CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free

Case Study Questions Chapter 1 Resources and Development
Please refer to the Case Study Questions Chapter 1 Resources and Development with answers provided for Class 10 Social Science. These solved case study based questions are expected to come in the Class 10 Economics exam in the current academic year. We have provided Case study for Class 10 Social Science for all chapters here. You should practise these solved case studies to get more marks in examinations.
Chapter 1 Resources and Development Case Study Questions Class 10 Social Science
1. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follows:
On the Basis of the Status of Development Potential Resources: Resources which are found in a region, but have not been utilised. For example, the western parts of India particularly Rajasthan and Gujarat have enormous potential for the development of wind and solar energy, but so far these have not been developed properly. Developed Resources: Resources which are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilisation. The development of resources depends on technology and level of their feasibility. Identify at least two resources from each category. Do you know that India has got the right to mine manganese nodules from the bed of the Indian Ocean from that area which lies beyond the exclusive economic zone. Identify some other resources which are international in nature. Stock: Materials in the environment which have the potential to satisfy human needs but human beings do not have the appropriate technology to access these, are included among stock. For example, water is a compound of two gases; hydrogen and oxygen. Hydrogen can be used as a rich source of energy. But we do not have advanced technical ‘know-how’ to use it for this purpose. Hence, it can be considered as stock. Reserves are the subset of the stock, which can be put into use with the help of existing technical ‘know-how’ but their use has not been started. These can be used for meeting future requirements. River water can be used for generating hydroelectric power but presently, it is being utilised only to a limited extent. Thus, the water in the dams, forests etc. is a reserve which can be used in the future.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
(i) Which one of the following statements is true about the term resources? (a) Resources are free gifts of nature. (b) They are the functions of human activities. (c) All those things which are found in nature. (d) Things which cannot be used to fulfill our needs.
(ii) Identify the correct basis of the Status of Development potential resources.
Choose the correct option-
(a) (a)-1, (b)–3, (c)–2, (d)–4 (b) (a)–2, (b)–1, (c)–4, (d)–3 (c) (a)–3, (b)–1, (c)–4, (d)–2 (d) (a)–4, (b)–2, (c)–3, (d)–1
(iii) Resources which are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilisation are __________. (a) Potential Resources (b) Individual Resources (c) Developed Resources (d) Stock
(iv) Resources that take long geological time for their formation are called: (a) Renewable resources (b) Reserve (c) Community resources (d) Non-renewable resources
2. Read the source given below and answer the following questions:
Energy is a basic requirement for economic development. Every sector of the national economy – agriculture, industry, transport, commercial and domestic – needs inputs of energy. The economic development plans implemented since Independence necessarily required increasing amounts of energy to remain operational. As a result, consumption of energy in all forms has been steadily rising all over the country. In this background, there is an urgent need to develop a sustainable path of energy development. Promotion of energy conservation and increased use of renewable energy sources are the twin planks of sustainable energy. India is presently one of the least energy efficient countries in the world. We have to adopt a cautious approach for the judicious use of our limited energy resources. For example, as concerned citizens we can do our bit by using public transport systems instead of individual vehicles; switching off electricity when not in use, using power-saving devices and using non-conventional sources of energy. After all, “energy saved is energy produced”.
(i) How will using public transport systems instead of individual vehicles help us? (a) saving resources (b) saving energy (c) saving vehicles (d) all the above
(ii) There is an urgent need of _________ development. (a) unsustainable (b) sustainable (c) non-energy (d) none of the above
(iii) Meaning of sustainable: (a) viable (b) temporary (c) conserve (d) none of the above
(iv) What is considered to be the basic requirement of economic development? (a) resources (b) energy (c) technology (d) citizens
3. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follows:
We have shared our land with the past generations and will have to do so with the future generations too. Ninety-five per cent of our basic needs for food, shelter and clothing are obtained from land. Human activities have not only brought about degradation of land but have also aggravated the pace of natural forces to cause damage to land. Some human activities such as deforestation, over grazing, mining and quarrying too have contributed significantly in land degradation. Mining sites are abandoned after excavation work is complete leaving deep scars and traces of over-burdening. In states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha deforestation due to mining have caused severe land degradation. In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra overgrazing is one of the main reasons for land degradation. In the states of Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh, over irrigation is responsible for land degradation due to water logging leading to increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil. The mineral processing like grinding of limestone for cement industry and calcite and soapstone for ceramic industry generate huge quantity of dust in the atmosphere. It retards the process of infiltration of water into the soil after it settles down on the land. In recent years, industrial effluents as waste have become a major source of land and water pollution in many parts of the country. There are many ways to solve the problems of land degradation. Afforestation and proper management of grazing can help to some extent. Planting of shelter belts of plants, control on over grazing, stabilisation of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes are some of the methods to check land degradation in arid areas. Proper management of waste lands, control of mining activities, proper discharge and disposal of industrial effluents and wastes after treatment can reduce land and water degradation in industrial and suburban areas.
(i) In which of the follo wing States mining has caused severe land degradation? (a) Gujarat (b) Jharkhand (c) Kerala (d) Uttarakhand
(ii) In which of the following states is overgrazing responsible for land degradation? (a) Jharkhand and Orissa (b) Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan (c) Punjab and Haryana (d) Kerala and Tamil Nadu
(iii) Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab? (a) Intensive cultivation (b) Deforestation (c) Over-irrigation (d) Overgrazing
(iv) One of the following which does not check land degradation- (a) control on overgrazing (b) creating shelter belts (c) deforestation (d) afforestation
4. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Resource planning is a complex process which involves: (i) identification and inventor of resources across the regions of the country. This involves surveying, mapping and qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of the resources. (ii) evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional set up for implementing resource development plans. (iii) Matching the resource development plans with overall national development plans. India has made concerted efforts for achieving the goals of resource planning right from the First Five Year Plan launched after Independence. The availability of resources is a necessary condition for the development of any region, but mere availability of resources in the absence of corresponding changes in technology and institutions may hinder development. There are many regions in our country that are rich in resources but these are included in economically backward regions. On the contrary there are some regions which have a poor resource base but they are economically developed. The history of colonisation reveals that rich resources in colonies were the main attractions for the foreign invaders. It was primarily the higher level of technological development of the colonising countries that helped them to exploit resources of other regions and establish their supremacy over the colonies. Therefore, resources can contribute to development only when they are accompanied by appropriate technological development and institutional changes.
India has experienced all this in different phases of colonisation. Therefore, in India, development in general, and resource development in particular do not only involve the availability of resources, but also the technology, quality of human resources and the historical experiences of the people.
(i) What was main attraction of foreign invaders to India? (a) architecture (b) resource (c) irrigation method (d) spices
(ii) Resource planning is essential for __________ existence of all forms of life. (a) ecological balance (b) sustainable (c) exploitation (d) None of these
(iii) Which of the following is essential for sustainable existence of all forms of life? (a) Resource planning (b) Resource management (c) Resource extraction (d) Resource generation
(iv) From which Five Year Plan has India made concerted efforts for achieving the goals of resource planning? (a) First Five Year Plan (b) Fifth Five Year Plan (c) Annual Plans (d) Tenth Five Year Plan
5. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follows:
Renewable Resources: The resources which can be renewed or reproduced by physical, chemical or mechanical processes are known as renewable or replenishable resources. For example, solar and wind energy, water, forests and wildlife, etc. The renewable resource may further be divided into continuous or flow Non-Renewable Resources: These occur over a very long geological time. Minerals and fossil fuels are examples of such resources. These resources take millions of years in their formation. Some of the resources like metals are recyclable and some like fossil fuels cannot be recycled and get exhausted with their use. On the Basis of Ownership Individual Resources: These are also owned privately by individuals. Many farmers own land which is allotted to them by government against the payment of revenue. In villages there are people with land ownership but there are many who are landless. Urban people own plots, houses and other property. Plantation, pasture lands, ponds, water in wells etc. are some of the examples of resources ownership by individuals. Make a list of resources owned by your household. Community Owned Resources: There are resources which are accessible to all the members of the community. Village commons (grazing grounds, burial grounds, village ponds, etc.) public parks, picnic spots, playgrounds in urban areas are de facto accessible to all the people living there. National Resources: Technically, all the resources belong to the nation. The country has legal powers to acquire even private property for public good. You might have seen roads, canals, railways being constructed on fields owned by some individuals. Urban Development Authorities get empowered by the government to acquire land. All the minerals, water resources, forests, wildlife, land within the political boundaries and oceanic area up to 12 nautical miles (22.2 km) from the coast termed as territorial water and resources therein belong to the nation. International Resources: There are international institutions which regulate some resources. The oceanic resources beyond 200 nautical miles of the Exclusive Economic Zone belong to open ocean and no individual country can utilise these without the concurrence of international institutions.
(i) Which one of the following is not the community owned resource? (a) Burial grounds (b) Grazing grounds (c) Privately owned house (d) village ponds
(ii) Match the following
Choose the correct option:
(a) 1–(a), 2–(c), 3–(d), 4–(b) (b) 1–(c), 2–(d), 3–(a), 4–(b) (c) 1–(b), 2–(a), 3–(c), 4–(b) (d) 1–(d), 2–(c), 3–(a), 4–(b)
(iii) Which among the following is a type of resources classified on the basis of exhaustibility? (a) National and individual (b) Renewable and non-renewable (c) Biotic and abiotic (d) Potential and reserves
6. Read the source given below and answer the following questions:
Individual Resources: These are also owned privately by individuals. Many farmers own land which is allotted to them by government against the payment of revenue.
In villages there are people with land ownership but there are many who are landless. Urban people own plots, houses and other property. Plantation, pasture lands, ponds, water in wells etc. are some of the examples of resources ownership by individuals.
Community owned resources: There are resources which are accessible to all the members of the community. Village commons (grazing grounds, burial grounds, village ponds, etc.) public parks, picnic spots, playgrounds in urban areas are de facto accessible to all the people living there.
National Resources: Technically, all the resources belong to the nation. The country has legal powers to acquire even private property for public good. You might have seen roads, canals, railways being constructed on fields owned by some individuals. Urban Development Authorities get empowered by the government to acquire land.
All the minerals, water resources, forests, wildlife, land within the political boundaries and oceanic area up to 12 nautical miles (22.2 km) from the coast termed as territorial water and resources therein belong to the nation. International Resources: There are international institutions which regulate some resources. The oceanic resources beyond 200 nautical miles of the Exclusive Economic Zone belong to open ocean and no individual country can utilise these without the concurrence of international institutions.
(i) Which one of the following is an example of Biotic Resources? (a) Rock (b) Mountain (c) Mineral (d) Flora
(ii) The resources which are owned by the community are: (a) plantation (b) pasture land (c) ponds (d) all the above
(iii) The oceanic resources beyond 200 km of the Exclusive Economic Zone can be termed as which of the following types of resource? (a) Individual resources (b) Community owned resources (c) National resources (d) International resources
(iv) On the basis of ownership, plantations can be better considered as which of the following types of resources? (a) Individual resource (b) Community owned resource (c) National resource (d) International resource
Resources and Development
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Question. Which one of the following type of resource is iron ore? (a) Renewable (b) Biotic (c) Flow (d) Non-renewable [Answer : (d)
Question. Under which of the following type of resource can tidal energy be put? (a) Replenishable (b) Human-made (c) Abiotic (d) Non-renewable [Answer : (a)
Question. Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab? (a) Intensive cultivation (b) Deforestation (c) Over-irrigation (d) Overgrazing [Answer : (c)
Question. In which one of the following States is terrace cultivation practised? (a) Punjab (b) Plains of U.P. (c) Haryana (d) Uttaranchal [Answer : (d)
Question. In which of the following States is black soil found? (a) Jammu & Kashmir (b) Gujarat (c) Rajasthan (d) Jharkhand [Answer : (b)
Question. What percentage of our land should be under forest according to the National Forest Policy (1952)? (a) 33 (b) 22.5 (c) 31 (d) 30 [Answer : (a)
Question. Materials in the environment which have the potential to satisfy human needs but human beings do not have appropriate technology to access them are called: (a) Potential resource (b) Stock (c) Developed resource (d) Reserves [Answer : (b)
Question. India’s territorial water extends upto a distance of: (a) 12 km (b) 12 nautical miles (c) 200 nautical miles (d) 19.2 miles [Answer : (b)
Question. Resources that take long geological time for their formation are called: (a) Renewable resources (b) Reserve (c) Community resources (d) Non-renewable resources [Answer : (d)
Question. Land that is left uncultivated for more than five agricultural years is called: (a) Pasture land (b) Culturable waste land (c) Current fallow (d) Barren land [Answer : (b)
Question. Area sown more than once in an agricultural year plus net sown area is known as: (a) Net sown area (b) Forest cover (c) Waste land (d) Gross cropped area [Answer : (d)
Question. The total degraded land in our country is: (a) 133 million hectares (b) 130 million sq. km. (c) 140 million hectares (d) 130 million hectares [Answer : (d)
Question. In which of the following States mining has caused severe land degradation? (a) Gujarat (b) Jharkhand (c) Kerala (d) Uttarakhand [Answer : (b)
Question. The main cause of land degradation in Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh is: (a) Mining (b) Over irrigation (c) Deforestation (d) Over grazing [Answer : (b)
Question. Which is the most common soil of Northern India? (a) Black soil (b) Laterite soil (c) Alluvial soil (d) Red soil [Answer : (c)
Question. Red soil is mostly found in: (a) Parts of Jammu & Kashmir (b) Upper Ganga Plains (c) Eastern and Southern part of Deccan Plateau (d) None of the above [Answer : (c)
Question. Red soil is reddish in colour due to: (a) high clay content. (b) presence of kankar nodules in the subsoil. (c) diffusion of iron in igneous and metamorphic rocks. (d) high moisture content. [Answer : (c)
Question. Which of the following is not important for soil formation? (a) Relief (c) Parent rock (c) Climate (d) Duration of day [Answer : (d)
Question. Black soil is also called: (a) Bangar (b) Khadar (c) Regur (d) Humus [Answer : (c)
Question. Black soils are common in: (a) Deccan trap region (b) Kashmir Valley (c) Ganga Valley (d) Northern Plains [Answer : (a)
Question. Laterite soil is very useful for growing: (a) Rice, wheat and mustard (b) Tea, coffee and cashewnut (c) Pulses, sugarcane and resin (d) None of the above [Answer : (b)
Question. Black soil is deficient in (a) Calcium carbonate (b) Magnesium (c) Potash (d) Phosphoric contents [Answer : (d)
Question. Which of the following soils has self-aeration capacity? (a) Alluvial soil (b) Mountain soil (c) Black soil (d) Red soil [Answer : (c)
Question. Ploughing along the contour lines to decelerate the flow of water down the slopes is called: (a) Strip cropping (b) Sheet erosion (c) Contour ploughing (d) Terrace cultivation [Answer : (c)
Question. Which of the following is not a measure for soil conservation? (a) Strip cropping (b) Terrace cultivation (c) Shelter belts (d) Overdrawing of ground water [Answer : (d)
Assertion-Reason Questions DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable: (a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion. (b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion. (c) If assertion is true but reason is false. (d) If both assertion and reason are false.
1. Assertion. Alluvial soil is ideal for growth of paddy, wheat, cereal and pulse crops. Reason. Alluvial soil is well-known for its capacity to hold moisture. Answer : (c) Assertion is true but reason is false. Alluvial soil contains adequate proportion of potash, phosphoric acid and lime which are ideal for the growth of sugarcane, paddy, wheat and other cereal and pulse crops. It is porous and this property makes it ideal for the growth of wheat, paddy, cereal and pulse crops.
2. Assertion. The availability of resources is not the only necessary condition for the development of any region. Reason. Not only availability of resources but also corresponding change in technology is necessary for the development of any region. Answer : (a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion. Mere availability of resources in the absence of corresponding changes in technology and institutions may hinder development. Thus, both resources and advanced technologies contribute in development of a region.
3. Assertion. Resources are free gifts of nature. Reason. Resources like soil, air, water are easily available in nature. Answer : (d) Both assertion and reason are false. Resources are not free gifts of nature but are present due to interaction of human beings with nature, technology and institutions. They are a function ofhuman activities. They transform material available in our environment into resources.
4. Assertion. Land is a natural resource of utmost importance. Reason. Land can be used for various purposes. Answer : (a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion. Land is a natural resource of utmost importance as it supports human life and wild life, economic activities like agriculture, mining, transport and communication system.
5. Assertion. Resource planning is an easy process in India. Reason. Resource planning involves planning structure, identification and inventory of resource across the regions. Answer : (d) Both assertion and reason are false. Resource planning is not an easy but a very complex process as it involves surveying, mapping, quantitative and qualitative estimation and measurement of the resources.
6. Assertion. Soil is the most important renewable natural resource. Reason. Soil supports different types of living organisms on earth. Answer : (a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion. Soil is a living system. Soil helps to grow plants, supports natural vegetation and economic activities like agriculture. Its universal usage proves that it is the most important renewable natural resource.
7. Assertion. Processes of soil formation and erosion go simultaneously and create a balance between the two. Reason. The denudation of the soil cover and subsequent washing down is soil erosion. Answer : (c) Assertion is true but reason is false. Soil formation and erosion go simultaneously but this balance is disturbed due to human activities like deforestation, over-grazing, construction and mining. Natural forces like wind, glacier and water lead to soil erosion.
8. Assertion. Arid soil is unsuitable for cultivation. Reason. Arid soil is generally sandy in texture and saline in nature. It restricts the filtration of water. Answer : (c) Assertion is true but reason is false. Due to dry climate and high temperature, evaporation is faster and the soil lacks humus and moisture that is why it becomes unfit for cultivation.
9. Assertion. Control on mining activities does not control land degradation. Reason. In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, deforestation has occurred due to overgrazing, not mining. Answer : (d) Both assertion and reason are false. Activities of mining cause land degradation because mining sites are abandoned after excavation work. This results in over-burdening. Mining activities in the mentioned states has contributed to deforestation.
10. Assertion. Terrace cultivation does not restrict erosion. Reason. Running water cuts through the clayey soils and makes deep channels as gullies. This helps to cultivate crops. Answer : (d) Both assertion and reason are false. Terraces, out on slopes in forms of steps break up the force of the wind, thus preventing erosion. The gullies render cultivation in those lands impossible
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Give one example of the main commercial crop cultivable in laterite soil. Ans. Tea/coffee.
Question. Which type of soil is most suitable for growing the crop of cashew nut ? Ans . Soil for the growth of Cashew nuts: Red Laterite soil. Question. Classify resources on the basis of exhaustibility. Ans. On the basis of exhaustibility, resources can be classified as: 1. Renewable/ Non-exhaustible resources 2. Non-renewable/ Exhaustible resources. Question. Read the features of a soil and name the related soil: 1. This soil ranges from red to brown in colour. 2. It is generally sandy in texture and is saline. 3. It lacks humus and moisture. Ans . Arid soil is the soil that has all these features.
Question. “Degradation of land is a cause of worry.” Give one reason to support the statement. Ans. Degradation of land is a cause of worry because it can cause ecological imbalance.
Question. How is overgrazing responsible for land degradation in Gujarat? Ans . Overgrazing is responsible for land degradation in Gujarat because the extensive grazing for long and repeated periods leaves less time for propre vegetation to grow and thus the land and it is soil particles are left loose thereby degrading the overall quality of the land. Related Theory Overgrazing refers to what happens when livestock feeds on pasture to the point where there is no vegetation left.
Question. “Conservation of resource is vital for development.” Give one example regarding the statement. Ans. Conservation of resources: afforestation, water treatment.
Question. How are mining activities responsible for land degradation in Jharkhand? Ans. Mining activities are responsible for land degradation in Jharkhand because mining sites are abandoned after the excavation work is complete, leaving deep scars on the land. Related Theory To get rid of this land degradation, proper management of wastelands and control of mining activities needs to be initiated.
Question. Water is a compound of two inflammable gases, hydrogen and oxygen, which can be used as a rich source of energy. However, we do not have the required technical ‘know-how’ to use them for this purpose. What kind of resources can these gases be put in? Ans. The gases can be put in: The Stock Resources.
Question. Highlight the reason for land being known as the utmost important natural resource. Ans. Land is known as the utmost important natural resource because all economic activities are performed on land and it also supports natural vegetation and wildlife.
Question. Give one example of community owned resources. Ans. Village grazing grounds, public parks and picnic spots.
Question. This type of soil is typical of the Deccan trap (Basalt) region spread over northwest Deccan plateau and is made up of lava flows. They are well- known for their capacity to hold moisture. in addition, they are rich in soil nutrients, such as calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash and lime. they are made up of extremely fine i.e. clayey material. Read the details given in the source above and identify the kind of soil whose features have been mentioned. Ans. Black Soil Explanation: Black soil is also known as ‘Regur Soil’ or ‘Cotton Soil’ as it is good for the cultivation of cotton crop in the states of Maharashtra and Gujarat in India.
Question. Favourable conditions for wind energy exist in Western Rajasthan and Gujarat, but they have not been utilised and developed to the maximum. It falls in which category of resources? Ans. Wind energy received in Western Rajasthan exist as: Potential Resources.
Question. Which soil is most retentive of moisture? Ans . Black Soil retains the most moisture.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. ‘‘Resource planning is a complex process.’’ Support the statement with arguments. Ans. Resource planning is a complex process because: (1) Resource planning involves identifying resources which are available in different parts of the country. This is a time consuming process as it involves surveying and mapping various regions of the country. Then, the quality and quantity of the available minerals also needs to be estimated. (2) Resource planning is a complicated process as it involves the use of specialised technology, skill sets and requires setting up many institutions for the execution of resource development plans. (3) One of the daunting tasks is to match and align resource development plans with national development plans. Related Theory Resource planning is the judicious use of resources. Resource planning becomes more important in a country like India, where resources are not distributed properly.
Question. Describe any three main features of ‘alluvial soil’ found in India. Ans . Features of the alluvial soil are as: (1) It is formed by the deposition of the river load as it flows from its upper to its lower course. (2) It is light and porous, therefore easily tillable. (3) It is a fertile soil as it is rich in minerals, especially potash and lime. (4) It is suitable for the growth of a large variety of rabi and kharif crops. (5) Soils in the drier areas are more alkaline.
Question. Classify resources of the basis of their origin. Ans. Types of resources on the basis of origin are as follows: (1) Biotic Resources: These resources are obtained from biosphere and have life such as human beings, flora and fauna, fisheries, livestock etc. (2) Abiotic Resources: All those things which are composed of non-living things are called abiotic resources. For example, rocks and metals etc.
Question. Describe the different steps of resource planning. Ans. The different steps of resource planning are : (1) Doing proper and strategic surveying, mapping, qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of resources, leading to identification and inventory of resources across the regions of the country. (2) Resource development plans are implemented by evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional setup. (3) The overall development plans are then matched and coincided with development plans.
Question. Describe any three main features of ‘black soil’ found in India. Ans. Features of the black soil found in India are: (1) Black soil is black in colour and is also known as regur soil. (2) Black soil is ideal for growing cotton and is also known as black cotton soil. (3) It is fine textured and clayey in nature. (4) It is formed from weathered lava rocks , which also gives it its black colour. (5) It has high water retention power.
Question. Mention three problems that are associated with the indiscriminate use of resources. Ans. The following three problems are the result of indiscriminate use of resources: (1) Depletion of resources for satisfying the greed of few individuals. (2) Accumulation of resources in few hands, which in turn has divided the society into two segments-rich and poor. (3) Indiscriminate exploitation of resources has led to global ecological crises such as global warming, ozone layer depletion, environmental pollution and land degradation.
Question. ‘Sustainable Development is a crucial step for the development of a country’. Explain with suitable examples. Ans. Sustainable development is crucial for development of a country as it: (1) Promotes use of renewable resources like solar energy, tidal energy, etc (2) Puts a check on over usage of resources (3) Promotes protection and conservation of resources for future generation
Question. Describe the importance of judicious use of resources. OR Why should we use natural resources properly and judiciously? Explain your views. Ans. The importance of judicious use of resources are : (1) Multiple environmental and socioeconomic problems may arise if resources are used in an indiscriminate manner. (2) Most of the resources are non-renewable. The continuous usage of these resources may result in exhaustion of the resources. This may stunt development and growth of the people. (3) It will enhance the status of a person and would not impede development in general for future generations. They have to be used with caution.
49. What were the main features of the Earth Summit held at Rio de Janeiro in 1992? Ans. Three main features of the Earth Summit of 1992 held at Rio de Janeiro: (1) It was the first international Earth Summit in which more than 100 heads of states met. (2) The Summit was convened for addressing urgent problems of environmental protection and socio-economic development at the global level. (3) This Convention endorsed the global, Forest Principles and adopted Agenda 21 for achieving Sustainable Development in the 21st century.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. What is meant by conservation of resources? Mention any four steps taken at global level to conserve resources. Ans . Resources are vital for development and also to satisfy human needs and aspirations. But irrational consumption and over-utilisation of resources may lead to socio-economic and environmental problems. To overcome these problems, resource conservation at various levels is important. Even once Mahatma Gandhi raised his concern about resource conservation in these words, “There is enough for everybody’s need and not for any body’s greed. He was against mass production and wanted to replace it with the production by the masses. Steps taken at global level for the conservation of resources are as follows: (1) The club of Rome advocated resource conservation for the first time in a more systematic way in 1968. (2) In 1974, Gandhi ji’s philosophy was presented by Schumacher in his book ‘Small is Beautiful’. (3) In 1987, the Brundtland Commission Report introduced the concept of sustainable development as a means for resource conservation. (4) In 1992, the first Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro in Brazil made significant contribution towards the conservation of resources.
Question. What is land degradation? Suggest any four steps to control land degradation. Ans. Continuous use of land over a long period of time without taking appropriate measures to conserve and manage it, has resulted in land degradation. This has serious repercussions on society and the environment. Following steps can be taken to control the land degradation: (1) Afforestation and proper management of grazing can help to some extent (2) Planting of shelter belts of plants. (3) Control on over grazing, stabilization of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes (4) Proper management of waste lands, control of mining activities, proper discharge and disposal of industrial effluents and wastes after treatment can reduce land and water degradation in industrial and suburban areas.
Question. Why is the issue of sustainability important for development? Explain. Ans. Sustainable economic development means development that is viable keeping the requirements of both the present and future generations at par. It is a development that doesn’t compromise with the environment, provides equal opportunities to grow, utilises resources for both the present and upcoming generations. The issue of sustainability is important for development because without the same, man will use resources without care, destroying the environment, preventing all chances of survival and development in future. If not for sustainability, people would start exploiting finitely available resources and end up finishing them soon, thus destroying Earth’s balance. Global warming, ozone layer depletion and environmental pollution have been caused due to this ignorance. Sustainability is vital for maintaining global peace and quality of life. So, the need of the hour is to use resources wisely so, as to sustain our planet Earth.
Question. What is resource planning? Why is resource planning essential? Explain. Ans. Resource planning is a technique of proper utilisation of resources which aimed at sustainable development. Resource planning is essential because of the following reasons: (1) Most of resources available on earth are limited in supply. (2) The resources available to us are distributed unevenly all over the country. (3) Overutilization of the resources may lead to environmental pollution and depletion of resources as well. Therefore, planning of resources can reduce pollution and overutilization of resources as well. (4) Planning of resources can lead to have a balanced development at national, state, regional and local levels.
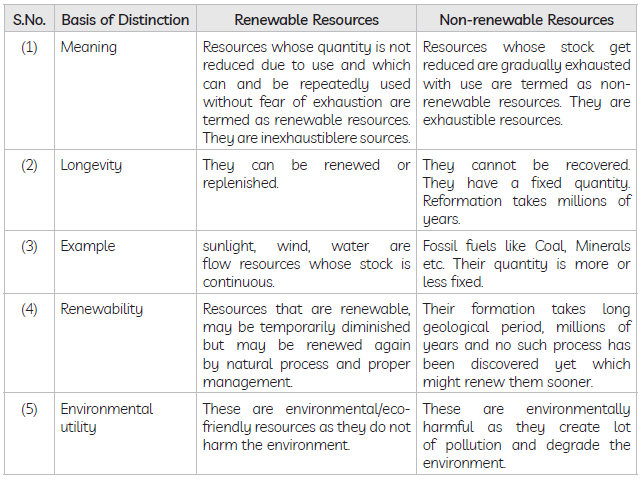
Question . Distinguish between renewable and non-renewable resources. Give examples.
Related Posts
Database management system class 10 information technology important questions.

