
India has varieties of climatic conditions and soil types .
These physical variations along with factors like availability of irrigation, use of machinery, modern agricultural inputs like High Yielding Varieties (HYV) of seeds, insecticides, and pesticides have played their important roles in the evolution of different farming practices in the Indian agriculture sector.
Table of Contents
Types of farming in India
Some of the major types of farming are discussed below.
i) Subsistence farming:
The majority of farmers in India practice subsistence farming- farming for their consumption. The entire production is largely consumed by the farmers and their families and they do not have any surplus to sell in the market.
In this type of farming, landholdings are small and fragmented; cultivation techniques are primitive and simple. There is a total absence of modern equipment like tractors and farm inputs like chemical fertilizers, insecticides, and pesticides. In this farming, farmers mostly cultivate cereals along with oilseeds, pulses, vegetables, and sugarcane.
Admissions Open: Join Prelims cum Mains Course 2025 Now
Subsistence farming is further classified into:
Primitive subsistence agriculture is practised on patches of land with the help of primitive tools like simple digging tools and community or family labour. This type of farming is monsoon depended along with the fertility of the soil and other environmental conditions. Examples of such types are shifting agriculture and nomadic herding.
- Shifting agriculture is practised in thickly forested regions like the Amazon basin, tropical Africa, parts of southeast Asia, and northeast India. These areas receive heavy rainfall hence the vegetation regenerates quickly.
- A patch of land is cleared by felling if tress and burning them. The ashes are then mixed with the soil and crops like maize, yam, potatoes, and cassava are grown. The land is abandoned once fertility is reduced.
- nomadic herding is practised in the semi-arid and arid regions of Sahara, Central Asia, and some parts of India like Rajasthan, Jammu and Kashmir.
- Herdsmen move from place to place with their animals for fodder and water, along defined routes and such movement arises due to seasonal changes. Animals like sheep, camel, yak, and goats are most commonly reared.
Intensive subsistence agriculture is done on small lands with simple tools and more labour. The produce is enough for local consumption and to be sold outside. The sunny climate and fertile soil for most of the year permit the cultivation of more than one crop annually on the same plot. Rice, wheat, maize, pulses, and oilseeds are generally cultivated.
ii) Intensive and Extensive farming
The basic difference between these two types of farming is the amount of production per unit of land. In comparison with temperate areas of the USA, Canada, India do not practice extensive cultivation.
When a large patch of land is used for cultivation then we call it extensive farming. Here, total production may be high due to the larger area but per unit are production is low.
Admissions Open: Join CSAT Course Now
Intensive Farming records high production per unit of land. An example of intensive cultivation is in Kerala where the availability of land for cultivation is very limited.
iii) Commercial farming
It is just the opposite of subsistence farming as most of the produce is sold in the market for earning money. In this system, farmers use inputs like irrigation, chemical fertilizers, insecticides, pesticides, High Yielding Varieties of seeds, etc.
Some of the major commercial crops grown in different parts of India are cotton , jute, sugarcane, groundnut, etc.
Rice farming in Harayana is mainly for commercial purposes as people of this area are predominantly wheat eaters. However, in East and North-Eastern states of India, rice cultivation would be large of subsistence type.
iv) Plantation Farming:
In this type, a single cash crop is grown for sale in national and international markets. This type of agriculture involves the growing and processing of a single cash crop purely meant for sale.
Admissions Open: Join Prelims Test Series Now
Tea, coffee, rubber, banana, and spices are all examples of plantation crops. Most of these crops were introduced in India by the Britishers in the 19th Century
v) Mixed Farming:
When both raising crops and rearing animals are carried on simultaneously it is called mixed farming. Farmers engaged in mixed farming have economical advantages as well.
All classifications are based on the nature and purpose of farming hence they may overlap in some cases. For example, Banana is a plantation type of farming but can also be classified as commercial farming.
Features of Indian Agriculture
Subsistence Agriculture : Most parts of India have subsistence agriculture which has been practised in India for several hundreds of years and still prevails.
The pressure of population on Agriculture : Despite the increase in urbanization and industrialization, about 70% of the population is still directly or indirectly dependent on agriculture.
Mechanization in agriculture: Even after more than forty years of the Green Revolution and revolution in agricultural machinery and equipment, complete mechanization is still not achieved.
Monsoon dependency: Despite the large-scale expansion, only about one-third of the total cropped area is irrigated today. As a consequence, two-thirds of cropped areas are still dependent upon the monsoon.
Variety of crops: Since India has both tropical and temperate climates, crops of both climates are found in India. There are very few countries in the world that have variety comparable to that of India. You would realize that when we would discuss the different types of crops in detail.
The predominance of food crops: The production of food crops is the priority of the farmers almost everywhere in the country.
Seasonal patterns: India has three distinct agricultural/cropping seasons- Kharif, rabi, and Zaid. In India, there are specific crops grown in these three seasons. For example, rice is a Kharif crop whereas wheat is a rabi crop.
Challenges for Indian Agriculture
The challenges faced by Indian agriculture can be broadly grouped into two categories- the long-standing problems and the emerging issues from the prevailing agricultural practices, system, changing climate, and economy.
Stagnation in Production of Major Crops: Production of some of the major staple food crops like rice and wheat has been stagnating for quite some time. This is a situation that is worrying our agricultural scientists, planners, and policymakers as it creates a huge gap between the demand of the ever-growing population and the production.
High cost of Farm Inputs: Farm inputs include fertilizer, insecticide, pesticides, HYV seeds, farm labour cost, etc. Such an increase puts low and medium-land-holding farmers at a disadvantage.
Soil Exhaustion: Green revolution has played a positive role in reducing hunger in India but has negative consequences also. One of which is Soil exhaustion which means the loss of nutrients in the soil from farming the same crop over and over again.
Ground Water depletion: The second negative consequence of the green revolution is the depletion of fresh groundwater. Most of the irrigation in dry areas of Punjab, Haryana, and Western Uttar Pradesh was carried out by excessive use of groundwater. Today fresh groundwater situation in these states is alarming.
Global Climatic Change: It has been predicted that climate change’s impact on Indian agriculture would be immense. It is predicted that due to climate change, the temperature would increase, leading to an increase in sea level, more intense cyclones, unpredictable rainfall, etc. These changes would adversely affect the production of rice and wheat. Specifically, a rise in temperature in winter would affect the production of wheat in north India. Production of rice would be affected in coastal areas of India due to the ingress of saline water and an increase in the frequency of cyclones.
Impact of Globalisation : All developing countries have been affected by globalization. The most evident effect is the reduction in farmers’ income and the threat to the viability of cultivation in India. This is due to the rising input costs and falling output prices. This reflects the combination of reduced subsidy and protection to farmers. Trade liberalization exposes these farmers to competition from highly subsidized production in the developed world.
Providing Food Security: Before the introduction of the green revolution in India, we were not self-sufficient in terms of our food grain production. But last few decades agriculture is not growing with the increasing population and to ensure food security factors like accessibility, affordability as well nutritional value of the food available should be catered to.
Farmers Suicides: The farmer suicides appear concentrated in regions of high commercialization of Indian agriculture and very high peasant debt. Cash crop farmers seemed far more vulnerable than those growing food crops. Commercialization of the countryside along with a massive decline in investment in agriculture was the beginning of the decline. Privatization of many resources has also compounded the problems.
Indian Agriculture: Important Facts
The Economic Survey of India 2020-21 report stated that in FY20:
- The total food grain production in the country was recorded at 296.65 million tonnes (up by 11.44 million tonnes compared with 285.21 million tonnes in FY19).
- The government has set a target to buy 42.74 million tonnes from the central pool in FY21; this is 10% more than the quantity purchased in FY20.
- For FY22, the government has set a record target for farmers to raise food grain production by 2% with 307.31 million tonnes of food grains.
- In FY21, production was recorded at 303.34 million tonnes against a target of 301 million tonnes
- Gross Value Added (GVA) by agriculture, forestry, and fishing was estimated at Rs. 19.48 lakh crore in FY20.
- The share of agriculture and allied sectors in GVA of India at current prices stood at 17.8 % in FY20.
- Consumer spending in India will return to growth in 2021 post the pandemic-led contraction, expanding by as much as 6.6%.
Also read: Agriculture export policy

