- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Critical Reviews

How to Write an Article Review
Last Updated: September 8, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 3,091,478 times.
An article review is both a summary and an evaluation of another writer's article. Teachers often assign article reviews to introduce students to the work of experts in the field. Experts also are often asked to review the work of other professionals. Understanding the main points and arguments of the article is essential for an accurate summation. Logical evaluation of the article's main theme, supporting arguments, and implications for further research is an important element of a review . Here are a few guidelines for writing an article review.
Education specialist Alexander Peterman recommends: "In the case of a review, your objective should be to reflect on the effectiveness of what has already been written, rather than writing to inform your audience about a subject."
Things You Should Know
- Read the article very closely, and then take time to reflect on your evaluation. Consider whether the article effectively achieves what it set out to.
- Write out a full article review by completing your intro, summary, evaluation, and conclusion. Don't forget to add a title, too!
- Proofread your review for mistakes (like grammar and usage), while also cutting down on needless information. [1] X Research source
Preparing to Write Your Review

- Article reviews present more than just an opinion. You will engage with the text to create a response to the scholarly writer's ideas. You will respond to and use ideas, theories, and research from your studies. Your critique of the article will be based on proof and your own thoughtful reasoning.
- An article review only responds to the author's research. It typically does not provide any new research. However, if you are correcting misleading or otherwise incorrect points, some new data may be presented.
- An article review both summarizes and evaluates the article.

- Summarize the article. Focus on the important points, claims, and information.
- Discuss the positive aspects of the article. Think about what the author does well, good points she makes, and insightful observations.
- Identify contradictions, gaps, and inconsistencies in the text. Determine if there is enough data or research included to support the author's claims. Find any unanswered questions left in the article.

- Make note of words or issues you don't understand and questions you have.
- Look up terms or concepts you are unfamiliar with, so you can fully understand the article. Read about concepts in-depth to make sure you understand their full context.

- Pay careful attention to the meaning of the article. Make sure you fully understand the article. The only way to write a good article review is to understand the article.

- With either method, make an outline of the main points made in the article and the supporting research or arguments. It is strictly a restatement of the main points of the article and does not include your opinions.
- After putting the article in your own words, decide which parts of the article you want to discuss in your review. You can focus on the theoretical approach, the content, the presentation or interpretation of evidence, or the style. You will always discuss the main issues of the article, but you can sometimes also focus on certain aspects. This comes in handy if you want to focus the review towards the content of a course.
- Review the summary outline to eliminate unnecessary items. Erase or cross out the less important arguments or supplemental information. Your revised summary can serve as the basis for the summary you provide at the beginning of your review.

- What does the article set out to do?
- What is the theoretical framework or assumptions?
- Are the central concepts clearly defined?
- How adequate is the evidence?
- How does the article fit into the literature and field?
- Does it advance the knowledge of the subject?
- How clear is the author's writing? Don't: include superficial opinions or your personal reaction. Do: pay attention to your biases, so you can overcome them.
Writing the Article Review

- For example, in MLA , a citation may look like: Duvall, John N. "The (Super)Marketplace of Images: Television as Unmediated Mediation in DeLillo's White Noise ." Arizona Quarterly 50.3 (1994): 127-53. Print. [10] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest.

- Your introduction should only be 10-25% of your review.
- End the introduction with your thesis. Your thesis should address the above issues. For example: Although the author has some good points, his article is biased and contains some misinterpretation of data from others’ analysis of the effectiveness of the condom.

- Use direct quotes from the author sparingly.
- Review the summary you have written. Read over your summary many times to ensure that your words are an accurate description of the author's article.

- Support your critique with evidence from the article or other texts.
- The summary portion is very important for your critique. You must make the author's argument clear in the summary section for your evaluation to make sense.
- Remember, this is not where you say if you liked the article or not. You are assessing the significance and relevance of the article.
- Use a topic sentence and supportive arguments for each opinion. For example, you might address a particular strength in the first sentence of the opinion section, followed by several sentences elaborating on the significance of the point.

- This should only be about 10% of your overall essay.
- For example: This critical review has evaluated the article "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS" by Anthony Zimmerman. The arguments in the article show the presence of bias, prejudice, argumentative writing without supporting details, and misinformation. These points weaken the author’s arguments and reduce his credibility.

- Make sure you have identified and discussed the 3-4 key issues in the article.
Sample Article Reviews

Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/grammarpunct/proofreading/
- ↑ https://libguides.cmich.edu/writinghelp/articlereview
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548566/
- ↑ Jake Adams. Academic Tutor & Test Prep Specialist. Expert Interview. 24 July 2020.
- ↑ https://guides.library.queensu.ca/introduction-research/writing/critical
- ↑ https://www.iup.edu/writingcenter/writing-resources/organization-and-structure/creating-an-outline.html
- ↑ https://writing.umn.edu/sws/assets/pdf/quicktips/titles.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_periodicals.html
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548565/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uconn.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/593/2014/06/How_to_Summarize_a_Research_Article1.pdf
- ↑ https://www.uis.edu/learning-hub/writing-resources/handouts/learning-hub/how-to-review-a-journal-article
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
About This Article

If you have to write an article review, read through the original article closely, taking notes and highlighting important sections as you read. Next, rewrite the article in your own words, either in a long paragraph or as an outline. Open your article review by citing the article, then write an introduction which states the article’s thesis. Next, summarize the article, followed by your opinion about whether the article was clear, thorough, and useful. Finish with a paragraph that summarizes the main points of the article and your opinions. To learn more about what to include in your personal critique of the article, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Prince Asiedu-Gyan
Apr 22, 2022
Did this article help you?
Sammy James
Sep 12, 2017
Juabin Matey
Aug 30, 2017
Oct 25, 2023
Vanita Meghrajani
Jul 21, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
How to Write an Article Review: Tips and Examples

Did you know that article reviews are not just academic exercises but also a valuable skill in today's information age? In a world inundated with content, being able to dissect and evaluate articles critically can help you separate the wheat from the chaff. Whether you're a student aiming to excel in your coursework or a professional looking to stay well-informed, mastering the art of writing article reviews is an invaluable skill.
Short Description
In this article, our research paper writing service experts will start by unraveling the concept of article reviews and discussing the various types. You'll also gain insights into the art of formatting your review effectively. To ensure you're well-prepared, we'll take you through the pre-writing process, offering tips on setting the stage for your review. But it doesn't stop there. You'll find a practical example of an article review to help you grasp the concepts in action. To complete your journey, we'll guide you through the post-writing process, equipping you with essential proofreading techniques to ensure your work shines with clarity and precision!
What Is an Article Review: Grasping the Concept
A review article is a type of professional paper writing that demands a high level of in-depth analysis and a well-structured presentation of arguments. It is a critical, constructive evaluation of literature in a particular field through summary, classification, analysis, and comparison.
If you write a scientific review, you have to use database searches to portray the research. Your primary goal is to summarize everything and present a clear understanding of the topic you've been working on.
Writing Involves:
- Summarization, classification, analysis, critiques, and comparison.
- The analysis, evaluation, and comparison require the use of theories, ideas, and research relevant to the subject area of the article.
- It is also worth nothing if a review does not introduce new information, but instead presents a response to another writer's work.
- Check out other samples to gain a better understanding of how to review the article.
Types of Review
When it comes to article reviews, there's more than one way to approach the task. Understanding the various types of reviews is like having a versatile toolkit at your disposal. In this section, we'll walk you through the different dimensions of review types, each offering a unique perspective and purpose. Whether you're dissecting a scholarly article, critiquing a piece of literature, or evaluating a product, you'll discover the diverse landscape of article reviews and how to navigate it effectively.
.webp)
Journal Article Review
Just like other types of reviews, a journal article review assesses the merits and shortcomings of a published work. To illustrate, consider a review of an academic paper on climate change, where the writer meticulously analyzes and interprets the article's significance within the context of environmental science.
Research Article Review
Distinguished by its focus on research methodologies, a research article review scrutinizes the techniques used in a study and evaluates them in light of the subsequent analysis and critique. For instance, when reviewing a research article on the effects of a new drug, the reviewer would delve into the methods employed to gather data and assess their reliability.
Science Article Review
In the realm of scientific literature, a science article review encompasses a wide array of subjects. Scientific publications often provide extensive background information, which can be instrumental in conducting a comprehensive analysis. For example, when reviewing an article about the latest breakthroughs in genetics, the reviewer may draw upon the background knowledge provided to facilitate a more in-depth evaluation of the publication.
Need a Hand From Professionals?
Address to Our Writers and Get Assistance in Any Questions!
Formatting an Article Review
The format of the article should always adhere to the citation style required by your professor. If you're not sure, seek clarification on the preferred format and ask him to clarify several other pointers to complete the formatting of an article review adequately.
How Many Publications Should You Review?
- In what format should you cite your articles (MLA, APA, ASA, Chicago, etc.)?
- What length should your review be?
- Should you include a summary, critique, or personal opinion in your assignment?
- Do you need to call attention to a theme or central idea within the articles?
- Does your instructor require background information?
When you know the answers to these questions, you may start writing your assignment. Below are examples of MLA and APA formats, as those are the two most common citation styles.
Using the APA Format
Articles appear most commonly in academic journals, newspapers, and websites. If you write an article review in the APA format, you will need to write bibliographical entries for the sources you use:
- Web : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Title. Retrieved from {link}
- Journal : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Publication Year). Publication Title. Periodical Title, Volume(Issue), pp.-pp.
- Newspaper : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Publication Title. Magazine Title, pp. xx-xx.
Using MLA Format
- Web : Last, First Middle Initial. “Publication Title.” Website Title. Website Publisher, Date Month Year Published. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
- Newspaper : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Newspaper Title [City] Date, Month, Year Published: Page(s). Print.
- Journal : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Journal Title Series Volume. Issue (Year Published): Page(s). Database Name. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
Enhance your writing effortlessly with EssayPro.com , where you can order an article review or any other writing task. Our team of expert writers specializes in various fields, ensuring your work is not just summarized, but deeply analyzed and professionally presented. Ideal for students and professionals alike, EssayPro offers top-notch writing assistance tailored to your needs. Elevate your writing today with our skilled team at your article review writing service !
.jpg)
The Pre-Writing Process
Facing this task for the first time can really get confusing and can leave you unsure of where to begin. To create a top-notch article review, start with a few preparatory steps. Here are the two main stages from our dissertation services to get you started:
Step 1: Define the right organization for your review. Knowing the future setup of your paper will help you define how you should read the article. Here are the steps to follow:
- Summarize the article — seek out the main points, ideas, claims, and general information presented in the article.
- Define the positive points — identify the strong aspects, ideas, and insightful observations the author has made.
- Find the gaps —- determine whether or not the author has any contradictions, gaps, or inconsistencies in the article and evaluate whether or not he or she used a sufficient amount of arguments and information to support his or her ideas.
- Identify unanswered questions — finally, identify if there are any questions left unanswered after reading the piece.
Step 2: Move on and review the article. Here is a small and simple guide to help you do it right:
- Start off by looking at and assessing the title of the piece, its abstract, introductory part, headings and subheadings, opening sentences in its paragraphs, and its conclusion.
- First, read only the beginning and the ending of the piece (introduction and conclusion). These are the parts where authors include all of their key arguments and points. Therefore, if you start with reading these parts, it will give you a good sense of the author's main points.
- Finally, read the article fully.
These three steps make up most of the prewriting process. After you are done with them, you can move on to writing your own review—and we are going to guide you through the writing process as well.
Outline and Template
As you progress with reading your article, organize your thoughts into coherent sections in an outline. As you read, jot down important facts, contributions, or contradictions. Identify the shortcomings and strengths of your publication. Begin to map your outline accordingly.
If your professor does not want a summary section or a personal critique section, then you must alleviate those parts from your writing. Much like other assignments, an article review must contain an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Thus, you might consider dividing your outline according to these sections as well as subheadings within the body. If you find yourself troubled with the pre-writing and the brainstorming process for this assignment, seek out a sample outline.
Your custom essay must contain these constituent parts:
- Pre-Title Page - Before diving into your review, start with essential details: article type, publication title, and author names with affiliations (position, department, institution, location, and email). Include corresponding author info if needed.
- Running Head - In APA format, use a concise title (under 40 characters) to ensure consistent formatting.
- Summary Page - Optional but useful. Summarize the article in 800 words, covering background, purpose, results, and methodology, avoiding verbatim text or references.
- Title Page - Include the full title, a 250-word abstract, and 4-6 keywords for discoverability.
- Introduction - Set the stage with an engaging overview of the article.
- Body - Organize your analysis with headings and subheadings.
- Works Cited/References - Properly cite all sources used in your review.
- Optional Suggested Reading Page - If permitted, suggest further readings for in-depth exploration.
- Tables and Figure Legends (if instructed by the professor) - Include visuals when requested by your professor for clarity.
Example of an Article Review
You might wonder why we've dedicated a section of this article to discuss an article review sample. Not everyone may realize it, but examining multiple well-constructed examples of review articles is a crucial step in the writing process. In the following section, our essay writing service experts will explain why.
Looking through relevant article review examples can be beneficial for you in the following ways:
- To get you introduced to the key works of experts in your field.
- To help you identify the key people engaged in a particular field of science.
- To help you define what significant discoveries and advances were made in your field.
- To help you unveil the major gaps within the existing knowledge of your field—which contributes to finding fresh solutions.
- To help you find solid references and arguments for your own review.
- To help you generate some ideas about any further field of research.
- To help you gain a better understanding of the area and become an expert in this specific field.
- To get a clear idea of how to write a good review.
View Our Writer’s Sample Before Crafting Your Own!
Why Have There Been No Great Female Artists?
Steps for Writing an Article Review
Here is a guide with critique paper format on how to write a review paper:
.webp)
Step 1: Write the Title
First of all, you need to write a title that reflects the main focus of your work. Respectively, the title can be either interrogative, descriptive, or declarative.
Step 2: Cite the Article
Next, create a proper citation for the reviewed article and input it following the title. At this step, the most important thing to keep in mind is the style of citation specified by your instructor in the requirements for the paper. For example, an article citation in the MLA style should look as follows:
Author's last and first name. "The title of the article." Journal's title and issue(publication date): page(s). Print
Abraham John. "The World of Dreams." Virginia Quarterly 60.2(1991): 125-67. Print.
Step 3: Article Identification
After your citation, you need to include the identification of your reviewed article:
- Title of the article
- Title of the journal
- Year of publication
All of this information should be included in the first paragraph of your paper.
The report "Poverty increases school drop-outs" was written by Brian Faith – a Health officer – in 2000.
Step 4: Introduction
Your organization in an assignment like this is of the utmost importance. Before embarking on your writing process, you should outline your assignment or use an article review template to organize your thoughts coherently.
- If you are wondering how to start an article review, begin with an introduction that mentions the article and your thesis for the review.
- Follow up with a summary of the main points of the article.
- Highlight the positive aspects and facts presented in the publication.
- Critique the publication by identifying gaps, contradictions, disparities in the text, and unanswered questions.
Step 5: Summarize the Article
Make a summary of the article by revisiting what the author has written about. Note any relevant facts and findings from the article. Include the author's conclusions in this section.
Step 6: Critique It
Present the strengths and weaknesses you have found in the publication. Highlight the knowledge that the author has contributed to the field. Also, write about any gaps and/or contradictions you have found in the article. Take a standpoint of either supporting or not supporting the author's assertions, but back up your arguments with facts and relevant theories that are pertinent to that area of knowledge. Rubrics and templates can also be used to evaluate and grade the person who wrote the article.
Step 7: Craft a Conclusion
In this section, revisit the critical points of your piece, your findings in the article, and your critique. Also, write about the accuracy, validity, and relevance of the results of the article review. Present a way forward for future research in the field of study. Before submitting your article, keep these pointers in mind:
- As you read the article, highlight the key points. This will help you pinpoint the article's main argument and the evidence that they used to support that argument.
- While you write your review, use evidence from your sources to make a point. This is best done using direct quotations.
- Select quotes and supporting evidence adequately and use direct quotations sparingly. Take time to analyze the article adequately.
- Every time you reference a publication or use a direct quotation, use a parenthetical citation to avoid accidentally plagiarizing your article.
- Re-read your piece a day after you finish writing it. This will help you to spot grammar mistakes and to notice any flaws in your organization.
- Use a spell-checker and get a second opinion on your paper.
The Post-Writing Process: Proofread Your Work
Finally, when all of the parts of your article review are set and ready, you have one last thing to take care of — proofreading. Although students often neglect this step, proofreading is a vital part of the writing process and will help you polish your paper to ensure that there are no mistakes or inconsistencies.
To proofread your paper properly, start by reading it fully and checking the following points:
- Punctuation
- Other mistakes
Afterward, take a moment to check for any unnecessary information in your paper and, if found, consider removing it to streamline your content. Finally, double-check that you've covered at least 3-4 key points in your discussion.
And remember, if you ever need help with proofreading, rewriting your essay, or even want to buy essay , our friendly team is always here to assist you.
Need an Article REVIEW WRITTEN?
Just send us the requirements to your paper and watch one of our writers crafting an original paper for you.
What Is A Review Article?
How to write an article review, how to write an article review in apa format, related articles.
%20(2).webp)
How to Write an Article Review: Template & Examples
An article review is an academic assignment that invites you to study a piece of academic research closely. Then, you should present its summary and critically evaluate it using the knowledge you’ve gained in class and during your independent study. If you get such a task at college or university, you shouldn’t confuse it with a response paper, which is a distinct assignment with other purposes (we’ll talk about it in detail below).
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
In this article, prepared by Custom-Writing experts, you’ll find:
- the intricacies of article review writing;
- the difference between an article review and similar assignments;
- a step-by-step algorithm for review composition;
- a couple of samples to guide you throughout the writing process.
So, if you wish to study our article review example and discover helpful writing tips, keep reading.
❓ What Is an Article Review?
- ✍️ Writing Steps
📑 Article Review Format
🔗 references.
An article review is an academic paper that summarizes and critically evaluates the information presented in your selected article.

The first thing you should note when approaching the task of an article review is that not every article is suitable for this assignment. Let’s have a look at the variety of articles to understand what you can choose from.
Popular Vs. Scholarly Articles
In most cases, you’ll be required to review a scholarly, peer-reviewed article – one composed in compliance with rigorous academic standards. Yet, the Web is also full of popular articles that don’t present original scientific value and shouldn’t be selected for a review.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
Not sure how to distinguish these two types? Here is a comparative table to help you out.
Article Review vs. Response Paper
Now, let’s consider the difference between an article review and a response paper:
- If you’re assigned to critique a scholarly article , you will need to compose an article review .
- If your subject of analysis is a popular article , you can respond to it with a well-crafted response paper .
The reason for such distinctions is the quality and structure of these two article types. Peer-reviewed, scholarly articles have clear-cut quality criteria, allowing you to conduct and present a structured assessment of the assigned material. Popular magazines have loose or non-existent quality criteria and don’t offer an opportunity for structured evaluation. So, they are only fit for a subjective response, in which you can summarize your reactions and emotions related to the reading material.
All in all, you can structure your response assignments as outlined in the tips below.
✍️ How to Write an Article Review: Step by Step
Here is a tried and tested algorithm for article review writing from our experts. We’ll consider only the critical review variety of this academic assignment. So, let’s get down to the stages you need to cover to get a stellar review.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 20% off your first order!
Read the Article
As with any reviews, reports, and critiques, you must first familiarize yourself with the assigned material. It’s impossible to review something you haven’t read, so set some time for close, careful reading of the article to identify:
- Its topic.
- Its type.
- The author’s main points and message.
- The arguments they use to prove their points.
- The methodology they use to approach the subject.
In terms of research type , your article will usually belong to one of three types explained below.
Summarize the Article
Now that you’ve read the text and have a general impression of the content, it’s time to summarize it for your readers. Look into the article’s text closely to determine:
- The thesis statement , or general message of the author.
- Research question, purpose, and context of research.
- Supporting points for the author’s assumptions and claims.
- Major findings and supporting evidence.
As you study the article thoroughly, make notes on the margins or write these elements out on a sheet of paper. You can also apply a different technique: read the text section by section and formulate its gist in one phrase or sentence. Once you’re done, you’ll have a summary skeleton in front of you.
Evaluate the Article
The next step of review is content evaluation. Keep in mind that various research types will require a different set of review questions. Here is a complete list of evaluation points you can include.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
Write the Text
After completing the critical review stage, it’s time to compose your article review.
The format of this assignment is standard – you will have an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. The introduction should present your article and summarize its content. The body will contain a structured review according to all four dimensions covered in the previous section. The concluding part will typically recap all the main points you’ve identified during your assessment.
It is essential to note that an article review is, first of all, an academic assignment. Therefore, it should follow all rules and conventions of academic composition, such as:
- No contractions . Don’t use short forms, such as “don’t,” “can’t,” “I’ll,” etc. in academic writing. You need to spell out all those words.
- Formal language and style . Avoid conversational phrasing and words that you would naturally use in blog posts or informal communication. For example, don’t use words like “pretty,” “kind of,” and “like.”
- Third-person narrative . Academic reviews should be written from the third-person point of view, avoiding statements like “I think,” “in my opinion,” and so on.
- No conversational forms . You shouldn’t turn to your readers directly in the text by addressing them with the pronoun “you.” It’s vital to keep the narrative neutral and impersonal.
- Proper abbreviation use . Consult the list of correct abbreviations , like “e.g.” or “i.e.,” for use in your academic writing. If you use informal abbreviations like “FYA” or “f.i.,” your professor will reduce the grade.
- Complete sentences . Make sure your sentences contain the subject and the predicate; avoid shortened or sketch-form phrases suitable for a draft only.
- No conjunctions at the beginning of a sentence . Remember the FANBOYS rule – don’t start a sentence with words like “and” or “but.” They often seem the right way to build a coherent narrative, but academic writing rules disfavor such usage.
- No abbreviations or figures at the beginning of a sentence . Never start a sentence with a number — spell it out if you need to use it anyway. Besides, sentences should never begin with abbreviations like “e.g.”
Finally, a vital rule for an article review is properly formatting the citations. We’ll discuss the correct use of citation styles in the following section.
When composing an article review, keep these points in mind:
- Start with a full reference to the reviewed article so the reader can locate it quickly.
- Ensure correct formatting of in-text references.
- Provide a complete list of used external sources on the last page of the review – your bibliographical entries .
You’ll need to understand the rules of your chosen citation style to meet all these requirements. Below, we’ll discuss the two most common referencing styles – APA and MLA.
Article Review in APA
When you need to compose an article review in the APA format , here is the general bibliographical entry format you should use for journal articles on your reference page:
- Author’s last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year of Publication). Name of the article. Name of the Journal, volume (number), pp. #-#. https://doi.org/xx.xxx/yyyy
Horigian, V. E., Schmidt, R. D., & Feaster, D. J. (2021). Loneliness, mental health, and substance use among US young adults during COVID-19. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 53 (1), pp. 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.2020.1836435
Your in-text citations should follow the author-date format like this:
- If you paraphrase the source and mention the author in the text: According to Horigian et al. (2021), young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic.
- If you paraphrase the source and don’t mention the author in the text: Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al., 2021).
- If you quote the source: As Horigian et al. (2021) point out, there were “elevated levels of loneliness, depression, anxiety, alcohol use, and drug use among young adults during COVID-19” (p. 6).
Note that your in-text citations should include “et al.,” as in the examples above, if your article has 3 or more authors. If you have one or two authors, your in-text citations would look like this:
- One author: “According to Smith (2020), depression is…” or “Depression is … (Smith, 2020).”
- Two authors: “According to Smith and Brown (2020), anxiety means…” or “Anxiety means (Smith & Brown, 2020).”
Finally, in case you have to review a book or a website article, here are the general formats for citing these source types on your APA reference list.
Article Review in MLA
If your assignment requires MLA-format referencing, here’s the general format you should use for citing journal articles on your Works Cited page:
- Author’s last name, First name. “Title of an Article.” Title of the Journal , vol. #, no. #, year, pp. #-#.
Horigian, Viviana E., et al. “Loneliness, Mental Health, and Substance Use Among US Young Adults During COVID-19.” Journal of Psychoactive Drugs , vol. 53, no. 1, 2021, pp. 1-9.
In-text citations in the MLA format follow the author-page citation format and look like this:
- According to Horigian et al., young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (6).
- Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al. 6).
Like in APA, the abbreviation “et al.” is only needed in MLA if your article has 3 or more authors.
If you need to cite a book or a website page, here are the general MLA formats for these types of sources.
✅ Article Review Template
Here is a handy, universal article review template to help you move on with any review assignment. We’ve tried to make it as generic as possible to guide you in the academic process.
📝 Article Review Examples
The theory is good, but practice is even better. Thus, we’ve created three brief examples to show you how to write an article review. You can study the full-text samples by following the links.
📃 Men, Women, & Money
This article review examines a famous piece, “Men, Women & Money – How the Sexes Differ with Their Finances,” published by Amy Livingston in 2020. The author of this article claims that men generally spend more money than women. She makes this conclusion from a close analysis of gender-specific expenditures across five main categories: food, clothing, cars, entertainment, and general spending patterns. Livingston also looks at men’s approach to saving to argue that counter to the common perception of women’s light-hearted attitude to money, men are those who spend more on average.
📃 When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism
This is a review of Jonathan Heidt’s 2016 article titled “When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism,” written as an advocacy of right-wing populism rising in many Western states. The author illustrates the case with the election of Donald Trump as the US President and the rise of right-wing rhetoric in many Western countries. These examples show how nationalist sentiment represents a reaction to global immigration and a failure of globalization.
📃 Sleep Deprivation
This is a review of the American Heart Association’s article titled “The Dangers of Sleep Deprivation.” It discusses how the national organization concerned with the American population’s cardiovascular health links the lack of high-quality sleep to far-reaching health consequences. The organization’s experts reveal how a consistent lack of sleep leads to Alzheimer’s disease development, obesity, type 2 diabetes, etc.
✏️ Article Review FAQ
A high-quality article review should summarize the assigned article’s content and offer data-backed reactions and evaluations of its quality in terms of the article’s purpose, methodology, and data used to argue the main points. It should be detailed, comprehensive, objective, and evidence-based.
The purpose of writing a review is to allow students to reflect on research quality and showcase their critical thinking and evaluation skills. Students should exhibit their mastery of close reading of research publications and their unbiased assessment.
The content of your article review will be the same in any format, with the only difference in the assignment’s formatting before submission. Ensure you have a separate title page made according to APA standards and cite sources using the parenthetical author-date referencing format.
You need to take a closer look at various dimensions of an assigned article to compose a valuable review. Study the author’s object of analysis, the purpose of their research, the chosen method, data, and findings. Evaluate all these dimensions critically to see whether the author has achieved the initial goals. Finally, offer improvement recommendations to add a critique aspect to your paper.
- Scientific Article Review: Duke University
- Book and Article Reviews: William & Mary, Writing Resources Center
- Sample Format for Reviewing a Journal Article: Boonshoft School of Medicine
- Research Paper Review – Structure and Format Guidelines: New Jersey Institute of Technology
- Article Review: University of Waterloo
- Article Review: University of South Australia
- How to Write a Journal Article Review: University of Newcastle Library Guides
- Writing Help: The Article Review: Central Michigan University Libraries
- Write a Critical Review of a Scientific Journal Article: McLaughlin Library
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Short essays answer a specific question on the subject. They usually are anywhere between 250 words and 750 words long. A paper with less than 250 words isn’t considered a finished text, so it doesn’t fall under the category of a short essay. Essays of such format are required for...