Human Eyes and Colourful World Class 10 Science Important Questions
Popular struggles and movements class 10 social science important questions.

- Lakhmir Singh
Case Study Questions Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 Resources and Development
Case study questions class 10 social science geography chapter 3 resources and development.
CBSE Class 10 Case Study Questions Social Science Geography Resources and Development. Important Case Study Questions for Class 10 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Resources and Development.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
Cast Study 1
Resources and development are interlinked concepts and serves as a important pillars of a country growth and development. As development is a multidimensional concept it relies heavily on sustainable use of available resources. Either it be natural resource like water ,minerals , forest and so on or be human resource like skilled labour ,education , healthcare the complex interaction between resources and development is a dynamic process that requires careful planning and management.
Natural resources serve as bedrock for country economic development as they provide raw material needed for manufacturing, energy and agriculture.
Human resource perhaps is the most critical part of development as skilled, educated, and healthy individual are more innovative, talented and productive.
Q1) Define resource and criteria’s to be called as a resource Mark 2
Answer Anything that is used to satisfy our needs is called as a resource.
Resource should be
Technologically assessable Economically affordable Culturally acceptable
Q2) Give an account of classification of natural resource with example. Mark1
Answer Natural resource can be classified in two ways
Q3) How resource and development are interlinked? Mark 1
Answer Human beings interact with nature through technology and create institutions to accelerate their economic development
Cast Study 2
Sustainable development is a global imperative, seeking to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It encompasses economic, social, and environmental dimensions, recognizing their interdependence. In pursuit of sustainable development, societies are adopting eco-friendly technologies, promoting renewable energy, and reducing waste. Social equity and inclusion are also vital aspects, ensuring that the benefits of development reach all strata of society. Sustainable development necessitates responsible consumption and production, conservation of biodiversity, and addressing climate change. As we grapple with global challenges, it is crucial to remember that a sustainable future is not an option but an imperative. It requires collective action, innovative solutions, and a commitment to leaving behind a world that is both prosperous and habitable for future generations.
Q1) What are the various problem arises due to irrational use of resources? 2
Answer Following problem arises due to irrational use of resources
Depletion of resources for satisfying the greed of a few individuals
Accumulation of resources in few hands, which, in turn, divided the society into two segments i.e. haves and have nots or rich and poor.
Indiscriminate exploitation of resources has led to global ecological crises such as, global warming, ozone layer depletion, environmental pollution and land degradation
Q2) What is Agenda 21 in sustainable development? 2
Answer Agenda 21 is to agenda to combat environmental damage, poverty, disease through global co-operation on common interests, mutual needs and shared responsibilities adopted in United national conference on Environment and development held in 1992 in Brazil.
Cast Study 3
Jharkhand is often cited as a victim of the “resource curse.” The state’s heavy reliance on mining and mineral extraction has led to environmental degradation, displacement of indigenous communities, and limited diversification of the economy. The revenue generated from mineral resources is often not reinvested effectively for the development of the state. While mining activities generate significant revenue, these benefits are not equitably distributed among the population. A substantial portion of the population, especially in rural areas, remains marginalized and lacks access to basic amenities, education, and healthcare
Large-scale mining projects often require land acquisition, leading to the displacement of local communities. This disruption can have long-lasting social and economic consequences, as many displaced individuals struggle to find alternative livelihoods. Improving governance and transparency is crucial to ensuring that mineral wealth benefits the broader population.
Q1) Why resource planning is important for India? Mark 1
Answer An equitable distribution of resources is essential for a sustained quality of life and global peace. If the present trend of resource depletion by a few individuals and countries continues, the future of our planet is in danger..
Q2) What are the steps involve in resource planning? Mark 1
Answer Following steps are involve in resource planning
Step 1 Identification and mapping of resource across the country
Step 2 Planning structure of skills , institution etc
Step 3 Matching resource development plans with national economic plans
Q3) “There is enough for everybody need but not for anybody greed”. Explain Mark 2
Answer Gandhi believed that the greedy and selfish individuals and exploitative nature of modern technology are the root cause for resource depletion at the global level. He was against mass production and wanted to replace it with the production by the masses.
Cast Study 4
Land is a critical and finite resource in India, serving as the foundation for various economic, social, and environmental activities. India’s vast and diverse landscape accommodates agriculture, industry, urbanization, infrastructure, and ecosystems. Agriculture remains the largest land-based sector, providing livelihoods for a significant portion of the population. However, the increasing demands for urbanization, industrialization, and infrastructure development have led to land use changes and pressures on agricultural land. Land resources are vital for food security, housing, and economic growth, but their sustainable management is a significant challenge. Issues such as land fragmentation, land degradation, and land disputes persist. Land reform measures aim to address issues of land ownership and equitable distribution. Additionally, environmental conservation efforts strive to protect ecosystems and biodiversity. Effective land-use planning, land-use policies, and land management practices are essential to ensure that India’s land resources are utilized sustainably for the benefit of current and future generations.
Q1) What are the factors that determines land use pattern in India? 1
Answer Land use pattern in India is determined by both physical and human factors. Physical Factor involves topography, climate, soil types while Human factor involves population density, technological capability and culture and traditions etc
Q2) Suggest some measure to solve the problem of land degradation? 2
Answer Afforestation and proper management of grazing ,planting of shelter belts of plants, stabilization of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes , proper management of waste lands, control of mining activities, proper discharge and disposal of industrial effluents and wastes after treatment can reduce land and water degradation in industrial and suburban areas can help in stopping land degradation.
Q3) Give an account of important relief features in India? 1
Answer India have variety of relief features, namely; mountains, plateaus, plains
and islands. About 43 % of the land area is plain. Mountains account for 30 % of the total surface area of the country About 27 % of the area of the country is the plateau region.
Also See: Water Resources Case Study Question and Answer
Cast Study 5
India’s agricultural success story is closely intertwined with its rich and diverse soil resources. With over 120 soil types across the country, India’s soil is as varied as its culture. Fertile alluvial soils in the Gangetic plains support the production of rice and wheat, while arid regions rely on hardy desert soils. However, soil degradation due to unsustainable agricultural practices, erosion, and urbanization poses a growing threat. To ensure food security and sustainable agriculture, India must prioritize soil conservation, nutrient management, and organic farming. The health of the nation’s soil is the bedrock of its agricultural future.
Q1) What do you mean by Bangar and khadar with reference to alluvial soil? Mark 1
Q2) Define soil erosion and factors associated with soil erosion? Mark 1
Answer The denudation of the soil cover and subsequent washing down is described as soil erosion. Factors responsible for soil erosion are deforestation, over-grazing, construction and mining etc., while natural forces like wind, glacier and water also play a key role.
Q3) How farming can also leads to soil erosion and write about methods to avoid it? Mark 2
Answer Soil erosion is also caused due to defective methods of farming. Ploughing in a wrong way leads to soil erosion. Steps can be cut out on the slopes making terraces.Terrace cultivation restricts erosion
Cast Study 7
India has been under colonial rule for several years. The colonising countries were able to use their technological advancements to establish their supremacy over other countries. Resource and raw materials were the main cause of colonial rule. They exploit the natural resources of the region for their own benefits. Because of this, development in the post-independence period does not involve only availability of resources but also technology, quality of human resources and historical experiences of people.
Based on the above paragraph answer the following questions-
1.) Find the incorrect pair of natural resources found in India
a.) Jharkhand – coal deposits
b.) Arunachal Pradesh- water resources
c.) Rajasthan- hydropower
d.) Chhattisgarh – mineral deposits
2.) Which one of the following Is not the correct reason for the colonial rule in India
a.) Britishers colonised India for exploiting its natural resources and developing their native country.
b.) Britishers colonised India for using its natural resources and developing it.
c.) India was devoid of any technological advancement of the contemporary period.
d.) India had a poor governance system based on traditional laws.
3.) What are the major changes which have been introduced in the post independence period for resource management in India. Elaborate your answer with examples.
The Government of India took up responsibility of resource management in the post independence period. There is a focus upon the equitable development and resource planning for overall development of the country. Some of the important to steps taken by the government are-
1.) Balanced resource planning was undertaken at the Central, state, district, and regional level.
2.) Quantitative and qualitative evaluation of the resources of the country to avoid its over exploitation. Example- mapping, surveying etc.
3.) Planned development through five year plans which give a certain perspective and direction to the development efforts of the government.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Worksheet for class 2 maths, counting by 2’s worksheet for class 2 as per nep pattern, the first war of independence 1857 class 10 icse complete notes pdf, west bengal board class 9 bengali ei tar porichay solution.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 Resources and Development
- Last modified on: 11 months ago
- Reading Time: 8 Minutes
Here we are providing case study questions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 Resources and Development.
Case Study Question 1:
Resources are vital for any developmental activity. But irrational consumption and over-utilisation of resources may lead to socioeconomic and environmental problems. To overcome these problems, resource conservation at various levels is important. This had been the main concern of the leaders and thinkers in the past. For example, Gandhiji was very apt in voicing his concern about resource conservation in these words: “There is enough for everybody’s need and not for any body’s greed.” He placed the greedy and selfish individuals and exploitative nature of modern technology as the root cause for resource depletion at the global level. He was against mass production and wanted to replace it with the production by the masses.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate options:
(i) Resources are vital for (a) Developmental activity (b) Commercial activity (c) Social activity (d) Environmental activity
(ii) Irrational consumption and over-utilisation of resources may lead to (a) Social Problems (b) Commercial Problems (c) Environmental Problems (d) All of the above
(iii) “There is enough for everybody’s need and not for any body’s greed.” Who said this? (a) Jawaharlal Nehru (b) Mahatma Gandhi (c) Rajendra Prasad (d) Vinoba Bhave
(iv) What had been the main concern of the leaders and thinkers in the past? (a) Ocean conservation (b) Soil conservation (c) Biodiversity conservation (d) Resource conservation
Related Posts
Tips to prepare for case study questions for class 10 social science.
Preparing for case study and passage-based questions in class 10 social science can be challenging, but it is important to remember that with the right approach, you can effectively tackle these types of questions. Here are some steps you can take to prepare for case study questions for class 10 social science:
- Understand the format of case study questions: Case study questions for class 10 social science usually require you to read a scenario or a passage and answer a set of questions based on it. These questions can be based on various topics like history, geography, economics, or civics.
- Read and analyze the case study or passage carefully: The first step in answering case study questions is to read the scenario or passage carefully. Try to identify the main idea or theme of the passage and note down any important details that you think are relevant. Pay attention to any maps, graphs, or charts that are included as they can be helpful in answering the questions.
- Identify the type of questions being asked: After reading the case study or passage, you should analyze the questions being asked. Try to identify the type of question, whether it is a factual question or an analytical question. Factual questions require you to provide specific details from the passage, while analytical questions require you to use your critical thinking skills to analyze the information presented in the passage.
- Use your textbook and notes: To prepare for case study questions for class 10 social science, it is important to have a thorough understanding of the topics covered in your textbook. Go through your notes and textbook to revise the relevant topics and concepts. This will help you to answer the questions more accurately.
- Practice sample questions: One of the best ways to prepare for case study questions is to practice answering sample questions. Try to find sample questions online or in your textbook and practice answering them. This will help you to get comfortable with the format of the questions and improve your speed and accuracy.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- Bihar Board
SRM University
Ap inter results.
- AP Board Results 2024
- UP Board Result 2024
- CBSE Board Result 2024
- MP Board Result 2024
- Rajasthan Board Result 2024
- Karnataka Board Result
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 10
Resources and Development Class 10 Notes: CBSE 10th Social Science Chapter 1 Geography, Download PDF
Cbse class 10 resources and development notes: find here the cbse 10th sst resources and development chapter notes based on the latest 10th class social science 2023-24 rationalised syllabus. you can also download these notes in pdf..

- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Syllabus 2023-24
Resources and Development Class 10 Notes
Classification of resources, development of resources.
People have been using resources without thinking, and that has caused some big problems.
First, some people have used up a lot of resources just because they want more and more. This is bad because it means there's not enough left for everyone else.
Second, a few people have gotten most of the resources, which has split society into two groups: the rich and the poor. This is unfair and creates a lot of inequality.
Third, using resources like this has caused global problems for the environment. Things like global warming, the hole in the ozone layer, pollution, and damage to land have happened because of it.
- Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit, 1992
Resource Planning
Resource planning in india.
- Identifying and assessing the resources available in different regions of the country. This involves conducting surveys, creating maps, and estimating the quality and quantity of resources.
- Establishing a planning framework with the necessary technology, skills, and institutions to implement resource development plans effectively.
- Aligning resource development plans with the overall national development plans to ensure coherence and synergy.
For resources to contribute to development, it is crucial to accompany them with appropriate technological advancements and institutional changes. Since the First Five Year Plan introduced after Independence, India has been actively working towards achieving the objectives of resource planning.
Land Resources
Land is a vital natural resource that plays a crucial role in supporting various aspects of life and economic activities. In India, the land encompasses diverse relief features such as mountains, plateaus, plains, and islands. It supports natural vegetation, wildlife, human settlements, transportation, and communication systems.
- Plains: 43%
- Mountains: 30%
- Plateaus: 27%
Land Utilisation
Land resources are used for the following purposes:
2 Land not available for cultivation
a) Barren and wasteland b) Land put to non-agricultural uses
3 Fallow lands
4 Other uncultivated lands (excluding fallow land)
Land Use Pattern in India
- Physical factors: such as topography, climate, soil types
- Human factors: such as population density, technological capability and culture and traditions etc.
Land Degradation and Conservation Measures
Land degradation has been largely influenced by human activities such as deforestation, overgrazing, and mining, which leave lasting scars on the land. Industrial waste, particularly in the form of effluents, has also emerged as a major cause of land and water pollution in various regions of the country.
- Afforestation and proper management of grazing.
- Planting of shelterbelts of plants.
- Stabilisation of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes.
- Proper management of wastelands.
- Control of mining activities.
- Proper discharge and disposal of industrial effluents and wastes after treatment.
Soil as a Resource
- It takes millions of years to form soil up to a few cms in depth. Natural factors such as changes in temperature, actions of running water, wind and glaciers, activities of decomposers, etc., contribute to the formation of soil.
- Parent rock or bedrock, climate, vegetation and other forms of life and time are important factors in the formation of soil.
- Chemical and organic changes in the soil play an important role.
- Soil also has organic (humus) and inorganic materials.
Classification of Soils
The soils in India are classified into various types based on factors such as soil formation processes, color, thickness, texture, age, as well as chemical and physical properties.
- - Alluvial soil covers the entire northern plains of India.
- - It is formed by the deposition of sediment carried by the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra rivers.
- - Alluvial soil is also found in regions like Rajasthan, Gujarat, and the eastern coastal plains, particularly in the deltas of the Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, and Kaveri rivers.
- - The composition of alluvial soil includes sand, silt, and clay, with the size of particles increasing as we move towards the river valleys.
- - Alluvial soils are classified into Old Alluvial (Bangar) and New Alluvial (Khadar) based on age.
- - Bangar soil has a higher concentration of kanker nodules, while Khadar soil is finer and more fertile.
- - Alluvial soils are highly fertile and contain essential nutrients like potash, phosphoric acid, and lime, making them suitable for growing crops such as sugarcane, paddy, wheat, and various cereals and pulses..
- Black soil, also known as regur soil, is characterized by its black color and is formed due to specific climatic conditions and parent rock material.
- This soil type is highly suitable for cultivating cotton and is commonly referred to as black cotton soil.
- It is primarily found in the Deccan trap (Basalt) region, which spans across the northwest Deccan plateau and is composed of lava flows.
- The distribution of black soil covers plateaus in Maharashtra, Saurashtra, Malwa, Madhya Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh, extending southeast along the Godavari and Krishna valleys.
- Black soils are predominantly composed of fine clayey material, known for their excellent moisture-retention capacity.
- The soil is rich in nutrients such as calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash, and lime.
- When wet, black soil becomes sticky and challenging to work with unless it is tilled immediately after the first rainfall or during the pre-monsoon season.
- This soil type forms on crystalline igneous rocks in regions with low rainfall, specifically in the eastern and southern areas of the Deccan plateau.
- The reddish color of this soil is a result of iron diffusion in crystalline and metamorphic rocks, while in its hydrated form, it appears yellow.
- It is predominantly found in certain regions, including parts of Odisha, Chhattisgarh, the southern portions of the middle Ganga plain, and along the Piedmont zone of the Western Ghats.
- Laterite soil is formed in tropical and subtropical climates characterized by alternating wet and dry seasons.
- It is the product of extensive leaching caused by heavy rainfall.
- Lateritic soils are generally acidic (pH<6.0) and often lack essential nutrients for plant growth.
- This type of soil is primarily found in southern states of India, the Western Ghats region of Maharashtra, Odisha, certain parts of West Bengal, and the northeastern regions.
- While laterite soil supports deciduous and evergreen forests, it is typically low in humus content.
- It is highly suitable for cultivating tea and coffee crops.
- Arid soils exhibit a colour spectrum ranging from red to brown.
- These soils are predominantly sandy in texture and have a high saline content. In certain regions, the salt content is so significant that common salt is obtained through water evaporation.
- Arid soils are deficient in humus and moisture.
- The lower layers of the soil contain Kankar, a calcareous deposit resulting from increasing calcium content downward. The presence of Kankar restricts water infiltration in the lower horizons.
- These soils are primarily located in hilly and mountainous regions.
- On the valley sides, the soil texture is loamy and silty, while it becomes coarse-grained on the upper slopes.
- In the snow-covered areas of the Himalayas, these soils undergo denudation and tend to be acidic with low humus content. However, on river terraces and alluvial fans, the soil is fertile.
Soil Erosion and Soil Conservation
Different ways for soil conservation.
- Contour ploughing is a technique where ploughing is done along the contour lines, which helps slow down the flow of water down slopes, reducing erosion.
- Terrace cultivation is another method used to control erosion, commonly practiced in the Western and Central Himalayas.
- Strip cropping involves dividing a large field into strips and leaving strips of grass to grow between the crops. This helps break up the force of the wind, mitigating erosion.
- Shelter belts are created by planting lines of trees, which provide protection and help stabilize sand dunes and desert areas, particularly in western India. These rows of trees are known as shelter belts.
CBSE Class 10 Syllabus (All Subject)
CBSE Resources and Development Class 10 Notes PDF Download
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- AP Board Result 2024
- AP Intermediate Result 2024
- AP Inter Result 2024 Live
- resultsbie.ap.gov.in Results 2024
- AP Inter Result 2024 Link
- Manabadi Inter Results 2024
- Manabadi AP Inter Result 2024
- Manabadi Inter Results 2024 AP
- AP Inter Results 2024 with Jagran Josh
- AP Inter Toppers List 2024
Latest Education News
AP Inter Results 2024 Manabadi Live: BIEAP Intermediate (1st, 2nd Year) Results Link at resultsbie.ap.gov.in; How to Check by Hall Ticket Number
Manabadi Inter Results 2024 AP: When, Where, and How to Check BIEAP 1st and 2nd Year Result Online
Manabadi AP Inter Results 2024 Today: Check BIEAP 1st, 2nd Year Result Link Details Here
AP Inter Results 2024 Link: List of Official Sites to Check BIEAP 1st, 2nd Year Result Online and Download Hall Ticket
AP Inter Results 2024 Manabadi Time Today: BIEAP 1st, 2nd Year Result at 11 AM, Stay Updated
AP Inter Toppers List 2024: Check BIEAP Intermediate 1st, 2nd Year Toppers Name, Pass Percentage, School and District-wise Details
AP Inter Results 2024 BIEAP: How to Check Manabadi 12th Results Online via SMS and Digilocker App
Inter Results 2024 AP Link: How to Check Manabadi 1st, 2nd Year Results Online via Official Website
AP Inter Results 2024 with Jagran Josh: Check BIEAP Intermediate 1st and 2nd Year Result
OSSC CHSL CV Admit Card 2024 Out at ossc.gov.in: Here's Download Link
resultsbie.ap.gov.in Results 2024 Link: Check How to Download the AP Inter 1st and 2nd Year Marks Memo?
CBSE Class 9 English Syllabus 2024-25: Download English Language and Literature Syllabus in PDF
AP Intermediate Results 2024 Manabadi: आंध्र प्रदेश इंटर 1st और 2nd ईयर का रिजल्ट ऑफिशियल वेबसाइट पर कैसे चेक करें?
AP Inter Results 2024: Check AP Intermediate Result Link at resultsbie.ap.gov.in and Jagran Josh
AP Inter 2nd Year VOC Results 2024: Check AP 12th Second Year Result Link at resultsbie.ap.gov.in and Jagran Josh
AP Board Results 2024: Check AP SSC, Intermediate Result Link at resultsbie.ap.gov.in and Jagran Josh
AP Inter 1st Year Results 2024: Check AP Intermediate First Year Result Link at resultsbie.ap.gov.in and Jagran Josh
AP Inter 1st Year VOC Results 2024: Check AP 12th First Year Result Link at resultsbie.ap.gov.in and Jagran Josh
AAI JE Recruitment 2024: Online application begins for 490 Junior Executive Posts, Check steps to apply
LIVE UP Board Result 2024: अप्रैल में upmsp.edu.in पर जारी होगा यूपी बोर्ड 10वीं 12वीं के नतीजे, जानें कितने नंबर वाले होंगे पास
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Resources and Development Class 10 Notes CBSE Geography Chapter 1 (Free PDF Download)
- Revision Notes