Aim IAS, IPS, or IFS?
About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...
Agriculture in India
India is a global agricultural powerhouse. It is the world’s largest producer of milk, pulses, and spices, and has the world’s largest cattle herd (buffaloes), as well as the largest area under wheat, rice and cotton. It manages to handle 65% rainfed area effectively.
It is the second largest producer of rice, wheat, cotton, sugarcane, farmed fish, sheep & goat meat, fruit, vegetables and tea.
Major Crops and Cropping Pattern in India
India is a country with an agrarian economy, with over 54% of the country’s land classified as arable and agriculture industry comprising half of labour market. India's climate varies from humid and dry tropical in the south to temperate alpine in the northern reaches. This diverse climate supports a variety of crops.

Major crops in India
Answer our survey to get FREE CONTENT

Feel free to get in touch! We will get back to you shortly
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Quality Enrichment Program (QEP)
- Total Enrichment Program (TEP)
- Ethics Marks Maximization Program
- Interview Mentorship Program (IMP)
- Prelims Crash Course for UPSC 2024
- Science of Answer Writing (SAW)
- Intensive News Analysis (INA)
- Topper's UPSC PYQ Answer
- Essay Marks Maximization Program
- PSIR Optional
- NEEV GS + CSAT Foundation
- News-CRUX-10
- Daily Headlines
- Geo. Optional Monthly Editorials
- Past Papers
- © Copyright 2024 - theIAShub
Talk To Our Counsellor
Final Result - CIVIL SERVICES EXAMINATION, 2023.
- UPSC Online
- UPSC offline and Hybrid
- UPSC Optional Coaching
- UPPCS Online
- BPSC Online
- MPSC Online
- MPPSC Online
- WBPSC Online
- OPSC Online
- UPPCS Offline Coaching
- BPSC Offline Coaching
- UPSC Test Series
- State PSC Test Series
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS
- SUBJECT WISE CURRENT AFFAIRS
- DAILY EDITORIAL ANALYSIS
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS QUIZ
- Daily Prelims(MCQs) Practice
- Daily Mains Answer Writing
- Free Resources