High school and college students often face challenges when crafting a compare-and-contrast essay. A well-written paper of this kind needs to be structured appropriately to earn you good grades. Knowing how to organize your ideas allows you to present your ideas in a coherent and logical manner This article by...

If you’re a student, you’ve heard about a formal essay: a factual, research-based paper written in 3rd person. Most students have to produce dozens of them during their educational career. Writing a formal essay may not be the easiest task. But fear not: our custom-writing team is here to guide...

Narrative essays are unlike anything you wrote throughout your academic career. Instead of writing a formal paper, you need to tell a story. Familiar elements such as evidence and arguments are replaced with exposition and character development. The importance of writing an outline for an essay like this is hard...

A précis is a brief synopsis of a written piece. It is used to summarize and analyze a text’s main points. If you need to write a précis for a research paper or the AP Lang exam, you’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide by Custom-Writing.org, you’ll...

A synthesis essay requires you to work with multiple sources. You combine the information gathered from them to present a well-rounded argument on a topic. Are you looking for the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing? You’ve come to the right place! In this guide by our custom writing team,...

Do you know how to make your essay stand out? One of the easiest ways is to start your introduction with a catchy hook. A hook is a phrase or a sentence that helps to grab the reader’s attention. After reading this article by Custom-Writing.org, you will be able to...

Critical thinking is the process of evaluating and analyzing information. People who use it in everyday life are open to different opinions. They rely on reason and logic when making conclusions about certain issues. A critical thinking essay shows how your thoughts change as you research your topic. This type...

Process analysis is an explanation of how something works or happens. Want to know more? Read the following article prepared by our custom writing specialists and learn about: process analysis and its typesa process analysis outline tipsfree examples and other tips that might be helpful for your college assignment So,...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any...
How to Write an Article Review That Stands Out

An article review is a critical assessment of another writer’s research paper or scholarly article. Such an activity aims to expand one’s knowledge by evaluating the original author’s research.
Of course, writing an article review could be tricky. But a few expert tips and tricks can get you on the right track. That’s what this interesting blog post is all about. So, ensure you read it till the end to make the most out of it.
Table of Contents
A Step-by-step Guide on How to Write an Article Review
Master the art of writing an article review with this step-by-step guide from professional paper help providers.
Step 1: Select the Right Article
The first step is to pick a suitable article for a review. Choose a scholarly source that’s connected to your area of study. You can look for pieces printed in trustworthy journals or by respected authors.
For Example:
For reviewing an article on climate change, consider selecting one from scientific journals like Nature or Science.
Step 2: Read and Understand the Article
It’s super important to read and understand the article before writing your review. Read the article a few times and jot down the notes as you go. Focus on the main arguments, major points, evidence, and how it’s structured.
Let’s say you’re looking at an article on how social media affects mental health. Ensure to take note of the following:
- The number of people involved
- How the data is analyzed
- The Results
Step 3: Structure and Introduction
To start a solid review, start with an introduction that gives readers the background info they need. Must include the article’s title, the author, and where it was published. Also, write a summary of the main point or argument in the article.
“In the article ‘The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health by John Smith, published in the Journal of Psychology:
The author examines the correlation between excessive social media usage and adolescent mental health disorders.”
Step 4: Summarize the Article
In this part, you’ll need to quickly go over the main points and arguments from the article. Make it short but must cover the most important elements and the evidence that backs them up. Leave your opinions and analysis out of it for now.
For instance, you could write:
“The author discusses various studies highlighting the negative effects of excessive social media usage on mental health.
Smith’s research reveals a significant correlation between
Increased social media consumption and higher rates of anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem among teenagers.
The article also explores the underlying mechanisms, such as social comparison and cyberbullying. All are contributing to the adverse mental health outcomes.”
Step 5: Critically Analyze and Evaluate
Now that you’ve given a rundown of the article, it’s time to take a closer look. Think about what the author did well and what could have been done better.
Check out the proof they used and if it seems solid. Give a thorough assessment, and use examples from the text to support your thoughts.
For Example
“While the article presents compelling evidence linking social media usage to mental health issues , it is important to acknowledge some limitations in Smith’s study.
The sample size of the research was relatively small. It comprises only 100 participants, which may limit the generalizability of the findings.
Additionally, the study primarily focused on one specific age group, namely adolescents. This way, there’s room for further research on other demographic groups.”
Step 6: Express Your Perspective
Here’s your chance to give your two cents and show off your smarts. Put your spin on the article by pointing out the pros, cons, and other potential improvements. Remember to back up your thoughts with facts and sound arguments.
Continuing with the Previous Example
Despite the limitations, Smith’s research offers valuable insights into the complex relationship between social media and mental health.
Future studies could expand the sample size and include a more diverse range of age groups. It is better to understand the broader impact of social media on mental well-being.
Furthermore, exploring strategies for developing digital literacy programs could be potential avenues for future research.
Step 7: Conclusion and Final Thoughts
At the end of your article review, wrap it up with a brief and powerful conclusion. Give a summary of your main points and overall thoughts about the article.
Point out its importance to the field and the impact of the study. Finish off with a thought-provoking conclusion. Give the reader a sense of finality and emphasize the need for additional research or discussion.
For instance
“In conclusion, John Smith’s article provides valuable insights into the detrimental effects of excessive social media usage on adolescent mental health.
While the research has limitations, it serves as a starting point for further investigation in this rapidly evolving field.
By addressing the research gaps and implementing targeted interventions:
We can strive to promote a healthier relationship between social media and mental well-being in our digitally connected society.”
Step 8: Editing and Proofreading
Before submission, set aside some time for editing and proofreading.
Ensure everything makes sense and everything is correct. Check out how it reads and if your points come across clearly. Get feedback from other people to get a different point of view and make it even better.
Types of Article Reviews
In college, you might be asked to write different types of review articles, including:
Narrative Review
This type of review needs you to look into the author’s background and experiences. You have to go through the specialist’s theories and practices and compare them. For the success of a narrative review, ensure that your arguments are qualitative and make sense.
Evidence Review
For a solid evidence paper, you got to put in the work and study the topic. You’ll need to research the facts, analyze the author’s ideas, their effects, and more.
Systematic Review
This task involves reviewing a bunch of research papers and summarizing the existing knowledge about a certain subject. A systematic paper type uses an organized approach and expects you to answer questions linked to the research.
Tips for Writing a Great Article Review
Here are some expert tips you could use to write an exceptional article review:
1. Figure out the main points you want to cover and why they matter.
- It will help you zero in on the key points.
2. Look for and assess pertinent sources, both from the past and present.
- It will give you a better understanding of the article you’re looking at.
3. Come Up with a Catchy Title, Summarize Your Topic in an Abstract, and Select Keywords
- It will help people read your review and get a good idea of what it’s about.
4. Write the main point of a review along with introducing the topic.
- It should help readers get a better grasp of the topic.
Outline for Writing a Good Article Review
Here’s an outline to write an excellent article review.
Introduction
– Begin with a summary of the article
– Put in background knowledge of the topic
– State why you are writing the review
– Give an overview of the article’s main points
– Figure out why the author choose to write something
– Look at the article and consider what it does well and what it could have done better.
– Highlight the shortcomings in the article
– Restate why you are writing the review
– Sum up the main points in a few sentences
– Suggest what could be achieved in the future research
Review Article Example
Title: “The Power of Vulnerability: A Review of Brené Brown’s Daring Greatly”
Introduction:
In her revolutionary book “Daring Greatly,”
Brené Brown, a renowned researcher and storyteller. Delves into vulnerability and how it can positively impact our lives, both professionally and personally.
Brown’s work has gained lots of praise. Since it resonates with people looking to build real connections in a world that often feels isolated.
This article looks to recap the main ideas and concepts from “Daring Greatly.” Also explains why it is such a captivating and insightful read.
Summary of Key Ideas:
“Daring Greatly” is all about how the vulnerability isn’t a sign of being weak. but it’s actually what it takes to be brave, strong and live a full life.
Brene Brown examines how society and culture can make it hard to be vulnerable. And, how fear of being judged or shamed stops us from being our authentic selves.
The book puts a lot of emphasis on shame and how it affects us.
Brown explains that shame thrives when it’s kept hidden away and can only be cured by being open, understanding, and compassionate.
By admitting our weaknesses, we can create meaningful connections and a sense of community.
Brown looks into the connection between being open to vulnerability and unleashing creative leadership and innovation.
She uses her own experiences and research to support her viewpoint. The book also gives useful advice on how to include vulnerability in different parts of life. Such as relationships, parenting, and the workplace.
Strengths of the Book:
Brown’s book is remarkable for her ability to mix her own experiences with comprehensive research. Combining her stories and evidence makes the material engaging and easy to understand.
Plus, her writing style is so friendly that readers feel they’re being acknowledged and accepted.
There’s advice on how to be kind to yourself. Set your limits, and accept that things won’t always be perfect. It’s like a toolkit to help you build strength and make positive changes.
Final Verdict
This book is really helpful for everyone, no matter who you are. It can help you figure out how to grow in life, have better relationships, and become a better leader. Plus, since it applies to all kinds of people, everyone can get something out of it.
If you want to write a great article review, it’s important to pick the right article, understand and analyze it critically. Finally, express your thoughts on it clearly. Ensure to stay impartial, back up your points with evidence, and write clearly and coherently.
Still if you are having troubles writing an article review, don’t hesitate to count on the expertise of our writers .
Order Original Papers & Essays
Your First Custom Paper Sample is on Us!
Timely Deliveries
No Plagiarism & AI
100% Refund
Try Our Free Paper Writing Service
Related blogs.

Connections with Writers and support
Privacy and Confidentiality Guarantee
Average Quality Score
How to Write an Article Review: Practical Tips and Examples
Table of contents
- 1 What Is an Article Review?
- 2 Different Types of Article Review
- 3.1 Critical review
- 3.2 Literature review
- 3.3 Mapping review/systematic map
- 3.4 Meta-analysis
- 3.5 Overview
- 3.6 Qualitative Systematic Review/Qualitative Evidence Synthesis
- 3.7 Rapid review
- 3.8 Scoping review
- 3.9 Systematic review
- 3.10 Umbrella review
- 4 Formatting
- 5 How To Write An Article Review
- 6 Article Review Outline
- 7 10 Tips for Writing an Article Review
- 8 An Article Review Example
What Is an Article Review?
Before you get started, learn what an article review is. It can be defined as a work that combines elements of summary and critical analysis. If you are writing an article review, you should take a close look at another author’s work. Many experts regularly practice evaluating the work of others. The purpose of this is to improve writing skills.
This kind of work belongs to professional pieces of writing because the process of crafting this paper requires reviewing, summarizing, and understanding the topic. Only experts are able to compose really good reviews containing a logical evaluation of a paper as well as a critique.
Your task is not to provide new information. You should process what you have in a certain publication.
Different Types of Article Review
In academic writing, the landscape of article reviews is diverse and nuanced, encompassing a variety of formats that cater to different research purposes and methodologies. Among these, three main types of article reviews stand out due to their distinct approaches and applications:
- Narrative. The basic focus here is the author’s personal experience. Judgments are presented through the prism of experiences and subsequent realizations. Besides, the use of emotional recollections is acceptable.
- Evidence. There is a significant difference from the narrative review. An in-depth study of the subject is assumed, and conclusions are built on arguments. The author may consider theories or concrete facts to support that.
- Systematic. The structure of the piece explains the approach to writing. The answer to what’s a systematic review lies on the surface. The writer should pay special attention to the chronology and logic of the narrative.
Understanding 10 Common Types
Don`t rush looking at meta-analysis vs. systematic review. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with other formats and topics of texts. This will allow you to understand the types of essays better and select them based on your request. For this purpose, we`ll discuss the typology of reviews below.
Critical review
The critical review definition says that the author must be objective and have arguments for each thought. Sometimes, amateur authors believe that they should “criticize” something. However, it is important to understand the difference since objectivity and the absence of emotional judgments are prioritized. The structure of this type of review article is as follows:
- Introduction;
- Conclusion.
“Stuffing” of the text is based on such elements as methodology, argumentation, evidence, and theory base. The subject of study is stated at the beginning of the material. Then follows the transition to the main part (facts). The final word summarizes all the information voiced earlier.
It is a mistake to believe that critical reviews are devoid of evaluation. The author’s art lies in maneuvering between facts. Smooth transition from one argument to another and lays out the conclusions in the reader. That is why such texts are used in science. The critical reviews meaning is especially tangible in medical topics.
Literature review
Literature is the basis for this type of work ─ books, essays, and articles become a source of information. Thus, the author should rethink the voiced information. After that, it is possible to proceed to conclusions. The methodology aims to find interconnections, repetitions, and even “gaps” in the literature. One important item is the referencing of sources. Footnotes are possible in the work itself or the list of resources used.
These types of research reviews often explore myths since there are often inconsistencies in mythology. Sometimes, there is contrary information. In this case, the author has to gather all existing theories. The essence does not always lie in the confirmation of facts. There are other different types of reviews for this purpose. In literary reviews, the object of study may be characters or traditions. This is where the author’s space for discovery opens up. Inconsistencies in the data can tell important details about particular periods or cultures. At the same time, patterns reveal well-established facts. Make sure to outline your work before you write. This will help you with essay writing .
Mapping review/systematic map
A mapping review, also known as a systematic map, is a unique approach to surveying and organizing existing literature, providing a panoramic view of the research landscape. This paper systematically categorizes and maps out the available literature on a particular topic, emphasizing breadth over depth. Its primary goal is to present a comprehensive visual representation of the research distribution, offering insights into the overall scope of a subject.
One of the strengths of systematic reviews is that they deeply focus on a research question with detailed analysis and synthesis, while mapping review prioritizes breadth. It identifies and categorizes a broad range of studies without necessarily providing in-depth critique or content synthesis. This approach allows for a broader understanding of the field, making it especially useful in the early stages of research. Mapping reviews excel in identifying gaps in the existing body of literature.
By systematically mapping the distribution of research, researchers can pinpoint areas where studies are scarce or nonexistent, helping to guide future research directions. This makes mapping reviews a valuable tool for researchers seeking to contribute meaningfully to a field by addressing unexplored or underexplored areas.
Meta-analysis
Meta-analysis is a powerful statistical technique. It systematically combines the results of multiple studies to derive comprehensive and nuanced insights. This method goes beyond the limitations of individual studies, offering a more robust understanding of a particular phenomenon by synthesizing data from diverse sources.
Meta-analysis employs a rigorous methodology. It involves the systematic collection and statistical integration of data from multiple studies. This methodological rigor ensures a standardized and unbiased approach to data synthesis. It is applied across various disciplines, from medicine and psychology to social sciences, providing a quantitative assessment of the overall effect of an intervention or the strength of an association.
In evidence-based fields, where informed decision-making relies on a thorough understanding of existing research, meta-analysis plays a pivotal role. It offers a quantitative overview of the collective evidence, helping researchers, policymakers, and practitioners make more informed decisions. By synthesizing results from diverse studies, meta-analysis contributes to the establishment of robust evidence-based practices, enhancing the reliability and credibility of findings in various fields. To present your research findings in the most readable way possible, learn how to write a summary of article .
If the key purpose of systematic review is to maximize the disclosure of facts, the opposite is true here. Imagine a video shot by a quadcopter from an altitude. The viewer sees a vast area of terrain without focusing on individual details. Overviews follow the same principle. The author gives a general picture of the events or objects described.
These types of reviews often seem simple. However, the role of the researcher becomes a very demanding one. The point is not just to list facts. Here, the search for information comes to the fore. After all, it is such reports that, in the future, will provide the basis for researching issues more narrowly. In essence, you yourself create a new source of information ─ students who worry that somebody may critique the author’s article love this type of material. However, there are no questions for the author; they just set the stage for discussions in different fields.
An example of this type of report would be a collection of research results from scientists. For example, statistics on the treatment of patients with certain diseases. In such a case, reference is made to scientific articles and doctrines. Based on this information, readers can speak about the effectiveness of certain treatment methods.
Qualitative Systematic Review/Qualitative Evidence Synthesis
One of the next types of review articles represents a meticulous effort to synthesize and analyze qualitative studies within a specific research domain.
The focus is synthesizing qualitative studies, employing a systematic and rigorous approach to extract meaningful insights. Its significance lies in its ability to provide a nuanced understanding of complex phenomena, offering a qualitative lens to complement quantitative analyses. Researchers can uncover patterns, themes, and contextual nuances that may elude traditional quantitative approaches by systematically reviewing and synthesizing qualitative data.
Often, you may meet discussion: is a systematic review quantitative or qualitative? The application of qualitative systematic reviews extends across diverse research domains, from healthcare and social sciences to education and psychology. For example, this approach can offer a comprehensive understanding of patient experiences and preferences in healthcare. In social sciences, it can illuminate cultural or societal dynamics. Its versatility makes it a valuable tool for researchers exploring, interpreting, and integrating qualitative findings to enrich their understanding of complex phenomena within their respective fields.
Rapid review
If you don’t know how to write an article review , try starting with this format. It is the complete opposite of everything we talked about above. The key advantage and feature is speed. Quick overviews are used when time is limited. The focus can go to individual details (key). Often, the focus is still on the principal points.
Often, these types of review papers are critically needed in politics. This method helps to communicate important information to the reader quickly. An example can be a comparison of the election programs of two politicians. The author can show the key differences. Or it can make an overview based on the theses of the opponents’ proposals on different topics.
Seeming simplicity becomes power. Such texts allow the reader to make a quick decision. The author’s task is to understand potential interests and needs. Then, highlight and present the most important data as concisely as possible. In addition to politics, such reports are often used in communications, advertising, and marketing. Experienced writers mention the one-minute principle. This means you can count on 60 seconds of the reader’s attention. If you managed to hook them ─ bravo, you have done the job!
Scoping review
If you read the official scoping review definition, you may find similarities with the systematic type of review. However, recall is a sequential and logical study in the second case. It’s like you stack things on a shelf by color, size, and texture.
This type of review can be more difficult to understand. The basic concept is to explore what is called the field of subjects. This means, on the one hand, exploring a particular topic through the existing data about it. The author tries to find gaps or patterns by drawing on sources of information.
Another good comparison between systematic and this type of review is imagining as if drawing a picture. In the first case, you will think through every nuance and detail, why it is there, and how it “moves the story.” In the second case, it is as if you are painting a picture with “broad strokes.” In doing so, you can explain your motives for choosing the primary color. For example: “I chose the emerald color because all the cultural publications say it’s a trend”. The same goes for texts.
Systematic review
Sometimes, you may encounter a battle: narrative review vs. systematic review. The point is not to compare but to understand the different types of papers. Once you understand their purpose, you can present your data better and choose a more readable format. The systematic approach can be called the most scientific. Such a review relies on the following steps:
- Literature search;
- Evaluating the information;
- Data processing;
- Careful analysis of the material.
It is the fourth point that is key. The writer should carefully process the information before using it. However, 80% of your work’s result depends on this stage’s seriousness.
A rigorous approach to data selection produces an array of factual data. That is why this method is so often used in science, education, and social fields. Where accuracy is important. At the same time, the popularity of this approach is growing in other directions.
Systematic reviews allow for using different data and methodologies,, but with one important caveat ─ if the author manages to keep the narrative structured and explain the reason for certain methods. It is not about rigor. The task of this type of review is to preserve the facts, which dictates consistency and rationality.
Umbrella review
An umbrella review is a distinctive approach that involves the review of existing reviews, providing a comprehensive synthesis of evidence on a specific topic. The methodology of an umbrella review entails systematically examining and summarizing findings from multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
This method ensures a rigorous and consolidated analysis of the existing evidence. The application of an umbrella review is broad, spanning various fields such as medicine, public health, and social sciences. It is particularly useful when a substantial body of systematic reviews exists, allowing researchers to draw overarching conclusions from the collective findings.
It allows the summarization of existing reviews and provides a new perspective on individual subtopics of the main object of study. In the context of the umbrella method, the comparison “bird’s eye view” is often cited. A bird in flight can see the whole panorama and shift its gaze to specific objects simultaneously. What becomes relevant at a particular moment? The author will face the same task.
On the one hand, you must delve into the offshoots of the researched topic. On the other hand, focus on the topic or object of study as a whole. Such a concept allows you to open up new perspectives and thoughts.

