

Why Is Art Important? – The Value of Creative Expression
The importance of art is an important topic and has been debated for many years. Some might think art is not as important as other disciplines like science or technology. Some might ask what art is able to offer the world in terms of evolution in culture and society, or perhaps how can art change us and the world. This article aims to explore these weighty questions and more. So, why is art important to our culture? Let us take a look.
Table of Contents
- 1.1 The Definition of Art
- 1.2 The Types and Genres of Art
- 2.1 Art Is a Universal Language
- 2.2 Art Allows for Self-Expression
- 2.3 Art Keeps Track of History and Culture
- 2.4 Art Assists in Education and Human Development
- 2.5 Art Adds Beauty for Art’s Sake
- 2.6 Art Is Socially and Financially Rewarding
- 2.7 Art Is a Powerful (Political) Tool
- 3 Art Will Always Be There
- 4.1 What Is the Importance of Arts?
- 4.2 Why Is Art Important to Culture?
- 4.3 What Are the Different Types of Art?
- 4.4 What Is the Definition of Art?
What Is Art?
There is no logical answer when we ponder the importance of arts. It is, instead, molded by centuries upon centuries of creation and philosophical ideas and concepts. These not only shaped and informed the way people did things, but they inspired people to do things and live certain ways.
We could even go so far as to say the importance of art is borne from the very act of making art. In other words, it is formulated from abstract ideas, which then turn into the action of creating something (designated as “art”, although this is also a contested topic). This then evokes an impetus or movement within the human individual.

This impetus or movement can be anything from stirred up emotions, crying, feeling inspired, education, the sheer pleasure of aesthetics, or the simple convenience of functional household items – as we said earlier, the importance of art does not have a logical answer.
Before we go deeper into this question and concept, we need some context. Below, we look at some definitions of art to help shape our understanding of art and what it is for us as humans, thus allowing us to better understand its importance.
The Definition of Art
Simply put, the definition of the word “art” originates from the Latin ars or artem , which means “skill”, “craft”, “work of art”, among other similar descriptions. According to Merriam-Webster’s online dictionary, the word has various meanings; art may be a “skill acquired by experience, study, or observation”, a “branch of learning”, “an occupation requiring knowledge or skill”, or “the conscious use of skill and creative imagination especially in the production of aesthetic objects”.
We might also tend to think of art in terms of the latter definition provided above, “the conscious use of skill” in the “production of aesthetic objects”. However, does art only serve aesthetic purposes? That will also depend on what art means to us personally, and not how it is collectively defined. If a painting done with great skill is considered to be art, would a piece of furniture that is also made with great skill receive the same label as being art?
Thus, art is defined by our very own perceptions.
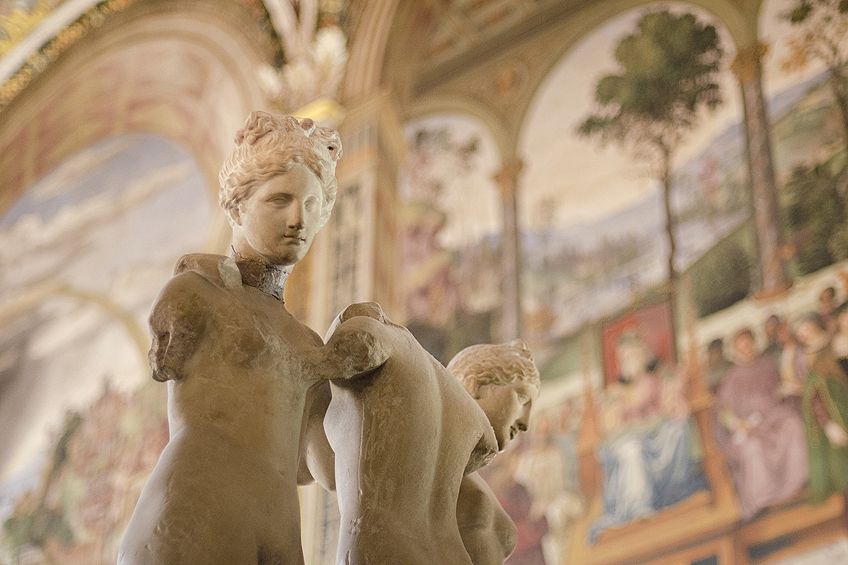

Art has also been molded by different definitions throughout history. When we look at it during the Classical or Renaissance periods , it was very much defined by a set of rules, especially through the various art academies in the major European regions like Italy (Academy and Company for the Arts of Drawing in Florence), France (French Academy of Fine Arts), and England (Royal Academy of Arts in London).
In other words, art had an academic component to it so as to distinguish artists from craftsmen.
The defining factor has always been between art for art’s sake , art for aesthetic purposes, and art that serves a purpose or a function, which is also referred to as “utilitarianism”. It was during the Classical and Renaissance periods that art was defined according to these various predetermined rules, but that leaves us with the question of whether these so-called rules are able to illustrate the deeper meaning of what art is?
If we move forward in time to the 20 th century and the more modern periods of art history, we find ourselves amidst a whole new art world. People have changed considerably between now and the Renaissance era, but we can count on art to be like a trusted friend, reflecting and expressing what is inherent in the cultures and people of the time.

During the 20 th century, art was not confined to rules like perspective, symmetry, religious subject matter, or only certain types of media like oil paints . Art was freed, so to say, and we see the definition of it changing (literally) in front of our very own eyes over a variety of canvases and objects. Art movements like Cubism , Fauvism, Dadaism, and Surrealism, among others, facilitated this newfound freedom in art.
Artists no longer subscribed to a set of rules and created art from a more subjective vantage point.
Additionally, more resources became available beyond only paint, and artists were able to explore new methods and techniques previously not available. This undoubtedly changed the preconceived notions of what art was. Art became commercialized, aestheticized, and devoid of the traditional Classical meaning from before. We can see this in other art movements like Pop Art and Abstract Expressionism, among others.
The Types and Genres of Art
There are also different types and genres of art, and all have had their own evolution in terms of being classified as art. These are the fine arts, consisting of painting, drawing, sculpting, and printmaking; applied arts like architecture; as well as different forms of design such as interior, graphic, and fashion design, which give day-to-day objects aesthetic value.
Other types of art include more decorative or ornamental pieces like ceramics, pottery, jewelry, mosaics, metalwork, woodwork, and fabrics like textiles. Performance arts involve theater and drama, music, and other forms of movement-based modalities like dancing, for example. Lastly, Plastic arts include works made with different materials that are pliable and able to be formed into the subject matter, thus becoming a more hands-on approach with three-dimensional interaction.

Top Reasons for the Importance of Art
Now that we have a reasonable understanding of what art is, and a definition that is ironically undefinable due to the ever-evolving and fluid nature of art, we can look at how the art that we have come to understand is important to culture and society. Below, we will outline some of the top reasons for the importance of art.
Art Is a Universal Language
Art does not need to explain in words how someone feels – it only shows. Almost anyone can create something that conveys a message on a personal or public level, whether it is political, social, cultural, historical, religious, or completely void of any message or purpose. Art becomes a universal language for all of us to tell our stories; it is the ultimate storyteller.
We can tell our stories through paintings, songs, poetry, and many other modalities.

Art connects us with others too. Whenever we view a specific artwork, which was painted by a person with a particular idea in mind, the viewer will feel or think a certain way, which is informed by the artwork (and artist’s) message. As a result, art becomes a universal language used to speak, paint, perform, or build that goes beyond different cultures, religions, ethnicities, or languages. It touches the deepest aspects of being human, which is something we all share.
Art Allows for Self-Expression
Touching on the above point, art touches the deepest aspects of being human and allows us to express these deeper aspects when words fail us. Art becomes like a best friend, giving us the freedom and space to be creative and explore our talents, gifts, and abilities. It can also help us when we need to express difficult emotions and feelings or when we need mental clarity – it gives us an outlet.
Art is widely utilized as a therapeutic tool for many people and is an important vehicle to maintain mental and emotional health. Art also allows us to create something new that will add value to the lives of others. Consistently expressing ourselves through a chosen art modality will also enable us to become more proficient and disciplined in our skills.
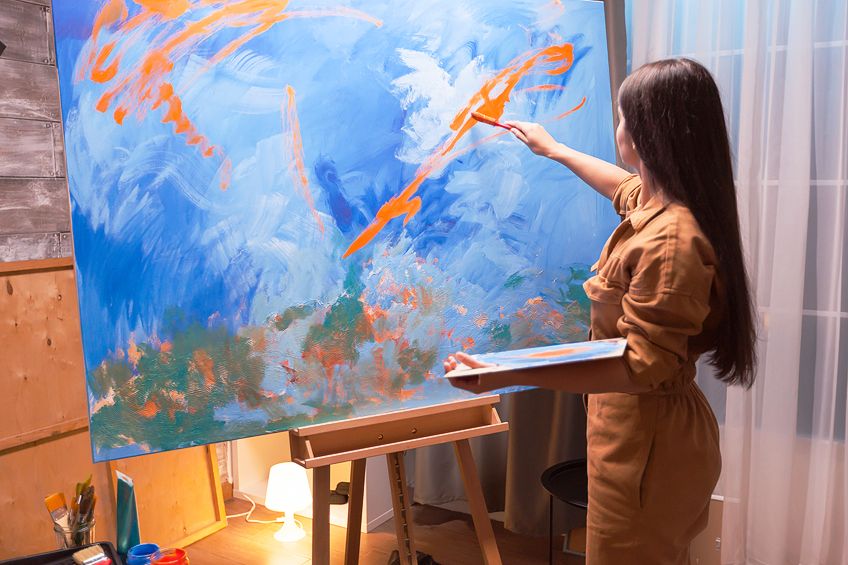

Art Keeps Track of History and Culture
We might wonder, why is art important to culture? As a universal language and an expression of our deepest human nature, art has always been the go-to to keep track of everyday events, almost like a visual diary. From the geometric motifs and animals found in early prehistoric cave paintings to portrait paintings from the Renaissance, every artwork is a small window into the ways of life of people from various periods in history. Art connects us with our ancestors and lineage.
When we find different artifacts from all over the world, we are shown how different cultures lived thousands of years ago. We can keep track of our current cultural trends and learn from past societal challenges. We can draw inspiration from past art and artifacts and in turn, create new forms of art.
Art is both timeless and a testament to the different times in our history.
Art Assists in Education and Human Development
Art helps with human development in terms of learning and understanding difficult concepts, as it accesses different parts of the human brain. It allows people to problem-solve as well as make more complex concepts easier to understand by providing a visual format instead of just words or numbers. Other areas that art assists learners in (range from children to adults) are the development of motor skills, critical thinking, creativity, social skills, as well as the ability to think from different perspectives.

Art subjects will also help students improve on other subjects like maths or science. Various research states the positive effects art has on students in public schools – it increases discipline and attendance and decreases the level of unruly behavior.
According to resources and questions asked to students about how art benefits them, they reported that they look forward to their art lesson more than all their other lessons during their school day. Additionally, others dislike the structured format of their school days, and art allows for more creativity and expression away from all the rules. It makes students feel free to do and be themselves.
Art Adds Beauty for Art’s Sake
Art is versatile. Not only can it help us in terms of more complex emotional and mental challenges and enhance our well-being, but it can also simply add beauty to our lives. It can be used in numerous ways to make spaces and areas visually appealing.
When we look at something beautiful, we immediately feel better. A piece of art in a room or office can either create a sense of calm and peace or a sense of movement and dynamism.
Art can lift a space either through a painting on a wall, a piece of colorful furniture, a sculpture, an ornamental object, or even the whole building itself, as we see from so many examples in the world of architecture. Sometimes, art can be just for art’s sake.

Art Is Socially and Financially Rewarding
Art can be socially and financially rewarding in so many ways. It can become a profession where artists of varying modalities can earn an income doing what they love. In turn, it becomes part of the economy. If artists sell their works, whether in an art gallery, a park, or online, this will attract more people to their location. Thus, it could even become a beacon for improved tourism to a city or country.
The best examples are cities in Europe where there are numerous art galleries and architectural landmarks celebrating artists from different periods in art history, from Gothic cathedrals like the Notre Dame in Paris to the Vincent van Gogh Museum in Amsterdam. Art can also encourage people to do exercise by hiking up mountains to visit pre-historic rock art caves.
Art Is a Powerful (Political) Tool
Knowing that art is so versatile, that it can be our best friend and teacher, makes it a very powerful tool. The history of humankind gives us thousands of examples that show how art has been used in the hands of people who mean well and people who do not mean well.
Therefore, understanding the role of art in our lives as a powerful tool gives us a strong indication of its importance.
Art is also used as a political medium. Examples include memorials to celebrate significant changemakers in our history, and conveying powerful messages to society in the form of posters, banners, murals, and even graffiti. It has been used throughout history by those who have rebelled as well as those who created propaganda to show the world their intentions, as extreme as wanting to take over the world or disrupt existing regimes.

The Futurist art movement is an example of art combined with a group of men who sought to change the way of the future, informed by significant changes in society like the industrial revolution. It also became a mode of expression of the political stances of its members.
Other movements like Constructivism and Suprematism used art to convey socialist ideals, also referred to as Socialist Realism.
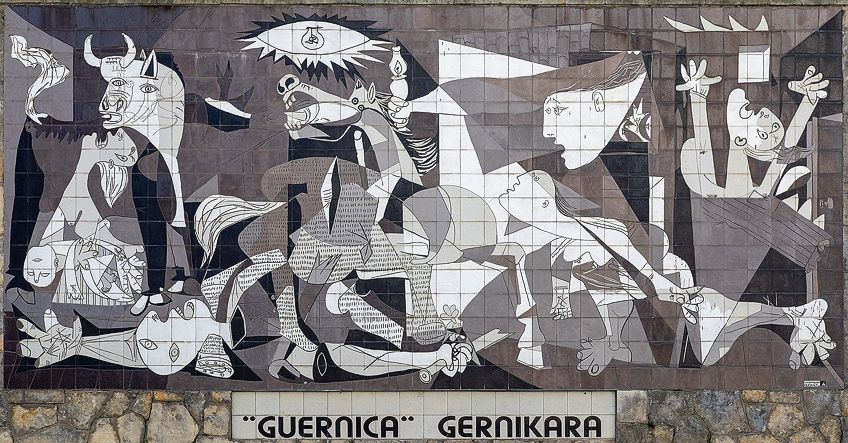
Other artists like Jacques-Louis David from the Neoclassical movement produced paintings influenced by political events; the subject matter also included themes like patriotism. Other artists include Pablo Picasso and his famous oil painting , Guernica (1937), which is a symbol and allegory intended to reach people with its message.
The above examples all illustrate to us that various wars, conflicts, and revolutions throughout history, notably World Wars I and II, have influenced both men and women to produce art that either celebrates or instigates changes in society. The power of art’s visual and symbolic impact has been able to convey and appeal to the masses.

Art Will Always Be There
The importance of art is an easy concept to understand because there are so many reasons that explain its benefits in our lives. We do not have to look too hard to determine its importance. We can also test it on our lives by the effects it has on how we feel and think when we engage with it as onlookers or as active participants – whether it is painting, sculpting, or standing in an art gallery.
What art continuously shows us is that it is a constant in our lives, our cultures, and the world. It has always been there to assist us in self-expression and telling our story in any way we want to. It has also given us glimpses of other cultures along the way.
Art is fluid and versatile, just like a piece of clay that can be molded into a beautiful bowl or a slab of marble carved into a statue. Art is also a powerful tool that can be used for the good of humanity good or as a political weapon.
Art is important because it gives us the power to mold and shape our lives and experiences. It allows us to respond to our circumstances on micro- and macroscopic levels, whether it is to appreciate beauty, enhance our wellbeing, delve deeper into the spiritual or metaphysical, celebrate changes, or to rebel and revolt.
Take a look at our purpose of art webstory here!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the importance of arts.
There are many reasons that explain the importance of art. It is a universal language because it crosses language and cultural barriers, making it a visual language that anyone can understand; it helps with self-expression and self-awareness because it acts as a vehicle wherein we can explore our emotions and thoughts; it is a record of past cultures and history; it helps with education and developing different skill sets; it can be financially rewarding, it can be a powerful political tool, and it adds beauty and ambiance to our lives and makes us feel good.
Why Is Art Important to Culture?
Art is important to culture because it can bridge the gap between different racial groups, religious groups, dialects, and ethnicities. It can express common values, virtues, and morals that we can all understand and feel. Art allows us to ask important questions about life and society. It allows reflection, it opens our hearts to empathy for others, as well as how we treat and relate to one another as human beings.
What Are the Different Types of Art?
There are many different types of art, including fine arts like painting, drawing, sculpture, and printmaking, as well as applied arts like architecture, design such as interior, graphic, and fashion. Other types of art include decorative arts like ceramics, pottery, jewelry, mosaics, metalwork, woodwork, and fabrics like textiles; performance arts like theater, music, dancing; and Plastic arts that work with different pliable materials.
What Is the Definition of Art?
The definition of the word “art” originates from the Latin ars or artem , which means “skill”, “craft”, and a “work of art”. The Merriam-Webster online dictionary offers several meanings, for example, art is a “skill acquired by experience, study, or observation”, it is a “branch of learning”, “an occupation requiring knowledge or skill”, or “the conscious use of skill and creative imagination especially in the production of aesthetic objects”.