- Offline Centers
- NCERT Notes
- UDAAN Notes
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Prelims PYQs
- UPSC Mains PYQs
- Prelims Preparation
NCERT NOTES
Elevate your upsc preparation with ncert notes – because every word matters on your journey to success..
- Indian Economy
- Physical Geography
- Indian Society
- Science & Tech
- Human Geography
- Art & Culture
Development of Agriculture in India: Evolution, Modern Reform and Challenges
Exploring the Dynamics of Development of Agriculture in India Worldwide
Agricultural development in India aims to increase farm production to meet rising population demands . It involves expanding cropped areas, crop diversity, irrigation, fertilizers, and mechanization.
Agriculture has developed at different places in different parts of the world. Developing countries with large populations usually practice intensive agriculture where crops are grown on small holdings mostly for subsistence
Sowing Progress: The Evolution of Indian Agriculture from Independence to Green Revolution
- Pre-Independence Challenges: Indian agriculture was primarily subsistence-based before Independence and faced challenges like droughts and famines in the first half of the 20th century.
- Partition Impact: During partition, a significant portion of irrigated land went to Pakistan, reducing the proportion of irrigated land in Independent India.
- Post-Independence Agricultural Strategy: After Independence, the government focused on increasing foodgrain production by switching from cash crops to food crops , intensifying cropping on existing land, and bringing fallow land under cultivation.
- To address this, Intensive Agricultural District Programme (IADP) and Intensive Agricultural Area Programme (IAAP) were launched, but two consecutive mid-1960s droughts led to a food crisis.
- This helped India to achieve self sufficiency in foodgrain production.
- However, the Green Revolution was initially limited to irrigated areas, creating regional disparities.
- Agricultural Diversification: Government promoted development of dairy farming, poultry, horticulture, livestock rearing, and aquaculture.
- The policy of liberalization and a free-market economy in the 1990s influenced the direction of Indian agricultural development.
Harvesting Progress: Advancements in Agricultural Output and Technology in India
- Crops like rice, wheat, sugarcane, oilseeds, and cotton have seen substantial production and yield growth.
- It paved the way for modern agricultural practices , including the adoption of high-yielding seed varieties, chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and farm machinery.
- The net irrigated area in the country has also expanded.
- The use of chemical fertilizers has increased 15-fold since the mid-1960s, contributing to enhanced agricultural productivity.
Nurturing Growth: Overcoming Challenges for Sustainable Development of Indian Agriculture
Indian agriculture is adversely affected by various issues impacting development of agriculture in India and livelihood of farmers.
- Poor monsoons and fluctuations in rainfall patterns in regions like Rajasthan result in both droughts and floods, impacting crop production.
- Rainfed areas, especially drylands, face low yields.
- As a result, many turn to credit from institutions and moneylenders, leading to indebtedness.
- Among the three revenue systems operational during the British period, i.e., Mahalwari, Ryotwari, and Zamindari , the last one was most exploitative for the peasants.
- Land holdings are often fragmented , making them economically unviable.
- Commercialization and modernization are more prevalent in irrigated regions.
- Vast Underemployment: The agricultural sector in India experiences substantial underemployment, especially in unirrigated areas, leading to seasonal unemployment.
- Issues like alkalization, salinization, waterlogging, and excessive chemical use have compromised soil fertility.
- Rainfed areas also face soil erosion and degradation due to human activities.
Tacking all these issues will surely contribute to development of agriculture in India.
Revitalizing Indian Agriculture through Technological and Institutional Reforms
To address the above problems comprehensively, various technological and Institutional measures has been initiated by the government.
- Collectivization: Efforts were made to consolidate land holdings and foster cooperation among farmers.
- Abolition of Zamindari : The zamindari system was abolished to ensure equitable land distribution.
- Land Reforms : Land reform laws were enacted, though their implementation varied.
- Green Revolution : The Green Revolution, driven by technology adoption, aimed to boost agricultural productivity.
- White Revolution : The White Revolution, or Operation Flood, focused on dairy production and distribution.
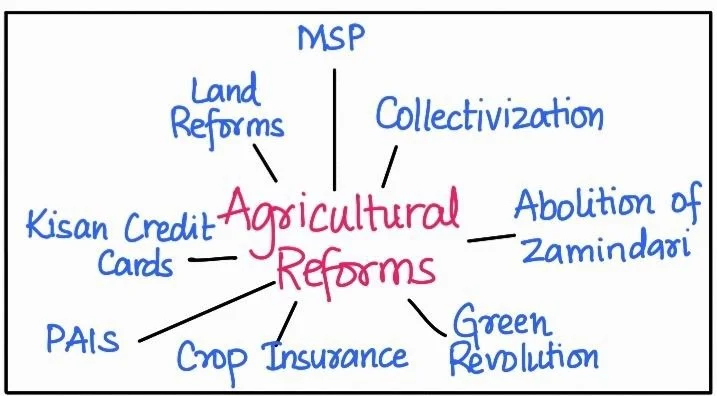
- Comprehensive Land Development : In the 1980s and 1990s, a comprehensive land development program was initiated, combining institutional and technical reforms.
- Crop Insurance: Crop insurance against natural disasters was introduced.
- Grameen Banks: Grameen banks and cooperative societies provided farmers with access to loans at lower interest rates.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC) : The KCC scheme aimed to provide credit to farmers.
- Personal Accident Insurance Scheme (PAIS) which aimed to offer insurance coverage to farmers.
- Weather Bulletins and Agricultural Programs: These were introduced on radio and television for better dissemination of information.
- Minimum Support Price (MSP) : The government announced MSPs for important crops to protect farmers from exploitation by middlemen and ensure sustainable development of Agriculture in India.
- Primary activities like hunting , gathering, pastoralism, mining, and mainly agriculture play a crucial role in meeting the demands of a growing population.
- As the majority of the population in the world is dependent on agriculture, the ongoing development of agriculture in India is essential for ensuring food security and fostering sustainable economic growth in both developing and developed regions.
Also Read: Diverse Types of Agriculture: Understanding Forms and Practices Worldwide
UPDATED :
Recommended For You
Latest comments, the most learning platform.
Learn From India's Best Faculty
Our Courses
Our initiatives, beginner’s roadmap, quick links.

PW-Only IAS came together specifically to carry their individual visions in a mission mode. Infusing affordability with quality and building a team where maximum members represent their experiences of Mains and Interview Stage and hence, their reliability to better understand and solve student issues.
Subscribe our Newsletter
Sign up now for our exclusive newsletter and be the first to know about our latest Initiatives, Quality Content, and much more.
Contact Details
G-Floor,4-B Pusha Road, New Delhi, 110060
- +91 9920613613
- [email protected]
Download Our App
Biginner's roadmap, suscribe now form, fill the required details to get early access of quality content..
Join Us Now
(Promise! We Will Not Spam You.)
CURRENT AF.
<div class="new-fform">
Select centre Online Mode Hybrid Mode PWonlyIAS Delhi (ORN) PWonlyIAS Delhi (MN) PWonlyIAS Lucknow PWonlyIAS Patna Other
Select course UPSC Online PSC ONline UPSC + PSC ONLINE UPSC Offline PSC Offline UPSC+PSC Offline UPSC Hybrid PSC Hybrid UPSC+PSC Hybrid Other
</div>