Different types of formatting styles are used for article review writing. It mainly depends on the guidelines that are provided by the instructor, sometimes, professors even provide an article review template that needs to be followed.
Here are some common types of formatting styles that you should be aware of when you start writing an article review:
- APA (American Psychological Association) – An APA format article review is commonly used for social sciences. It has guidelines for formatting the title, abstract, body paragraphs, and references. For example, the title of an article in APA format is in sentence case, whereas the publication title is in title case.
- MLA (Modern Language Association): This is a formatting style often used in humanities, such as language studies and literature. There are specific guidelines for the formatting of the title page, header, footer, and citation style.
- Chicago Manual of Style: This is one of the most commonly used formatting styles. It is often used for subjects in humanities and social sciences, but also commonly found in a newspaper title. This includes guidelines for formatting the title page, end notes, footnotes, publication title, article citation, and bibliography.
- Harvard Style: Harvard style is commonly used for social sciences and provides specific guidelines for formatting different sections of the pages, including publication title, summary page, website publisher, and more.
To ensure that your article review paper is properly formatted and meets the requirements, it is crucial to adhere to the specific guidelines for the formatting style you are using. This helps you write a good article review.
- Free unlimited checks
- All common file formats
- Accurate results
- Intuitive interface
How To Write An Article Review
There are several steps that must be followed when you are starting to review articles. You need to follow these to make sure that your thoughts are organized properly. In this way, you can present your ideas in a more concise and clear manner. Here are some tips on how to start an article review and how to cater to each writing stage.
- Read the Article Closely: Even before you start to write an article review, it’s important to make sure that you have read the specific article thoroughly. Write down the central points and all the supporting ideas. It’s important also to note any questions or comments that you have about the content.
- Identify the Thesis: Make sure that you understand the author’s main points, and identify the main thesis of the article. This will help you focus on your review and ensure that you are addressing all of the key points.
- Formulate an Introduction: The piece should start with an introduction that has all the necessary background information, possibly in the first paragraph or in the first few paragraphs. This can include a brief summary of the important points or an explanation of the importance.
- Summarize the Article : Summarize the main points when you review the article, and make sure that you include all supporting elements of the author’s thesis.
- Start with Personal Critique : Now is the time to include a personal opinion on the research article or the journal article review. Start with evaluating all the strengths and weaknesses of the reviewed article. Discuss all of the flaws that you found in the author’s evidence and reasoning. Also, point out whether the conclusion provided by the author was well presented or not.
- Add Personal Perspective: Offer your perspective on the original article, do you agree or disagree with the ideas that the article supports or not. Your critical review, in your own words, is an essential part of a good review. Make sure you address all unanswered questions in your review.
- Conclude the Article Review : In this section of the writing process, you need to be very careful and wrap up the whole discussion in a coherent manner. This is should summarize all the main points and offer an overall assessment.
Make sure to stay impartial and provide proof to back up your assessment. By adhering to these guidelines, you can create a reflective and well-structured article review.
Article Review Outline
Here is a basic, detailed outline for an article review you should be aware of as a pre-writing process if you are wondering how to write an article review.
Introduction
- Introduce the article that you are reviewing (author name, publication date, title, etc.) Now provide an overview of the article’s main topic
Summary section
- Summarize the key points in the article as well as any arguments Identify the findings and conclusion
Critical Review
- Assess and evaluate the positive aspects and the drawbacks
- Discuss if the authors arguments were verified by the evidence of the article
- Identify if the text provides substantial information for any future paper or further research
- Assess any gaps in the arguments
- Restate the thesis statement
- Provide a summary for all sections
- Write any recommendations and thoughts that you have on the article
- Never forget to add and cite any references that you used in your article
10 Tips for Writing an Article Review
Have you ever written such an assignment? If not, study the helpful tips for composing a paper. If you follow the recommendations provided here, the process of writing a summary of the article won’t be so time-consuming, and you will be able to write an article in the most effective manner.
The guidelines below will help to make the process of preparing a paper much more productive. Let’s get started!
- Check what kind of information your work should contain. After answering the key question “What is an article review?” you should learn how to structure it the right way. To succeed, you need to know what your work should be based on. An analysis with insightful observations is a must for your piece of writing.
- Identify the central idea: In your first reading, focus on the overall impression. Gather ideas about what the writer wants to tell, and consider whether he or she managed to achieve it.
- Look up unfamiliar terms. Don’t know what certain words and expressions mean? Highlight them, and don’t forget to check what they mean with a reliable source of information.
- Highlight the most important ideas. If you are reading it a second time, use a highlighter to highlight the points that are most important to understanding the passage.
- Write an outline. A well-written outline will make your life a lot easier. All your thoughts will be grouped. Detailed planning helps not to miss anything important. Think about the questions you should answer when writing.
- Brainstorm headline ideas. When choosing a project, remember: it should reflect the main idea. Make it bold and concise.
- Check an article review format example. You should check that you know how to cite an article properly. Note that citation rules are different in APA and MLA formats. Ask your teacher which one to prioritize.
- Write a good introduction. Use only one short paragraph to state the central idea of the work. Emphasize the author’s key concepts and arguments. Add the thesis at the end of the Introduction.
- Write in a formal style. Use the third person, remembering that this assignment should be written in a formal academic writing style.
- Wrap up, offer your critique, and close. Give your opinion on whether the author achieved his goals. Mention the shortcomings of the job, if any, and highlight its strengths.
If you have checked the tips and you still doubt whether you have all the necessary skills and time to prepare this kind of educational work, follow one more tip that guarantees 100% success- ask for professional assistance by asking the custom writing service PapersOwl to craft your paper instead of you. Just submit an order online and get the paper completed by experts.

An Article Review Example
If you have a task to prepare an analysis of a certain piece of literature, have a look at the article review sample. There is an article review example for you to have a clear picture of what it must look like.
Journal Article on Ayn Rand’s Works Review Example
“The purpose of the article is to consider the features of the poetics of Ayn Rand’s novels “Atlas Shrugged,” “We the living,” and “The Fountainhead.” In the analysis of the novels, the structural-semantic and the method of comparative analysis were used.
With the help of these methods, genre features of the novels were revealed, and a single conflict and a cyclic hero were identified.
In-depth reading allows us to more fully reveal the worldview of the author reflected in the novels. It becomes easier to understand the essence of the author’s ideas about the connection between being and consciousness, embodied in cyclic ideas and images of plot twists and heroes. The author did a good job highlighting the strong points of the works and mentioning the reasons for the obvious success of Ayn Rand.“
You can also search for other relevant article review examples before you start.
In conclusion, article reviews play an important role in evaluating and analyzing different scholarly articles. Writing a review requires critical thinking skills and a deep understanding of the article’s content, style, and structure. It is crucial to identify the type of article review and follow the specific guidelines for formatting style provided by the instructor or professor.
The process of writing an article review requires several steps, such as reading the article attentively, identifying the thesis, and formulating an introduction. By following the tips and examples provided in this article, students can write a worthy review that demonstrates their ability to evaluate and critique another writer’s work.
Learning how to write an article review is a critical skill for students and professionals alike. Before diving into the nitty-gritty of reviewing an article, it’s important to understand what an article review is and the elements it should include. An article review is an assessment of a piece of writing that summarizes and evaluates a work. To complete a quality article review, the author should consider the text’s purpose and content, its organization, the author’s style, and how the article fits into a larger conversation. But if you don’t have the time to do all of this work, you can always purchase a literature review from Papers Owl .
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
The Tech Edvocate
- Advertisement
- Home Page Five (No Sidebar)
- Home Page Four
- Home Page Three
- Home Page Two
- Icons [No Sidebar]
- Left Sidbear Page
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- My Speaking Page
- Newsletter Sign Up Confirmation
- Newsletter Unsubscription
- Page Example
- Privacy Policy
- Protected Content
- Request a Product Review
- Shortcodes Examples
- Terms and Conditions
- The Edvocate
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- Write For Us
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Assistive Technology
- Child Development Tech
- Early Childhood & K-12 EdTech
- EdTech Futures
- EdTech News
- EdTech Policy & Reform
- EdTech Startups & Businesses
- Higher Education EdTech
- Online Learning & eLearning
- Parent & Family Tech
- Personalized Learning
- Product Reviews
- Tech Edvocate Awards
- School Ratings
Reading Anxiety In Children: Everything You Need to Know
Iep meetings and parent-teacher conferences: everything you need to know, college disability services and accommodations: everything you need to know, spam vs. phishing: how are these unwanted messages different, how to charge your iphone properly, encouraging your teenager to read: everything you need to know, 8 ways to service an air conditioner, 3 ways to stop a baby from vomiting, 3 ways to save instagram highlights, skills needed for reading comprehension: everything you need to know, how to write an article review (with sample reviews) .

An article review is a critical evaluation of a scholarly or scientific piece, which aims to summarize its main ideas, assess its contributions, and provide constructive feedback. A well-written review not only benefits the author of the article under scrutiny but also serves as a valuable resource for fellow researchers and scholars. Follow these steps to create an effective and informative article review:
1. Understand the purpose: Before diving into the article, it is important to understand the intent of writing a review. This helps in focusing your thoughts, directing your analysis, and ensuring your review adds value to the academic community.
2. Read the article thoroughly: Carefully read the article multiple times to get a complete understanding of its content, arguments, and conclusions. As you read, take notes on key points, supporting evidence, and any areas that require further exploration or clarification.
3. Summarize the main ideas: In your review’s introduction, briefly outline the primary themes and arguments presented by the author(s). Keep it concise but sufficiently informative so that readers can quickly grasp the essence of the article.
4. Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses: In subsequent paragraphs, assess the strengths and limitations of the article based on factors such as methodology, quality of evidence presented, coherence of arguments, and alignment with existing literature in the field. Be fair and objective while providing your critique.
5. Discuss any implications: Deliberate on how this particular piece contributes to or challenges existing knowledge in its discipline. You may also discuss potential improvements for future research or explore real-world applications stemming from this study.
6. Provide recommendations: Finally, offer suggestions for both the author(s) and readers regarding how they can further build on this work or apply its findings in practice.
7. Proofread and revise: Once your initial draft is complete, go through it carefully for clarity, accuracy, and coherence. Revise as necessary, ensuring your review is both informative and engaging for readers.
Sample Review:
A Critical Review of “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health”
Introduction:
“The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health” is a timely article which investigates the relationship between social media usage and psychological well-being. The authors present compelling evidence to support their argument that excessive use of social media can result in decreased self-esteem, increased anxiety, and a negative impact on interpersonal relationships.
Strengths and weaknesses:
One of the strengths of this article lies in its well-structured methodology utilizing a variety of sources, including quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews. This approach provides a comprehensive view of the topic, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of the effects of social media on mental health. However, it would have been beneficial if the authors included a larger sample size to increase the reliability of their conclusions. Additionally, exploring how different platforms may influence mental health differently could have added depth to the analysis.
Implications:
The findings in this article contribute significantly to ongoing debates surrounding the psychological implications of social media use. It highlights the potential dangers that excessive engagement with online platforms may pose to one’s mental well-being and encourages further research into interventions that could mitigate these risks. The study also offers an opportunity for educators and policy-makers to take note and develop strategies to foster healthier online behavior.
Recommendations:
Future researchers should consider investigating how specific social media platforms impact mental health outcomes, as this could lead to more targeted interventions. For practitioners, implementing educational programs aimed at promoting healthy online habits may be beneficial in mitigating the potential negative consequences associated with excessive social media use.
Conclusion:
Overall, “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health” is an important and informative piece that raises awareness about a pressing issue in today’s digital age. Given its minor limitations, it provides valuable
3 Ways to Make a Mini Greenhouse ...
3 ways to teach yourself to play ....
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.

3 Ways to Neutralize Ammonia

How to Play Dice 4, 5, 6: 14 Steps

How to Impress a French Girl: 4 Steps
How to Put Feathers in Your Hair

3 Ways to Drive a Car in Reverse Gear

3 Ways to Give Yourself a Facial Massage
- All eBooks & Audiobooks
- Academic eBook Collection
- Home Grown eBook Collection
- Off-Campus Access
- Literature Resource Center
- Opposing Viewpoints
- ProQuest Central
- Course Guides
- Citing Sources
- Library Research
- Websites by Topic
- Book-a-Librarian
- Research Tutorials
- Use the Catalog
- Use Databases
- Use Films on Demand
- Use Home Grown eBooks
- Use NC LIVE
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary vs. Secondary
- Scholarly vs. Popular
- Make an Appointment
- Writing Tools
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing Center
Service Alert

Article Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing an article SUMMARY
Writing an article REVIEW
- Writing an article CRITIQUE
- Citing Sources This link opens in a new window
- About RCC Library
Text: 336-308-8801
Email: [email protected]
Call: 336-633-0204
Schedule: Book-a-Librarian
Like us on Facebook
Links on this guide may go to external web sites not connected with Randolph Community College. Their inclusion is not an endorsement by Randolph Community College and the College is not responsible for the accuracy of their content or the security of their site.
A journal article review is written for a reader who is knowledgeable in the discipline and is interested not just in the coverage and content of the article being reviewed, but also in your critical assessment of the ideas and argument that are being presented by the author.
Your review might be guided by the following questions:
Additional Resources
All links open in a new window.
How to Write an Article Review (from Essaypro.com)
How to Review a Journal Article (from University of Illinois Springfield)
Writing Critical Reviews (from Queen's University Library)
- << Previous: Writing an article SUMMARY
- Next: Writing an article CRITIQUE >>
- Last Updated: Mar 15, 2024 9:32 AM
- URL: https://libguides.randolph.edu/summaries

How to Write an Article Review
a scholarly article, scientific paper, political article, book report, research paper, or any publication your teacher or professor assigns. It requires an in-depth understanding of the subject matter as well as the ability to critique someone else work.
What Is an Article Review
An article review asks the writer to evaluate another person’s work - understand it, analyze it, present it concisely, and question the conclusions drawn by the author. They are often used by teachers to introduce students to experts’ work in the field and to test their critical thinking skills.
This assignment isn’t like a typical essay. It answers how to review an article, but it doesn’t follow the classic 5 paragraph style of formal essay writing - there are other steps you have to follow. This makes writing one a new challenge for students, but don’t worry, this article will cover everything you need to know about how to write article review.
Article Review Types
There are several different types of article reviews, most of which you don’t have to worry about because they are either very specialized or are meant for professionals. Some examples of these are scoping review, systematic review, umbrella review, meta-analyses, and more complicated sounding names. Here, we’ll talk about the types of article reviews students usually have to deal with.
Narrative Article Review
A summation and analysis of a particular publication. It focuses on critiquing the biases of the author as well as logical inconsistencies. These can be book reports, film critiques, story critiques, etc.
Systematic Article Review
Using multiple sources to summarize information about a specific topic. This is a more complex type of article review that uses systematic methods to evaluate available research. These tend to be more technical in nature and are used often in the sciences and quantitative humanities.
Evidence Article Review
Focuses on analyzing the evidence and the findings based on that evidence. Whereas a systematic review’s primary focus isn’t the evidence, it is for this type of review.
Journal Article Review
An analysis of any type of publication focusing on the article’s opinion and subject matter. It answers how important the article is as well as analyzing the article itself.
Research Article Review
A subset of a journal article review that analyzes literary publications. It summarizes the presented research and evaluates the conclusions the original author draws.
Science Article Review
A subset of journal article reviews that analyzes scientific journals. As such, it focuses on the research methodology used and the conclusions based on the evidence.
Struggling with your Article Review Homework?
Get your assignments done by real pros. Save your precious time and boost your marks with ease.
Article Review Format
Following instructions is absolutely critical to getting a good grade. An article review has a very particular format that must be followed. Read an article review example to get a sense of what it’s like and take a look at the Template and Outline section further down for a step by step guide on how to structure your paper.
One key thing to note is the citation style. Your professor or teacher will specify which citation style to use between MLA and APA. While both styles require in-text parenthetical citations, how to write an article review APA or MLA differ slightly in style.
APA Article Review Citation
APA stands for American Psychological Association and is generally used for social studies. If you need to write an APA format article review, these are the structures.
Journal: Author’s last name, Author’s first initial. Author’s middle initial. (Year, Month Date Published). Article title. Journal Name, Volume (Issue), page number(s).
Newspaper Print: Author, A. (Year, Month Date of Publication). Article title. Newspaper Title, pp. Xx-xx.
Newspaper Online: Author, A. (Year, Month Date of Publication). Article title. Newspaper Title, Retrieved from newspaper homepage URL
Website: Author’s last name, Initial(s). (Year, Month Day of publication). Title of work. Website. https://URL
Follow this citation article review examples to write a perfect apa style article review.
MLA Article Review Citation
MLA stands for Modern Language Association and is generally used for arts and humanities subjects. For the MLA format , these are the structures.
Journal: Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Journal Title Series Volume. Issue (Year Published): Page(s). Database Name. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
Newspaper Print: Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Article: Subtitle if Any." Name of Newspaper, Date of Publication, p. Page Number.
Newspaper Online: Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Article: Subtitle if Any." Title of Website, Date of Publication, URL. Accessed Day Month Year site was visited.
Website: Author's Last Name, First Name. Title of Website, Name of Organization Affiliated with the Website, Date of copyright or date last modified/updated, URL. Accessed Day Month Year site was visited.
The Planning Stage
What’s the structure going to be.
Knowing the different sections of a review article before reading the original article will help you process information in a useful way. Read an example of an article review to give you an idea of what to expect. There are 3 main parts to keep in mind.
- Summarize the article by identifying the most important points of information and the main claims made by the author
- Talk about what the author gets right. An analysis of the positive elements of the author’s opinions, research, and conclusions
- Discuss what the author could have done better. Think about shaky conclusions, inconsistent research, and unanswered questions.
Your first read
Do a quick read of the article. Start by reading the title, abstract, introduction, headings, the first few lines of every paragraph, and the conclusion. This should give you an idea of what the article will be about. Then read the article taking note of terms or concepts you don’t understand. After your first quick read, research the concepts that you aren’t familiar with to make sure to get a better understanding on your next read-through.
Your second read
Now read the article slowly and deliberately, highlighting important information and taking notes. Connect information with knowledge you already have on the subject. Think about what new information is being presented in the article and how it differs or supports what you already know. Read the article as many times as you need to so that you understand it perfectly. It’s impossible to write a good review if you don’t understand the article itself!
Collecting information
Write the article again in your own words. This will help you identify the main points, arguments, and conclusions of the article and deepen your understanding. Don’t worry about editing, this is just for yourself.
Creating an outline
Now that you’ve dissected the article and noted down the main points and arguments, you’re well prepared to work on your review outline. Creating an outline helps plan your essay and cuts down on a lot of writing and reviewing time.
Did you like our inspiring Article Review Writing Guide?
For more help, tap into our pool of professional writers and get expert essay editing services!
Article Review Template & Outline
Use the outline as a guide to help plan and write your review. An article review, though a unique form of writing, still follows the traditional introduction, body, and conclusion format of essays, but has several specific sections that must be included as well. Fit these into your body paragraphs.
Pre-Title Page - This section states the basics. What type of article it is, the title of the article, contributing authors, and the authors’ credentials.
Optional Corresponding Author Details - Specific details of the authors including phone numbers, email addresses, etc.
Running Head - The title of your paper shortened to 40 characters or less (only required for APA format).
Summary Page - Some teachers ask for a summary page. It’s an 800 word or less summary that gives background information, explains the purpose of the review and summarizes the results. Don’t copy pieces of text from the article or the review itself, keep the language simple, and there’s no need to use references.
Title Page - This page can be thought of as the official start of your paper. You need to include the full title, a 250 word abstract, and a few keywords.
Introduction - The beginning of your review including a thesis statement.
Body Paragraphs - Include headings and subheadings to lay out your analysis clearly.
Works Cited/References - Differs in style based on MLA or APA format. Get clarification from your teacher if it isn’t clear.
Optional Suggested Reading List - If required by the professor.
Tables and Figure Legends - If required by the type of article or professor.
Article Review Writing: Step by Step
Step 1: title selection.
Spend some time crafting an interesting and representative title. A good title is both catchy as well as informative. It often helps to start with a tentative title and modify it as you write your paper. Your title should guide you as you write your paper, but it should also be reflective of the main purpose of the review.
Step 2: Article Citation
You need to properly cite the reviewed article. The most important thing is to make sure you are citing it in either APA or MLA format, whichever one is required by your teacher.
Step 3: Brief Article Description
After citing the article, start your first paragraph by stating the title of the article, the author, the name of the journal, and the year of publication.
Step 4: Introduction
Once you’ve identified the article, give a brief description of the main points of the article. Carefully analyze the article to identify and highlight the author’s thesis. Understanding the thesis of the main article is crucial to writing a good review, so make sure you include any sub thesis. End the introduction with your own thesis, this could include accepting and expanding on the original author’s main points, or proposing reasons why the author’s conclusions were flawed.
Step 5: Article Summary
The first body paragraph should summarize the main points of the original article including the author’s arguments and takeaways. Don’t hold yourself to just 3 body paragraphs unless specifically told so by your teacher. Explore a different main point in each paragraph and explain the author’s perspective on the issues. Make sure you review the summary paragraphs so that they accurately reflect the content of the original article and the views of the author.
Step 6: Analysis
Start with a general assessment of the clarity and usefulness of the article. Analyze each point of your summary and express your opinions on what the author did well or badly. Critiquing the article is the most important element of an article review, so devote a majority of your time and effort to this section. Analyze the main points of the article and determine if the author did a good job of backing their claims with logic and fact. Finally decide if you agree with the author’s conclusions and provide supporting evidence to substantiate your claims.
Step 7: Conclusion
Summarize the main points and lessons of the original article and then state your main critiques of the article. Specify why you believe the author made specific mistakes, and how the key takeaways should be different. If possible pose a question about further research or analysis on the topic.
The Post-Writing Process: Revision
Finishing your first draft isn’t the end of the process! If you spent enough time during the prewriting stage and made a good outline you will have to spend much less time during revision.
Checklist for revision
- Do a quick read-through of the entire paper
- Make sure it flows logically from one section to another
- Make sure sentences are clear
- Make sure each paragraph only talks about one main point
- Get rid of unnecessary information
- Check your summary to make sure it represents the original paper accurately
- Check your critique to make sure it is fair and backed up by evidence
- Check the grammar
- Check the punctuation
- Check for typos
- Check your citations
Tips for Writing an Article Review
An article review is a unique form of academic writing that has a well-defined structure and specific requirements. Follow these tips to make writing one easier.
- Make sure you understand the overall structure and format
- On the first read through of the article focus on the big picture impressions
- Do research on terms and concepts you aren’t familiar with
- On the second read through, note down key points
- Spend time preparing a thorough outline
- Come up with several title ideas and choose amongst the best
- Confirm which citation style you need to use between APA and MLA
- Follow the standard introduction paragraph style but include specific requirements
- This is a formal academic paper so keep the tone and style formal as well
- The main body consists of a summary, and then a critique of the original article
- Conclude the review by summarizing your main critiques of the article
An article review tests your formal writing skills, critical thinking, ability to summarize and synthesize information, and evaluative powers. Learning how to craft a critical review of an article isn’t just helpful in academics. The skills you learn and the format will be useful when evaluating anything in your life, whether it be a movie, game review, or social media content.
This comprehensive article provides all the necessary information on how to write a review of an article, but it's clear that the process isn't straightforward. Studyfy boasts a vast team of experts who have assisted numerous students with their homework. If you need assistance, don't hesitate to reach out to them via email for services such as proofreading, essay editing, or expert advice. Whether you require a biology essay writing service , want to write essays for money online , need a custom research paper , or are looking to pay for an essay , Studyfy is here to help!
Featured Posts
How to write a scholarship essay.

How to Write a Movie Review

How to Write an Argumentative Essay

How to Write a Cause and Effect Essay
.jpg)
How to Write an Expository Essay

How to Write an Analytical Essay


The Portable Mentor pp 163–173 Cite as
How to Write an Effective Journal Article Review
- Dennis Drotar PhD 2 ,
- Yelena P. Wu PhD 3 &
- Jennifer M. Rohan MA 4
- First Online: 01 January 2012
5613 Accesses
2 Citations
The experience of reviewing manuscripts for scientific journals is an important one in professional development. Reviewing articles gives trainees familiarity with the peer review process in ways that facilitate their writing. For example, reviewing manuscripts can help students and early career psychologists understand what reviewers and editors look for in a peer-reviewed article and ways to critique and enhance a manuscript based on peer review. Experiences in review can facilitate early career faculty with early entry into and experience being a reviewer for a professional journal. The experience of journal reviews also gives students a broader connection to the field of science in areas of their primary professional interest. At the same time reviewing articles for scientific journals poses a number of difficult challenges (see Hyman, 1995; Drotar, 2000a, 2009a, 2009b, 2009c, 2009d, 2010, 2011; Lovejoy, Revenson, & France, 2011). The purpose of this chapter is to provide an introduction to the review process and give step by step guidance in conducting reviews for scientific journals. Interested readers might wish to read Lovejoy et al.’s (2011) primer for manuscript review, which contains annotated examples of reviews and an editor’s decision letter.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
American Psychological Association. (2010). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (6th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Google Scholar
American Psychological Association Science Student Council. (2007). A graduate students’ guide to involvement in the peer review process. Retrieved July 15, 2011, from http://www.apa.org/research/publishing/
APA Publications and Communications Working Group on Journal Article Reporting Standards. (2008). Reporting standards for research in psychology. Why do we need them? What do they need to be? American Psychologist, 63 , 839–851.
Article Google Scholar
Cumming, G., & Finch, S. (2008). Putting research in context: Understanding confidence intervals from one or more studies. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 34 (9), 903–916.
PubMed Google Scholar
Drotar, D. (2000a). Reviewing and editing manuscripts for scientific journals. In D. Drotar (Ed.), Handbook of research methods in clinical child and pediatric psychology (pp. 409–425). New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum.
Chapter Google Scholar
Drotar, D. (2000b). Training professional psychologists to write and publish. The utility of a writer’s workshop seminar. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 31 , 453–457.
Drotar, D. (2009a). Editorial: How to write effective reviews for the Journal of Pediatric Psychology . Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 34 , 113–117.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Drotar, D. (2009b). Editorial: Thoughts in improving the quality of manuscripts submitted to the Journal of Pediatric Psychology: How to write a convincing introduction. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 34 , 1–3.
Drotar, D. (2009c). Editorial: How to report methods in the Journal of Pediatric Psychology . Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 34 , 227–230.
Drotar, D. (2009d). How to write an effective results and discussion section for the Journal of Pediatric Psychology . Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 34 , 339–343.
Drotar, D. (2010). Editorial: Guidance for submission and review of multiple publications derived from the same study. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 35 , 225–230.
Drotar, D. (2011). Editorial: How to write more effective, user friendly reviews for the Journal of Pediatric Psychology . Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 36 , 1–3.
Durlak, J. A. (2009). How to select, calculate, and interpret effect sizes. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 34 , 917–928.
Fiske, D. W., & Fogg, L. (1990). But the reviewers are making different criticisms of my paper: Diversity and uniqueness in reviewer comments. American Psychologist, 40 , 591–598.
Holmbeck, G. N., & Devine, K. A. (2009). Editorial: An author’s checklist for measure development and validation manuscripts. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 34 (7), 691–696.
Hyman, R. (1995). How to critique a published article. Psychological Bulletin, 118 , 178–182.
Journal of Pediatric Psychology mentoring policy & suggestions for conducting mentored reviews (2009). Retrieved July 15, 2011, from http://www.oxfordjournals.org/our_journals/jpepsy/for_authors/msprep_submission.html
Lovejoy, T. I., Revenson, T. A., & France, C. R. (2011). Reviewing manuscripts for peer-review journals: A primer for novice and seasoned reviewers. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 42 , 1–13.
Palermo, T. M. (2010). Editorial: Exploring ethical issues in peer review for the Journal of Pediatric Psychology. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 35 (3), 221–224.
Routh, D. K. (1995). Confessions of an editor, including mistakes I have made. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 24 , 236–241.
Sternberg, R. J. (Ed.). (2006). Reviewing scientific works in psychology . Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Stinson, J. N., McGrath, P. J., & Yamada, J. T. (2003). Clinical trials in the Journal of Pediatric Psychology : Applying the CONSORT statement. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 28 , 159–167.
Weller, A. C. (2001). Editorial peer review: Its strengths and weaknesses . Medford, NY: Information Today, Inc.
Wu, Y. P., Nassau, J. H., & Drotar, D. (2011). Mentoring reviewers: The Journal of Pediatric Psychology experience. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 36 , 258–264.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Division of Behavioral Medicine and Clinical Psychology, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, MLC 7039, 3333 Burnet Avenue, Cincinnati, OH, 45229-3039, USA
Dennis Drotar PhD
Division of Behavioral Medicine and Clinical Psychology, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH, 45229-3039, USA
Yelena P. Wu PhD
Division of Behavioral Medicine and Clinical Psychology, Department of Psychology, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH, 45229-3039, USA
Jennifer M. Rohan MA
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Dennis Drotar PhD .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
, Department of Psychology, University of North Carolina at Chapel H, Davie Hall, Campus Box 3270, Chapel Hill, 27599-3270, North Carolina, USA
Mitchell J. Prinstein
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Drotar, D., Wu, Y.P., Rohan, J.M. (2013). How to Write an Effective Journal Article Review. In: Prinstein, M. (eds) The Portable Mentor. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-3994-3_11
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-3994-3_11
Published : 25 July 2012
Publisher Name : Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN : 978-1-4614-3993-6
Online ISBN : 978-1-4614-3994-3
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science Behavioral Science and Psychology (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