Isabella studied at the University of Cape Town in South Africa and graduated with a Bachelor of Arts majoring in English Literature & Language and Psychology. Throughout her undergraduate years, she took Art History as an additional subject and absolutely loved it. Building on from her art history knowledge that began in high school, art has always been a particular area of fascination for her. From learning about artworks previously unknown to her, or sharpening her existing understanding of specific works, the ability to continue learning within this interesting sphere excites her greatly.
Her focal points of interest in art history encompass profiling specific artists and art movements, as it is these areas where she is able to really dig deep into the rich narrative of the art world. Additionally, she particularly enjoys exploring the different artistic styles of the 20 th century, as well as the important impact that female artists have had on the development of art history.
Learn more about Isabella Meyer and the Art in Context Team .
Cite this Article
Isabella, Meyer, “Why Is Art Important? – The Value of Creative Expression.” Art in Context. July 26, 2021. URL: https://artincontext.org/why-is-art-important/
Meyer, I. (2021, 26 July). Why Is Art Important? – The Value of Creative Expression. Art in Context. https://artincontext.org/why-is-art-important/
Meyer, Isabella. “Why Is Art Important? – The Value of Creative Expression.” Art in Context , July 26, 2021. https://artincontext.org/why-is-art-important/ .
Similar Posts

Relief Sculpture – Carving Dimensions in Art

Cyanotype Art – Unveiling the Timeless Beauty of Blue Prints

Early Christian Art – Christian Artwork and Biblical Paintings

Byzantine Art – Traversing the Byzantine Empire Art Period

Hellenistic Art – Ancient Greek Multiculturalism

Impressionism – A Detailed Movement Overview
One comment.
It’s great that you talked about how there are various kinds and genres of art. I was reading an art book earlier and it was quite interesting to learn more about the history of art. I also learned other things, like the existence of online american indian art auctions.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
The Most Famous Artists and Artworks
Discover the most famous artists, paintings, sculptors…in all of history!

MOST FAMOUS ARTISTS AND ARTWORKS
Discover the most famous artists, paintings, sculptors!

Essay on Art
500 words essay on art.
Each morning we see the sunshine outside and relax while some draw it to feel relaxed. Thus, you see that art is everywhere and anywhere if we look closely. In other words, everything in life is artwork. The essay on art will help us go through the importance of art and its meaning for a better understanding.

What is Art?
For as long as humanity has existed, art has been part of our lives. For many years, people have been creating and enjoying art. It expresses emotions or expression of life. It is one such creation that enables interpretation of any kind.
It is a skill that applies to music, painting, poetry, dance and more. Moreover, nature is no less than art. For instance, if nature creates something unique, it is also art. Artists use their artwork for passing along their feelings.
Thus, art and artists bring value to society and have been doing so throughout history. Art gives us an innovative way to view the world or society around us. Most important thing is that it lets us interpret it on our own individual experiences and associations.
Art is similar to live which has many definitions and examples. What is constant is that art is not perfect or does not revolve around perfection. It is something that continues growing and developing to express emotions, thoughts and human capacities.
Importance of Art
Art comes in many different forms which include audios, visuals and more. Audios comprise songs, music, poems and more whereas visuals include painting, photography, movies and more.
You will notice that we consume a lot of audio art in the form of music, songs and more. It is because they help us to relax our mind. Moreover, it also has the ability to change our mood and brighten it up.
After that, it also motivates us and strengthens our emotions. Poetries are audio arts that help the author express their feelings in writings. We also have music that requires musical instruments to create a piece of art.
Other than that, visual arts help artists communicate with the viewer. It also allows the viewer to interpret the art in their own way. Thus, it invokes a variety of emotions among us. Thus, you see how essential art is for humankind.
Without art, the world would be a dull place. Take the recent pandemic, for example, it was not the sports or news which kept us entertained but the artists. Their work of arts in the form of shows, songs, music and more added meaning to our boring lives.
Therefore, art adds happiness and colours to our lives and save us from the boring monotony of daily life.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Conclusion of the Essay on Art
All in all, art is universal and can be found everywhere. It is not only for people who exercise work art but for those who consume it. If there were no art, we wouldn’t have been able to see the beauty in things. In other words, art helps us feel relaxed and forget about our problems.
FAQ of Essay on Art
Question 1: How can art help us?
Answer 1: Art can help us in a lot of ways. It can stimulate the release of dopamine in your bodies. This will in turn lower the feelings of depression and increase the feeling of confidence. Moreover, it makes us feel better about ourselves.
Question 2: What is the importance of art?
Answer 2: Art is essential as it covers all the developmental domains in child development. Moreover, it helps in physical development and enhancing gross and motor skills. For example, playing with dough can fine-tune your muscle control in your fingers.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

10 Famous Artworks of Anish Kapoor
Top 25 paintings of jan van eyck, 11 famous artworks of robert rauschenberg, subscribe to updates.
Get the latest creative news from FooBar about art, design and business.
By signing up, you agree to the our terms and our Privacy Policy agreement.

What is Art? Why is Art Important?

What is art? – The dictionary definition of art says that it is “the conscious use of skill and creative imagination , especially in the production of aesthetic objects” (Merriam-Webster). Art is essential to society as it stimulates creativity , reflects culture, fosters empathy, provokes thought, and offers a medium for expression. It enhances society’s intellectual and emotional understanding of the world.
But the thing about art is that it’s so diverse that there are as many ways to understand it as there are people.
That’s why there are scholars who give their special definition of the word, such as the one penned by this famous Russian novelist, which goes:
“Art is the activity by which a person, having experienced an emotion, intentionally transmits it to others” – Leo Tolstoy
During his life, Tolstoy was known to write based on his life experiences, such as his most famous work, “War and Peace,” which used much of his experience during the Crimean War.
Whether or not his definition of art is the best, the point is that people look at art based on how they have experienced it.
What is Art?
There are many common definitions of art as per many books by famous artists and authors . Few to quote:
- any creative work of a human being
- a form of expressing oneself
- resides in the quality of doing; the process is not magic
- an act of making something visually entertaining
- an activity that manifests beauty ( What is Beauty in Art? )
- the mastery, an ideal way of doing things
- not a thing — it is a way (Elbert Hubbard)
- the most intense mode of individualism that the world has known
- discovery and development of elementary principles of nature into beautiful forms suitable for human use (Frank Lloyd Wright)
Why is Art Important?
Probably, the most prominent theory which best explains – Why is art important – is from Van Jones, which subtly provides a great response to What is art?
Van Jones presented a graph that accurately represents the interaction between the four aspects of society and its different members.
Consequently, Vones depicts why art is important to our society.
The graph (below) represents our society.
Society is driven by the powerful elites, the dependent masses, the government, cultural producers, and artists

On the left, you have action, and on the right, ideas; elites are at the top, and the masses are below. There’s an inside act and an outside act.
On the inside, there’s big money: elites are spending millions of dollars to influence politicians and policymakers. The inside act has the power to influence policy creators.
On the outside, we at the grassroots set our expectations and needs so that the elected candidates pass laws that give us power. Masses reflect what society wants (heart)
The left side, “action,” often means quantifiable policy changes. The right side, “ideas,” can be harder to see. We are not necessarily talking about concrete things here, but rather, a “headspace.”
Academic institutions and think tanks, which are not always involved in the immediate policy wins, are significant in creating a culture of thought
While the left side, “action,” continues to produce quantifiable policy changes and new laws, the right side, “ïdeas,” can be hard to quantify its outcome. Although “head” talks about theories and academics, it fails to contribute significantly to policymakers.
Artists come into the play here at this moment
Artists are represented here on the side of ideas, in the “heart space.”
Art is uniquely positioned to move people—inspiring us, inciting new questions, and provoking curiosity, excitement, and outrage.
Artists can strengthen the will and push people to act. They do not think like policymakers or academics people.
Artists think from their heart – big, revolutionary, and visionary ideas.
This is why artists are able to move people to action, thus creates a significant cultural and political contributions.
This is what makes art powerful.
Impact of Art on Politics, Culture, and People
Art is essential in society because it is an essential ingredient in empowering people’s hearts.
When activists show images of children suffering from poverty or oppression in their campaigns, this is the art of pulling the heartstrings of society’s elite and powerful to make changes.
Similarly, when photographers publish photos of war-torn areas, it catches the attention of the masses whose hearts reach out to those who need help.
When an artist creates great music and movies, it entertains people worldwide. This is art, making a difference in society.
A very modern example of art in action is street art. When the famous Italian street artist Blu created the mural in Kreuzberg , it sparked a lot of solid and different reactions rooted deeply in the differences between East and West Berlin.
Who would have thought that a wall painting depicting two masked figures trying to unmask each other could elicit such strong reactions?

Now, the issue behind this mural is a different matter to discuss. But whether or not the effect of the mural was good, it cannot be denied how a well-crafted piece of art can have a significant impact on society.
Art is also a remarkable mode of depicting culture from all over the world
When you see a Zen garden in Sydney or San Francisco, you know that it’s a practice that originated from China.
Likewise, when you see paper swans swarming a beautiful wedding ceremony, you know that this is origami, an art from Japan.
When you see films featuring Bollywood music and dancing, you know that it’s a movie from India. Art can take cultural practices from their origins and transport and integrate them into different parts of the world without losing their identity.
There, these art forms can entertain, create awareness, and even inspire foreigners to accept these cultures, no matter how strange or alien they may seem.
And that’s precisely what John Dewey implies in Art as an Experience:
“Barriers are dissolved; limiting prejudices melt away when we enter into the spirit of Negro or Polynesian Art. This insensible melting is far more efficacious than the change effected by reasoning, because it enters directly into attitude.”
This is especially important in our highly globalized world.
Art has played an essential role in helping fight against intolerance of different cultures, racism, and other forms of unjust societal segregation.
With immigration becoming a trend, the world’s countries are expected to be more tolerant and accepting of those who enter their borders.
Art helps make that happen by making sure that identities and their cultures are given due recognition around the world.
Art stimulates creativity and innovation.
Art inspires creativity and innovation beyond boundaries, encouraging imagination, lateral thinking, and risk-taking. The process of creating art involves experimentation and novel ideas, which can influence progress in various industries.
Art also challenges perceptions and assumptions, encouraging critical thinking and open-mindedness, which are essential for innovation. By presenting alternative realities or questioning the status quo, art inspires individuals to think differently and to approach problems from unique angles.
Furthermore, the aesthetic experience of art can lead to epiphanies and insights.
The beauty or emotional impact of a piece of art can trigger ideas and spark the imagination in ways that logical reasoning alone may not. This can lead to breakthroughs in creative and scientific endeavors, as individuals draw inspiration from the emotions evoked by art.
Art plays a subtle yet significant role in our daily lives.
For instance, when a child takes part in a school art project, they are given a variety of materials to create a collage. As they construct a 3D model of an imaginary winged vehicle with multiple wheels, the textures and shapes inspire them. This hands-on exploration of materials and forms sparks the child’s interest in engineering and design, planting the seeds for future innovation.
The above example illustrates how art can engage young minds, encouraging them to think creatively and envision innovative solutions beyond conventional boundaries.
In essence, art fuels the creative fire, providing the sparks that can ignite the next wave of innovation in society.
Great Art elicits powerful sentiments and tells meaningful stories
Art can take the form of film, music, theatre, and pop culture , all of which aim to entertain and make people happy. But when films, songs, or plays are made for a specific audience or purpose, the art begins to diversify.
Films, for example, can be made to spread awareness or cultural appreciation. Songs can also be composed in a way that brings out certain emotions, give inspiration, or boost the morale of people.
During the Victorian period in England, women started to make a name for themselves with classic artworks such as Elizabeth Sirani’s “ Portia Wounding Her Thigh ”, a painting that signifies the message that a woman is now willing to distance herself from gender biasedness.

The painting’s subject depicts an act of a woman possessing the same strength as that of a man. “Portia” represents surrender because she isn’t the same type of woman known in society as weak and prone to gossip.
One of the revolutionary works in history that ultimately opened the doors of art to women in general showed the power of women in art
There are also works of art that illicit intellectual solid discourse – the kind that can question norms and change the behavior of society.
Sometimes, still, art is there to reach out to a person who shares the same thoughts, feelings, and experiences as the artist.
The truth is that art is more than just a practice – it is a way of life. Art is more than just a skill – it is a passion. Art is more than just an image – each one tells a story.
The fact that art is quite connected to human experience makes it unsurprising that we have always made it part of our ways of living.
This is why ancient and present-day indigenous groups from all over the world have a knack for mixing art and their traditional artifacts or rituals without them knowing, which in fact one of the fundamental reasons why art is essential.
Why is Art so Powerful? Why is art important to human society?
Perhaps the most straightforward answer to this question is that art touches us emotionally.
Art is influential because it can potentially influence our culture, politics, and even the economy. When we see a powerful work of art, we feel it touching deep within our core, giving us the power to make real-life changes.
In the words of Leo Tolstoy:
“The activity of art is based on the capacity of people to infect others with their own emotions and to be infected by the emotions of others. Strong emotions, weak emotions, important emotions or irrelevant emotions, good emotions or bad emotions – if they contaminate the reader, the spectator, or the listener – it attains the function of art.”
In sum, art can be considered powerful because of the following reasons, among others:
- It has the power to educate people about almost anything. It can create awareness and present information in a way that could be absorbed by many quickly. In a world where some don’t even have access to good education, art makes education an even greater equalizer of society.
- It promotes cultural appreciation among a generation that’s currently preoccupied with their technology. It can be said that if it weren’t for art, our history, culture, and traditions would be in more danger of being forgotten than they already are.
- It breaks cultural, social, and economic barriers . While art can’t solve poverty or promote social justice alone, it can be a leveled playing field for discourse and expression. The reason why everyone can relate to art is that everyone has emotions and personal experiences. Therefore, anyone can learn to appreciate art regardless of social background, economic standing, or political affiliation.
- It accesses higher orders of thinking . Art doesn’t just make you absorb information. Instead, it makes you think about current ideas and inspire you to make your own. This is why creativity is a form of intelligence – it is a unique ability that unlocks the potential of the human mind. Studies have shown that exposure to art can improve you in other fields of knowledge.
The truth is that people have recognized how influential art can be.
Many times in history, I have heard of people being criticized, threatened, censored, and even killed because of their artwork.
Those responsible for these reactions, whether a belligerent government or a dissident group, take these measures against artists, knowing how much their works can affect the politics in a given area.
In the hands of good people, however, art can be used to give back hope or instill courage in a society that’s undergoing a lot of hardships.
Art is a powerful form of therapy .