Exam-Focused Revision Notes for CBSE Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 - Resources and Development
CBSE Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1 in Geography is about Resources and Development. The Resources and Development Class 10 is one of the important chapters in Geography for Class 10 students.
CBSE revision Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 - Resources and Development provides a comprehensive overview of the chapter, including the classification of resources on the basis of origin, ownership, exhaustibility, and the status of development. It also discusses how essential resources are in our day-to-day lives and what role they play in development. The notes cover important topics such as land resources, the development of resources, and resource planning in India. Students can also find information on the types of resources and their classification. Let’s get started with the CBSE Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 1
Overview of Deleted Syllabus for CBSE Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India Chapter 1 Resources and Development

Related Chapters
An Overview on Resources and Development CBSE Class 10 Social Science
CBSE revision Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 - Resources and Development cover important topics such as the classification of resources, land resources, the development of resources, and resource planning in India. These notes are available on our Vedantu website. The notes provide a comprehensive overview of the chapter and are prepared by expert teachers. Students can also find information on the types of resources and their classification.
Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 - Resources and Development introduces students to the concept of resources and their classification. Everything in our environment that we can use to satisfy our needs and is technologically accessible, economically affordable and acceptable culturally is termed as ‘Resource’. Humans are dominant components of resources. They convert materials available in the environment into resources and use them. Students can refer to various resources such as NCERT books, CBSE revision notes, and video lectures to understand the chapter better. These resources are available on the Vedantu website and our YouTube Channel.
Types of Resources
On the Basis of Origin
Biotic- Obtained from the biospheres such as flora, fauna, fisheries etc.
Abiotic - Obtained from non-living resources such as rocks and metals.
On the Basis of Exhaustibility
Renewable
These resources are the ones that can replenish once they are exhausted.
Example: solar energy, wind energy
Non-Renewable
Once exhausted these resources cannot replenish themselves again. If we consume them completely without planning we can lose them forever.
Example: Fossil fuels and minerals
On the basis of ownership
Owned privately by individuals
Example: Plantation, pasture lands
All the members of the community can access these resources
Example: Grazing grounds, burial grounds
National
All the resources belong to the nation and the country has legal autonomy over them.
Private property can be acquired by the government for the public good.
Example: Roads, railways etc.
International
The oceanic resources beyond 200 nautical miles of the Exclusive Economic Zone belong to the open ocean.
No individual country is allowed to utilize these without prior permission from international organizations.
On the basis of the status of development
Resources that are found in a region, but have not been utilized to their full potential are termed as potential resources.
Example: Rajasthan and Gujarat have enormous potential for the development of wind and solar energy, but so far these resources have not been utilized properly.
Developed
Resources whose quality and quantity have been determined for utilization are termed as developed resources.
The extent to which these resources are utilized depends on technology and the level of their feasibility.
Hydrogen can be used as a rich source of energy. But we do not have advanced technology to use it.
Stock
Resources that are available in the nature to be used but human beings don’t have the right equipment and technology to utilize these resources.
Example: Water can be broken down to extract hydrogen and oxygen. Hydrogen is a great source of energy but we don’t know how to carry out this process on a large scale.
Human civilization has proper technology to utilize these resources but a further development of technology is required to exploit these resources to their fullest potential.
Example: Hydropower is being generated from water and hence only put out for limited use.
Development of Resources
Human beings have excessively exploited resources which have led to the following problems:
Depletion of resources for satisfying the greedy of a few individuals.
Accumulation of resources in few hands which has created two class of people, i.e. haves and have nots or rich and poor.
Indiscriminate exploitation of resources that led to the global ecological crises such as, global warming, ozone layer depletion, environmental pollution and land degradation
Sustainable Development
Development that takes place without over-exploiting the nature is termed as sustainable development.
It focuses on the idea that ‘the development in the present should not compromise with the needs of the future generations.’
Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit, held in June 1992 was a global submit where more than 100 heads of states met in Rio de Janeiro in Brazil, for the first International Earth Summit.
The Summit was convened for addressing urgent problems of environmental protection and socio-economic development at the global level.
A declaration was signed by the global leaders on Global Climatic Change and Biological Diversity.
The Rio Convention endorsed the global Forest Principles and adopted the Agenda 21 for achieving Sustainable Development in the 21st century.
It aimed at achieving global sustainable development.
It is an agenda that aims at combating environmental damage, poverty, disease through global co-operation on common interests, mutual needs and shared responsibilities.
One major objective of the Agenda 21 includes every local government should draw its own local Agenda 21.
Resource Planning in India
Planning is the widely accepted strategy for judicious use of resources as there are certain areas that have sufficient resources while others don't have enough.
For example, the states of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh that are rich in minerals and coal deposits. Arunachal Pradesh has an abundance of water resources but lacks in infrastructural development.
The state of Rajasthan is very well endowed with solar and wind energy but there is lack in water resources.
The cold desert of Ladakh is isolated from the rest of the country. As it has an extraordinarily rich cultural heritage but it is deficient in water, infrastructure, and some vital minerals.
Resource Planning is a Complex Process That Involves:
(i) Identification and inventory of resources across the regions of the country. This involves surveying, mapping and qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of the resources.
(ii) Evolve a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional set up for implementing resource development plans.
(iii) Matching the resource development plans along with overall national development plans.
Land Resources
They form a major share of resources that mankind has.
Land Utilization
Land resources are used for the following purposes:
2. Land not available for cultivation
(a) Barren and waste land
(b) Land put to non-agricultural uses, e.g. buildings, roads, factories, etc.
3. Other uncultivated land (excluding fallow land)
(a) Permanent pastures and grazing land,
(b) Land under miscellaneous tree crops groves (that are not included in the net sown area),
(c) Culturable waste land ( That are left uncultivated for more than 5 agricultural years).
4. Fallow lands
(a) Current fallow-(they are left without cultivation for one or less than one agricultural year),
(b) Other than current fallow-(they are left uncultivated for the past 1 to 5 agricultural years).
5. Net sown area: Area that are sowed more than once in an agricultural year plus net sown area is known as gross cropped area.
Land Use Pattern in India
The use of land is determined by using both physical factors such as topography, climate, soil types as well as human factors such as population density, technological capability and culture and traditions
The land under permanent pasture has also decreased.
The pattern of net sown area varies greatly from one state to another. It is over 80 per cent of the total area in Punjab and Haryana and less than 10 per cent in Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Manipur and Andaman Nicobar Islands.
Forest area in the country is far lower than the desired 33 per cent of geographical area, which was stated in the National Forest Policy (1952).
A part of the land is termed as waste land and land put to other non-agricultural uses.
Waste land includes rocky, arid and desert areas. Land put to other non-agricultural uses includes settlements, roads, railways, industry etc.
Land Degradation and Conservation Patterns
Human activities like deforestation, overgrazing, mining and quarrying, excessively for a very long period of time over an area can lead to land degradation.
Mining sites are abandoned after excavation work is complete and that leaves deep scars and traces of over-burdening.
In states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha deforestation happens due to mining have caused severe land degradation.
In other states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra overgrazing is a major contributor to land degradation.
In the states of Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh, over irrigation is responsible for land degradation which occurs due to water logging that lead to an increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil.
The mineral processing like grinding of limestone for cement industry and calcite and soapstone for ceramic industry generate huge quantity of dust in the atmosphere. It retards the process of infiltration of water into the soil after it settles down on the land.
Conservation
Afforestation or planting of more trees and proper management of grazing can help to control land degradation.
Planting of shelter belts of plants, stabilisation of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes are some of the methods to check land degradation in arid areas.
Proper management of waste lands, control of mining activities, proper discharge and disposal of industrial effluents and wastes after treatment can reduce land and water degradation in industrial and suburban areas.
Types of Soil
Alluvial soils.
Himalayan river system- the Indus, Brahmaputra and Ganga carry sediments with them and form the regions of alluvial deposits. The entire northern plains are made of alluvial soil.
These soils also extend in some part of Rajasthan and Gujarat through a narrow corridor.
Alluvial soil is also found in the eastern coastal plains particularly in the deltas of the Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna and the Kaveri rivers.
This type of soil has various proportions of sand, silt and clay.
According to their age alluvial soils can be classified as old alluvial (Bangar) and new alluvial (Khadar).
The bangar soil has higher concentration of kanker nodules and has more fine particles and is more fertile than the bangar.
Alluvial soil is highly fertile and has adequate proportions of potash, phosphoric acid and lime which are ideal for the growth of sugarcane, paddy, wheat and other cereal and pulse crops.
It is black in colour and is also known as regur soil.
Black soil is ideal for growing cotton and is also known as black cotton soil and is made up of lava flows.
This type of soil is found in the Deccan trap (Basalt) region and it is spread over the northwest Deccan plateau.
They mostly cover the plateaus of Maharashtra, Saurashtra, Malwa, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh and extend in the south east direction along the Godavari and the Krishna valleys.
They are made up of clayey material. They retain moisture and also rich in soil nutrients, such as calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash and lime
They develop deep cracks during hot weather, which promotes aeration of the soil but do get sticky when wet and difficult to work on.
Red and Yellow Soils
Red soil develops on crystalline igneous rocks in areas of low rainfall in the eastern and southern parts of the Deccan plateau.
Yellow and red soils are also found in some parts of Odisha, Chhattisgarh, southern parts of the middle Ganga plain and along the piedmont zone of the Western Ghats.
Laterite Soil
The laterite soil develops under the tropical and subtropical climates with an alternate wet and dry season.
Lateritic soils are acidic (pH<6.0), and deficient in plant nutrients.
They occur in southern states, Western Ghats region of Maharashtra, Odisha, some parts of West Bengal and North-east regions
Arid soils range from red to brown in colour.
Are sandy in texture and saline in nature.
The soil lacks humus and moisture.
The lower horizons of the soil are occupied by Kankar because of the increasing calcium content downwards and it restricts infiltration.
Forest Soils
The soils texture varies according to the mountain environment where they are formed.
They are loamy and silty in valley sides and coarse grained in the upper slopes.
Soil Erosion and Soil Conservation
The denudation of the soil cover and subsequent washing down is described as soil erosion.
Soil formation and soil erosion go hand in hand but if it goes beyond control then can lead to disastrous outcomes.
Activities like deforestation, overgrazing, construction and mining etc., and natural forces like wind, glaciers and water lead to soil erosion cause a lot of soil erosion.
The running water cuts through the clayey soils and makes deep channels as gullies and makes land unfit for cultivation and is known as bad land.
In the Chambal basin, such lands are called ravines.
Sometimes water flows as a sheet over large areas down the slope. In such cases, the top soil is washed away. This is known as sheet erosion.
Ploughing along the contour lines can decelerate the flow of water down the slopes. This is known as contour ploughing.
Steps can be cut out on the slopes making terraces. Terrace cultivation restricts erosion. In this steps are cut down to create terraces which help to retain water.
Large fields can be divided into strips. Strips of grass are left to grow between the crops. This breaks up the force of the wind. This method is known as strip cropping.
Planting lines of trees to create shelter also works in a similar way. Rows of such trees are called shelter belts. These shelter belts have contributed significantly to the stabilisation of sand dunes and in stabilising the desert in western India.
Important Questions and Answer:
1. Explain briefly about the ‘Agenda 21’?
Ans: Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit, held in June 1992 was a global submit where more than 100 heads of states met in Rio de Janeiro in Brazil, for the first International Earth Summit. The Summit was convened for addressing urgent problems of environmental protection and socioeconomic development at the global level. A declaration was signed by the global leaders on Global Climatic Change and Biological Diversity. The Rio Convention endorsed the global Forest Principles and adopted Agenda 21 for achieving Sustainable Development in the 21st century. It is aimed at achieving global sustainable development.
It is an agenda that aims at combating environmental damage, poverty, disease through global co-operation on common interests, mutual needs and shared responsibilities. One major objective of the Agenda 21 is that every local government should draw its own local Agenda 21.
2. What are the different types of soil erosion?
Ans: The following are different types of soil erosion:
Gully Erosion: The running water cuts through the clayey soils and makes deep channels as gullies and makes land unfit for cultivation and is known as bad land.
Sheet Erosion: Sometimes water flows as a sheet over large areas down a slope. In such cases, the top soil is washed away. This is known as sheet erosion.
Wind Erosion: When the top fertile layer of soil gets eroded by the wind then it is called as wind erosion. Planting trees can help to reduce soil erosion by wind.
3. Mention the factors that determine land use in India.
Ans: The use of land is determined both by physical factors such as topography, climate, soil types as well as human factors such as population density, technological capability and culture and traditions. The land under permanent pasture has also decreased.
Forest area in the country is far lower than the desired 33 per cent of geographical area, which was stated in the National Forest Policy (1952). A part of the land is termed as waste land and land put to other non-agricultural uses.
Waste land includes rocky, arid and desert areas and land put to other non-agricultural uses includes settlements, roads, railways, industry etc.
4. “Resource planning is essential for sustainable development.” Elaborate
Ans: Planning is the widely accepted strategy for judicious use of resources as there are certain areas that have sufficient resources while others don't have enough.
For example, the states of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh are rich in minerals and coal deposits. Arunachal Pradesh has an abundance of water resources but lacks in infrastructural development. The state of Rajasthan is very well endowed with solar and wind energy but lacks in water resources. The cold desert of Ladakh is isolated from the rest of the country. It has an extraordinarily rich cultural heritage but it is deficient in water, infrastructure, and some vital minerals.
Resource planning is a complex process that involves:
(ii) Evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional set up for implementing resource development plans.
(iii) Matching the resource development plans with overall national development plans.
CBSE Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 - Resources and Development
Everything in our environment that we can use to satisfy our needs and is technologically accessible, economically affordable and acceptable culturally is termed as ‘Resource’. Humans are dominant components of resources. They convert materials available in the environment into resources and use them.
Classification of Resources
Classification of Resources is done in the following ways:
On the basis of Origin-Biotic and Abiotic.
On the basis of Exhaustibility-Renewable and Non-Renewable.
On the basis of Ownership-Individual, community, national and international.
On the basis of the status of development-potential, developed stock and reserves.
On the Basis of Origin – Biotic and Abiotic
Biotic Resources
These are obtained from living things in the environment. They are obtained from plants, animals, birds etc.
Abiotic Resources
These are obtained from non-living things in the environment. They are obtained from rocks, mountains, soil etc.
On the Basis of Exhaustibility – Renewable and Non-Renewable
Renewable or Replenishable Resources
Non-Renewable Resources
On the Basis of Ownership – Individual, Community, National and International
Individual Resources
These resources are owned by individuals. Examples of private plots, farms, houses etc.
Community Owned Resources
These resources are over by a community and accessible to all the members of the community. Example burial grounds, playground, wells etc.
National Resources
These resources are owned by a country or nation. Example mineral resources water resources forest.
International Resources
These resources are under the rules and regulations of international institutions. Example the water of the ocean beyond 200 nautical miles.
On the Basis of the Status of Development – Potential, Developed Stock and Reserves
Potential Resources
These resources are the resources which have been found in a region but yet to be utilised.
Developed Resources
These resources are the resources which have been researched upon and their quality and quantity have been already decided by making utilisation of them.
These are the sources which have the potential to be utilised by human beings but we do not have adequate technology to utilise them.
Reserve just like ‘Stock’ but these are resources which can be put to use with technology but they have not been used.
Human utilised resources indiscriminately which has led to many problems. The resources have got concentrated in few hands and this has caused rapid depletion of certain resources.
The rapid depletion of resources has also resulted in various environmental issues like global warming ozone layer depletion and environmental pollution.
At this point, resource planning has become an essential thing.
Note: Sustainable economic development is a development which takes place without damaging the environment of the present generation does not compromise with the needs of the future generation.
Resource Planning
Resource planning is very essential to ensure that the proper distribution of resources takes place in a region. Resource distribution should be equal so that everyone has access to it.
For a country like India, resource planning is essential because we have a diverse population and a very large one at that which needs a management system.
India has a varied distribution of resources all over the country. This requires a central management system to see that every part of the country receives the resources and utilizes it according to needs. Therefore, the country considered most of the resources found in nature as national resources. All the resources are taken inventory of, and the needs of various regions are estimated and distributed accordingly.
Conservation of Resources
The irrational consumption and overutilization of resources have created an imbalance in the system. This has led to many environmental as well as economic and social issues. To combat these issues, the conservation of resources is essential for survival.
Land as a resource is a very important one as it supports life on earth. Apart from supporting life land also, various uses are carefully planned.
The various relief features of the land are categorised into three mountains which constitutes 30% of the land, plateaus which constitute 27% of the land and plains which constitutes 43% of the land.
Land Utilisation
The various purpose of land utilisation is as follows:
Land not available for cultivation.
Barren and wasteland.
Land put to non-agricultural uses.
Fallow lands.
Other uncultivated lands (excluding fallow land).
Net sown area.
The land use pattern is determined by physical factors and human factors. Physical factors are topography climate and soil types while human factors are population density, technological capability, culture, tradition etc.
Land Degradation and Conservation Measures
Due to human activities, as well as some natural phenomena, the land in recent times has started degrading. Some activities such as deforestation mining, quarrying, overgrazing have significantly increased the rate of Land Degradation. Industrial waste has also contributed to degrading the quality of land especially in areas where industrial belts are found. Land Degradation has also affected the quality of water in our natural resources.
To conserve our Land and ensure the land degradation rate declines, we can take certain measures such as control mining activities proper disposal of Industrial waste planting shelterbelts etc.
Soil as a Resource
Soil is one of the important natural resources which is renewable. It takes millions of years to form every centimetre of soil. Soil formation depends upon various factors like temperature, the action of running water, wind, glaciers, the activity of decomposers, parent rock, chemical and organic changes etc.
Classification of Soils
India has various types of soil due to various natural factors that have contributed to creating soil which differs in terms of thickness, colour, texture, chemical and physical properties.
The Northern Plains are made of Alluvial soil. Alluvial soil is formed due to deposits from the Himalayan rivers Indus, Ganga and Brahmaputra.
It consists mainly of sand, silt and clay. Based on age Alluvial soils are classified into old Alluvial known as ‘Bhangar’ and new alluvial known as ‘khadar’.
The black soil is famous for growing cotton crops. It is mainly found in the Deccan trap and made of Lava.
It has more amount of clay and is known for its moisture holding capacity.
This type of soil is found mainly in areas with low rainfall the soil has iron and is formed of igneous which gives it its reddish colour.
The soil changes colour from red to yellow when it is hydrated.
Laterite soil forms in subtropical and tropical climates where intense leaching happens due to heavy rainfall this soil is acidic and is found mostly in the southern States Maharashtra.
It is very useful for growing tea and coffee.
Soil is generally sandy and saline in nature; it lacks humus and moisture.
The soil is red to brown in colour and has got high calcium content while going deeper.
This is found in forest areas especially in the hills and mountains the soil is loamy and silty while of course in the upper slopes.
It is acidic in nature with low humus content.
Soil erosion occurs due to human as well as Natural activities. It needs to be controlled as high soil erosion will lead to many problems. Soil erosion can be controlled by using soil conservation methods.
Different Ways for Soil Conservation
Various ways to conserve soil such as given below:
Contour ploughing where contours are created to stop direct water flowing down the slopes.
Terrace farming is a method which restricts erosion and helps with soil conservation.
Strip farming is a method where strips of grasses are grown between the crops to minimise erosion.
Shelterbelt is a method in which trees are planted in rows to break wind and minimise the shifting of the desert.