How to write a journal article review: Do the writing
- What's in this Guide
- What is a journal article?
- Create a template
- Choose your article to review
- Read your article carefully
Do the writing
- Remember to edit
- Additional resources
Start to write. Follow the instructions of your assessment, then structure your writing accordingly.
The four key parts of a journal article review are:
3. A critique, or a discussion about the key points of the journal article.
A critique is a discussion about the key points of the journal article. It should be a balanced discussion about the strengths and weaknesses of the key points and structure of the article.
You will also need to discuss if the author(s) points are valid (supported by other literature) and robust (would you get the same outcome if the way the information was gathered was repeated).
Example of part of a critique
4. A conclusion - a final evaluation of the article
1. Give an overall opinion of the text.
2. Briefly summarise key points and determine if they are valid, useful, accurate etc.
3. Remember, do not include new ideas or opinions in the conclusion.
Pathways and Academic Learning Support

- << Previous: Read your article carefully
- Next: Remember to edit >>
- Last Updated: Apr 27, 2023 4:28 PM
- URL: https://libguides.newcastle.edu.au/how-to-write-a-journal-article-review

10 Best Tips On How To Write An Article Review
Are you stressed because you don’t know How To Write An Article Review? Don’t panic! Practice helps you out in article review writing . As a student, we understand it is a challenging task. But it is a great way to improve your reading, analytical, writing, and scientific skills. So let’s start!
Before getting straight to reviewing an article, you should have some knowledge of what an article review is. So, an article review is a study of writing when you compile and access someone else’s article.
It involves a sensible evaluation of the theme of an article i.e. when you evaluate another persona’s article then there should be some point of reviewing the article.
A review can be a critical review or it can be a literature review i.e. you may or may not agree with the point the writer has made in his/her article.
A critical analysis is a comprehensive type of text dealing with a particular article or book in detail.
Sure, you can archive that dynamic content on How To Write An Article Review.
What Is An Article Review?
Table of Contents
An article review is a critical analysis of an academic article or research paper. It is written by experts in a particular field. The goal of an article review is to evaluate the quality, relevance, and significance of the article to the field and to provide a summary of its key points and arguments.
Moreover, article reviews are typically written by scholars, researchers, or students as a way to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in their field. It is used to assess the quality of published research critically. They are often published in academic journals or other educational publications.
The structure of an article review varies depending on the requirements of the assignment or the publication. However, most article reviews include an introduction that provides context for the article being reviewed, a summary of the article’s main points and arguments, a critical evaluation of the article’s strengths and weaknesses, and a conclusion that synthesizes the reviewer’s overall assessment of the article.
5 Types of article review
An article review is an evaluation and summary of someone else’s work, and it has a particular format and some guidelines to write, which you have to follow to review an article. Here, in this blog, we will provide you a complete guide on how to write an article review.
Reviewing an article is essential
- Because it helps the readers to understand the indefinite terms.
- Reviewing the article clarifies so many questions.
- As the review provides suggestion or analysis of the article to the author and that assists or helps the author to execute the work in a better way next time.
How To Write An Article Review: The pre-writing process
For reviewing an article in an excellent way, one should first prepare and then write the review.
And the formation of a review includes the following steps for How To Write A Good Article Review that you should follow: –
Step 1: – Understanding what the article review is
You should never underestimate the viewers as the viewers of the review already has information and knowledge on the topic and is not the general audience.
So first of all, you need to summarize all the main ideas of the article, the thoughts and all.
And you should also critique the participation of the matter and effectiveness of the field. The review of the article responds to the research of the authors and it does not include new analysis. The review assesses and summarizes the article.
Step 2: – Identify the organization of the review article
Before you even start to read the article you will review, you should know how your articles review will be set up and how does it work.
This will help you understand how to read the article. so that, you can get the maximum information out of it and write an effective review.
You should summarize the article and you should concentrate on the major points and information.
You should discuss the positive viewpoints of the article and think about what the author does well.
Identify all the contradictions and gaps in the text. You should also check if the author has done enough research on the topic he has written. And find if there are any questions left which are not being answered in the article.
Step 3: – Preview the article
Start by looking at the tile of the article, abstract and introduction and the headings of each paragraph of the article and the conclusion which the author has concluded.
Read the first few paragraphs just to get the idea of what the author wants to say and the article’s main point.
These steps should help you get the brief idea of the article and you will surely get the bigger picture of what is going on in the article and what the author wants to say. And by doing this you will get the look of the overall argument.

As soon as you start getting the idea of what is going on in the article, start making notes of it and start writing the questions you have in mind. Try to look for the terms and concepts you are unknown with so that you can read about those concepts and get some knowledge about it before writing the review.
Step 4: – Read the article carefully
Read the article very carefully just to make sure that you didn’t left any point the author wants to highlight.
Give it a few readings and the make notes of the essential sections. Just to highlight the main points and details.
Compare what you have read with to your actual understanding of the topic.
Pay careful attention to the meaning of the article. Make sure that you understand the article completely because half knowledge is the worst thing and by understanding the article completely you can write a good review.
Step 5: – Write the article in your own words.
After reading the article and writing the important points you should write the article again but in your own words and keep it in mind that you write the entire essential points accurately and in a logical manner. So, that it becomes easier for us to get any sort of info from the article by doing this. And then you should review the summary to discard useless items if any.
Step 6: – Write an outline of your evaluation.
After, reading and writing the article in your own words, review each and every detail in the article to discover.
Whether the author was correct and clear or not.
Write down all the instances of a productive script. And the articles that you feel, needs improvement with.
Create a record of strengths and weaknesses. The strength of the article can be a clear summation of any particular issue.
And the list of weaknesses that may any kind of weakness like it is not providing any new information on the topic or any information that you feel like that they are contradicting the facts.
And then, think about a few questions to help you critique and interconnect with the article: –
Here are some questions that you can think of to critique and engage with the article:-
- What is the point of the article?
- What is the theoretical structure and assumptions?
- Does the author define the concepts clearly?
- How satisfactory is the evidence?
- Is there transparency in the author’s writing?
- Transparency is the author’s writing?
- Does it advance the knowledge of the subject or it’s just the knowledge we can find anywhere?
Format of How To Write An Article Review: you must follow
1. Title page 2. Title ( Article name) 3. Your name 4. Date 5. Abstract: It must include around 200 to 30o words. It involves a review question summary, the study reviewed, and the study’s conclusions.
6. Introduction: It involves what the article contains. Also, it gives hints to the reader about the article and involves the background information to help the reader understand the article sections.
7. Body: It involves the main points in detail.
8. Conclusion: It sums up all the main points of your article review and states the article’s purpose.
9. Citation: You have to use a standardized reference system such as MLA, APA style , etc.
10. Format applications: Articles are commonly written in newspapers, websites, and academic journals.
Steps For How To Write An Article Review – Step-by-Step Guide
Now the answer to your question about How To Write An Article Review is here. Follow the steps while writing an article review-
step 1: – Come up with a unique title for the review.
The title you are thinking of giving to the review should consider the center of your review. You should choose between a declarative title, a descriptive title or interrogative title whichever suits the best according to your article needs.
step 2: – Cite the article.
Under the title of the article, Place a complete reference of the article in the proper form and manner. And then move to the next line to begin your article. And don’t skip a line between the citation and sentence.
step 3: – Identify the article
After the title and summoning the article you should start your review by relating to the title you have chosen for your review and author of the article and the title of the publication. And the year in the article was published should be written in the first paragraph.
steps 4: – Write the introduction of the review
The introduction of the article review should have the identifying sentence. It should also mention the fundamental theme of the article and the main aspect of the article and the thoughts and the claims by the author.
You also need to pronounce the author’s opinion.
Sometimes, there are multiple viewpoints in the thesis and the thesis may not the clearly stated than in that case, you may have to determine the thesis yourself and should write it by your own understanding and your own point of view.
step 5: – Summarizing the article
Now you have to start summarizing the main details, thoughts, and conclusions of the article in your words, pointing to your summary for assistance.
Then show how the article supports its claims and conclusions. Make sure that you don’t forget to add the conclusions of the article. Moreover, This may be done in some paragraphs, and its length will depend on the conditions established by your publisher.
step 6: – Write the critique
Now, you have to use all your article study and you have to write how thoroughly the author addressed the topic, by using your judgment.
And you should also write your opinion on how precise and useful the explanation of the subject you found in the article.
Write if you agree with the writer’s point or not.
If yes, then provide the reasons why you support the writer and if not then give the reason behind your judgment.
And then indicate the type of audience that can get benefit from reading the article.
Quick Links
- A Definitive Guide On How To Write A Literature Review Outline
- Best Of The Best Ways On How To Write A Critical Review By Experts
step 7: – Write what you have concluded from the article review.
After compiling all the main points in a paragraph. Write your own opinion about accuracy and clarity and the significance of the article in that paragraph. You can also mention if that implication is connected or not.
The conclusion should always only be at max 10% of the overall essay.
Step 8:- Proofread the work you have done: The post-writing process
To ensure that there is no mistake in the review you have written, you should always check on grammar and mechanics and check if there should not be any mistake.
Remove all sort of unnecessary information. And just for the sake of a good review you should identify and discuss 3-4 critical issues in the article.
Conclusion (How To Write An Article Review)
We all know writing a compelling and well-formatted article review is a difficult task, but now from the above discussion, we hope you get the answer to your question about How To Write An Article Review. It needs you to find the article from reliable sources, read it completely, analyze the information. So, follow the above steps carefully to write an impressive article review.
If you need any Article Review Help you can contact to Call Tutors . For more information, stay tuned with our blogs!
What are the five qualities of a good article?
The following is a brief description of five qualities of good writing: focus, development, unity, coherence, and correctness.
What makes a successful article?
An effective article is an article that achieves its goal. Now, that goal can be anything: To entertain, inform, or persuade someone to act.
What makes an article high quality?
High-quality content means writing about things your audience will find useful in a clear, understandable way.
Similar Articles

How To Do Homework Fast – 11 Tips To Do Homework Fast
Homework is one of the most important parts that have to be done by students. It has been around for…

How to Write an Assignment Introduction – 6 Best Tips
In essence, the writing tasks in academic tenure students are an integral part of any curriculum. Whether in high school,…
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Article Review
Article Review Writing: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide with Examples

People also read
Learn How to Write an Editorial on Any Topic
Best Tips on How to Avoid Plagiarism
How to Write a Movie Review - Guide & Examples
A Complete Guide on How to Write a Summary for Students
Write Opinion Essay Like a Pro: A Detailed Guide
Evaluation Essay - Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
How to Write a Thematic Statement - Tips & Examples
How to Write a Bio - Quick Tips, Structure & Examples
How to Write a Synopsis – A Simple Format & Guide
How to Write a Comparative Essay – A Complete Guide
Visual Analysis Essay - A Writing Guide with Format & Sample
List of Common Social Issues Around the World
Writing Character Analysis - Outline, Steps, and Examples
11 Common Types of Plagiarism Explained Through Examples
A Detailed Guide on How to Write a Poem Step by Step
Detailed Guide on Appendix Writing: With Tips and Examples
Struggling to write a review that people actually want to read? Feeling lost in the details and wondering how to make your analysis stand out?
You're not alone!
Many writers find it tough to navigate the world of article reviews, not sure where to start or how to make their reviews really grab attention.
No worries!
In this blog, we're going to guide you through the process of writing an article review that stands out. We'll also share tips, and examples to make this process easier for you.
Let’s get started.
- 1. What is an Article Review?
- 2. Types of Article Reviews
- 3. Article Review Format
- 4. How to Write an Article Review? 10 Easy Steps
- 5. Article Review Outline
- 6. Article Review Examples
- 7. Tips for Writing an Effective Article Review

What is an Article Review?
An article review is a critical evaluation and analysis of a piece of writing, typically an academic or journalistic article.
It goes beyond summarizing the content; it involves an in-depth examination of the author's ideas, arguments, and methodologies.
The goal is to provide a well-rounded understanding of the article's strengths, weaknesses, and overall contribution to the field.

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Types of Article Reviews
Article reviews come in various forms, each serving a distinct purpose in the realm of academic or professional discourse. Understanding these types is crucial for tailoring your approach.
Here are some common types of article reviews:
Journal Article Review
A journal article review involves a thorough evaluation of scholarly articles published in academic journals.
It requires summarizing the article's key points, methodology, and findings, emphasizing its contributions to the academic field.
Take a look at the following example to help you understand better.
Example of Journal Article Review
Research Article Review
A research article review focuses on scrutinizing articles with a primary emphasis on research.
This type of review involves evaluating the research design, methodology, results, and their broader implications.
Discussions on the interpretation of results, limitations, and the article's overall contributions are key.
Here is a sample for you to get an idea.
Example of Research Article Review
Science Article Review
A science article review specifically addresses articles within scientific disciplines. It includes summarizing scientific concepts, hypotheses, and experimental methods.
The type of review assesses the reliability of the experimental design, and evaluates the author's interpretation of findings.
Take a look at the following example.
Example of Science Article Review
Critical Review
A critical review involves a balanced critique of a given article. It encompasses providing a comprehensive summary, highlighting key points, and engaging in a critical analysis of strengths and weaknesses.
To get a clearer idea of a critical review, take a look at this example.
Critical Review Example
Article Review Format
When crafting an article review in either APA or MLA format, it's crucial to adhere to the specific guidelines for citing sources.
Below are the bibliographical entries for different types of sources in both APA and MLA styles:
How to Write an Article Review? 10 Easy Steps
Writing an effective article review involves a systematic approach. Follow this step-by-step process to ensure a comprehensive and well-structured analysis.
Step 1: Understand the Assignment
Before diving into the review, carefully read and understand the assignment guidelines.
Pay attention to specific requirements, such as word count, formatting style (APA, MLA), and the aspects your instructor wants you to focus on.
Step 2: Read the Article Thoroughly
Begin by thoroughly reading the article. Take notes on key points, arguments, and evidence presented by the author.
Understand the author's main thesis and the context in which the article was written.
Step 3: Create a Summary
Summarize the main points of the article. Highlight the author's key arguments and findings.
While writing the summary ensure that you capture the essential elements of the article to provide context for your analysis.
Step 4: Identify the Author's Thesis
In this step, pinpoint the author's main thesis or central argument. Understand the purpose of the article and how the author supports their position.
This will serve as a foundation for your critique.
Step 5: Evaluate the Author's Evidence and Methodology
Examine the evidence provided by the author to support their thesis. Assess the reliability and validity of the methodology used.
Consider the sources, data collection methods, and any potential biases.
Step 6: Analyze the Author's Writing Style
Evaluate the author's writing style and how effectively they communicate their ideas.
Consider the clarity of the language, the organization of the content, and the overall persuasiveness of the article.
Step 7: Consider the Article's Contribution
Reflect on the article's contribution to its field of study. Analyze how it fits into the existing literature, its significance, and any potential implications for future research or applications.
Step 8: Write the Introduction
Craft an introduction that includes the article's title, author, publication date, and a brief overview.
State the purpose of your review and your thesis—the main point you'll be analyzing in your review.
Step 9: Develop the Body of the Review
Organize your review by addressing specific aspects such as the author's thesis, methodology, writing style, and the article's contribution.
Use clear paragraphs to structure your analysis logically.
Step 10: Conclude with a Summary and Evaluation
Summarize your main points and restate your overall assessment of the article.
Offer insights into its strengths and weaknesses, and conclude with any recommendations for improvement or suggestions for further research.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Article Review Outline
Creating a well-organized outline is an essential part of writing a coherent and insightful article review.
This outline given below will guide you through the key sections of your review, ensuring that your analysis is comprehensive and logically structured.
Refer to the following template to understand outlining the article review in detail.
Article Review Format Template
Article Review Examples
Examining article review examples can provide valuable insights into the structure, tone, and depth of analysis expected.
Below are sample article reviews, each illustrating a different approach and focus.
Example of Article Review
Sample of article review assignment pdf
Tips for Writing an Effective Article Review
Crafting an effective article review involves a combination of critical analysis, clarity, and structure.
Here are some valuable tips to guide you through the process:
- Start with a Clear Introduction
Kick off your article review by introducing the article's main points and mentioning the publication date, which you can find on the re-title page. Outline the topics you'll cover in your review.
- Concise Summary with Unanswered Questions
Provide a short summary of the article, emphasizing its main ideas. Highlight any lingering questions, known as "unanswered questions," that the article may have triggered. Use a basic article review template to help structure your thoughts.
- Illustrate with Examples
Use examples from the article to illustrate your points. If there are tables or figures in the article, discuss them to make your review more concrete and easily understandable.
- Organize Clearly with a Summary Section
Keep your review straightforward and well-organized. Begin with the start of the article, express your thoughts on what you liked or didn't like, and conclude with a summary section. This follows a basic plan for clarity.
- Constructive Criticism
When providing criticism, be constructive. If there are elements you don't understand, frame them as "unanswered questions." This approach shows engagement and curiosity.
- Smoothly Connect Your Ideas
Ensure your thoughts flow naturally throughout your review. Use simple words and sentences. If you have questions about the article, let them guide your review organically.
- Revise and Check for Clarity
Before finishing, go through your review. Correct any mistakes and ensure it sounds clear. Check if you followed your plan, used simple words, and incorporated the keywords effectively. This makes your review better and more accessible for others.
In conclusion , writing an effective article review involves a thoughtful balance of summarizing key points, and addressing unanswered questions.
By following a simple and structured approach, you can create a review that not only analyzes the content but also adds value to the reader's understanding.
Remember to organize your thoughts logically, use clear language, and provide examples from the article to support your points.
Ready to elevate your article reviewing skills? Explore the valuable resources and expert assistance at MyPerfectWords.com.
Our team of experienced writers is here to help you with article reviews and other school tasks.
So why wait? Get our essay writing service today!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
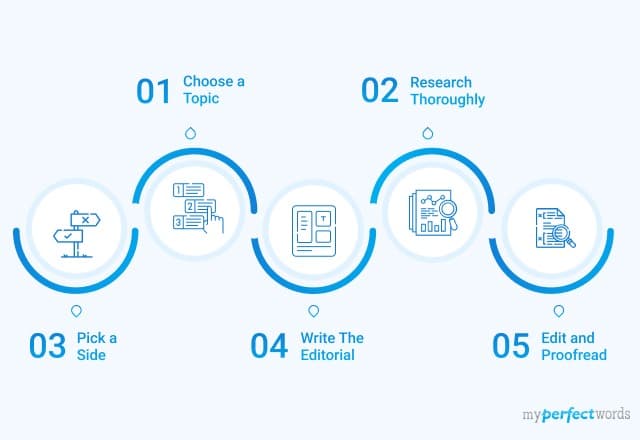
How to Write an Article Review: Examples and Tips
.webp)
In today's information-rich world, mastering the skill of discerning valuable insights from the overwhelming noise is a game-changer. Whether you're a student striving for success or a professional aiming to stay sharp, knowing how to critique an article is your key.
Our custom article review service explains the intricacies of writing an article review, categorizes different types and shares insights into impactful formatting. It's not just theory – we'll guide you step by step, from pre-writing to a tangible review article example, and refine your abilities with essential proofreading tips.
What Is an Article Review
An article review is more than a mere summary; it is a thoughtful analysis and critique that goes beyond the surface of the title. It's an intellectual exercise that challenges you to engage deeply with the author's ideas, question their methodology, and evaluate the significance of their findings.
Consider it as a journey through the landscape of someone else's thoughts. It's not just about where the writer takes you; it's about the path they choose, the landmarks they highlight, and the potential detours they overlook. An effective examination is a conversation with the author, a dialogue where you appreciate their insights, challenge assumptions, and perhaps even find alternative routes through the intellectual terrain they've explored.
As you start to understand how to review the article, encourage thought by asking questions.
- What assumptions underlie the author's arguments?
- Are there alternative perspectives that could enrich the discussion?
- How does the author's methodology shape their conclusions, and are there potential biases to consider?
- How does the title contribute to the clarity and coherence of the author's arguments?
- In what ways does the title influence the reader's perception of the author's
At EssayHub, our book review writing service experts believe an article review is an opportunity not just to absorb information but to actively engage with it, to question, to ponder, and to contribute your own insights to the scholarly conversation.
Types of Review
When tackling article reviews, there isn't a one-size-fits-all approach; it's a task that allows for versatile strategies. Think of understanding the different types of reviews as having a multifaceted toolkit ready for use. In this part, we'll guide you through the varied types of a review article, each showing a unique viewpoint and serving a specific purpose. Whether you're analyzing a scholarly piece on your own or asking someone to 'write an article review for me,' you'll get valuable insights.
.webp)
Journal Article Review
A journal article review involves critically evaluating and analyzing scholarly pieces published in an academic journal. It requires a thorough understanding of the author's research, methodology, results, and conclusions. The reviewer assesses the journal's contributions to the field, its theoretical framework, and the validity of the research methods employed. The goal is to provide a comprehensive summary and critique that highlights both the strengths and limitations of the piece.
Research Article Review
A research article review focuses on the evaluation of a scientific or academic research paper. This type of examination involves examining the research question, experimental design, data collection methods, statistical analysis, and the interpretation of findings. The reviewer assesses the reliability and validity of the research, considers the implications of the study, and offers insights into its potential impact on the broader academic community.
Science Article Review
A science article review encompasses a critical analysis of a piece in the field of science, covering disciplines such as physics, chemistry, biology, or any other scientific domain. This review type involves assessing the clarity of scientific concepts presented, the validity of experimental procedures, and the significance of the study's findings. According to our literature review writing service , reviewers may also consider the article's potential contributions to advancing scientific knowledge and its relevance to current scientific debates or issues.