Some say art is boring . But the fact remains that art has the power to take cultural practices from where they are from and then transport and integrate them into different parts of the world without losing their identity.
Art helps make that happen by making sure that identities and their cultures are given due recognition around the world. Thus, it is essential to reflect upon – Why art is critical – which, in fact, provides you the answer to – What is art?
This is why we at The Artist believe that art is a form of creative human expression, a way of enriching the human experience.
NFTs: The Future of Art
Now, the world of art is shifting towards a digital and alternative world. And NFT is becoming a game-changing variable in the future of art .
What is NFT artwork?
An NFT , which stands for “non-fungible token” can be defined as a digital file that can be simply and easily transferred across a blockchain network.
Many people around the world are seeking out these digital assets to sell and trade in their everyday market trading, since these items are able to be traced, have value and oftentimes also have considerable rarity for collectors.
While artistic works are certainly a part of the NFT market, a variety of different players are getting involved through gaming systems, avatars, and even entire virtual worlds.
Such tokens have a wide variety of usage and while for many these are out of reach, for serious investors NFTs can prove to be a profitable source of income.
Art plays a significant role in society by acting as an educational equalizer, fostering cultural appreciation, bridging cultural and social divides, and stimulating higher orders of thinking and creativity.
Art and its definition will always be controversial.
There will always be debates about what art is and what is not.
But no matter what the definition may be, it has been around us for as long as humans have existed (i.e. cave paintings, hieroglyphics).
Whether or not we are aware of it, we allow art to affect our lives one way or another, and the reasons why we make art are many!
We use the arts for our entertainment, cultural appreciation, aesthetics, personal improvement, and even social change. We use the arts to thrive in this world.
So, share your thoughts – What does art mean to you? Art plays a subtle yet significant role in our daily lives. For instance, when a child takes part in a school art project, they are given a variety of materials to create a collage. As they construct a 3D model of an imaginary winged vehicle with multiple wheels, the textures and shapes inspire them. This hands-on exploration of materials and forms sparks the child’s interest in engineering and design, planting the seeds for future innovation. This example illustrates how art can engage young minds, encouraging them to think creatively and envision innovative solutions beyond conventional boundaries.
Passionate experimenter with a heart for art, design, and tech. A relentless explorer of the culture, creative and innovative realms.
Related Posts
16 comments.
Pingback: 7 Functions of Art That Make Us Empathetic Human Beings
Pingback: A world full of colors | Ashley's blog
Pingback: The importance of art and fashion. – BlissfulReject
Pingback: Art is Important – {thy smile is quite toothy}
Pingback: Arts influence society, change the world - The Feather Online
Hello there! This is my first comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and tell you I genuinely enjoy reading your posts. Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that cover the same topics? Thanks a lot!
Agreed with the summation, that art is a tricky thing to define. Shall we leave it at that and let the artist get on with it?
Hello! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this page to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
I got this web site from my pal who informed me on the topic of this website and at the moment this time I am browsing this website and reading very informative articles or reviews at this place.
Very good article! We will be linjking to this particularly great content onn our website. Keep up thhe great writing.
Every day we Delhiites shorten our lives due too choking air. This blog was extremely useful!
Great! Thank you so much. Keep up the good work.
Amazing! This has helped me out so much!
I do consider all the concepts you have introduced for your post. They are really convincing and can certainly work. Nonetheless, the posts are too quick for novices. Could you please extend them a little from subsequent time? Thanks for the post.
I love this! It was so interesting to read this!
Appreciating the commitment you put into your website and detailed information you offer. It’s good to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same unwanted rehashed information. Excellent read!
I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m including your RSS feeds to my Google account.
Leave A Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
Arts on the Brain
Emory undergrads experience & explore!
How does art affect us?
It’s no secret that art can impact lots of people’s lives in very meaningful and deep ways. “Beauty is in the eye of the beholder” can attest to this much at the very least. Whether you think art is paint on a canvas or scenes from the nature that surrounds you, what we as a society deem art has an impact on us all.
Art is actually part of what historians deem necessary for a group of people to be considered a society! Art, along with writing, cities, government, religion, and social structure, is the very basis of life as we as humans have known it for millennia. So, it shouldn’t be surprising that art has both a mental and physical effect on the human being.
To begin, music can have a significant effect on concentration. A lot of research has gone into its ability to help people hone their concentration, and theories such as the Mozart effect suggest that this effect extends to even spatial awareness. Physically, dancing is something that most people universally feel compelled to do when hearing a catchy beat. However, there is a physical effect besides dancing that not everyone feels: goosebumps. Studies suggest that 50% of all people experience this phenomena (Salimpoor, Benovoy, Larcher, Dagher, Zatorre, 2011), and is a result of excitement from music. It was found that dopamine production was very high while participants were listening to music, and this could suggest why music has been such a large part of cultures across the ages.
Visual art can produce a lot of the same effects that music does. General feelings of happiness and calmness can be found and utilized via art therapy. Many people use these benefits of art to quell distress and solve problems in their own lives, and part of this effect is suggested to be caused by being involved in something tangible (Malchiodi, 2012). Tangibility is something that isn’t often seen when dealing with mental issues. Most all of our mental issues stem from the chemicals within us that dictate how we view situations and the reactions we have in regards to them, and while it may be possible to visualize how these chemicals work, you cannot mold your reactions and chemical outputs like you can mold a block of clay or paint a piece of canvas. Control is something that many who are struggling with internal battles such as mental illness or grief are desiring to achieve, and art therapy and other physical-emotional therapies can help achieve a more tangible version of this.
The picture I’ve included displays the ventral striatum, which has also been shown to be activated and produce dopamine when shown art via a study at Emory (Eastman, 2011). When shown a photograph versus an artistic rendition of the subject, participants were seen to have much more activity in the ventral striatum while looking at the art. This part of your brain is very close to the midbrain and plays a role in the decision making vs reward system. So, looking at art may actually be a reward from our brain’s point of view!
Overall, art is an essential part of the human experience. Even if it doesn’t play a big role in someone’s personal life, art shapes the world around us and almost everything we experience when we interact with others. Art impacts what’s on the T.V. when you turn it on, it impacts what you see in textbooks on ancient civilizations (be it cave paintings, classical works, or folk art), it impacts what comes on on your radio and what reaches the tops of the charts on your streaming services. Art impacts us all, whether it makes you sad, happy, or anywhere in between.
Eastman Q. 2011 Jan 6. Viewing Art Activates Brain’s Reward Circuits.
Malchiodi CA. 2012. Handbook of Art Therapy, Second Edition.
Salimpoor VN, Benovoy M, Larcher K, Dagher A, Zatorre RJ. 2011. Anatomically distinct dopamine release during anticipation and experience of peak emotion to music. Nature Neuroscience 14:257–262.
3 Comments Add yours
I love the subject of you blog post! I find it fascinating that humain beings are related by art. You do not need to speak the same language as the artist to understand his work. However, it is very personal at the same time since everyone has their own interpretation of what they see. It is also true art can become very useful for our everyday life, with Art Therapy for example. We can see the emotional impact it can have on humain beings.
Katie, fascinating ideas! I totally agree with what you explained about how art has a significant impact on our lives even if many of us don’t think about it usually. Art, as a way of expression,. should be taken more seriously as it is inseparable from our daily life. We can see art almost everywhere around us and in almost everything we do. I liked how you introduce and literate the ideas on that. I am inspired in many ways!
I really like your post. The concept and definition of art is very broad and obscure, but it is also what makes it so interesting. Ranging from visual, to auditory, to a combo of both, or even though, art can mean a lot of things, yet they are hoping to communicate a message or feeling through the works. I think what is important, like what you mentioned in the end, is to realize the essential role of all forms of arts in our lives and appreciation the impacts they bring.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of followup comments via e-mail
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
National Endowment for the Arts
- Grants for Arts Projects
- Challenge America
- Research Awards
- Partnership Agreement Grants
- Creative Writing
- Translation Projects
- Volunteer to be an NEA Panelist
- Manage Your Award
- Recent Grants
- Arts & Human Development Task Force
- Arts Education Partnership
- Blue Star Museums
- Citizens' Institute on Rural Design
- Creative Forces: NEA Military Healing Arts Network
- GSA's Art in Architecture
- Independent Film & Media Arts Field-Building Initiative
- Interagency Working Group on Arts, Health, & Civic Infrastructure
- International
- Mayors' Institute on City Design
- Musical Theater Songwriting Challenge
- National Folklife Network
- NEA Big Read
- NEA Research Labs
- Poetry Out Loud
- Save America's Treasures
- Shakespeare in American Communities
- Sound Health Network
- United We Stand
- American Artscape Magazine
- NEA Art Works Podcast
- National Endowment for the Arts Blog
- States and Regions
- Accessibility
- Arts & Artifacts Indemnity Program
- Arts and Health
- Arts Education
- Creative Placemaking
- Equity Action Plan
- Historically Black Colleges and Universities (HBCUs)
- Literary Arts
- Native Arts and Culture
- NEA Jazz Masters Fellowships
- National Heritage Fellowships
- National Medal of Arts
- Press Releases
- Upcoming Events
- NEA Chair's Page
- Leadership and Staff
- What Is the NEA
- Publications
- National Endowment for the Arts on COVID-19
- Open Government
- Freedom of Information Act (FOIA)
- Office of the Inspector General
- Civil Rights Office
- Appropriations History
- Make a Donation
Why The Arts Matter

Recent Blog Posts

The Artful Life Questionnaire: Santina Protopapa (Cleveland, OH)

National Poetry Month Spotlight: Zoeglossia

Performing Arts “Crossover” Strategies Fail to Diversify Core Audiences, According to New Report
Stay connected to the national endowment for the arts.
The Value of Art Why should we care about art?
One of the first questions raised when talking about art is simple—why should we care? Art in the contemporary era is easy to dismiss as a selfish pastime for people who have too much time on their hands. Creating art doesn't cure disease, build roads, or feed the poor. So to understand the value of art, let’s look at how art has been valued through history and consider how it is valuable today.
The value of creating
At its most basic level, the act of creating is rewarding in itself. Children draw for the joy of it before they can speak, and creating pictures, sculptures and writing is both a valuable means of communicating ideas and simply fun. Creating is instinctive in humans, for the pleasure of exercising creativity. While applied creativity is valueable in a work context, free-form creativity leads to new ideas.
Material value
Through the ages, art has often been created from valuable materials. Gold , ivory and gemstones adorn medieval crowns , and even the paints used by renaissance artists were made from rare materials like lapis lazuli , ground into pigment. These objects have creative value for their beauty and craftsmanship, but they are also intrinsically valuable because of the materials they contain.
Historical value
Artwork is a record of cultural history. Many ancient cultures are entirely lost to time except for the artworks they created, a legacy that helps us understand our human past. Even recent work can help us understand the lives and times of its creators, like the artwork of African-American artists during the Harlem Renaissance . Artwork is inextricably tied to the time and cultural context it was created in, a relationship called zeitgeist , making art a window into history.
Religious value
For religions around the world, artwork is often used to illustrate their beliefs. Depicting gods and goddesses, from Shiva to the Madonna , make the concepts of faith real to the faithful. Artwork has been believed to contain the spirits of gods or ancestors, or may be used to imbue architecture with an aura of awe and worship like the Badshahi Mosque .
Patriotic value
Art has long been a source of national pride, both as an example of the skill and dedication of a country’s artisans and as expressions of national accomplishments and history, like the Arc de Triomphe , a heroic monument honoring the soldiers who died in the Napoleonic Wars. The patriotic value of art slides into propaganda as well, used to sway the populace towards a political agenda.
Symbolic value
Art is uniquely suited to communicating ideas. Whether it’s writing or painting or sculpture, artwork can distill complex concepts into symbols that can be understood, even sometimes across language barriers and cultures. When art achieves symbolic value it can become a rallying point for a movement, like J. Howard Miller’s 1942 illustration of Rosie the Riveter, which has become an icon of feminism and women’s economic impact across the western world.
Societal value
And here’s where the rubber meets the road: when we look at our world today, we see a seemingly insurmountable wave of fear, bigotry, and hatred expressed by groups of people against anyone who is different from them. While issues of racial and gender bias, homophobia and religious intolerance run deep, and have many complex sources, much of the problem lies with a lack of empathy. When you look at another person and don't see them as human, that’s the beginning of fear, violence and war. Art is communication. And in the contemporary world, it’s often a deeply personal communication. When you create art, you share your worldview, your history, your culture and yourself with the world. Art is a window, however small, into the human struggles and stories of all people. So go see art, find art from other cultures, other religions, other orientations and perspectives. If we learn about each other, maybe we can finally see that we're all in this together. Art is a uniquely human expression of creativity. It helps us understand our past, people who are different from us, and ultimately, ourselves.
Reed Enger, "The Value of Art, Why should we care about art?," in Obelisk Art History , Published June 24, 2017; last modified November 08, 2022, http://www.arthistoryproject.com/essays/the-value-of-art/.

Basic Composition Techniques
A few easy tips

Art History Methodologies
Eight ways to understand art
The Elements of Art
Eight tools, infinite expression
By continuing to browse Obelisk you agree to our Cookie Policy