Agricultural Challenges to Overcome in India | UPSC Mains Essay Preparation PDF Download
To create an essay on "Agricultural Challenges to Overcome in India" for the UPSC exam, we need to structure it effectively with an introduction, body, and conclusion. Here's the proposed structure, followed by the essay:
Introduction
- Quote or Phrase: Start with a relevant quote or phrase to set the tone.
- Context Setting: Briefly introduce the importance of agriculture in India.
- Thesis Statement: Present the main argument or perspective of the essay.
- Discuss the Green Revolution and its impact.
- Present the current state of agriculture in India.
- Environmental Issues: Climate change, water scarcity, soil degradation.
- Economic and Policy Challenges: Subsidies, pricing issues, trade policies.
- Technological and Infrastructure Challenges: Lack of modern technology, storage, and transportation issues.
- Social Challenges: Farmer distress, rural-urban migration.
- Compare with countries like China or the US in terms of agricultural policies and outcomes.
- Discuss recent government initiatives and their effectiveness.
- How technology can be a game-changer in overcoming challenges.
- Impact on rural livelihood, economy, and overall food security.
- Reiterate the Thesis: Summarize the main points made in the essay.
- Future Outlook: Present a vision of what Indian agriculture could look like with the right interventions.
- Closing Quote or Phrase: End with a powerful quote or phrase that encapsulates the essence of the essay.
Sample Essay
The following essay serves as a sample for the given topic. Students can add their own ideas and points as well.
"The destiny of nations depends on the manner in which they feed themselves." - Jean Anthelme Brillat-Savarin
Agriculture, the backbone of the Indian economy, reflects the soul of its rural essence and sustains the lifeline of over a billion. However, as we traverse through the annals of time, we realize the journey of Indian agriculture is marked with both triumphs and trials. This essay delves into the multifaceted agricultural challenges India faces, seeking not just to underline the crises but also to envision a greener and more prosperous agrarian future.
Historically, India's agricultural saga witnessed a watershed moment with the Green Revolution in the 1960s, spearheaded by visionaries like M.S. Swaminathan. This revolution, a harbinger of hope, catapulted India from the shadows of famines to self-sufficiency in food grains. However, fast forward to the contemporary era, Indian agriculture grapples with myriad challenges, despite being the primary source of livelihood for about 58% of the population.
Environmental issues such as unpredictable climate patterns, dwindling water resources, and soil degradation pose significant threats. The over-exploitation of water resources for irrigation, aided by subsidized electricity, has led to alarming drops in groundwater levels. Furthermore, climate change exacerbates the unpredictability of monsoons, vital for rain-fed agriculture dominating large tracts of the country.
Economic and policy challenges are equally daunting. The agrarian distress is often attributed to inadequate pricing, inefficient subsidy regimes, and skewed trade policies. The plight of small and marginal farmers, who constitute a significant portion of the agrarian community, is worsened by inadequate market access and lack of bargaining power.
Technological and infrastructure challenges further stifle the sector's potential. Despite the digital age, a significant portion of India's agriculture remains bereft of modern technology and innovation. Post-harvest losses due to inadequate storage and transportation facilities further dent the farmers' income.
Social challenges are reflected in the grim reality of farmer suicides and the growing trend of rural-urban migration. The distress in the agricultural sector has profound implications on the socio-economic fabric of rural India.
A comparative analysis with other nations like China reveals stark differences in policy approaches. China's early focus on agricultural reforms and rural poverty reduction presents a contrasting trajectory compared to India's emphasis on manufacturing and services.
Government initiatives , though well-intentioned, often fall short in execution. Schemes like PM-KISAN, crop insurance schemes, and e-NAM (National Agriculture Market) are steps in the right direction but require more robust implementation and wider reach.
Technology and innovation hold the key to revolutionizing Indian agriculture. Initiatives like digital agriculture, precision farming, and genetically modified crops could potentially increase yields, reduce input costs, and make farming more sustainable.
The socio-economic impact of these challenges and interventions is profound. Agriculture, being intrinsically linked to the rural economy, has a cascading effect on overall economic growth and food security.
In conclusion, as we stand at the crossroads, the path to a resurgent and resilient agricultural sector in India requires a multi-pronged approach. It demands a concerted effort from all stakeholders - government, farmers, scientists, and the private sector. A holistic policy framework, blending traditional wisdom with modern technology, can propel Indian agriculture towards a future where it not only feeds its population but also becomes a beacon of sustainable and efficient farming globally. In the words of Mahatma Gandhi, "The future depends on what you do today." It is high time that the agricultural sector in India is given the impetus it deserves, for it is not just about food security, but about securing the future of a nation.
"To forget how to dig the earth and to tend the soil is to forget ourselves." - Mahatma Gandhi
Top Courses for UPSC
Faqs on agricultural challenges to overcome in india - upsc mains essay preparation, how to prepare for upsc, study material, mock tests for examination, agricultural challenges to overcome in india | upsc mains essay preparation, viva questions, sample paper, important questions, extra questions, practice quizzes, previous year questions with solutions, past year papers, video lectures, shortcuts and tricks, objective type questions, semester notes.

Agricultural Challenges to Overcome in India Free PDF Download
Importance of agricultural challenges to overcome in india, agricultural challenges to overcome in india notes, agricultural challenges to overcome in india upsc questions, study agricultural challenges to overcome in india on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country.
- Essay On Agriculture
Essay on Agriculture
500+ words essay on agriculture.
In India, agriculture is considered a primary livelihood for most of the population, which can never be underestimated. Agriculture has existed for thousands of years in our country and has developed with new technologies and equipment that have replaced traditional farming methods. In India, few farmers still use the traditional farming method because they lack the resources to use modern techniques. Agriculture is the only sector that contributes to itself and other country sectors. India is the second-largest wheat, rice, cotton, fruit, vegetables, and tea producer. It is also a global powerhouse of agricultural production. It is the world’s largest producer of spices, milk, wheat, rice and cotton.
Role of Agricultural in Economic Development
The population of India largely depends on agriculture, and it is not only just a means of livelihood but a way of living. The Government of India is continuously developing the agricultural sector by framing new laws, implementing modern technology, etc. In India, the entire nation depends on agriculture for food. In earlier times, agriculture was mainly dependent on the monsoon, but dams, canals, pump sets, and tube wells are now being constructed.
Agriculture plays a crucial role in the economic development of India as 3/4th of the population is based on agriculture. It is one of the largest sources of livelihood for the country. The country was dependent on agriculture for a thousand years.
The agricultural sector also benefits the industries in getting their raw materials, which clearly states that a large part of the economy will freeze without a flourishing agriculture sector. It leads to the expansion of the industrial sector. Indian agriculture provides employment opportunities to most people, and 70% of the population, especially in rural areas, earn their livelihood from cultivation.
In India, agriculture plays an imperative role in enhancing foreign exchange. To other nations, India exports commodities such as coffee, spices, tea, vegetables, tobacco, etc. Agriculture contributes to Indian exports. With the invention of organic farming, exports have also increased in the last few decades.
Agriculture is the Indian economy’s most important sector, and India’s farm sector is the largest industry. With constant changes and developments happening and introduced policies, it will only go upwards. It will always remain a significant factor in the nation’s economic growth.
An essay on Agriculture is crucial that can be asked during the exam. Students can also access CBSE Essays from our BYJU’S website.
Frequently Asked Questions on Agriculture Essay
Where was agriculture originally developed.
Agriculture was developed in modern-day Iraq, Jordan, Palestine, Israel, parts of Turkey and Iran which was also known as the Fertile Crescent.
What are the main types of agriculture?
The four main types of agricultural activities include livestock production, crop production, agricultural economics and agricultural engineering.
What are agricultural methods which are famous in India?
The majority of Indian farmers practice subsistence farming which involves the cultivation of crops on small pieces of land.