Article Review Format
Ensuring the proper formatting of an article examination is crucial, and it should consistently align with the citation style specified by your instructor. If you're uncertain, don't hesitate to ask us - write my article review for me, along with additional guidelines to effectively structure your piece.
Meanwhile, here are some questions to consider:
- What citation style (MLA, APA, ASA, Chicago, etc.) should you employ?
- What is the recommended length for your article review?
- Should your assignment encompass a summary, critique, or include personal opinions?
- Is it necessary to highlight a theme or central idea from the articles?
- Does your instructor expect background information to be incorporated?
APA Format Article Review
An APA review sticks to the rules of the American Psychological Association. When unsure how to write an article review in APA format, remember that it carefully cites the article, using a title page, intro, summary, critique, conclusion, and references. Citations follow the author-date format, focusing on being clear and objective. The review digs into the article's methods, results, and overall impact.
When you write an article review in APA, your in-text citation might read: (Anderson & Ramirez, 2019)
The corresponding entry in the reference list would be: Anderson, L., & Ramirez, C. (2019). Unveiling the Dynamics of Urban Green Spaces. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 25(3), 112-128.
MLA Format Article Review
For an MLA writing review, it follows the Modern Language Association's style. It's important to know how sources are cited in the text and in the Works Cited page. The structure usually has an intro, summary, critique, and conclusion. MLA citations often have the author's last name and page number in brackets in the text. This review might highlight the document's literary or humanities aspects, such as style, language, and cultural context.
In an MLA format publication, the citation within the text could look like: (Anderson and Ramirez 112)
The Works Cited entry for this publication: Anderson, Laura, and Carlos Ramirez. 'Exploring the Impact of Urban Green Spaces on Well-being.' Journal of Environmental Psychology, vol. 25, no. 3, 2019, pp. 112-128.
Review Article Outline
As you read your writing piece, organize your thoughts into sections in an outline. Note down key facts, contributions, and any contradictions. Identify strengths and weaknesses, and start mapping your outline.
If your professor doesn't want a summary or personal critique, skip those parts. Like other assignments, your examination needs an introduction, body, and conclusion. Consider dividing your outline accordingly, with subheadings in the body. If you need help starting, find a sample outline.
Your article assessment should have the following:
- Pre-Title Page: Essential details like publication type, publication title, author names with affiliations, and corresponding author info.
- Running Head (APA format): A concise title for consistent formatting.
- Summary Page (optional but useful): Summarize the document in 800 words, covering background, purpose, results, and methodology.
- Title Page: Full title, a 250-word abstract, and 4-6 keywords for discoverability.
- Introduction: Engage your reader with an overview.
- Body: Organize your analysis with headings and subheadings.
- Works Cited/References: Properly cite all sources.
- Optional Suggested Reading Page: If allowed, suggest further readings.
- Tables and Figure Legends (if instructed): Include visuals when requested for clarity.
Writing an Article Review in 7 Steps
Now, let's move on to understanding how to write a review paper covering everything from creating the title to summarizing key points. This step-by-step guide breaks it down into seven simple steps, making the entire process more manageable.
.webp)
Step 1: Create the Title
The very first question you might have is how to start an article review. It's crucial to develop a title that not only captures the essence of the publication but also reflects your perspective. For instance, consider the title: ' Decoding Data: A Critical Exploration of Privacy Concerns in Online Health Platforms. ' This title not only introduces the main theme but also hints at the critical evaluation that will unfold in the writing. It sets the tone for your analysis and sparks interest from the outset.
Step 2: Reference the Article
In the second step, it's essential to ensure accurate citation by providing specific details. Take a look at this example:
- Author: Rodriguez, M., & Chen, L.
- Title: 'Privacy Matters: Analyzing the Impact of Health Apps on User Data'
- Publication Date: 2023
- Source: Journal of Digital Ethics, 8(2), 87-105.
By including these details, you not only acknowledge the authors and the publication but also provide your readers with the necessary information to locate and verify the article. This step lays the foundation for a credible and well-referenced examination.
Step 3: Article Identification
Identify key elements of the publication, such as the writer's main argument, methodology, and key findings. Pinpoint any theoretical frameworks or models used in the title.
For example: The writing by Garcia and Kim examines the correlation between social media usage and mental health outcomes among adolescents. The authors employ a longitudinal study approach, utilizing surveys and interviews to gather data.
Step 4: Make an Introduction
In your introduction, provide a brief overview of the title's subject and purpose. Capture the reader's attention and clearly state your thesis or main point related to the title. For instance, you might start your article review template like this.
In the digital age, the impact of social media on mental health has become a topic of increasing concern. Garcia and Kim's recent study delves into this issue, aiming to uncover the nuanced relationship between social media engagement and the psychological well-being of adolescents. This writing piece critically analyzes the methodology, findings, and implications of their research.
Step 5: Summarize the Article
Summarize the main points of your assessment, highlighting key arguments, evidence, and results. Offer a concise overview without adding personal opinions.
Example: Garcia and Kim's study reveals a significant positive association between increased social media use and heightened levels of anxiety and depression among the adolescent population. The longitudinal study tracked participants over a two-year period, employing both quantitative and qualitative measures to assess mental health outcomes.
Step 6: Provide Critique
Critically assess the strengths and weaknesses of the writing. Well, how to critique an article , you might wonder. Discuss aspects such as methodology, data interpretation, and potential biases.
Example: While the study offers valuable insights, the reliance on self-reported data may introduce response bias. Additionally, the research predominantly focuses on mainstream social media platforms, potentially overlooking the impact of emerging platforms. Despite these limitations, the study's comprehensive approach contributes to the ongoing discourse surrounding the intersection of social media and mental health.
Step 7: Conclude
In the conclusion, summarize your overall assessment of the article and restate your main points. Offer insights into the broader implications of the research and suggest areas for future exploration.
For example: To conclude, Garcia and Kim's study sheds light on the complex relationship between social media use and adolescent mental health. Despite certain methodological limitations, the research underscores the need for continued investigation in this field. As we navigate the digital landscape, understanding these dynamics becomes crucial for devising effective interventions and support systems for the well-being of our youth.
Example of an Article Review
Why are we taking the time to discuss article review examples in this article? It might not be immediately apparent, but exploring a well-crafted article review sample is a vital step in the writing process for the following reasons:
- Introduction to Key Works: Helps you to familiarize yourself with the important works of experts in your field.
- Identification of Key Figures: You can recognize key figures contributing to a specific scientific field.
- Understanding Field Advancements: Helps you define significant discoveries and advances made in your area of study.
- Identification of Knowledge Gaps: You can uncover major gaps in existing knowledge, contributing to the formulation of fresh solutions.
- Reference and Argumentation Resources: You discover solid references and arguments that can enhance your own writing.
- Idea Generation: Helps you generate ideas for potential future research directions.
- Becoming an Expert: Assists in gaining a deeper understanding of the subject area, moving towards expertise.
- Writing Guidance: You acquire a clear idea of how to craft a well-structured review.

Can Anyone Write an Article Review for Me?
Is writing a review article worth it, how to write an apa format article review, how do you write an article review from the beginning, what is the proper article review format.

- Plagiarism Report
- Unlimited Revisions
- 24/7 Support

How to Write an Article Review: Tips, Outline, Format

Have you been assigned an article review paper, but you are unsure where to start, or what is a review article at all? There is no need to worry, as EssayService has put together a top guide for you! Find out all about an article review to master your assignment.
What is an Article Review?
In simple terms, an article review essay is like a summary and evaluation of another professional or expert's work. It may also be referred to as a literature review that includes an outline of the most recent research on the subject, or a critical review that focuses on a specific article with smaller scope. Article review can be used for many reasons; for example, a teacher or lecturer may wish to introduce their students to a new subject by reviewing a professional's piece. You can also learn about the most important works of specialists in your industry by looking at relevant article review examples.
Also, a newspaper article review example could be a journalist writing a critique about another competitor's published work.
In comparison, a book review article example could be critiqued by a fellow author or even a student in the chosen field.
Depending on the critique criteria and the work being reviewed, there could also be certain points asked for addition which should be checked and noted by the lecturer or supervisor. Otherwise, follow the article review guidelines from our write my essay service to complete the assignment in no time.
Key points when writing an article review:
Use the article review template from our paper writing service to get through the assignment as fast as possible so you will not waste any time.

How to Start an Article Review?
- Firstly read the work being reviewed as much as possible and look up key phrases and words that are not understood.
- Discuss the work with other professionals or colleagues to collect more opinions and get a more balanced impression.
- Highlight important sections or sentences and refer this to your knowledge in the topic, do you agree or disagree and what does this contribute to the field?
- Then re-write the key arguments and findings into your own words this will help gain better understanding into the paper. This can be just written as an outline also and will help decide which points are wanted to discuss later.
If you feel you do not have enough time to create a critique worthy of your time, then come to EssayService and order a custom Article review online.
You can order essay independent of type, for example:
- nursing essay;
- law essay writing;
- history essays.
The best way to write an effective essay would be to draw up a plan or outline of what needs to be covered and use it for guidance throughout the critique.

Article Review Formatting
There is no one-fits-all article format you can follow in your review. In fact, the formatting is dictated by the citation style specified by your professor in the task requirements. Thus, be sure to clarify the preferred style before you jump straight to writing to handle the given assignment right.
APA Format Article Review
Writing an APA style article review, you will most likely use articles from journals, websites, and newspapers. For each source, you will have to create properly formatted bibliographical entries.
Here is how to write an article review APA:
- Journal: Author’s last name, First and middle initial. (Year of Publication). Publication Title. Periodical Title, Volume(Issue), pp.-pp.
- Website: Last name, initials. (Date of Publication). Title. Retrieved from {link}
- Newspaper: Last name, initials. (Date of Publication). Title. Magazine Title, pp. xx-xx.
MLA Format Article Review
Tips for citing sources in an article review MLA format:
- Journal: Last name, First name Middle initial. “Title.” Journal Title Series Volume. Issue (Year of Publication): Page(s). Database Name. Web. Date Accessed.
- Website: Last, First M. “Title.” Website Title. Publisher, Date Published. Web. Date Accessed.
- Newspaper: Last, First M. “Title.” Newspaper Title [City] Date of Publication: Page(s). Print.
Article Review Outline
Planning out an outline for your paper will help writing and to put it together so therefore saving you time in the long run.
Some questions to help with the outline of a critique:
- What does the article set out to do or prove?
- Are the main ideas clear and defined?
- How substantial is the evidence?
- Where does the article fit in its specific field?
- Does it provide new knowledge on the topic?
- What are the central theories and assumptions?
- Is the writer conclusive at getting their point across?
Here is a typical article review format to follow:

Use our article review template to get through the assignment as fast as possible so you will not waste any time.
Article Review Title
Firstly start with creating a title for your critique, this should be something to do with the focus of the work that is being reviewed. An approach could be to make it descriptive or also in a more creative way think of something that intrigues the reader. After the title, this is a good place to correctly cite the paper being critiqued and include the important details for example, the author, title of publication, any page references. The style in which the citation is written will depend on which is best for this type of work being reviewed.
Article Review Introduction
The introduction should be a brief glimpse into what the author was writing about and any other details the audience will find interesting. Maybe some background details on the piece that is not already known or something that contributes to the review itself. It is a good idea to start by introducing the work at the start of the paragraph and then include a ' hook '. Include the writer's thesis if there is one and put it at the end but include your own thesis towards the critique near the beginning of this section.
Article Review Body
When constructing the summary section, write down the important points and findings in the piece in your own words. Include how the claims are supported and backed up with evidence but use direct quotes as sparing as possible. Do not put in any information known to professionals in the field or topic, but detail any conclusions the work came to. Make sure the paper is not just copied word for word and is actually summarized by yourself; this will also help the review stage.
To make an accurate critique, break down the work and express opinions on whether it achieves its goals and how useful it is in explaining the topics for an article review. Decide if the paper contributes to its field and is important and credible to the given field. Back up all the claims with evidence from the summary or another source. If using another text, remember to cite it correctly in the bibliography section. Look at how strong the points are and do they contribute to the argument. Try to identify any biases the writer might have and use this to make a fair critique. This part is only for opinions of the piece's significance, not including whether you liked it. Furthermore, the different types of audiences that would benefit from the paper can be mentioned in this section.
Article Review Conclusion
In the conclusion section of the critique, there should only be one or two paragraphs in which a summary of key points and opinions in the piece are included. Also, summarize the paper's significance to its field and how accurate the work is. Depending on the type of critique or work evaluated, it is also possible to include comments on future research or the topic to be discussed further.
If other sources have been used, construct a bibliography section and correctly cite all works utilized in the critique.
The APA format is very common in an article review and stands for American Psychology Association. This will include a 'references list' at the end of the critique and in-text citations, mentioning the author's last name, page number, and publication date.
There are also MLA and Chicago formats for citations with slight differences in a name, like using a 'works cited' page for MLA. More can be found in this guide on the subtle differences between the types of citation methods under the heading 'Creating a bibliography.'
Article Review Example
Article review writing tips.
If you are interested in best scholarships for high school seniors , the following tips will be handy while writing your essay or article:
- Allow enough time to complete the research and writing of the critique. The number one problem with creating a critique is running out of time to make it the best it can be. This can be avoided by effective planning and keeping on time with the deadlines you set out.
- Collect twice more research than you think is needed to write a review. This will help when coming to the writing stage as not all the information collected will be used in the final draft.
- Write in a style that is compatible with the work being critiqued. This will be better for whoever requested the critique and also will make paper easier to construct.
- A summary and evaluation must be written. Do not leave out either part as one complements the other and is vital to create a critique worth reading.
- Be clear and explain well every statement made about the piece . Everything that is unknown to professionals in the field should be explained and all comments should be easy to follow for the reader.
- Do not just describe the work, analyze and interpret it. The critique should be in depth and give the audience some detailed interpretations of the work in a professional way.
- Give an assessment of the quality in the writing and of what standard it is. Evaluate every aspect in the paper so that the audience can see where it fits into the rest of the related works. Give opinions based on fact and do not leave any comments without reason as this will not count for anything.
How to Write an Article Review?
Writing a review article is not that hard if you know what steps to take. Below is a step-by-step guide on how to write a review example quickly and easily.
- Before You Start
Before you start writing your review essay, there are a few pre-writing steps to take. The pre-writing process should consist of the following steps:
- Pick the subject of your review (if it wasn’t specified by your professor);
- Read the article fully multiple times;
- Summarize the main ideas, points, and claims made in the article;
- Define the positive (strong) aspects;
- Identify the gaps or inconsistencies;
- Find the questions that remained unanswered.
All these steps are needed to help you define the direction for your review article and find the main ideas you’d like to cover in it.
After you review articles and define the key ideas, gaps, and other details, map out your future paper by creating a detailed outline.
Here are the core elements that must be included:
- Pre-title page;
- Corresponding author details (optional);
- Running head (only for the APA style);
- Summary page (optional);
- Title page;
- Introduction;
- References/Works Cited;
- Suggested Reading page (optional);
- Tables and Figure Legends (if required by the professor).
This step is vital to organize your thoughts and ensure a proper structure of your work. Thus, be sure not to skip this step.
When you have an outline, students can move on to the writing stage by formulating compelling titles for their article reviews. Titles should be declarative, interrogative, or descriptive to reflect the core focus of the paper.
- Article Citation
After the title should follow a proper citation of the piece you are going to review. Write a citation according to the required style, and feel free to check out a well-written article review example to see how it should look like.
- Article Identification
Start the first paragraph of your review with concise and clear article identification that specifies its title, author, name of the resource (e.g., journal, web, etc.), and the year of publication.
Following the identification, write a short introductory paragraph. It should be to the point and state a clear thesis for your review.
- Summary and Critique
In the main body of your article review, you should first make a detailed but not too extensive summary of the article you reviewed, its main ideas, statements, and findings. In this part, you should also reflect on the conclusion made by the author of the original article.
After a general summary should follow an objective critique. In this part of your paper, you have to state and analyze the main strengths and weaknesses of the article. Also, you need to point out any gaps or unanswered questions that are still there. And clarify your stance on the author’s assertions.
Lastly, you need to craft a compelling conclusion that recaps the key points of your review and gives the final, logical evaluation of the piece that was reviewed.
After this, proofread your work and submit it.
No Time Left For Your Due Assignment
Now we hope you understand how to write a review of an article. However, we know that writing a great article review requires a lot of time to properly research the work. To save your precious time, visit EssayService, where our team of top essay writers will help you. The team can even provide you with the best article review topics! You can learn more at the college essay writing service page where we have free guides with all the essay writing tips and tricks!
Frequently asked questions
She was flawless! first time using a website like this, I've ordered article review and i totally adored it! grammar punctuation, content - everything was on point
This writer is my go to, because whenever I need someone who I can trust my task to - I hire Joy. She wrote almost every paper for me for the last 2 years
Term paper done up to a highest standard, no revisions, perfect communication. 10s across the board!!!!!!!
I send him instructions and that's it. my paper was done 10 hours later, no stupid questions, he nailed it.
Sometimes I wonder if Michael is secretly a professor because he literally knows everything. HE DID SO WELL THAT MY PROF SHOWED MY PAPER AS AN EXAMPLE. unbelievable, many thanks
You Might Also Like

New Posts to Your Inbox!
Stay in touch

- Research Process
Writing a good review article
- 3 minute read
- 73.3K views
Table of Contents
As a young researcher, you might wonder how to start writing your first review article, and the extent of the information that it should contain. A review article is a comprehensive summary of the current understanding of a specific research topic and is based on previously published research. Unlike research papers, it does not contain new results, but can propose new inferences based on the combined findings of previous research.
Types of review articles
Review articles are typically of three types: literature reviews, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses.
A literature review is a general survey of the research topic and aims to provide a reliable and unbiased account of the current understanding of the topic.
A systematic review , in contrast, is more specific and attempts to address a highly focused research question. Its presentation is more detailed, with information on the search strategy used, the eligibility criteria for inclusion of studies, the methods utilized to review the collected information, and more.
A meta-analysis is similar to a systematic review in that both are systematically conducted with a properly defined research question. However, unlike the latter, a meta-analysis compares and evaluates a defined number of similar studies. It is quantitative in nature and can help assess contrasting study findings.
Tips for writing a good review article
Here are a few practices that can make the time-consuming process of writing a review article easier:
- Define your question: Take your time to identify the research question and carefully articulate the topic of your review paper. A good review should also add something new to the field in terms of a hypothesis, inference, or conclusion. A carefully defined scientific question will give you more clarity in determining the novelty of your inferences.
- Identify credible sources: Identify relevant as well as credible studies that you can base your review on, with the help of multiple databases or search engines. It is also a good idea to conduct another search once you have finished your article to avoid missing relevant studies published during the course of your writing.
- Take notes: A literature search involves extensive reading, which can make it difficult to recall relevant information subsequently. Therefore, make notes while conducting the literature search and note down the source references. This will ensure that you have sufficient information to start with when you finally get to writing.
- Describe the title, abstract, and introduction: A good starting point to begin structuring your review is by drafting the title, abstract, and introduction. Explicitly writing down what your review aims to address in the field will help shape the rest of your article.
- Be unbiased and critical: Evaluate every piece of evidence in a critical but unbiased manner. This will help you present a proper assessment and a critical discussion in your article.
- Include a good summary: End by stating the take-home message and identify the limitations of existing studies that need to be addressed through future studies.
- Ask for feedback: Ask a colleague to provide feedback on both the content and the language or tone of your article before you submit it.
- Check your journal’s guidelines: Some journals only publish reviews, while some only publish research articles. Further, all journals clearly indicate their aims and scope. Therefore, make sure to check the appropriateness of a journal before submitting your article.
Writing review articles, especially systematic reviews or meta-analyses, can seem like a daunting task. However, Elsevier Author Services can guide you by providing useful tips on how to write an impressive review article that stands out and gets published!

- Manuscript Preparation
What are Implications in Research?

How to write the results section of a research paper
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Scholarly Sources: What are They and Where can You Find Them?
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, what is your plagiarism score.

- Cancer Cell
- Cell Chemical Biology
- Cell Host & Microbe
- Cell Metabolism
- Cell Reports
- Cell Stem Cell
- Cell Systems
- Current Biology
- Developmental Cell
- Molecular Cell
- Biochemical Sciences
- Biotechnology
- Cell Biology
- Cognitive Sciences
- Ecology & Evolution
- Endocrinology & Metabolism
- Microbiology
- Molecular Medicine
- Neurosciences
- Parisitology
- Pharmacological Sciences
- Plant Science
- Biophysical Journal
- EBioMedicine
- Molecular Plant
- Molecular Therapy Family
- Stem Cell Reports
- Get Inspired
- Get Techncal
- Get Published
- Cell Mentor China
- And They're Scientists, Too
- Biology in 3D
- Careers Under the Microscope
- Cell Insider
- Emilie, Can I Ask You?
- Random Walk
- The Female Scientist
- The Scientific Communicator
- Cell Symposia
- Cell Press Reviews
- China Gateway
- Snapshot Archive
- Cell Picture Show
- Cell Press Podcast
- Cell Press Videos
- Cell Career Network
- CrossTalk Blog
- Cell Selections
- Spotlight on China
- Trends: Limited Edition
- Chemistry & Biology
- Parasitology
- For Advertisers
- For Librarians
- For Recruiters

How to get started writing a review article
So you've been invited to write a review article.
Congratulations! Some editor, somewhere, thinks you're the best person for the job, with the right expertise and something interesting to say. Maybe you've done your homework and read our advice for writing a review article that people will read , or perhaps you've watched our webinar " An editor’s guide to writing a review article " and read our answers to the audience’s questions . You've thought through the arguments that you want to make, and your favorite citation manager is full of the latest research on the topic.
Settling down to business and putting words on a page—taking that invitation from an editor and making it your own or fleshing out your proposal into a real article—can be intimidating. But we're here to help: I've asked the Trends editors, and a few other reviews editors from around Cell Press, to share their best tips to go from a blinking cursor on a blank page to a real manuscript.
Understand your audience
Even before you start writing, make sure you have a good sense of who is going to read the article. It may sound like an obvious point, but keeping a consistent tone throughout the manuscript is going to save you a lot of time in revision. Is this a tutorial review, aimed toward people who are totally new to the field? You'll want to include lots of context and define terms that may seem obvious to you. A historical perspective? Don't be afraid to dig far back in the literature to the seminal publications. A digest or highlight piece? Worry less about assembling every single paper on the topic and focus more on what the most interesting handful of results say right now.
Pengfei Kong, editor of Trends in Parasitology , suggests thinking about the scope of the review as a function of the expertise of the audience: if it's meant for readers actively engaged in a specific field, then you can go deeper, whereas if you want it to be more accessible to a general audience, you should go wider. Former Cell Stem Cell reviews editor Anh Nguyen also advises you to "make sure your article has the type of breadth and depth that the journal typically publishes."
Understand what the journal wants
Most journals, including the Trends journals, have a dense array of author guidelines that provide instructions on everything from how to format a glossary (put each term in bold the first time it appears in the main text) to how long an abstract can be (strictly no more than 120 words for longer formats and 50 words for shorter formats) to how to prepare print-quality figures (300 dpi, .tif format preferred). These items are important and may delay or preclude publication if they're not followed, but they're things that can be addressed as you're polishing a manuscript for submission.
Before you start writing, though, get a general sense of what the journal expects from you. In particular, Trends in Pharmacological Sciences editor Kushi Mukherjee emphasizes how understanding the journal's length requirements before you start writing can prevent significant frustration later on. Trends journals advise submitting Review articles between 3,000 and 3,500 words on initial submission. If you keep this goal in mind from the beginning and end up a few hundred words long or short, then it's relatively straightforward to cut or add to reach the appropriate length. But if you choose to ignore the instruction and end up with a 9,000-word albatross, then you'll have to discard 60% of your effort, in many cases before the journal will even send your manuscript out for review.
Figure out what you want to say
Danielle Loughlin, editor of Trends in Cell Biology , puts it well: "First, define the overall goal of the manuscript. What do you want to convey to the reader? What are the major points that you want to make?" Claudia Willmes from Trends in Molecular Medicine agrees: "Start with the motivation for why you're writing this review and make sure this is your running thread." Claudia explains this by encouraging authors to think back to where the idea for the review came from in the first place. For instance, if an editor invited you to write after listening to you give a talk, then it makes sense to write the review with a similar take-home message to the talk.
After you've decided what to convey to the reader, Anh reminds you to "make sure you are aware of other reviews in this area over the past few years to ensure yours offers a unique angle on the topic." It's worth re-examining the literature once you have a good sense of audience, journal requirements, and scope just to make sure that you're not inadvertently writing the same article that someone else published a few months ago.

Make an outline
This is the single most common piece of advice I got. Claudia says, "plan a structure to see what are the core topics that need to be addressed in dedicated sections," while Danielle's advice is to "create an outline, bullet point major areas or publications," and Kushi's is to "write out an outline of main subtopics that the article will cover." Trends in Cognitive Sciences editor Lindsey Drayton and I also covered the importance of the outline in our webinar on writing reviews , and you may have even created an outline if you proposed the review to the editor.
Nearly every editor who shared their thoughts brought up outlining in some capacity, so take heed. An outline doesn't have to be a hierarchical list of bullet points, though it certainly can be if that's what will help you organize. You might also consider a mind map or other diagram or simple clusters of publications that are related to each other. To structure smaller sections or single paragraphs, Trends in Microbiology editor Gail Teitzel (inspired by her 9-year-old son's homework) suggests that food-themed graphical organizers can be surprisingly useful for adult writers too.
Why outline? As Lindsey talked about in the webinar, the outline helps you understand the relationship between the different parts of the review and to elevate your review from a collection of results into a compelling narrative. Understanding which publications you want to cite in which section, or which elements of your argument you want to advance in which order, before you begin writing will let you focus on how to tell the most interesting story possible. Outlining beforehand will also help you to spot structural weaknesses in the manuscript before they become problems: if what you thought could be a main section only ends up with one paragraph's worth of content, you might consider reorganizing to bolster the section or move that paragraph elsewhere.
Think about figures
"Even if the actual design of the figures is left to a later stage," advises Moran Furman, editor of Trends in Neurosciences, "I think it can be helpful to start thinking about the figures from the outset." Anh agrees: "It's helpful to devise figures conceptually early on because schematics can be worth a thousand words and help you focus your text." Moran also advises against what we around the Cell Press office have taken to calling "Frankenfigures": "figures that tend to work well in Review or Opinion articles are ones that summarize findings or highlight new ideas, rather than just reproduce primary source data."
Start with the introductory section
Just as with research articles, there is no one correct place to begin writing, but the introduction came up frequently as a reasonable place to start. Consider the right level of specificity, again keeping your audience in mind: if you're writing a review of algal biofuels for a biomolecular engineering audience, you probably don't need to motivate the entire concept of biofuels.
There are three critical elements of introductory sections that I encourage every Trends in Biotechnology author to include: a basic scientific overview (for a biotechnology journal, this should encompass both the biological system being exploited as a technology and the practical problem that technology is intended to solve), the unique selling point of the review, and a preview of the specific content of the review.
Most authors do well with the scientific overview and the preview of the article. But the unique selling point often takes a little more encouragement. As an author, this should be the most exciting part: this is your chance to tell the world why it should be interested in what you have to say. If you can express this in a succinct and compelling manner, while also explaining how your review advances the conversation beyond any other reviews that may have been published on the topic, then you are putting yourself in a position to succeed as you compose the rest of the manuscript.
Engage co-authors, editors, and colleagues early and often
Finally, as we have explained before, never submit the first draft of your manuscript. Instead, read it again and expect to make significant revisions even before you submit: make sure that all of the sections feel like they're part of the same coherent work, terms are used consistently, and the level of scientific detail doesn't vary significantly from one paragraph to the next.
You're not writing a review in a vacuum. Often, you'll be writing in collaboration with co-authors, who should ideally be involved with every stage of writing, but especially when they’re contributing specific technical expertise. If you're writing for Trends, you're working with an editor whose job it is to help you write the best review possible. And you almost certainly have colleagues who are educated and interested in science yet not subject-matter experts in the precise topic of the review. Use these resources to make sure that the article you’ve started writing captures the most recent and exciting literature, conforms to the journal’s specifications, and is comprehensible to a wide audience.
As Cell Leading Edge Editor (and former editor of Trends in Biochemical Sciences ) Nicole Neuman rightly points out, writing a review is much different from editing one, so we would love to hear additional suggestions from our authors: how do you embark on the review-writing process?