How Art Makes Us More Human: Why Being Creative is So Important in Life

Art is an important part of life, as it helps us to explore our creativity and express ourselves in unique ways. Art is more than just a form of expression - it’s a way of understanding the world and our place in it. In this blog post, we’ll discuss the psychological, social, and cognitive benefits of creating art and how it can bring joy and purpose to our lives.
What is art?
Art is a form of expression that values creativity and self-expression. It can take many forms, from paintings and sculptures to photography and even digital art. Art has the power to move us, to make us feel something, and to tell stories. Art can be used as a way of connecting with ourselves and with each other, and its power lies in its ability to inspire, create joy, and provoke thought. Art is an expression of the human experience, and its value lies in its ability to bring people together.
The connection between art and emotion
The value of art lies in its ability to evoke emotion. Whether you’re looking at a painting, watching a performance, or listening to music, art allows us to experience a range of emotions from joy to sorrow and everything in between. Art can help us make sense of our own emotions and gain a better understanding of how other people are feeling. It can even bring us closer together as it enables us to feel connected with the artist, even if we have never met them. When we interact with art, it can often spark a dialogue, creating a feeling of understanding and empathy within us.
One way in which art can be especially powerful is when it reflects our personal experiences and values. By connecting with a piece of art that speaks to our values, we can often feel a strong emotional connection with it, enabling us to recognize ourselves in the work and appreciate its beauty and meaning.
The link between art and mental health
Art can be an incredibly powerful tool in helping us to manage our mental health and well-being. Studies have found that art can reduce stress, increase self-esteem, and improve our ability to cope with difficult emotions. Art provides a safe space for us to express our thoughts and feelings, allowing us to connect with ourselves on a deeper level.
One of the main ways that art benefits mental health is through its ability to help us process and make sense of our emotions. Art enables us to externalize our inner struggles, allowing us to make sense of them in a new way. By engaging in creative activities, we can gain insight into our own feelings, giving us the opportunity to recognize patterns and reflect on them in a non-judgmental manner. This can help us to gain a better understanding of our emotions and allow us to find healthier ways of managing them.
Art can also help to decrease symptoms of depression and anxiety. Studies have found that engaging in creative activities such as painting, drawing, or sculpting can reduce symptoms of both depression and anxiety. It also can increase positive moods and overall life satisfaction. In addition, engaging in art can give us a sense of control over our lives, providing us with the opportunity to express ourselves without fear of judgment.
Finally, creating art can provide a sense of purpose and accomplishment, helping us to feel connected to something larger than ourselves. Art gives us a way to channel our energy into something meaningful, allowing us to have a tangible outcome at the end of our creative journey. The act of creation itself can be incredibly empowering, giving us the confidence to take on new challenges and set goals for ourselves.
Overall, engaging in art has been proven to have a positive impact on mental health. Through its ability to help us process emotions, decrease symptoms of depression and anxiety, and provide us with a sense of purpose and accomplishment, art has the power to truly transform our lives.
The benefits of creating art
Creating art can be an immensely rewarding experience that has both psychological and physical benefits. It can provide a sense of purpose, satisfaction, and accomplishment. Art can also help reduce stress, build self-confidence, and improve problem solving skills.
Art can be used to express feelings and emotions, helping to better understand and cope with difficult experiences. It can also be used to relieve anxiety, improve mental health, and enhance positive self-image. Additionally, engaging in creative activities encourages creative thinking, which can foster innovation and creativity in other areas of life.
Creating art can also improve physical well-being. It has been linked to reducing chronic pain and boosting the immune system. It can also help with motor coordination, providing relief for conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome. Furthermore, it can help with hand-eye coordination, increasing dexterity and making everyday tasks easier.
Finally, creating art is a great way to relax and unwind after a long day. It can provide an outlet for pent-up emotions and help to restore a sense of balance and wellbeing. Even if your work is not immediately appreciated, it’s important to remember that art is subjective and it should be created for yourself, not for the approval of others.
The power of art in storytelling
Storytelling is a powerful tool for communication, and art is an important part of this process. Through art, we can express ourselves in ways that words alone cannot do justice to. Art allows us to show the emotion behind our stories, to add nuance and depth to our tales, and to create visuals that can leave a lasting impression.
Stories told through art have a special power. Whether it's through painting, drawing, sculpture, or even film, art has the potential to bring our stories to life in a way that words simply cannot do. With art, we can bring our characters and stories to life in vivid detail, making them more vivid and alive than if we were to tell the story with just words. We can also add layers of symbolism and meaning to our stories which can make them more meaningful and powerful.
Art has been used as a storytelling device for thousands of years. Ancient cultures used drawings and sculptures to tell their stories, and today, the tradition continues with all forms of visual arts. From street art to museum installations, art is used to tell stories of cultures, histories, beliefs, and emotions. By using art to tell stories, we can move people emotionally and capture their attention in a unique way.
In today's world, where we are bombarded with information from all sides, it can be hard to stand out. Art gives us the chance to do that in a powerful way. By creating art, we can tell stories that resonate with people, inspiring them and showing them something new. The power of storytelling through art is immense and should not be underestimated.
The importance of art in education
Art plays an important role in education, as it encourages creative thinking and provides a platform for students to express their feelings and ideas. It can also be used as a form of communication, allowing students to interpret and create meaning from what they observe. Additionally, the visual representation of art helps children to develop skills such as analyzing information, forming arguments, and making connections.
In the classroom, art can help to introduce new concepts, convey complex topics, and build relationships between students. By incorporating art into lesson plans, teachers are able to engage students in learning and make the material more interesting. Art also helps students to identify patterns and practice critical thinking skills by exploring how elements interact to create a bigger picture.
Furthermore, art allows for students to practice collaboration, problem-solving, and social interaction. Through group projects, students can work together to plan, organize, and execute a project from start to finish. This helps to teach kids essential teamwork skills while also giving them the opportunity to explore their individual strengths and weaknesses.
Overall, art is an integral part of education that helps students develop important skills and encourages creative expression. It is an important tool for teaching and can be used in various ways to make learning more engaging and meaningful.
The role of art in social change
The power of art in creating social change is undeniable. It has been used throughout history as a tool to inspire, educate, and challenge the status quo. Art can be used to bring attention to injustices, advocate for different perspectives, and to create positive cultural shifts.
One example of how art has been used to inspire social change is through protest art. This type of art is often seen at protests and marches, or used to create powerful visuals for political campaigns. Protest art can be anything from signs and banners to sculptures, graffiti, or public installations. It can also take the form of music, film, theater, and literature. By combining art and activism, people are able to communicate their message in an effective way that captures the attention of the public.
Another example of how art can be used to create social change is through digital media platforms such as Instagram and Twitter. These platforms allow anyone with an internet connection to share their creative works and connect with other like-minded individuals. Art has been used on these platforms to raise awareness about important issues, tell stories that inspire change, and even challenge oppressive systems.
Finally, art can be used to help those who are oppressed find strength and resilience. Art provides a platform for those who are marginalized to tell their stories and express their experiences in a safe space. Through art, people are able to connect with each other and find solidarity in the face of adversity.
Art plays an important role in social change and is an invaluable tool for anyone looking to create positive impact in the world. Whether it’s used to create powerful visuals for a protest or to tell stories that inspire action, art has the power to bring people together and spark meaningful conversations about important topics.
Art is essential for all our lives
No matter who you are or where you come from, art plays a vital role in helping us make sense of our lives and the world around us. Art helps us to express our emotions, to communicate our thoughts and feelings, and to explore the depths of our imaginations. By engaging with art, we can discover more about ourselves and the world around us, and cultivate empathy and understanding.
- Cultivate News
Recent Posts
March Volunteer of the Month: May Southavilai
Press Release: Announcing 2024 ArtPrize Education Partnership
Volunteer of the Month: Aude Shattuck
Hello! I really liked your article! You can be creative not only by making paintings, but you can also lead social networks in any manifestation and be an inspiration to other people. The most important manifestation of your creativity in social networks is to create content. Shoot videos, take photos, etc. To do this, I can recommend this article for the further development of your content and social networks.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.1: What Is Art Appreciation?
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 31973

- Deborah Gustlin & Zoe Gustlin
- Evergreen Valley College via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative

What Is Art Appreciation?
Appreciation of the visual arts goes beyond staring at a painting hanging on the wall of a museum—art is in everything and everywhere you look. Opening your eyes to the world of art is essential in understanding the world around you. Art is more than pretentious museums; only a few enter and comprehend. Instead, art appreciation is:
- Gaining the knowledge to understand the art.
- Acquire the art methods and materials to discuss art verbally or by the written word.
- Ability to identify the movements from ancient cultures to today's contemporary art.
Learning how to appreciate art is a necessary cultural foundation enabling people to critically analyze art, art forms, and how cultures used art. All it takes to understand the art is just to look!
Art appreciation centers on the ability to view art throughout history, focusing on the cultures and the people, and how art developed in the specific periods. It is difficult to understand art without understanding the culture, their use of materials, and a sense of beauty. Art is conveyed by the simple act of creating art for art's sake. Every person is born with the innate desire to create art, and similar to other professions, training is essential in honing skills to produce art. Art education broadens a person's comprehension, development, and visions of art. Art brings an understanding of diversity, how people lived in the past, and connects the issues concerning contemporary life and art today.
The history of the world is similarly the history of art, continually intertwined. For millions of years, as humans roamed the earth, evolution, and environment shaped many different cultures depending on location, weather, natural resources, and food. These cultures formed the foundation of all art today. Art appreciation analyzes art using the methods and materials, allowing people to make connections to the context of art and the interactions of societies.
It is difficult to understand the art without understanding the culture.

Essay on Importance Of Art In Our Life
Students are often asked to write an essay on Importance Of Art In Our Life in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Importance Of Art In Our Life
Art sparks creativity.
Art is like a key that unlocks our imagination. When we make or look at art, our minds start to think in new and exciting ways. This creativity can help us in school, work, and solving problems. It’s like art gives our brain a fun workout.

Art Shows Feelings
Sometimes it’s hard to say how we feel. Art can help with that. By drawing or painting, we can show our emotions. This can make us feel better and help others understand us more.
Art Connects People
Art is a language that everyone speaks, no matter where they are from. It brings people together. When we share our art, we share a part of ourselves. This can create friendships and make our community stronger.
Art Teaches Us
Art is full of stories and lessons. By looking at art from the past, we can learn about different times and places. It’s like a time machine that teaches us history in a fun way.
Art Adds Beauty
Art makes our world beautiful. A painting on a wall or a song in the air can make our day better. It’s like a splash of color on a grey day, making life more enjoyable.
250 Words Essay on Importance Of Art In Our Life
Art brightens our world.
Art is like a splash of color on a blank canvas. It makes our world more interesting and beautiful. When you see a painting or a sculpture, it can make you feel happy, sad, or excited. Art is not just about creating; it’s also about sharing. When artists share their work, they share a piece of their heart and mind.
Art Helps Us Express Ourselves
Sometimes, it’s hard to say how we feel using just words. This is where art comes in. It gives us a way to show our feelings without speaking. You can draw or paint your emotions, and this can help you feel better. It’s like art understands you and can help you understand yourself.
Art Teaches Us New Things
Art is not only about looking at pretty pictures. It can teach us about different places, people, and times in history. By looking at art, we can learn stories from all over the world. It’s like a window to different cultures and helps us see how others live and think.
Art has a special power to bring people together. When you make art with others, you create a bond. It’s fun to work on art projects with friends or family. You can learn from each other and create something special together. Also, when you look at someone else’s art, you can feel connected to them, even if they are far away or from a different time.
In short, art is very important in our lives. It adds color to our world, lets us say what we feel, teaches us new things, and helps us make friends. Art is not just something nice to look at; it is a part of us and our way of living.
500 Words Essay on Importance Of Art In Our Life
Art is everywhere.
Art is a big part of our lives, even if we might not always notice it. Think about the music you listen to, the cartoons you watch, and the pictures you draw. These are all forms of art. Art is not just something you see in a museum; it’s in the games you play, the clothes you wear, and the way you decorate your room. It makes our world more colorful and interesting.
Expressing Ourselves
One of the most important things about art is that it lets us show who we are and how we feel. When you make a drawing or write a story, you are telling people something about yourself without even using words. This can be really helpful when you have big feelings that are hard to talk about. Art gives us a way to share our thoughts and feelings with others.
Learning and Thinking
Art is also a great way to learn. When you make art, you think about colors, shapes, and how to make your idea come to life. This helps your brain grow and helps you solve problems better. In school, teachers use art to make learning more fun and to help you remember things. For example, when you draw a picture of a plant and label its parts, you’re more likely to remember what each part is called.
Bringing People Together
Art can bring people together. When you look at someone’s art or listen to their music, you can feel what they feel and see things from their point of view. This can help you understand people who are different from you. Art can also bring people together to work on things, like when you and your friends make a big poster or put on a play.
Jobs and the Economy
Art is not just for fun; it’s also a way for people to make a living. There are many jobs in art, like being a painter, a musician, a dancer, or a movie maker. These jobs are important because they give people work and help the economy. When people buy art or tickets to a show, they are supporting artists and helping them to keep making more art.
Health and Happiness
Making and enjoying art is good for your health. It can make you feel happy and relaxed. When you are stressed, doing something creative like drawing or playing an instrument can calm you down. Doctors have found that looking at art can make people feel better when they are sick or sad.
In conclusion, art is very important in our lives. It is all around us, helping us to express ourselves, learn, and bring people together. Art also creates jobs and can make us healthier and happier. Even if we are not all artists, art touches everyone in some way. So next time you see a painting or hear a song, think about how art is making your life better.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Importance Of Art
- Essay on Importance Of Agriculture
- Essay on Importance Of Agrarian Reform
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
The Importance Of Art In Society And How It Helps Us Flourish
- By The Studio Director Team
- November 2, 2023
Stay up to date with the latest blogs!
" * " indicates required fields
As a teacher or studio owner, you have an undeniable passion for the arts. Whether you specialize in ballet, piano, or oil painting, you know what it’s like to fall in love with art. The importance of art in society can’t be overstated, and it transcends far beyond borders or cultures. This is what we know about its major tangible and intangible benefits.
Why Is Art Important?
Art is all around us. Whether you hear your favorite song on the radio or drive by a gorgeous mural, you experience art every day. We know that these meeting points elevate our everyday experiences, but it’s common to lose sight of the overall impact of the arts on communities .
Our goal here is to dive into this topic and answer that question: “Why is art important?” By answering it with insights from research, we hope to provide studio owners and teachers alike with the solid information they need to share their love of the arts with their wider communities.
1. It promotes expression and creativity
As humans, we’re naturally drawn to art as a form of expression and communication. Toddlers love to draw, sing, and dance. It’s a way for them to express themselves before they’re verbal.
In fact, participation in the arts may even assist kids with language, motor skills, and visual learning development. Research indicates that young people who regularly participate in the arts are four times more likely to be recognized for academic achievement later on.
In therapy settings, art also provides an opportunity for digging deeper and expressing emotions that are difficult to discuss.
Art therapy activities can help children (and adults) cope with their circumstances, both past and present. In one important study, children between six and 12 were asked to draw a house as a distraction after thinking about something upsetting. This group was able to improve their mood when compared with children who were instructed to draw the negative event or simply copy another drawing.
2. It helps all of us develop necessary soft skills
The importance of art in society goes far beyond what we do in our free time. It can also help people work better.
When someone applies for a job, there are certain hard skills they need to have like data analysis or bookkeeping. However, many employers also understand the very important need for soft skills . These intangible attributes are hard to measure and often difficult to define. Some examples include a person’s ability to adapt to change, think creatively, or collaborate with team members.
The arts are a universal way to develop these necessary soft skills that make us better people and coworkers in the workplace.

3. It provides historical context
Art and human history go hand-in-hand. This is why people dedicate their lives to studying cave art, Shakespearean plays, and so much more.
When we take the time to dive into art created in the past, we can learn about other generations and eras. We can study art to find out what those before us were facing and how they overcame it. In the same way, future generations will learn about our current events through the art we leave behind.
As the The Metropolitan Museum of Art puts it: “Looking at art from the past contributes to who we are as people. By looking at what has been done before, we gather knowledge and inspiration that contribute to how we speak, feel, and view the world around us.”

4. Art leads to healthy and thoughtful cultural discussions
Art is often controversial or groundbreaking. And when art creates a stir, it has the potential to spark healthy conversations that lead to improvements across a society. Rather than impassioned debate, art gives us an opportunity to analyze, respond to, and create social change.
How does this play out in direct impacts? Surveys show that high school students in the United States who engage in the arts at school are twice as likely to volunteer than those who don’t. They are also 20% more likely to vote when they become young adults.

5. It gives us a place to gather as a society
Beyond personal development, the overall social impact of the arts is essential to understand. Cultures big and small unite through the arts to build better communities.
From fine art showings to community theatre in the park, the arts provide an opportunity to gather with other people from all walks of life. Several case studies have actually demonstrated that art in rural communities specifically can help boost economic growth. Further, it strengthens the bonds between people in these places.
It’s also worth noting the importance of art in society when it comes to tourism. Cities like New York City and Seattle are full of endless museums and theatres. But even in smaller communities across the United States, and the rest of the world, the arts provide unique economic opportunities. This type of tourism leads to jobs, revenue, and areas for growth.
The Art World Makes Life More Beautiful
Immersed in the art world, your commitment as an educator or studio owner is undeniable. Whether it’s ballet, piano, or oil painting that has captivated your heart, you understand what it means to truly experience art. The role of art forms in society is monumental, extending beyond any geographical or cultural boundaries. Here’s what we’ve learned about its profound and far-reaching impacts.
Art, particularly fine arts, serves as a powerful tool for self-expression. It provides a platform for human beings to articulate their deepest emotions and thoughts, fostering self-awareness and promoting healthy conversations. From the intricate brushstrokes of oil paintings to the rhythmic movements in ballet, each art form speaks a unique language that resonates with different perspectives.
The importance of art extends to our youth and future generations. By incorporating art subjects into education, we encourage young people to develop critical thinking and motor skills. Art lessons aren’t just about producing pop art or mastering ballet; they’re about understanding human history, from cave paintings to contemporary installations in art galleries.
Moreover, the study of art fosters a deeper understanding of the creative process. As art students delve into various art forms, they gain insights into the workings of the human brain and the power of creative expression. This knowledge prepares students to approach other subjects with an open mind and a keen eye for detail.
Furthermore, arts education fuels economic growth. By nurturing critical thinking, creativity, and innovation, we are equipping our future workforce with essential skills needed in the 21st-century economy. The arts provide a robust foundation for a well-rounded education, one that interweaves the beauty of fine arts with the practicality of real-world applications.
In essence, to study art is to engage in a timeless tradition of exploration and discovery. Through art, we can forge connections, facilitate dialogues, and inspire change. So let’s continue to celebrate and champion the arts, for the benefit of our society and generations to come.
Your Studio Makes An Impact
Whether you teach online art classes , lead a music school, or instruct dancers in a ballet studio, the work you do is so incredibly important. As an active member of your local arts scene, you have a direct impact on your students and larger community.
Studio Director is an all-in-one studio management software that gives you the gift of more time and flexibility to focus on these creative pursuits. We’re your behind-the-scenes partner that can automate the key administrative tasks that help your studio run smoothly. Want to learn how Studio Director can help your team focus on the work they love? Schedule a free demo today !
Discover How Our Software
Can help your studio, more from the blog.