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling
- UPSC IAS Exam Pattern
- UPSC IAS Prelims
- UPSC IAS Mains
- UPSC IAS Interview
- UPSC IAS Optionals
- UPSC Notification
- UPSC Eligibility Criteria
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Admit Card
- UPSC Results
- UPSC Cut-Off
- UPSC Calendar
- Documents Required for UPSC IAS Exam
- UPSC IAS Prelims Syllabus
- General Studies 1
- General Studies 2
- General Studies 3
- General Studies 4
- UPSC IAS Interview Syllabus
- UPSC IAS Optional Syllabus

Agricultural Productivity in India – UPSC Economy Notes
Agricultural productivity, reflecting the efficiency of input utilization, is a critical measure defined as the ratio of output to inputs. Several factors contribute to agricultural productivity, and its enhancement is pivotal for numerous benefits:
- Availability of Water: Adequate water supply is crucial for crop growth.
- Quality of Soil: The fertility and composition of soil directly impact productivity.
- Farm Size: Larger farms may benefit from economies of scale.
- Mechanization: The use of machinery enhances efficiency.
- HYV Seeds: High-yielding and genetically improved seeds contribute to higher yields.
- Optimal Fertilizer Application: Proper use of fertilizers supports plant growth.
- Extension Services: Knowledge dissemination and support services play a vital role.
- Farmer Knowledge: Informed farmers can make better decisions.
- Credit Availability: Timely and affordable credit enables investment in inputs.
- Tenant Security: Secure land tenure encourages long-term investment.
- Increased Production: Higher yields lead to increased agricultural output.
- Food Security: Enhanced productivity contributes to a more secure food supply.
- Resource Conservation: Minimization of resource wastage.
- Income Generation: Improved productivity results in higher incomes for farmers.
- Wage Growth: Higher wages for agricultural labor.
- Reduced Migration: Mitigation of labor migration from rural to urban areas.
- Export Opportunities: Comparative advantage in global markets.
- Agricultural Growth: Contributes to overall growth in the agricultural sector.
- Poverty Alleviation: Reduced poverty through increased incomes.
- It is essential to ensure that productivity gains are sustainable, avoiding the pitfalls of practices that may harm the environment, as seen in the aftermath of the Green Revolution in India.
- Landholding Size: Small and diminishing land holdings.
- Irrigation Insufficiency: Inadequate irrigation facilities.
- Marketing Policy Issues: Lack of remunerative and secure marketing policies.
- Financial Inclusion: Insufficient financial access for farmers.
- Soil Quality: Concerns about soil quality and degradation.
- Extension Services: Sub-optimal extension services in terms of coverage and quality.
- Knowledge Gaps: Information and knowledge disparities among farmers.
- Numerous schemes in India aim at enhancing agricultural productivity.
In conclusion, the multifaceted nature of agricultural productivity requires a holistic approach. Addressing challenges, promoting sustainable practices, and ensuring inclusive policies are crucial for unlocking the full potential of agriculture in India. The ongoing government schemes attest to the concerted efforts being made to boost agricultural productivity and uplift the farming community.
Table of Contents
1. What factors contribute to agricultural productivity in India?
- Agricultural productivity in India is influenced by several factors, including access to irrigation, availability of high-quality seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides, adoption of modern farming techniques, land consolidation, mechanization, and government policies supporting agriculture.
2. How does irrigation impact agricultural productivity in India?
- Irrigation plays a crucial role in enhancing agricultural productivity in India by providing water to crops, especially during dry spells. Improved irrigation infrastructure, such as drip and sprinkler systems, helps conserve water and optimize its usage, leading to increased crop yields and better quality produce.
3. What initiatives has the Indian government undertaken to improve agricultural productivity?
- The Indian government has implemented various initiatives like the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) to promote efficient water usage in agriculture, the National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) to promote climate-resilient farming practices, and the Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) to support agricultural development at the state level.
4. How do technological advancements contribute to agricultural productivity in India?
- Technological advancements such as precision agriculture, genetic engineering, and remote sensing techniques have revolutionized Indian agriculture. These technologies enable farmers to optimize inputs like water, fertilizers, and pesticides, leading to higher yields, reduced production costs, and improved sustainability.
5. What are the challenges hindering agricultural productivity growth in India?
- Challenges such as fragmented landholdings, lack of access to credit and markets, inadequate infrastructure, climate change impacts, and pest and disease outbreaks pose significant hurdles to agricultural productivity growth in India. Addressing these challenges requires concerted efforts from the government, farmers, and other stakeholders to promote sustainable and inclusive agricultural development.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here
Visit our YouTube Channel – here
- Business Cycles: Slowdown, Recession, Great Recession, and Depression – UPSC Economy Notes
- Swiss Challenge – UPSC Economy Notes
- Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) – UPSC Economy Notes
- Electronic Way Bill (E-Way Bill) – UPSC Economy Notes
Edukemy Team
Imf and the great recession 2008 – upsc economy notes, gross national happiness (gnh) – upsc economy notes, protection of plant variety and farmers’ rights act, 2001 (ppvfr..., priority sector lending – upsc economy notes, challenges to boosting india’s exports: a comprehensive overview – upsc..., toll-operate-transfer (tot) – upsc economy notes, stock exchanges in india – upsc economy notes, consumer price index + new cpi series 2015 – upsc..., world bank classification – upsc economy notes, keynesian economics – upsc economy notes, leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Our website uses cookies to improve your experience. By using our services, you agree to our use of cookies Got it
Keep me signed in until I sign out
Forgot your password?
A new password will be emailed to you.
Have received a new password? Login here

UPSC All India Mock Test – Edukemy Open Mock
Essay on Agriculture for Students and Children
500+ words essay on agriculture.
Agriculture is one of the major sectors of the Indian economy. It is present in the country for thousands of years. Over the years it has developed and the use of new technologies and equipment replaced almost all the traditional methods of farming. Besides, in India, there are still some small farmers that use the old traditional methods of agriculture because they lack the resources to use modern methods. Furthermore, this is the only sector that contributed to the growth of not only itself but also of the other sector of the country.

