Organizational Structure

Functional Organizational Structure
By Mike Baumgarten
Last updated: May 4, 2023
Table of contents
What is a functional organizational structure?
Which characteristics does a functional structure organization have, pros and cons of a functional organizational structure, who is the functional structure optimal for, example of a functionally structured organization, learn more about organizational design.
In this article, we’ll cover what a functional organizational structure is and what characterizes this type of structure. Finally, we’ll explore the pros and cons of the model.

A functional organizational structure is a safe way to ensure that employees are focused and decision-making processes are streamlined. Due to a strict focus on efficiency and a clear chain of command, functional structures are especially popular among larger companies.
Every time an organizational structure has benefits, however, it also has downsides. In this article, we’ll cover what a functional organizational structure is and what characterizes this type of structure. Finally, we’ll explore the pros and cons of the model.
Let’s get into it!
A functional structure is defined as a system where employees are grouped in different departments based on expertise, each having a functional head. Unlike a hierarchical chart, employees are organized by function rather than by authority.
These departments are referred to as “silos”. This term comes from the metaphor of grain silos that are tall, slim, and isolated to each store different types of grain. Similarly, employees in a functional organizational structure are isolated from other departments.
There are three main areas where a functional organizational structure is distinctive in its design. These are:
- Departmental specialization
In a functional organization, every department is specialized in a particular field, such as sales, marketing, engineering, or finance.
- Clear hierarchy
Employees within the department report to the department head who reports to the executives.
- Limited cross-collaboration
As employees work in silos, they are entirely focused on their own work and do not work cross-functionally.
The characteristics of a functional organizational structure can be both good and bad, depending on the needs of the organization. Here are some of the pros and cons of the structure:
- Clear decision-making process
Because each employee isn’t individually managed, functional organizational designs allow for more flexibility and autonomy within each department, while still keeping an effective chain of command through the head of each department.
- Grouped based on expertise
By strictly working within their field, employees can focus entirely on their own domain of expertise. This can increase efficiency and lead to higher satisfaction since employees don’t have to work in fields they aren’t interested in.
- Easier measurement and development
Because employees are grouped by fields of expertise, it becomes easier to evaluate their performance, as employees can be measured against each other. New skill development also becomes easier since training can be focused on a particular skill set within that field.
- Internal isolation
Within a functional org structure, there is a risk of professional as well as personal isolation. As employees are grouped by expertise, cross-functional collaboration is not encouraged. This can lead to social issues if teams do not socialize with others.
- Less innovation
Innovation often happens when different perspectives meet to come up with a solution. Functional structures can prevent this creativity from unfolding, as the model discourages employees from cross-functional collaboration.
- Slower decision-making
The chain of command in functional organizational structures goes through the department head further up to the executives. Though the decision-making process in functional structures is clear and well-defined, it is slow when compared to flatter structures.
Functional organizational structures are suitable for larger companies that want to keep their employees focused on their specific areas of expertise.
These structures do not prioritize fostering innovation through cross-functional collaboration. Instead, they focus on efficient workflows and a streamlined decision-making process.
A large company that operates with a structure that has functional elements is Unilever , the owner of brands such as Knorr, Dove, and Ben & Jerry’s. In late 2022, Unilever announced changes to its organizational structure to make it “simpler, more category-focused”.
It moved away from its matrix structure and organized into five departments focused on Beauty & Well-Being, Personal Care, Nutrition, Home Care, and Ice Cream. Each department, or Business Group as Unilever calls it, is responsible for its own operations.
This structure has elements of a divisional organizational structure, but also of a functional structure, since the departments each have a specialized focus and operate in isolation from each other.
Want to learn more about organizational structures? At The Org , we have the world’s largest network of publicly available org charts and a ton of resources that will teach you more about management, organizational design, and how you can make your own org chart.