Running A Successful Gymnastics Training Center: 8 Tips

How To Teach Online Art Classes: 10 Tips

31 Fun And Catchy Dance Studio Names Ideas
The Importance of Arts Education Essay
Introduction, the importance of teaching arts education.
Art has been in existence for since the beginning of human civilisation. The field, in most cases, is viewed as a way of action and knowing. Art has played a key role in the development of human identities. It has also been significant to the evolution of cultural practices in all human societies. Consequently, art is regarded as one of the defining elements of humanity. To some advocates of this field, art is believed to be the window to the soul of humanity. According to Nathan (2008), art is used to communicate and provide a framework for the understanding of passions, emotions, and the enduring conflicts that humans have always indulged in. The scholars who advocate for the centrality of arts in the development of humanity observe that even the cavemen recorded their history, experiences, and events through drawings of pageants that marked the passing of time and seasons (Anderson, 2014).
In this paper, the author explores the importance of art its contribution in the development of cognitive and cultural attributes among children. To this end, the author will demonstrate that art provides human societies with lens through which they can view both historical and contemporary issues. Finally, the paper will be used to support the argument that teaching art processes can improve the ability of students to shape the learning process and the way it is conceived in schools.
Arts in Traditional and Contemporary Societies
Arts are a common feature in both traditional and modern societies. In most traditional communities, trumpets and drums were used to herald the commencement of battle. In addition, birth and death in these societies were received with songs and dance. Consequently, theatre was viewed as an avenue through which solutions to dilemmas faced by mankind were provided. It can also be observed that in most communities, the portraits of heroes, kings, villains, and other important figures in the society were painted to record these particular moments in time ( Learning area, n.d).
To recognise the centrality of arts to experiences among humans, the Universal Declaration of Human Rights was adopted several decades ago ( The future of the Australian curriculum, 2014). The declaration observed that everybody has a right to participate in the cultural life of their community. In addition, each person should be able to enjoy and share arts in the scientific advancement of its benefits. In the western world, arts subjects have been neglected and pushed to the periphery of the academic field in favour of the sciences. The curriculums used in most schools focus on literacy, sciences, and numeracy. However, in the last few decades, the intrinsic values of arts have been recognised (Ross, 2014).
According to some advocates of this field, arts have the ability to release people’s imaginations to new perspectives. In addition, they can help people identify new solutions and alternative views to life. As a result, the vistas that could be opened, as well as the connections that could be made, are phenomenal. It is also noted that the encounter between the individual and the world around them would be newly informed with the help of arts. In addition, immersion in arts has been found to improve individuals’ sense of enjoyment and identity. The immersion can also offer positive changes in the direction taken by the life of the individual (Anderson, 2014). In most cases, it is argued that arts can transform learning in education contexts. They can also ensure improve the link between the learners and the curriculum.
A Working Definition of Arts
There are many ways through which arts can be defined. According to Bamford (2006), arts can be used to reflect the uniqueness of the cultural circumstances of a particular nation. Bamford (2006) further observes that art is characterised by fluidity and dynamism. In their attempts to arrive at a working definition of arts, Bamford (2006) recognises the impossibility of giving static definitions to this field. The reason is that the definitions become obsolete as soon as they are provided. As such, scholars should be conscious of the dynamism of contemporary art practices. In addition, the art terminology can be used to represent the important creative disciplines. The disciplines include dance, literature, drama, music, visual arts, film, as well as other forms of media arts. All these disciplines have a significant role in formal education contexts. They also play a significant role in the cohesion of the community.
The forms of art described above can be viewed as a representation of different languages. Their varying modes are used to communicate a wide range of skills, knowledge, and symbols. In light of this, it is imperative to study each form of art (Burton, 2010). Each form of art should be explored for its intrinsic values. The reason is that each of them has different ways of creating knowledge and improving communication (Sinclair & O’Toole, 2008). The various forms of art should be viewed and understood as different types of literary elements. However, it is important to note that all of them involve some kind of design, experimentation, play, provocation, and exploration. In addition, they entail expression, communication, representation, and visualisation. All these elements are used to shape other forms of media (Ross, 2014).
Developmental Benefits of Arts
Arts play a significant role in the development of a child’s motor skills. For instance, most of the motions involved in the creation of art, such as scribbling with a pencil or a crayon, are important in the development of fine motor skills ( The future of the Australian curriculum, 2014). Participation helps learners to improve their skills in mathematics and reading. It also improves one’s cognitive and verbal competencies. According to Burton (2010), engaging in arts has a positive correlation with verbal capabilities. Learning these subjects is also associated with an increase in levels of motivation and enhanced confidence. It also improves concentration and teamwork among the learners ( Why art matters, 2011).
Many scholars observe that the intrinsic pleasures derived from arts entail more than just the ‘sweetening’ of a person’s life (Burton, 2010). Such experiences help to deepen the connection between the individual and the world around them. They also provide them with new ways to view the world. The development lays the foundation for strong social bonds and improved cohesion in the community. A strong programming of arts within the curriculum also helps to close the intellectual gap that has made many children lag behind in intellectual achievement. It is noted that the children from affluent backgrounds are exposed to arts through visits to museums and attending Mozart concerts and other platforms. As a result, their interaction with the arts is assured regardless of whether or not the subjects are provided in their schools. However, teaching arts in schools provides children from poor economic backgrounds a level playing field (Nathan, 2008).
Arts Education and Academic Achievement
A new picture is emerging in the new educational era. School districts have started to focus on the field of arts. The emerging models are anchored on new brain research findings and cognitive development. The new models have embraced a variety of approaches that regard arts as a significant learning tool. For instance, musical notes are increasingly being used to teach fractions (Nathan, 2008). The models have also incorporated arts into the teaching of the core classes. For example, the teaching of slavery and other historical themes can be delivered by having the students act a play that dramatises those events.
In the US, Australia, and Europe, it is widely acknowledged that the students exposed to a learning process embedded in arts achieve improved grades and better test scores compared to those who are not exposed to this field. The students are less likely to play truants. In addition, they are rarely bored and have a healthy and positive self concept (Marshall, 2010). They are also most likely to participate in community service. Nascent studies have demonstrated that learning through arts can improve educational outcomes for other academic disciplines (Burton, 2010). For instance, the studies have observed that the students who partake in drama and music attain higher levels of success in reading and mathematics than those who do not take part in such ventures. Consequently, arts are seen as strategies to engage difficult students. The subjects connect learners to self, others, and the world. Engaging in arts also helps the teacher to transform the classroom environment. Most importantly, it challenges the students who may already be successful to work harder (Burton, 2010).
Specific Connections
Experimental evidence demonstrates a strong link between non-arts and arts skills. For example, I carried out an experiment on 10 children who were involved in a family theatre program. The program demonstrated that an exposure in theatrical activities for a year improves the empathy and emotional regulation among the children. For the adolescents involved in a similar program, it was shown that arts helped them improve their empathy. It also improved their understanding and appreciation of the mental status of other participants. The linkage makes sense to the advocates of arts education (Marshall, 2010). Training in arts, acting, and theatre puts the participants in other people’s shoes. The experience helps them to imagine how other people feel. In addition, it enables them to understand their emotions and view the world differently. After undertaking the program, I concluded that students should be given the opportunity to study arts in school irrespective of whether or not the subjects have discernible positive effects.
Cognitive Benefits of Arts
The cognitive benefits that are derived from arts include the development of skills needed in learning, improvement of academic performance, as well as enhancement of reading and mathematical capabilities. In addition, arts improve creative thinking among the learners (Marshall, 2010). The experiment mentioned above also showed that participation in theatre helped students from low socioeconomic backgrounds improve their academic performance. Consequently, I can conclude that the effects of arts education are transformative. The effects hold true across the socioeconomic divide. The impacts are cumulative and increase as the students from poor background get more exposure to the study of arts. It can also be emphasised that the students who are exposed to arts had better scores, which are higher than those of learners who are less engaged. The scores are especially better in such educational areas as creative thinking and originality (Burton, 2010).
The Benefits of Arts with Regards to Behaviour and Attitude
The study of arts has a positive impact on the attitudes and behaviour of the students. The benefits of behavioural and attitude change include improved self-efficacy and self-discipline. The advantages are easily associated and directly linked to improved school attendance, as well as reduced rates of drop-outs (Burton, 2010). In addition, the benefits are associated with the development of social skills. Such social and life skills include better understanding and appreciation of the consequences of an individual behaviour. The students also portray an increased ability to participate in teamwork, acceptance of constructive critiquing from fellow students, and the willingness to adopt pro-social behaviours.
Health Benefits of Arts Education
I must recognise that art has many health benefits. The therapeutic effects include improved physical and mental health. In Australia, the benefits are beginning to be recognised with several ongoing projects in schools reporting positive outcomes. It is argued that people who engage in relaxing activities, such as reading a novel, playing a musical instrument, painting, or singing, develop a healthy mind ( Why art matters , 2011). It is also observed that people who enjoy attending a good concert, a dance, a movie, or an art exhibition exercise their body and mind through the enjoyment, social inclusion, and relaxation. The individuals also improve their confidence, resilience, and self-esteem (Marshall, 2010). An art-mental paradigm can deliver significant health benefits to the students at school and in their adult life.
Arts Education in Australian Curricula
There are three different approaches to the learning of arts in Australia. The first can be described as the appreciation of Australian arts heritage. In this approach, the field is conceptualised as a domain for the talented. The approach points to the belief that the talented artist will provide the Australian society with its cultural artefacts ( Learning area , n.d). The second approach is the identification of the students who demonstrate artistic potential. The teachers focus on these learners and prepare them for future careers. The third approach is the desire to avail every student with an opportunity to engage with art and to appreciate it (Marshall, 2010). As such, the Australian curriculum anticipates that the students will actively learn, engage in artistic activities and processes, as well as appreciate the works of art done by others.
It must be remembered that the role of arts is to enhance learning by increasing enjoyment, fostering creativity, and enhancing imaginative activities. The objectives can only be achieved through participation in arts programs. It is also observed that students become more cognisant of the larger spectrum of world experiences by engaging in this field. The role of arts is to transform the students’ learning experiences by celebrating creativity. As such, teaching of arts should be encouraged and promoted at all levels of learning. Every student should be provided with the opportunity to participate in arts so as to improve their academic performance and develop into healthy adults with enhanced social skills.
Anderson, M. (2014). Why this elitist attack on arts education is wrong . Web.
Bamford, A. (2006). The wow factor: Global research compendium on the impact of the arts in education . Berlin, Germany: Waxmann Verlag.
Burton, B. (2010). Dramatising the hidden hurt: Acting against covert bullying by adolescent girls: Research in drama education. The Journal of Applied Theatre & Performance, 15 (2), 255-278.
Learning area. (n.d). Web.
Marshall, J. (2010). Five ways to integrate: Using strategies from contemporary art. Art Education, 63 (3), 13-19.
Nathan, L. (2008). Why the arts make sense in education. Phi Delta Kappan, 90 (3), 177-181.
Ross, M. (2014). The aesthetic imperative: Relevance and responsibility in arts education. New York: Pergamon.
Sinclair, C., & O’Toole, J. (2008). Education in the arts: Teaching and learning in the contemporary curriculum: Principles and practices for teaching. South Melbourne, Australia: Oxford University Press.
The future of the Australian curriculum: The arts: A response to the review of the Australian curriculum . (2014). Web.
Why art matters . (2011). Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 1). The Importance of Arts Education. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-importance-of-arts-education/
"The Importance of Arts Education." IvyPanda , 1 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/the-importance-of-arts-education/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'The Importance of Arts Education'. 1 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "The Importance of Arts Education." February 1, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-importance-of-arts-education/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Importance of Arts Education." February 1, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-importance-of-arts-education/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Importance of Arts Education." February 1, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-importance-of-arts-education/.
- Discipline and Student Engagement
- Architecture as an Academic Discipline
- Comprehensive Art Education
- Art and Design: History of Art Teaching
- Humanities as Academic Disciplines
- Current Issues in Art Education
- Teaching in Schools and Creativity of Students
- Art Education Principles Analysis
- Discipline and Managing Behavior in the Classroom
- Teaching Strategies: The Art and Science of Teaching
- "Assessment Balance and Quality" by Commodore et al.
- Cognitive Coaching: A Foundation for Renaissance Schools
- Teaching and Research Philosophy
- What Impacts and Enhances Learning?
- The Culture of Smartness in Education
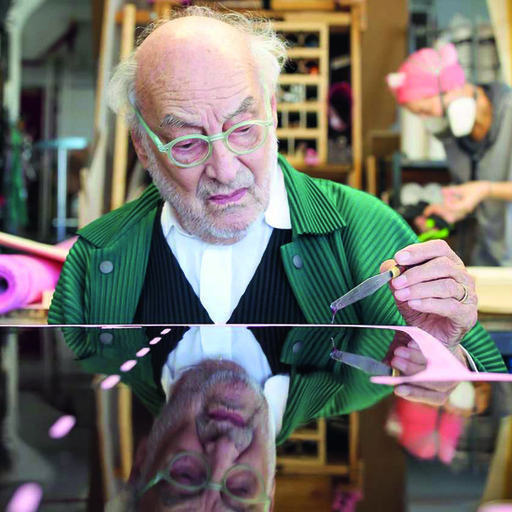

By Will Fenstermaker
June 14, 2017

There has never been a time when art critics held more power than during the second half of the twentieth century. Following the Second World War, with the relocation of the world’s artistic epicenter from Paris to New York, a different kind of war was waged in the pages of magazines across the country. As part of the larger “culture wars” of the mid-century, art critics began to take on greater influence than they’d ever held before. For a time, two critics in particular—who began as friends, and remained in the same social circles for much of their lives—set the stakes of the debates surrounding the maturation of American art that would continue for decades. The ideas about art outlined by Clement Greenberg and Harold Rosenberg are still debated today, and the extent to which they were debated in the past has shaped entire movements of the arts. Below are ten works of criticism through which one can trace the mainstreaming of Clement Greenberg’s formalist theory, and how its dismantling led us into institutional critique and conceptual art today.
The American Action Painters
Harold Rosenberg

Harold Rosenberg, a poet who came to art through his involvement with the Artist’s Union and the WPA, was introduced to Jean-Paul Sartre as the “first American existentialist.” Soon, Rosenberg became a contributor to Sartre’s publication in France, for which he first drafted his influential essay. However, when Sartre supported Soviet aggression against Korea, Rosenberg brought his essay to Elaine de Kooning , then the editor of ARTnews , who ran “The American Action Painters” in December, 1952.
RELATED: What Did Harold Rosenberg Do? An Introduction to the Champion of “Action Painting”
Rosenberg’s essay on the emerging school of American Painters omitted particular names—because they’d have been unfamiliar to its original French audience—but it was nonetheless extraordinarily influential for the burgeoning scene of post-WWII American artists. Jackson Pollock claimed to be the influence of “action painting,” despite Rosenberg’s rumored lack of respect for the artist because Pollock wasn’t particularly well-read. Influenced by Marxist theory and French existentialism, Rosenberg conceives of a painting as an “arena,” in which the artist acts upon, wrestles, or otherwise engages with the canvas, in what ultimately amounts to an expressive record of a struggle. “What was to go on the canvas,” Rosenberg wrote, “was not a picture but an event.”
Notable Quote
Weak mysticism, the “Christian Science” side of the new movement, tends … toward easy painting—never so many unearned masterpieces! Works of this sort lack the dialectical tension of a genuine act, associated with risk and will. When a tube of paint is squeezed by the Absolute, the result can only be a Success. The painter need keep himself on hand solely to collect the benefits of an endless series of strokes of luck. His gesture completes itself without arousing either an opposing movement within itself nor the desire in the artist to make the act more fully his own. Satisfied with wonders that remain safely inside the canvas, the artist accepts the permanence of the commonplace and decorates it with his own daily annihilation. The result is an apocalyptic wallpaper.
‘American-Type’ Painting
Clement Greenberg