FAQs on Resources and Development Class 10 Notes CBSE Geography Chapter 1 (Free PDF Download)
1. How are Resources Important to us?
Resources are important to us because they make our life easier. Resources support the life of human beings as well as animals and help us in surviving. Natural resources like water, food and air are basic necessities for the survival of human beings. Man-made resources search schools, colleges hospitals etc help in the development of human beings.
The utility of each resource has been determined according to the needs of the humans and the possible ways in which each of the resources has been used to date. The various utilities of each resource are not yet known and it is a possibility that many resources have uses which we might get to know in the future. There are also resources available which are not yet in use due to lack of adequate technology. Refer to Resources and Development Class 10 notes or master class to clear any further doubts.
2. Why is the Conservation of Resources Necessary?
Conservation of resources is necessary because resources are a support system of all living beings. Humans need a lot of resources to survive. They need natural as well as human-made resources to survive the day to day life. Some of the resources that humans need are basic like air, water, and food. Some other resources like hospitals, schools and colleges or man-made resources which are necessary for the development of human beings.
We all need resources for our survival. It is very necessary that we conserve it for the future. Concepts of conservation like sustainable development enable us to use the resources in a careful manner which lets us fulfil the needs of this generation while taking care of the needs of future generations also. There are various ways in which resources can be conserved. For more information conservation of resources, please refer to the notes of CBSE 10 Social Science Chapter 1 in Geography.
3. How will you define natural resources?
Natural resources are defined as the resources that are available in nature. Such resources are available naturally. For example, plants, animals, and minerals are all called natural resources. Natural resources are used for making other useful products. The cutting of trees has led to deforestation. Destruction of forests has affected the lives of animals that live in the forest. It has also affected the climate and has increased the greenhouse effect.
4. What do you mean by conservation of resources and why is it important?
Conservation of resources means that the resources available in nature should be used wisely so that we can preserve them for future generations. We should not waste natural resources that are non-renewable as these won’t get renewed once they are depleted. It is important to conserve resources for the survival of living beings. Coal and petroleum are examples of non-renewable resources. We should start using renewable resources such as solar energy, wind energy, water energy to preserve non-renewable resources.
5. How should I study to score high marks in Class 10 Geography?
Geography is a part of social science. It is an easy part of social science. Students learn about natural resources, earth, minerals, and such topics in Geography. Students can read the chapters carefully to understand the basic concepts and score high marks in Class 10 Geography. Students can refer to the Class 10 Geography notes available on the Vedantu website and on the Vedantu app for free. Class 10 Geography notes can help students to understand the concepts and score high marks in class 10 Geography.
6. What is the benefit of studying from CBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 notes on Vedantu?
Vedantu provides notes for Chapter 1 of Class 10 Geography in simple language. Students can understand the notes easily and prepare for their board exams. These revision notes for Chapter 1 of Class 10 Geography are prepared by expert and professional teachers from different schools based on their experience. The notes will help students to prepare for the important questions. The notes are prepared after consulting different sources such as previous year papers, NCERT books, and other textbooks. These study materials are available on the Vedantu app and the Vedantu website at free of cost.
7. Can you write some ways to conserve soil?
Soil is an important natural resource. It is important to conserve soil for future use. There are several ways to conserve soil. These include adopting different types of farming that can help in preserving the soil. For example, contour farming helps to flow down the soil due to water. Therefore, contour ploughing helps in soil conservation. Terrace farming is another method that can help in soil conservation. It also increases soil fertility.
- RS Aggarwal
- ML Aggarwal
- Merchant of Venice
- NCERT Books
- Questions and Answers
- NCERT Notes
- Important Questions
- Resources and Development
Revision Notes for Chapter 1 Resources and Development Class 10 Geography
On the basis of the factors responsible for soil formation, colour, thickness, texture, age, chemical and physical properties, the soils of India can be classified in different types:
• Alluvial Soils :
→ Entire northern plains are made of alluvial soil.
→ Also found in the eastern coastal plains particularly in the deltas of the Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna and the Kaveri rivers.
→ Fertile soil therefore, fit for agriculture purpose.
→ Regions of alluvial soils are intensively cultivated and densely populated.
→ Rich in potash, phosphoric acid and lime which are ideal for the growth of sugarcane, paddy, wheat and other cereal and pulse crops.
• Black Soil :
→ Black in colour and are also known as regur soils.
→ Ideal for growing cotton and is also known as black cotton soil.
→ Found in the plateaus of Maharashtra, Saurashtra, Malwa, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh also along the Godavari and the Krishna valleys.
→ Made up of extremely fine i.e. clayey material.
→ Well-known for their capacity to hold moisture.
→ Rich in calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash and lime.
• Red and Yellow Soils :
→ Found in the areas of low rainfall in the eastern and southern parts of the Deccan plateau.
→ Also found in parts of Odisha, Chhattisgarh, southern parts of the middle Ganga plain and along the piedmont zone of the Western Ghats.
→ Develop a reddish colour due to diffusion of iron in crystalline and metamorphic rocks.
• Laterite Soils :
→ Develops in areas with high temperature and heavy rainfall.
→ Found in Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, and the hilly areas of Odisha and Assam.
→ Suitable for cultivation with adequate doses of manures and fertilizers.
→ Low Humus content because decomposers, like bacteria, get destroyed due to high temperature.
• Arid Soils :
→ Found in the western parts of Rajasthan.
→ After proper irrigation these soils become cultivable.
→ Lacks humus and moisture because dry climate, high temperature make evaporation faster.
→ Salt content is very high and common salt is obtained by evaporating the water.
• Forest Soils :
→ Found in the hilly and mountainous areas where sufficient rain forests are available.
→ Feature differs based on location.
→ Loamy and silty in valley sides and coarse grained in the upper slopes.
→ Silt in the lower parts of the valleys particularly on the river terraces and alluvial fans are fertile.
• Natural ways of Soil erosion: Wind, glacier and water lead to soil erosion. • Human activities: Deforestation, over-grazing, construction and mining etc., contributes in soil erosion. • Measures to control Soil erosion: → Strip cropping → Planting shelter belts → In the hilly areas, using contour ploughing and terrace farming.
NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialisation Class 10 History
Related chapters.
- Forest and Wildlife Resources
- Water Resources
- Agriculture
- Minerals and Energy Resources
Related Questions
- NCERT Solutions for Chapter 1 Resources and Development Class 10 Geography
- Important Questions for Chapter 1 Resources and Development Class 10 Geography
Report a problem
- Question is incorrect
- Answer is Incorrect
- Spelling Mistakes
- Not explained in detail

Resources and Development Class 10 Geography Solutions
We are providing you with the detailed notes of geography lesson 1 resources and development class 10 along with the ncert solutions, multiple-choice questions, and some value-based questions so that the students can cope with the new assessment scheme. Students after going through these short notes will be able to understand the new pattern and the concepts will be on fingertips.
What are Resources and What are their types?
Resource- Everything available in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs, provided it is technologically accessible, economically feasible, and culturally acceptable can be termed as a resource.
Types of resources –
These resources can be classified in the following ways-
- Based on origin- biotic and abiotic
- Based on exhaustibility- renewable and non-renewable
- Based on ownership- individual, community, national and international
- Based on the status of development- potential developed stock and reserves.
Biotic resources are obtained from the biosphere and have life such as human beings, flora, and fauna, fisheries, livestock, etc.
All those things which are composed of non-living things are called abiotic resources. For example- rocks and metals.
Renewable resources can be renewed or reproduced by physical, chemical, or mechanical processes. For example; solar and wind energy, forests, and wildlife, etc.
Non-renewable resources occur over a long period of time. Minerals and fossil fuels are examples of such resources. These resources take millions of years in their formation.
Individual resources are owned privately by individuals. For example; many farmers own land which is allotted to them by the government against the payment of revenue.
Community-owned resources are resources that are accessible to all the members of the community. Example- village commons, public parks, picnic spots, playgrounds in urban areas, etc.
National resources technically, all the resources belong to the nation. The computer has legal powers to acquire even private property for the public good.
International resources are international institutions that regulate some resources. The oceanic resources beyond 200 KM of Exclusive Economic Zone to open oceans and no individual country can utilize these without the occurrence of international institutions.
Potential resources- resources that are found in a region, but have not been utilized. For example; the western parts of India particularly Rajasthan and Gujarat. Have enormous potential for the development of wind and solar energy, but so far these have not been developed properly.
Developed resources- these are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilization.
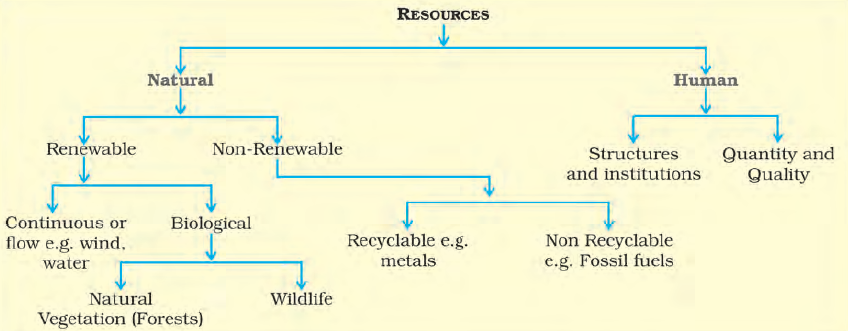
Development of resources
Resources are vital for human survival as well as for maintaining the quality of life. It was believed that resources are gifts of nature. Human beings used them indiscriminately and this has led to the following major problems:
- Depletion of resources for satisfying
- Accumulation of resources in few hands, which in turn, divided the society into two segments i.ee. Haves and have not or rich and poor.
- Indiscriminate exploitation of resources has led to global ecological crises such as global warming, ozone layer depletion, environmental pollution, and land degradation.
Resources planning in India-
- Identification and inventory across the regions of the country. This involves surveying, mapping, and qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of the resources.
- Evolving planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill, and institutional setup for implementing resource developmental plans.
- Matching the resource development plans with overall national developmental plans.
Conservation of resources-
- Resource conservation at various levels is important.
- Gandhi was very apt in voicing his concern about resource conservation in these words: “There is enough for everybody’s need and not for anybody’s greed”
Land Utilization-
Land resources are used for the following purposes-
Land not available for cultivation-
- Barren and wasteland
- Land put to non-agricultural uses: buildings, roads, factories. Etc.
- Other uncultivated lands ( excluding fallow land )
- Permanent pastures and grazing land
- Land under miscellaneous tree crops groves( not included in the net sown area)
- Other than current fallow land which is left for th past 1 to 5 agricultural year.
- Net sown area – area sown more than once in an agricultural year plus the sown area is known as gross cropped area.
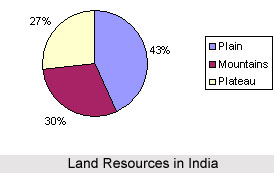
Land use pattern in India-
- The total geographical area of India is 3.28 Million sq. km.
- Land use data however is available only for 93% of the total area because the land use reporting for most of the Northeast states except Assam has not been done fully surveyed.
- Some are of Jammu and Kashmir occupied by Pakistan and China have also not been surveyed.
- The land under permanent pasture has also decreased.
- Fallow land- left without cultivation for one or less than one agricultural year.
- Net sown area total- total area seen in an agricultural year.
- More net sown area in Punjab and Haryana.
- Less net sown area in Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Manipur and Andaman, and Nicobar islands.
- National Forest Policy in India in 1952.
- Wasteland includes rocky, arid, and desert areas, and land put to other non-agricultural uses include settlements, roads, railways, industry, etc.
Land degradation and conservation measures-
At present, there are about 130 million hectares of degraded land in India.
Some human activities such as deforestation, over-grazing, mining, and quarrying have contributed significantly to land degradation.
In states, like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Orissa deforestation due to mining has caused severe land degradation.
In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra overgrazing are one of the main reasons for land degradation.
In the states of Punjab, Haryana, Western Uttar Pradesh, over-irrigation is responsible for land degradation.
NCERT SOLUTIONS For Resources and Development Class 10th
Q1. Multiple-choice questions-
1. Which one of the following types of resources is iron ore?
- Non-renewable
Ans- Non-renewable
2. Under which of the following type of resources can tidal energy be puy?
- Replenishable
- non-recyclable
Ans- Replenishable
3. Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab?
- Intensive cultivation
- Over irrigation
- Deforestation
- Overgrazing
Ans- over-irrigation
4. In which one of the following states is terrace cultivation practiced?
- Plains of Uttar Pradesh
- Uttarakhand
Ans- Uttarakhand
5. In which of the following states is black soil found?
- Jammu and Kashmir
Ans- Gujarat
Q2. name three states having black soil and the crop which is mainly grown in it?
Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, and Chhatisgarh.
Q3. what type of soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast? Give three main features of this type of soil.
Alluvial soil is found in the river delays of the eastern crops. Alluvial soil is rich in p[otash, phosphoric acid, and lime. It has a high water retention capacity and is highly fertile soil.
Q4. what steps can be taken to control soil erosion in the hilly areas?
Terrace farming and shelterbelts.
Q5. what are the biotic and abiotic resources? Give examples?
Biotic resources- All living organisms in our environment are called biotic resources. For example; trees, animals, insects, etc.
Abiotic resources- All non-living things present in our environment are termed biotic resources. For example- earth, air, water, metals, rocks, etc.
Q6. Explain land use pattern in India and why has the land under forest not increased much since 1960-61?
About 45% of the land is used as net sown area, i.e. for farming. About 22% of the land is under forest and the rest of the land is used for various purposes; like housing, recreation, and industrial activities. Increasing population and subsequent increase in demand for resources is the main reason that forested land has not increased much during this period.
Q7. How has technical and economic development led to more consumption of resources?
Economic development creates demand for various resources and technical development gives the knowledge to exploit those resources.
Thus, technical and economic development; together lead to more consumption of resources.
Multiple Choice Questions For Resources and Development
1. The availability of resources is a necessary condition for the development of:
Any country
- None of the above
Ans- any region
2. Some countries colonized other countries because of their:
- Natural beauty
- Rich resources
Ans- rich resources
3. In which of the following books, Schumacher presented Gandhian philosophy
- Big is beautiful
- Large is beautiful
- Small is beautiful
- Everything is beautiful
Ans- small is beautiful
4. What % of Indian land areas is plain area :
5. What % of Indian land area is mountain area:
6.What is the total geographical area of India?
- 2.28 million sq. km.
- 3.28 million sq. km.
- 4.28 million sq. km.
- 5.28 million sq. km.
Ans- 3.38 million sq. km.
7.What % of Geographical area is desired forested area?
- 23 percent of geographical area
- 33 percent of geographical area
- 43 percent of geographical area
- 53 percent of geographical area
Ans- 33 percent of geographical area
8.How many million hectares of Indian land is degraded land?
- 110 million hectares
- 120 million hectares
- 130 million hectares
- 140 million hectares
Ans- 130 million hectares
9. Which of the following is the main reasons for land degradation in the states of Gujarat, Rajasthan, M.P., and Maharashtra?
- Over-grazing
- All of the above
Ans- over-grazing
10. Which is the most widely spread and important soil?
Ans- alluvial
11. The soil which has a higher concentration of Kanker nodules is called-
- Alluvial soil
Ans- hangar
12. Black soil is also known as-
13. The soil which develops in areas with high temperatures and heavy rainfall is called-
Ans- laterite
14.Red laterite soil is suitable for growing which of the following crops-
- Cashew nuts
Ans- cashew nuts
15. When the topsoil is washed away when water flow as a sheet over large areas down a slope is known as-
- Land erosion
- Water erosion Sheet erosion
Ans- sheet erosion
16. Resources are a function of –
- National activities
- Human activities
- Both a and b
Ans- human activities
17. Biotic resources are obtained from-
- Biosphere and include living organisms
- Biosphere and include non-living organisms
Ans- Biosphere and include living organisms
18. Rocks and metals are examples of-
- Biotic resources
- Abiotic resources
- Natural resources
Ans- abiotic resources
19. Many farmers own land which is allotted to them by the government:
- Against the payment by cash
- Against property in towns
- Against the payment or revenue
Ans- against the payment of revenue
20. Plantation, pasture lands, ponds, water in wells, etc are some examples of-
- Resources owned by the government
- Resources owned by the private
- Resources owned by individual
Ans- resources owned by individual
21. Resources that are accessible to all the embers of the community are called-
- Private owned resources
- Public owned resources
- Community-owned resources
- Individual owned resources
Ans- community-owned resources
22. Resources belonging to the nation are called-
- State resources
- Country resources
- National resources
- Individual resources
Ans- national resources
23. Resources that are found in a region, but have not been utilized are called-
- Developed resources
- International resources
- Potential resources
Ans- potential resources
24. Resources that are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilization are called-
Ans- developed resources
25. Materials in the environment that have the potential to satisfy human needs but human beings do not have the appropriate technical knowhow to access them are called-
Case Study Questions For Resources and Development
Read the extract given below and answer the following questions
We have shared our land with the past generations and will have to do so with the future generation too. Ninety-five percent of our basic needs of food, shelters, and clothing are obtained from the land.
Human activities have not only brought about the degradation of the land but have also aggravated the pace of natural forces to cause damage to the land. Some human activities such as deforestation, overgrazing, mining, and quarrying too have contributed significantly and land degradation.
Mining sites are abandoned, after excavation work is complete, leaving deep scars and traces over-burdening. In states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, M.P., and Odisha, deforestation sure to mining has caused severe land degradation. In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, M.P., and Maharashtra overgrazing are one of the main reasons for land degradation. In the states like Punjab, Haryana, Western Uttar Pradesh, over-irrigation is responsible for land degradation due to waterlogging leading to an increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil.
Answer the questions-
1. Most of the basic needs for food, shelter, and clothing are obtained from
- Land degradation
2. Deforestation due to mining has caused severe land degradation in the state of-
Ans-Jharkhand
3. Over irrigation is responsible for land degradation due to the following reasons-
- Deforestation and over grazing’
- Increase in alkalinity of the soil
- Waterlogging leading to an increase in salinity in soil
- Noen of these
Ans- water logging due to an increase in salinity of the soil
4. Human is considered as the main culprit for land degradation because
- Of his excavation work at mining sites
- Of his significant contribution to deforestation
- He has aggravated the pace of natural forces causing damage to land
- All of these.
Ans- he has aggravated the pace of natural forces causing damage to land
We have penned down the summary of the lesson resources and development class 10 along with the ncert solutions and MCQs. we have also mentioned some value-based questions. Students after reading the lesson can go through these to get the gist of the lesson at just one stroke.
Hi, I am Kavisha Bagga, a teacher by profession and a part-time blogger. I love sharing knowledge, which is why I have started this blog.
myCBSEguide
- Social Science
- NCERT solutions for Class...
NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Resources and Development
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Resources and Development Chapter 1 are available in PDF format for free download. These ncert book chapter wise questions and answers are very helpful for CBSE exam. CBSE recommends NCERT books and most of the questions in CBSE exam are asked from NCERT textbooks Social Science chapter wise NCERT solution for Social Science part 1 part 2 Part 3 and Part 4 for all the chapters can be downloaded from our website and myCBSEguide mobile app for free.
NCERT Solutions for Geography Class 10 Download as PDF
NCERT Class 10 Social Science Chapter-wise Solutions
- Development
- Sector of Indian Economy
- Money and Credit
- Globalization of Indian Sector
- Consumer Rights
- Resources and Development
- Forest and Wildlife Resources
- Water Resources
- Agriculture
- Minerals and Energy Resources
- Manufacturing Industries
- Lifelines of National Economy
- The Rise of Nationalism in Europe
- The Nationalist Movement in Indo China
- Nationalism in India
- The Making of a Global World
- The Age of Industrialisation
- Work Life and Leisure
- Print Culture and The Modern World
- Novels Society and History
- Power Sharing
- Democracy and Diversity
- Gender Religion Caste
- Popular Struggle and Movements
- Political Parties
- Outcomes of Democracy