The ORG helps you hire great candidates
Free to use – try today
Which Org Structure Fits You?
Matrix organizational structure, flat organizational structure, the best organizational chart software of 2023.
22 min read
Functional Organizational Structure: Everything You Need to Know
A functional organization structure is a structure used to organize workers. 3 min read updated on February 01, 2023
Updated August 10, 2020:
What Is a Functional Organizational Structure?
A functional organizational structure is a structure used to organize workers. They are grouped based on their specific skills and knowledge. It vertically structures each department with roles from the president to finance and sales departments, to customer service, to employees assigned to one product or service. Functional organizations contain specialized units that report to a single authority, usually called top management.
Each functional unit handles one aspect of the product or service provided such as:
- information technology
- development
- research, etc.
They are referred to as "silos" because the function independently and have their own vertical management structure. Workers within each functional department communicate with each other exclusively, and then department heads communicate with each other. This structure works well in a stable environment that has continuous operations. The goal of a functional structure is to put together every informational and human resource necessary for one activity in a single place. The functional organizational structure helps organizations run their business and earn a profit.
Advantages of a Functional Structure
When employees who have similar skills and experiences are grouped together, it makes production more efficient and of a higher quality. Roles and tasks do not change very much so there is little time spent learning, and accountability is clear. Since the hierarchy is simple, employees know the one manager they are to answer to, instead of multiple people. This streamlines communication and reduces confusion among employees. Employees can feel confident about what they're doing because it is standardized. They are more likely to feel a loyalty to their department and the organization as a whole. This increases morale and work ethic, as there is more job security . There is a clear path of growth for employees which provides motivation, and they are more likely to be corporative with people in their department. A functional organizational structure provides a perfect environment for learning for new employees (especially new college graduates) to be taught the real-world application of theoretical information.
Disadvantages of the Functional Organizational Structure
Employees may find it boring to repeat the same task over and over, and become less enthusiastic over time. If promotions are not handled well, an employee may be discouraged if a lower-performing peer is promoted over them. Problems may arise among management if department heads are only focused on their department and do not communicate effectively with other departments. This can cause poor communication and "silos" that are too independent from one another. If employees and management are only loyal to their teams, there will be a lack of teamwork and coordination.
It is a rigid structure where changes, innovations, and flexibility can be difficult to implement. An employee in any department may lack knowledge of information about all other departments. Managers tend to make decisions without consulting the department first, which can lead to problems. A department can become too autocratic and put its goals above those of the organization as a whole. With so many specialists involved in a process, it is difficult to pin the blame for a specific product or service malfunction on any individual.
Who Is Best Suited for a Functional Organizational Structure?
Larger companies are better suited to use the functional organizational structure, especially ones that produce just a few types of goods or services. Smaller companies may not need the structure or may find it too constraining. For projects in which the depth of knowledge is more important than the breadth of information, a functional organizational structure is appropriate. For instance, a fundamental research and development program is well-suited to a functional organizational structure since the project can capitalize on the expertise of the department.
The functional organizational structure helps organizations run their business and earn a profit by grouping employees based on their skills and expertise. It provides a clear hierarchy and minimizes confusion among employees who may be unsure who they are to report to. It is an efficient way to run a business but can have drawbacks as it can lead to a lack of communication between departments and unenthusiastic employees.
If you need help with learning more about a functional organizational structure, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel’s marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- What Does Company Structure Mean?
- Matrix Organizational Structure
- Definition of Organizational Structure and Culture
- Different Types of Business Organization Structure
- What Is the Organizational Structure of a Corporation?
- Organizational Communication
- Business Plan Management Structure: What You Need to Know
- Matrix Structure
- Can You Change Your Business Structure
- Employee Development
10.1 Organizational Structures and Design
- What are mechanistic versus organic organizational structures?
First, an organizational structure is a system for accomplishing and connecting the activities that occur within a work organization. People rely on structures to know what work they should do, how their work supports or relies on other employees, and how these work activities fulfill the purpose of the organization itself.
Second, organizational design is the process of setting up organizational structures to address the needs of an organization and account for the complexity involved in accomplishing business objectives.
Next, organizational change refers to the constant shifts that occur within an organizational system—for example, as people enter or leave the organization, market conditions shift, supply sources change, or adaptations are introduced in the processes for accomplishing work. Through managed change , leaders in an organization can intentionally shape how these shifts occur over time.
Finally, organizational development (OD) is the label for a field that specializes in change management. OD specialists draw on social science to guide change processes that simultaneously help a business achieve its objectives while generating well-being for employees and sustainable benefits for society. An understanding of OD practices is essential for leaders who want to maximize the potential of their organizations over a long period of time.
Together, an understanding of these concepts can help managers know how to create and direct organizations that are positioned to successfully accomplish strategic goals and objectives. 1
To understand the role of organizational structure, consider the experience of Justin, a young manager who worked for a logistics and transportation company. Their success at leading change in the United States gave their leaders the confidence that Justin could handle a challenging assignment: organize a new supply chain and distribution system for a company in Northern Europe. Almost overnight, Justin was responsible for hiring competent people, forming them into a coherent organization, training them, and establishing the needed infrastructure for sustained success in this new market.
If you were given this assignment, what would you do? How would you organize your employees? How would you help them understand the challenge of setting up a new organization and system? These are the kinds of questions that require an understanding of organizational structure, organizational design, organizational change, and organizational development.
One of the first issues Justin will need to address deals with how they will organize the system. “The decisions about the structure of an organization are all related to the concept of organizational design. There are two fundamental forms of structure to remember when designing an organization.
To address these questions, we need to be familiar with two fundamental ways of building an organization.
The formal organization is an officially defined set of relationships, responsibilities, and connections that exist across an organization. The traditional organizational chart, as illustrated in Exhibit 10.2 , is perhaps the most common way of depicting the formal organization. The typical organization has a hierarchical form with clearly defined roles and responsibilities.
When Justin sets up the formal organization, they will need to design the administrative responsibilities and communication structures that should function within an organizational system. The formal systems describe how flow of information and resources should occur within an organization. To establish the formal organization, they will identify the essential functions that need to be part of the system, and they will hire people to fill these functions. They will then need to help employees learn their functions and how these functions should relate to one another.
The informal organization is sometimes referred to as the invisible network of interpersonal relationships that shape how people actually connect with one another to carry out their activities. The informal organization is emergent, meaning that it is formed through the common conversations and relationships that often naturally occur as people interact with one another in their day-to-day relationships. It is usually complex, impossible to control, and has the potential to significantly influence an organization’s success.
As depicted in Exhibit 10.3 , the informal organization can also be mapped, but it is usually very different than the formal organization. The chart you see in this example is called a network map, because it depicts the relationships that exist between different members of a system. Some members are more central than others, and the strength of relationships may vary between any two pairs or groups of individuals. These relationships are constantly in flux, as people interact with new individuals, current relationships evolve, and the organization itself changes over time. 2
The informal organization in Justin’s design will form as people begin interacting with one another to accomplish their work. As this occurs, people will begin connecting with one another as they make sense of their new roles and relationships. Usually, the informal organization closely mirrors the formal organization, but often it is different. People quickly learn who the key influencers are within the system, and they will begin to rely on these individuals to accomplish the work of the organization. The informal organization can either help or hinder an organization’s overall success.
In sum, the formal organization explains how an organization should function, while the informal organization is how the organizational actually functions. Formal organization will come as Justin hires and assigns people to different roles. They can influence the shape of the informal organization by giving people opportunities to build relationships as they work together. Both types of structures shape the patterns of influence, administration, and leadership that may occur through an organizational system.
As we continue our discussion of structure and design, we will next examine different ways of understanding formal structure.
Types of Formal Organizational Structures
Now, Justin will need to choose and implement an administrative system for delegating duties, establishing oversight, and reporting on performance. They will do this by designing a formal structure that defines the responsibilities and accountability that correspond to specific duties throughout an organizational system. In this section, we’ll discuss the factors that any manager should consider when designing an organizational structure.
Bureaucracy
One of the most common frameworks for thinking about these issues is called the bureaucratic model . It was developed by Max Weber, a 19th-century sociologist. Weber’s central assumption was that organizations will find efficiencies when they divide the duties of labor, allow people to specialize, and create structure for coordinating their differentiated efforts, usually within a hierarchy of responsibility. He proposed five elements of bureaucracy that serve as a foundation for determining an appropriate structure: specialization, command-and-control, span of control, centralization, and formalization. 3
Specialization
The degree to which people are organized into subunits according to their expertise is referred to as specialization —for example, human resources, finance, marketing, or manufacturing. It may also include specialization within those functions. For instance, people who work in a manufacturing facility may be well-versed in every part of a manufacturing process, or they may be organized into specialty units that focus on different parts of the manufacturing process, such as procurement, material preparation, assembly, quality control, and the like.
Command-and-Control
The next element to consider is the reporting and oversight structure of the organization. Command-and-control refers to the way in which people report to one another or connect to coordinate their efforts in accomplishing the work of the organization.
Span of Control
Another question addresses the scope of the work that any one person in the organization will be accountable for, referred to as span of control . For instance, top-level leaders are usually responsible for all of the work of their subordinates, mid-level leaders are responsible for a narrower set of responsibilities, and ground-level employees usually perform very specific tasks. Each manager in a hierarchy works within the span of control of another manager at a level of the organization.
Centralization
The next element to consider is how to manage the flows of resources and information in an organization, or its centralization . A highly centralized organization concentrates resources in only one or very few locations, or only a few individuals are authorized to make decisions about the use of resources. In contrast, a diffuse organization distributes resources more broadly throughout an organizational system along with the authority to make decisions about how to use those resources.
Formalization
The last element of bureaucracy, formalization , refers to the degree of definition in the roles that exist throughout an organization. A highly formalized system (e.g., the military) has a very defined organization, a tightly structured system, in which all of the jobs, responsibilities, and accountability structures are very clearly understood. In contrast, a loosely structured system (e.g., a small, volunteer nonprofit) relies heavily on the emergent relationships of informal organization.
Mechanistic and Organic Structures
Using the principles of bureaucracy outlined above, managers like Justin have experimented with many different structures as way to shape the formal organization and potentially to capture some of the advantages of the informal organization. Generally, the application of these principles leads to some combination of the two kinds of structures that can be seen as anchors on a continuum (see Table 10.1 ).
On one end of the continuum is mechanistic bureaucratic structure . This is a strongly hierarchical form of organizing that is designed to generate a high degree of standardization and control. Mechanistic organizations are often characterized by a highly vertical organizational structure , or a “tall” structure, due to the presence of many levels of management. A mechanistic structure tends to dictate roles and procedure through strong routines and standard operating practices.
In contrast, an organic bureaucratic structure relies on the ability of people to self-organize and make decisions without much direction such that they can adapt quickly to changing circumstances. In an organic organization, it is common to see a horizontal organizational structure , in which many individuals across the whole system are empowered to make organizational decision. An organization with a horizontal structure is also known as a flat organization because it often features only a few levels of organizational hierarchy.
The principles of bureaucracy outlined earlier can be applied in different ways, depending on the context of the organization and the managers’ objectives, to create structures that have features of either mechanistic or organic structures.
For example, the degree of specialization required in an organization depends both on the complexity of the activities the organization needs to account for and on the scale of the organization. A more organic organization may encourage employees to be both specialists and generalists so that they are more aware of opportunities for innovation within a system. A mechanistic organization may emphasize a strong degree of specialization so that essential procedures or practices are carried out with consistency and predictable precision. Thus, an organization’s overall objectives drive how specialization should be viewed. For example, an organization that produces innovation needs to be more organic, while an organization that seeks reliability needs to be more mechanistic.
Similarly, the need for a strong environment of command-and-control varies by the circumstances of each organization. An organization that has a strong command-and-control system usually requires a vertical, tall organizational administrative structure. Organizations that exist in loosely defined or ambiguous environments need to distribute decision-making authority to employees, and thus will often feature a flat organizational structure.
The span of control assigned to any specific manager is commonly used to encourage either mechanistic or organic bureaucracy. Any manager’s ability to attend to responsibilities has limits; indeed, the amount of work anyone can accomplish is finite. A manager in an organic structure usually has a broad span of control, forcing her to rely more on subordinates to make decisions. A manager in a mechanistic structure usually has a narrow span of control so that they can provide more oversight. Thus, increasing span of control for a manager tends to flatten the hierarchy while narrowing span of control tends to reinforce the hierarchy.
Centralization addresses assumptions about how an organization can best achieve efficiencies in its operations. In a mechanistic structure, it is assumed that efficiencies will occur in the system if the resources and decisions flow through in a centralized way. In an organic system, it is assumed that greater efficiencies will be seen by distributing those resources and having the resources sorted by the users of the resources. Either perspective may work, depending on the circumstances.
Finally, managers also have discretion in how tightly they choose to define the formal roles and responsibilities of individuals within an organization. Managers who want to encourage organic bureaucracy will resist the idea of writing out and tightly defining roles and responsibilities. They will encourage and empower employees to self-organize and define for themselves the roles they wish to fill. In contrast, managers who wish to encourage more mechanistic bureaucracy will use tools such as standard operating procedures (SOPs) or written policies to set expectations and exercise clear controls around those expectations for employees.
When a bureaucratic structure works well, an organization achieves an appropriate balance across all of these considerations. Employees specialize in and become highly advanced in their ability to perform specific functions while also attending to broader organizational needs. They receive sufficient guidance from managers to stay aligned with overall organizational goals. The span of control given to any one manager encourages them to provide appropriate oversight while also relying on employees to do their part. The resources and decision-making necessary to accomplish the goals of the organization are efficiently managed. There is an appropriate balance between compliance with formal policy and innovative action.
Business Structures
Aside from the considerations outlined above, organizations will often set structures according to the functional needs of the organization. A functional need refers to a feature of the organization or its environment that is necessary for organizational success. A business structure is designed to address these organizational needs. There are two common examples of functional structures illustrated here.
Product structures exist where the business organizes its employees according to product lines or lines of business. For example, employees in a car company might be organized according to the model of the vehicle that they help to support or produce. Employees in a consulting firm might be organized around a particular kind of practice that they work in or support. Where a functional structure exists, employees become highly attuned to their own line of business or their own product.
Geographic structures exist where organizations are set up to deliver a range of products within a geographic area or region. Here, the business is set up based on a territory or region. Managers of a particular unit oversee all of the operations of the business for that geographical area.
In either functional structure, the manager will oversee all the activities that correspond to that function: marketing, manufacturing, delivery, client support systems, and so forth. In some ways, a functional structure is like a smaller version of the larger organization—a smaller version of the bureaucracy that exists within the larger organization.
One common weakness of a bureaucratic structure is that people can become so focused on their own part of the organization that they fail to understand or connect with broader organizational activities. In the extreme, bureaucracy separates and alienates workers from one another. These problems can occur when different parts of an organization fail to communicate effectively with one another.
Some organizations set up a matrix structure to minimize the potential for these problems. A matrix structure describes an organization that has multiple reporting lines of authority. For example, an employee who specializes in a particular product might have both the functional reporting line and a geographic reporting line. This employee has accountability in both directions. The functional responsibility has to do with her specialty as it correlates with the strategy of the company as a whole. However, her geographic accountability is to the manager who is responsible for the region or part of the organization in which she is currently working. The challenge is that an employee may be accountable to two or more managers, and this can create conflict if those managers are not aligned. The potential benefit, however, is that employees may be more inclined to pay attention to the needs of multiple parts of the business simultaneously.
Concept Check
- What is an organizational structure?
- What are different types of organizational structures?
- What is organizational design?
- What concepts should guide decisions about how to design structures?
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-management/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: David S. Bright, Anastasia H. Cortes
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Principles of Management
- Publication date: Mar 20, 2019
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-management/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-management/pages/10-1-organizational-structures-and-design
© Jan 9, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