Throughout the preceding decade, Clement Greenberg, also a former poet, had established a reputation as a leftist critic through his writings with The Partisan Review —a publication run by the John Reed Club, a New York City-centered organization affiliated with the American Communist Party—and his time as an art critic with The Nation . In 1955, The Partisan Review published Greenberg’s “‘American-Type’ Painting,” in which the critic defined the now-ubiquitous term “abstract expressionism.”
RELATED: What Did Clement Greenberg Do? A Primer on the Powerful AbEx Theorist’s Key Ideas
In contrast to Rosenberg’s conception of painting as a performative act, Greenberg’s theory, influenced by Clive Bell and T. S. Eliot, was essentially a formal one—in fact, it eventually evolved into what would be called “formalism.” Greenberg argued that the evolution of painting was one of historical determinacy—that ever since the Renaissance, pictures moved toward flatness, and the painted line moved away from representation. Henri Matisse and Pablo Picasso were two of the landmarks of this view. Pollock, who exhibited his drip paintings in 1951, freeing the line from figuration, was for Greenberg the pinnacle of American Modernism, the most important artist since Picasso. (Pollock’s paintings exhibited in 1954, with which he returned to semi-representational form, were regarded by Greenberg as a regression. This lead him to adopt Barnett Newman as his new poster-boy, despite the artist’s possessing vastly different ideas on the nature of painting. For one, Greenberg mostly ignored the Biblical titles of Newman’s paintings.)
Greenberg’s formalist theories were immensely influential over the subsequent decades. Artforum in particular grew into a locus for formalist discourse, which had the early effect of providing an aesthetic toolkit divorced from politic. Certain curators of the Museum of Modern Art, particularly William Rubin, Kirk Varnedoe, and to an extent Alfred Barr are credited for steering the museum in an essentially formalist direction. Some painters, such as Frank Stella , Helen Frankenthaler , and Kenneth Noland, had even been accused of illustrating Greenberg’s theories (and those of Michael Fried, a prominent Greenbergian disciple) in attempt to embody the theory, which was restrictive in its failure to account for narrative content, figuration, identity, politics, and more. In addition, Greenberg’s theories proved well-suited for a burgeoning art market, which found connoisseurship an easy sell. (As the writer Mary McCarthy said, “You can’t hang an event on your wall.”) In fact, the dominance of the term “abstract expressionism” over “action painting,” which seemed more applicable to Pollock and Willem de Kooning than any other members of the New York School, is emblematic of the influence of formalist discourse.
The justification for the term, “abstract expressionist,” lies in the fact that most of the painters covered by it took their lead from German, Russian, or Jewish expressionism in breaking away from late Cubist abstract art. But they all started from French painting, for their fundamental sense of style from it, and still maintain some sort of continuity with it. Not least of all, they got from it their most vivid notion of an ambitious, major art, and of the general direction in which it had to go in their time.
Barbara Rose

Like many critics in the 1950s and 60s, Barbara Rose had clearly staked her allegiance to one camp or the other. She was, firmly, a formalist, and along with Fried and Rosalind Krauss is largely credited with expanding the theory beyond abstract expressionist painting. By 1965, however, Rose recognized a limitation of the theory as outlined by Greenberg—that it was reductionist and only capable of account for a certain style of painting, and not much at all in other mediums.
RELATED: The Intellectual Origins Of Minimalism
In “ABC Art,” published in Art in America where Rose was a contributing editor, Rose opens up formalism to encompass sculpture, which Greenberg was largely unable to account for. The simple idea that art moves toward flatness and abstraction leads, for Rose, into Minimalism, and “ABC Art” is often considered the first landmark essay on Minimalist art. By linking the Minimalist sculptures of artists like Donald Judd to the Russian supremacist paintings of Kasimir Malevich and readymades of Duchamp, she extends the determinist history that formalism relies on into sculpture and movements beyond abstract expressionism.
I do not agree with critic Michael Fried’s view that Duchamp, at any rate, was a failed Cubist. Rather, the inevitability of a logical evolution toward a reductive art was obvious to them already. For Malevich, the poetic Slav, this realization forced a turning inward toward an inspirational mysticism, whereas for Duchamp, the rational Frenchman, it meant a fatigue so enervating that finally the wish to paint at all was killed. Both the yearnings of Malevich’s Slavic soul and the deductions of Duchamp’s rationalist mind led both men ultimately to reject and exclude from their work many of the most cherished premises of Western art in favor of an art stripped to its bare, irreducible minimum.
How I Spent My Summer Vacation
Philip Leider

Despite the rhetorical tendency to suggest the social upheaval of the '60s ended with the actual decade, 1970 remained a year of unrest. And Artforum was still the locus of formalist criticism, which was proving increasingly unable to account for art that contributed to larger cultural movements, like Civil Rights, women’s liberation, anti-war protests, and more. (Tellingly, The Partisan Review , which birthed formalism, had by then distanced itself from its communist associations and, as an editorial body, was supportive of American Interventionism in Vietnam. Greenberg was a vocal hawk.) Subtitled “Art and Politics in Nevada, Berkeley, San Francisco, and Utah,” the editor’s note to the September 1970 issue of Artforum , written by Philip Leider, ostensibly recounts a road trip undertaken with Richard Serra and Abbie Hoffman to see Michael Heizer’s Double Negative in the Nevada desert.
RELATED: A City of Art in the Desert: Behind Michael Heizer’s Monumental Visions for Nevada
However, the essay is also an account of an onsetting disillusion with formalism, which Leider found left him woefully unequipped to process the protests that had erupted surrounding an exhibition of prints by Paul Wunderlich at the Phoenix Gallery in Berkeley. Wunderlich’s depictions of nude women were shown concurrently to an exhibition of drawings sold to raise money for Vietnamese orphans. The juxtaposition of a canonical, patriarchal form of representation and liberal posturing, to which the protestors objected, showcased the limitations of a methodology that placed the aesthetic elements of a picture plane far above the actual world in which it existed. Less than a year later, Leider stepped down as editor-in-chief and Artforum began to lose its emphasis on late Modernism.
I thought the women were probably with me—if they were, I was with them. I thought the women were picketing the show because it was reactionary art. To the women, [Piet] Mondrian must be a great revolutionary artist. Abstract art broke all of those chains thirty years ago! What is a Movement gallery showing dumb stuff like this for? But if it were just a matter of reactionary art , why would the women picket it? Why not? Women care as much about art as men do—maybe more. The question is, why weren’t the men right there with them?
Why Have There Been No Great Women Artists?
Linda Nochlin

While Artforum , in its early history, had established a reputation as a generator for formalist theory, ARTnews had followed a decidedly more Rosenberg-ian course, emphasizing art as a practice for investigating the world. The January 1971 issue of the magazine was dedicated to “Women’s Liberation, Woman Artists, and Art History” and included an iconoclastic essay by Linda Nochlin titled “Why Have There Been No Great Women Artists?”
RELATED: An Introduction to Feminist Art
Nochlin notes that it’s tempting to answer the question “why have there been no great women artists?” by listing examples of those overlooked by critical and institutional organizations (a labor that Nochlin admits has great merit). However, she notes, “by attempting to answer it, they tacitly reinforce its negative implications,” namely that women are intrinsically less capable of achieving artistic merit than men. Instead, Nochlin’s essay functions as a critique of art institutions, beginning with European salons, which were structured in such a way as to deter women from rising to the highest echelons. Nochlin’s essay is considered the beginning of modern feminist art history and a textbook example of institutional critique.
There are no women equivalents for Michelangelo or Rembrandt, Delacroix or Cézanne, Picasso or Matisse, or even in very recent times, for de Kooning or Warhol, any more than there are black American equivalents for the same. If there actually were large numbers of “hidden” great women artists, or if there really should be different standards for women’s art as opposed to men’s—and one can’t have it both ways—then what are feminists fighting for? If women have in fact achieved the same status as men in the arts, then the status quo is fine as it is. But in actuality, as we all know, things as they are and as they have been, in the arts as in a hundred other areas, are stultifying, oppressive, and discouraging to all those, women among them, who did not have the good fortune to be born white, preferably middle class and above all, male. The fault lies not in our stars, our hormones, our menstrual cycles, or our empty internal spaces, but in our institutions and our education.
Doctor, Lawyer, Indian Chief
Thomas McEvilley

One of the many extrapolations of Nochlin’s essay is that contemporary museum institutions continue to reflect the gendered and racist biases of preceding centuries by reinforcing the supremacy of specific master artists. In a 1984 Artforum review, Thomas McEvilley, a classicist new to the world of contemporary art, made the case that the Museum of Modern Art in New York served as an exclusionary temple to certain high-minded Modernists—namely, Picasso, Matisse, and Pollock—who, in fact, took many of their innovations from native cultures.
RELATED: MoMA Curator Laura Hoptman on How to Tell a Good Painting From a “Bogus” Painting
In 1984, MoMA organized a blockbuster exhibition. Curated by William Rubin and Kirk Varnedoe, both of whom were avowed formalists, “‘Primitivism’ in 20th Century Art: Affinity of the Tribal and the Modern” collected works by European painters like Paul Gaugin and Picasso with cultural artifacts from Zaire, arctic communities, and elsewhere. McEvilley takes aim at the “the absolutist view of formalist Modernism” in which MoMA is rooted. He argues that the removal tribal artifacts from their contexts (for example, many were ritual items intended for ceremonies, not display) and placement of them, unattributed, near works by European artists, censors the cultural contributions of non-Western civilizations in deference to an idealized European genius.
The fact that the primitive “looks like” the Modern is interpreted as validating the Modern by showing that its values are universal, while at the same time projecting it—and with it MoMA—into the future as a permanent canon. A counter view is possible: that primitivism on the contrary invalidates Modernism by showing it to be derivative and subject to external causation. At one level this show undertakes precisely to coopt that question by answering it before it has really been asked, and by burying it under a mass of information.
Please Wait By the Coatroom
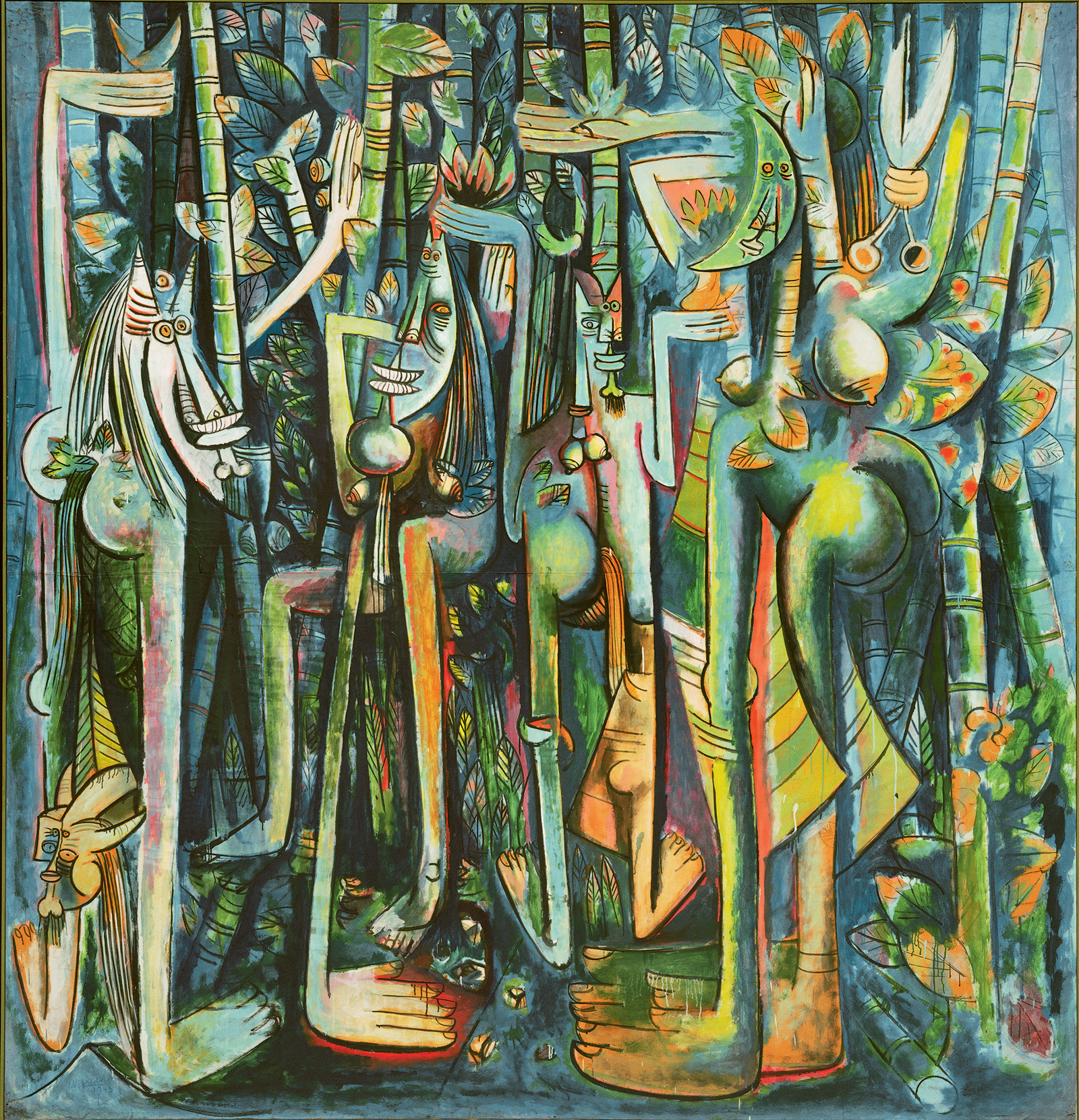

Not content to let MoMA and the last vestiges of formalism off the hook yet, John Yau wrote in 1988 an essay on Wifredo Lam, a Cuban painter who lived and worked in Paris among Picasso, Matisse, Georges Braque, and others. Noting Lam’s many influences—his Afro-Cuban mother, Chinese father, and Yoruba godmother—Yau laments the placement of Lam’s The Jungle near the coatroom in the Museum of Modern Art, as opposed to within the Modernist galleries several floors above. The painting was accompanied by a brief entry written by former curator William Rubin, who, Yau argues, adopted Greenberg’s theories because they endowed him with “a connoisseur’s lens with which one can scan all art.”
RELATED: From Cuba With Love: Artist Bill Claps on the Island’s DIY Art Scene
Here, as with with McEvilley’s essay, Yau illustrates how formalism, as adapted by museum institutions, became a (perhaps unintentional) method for reinforcing the exclusionary framework that Nochlin argued excluded women and black artists for centuries.
Rubin sees in Lam only what is in his own eyes: colorless or white artists. For Lam to have achieved the status of unique individual, he would have had to successfully adapt to the conditions of imprisonment (the aesthetic standards of a fixed tradition) Rubin and others both construct and watch over. To enter this prison, which takes the alluring form of museums, art history textbooks, galleries, and magazines, an individual must suppress his cultural differences and become a colorless ghost. The bind every hybrid American artist finds themselves in is this: should they try and deal with the constantly changing polymorphous conditions effecting identity, tradition, and reality? Or should they assimilate into the mainstream art world by focusing on approved-of aesthetic issues? Lam’s response to this bind sets an important precedent. Instead of assimilating, Lam infiltrates the syntactical rules of “the exploiters” with his own specific language. He becomes, as he says, “a Trojan horse.”
Black Culture and Postmodernism
Cornel West

The opening up of cultural discourse did not mean that it immediately made room for voices of all dimensions. Cornel West notes as much in his 1989 essay “Black Culture and Postmodernism,” in which he argues that postmodernism, much like Modernism before it, remains primarily ahistorical, which makes it difficult for “oppressed peoples to exercise their opposition to hierarchies of power.” West’s position is that the proliferation of theory and criticism that accompanied the rise of postmodernism provided mechanisms by which black culture could “be conversant with and, to a degree, participants in the debate.” Without their voices, postmodernism would remain yet another exclusionary movements.
RELATED: Kerry James Marshall on Painting Blackness as a Noun Vs. Verb
As the consumption cycle of advanced multinational corporate capitalism was sped up in order to sustain the production of luxury goods, cultural production became more and more mass-commodity production. The stress here is not simply on the new and fashionable but also on the exotic and primitive. Black cultural products have historically served as a major source for European and Euro-American exotic interests—interests that issue from a healthy critique of the mechanistic, puritanical, utilitarian, and productivity aspects of modern life.
Minimalism and the Rhetoric of Power
Anna C. Chave