Question 1: Multiple choice questions.
(i) Which one of the following type of resource is iron ore? (a) Renewable (b) Biotic (c) Flow (d) Non-renewable
(ii) Under which of the following type of resource can tidal energy be put? (a) Replenishable (b) Human-made (c) Abiotic (d) Non-recyclable
(iii) Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab? (a) Intensive cultivation (b) Deforestation (c) Over irrigation (d) Overgrazing
(iv) In which one of the following states is terrace cultivation practised ? (a) Punjab (b) Plains of Uttar Pradesh (c) Haryana (d) Uttarakhand
(v) In which of the following states is black soil found? (a) Jammu and Kashmir (b) Gujarat (c) Rajasthan (d) Jharkhand
Answer: (i) (d) non–renewable Explanation: Once they have been used up, there will be no more. Most non-renewable resources are minerals, which are mined, for example, gold, iron ore, titanium. Coal and oil are known as fossil fuels and are also non-renewable.
(ii) (a) Replenishable Explanation: Tidal energy is a replenishable resource since tides keep coming over and over again due to the moon’s force.
(iii) (c) over irrigation Explanation: In Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh, over irrigation is responsible for land degradation due to waterlogging leading to increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil.
(iv) (d) Uttarakhand Explanation: Terrace farming is done on hill slopes and Uttarakhand is the region having hill slopes and here terrace farming is practiced.
(v) (b) Gujrat Explanation: It is mostly found in areas such as Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra. It is formed by weathering of deccan basalt from last 60 million years and paleo organic carbon resource.
Question 2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
- Name three states having black soil and the crop which is mainly grown in it.
- What type of soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast? Give three main features of this type of soil.
- What steps can be taken to control soil erosion in the hilly areas?
- What are the biotic and abiotic resources? Give some examples.
- Maharashtra, Gujrat, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh are states having black soil. Cotton is mainly grown in black soil. Other crops which can be grown in black soil are rice, sugarcane, wheat, Jawar, linseed etc
- Alluvial soils are very fertile.
- It contains varied amounts of sand, silt and clay.
- These soils contain ample amount of phosphoric acid, potash and lime so they are ideal for growing sugarcane, wheat and paddy.
- The regions of alluvial soils are intensively cultivated and densely populated.
- In hilly areas, soil erosion can be controlled by contour which refers ploughing across contour-lines, making use of terrace farming techniques and using strips of grasses to check soil erosion by wind and water.
- Biotic Resources: The resources which are obtained from the biosphere, from forest and the materials derived from them and have life are called Biotic Resources. For example, animals and plants including human beings. Abiotic Resources: The resources which are composed of non-living things are called Abiotic Resources. For example rocks ,water, minerals, metals, wind, solar energy etc.
Question 3. Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
- Explain land use pattern in India and why has the land under forest not increased much since 1960-61?
- How has technical and economic development led to more consumption of resources?
Answer: (i) The use of land is determined by both physical factors such as topography, climate, soil types as well as human factors such as population density, technological capability and culture and traditions. Land resources in India are primarily divided into agricultural land, forest land, land meant for pasture and grazing, and waste land. Wasteland includes rocky, arid and desert areas and land used for other non-agricultural purposes such as housing, roads and industry. According to the recent data, about 54% of the total land area is cultivable or fallow, 22.5% is covered by forests and 3.45% is used for grazing. The rest is wasteland, with traces of miscellaneous cultivation. The land under forest has not increased since 1960–61 because in the post-independence era demand for more land to expand agriculture, mainly after Green Revolution, developmental works and infrastructural facilities, led to clearance of forests areas. Industrialisation and urbanisation also decreased the forest area. Thus, land under forest has increased by only about 4% since 1960-61. (ii) Technical and economic development has led to more consumption of resources on account of various factors such as:
- Technological development provides sophisticated equipment. As a result, production increases ultimately leading to consumption of more resources. Technological advancement leads to the conversion of more natural resources into useful resources thus the consumption also increases.
- Technological development also leads to economic development. When the economic condition of a country rises, the needs of people also rise. It again results in more consumption of resources.
- Economic development provides favourable environment for the development of latest technologies. It helps to make or convert various materials found around us into resources. Finally, it results in the consumption of newly available resources too.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Resources and Development
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science PDF (Download) Free from myCBSEguide app and myCBSEguide website. Ncert solution class 10 Social Science includes text book solutions from part 1 and part 2 part 3 and part 4. NCERT Solutions for CBSE Class 10 Social Science have total 27 chapters. 10 Social Science NCERT Solutions in PDF for free Download on our website. Ncert Social Science class 10 solutions PDF and Social Science ncert class 10 PDF solutions with latest modifications and as per the latest CBSE syllabus are only available in myCBSEguide.
CBSE app for Class 10
To download NCERT Solutions for class 10 Social Science, Computer Science, Home Science, Hindi, English, Maths Science do check myCBSEguide app or website. myCBSEguide provides sample papers with solution, test papers for chapter-wise practice, NCERT solutions, NCERT Exemplar solutions, quick revision notes for ready reference, CBSE guess papers and CBSE important question papers. Sample Paper all are made available through the best app for CBSE students and myCBSEguide website.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Minerals and Energy Resources
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science Economics Development
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Economics Sector of Indian Economy
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Economics Money and Credit
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Economics Globalisation of Indian sector
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Economics Consumer rights
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Water Resources
4 thoughts on “NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Resources and Development”
Thank you so much
GK MCQ Questions
Class 10 Science MCQ
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Class 10 Social Science (Geography) Chapter 1 Resources and Development Lesson Plan

Written By Avinash Sharan
Class 10 | lesson plan 10, 2 comment(s), 7th march 2023, resources and development lesson plan: activity based.
Resources and Development Lesson Plan includes the various natural resources available on our planet and how they can be used sustainably for development. The Resources and Development Lesson Plan covers topics such as the classification of resources, their distribution and utilization, conservation and management of resources, and sustainable development. It also deals with the impact of human activities on the environment and the measures that can be taken to mitigate them.
This Lesson Plan on Resources and Development deals with the interdependence of various resources and the need for their judicious use. The lesson plan also highlights the importance of preserving resources for future generations and the role of individuals, communities, and governments in achieving sustainable development through activities.
Table of Contents
Topic: Resources and Development
No. of Periods required: 7-8
General Objective:
- To create interest in the subject.
- To understand the importance of resources.
Specific Objective:
The objective of teaching Resources and Development to class X students is to:
- introduce the concept of resources and their types to students, including natural, human, and capital resources.
- make students aware of the importance of sustainable use of resources and the impact of overuse on the environment.
- teach students about the distribution of resources across the world and the factors that influence their distribution.
- help students understand the concept of resource planning and its importance in sustainable development.
- familiarize students with the various methods of conservation of resources, such as reuse, recycling, and reducing waste.
- enable students to identify the natural resources available in their local area and their uses.
- develop students’ critical thinking skills by analyzing the impact of resource use on the environment and society.
- educate students on the role of technology in resource development and its impact on society and the environment.
- encourage students to take responsibility for sustainable resource use in their daily lives and future careers and to
- prepare students for further studies in geography, environmental science, or related fields
Teaching Points:
- Definition of resource
- Types & Classification of resources
- Development of resources
- The concept of Sustainable Development
- Resource Planning
- Resource planning in India
- Land Resources
- Land use pattern
- degradation and conservation of land
- Soil as a resource
- Classification of soils
- Soil erosion and conservation
Teaching Aids:
- Physical and Political map of India.
- Map of soils.
- Audio and videos
- Blackboard and chalk.
Checking Prior Knowledge:
Before starting the chapter, the teacher checks the prior knowledge of the students about resources by asking a few questions:
- What is meant by the term ‘natural resources’?
- Can you give examples of renewable and non-renewable resources?
- Do you know what is meant by sustainable development?
- How do human activities impact the environment and natural resources?
- What will happen if there is an over-exploitation of natural resources?
Teaching Methodology:
The teacher will apply the following methodologies to explain the chapter:
Active learning:
Through this methodology, the teacher will emphasize the participation of students in the learning process. Through this approach, The teacher will encourage students to participate in discussions, group activities, problem-solving, and critical thinking to explore the topic of resources and development. This approach will help students to apply their knowledge, learn through experimentation and discovery, and develop a deeper understanding of the subject.
Inquiry-based learning:
By adopting Inquiry-based learning the teacher will encourage students to ask questions. Children will explore and investigate the topic of resources and development on their own. The teacher provides guidance, resources, and feedback to help students find answers to their questions and develop a better understanding of the topic. This approach will help students to develop critical thinking skills, problem-solving skills, and independent learning skills.
Project-based learning:
Through Project-based learning, the teacher will involve students in an extended project that requires them to explore and investigate a topic related to resources and development. Of course, the teacher will provide guidance and support to help students plan and execute the project. This approach will help students to develop research skills, teamwork skills, and problem-solving skills.
Flipped classroom:
Lastly, the teacher will apply the flipped classroom teaching methodology that involves students in a self-directed learning process. In this approach, the teacher will provide students with online resources such as videos, podcasts, and readings before the class. During the class, students will engage themselves in discussions, group activities, and problem-solving exercises related to the topic. This approach will help students to develop self-directed learning skills and critical and collaboration skills.
Activities To Be Conducted:
The teacher will conduct the following classroom activities while teaching the chapter Resources and Development:
Activity 1 Resource mapping
The teacher will divide students into groups.
Each group will be assigned a different region or country to research.
The students have to create a resource map of the region/ state or country,
They will identify and categorize the natural resources available.
Then, each group will present its map to the class.
They will also compare and contrast the availability and distribution of resources in different regions.
Activity 2 Debate
Here, the teacher will divide the class into two groups.
One group will argue for the conservation and sustainable use of resources.
The other group will argue for economic development and the exploitation of resources.
The teacher will give each group time to research and prepare their arguments.
He/she will hold a structured debate with clear rules and time limits.
The teacher will also encourage students to use evidence and examples to support their arguments.
Activity 3 Case study analysis:
In this activity, the teacher will provide students with a case study of a real-world resource management issue.
It can be any topic such as water scarcity in a particular region, or the impact of mining on a local community.
Students have to read and analyze the case study in small groups.
They have to identify the key stakeholders, the causes and effects of the issue, and potential solutions.
Then, each group will be given a chance to present their analysis to the class.
This will facilitate a discussion about the complex issues involved in resource management.
Activity 4 Simulation game
The teacher divide the class into small groups and provide each group with a different scenario related to resource management.
Such as managing a fishery or allocating water resources during a drought.
Students will work together to make decisions and take actions in response to the scenario, and provide feedback and consequences based
on the outcomes.
This will help students to reflect on the trade-offs and challenges involved in resource management and resource planning .
Students will have to prepare a map related to the types of soils found in India.
Sohot questions, MCQ, and source-based questions will be done in the class.
The teacher will also guide the students in writing perfect answers in Board exams.
Read about the Rio de Janeiro earth summit.
Also, read about the views of Mahatma Gandhi on resource development.
मेघालय : रैट होल माइनिंग
Learning Outcome:
“Resources and Development” is a topic within the field of Geography that deals with the availability, management, and utilization of
resources by humans.
Here are five possible learning outcomes from studying this topic:
Understanding the different types of natural resources
By studying Resources and Development , learners can learn about different types of natural resources such as land, water, forests, minerals,
and energy resources.
They can also understand the concept of resource depletion and the consequences of over-exploitation.
Understanding the impact of human activities on the environment:
Resources and Development involve studying the impact of human activities on the environment, including issues such as deforestation, soil
erosion, and climate change .
Learners can understand how human activities affect the environment and how they can contribute to sustainable development.
Understanding the importance of resource management:
Resource management is a critical component of sustainable development .
Learners can gain an understanding of the principles of resource management, including the sustainable use of resources, the protection of
ecosystems , and the importance of conservation.
Understanding the role of technology in resource development:
Technology plays a crucial role in the development and utilization of resources.
Learners can learn about the various technologies used in resource development, such as irrigation systems, hydroelectric power, and mining
equipment, and how they impact the environment.
Understanding global resource distribution and economic development:
Resources and Development also involve studying the distribution of resources around the world and how they are used to support economic
development.
Learners can gain an understanding of the relationship between resource distribution and economic development, and how it impacts
different regions of the world.
Remedial Measures:
Pair and share:.
It’s a very popular method used by teachers to help slow learners.
A student sitting to the right will read a paragraph from the chapter and will explain it to his partner sitting to his left.
Then, the student sitting to the left will read a paragraph from the chapter and will explain it to his partner sitting to his right.
The teacher asks the slow learners to prepare 10 quiz questions which they have to conduct in the class.
Note: The teacher must not prepare the questions.
Conclusion:
I hope that this Resources and Development Lesson Plan will cater to the need of all students. New classroom activities involved in the Resources and Development Lesson Plan will involve the students in the teaching-learning process. However, the chapter is very big and contains lots of concepts e.g. resource planning, Sustainable development, soil erosion and conservation, Land use planning, etc. Therefore, it also requires detailed Resources and Development lesson plans beforehand.
If you have conducted any classroom activity, you are free to share.
Hot Question for my readers:
which resources have been found recently found in Jammu and Kashmir and what is their use?
Blended Learning: Combining Digital Tools With Traditional Classrooms
How to complete your Economics Project On India’s First Digital Currency in 60 minutes
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
Related Posts

Traditional Hydrological Surveys: A Project On Tools and Techniques For Water Detection
Mar 8, 2024
Traditional Hydrological Surveys: Merits & Demerits In India, Traditional Hydrological Surveys play an important...

Revising Class X Geography: A Deep Dive Into Key Concepts
Jan 19, 2024
Unlocking The Secrets Of Revising Class X Geography Unlocking The Secrets Of Revising Class X Geography is going to...