- Calculators
- Swot Analysis
- Pestle Analysis
- Five Forces Analysis
- Organizational Structure
- Copywriting
- Research Topics
- Student Resources
Services We Provide

Resources We Provide

Login / Register

- A Comprehensive Guide on Functional Organizational Structure
- An Exegesis Study on the Types of Organizational Structures
- What is Functional Organizational Structure
As the term depicts, the functional organizational structure is a type of organizational structure that groups the employees based on their roles, skills, and specialty. Under this organizational structure, different departments are established and each department head is responsible to manage the performance of employees in the department. Moreover, each employee reports directly to the departmental head or manager in the specific functional area. Thus, top-level managers centrally coordinate and manage the different departments. Hence, the use of this organizational structure helps to ensure a higher degree of specialization. The different functions in the organization can include production, marketing, research, IT, human resource, etc.
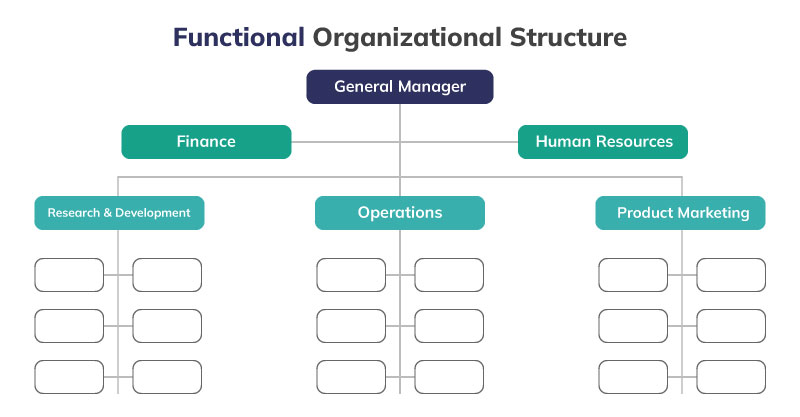
The use of this organizational structure is mainly suitable for the organization that is centralized i.e. majority of decisions are taken at the top level and a degree of specialization is needed in the organizational products and services.
Table of Contents
- Advantages of Functional organizational structure
- Disadvantages of Functional organizational structure
- Example of Functional organizational structure
Advantages of Functional Organizational Structure
Till now, you must have got the idea that the functional organizational structure includes structuring organizational processes in a manner that ensures grouping of employees with similar skills and knowledge together. Some of the advantages of the functional organizational structure are discussed as follows-
Improved productivity- The functional organizational structure helps to enhance the productivity of the organization as the individuals in the functional organizational structure having specialized skills are grouped which helps them to work quickly and efficiently. Moreover, all the employees are engaged in performing only the tasks in which they are proficient which also helps in ensuring higher productivity.
Enhance employee skills- The employees in the functional organizational structure work under experienced managers which helps to enhance the skills and abilities of the employees. Moreover, the employees working in teams also get the opportunity to learn from the soft skills and abilities of other employees.
Clarity- The functional organizational structure also helps to ensure greater clarity in the organizational operations as each departmental head is held responsible for managing the performance of the employees in the same department. Moreover, the collaboration of the employees with similar skill sets also helps to improve the work effectiveness of the employees and clarity of operations.
Disadvantages of Functional Organizational Structure
You must be thinking that the functional organizational structure is suitable for all organizations. However, this is not true in all cases. The functional organizational structure also suffers from various disadvantages which are discussed as follows-
Hindered decision making- We all know that the organizations in the current times thrive to maintain flexibility in the organizations. However, we need to consider that the employees working under the functional organizational structure are required to seek approval for various decisions from the management which increases the chance of delays in the decision making.
Communication barriers- In the functional organizational structure, there is limited communication in the cross-functional departments which can also cause problems in innovation in the organization. For instance, the marketing department may fail to communicate the product needs of the customers to the production department due to a lack of interdepartmental communication in the functional organizational structure which can then lead to the inability of the organization to effectively meet the customer needs.
Silos within an organization- The organizational silos can be defined as the business units or divisions operating independently. The chance of silos in the organization operating under the functional organizational structure is very high as each functional department may operate independently under the functional organizational structure.
Unhealthy competition- You may be surprised by the fact that the functional organizational structure can cause unhealthy competition within the organization as each department may have its own goals and may work towards achieving the department-specific goals. This can prompt competition between the departments and can deviate the organizational operations from the organizational goals.
Example of Functional Organizational Structure
The best example of the functional organizational structure is that of Apple as Apple does not divide its operations based on the product line but instead focuses on various functions like marketing, retail, engineering, and operations. The company employs a unitary organizational form where the operations are organized around the areas of expertise rather than the different types of products. This helps Apple to maintain specialization in its product and ensure manufacturing of higher quality products and services. The different areas of expertise of Apple include product marketing, operations, hardware engineering, software engineering, hardware Technologies, etc. The organizational structure of Apple is further represented as follows-
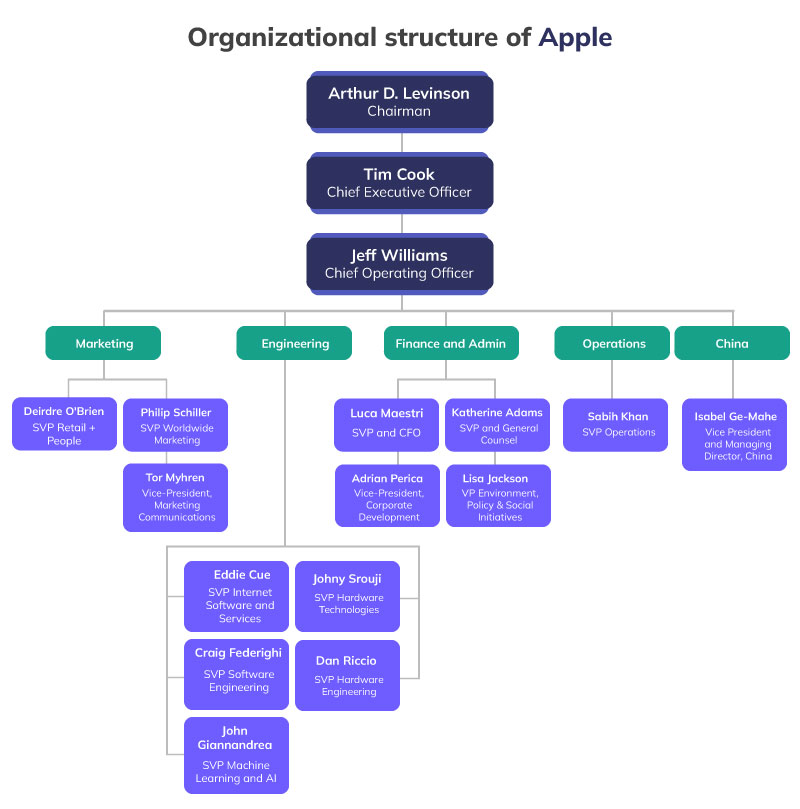
The organizational structure of Apple represents that the operations of Apple are organized in different departments based on the functions and each department has its role and responsibility. For instance, the marketing department of Apple is responsible to identify the customer needs and identify the products that can best meet the market needs of the customers. The designing team at Apple is held responsible for crafting the appearance of the Apple products like the Apple Macintosh computer line. The software engineering department is held responsible for developing the operating system OS and other software products such as iWork.
Jeff Williams, Chief Operating Officer is responsible for managing the performance of departments. The different departments of Apple include Marketing, engineering, finance and admin, and operations. Moreover, each department is further headed by the upper management team and vice presidents who then supervise the performance of employees. Thus, the functional organizational structure helps the organization to effectively manage the organizational operations in different departments and areas of expertise along with effective task allocation, coordination, and supervision. The individual divisions departments under the expertise-focused hierarchy system of Apple also enjoy autonomy in various decisions and processes which further enable them to perform effectively and help Apple to achieve a market-leading position for its products.
What types of industries or sectors commonly adopt a Functional Organizational Structure?
Industries that rely on specialized expertise, such as manufacturing, healthcare, and professional services, often adopt a Functional Organizational Structure.
How does a Functional Organizational Structure differ from other organizational structures like Matrix or Divisional?
A Functional Organizational Structure groups employees based on their specialized functions, while a Matrix Structure combines functional and project-based teams. A Divisional Structure groups employees by products, regions, or customer segments.
Next Structure
Copyright © 2023 CrowJack. All Rights Reserved
Functional Structure vs. Matrix
What's the difference.
Functional structure is a traditional organizational structure where employees are grouped based on their specific functions or areas of expertise. Each department or function operates independently and has its own hierarchy. On the other hand, matrix structure is a more flexible and dynamic organizational structure where employees are grouped based on both their functions and projects. In a matrix structure, employees report to both a functional manager and a project manager, allowing for better coordination and communication across different functions. While functional structure promotes specialization and efficiency within each department, matrix structure encourages collaboration and cross-functional teamwork.
Further Detail
Introduction.
Organizational structure plays a crucial role in determining how a company operates and achieves its goals. Two commonly used structures are functional structure and matrix structure. While both have their own advantages and disadvantages, understanding their attributes can help organizations make informed decisions about which structure best suits their needs. In this article, we will compare the attributes of functional structure and matrix structure, highlighting their key differences and similarities.
Functional Structure
Functional structure is a traditional organizational design where employees are grouped based on their specialized functions or areas of expertise. Each department focuses on a specific function, such as marketing, finance, operations, or human resources. Here are some key attributes of functional structure:
- Clear Specialization: Functional structure allows employees to specialize in their respective areas, leading to deep expertise and efficiency within each department.
- Clear Reporting Lines: In this structure, employees report to a single manager within their functional department, ensuring clear lines of authority and accountability.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Functional structure enables efficient allocation of resources as each department can focus on its specific function and optimize resource utilization accordingly.
- Enhanced Skill Development: Employees have the opportunity to develop specialized skills within their functional area, leading to career growth and expertise.
- Limited Cross-Functional Collaboration: Due to the siloed nature of functional structure, cross-functional collaboration may be limited, potentially hindering innovation and communication between departments.
Matrix Structure
Matrix structure is a more complex organizational design that combines functional and project-based reporting lines. It aims to leverage the benefits of both functional specialization and cross-functional collaboration. Here are some key attributes of matrix structure:
- Dual Reporting Lines: In matrix structure, employees have two reporting lines: one to their functional manager and another to the project or product manager. This allows for a balance between functional expertise and project-specific goals.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Matrix structure promotes collaboration across departments, as employees from different functions work together on projects, sharing knowledge and expertise.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Matrix structure enables organizations to quickly adapt to changing market conditions or project requirements by assembling cross-functional teams with the necessary skills and expertise.
- Improved Communication: With employees from different functions working closely together, matrix structure fosters better communication and information sharing, leading to more informed decision-making.
- Potential for Role Confusion: The dual reporting lines in matrix structure can sometimes lead to role confusion or conflicts, as employees may receive conflicting instructions or priorities from their functional and project managers.
Now that we have explored the attributes of both functional structure and matrix structure, let's compare them in various aspects:
Organizational Focus
In functional structure, the focus is primarily on specialized functions or departments. Each department operates independently, optimizing its function's performance. In contrast, matrix structure emphasizes both functional expertise and project-specific goals, striking a balance between the two.
Communication and Collaboration
Functional structure may limit cross-functional collaboration due to its siloed nature. Communication primarily occurs within departments, potentially hindering information sharing and innovation. On the other hand, matrix structure promotes collaboration and communication across functions, fostering a more integrated and collaborative work environment.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Functional structure may struggle with flexibility and adaptability, as changes or new projects may require reorganizing departments or creating new ones. Matrix structure, on the other hand, offers greater flexibility and adaptability by assembling cross-functional teams based on project requirements, allowing organizations to respond quickly to market changes.
Decision-Making Authority
In functional structure, decision-making authority lies primarily with functional managers who have expertise in their respective areas. On the contrary, matrix structure involves shared decision-making between functional and project managers, considering both functional requirements and project goals.
Employee Development
Functional structure provides employees with the opportunity to develop specialized skills within their functional area, leading to career growth and expertise. Matrix structure, however, offers employees the chance to develop a broader skill set by working on cross-functional projects, enhancing their versatility and adaptability.
Choosing the right organizational structure is crucial for any company's success. Functional structure and matrix structure are two popular options, each with its own attributes and implications. Functional structure offers clear specialization and efficient resource allocation but may limit cross-functional collaboration. On the other hand, matrix structure promotes collaboration, flexibility, and adaptability but can lead to role confusion. Ultimately, organizations must carefully consider their goals, culture, and industry dynamics to determine which structure aligns best with their needs and objectives.
Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or facts. Please report any issues.