In recent years, formalist analysis has been deployed as a single tool within a more varied approach to art. Its methodology—that of analyzing a picture as an isolated phenomena—remains prevalent, and has its uses. Yet, many of the works and movements that rose to prominence under formalist critics and curators, in no small part because of their institutional acceptance, have since become part of the rearguard rather than the vanguard.
In a 1990 essay for Arts Magazine , Anna Chave analyzes how Minimalist sculpture possesses a “domineering, sometimes brutal rhetoric” that was aligned with “both the American military in Vietnam, and the police at home in the streets and on university campuses across the country.” In particular, Chave is concerned with the way Minimalist sculptures define themselves through a process of negation. Of particular relevance to Chave’s argument are the massive steel sculptures by Minimalist artist Richard Serra.
Tilted Arc was installed in Federal Plaza in lower Manhattan in 1981. Chave describes the work as a “mammoth, perilously tilted steel arc [that] formed a divisive barrier too tall to see over, and a protracted trip to walk around.” She writes, “it is more often the case with Serra that his work doesn’t simply exemplify aggression or domination, but acts it out.” Tilted Arc was so controversial upon its erecting that the General Services Administration, which commissioned the work, held hearings in response to petitions demanding the work be removed. Worth quoting at length, Chave writes:
A predictable defense of Serra’s work was mounted by critics, curators, dealers, collectors, and some fellow artists…. The principle arguments mustered on Serra’s behalf were old ones concerning the nature and function of the avant-garde…. What Rubin and Serra’s other supporters declined to ask is whether the sculptor really is, in the most meaningful sense of the term, an avant-garde artist. Being avant-garde implies being ahead of, outside, or against the dominant culture; proffering a vision that implicitly stands (at least when it is conceived) as a critique of entrenched forms and structures…. But Serra’s work is securely embedded within the system: when the brouhaha over Arc was at its height, he was enjoying a retrospective at the Museum of Modern Art…. [The defense’s] arguments locate Serra not with the vanguard but with the standing army or “status quo.” … More thoughtful, sensible, and eloquent testimony at the hearing came instead from some of the uncouth:
My name is Danny Katz and I work in this building as a clerk. My friend Vito told me this morning that I am a philistine. Despite that I am getting up to speak…. I don’t think this issue should be elevated into a dispute between the forces of ignorance and art, or art versus government. I really blame government less because it has long ago outgrown its human dimension. But from the artists I expected a lot more. I didn’t expect to hear them rely on the tired and dangerous reasoning that the government has made a deal, so let the rabble live with the steel because it’s a deal. That kind of mentality leads to wars. We had a deal with Vietnam. I didn’t expect to hear the arrogant position that art justifies interference with the simple joys of human activity in a plaza. It’s not a great plaza by international standards, but it is a small refuge and place of revival for people who ride to work in steel containers, work in sealed rooms, and breathe recirculated air all day. Is the purpose of art in public places to seal off a route of escape, to stress the absence of joy and hope? I can’t believe this was the artistic intention, yet to my sadness this for me has become the dominant effect of the work, and it’s all the fault of its position and location. I can accept anything in art, but I can’t accept physical assault and complete destruction of pathetic human activity. No work of art created with a contempt for ordinary humanity and without respect for the common element of human experience can be great. It will always lack dimension.
The terms Katz associated with Serra’s project include arrogance and contempt, assault, and destruction; he saw the Minimalist idiom, in other words, as continuous with the master discourse of our imperious and violent technocracy.
The End of Art
Arthur Danto

Like Greenberg, Arthur Danto was an art critic for The Nation . However, Danto was overtly critical of Greenberg’s ideology and the influence he wielded over Modern and contemporary art. Nor was he a follower of Harold Rosenberg, though they shared influences, among them the phenomenologist Maurice Merleau-Ponty. Danto’s chief contribution to contemporary art was his advancing of Pop Artists, particularly Andy Warhol and Roy Lichtenstein .
In “The End of Art” Danto argues that society at large determines and accepts art, which no longer progresses linearly, categorized by movements. Instead, viewers each possess a theory or two, which they use to interpret works, and art institutions are largely tasked with developing, testing, and modifying various interpretive methods. In this way, art differs little from philosophy. After decades of infighting regarding the proper way to interpret works of art, Danto essentially sanctioned each approach and the institutions that gave rise to them. He came to call this “pluralism.”
RELATED: What Was the Pictures Generation?
Similarly, in “Painting, Politics, and Post-Historical Art,” Danto makes the case for an armistice between formalism and the various theories that arose in opposition, noting that postmodern critics like Douglas Crimp in the 1980s, who positioned themselves against formalism, nonetheless adopted the same constrictive air, minus the revolutionary beginnings.
Modernist critical practice was out of phase with what was happening in the art world itself in the late 60s and through the 1970s. It remained the basis for most critical practice, especially on the part of the curatoriat, and the art-history professoriat as well, to the degree that it descended to criticism. It became the language of the museum panel, the catalog essay, the article in the art periodical. It was a daunting paradigm, and it was the counterpart in discourse to the “broadening of taste” which reduced art of all cultures and times to its formalist skeleton, and thus, as I phrased it, transformed every museum into a Museum of Modern Art, whatever that museum’s contents. It was the stable of the docent’s gallery talk and the art appreciation course—and it was replaced, not totally but massively, by the postmodernist discourse that was imported from Paris in the late 70s, in the texts of Michel Foucault, Jacques Derrida, Jean Baudrillard, Jean-François Lyotard, and Jacques Lacan, and of the French feminists Hélène Cixous and Luce Irigaray. That is the discourse [Douglas] Crimp internalizes, and it came to be lingua artspeak everywhere. Like modernist discourse, it applied to everything, so that there was room for deconstructive and “archeological” discussion of art of every period.
Editor’s Note: This list was drawn in part from a 2014 seminar taught by Debra Bricker Balken in the MFA program in Art Writing at the School of Visual Arts titled Critical Strategies: Late Modernism/Postmodernism. Additional sources can be found here , here , here (paywall), and here . Also relevant are reviews of the 2008 exhibition at the Jewish Museum, “Action/Abstraction: Pollock, de Kooning, and American Art, 1940–1976,” notably those by Roberta Smith , Peter Schjeldahl , and Martha Schwendener .

Related Articles
Know your critics.
Current Shows
Receive our award winning emails & enjoy 10% off your first purchase, thanks for signing up for our newsletter., that email has already been subscribed..
Now, personalize your account so you can discover more art you'll love.
a treasure trove of fine art from the world's most renowned artists, galleries, museums and cultural institutions. We offer exclusive works you can't find anywhere else.
through exclusive content featuring art news, collecting guides, and interviews with artists, dealers, collectors, curators and influencers.
authentic artworks from across the globe. Collecting with us means you're helping to sustain creative culture and supporting organizations that are making the world a better place.
with our art advisors for buying advice or to help you find the art that's perfect for you. We have the resources to find works that suit your needs.

INSIDER ACCESS TO THE WORLD'S BEST ART
Artspace offers you authentic, exclusive works from world-renowned artists, galleries, museums and cultural institutions. Collecting with us helps support creative culture while bringing you art news, interviews and access to global art resources.
COLLECT FROM 300+ GALLERIES & MUSEUMS
Sign in for personalized experiences, exclusive access to new works, special offers, invitations and features.
Collect the world's best
Sign up to view price and receive personalized experiences exclusive access to new works, special offers, invitations and features.
Thank you for signing up
Tailor your art, news & information to your preferences.
THANK YOU FOR SIGNING-UP TO ARTSPACE
Welcome to the world's premier online marketplace for fine art.
Enjoy 10% on your next purchase by using coupon code WELCOME10 at checkout.
THANK YOU FOR RETURNING TO ARTSPACE
The world's premier online marketplace for fine art.
Enjoy 10% on your next purchase by using coupon code PHAIDON10 at checkout.
Forgot your password?
Please enter your email below and we will send you a new password.
We've emailed you a new password. Sign In
Interested in Firstname Lastname?
To follow this artist and get updates on new work & exclusives, you must be signed into your Artspace account. Don't have one? Create one now.
You are now following first name last name
Interested in saving this work.
To save this work to your personal gallery and to access other features like this, you must be signed into your Artspace account.
prompt placeholder
The 10 Essays That Changed Art Criticism Forever
Share this article
Use this form to share great articles with your friends.
Enter your email
Enter your friend's email
Your message was sent
Thank you for sharing with your friends.
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Pinterest
Your email has been submitted and a 10% off discount code sent to you. Next, personalize your Artspace experience by creating an account.
Please select the statement that best describes you:
- I am an existing collector.
- I am a new and aspiring collector.
Types of art that interest you
Select all that interest you:, partners you'd like to follow, enter or select all partners that interest you:.
Your preferences have been saved to your account. Update them at any time in your Preference Center
How it Works
How bidding works.
To place a bid, enter the maximum amount you are willing to pay for the work. Artspace will accept a bid at the next increment, and save any excess amount as a maximum bid. If you are outbid, we will continue bid on your behalf up to your maximum bid.
Bid Increments
Bidding increments increase at the following intervals:
- Below $400: $50
- Between $400 and $699: $100
- Between $700 and $1,499: $200
- Between $1,500 and $2,499: $300
- Between $2,500 and $4,999: $500
- Between $5,000 and $9,999: $1,000
- Between $10,000 and $19,999: $2,000
- Between $20,000 and $29,999: $3,000
- Between $30,000 and $49,999: $4,000
- Between $50,000 and $99,999: $5,000
- Above $100,000: $10,000
You will receive an email confirmation of your bid and when you are outbid.
If you are the winning bidder, you will be contacted 48 hours after of the close of the auction.
Maximum Bidding
Every bid submitted is treated as a maximum bid. You should always bid the maximum you are willing to spend for a work, though this does not necessarily mean you will pay that price. As the auction unfolds, we will increase your bid by increments to ensure you remain the highest bidder. If the winning amount is less than your maximum bid, you will pay the current increment. If your maximum bid no longer exceeds the current bid, you will receive an outbid notification email, and have the option to bid again.
In the case of multiple bidders placing the same maximum bid, the first person to place the maximum amount takes precedence as the highest bid until another bidder exceeds the maximum amount.
Buyer's Premium & Additional Charges
For Artspace Auctions winning bidders are charged a 15% Buyer's Premium on top of the hammer price. For Artspace Benefit Auctions, Buyer's Premiums are not applied. If they are, this will be clearly noted. Purchases made from all auctions, including benefit auctions, are subject to sales tax.
Winning bidders will be contacted within 48 hours to arrange shipping and to provide final price including commission, shipping, and taxes and duties when applicable. Promotion codes cannot be applied to auction works.
Auction Pre-Registration
Credit Card Validation
In order to secure a bid, please enter your credit card details below. We will not charge your card but only use it to validate your bid. We only need to validate your card once. You will be notified that you are the winning bidder before your card is charged, and you will have the option to change your payment method at that time.

Create an Artspace account
All our frames are manufactured in the USA, using eco-friendly & sustainably sourced engineered hardwood for durability and a uniform finish that is free of defects. Frames are available in Black or White Satin and Honey Pecan.
- White Satin
- Honey Pecan
- Black Satin
All prints are hinged to a conservation quality, acid-free and lignin-free Alpha Cellulose matboard, using an acid-free linen tape. The mat's surface paper is fade and bleed resistant and is attached to a conservation quality foam-core mounting board that will keep the work safe from deterioration over time. Artworks with a deckled or decorative edges will be floated on the matboard, with acrylic spacers to separate the art from the glazing. All mounting is fully reversible, without any potential damage to the art.
Acrylic Glazing
All of our frames come with picture quality .090 mm plexiglass, which blocks 66% of UV to prevent color fading from exposure to light, keeping your art protected for years to come. It is now considered the industry standard for artists, museums and galleries throughout the world.
For images up to 30" x 40"
- 1 1/4” wide, 3/4” deep, with a 2 1/2” wide mat.
- We generally leave 1/4” - 1/2” of paper showing around the image, to accommodate signatures and for visual appeal.
For sheet sizes larger than 30” x 40”
- Please contact an Artspace advisor for a custom quote.
Artists you'd like to follow
Enter or select all artists that interest you:.

Press ESC to close

Art is Considered an Important Part of Society: IELTS Essay on Art and Society
You will be asked to write a variety of essays in IELTS Writing Task 2. This includes Opinion Essays, Argumentative Essays, Advantages and Disadvantages Essays, Problem & Answer Essays, and Mixed Essays. The type of essay required must be determined, and your responses must be written accordingly. You are expected to use your skills, experience, and examples when answering.
To be more specific, IELTS Writing Task 2 requires you to write a 250-word essay on a given topic. Not to mention the fact that the task is time-limited. You have 40 minutes to cleverly answer the specific topic with your own language, obviously without any mistakes. This article provides an example of an essay on “Art is considered an important part of a society.”
Art is Considered an Important Part of Society: IELTS Essay Topic
Will you be able to write an essay on art? If you don’t have the idea to approach a topic like that, you must read the section below carefully.
Art is Considered an Important Part of Society Sample 1
Introduction.
Art is widely regarded as an important aspect of society, and works of art often offer important insights into current communities. I am fully in favour of art education playing a significant part in the lives of children. I assume that children should be encouraged to value art as much as they value other topics such as science, math, and so on. This article would address two advantages of combining art education to include a rationale for why prioritising other topics is so beneficial.
Since the movements and methods used in making it include finely tuned motor abilities, one of the main benefits of incorporating art instruction in a school curriculum is that it aids in the learning of motor skills.

Also Read: Describe Your Favourite Clothes Cue Card Topic: IELTS Exam Speaking Test
Art is Considered an Important Part of Society IELTS Essay: Body
Swirling a paintbrush, colouring between multiple lines, and erasing minor aspects of a sketch are all examples of this, and they all include particular concentrations and smooth hand motions. Drawing various shapes and chopping papers would not only improve general dexterity, but it would also make children even more concise and effective. Another advantage in delivering art lessons is the production of total trust. Take, for example, the usually egocentric visual arts. To put it another way, when a kid sketches or paints, it is an expression of themselves and how they think. As a result, if teachers and others encourage young people to participate in visual art by complementing their work and showing the images in an exhibition, this type of project is likely to improve children’s morale and personal growth.
Art is Considered an Important Part of Society IELTS Essay: Conclusion
Children must be encouraged to pursue painting as well as academic subjects such as algebra, astronomy, and others. Using detailed perceptions of both subjects, the study of astronomy was made perfectly possible, just as the scale of the earth, our distance from the sun, and the advent of satellites were made perfectly possible. Without it, we wouldn’t have any of our new technological marvels and would have remained uncivilised for all time.
Finally, it is obvious that spare subjects are just as important as art subjects. Furthermore, regardless of the incorporation of a creative approach and determinations, providing art education remains a truly fundamental mission.
Art is Considered an Important Part of Society Sample 2
One of the most contentious issues currently is whether or not art is a necessary subject for school children. In this article, I’ll look at both sides of the debate and then offer my own thoughts on the topic.
On one side of the debate, others contend that the advantages of it as an intellectual topic far outweigh the drawbacks. The primary explanation for this is that it is the transformation of an individual’s creativity into paper; as a result, it assists students in broadening their thinking. It’s also plausible to argue that it serves as a vehicle for shy students to articulate themselves directly.
Also Read: Describe a Person Who has Apologized to You: An Important IELTS Cue Card Topic
One clear example is when children show their love and feelings towards their parents by using their imagination to create a birthday card, assuming they studied this craft in kindergarten. As a result, it’s easy to see why this viewpoint has gained traction.
Individuals, on the other hand, often contend that it is a waste of time. People also believe this because students are already overburdened with other academic topics, and having a class would add to their workload. Furthermore, there are no career opportunities for art students nowadays; as a result, they choose other vocational subjects. For example, students should choose between science and commerce, all of which have plenty of job opportunities.
As a result, it can go without saying that this point of view is both plausible and rational.
Both points, in my view, have substance. Overall, however, I agree that it should be an elective subject, bearing in mind that students’ work prospects are paramount.
Art is Considered an Important Part of Society Sample 3
Art is a significant cultural legacy that represents individuality and reflects national characteristics, values, and customs. Despite its relevance, people’s engagement with and participation in it has declined in recent years, as science and technology have taken precedence. There are some reasons for this ignorance that can be found, but there are also some remedies that can be used to change this perspective.
There are some key explanations for the change in focus and mindset toward technological fields. To begin with, painting is a profession that does not promise a high wage. People are most likely to study high-demand careers such as science, which are more indispensable and in-demand in the community. Second, humans are heavily reliant on technology, as gadgets make everyday activities easier, medical services help to avoid and treat illnesses, and technology, in general, makes our lives easier. People began creating science spheres after seeing the advantages and successes of innovations. Because of these possibilities, people choose technological and business capabilities over creative talent.
To solve a dilemma, one can engage in a variety of tasks. To continue, the government should fund galleries and art-related subjects in schools to raise public consciousness of the importance of it and to develop creative skills in children. Similarly, sentimental appeals, such as musicals, operas, and plays, will stimulate and inspire a culture to cultivate the arts. Regrettably, due to their busy schedules, people are unable to visit museums and galleries in their free time. As a result, the government will open cultural centres at night and organise festivals, allowing people to visit them on weekends. Those solutions have the potential to strengthen the present situation and change people’s attitudes about it for the better.
To summarise, it is an essential aspect of life that has fallen out of favour. However, the dilemma can be addressed if the government and individuals take the appropriate action.
The IELTS Writing Task 2 is an essential part of the test. To write an excellent essay, you must be well-versed in a wide range of statistics and subjects. This breadth of experience will assist you in easily relating something to the subject in order to bolster your argument. Since there are various types of essays, you must practise one thoroughly in order to achieve a good band score on your IELTS test.
If you want to avoid making such mistakes, go to IELTS Ninja for more advice and guidance on the IELTS test.
Also Read: Describe An Intelligent Person You Know: Cue Card Topic For IELTS Speaking Test

Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Share Article:
About the Author
Madhurjya chowdhury.
Madhurjya Chowdhury, a web content writer in Ufaber EduTech has a very strong passion for writing and alluring the readers. You can find him writing articles for the betterment of exam aspirants and children. With immense interest in research-based content writing and copywriting, he likes to reach out to more and more people with his creative writing style. On the other side, he is an Electronics and Communication Engineer from LPU, Jalandhar. In his leisure time, he likes to play badminton or read about space discoveries. Apart from this, he is a pro gamer on PC, PS and Mobile gaming platforms.
You might also like

Describe Something Important that has been Kept in Your Family: A Cue Card Sample Topic for IELTS Speaking

How to Use an IELTS Calculator? Calculate Your Overall IELTS Exam Score

What is a Good IELTS Score? Is 7.5 a Good IELTS Score? Here’s All You Need to Know
Other stories, describe a company where you live that employs a lot of people: sample ielts cue card topic, art or craft ielts reading answers: how to achieve 8+ band score in ielts reading.
Whispering Trees: the Art of Silent Conservation
This essay is about the silent symphony of conservation orchestrated by whispering trees. As a biologist, I explore the subtle yet crucial communication methods employed by trees in forests, revealing a world of chemical conversations and underground networks. The intricate dance of volatile organic compounds and mycorrhizal fungi forms the foundation of silent conservation, fostering cooperation and resilience in ecosystems. Understanding the interconnectedness of trees and the delicate balance they maintain offers profound insights for effective conservation. The essay emphasizes the need to go beyond traditional approaches and recognize the invisible threads that bind entire ecosystems. Silent conservation urges a holistic perspective, acknowledging the intrinsic value of each tree in sustaining ecological harmony. Biologists play a vital role in conveying the wonders of silent communication, inspiring the public to appreciate and protect the intricate symphony of nature. In essence, this essay advocates for a paradigm shift in conservation, embracing the art of silent conservation to ensure the longevity of the whispers that resonate within the heart of the forest.
On PapersOwl, there’s also a selection of free essay templates associated with Conservation.
How it works
Where the tapestry of life unfolds in myriad hues, a phenomenon often goes unnoticed—the whispering trees. As a biologist immersed in the study of ecosystems, I have come to appreciate the profound importance of these arboreal murmurs, which serve as the art of silent conservation.
From the mighty redwoods to the delicate aspens, trees communicate with each other through a language imperceptible to the human ear. Recent research has unveiled the intricacies of this arboreal dialogue, shedding light on the profound interconnectedness that underlies forest ecosystems.
It is a symphony performed not with boisterous sounds but through subtle cues, a symphony that plays a crucial role in the delicate dance of ecological balance.
The scientific exploration of tree communication has revealed a fascinating world of chemical conversations and underground networks. Trees, it turns out, engage in a form of silent conversation by releasing chemical compounds into the air. When under attack by pests, for instance, a tree can emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) to alert neighboring trees of the impending threat. This chemical signaling not only prepares nearby trees for defense but also triggers responses in insects that prey on the invaders, creating a natural and intricate web of protection.
Beneath the soil, a silent network of mycorrhizal fungi serves as nature’s internet, connecting trees in a web of symbiotic relationships. This mycorrhizal network allows trees to exchange nutrients, information, and even warnings about potential threats. It is a subterranean symphony of cooperation, where the silent language of the roots fosters the survival of the entire forest community.
As a biologist, my fascination with these silent conversations has grown into a deep appreciation for the art of silent conservation. In a world often dominated by human activities, the whispers of trees remind us of the delicate balance that sustains life on Earth. The silent communication among trees is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of nature, offering valuable lessons for conservation efforts.
The implications of understanding and respecting the silent language of trees are profound. Conservation practices must go beyond traditional approaches and embrace a holistic understanding of ecosystems. Instead of focusing solely on individual species, we must recognize the interconnectedness of entire forests and the vital role that each tree plays in maintaining ecological harmony.
Silent conservation involves preserving not only the visible aspects of a forest but also the invisible threads that bind it together. It requires acknowledging the intricate relationships between trees, fungi, and the myriad organisms that coexist within these ecosystems. By doing so, we can develop more effective conservation strategies that address the needs of entire ecosystems rather than isolated components.
One of the challenges in promoting silent conservation lies in making it tangible and accessible to the general public. Unlike grand conservation projects that capture headlines, the subtlety of tree communication often eludes casual observers. It is here that the role of science communication becomes crucial. As biologists, we must convey the wonders of silent conservation in a way that resonates with people, inspiring them to appreciate and protect the intricate symphony of nature.
In conclusion, the art of silent conservation embodied by whispering trees is a testament to the resilience and interconnectedness of ecosystems. As a biologist, I find myself drawn to the beauty of this silent symphony and the lessons it imparts. It is a call to action, urging us to reevaluate our approach to conservation and embrace a more holistic understanding of the intricate dance of life that unfolds in the heart of the forest. Through the art of silent conservation, we can ensure that the whispers of trees continue to resonate for generations to come, weaving a harmonious narrative of ecological coexistence.
Cite this page
Whispering Trees: The Art of Silent Conservation. (2024, Mar 01). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/whispering-trees-the-art-of-silent-conservation/
"Whispering Trees: The Art of Silent Conservation." PapersOwl.com , 1 Mar 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/whispering-trees-the-art-of-silent-conservation/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Whispering Trees: The Art of Silent Conservation . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/whispering-trees-the-art-of-silent-conservation/ [Accessed: 11 Apr. 2024]
"Whispering Trees: The Art of Silent Conservation." PapersOwl.com, Mar 01, 2024. Accessed April 11, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/whispering-trees-the-art-of-silent-conservation/
"Whispering Trees: The Art of Silent Conservation," PapersOwl.com , 01-Mar-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/whispering-trees-the-art-of-silent-conservation/. [Accessed: 11-Apr-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Whispering Trees: The Art of Silent Conservation . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/whispering-trees-the-art-of-silent-conservation/ [Accessed: 11-Apr-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
The Next Frontier? Philosophy in Space.

By Joseph O. Chapa
Dr. Chapa is a U.S. Air Force officer and the author of “Is Remote Warfare Moral?”
The window to apply to be a NASA astronaut — a window that opens only about every four years — closes this month, on April 16. Though I’ve submitted an application, I don’t expect to make the cut.
The educational requirements for the astronaut program are clear: Applicants must possess at least a master’s degree in a STEM field (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics), a doctorate in medicine or a test pilot school graduate patch. Though I have a Ph.D., it’s in philosophy. (And though I’m an Air Force pilot, I’m not a test pilot.)
I hesitate to tell NASA its business. But I think its requirements are closing the astronaut program off from important insights from the humanities and social sciences.
Of course, the requirement for astronauts to have technical training makes some intuitive sense. NASA was founded in 1958 “to provide for research into problems of flight within and outside the earth’s atmosphere.” Who better to solve flight problems than scientists and engineers? What’s more, NASA’s space missions have long conducted science experiments to learn how plant and animal life behaves in the far-flung emptiness between us and the moon.
But the need for STEM in space might be waning — just as the need for humanities and the social sciences waxes. After all, the “problems of flight” that once tethered us to this planet have largely been solved, thanks in no small part to all those scientist and engineer astronauts who blazed the trail to space.
By contrast, the future of our relationship with the cosmos — a colony on the moon? Humans on Mars? Contact with intelligent alien life? — will require thoughtful inquiry from many disciplines. We will need sociologists and anthropologists to help us imagine new communities; theologians and linguists if we find we are not alone in the universe; political and legal theorists to sort out the governing principles of interstellar life.
Naturally, some scholars can study these topics while still earthbound. But so can many of today’s astronauts, who often end up working on projects unrelated to their academic training. The idea behind sending people with a wider array of academic disciplines into the cosmos is not just to give scholars a taste of outer space, but also to put them in fruitful conversation with one another.
My own discipline, philosophy, may be better suited for this kind of exploration than some might think. To be sure, much philosophy can be done from an armchair. Descartes arrived at his famous conclusion, “I think, therefore, I am,” while warming himself by the fire and, as he noted, “wearing a winter dressing gown.”
But some of the greatest philosophical breakthroughs occurred only because their authors had firsthand experience with extreme and uncomfortable conditions. We might not have the Stoic philosophy of Epictetus had he not faced the hardship of slavery in Nero’s court. We might not have Thomas Hobbes’s “Leviathan” (and his principle of the “consent of the governed,” so central to the American experiment), but for his flight from the English Civil War. And we might not have Hannah Arendt’s insights on the “banality of evil” had she not attended the trial of Adolf Eichmann, a chief architect of the Holocaust.
Not all philosophers who want to learn what it means to be human in this vast and expanding universe need to experience living in space. But perhaps some of us should.
Throughout the history of Western philosophy, space has often served as stand-in for life’s deepest truths. Plato thought that the things of this world were mere images of true reality, and that true reality existed in the heavens beyond. What inspired admiration and awe in Immanuel Kant was not just the moral law within all of us but also the “starry heavens above.” The Platos and Kants of today are in a position to take a much closer look at those very heavens.
In general, the work of philosophy is to ask, “And suppose this proposition is right, what then?” When faced with a proposition — say, “The mind and body are separable,” or “One must always act to achieve the greatest happiness for the greatest number” — the philosopher takes another step and asks, “What are the implications of such a view?”
Though Earth has been our only home, it may not be our home forever. What are the implications of that proposition? What might that mean for our conception of nationhood? Of community? Of ourselves and our place in the world? This would be the work of space philosophers.
These days, unfortunately, the prestige of STEM continues to eclipse that of the social sciences and humanities. It seems unlikely that NASA will buck this trend.
That would be bad news for me, personally — but I think also for humanity at large. One day we may all echo Jodie Foster’s character in the sci-fi movie “Contact . ” When the mysteries of space-time were unfurled before her, all she could manage to say was, “They should have sent a poet.”
Joseph O. Chapa ( @JosephOChapa ) is a U.S. Air Force officer and the author of “Is Remote Warfare Moral?”
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Art is important to culture because it can bridge the gap between different racial groups, religious groups, dialects, and ethnicities. It can express common values, virtues, and morals that we can all understand and feel. Art allows us to ask important questions about life and society.
Answer 2: Art is essential as it covers all the developmental domains in child development. Moreover, it helps in physical development and enhancing gross and motor skills. For example, playing with dough can fine-tune your muscle control in your fingers. Share with friends. Previous.
Art is uniquely positioned to move people—inspiring us, inciting new questions, and provoking curiosity, excitement, and outrage. Artists can strengthen the will and push people to act. They do not think like policymakers or academics people. Artists think from their heart - big, revolutionary, and visionary ideas.
9 years ago. Art is important because it makes you feel beauty of freedom. It is free expression of human mind and senses. An expression which is not subdue to any kind of utility, if you don't desire; an expression which only aims at her own existence, at her own beauty. •.
This part of your brain is very close to the midbrain and plays a role in the decision making vs reward system. So, looking at art may actually be a reward from our brain's point of view! Overall, art is an essential part of the human experience. Even if it doesn't play a big role in someone's personal life, art shapes the world around us ...
The arts are transformative.". - Beth Bienvenu "The arts matter because they allow you to experience different ways of seeing and thinking about life.". - Don Ball "The arts matter because life is dull without perspective. All art, good and bad, made by an individual or a team, brings the perspective of an artist to others.
The value of creating. At its most basic level, the act of creating is rewarding in itself. Children draw for the joy of it before they can speak, and creating pictures, sculptures and writing is both a valuable means of communicating ideas and simply fun. Creating is instinctive in humans, for the pleasure of exercising creativity.
The scale, visibility, and accessibility of these objects and images are further sources of information about their cultural significance. In the rest of this essay, we present a range of examples to consider the varied ways in which art makes society. We consider: (1) the ways art can frame a setting; (2) art as participation; (3) art as ...
This is the essay is part of The Big Ideas, ... I would contend that art and culture are the most important vehicles by which we come to understand one another. They make us curious about that ...
Here are seven significant examples of art essays written by some of most influential intellectuals such as Walter Benjamin and Susan Sontag.
100 Words Essay on Importance Of Art Art Sparks Creativity. Art is like a key that unlocks the door to imagination. When kids draw, paint or make crafts, they think of new ideas. This helps their brains grow and teaches them to think in different ways. Art can turn a plain white paper into a world of colors and stories, showing that with a bit ...
The benefits of creating art. Creating art can be an immensely rewarding experience that has both psychological and physical benefits. It can provide a sense of purpose, satisfaction, and accomplishment. Art can also help reduce stress, build self-confidence, and improve problem solving skills.
philosophy of art, the study of the nature of art, including concepts such as interpretation, representation and expression, and form.It is closely related to aesthetics, the philosophical study of beauty and taste.. Distinguishing characteristics. The philosophy of art is distinguished from art criticism, which is concerned with the analysis and evaluation of particular works of art.
Instead, art appreciation is: Gaining the knowledge to understand the art. Acquire the art methods and materials to discuss art verbally or by the written word. Ability to identify the movements from ancient cultures to today's contemporary art. Learning how to appreciate art is a necessary cultural foundation enabling people to critically ...
Appreciating and Admiring Art. Art is not meant to be overlooked. People need to appreciate it, admire it, and be inspired by it as it can teach us many things that we can't even imagine. Art is meant to be looked at for what it is, as it tells us who we are and what we can become in the eyes of the beholder. Art can stimulate thought and reason.
500 Words Essay on Importance Of Art In Our Life Art is Everywhere. Art is a big part of our lives, even if we might not always notice it. Think about the music you listen to, the cartoons you watch, and the pictures you draw. These are all forms of art. Art is not just something you see in a museum; it's in the games you play, the clothes ...
ART HISTORY: GUIDE TO ESSAY WRITING . The aim of formal essay writing is to engage your critical reading and writing skills to craft an articulate and polished essay. It provides an opportunity to consider a topic in depth, combining the synthesis of source materials with your own conclusions based on those materials.
2. It helps all of us develop necessary soft skills. The importance of art in society goes far beyond what we do in our free time. It can also help people work better. When someone applies for a job, there are certain hard skills they need to have like data analysis or bookkeeping.
Victor Merida, " Excited Delirium: Graffiti and Miami ," The Miami Rail, Winter 2014. Some sober, sobering reflections on graffiti art's place in the branding of Miami, made more resonant by ...
The Importance Of Art Essay. 867 Words4 Pages. Imagine living in a world where there is clean water, fresh air to breathe in and natural food stuffs to eat. Many governments are saving more money than they used to do, in the past years. This has been made possible by the use of artwork. Today in this world people have used art to develop new ...
Developmental Benefits of Arts. Arts play a significant role in the development of a child's motor skills. For instance, most of the motions involved in the creation of art, such as scribbling with a pencil or a crayon, are important in the development of fine motor skills (The future of the Australian curriculum, 2014).Participation helps learners to improve their skills in mathematics and ...
The 10 Essays That Changed Art Criticism Forever. By Will Fenstermaker. June 14, 2017. Dr. Cornel West. There has never been a time when art critics held more power than during the second half of the twentieth century. Following the Second World War, with the relocation of the world's artistic epicenter from Paris to New York, a different ...
Art is Considered an Important Part of Society IELTS Essay: Conclusion Children must be encouraged to pursue painting as well as academic subjects such as algebra, astronomy, and others. Using detailed perceptions of both subjects, the study of astronomy was made perfectly possible, just as the scale of the earth, our distance from the sun, and ...
Essay Example: Where the tapestry of life unfolds in myriad hues, a phenomenon often goes unnoticed—the whispering trees. As a biologist immersed in the study of ecosystems, I have come to appreciate the profound importance of these arboreal murmurs, which serve as the art of silent conservation
Here are some tips. And here's our email: [email protected]. Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, WhatsApp, X and Threads. A version of this article ...