Posted by Matt Pavlovich Matt is the editor of Trends in Biotechnology , Cell Press's home for reviews in the applied biological sciences. His background is not so secretly in engineering rather than biology, but he hopes you won't hold that against him. He can often be found crafting and enjoying fine beverages (which is definitely biotechnology) and blogging about strategy game design (which is surprisingly similar to managing a reviews journal).
Filed to Reviews , Cell Stem Cell , Trends in Cognitive Sciences , Trends in Molecular Medicine , Trends in Neurosciences , Cell , Trends in Biotechnology , Trends in Cell Biology , Trends in Parasitology , Trends in Pharmacological Sciences , Get published , Cell Mentor

About Cell Mentor
Cell Mentor—an online resource from Cell Press and Cell Signaling Technology—empowers early-career researchers with career insights, publishing advice, and techniques on experimental processes and procedures. Now it’s even easier to tap into the knowledge and experience of experts who’ve walked in your shoes.
Subscribe to Cell Mentor
Browse cell mentor by topic and type.
- Get Technical
Contact Cell Mentor
Explore cell mentor:, stay connected:.
Research Journals
- Cell Genomics
- Cell Reports Medicine
- Cell Reports Methods
- Chem Catalysis
- STAR Protocols
Trends Reviews Journals
Partner journals.
- HGG Advances
- Plant Communications
- The Innovation
Collections
- Best of Cell Press
- Cell Press Selections
- Consortia Hub
- Nucleus Collections
- SnapShot Archive
- Trends Limited Editions
EVOLVING THE ARTICLE
- STAR Methods
- Read-It-Now
- Recommend to Librarian
Information
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Accessibility
BEYOND THE JOURNAL
- Cell Mentor
Science in Society
- Coloring and Comics
- Research Arc
- About Cell Press
- Help & Support
- Publication Alerts
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. except certain content provided by third parties
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
- AI Content Shield
- AI KW Research
- AI Assistant
- SEO Optimizer
- AI KW Clustering
- Customer reviews
- The NLO Revolution
- Press Center
- Help Center
- Content Resources
- Facebook Group
Winning Intro Examples For Article Reviews
Table of Contents
Writing an article review is a great way to analyze and evaluate the work of other experts in your field. It is typically done to demonstrate clarity, originality, and how significant a certain article’s contribution is. As with most pieces of writing, your introduction is a critical element for an article review. It can be beneficial to refer to an example introduction for article review to help you make a winning intro.
This article has gathered some great introduction examples you can refer to. We’ve also listed some great tips to help you get started on your article.
Your introduction is often the determining factor in whether or not someone will be interested in reading your article. It needs to capture your audience’s attention immediately and state the purpose of your review.
What Is an Article Review?
An article review is a piece of writing that summarises and assesses someone else’s article. It aims to understand the central theme, supporting arguments, and implications of an article for future research.
There are specific guidelines and formats that an article review has to abide by. Reviews can either be critical, literature-based, or both. Literature reviews cover broad topics, while critical reviews focus on specific texts.

The Significance of Article Reviews
Article reviews are often required for school writing assignments. But scholars or students can also use it outside the educational system to conduct preliminary research before writing a paper. An article review can help you with:
- Clarifying questions
- See other people’s thoughts and perspectives regarding current issues.
- Correct grammar errors and sentence structure.
- Get out of personal biases after reading various reviews
- Improve grammar as well as writing skills
- Provide suggestions or criticism on the article for future research.
How to Start an Article Review
Your introduction in an article review is of the utmost importance. Before you begin writing, you should first outline your assignment. You can also use an article review template to organize your thoughts. Here are some things your intro should accomplish:
- Introduce the article and the thesis you will be reviewing.
- Establish the significance of the study.
- Summarize the main points of the article.
- Present the positive aspects and facts contained in the article.
- Mention knowledge gaps, contradictions, disparities in the text, and unanswered questions in the publication.
In journals, an introduction usually takes up one paragraph, but in longer book reviews, it can take two or three paragraphs.
Include a few opening sentences that explain the subject of the text and introduce the author . Present the main finding or key argument and describe the aim of the text. After this, make a brief statement about your evaluation of the text in your introduction.
Example Introduction for Article Review
As Olsen (2015) states, grasping mathematics concepts is not something that happens spontaneously or independently. To improve one’s mathematics proficiency, one must appropriately use mental math to enhance their knowledge. Olsen (2015) suggests increasing a student’s mental abilities is possible.
George Hammond’s book “The Role of God” was first published in the opinion magazine Grass over Grass. It is ambitious in its primary focus being a perception of infinity. Hammond points out that God cannot be seen in its pure form. This cancels out a specific role since we cannot get acquainted with it physically. According to the author, “the roleless God has a role in our lives.” It causes us to look deeply at nothingness, mystery, and what we cannot explain.” (Hammond 56).
The growth of technology has had a huge effect on the political ratings that candidates achieve. The article, Impact of Technology on Politics by Housley explores how technology and politics interrelate. And it also analyzes what consequences they have.
There are many ways political candidates use technology. Different communication channels have the power to influence the growth of individuals in their respective political spheres. The likes of Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube are powerful platforms that can easily increase the ratings of political candidates. According to Housley, technology is a decisive factor in politics, regardless of whether we recognize it.
Article reviews analyze and evaluate a body of written text. Its goal is to pull out a certain theme that the author is trying to convey, interpret the text, and synthesize your findings.
A review stands out with specific use of language and clear articulation of observations and conclusions. For this reason, reviewing an article or book can be an exercise in analytical writing. And it may prepare you for your future in various careers, from teaching to business writing. So start your article review right by referring to an example introduction for article review .

Abir Ghenaiet
Abir is a data analyst and researcher. Among her interests are artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing. As a humanitarian and educator, she actively supports women in tech and promotes diversity.
Explore All Essay Intro Generator Articles
The different ways to start a comparative essay.
Some writers intend to compare two specific things or ideas through their articles. They write these essays to compare and…
- Essay Intro Generator
Know The Best Way to Start an Expository Essay
Are you into writing essays that tackle a still-unknown fact? Do you know how to write an expository essay? Before…
Writing an Opinion Essay? Read This First!
Students are required to express their opinions on a topic in an opinion essay. Pertinent illustrations and explanations support their…
Identifying the Best Transitions to Start an Essay
A typical academic assignment is the essay, which must meet certain requirements in order to be written properly. Even students…
How to Write Introductions for Synthesis Essays
One of the most exciting assignments you could have is writing a synthesis essay. For a college or university student,…
How to Write Introductions for Music Essays
Music is food for the soul, or so they say. A music essay analyzes or describes a piece of music,…

- An Introduction to Writing Review Articl ...
An Introduction to Writing Review Articles
Posted by Seema Grewal , on 7 April 2020
Last week, I gave a talk (online, of course) about ‘Writing review articles’. It was aimed at graduate students who, as part of their training, had to identify a topic in the field of developmental biology and write a mini-review on that particular topic. However, my talk contained some general advice about writing review-type articles, as well as some general writing tips, so I thought I’d share a summary of it here.
Types of Review articles
I guess the first thing to point out is that review-type articles come in lots of different ‘flavours’. They all vary with regard to length, scope, style and overall purpose, and are given different names by different journals. But they all aim to summarise and distill research findings. This makes them very different to primary research articles, whic h aim to present data, although they are handled in similar way, i.e. they are submitted to a journal and peer-reviewed by 2-3 experts in the field.
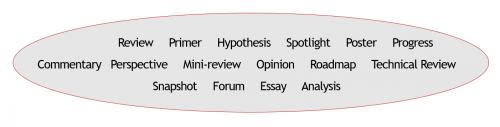
What’s the purpose of a (good) Review article?
A good review article might aim to:
- summarise key research findings
- highlight ‘must-read’ articles in the field
- act as educational material
However, an excellent review article will also:
- provide critique of studies
- highlight areas of agreement as well as controversies and debates
- point out gaps in knowledge and unanswered questions
- highlight current technologies that are helping/can help the field
- suggest directions for future research
But remember that readers are usually a mix of experts and non-experts who will be looking for very different things so a good review will cater for both of these audiences. For example, a graduate student might turn to a review article when they start in a new lab to find out more about the history of a field, or to get a summary of key findings. By contrast, an experienced post-doc or PI might want to read a review written by one of their peers to find out what the current state of thinking in a field is. Ideally, a good review should therefore aim to provide a combination of balanced summaries and critique whilst being authoritative, forward-looking and inspirational. However, note that the exact ‘flavour’ or format of the review will also dictate its purpose, e.g. a ‘Perspective’ article in Journal X might aim to summarise a handful of recent studies, whereas an ‘Essay’ in Journal Y might aim to provide a more comprehensive analysis of the last decade of research.
Where to begin?
The first step is to choose the topic you want to write on and come up with a rough idea of the scope of your article. You may already have this in mind but it’s important, before you begin writing, to really nail the exact purpose of your article. To help you do this, I‘d suggest the following:
- Identify the particular theme/topic/idea that you want to focus on. In most cases, this will be something that’s closely related to the topic you work on, e.g. you might be working on something, or reading up on a particular area, and feel that a review would be helpful. If you need inspiration (i.e. if you want to write but aren’t sure what to write about), read, speak to people, and think about talks you’ve been to. What’s exciting in your field right now? Are there papers that change the way we think about something? Have you seen/read papers that converge on a similar theme/idea?
- Check that there aren’t already reviews on this topic, i.e. something that’s been published within the past year or so. This is important; no-one wants to read a review that doesn’t offer anything new.
- Decide if there is enough recent material to include (or too much). At this point, you may need to go back to the drawing board to either expand on or refine the scope of your article. It’s also helpful to read a few reviews (mini-reviews vs longer reviews) to get a feel for how much material a review can cover.
- Identify and write down the main aim/purpose of your article. What’s the key message you want to get across? Why is this important and timely? Why would people want to read your article?
Note that lots of reviews are commissioned, i.e. the author is invited to write by a journal/editor. So, if you know you want to write a review on a particular topic and have a pretty clear idea of what your review will cover, a good place to start is by contacting a journal to see if they’d consider it. This also then means that you’ll (hopefully) be working alongside an editor from the outset to develop and refine the scope of your article. You’ll also have your target audience, article format and word limit in mind while you’re writing so can tailor the review accordingly.
Before you begin writing
Plan, plan and plan some more! Having worked with authors on review-type articles for years now, I can’t stress this enough.
- Think about the sections/sub-sections you might use. What material would you cover in each of these? What’s the message of each section? How can you link the sections?
- Think about the key concepts/words/specialist terms that you need to introduce and define. Where, when and how should you introduce these? (e.g. in Intro, in a figure, in a text box). What needs to be introduced first? What’s the best order in which to discuss these?
- Think about the display items (figures, text boxes, tables) that might be helpful. How/when should they be used? What material would they contain?
When you start writing
Once you have a plan, you can start writing. I’d suggest that you start with the Title, Abstract and Introduction – these are the first parts that the reader sees of the article so they need careful thought. By starting off with these, you’ll also have the scope/purpose of the article clear in your own mind. You can then work on the main text of the article (the ‘meaty’ bit) and the Conclusions with this scope/purpose in mind, although you’ll need to return to the Title, Abstract and Introduction for a tidy up once you’ve written the main text.
Things to think about:
- Title, Abstract and Introduction: These should be short and self-contained, and should complement each other. Each one in turn should provide more detail, aiming to draw the reader in. Remember: lots of readers will only read the title and abstract (e.g. when they search for articles in Pubmed) so these basically act as a ‘hook’ to grab their attention. They also need to be ‘discoverable’ on the Web, i.e. database friendly and containing the relevant keywords.
- Choosing a title: Choose something that is short, clear and self-explanatory; try to avoid puns/idioms and colloquial phrases or references. Try to convey the key message but also provide context.
- Abstract: The abstract should then aim to highlight the most important parts of the article. The answers to the following 5 questions provide a good starting point: What is the main topic you’re going to focus on? What do we know so far? What is new/why is this now an interesting time for this field? What are the broad implications of these newer findings? What does your review aim to do?
- Introduction: The Introduction should then expand on the Abstract and set the scene. Provide context by first introducing the topic: why is this topic interesting/significant, what do we know about it so far, how has the field progressed, what has the new progress shown? Ideally, the Introduction should end with a clear description of the article’s scope, aims and structure, i.e. a walk-through of the main topics that will be discussed and the order in which these will be covered. This just lets the reader know what they can expect from the article. If possible, introduce or re-iterate the main ‘message’ of the article.
- Conclusions: Emphasize the key message or theme of the article and, if needed, reiterate the data that support this message. Highlight the broader significance of this conclusion. Finally, if possible, bring your voice to the article: What do you think are the most compelling questions raised by these studies? What approach(es) could be taken to address these open questions? Are there technical hurdles that need to be overcome? What are the broader implications of this, i.e. why are further studies needed and what benefits might they offer?
- Display items: Use figures to emphasize or illustrate key concepts/processes, or to introduce or summarize . Remember that figures should ideally act as stand-alone items; you should be able to follow them by eye and without referring to the main text, although each figure should have a clear title and a figure legend the walks the reader through the figure. In general, schematics are easier to follow than images reproduced from primary articles. Tables can be useful for summarizing lots of information, for comparing/contrasting things, or for highlighting advantages and disadvantages. Some journals encourage the use of text boxes, which can house additional or background information or material that is peripheral to the main theme of the text.
General things to think about while you’re writing (and to re-visit before you finish off!)
- Try to group your discussion into sections/sub-sections. This just helps to break up long chunks of text (and helps to keep the reader interested). If you already have a plan (e.g. a list of headings/sub-headings) this structuring will be much easier.
- Each section should begin with a small introduction.
- Each sub-section (and/or even each paragraph) should then have a clear message/point to it, e.g. What question did particular sets/types of studies set out to address? What did these show (and here you can go into the detail)? What could be concluded from these?
- It’s also helpful to add in a few lines to wrap up each section and ease transition into the next section.
- Make sure that all statements are adequately supported by a citation. Cite the source/primary article whenever possible (but note that it is okay to cite Reviews for established concepts or to refer to a large body of evidence).
- Think about the word count and how much can be covered/how much detail you can go in to; you may find that it’s easier to write lots first then trim at a later stage.
- Avoid regurgitating the conclusions drawn in the papers you cite without giving them some thought.
- Don’t shy away from discussing findings that contradict each other. It’s better to highlight what can/cannot be reconciled and the possible cause of any discrepancies. Also use this as an opportunity to draw out the questions that remain and discuss how these questions could be addressed.
- Similarly, remain balanced – make sure you discuss the findings from the field as a whole (and not just the data from a few select labs).
- Make it clear when you are stating results versus providing speculation or alternative interpretations.
- Provide critique if you can…but keep it polite and constructive.
Accessibility
- Remember your audience: the article needs to accessible to expert and non-expert readers alike.
- Introduce/define/explain specialist terms, cell types, tissues, phrases on first mention.
- Consider using display items to house any material that a non-expert reader might find useful.
- Don’t assume the reader knows what you’re thinking and how things link together; you might feel like you’re sometimes stating the obvious but it’s better to do this than to leave readers feeling lost.
- Stick to using clear and simple sentences…but try to vary the pace of your writing, e.g. by using a mixture of long and short sentences.
- A general rule is to write as you would speak, using active rather than passive tense/sentence construction.
- Be thrifty with your words: completely eliminate any that aren’t needed.
- Avoid vague sentences. For example, say ‘Factor A causes an increase/decrease in Factor B’, rather than ‘Factor A modulates Factor B’.
Importantly, be patient and don’t get frustrated! A good writing style needs to be developed over time and comes with practice. Of all the things highlighted above (structure, content, accessibility and style), I’d say that style is the hardest to really nail. Getting a good and consistent writing style is also challenging if you have multiple authors working on the same article. In this case, I’d recommend that you nominate one author to do a final comb-through to iron out any inconsistencies, although hopefully you’ll have an editor who’ll also assist with this! On this note, I should point out that the amount of input you receive from an editor will vary from journal to journal, e.g. some journals have dedicated editors who spend a significant amount of time, working alongside the authors, to edit and improve a review.

Finally, some tips from fellow editors!
We have a bunch of experienced editors here at the Company of Biologists so I asked them all for their key pieces of advice. Here are just some of the things they suggested:
- Plan, plan, plan – make sure you have a good idea of the overall structure before you think about details
- Get feedback. Before you submit your review, send it to someone whose opinion you trust and ask them for their honest thoughts. Don’t be discouraged if they give lots of feedback – this is exactly what you want!
- A review shouldn’t just be a list of facts, e.g. X showed this, Y showed this, Z showed this. A narrative thread or argument that connects is much more engaging.
- Take time to pull back and look at the overall structure. Does it make sense? Can you see how the ideas join together and flow from beginning to end?
- Remember that readers aren’t psychic. Explain why you’ve chosen the scope you have, why you’ve chosen to discuss particular examples, why you’re moving on to the next topic. Also make sure you clearly link up relevant observations and state conclusions rather than expecting the reader to make connections.
- Don’t assume that the reader can link two statements that you might be able to link in your mind; you have to explain the link.
- Think about the graphics at an early stage – figures can often feel like a bit of an afterthought but good figures can really help to get the message across far more concisely than text.
- Break the article up into sections so that people can easily find the particular piece of information they might be looking for; recognize that not everyone is going to read from start to finish.
- Remember that your readers will know far less about the topic than you do. So before you dive into the new and exciting findings in the field, make sure you’ve given a clear overview of the system you’re writing about. Imagine that you’re writing for a new PhD student who’s never worked in this particular field.
One final point: there’s no ‘winning formula’. This is just my advice based on the articles I’ve handled and the authors I’ve dealt with, so you may find that some of it doesn’t work for you or that someone else’s advice differs. Ultimately, you should aim to develop a writing approach, technique and style that works for you.
Happy writing!

Tags: how to Categories: Careers , Education , Lab Life , Outreach , Research , Resources
5 thoughts on “An Introduction to Writing Review Articles”
I want to say that was really simple and pragmatic. Thank you very much!

Thank you very much. I got good hint from this written piece. please don’t back to comment and help others on the topic of what you know.
its a pleasure interaction with you and the kind written piece advice on how to approach introduction review has been productive. looking forward to have you again. than you
This blog is informative for my research, but what are the resources I should use for writing my review paper to make it more specific or provide additional information so it can easily get published?
Thank You for sharing this information regarding introduction to write review article. if you want to know more information related to review article and other research related things you can visit our website pubmanu.com
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Get involved
Create an account or log in to post your story on the Node.
Sign up for emails
Subscribe to our mailing lists.
Most-read posts in March
- Can the post-doc shortage get even worse? by J Guillermo Sanchez
- Lab meeting with the Mohlin lab
- SciArt profile: Brent Foster
- Lab meeting with the Soiza-Reilly lab
- Exploring multi-hub conferences: interview with Sally Lowell by Teodora Andreea Rinciog
- An afternoon in the museum with an exploded skull and a 3.5m python skeleton by Joyce Yu
Do you have any news to share?
Our ‘Developing news’ posts celebrate the various achievements of the people in the developmental and stem cell biology community. Let us know if you would like to share some news.
Browse our topic pages
- A day in the life…
- Alternative careers
- Behind the paper stories
- Forgotten classics
- Honest conversations
- Lab meetings
- Meeting reports
- Monthly preprint list
- New PI diaries
- SciArt profiles
- About the Node
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- The Company of Biologists
- Development
© 2024. The Company of Biologists Ltd | Registered Charity 277992 Registered in England and Wales | Company Limited by Guarantee No 514735 Registered office: Bidder Building, Station Road, Histon, Cambridge CB24 9LF, UK

Our expert, award-winning staff selects the products we cover and rigorously researches and tests our top picks. If you buy through our links, we may get a commission. Reviews ethics statement
- Services & Software
NBA Playoffs 2024: Play-in Tournament Schedule, Matchups, TV Times, How to Watch Wednesday
Play-in games continue tonight starting with the Heat and Sixers, and you don't need cable to watch.

The NBA play-in tournament on Wednesday with two more games on the docket. After the Lakers took down the Pelicans to become the West's seventh seed and the Kings eliminated the Warriors, tonight's focus shifts to the East. First up is Joel Embiid and the 76ers hosting Jimmy Butler and the Heat at 7 p.m. ET (4 p.m. PT) on ESPN.
The winner will become the seventh seed in the Eastern Conference and take on the Knicks while the loser will play the winner of tonight's second game between the Hawks and Bulls, for a chance at the eighth and final playoff spot Friday night.
The Western Conference play-in games, including Friday's Kings-Pelicans showdown, will be shown on TNT while the Eastern Conference games will be on ESPN. Here's everything you need to know to watch or stream the start of the NBA Playoffs.

Jimmy Butler and the Miami Heat will look to repeat their playoff run from last year.
What are the play-in tournament matchups?
In the West, the No. 7 Pelicans lost to the No. 8 Lakers on Tuesday night, with LeBron James and company now becoming the seventh seed and taking on the Nuggets in the first round. The Pelicans will take on the Kings, who defeated the Warriors, on Friday for a chance to become the West's eighth and final playoff team and play the Thunder.
In the East, the No. 7 76ers host the No. 8 Heat in a game that will feature reigning league MVP Joel Embiid, who just returned from injury near the end of the regular season, going up against Miami center Bam Adebayo and former playoff hero Jimmy Butler. In the game between the No. 9 Bulls and No. 10 Hawks, the focus will be less on big men and more on guards and wings, such as DeMar DeRozan and Zach LaVine of the Bulls and the Hawks' Trae Young and Dejounte Murray.
What is the play-in tournament and playoff schedule?
Here is the schedule for the next few days of NBA action (all times ET):
Wednesday, April 17 (Play-in)
- No. 7 76ers vs. No. 8 Heat, 7 p.m. on ESPN; winner plays the Knicks and is the seventh seed in the East.
- No. 9 Bulls vs. No. 10 Hawks, 9:30 p.m. on ESPN
Friday, April 19 (Play-in)
- Winner of Bulls/Hawks vs. Loser of 76ers/Heat, 7 p.m. on ESPN, winner plays the Celtics and is the eighth seed in the East.
- Kings vs. Pelicans, 9:30 p.m. on TNT, winner plays the Thunder and is the eighth seed in the West.
Saturday, April 20 (Playoffs)
- Magic vs. Cavaliers, 1 p.m. on ESPN
- Suns vs. Timberwolves, 3:30 p.m. on ESPN
- Winner of 76ers/Heat vs. Knicks, 6 p.m. on ESPN
- Lakers vs. Nuggets, 8:30 p.m. on ABC
Sunday, April 21
- East eighth seed vs. Celtics, 1 p.m. on ABC
- Mavericks vs. Clippers, 3:30 p.m. on ABC
- Pacers vs. Bucks, 7 p.m. on TNT
- Winner of Pelicans/Kings vs. Thunder, 9:30 p.m. on TNT
What does the NBA playoff bracket look like?
The Boston Celtics earned the top spot in the East, and the Oklahoma City Thunder edged the defending champion Denver Nuggets for the top seed in the West. Here's what the matchups look like for the 2024 NBA Playoffs that begin Saturday:
Saturday, April 20
- No. 2 New York Knicks vs. East No. 7
- No. 4 Cleveland Cavaliers vs. No. 5 Orlando Magic
- No. 2 Denver Nuggets vs. No. 7 Los Angeles Lakers
- No. 3 Minnesota Timberwolves vs. No. 6 Phoenix Suns
- No. 1 Boston Celtics vs. East No. 8
- No. 3 Milwaukee Bucks vs. No. 6 Indiana Pacers
- No. 1 Oklahoma City Thunder vs. West No. 8
- No. 4 Los Angeles Clippers vs. No. 5 Dallas Mavericks
How to watch the NBA play-in tournament
You can watch the play-in games on TNT and ESPN with a cable subscription or a live TV streaming service . Four of the five major services (all but Fubo) offer both channels. You can also watch the TNT broadcast of the Western Conference play-in games with Max.
The rest of the playoffs will be shown on ABC, ESPN, TNT and NBA TV.