Benefits & Disadvantages of a Functional Organizational Structure
- Small Business
- Business Models & Organizational Structure
- Organizational Structure
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
Advantages & Disadvantages of Team-Based Organizations
What are the disadvantages and advantages of using employment teams in an organization, models of organizational structure.
- Functional Structure Organization Strength & Weakness
- Strengths & Weaknesses of Cross Functional Teams
A functional organizational structure is the most common of the three organizational structures adopted by most companies. Companies organized by function group employees according to their activities in the organization. Human Resources employees have their own HR department, for example, as do employees working in sales, marketing, finance and technical support. Organizing a company in this way has inherent advantages and disadvantages.
Advantage: Specialization
The most obvious advantage of a functional organization is that grouping employees by specialization ensures a dependable level of departmental competence. This is particularly so for large organizations that have several functional levels within a department – a particular tech group that follows up on tech issues not resolved by the primary telephone tech support group, for example.
Membership in this group could require a bachelor's degree in computer science, a manager's recommendation and a minimum number of years of field experience. This ensures that support issues moved up to the follow-up group are handled by fully qualified personnel, which increases customer satisfaction and retention.
Advantage: Operational Speed
A related benefit of this kind of organizational specialization is operational speed. By and large, a senior tech is going to handle a support problem faster than someone with less experience. There're probably going to train new staff members faster, too.
Advantage: Operational Clarity
Segregating the workforce according to function clarifies organizational responsibility and allocation of tasks. This tends to eliminate duplication of assignments that waste time and effort and makes it easier for management to direct work to appropriate employees.
Disadvantage: Segregation
Having departments populated by employees specializing in specific work areas means that teams become siloed. Employees in different teams do not get the opportunity to meet and share perspectives, which can be harmful for the progress of the business in the long run.
Disadvantage: Weakening of Common Bonds
Having a common organizational purpose improves employee morale and performance and is an important predictor of organizational success. When each group of specialists in a functional organization is relatively isolated, the common bond that emphasizes a single overarching organizational purpose is almost inevitably weaker than in an organization where different kinds of employees regularly interact.
Disadvantage: Lack of Coordination
In a perfect functional organization, each group's tasks would require no input from other functional groups, but this is often not the case. As communication becomes increasingly dominant in organizations, isolated groups may underperform or even fail because they have no institutionally recognized way of communicating needs and issues to other functional groups that might have helped.
In some instances, managers of other functional groups may not respond helpfully or in a timely way because "it's not our problem." By the time the need for cooperation has been established, the moment when cooperation would have been most effective may already have passed.
Disadvantage: Territorial Disputes
A further disadvantage of a functional organization closely related to the failure of functional groups to cooperate with one another is the possibility of territorial disputes. These disputes may have to do with disagreements over goals, budgetary competition or any number of issues that stem from a clash of egos that occur when each department has its own separate functional structure or where a strong sense of a common purpose is lacking.
- LetsLearnFinance: Advantages and Disadvantages of Functional Organization
- Master of Projects Academy: Organizational Structure | 3 Common Types of Organization Structure in Corporate Companies
I am a retired Registered Investment Advisor with 12 years experience as head of an investment management firm. I also have a Ph.D. in English and have written more than 4,000 articles for regional and national publications.
Related Articles
Features of a functional organization structure, describe each of the three major types of organizational structure, what is an autonomous work group, types of team project organization, the advantages of group performance awards, functional organizational structure advantages, the organizational structure of a company, how to improve cross-functional teamwork, what is the difference between a flat organization & a matrixed organization, most popular.
- 1 Features of a Functional Organization Structure
- 2 Describe Each of the Three Major Types of Organizational Structure
- 3 What Is an Autonomous Work Group?
- 4 Types of Team Project Organization
The Amazon Firm’s Organizational Structure Essay
Being one of the largest multinational corporations in the world, Amazon.com has an organizational structure that reflects the complexity of governing a business on that scale. First and foremost, it is important to note that Amazon’s structure is functional rather than divisional. The company creates departments, such as “worldwide Consumer,” Web Services,” or “Media & Entertainment” based on their function rather than geographical affinity (Amazon, 2021). The advantage of this model is that it offers greater centralization than the divisional structure, in which regional divisions may even begin conflicting with each other to the detriment of global value creation (Luo & Shenkar, 2017). At the same time, functional structure, especially in the business of Amazon’s size, often comes at the cost of restricted adaptability to the specific conditions of regional markets (Luo & Shenkar, 2017). In short, Amazon’s functional structure reflects the leadership’s preference for centralized control and global guidance as opposed to the greater autonomy of regional divisions.
This preference also manifests in the company’s dedication to ensuring stable long-term leadership. Amazon is known for very limited turnover when it comes to its principal executives, such as Jeff Bezos, Andy Jassy, Jamie Gorelick, and others (Kim, 2019). Moreover, research indicates that the high level of trust and camaraderie built over the years among Amazon’s senior managers is one of the defining features of the company’s organizational structure (Kim, 2019). Maintaining a cohesive team with very little turnover signifies Amazon’s dedication to centralization and concentration of control on the top level at the expense of unit autonomy. With this in mind, one may conclude that Amazon maintains a functional organizational structure with a strong emphasis on centralization and top-down control.
Amazon. (2021). Org chart – The official board . Web.
Kim. E. (2019). Amazon’s executive org chart, revealed . CNBC. Web.
Luo, Y., & Shenkar, O. 92017). The multinational corporation as a multilingual community: Language and organization in a global context. In M. Y. Branen & T. Mughan (Eds.), Language in International Business (pp. 59-92). Springer.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, November 28). The Amazon Firm’s Organizational Structure. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-amazon-firms-organizational-structure/
"The Amazon Firm’s Organizational Structure." IvyPanda , 28 Nov. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/the-amazon-firms-organizational-structure/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'The Amazon Firm’s Organizational Structure'. 28 November.
IvyPanda . 2022. "The Amazon Firm’s Organizational Structure." November 28, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-amazon-firms-organizational-structure/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Amazon Firm’s Organizational Structure." November 28, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-amazon-firms-organizational-structure/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Amazon Firm’s Organizational Structure." November 28, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-amazon-firms-organizational-structure/.
- Jeff Bezos’ Managerial Philosophy
- “Invent and Wonder” by Jeff Bezos: Book Review
- Servant Leadership of Jeff Bezos
- Jeff Bezos: The Richest Man in Modern History
- Jamie Dodge Company’s Entry into Japanese Market
- Jeff Bezos and Gladwell’s Success Principles
- Invent and Wander: The Collected Writing of Jeff Bezos
- Jeff Bezos's Leadership and the Amazon Revolution
- Interesting Facts in “Invent & Wander” by Jeffrey Bezos
- "Bullied: The Jamie Nabozny Story" Documentary
- Target Costing Extent Profit: Critical Report
- Cameron Mechanical & Automation, Inc.
- Walmart Organizational Structure
- Holocracy, Heterarchy, and Fractal Organisation
- Business Plan on Fawz Olympic Academy