History & D P Sample Questions 2023-2024 – Navigating Success
Dec 30, 2023
CLASS 10 HISTORY & D P SAMPLE QUESTIONS 2023-24 Welcome to the History & D P Sample Questions 2023-24, your...
This lesson plans are really helpfull.so many strategies are there .really interesting
Thanks Suhani.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Submit Comment
Resources and Development Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Extra Questions and Answers
CBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Resources and Development Extra Questions and Answers is available here. Students can learn and download PDF of these questions for free. These extra questions and answers are prepared by our expert teachers as per the latest NCERT textbook and guidelines. Learning these questions will help you to score excellent marks in the board exams.
Resources and Development Class 10 Extra Questions Geography Chapter 1
Very short answer type questions.
1. What is a Resource? Give two examples.
Answer: Everything available in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs, provided, it is technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally acceptable can be termed as Resource. Coal, water, air, minerals etc. are some examples of resource.
2. What is the role of humans in resource development ?
Answer: (i) Human beings interact with nature through technology and create institutions to accelerate their economic development. (ii) Human beings transfer material available in our environment into resource and use them.
3. How can the resources be classified on the basis of origin ? [CBSE 2010] Answer: Biotic and Abiotic.
4. What are abiotic resources? [CBSE 2014] Answer: All those things which are composed of non – living things are called abiotic resources.
5. A gas reserve has been discovered in an Ocean. The reserve is 19 km from the coast of the nation. Will it be considered an international resource or a national resource. Answer: All the resources upto 12 nautical miles (19.2 km) from the coast are termed as national resources. So this will be a national resource.
6. “There is enough for everybody’s need and not for anybody’s greed”. Who said these words? Answer: Mahatma Gandhi
7. It is important to use the available land for various purposes with careful planning”. Give reason. Answer: Because land is an asset of a finite magnitude.
8. How can the resources be divided on the basis of exhaustibility? Answer: Renewable and Non-renewable.
9. Classify the following resources as biotic and abiotic. (i) Metals (ii) Fauna
Answer: (i) Metals – abiotic (ii) Fauna – biotic
10. Give a single word for the following : (i) Materials which have the potential to satisfy human needs but human beings do not have the appropriate technology. (ii) The resources which can be renewed or reproduced by physical, chemical or mechanical processes. Answer: (i) Stock (ii) Renewable
11. Name any two states of India which are well endowed with solar energy. Answer: Gujarat and Rajasthan.
12. Name any two factors on which resource development depends. Answer: (i) Technology (ii) Quality of human resources.
13. What is total geographical area of India? Answer: 3.28 million s km.
14. Mention any two factors which determines the land use pattern of a nation. Answer: (i) Topography (ii) Population
15. What is wasteland? Answer: An unused area of land like rocky, arid and desert areas.
16. What is net sown area? [CBSE 2014] Answer: Area sown once a year is known as net sown area.
17. What is gross sown area? Answer: This represents the total sown area once/or more than once in a particular year i.e. the area is counted as many as times as there are sowings in a year.
18. Name any two states which have high percentage of net sown area. Answer: Punjab and Haryana
19. Name any two states Which have very low percentage of net sown area. Answer: Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram
20. How much degraded land is present in India ? Answer: 130 million hectares.
21. Name any two states where over grazing is one of the main reasons for land degradation. Answer: (i) Madhya Pradesh (ii) Rajasthan
22. What are biotic resources? [CBSE 2014] Answer: These are obtained from biosphere and have life such as human beings, flora and fauna, fisheries, livestock etc.
23. Name any two states where over irrigation is responsible for land degradation. Answer: (i) Punjab (ii) Haryana
24. Name any two states where mining is responsible for land degradation. Answer: Jharkhand and Madhya Pradesh.
25. How over-irrigation leads to land degradation? Answer: Over-irrigation degrades land due to water logging leading to increase in salinity and alkalinity of the soil.
26. How can land degradation be checked in Rajasthan as the state is having arid soil? Mention any two methods. Answer: (i) Control on over grazing. (ii) Stabilisation of sand dunes.
27. Suggest any two ways to check land degradation. [CBSE 2013, 14] Answer: (i) Afforestation (ii) Proper management of grazing
28. Mention any two factors which have contributed in the development of various types of soils. Answer: (i) Varied relief features. (ii) Varied climatic conditions.
29. ‘The entire northern plains are made of alluvial soils. Name the rivers due to which the soils have been deposited. Answer: The Indus, the Ganga and the Brahmaputra.
30. How can the alluvial soil be classified according to their age ? Answer: (i) Khadar (ii) Bangar
31. Out of Khadar and Bangar soil which is more fertile ? Give one reason. Answer: Khadar soil is more fertile because it has more fine particles.
32. Name any two minerals present in alluvial soil which makes it ideal for the growth of sugarcane, paddy, wheat and other cereals. Answer: Potash and lime.
33. Name one important crop cultivated in : (i) Alluvial soil (ii) Black-soil Answer: (i) Alluvial – Wheat (ii) Black – Cotton.
34. Which soil is ideal for growing cotton ? [CBSE 2014] Answer: Black soil.
35. Which soil is well known for their capacity to hold moisture ? Give reason. Answer: Black soil. Because black soil is made up of extremely fine clayey material.
36. Name a mineral in which the black soil is poor. Answer: Phosphoric contents.
37. Why black soil is tilled immediately after the first shower ? Answer: These soils are sticky when wet and difficult to work on.
38. Name the soil which develops on crystalline igneous rocks. Answer: Red soil.
39. ‘Laterite’ has been derived from the Greek word ‘later’. What does the term later mean? Answer: Brick.
40. The running water cuts through clayey soils and makes deep channels. What are they called?
Answer: Gully erosion.
41. Which state has mostly laterite soil? Answer: Karnataka.
42. Which soil types is the result of intense leaching due to heavy rainfall? Answer: Laterite soil.
43. Name the soil which develops in areas with high temperature and heavy rainfall. Answer: Laterite soil.
44. Name any two crops associated with laterite soil. Answer: Tea and coffee.
45. Which soils are generally sandy in texture and saline in nature? Answer: Arid soils.
46. ‘The lower horizon of the arid soils are occupied by kankar’. Give reason. Answer: This is because of increasing calcium content downwards.
47. Name any two natural factors which are responsible for soil erosion. Answer: Wind and glacier.
48. By which name is the bad land known in chambal basin? Answer: Ravines.
49. What is sheet erosion? Answer: When the top layer of the soil is removed over a large area by running water, it is called sheet erosion.
50. What is wind erosion? Answer: Wind blows loose soil off flat or sloping land. This is known as wind erosion.
51. What is contour ploughing? Answer: Ploughing along the contour lines is known as contour ploughing.
52. How contour ploughing helps in the soil conservation? Answer: Ploughing along the contour lines decelerates the flow of water down the slopes.
53. What are shelter belts? Answer: Rows of trees which are planted in between the crops are known as shelter belts.
54. How shelter belts help in file conservation of soil? Answer: The shelter belts break up the force of the wind.
55. Name a method which has contributed significantly in soil conservation in western India. Answer: Shelter belts.
56. What is net sown area? What percentage of total area is under net sown area in India? Answer: Area sown once in a year is known as net sown area. In 2008-2009, 46.24% of India’s area was under net sown area.
57. What is gross sown area? Answer: Area sown more than once in an agricultural year plus net sown area is known as gross sown area.
58. Which soils is the most widely spread in India? Answer: Alluvial soil.
59. What is bad land? Answer: It is a land which is unsuitable for cultivation. Mainly soil erosion converts a fertile land into a bad land.
60. What is gully erosion? Answer: Gully erosion takes place when running water cuts deep ravines in the absence of vegetation. This type of erosion makes soil unfit for cultivation.
61. What is strip cropping? Answer: Under strip cropping large fields are divided into strips and different types of crops are grown on alternative strips along contours or across the prevailing direction of winds. This breaks up the force of the wind.
62. Mention any two man-made and two natural factors responsible for land degradation. [CBSE 2014]
Answer: (i) Man-made: Deforestation, over- grazing, mining, quarrying. (ii) Natural: Water logging, wind, running water
63. Name any four minerals in which the black soil is rich. Answer: (i) Calcium carbonate (ii) Magnesium (iii) Potash (iv) Lime
64. What is leaching? Name the soils which develop due to leaching. Answer: Leaching is a process by which the nutrients in the soil are washed away by heavy rains. Laterite soils develop due to leaching.
65. Mention any four proper farming technique which can be helpful in conservation of soil. Answer: (a) Strip cropping (b) Shelter belt (c) Contour ploughing (d) Terracing
66. State two disadvantages of the red soil. Answer: (i) The soil lacks in nitrogen, organic and phosphoric acid contents and is less fertile. (ii) Red soils are porous in nature but not retentive to moisture.
67. ‘It is important to use the available land for various purposes with careful planning’. Give reason. Answer: Because it is an asset of a finite magnitude.
68. Mention the various forces of nature which contribute to the formation of soil. Answer: Change in temperature, action of running water, wind and glaciers, activities of decomposers etc. contribute to the formation of soil.
Short Answer Type Questions
Answer: Everything available in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs, provided, it is technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally acceptable can be termed as Resource. Examples, coal, water, air, minerals, etc.
2. What is the importance of natural resource? Why is it necessary to conserve them?
Answer: Resources are important for the development of any country. For example, fossil fuels are essential to generate energy, mineral resources are important for industrial development, etc. Necessary to conserve resources because: (i) Their irrational consumption and over utilisation have led to socio-economic and environmental problems. (ii) It takes million of years for the formation of natural resources. (iii) Natural resources are available in fixed quantity and they are non – renewable.
3. What are the ways to classify resources?
Answer: (i) On the basis of origin – biotic and abiotic. (ii) On the basis of exhaustibility – renewable and non-renewable. (iii) On the basis of ownership-individual, community, national and international. (iv) On the basis of the state of development- potential, developed and stock.
4. What is the role of humans in resource development ? [CBSE 2014] Or Explain the role of humans in resource development. [CBSE Sept. 2010, 2011],
Answer: (i) Resources are function of human activities. (ii) Human beings interact with-nature through technology, and create institutions to accelerate their economic development. (iii) Human beings transfer materials available in our environment into resource, and use them. (iv) For example, river is a natural endowment and it becomes resource when its water is used for irrigation or power production.
5. What are renewable resources? Give two examples.
Answer: The resources which can be renewed or reproduced by physical, chemical or mechanical processes are known as renewable or replenishable resources. For example, solar and wind energy, water, forests and wildlife, etc. The renewable resource may further be divided into continuous or flow.
6. What are non renewable resources? Give two examples.
Answer: These occur over a very long geological time. These resources take millions of years in their formation. Some of the resources like metals are recyclable and some like fossil fuels cannot be recycled and get exhausted with their use. For example, coal, bauxite.
7. What are individual resources? Give two examples.
Answer: Resources which are owned by private individuals are known as individual resources. Plots, fields, house, car, book, etc. are some examples of individual resources.
8. What are community owned resources? Give two examples.
Answer: The resources which are accessible to all the members of the community are known as community resources. Village ponds, public parks, playgrounds, etc. are some examples of community resources.
9. What are national resources? Give two examples.
Answer: All the resources which are under the control of state or union government are known as national resources. All the resources within political boundaries are national resources because the government has the power to acquire even private property. For example, Indian railway, Bhakra dam.
10. What are potential resources? Give two examples.
Answer: Resources which are found in a region, but have not been utilised due to lack of capital or other reasons. For example, the western parts of India particularly Rajasthan and Gujarat have enormous potential for the development of wind and solar energy, but so far these have not been developed properly.
11. What are developed resources? Give two examples.
Answer: These are resources which have been surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilisation. The development of resources depends on technology and level of their feasibility. For example, India has a cumulative total of 2,47,847 million tones of coal resources.
12. What is stock? Give two examples.
Answer: These are material in the environment which have the potential to satisfy the human needs but could not be used as the human beings do not have the appropriate technology to convert them into usable form. For example, water (H20) is a compound of two inflammable gases i.e., hydrogen and oxygen but human beings do not have the required technology to use them as a source of energy.
13. What are reserves? Explain with examples.
Answer: Reserves are the subset of the stock, which can be put into use with the help of existing technical ‘know-how’ but their use has not been started. These can be used for meeting future requirements. River water can be used for generating hydroelectric power but presently, it is being utilised only to a limited extent. Thus, the water in the dams, forests etc. is a reserve which can be used in the future. ‘
14. “Planning of resources is very important for a country like India”. Justify by giving three reasons.
Answer: (i) India has enormous diversity in the availability of resources. There are many regions which are rich in certain type of resources but are deficient in some other resources. (ii) The states of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh are rich in minerals and coal deposits but lacks in infrastructural development. (iii) The states like Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh are rich in soil but lacks minerals.
15. ‘The availability of resources is the only condition for the development of any region’. What is your opinion on the statement? Explain. Or Mention any three necessary conditions for the development of resources.
Answer: (i) Resources can contribute to development only when they are accompanied by appropriate technological development and institutional changes. (ii) There is need for quality of human resources i.e., skilled workers who can convert natural resources into more useable form. (iii) There is also a need for capital which is required to develop technology.
16. Explain the relationship between nature, technology and institutions.
Answer: Nature contains resources. These resources are converted into usable form with the help of technology. Human beings interact with nature through technology, and create institutions to accelerate their economic development.
17. ‘India has enormous diversity in the availability of resources.’ Explain. Or “India is rich in certain types of resources but deficient in some other resources.” Support your answer with examples. [CBSE Sept. 2012, 2014]
Answer: (i) The states of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh are rich in mineral resources but lack industrialisation. (ii) Arunachal Pradesh has an abundance of water resources, but lacks in infrastructural development. The state of Rajasthan is very well endowed with solar and wind energy but lacks in water resources. The cold desert area of Ladakh is relatively isolated from the rest of the country due to lack of means of transportation and communication. (iii) Most of North-Eastern states are rich in natural vegetation but lacks in fertile soil.
18. Study the following data carefully and answer the questions that follow: LAND FEATURES OF INDIA Land Features Area Covered (in percentage) (i) Plains 43% (ii) Mountains 30% (iii) Plateaus 27% Total 100% (i) Name the land feature which occupies the highest surface area of India. (ii) Give two advantages of the above land feature.
Answer: (i) The plains (43%) occupy the highest surface area of India. (ii) (a) The plains provide opportunity for crop farming. (b) The plains have good climatic conditions for human habitation.
19. How over-irrigation and mining lead to land degradation? Or How is over-irrigation responsible for land degradation? Which states of India face this problem? [CBSE 2013]
Answer: Over-irrigation and mining lead to land degradation as : (i) Over-irrigation is responsible for land degradation due to waterlogging which leads to increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil. Water logging is a major issue in Punjab, Haryana, UR (ii) The mineral processing like grinding of limestone for cement industry calcite and soapstone for ceramic industry generate huge quantities of dust in the atmosphere. It retards the process of infiltration of water into the soil after it settles down on the land.
20. Explain the major factors which are responsible for the formation of soil. [CBSE 2009 (O), Sept. 2011] Or Explain any three factors responsible for the formation of soil. [CBSE 2013]
Answer: (i) Relief, parent rock or bedrock, climate, vegetation and other forms of life and time are important factors in the formation of soil. (ii) Various forces of nature such as change in temperature, actions of running water, wind and glaciers, activities of decomposers, etc. contribute to the formation of soil. (iii) Chemical and organic changes which take place in the soil are equally important. (iv) Soil also consists of organic (humus) and inorganic materials.
21. Mention the criteria on the basis of which Indian soils can be classified.
Answer: (i) Factors responsible for soil formation. (ii) Colour (iii) Thickness (iv) Texture (v) Age (vi) Chemical and Physical properties.
22. Explain the distribution of alluvial soils.
Answer: (i) This is the most widely spread and important soil of India. (ii)These soils also extend in Rajasthan and Gujarat through a narrow corridor. (iii)Alluvial soil is also found in the eastern coastal plains particularly in the deltas of the Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna and Kaveri rivers.
23. With reference to alluvial soil answer the following questions- (i) How is it classified on the basis of its age? (ii) Alluvial soil as a whole is very fertile. Give reasons.
Answer: (i) On the basis of age alluvial soil is classified as Bangar and Khadar. (ii) Mostly these soils contain adequate proportion of potash, phosphoric acid and lime.
24. Explain the distribution of black soil.
Answer: (i) Black soil is typical of the Deccan trap region spread over northwest Deccan plateau. (ii) They cover the plateau of Maharashtra, Saurashtra, Malwa, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh. (iii) They are also found in the Godavari and Krishna valleys.
25. Which soil is considered ideal for growing cotton? How is the soil formed?
Answer: Black soil. These soils have been formed due to the weathering of the lava spread over large areas during volcanic activity in the Deccan Plateau and different climatic conditions.
26. (I) Which soils develop on crystalline igneous rocks? (ii) Why do the soils develop a reddish colour? (iii) Name any two states where this soil is found.
Answer: (i) Red soil (ii) The soils develop a reddish colour due to diffusion of iron crystalline and metamorphic rocks. (iii) Odisha and Chhattisgarh
27. Mention the factors on which the land- use pattern of India depends upon. [CBSE Sept. 2012]
Answer: The use of land is determined by physical as well as human factors. (i) Physical factors: Topography, climate and soil types. (ii) Human factors: Population density, technological capability, culture and traditions.
28. (i) ‘Humus content of the laterite soil is very low.’ Explain by giving two reasons. (ii) Mention any two crops associated with the soil.
Answer: (i) (a) The soil is formed due to intense leaching. So the nutrients of the soil are washed away by heavy rains. (b) The soil is formed in the regions of high temperature. So most of the microorganisms, particularly the decomposers, like bacteria, get destroyed. (ii) Tea and Coffee.
29. (i) ‘The arid soil lacks humus and moisture.’ Explain. (ii) Name any two states where this soil is formed.
Answer: (i) The arid soil is found in dry climatic conditions. Due to dry climate and high temperature, evaporation is faster and the soil lacks humus and moisture. (ii) Rajasthan and Gujarat
30. What is soil erosion? Name any four states which have been affected by gully erosion.
Answer: The removal of soil by the forces of nature, particularly wind and water is called soil erosion. Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Bihar and Rajasthan.
31. How does the soil of the Ganga-Yamuna plain differ from that of central Maharashtra?
Answer: The Ganga-Yamuna plain has alluvial soils, whereas the central Maharashtra has black soils. The alluvial soils are formed by the depositional work of rivers in the river ualleys, flood plains and deltas. The black soils develop from volcanic rocks from where the lava flows.
32. What are the causes of soil erosion in : (I) Shiwaliks or the Outer Himalayas. (ii) North-Eastern parts of India. (iii) Arid regions of India.
Answer: (I) Shiwaliks or the Outer Himalayas : Destruction of vegetation is the main cause of soil erosion in hilly areas because when vegetation is removed, the soil surface becomes loose, and is more easily removed by the running water. (ii) North-Eastern parts of India : Heavy rainfall which leads to frequent floods is responsible for soil erosion. (iii) Arid regions of India : In deserts and dry regions, where there is little or no vegetation, wind is the most powerful agent of soil erosion, blowing away fine particles of sand depositing them in other areas making both the areas unproductive.
33. Which is the main cause of land degradation in Gujarat, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh? How can it be checked? Explain. [CBSE 2012] Answer: Large scale over-grazing has caused severe land degradation. Measures to check : (i)Afforestation and proper management of grazing. (ii)Planting of shelter belts. (iii)Stabilisation of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes. (iv) Control on overgrazing.
Long Answer Type Questions
1. What is resource planning? Mention the steps which are involved in resource planning. [CBSE 2009 (F); Sept. 2010, 14] Or Explain the three steps involved in the resource planning in India. [CBSE Sept. 20W] Or What are the three stages of resource planning in India?
Answer: “Resource planning is a technique or skill of proper or judicious use of resources. ” Resource planning is a complex process which involves : (i) Identification and inventory of resources across the regions of the country. This involves surveying, mapping, qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of the resources. (ii) Evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional set up for implementing resource development plans (iii) Matching the resource development plans with overall national development plans.
2. Explain the classification of resources on the basis of exhaustibility. [CBSE 2009 (D), Sept. 2010, 2011]
Answer: (i) Renewable resources: “Renewable resources are the natural resources which can be used again and again or can be reproduced by physical, mechanical and chemical processes.” Solar energy, air, water and soil are some of the renewable resources of energy.
(ii) Non-renewable resources: “Non renewable resources are the natural resources that cannot be replaced at all or within a reasonable time.” Fossil fuels such as oil, gas and coal are examples of non renewable resources. These resources are accumulated over millions of years. They are considered to be non-renewable resources because once they are used up, they are gone forever.
3. Explain the classification of resources on the basis of ownership. [CBSE 2009 (O), 2014] Or Explain what is meant by national resources and individual resources. [CBSE Sept. 2010, 2014]
Answer: (a) Individual Resources: Resources which are owned by private individuals are known as individual resources. Plots, fields, houses, cars, books, etc., are some examples of individual resources.
(b) Community Owned Resources: The resources which are accessible .to all the members of the community are known as community resources. Village ponds, public parks, playgrounds, etc., are some examples of community resources.
(c) National Resources: All the resources which are under the control of state or union government are known as national resources. All the resources within political boundaries are national resources because the government has the power to acquire even the private properties.
(d) International Resources: These resources are owned and regulated by international institutions. The oceanic resources beyond 200 km of the Exclusive Economic Zone belong to the open ocean, and no individual country can utilise these without the concurrence of international institutions. India has got the right to mine manganese nodules from the bed of the Indian Ocean from that area which lies beyond the Exclusive Economic Zone.
4. Explain the classification of resources on the basis of the state of development. [CBSE 2008] Or Distinguish between stock resources and reserve resources. [CBSE Sept. 2010,12]
Answer: (i) Potential Resources : Resources which are found in a region, but have not been utilised due to lack of capital or other reasons. For example: the western parts of India, particularly Rajasthan and Gujarat have enormous potential for the development of wind and solar energy, but so far, these have not been developed properly.
(ii) Developed Resources : These are resources which have been surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilisation. The development of resources depends on technology and the level of their feasibility. For example, India has a cumulative total of about 2,47,847 million tonnes of coal resources.
(iii) Stock : These are the materials in the environment which have the potential to satisfy the human needs but cannot be used as the human beings do not have the appropriate technology to convert them into usable form. For example, water (H20) is a compound of two inflammable gases, i.e., hydrogen and oxygen, but human beings do not have the required technology to use them as a source of energy.
(iv) Reserves : These are the subset of the stock, which can be put into use with the existing technology, but their uses have been postponed keeping in mind the needs of the future generations. For example, India has sufficient amount of forests to fulfil the needs of the present generation, but they are being protected for the future generations.
5. How is land a natural resource of utmost importance ? Explain with four facts. [CBSE 2008 (O), 2012, 2013] Or “Land is a natural resource of utmost importance.” Elaborate the statement with the help of suitable examples highlighting the value of land resource. [CBSE 2013]
Answer: Land is an important natural resource, because : (i)All economic activities are performed on land. (ii)It supports natural vegetation and wildlife. (iii)Most of the minerals are formed in land. (iv)It is used for transport and communication system.
6. Which is the most widely spread and important soil of India? State any six characteristics of this type of soil. [CBSE 2008 (F), Sept. 2010] Or Mention any four characteristics of alluvial soils. Or How are alluvial soils formed? How is Bangar different from Khadar? [CBSE 2012]
Answer: Characteristics of the Alluvial soil are :
(i) Alluvial soils are transported soils. Most of the soils are derived from the sediments deposited by rivers as in the Indo-Gangetic plain. Thus, the parent material of these soils is of transported origin.
(ii) These soils consist of varying proportion of sand, silt and clay. In the upper course of the river, the soil is coarse. In the middle course, it is medium, and fine grained in the lower course.
(iii) Apart from the size of their grains or particles, soils are described according to their age as well. They are old alluvium and new alluvium. Locally, the old alluvium is called ‘Bhangar’ and the new alluvium is called ‘Khadar’.
(iv) The old alluvium often contains ‘kankar, nodules, with calcium carbonates in the sub-soil. The new alluvium is more fertile than the old alluvium.
7. Which soil is called ‘regur soil? Mention any four characteristics of this type of soil. [CBSE 2009 (F), Sept. 2010, 2012, 2013]
Answer: (i) These have been formed due to withering of lava. (if) The black soils are made of extremely fine materials, i.e., clayey materials. (iii)These soils are rich in soil nutrients such as calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate, potash and lime. (iv)These soils are generally poor in phosphoric content. (v)The soil is well known for its capacity to hold moisture.
8. How is red soil formed? Mention its three characteristics. [CBSE Sept. 2010] Or How does red soil develop? What makes it look red and yellow? [CBSE 2014]
Answer: Formation : Most of the red soils have come into existence due to weathering of ancient crystalline igneous rocks. Characteristics/Features : (i) Soils are loamy in deep depressions and in uplands. They consist of loose gravels and highly coarse materials. (ii) The colour of these soils is generally red, often grading into brown, chocolate or yellow. The red colour is due to wide diffusion rather than high percentage of iron content. It looks yellow when it occurs in a hydrated form. (iii) Soils are deficient in phosphoric acid, organic matter and nitrogenous materials but are fairly rich in potash. But crops are cultivated with the use of fertilizers.
9. Which geographical factors are responsible for the evolution of black soil? Why is it considered the most suitable for growing cotton? [CBSE 2012, 2013]
Answer: (1) Climatic conditions like temperature, rainfall etc. along with present rock material are important factors for making of black soil. The parent rock is volcanic rock.
(2) It is ideal for growing cotton because: (i)It has capacity to hold moisture. (ii)They are rich in calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash and lime. (iii)This soil is also known as black cotton soil, (iv) They develop deep cracks during hot weather, which help in the proper aeration of the soil.
10. How is mountain soil (forest soil) formed? Mention any four characteristics of forest soil. .
Answer: Formation: The soils are formed due to mechanical weathering caused by snow, rain, temperature variation, etc. Characteristics/Features: (i) These soils are heterogeneous in nature, and their character changes with mountainous environment and altitude. (ii) The soils are very rich in humus, but are deficient in potash, phosphorus and lime. (iii) The soils are especially suitable for plantation of tea, coffee, spices and tropical fruits. (iv) The soil is loamy and silty in valley sides and coarse grained in the upper slopes. It is acidic with low humus content in the snow covered areas. It is fertile in the lower parts of the valleys.
11. Mention any four features of the arid soils. Or Name the soil type which is widely found in Western Rajasthan. Explain two important characteristics of this soil type which make it unsuitable for cultivation. [CBSE 2012]
Answer: Arid soil is widely found in Western Rajasthan. (i) The soil ranges red to brown in colour. (ii) The soils contain considerable amount of soluble salts. (iii) The soils contain a low percentage of organic matter due to dry climate and absence of vegetation. (iv) The soil is alkaline in nature as there is no rainfall to wash soluble salts. (v) The lower horizon of the soil is occupied by ‘kankar’ because of the increasing calcium content downwards. The ‘kankar’ layer formations in the bottom horizons restrict the infiltration of water. (vi) The soils are infertile but with irrigation and fertilizers, the drought resistant and salt tolerant dry crops such as barley, cotton, wheat, millets, maize, pulses, etc., are grown. (Any Four)
12. Explain the formation and important features of the laterite soil. [CBSE 2013, 14]
Answer: Formation: It develops in areas with high temperature and heavy rainfall. The laterite soil is a result of intense leaching owing to heavy tropical rains. Features : (i) The soils are acidic in nature, coarser and crumbly in texture. (ii) Due to lack of nitrogen, potassium and organic elements, the laterite soils lack fertility, and are not suitable for cultivation. But when the soils are manured and irrigated, some crops can be cultivated. (iii) As the soils are indefinitely durable, so they provide valuable building materials.
13. What is soil erosion? Explain the major types of soil erosions prevailing in India. [CBSE Sept. 2010]
Answer: “Soil erosion is the removal of soil by the forces of nature like wind and water, more rapidly than the various soil forming processes can replace it.” Generally, there is a balance between the soil forming process and the erosional process. The balance can be disturbed by natural or human factors.
Types of Soil Erosion : (a) Water Erosion : Water is a powerful agent of soil erosion. Following are the major types of erosion caused by water.
(i) Sheet Erosion : When the top layer of the soil is removed over a large area by the running water, it is called as sheet erosion.
(ii) Rill Erosion : This is the second stage of sheet erosion. If erosion continues unchecked for a sufficient time, (rills) or small finger-shaped grooves which are a few centimetres in depth, may develop on the landscape. Over a period of time, the fine rills increase in number and also become deeper and wider, and resemble the twigs, branches and trunk of a tree. This is called as rill erosion.
(iii) Gully Erosion : This is the third stage of sheet erosion. With further erosion of the soil, the rills may deepen and become enlarged, and are ultimately turned into gullies. The main cause of gully erosion is the removal of vegetation, particularly of trees with their widespread binding roots. Gullies cut up agricultural land and the entire area may be turned into a bad land topography. Gully erosion is also responsible for the formation of ravines.
(b) Wind erosion : Wind is a powerful agent of erosion in arid and semi-arid lands with little rainfall. Wind can lift the valuable top soil from one area and deposits in another area. The wind erosion is very dangerous type of erosion because due to wind most of the deserts of the world are expanding.
14. Give reasons : (i) Alluvial soil can hold moisture, and is very fertile. (ii) Black soil needs to be tilled after the first rain. (iii) Red soil is ideal for dry farming. (iv) The percentage of organic matter in desert soil is very low. (v) Red soil is less fertile.
Answer: (i) Because the alluvial soil is made up of fine particles. The soil is very fertile because it is rich in mineral nutrients like potash and lime. (ii) The soil is sticky, and difficult to work unless tilled immediately after the first rain. (iii) Because it does not require much moisture. (iv) Because of the dry climate and absence of vegetation. (v) Because it is deficient in phosphorus, nitrogen, lime and humus.
15. Name two important crops associated with the following types of soil : (a) Alluvial soil (b) Black soil (c) Desert soil (d) Laterite soil
Answer: (a) Alluvial: Wheat and rice. (b) Black: Cotton and sugarcane. (c) Desert: Barley and ragi. (d) Laterite: Coffee and tea.
16. Explain the land-use pattern of India.
Answer: (i) The net sown area in India has decreased from 45.26% to 43.41%. This means that more and more agricultural land is being shifted to other activities. This is not a healthy trend, and must be checked. The steps taken by government has resulted in increase of net sown area to 47% in 2005-06.
(ii) The pattern of the net sown area varies greatly from one state to another. It is over 80 per cent of the total area in Punjab and Haryana, and less than 10 per cent in Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Manipur and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
(iii) The area under forests has increased from 18.11% in 1960-61 to 22.57% in 2000-03 and to 23% in 2005-06 yet it is far below than the scientific norms.
(iv) The land under permanent pasture is very low, i.e., only 3.45% (Fallen to 3%). This shows the tremendous pressure of livestock population on agricultural land. Cattle are reared mainly on the farm wastes, grain chaff and a few fodder crops.
(v) Area under fallow land has also decreased which shows, that subsistence agriculture is being replaced by commercial agriculture.
(vi) A part of the land is termed as waste land, and land put to other non-agricultural uses. Waste land includes rocky, arid and desert areas, and land put to other non- agricultural uses includes settlements, roads, railways, industries, etc.
17. Explain any four proper fanning techniques which can be used for soil conservation. Or Suggest any three measures of soil conservation. [CBSE Sept. 2010, 2011] Or What is soil conservation? Explain any three methods of soil conservation suitable to Indian conditions. [CBSE 2013, 14]
Answer: Soil conservation includes all those measures which help in protecting the soil from erosion or degradation.
(i) Crop rotation : If the same crop is sown in the same field, year after year, this consumes certain nutrients from the soil making it infertile. Crop rotation can check this type of erosion.
(ii) Settled agriculture : Checking and reducing shifting agriculture by persuading the tribal people to switch over to settled agriculture.
(iii) Terracing and contour bunding : Terracing and contour bunding across the hill slopes is a very effective, and one of the oldest methods of soil conservation. Hill slope is cut into a number of terraces having horizontal top and steep slopes on the back and front. Contour bunding involves the construction of bank along the contour.
(iv) Strip cropping : Large fields can be divided into strips. Strips of grass are left to grow between the crops. This breaks up the force of the wind. This method is known as strip cropping.
(v) Shelter Belt : Planting lines of trees to create shelter also works in a similar way. Rows of such trees are called shelter belts. These shelter belts have contributed significantly to the stabilisation of sand dunes and in establishing the desert in western India.
HOTS Questions and Answers
1. Do you think that resources are free gifts of nature as is assumed by many? Justify your answer with any three suitable arguments. [CBSE 2012]
Answer: They are not free gifts of nature as : (i) Resources are a function of human activities, (ii) Human beings themselves are essential components of resources. (iii) They transform material available in our environment into resources and use them. For example river is a natural resource but river become a resource when its water is used for irrigation or power production.
2. What is the importance of natural resources? [CBSE 2014]
Answer: (i) Resources are used to satisfy human wants. (ii) Resources are base for economic development for example water, fossil fuel, solar energy is required for power production. (iii) Resources are vital for human survival as well as maintaining the quality of life. (iv) Land which is a natural resource support natural vegetation, wild life, human life and all economic activities. (v) Water which is another natural resource is essential for human, plant and wild life.
3. “India has land under a variety of relief features.” Justify. [CBSE 2014] Or What are the main advantages of India’s land under a variety of relief features? [CBSE 2010, 2011]
Answer: India has land under a variety of relief features, namely: mountains, plateaus, plains and islands. (i) About 43 per cent of the land area is plain, which provides facilities for agriculture and industry. (ii) Mountains account for 30 per cent of the total surface area. They ensure perennial flow of some rivers, provide facilities for tourism and ecological aspects. (iii) About 27 per cent of the land area is plateau. It possesses reserves of minerals, fossil fuels and forests.
4. Discuss the problems which have been caused due to over-utilisation of resources. Suggest any two ways to save the resources. Or “Indiscriminate use of resources has led to numerous problems”. Justify the statement in three points. [GBSE 2012, 14]
Answer: (I) Depletion of resources : Over-utilisation has led to the depletion of the resources for meeting the greed of a few individuals. For example, over-utilisation of petroleum products has led to a situation where most of the countries of the world are facing energy crisis.
(ii) Concentration of resources: This has divided the society into ‘haves’ and ‘have nots’ or the rich and the poor.
(iii) Global ecological crisis : Over utilisation of resources has led to the global ecological crisis such as global warming, depletion of ozone layer, pollution and land degradation.
Suggestions : (i) Minimising wastage. (ii) Use of renewable resources.
5. “The earth has enough resources to meet the need of all but not enough to satisfy the greed of even one person.” How is this statement relevant to the discussion of development? Discuss. [CBSE 2013]
Answer: (i) Resources are vital for any developmental activity. (ii) The irrational consumption and over utilization of resources may lead to socio economic and environmental problems. (iii) Indiscriminate exploitation of resources led to global ecological crises such as global warming, environmental pollution, etc (iv) The greedy and selfish individuals and exploitative nature of modem technology is the root cause for resource depletion at the global level. (v) If the present trend of resource depletion by a few individuals and countries continues, the future of our planet is in danger. (vi) There is need for sustainable development. It means development should take place without damaging the environment and development in the present shout not compromise with the need of future generations’.
6. Why is there a need to conserve resources? What was Gandhiji’s opinion regarding the conservation of resources? [CBSE Sept. 2012] Or Explain the importance of conservation of resources. [CBSE Sept. 2010, 2011,2014] Or Why is it essential to have resource planning? Give three reasons. [CBSE 2014]
Answer: (i) Limited supply : Most of the resources have limited supply as compared to their demand for example supply of fossil fuels is limited.
(ii) Pollution and global warming : Overutilisation of natural resources may lead to environmental pollution for example over use of fossil fuel is a major factor responsible for global warming.
(iii) Socio economic problem : The destruction of forests and wildlife is not just a biological issue. The biological loss is strongly correlated with the loss of cultural diversity. Such losses have increasingly marginalised and impoverished many indigenous and other forest-dependent communities, who directly depend on various components of the forest and wildlife for food, drink, medicine, culture, spirituality, etc. Within the poor, women are affected more than men. In many societies, women bear the major responsibility of collection of fuel, fodder, water and other basic subsistence needs. As these resources are depleted, the drudgery of women increases and sometimes they have to walk for more than 10 km to collect these resources. This causes serious health problems for women and negligence of home and children because of the increased hours of work, which often has serious social implications. Gandhiji was very apt in voicing his concern about resource conservation. He said, “There is enough for everybody’s need, and not for anybody’s greed. ” According to him, they were the greedy and selfish individuals who were responsible for depletion of resources. He was in favour of producing for the masses than mass production.
7. Why is there a need for resource planning? What can happen if we don’t follow the principle of resource planning?
Answer: (i) Most of the resources are limited in supply. (ii) Most of the resources are unevenly distributed over the country. (iii) Overutilisation of the resources may lead to pollution of the environment. (iv) There is a need to plan the human resources because only then we would be able to develop our natural resources. Effects : (i) Energy crisis (ii) Global warming
8. Explain any four reasons responsible for land degradation in India. Or Explain any four human activities which are mainly responsible for land degradation in India. Give any two suggestions to check land degradation. [CBSE 2014]
Answer: (i) Mining : Mining is one of the major factors responsible for land degradation. In states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha, deforestation due to mining have caused severe land degradation.
(ii) Overgrazing : During the long dry period, grass is grazed to the ground and torn out by the roots by animals. This leads to loosening of soil and it is easily washed away by rains. In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra overgrazing is one of the main reasons for land degradation.
(iii) Overirrigation : In the states of Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh, overirrigation is responsible for land degradation due to waterlogging which leads to increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil.
(iv) Processing of minerals : The mineral processing like grinding of limestone for cement industry and calcite and soapstone for ceramic industry generate huge quantity of dust in the atmosphere. It retards the process of infiltration of water into the soil after it settles down on the land. In recent years, industrial effluents as waste have become a major source of land and water pollution in many parts of the country.
Suggestions : (i) Plant more trees (ii) We should not waste paper.
- School Guide
- Class 10 Syllabus
- Maths Notes Class 10
- Science Notes Class 10
- History Notes Class 10
- Geography Notes Class 10
- Political Science Notes Class 10
- NCERT Soln. Class 10 Maths
- RD Sharma Soln. Class 10
- Math Formulas Class 10
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Notes
Class 10: History Notes
- CBSE Class 10 History Notes
- The Rise of Nationalism in Europe Class 10 History Notes Chapter 1
- Nationalism in India - CBSE Class 10 History Notes Chapter 2
- The Making of Global World Class 10 History Notes Chapter 3
- The Age of Industrialisation Class 10 History Notes Chapter 4
- Print Culture and the Modern World Class 10 Notes History Chapter 5
Class 10: Geography Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Geography Notes
CBSE Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 1- Resources and Development
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 2- Forest and Wildlife Resources
- CBSE Class 10 Geography Notes Chapter 3 : Water Resources
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 4 - Agriculture
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 5: Minerals and Energy Resources
- Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Geography Notes Chapter 6
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 7- Lifelines of National Economy
Class 10: Polity Notes
- Class 10 Political Science Notes
- Power Sharing Class 10 Civics Notes Chapter 1
- Federalism Class 10 Notes Civics Chapter 2
- Gender, Religion and Caste Class 10 Notes Chapter 4 Civics
- Political Parties Class 10 Notes Civics Chapter 6
- Chapter 7 Outcomes of Democracy : CBSE Notes Class 10 Political Science (Civics)
Class 10: Economics Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Economics Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Notes Economics Chapter 1: Development
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Economics Chapter 2 : Sectors of the Indian Economy
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Economics Chapter 3: Money and Credit
- Globalisation and the Indian Economy : CBSE Class 10 Economics Notes Chapter 4
- Consumer Rights Class 10 Notes
Resources and Development is the first chapter in CBSE Class 10 Geography , which discusses the concept of resources and their various forms. The chapter covers the different types of resources such as natural, human-made, and human resources, and their utilization for the development of society. It also discusses the process of resource development and planning in India, focusing on the need for sustainable development.
Additionally, the chapter covers the topics of soil conservation and erosion, highlighting the causes and effects of soil erosion and various methods of soil conservation. Overall, this chapter provides an overview of the various resources available on Earth and their importance in the development of human society. The Resources and Development notes cover all the necessary topics that are extremely important for the board examination 2024. It can save you time and will positively affect your result.
Class 10 Geography Chapter 1: Resources and Development
1. Resources
Everything in the environment around us that can be used to fulfil our requirements, and is technologically accessible, economically practical, and culturally acceptable, is referred to as a ‘Resource’. Human actions also function as resources. Humans are necessary components of resources. They convert the components in our surroundings into resources and consume them.
Classification of Resources
Resources can be classified in the following ways and types:
- On the basis of origin – biotic and abiotic
- On the basis of exhaustibility – renewable and non-renewable
- On the basis of ownership – individual, community, national and international
- On the basis of the status of development – potential, developed stock, and reserves.