Carries TNT and ESPN for $40 per month
Sling TV's $40-per-month Orange plan includes TNT and ESPN for the play-in games, but you'll need the combined Orange-and-Blue plan for $55 a month to get both ESPN and ABC for the rest of the playoffs. You'll also need to live in one of the few markets where Sling offers ABC .
Read our Sling TV review .

Carries TNT and ESPN for $73 per month
YouTube TV costs $73 per month and includes TNT and ESPN for the play-in tournament. For future rounds of the playoffs, it also includes ABC and is the only service to include NBA TV in its basic plan. Plug in your ZIP code on its welcome page to see which local networks are available in your area.
Read our YouTube TV review .

Hulu with Live TV
Carries tnt and espn for $77 per month.
Hulu with Live TV costs $77 per month and includes TNT and ESPN. It also offers ABC for future rounds; click the "View channels in your area" link on its welcome page to see which local channels are offered in your ZIP code. It's the only service, however, that doesn't offer NBA TV, even as part of an add-on package.
Read our Hulu with Live TV review .

DirecTV Stream
Carries tnt and espn for $80 per month.
DirecTV Stream's basic $80-per-month plan includes TNT and ESPN. For future rounds, you can use its channel lookup tool to see if ABC is available where you live.
Read our DirecTV Stream review .

Western Conference play-in games for $10 per month
The ad-supported plan for Max costs $10 per month and will show the three Western Conference play-in games and well as some games in future rounds of the NBA playoffs. With just Max, however, you'll miss games on ESPN and ABC.
Live sports on Max will soon require the $10-per-month B/R Sports add-on, but you won't need to shell out for it just yet. Warner Bros. Discovery is delaying charging customers for the add-on for now and includes it in the standard subscription.
Read our Max review .
All of the live TV streaming services above offer free trials, allow you to cancel anytime and require a solid internet connection. Looking for more information? Check out our live TV streaming services guide .
Services and Software Guides
- Best iPhone VPN
- Best Free VPN
- Best Android VPN
- Best Mac VPN
- Best Mobile VPN
- Best VPN for Firestick
- Best VPN for Windows
- Fastest VPN
- Best Cheap VPN
- Best Password Manager
- Best Antivirus
- Best Identity Theft Protection
- Best LastPass Alternative
- Best Live TV Streaming Service
- Best Streaming Service
- Best Free TV Streaming Service
- Best Music Streaming Services
- Best Web Hosting
- Best Minecraft Server Hosting
- Best Website Builder
- Best Dating Sites
- Best Language Learning Apps
- Best Weather App
- Best Stargazing Apps
- Best Cloud Storage
- Best Resume Writing Services
- New Coverage on Operating Systems
- Hostinger Coupon Codes
- HR&R Block Coupons
- ShutterStock Coupon Codes
- FedEx Office Coupons
- Coursera Coupons
- Autodesk Coupons
- Codeacademy Coupon Codes
- iolo Techologies Coupons
- Norton Coupon Codes
2024 Masters Tiger updates: Recap Thursday, Woods through No. 13 when Round 1 suspended
14 Min Read

AUGUSTA, GEORGIA - APRIL 11: Tiger Woods of the United States follows his shot from the fifth tee during the first round of the 2024 Masters Tournament at Augusta National Golf Club on April 11, 2024 in Augusta, Georgia. (Photo by Maddie Meyer/Getty Images)
Woods stood 1-under through 13 holes, two inside projected cut line
Change Text Size
You can't win the Masters on Thursday, but you can lose it, as the adage goes. Tiger Woods didn't lose it.
After heavy storms overnight delayed the Masters' start by two-and-a-half hours Thursday morning, Woods teed off at 3:54 p.m. ET and stood 1 under through 13 holes as play was suspended due to darkness, an encouraging start as he seeks his sixth green jacket – and a record 24th consecutive Masters made cut.
But Friday will be a different animal for Woods. The first round resumed at 7:50 a.m. ET, just over 12 hours from when play was suspended Thursday night. Woods will finish the final five holes of his first round, take a short break and then head out for his second round tee time at 10:18 ET. How will his body hold up with the short recovery time and 23 holes on Friday? That's the central question.
"The body is okay," Woods said Thursday night. "We've got some work to do yet tonight."
After undergoing ankle surgery following a WD during the third round of last year’s Masters, Woods returned to PGA TOUR competition at The Genesis Invitational in February, where he opened in 1-over 72 but withdrew during the second round due to flu-like symptoms. The Masters is Woods’ first start since withdrawing at The Genesis, and he said Tuesday that he still believes he can contend and win. That’s why he’s here, after all.
“If everything comes together, I think I can get one more,” said the five-time Masters winner on Tuesday.
His play so far validates that belief.
Woods started fast on Thursday with a birdie at the par-4 opening hole, his first Masters-opening birdie since 1999, and he remained steady as the conditions dried out in the afternoon. Woods, 48, made bogey at the par-3 fourth but responded with a two-putt birdie at the par-5 eighth, turning in 1-under 35. He made three straight crafty up-and-down pars on Nos. 10-12, then escaped the trees en route to par at the par-5 13th, his final hole of the day.
"The wind was all over the place," Woods said Thursday evening. "It was one of the most tricky days that I've ever been a part of. It was hard to get a beat not only on what direction it was going, but the intensity, and it kept switching all over the place, and then you had to – the timing was affecting putts on the greens. It was a very difficult day."
Woods entered the week on a streak of 23 consecutive made cuts at the Masters, sharing the all-time record with Fred Couples and Gary Player. He'll have a chance Friday to hold that record alone, but expected windy conditions (up to 34 mph) should offer a challenge for Woods and the field at large. Woods was tied for 17th, six back of leader Bryson DeChambeau, as play was halted for the evening. DeChambeau posted 7-under 65 earlier in the day, one clear of world No. 1 Scottie Scheffler's 6-under 66.
Read below for a hole-by-hole look at Woods' opening round at Augusta National.
Hole 18 (par 4, 465 yards): Tiger has great rhythm with the driver, with another perfectly placed tee shot in the 18th fairway. It's a mighty encouraging sign as the first round finishes up and Woods readies for 18 more holes. It's a 287-yard drive. He has 171 yards into the closing par 4.
After Max Homa's approach got swallowed up by the wind and found the right greenside bunker, Woods plays a nearly identical shot. The wind impacted those shots much more than either player anticipated. Woods will need an up-and-down to finish even-par for the first round.
Nearly more short game magic for Woods! His bunker shot comes just inches from hitting the flagstick. Instead, it races by and Woods has more than he bargained for -- 16 feet for par. He gets the putt to the hole but doesn't play enough break. He closes with a bogey.
Woods finishes with an opening-round 73. That's a solid result given his lack of competitive reps, though Woods is surely disappointed after he was 1 under through 13 holes when play suspended Thursday night. He won't have much time to dwell on the finish. His second round tee time is scheduled for 10:18 a.m. ET. He has around 45 minutes to grab some food, keep the body loose and get ready for 18 more holes.
Woods shoots 1-over 73
Hole 17 (par 4, 440 yards): It's another low, fading bullet with the driver that finds the fairway. Woods is 3-for-3 in fairways hit this morning. That's a great sign. He's hit 77% of the fairways in this first round, slightly better than the field average.
With 158 yards into the green, Woods pulls 9-iron and plays the smart shot, leaving himself below the hole. He will have 23 feet for birdie. After a few shaky iron swings to start the morning, Woods has hit two solid ones with his tee shot on 16 and now this approach.
Woods leaves his birdie putt short. That's three putts left short in his opening four holes of the day. But it is another stress-free par. Those are always welcome at Augusta National, particularly on the 17th.
Woods even-par thru 17
Hole 16 (par 3, 170 yards): Woods pulls 7-iron after watching Jason Day put one in the water with the same club. The 82-time PGA TOUR winner doesn't make the same mistake. Woods safely lands it 20 feet past the pin and uses the slope to get it on the same plateau as the hole. He will have 20 feet for birdie.
It's a quick putt, meandering slightly left to right. Woods handles it with care but doesn't give it quite enough pace. That will be another par for Woods. He's 1-over since play resumed today but has made two relatively easy pars after that opening bogey.
Woods even-par thru 16
Hole 15 (par 5, 550 yards): Woods’ drive finds the fairway but it will be a lay-up with 273 yards remaining into the green. He does just that, leaving himself 70 yards. It's a tricky wedge shot on a severe downslope and Woods can't control the spin as the ball rolls off the back of the green. Woods' ball-striking has been iffy to start, but his touch is fully activated as he nearly holes the chip for birdie. He makes the comebacker for par.
It's a hole you'd like to make birdie, but Woods will take the par. He is clearly laboring this morning; the short turnaround time was likely going to be problematic. As the weather warms and Woods gets a few more swings, let's see how his body progresses.
Woods even-par thru 15
Hole 14 (par 4, 440 yards): Play resumed as scheduled at 7:50 a.m. ET. Woods plays his patented cut off the tee and finds the fairway. The 315-yard drive leaves him just 119 yards into the green, but Woods lays the sod over a wedge and comes up short of the green. That leaves Woods with a delicate chip, with the pin sitting on the top of a slope on the back of the green. Woods opts to hit a low spinner, but the ball releases out and Woods has 22 feet for par. The curling right-to-left putt come up just short. Woods makes bogey and drops a shot.
Woods even-par thru 14
Hole 13 (par 5, 545 yards): Woods plays a fade off the tee but overcooks it, as the ball sails into the collection of pine straw amidst a dense tree line right of the fairway. It means he can't go for the green, and he escapes the trees with a low punch shot that reaches the first cut just short of the fairway, leaving a 191-yard approach for his third shot.
Faced with a hanging lie and Rae's Creek closely guarding the green, Woods strikes a crisp iron shot that lands hole-high and stops on a dime, leaving a reasonable look from roughly 20 feet. The horn blows for darkness, allowing players to finish their current hole if they choose, as Woods walks to the green.
Woods opts to complete the hole; his right-to-left breaking birdie try pulls up a couple feet short. He makes his par to remain in red figures overnight. All in all, a promising start for the five-time Masters winner. It will be a marathon Friday as he eyes a record 24th consecutive made cut at Augusta National.
Woods 1-under thru 13
Hole 12 (par 3, 150 yards): As the twilight begins and the wind continues to gust, Woods pulls 7-iron and flies it over the green, a trend that has emerged with his mid-irons on this Thursday. The ball settles in the pine straw roughly 30 feet past the hole, but once again he displays a sublime short game with a softly played bump-and-run that trundles to 6 feet.
Woods drains the par putt, his third straight crafty par save as darkness approaches at Augusta National. He'll head to the par-5 13th tee.
Woods 1-under thru 12
Hole 11 (par 4, 520 yards): Woods has played this hole a cumulative 17 over across his career, but he has no such trouble on the tee shot Thursday, striping it down the fairway's left side as he begins Augusta National's famed Amen Corner. Faced with a lengthy second shot from 209 yards, he strikes it well with a long iron but the ball perhaps catches a gust of wind; it lands in the front fairway and settles some 80 feet short of the hole.
Woods' magnificent short game is on display once again, as he executes a high flop shot that lands softly and releases to tap-in range. He saves par, his second straight impressive up-and-down to begin the back nine. Darkness will approach soon; it appears he might only complete one more hole Thursday. Onward to the famed par-3 12th across Rae's Creek.
Woods 1-under thru 11
Hole 10 (par 4, 495 yards): Woods positions a fairway metal safely in the fairway's right side on the majestic downhill par 4, but he misses the green right with his second shot from 216 yards, leaving a slippery greenside bunker shot.
Ever a short-game magician, Woods has no troubles with his third shot from the bunker, playing a nifty splash shot that lands in the fairway cut and releases to leave a 4-foot uphill par putt. The patrons roar with deserving approval. He drains the par putt, dead center, to stay in red figures.
Woods 1-under thru 10
Hole 9 (par 4, 460 yards): Woods is finding a comfort zone off the tee, striping this drive 312 yards, perfectly positioned in the fairway's right side, leaving a good angle from 169 yards. He selects an 8-iron that tracks toward the hole, but the ball can't reach the back tier on which the hole is positioned; the ball lands on the ridge beween tiers and rolls back onto the green's middle tier, leaving a 33-foot birdie putt.
Woods' uphill birdie putt has solid pace but grinds to a halt 2 feet short. He cleans up his par to turn in 1-under 35, a promising start to the Masters. He stands T15 at the turn, six back of leader Bryson DeChambeau. He's two inside the current projected cut line of 1 over.
Woods' playing partner Max Homa turns in 3-under 32. Safe to say the group's vibes are high.
Woods 1-under thru 9
Hole 8 (par 5, 570 yards): Woods blisters driver down the right-center of the fairway, utilizing a high cut that puts him in position to reach the green in two. He does just that with a bold strike from 242 yards, the ball landing softly on the green's right collar to leave a 40-foot eagle putt.
Woods leaves his eagle try 5 feet short, but the birdie putt slides into the cup's right side. With his second birdie of the day, he's in red figures once again.
Woods 1-under thru 8
Hole 7 (par 4, 450 yards): Woods tugs a fairway metal just left of the fairway, the ball settling in the first cut but requiring a low punch to elude a dense grove of trees. He plays his 171-yard second shot accordingly, a low bullet that tracks toward the hole but can't clear a front greenside bunker.
Woods' bunker shot is a short-game master class, the ball landing some 10 feet short of the hole and releasing beautifully, leaving a 2-footer to save par. He has no trouble doing so.
Woods even-par thru 7
Hole 6 (par 3, 192 yards): Woods takes an aggressive line with a mid-iron; the ball tracks toward the hole's left side and lands roughly 15 feet short-right of the hole, but it catches the slope and feeds back onto the green's front portion, leaving a cross-country birdie try up a tier from 42 feet.
In what could be either a misread or a mis-hit, Woods' birdie putt misses short and right of the hole, leaving a knee-knocker for par. He has no trouble, though, draining the 5-footer for an adventurous two-putt par.
Woods even-par thru 6
Hole 5 (par 4, 495 yards): Woods pulls driver on the demanding par 4 and plays a feathery cut that splits the fairway's right-center portion. The five-time Masters winner hoists a mid-iron from 200 yards that lands softly on the green's proper level, offering a mid-range birdie try.
Woods' 16-foot birdie try has a good line but isn't struck hard enough, settling a couple feet short. He cleans up his par to remain level on the round.
Woods even-par thru 5
Hole 4 (par 3, 177 yards): Woods flushes an iron on Augusta National's first par 3; similar to his third shot on the par-5 second, the ball flies too far, settling in the second cut just beyond the green. He faces a slippery downhill chip, the green sloping away, and bumps the ball into the fringe on a line some 20 feet left of the hole; the ball releases onto the green and rolls well past, leaving a 25-foot par attempt from the front portion of the green's back section.
Woods' par putt is well judged, but the right-to-left bender just misses on the hole's right edge. He taps in for his first bogey of the week.
Woods even-par thru 4
Hole 3 (par 4, 350 yards): Woods settles in with the driver, playing a tight cut that eludes the short par 4's myriad fairway bunkers, the ball traveling 334 yards down the middle. From roughly 70 feet, he plays a bump-and-run second shot into the hill that releases just past the hole, leaving a 12-foot birdie try.
Woods can't convert the birdie, as he plays too much break on the left-to-right slider; the ball stays out on the left side. He taps in for a comfortable par, remaining in the Thursday red.
Woods 1-under thru 3
Hole 2 (par 5, 585 yards): Woods pulls driver but is unhappy with the swing immediately; he points to the left as the ball misses the fairway on the left side. The ball travels 319 yards, but it settles just inches from a tree's thick base, with 237 yards remaining to the hole. After some analysis and deliberation, he turns an iron upside-down and makes a left-handed swing, advancing the ball roughly 40 yards back into the fairway, enough to offer a clear angle for his third shot to the green.
Woods selects a 6-iron for his third shot from 190 yards; he stripes it but the ball flies too far, settling in the fairway cut beyond the green's back side. He plays a pitch-and-run with a mid-iron for his fourth, the ball not getting more than a few inches above surface level; it releases through the fringe and rolls to 5 feet. "Absolutely brilliant," said analyst Dottie Pepper. The slippery downhiller has some right-to-left movement, but he drips the par putt into the hole's left center with sublime pace. Crisis averted.
Woods 1-under thru 2
Hole 1 (par 4, 445 yards): Sporting a salmon shirt in his new Sun Day Red branding, Woods stripes a fairway metal with plenty of left-to-right movement, the ball starting down the left side but cutting back perfectly to the center of the fairway. He doesn't miss a beat on his second shot from 169 yards, striping a short iron to 8 feet. The patrons roar in approval.
Woods takes advantage of the early opportunity, as the right-to-left breaker curves into the center of the cup with perfect pace. Birdie to start. It's the first time since 1999 that he has carded birdie on his first hole of the Masters.
Woods 1-under thru 1
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Transformations That Work
- Michael Mankins
- Patrick Litre

More than a third of large organizations have some type of transformation program underway at any given time, and many launch one major change initiative after another. Though they kick off with a lot of fanfare, most of these efforts fail to deliver. Only 12% produce lasting results, and that figure hasn’t budged in the past two decades, despite everything we’ve learned over the years about how to lead change.
Clearly, businesses need a new model for transformation. In this article the authors present one based on research with dozens of leading companies that have defied the odds, such as Ford, Dell, Amgen, T-Mobile, Adobe, and Virgin Australia. The successful programs, the authors found, employed six critical practices: treating transformation as a continuous process; building it into the company’s operating rhythm; explicitly managing organizational energy; using aspirations, not benchmarks, to set goals; driving change from the middle of the organization out; and tapping significant external capital to fund the effort from the start.
Lessons from companies that are defying the odds
Idea in Brief
The problem.
Although companies frequently engage in transformation initiatives, few are actually transformative. Research indicates that only 12% of major change programs produce lasting results.
Why It Happens
Leaders are increasingly content with incremental improvements. As a result, they experience fewer outright failures but equally fewer real transformations.
The Solution
To deliver, change programs must treat transformation as a continuous process, build it into the company’s operating rhythm, explicitly manage organizational energy, state aspirations rather than set targets, drive change from the middle out, and be funded by serious capital investments.
Nearly every major corporation has embarked on some sort of transformation in recent years. By our estimates, at any given time more than a third of large organizations have a transformation program underway. When asked, roughly 50% of CEOs we’ve interviewed report that their company has undertaken two or more major change efforts within the past five years, with nearly 20% reporting three or more.
- Michael Mankins is a leader in Bain’s Organization and Strategy practices and is a partner based in Austin, Texas. He is a coauthor of Time, Talent, Energy: Overcome Organizational Drag and Unleash Your Team’s Productive Power (Harvard Business Review Press, 2017).
- PL Patrick Litre leads Bain’s Global Transformation and Change practice and is a partner based in Atlanta.
Partner Center

‘Fake drama’: NYC thug accused of shoving woman, 68, off church steps arrested – tries to hang himself
The underage thug who pushed a woman off the top step of a church stairway has tried to commit suicide after being arrested by the police.
“Jayvaun Prince, 16 — who was arrested Thursday in the brutal mugging of 68-year-old Irene Tahliambouris — took his shirt off and wrapped it around his neck inside the NYPD’s 107th Precinct stationhouse,” the New York Post has confirmed via sources.
“He was brought out in a stretcher and hospitalized, but was not seriously injured, the sources said,” according to the Post.
Responding to the reports of his attempted suicide, some critics alleged that he’d tried to kill himself for the sympathy.
Fake drama to get away with felony — Lux Argenti (@tvgts8g4z4) April 12, 2024
*tries to get sympathy. Fixed it for you. He gets none. — CKirk (@cynkirkland) April 12, 2024
Good way to cop an insanity plea. Bold move. — ZNO (@therealZNO) April 12, 2024
He had no intentions of killing himself he is seeking sympathy. — Carolina Girl (@DollyEllington) April 12, 2024
I am guessing he will play the victim card now. Life must be horrible for people who try to exist and identify under the victim hood basis to justify being horribly terrible people that provide benefit for society. — Brett (@Thee_G_spot_) April 13, 2024
Other critics meanwhile expressed disappointment that he hadn’t succeeded in killing himself and that the police had sought to stop him from hurting himself.
To bad he wasn’t successful. — Whirley (@WhirlaWhirla1) April 12, 2024
They should have done the world a favor and just let him. — Eddie Mush (@MrEddieMush1) April 13, 2024
and why they stopped it? Dude shoved a 68 year old grandma down the steps and left her to die. — The Lock$mith (@RipsAndSlips) April 12, 2024
Next time, he should work a tiny harder so that he can at least succeed at that since he couldn’t be successful in being a normal human being. — Nevada Liberty 1864 (@NevadaLiberty64) April 12, 2024
They can’t even take themselves out of the gene pool properly. What a burden to society. pic.twitter.com/vieLSsgdnm — MuhSocioFactors (@MuhSociofactor) April 12, 2024
Prince was formally arraigned in a juvenile court on Friday after being charged with robbery and grand larceny for the April 7th attack on Tahliambouris.
As previously reported, as Tahliambouris was climbing the outside stairs of the Saint Demetrios Greek Orthodox Church in Queens, Prince rushed up to the top step and then pushed her down.
Tahliambouris hit the ground below landing on her head, after which Prince robbed her as she lay there motionless, first stealing her purse and then later her 2006 Nissan Altima.
“Horrible. I could not believe my eyes. Seeing what he did to this lady,” Rev. Konstantinos Kalogridis of St. Demetrios later told reporters. “She was coming to church to pray, to participate. I don’t know what kind of a person this is but evil. Pure evil.”
He added that it was a miracle that she survived.
“She is in stable condition,” he said. “She is such a sweet lady. She is a very humble low-key person.”
Thankfully Prince’s actions against her were caught on surveillance camera.
REPORT: The 16-year-old teen who cracked a 68-year-old woman’s skull outside of her church, had been arrested & released 9 times before the brutal attack. Progressivism is evil. Just *three days* before the attack outside of the church, Jayvaun Prince had reportedly mugged a… pic.twitter.com/Cke3lUiKg4 — Collin Rugg (@CollinRugg) April 14, 2024
Prince reportedly also faces charges for robbing another woman inside an apartment building and then feeling in her car earlier this month. He was previously arrested nine times for other crimes but also let out.
“The viciousness with which the defendant is accused of having committed the robbery at the church struck the city at its core,” Queens District Attorney Melinda Katz said in a statement about Prince’s latest attack on women.
“As alleged, he chose to rob an elderly woman by first pushing her down the stairs and then proceeded to take her purse and leave her to suffer while he took off in her car. He will now have to answer for the serious charges levied against him by my Office,” Katz added.
Jayvaun Prince (16) cracked a 68-year-old woman’s skull outside of her church. He was arrested NINE TIMES before this, including 2x for assault. He was let out. Just 3 days prior to the church attack, he targeted a different lady, mugged her, & carjacked her car. pic.twitter.com/dyxXgoWYuG — End Wokeness (@EndWokeness) April 14, 2024
DONATE TO BIZPAC REVIEW
Please help us! If you are fed up with letting radical big tech execs, phony fact-checkers, tyrannical liberals and a lying mainstream media have unprecedented power over your news please consider making a donation to BPR to help us fight them. Now is the time. Truth has never been more critical!
- Recent Posts
- ‘Fake drama’: NYC thug accused of shoving woman, 68, off church steps arrested – tries to hang himself - April 14, 2024
- Bundy family say they’re ‘still ranching’ 10 years after armed standoff with feds - April 14, 2024
- INSIDER: News outlets seek specific election commitment from Biden, Trump - April 14, 2024
We have no tolerance for comments containing violence, racism, profanity, vulgarity, doxing, or discourteous behavior. If a comment is spam, instead of replying to it please click the ∨ icon below and to the right of that comment. Thank you for partnering with us to maintain fruitful conversation.
BPR INSIDER COMMENTS
Scroll down for non-member comments or join our insider conversations by becoming a member . We'd love to have you!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Latest Articles

- job opportunities
- privacy policy
- DUMPSTER FIRE NEWS
- * NEW * WE THE PEOPLE WINE
- * NEW * WE THE PEOPLE STORE
Everything to know about the 2024 Masters, from tee times to TV schedule

Professional golf makes its annual visit to Augusta National with this week’s Masters. Here’s a look at the first major of the season, which begins Thursday.
All time listed are Eastern.
The Masters 2024
Scottie Scheffler won his second green jacket in the past three years at Augusta National Golf Club, holding off several final-round challenges to claim his second major title.
Who played: The Masters field had 89 players, including five-time winner Tiger Woods , defending champion Jon Rahm and Scheffler . Five amateur golfers were also in the field , but only one — American Neal Shipley — made the cut.
Lundquist signs off: The legendary Verne Lundquist made his final call from No. 16 on Sunday. After 40 tournaments, the 83-year-old play-by-play announcer is retiring .
LIV and PGA: Thirteen LIV players were at the Masters with their PGA Tour counterparts, distinguishable only by the LIV team gear they’ve been sporting. More than 10 months have passed since the PGA Tour announced plans to partner with LIV Golf’s Saudi backers, but no deal is imminent.