ESSAY SAUCE
FOR STUDENTS : ALL THE INGREDIENTS OF A GOOD ESSAY
Essay: Organisational structure
Essay details and download:.
- Subject area(s): Management essays
- Reading time: 9 minutes
- Price: Free download
- Published: 24 November 2015*
- File format: Text
- Words: 2,568 (approx)
- Number of pages: 11 (approx)
Text preview of this essay:
This page of the essay has 2,568 words. Download the full version above.
INTRODUCTION AND DEFINATION OF ORGANIZATION According to the (council dictionary fourth edition, p 1103) organisation means means union organization comprising parts and other people in a body (association, corporation, etc.) for specific purposes (mutual interest ). According to (Professor Schein (1973), the organization serves as a rational adjustment of human activity in order to achieve the goals set by the division of labor, and also functions through authoritative hierarchy ) . (Ralph Davis (1951) also quote that the organization is a group of a number of a group of large men who worked under one head or manager to achieve an objective) Chester Barnard in his book, “The Function of the Executive” published by Harvard University Press, 1938, said that the organization is a system of personal power activity, consciously coordinated to achieve organsation goal. (Ralph M. Stogdill, the author of “Dimensions of Organizational Design” output of Pittsbury University Press, 1966,) defines the organization as a system of work that is done with structure that contains position and feelings are shaped and determined in advance of the role and the position filled by actors or workers. However what is important in the definition of organization is that it is a group that has certain parts in it which consists of a group of people who work together and help each other and their surroundings are interwined with each other in order to achieve the objectives and goals of individuals, groups or organization. Based on the chart, the Department of YAYASAN TERENGGANU has established the functional structure of different tasks or work to achieve the objectives and goals of the plan. Refering to a functional structure that has formed above, the Director General of YAYASAN TERENGGANU has the highest function power where he is responsible for administering and directing an organization with established policies, rules, working methods, making legal advise, coordinate the activities of the organization, department or unit / interior and goals of the organization , There are two parts function under the direct order Director General which is the Deputy Director (Operations) and Director General (Development) where both the function serves as chairman of the unit / section below. The parts have different functions or tasks workflow. In addition, the functional structure is also designed to enable many individuals with expertise and experience in controlling and supervising the work of each taskforce . Besides, it can provide opportunities for member organizations to learn from other people and become more efficient in their job. Thus, indirectly it has facilitated the process of controlling and adjusting the good work. In addition, the functional structure has been set up to facilitate the work and service operation which is designed to run more smoothly. In addition, the functional structure serves as the focus and gather members or employees to facilitate organisational needed skills and use certain skills where the staff are needed. This functional structure allows the division of labor as a whole and indirectly facilitate the process of communication and interaction that can improve the ability and efficiency in producing the best technique in performing its obligations and is the best way to resolve any problem Moreover, it also facilitates the performance of some top managers know- how divisions, units or departments within an organization. The work done or carried as a whole can be adjusted for all activities and skills will be classified or grouped in one place / divisions under one head. In addition, the division function makes supervision easier because each unit has a chief and specific skills. In addition, the function can be used according to the change of the work, fast and effectively done
THE BENEFITS OF FUNCTIONAL STRUCTURE 1) The task of supervision becomes easier because each head of department has and equipped with specific skills. 2) Any functional problem between units, departments and divisions can be easily identified and brought to attention immediately 3) Resources can be used efficiently 4) The functions and individual position is clear. 5) Expertise, knowledge, skills and experience can be consolidated or combined among individuals.
THE DISADVANTAGES OF FUNCTIONAL STRUCTURE 1) The response time might be slow and interupted because of waiting above from higher authority 2) It does not encourage innovation between staff and its perspective of view is narrow 3) Recaiving feedback may be slow because of the units, departments and divisions current un-done task 4) It contributes unto the lack of communication between units, departments and divisions. 5) It is weak in addressing all individual needs because of the slowness might occured in terms of action plan that can leads to un-achievable organisational objectives
Retrieved from : http://www.airasia.com/iwov-resources/my/common/pdf/AirAsia/IR/annual-report-2007b.pdf1.2 THE GEOGRAFIC STRUCTURE OF AIR ASIA ORGANISATIONAL BRANCHES IN VARIOUS COUNTRIES
The organizational structure of geography divide the workers by geographical area designated as below at different part of its bracnches operation . It was formed on the request of customers who are far away or outside an organization’s operations center. The organizational structure of geography in operation among different staff is responsible for carrying out business activities in designated locations. The chart below shows an example of the organization of geographical structure adopted by The Air Asia Management . At below of the image, I also present the advantages and disadvantages of the organizational structure of geography. In this geographic structure, units and divisions based on the places and the geographical area. This structure is suitable when companies or offices operate in many different geographical areas in which the state, religion and country. In addition, the geographical structure is the coordination of work and workers in the unit or where different parts are all responsible for each of the organization or activity in a specific geographical area. Based on the geographical structure chart of the Air Asian Management , it has expanded its production in some specific geographical area. The advantage gained is the company able to expand its business across borders including financial markets, social relationships and the resulting product or products to the local market. In addition, the company is able to foster a closer relationship between places worldwide. The company is also able to expand the understanding and friendship between the peoples of the world with opportunities for personal conversion that is progressively emerged. Thus indirectly the company has formed or able to meet its own slogan which is “Now, Everyone Can Fly”. In addition, the company is also able to improve the standards prescribed or used in the ranking of global requirements such as the standards prescribed or used in the ranking of global requirements such as copyright law. The company on the other hand is also able to shape the universal’s value and get the technology needed to help in spreading its market (marketing) throughout the world. The company is also conducting management activities between the border and the processes of development which will be adopted when the emergence of a global market in the future. In addition, these companies are also more frequent use of advanced technologies because it often built connection or get connected between the border and to develop a global telecommunications infrastructure
ADVANTAGES OF GEOGRAFIC STRUCTURE 1) The whole organisation is able to use the expertise of all staff in ‘worldwide’ speaking according to the geographical location of the organization. 2) Products and services can be produced and marketed to different countries thus, make marketing job easier and effective 3) It is able introduce the organization to the world. 4) The organization becomes larger. 5) ) It can reduce organisation costs by putting the resources of the organization closer to the geographical area specified.
DISADVANTAGES OF GEOGRAFICAL STRUCTURE 1) There might be difficulty in coordinating the departments in the geographical area because its location that isfar from each other.
2) Lack of control might occur to each geographical department of the organization
3) Redundancies can happen
4) It can not guarantee the full loyalty of employees to the organisation
5) The existence of a change in products ( travelling ) and services as cultural factors, physical and weather
Retrieved from : http://kamarularnizam.blogspot.com/2015/02/contoh-pbs-pengajian-perniagaan.html
1.3 THE PRODUCT STRUCTURE OF SAMSUNG COMPANY The product is the output of an organization that can be produced in the form of goods or service . This refers to the coordination of work between workers in a unit or the other. This means each unit hold different responsibility to produce the output of products or services that have been set. The advantage of this section is to allow employers and employees to broaden their experience and expertise in relation to the overall activities of the products or services to be offerd. Accordingly, this allows management to assess the performance of work done in each work unit. From the image of product structure below , SAMSUNG company is capable of designing and producing a wide range of different products which generally meet the needs of everyone. All of these products are produced in different part or unit of work and function. Each division will be headed by a chairman and a chief that is responsible for coordinating the work or production activities as well as other activities such as purchasing, marketing and distribution of any products. Products produced by SAMSUNG company headed by a chairman with responsibility to ensure the product is produced in accordance with the criteria set and ensure marketing, distribution is done correctly. Thus working to produce each product is easy because each product will be distributed to the head that will manage it and supervise it The separation of individual products and these products have facilitated the production of such products. This separation is important because it can generate and collect ideas and brilliant creative in producing these products to market s. Each product has a function, purpose, use, benefits and advantages of its own. The resulting product is equipped with features such as it is psysicalll attractive, colorful, and the materials used to form the product . ( in eaxample: how a new I-Phone is formed with its colourful structure and its function) Apart from the physical characteristics SAMSUNG companies also produce products based on non-physical characteristics such the image, concept and its flexibility to use. These features make the users and buyers interested in purchasing. With the diversity of the products it can also solve the needs of purchasers or users and the importance of such a requirement in other words, the higher term needs of a person, the higher the consumer is willing to buy The company further then makes high quality products and good price comparable with other competitors after a thorough discussion of each of the products made