1. On the Basis of Origin- Biotic and Abiotic
Biotic Resouces: These are taken from the biosphere and contain life, such as humans, plants and wildlife, fisheries, ruminants, and so on.
Abiotic Resouces: The abiotic resource is anything that is made up of nonliving items such as rocks and metals.
2. On the Basis of Exhaustibility- Renewable and Non-Renewable
Renewable Resources: Renewable or replenishable resources are those that can be replaced or reproduced by physical, chemical, or mechanical processes, such as solar and wind energy, water, forests and wildlife, and so on. Renewable resources can be further divided into continuous or flow.
Non-renewable Resources: These occur throughout a wide range of geological periods. These resources take millions of years to form. Minerals and fossil fuels are examples of resources that take millions of years to create. Some resources take like metals are recyclable, whereas some fossil fuels cannot be recycled and get exhausted.
3. On the Basis of Ownership- Individual, Community, National, and International
Individual Resources: These are privately held by people. Personal resource ownership includes plantations, pasture fields, ponds, water in wells, and various other things.
Community Resources: These are communal resources that are available to all members of the community, such as grazing fields, burial sites, village ponds, public spaces, picnic areas, playgrounds, and so on.
National Resources: Technically, the country owns all of the resources. The nation has the legal authority to acquire private property for the public interest. The nation owns all minerals, water resources, forests, animals, and land within its political limits, as well as the oceanic region up to 12 nautical miles (22.2 km) from the shore, referred to as territorial water and its resources.
International Resources: Some resources are regulated by international institutions. Beyond 200 nautical miles of the Exclusive Economic Zone, marine resources belong to open waters, and no one country can use them without the approval of an international authority.
4. On the basis of the Status of Development- Potential, Developed Stock, and Reserves
Potential Resources: These resources exist in a region but have not been used. For example, the western areas of India, notably Rajasthan, and Gujarat offer huge potential for wind and solar energy development, but they have yet to be completely developed.
Developed Resources: These are resources that have been surveyed and their quality and quantity determined for use. The development of resources is determined by technologies and their level of sustainability.
Stock: Stock refers to materials in the environment that have the potential to meet human requirements but lack the required technology to accomplish so. For example, Hydrogen is a valuable source of energy. However, we need advanced technology to put it to use.
Reserves: Reserves are a subset of the stock that can be used with the technology ‘know-how’ but has not yet been used. These can be utilized to satisfy requirements in the future. For example, Water in dams, woods, and other sources of water is a reserve that can be utilized in the future.
Read More: Resources and its Types
2. Development of Resources
Resources are essential for human life; however, they have been utilized indiscriminately by humans, resulting in problems such as:
- The centralized control of resources in a few hands split society into two groups, rich and poor.
- Consumption of resources to satisfy the avarice of a few people.
- It has resulted in worldwide environmental issues such as global warming, ozone depletion, pollution, and land degradation.
A fair utilization of resources has become critical for long-term quality of life and world peace. However, its abolition by a few individuals or countries may endanger the planet. Resource planning is important for the sustainable existence of different forms of life and Sustainable Economic Development refers to the development which takes place without damaging the environment, and development happening at the present shouldn’t compromise with the generations to come.
3. Resource Planning
The commonly acknowledged technique for prudent resource utilization is planning. There are locations in India that are rich in certain sorts of resources but poor in others. There are certain locations that can be called self-sufficient in terms of resource availability, while others have severe shortages of critical resources. This necessitates resource planning that is balanced at the national, state, regional, and local levels.
Resource Planning in India
Resource planning is a complicated process that includes:
- Identifying and inventorying resources across the country. This includes collecting data, mapping, and both quantitative and qualitative resource estimates and measurements.
- Developing a planning framework that is equipped with the necessary technology, skills, and institutional infrastructure to carry out resource development plans.
- Linking resource development strategies with long-term national development goals.
From the First Five Year Plan, released after independence, India has made coordinated efforts to achieve resource planning goals. The availability of resources alone may hinder progress in the absence of equivalent advances in technology and institutions. Resources when accompanied by proper technical progress and institutional adjustments, contribute to development.
Resource conservation at many levels is critical for overcoming irrational consumption and over-utilization of resources.
4. Land Resources
Land is a vital natural resource, but it is a finite property; thus, it is critical to use the existing land for varied purposes with careful consideration. India contains land with a range of relief features, including mountains, plateaus, plains, and islands.

Land Resources
Land Utilization
The following uses are made of land resources:.
- Barren and Wasteland
- Land put out for non-agricultural uses
- Fallow lands
- Other uncultivated lands which exclude fallow land
- Net Sown area
Land Use Pattern in India
The usage of land is influenced by both physical and human causes:
- Physical Factors: These refer to the factors such as topography, climate, and soil types.
- Human Factors: The human factors include population density, technological capability, culture, traditions, etc.

General Land Use Categories
Wasteland refers to the land which has been put out for other non-agricultural uses and includes rocky, arid, and desert regions, roads, railways, and so forth. The continuous use of the land resource over a long period of time, without taking appropriate measures for management and conservation, results in what is known as land degradation.
Read More: Land Utilization and Land Use Pattern in India
Land Degradation and Conservation Measures
Human activities including deforestation, overgrazing, mining, and extraction have not only caused land degradation but have also accelerated the rate at which natural processes cause land harm.
There are several approaches for resolving land degradation issues:
- Afforestation and adequate grazing maintenance.
- Planting of plant shelter zones.
- Sand dunes are stabilized by the growth of prickly shrubs.
- Wastelands must be managed properly.
- Mining activity supervision.
- After-treatment release and removal of industrial wastewater and wastes.
Read More: Land Degradation and Conservation
5. Soil as a Resource
The most significant renewable natural resource is soil. Various natural factors such as temperature variations, the acts of running water, wind, glaciers, decomposer activities, and chemical and organic changes that occur in the soil all contribute to the development of soil:
- Soil takes millions of years to be formed up to only a few cm in depth. There are various factors and forces of nature such as temperature, actions of running water, wind, etc. which contribute to the formation of soil.
- The parent rock or bedrock, climate, vegetation, etc. are forms of life and time, important in the formation of soil.
- Chemical and also organic changes also play important roles in soil formation.
- Soil consists of both organic as well as inorganic materials.
6. Classification of Soils
India has a wide range of environmental characteristics, landforms, climate zones, and flora kinds. These have aided in the formation of distinct soil formations, color, thickness, texture, age, chemical as well as physical properties, soils of India can be classified as:
Alluvial Soils
- This is the most widely distributed and significant soil. Alluvial soil covers the whole northern plains.
- It can also be found in Rajasthan, Gujarat, and the eastern coastal plains, namely in the deltas of the Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, and Kaveri rivers.
- These were deposited by three major Himalayan river systems: the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra.
- Sand, silt, and clay are the components of alluvial soil.
- Based on age, Alluvial soils can be classified as:
- Old Alluvial (Bangar): The Bangar soil has a higher concentration of Kanker nodules than that of Khadar.
- New Alluvial (Khadar): It has more fine particles and is more fertile as compared to Bangar.
- Alluvial soils are mostly very fertile and contain an adequate amount of potash, phosphoric acid, and lime, ideal for the growth of sugarcane, paddy, wheat, and other pulses crops.

Alluvial Soil
- These black soils are also referred to as regur soils. These are great for cotton cultivation.
- The parent rock material, as well as the climatic conditions, are essential elements in the production of black soil.
- The soil extends southeast along the Godavari and Krishna basins and covers the plateaus of Maharashtra, Saurashtra, Malwa, Madhya Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh.
- The black soils are composed of exceedingly fine clayey minerals. They are widely known for their ability to retain moisture.
- They are high in soil nutrients such as calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash, and lime.
- This type of soil is found mostly in the Deccan Trap region and spread over the northwest Deccan plateau and is also made up of lava flows.
- The soil has a sticky nature and is difficult to work with unless it is tilled immediately after the first shower during pre-monsoon periods.
.webp)
Red and Yellow Soils
- Red soil forms on crystalline igneous rocks in low-rainfall sections of the Deccan plateau’s eastern and southern regions.
- Yellow and red soils may be found in regions of Odisha, Chhattisgarh, the southern Ganga plain, and the Piedmont zone of the Western Ghats.
- The reddish color of these soils is caused by iron diffusion in crystalline and metamorphic rocks.
- When it is hydrated, it has a yellow appearance.
.webp)
Red and Yellow Soil
Laterite Soils
- Laterite soil forms in tropical and subtropical climates with alternating wet and dry seasons.
- This soil is the product of heavy rain’s extensive leaching.
- They are mainly deep to variable depths, acidic in nature (pH 6.0), and often low in plant nutrients. This type of soil is generally found in the southern states, the western Ghats area of Maharashtra, Odissa, some portions of West Bengal, and the Northeastern states.
- The soil supports deciduous and evergreen woods, but it is deficient in humus.
- This soil is extremely beneficial for growing tea and coffee.
.webp)
Laterite Soil
- Arid soils have a sandy texture and are salty in character.
- Evaporation occurs faster due to the dry environment and high temperatures, and the soil lacks humus and moisture.
- Kankar occupies the bottom layer of the soil because of the rising calcium concentration downwards.
- The colour of arid soils ranges from red to brown.

Forest Soils
- These soils are found in hilly and mountainous areas where there is enough rainforest.
- The valley sides are loamy and silty, whereas the top slopes are coarse-grained.
- The texture of the soil changes depending on the alpine environment in which it is generated.
- Fertile soils may be found in the lower valleys, particularly on river terraces and alluvial fans.

Forests Soils
The map below shows the distribution of soil in India:

Major types of soil
Read More: Soil Formation
7. Soil Erosion and Soil Conservation
Soil erosion is defined as the degradation of the soil cover and subsequent washing away. Soil erosion is caused by human activities such as deforestation, overgrazing, building, and mining, as well as natural processes such as wind, glaciers, and water. Running water breaks through the clayey soils, forming deep channels known as gullies.
The land has become unsuited for agriculture and is referred to as bad land. Such regions are known as ravines in the Chambal basin. Water can flow in a sheet across huge portions of the slope at times. This is referred to as sheet erosion. Wind erosion occurs when the wind sweeps loose dirt off the flat or sloping ground. Defective agricultural techniques also contribute to soil erosion.
Read More: Soil Erosion
Different Ways for Soil Conservation
- Ploughing following contour lines slows the flow of water down the hills. This is known as contour ploughing.
- Terrace cultivation helps to prevent erosion. This form of farming is practised in the Western and Central Himalayas.
- When a vast field is split into strips and grass is allowed to grow in between the crops. This then splits up the wind’s power. Strip cropping is the name given to this technique.
- Planting lines of trees to provide cover aids in the stability of sand dunes in the western Indian desert. Shelter Belts are rows of such trees.
FAQs on CBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 1: Resources and Development
Q 1. what is a resource.
Everything in the environment around us that can be used to fulfill our requirements, and is technologically accessible, economically practical, and culturally acceptable, is referred to as a ‘Resource’.
Q 2. Name the types of Resources.
The types of resources include Natural, Human and Human Made resources.
Q 3. Why are resources important?
Resources are important as without resources none of our needs are satisfied and all the raw materials are obtained mostly from resources.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- School Geography
- School Learning
- 10 Best Slack Integrations to Enhance Your Team's Productivity
- 10 Best Zendesk Alternatives and Competitors
- 10 Best Trello Power-Ups for Maximizing Project Management
- Google Rolls Out Gemini In Android Studio For Coding Assistance
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

NCERT Solutions for Class 10th: Ch 1 Resources and Development Geography
Ncert solutions for class 10th: ch 1 resources and development geography social studies (s.st), contact form.
Question and Answer forum for K12 Students

Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Extra Questions and Answers Resource and Development
In this page, you can find CBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Extra Questions and Answers Resource and Development Pdf free download, NCERT Extra Questions for Class 10 Social Science will make your practice complete.
Resource and Development World Class 10 Extra Questions and Answer Geography Chapter 1 Very Short Answers Type
Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Extra Questions
Question 1. Mention two factors on which resource development depends. Answer:
- Latest technology
- Quality of humans as resource

Question 2. What is resource? Give one example. Answer: Everything available in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs, and which is technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally acceptable can be termed as ‘resource’. For example, water is a resource.