Growth and Development of the Agriculture Sector
India largely depends on the agriculture sector. Besides, agriculture is not just a mean of livelihood but a way of living life in India. Moreover, the government is continuously making efforts to develop this sector as the whole nation depends on it for food.
For thousands of years, we are practicing agriculture but still, it remained underdeveloped for a long time. Moreover, after independence, we use to import food grains from other countries to fulfill our demand. But, after the green revolution, we become self-sufficient and started exporting our surplus to other countries.
Besides, these earlier we use to depend completely on monsoon for the cultivation of food grains but now we have constructed dams, canals, tube-wells, and pump-sets. Also, we now have a better variety of fertilizers, pesticides, and seeds, which help us to grow more food in comparison to what we produce during old times.
With the advancement of technology, advanced equipment, better irrigation facility and the specialized knowledge of agriculture started improving.
Furthermore, our agriculture sector has grown stronger than many countries and we are the largest exporter of many food grains.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Significance of Agriculture
It is not wrong to say that the food we eat is the gift of agriculture activities and Indian farmers who work their sweat to provide us this food.
In addition, the agricultural sector is one of the major contributors to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and national income of the country.
Also, it requires a large labor force and employees around 80% of the total employed people. The agriculture sector not only employees directly but also indirectly.
Moreover, agriculture forms around 70% of our total exports. The main export items are tea, cotton, textiles, tobacco, sugar, jute products, spices, rice, and many other items.
Negative Impacts of Agriculture
Although agriculture is very beneficial for the economy and the people there are some negative impacts too. These impacts are harmful to both environments as the people involved in this sector.
Deforestation is the first negative impact of agriculture as many forests have been cut downed to turn them into agricultural land. Also, the use of river water for irrigation causes many small rivers and ponds to dry off which disturb the natural habitat.
Moreover, most of the chemical fertilizers and pesticides contaminate the land as well as water bodies nearby. Ultimately it leads to topsoil depletion and contamination of groundwater.
In conclusion, Agriculture has given so much to society. But it has its own pros and cons that we can’t overlook. Furthermore, the government is doing his every bit to help in the growth and development of agriculture; still, it needs to do something for the negative impacts of agriculture. To save the environment and the people involved in it.
FAQs about Essay on Agriculture
Q.1 Name the four types of agriculture? A.1 The four types of agriculture are nomadic herding, shifting cultivation, commercial plantation, and intensive subsistence farming.
Q.2 What are the components of the agriculture revolution? A.2 The agriculture revolution has five components namely, machinery, land under cultivation, fertilizers, and pesticides, irrigation, and high-yielding variety of seeds.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- Education News
- UPSC 2023 Topper's Mock Essay Goes Viral, Sparking Debate on Exam Relevance
UPSC 2023 Topper's Mock Essay Goes Viral, Sparking Debate on Exam Relevance

Visual Stories

UPSC 2023 topper Aditya Srivastava's mock essay copy goes viral, internet reacts
Upsc topper 2023 aditya srivastava's essay mock test copy has gone viral, sparking various reactions from the internet..
Listen to Story

- UPSC topper Aditya Srivastava's essay mock test goes viral
- Netizens debate essay's relevance in UPSC
- Lucknow's Aditya Srivastava became UPSC 2023 topper
The UPSC 2023 results were recently announced, with Lucknow's Aditya Srivastava emerging as the IAS topper. As aspirants gear up for UPSC prelims 2024, many are eager to learn from the strategies of Aditya and other toppers. Aditya's essay mock test copy has gone viral, sparking various reactions from netizens. Some are questioning the relevance of the essay in UPSC CSE.
The essay, which begins with a reference to Oppenheimer's idea of the Manhattan Project, discusses the balance between logic and emotion--"A mind all logic is like a knife all blade, it makes the hand bleed that uses it."
IAS Topper Aditya Srivastava CSE AIR-1 Essay Mock Test Copy 👇 A Thread ðŸçµ pic.twitter.com/Y2SjL2Igff — UPSC NOTES (@UPSC_Notes) April 17, 2024
The Internet is giving the viral essay a mixed response. Some like the reference, while some are unhappy with the curation:
"Not at all impressed," a user commented.
"Salute to perfection," another user posted on X.
"Kids, the only thing matters is a good handwriting," another comment reads.

Call us @ 08069405205

Search Here

- An Introduction to the CSE Exam
- Personality Test
- Annual Calendar by UPSC-2024
- Common Myths about the Exam
- About Insights IAS
- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director's Desk
- Meet Our Team
- Our Branches
- Careers at Insights IAS
- Daily Current Affairs+PIB Summary
- Insights into Editorials
- Insta Revision Modules for Prelims
- Current Affairs Quiz
- Static Quiz
- Current Affairs RTM
- Insta-DART(CSAT)
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Prelims 2024
- Secure (Mains Answer writing)
- Secure Synopsis
- Ethics Case Studies
- Insta Ethics
- Weekly Essay Challenge
- Insta Revision Modules-Mains
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Mains
- Secure (Archive)
- Anthropology
- Law Optional
- Kannada Literature
- Public Administration
- English Literature
- Medical Science
- Mathematics
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Monthly Magazine: CURRENT AFFAIRS 30
- Content for Mains Enrichment (CME)
- InstaMaps: Important Places in News
- Weekly CA Magazine
- The PRIME Magazine
- Insta Revision Modules-Prelims
- Insta-DART(CSAT) Quiz
- Insta 75 days Revision Tests for Prelims 2022
- Insights SECURE(Mains Answer Writing)
- Interview Transcripts
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Prelims
- Answer Keys for Prelims PYQs
- Solve Prelims PYQs
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Mains
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- Toppers from Insights IAS
- Testimonials
- Felicitation
- UPSC Results
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- World History
- World Geography
- Indian Geography
- Indian Society
- Social Justice
- International Relations
- Agriculture
- Environment & Ecology
- Disaster Management
- Science & Technology
- Security Issues
- Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude

- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Enivornment & Ecology
Day: April 20, 2024
Day – 39 insta 75 days revision plan-2024: topic – modern india, subject-wise test 19, textbook-based test – 24 and april 2024 ca.
Join our Official Telegram Channel HERE Please subscribe to Our podcast channel HERE Subscribe to our YouTube ChannelHERE Follow our Twitter Account HERE Follow our Instagram ID HERE Follow us on LinkedIn : HERE
[Mission 2024] INSIGHTS DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS + PIB SUMMARY 20 April 2024
InstaLinks : Insta Links help you think beyond the issue but relevant to the issue from UPSC prelims and Mains exam point of view. These linkages provided in this ‘hint’ format help you frame possible questions in your mind that might arise(or an examiner might imagine) from each current event. InstaLinks also connect every issue …
Continue reading “[Mission 2024] INSIGHTS DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS + PIB SUMMARY 20 April 2024”
Mapping Source: DTE Context: The drying of the Aral Sea in Central Asia has led to the emergence of the Aralkum Desert, making the region much dustier. Dust emissions from the desert have almost doubled over the past 30 years, impacting air quality and climate. The dust contains residues of fertilizers and pesticides from …
Continue reading “Aral Sea”
Exoskeleton
Facts for Prelims (FFP) Source: PIB Context: DRDO organized the first international workshop on ‘Emerging Technologies & Challenges for Exoskeleton’ in Bengaluru. What is Exoskeleton? An exoskeleton is a mobile machine resembling an insect’s exoskeleton, worn by a person. It’s powered by motors, hydraulics, or pneumatics to aid limb movement. Applications include aiding …
Continue reading “Exoskeleton”
Indigenous Technology Cruise Missile (ITCM)
Tags: Indigenous Technology Cruise Missile (ITCM) , ITCM
Facts for Prelims (FFP) Source: TH Context: DRDO conducts a successful test of an indigenous long-range subsonic cruise missile (Indigenous Technology Cruise Missile (ITCM)) from Chandipur, Odisha. The missile, similar to Nirbhay, showcased low-altitude sea-skimming flight with all subsystems performing as expected.
Artemis Accords
Tags: Artemis Accords
Facts for Prelims (FFP) Source: IE Context: Sweden joined the Artemis Accords, becoming the 38th country to do so. These non-binding arrangements aim to establish norms for outer space activities. About the Artemis Accords: The Artemis Accords are non-binding principles based on the Outer Space Treaty (OST) of 1967, aiming to guide …
Continue reading “Artemis Accords”
Tags: Tachyons
Facts for Prelims (FFP) Source: Live Science Context: A new paper suggests that the universe may be dominated by particles called tachyons, which move faster than light. About Tachyons: They are hypothetical subatomic particles that move faster than the speed of light. Coined by physicist Gerald Feinberg in 1967, they’re distinct from bradyons, …
Continue reading “Tachyons “
Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF)
Tags: Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF)
Facts for Prelims (FFP) Source: TH Context: Private investment in India, measured by Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) as a percentage of GDP, has seen a decline since 2011-12. Despite government efforts like corporate tax cuts, private investment hasn’t picked up. What is GFCF? Gross Fixed Capital Formation, measures the growth in …
Continue reading “Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF)”
Reports in News
Tags: Arctic’s Plastic Crisis Report , Global Forest Watch (GFW) Report , State of World Population 2024 report , Survival International Report
Facts for Prelims (FFP)
Srinagar (considered for World Craft City)
Tags: Srinagar , World Craft City
Facts for Prelims (FFP) Source: TH Context: Srinagar is being considered for the prestigious World Craft City (WCC) title by the World Crafts Council International (WCCI). Arts and Crafts of Srinagar City:
Innovation Trap
Tags: Innovation Trap
Content for Mains Enrichment (CME) Source: LM What is the Innovation trap? It refers to a situation where organizations strive to innovate but inadvertently fall into patterns of thinking and behaviour that stifle genuine creativity and progress. This trap often arises when organizations prioritize conformity, rely too heavily on past successes, or resist …
Continue reading “Innovation Trap”
4Ps (Political Leadership, Public Financing, Partnerships, and Participation)
Tags: 4Ps (Political Leadership , and Participation) , Partnerships , Public Financing
Content for Mains Enrichment (CME) Source: IE Context: India’s development strategy, characterized by the 4Ps (Political Leadership, Public Financing, Partnerships, and Participation), has led to significant success in national programs. Explanation of each of the 4Ps using Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) Example: Usage: The 4Ps framework can be used to explain the …
Continue reading “4Ps (Political Leadership, Public Financing, Partnerships, and Participation)”
Examples of Ethics
Tags: Longevity India Initiative , Misuse of Public Money by three IAS officers , Nestle infant milk in poorer countries has a higher sugar content
GS4 Paper Syllabus: Applications of Ethics Source: IE, IE Example 1: Longevity India Initiative Context: The Indian Institute of Science (IISc) has launched the ‘Longevity India Initiative’ to promote healthy ageing by researching overcoming challenges associated with growing older. The initiative focuses on identifying early disease indicators, researching ageing biomarkers, and developing new …
Continue reading “Examples of Ethics”
[ Reminder for CSAT Test 1 ] STEP UP – Free All India Prelims Test Series 2024 | 21st April 2024
Tags: STEP UP CSAT Test 1
CLICK HERE TO REGISTER FOR STEP UP Prelims Test Series 2024 (Ignore if already registered) All the Tests will be available in both Online mode and Offline mode at all our centres( Bengaluru, Delhi, Hyderabad, Lucknow, Srinagar, Dharwad, Mysuru) Students who have missed GS Test 1, Test 2 & Test 3 can …
Continue reading “[ Reminder for CSAT Test 1 ] STEP UP – Free All India Prelims Test Series 2024 | 21st April 2024”
[Mission 2024] Insta–DART (Daily Aptitude and Reasoning Test) 19 April 2024
Follow us on our Official TELEGRAM Channel HERE Subscribe to Our Official YouTube Channel HERE Official Facebook Page HERE Follow our Twitter Account HERE
[Mission 2024] Insta–DART (Daily Aptitude and Reasoning Test) 18 April 2024
[mission 2024] insta–dart (daily aptitude and reasoning test) 17 april 2024, [mission 2024] insta–dart (daily aptitude and reasoning test) 15-16 april 2024, [mission 2024] static quiz, 20 april 2024 – environment.
Join our Official Telegram Channel HERE for Motivation and Fast Updates Subscribe to our YouTube Channel HERE to watch Motivational and New Join our Twitter Channel HERE Follow our Instagram Channel HERE Follow us on LinkedIn : HERE
[Mission 2024] Current Affairs Quiz , 20 April 2024

- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director’s Desk
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Prelims
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Mains
- Environment & Ecology
- Science & Technology

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Agriculture is the primary source of livelihood for about 58% of India's population. Read here to know more about Indian agriculture. India has one of the largest plain areas of the world-the Indo-Gangetic plain which is immensely fertile. India has varieties of climatic conditions and soil types.
The absence of direct measures to promote farmers' welfare is also one of the main reasons for agricultural distress. Declining Average Size of Farm Holdings: Increasing demographic pressure, disguised employment in agriculture and conversion of agricultural land for alternative uses, have drastically reduced the average land holding.
Agriculture is an important sector of Indian economy as it contributes about 17% to the total GDP and provides employment to around 58% of the population. Indian agriculture has registered impressive growth over last few decades. The foodgrains production has increased from 51 million tonnes (MT) in 1950-51 to 250MT during 2011-12 highest ever ...
Agriculture UPSC. Candidates can expect an essay on agriculture in the upcoming UPSC Exam. Agriculture in India is a significant topic in the UPSC syllabus, and the candidates need to be well-versed in the subject. Moreover, Agriculture is covered in detail under UPSC GS Paper 3 Syllabus.
Agriculture is the backbone of the Indian economy. Even, with the growth of other sectors, agriculture still continues to play a dominant part in the overall economic scenario of India. Agricultural marketing is mainly a state entitlement with the Central Government providing support under central sector schemes.
Since independence India has made much progress in agriculture. Indian agriculture, which grew at the rate of about 1 percent per annum during the fifty years before Independence, has grown at the rate of about 2.6 percent per annum in the post-Independence era. Expansion of area was the main source of growth in the period of fifties and ...
Expert guidance, comprehensive IAS coaching, and proven success. Best IAS|UPSC coaching in India. Call us @ 08069405205; Search Here. Search. Search Here. Search. Call us @ 08069405205. Blog ... Role of Agriculture in Indian Economy. ... Previous Years' Question Papers-Mains; UPSC CSE Syllabus; Booklist; FAQs; Toppers. Toppers from Insights ...
Current scenario of agriculture. Over 70 per cent of the rural households depend on agriculture. It contributes about 18.8% to the total GDP. Accounting for 18.8% (2021-22) in Gross Value Added (GVA) of the country registering a growth of 3.6% in 2020-21 and 3.9% in 2021-22. Indian agriculture sector has been growing at an average annual growth ...
Agricultural development in India aims to increase farm production to meet rising population demands. It involves expanding cropped areas, crop diversity, irrigation, fertilizers, and mechanization. Agriculture has developed at different places in different parts of the world. Developing countries with large populations usually practice ...
Reforming Indian Agriculture. This article is based on Farm reforms must be oriented towards minimising risk and increasing returns for farmers which was published in The Indian Express on 29/07/2021. It talks about issues emerging from the present Indian agriculture setup and recommendation to eliminate such issues.
Agriculture in India is an important topic from the civil services examination's point of view. It comes under UPSC Mains GS 3. This article talks about various issues regarding Indian Agriculture. It will aspirants of the IAS Exam and other competitive examinations. UPSC Current Affairs: Issues in News - Agriculture in India Why in news?
Previous Year Papers. IAS Exam. Latest Updates 19 April, 2024: ... From the perspective of the UPSC civil services examination, agriculture in India is a critical subject. It falls under GS3 of the UPSC Mains and Questions in prelims can be framed on the basis of Important concepts , facts related to Indian. ... UPSC : Geography - Agriculture ...
Document Description: Agricultural Challenges to Overcome in India for UPSC 2024 is part of UPSC Mains Essay Preparation preparation. The notes and questions for Agricultural Challenges to Overcome in India have been prepared according to the UPSC exam syllabus. Information about Agricultural Challenges to Overcome in India covers topics like Structure, Sample Essay and Agricultural Challenges ...
Indian agriculture in the present times. Growth trajectory; Issues plaguing Indian agriculture; Programmes and policies introduced in India in recent times to address the issues; Some more measures or recommendations made by the committee to improve agricultural growth in India; Indian industries and economic growth. Indian industry at the eve ...
Importance of Agriculture in India: Two third of the livelihood of the Indian population is directly or indirectly dependent on Agriculture. 55% of the labour force is directly or indirectly involved in Agriculture. Agricultural sector accounts for 15% of the export earnings and 14%-17% of India's GDP. Agricultural sector provides raw ...
Agriculture Reforms. This article is based on "Reforming Indian Agriculture" which was published in Economic and Political Weekly on 14/03/2020. It talks about challenges and solutions pertaining to India's Agriculture sector. India's agriculture policies have had multiple mandates, including a production imperative (national food ...
Agriculture plays a crucial role in the economic development of India as 3/4th of the population is based on agriculture. It is one of the largest sources of livelihood for the country. The country was dependent on agriculture for a thousand years. The agricultural sector also benefits the industries in getting their raw materials, which ...
Agricultural Productivity in India - UPSC Economy Notes. by Edukemy Team March 29, 2024. Agricultural productivity, reflecting the efficiency of input utilization, is a critical measure defined as the ratio of output to inputs. Several factors contribute to agricultural productivity, and its enhancement is pivotal for numerous benefits:
Agricultural influence on national income: The contribution of agriculture during the first two decades towards the gross domestic product ranged between 48 and 60%. In the year 2001-2002, this contribution declined to only about 26%. Agriculture plays vital role in generating employment: In India at least two-thirds of the working population ...
10 Lines On Agriculture in India Essay. Agriculture contributes to more than 15% of India's GDP and has provided employment to millions of people in the country. India is the second-highest producer of agricultural products in the world. Agriculture forms over more than 70% of India's export capacity.
A.1 The four types of agriculture are nomadic herding, shifting cultivation, commercial plantation, and intensive subsistence farming. Q.2 What are the components of the agriculture revolution? A.2 The agriculture revolution has five components namely, machinery, land under cultivation, fertilizers, and pesticides, irrigation, and high-yielding ...
Role of Agriculture in India. Agriculture is one of the most important sectors of Indian economy. It is the supplier of food and raw materials in the country. At the time of independence more than 70 per cent of India's population depended on agriculture to earn livelihood. Accordingly the share of agriculture in the national product/income ...
Aditya Srivastava. NEW DELHI: The Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) recently declared its Civil Services Examination (CSE) results, with Lucknow's Aditya Srivastava emerging as the top scorer ...
In Short. The UPSC 2023 results were recently announced, with Lucknow's Aditya Srivastava emerging as the IAS topper. As aspirants gear up for UPSC prelims 2024, many are eager to learn from the strategies of Aditya and other toppers. Aditya's essay mock test copy has gone viral, sparking various reactions from netizens.
Insights Weekly Essay Challenges 2020 - Week 51. Archives. 20 September 2020. Write an essay on the following topic in not more than 1000-1200 words: "In India Agriculture and the Farmer are both the Victims of Narrow Political Vision"
Insights IAS: Simplifying UPSC IAS Exam Preparation. InsightsIAS has redefined, revolutionized and simplified the way aspirants prepare for UPSC IAS Civil Services Exam. Today, it's India's top website and institution when it comes to imparting quality content, guidance and teaching for the IAS Exam.
DAY - 39 Insta 75 Days Revision Plan-2024: Topic - MODERN INDIA, Subject-wise Test 19, Textbook-based Test - 24 and April 2024 CA. Join our Official Telegram Channel HERE Please subscribe to Our podcast channel HERE Subscribe to our YouTube ChannelHERE Follow our Twitter Account HERE Follow our Instagram ID HERE Follow us on LinkedIn : HERE.