THE BENEFITS OF PRODUCTS STRUCTURE 1) Managers and employees can develop their talents, their experience and expertise in product development activities. 2) Managers in every department can monitor the activity of each unit and staff in the production of the product under operation. 3) A very clear lines of responsibility between departments. 4) The structure of the product is very suitable for large-sized organizations. 5) It is appropriate for organizations that produce various kind of products
THE DISADVANTAGES OF PRODUCTS STRUCTURE 1) The Manager is focused only in products management 2) There is a lack of communication between departments and its staff 3) The cost of the operation is big because each department has its own managers and experts. 4) It requires a high amount of workforces . 5) It does not promote cooperation which is a very important value because each department is of different expertise
Retrieved from : http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/rational/library/apr05/hanford/
1.4 MATRIX STRUCTURE OF AN ORGANISATION DOING SITE PROJECT( IBM INTERNATIONAL COMPANY
Matrix structure is a result of two or more of the combined organization at the same time and the matrix structure is suitable for use when an organization has to handle a large project or task at a time. It is very complicated and complex structure as of individuals from different organizational structures work together to control and ensure the success of a project to achieve the intended purpose. There are some factors that distinguish this matrix structure that differentiates with other structures such workers report and work-related contact of two ifferent supervisors or managers. “Matrix structure developed as a way to improve horizontal coordination and information sharing” (Richard. L Daft, 2008). Managers have a responsibility to ensure the success of the projects undertaken while the departments of other acts to maintain technical competence in their work. (Harold Kerzner, 2003) also quote that there were certain rules that exist for the construction of a matrix structure 1) “participant must spend full time on this project to ensure the loyalty” 2) “there must be good communication channels between managers and independent access” 4) “there must be a quick and effective methodto resolve the conflict ”
For organizations like this ( image 1.4 ) that are experts iin commissioning employees from different units and parts to perform tasks for one or more projects led by a project manager. The project was carried out on a temporary or contract where its members consist of different functional departments that collaborate in carrying out the project. In this structure, the manager will be responsible to his supervisor or the head. There are lots of advantages to be obtained. Including the presence of matrix functions provide flexibility (flexibility) to the organization. Besides, it enable the employee to discipline themselves to do two or more tasks provided with full responsibility. It also stimulates the matrix function of co-operation between the employees and other employees in two or more work done. Among other advantages derived from this organizational structure is that they can learn new skill at one time during the working process. Matrix organizational structure also allows them to transfer skills to the other participant workers to the areas that are and this in turns help when desperation of skills workes are in demand in certain areas. In addition, the matrix structure of this organization can strengthen the relationship between each worker because they are connected and can carry out their duties in accordance with the requirements set. This organizational matrix structure will also be able to further develop desired goals and is of good use when the organisation need to use two or more employees to perform two or more tasks / work in an organosation ADVANTAGES OF MATRIX STRUCTURE IN AN ORGANISATION 1) It encourage the staff to use resources more effectively. 2) It provides more accurate and extensive information. 3) Collaboration between disciplines and expertise is available to all sections. 4) Flexibility and adaptation to the changing environment. 5) It fosters the spirit of cooperation which is an important asset for all organisation
THE DISADVANTAGES OF A MATRIX STRUCTURED’S ORGANISATION 1) Confusion can happen because there are two directions. 2) It can be a complicated approach because instructions can come between the two sides of different departments 3) More meetings and discussions need to be held to determine action plan 4) Distribution of resources becomes difficult when many projects are carried out simultaneously. 5) There will be a dominant power struggle when there are managers who are more prominent.
Each organization has a clearly established objectives and goals of its own. In general, the organizational chart has been used by many organizations to assist their operations. Without careful planning and the right implication or action plan, the organization would not be able to operate at the level best to achieve the goals set. It also requires knowledge and efficient management of the organization is to ensure great success. In short every organization should take into account every factors either internal or external to make sure every task is done accordingly and smoothly in line with the goals set
...(download the rest of the essay above)
About this essay:
If you use part of this page in your own work, you need to provide a citation, as follows:
Essay Sauce, Organisational structure . Available from:<https://www.essaysauce.com/management-essays/essay-organisational-structure/> [Accessed 12-04-24].
These Management essays have been submitted to us by students in order to help you with your studies.
* This essay may have been previously published on Essay.uk.com at an earlier date.
Essay Categories:
- Accounting essays
- Architecture essays
- Business essays
- Computer science essays
- Criminology essays
- Economics essays
- Education essays
- Engineering essays
- English language essays
- Environmental studies essays
- Essay examples
- Finance essays
- Geography essays
- Health essays
- History essays
- Hospitality and tourism essays
- Human rights essays
- Information technology essays
- International relations
- Leadership essays
- Linguistics essays
- Literature essays
- Management essays
- Marketing essays
- Mathematics essays
- Media essays
- Medicine essays
- Military essays
- Miscellaneous essays
- Music Essays
- Nursing essays
- Philosophy essays
- Photography and arts essays
- Politics essays
- Project management essays
- Psychology essays
- Religious studies and theology essays
- Sample essays
- Science essays
- Social work essays
- Sociology essays
- Sports essays
- Types of essay
- Zoology essays
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essays Examples >
- Essay Topics
Essays on Functional Structure
25 samples on this topic
Writing gobs of Functional Structure papers is an implicit part of present-day studying, be it in high-school, college, or university. If you can do that single-handedly, that's just awesome; yet, other students might not be that lucky, as Functional Structure writing can be quite difficult. The catalog of free sample Functional Structure papers presented below was assembled in order to help lagging students rise up to the challenge.
On the one hand, Functional Structure essays we showcase here evidently demonstrate how a really well-written academic paper should be developed. On the other hand, upon your request and for an affordable cost, a pro essay helper with the relevant academic background can put together a fine paper example on Functional Structure from scratch.
Free Essay On Problems Addressed: Its Similarity To Traditional Structures Enabled Clarity Of Reporting And Responsibility Structures.
Free unique supplies (wales) limited case study sample.
Organizational Structure
Free Essay About Organizational Structures
Good example of essay on understanding the success of ryanair ltd..
INTRODUCTION
Good Term Paper On Corporate Level Analysis
Organization of Focus
Good Organizational Structure Essay Example
Learning Activity 1
Good Case Study On Mini-Case Study Of IKEA
Course works on participant observation wow essays, sample report on system integration.
INTERNATIONAL HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
Southwest Airlines: Organizational Structure And Design Analysis Essay Samples
Types of organizational structures essays example, free essay about work.
You have just been hired by a large organization to serve as a first line supervisor, but because you are in an influential department, you have the opportunity to meet the top managers at a company party and to dialogue with the CEO on his responsibilities. Knowing the responsibilities and types of decisions made by top management as we studied them in organization theory, what would you discuss the organization with the CEO?
Closing Case: Strategy Implementation At Dell Computer Case Study Samples
- Use electronic and non-electronic sources to find out how Dell utilized its different kinds of organizational structures over time in capturing the following performance area: - Motivation / Goal Setting Process - Decision making/ Problem solving process - Conflict Resolution - Team building/ team process
Designation Dell utilized its different kinds of organizational structures over time in capturing motivation and goal setting process, decision making, conflict resolution and team building in the following manner.
Motivation / Goal Setting Process
Free Ayala Land, Inc Term Paper Sample
Organizational structure and culture essays example.
Every organization has a specific aim with which it wishes to achieve to gain excellence and business satisfaction. Organizational structure may be defined as the way job tasks can be divided allocated and carried out by specified individuals in an organization. Culture may be defined as a set of beliefs or norms that are shared and accepted by a particular group of people in the society. Organizational culture can then be defined as a set of values that are shared by the employees at a particular organization (Baligh 2011, P. 38).
Different organizational structures and culture
Organizing Concepts And Change Principles Essay Sample
Functional, divisional and adaptive organizational structure essay, apple inc. organizational structure essay, project scope report examples.
Executive Summary
Free Critical Thinking On Organizational Structure
Companies today set up their organization structure based on their mission, goal and objectives. An organization can increase revenues and widen their profits margin if they select organization structures that match the needs of their operations. There many types of organization structures that exist today with the common ones been divisional, functional and matrix.
Woolworth’s organization structure
Strategic Capabilities Case Study
4.0 Structural Type that will maximize the Strategic Capabilities of eBay 4.1 Critical analytical discussion of structural theories 4.2. The structural and generic approach strategy
Problem/issue Statement Case Study
As the president of the company, the two major problems that I think are facing the company is inflexibility or rigidity in responding to market concentration issues and getting the right leadership which will propel the company based on the current business environmental conditions.
275 words = 1 page double-spaced

Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline

Dissertation
Research Paper
- Testimonials
Research Papers
Dissertations
Term Papers

Essay Paper on Organizational Structure
by George Grant
Organizational structure is one of the breaking factors that may foster or hinder the organization success rate. Project organizational structure was one issue of project management that grabbed attention in the fifties and sixties. Lately among the last two decades various organizational structures have emerged on the picture but still need efficiency and quality. Eventually, project managers look for better organizational techniques to smoothen the progress of execution. They look forward to enhance teamwork tasks, increase flexibility in dealing with resources and how to get the best of them. Managers also look forward to add efficiency and quality to all project aspects to meet their goals. We here will examine three of the major organizational structures for project management. Those structures are mainly named functional, project and matrix organization. Among each organizational structure the role and power of the project manager varies accordingly (Russell, 2011).
Functional structures are accepted by lots of the conventional manufacturing and industrialized companies. They are somehow hierarchical in arrangement through which each employee is managed by one known boss. (Figure1).
“Functional Organization structure” is one of the oldest processes yet one of the most successful. This structure achieves in a better way when applied for schedules and regular everyday tasks and meant to keep up quality and work principles and standards. The “Functional Organization structures” allocate plans in 2 unlike ways. One way looks after the project being given to a particular functional manager; coordination takes place to involve all other departments for their contribution. Then again, projects can be trundled around to several divisions where each division manager guarantees that their duties and tasks have been finished. This way is not so efficient when applied to make complex or multifaceted projects easier. One of the most important disadvantages of this organizational structure is the need of integrated employee recognition plus evaluation and compensation for project performance. Similarly employee accountability is very low for all allocated duties carried out through the project (Russell, 2011). Accepted projects by functional organizations are usually of a low profile. And projects more often than not are carried out inside one functional unit e.g. a design project for a signage company is taken on by the engineering division. This project does not require cross-functional collaboration or integration. Also the team working on the project is not allocated on a full-time starting point concept. As well the power and authority of the project manager within this structure is low or almost none existing.
Projectised structures are very exceptional (Figure 2). They are accepted by companies such as architectural organizations, usually the bulk of the staff is occupied in the project tasks. Regularly project is dedicated for an external customer. Project structures are controlled just by project teams where each team is self-sufficient and independent in administration and support meanings. In this kind of structure the Project Manager has more power and authority than the functional style and also has more independence in achieving the tasks. This project structure is practicable and reasonable for very small companies; the overhead of extra staff and support is unaffordable. The staff members working together within a team report to one specific boss and finally this boss reports to the project manager where the project manager is holds the highest power in the configuration.
In this projectised structure, everybody is allocated to a project. After finishing the project, resources are allocated to another project. The Project Organization structure is purposely considered for implementing projects. It is specially adapted to fit for the needs and requirements of complex projects by separating exclusive work and preserving a strapping focus on finishing the project. Once the project is finished, this structure breaks up. It is effectual in sustaining fanatical resources throughout the existence of the project. The main disadvantage of the projectised structure is that it is ineffective in reassigning resources and technology. Also, by the time the staff in point of fact starts performing as a unified team, when the project is ended it’s hard as the organization breaks up. As this project has fanatical resources throughout its time, ineffectiveness and disorganization may result as there could be underutilized employees at some stages of the project (Russell, 2011).
Matrix Organization (Figure 3) is a structure for project management that came up from the acknowledgment of intrinsic faults and errors in both the “Functional Organization” and “Project Organization” structures. It shared the best mechanisms of the two structures. It operates greatly when several projects are synchronized at the same time. The functional managers supervise and monitor staff, training, job duties and assessment of the project’s employees. The functional individuals are allocated one or more projects and ensure that projects are meeting their goals through high levels of performance. The “matrix organizational structure” (Figure 3) is in the middle of functional and projectised. The team working for the project is consisted of staff employees selected from several functional divisions that could be marketing, sales or other divisions. The team staff in this structure should report to both the functional manager and the project manager. A lot of global organizations approve the matrix form with tasks jointed between either the product or th services departments and geographical division. The “global matrix organization” was created to maintain equilibrium by merging global effectiveness including infrastructure, and strategies with local receptiveness and awareness. Project Managers play a significant role in running the clashes and strains between different departments and state executives, for better interaction between global effectiveness and local receptiveness. Among this strong matrix structures, Project managers are powerful and hold up decisions for the whole project. There are different forms of matrix organizations; strong, weak and balanced. For the strong matrix, power is seized to the Project Manager and is more close to the Projectised structure. Among the weak matrix, Power is seized to the Functional Manager and is more close to Functional structure. Concerning the balanced matrix model, the power is communal and it’s a mix of the Functional and the Projectised. The Project Manager and the Functional Manager manage the resources and later after the project is finished the resources are returned back to the functional division. Nowadays projects are often taken on under the matrix structure. Accordingly, organizations are more and more altering their shapes into “strong matrix organizations”. The huge bulk of bulky projects are performed within “matrix structures” today. Approximately all global services organizations approve this structure. The work could be carried out transversely among several geographies, yet the client may exist in other geography. In spite of avoiding the flaws existing in other structures, Matrix Organization still enclose some troubles. One of which is that employees report and refer to at least two managers, which may over and over lead to vagueness and divergence. These troubles could be avoided with advanced communication and firm leadership for better understanding and control (Russell, 2011).
This clarification on the whole presented a general idea of some “project management organizational structures”. The three styles “Functional Organization, Project Organization and Matrix Organization” are considered to be the most conventional project management structures that are commonly used because of their efficiency and usefulness. Moreover, there are a lot of other techniques accessible that may better fit in different situations. However, the sort of organizational structure that is supposed to be preferred by any corporation depends on the nature of the project and goals to be accomplished.
This is just a free sample of the research paper, or part of the research paper on the given topic you have found at ProfEssays.com. If you feel you need professional writing assistance contact us! We will help you to create perfect research paper on any topic. ProfEssays.com – Leading custom essay and dissertation writing company and we are 24/7 open to serve you writing needs!
Don ‘ t hesitate! ORDER NOW !
Looking for an exceptional company to do some custom writing for you? Look no further than ProfEssays.com! You simply place an order with the writing instructions you have been given, and before you know it, your essay or term paper, completely finished and unique, will be completed and sent back to you. At ProfEssays.com, we have over 500 highly educated, professional writers standing by waiting to help you with any writing needs you may have! We understand students have plenty on their plates, which is why we love to help them out. Let us do the work for you, so you have time to do what you want to do!
- Customers' Testimonials
- Custom Book Report
- Help with Case Studies
- Personal Essays
- Custom Movie Review
- Narrative Essays
- Argumentative Essays
- Homework Help
- Essay Format
- Essay Outline
- Essay Topics
- Essay Questions
- How to Write a Research Paper
- Research Paper Format
- Research Paper Introduction
- Research Paper Outline
- Research Paper Abstract
- Research Paper Topics

Client Lounge
Deadline approaching.
- How it works
Functional Organization Structure - Essay Sample
The above diagram represents a functional structure used by Sudair pharmaceutical company where the organization is divided into different departments. In this arrangement, every individual serves his/her responsibility and handles a large volume of transactions within the departments (Al-Thuneibat et al., 2015).
Benefits of functional structure
Functional type of structure offers several benefits to sudair pharmaceutical company. First, it provides a chance for specialization where each department operates by itself without depending on other departments. Each department has got its staff, machines, and operations without having to share any of this. The team in each department, therefore, has a chance to concentrate on their specific jobs on a daily basis developing their skills. Example the finance department is dependent, and its staff only operates in this office without being shifted to the quality management department or any other department. Experience over time make them extra competitive, and the company can highly benefit from their expertise (Malik, 2014).
Additionally, production and efficiency are improved by this type of structure in that every worker becomes an expert in his/her functional area and can perform duties with a high speed, accuracy, and efficiency. There are minimum mistakes noted at work when this structure is applied since the workers keep upgrading in their areas of specialization (Momani & Fadil 2013). The IT specialist, for example, will develop more passion on the field of IT and yield the best results on that field.
Notably, there is the minimization of duplication of work since every function has a department in which it is carried out exhaustively, so the task is not done in any other division within that organization. The company can as well train the staff from their specific departments on their specialization to improve performance (Saudi Pharmaceuticals company, 2017). Sales, for example, are only within the marketing and sales department while all budgets are completed in the finance department as opposed to other approaches where a department dealing with sales and marketing would be handling their budgets as well.
Challenges of functional structure
This type of organizational structure poses some challenges to the company. First, there is lack of teamwork within the staff of the company since each department works as a unit and the staff members have no chance to work together as a team. Each department has its objectives and goals and therefore operates independently without minding the purposes nor the efficiency or production of the other units. Lack of cooperation between different departments of the same company might lead to failure of the company. Its important for the company to note that the failure of a single department alters with the whole operations of the organization (Whitmarsh et., al 2012). The research and development department, for example, needs to coordinate with the quality management department to yield the best production results. However, this approach discourages this.
Secondly, this structure makes it difficult for the management to have control over the company. The top management may find it hard to maintain control over the organization as it keeps expanding. When the need arises for delegation of more decision making responsibilities to the departments, the extent of autonomy also may increase making coordination of duties difficult. In this organization, for example, the top management may not even be aware of where specific units fall in the departments or how they operate because there is too little face to face coordination between the subunits and the top management. In case the company expands to cover new geographical areas it would be tough to maintain control and manage separate functions. Also, this type of structure can be quite expensive to implement. Modern infrastructure and staff are required to enable the development of independent units (Welsh & Ordonez 2014). Example the administrative department will have their separate computers, printers, and staff members as well as the finance department; however, in a different approach same computers and printers could be shared to save on cost.
Behavior changes needed to adopt functional structure
The types of behavior changes needed to adopt the functional organizational structure include structural changes where the company will have to abandon its previous structure and shift to a new one. This requires implementation of new infrastructure and power. Settings of the prior equipments and buildings have to be changed so that all the staff and equipment if one department is set to a specific standard location. In a case where the sales and marketing department and the finance department were under same management and operations, they have to be broken down and each located separately (Fan et al. 2013). If the equipment were being shared before, new ones have to be purchased, and the duties reassigned to staff members so that they stick to their specific departments. Modern computers, printers staff members among other things need to be incorporated. There may be a need for new buildings also to ensure that each unit has its location to operate from the approach does not allow two different, e.g., administration and finance to work together. Instead, they have to be separate and independent. The whole process, therefore, requires planning due to large budgets that may be involved in implementation. This change needs to be managed to avoid resistance from people and to ensure that it becomes successful by concerning the staff and the clients of the company (Spector, 2013). This can be done by informing the stakeholders of changes that the organization is about to adopt, the effects pose and the operation of the new organizational structure.
In conclusion, the functional organizational structure is an appropriate type of arrangement because it ensures that activities of the company are all controlled from the department level, reducing the work of the top management. Accuracy and effectiveness are improved since the checks are done in the specific working units. Every individual gets to love what they do in the company and works to the maximum to achieve their long-term and short-term goals. The employee work keeping in mind their specific daily task as opposed to other types where the staff have a tension that they might be shifted to other jobs at any time and therefore don't have to focus on quality. The company reduces the burden of overspending since there is no duplication of work. Training and specialization help the organizations to achieve good quality and production through the functional organizational structure (Tan et al., 2007).
Al-Thuneibat, A. A., Al-Rehaily, A. S., & Basodan, Y. A. (2015). The impact of internal control requirements on the profitability of Saudi shareholding companies. International Journal of Commerce and Management, 25(2), 196-217.
Malik, S. Z. (2014). Strategic Change and Organizational Reforms: Case of a Pakistani University. Journal of Research & Reflections in Education (JRRE), 8(1).
Momani, N. M., & Fadil, A. S. (2013). Risk management practices in the Saudi business organizations: A case study of the city of Jeddah. Journal of Business and Retail Management Research, 7(2).
Saudi Pharmaceuticals company, SPC. (2017).Building front lines against cancer and life threatening diseases. Retrieved from http://www.sudairpharma.com/web/index.html
Spector, B. (2013). Implementing Organizational Change: Theory and practice (3rd ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson. ISBN-13: 9780132729840
Tan, W. L., Menkhoff, T., & Chay, Y. W. (2007). The effects of entrepreneurial growth orientation on organizational change and firm growth. Small Enterprise Research, 15(2), 88-99.
Welsh, D. T., & Ordonez, L. D. (2014). Conscience without cognition: The effects of subconscious priming on ethical behaviour. Academy of Management Journal, 57(3), 723-742.
Whitmarsh, L., Lorenzoni, I., & O'Neill, S. (Eds.). (2012). Engaging the public with climate change: Behaviour change and communication. Routledge.
Fan, J. P., Wong, T. J., & Zhang, T. (2013). Institutions and organizational structure: The case of state-owned corporate pyramids. The Journal of Law, Economics, and Organization, 29(6), 1217-1252.