Question 3. How can you say that resources are not free gifts of nature? Answer: Resources are, in fact, a function of human activities. Human beings, who themselves are essential components of resources, transform materials available in our environment into resources and use them. So, it is wrong to say that resources are free gifts of nature.
Question 4. What is meant by sustainable development? Answer: Sustainable development means ‘development should take place without damaging the environment, and development in the present should not compromise with the needs of the future generations.
Question 5. Why was Rio de Janeiro Earth Summit convened in 1992? Answer: The Summit was convened for addressing urgent problems of environmental protection and socio-economic development at the global level.
Question 6. What is Net Sown Area (NSA)? Answer: Area sown more than once in an agricultural year is known as Net Sown Area.
Question 7. What is meant by gross cropped area? Answer: Area sown more than once in an agricultural year plus net sown area is known as gross cropped area.
Question 8. What are the physical factors that determine the use of land? Answer: The physical factors that determine the use of land are — topography, climate and soil types.
Question 9. What are the human factors that determine the use of land? Answer: The human factors that determine the use of land are – population density, technological capability and culture and traditions etc.
Question 10. India has land under a variety of relief features. Name them. Answer: Mountains, plateaus, plains and islands.
Question 11. What are shelter belts? How have they proved helpful? Answer: Rows of trees which are planted in between the crops are called shelter belts. These shelter belts have proved helpful in the stabilisation of sand dunes and in stabilising the desert in western India.
Question 12. What do you mean by international resources? Answer: Resources that are owned and regulated by international institutions is called international resources. The oceanic resources beyond 200 nautical miles of the Exclusive Economic Zone belong to open ocean and no individual country can utilise these without the concurrence of international institutions.
Question 13. How does the contour farming help in the soil conservation? Answer: Ploughing along the contour lines can decelerate the flow of water down the slopes and thus helpful in the soil conservation.
Question 14. Name the four states where mining have caused severe land degradation. Answer: These states are- Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha.
Question 15. What are the important factors in the formation of soil? Answer: The important factors in the formation of soil include relief, parent rock or bed rock, climate, vegetation and other forms of life and time.
Question 16. What is gully erosion? Answer: Gully erosion takes place when running water cuts deep ravines in the absence of vegetation. This type of erosion makes soil unfit for cultivation.
Question 17. Name the areas where red and yellow soils are found. Answer: The eastern and southern parts of the Deccan plateau, parts of Odisha, Chhattisgarh, southern parts of the middle Ganga plain and the piedmont zone of the Western Ghats.
Question 18. Where does the laterite soil develop? Answer: The laterite soil develops in areas with high temperature and heavy rainfall. This is the result of intense leaching due to heavy rainfall.
Question 19. What causes land degradation? Answer: Continuous use of land over a long period of time without taking appropriate measures to conserve and manage it causes land degradation.
Question 20. What is Agenda 21? Answer: Agenda 21 is a declaration signed by the world leaders in the Earth Summit held at Rio de Janeiro (Brazil) in 1992 in order to achieve global sustainable development.
Question 21. Which human factors have contributed to land degradation? Answer: Deforestation, overgrazing, mining and quarrying are some of the human factors which have contributed to land degradation.
Question 22. Name the states where overgrazing has caused land degradation. Answer: Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra.
Question 23. What are the necessary conditions for the development of any region? Answer: The availability of resources and corresponding changes in technology and institutions are the necessary conditions for the development of any region.
Question 24. How is over-irrigation responsible for land degradation? Answer: Over irrigation leads to waterlogging in the field which further leads to increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil.
Question 25. What do you mean by bad land? Answer: Land that is highly unsuitable for cultivation is called bad land. Soil erosion is the factor which converts a fertile land into a bad land.
Resource and Development World Class 10 Extra Questions and Answer Geography Chapter 1 Short Answers Type
Question 1. Mention any two human activities which are responsible for the process of soil erosion. Explain the two types of soil erosion mostly observed in India. Answer: Large scale deforestation and mining are some of the human activities responsible for the process of soil erosion. The most common types of soil erosion in India are (a) Gully erosion, and (b) Sheet erosion.
(a) Gully erosion: It is the removal of soil along drainage lines by surface water run off. Once started, gullies will continue to move by head ward erosion or by slumping of the side walls unless steps are taken to stabilise the disturbance.
(b) Sheet erosion: Sometimes water flows as a sheet over large areas down a slope. In such cases the top soil is washed away. This is known as sheet erosion.
Question 2. Discuss the role of humans in resource development. (Imp) Answer: (i) Humans play an important role in resource development. They interact with nature through technology and create institutions to accelerate their economic development.
(ii) They convert materials available in our environment into resources. To fulfil their needs, they make the natural elements useful and valuable by dint of their intelligence, skill and technical knowledge.
(iii) For example, running water of rivers is a natural gift and it becomes a resource when man uses it (river water) for irrigation by constructing a canal. Man can also use this water for power generation by building dams on rivers. Thus, in the process of conversion of materials to resource creation, man’s role is more important.
Question 3. Classify resources on the basis of exhaustibility. OR Distinguish between renewable and non-renewable resources. Answer: On the basis of exhaustibility, resources are of two types: (i) Renewable resources, and (ii) Non-renewable resources. (i) Renewable resources: These resources can be renewed or reproduced by physical, chemical or mechanical processes. These are also known as replenishable resources. For example, solar and wind energy, water, forest and wildlife.
(ii) Non-renewable resources: These resources occur over a long geological time. For example, minerals and fossil fuels take millions of years in their formation. Some of the resources like metals are recyclable and some like fossil fuels cannot be recycled and get exhausted with their use.
Question 4. What is Agenda 21? What does it aim at? Answer: Agenda 21 is a non-binding, voluntarily implemented action plan of the United Nations with regard to sustainable development. It is a product of the Earth Summit i.e. UN Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) which took place at Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, in 1992. The ‘21’ in Agenda 21 refers to the 21st century.
It aims at achieving global sustainable development. It is an agenda to combat environmental damage, poverty, disease through global co-operation on common interests, mutual needs and shared responsibilities. One major objective of Agenda 21 is that every local government should draw its own local agenda 21.
Question 5. Mention three factors that are involved in resource planning. OR ‘Resource planning is a complex process’. Explain. Answer: Resource planning is a complex process and it involves the following factors: (i) Identification and inventory of resources across the regions of the country. This involves survey¬ing, mapping and qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of the resources.
(ii) Evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional set up for implementing resource development plans.
(iii) Matching the resources development plans with overall national development plans.
Question 6. Mention any three characteristics of arid soils. Answer: The three characteristics of arid soils are- (i) These soils range from red to brown in colour. They are generally sandy in texture and saline in nature. In some areas, the salt content is very high and common salt is obtained by evaporating the water.
(ii) These soils are mainly found in Western Rajasthan. As the region is characterised by dry climate and high temperature, evaporation is faster. That is why soil lacks humus and moisture.
(iii) The lower horizons of the soil are occupied by kanker because of the increasing calcium content downwards. The kanker layer formations in the bottom horizons restrict the infiltration of water up. This makes the soil unsuitable for cultivation.
(iv) These soils can be converted into cultivable land by proper irrigation.
Question 7. Distinguish between khadar and bangar soils. (Imp) OR Classify alluvial soils on the basis of their age
Question 8. Which is called regur soil? Mention any three characteristics of this soil. (Imp) Answer: Black soil is also called regur soil. This soil is ideal for growing cotton and is also known as black cotton soil. Three characteristic features of this soil are-
- The black soils are made up of extremely fine (clayey) material. They are well-known for their capacity to hold moisture.
- These soils are rich in soil nutrients, such as calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash and lime but are deficient in phosphoric contents.
- They become sticky when wet and develop cracks on drying up. These cracks help in mixing air in the soil.
Question 9. How does red soil develop and in which part of India? What makes it look red and yellow? Or How is red soil formed? Mention its three characteristics. Answer: Red soil develops on crystalline igneous rocks in areas of low rainfall in the eastern and southern parts of the Deccan plateau. Three characteristics of red soil-
- This soil develops a reddish colour due to diffusion of iron in crystalline and metamorphic rocks. It looks yellow when it occurs in a hydrated form.
- It is porous in nature and more fertile. It is also very thick.
- On the uplands, this soil consists of loose gravels and highly coarse materials, but in the lowlands it is rich, deep dark coloured, fertile and red.
Question 10. Which is the most widespread and important soil of India? Mention its important characteristics. Answer: Alluvial soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast. Three main features of this type of soil are –
- This soil consists of various proportions of sand, silt and clay. It is a very fertile soil.
- Mostly these soils contain adequate proportion of potash, phosphoric acid and lime which are ideal for the growth of sugarcane, paddy, wheat etc.
- Due to its high fertility, regions of alluvial soils are intensively cultivated and densely populated.
Question 11. Name the soil type which is widely found in Western Rajasthan. Explain two important characteristics of this soil type which make it unsuitable for cultivation. (Imp) Answer: The three characteristics of arid soils are- (i) These soils range from red to brown in colour. They are generally sandy in texture and saline in nature. In some areas, the salt content is very high and common salt is obtained by evaporating the water.
Question 12. Explain the distribution of the black soil. Answer: This type of soil is typical of the Deccan trap region spread over northwest Deccan plateau and is made up of lava flows. They cover the plateaus of Maharashtra, Saurashtra, Malwa, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh and extend in the south east direction along the Godavari and the Krishna valleys.
Question 13. Describe the laterite soil under the following headings: (i) Why are they called laterite? (ii) Distribution of this soil (iii) Crops grown in these soils Answer: (i) The word ‘laterite’ has been derived from the Latin word ‘later’ which means brick. Since its colour is red and resembles brick colour that is why it is called laterite soil. (ii) Laterite soils are mainly found in Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, and the hilly areas of Odisha and Assam. (iii) Crops grown in these soils are tea, coffee and cashew nuts.
Question 14. What do you mean by land degradation? What is the area of degraded land in India? Mention the name of various types of wasteland and their percentage share. Answer: Land degradation is a process in which the value of the biophysical environment is affected by a combination of human-included processes acting upon the land. At present, there are about 130 million hectares of degraded land in India. Approximately, 28 percent of it belongs to the category of forest degraded area, 56 percent of it is water eroded area, 6 percent of it is saline and alkaline land and 10 percent of it is wind eroded area.
Question 15. Where are forest soils found in India? Mention the major characteristics of these soils. Answer: Forest soils are found in the hilly and mountainous areas where sufficient rainforests are available. Major characteristics of these soils are:
- The texture of these soil varies according to the mountain environment where they are formed. They are loamy and salty in valley sides and coarse grained in the upper slopes.
- In the snow-covered areas of the Himalayas, these soils experience denudation and are acidic with low humus content.
- The soils found in the lower parts of the valleys particularly on the river terraces and alluvial fans are fertile.
Resource and Development World Class 10 Extra Questions and Answer Geography Chapter 1 Long Answers Type
Question 1. Classify resources on the basis of ownership. Mention major features of these resources. OR Explain the classification of resources on the basis of ownership. (Imp) Answer: On the basis of ownership, there are four types of resources-
- Individual resources
- Community owned resources
- National resources
- International resources
Individual resources: These resources are owned privately by individuals. Many farmers own land which is allotted to them by government against the payment of revenue. People in urban areas also own plots, houses and other property. Other examples of resources owned by individu¬als include plantation, pasture lands, ponds, water in wells, etc.
Community owned resources: These resources are accessible to all the members of the commu¬nity. Village commons, public parks, picnic spots, playgrounds etc. are accessible to all the people living in that area.
National resources: All the resources such as water resources, forests, wildlife, land within the political boundaries and oceanic area upto 12 nautical miles from the coast termed as territorial water and resources therein belong to the nation and therefore, known as national resources.
International resources: There are international institutions which regulate some resources. The oceanic resources beyond 200 nautical miles of the Exclusive Economic Zone belong to open ocean and no individual country can utilise these resources without the concurrence of international institutions.
Question 2. Explain the classification of resources on the basis of the status of development. (Imp) OR Distinguish between stock resources and reserve resources. (Imp) Answer: On the basis of the status of development resources are classified in the following categories:
- Potential resources
- Developed resources
Potential resources: Potential resources are those resources which are found in a region, but have not been utilised. For example, the western parts of India particularly Rajasthan and Gujarat have huge potential for the development of wind and solar energy. But these have not been developed properly till date.
Developed resources: These resources are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilisation. The development of resources depends on technology and level of their feasibility.
Stock: Materials in the environment which have the potential to satisfy human needs but they are not accessible due to lack of appropriate technology, are included among stock resources. For example, water is a compound of two inflammable gases hydrogen and oxygen, which can be used as a rich source of energy. But in absence of required technology to use them for this purpose, it is considered as stock resources.
Reserves: These are the subset of the stock, which can be put into use with the help of existing technology but their use has not been started. These can be used for meeting future requirements. River water can be used for generating hydroelectric power but presently, it is being utilised only to a limited extent. Thus, water in the dams, forests etc. is a reserve which can be utilised in the future.
Question 3. What is soil? What is its importance in human life? Explain the factors that contribute to soil formation. Answer: Soil is the uppermost layer of the unconsolidated particles found on the surface of the earth. It is made up of parent rocks and vegetation. It is rich in both organic and inorganic materials and supports the growth of plants.
Soil is the most important renewable natural resource. It is the medium of plant growth and supports different types of living organisms on the earth.
Soil is a living system. It takes millions of years to form soil upto a few cm in depth. There are different factors which help in formation of soil:
- Relief, parent rock or bed rock, climate, vegetation and other forms of life and time are important factors in the formation of soil.
- Various forces of nature such as change in temperature, actions of running water, wind and glaciers, activities of decomposers, etc. contribute to the formation of soil.
- Chemical and organic changes which take place in the soil also contribute to soil formation.
Question 4. What is meant by soil profile? Draw a labelled diagram of soil profile. Answer: Soil profile is the sequence, colour, texture and nature of the horizons superimposed one above the other and exposed in a pit-section dug through the soil mantle.

The various layers of soil profile are:
- Top soil or the upper soil layer
- Sub soil weathered rocks sand and silt clay
- Substratum weathered parent rock material
- Unweathered parent bed rock
Top soil of the uppermost layer is the real soil. It contains humus and inorganic materials. Below it is the subsoil which consists of rocks. sand particles and clay. The third layer, which comes below the second layer is made up of weathered parent rock material and the fourth layer is made up of parent bed rock.
Question 5. What is soil erosion? What factors contribute to it? Mention various types of soil erosion. Answer: Soil erosion is the washing or blowing away (by wind or water) of the top layer of soil. This is a serious problem particularly for farmers. The process of soil formation and erosion, go on side by side. Generally, there is a balance between the two. But when this balance is disturbed, soil erosion takes place. The factors that contribute to soil erosion are-
- Deforestation
- Over grazing
- Construction and mining activities
- Natural forces such as wind, glacier and water.
There are different types of soil erosion-
Water erosion and surface water runoff: The loss of top soil due to water is called water erosion. During rainy season, when raindrops fall directly on top soil, they loosen the material binding it together. As a result, small fragments get detached. If the rainfall continues, water gathers on the ground, causing water flow on the land surface, known as surface water runoff. This runoff carries the detached soil away.
Sheet erosion: Sometimes water flows as a sheet over large areas down a slope. In such cases the top soil is washed away. This is known as ‘sheet erosion’.
Rill erosion: Sometimes rainfall does not soak into the soil, and gathers on the surface and runs downhill, forming small channels of water called rills. These rills get dry up after the rainfall but the stream bed created by the temporary stream becomes prominent.
Gully erosion: The running water cuts through the clayey soils and makes deep channels as gullies. This type of erosion poses problems for farmers because the affected land is not put for cultivation.
Wind erosion: Wind blows loose soil off flat or sloping land known as wind erosion.
Defective methods of farming: Due to defective farming methods, there arises the problem of soil erosion. Ploughing in a wrong way i.e. up and down the slope form channels for the quick flow of water leading to soil erosion.
Question 6. What is meant by land degradation? Write five human activities which are mainly responsible for land degradation in India. (Imp) Answer: Land degradation is a process through which the land becomes unsuitable for agricultural activities. The following human activities are responsible for land degradation:
(i) Mining: Mining sites are abandoned after excavation work is complete leaving deep scars and traces of over burdening. In states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha deforestation due to mining have caused severe land degradation.
(ii) Overgrazing: Overgrazing occurs when plants are exposed to intensive grazing for extended periods of time, or without sufficient recovery periods. In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra overgrazing is one of the main reasons for land degradation.
(iii) Over irrigation: In states of Punjab, Haryana and western Uttar Pradesh, over irrigation is responsible for land degradation. It occurs due to water logging that leads to increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil.
(iv) Mineral processing: The mineral processing like grinding of limestone for cement industry and calcite and soapstone for ceramic industry generate huge quantity of dust in the atmosphere. It retards the process of infiltration of water into the soil after it settles down on the land.
(v) Industrial effluents as waste have also become a major source of land degradation in many parts of the country.
Resource and Development World Class 10 Extra Questions and Answer Geography Chapter 1 Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) Questions
Question 1. Why is resource planning so important in a country like India? Give reasons. Answer: (i) India has enormous diversity in the availability of resources. There are regions which are rich in certain types of resources but are deficient in some other resources.
(ii) There are some regions which can be considered self-sufficient in terms of the availability of resources and there are some regions which have acute shortage of some vital resources.
(iii) The states of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh are rich in minerals and coal deposits. Arunachal Pradesh has no dearth of water resources but lacks in infrastructrual development. The state of Rajasthan is gifted with solar and wind energy but lacks in water resources. Ladakh has rich cultural heritage but it is deficient in water; infrastructure etc. This calls for balanced resource planning at the national, state, regional and local levels.
Question 2. What are the various methods of conservation of soil? Explain. Answer: There are various methods of soil conservation:
- Contour farming in mountainous regions: Ploughing along the contour lines can decelerate the flow of water down the slopes.
- Terrace farming: Steps can be cut out on the slopes making terraces. Terrace cultivation restricts erosion.
- Strip farming: Large fields can be divided into strips. Strips of grass are left to grow between the crops. This breaks up the force of the wind.
- Shelter belts: Planting lines of trees to create shelters have contributed significantly to the stabilisation of sand dunes and in stabilising the desert in western India.
- Other methods include afforestation, control on grazing, etc.
Question 3. Why is there a need to conserve resources? What was Gandhiji’s opinion regarding the conservation of resources? Answer: Resources are vital for any developmental activity. But irrational consumption and over-use of resources for selfish purposes may lead to socio-economic and environmental problems. In order to overcome these problems, resource conservation at various levels is important.
Gandhiji voiced his concern about resource conservation in these words, “There is enough for everybody’s need and not for anybody’s greed”. He placed the greedy and selfish individuals and exploitative nature of modern technology as the root cause for resource depletion at the global level. He didn’t believe in mass production and wanted to replace it with the production by the masses.
Question 4. ‘India has land under a variety of relief features’. Support the statement with the help of a pie chart. Answer: The name of these relief features are mountains, plateaus, plains and islands.

- About 43 percent of the land area is plain which provides facilities for agricultural and industrial activities.
- Mountains account for 30 percent of the total surface area of the country and ensure perennial flow of some rivers. They also provide facilities for tourism and ecological aspects.
- About 27 percent of the area of the country is the plateau region. It possesses rich reserves of minerals, fossil fuels and forests.
Resource and Development World Class 10 Extra Questions and Answer Geography Chapter 1 Value-based Questions (VBQs)
Question 1. Natural resources are of great importance. Which values are associated with them? Answer: The values associated with resources are-
- They are used to satisfy human needs. For example, water is a resource and it is used for drinking, irrigation, cleaning purposes and cooking.
- Resources make human life simpler and happier. They bring quality change in man’s life.
- Resources are the basic requirements for country’s economic development. Today the countries which have more resources are considered as developed and prosperous.
- Land resources support natural vegetation, wildlife, human life as well as man’s economic activities.
- Water is an important resource because we cannot survive without it.
Question 2. Mention three problems which have been caused due to indiscriminate use of resources. Answer:
- Depletion of resources for satisfying the greed of few individuals.
- Accumulation of resources in few hands, which, in turn, divided the society into two groups- haves and have nots (the rich and the poor).
- Indiscriminate exploitation of resources has led to global ecological crises such as, global warming, ozone layer depletion, environmental pollution and land degradation.
Resource and Development World Class 10 Extra Questions and Answer Geography Chapter 1 Map-based Questions
Question 1. Identify six major soil types shown in the given map of India. Answer:
- Forest and mountainous soil
- Alluvial soil
- Red and yellow soil
- Laterite soil and


COMMENTS
Chapter 1 Resources and Development Case Study Questions Class 10 Social Science. 1. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follows: On the Basis of the Status of Development Potential Resources: Resources which are found in a region, but have not been utilised. For example, the western parts of India particularly Rajasthan ...
Human resource perhaps is the most critical part of development as skilled, educated, and healthy individual are more innovative, talented and productive. Q1) Define resource and criteria's to be called as a resource Mark 2. Answer Anything that is used to satisfy our needs is called as a resource. Resource should be.
Class 10 Social Science Case Study Question 4. Class 10 ECONOMICS: Development. Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow: Besides seeking more income, oneway or the other, people also seek things like equal treatment, freedom, security, and respect of others. They resent discrimination.
Here are some steps you can take to prepare for case study questions for class 10 social science: Understand the format of case study questions: Case study questions for class 10 social science usually require you to read a scenario or a passage and answer a set of questions based on it. These questions can be based on various topics like ...
Practice Tests. Timed Tests. Select the number of questions for the test: Select the number of questions for the test: TopperLearning provides a complete collection of case studies for CBSE Class 10 Geography Resources and Development chapter. Improve your understanding of biological concepts and develop problem-solving skills with expert advice.
NCERT Book Solutions For Class 10 Geography Contemporary India - II Chapter 1 Resources and Development - CBSE Free PDF Download. NCERT Solutions Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 - Resources and Development are important resources for students to prepare for CBSE exams. By going through these solutions, students will get to know the answer writing style, which will help them in fetching more ...
Resources can be classified in the following ways: (a) On the basis of origin - biotic and abiotic. (b) On the basis of exhaustibility - renewable and non-renewable. (c) On the basis of ownership - individual, community, national and international. (d) On the basis of the status of development - potential, developed stock and reserves.
Jun 21, 2023, 14:28 IST. Download PDF for CBSE Class 10 Chapter 1 Resources and Development Notes. Resources and Development Class 10 Notes: In chapter 1 of CBSE 10th class SST, we get to learn ...
CBSE revision Notes Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 - Resources and Development provides a comprehensive overview of the chapter, including the classification of resources on the basis of origin, ownership, exhaustibility, and the status of development. It also discusses how essential resources are in our day-to-day lives and what role they play ...
Template 3. Chapter 1 of Class 10 Geography introduces you to resources and its classification. Furthermore, going into the depth of the chapter, you will learn the development of resources and resource planning in India. You will know about land resources and the classification of different types of soils found in India.
Answer. • Renewable Resources: The resources which can be renewed or reproduced by physical, chemical or mechanical processes are known as renewable resources. For example, solar and wind energy, water, forests and wildlife, etc. • Non-Renewable Resources: The resources once consumed cannot be replaced are known as non-renewable resources.
Which one of the following types of resources is iron ore? (a) Renewable. (b) Flow. (c) Biotic. (d) Non-renewable. 2. Justify the statement, "Resources are a function of human activities". 3. Explain the classification of resources on the basis of exhaustibility and give two examples each.
Resources and Development Class 10 Geography Solutions — CBSE Guides. We are providing you with the detailed notes of geography lesson 1 resources and development class 10 along with the ncert solutions, multiple-choice questions, and some value-based questions so that the students can cope with the new assessment scheme.
NCERT solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Resources and Development Chapter 1 are available in PDF format for free download. These ncert book chapter wise questions and answers are very helpful for CBSE exam. CBSE recommends NCERT books and most of the questions in CBSE exam are asked from NCERT textbooks Social Science chapter wise ...
Activity 3 Case study analysis: In this activity, the teacher will provide students with a case study of a real-world resource management issue. It can be any topic such as water scarcity in a particular region, or the impact of mining on a local community. Students have to read and analyze the case study in small groups.
Answer: (i) Stock. (ii) Renewable. 11. Name any two states of India which are well endowed with solar energy. Answer: Gujarat and Rajasthan. 12. Name any two factors on which resource development depends. Answer: (i) Technology. (ii) Quality of human resources.
The main topics which are included in Chapter 1 of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Geography are: Types of Resources- This is divided further into 4 categories: On the basis of origin- Biotic and Abiotic resources. On the basis of exhaustibility- Renewable and Non- Renewable resources. On the basis of ownership- Individual, community, and so forth.
Resources and Development class 10 Part 1 in Animation | CBSE | NCERTPart 2~ https://youtu.be/QvVZ6Cvnwrcother channels links ~Sunlike study Sciencehttps://y...
Resources and Development is the first chapter in CBSE Class 10 Geography, which discusses the concept of resources and their various forms. The chapter covers the different types of resources such as natural, human-made, and human resources, and their utilization for the development of society. It also discusses the process of resource ...
On the Basis of Origin. • Biotic Resources: These are obtained from biosphere and have life such as human beings, flora and fauna, fisheries, livestock etc. • Abiotic Resources: All those things which are composed of non-living things are called abiotic resources. For example, rocks and metals. On the Basis of Exhaustibility.
Here we present The Resources and Development Class 10 Important Questions and Answers Pdf Social Science Geography Chapter 1, We have collected all the important questions which came in the previous year exams. You can also find Social Science Class 10 Important Questions With Answers Pdf from the year 2010 to 2020 CBSE board exams. These […]
4. Solve the puzzle by following your search horizontally and vertically to find the hidden answers. (i) Natural endowments in the form of land, water, vegetation and minerals. (ii) A type of non-renewable resource. (iii) Soil with high water retaining capacity. (iv) Intensively leached soils of the monsoon climate.
Resource and Development World Class 10 Extra Questions and Answer Geography Chapter 1 Very Short Answers Type. Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Extra Questions. Question 1. Mention two factors on which resource development depends. Answer: Latest technology. Quality of humans as resource. Question 2.
1. A Make It Happen-Leadership Development Workshop. Date and Time: From 5-7 p.m. on Tuesday, April 16. Location: Olscamp 117 Register for this workshop. Description: Join us for a Leadership Development and Social Event! Don Adamski Sr. Human Resources Organizational Effectiveness Consultant at ProMedica of Toledo will be discussing effective Leadership with our NSLS Members!