2024 federal budget's key takeaways: Housing and carbon rebates, students and sin taxes
Budget sees nearly $53b in new spending over the next 5 years.

What's in the new federal budget?
Social sharing.
Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland today tabled a 400-page-plus budget her government is pitching as a balm for anxious millennials and Generation Z.
The budget proposes $52.9 billion in new spending over five years, including $8.5 billion in new spending for housing. To offset some of that new spending, Ottawa is pitching policy changes to bring in new revenue.
Here are some of the notable funding initiatives and legislative commitments in budget 2024.
Ottawa unloading unused offices to meet housing targets
One of the biggest pillars of the budget is its housing commitments. Before releasing the budget, the government laid out what it's calling Canada's Housing Plan — a pledge to "unlock" nearly 3.9 million homes by 2031.

The government says two million of those would be net new homes and it believes it can contribute to more than half of them.
It plans to do that by:
- Converting underused federal offices into homes. The budget promises $1.1 billion over ten years to transform 50 per cent of the federal office portfolio into housing.
- Building homes on Canada Post properties. The government says the 1,700-plus Canada Post offices across the country can be used to build new homes while maintaining postal services. The federal government says it's assessing six Canada Post properties in Quebec, Alberta and British Columbia for development potential "as a start."
- Rethinking National Defence properties. The government is promising to look at redeveloping properties and buildings on National Defence lands for military and civilian use.
- Building apartments. Ottawa is pledging a $15 billion top-up to the Apartment Construction Loan Program, which says it will build 30,000 new homes across Canada.
Taxing vacant land?
As part of its push on housing, the federal government also says it's looking at vacant land that could be used to build homes.
It's not yet committing to new measures but the budget says the government will consider introducing a new tax on residentially zoned vacant land.
- Freeland's new federal budget hikes taxes on the rich to cover billions in new spending
- Are you renting with no plans to buy? Here's what the federal budget has for you
The government said it plans to launch consultations on the measure later this year.
Help for students
There's also something in the budget for students hunting for housing.
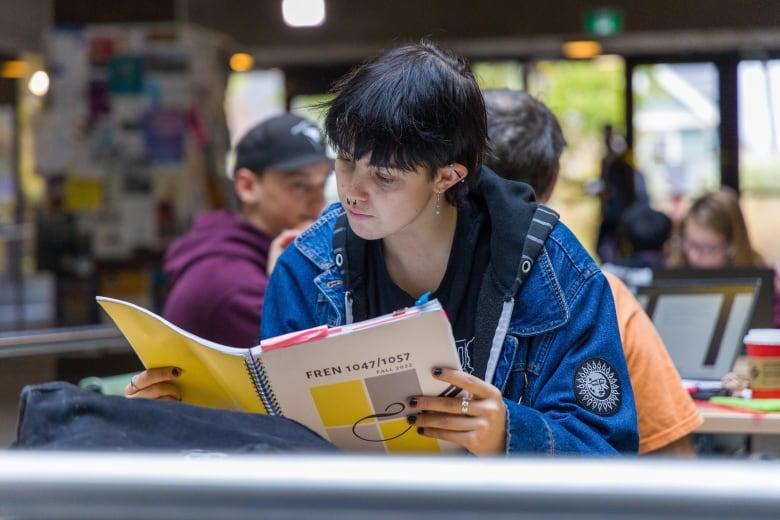

The government says it will update the formula used by the Canada Student Financial Assistance Program to calculate housing costs when determining financial need, to better reflect the cost of housing in the current climate.
The government estimates this could deliver more aid for rent to approximately 79,000 students each year, at an estimated cost of $154.6 million over five years.
- Updated Federal budget's funding boost for defence spread out over multiple years
- Liberals pledge $9B in new money for Indigenous communities in 2024 budget
The government is also promising to extend increased student grants and interest-free loans, at an estimated total cost of $1.1 billion this year.
Increase in taxes on capital gains
To help cover some of its multi-billion dollar commitments, the government is proposing a tax hike on capital gains — the profit individuals make when assets like stocks and second properties are sold.
The government is proposing an increase in the taxable portion of capital gains, up from the current 50 per cent to two thirds for annual capital gains over $250,000.
New investment to lead 'housing revolution in Canada,' Freeland says
Freeland said the change would impact the wealthiest 0.1 per cent.
There's still some protection for small businesses. There's been a lifetime capital gains exemption which allows Canadians to exempt up to $1,016,836 in capital gains tax-free on the sale of small business shares and farming and fishing property. This June the tax-free limit will be increased to $1.25 million and will continue to be indexed to inflation thereafter, according to the budget.
The federal government estimates this could bring in more than $19 billion over five years, although some analysts are not convinced.
Disability benefit amounts to $200 per month
Parliament last year passed the Canada Disability Benefit Act, which promised to send a direct benefit to low-income, working-age people with disabilities.
Budget 2024 proposes funding of $6.1 billion over six years, beginning this fiscal year, and $1.4 billion per year ongoing, for a new Canada Disability Benefit.
Advocates had been hoping for something along the lines of $1,000 per month per person . They'll be disappointed.
According to the budget document, the maximum benefit will amount to $2,400 per year for low income individuals with disabilities between the ages of 18 and 64 — about $200 a month.
- Federal government plans to lease public lands for construction through new housing strategy
- Alberta premier says she's prepared to take Ottawa to court over housing deals
The government said it plans for the Canada Disability Benefit Act to come into force in June 2024 and for payments to start in July 2025.
Carbon rebate for small businesses coming
The federal government has heard an earful from small business advocates who accuse it of reneging on a promise to return a portion of carbon pricing revenues to small businesses to mitigate the tax's economic costs.
- What's behind the carbon tax, and does it work?
- Federal government scales back carbon tax rebates for small businesses
The budget proposes to return fuel charge proceeds from 2019-20 through 2023-24 to an estimated 600,000 businesses with 499 or fewer employees through a new refundable tax credit.
The government said this would deliver $2.5 billion directly to Canada's small- and medium-sized businesses.
Darts and vape pods will cost more
Pitching it as a measure to cut the number of people smoking and vaping, the Liberals are promising to raise revenues on tobacco and smoking products.
- Just Asking wants to know: What questions do you have about quitting smoking or vaping? Do you think sin taxes will encourage smoking cessation? Fill out the details on this form and send us your questions ahead of our show on April 20.
Starting Wednesday, the total tobacco excise duty will be $5.49 per carton. The government estimates this could increase federal revenue by $1.36 billion over five years starting in 2024-25.

The budget also proposes to increase the vaping excise duty rates by 12 per cent effective July 1. That means an increase of 12 to 24 cents per pod, depending on where you live.
- 'Stay the hell away from our kids': Health minister vows to restrict nicotine pouches — but how?
Ottawa hopes this increase in sin taxes will bring in $310 million over five years, starting in 2024-25.
More money for CBC
Heritage Minister Pascale St-Onge has mused about redefining the role of the public broadcaster before the next federal election . But before that happens, CBC/Radio-Canada is getting a top-up this year.

The budget promises $42 million more in 2024-25 for CBC/Radio-Canada for "news and entertainment programming." CBC/Radio-Canada received about $1.3 billion in total federal funding last year.
The government says it's doing this to ensure that Canadians across the country, including rural, remote, Indigenous and minority language communities, have access to independent journalism and entertainment.
Last year, the CBC announced a financial shortfall, cut 141 employees and eliminated 205 vacant positions. In a statement issued Tuesday, CBC spokesperson Leon Mar said the new funding means the corporation can balance its budget "without significant additional reductions this year."
Boost for Canada's spy agency

As the government takes heat over how it has handled the threat of foreign election interference, it's promising more money to bolster its spy service.
The Canadian Security Intelligence Service is in line to receive $655.7 million over eight years, starting this fiscal year, to enhance its intelligence capabilities and its presence in Toronto.
- CSIS chief defends his spies' work after PM casts doubt on reliability of agency's reports
- Trudeau says it's his job to question CSIS intelligence, call out 'contradictions'
The budget also promises to guarantee up to $5 billion in loans for Indigenous communities to participate in natural resource development and energy projects in their territories.
These loans would be provided by financial institutions or other lenders and guaranteed by the federal government, meaning Indigenous borrowers who opt in could benefit from lower interest rates, the budget says.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Catharine Tunney is a reporter with CBC's Parliament Hill bureau, where she covers national security and the RCMP. She worked previously for CBC in Nova Scotia. You can reach her at [email protected]
- Follow Cat on Twitter
Add some “good” to your morning and evening.
Your weekly guide to what you need to know about federal politics and the minority Liberal government. Get the latest news and sharp analysis delivered to your inbox every Sunday morning.

Advertisement

How Dan Hurley, UConn beat Zach Edey, Purdue to win second straight national championship
UConn beats Purdue to go back to back
GLENDALE, Ariz. — With exactly six minutes left in Monday night’s national championship game, UConn guard Tristen Newton zoomed a pass to a cutting Stephon Castle, who skipped past Zach Edey in the paint and laid in an ordinary layup. Except, it was only ordinary in execution — because that basket put the Huskies up 17 points, their largest lead of the night.
Consider that the moment the hourglass flipped, and time started ticking until UConn’s looming championship celebration.
Minutes later, the confetti cannons inside State Farm Arena erupted, finalizing UConn’s 75-60 win over Purdue in Monday’s national title game — and immortalizing Dan Hurley’s Huskies , who accomplished what no college basketball team had since Florida in 2006-07: winning consecutive NCAA championships.
That feat alone is historic. Other than Florida , only Duke in 1991-92 had gone back-to-back since John Wooden’s UCLA dynasty in the 1960s and 1970s. But it’s the way that UConn won its 12th straight NCAA Tournament game — by, effectively, turning into the basketball version of a wood chipper — that lifts this two-year stretch to legendary status.
Last season, UConn won its six games in the Big Dance by a staggering average of 20 points per contest … yet somehow Hurley’s encore squad was even more dominant. After UConn’s 15-point victory over the Boilermakers, who were playing in their first national title game since 1969, the Huskies’ average victory margin this tournament? A whopping 23.3 points per game. That not even the Boilermakers — a No. 1 seed with two-time Wooden Award winner Zach Edey — could keep the final score to single digits speaks to UConn’s overwhelming dominance. The 7-foot-4 Edey finished Monday’s game, likely his last in college, with 37 points and 10 rebounds… and it mattered little.
And if this wasn’t already the case, go ahead and formally welcome UConn’s to the blue-blood club. Monday’s win was the Huskies’ sixth NCAA title, pushing them past Duke — which has five — and into a tie for third all-time with North Carolina ; only UCLA (11) and Kentucky (eight) have more. That all six championships have come in a 25-year span since 1999, and under three different coaches, only further validates Connecticut’s place in college basketball’s historic hierarchy.
The same can be said of Hurley; the 51-year-old is now only the third active Division-I men’s coach with multiple national titles, joining Bill Self and Rick Pitino.
And it’s Hurley who deserves plenty of credit for UConn’s masterful game plan Monday night. Stopping Edey is an impossible task. Even in a battle of the two best bigs in America — Edey vs. 7-2 UConn’s center Donovan Clingan , who managed 11 points and five rebounds despite foul trouble — the Big Maple was always going to get his. He scored 16 of Purdue’s 30 first-half points, especially early on, when he feasted with his patented array of hook shots. But UConn countered well late, holding Edey without a basket over the final 5:47 before halftime — and during that stretch, the Huskies stretched their lead to six.
At the same time, UConn completely smothered Purdue — which entered as the second-best 3-point shooting team in America, making 40.6 percent from deep — from behind the arc. Hurley’s strategy of not having UConn’s guards help when Edey got the ball inside meant Purdue’s perimeter players had no breathing room. Case in point: Purdue only attempted one 3-pointer in the first 17 minutes of the game; it wasn’t until Braden Smith canned a fadeaway 3 with the shot clock expiring, 2:17 before intermission, that the Boilermakers actually made a triple.
Offensively, the difference between the two teams’ philosophies couldn’t have been more pronounced. Edey took 12 of Purdue’s 28 first-half attempts, making more shots than the rest of the Boilermakers did combined. On the flip side, while Cam Spencer scored seven of UConn’s first 11 points, the Huskies leaned on their balance and depth. Four different Huskies — Spencer, Clingan, Tristen Newton, and Hassan Diarra — had at least three made shots before any non-Edey Boilermaker did so.
That dichotomy became untenable for Purdue from the very first possession of the second half. Edey missed a bunny inside, and UConn turned it into a Newton 3 on the other end — a critical five-point swing that pushed Purdue into an early danger zone. From then on, what had been a back-and-forth battle between KenPom’s No. 1 and 2 teams — only the fourth time that’s happened since 2005 —became a lopsided, 20-minute-long UConn’s coronation. A surprise putback dunk from freshman Camden Heide , off another Edey miss, only briefly revived the Boilermakers’ hopes… until, soon after, they went 4:29 without a made field goal, during which UConn pushed its lead to 16. Newton — who finished with 20 points, seven assists and five rebounds — was the maestro making it all happen.
The last made shot of that run was a Diarra layup in transition; Purdue coach Matt Painter couldn’t have called timeout more quickly, sensing the game getting away from his team.
And he was almost right.
Except the game wasn’t getting away by then; it was gone.

Inside the UConn defensive strategy that won a national title

(Photo: Michael Chow / USA Today)
GLENDALE, Ariz. — Connecticut assistant coach Luke Murray went to sophomore center Donovan Clingan sometime in the middle of this season with a declaration. UConn was going to face Purdue in the national championship, and he’d better get familiar with Zach Edey. Murray and Clingan discussed how they would play the hypothetical matchup, and Clingan said he wanted to play him one-on-one and let the rest of the Huskies win the game.
Continue reading.

Inside the UConn defensive strategy that stopped Purdue and won a national title

How UConn became the unlikeliest modern Camelot
GLENDALE, Ariz. — That this started, or restarted, with a then-75-year-old Jim Calhoun nearly kicking Dan Hurley’s ass is so perfectly Connecticut that the scene should replace the state flag. It was early spring of 2018. Hurley was the recently named UConn head coach and Calhoun was the retired patriarch of the program, one whose endorsement helped secure Hurley’s hiring.

How UConn became college basketball’s unlikeliest modern Camelot
Tristen Newton, Dan Hurley met in the middle. It led to two titles

(Photo: Bob Donnan / USA Today)
GLENDALE, Ariz. — During Tristen Newton’s first Connecticut practice, right after he transferred from East Carolina in the summer of 2022, UConn’s coaching staff put him through a normal shooting drill: make 50 3-pointers, timed, to see how quickly you can do it.
Newton got to 37 … and started cramping in his right arm.

UConn’s Tristen Newton and Dan Hurley met in the middle. It led to two titles

UConn, Purdue showed blueprint for building NCAA championship rosters

(Photo: Joe Rondone / USA Today)
GLENDALE, Ariz. — The master plan for men’s college basketball was in plain sight again Monday night, but for distracting confetti flakes floating into the area. Connecticut won another national championship, its second straight, which is an extremely hard thing to do. But the imprints and spoor leading directly to masses of happy humanity in April were right there, for any coach or administrator who cares to look. This is what wins now. It is intricate and tenuous and, honestly, not that hard to figure out.

UConn, Purdue showed blueprint for building NCAA championship rosters — again

Zach Edey came up one win short of title, but his legacy is towering

(Photo: Grace Hollars / USA Today)
GLENDALE, Ariz. — Will Berg arrived in West Lafayette, Ind., last year from Sweden, desperately homesick and missing his father, Martin. The two are incredibly close, bonded after they lost Berg’s mother to a battle with alcoholism. Berg didn’t talk about it much to anyone, trying to find a way to fit in with his new team, but as the months continued, the gnaw in his stomach grew. One afternoon in practice, maybe about a month into the season, Zach Edey told Berg to hang in there, that though Canada isn’t quite as far as Sweden, he understood what it was like to transplant yourself entirely on your own.

Purdue’s Zach Edey came up one win short of a title, but his legacy is towering
Too-early men’s college basketball Top 25
Those in the industry have always called this exercise the way-too-early Top 25. A more appropriate title in this transfer portal era of college basketball would be the almost-impossible Top 25.
We realize this is a tough task, trying to speculate on who might return and who might leave and who might even be the coach. (Thanks, John Calipari.) We have done our best to make those projections. If we anticipate that you’ll leave for the NBA Draft based on our projections, then you are not included. There are probably some players listed here who think right now that they are leaving for the NBA but will ultimately return when they receive their feedback. This will be a lot easier in a few months when we have clarity on the rosters but, hey, the national champion has been crowned. We are starting to think about next year. And it’s always fun to project ahead. With that, here is your don’t-hold-us-to-it-super-early Top 25.

Too-early men’s college basketball Top 25: Duke, Gonzaga, Houston start in front

Hurley says 'No way' about taking Kentucky job
GLENDALE, Ariz. — Dan Hurley entered rare air on Monday night, becoming just the third men’s college basketball coach to repeat as a national champion since the end of John Wooden’s UCLA dynasty in the 1970s. And when it was over — a 75-60 victory over Purdue marking Connecticut’s 12th consecutive NCAA Tournament win by double digits — Hurley found himself in another very small club: coaches who’ve won it all and immediately had to address the possibility of leaving for another program. Such is life when you’re the hottest coach in the sport and the Kentucky job unexpectedly becomes available on the eve of the championship game.

UConn’s Dan Hurley: ‘No way’ he would entertain Kentucky coaching job
Cutting down the nets
The Huskies get their prize.
The all-tournament team is out
Tristen Newton leads the way as the Most Outstanding Player.
One Shining Moment
Always a fan favorite, let's look back on the tournament.
Reason to celebrate
UConn goes back to back.
Dan Hurley: “For the last 25, 30 years, UConn’s been running college basketball.”
Six titles in 25 years, hard to argue.

No college in the western side of the United States has won a national championship in football or basketball in at least 20 years.
27 in basketball (Arizona) and 20 in football (USC).

(Dana O'Neil)
The UConn locker room gets an update: national champion signage.
GLENDALE, Ariz. — Another television duty with a new man in charge in 2024: Ernie Johnson takes over as the man interviewing the champions on the dais.
That, too, was a Jim Nantz job. And while Ian Eagle took over for Nantz as the primary television play-by-play voice for the Final Four, he indicated to me way back in February that being on the stage after the game was not going to be a job for him.

(Photo: Robert Deutsch / USA Today)
UConn claimed its sixth national title with its win over Purdue on Monday night. That breaks a tie with Duke and Indiana at five titles.
It moves UConn into a tie for third with six titles with North Carolina. Only UCLA (11) and Kentucky (eight) have more.
UConn is the eighth program to repeat as the national champion and the first since Florida in 2006 and 2007. Before that, Duke (1991-1992) was the last program to repeat since UCLA's run of 10 straight from 1964-1973.
The other programs to repeat:
- Oklahoma State: 1945-1946
- Kentucky: 1948-1949
- San Francisco: 1955-1956
- Cincinnati: 1961-1962
GLENDALE, Ariz. — With a minute left, Purdue called off the fouls. Zach Edey wiped his face with his jersey. The Connecticut celebration began.
And with 36 seconds left, Edey left the floor.
The UConn Huskies, are national champions. Again.
GLENDALE, Ariz. — The UConn family section is relentless and vicious. During Tristen Newton's free throws after the under-4 timeout, one of them cut through the silence, trying to get the attention of Purdue's Lance Jones.
"Hey! Lance!" he said. "L for loss!"
Jones just smiled.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Identify the article. Start your review by referring to the title and author of the article, the title of the journal, and the year of publication in the first paragraph. For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest. 4.
Step 1: Define the right organization for your review. Knowing the future setup of your paper will help you define how you should read the article. Here are the steps to follow: Summarize the article — seek out the main points, ideas, claims, and general information presented in the article.
Both a reaction paper and an article review will start with a content summary. ️. For scholarly material, you will present a structured review after the summary. ️. For popular magazine content, you will write a response that sums up your emotions, thoughts, and reactions that the material aroused.
Step 2: Read and Understand the Article. It's super important to read and understand the article before writing your review. Read the article a few times and jot down the notes as you go. Focus on the main arguments, major points, evidence, and how it's structured. For Example:
Here is a basic, detailed outline for an article review you should be aware of as a pre-writing process if you are wondering how to write an article review. Introduction. Introduce the article that you are reviewing (author name, publication date, title, etc.) Now provide an overview of the article's main topic.
2. Read the article thoroughly: Carefully read the article multiple times to get a complete understanding of its content, arguments, and conclusions. As you read, take notes on key points, supporting evidence, and any areas that require further exploration or clarification. 3. Summarize the main ideas: In your review's introduction, briefly ...
A journal article review is written for a reader who is knowledgeable in the discipline and is interested not just in the coverage and content of the article being reviewed, but also in your critical assessment of the ideas and argument that are being presented by the author. Your review might be guided by the following questions:
For an article review, your task is to identify, summarize, and evaluate the ideas and information the author has presented. You are being asked to make judgments, positive or negative, about the content of the article. The criteria you follow to do this will vary based upon your particular academic discipline and the parameters of your ...
Step 4: Introduction. Once you've identified the article, give a brief description of the main points of the article. Carefully analyze the article to identify and highlight the author's thesis. Understanding the thesis of the main article is crucial to writing a good review, so make sure you include any sub thesis.
The most critical characteristics of an effective review are clarity, specificity, constructiveness, and thoroughness (Hyman, 1995 ). A journal article review should inform the managing editor and author of the primary strengths and weaknesses of a manuscript in a focused way (see Table 11.1 ).
3. A critique, or a discussion about the key points of the journal article. A critique is a discussion about the key points of the journal article. It should be a balanced discussion about the strengths and weaknesses of the key points and structure of the article.. You will also need to discuss if the author(s) points are valid (supported by other literature) and robust (would you get the ...
2. Theories, research, ideas that are relevant to the article area must be used. 3. It must remember that a review does not include the new information. Instead, it shows another writer's work quality. Tip- "Check the other review samples to understand how to write an article review in a better way.".
Crafting an effective article review involves a combination of critical analysis, clarity, and structure. Here are some valuable tips to guide you through the process: Start with a Clear Introduction; Kick off your article review by introducing the article's main points and mentioning the publication date, which you can find on the re-title page.
Step 4: Make an Introduction. In your introduction, provide a brief overview of the title's subject and purpose. Capture the reader's attention and clearly state your thesis or main point related to the title. For instance, you might start your article review template like this.
Article Identification. Start the first paragraph of your review with concise and clear article identification that specifies its title, author, name of the resource (e.g., journal, web, etc.), and the year of publication. Intro. Following the identification, write a short introductory paragraph.
Describe the title, abstract, and introduction: A good starting point to begin structuring your review is by drafting the title, abstract, and introduction. Explicitly writing down what your review aims to address in the field will help shape the rest of your article. Be unbiased and critical: Evaluate every piece of evidence in a critical but ...
1 A thesis. Before you write, make sure you know the general message you want to convey. A simple thesis will help keep your review from straying off-topic. This could be as straightforward as "I really liked this meal!" or as complex as "These shoes took a while to wear in." Think to yourself: If I were telling a friend about this ...
A review article can also be called a literature review, or a review of literature. It is a survey of previously published research on a topic. It should give an overview of current thinking on the topic. And, unlike an original research article, it will not present new experimental results. Writing a review of literature is to provide a ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Claudia Willmes from Trends in Molecular Medicine agrees: "Start with the motivation for why you're writing this review and make sure this is your running thread." Claudia explains this by encouraging authors to think back to where the idea for the review came from in the first place. For instance, if an editor invited you to write after ...
Writing a Literature Review. A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels ...
How to Start an Article Review. Example Introduction for Article Review. Example 1: Example 2: Example 3: Conclusion. Writing an article review is a great way to analyze and evaluate the work of other experts in your field. It is typically done to demonstrate clarity, originality, and how significant a certain article's contribution is.
For example, a graduate student might turn to a review article when they start in a new lab to find out more about the history of a field, or to get a summary of key findings. By contrast, an experienced post-doc or PI might want to read a review written by one of their peers to find out what the current state of thinking in a field is ...
The NBA Playoffs tip off Tuesday with the start of the play-in tournament. The top six teams in each conference have qualified for the actual playoffs, and teams seven through 10 must get through ...
After heavy storms overnight delayed the Masters' start by two-and-a-half hours Thursday morning, Woods teed off at 3:54 p.m. ET and stood 1 under through 13 holes as play was suspended due to ...
The successful programs, the authors found, employed six critical practices: treating transformation as a continuous process; building it into the company's operating rhythm; explicitly managing ...
Senior Staff Writer [email protected] V. Saxena is a staff writer for BizPac Review with a decade of experience as a professional writer, and a lifetime of experience as an avid news junkie. He ...
Professional golf makes its annual visit to Augusta National with this week's Masters. Here's a look at the first major of the season, which begins Thursday.
Starting Wednesday, the total tobacco excise duty will be $5.49 per carton. The government estimates this could increase federal revenue by $1.36 billion over five years starting in 2024-25.
GLENDALE, Ariz. — That this started, or restarted, with a then-75-year-old Jim Calhoun nearly kicking Dan Hurley's ass is so perfectly Connecticut that the scene should replace the state flag.