Request Removal
If you are the original author of this essay and no longer wish to have it published on the collegeessaywriter.net website, please click below to request its removal:
- Need for Alignment of Manager Roles and Organizational Structures - Essay Example
- Essay on Personality Testing in Employee Selection
- The Role of Managerial Accounting in Contemporary Business - An Essay Example
- Nompumelelo Hospital Website Report Paper Example
- Coursework Example on Lean Six Sigma: Prescription Errors Process Improvement
- Project Quality Management: Background to the BP Oil Spill Case - Paper Example
- Management Report: First Few Weeks as a New Junior Project Manager
Submit your request
Sorry, but it's not possible to copy the text due to security reasons.
Would you like to get this essay by email?
Sorry, you can’t copy this text :(
Enter your email to get this essay sample.
Don’t print this from here
Enter your email and we'll send you a properly formatted printable version of this essay right away.
How about making it original at only $7.00/page
Let us edit it for you at only $7.00 to make it 100% original!

Essay: What is a Functional Structure
Business / Samples May 9, 2011
Sample Essay
The functional structure is found in many organizations and it groups the employees of the organization together and this grouping is based on the jobs characteristics within the organization. The sample functional structure can be given as:
Vice president
Sales Department
Customer Service
Engineering department
Marketing department
Administration department
This structure depicts that the different heads are working under the leadership of the Vice president. There are certain advantages and disadvantages of this structure which are given below:
Advantages of Functional Structure: When the specialists are grouped together than it would result in the economies of scale and it definitely minimizes the duplication of equipment. The employees are a bit satisfied with the functional structure because they can talk with the same language with their peers. The element of training is also simplified with it and the decision making of an organization is simplified an employees receive unified direction from the top. The elements of communication and coordination are quite excellent within the departments and this is because of the simplified nature of functional structure (Gibson, 2008). At last, it can be said that when an organizations implements a functional structure then the element of problem solving especially technical problem solving increases and employees make quick decisions because of this.
Disadvantages of Functional Structure: Besides certain advantages there are certain disadvantages that are associated with functional structure. Employees only have knowledge of their respective areas and they have no knowledge and concern outside their functional area. It can also lead to barriers in communications because functional structure can result in narrowness and this would also create problems in cooperation and coordination. The employees would only focus on their departments and they would not focus on the mission. Similarly, this structure possesses rigidity and separate chains of command that is the reason why in changing environments their response time slow.
Kindly order term papers, essays, research papers, dissertations, thesis , book reports from the order page.
Related Pages
- Data Privacy Compliance in E-Commerce Essay
- Music in Contemporary American Fiction Essay
- Magic Realism in Angela Carter’s Novels Research Paper
- Ways to Deal with Oil Spills Essay
- Wellness and Pathology in Plastic Surgery Research Paper
You may also like this

Best Ways to Avoid Plagiarism in your Essays

How to write an essay on the use of Nursing

Herding in Financial Markets
Importance of hand hygiene, higher global temperatures.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A functional organizational structure is a safe way to ensure that employees are focused and decision-making processes are streamlined. Due to a strict focus on efficiency and a clear chain of command, functional structures are especially popular among larger companies. Every time an organizational structure has benefits, however, it also has ...
The functional organizational structure helps organizations run their business and earn a profit by grouping employees based on their skills and expertise. It provides a clear hierarchy and minimizes confusion among employees who may be unsure who they are to report to. It is an efficient way to run a business but can have drawbacks as it can ...
In conclusion, the Functional Organization is a well-established structure known for its efficiency and specialization. It thrives in industries with a clear separation of functions. Organizations ...
A functional structure—especially when it is mapped out using org chart software and distributed to your employees—creates clarity within the organization. It presents everyone with their individual place and role in the organization clearly and without ambiguity. This reduces the number of communication channels, enabling information to ...
Aside from the considerations outlined above, organizations will often set structures according to the functional needs of the organization. A functional need refers to a feature of the organization or its environment that is necessary for organizational success. A business structure is designed to address these organizational needs.
An organizational structure refers to a system established to oversee the organization's flow of activities to achieve its goals, which include roles, rules, and responsibilities. There are several organizational structures, such as product, functional, matrix, customer, and geographic. I prefer the functional one because it categorizes ...
Functional Structure: 3 Characteristics of Functional Structure. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Dec 17, 2021 • 5 min read. In an effort to organize teams, some companies opt for a functional organizational structure where decision-making and operations run through functional departments with precise areas of specialization. In an ...
Functional organizational structure is ideal for the company 1. Its structure should have two functional levels: managerial team at the top level hierarchy while programmers and supporting personnel - under it. Below, there is a chart to illustrate company 1 functional organizational structure: We will write a custom essay on your topic.
The divisional structure classifies the operations of an organization along with market, service, product, or geographical lines. In this aspect, a business managed in a divisional method may have operations dealing with farm produce located in the US, for example, and the ones handling green products in Europe where every division holds a ...
Most management students have had limited exposure to issues concerning organizational structure. This exercise offers a brief in-class experience of the differences of working in a functional structure versus a divisional structure. The instructor guides students to think about certain events, or challenges, confronting their simulated ...
What is Functional Organizational Structure. As the term depicts, the functional organizational structure is a type of organizational structure that groups the employees based on their roles, skills, and specialty. Under this organizational structure, different departments are established and each department head is responsible to manage the ...
Functional/Role-Based Structure. A functional—or role-based—structure is one of the most common organizational structures. This structure has centralized leadership and the vertical ...
7 other types of organizational structures Besides the functional organizational structure, there are other types of organizational structures that help businesses achieve their goals, such as:. Divisional: Organizations are split into divisions based on specific products, services or geographies. For this reason, this structure is typically used by large companies that operate in wide ...
Organizational Focus. In functional structure, the focus is primarily on specialized functions or departments. Each department operates independently, optimizing its function's performance. In contrast, matrix structure emphasizes both functional expertise and project-specific goals, striking a balance between the two.
A functional organizational structure is the most common of the three organizational structures adopted by most companies. Companies organized by function group employees according to their ...
3) Matrix. Functional Structure. A functional organisation structure is hierarchical where people are grouped together in line with their area of expertise. The functional manager will assume control of employees and will have expertise in the same field this will help the functional manager effectively utilise all the skills of employees in ...
Common types of organizational structures include: Functional Structure: Organized around specialized functions or departments, such as marketing, finance, and operations. Divisional Structure: Organized by product lines, geographic regions, or customer segments. Matrix Structure: Combines functional and divisional structures, creating dual ...
Being one of the largest multinational corporations in the world, Amazon.com has an organizational structure that reflects the complexity of governing a business on that scale. First and foremost, it is important to note that Amazon's structure is functional rather than divisional. The company creates departments, such as "worldwide ...
3) A very clear lines of responsibility between departments. 4) The structure of the product is very suitable for large-sized organizations. 3) The cost of the operation is big because each department has its own managers and experts. 4) It requires a high amount of workforces .
The organizational structure that is presently in the organization is functional structure. In the functional structure, each organization's portion is grouped in accordance with its objective and purpose (Daft & Marcic, 2010). For example, in company Jimi's Jammers there are four departments, guitar manufacturing department, guitar design ...
Those structures are mainly named functional, project and matrix organization. Among each organizational structure the role and power of the project manager varies accordingly (Russell, 2011). Functional structures are accepted by lots of the conventional manufacturing and industrialized companies.
The above diagram represents a functional structure used by Sudair pharmaceutical company where the organization is divided into different departments. In this arrangement, every individual serves his/her responsibility and handles a large volume of transactions within the departments (Al-Thuneibat et al., 2015). Benefits of functional structure.
Organizational structure is a hierarchy of people and their functions. The structure of an organization can be functional, organizational, divisional, and matrix, and it is shown similarly in the work culture of the organization. Every organization needs a design and structure in order to operate systematically.
Essay: What is a Functional Structure. Business / Samples May 9, 2011. Sample Essay. The functional structure is found in many organizations and it groups the employees of the organization together and this grouping is based on the jobs characteristics within the organization. The sample functional structure can be given as: