

Pathos Definition
What is pathos? Here’s a quick and simple definition:
Pathos , along with logos and ethos , is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Pathos is an argument that appeals to an audience's emotions. When a speaker tells a personal story, presents an audience with a powerful visual image, or appeals to an audience's sense of duty or purpose in order to influence listeners' emotions in favor of adopting the speaker's point of view, he or she is using pathos .
Some additional key details about pathos:
- You may also hear the word "pathos" used to mean "a quality that invokes sadness or pity," as in the statement, "The actor's performance was full of pathos." However, this guide focuses specifically on the rhetorical technique of pathos used in literature and public speaking to persuade readers and listeners through an appeal to emotion.
- The three "modes of persuasion"— pathos , logos , and ethos —were originally defined by Aristotle.
- In contrast to pathos, which appeals to the listener's emotions, logos appeals to the audience's sense of reason, while ethos appeals to the audience based on the speaker's authority.
- Although Aristotle developed the concept of pathos in the context of oratory and speechmaking, authors, poets, and advertisers also use pathos frequently.
Pathos Pronunciation
Here's how to pronounce pathos : pay -thos
Pathos in Depth
Aristotle (the ancient Greek philosopher and scientist) first defined pathos , along with logos and ethos , in his treatise on rhetoric, Ars Rhetorica. Together, he referred to pathos , logos , and ethos as the three modes of persuasion, or sometimes simply as "the appeals." Aristotle defined pathos as "putting the audience in a certain frame of mind," and argued that to achieve this task a speaker must truly know and understand his or her audience. For instance, in Ars Rhetorica, Aristotle describes the information a speaker needs to rile up a feeling of anger in his or her audience:
Take, for instance, the emotion of anger: here we must discover (1) what the state of mind of angry people is, (2) who the people are with whom they usually get angry, and (3) on what grounds they get angry with them. It is not enough to know one or even two of these points; unless we know all three, we shall be unable to arouse anger in any one.
Here, Aristotle articulates that it's not enough to know the dominant emotions that move one's listeners: you also need to have a deeper understanding of the listeners' values, and how these values motivate their emotional responses to specific individuals and behaviors.
Pathos vs Logos and Ethos
Pathos is often criticized as being the least substantial or legitimate of the three persuasive modest. Arguments using logos appeal to listeners' sense of reason through the presentation of facts and a well-structured argument. Meanwhile, arguments using ethos generally try to achieve credibility by relying on the speaker's credentials and reputation. Therefore, both logos and ethos may seem more concrete—in the sense of being more evidence-based—than pathos, which "merely" appeals to listeners' emotions. But people often forget that facts, statistics, credentials, and personal history can be easily manipulated or fabricated in order to win the confidence of an audience, while people at the same time underestimate the power and importance of being able to expertly direct the emotional current of an audience to win their allegiance or sympathy.
Pathos Examples
Pathos in literature.
Characters in literature often use pathos to convince one another, or themselves, of a certain viewpoint. It's important to remember that pathos , perhaps more than the other modes of persuasion, relies not only on the content of what is said, but also on the tone and expressiveness of the delivery . For that reason, depictions of characters using pathos can be dramatic and revealing of character.
Pathos in Jane Austen's Pride and Prejudice
In this example from Chapter 16 of Pride and Prejudice , George Wickham describes the history of his relationship with Mr. Darcy to Elizabeth Bennet—or at least, he describes his version of their shared history. Wickham's goal is to endear himself to Elizabeth, turn her against Mr. Darcy, and cover up the truth. (Wickham actually squanders his inheritance from Mr. Darcy's father and, out of laziness, turns down Darcy Senior's offer help him obtain a "living" as a clergyman.)
"The church ought to have been my profession...had it pleased [Mr. Darcy]... Yes—the late Mr. Darcy bequeathed me the next presentation of the best living in his gift. He was my godfather, and excessively attached to me. I cannot do justice to his kindness. He meant to provide for me amply, and thought he had done it; but when the living fell it was given elsewhere...There was just such an informality in the terms of the bequest as to give me no hope from law. A man of honor could not have doubted the intention, but Mr. Darcy chose to doubt it—or to treat it as a merely conditional recommendation, and to assert that I had forfeited all claim to it by extravagance, imprudence, in short any thing or nothing. Certain it is, that the living became vacant two years ago, exactly as I was of an age to hold it, and that it was given to another man; and no less certain is it, that I cannot accuse myself of having really done anything to deserve to lose it. I have a warm, unguarded temper, and I may perhaps have sometimes spoken my opinion of him, and to him, too freely. I can recall nothing worse. But the fact is, that we are very different sort of men, and that he hates me." "This is quite shocking!—he deserves to be publicly disgraced." "Some time or other he will be—but it shall not be by me. Till I can forget his father, I can never defy or expose him." Elizabeth honored him for such feelings, and thought him handsomer than ever as he expressed them.
Here, Wickham claims that Darcy robbed him of his intended profession out of greed, and that he, Wickham, is too virtuous to reveal Mr. Darcy's "true" nature with respect to this issue. By doing so, Wickham successfully uses pathos in the form of a personal story, inspiring Elizabeth to feel sympathy, admiration, and romantic interest towards him. In this example, Wickham's use of pathos indicates a shifty, manipulative character and lack of substance.
Pathos in Nathaniel Hawthorne's The Scarlet Letter
In The Scarlet Letter , Hawthorne tells the story of Hester Prynne, a young woman living in seventeenth-century Boston. As punishment for committing the sin of adultery, she is sentenced to public humiliation on the scaffold, and forced to wear the scarlet letter "A" on her clothing for the rest of her life. Even though Hester's punishment exposes her before the community, she refuses to reveal the identity of the man she slept with. In the following passage from Chapter 3, two reverends—first, Arthur Dimmesdale and then John Wilson—urge her to reveal the name of her partner:
"What can thy silence do for him, except it tempt him—yea, compel him, as it were—to add hypocrisy to sin? Heaven hath granted thee an open ignominy, that thereby thou mayest work out an open triumph over the evil within thee and the sorrow without. Take heed how thou deniest to him—who, perchance, hath not the courage to grasp it for himself—the bitter, but wholesome, cup that is now presented to thy lips!’ The young pastor’s voice was tremulously sweet, rich, deep, and broken. The feeling that it so evidently manifested, rather than the direct purport of the words, caused it to vibrate within all hearts, and brought the listeners into one accord of sympathy. Even the poor baby at Hester’s bosom was affected by the same influence, for it directed its hitherto vacant gaze towards Mr. Dimmesdale, and held up its little arms with a half-pleased, half-plaintive murmur... "Woman, transgress not beyond the limits of Heaven’s mercy!’ cried the Reverend Mr. Wilson, more harshly than before. ‘That little babe hath been gifted with a voice, to second and confirm the counsel which thou hast heard. Speak out the name! That, and thy repentance, may avail to take the scarlet letter off thy breast."
The reverends call upon Hester's love for the father of her child—the same love they are condemning—to convince her to reveal his identity. Their attempts to move her by appealing to her sense of duty, compassion and morality are examples of pathos. Once again, this example of pathos reveals a lack of moral fiber in the reverends who are attempting to manipulate Hester by appealing to her emotions, particularly since (spoiler alert!) Reverend Dimmesdale is in fact the father.
Pathos in Dylan Thomas' "Do Not Go Gentle Into That Good Night"
In " Do Not Go Gentle Into That Good Night," Thomas urges his dying father to cling to life and his love of it. The poem is a villanelle , a specific form of verse that originated as a ballad or "country song" and is known for its repetition. Thomas' selection of the repetitive villanelle form contributes to the pathos of his insistent message to his father—his appeal to his father's inner strength:
Do not go gentle into that good night, Old age should burn and rave at close of day; Rage, rage against the dying of the light. Though wise men at their end know dark is right, Because their words had forked no lightning they Do not go gentle into that good night. Good men, the last wave by, crying how bright Their frail deeds might have danced in a green bay, Rage, rage against the dying of the light. Wild men who caught and sang the sun in flight, And learn, too late, they grieved it on its way, Do not go gentle into that good night. Grave men, near death, who see with blinding sight Blind eyes could blaze like meteors and be gay, Rage, rage against the dying of the light.
It's worth noting that, in this poem, pathos is not in any way connected to a lack of morals or inner strength. Quite the opposite, the appeal to emotion is connected to a profound love—the poet's own love for his father.
Pathos in Political Speeches
Politicians understand the power of emotion, and successful politicians are adept at harnessing people's emotions to curry favor for themselves, as well as their policies and ideologies.
Pathos in Barack Obama's 2013 Address to the Nation on Syria
In August 2013, the Syrian government, led by Bashar al-Assad, used chemical weapons against Syrians who opposed his regime, causing several countries—including the United States—to consider military intervention in the conflict. Obama's tragic descriptions of civilians who died as a result of the attack are an example of pathos : they provoke an emotional response and help him mobilize American sentiment in favor of U.S. intervention.
Over the past two years, what began as a series of peaceful protests against the oppressive regime of Bashar al-Assad has turned into a brutal civil war. Over 100,000 people have been killed. Millions have fled the country...The situation profoundly changed, though, on August 21st, when Assad’s government gassed to death over 1,000 people, including hundreds of children. The images from this massacre are sickening: men, women, children lying in rows, killed by poison gas, others foaming at the mouth, gasping for breath, a father clutching his dead children, imploring them to get up and walk.
Pathos in Ronald Reagan's 1987 " Tear Down This Wall!" Speech
In 1987, the Berlin Wall divided Communist East Berlin from Democratic West Berlin. The Wall was a symbol of the divide between the communist Soviet Union, or Eastern Bloc, and the Western Bloc which included the United States, NATO and its allies. The wall also split Berlin in two, obstructing one of Berlin's most famous landmarks: the Brandenburg Gate.
Reagan's speech, delivered to a crowd in front of the Brandenburg Gate, contains many examples of pathos:
Behind me stands a wall that encircles the free sectors of this city, part of a vast system of barriers that divides the entire continent of Europe...Yet it is here in Berlin where the wall emerges most clearly...Every man is a Berliner, forced to look upon a scar... General Secretary Gorbachev, if you seek peace, if you seek prosperity for the Soviet Union and Eastern Europe, if you seek liberalization: Come here to this gate! Mr. Gorbachev, open this gate! Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall!
Reagan moves his listeners to feel outrage at the Wall's existence by calling it a "scar." He assures Germans that the world is invested in the city's problems by telling the crowd that "Every man is a Berliner." Finally, he excites and invigorates the listener by boldly daring Gorbachev, president of the Soviet Union, to "tear down this wall!"
Pathos in Advertising
Few appreciate the complexity of pathos better than advertisers. Consider all the ads you've seen in the past week. Whether you're thinking of billboards, magazine ads, or TV commercials, its almost a guarantee that the ones you remember contained very little specific information about the product, and were instead designed to create an emotional association with the brand. Advertisers spend incredible amounts of money trying to understand exactly what Aristotle describes as the building blocks of pathos: the emotional "who, what, and why" of their target audience. Take a look at this advertisement for the watch company, Rolex, featuring David Beckham:

Notice that the ad doesn't convey anything specific about the watch itself to make someone think it's a high quality or useful product. Instead, the ad caters to Rolex's target audience of successful male professionals by causing them to associate the Rolex brand with soccer player David Beckham, a celebrity who embodies the values of the advertisement's target audience: physical fitness and attractiveness, style, charisma, and good hair.
Why Do Writers Use Pathos?
The philosopher and psychologist William James once said, “The emotions aren’t always immediately subject to reason, but they are always immediately subject to action.” Pathos is a powerful tool, enabling speakers to galvanize their listeners into action, or persuade them to support a desired cause. Speechwriters, politicians, and advertisers use pathos for precisely this reason: to influence their audience to a desired belief or action.
The use of pathos in literature is often different than in public speeches, since it's less common for authors to try to directly influence their readers in the way politicians might try to influence their audiences. Rather, authors often employ pathos by having a character make use of it in their own speech. In doing so, the author may be giving the reader some insight into a character's values, motives, or their perception of another character.
Consider the above example from The Scarlet Letter. The clergymen in Hester's town punish her by publicly humiliating her in front of the community and holding her up as an example of sin for conceiving a child outside of marriage. The reverends make an effort to get Hester to tell them the name of her child's father by making a dramatic appeal to a sense of shame that Hester plainly does not feel over her sin. As a result, this use of pathos only serves to expose the the manipulative intent of the reverends, offering readers some insight into their moral character as well as that of Puritan society at large. Ultimately, it's a good example of an ineffective use of pathos , since what the reverends lack is the key to eliciting the response they want: a strong grasp of what their listener values.
Other Helpful Pathos Resources
- The Wikipedia Page on Pathos: A detailed explanation which covers Aristotle's original ideas on pathos and discusses how the term's meaning has changed over time.
- The Dictionary Definition of Pathos: A definition and etymology of the term, which comes from the Greek pàthos, meaning "suffering or sensation."
- An excellent video from TED-Ed about the three modes of persuasion.
- A pathos -laden recording of Dylan Thomas reading his poem "Do Not Go Gentle Into That Good Night"

- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1886 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 39,697 quotes across 1886 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
- Red Herring
- Flat Character
- Figure of Speech
- Understatement
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Protagonist
- Climax (Figure of Speech)
- Climax (Plot)
- External Conflict
- Falling Action
- Figurative Language

Definition of Pathos
Pathos is a literary device that is designed to inspire emotions from readers. Pathos, Greek for “suffering” or “experience,” originated as a conceptual mode of persuasion by the Greek philosopher, Aristotle. Aristotle believed that utilizing pathos as a means of stirring people’s emotions is effective in turning their opinion towards the speaker . This is due in part because emotions and passion can be engulfing and compelling, even going against a sense of logic or reason.
Pathos, as an appeal to an audience ’s emotions, is a valuable device in literature as well as rhetoric and other forms of writing. Like all art, literature is intended to evoke a feeling in a reader and, when done effectively, generate greater meaning and understanding of existence. For example, in his poem “No Man Is an Island,” John Donne appeals to the reader’s emotions of acceptance, belonging, and empathy:
No man is an island, Entire of itself, Every man is a piece of the continent, A part of the main. If a clod be washed away by the sea, Europe is the less. As well as if a promontory were. As well as if a manor of thy friend’s Or of thine own were: Any man’s death diminishes me, Because I am involved in mankind, And therefore never send to know for whom the bell tolls ; It tolls for thee.
By describing how all men are connected rather than isolated, Donne utilizes pathos as an emotional appeal to readers of his poem. The feelings evoked by the poet are grief and sympathy for all who die, because all death is an individual loss and a loss for mankind as a whole.
Common Examples of Emotions Evoked by Pathos
Pathos has the power to evoke many emotions in a reader or audience of a literary work. Here are some common examples of emotions evoked by pathos in literature:
Examples of Pathos in Advertisement
Advertisers heavily rely on pathos to provoke an emotional reaction in an audience of consumers, thereby persuading them to take action in the form of patronage or other monetary support. Here are some examples of pathos in an advertisement:
- television commercial showing neglected or mistreated animals
- political ad utilizing fear tactics
- holiday commercial showing a family coming together for a meal
- cologne commercial displaying sexual tension
- diaper ad featuring a crying baby
- ad for cleaning product featuring a messy house and frustrated homeowner
- jewelry commercial showing a marriage proposal
- insurance ad showing a terrible car accident
- ad for a line of toys showing children playing together
- commercial for make-up displaying a woman receiving attention from men
Famous Examples of Pathos in Movie Lines
Many films feature dialogue that generates pathos and emotional reactions in viewers. Here are some famous examples of pathos in well-known movie lines:
- Love means never having to say you’re sorry. (Love Story )
- The jail you planned for me is the one you’re gonna rot in. ( The Color Purple )
- I’m mad as hell and I’m not going to take it anymore. (Network)
- The marks humans leave are too often scars. (The Fault in Our Stars)
- I have to remind myself that some birds aren’t meant to be caged. (The Shawshank Redemption)
- And just like that, she was gone, out of my life again. (Forrest Gump)
- There are two types of people in the world: The people who naturally excel at life. And the people who hope all those people die in a big explosion. (The Edge of Being Seventeen)
- You have to get through your fear to see the beauty on the other side. (The Good Dinosaur)
- Hate never solved nothing, but calm did. And thought did. Try it. Try it just for a change . (Three Billboards Outside Ebbing, Missouri)
- Things change, friends leave. And life doesn’t stop for anybody. (The Perks of Being a Wallflower)
Difference Between Pathos, Logos, and Ethos
Aristotle outlined three forms of rhetoric, which is the art of effective speaking and writing. These forms are pathos, logos , and ethos . As a matter of rhetorical persuasion, it is important for these forms (or “appeals”) to be balanced. This is especially true for pathos in that overuse of emotional appeal can lead to a flawed argument without the balance of logic or credibility.
Logos is an appeal to logic. It is considered a methodical and rational approach to rhetoric. In a sense, logos is an appeal that is devoid of pathos. Ethos is an appeal to ethics. As an effective rhetorical form, a writer or speaker must have knowledge and credibility regarding the subject . Ethos, therefore, builds trust with an audience as an ethical and character -driven approach.
Pathos is a common form of rhetoric and persuasive tactic. Emotion and passion can be powerful forces in motivating an audience or readership. However, pathos has minimal effect without the balance of logos and ethos as appeals.
Effect of Pathos on Logos
Aa a logo appeals to logic, and pathos appeals to emotions. It is a well-known fact that not everybody gets convinced by logic and the same is the case of pathos which not everybody gets convinced with pathos only. Therefore, orators and speakers use both in a combination. When a pathos is added to logos, it becomes convincing, persuasive, strong, and touches beliefs and values.
Effect of Pathos on Ethos
Although ethos is itself a strong rhetorical device and works wonders when it comes to persuasion and convincing the audience, when a touch of pathos is added to it, it becomes a lethal weapon. It has happened in I Have a Dream , a powerful rhetorical piece of Martin Luther King and the speech is still a memorable rhetorical piece. The reason is that not only does it enhance the power of argument when added with an ethos, it also increases the trust and credibility of the speaker or orator.
How To Build Arguments Using Pathos
When using pathos, keep these points in mind.
- What is the touching event for the audience?
- Evaluate how the audiences or readers respond to the gravity of the situation?
- Use pathos with ethos first and then use l0gos to add pathos later.
- Pathos is always the last weapon after ethos and logos.
Fallacy Of Emotion (Pathos) / Fallacious Pathos
As pathos is also called a fallacy of emotion, the use of only pathos is highly damaging for argumentative writing and speaking. The reason is that audiences if they are not directly concerned with the pathetic event or tragedy , become bored with excessive targetting of their emotions and eventually lose interest. At this point, it becomes a fallacy. Therefore, always avoid fallacious pathos. Add a touch of veracity to your pathos and use it in conjunction with ethos first and add logos later.
Three Characteristics Of Pathos
There are three important characteristics of pathos.
- It is relevant to the target audience or readers and is couched in simple and strong language.
- It is intended to achieve a specific purpose.
- It is not excessive that it should become fallacious pathos.
Using Pathos in Sentences
- The Holocaust has done more harm to the entire Jewish nation than any other such event.
- If you love me, you’ll get me a cell phone for my safety.
- I have to pick up my children from school every day, can you give me a good deal on this car?
- Look at these innocent street children. By seeing this, you can give us good donations.
- If you let me eat chips everyday, it will prove that you love me and I will do the dishes.
Examples of Pathos in Literature
Though Aristotle defined pathos as a rhetorical technique for persuasion, literary writers rely on pathos as well to evoke emotion and understanding in readers. As a literary device, pathos allows readers to connect to and find meaning in characters and narratives. Here are some examples of pathos in literature and the impact this literary device has on the work and the reader:
Example 1: Funeral Blues by W.H. Auden
He was my North, my South, my East and West, My working week and my Sunday rest, My noon, my midnight, my talk, my song; I thought that love would last forever: I was wrong. The stars are not wanted now ; put out every one, Pack up the moon and dismantle the sun, Pour away the ocean and sweep up the wood; For nothing now can ever come to any good.
In his poem, Auden relies on pathos as a literary device to evoke feelings of grief and inspire sympathy in the reader. The poet cannot cope with the loss of his loved one and companion, yet the world around him continues to function as if nothing is different and as if the funeral is not taking place. The poet’s passion for his loved one, that he was all cardinal directions and days and times, followed by the poet’s desperation to remove elements of nature, inspires sympathetic mourning in readers.
Though the poet cannot get the world to pause in grief for his loved one, by utilizing pathos as a literary device in this poem, Auden is able to momentarily capture the reader’s attention and understanding. This pause for grief and sympathy on the part of the reader fulfills, on some level, the emotional need of the poet to be recognized and validated in his mourning. This reciprocal exchange of feeling enhances the connection between the poet and reader through pathos.
Example 2: I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings by Maya Angelou
If growing up is painful for the Southern Black girl, being aware of her displacement is the rust on the razor that threatens the throat. It is an unnecessary insult.
In her memoir , Angelou focuses on the emotional events of her life from early childhood through adolescence. While recounting her story, Angelou utilizes pathos to appeal to the reader’s emotions and to evoke empathy for her experiences, especially in terms of trauma, abuse, and racism.
In this particular passage from her memoir, Angelou appeals to the reader’s feelings of shame, empathy, and fear by describing her experience and how she felt as a Black girl growing up in the South. This allows the reader to connect with and find meaning in Angelou’s writing and experiences, especially if those experiences are unfamiliar or personally unknown to the reader. In addition, the pathos in this passage is an effective literary device through confronting the reader with the pain, displacement, and insult experienced not just by Angelou as a Southern Black girl, but in a generalized manner for all Southern Black girls. Angelou’s readers are therefore encouraged through pathos to identify this experience and share in the resulting emotional anger and pain.
Example 3: Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare
Two households, both alike in dignity In fair Verona, where we lay our scene From ancient grudge break to new mutiny Where civil blood makes civil hands unclean. From forth the fatal loins of these two foes A pair of star- cross ’d lovers take their life Whose misadventured piteous overthrows Do with their death bury their parents’ strife.
In the prologue , Shakespeare foreshadows the events that take place in the play between Romeo and Juliet and their families. He also foreshadows the feelings and struggles of the characters, which is an appeal to the pathos of the audience/reader. For example, by stating that “civil blood makes civil hands unclean,” Shakespeare evokes feelings of dread and uncertainty in the audience, knowing that there is impending violence. By categorizing Romeo and Juliet as “star-crossed” lovers, Shakespeare appeals to the audience’s feelings of passion and unrequited love. Finally, in announcing the deaths of the lovers, Shakespeare inspires sadness, grief, and possibly anger or frustration in the audience at the foretold outcome.
With these emotional appeals in his prologue, Shakespeare not only prepares his audience for what is to come in the plot of the play but also sets the tone and prepares the appropriate emotional reactions for the audience to the events that will happen. This is a unique use of pathos as a literary device. Rather than allowing the audience to feel and react to the play’s narrative as it unfolds, Shakespeare “primes” emotional responses through pathos before the play even begins. This technique is effective because the audience is able to focus on the nuances of the play since they are already aware of the main events and outcomes, as well as how to feel about it.
Synonyms of Pathos
Pathos has a few synonyms that follow but they are only distant meanings. Some of them are tragedy, sadness, pitifulness, piteousness, sorrowfulness, lugubrious, poignant, and poignancy.
Related posts:
- Et Tu, Brute?
Post navigation
What Are Logos, Pathos & Ethos?
A straight-forward explainer (with examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | June 2023
If you spend any amount of time exploring the wonderful world of philosophy, you’re bound to run into the dynamic trio of rhetorical appeals: logos , ethos and pathos . But, what exactly do they mean and how can you use them in your writing or speaking? In this post, we’ll unpack the rhetorical love triangle in simple terms, using loads of practical examples along the way.
Overview: The Rhetorical Triangle
- What are logos , pathos and ethos ?
- Logos unpacked (+ examples)
- Pathos unpacked (+ examples)
- Ethos unpacked (+ examples)
- The rhetorical triangle
What are logos, ethos and pathos?
Simply put, logos, ethos and pathos are three powerful tools that you can use to persuade an audience of your argument . At the most basic level, logos appeals to logic and reason, while pathos appeals to emotions and ethos emphasises credibility or authority.
Naturally, a combination of all three rhetorical appeals packs the biggest punch, but it’s important to consider a few different factors to determine the best mix for any given context. Let’s look at each rhetorical appeal in a little more detail to understand how best to use them to your advantage.

Logos appeals to the logical, reason-driven side of our minds. Using logos in an argument typically means presenting a strong body of evidence and facts to support your position. This evidence should then be accompanied by sound logic and well-articulated reasoning .
Let’s look at some examples of logos in action:
- A friend trying to persuade you to eat healthier might present scientific studies that show the benefits of a balanced diet and explain how certain nutrients contribute to overall health and longevity.
- A scientist giving a presentation on climate change might use data from reputable studies, along with well-presented graphs and statistical analyses to demonstrate the rising global temperatures and their impact on the environment.
- An advertisement for a new smartphone might highlight its technological features, such as a faster processor, longer battery life, and a high-resolution camera. This could also be accompanied by technical specifications and comparisons with competitors’ models.
In short, logos is all about using evidence , logic and reason to build a strong argument that will win over an audience on the basis of its objective merit . This contrasts quite sharply against pathos, which we’ll look at next.

Contrasted to logos, pathos appeals to the softer side of us mushy humans. Specifically, it focuses on evoking feelings and emotions in the audience. When utilising pathos in an argument, the aim is to cultivate some feeling of connection in the audience toward either yourself or the point that you’re trying to make.
In practical terms, pathos often uses storytelling , vivid language and personal anecdotes to tap into the audience’s emotions. Unlike logos, the focus here is not on facts and figures, but rather on psychological affect . Simply put, pathos utilises our shared humanness to foster agreement.
Let’s look at some examples of pathos in action:
- An advertisement for a charity might incorporate images of starving children and highlight their desperate living conditions to evoke sympathy, compassion and, ultimately, donations.
- A politician on the campaign trail might appeal to feelings of hope, unity, and patriotism to rally supporters and motivate them to vote for his or her party.
- A fundraising event may include a heartfelt personal story shared by a cancer survivor, with the aim of evoking empathy and encouraging donations to support cancer research.
As you can see, pathos is all about appealing to the human side of us – playing on our emotions to create buy-in and agreement.

Last but not least, we’ve got ethos. Ethos is all about emphasising the credibility and authority of the person making the argument, or leveraging off of someone else’s credibility to support your own argument.
The ethos card can be played by highlighting expertise, achievements, qualifications and accreditations , or even personal and professional associations and connections. Ultimately, the aim here is to foster some level of trust within the audience by demonstrating your competence, as this will make them more likely to take your word as fact.
Let’s look at some examples of ethos in action:
- A fitness equipment brand might hire a well-known athlete to endorse their product.
- A toothpaste brand might make claims highlighting that a large percentage of dentists recommend their product.
- A financial advisor might present their qualifications, certifications and professional memberships when meeting with a prospective client.
As you can see, using ethos in an argument is largely about emphasising the credibility of the person rather than the logical soundness of the argument itself (which would reflect a logos-based approach). This is particularly helpful when there isn’t a large body of evidence to support the argument.
Ethos can also overlap somewhat with pathos in that positive emotions and feelings toward a specific person can oftentimes be extended to someone else’s argument. For example, a brand that has nothing to do with sports could still benefit from the endorsement of a well-loved athlete, just because people feel positive feelings about the athlete – not because of that athlete’s expertise in the product they’re endorsing.

How to use logos, pathos and ethos
Logos, pathos and ethos combine to form the rhetorical triangle , also known as the Aristotelian triangle. As you’d expect, the three sides (or corners) of the triangle reflect the three appeals, but there’s also another layer of meaning. Specifically, the three sides symbolise the relationship between the speaker , the audience and the message .
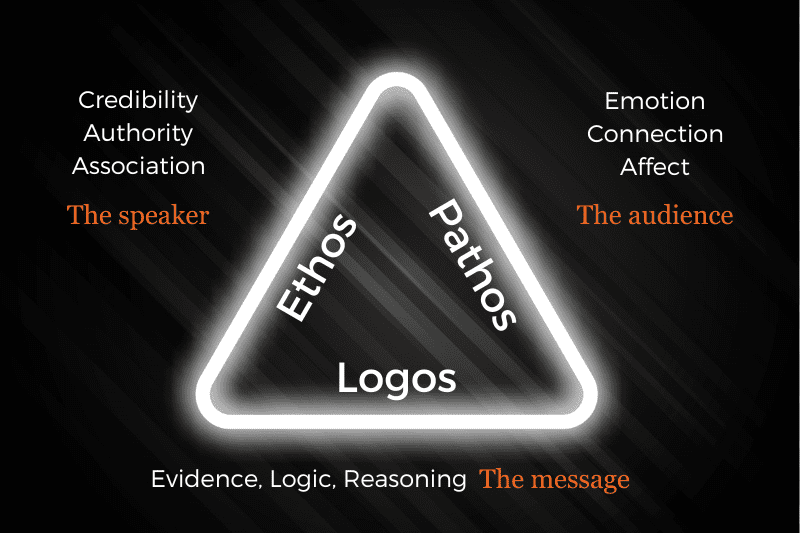
Without getting too philosophical, the key takeaway here is that logos, pathos and ethos are all tools that you can use to present a persuasive argument . However, how much you use each tool needs to be informed by careful consideration of who your audience is and what message you’re trying to convey to them.
For example, if you’re writing a research paper for a largely scientific audience, you’ll likely lean more heavily on the logos . Conversely, if you’re presenting a speech in which you argue for greater social justice, you may lean more heavily on the pathos to win over the hearts and minds of your audience.
Simply put, by understanding the relationship between yourself (as the person making the argument), your audience , and your message , you can strategically employ the three rhetorical appeals to persuade, engage, and connect with your audience more effectively in any context. Use these tools wisely and you’ll quickly notice what a difference they can make to your ability to communicate and more importantly, to persuade .

Psst… there’s more (for free)
This post is part of our dissertation mini-course, which covers everything you need to get started with your dissertation, thesis or research project.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos – A Simple Guide

4-minute read
- 12th April 2023
Ethos, logos, and pathos are three essential components of persuasive communication . They’ve been used for centuries by great communicators to influence the beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors of their audiences. In this simple guide, we’ll take a closer look at these three components using examples from famous writing and speeches.
What Is Ethos?
Ethos is a persuasive appeal based on the credibility or character of the speaker or writer. It refers to the trustworthiness, expertise, or authority that they bring to the argument. It’s crucial in establishing the credibility of the speaker or writer and can be built in through a variety of means, such as reputation and sources, or language and tone.
How To Use Ethos
Ethos can be established through the speaker or writer’s reputation: if they are known for being knowledgeable, honest, and trustworthy, this can lend credibility to their argument. For example, in his famous “I Have a Dream” speech, Martin Luther King Jr. established his ethos by highlighting his role as a civil rights leader and his personal experience with racial injustice.
Another way you can achieve ethos in speech or writing is through the use of credible sources. For example, Rachel Carson established ethos in her book Silent Spring by providing extensive scientific evidence to support her argument that pesticides were harming the environment.
Finally, ethos can be accomplished through the use of language and tone . Using a professional and respectful tone can create the impression of credibility and authority. For instance, in his second inaugural address, President Abraham Lincoln employed ethos by using a solemn, reflective tone to convey the gravity of the situation.
What Is Logos?
Logos is a persuasive appeal based on logic and reasoning. It refers to the use of evidence and logical arguments to support the speaker or writer’s position.
How To Use Logos
One way you can implement logos in your speech or writing is through the use of statistics and data. When writing, or constructing a speech, try to incorporate reliable and credible stats or figures to strengthen your claims or argument and persuade your audience.
You can also employ examples and analogies to achieve logos. These can make your argument more accessible and understandable to a wider audience. For example, in his book The Tipping Point , Malcolm Gladwell uses the example of “the broken windows” theory to illustrate his argument that small changes can have a big impact on social behavior.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Finally, logos can be established through the use of logical arguments . To ensure you have a logical argument, you should have a clear statement with definitions, examples, and evidence to support it. For instance, in his essay “Civil Disobedience,” Henry David Thoreau made a logical argument that individuals have a moral obligation to resist unjust laws.
What Is Pathos?
Pathos is a persuasive appeal based on emotion. It refers to the use of language and imagery that elicits an emotional response. Pathos can be used to create a sense of urgency, inspire empathy, or evoke a particular mood.
How To Use Pathos
Vivid imagery is a great way in which a writer or speaker can implement pathos. Using descriptive language to paint a picture in your audience’s mind is a powerful and persuasive skill. For example, in his poem “Dulce et Decorum Est,” Wilfred Owen used vivid imagery to describe the horrors of war and elicit an emotional response in his readers.
Pathos can also be accomplished by using personal anecdotes. The power of storytelling is an invaluable skill for any writer or speaker because it creates rapport and an emotional connection with your audience. For example, in her TED talk “The Power of Vulnerability,” Brene Brown shares personal stories about her struggles with shame and vulnerability to inspire empathy and connection with her audience.
Finally, pathos can be established through the use of rhetorical questions and appeals to shared values. A good example can be heard in Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech. He poses his biggest question to his audience (and the world): “Now, what does all of this mean in this great period of history?” In response to this rhetorical question, he beautifully tries to persuade the audience to work together toward a common goal, stating, “It means that we’ve got to stay together. We’ve got to stay together and maintain unity.”
Ethos, logos, and pathos are powerful tools for persuasive speech and writing. By establishing credibility, using logical arguments, and appealing to emotion, speakers and writers can influence the beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors of their audiences. When used effectively, these elements can help to create meaningful and lasting change in the world.
Interested in learning how to elevate your writing with more literary devices? Check our other articles .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
3-minute read
The 5 Best Ecommerce Website Design Tools
A visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for success in today’s competitive ecommerce landscape....
The 7 Best Market Research Tools in 2024
Market research is the backbone of successful marketing strategies. To gain a competitive edge, businesses...
Google Patents: Tutorial and Guide
Google Patents is a valuable resource for anyone who wants to learn more about patents, whether...
How to Come Up With Newsletter Ideas
If used strategically, email can have a substantial impact on your business. In fact, according...
Free Online Peer Review Template
Having your writing peer-reviewed is a valuable process that can showcase the strengths and weaknesses...
How to Embed a Video in PowerPoint
Including a video in your PowerPoint presentation can make it more exciting and engaging. And...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Pathos, Logos, and Ethos
Most people are able to drive a car without fully understanding how the car operates. Making an argument is the same way. Most of us attempt to persuade people every day without understanding how persuasion works. Learning how a strong argument is crafted empowers us to better communicate and persuade others to understand our viewpoints.
What Are Pathos, Logos, and Ethos?
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos are three strategies commonly employed when attempting to persuade a reader.
Pathos , or the appeal to emotion, means to persuade an audience by purposely evoking certain emotions to make them feel the way the author wants them to feel. Authors make deliberate word choices, use meaningful language, and use examples and stories that evoke emotion. Authors can desire a range of emotional responses, including sympathy, anger, frustration, or even amusement.
Logos , or the appeal to logic, means to appeal to the audiences’ sense of reason or logic. To use logos, the author makes clear, logical connections between ideas, and includes the use of facts and statistics. Using historical and literal analogies to make a logical argument is another strategy. There should be no holes in the argument, also known as logical fallacies, which are unclear or wrong assumptions or connections between ideas.
Ethos is used to convey the writer’s credibility and authority. When evaluating a piece of writing, the reader must know if the writer is qualified to comment on this issue. The writer can communicate their authority by using credible sources; choosing appropriate language; demonstrating that they have fairly examined the issue (by considering the counterargument); introducing their own professional, academic or authorial credentials; introducing their own personal experience with the issue; and using correct grammar and syntax.
Sample Paragraph
Imagine this: a small dog sits in a dark, cold garage. His hair is matted and dirty; he is skinny and weak from going days without food. There is no water for him to drink, no person to give him love and no blanket to keep him warm at night. 1 While this might be a hard scenario to imagine, it is not an uncommon one in America today. According to the Humane Society of the United States, nearly 1,000,000 animals are abused or die from abuse every year. 2 As a veterinarian with 30 years of experience, I have seen how even one incident of abuse can affect an animal for the rest of its life. 3 As a society, we need to be more aware of this terrible problem and address this issue before it gets worse.
1 Pathos: the author paints a vivid picture to evoke a feeling from the reader—sadness and pity for the abused animal.
2 Logos: the author uses a startling statistic to appeal to our intellect. Keep in mind that these three strategies can often overlap. This sentence qualifies as both Logos and Ethos because it cites a reputable organization, so we know the author is using credible sources.
3 Ethos: the author establishes their own credibility by stating their occupation and experience.>
How Do I Know if the Author is Using Pathos, Logos or Ethos?
Pathos—does the writer appeal to the emotions of their reader.
- Do they use individuals’ stories to “put a face” on the problem you’re exploring? For example, using an individual’s story about losing their home during the mortgage crisis of the 2008 Recession may be more powerful than using only statistics.
- Do they use charged language or words that carry appropriate connotations? For example, if a writer describes a gun as a “sleek, silver piece of sophisticated weaponry,” they are delivering a much different image than if she writes, “a cold hunk of metal, dark and barbaric and ready to kill.”
Logos—does the writer appeal to the rational mind by using logic and evidence?
- Do they include facts and statistics that support their point? It’s more convincing to tell the reader that “80% of students have committed some form of plagiarism,” than simply saying that “Lots of students have plagiarized.”
- Do they walk us through the logical quality of their argument? Do they show us how ideas connect in a rational way? For example: “English students have been able to raise their overall grade by meeting with peer tutors, so it’s safe to assume that math students could also benefit from frequent tutoring sessions.” This example points out that logically, if the result has been seen in one situation, then it should be seen in a different but similar situation.
- Hasty generalizations: “Even though the movie just started, I know it’s going to be boring.”
- Slippery Slope: “If the government legalizes marijuana, eventually they’ll legalize all drugs.”
- Circular Argument: “Barack Obama is a good communicator because he speaks effectively.”
Ethos—is this writer trustworthy?
- What are their credentials? Are they an expert in the field? Have they written past essays, articles or books about this topic?
- Do they use reputable sources? Do they support her statements with sources from established publications like The New York Times or a government census report? Do they fail to mention any sources?
- Are they a fair-minded person who has considered all sides of this issue? Have they acknowledged any common ground they share with the opposite side? Do they include a counterargument and refutation?
Learn more about the Rhetorical Analysis Graphic Organizer .
Learn more about the Rhetorical Analysis Sample Essay .
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Sociology Rhetorical Strategies
How to Use Pathos in an Essay: Connecting Emotion and Persuasion
Table of contents, the power of pathos, techniques for utilizing pathos, balance and ethical considerations.
- Aristotle. (n.d.). Rhetoric. Project Gutenberg. https://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/16357
- Edlund, J. R. (2019). The Ethos-Pathos-Logos of Aristotle's Rhetoric. Humanities Commons. https://hcommons.org/deposits/item/hc:24300/
- Perloff, M. (2009). The dynamics of persuasion: Communication and attitudes in the 21st century. Routledge.
- Johnson, R. H. (2005). Imagining the audience in audience appeals: Audience invoked in American public address textbooks, 1830-1930. Rhetoric & Public Affairs, 8(3), 429-453.
- Walton, D. N. (2013). The new dialectic: Conversational contexts of argument. University of Toronto Press.
- Kellner, D. (2009). Critical theory, Marxism, and modernity. In The Routledge companion to social and political philosophy (pp. 381-395). Routledge.
- Gardner, R. C. (2019). Environmental psychology: An introduction. Routledge.
- Pinker, S. (2014). The sense of style: The thinking person's guide to writing in the 21st century. Penguin Books.
- Cialdini, R. B. (2008). Influence: Science and practice (Vol. 4). Pearson Education.
- Sobieraj, S., & Berry, J. M. (2011). From incivility to outrage: Political discourse in blogs, talk radio, and cable news. Political Communication, 28(1), 19-41.
*minimum deadline
Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below

- Money and Class in America
- Gender Differences
- National Honor Society
- Divorce Rate
Related Essays
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.

AFS Programs
Understanding Pathos, Logos, and Ethos: The Power of Persuasion

When it comes to effective communication, knowing how to use pathos, logos, and ethos can mean the difference between a persuasive argument and one that falls flat. These three rhetorical appeals are frequently used in speeches, essays, and other forms of communication to establish credibility, evoke emotions, and provide logical evidence to support ideas.
Let’s start with pathos–does the word sound familiar? It should, as it comes from the Greek word for “suffering” or “experience.” Pathos is all about appealing to the emotions of the audience. By using phrases, examples, or anecdotes that evoke pity or sympathy, a speaker or writer can establish a connection with the audience on a more emotional level. It’s a powerful tool to unleash whenever you want your message to be more persuasive.
On the other hand, logos is all about using logical reasoning and evidence to support arguments. It appeals to the rationality and intellect of the audience. Logos is often used in conjunction with facts, statistics, and logical statements to establish the credibility of the speaker or author. When applying logos in your writing, be sure to use clear and concise sentences, provide examples or case studies, and keep your audience engaged with logical analysis.
Lastly, we have ethos, which is all about the character or authority of the speaker or author. Ethos is used to establish the credibility and trustworthiness of the person presenting the arguments. By showcasing your expertise, professional background, or previous works, you can establish yourself as a credible source on the subject matter. This is especially important when writing persuasive essays or presenting arguments on certain topics.
Now that we have a general understanding of pathos, logos, and ethos, let’s clarify some common fallacies and abuses of these rhetorical appeals. It’s important to note that while pathos, logos, and ethos can be powerful tools, they can also be misused. For example, appealing to someone’s emotions without providing any additional evidence or logical reasoning can lead to a biased and irrational argument.
Understanding Pathos, Logos, and Ethos
Let’s start by clarifying what pathos, logos, and ethos mean in the context of persuasive writing. Pathos appeals to the emotions of the reader or listener, making them feel pity, anger, or other strong feelings. Logos focuses on the logical reasoning and evidence used to support an argument. Ethos, on the other hand, establishes the credibility and authority of the writer or speaker.
Pathos–Evoke Emotions
The use of pathos is crucial in persuading others. By using language that connects with the reader’s emotions, writers can create a climate of sympathy or urgency. Pathos can be evoked through vivid imagery, personal anecdotes, or by appealing to shared values and beliefs. It is often employed in advertising campaigns or when discussing issues that require an emotional response from the audience.
Logos–Use Logic and Reasoning
While pathos appeals to emotions, logos relies on logical reasoning and evidence. This includes presenting facts, statistics, and logical arguments to support the writer’s or speaker’s point of view. By structuring sentences and paragraphs in a logical manner, writers can strengthen their arguments and make them more persuasive. Logos is commonly used in academic and argumentative writing, as well as in government reports and scientific research.
Ethos–Establish Credibility
Lastly, ethos plays a crucial role in persuading your audience. By presenting yourself as a credible and knowledgeable authority on the subject, you gain the trust of your readers or listeners. This can be achieved through the use of reliable sources, professional language, and a well-structured and organized argument. Ethos is particularly important when dealing with contentious or controversial topics, as it helps establish your credibility and persuasiveness.
The Importance of Pathos in Persuasive Writing
Pathos is the appeal to the emotions and experiences of the audience. It allows writers to tap into the readers’ feelings, such as empathy, sympathy, pity, or even anger, in order to persuade them to agree with their arguments. By using emotionally charged language, vivid descriptions, and relatable anecdotes, writers can create a connection with their audience and make them more likely to be swayed by their ideas.
In persuasive writing, pathos can be especially effective when discussing personal stories or real-life examples that evoke strong emotions. For example, when writing about the impact of climate change, a writer could describe the devastating effects of rising sea levels on coastal communities, like the loss of homes and beaches, to evoke a sense of urgency and concern in the reader.
Furthermore, pathos can also be used to establish the credibility of the writer. By connecting emotionally with the audience, the writer can be seen as someone who understands their concerns and experiences, making them more likely to be trusted and listened to. This is particularly important when addressing controversial or sensitive topics, as it helps the writer establish a connection and gain the readers’ trust before presenting their arguments.
It is important to note, however, that pathos should not overshadow the other rhetorical appeals. Persuasive writing should also include logical and rational arguments (logos) and establish the credibility of the writer (ethos). By combining all three appeals, writers can create a well-rounded persuasive essay that appeals to both the emotions and the intellect of their audience.
So, when writing a persuasive essay, make sure to incorporate pathos effectively by using emotionally compelling language, personal anecdotes, and real-life examples. By appealing to the emotions of your audience, you can establish a stronger connection and make your arguments more persuasive. Remember to balance pathos with logos and ethos, and always provide evidence and logical analysis to support your points. Thank you for reading!
Tapping Into Emotions to Influence Your Audience
Emotions have a way of connecting people on a deeper level. By evoking certain emotions in your audience, you can create a strong bond and make your message or argument much more impactful. This is where pathos, one of Aristotle’s three appeals, comes into play.
Pathos appeals to the emotions of the audience and is often used to elicit empathy, sympathy, or even anger. By appealing to the emotions, you can make your audience more receptive to your ideas and more likely to take action.
One way to tap into emotions is by using powerful and descriptive language. Paint a vivid image in the minds of your audience, allowing them to truly feel what you are saying. Use words that evoke specific emotions such as joy, sadness, fear, or anger, depending on the desired effect.
Another effective technique is to tell stories or share personal anecdotes that relate to the subject matter. This allows the audience to connect with the topic on a personal level and feel a sense of empathy or sympathy. It can also make your message more relatable and memorable.
As with any persuasive writing, it is important to keep in mind the audience you are addressing. Different emotions will resonate with different audiences, so it is important to tailor your message accordingly. Consider what emotions are most likely to resonate with your specific audience and craft your arguments and evidence in a way that appeals to those emotions.
While emotions are a powerful tool, it is important to use them ethically. Always be credible and honest in your arguments and avoid using emotions in a manipulative or exploitative way. The goal is to evoke genuine emotions and create a connection with your audience, not to deceive or manipulate them.
Remember, a persuasive essay or speech doesn’t necessarily have to make the audience angry or sad. It can also inspire happiness, hope, or motivation. The key is to unleash the power of emotions in a way that supports your overall message and objectives.
So, the next time you’re writing an argumentative essay or preparing a speech, remember to keep your audience’s emotions in mind. Use the tips and techniques mentioned above to create a strong emotional appeal, and you’ll be on your way to delivering a persuasive message that resonates with your audience.
Utilizing Logos to Strengthen Your Argument
Logos is derived from the Greek word meaning “logic,” and it emphasizes the use of reasoning and evidence to convince your audience. When you use logos in your writing, you are relying on facts, statistics, expert opinions, and logical reasoning to support your claims and persuade your readers or listeners.
Why is logos important?
Using logos in your arguments is essential because it helps to establish your credibility and makes your argument more persuasive and convincing. By providing clear and logical evidence, you show that you have done your research and have a deep understanding of the subject matter. This can help build trust with your audience and make them more likely to agree with your point of view.
When you use logos effectively, it also helps to counter any potential fallacies or weak arguments that may arise. By presenting strong evidence and using rational reasoning, you can effectively debunk any faulty or misleading statements made by others. This helps to strengthen your own position and make your argument more convincing.
Strategies for using logos
Here are some tips for effectively utilizing logos in your writing:
- Research and gather relevant data and evidence to support your claims.
- Cite credible sources and expert opinions to add credibility to your argument.
- Use logical reasoning to connect your evidence to your main points.
- Address counterarguments and provide refutations to strengthen your argument.
- Keep your language clear, concise, and free from any logical fallacies.
- Structure your argument in a logical and organized manner.
It is important to note that while logos is crucial for making a strong and persuasive argument, it can be even more effective when combined with pathos and ethos. By appealing to both the emotions and ethics of your audience, you create a well-rounded and compelling argument that is more likely to resonate with them.
Building a Solid Reasoning and Evidence-based Approach
To use logos–logical appeal–in your writing, you need to develop clear and sound arguments. Make sure that your statements are supported by evidence, such as facts, statistics, or expert opinions. This helps to strengthen your message and convince the audience that your ideas are valid and well-reasoned.
In an argumentative essay, for example, you can use logos to clarify your main points and counter any potential fallacies or opposing arguments. By using logical reasoning, you can demonstrate that your position is well-founded and supported by evidence.
On the other hand, pathos–emotional appeal–can also be a powerful tool in persuasive writing. By evoking emotions in your readers, you can create a connection and make your message more relatable. This can be done by telling personal stories, using descriptive language, or appealing to the values and beliefs of your audience.
However, it’s important to use pathos responsibly and without abuse. While emotions can be powerful, relying solely on emotional appeal without logical reasoning may undermine the credibility of your argument. It’s crucial to strike a balance between emotional appeal and logical reasoning to create a convincing and compelling message.
In addition to logos and pathos, ethos–is the character and credibility of the author–also plays a significant role in persuasive writing. To establish ethos, the writer needs to demonstrate expertise and credibility on the subject matter. This can be done by including relevant credentials, citing reputable sources, and displaying a deep understanding of the topic.
When building a solid reasoning and evidence-based approach, it is essential to consider your audience. Different strategies may be necessary for different audiences. For example, if you are writing a persuasive speech to a government body, you may need to use more formal language and rely heavily on statistics and expert opinions. On the other hand, if your purpose is to appeal to a broader audience, you may use storytelling and personal anecdotes to create a connection.
To further strengthen your reasoning and evidence-based approach, here are some tips and resources:
1. Use clear and concise language:
Avoid using complicated or ambiguous language that may confuse your audience. Keep your paragraphs and sentences short and to the point.
2. Know your audience:
Understanding the interests, values, and knowledge of your audience can help you tailor your message and arguments to their needs.
3. Keep the focus on your main message:
Avoid getting sidetracked or including irrelevant information that may weaken your argument. Stay focused on your main points and keep the audience engaged.
By following these strategies and applying a solid reasoning and evidence-based approach, you can create persuasive essays that resonate with your audiences. Remember to use logos, pathos, and ethos effectively and responsibly to build a strong and convincing message.
If you’re unsure about the effectiveness of your writing or want to check for any grammar or spelling mistakes, you can use resources like LanguageTool or seek editing assistance from others. With practice, you’ll become more adept at applying these strategies and connecting with your readers on a deeper level.
Developing Ethos for Effective Persuasion
To develop ethos, it is important to consider your audience and tailor your approach accordingly. Start by asking yourself questions such as: What level of expertise do my readers have? What kind of language and examples would resonate with them? Knowing your audience will help you structure your arguments and better appeal to their emotions and intellect.
A well-developed ethos also includes using professional language and avoiding fallacies or abuses of logic. Show that you have done your research and provide evidence to support your claims. Use words and phrases that express certainty and authority, but be careful not to come across as arrogant or condescending.
Another important aspect of ethos is acknowledging and addressing potential counterarguments. By showing that you have considered other viewpoints and have a well-rounded understanding of the topic, you demonstrate fairness and openness. This can further establish your credibility and make your arguments more persuasive.
Developing ethos requires practice and continuous improvement. Read sample speeches, articles, or essays written by professionals to learn from their techniques. Take additional classes or workshops to further enhance your persuasive skills. The more you unleash the power of ethos, the more effective you will be in making your point and influencing others.
Remember, ethos is just one of the three pillars of persuasion. Pathos appeals to emotions, while logos–logic–does so with rational arguments. By using a combination of ethos, pathos, and logos, you can create a well-rounded persuasive piece that communicates your ideas effectively and ethically.
Thank you for reading!
Does appealing to emotions make a persuasive argument stronger?
Yes, appealing to emotions can make a persuasive argument stronger. By tapping into the reader’s emotions, the writer can create a stronger connection and engage the reader on a more personal level. Emotions can help to evoke empathy, create a sense of urgency, and ultimately motivate the reader to take action.

How can a writer appeal to the emotions of their reader?
A writer can appeal to the emotions of their reader by using vivid and descriptive language, storytelling, personal anecdotes, and powerful imagery. They can also use rhetorical devices such as metaphors, similes, and hyperbole to evoke strong emotions. Additionally, the writer can focus on relatable topics and issues that resonate with the reader’s own experiences and emotions.
Is it more effective to appeal to emotions when trying to persuade someone?
It depends on the situation and the audience. Appealing to emotions can be very effective in certain circumstances, especially when the topic is highly personal or sensitive. However, in other situations where the audience values logic and reason, appealing to emotions may be less effective and could even backfire. It’s important for the writer to understand their audience and tailor their persuasive techniques accordingly.
What are the benefits of appealing to emotions in persuasive writing?
Appealing to emotions in persuasive writing can have several benefits. Firstly, it can create a strong connection between the writer and the reader, enhancing the reader’s engagement with the argument. Secondly, emotions can help to evoke empathy and compassion, making the reader more likely to take action or support the writer’s cause. Lastly, appealing to emotions can make the argument more memorable and impactful, as emotions tend to leave a lasting impression on the reader.
Are there any risks associated with appealing to emotions in persuasive writing?
Yes, there are some risks associated with appealing to emotions in persuasive writing. If the emotions are not effectively supported by evidence and logical reasoning, the argument may come across as manipulative or disingenuous. Additionally, different people may have different emotional responses to the same argument, so it’s important for the writer to consider the diverse perspectives and emotional reactions of their audience. Overall, the writer should strike a balance between appealing to emotions and presenting a well-supported and logical argument.
Does using pathos make the writer’s argument more persuasive?
Yes, using pathos can make the writer’s argument more persuasive. By appealing to the emotions of their reader, the writer can create a strong emotional connection and make their argument more relatable, memorable, and convincing.

By Alex Koliada, PhD
Alex Koliada, PhD, is a well-known doctor. He is famous for studying aging, genetics, and other medical conditions. He works at the Institute of Food Biotechnology and Genomics. His scientific research has been published in the most reputable international magazines. Alex holds a BA in English and Comparative Literature from the University of Southern California , and a TEFL certification from The Boston Language Institute.

The Essential AP Guide to Ethos, Pathos, and Logos
The goal of argumentative writing is to persuade your audience that your ideas are convincing. Basically, there are three ways of doing this:
- You can convince your reader that your authority is indisputable (ethos)
- You can convince your reader by appealing to his emotions (pathos)
- You can convince your reader by appealing to his sense of logic and reason (logos)
Think of these different modes of persuasion, ethos, pathos, and logos, as tactics or strategies. Tactics you’ve used all your life when you use words to try to persuade someone to do something, be that agree with your opinion or buy you a new bike.
Yes, you use ethos, pathos, and logos every day.
To succeed in AP English, you need to know how to identify ethos, pathos, and logos quickly. Below is our quick guide that gives you everything you need to know to identify ethos, pathos, and logos and ace AP English.


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Elizabeth Browning
The Appeal to Pathos
Literally translated, pathos means “suffering.” In this case, it refers to emotion, or more specifically, the writer’s appeal to the audience’s emotions. When a writer establishes an effective pathetic appeal, he/she is able to make the audience care about what the writer is saying. If the audience does not care about the message, then they will not engage with the argument being made.
For example, say that a writer is crafting a speech for a politician who is running for office, and in it he raises a point about Social Security benefits. In order to make this point more appealing to the audience so that they will feel more emotionally connected to what the politician says, the writer inserts a story about Mary, an 80-year-old widow who relies on her Social Security benefits to supplement her income. While visiting Mary the other day, sitting at her kitchen table and eating a piece of her delicious homemade apple pie, the writer recounts how the politician held Mary’s delicate hand and promised that her benefits would be safe if he were elected. Ideally, the writer wants the audience to feel sympathy or compassion for Mary, and thus they will feel more open to considering the politician’s views on Social Security (and maybe even other issues).
When evaluating a writer’s pathetic appeal, ask the following questions:
- Does the writer try to engage or connect with the audience by making the subject matter relatable in some way?
- Does the writer have an interesting writing style?
- Does the writer use humor at any point?
- Does the writer use narration, such as storytelling or anecdotes, to add interest or to help humanize a certain issue within the text?
- Does the writer use descriptive or attention-grabbing details?
- Are there hypothetical examples that help the audience to imagine themselves in certain scenarios?
- Does the writer use any other examples in the text that might emotionally appeal to the audience?
- Are there any visual appeals to pathos, such as photographs or illustrations?
Appealing to Emotions
When an author relies on pathos, it means that they are trying to tap into the audience’s emotions to get them to agree with the author’s claim. An author using pathos appeals wants the audience to feel something: anger, pride, joy, rage, or happiness. For example, many of us have seen the ASPCA commercials that use photographs of injured puppies, or sad-looking kittens, and slow, depressing music to emotionally persuade their audience to donate money. This is a classic example of the use of pathos in argument.
Pathos-based rhetorical strategies are any strategies that get the audience to “open up” to the topic, the argument, or to the author through an emotional connection. Emotions can make us vulnerable, and an author can use this vulnerability to get the audience to believe that their argument is a compelling one.
Pathetic appeals might include:
- Expressive descriptions of people, places, or events that help the reader to feel or experience those events
- Vivid imagery of people, places or events that help the reader to feel like they are seeing those events
- Sharing personal stories that make the reader feel a connection to, or empathy for, the person being described
- Using emotion-laden vocabulary as a way to put the reader into that specific emotional mindset (what is the author trying to make the audience feel? and how are they doing that?)
- Using any information that will evoke an emotional response from the audience. This could involve making the audience feel empathy or disgust for the person/group/event being discussed, or perhaps connection to or rejection of the person/group/event being discussed.
Consider the use of pathos in one of the most common forms of media, the TV commercial, where advertisers use emotionally driven images or language to sway the audience.
Car Commercial: Images of a pregnant woman being safely rushed to a hospital. Flash to two car seats in the back seat. Flash to family hopping out of their Ford Escape and witnessing the majesty of the Grand Canyon.
After an image of a worried mother watching her sixteen-year-old daughter drive away: “Ford Escape takes the fear out of driving.”
The use of examples and language that evoke an appropriate emotional response in the viewer or reader—that gets them to care about your topic—can be helpful in argument.
For academic essays, pathos may be useful in introductory sections, concluding sections, or as ways to link various parts of the paper together. However, if your argument is based solely or primarily upon emotional appeals, it will be viewed as weak in an academic setting, especially when data or ethical sources can disprove your claims. Therefore, college writing often puts more emphasis on logos and ethos.
Understanding “Emotional” Appeal
Pathos does not always necessarily mean that you are appealing to the way your audience “feels.”
Instead, “emotion” in pathos refers to beliefs and values and how you react when those beliefs and values are alluded to, questioned, or threatened. Please note that this is different from the usual way we think of “emotions.”
For example, let’s say that I am the director of some program that is a “worthy cause,” like a food bank. I need your money to keep the place going (a place that provides food for people who are really hungry). The simplest thing to do might be to write you a letter and ask you for the money, perhaps even giving you a figure (“send one single 20-dollar bill for the whole year”). I will probably be successful, up to a point. I might be more successful, however, if I appealed to your pathos. I could do this by including an 8×10 black and white photograph of a big-eyed, sad-faced, raggedly dressed child, with a caption that says, “Amy is hoping you can make the hunger pains go away. Amy is saying ‘help me’.” Now the appeal is to your reaction when your beliefs and values are alluded to, questioned, or threatened.
When writing an academic essay, your essay is probably equivalent to only writing the letter above, not the picture. However, be careful with the next few questions below. A little pathos goes a long way.
Connecting with Your Audience through Appropriate Language
Do i use honorific language.
Make sure your writing includes honorific language – language that is respectful, polite, courteous. Any language that shows respect for other points of view tends to increase the audience’s respect for you.
Do this: While Dr. Alvarez makes a valid point regarding the benefit of GMOs when it comes to increased crop yields for developing countries, he fails to take into account some of the greater risks that are still being investigated, such as antibacterial resistance being transferred from GMO crops to the humans who eat them.
Not this: John Alvarez refuses to see any other side of the issue but his own, even leaving out something as important as antibacterial resistance when making his point about GMOs.
When you have reread your entire essay and inserted honorific language, go to the next question.
Do I use pejorative language?
Pejorative language is language that puts down, belittles, sounds sarcastic. As much fun as it may seem to make fun of an opposing view, it makes your audience suspicious of you, particularly if your audience holds an opposing view. This kind of language should be eliminated from your writing.
When revising your own writing, be sure to eliminate any pejorative language. This may include phrases, punctuation, or the use of qualifiers and adjectives that make you look like you can only make fun of an opposing view, rather than make a serious point.
Do this: Soil scientist, Dr. Linda McAllister, conducted a recent study on the efficacy of glyphosate on commercial crops, and while her findings seem mostly positive and mention very few downsides to crop spraying, it is important to note that Monsanto, one of the largest agricultural companies in the world that regularly uses glyphosate as a pesticide for crops, was a major funder of the study.
Not this: Clearly, “Doctor” Linda is in the bulging pocket of greedy Monsanto, which is arguably the worst culprit of poisoning America’s farmland, thus revealing that her “scientific” study is entirely bogus.
When you have reread your writing and eliminated pejorative language, go to the next question.
Do I use an anecdote?
You could very easily insert a number of anecdotes to highlight what you are claiming, in the same way I included the photograph in the above example of the letter. You could include a single anecdote in your introductory paragraph of an essay. However, most readers of persuasive essays at the college level and higher do not appreciate many direct emotional appeals. It may be best to limit your anecdote to just the one in your Introduction, though the more anecdotes you use, the more emotional the argument. This includes anecdotes you tell yourself and anecdotes you find in other places.
When you are satisfied that you have used a number of anecdotes appropriate for the audience, go to the next question.
Do I use allusions?
Do you allude (or refer) to your anecdotes or other well-known symbols? At most, it may be best if you only allude to your one anecdote in your introduction. Pathos in writing like this should be limited to the kind of language you use, and the way you use it. However, you may also allude to anything that puts you and the audience in the same system of beliefs, or values, or assumptions about life. In a long persuasive essay, it is probably enough to remind the reader of the introductory anecdote by alluding to it indirectly in the conclusion.
Recognizing a Manipulative Appeal to Pathos:
Up to a certain point, an appeal to pathos can be a legitimate part of an argument. For example, a writer or speaker may begin with an anecdote showing the effect of a law on an individual. This anecdote will be a means of gaining an audience’s attention for an argument in which she uses evidence and reason to present her full case as to why the law should/should not be repealed or amended. In such a context, engaging the emotions, values, or beliefs of the audience is a legitimate tool whose effective use should lead you to give the author high marks.
An appropriate appeal to pathos is different than trying to unfairly play upon the audience’s feelings and emotions through fallacious, misleading, or excessively emotional appeals. Such a manipulative use of pathos may alienate the audience or cause them to “tune out”. An example would be the American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (ASPCA) commercials featuring the song “In the Arms on an Angel” and footage of abused animals. Even Sarah McLachlan, the singer and spokesperson featured in the commercials, admits that she changes the channel because they are too depressing (Brekke, 2014).
Even if an appeal to pathos is not manipulative, such an appeal should complement rather than replace reason and evidence-based argument. In addition to making use of pathos, the author must establish her credibility (ethos) and must supply reasons and evidence (logos) in support of her position. An author who essentially replaces logos and ethos with pathos alone should be given low marks.
When identifying pathos in written communication, try to locate where the author is trying to convince the reader by strictly using emotions because, if used to excess, pathos appeals can indicate a lack of substance or emotional manipulation of the audience. If the only way in which an author can persuade the readers is by making them sad or angry, does that make for a solid, valid argument?
In the movie Braveheart, the Scottish military leader, William Wallace, played by Mel Gibson, gives a speech to his troops just before they get ready to go into battle against the English army of King Edward I.
See clip here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h2vW-rr9ibE
Transcript here: https://www.virginiawestern.edu/eng111/WilliamWallaceSpeech-Braveheart.pdf
Step 1: When you watch the movie clip, try to gauge the general emotional atmosphere. Do the men seem calm or nervous? Confident or skeptical? Are they eager to go into battle, or are they ready to retreat? Assessing the situation from the start will make it easier to answer more specific, probing rhetorical questions after watching it.
Step 2: Consider these questions:
- What issues does Wallace address?
- Who is his audience?
- How does the audience view the issues at hand?
Step 3: Next, analyze Wallace’s use of pathos in his speech.
- How does he try to connect with his audience emotionally? Because this is a speech, and he’s appealing to the audience in person, consider his overall look as well as what he says.
- How would you describe his manner or attitude?
- Does he use any humor, and if so, to what effect?
- How would you describe his tone?
- Identify some examples of language that show an appeal to pathos: words, phrases, imagery, collective pronouns (we, us, our).
- How do all of these factors help him establish a pathetic appeal?
Step 4: Once you’ve identified the various ways that Wallace tries to establish his appeal to pathos, the final step is to evaluate the effectiveness of that appeal.
- Do you think he has successfully established a pathetic appeal? Why or why not?
- What does he do well in establishing pathos?
- What could he improve, or what could he do differently to make his pathetic appeal even stronger?
Information in this chapter was remixed from the following sources:
Frameworks for Academic Writing by Stephen V. Poulter is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License .
Informed Arguments: A Guide to Writing and Research by Terri Pantuso, Sarah LeMire, and Kathy Anders, which was published in 2019 by Texas A&M University with an attribution, non-commerical, share-alike creative commons license . It was accessed through the Open Textbook Library.
Let’s Get Writing by Elizabeth Browning, Kirsten DeVries, Kathy Boylan, Jenifer Kurtz, and Katelyn Burton, which was published by Virginia Western Community Colleges and uses a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ,
Pathos Copyright © 2021 by Elizabeth Browning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Understand The Difference Between Ethos, Pathos, And Logos To Make Your Point
- What Is Ethos?
- What Is Pathos?
- What Is Logos?
- Examples Of Each
- What Are Mythos And Kairos?
During an argument, people will often say whatever is necessary to win. If that is the case, they would certainly need to understand the three modes of persuasion, also commonly known as the three rhetorical appeals: ethos , pathos , and logos . In short, these three words refer to three main methods that a person can use to speak or write persuasively. As you’re about to find out, the modes of persuasion are important because a speaker who knows how to effectively use them will have a significant advantage over someone who doesn’t.
The terms ethos , pathos , and logos and the theory of their use can be traced back to ancient Greece to the philosophy of Aristotle . Aristotle used these three concepts in his explanations of rhetoric , or the art of influencing the thought and conduct of an audience. For Aristotle, the three modes of persuasion specifically referred to the three major parts of an argument: the speaker ( ethos ), the argument itself ( logos ), and the audience ( pathos ). In particular, Aristotle focused on the speaker’s character, the logic and reason presented by an argument, and the emotional impact the argument had on an audience.
While they have ancient roots, these modes of persuasion are alive and well today. Put simply, ethos refers to persuasion based on the credibility or authority of the speaker, pathos refers to persuasion based on emotion, and logos refers to persuasion based on logic or reason.
By effectively using the three modes of persuasion with a large supply of rhetorical devices, a speaker or writer can become a master of rhetoric and win nearly any argument or win over any audience. Before they can do that, though, they must know exactly what ethos , pathos , and logos mean. Fortunately, we are going to look closely at each of these three ideas and see if they are really as effective as they are said to be.
⚡️ Quick summary
Ethos , pathos , and logos are the three classical modes of persuasion that a person can use to speak or write persuasively. Specifically:
- ethos (character): known as “the appeal to authority” or “the appeal to credibility.” This is the method in which a person relies on their credibility or character when making an appeal or an argument.
- pathos (emotions): known as “the appeal to emotion.” Pathos refers to the method of trying to persuade an audience by eliciting some kind of emotional reaction.
- logos (logic): known as “the appeal to reason.” This method involves using facts and logical reasoning to support an argument and persuade an audience.
What is ethos ?
The word ethos comes straight from Greek. In Greek, ethos literally translates to “habit,” “custom,” or “character.” Ethos is related to the words ethic and ethical , which are typically used to refer to behavior that is or isn’t acceptable for a particular person.
In rhetoric, the word ethos is used to refer to the character or reputation of the speaker. As a rhetorical appeal, ethos is known as “the appeal to authority” or “the appeal to credibility.” When it comes to ethos , one important consideration is how the speaker carries themself and how they present themselves to the audience: Does it seem like they know what they are talking about? Do they even believe the words they are saying? Are they an expert? Do they have some experience or skills that tell us we should listen to them?
Ethos is important in rhetoric because it often influences the opinion or mood of the audience. If a speaker seems unenthusiastic, unprepared, or inexperienced, the audience is more likely to discount the speaker’s argument regardless of what it even is. On the other hand, a knowledgeable, authoritative, confident speaker is much more likely to win an audience over.
Ethos often depends on more than just the argument itself. For example, a speaker’s word choice, grammar, and diction also contribute to ethos ; an audience may react more favorably toward a professional speaker who has a good grasp of industry jargon and enunciates clearly versus a speaker who lacks the necessary vocabulary and fails to enunciate. Ethos can also be influenced by nonverbal factors as well, such as posture, body language, eye contact, and even the speaker’s choice of clothing. For example, a military officer proudly wearing their uniform bedecked with medals will go a long way to establishing ethos without them saying a single word.
Here as a simple example of ethos :
- “As a former mayor of this city, I believe we can solve this crisis if we band together.”
The speaker uses ethos by alerting the audience of their credentials and experience. By doing so, they rely on their reputation to be more persuasive. This “as a…” method of establishing ethos is common, and you have probably seen it used in many persuasive advertisements and speeches.
What are open-ended questions and how can you use them effectively? Find out here.
What is pathos ?
In Greek, pathos literally translates to “suffering, experience, or sensation.” The word pathos is related to the words pathetic , sympathy , and empathy , which all have to do with emotions or emotional connections. Aristotle used the word pathos to refer to the emotional impact that an argument had on an audience; this usage is still mainly how pathos is used in rhetoric today.
As a rhetorical appeal, pathos is referred to as “the appeal to emotion.” Generally speaking, an author or speaker is using pathos when they are trying to persuade an audience by causing some kind of emotional reaction. When it comes to pathos , any and all emotions are on the table: sadness, fear, hope, joy, anger, lust, pity, etc.
As you probably know from your own life, emotions are a powerful motivating factor. For this reason, relying on pathos is often a smart and effective strategy for persuading an audience. Both positive and negative emotions can heavily influence an audience: for example, an audience will want to support a speaker whose position will make them happy, a speaker who wants to end their sadness, or a speaker who is opposed to something that makes them angry.
Here is a simple example of pathos :
- “Every day, the rainforests shrink and innocent animals are killed. We must do something about this calamitous trend before the planet we call our home is damaged beyond repair.”
Here, the author is trying to win over an audience by making them feel sad, concerned, or afraid. The author’s choice of words like “innocent” and “calamitous” enforce the fact that they are trying to rely on pathos .
What is logos ?
In Greek, the word logos literally translates to “word, reason, or discourse.” The word logos is related to many different words that have to do with reason, discourse, or knowledge, such as logic , logical , and any words that end in the suffixes -logy or -logue .
As a mode of persuasion and rhetorical appeal, logos is often referred to as “the appeal to reason.” If a speaker or author is relying on logos , they are typically reciting facts or providing data and statistics that support their argument. In a manner of speaking, logos does away with all of the bells and whistles of ethos and pathos and cuts to the chase by trying to present a rational argument.
Logos can be effective in arguments because, in theory, it is impossible to argue against truth and facts. An audience is more likely to agree with a speaker who can provide strong, factual evidence that shows their position is correct. On the flip side, an audience is less likely to support an argument that is flawed or entirely wrong. Going further, a speaker that presents a lot of supporting evidence and data to the audience is likely to come across as knowledgeable and someone to be listened to, which earns bonus points in ethos as well.
While Aristotle clearly valued an argument based on reason very highly, we know that logos alone doesn’t always effectively persuade an audience. In your own life, you have likely seen a rational, correct speaker lose an argument to a charismatic, authoritative speaker who may not have the facts right.
Here is a simple example of logos :
- “According to market research, sales of computer chips have increased by 300% in the last five years. Analysis of the industry tells us that the market share of computer chips is dominated by Asian manufacturers. It is clear that the Asian technology sector will continue to experience rapid growth for the foreseeable future.”
In this paragraph, the author is using data, statistics, and logical reasoning to make their argument. They clearly hope to use logos to try to convince an audience to agree with them.
Do you need persuading to take this quiz on identifying ethos, pathos, and logos? We think you’ll be a champion at it.
Examples of ethos , pathos , and logos
Ethos , pathos , and logos can all be employed to deliver compelling and persuasive arguments or to win over an audience. Let’s look at a variety of examples to see how different speakers and authors have turned to these modes of persuasion over the years.
“Come I to speak in Caesar’s funeral. He was my friend, faithful and just to me […] You all did see that on the Lupercal I thrice presented him a kingly crown, Which he did thrice refuse: was this ambition?” —Marc Antony, Julius Caesar by William Shakespeare
In this scene, Marc Antony is trying to win over the Roman people, so Shakespeare has Antony rely on ethos . Antony is establishing himself as both a person of authority in Rome (having the power to offer Caesar a crown) and an expert on Caesar’s true character (Antony was Caesar’s close friend and advisor).
“During the next five years, I started a company named NeXT, another company named Pixar, and fell in love with an amazing woman who would become my wife. Pixar went on to create the world’s first computer animated feature film, Toy Story , and is now the most successful animation studio in the world. In a remarkable turn of events, Apple bought NeXT, I returned to Apple, and the technology we developed at NeXT is at the heart of Apple’s current renaissance.” —Steve Jobs, 2005
Here, Steve Jobs is providing his background–via humblebrag – of being a major figure in several different highly successful tech companies. Jobs is using ethos to provide substance to his words and make it clear to the audience that he knows what he is talking about and they should listen to him.
Make Your Writing Shine!
- By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy policies.
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
“Moreover, though you hate both him and his gifts with all your heart, yet pity the rest of the Achaeans who are being harassed in all their host; they will honour you as a god, and you will earn great glory at their hands. You might even kill Hector; he will come within your reach, for he is infatuated, and declares that not a Danaan whom the ships have brought can hold his own against him.” —Ulysses to Achilles, The Iliad by Homer
In this plea, Ulysses is doing his best to pile on the pathos . In one paragraph, Ulysses is attempting to appeal to several of Achilles’s emotions: his hatred of Hector, his infamous stubborn pride, his sympathy for civilians, and his desire for vengeance.
“I am not unmindful that some of you have come here out of great trials and tribulations. Some of you have come fresh from narrow jail cells. Some of you have come from areas where your quest—quest for freedom left you battered by the storms of persecution and staggered by the winds of police brutality.” —Dr. Martin Luther King Jr., 1963
In this excerpt from his “I Have A Dream” speech, King is using pathos to accomplish two goals at once. First, he is connecting with his audience by making it clear is aware of their plight and suffering. Second, he is citing these examples to cause sadness or outrage in the audience. Both of these effects will make an audience interested in what he has to say and more likely to support his position.
Dr. King’s “I Have A Dream” speech is recognizable and noteworthy for many reasons, including the rhetorical device he employs. Learn about it here.
“Let it be remembered how powerful the influence of a single introduced tree or mammal has been shown to be. But in the case of an island, or of a country partly surrounded by barriers, into which new and better adapted forms could not freely enter, we should then have places in the economy of nature which would assuredly be better filled up if some of the original inhabitants were in some manner modified; for, had the area been open to immigration, these same places would have been seized on by intruders. In such case, every slight modification, which in the course of ages chanced to arise, and which in any way favoured the individuals of any of the species, by better adapting them to their altered conditions, would tend to be preserved; and natural selection would have free scope for the work of improvement.” —Charles Darwin, On the Origin of the Species , 1859
In this passage, Darwin is using logos by presenting a rational argument in support of natural selection. Darwin connects natural selection to established scientific knowledge to argue that it makes logical sense that animals would adapt to better survive in their environment.
“I often echo the point made by the climate scientist James Hansen: The accumulation of carbon dioxide, methane and other greenhouse gases—some of which will envelop the planet for hundreds and possibly thousands of years—is now trapping as much extra energy daily as 500,000 Hiroshima-class atomic bombs would release every 24 hours. This is the crisis we face.” —Al Gore, “The Climate Crisis Is the Battle of Our Time, and We Can Win,” 2019
In this call to action, Al Gore uses logos to attempt to convince his audience of the significance of climate change. In order to do this, Gore both cites an expert in the field and provides a scientifically accurate simile to explain the scale of the effect that greenhouse gases have on Earth’s atmosphere.
What are mythos and kairos ?
Some modern scholars may also use terms mythos and kairos when discussing modes of persuasion or rhetoric in general.
Aristotle used the term mythos to refer to the plot or story structure of Greek tragedies, i.e., how a playwright ordered the events of the story to affect the audience. Today, mythos is most often discussed as a literary or poetic term rather than a rhetorical one. However, mythos may rarely be referred to as the “appeal to culture” or the “appeal to myth” if it is treated as an additional mode of persuasion. According to this viewpoint, a speaker/writer is using mythos if they try to persuade an audience using shared cultural customs or societal values.
A commonly cited example of mythos is King’s “I Have a Dream” speech quoted earlier. King says:
“When the architects of our republic wrote the magnificent words of the Constitution and the Declaration of Independence, they were signing a promissory note to which every American was to fall heir. This note was a promise that all men—yes, black men as well as white men—would be guaranteed the ‘unalienable rights’ of ‘life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness.’ ”
Throughout the speech, King repeatedly uses American symbols and American history ( mythos ) to argue that all Americans should be outraged that Black Americans have been denied freedom and civil rights.
Some modern scholars may also consider kairos as an additional mode of persuasion. Kairos is usually defined as referring to the specific time and place that a speaker chooses to deliver their speech. For written rhetoric, the “place” instead refers to the specific medium or publication in which a piece of writing appears.
Unlike the other modes of persuasion, kairos relates to the context of a speech and how the appropriateness (or not) of a setting affects how effective a speaker is. Once again, King’s “I Have a Dream” speech is a great example of the use of kairos . This speech was delivered at the steps of the Lincoln Memorial during the 100th anniversary of the Emancipation Proclamation at the end of the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. Clearly, King intended to use kairos to enhance the importance and timeliness of this landmark speech.
Make your communication as smooth as can be by learning about filler words and when you should, and shouldn't, use them.

Ways To Say
Synonym of the day
Table of Contents
Collaboration, information literacy, writing process, using pathos in persuasive writing.
- CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 by Angela Eward-Mangione - Hillsborough Community College
Incorporating appeals to pathos into persuasive writing increases a writer’s chances of achieving his or her purpose. Read “ Pathos ” to define and understand pathos and methods for appealing to it. The following brief article discusses examples of these appeals in persuasive writing.
An important key to incorporating pathos into your persuasive writing effectively is appealing to your audience’s commonly held emotions. To do this, one must be able to identify common emotions, as well as understand what situations typically evoke such emotions. The blog post “ The 10 Most Common Feelings Worldwide, We Feel Fine ,” offers an interview with Seth Kamvar, co-author of We Feel Fine. According to the post, the 10 most commonly held emotions in 2006-2009 were: better, bad, good, guilty, sorry, sick, well, comfortable, great, and happy (qtd. in Whelan).
Let’s take a look at some potential essay topics, what emotions they might evoke, and what methods can be used to appeal to those emotions.
Example: Animal Cruelty
Related Emotions:
Method Narrative
In “To Kill a Chicken,” Nicholas Kristof describes footage taken by an undercover investigator for Mercy with Animals at a North Carolina poultry slaughterhouse: “some chickens aren’t completely knocked out by the electric current and can be seen struggling frantically. Others avoid the circular saw somehow. A backup worker is supposed to cut the throat of those missed by the saw, but any that get by him are scalded alive, the investigator said” (Kristof).
This narrative account, which creates a cruel picture in readers’ minds, will evoke anger, horror, sadness, and sympathy.
Example: Human Trafficking
- Sadness (sorry)
- Sympathy
Method: Direct Quote
“From Victim to Impassioned Voice” provides the perspective of Asia Graves, a victim of a vicious child prostitution ring who attributes her survival to a group of women: “If I didn’t have those strong women, I’d be nowhere” (McKin).
A quote from a victim of human trafficking humanizes the topic, eliciting sadness and sympathy for the victim(s).
Example: Cyberbullying
Method: empathy for an opposing view.
The concerns of some people who oppose the criminalization of cyberbullying are understandable. For example, Justin W. Patchin, coauthor of Bullying Beyond the Schoolyard: Preventing and Responding to Cyberbullying , opposes making cyberbullying a crime because he views the federal and state governments’ role as one to educate local school districts and provide resources for them (“Cyberbullying”). Patchin does not oppose cyberbullying itself; rather, he takes issue with the government responding to it through criminalization.
Identifying and articulating the opposing view as well as the concerns that underpin it helps the audience experience a full range of sympathy, a commonly held emotion, as a consequence of sincerely investigating and acknowledging another view.
The method a writer uses to persuade emotionally his or her audience will depend on the situation. However, any writer who uses at least one approach will be more persuasive than a writer who ignores opportunities to entreat one of the most powerful aspects of the human experience—emotions.
Works Cited
“Cyberbullying.” Opposing Viewpoints Online Collection . Detroit: Gale, 2015. Opposing Viewpoints in Context . Web. 21 July 2016.
Kristof, Nicholas. “To Kill a Chicken.” The New York Times . The New York Times, 3 May 2015. Web. 20 July 2016.
McKin, Jenifer. “From victim to impassioned voice: Women exploited as a teen fights sexual trafficking of children.” The Boston Globe . Boston Globe Media Partners, 27 Nov. 2012. Web. 20 July 2016.
Whelan, Christine. “The 10 Most Common Feelings Worldwide: We Feel Fine.” The Huffington Post . The Huffington Post, 18 March 2012. Web. 21 July 2016.

Brevity – Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence – How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow – How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity – Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style – The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority – How to Establish Credibility in Speech & Writing
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a rhetorical analysis | Key concepts & examples
How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis | Key Concepts & Examples
Published on August 28, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
A rhetorical analysis is a type of essay that looks at a text in terms of rhetoric. This means it is less concerned with what the author is saying than with how they say it: their goals, techniques, and appeals to the audience.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Key concepts in rhetoric, analyzing the text, introducing your rhetorical analysis, the body: doing the analysis, concluding a rhetorical analysis, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about rhetorical analysis.
Rhetoric, the art of effective speaking and writing, is a subject that trains you to look at texts, arguments and speeches in terms of how they are designed to persuade the audience. This section introduces a few of the key concepts of this field.
Appeals: Logos, ethos, pathos
Appeals are how the author convinces their audience. Three central appeals are discussed in rhetoric, established by the philosopher Aristotle and sometimes called the rhetorical triangle: logos, ethos, and pathos.
Logos , or the logical appeal, refers to the use of reasoned argument to persuade. This is the dominant approach in academic writing , where arguments are built up using reasoning and evidence.
Ethos , or the ethical appeal, involves the author presenting themselves as an authority on their subject. For example, someone making a moral argument might highlight their own morally admirable behavior; someone speaking about a technical subject might present themselves as an expert by mentioning their qualifications.
Pathos , or the pathetic appeal, evokes the audience’s emotions. This might involve speaking in a passionate way, employing vivid imagery, or trying to provoke anger, sympathy, or any other emotional response in the audience.
These three appeals are all treated as integral parts of rhetoric, and a given author may combine all three of them to convince their audience.
Text and context
In rhetoric, a text is not necessarily a piece of writing (though it may be this). A text is whatever piece of communication you are analyzing. This could be, for example, a speech, an advertisement, or a satirical image.
In these cases, your analysis would focus on more than just language—you might look at visual or sonic elements of the text too.
The context is everything surrounding the text: Who is the author (or speaker, designer, etc.)? Who is their (intended or actual) audience? When and where was the text produced, and for what purpose?
Looking at the context can help to inform your rhetorical analysis. For example, Martin Luther King, Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech has universal power, but the context of the civil rights movement is an important part of understanding why.
Claims, supports, and warrants
A piece of rhetoric is always making some sort of argument, whether it’s a very clearly defined and logical one (e.g. in a philosophy essay) or one that the reader has to infer (e.g. in a satirical article). These arguments are built up with claims, supports, and warrants.
A claim is the fact or idea the author wants to convince the reader of. An argument might center on a single claim, or be built up out of many. Claims are usually explicitly stated, but they may also just be implied in some kinds of text.
The author uses supports to back up each claim they make. These might range from hard evidence to emotional appeals—anything that is used to convince the reader to accept a claim.
The warrant is the logic or assumption that connects a support with a claim. Outside of quite formal argumentation, the warrant is often unstated—the author assumes their audience will understand the connection without it. But that doesn’t mean you can’t still explore the implicit warrant in these cases.
For example, look at the following statement:
We can see a claim and a support here, but the warrant is implicit. Here, the warrant is the assumption that more likeable candidates would have inspired greater turnout. We might be more or less convinced by the argument depending on whether we think this is a fair assumption.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Rhetorical analysis isn’t a matter of choosing concepts in advance and applying them to a text. Instead, it starts with looking at the text in detail and asking the appropriate questions about how it works:
- What is the author’s purpose?
- Do they focus closely on their key claims, or do they discuss various topics?
- What tone do they take—angry or sympathetic? Personal or authoritative? Formal or informal?
- Who seems to be the intended audience? Is this audience likely to be successfully reached and convinced?
- What kinds of evidence are presented?
By asking these questions, you’ll discover the various rhetorical devices the text uses. Don’t feel that you have to cram in every rhetorical term you know—focus on those that are most important to the text.
The following sections show how to write the different parts of a rhetorical analysis.
Like all essays, a rhetorical analysis begins with an introduction . The introduction tells readers what text you’ll be discussing, provides relevant background information, and presents your thesis statement .
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how an introduction works.
Martin Luther King, Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech is widely regarded as one of the most important pieces of oratory in American history. Delivered in 1963 to thousands of civil rights activists outside the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C., the speech has come to symbolize the spirit of the civil rights movement and even to function as a major part of the American national myth. This rhetorical analysis argues that King’s assumption of the prophetic voice, amplified by the historic size of his audience, creates a powerful sense of ethos that has retained its inspirational power over the years.
The body of your rhetorical analysis is where you’ll tackle the text directly. It’s often divided into three paragraphs, although it may be more in a longer essay.
Each paragraph should focus on a different element of the text, and they should all contribute to your overall argument for your thesis statement.
Hover over the example to explore how a typical body paragraph is constructed.
King’s speech is infused with prophetic language throughout. Even before the famous “dream” part of the speech, King’s language consistently strikes a prophetic tone. He refers to the Lincoln Memorial as a “hallowed spot” and speaks of rising “from the dark and desolate valley of segregation” to “make justice a reality for all of God’s children.” The assumption of this prophetic voice constitutes the text’s strongest ethical appeal; after linking himself with political figures like Lincoln and the Founding Fathers, King’s ethos adopts a distinctly religious tone, recalling Biblical prophets and preachers of change from across history. This adds significant force to his words; standing before an audience of hundreds of thousands, he states not just what the future should be, but what it will be: “The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.” This warning is almost apocalyptic in tone, though it concludes with the positive image of the “bright day of justice.” The power of King’s rhetoric thus stems not only from the pathos of his vision of a brighter future, but from the ethos of the prophetic voice he adopts in expressing this vision.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The conclusion of a rhetorical analysis wraps up the essay by restating the main argument and showing how it has been developed by your analysis. It may also try to link the text, and your analysis of it, with broader concerns.
Explore the example below to get a sense of the conclusion.
It is clear from this analysis that the effectiveness of King’s rhetoric stems less from the pathetic appeal of his utopian “dream” than it does from the ethos he carefully constructs to give force to his statements. By framing contemporary upheavals as part of a prophecy whose fulfillment will result in the better future he imagines, King ensures not only the effectiveness of his words in the moment but their continuing resonance today. Even if we have not yet achieved King’s dream, we cannot deny the role his words played in setting us on the path toward it.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The goal of a rhetorical analysis is to explain the effect a piece of writing or oratory has on its audience, how successful it is, and the devices and appeals it uses to achieve its goals.
Unlike a standard argumentative essay , it’s less about taking a position on the arguments presented, and more about exploring how they are constructed.
The term “text” in a rhetorical analysis essay refers to whatever object you’re analyzing. It’s frequently a piece of writing or a speech, but it doesn’t have to be. For example, you could also treat an advertisement or political cartoon as a text.
Logos appeals to the audience’s reason, building up logical arguments . Ethos appeals to the speaker’s status or authority, making the audience more likely to trust them. Pathos appeals to the emotions, trying to make the audience feel angry or sympathetic, for example.
Collectively, these three appeals are sometimes called the rhetorical triangle . They are central to rhetorical analysis , though a piece of rhetoric might not necessarily use all of them.
In rhetorical analysis , a claim is something the author wants the audience to believe. A support is the evidence or appeal they use to convince the reader to believe the claim. A warrant is the (often implicit) assumption that links the support with the claim.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis | Key Concepts & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 14, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/rhetorical-analysis/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, how to write a literary analysis essay | a step-by-step guide, comparing and contrasting in an essay | tips & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
10 Pathos Examples

Pathos is a rhetorical device that stirs emotions such as pity, sadness, or sympathy in the audience.
Pathos refers to one corner of the rhetorical triangle, which means that it is one of the three main technical means of persuasion .
Aristotle claims that there are three technical means of persuasion:
“Now the proofs furnished by the speech are of three kinds. The first depends upon the moral character of the speaker, the second upon putting the hearer into a certain frame of mind, the third upon the speech itself, in so far as it proves or seems to prove” (Aristotle, Rhetoric, ca. 367-322 B.C.E./1926, Book 1, Chapter 2, Section 3).
Each of these corresponds to the three means of persuasion:
- Ethos (Appeal to credibility) : Persuasion through establishing the character of the speaker.
- Pathos ( Appeal to emotion ): Persuasion through putting the hearer into a certain frame of mind.
- Logos (Appeal to logic) : Persuasion through proof or seeming proof.
For Aristotle, speech consists of three things: the speaker, the hearer, and the speech. These correspond to ethos, pathos, and logos , respectively. Pathos is the means of persuasion that is concerned with the audience and it is the subject of this article.

Pathos Definition
Pathos refers to appeals to the emotions of the audience. Whenever the audience is led to feel a certain way, and that feeling influences their judgment of a speech, the speaker is using pathos.
Aristotle’s underlying assumption is that people’s emotional states influence their evaluations, which is quite reasonable to suppose.
The rhetorical method, therefore, requires one to sway the emotional states of the hearers:
“… for the judgements we deliver are not the same when we are influenced by joy or sorrow, love or hate” (Aristotle, Rhetoric, ca. 367-322 B.C.E./1926, Book 1, Chapter 2, Section 5).
You can appeal to people’s emotions in many ways: through storytelling hooks, passionate speech, personal anecdotes , and so on.
In some sense, most pieces of writing and most speeches that have an agenda to persuade necessarily have some forms of pathos built into them. For example, even a math textbook may give rise to feelings of awe.
Pathos probably has the worst reputation out of the three technical means of persuasion because people believe that all appeals to emotion are somehow dishonest or manipulative, but this is not so.
There is simply no getting away from elements of pathos, no matter how hard the persuader tries.
Furthermore, the use of pathos to persuade can be just as honest and harmless as the most seemingly objective uses of logos or ethos.
Pathos Examples
Example 1: advertising.
Pathos is an especially common persuasion tool in advertising. Since emotions influence people’s decision-making, pathos is well-suited to the task of persuading customers to buy products (Ho & Siu, 2012).
For example, advertising is to appeal to empathy, which would be part of pathos. Animal welfare organizations like the SPCA, for instance, may appeal to people’s empathy by using pictures of stray dogs accompanied by sad music.
In this context, the power of pathos can be leveraged to not only promote immediate action, such as a donation, but also to build long-term brand associations and loyalty, embedding a sense of empathy and compassion in the perception of the organization’s mission.
Example 2: Art
Most forms of art use pathos in some form. This is more apparent in art that has a clear agenda, for example, political cartoons.
In political cartoons, the application of pathos is often used to generate empathy or outrage, thus persuading viewers to consider the artist’s perspective on social or political issues.
Similarly, in paintings, sculptures, or installation art, artists often use symbolic imagery, dramatic contrasts, and evocative themes to arouse feelings of sorrow, compassion, or introspection .
Example 3: In the ad hominem Argument
Arguments that commit the ad hominem fallacy tend to be persuasive because of pathos.
The ad hominem fallacy involves attacking the arguer’s personal situation or traits (Hansen, 2020). There are three commonly recognized kinds of ad hominem: (1) the abusive ad hominem, (2) the circumstantial ad hominem, and (3) the tu quoque.
The first kind involves arguing that someone’s view should not be accepted because they have some negative property. For example: “Alice’s view that breaking promises is immoral should be rejected because Alice is rude.”
The second kind involves arguing that someone’s view should not be accepted because their view is supported by self-interest. For example: “Bob’s recommendation to exercise regularly should be rejected because Bob owns a gym.”
The tu quoque involves arguing that someone’s view should not be accepted because their actions are inconsistent with that view. For example: “Clarence’s view that people should not drive cars should not be accepted because Clarence drives a car.”
Example 4: In the Slippery Slope Argument
Another form of persuasive but fallacious argument is the slippery slope. It is a fallacy that occurs when one unjustifiably assumes that a small step leads to a chain of related events culminating in some significant effect.
Such arguments may sometimes be reasonable, but they are not deductively correct.
Moreover, they usually rely on generating fear on the part of the audience. Alfred Sidgwick described slippery slope arguments in the following way:
“We must not do this or that, it is often said, because if we did we should be logically bound to do something else which is plainly absurd or wrong. If we once begin to take a certain course there is no knowing where we shall be able to stop within any show of consistency; there would be no reason for stopping anywhere in particular, and we should be led on, step by step into action or opinions that we all agree to call undesirable or untrue.” (Sidgwick, 1910, p. 40)
Example 5: In Music
The use of emotional music in a piece of media the purpose of which is to persuade is an example of pathos.
Such music can intensify the emotional impact of, for example, an advertisement and thereby make it more persuasive.
Since logic is rarely used to advertise products, pathos is often the most important means of persuasion in such cases.
Example 6: In Political Rhetoric
Word choice in political speech is particularly important for the effective use of pathos.
For example, the conflicting uses of terms like “unborn life” and ”fetus” in women’s reproductive rights debates appeal to people’s emotions in different ways.
Whereas one side would appeal to the emotion of saving life, the other would appeal to the emotion of freedom and bodily autonomy.
It is virtually impossible for an effective political speech not to contain pathos, especially in democratic contexts. How skillfully a politician appeals to the emotions of the voters will, to a large extent, determine the success of their campaign.
Example 7: In Social Media Campaigns
Pathos is frequently utilized in social media campaigns, often leveraging user-generated content to create a sense of empathy or community around a product or cause.
User stories that feature personal triumphs, challenges overcome, or emotional experiences related to the product or cause in question are designed to invoke emotional responses that foster brand loyalty or advocacy.
The use of pathos in social media campaigns often involves images, videos, and narratives that are likely to resonate emotionally with the target audience, effectively fostering a deeper connection to the brand or cause, and enhancing audience engagement and interaction.
Example 8: In Public Health Campaigns
Pathos is also evident in public health campaigns. For instance, anti-drinking ads often show the severe health effects of drinking, such as patients unable to play with their children due to health issues.
These campaigns are intended to evoke fear or concern, stimulating the public to change their behavior and adopt healthier habits.
By emphasizing the grave consequences and personal costs of unhealthy choices, public health campaigns that use pathos aim to foster a more emotional and personal connection to health issues, making the audience more likely to take preventive actions or change unhealthy habits.
Example 9: In Philanthropy and Fundraising
Pathos is used extensively in philanthropy and fundraising, with organizations sharing stories of individuals or communities in need to evoke empathy and provoke action.
Charitable campaigns that depict the harsh realities of poverty, disease, or disaster aim to stir feelings of compassion, guilt, or responsibility, encouraging donations and aid.
Through the strategic use of pathos, philanthropy and fundraising campaigns can make the plight of those in need feel more immediate and tangible, thereby increasing the likelihood of donations and encouraging more active involvement in the cause or issue at hand.
Example 10: In Literature
In literature, authors often use pathos to create an emotional connection between readers and characters or situations.
This might involve crafting narratives around heart-wrenching tragedies, touching moments, or stirring triumphs to make the readers feel a range of emotions, thereby enhancing their engagement and investment in the storyline.
By evoking deep emotional responses through the use of pathos, authors can make the characters and situations in their works more relatable and real, intensifying readers’ engagement and creating a lasting impact that goes beyond mere enjoyment of the story.
Strengths of Pathos
- Memorability: Appeals to emotion tend to stick. While you’re unlikely to remember the speaker’s logical reasoning or their credentials perfectly, you probably will remember how the speech made you feel.
- Decision-making : appeals to pathos typically affect the actions of the audience more than appeals to ethos or logos.
- Subjective topics: similar to ethos, pathos is an especially powerful persuasion technique in matters that don’t rely on objective criteria. In such a case, logical arguments alone won’t be enough. For example, the orator will make greater use of pathos when speaking about a work of art than when debating the merits of a mathematical proof.
Weaknesses of Pathos
- Manipulation: The use of pathos can be morally questionable since it can exploit people’s emotional vulnerabilities.
- Insincerity: It is easy for the audience to perceive the speaker’s appeals to pathos as insincere. Some people view all appeals to emotion as attempts to mask or modify the truth, so the orator must know their audience before resorting to pathos.
The term pathos comes from the Greek word for “experience” or “suffering.” In the context of rhetoric, it refers to appeals to the emotions of the audience.
See Also: The 5 Types of Rhetorical Situations
Aristotle. (1926). Rhetoric. In Aristotle in 23 Volumes, Vol. 22, translated by J. H. Freese. Harvard University Press. (Original work published ca. 367-322 B.C.E.)
Hansen, H. (2020). Fallacies. In E. N. Zalta (Ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Summer 2020). Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/sum2020/entries/fallacies/
Ho, A. G., & Siu, K. W. M. G. (2012). Emotion Design, Emotional Design, Emotionalize Design: A Review on Their Relationships from a New Perspective. The Design Journal, 15(1), 9–32. https://doi.org/10.2752/175630612X13192035508462
Rapp, C. (2022). Aristotle’s Rhetoric. In E. N. Zalta (Ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Spring 2022). Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/spr2022/entries/aristotle-rhetoric/
Sidgwick, A. (1910). The application of logic. London : Macmillan and Co., limited. http://archive.org/details/applicationoflog00sidgiala

Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch)
Tio Gabunia is an academic writer and architect based in Tbilisi. He has studied architecture, design, and urban planning at the Georgian Technical University and the University of Lisbon. He has worked in these fields in Georgia, Portugal, and France. Most of Tio’s writings concern philosophy. Other writings include architecture, sociology, urban planning, and economics.
- Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch) #molongui-disabled-link 6 Types of Societies (With 21 Examples)
- Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch) #molongui-disabled-link 25 Public Health Policy Examples
- Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch) #molongui-disabled-link 15 Cultural Differences Examples
- Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch) #molongui-disabled-link Social Interaction Types & Examples (Sociology)

Chris Drew (PhD)
This article was peer-reviewed and edited by Chris Drew (PhD). The review process on Helpful Professor involves having a PhD level expert fact check, edit, and contribute to articles. Reviewers ensure all content reflects expert academic consensus and is backed up with reference to academic studies. Dr. Drew has published over 20 academic articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education and holds a PhD in Education from ACU.
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 25 Positive Punishment Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 25 Dissociation Examples (Psychology)
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 15 Zone of Proximal Development Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link Perception Checking: 15 Examples and Definition
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Home — Essay Samples — Literature — The Tragedy of Julius Caesar — Theme Of Pathos In Antony’s Speech
Theme of Pathos in Antony's Speech
- Categories: The Tragedy of Julius Caesar
About this sample

Words: 539 |
Published: Mar 6, 2024
Words: 539 | Page: 1 | 3 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr Jacklynne
Verified writer
- Expert in: Literature

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3.5 pages / 1637 words
1 pages / 592 words
3.5 pages / 1580 words
6 pages / 2816 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on The Tragedy of Julius Caesar
In The Tragedy of Julius Caesar speech plays an important role in the plot. The people in play are easily persuaded into opposing viewpoints though both Anthony’s and Brutus’s speeches. In Brutus’s speech he says “Not that I [...]
The legacy of Brutus, one of the central figures in William Shakespeare's play "Julius Caesar," continues to spark debates over his motivations and actions. In this essay, I will delve into the complex character of Brutus and [...]
Shakespeare, William. Julius Caesar. 1599. Blits, Jan. "Julius Caesar and Political Philosophy: The Lessons of Leadership and the Rules of Righteousness." Harvard University Press, 2015. Greenblatt, Stephen. "Shakespeare's [...]
William Shakespeare’s early writing aims to advance a philosophy of history. It asks how kingdoms are built and destroyed. The author approaches theater as a tool which might potentially elucidate key events by studying [...]
In the play Tragedy of Julius Caesar by William Shakespeare, both of these characters Calpurnia and Decius try to persuade Caesar either into continued life, or into betrayal and death. Calpurnia had a vision that Caesar would [...]
All great speakers have one thing in common: a seamless ability to use persuasive techniques in order to push a point across. In William Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar, after Caesar’s assassination, nobleman and conspirator Brutus [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Advertisement
Supported by
‘The Notebook’ Review: A Musical Tear-Jerker or Just All Wet?
The 2004 weepie comes to Broadway with songs by Ingrid Michaelson and a $5 box of tissues.
- Share full article

By Jesse Green
Romantic musicals are as personal as romance itself. What makes you sigh and weep may leave the person next to you bored and stony.
At “The Notebook,” I was the person next to you.
You were sniffling even before anything much happened onstage. As the lights came up, an old man dozed while a teenage boy and girl frisked nearby in an unconvincing body of water. A wispy song called “Time” wafted over the footlights: “Time time time time/It was never mine mine mine.”
But having seen (I’m guessing more than once) the 2004 movie on which “The Notebook” is based, and possibly having read the 1996 novel by Nicholas Sparks, you perfectly well knew what was coming. That was the point of mounting the show, which opened on Thursday at the Gerald Schoenfeld Theater , in the first place.
It therefore cannot be a spoiler — and anyway this block of cheese is impervious — to reveal that over the course of the 54 years covered by the musical, the frisky boy, Noah, turns into the dozing man. And that Allie, the frisky girl, having overcome various impediments to their love, winds up his wife. Nor does it give anything away to add that Allie, now 70 and in a nursing home with dementia, will not remember Noah until he recites their story from a notebook she prepared long ago for that purpose.
So there’s a reason the producers are selling teeny $5 “Notebook”-themed boxes of tissues in the lobby. Love is powerful. Dementia is sad. The result can be heartbreaking.
Or maybe, seen with a cold eye, meretricious.
The movie, a super-slick Hollywood affair, did everything it could to keep the eye warm. Ryan Gosling and Rachel McAdams, as the young couple, could not have been glowier. The soundtrack relied on precision-crafted standards like “I’ll Be Seeing You” to yank at your tear ducts. The production design, like a montage of greeting cards come to life , celebrated valentine passion, anniversary tenderness and golden sympathy, releasing flocks of trained geese into a technicolor sunset to symbolize lifelong pair bonding.
The musical, unwilling except at the margins to alter a plot so beloved — or at least so familiar — tries to distinguish itself in other ways. It aims for a rougher, hand-hewn texture, befitting Noah’s career as a carpenter and the indie-folk sound of its songwriter, Ingrid Michaelson . The directors, Michael Greif and Schele Williams, have cast the couples regardless of race: a nice, universalizing touch.
In other updates, the book writer, Bekah Brunstetter, has shifted the period by two decades — Noah fights in Vietnam, not at the Battle of the Bulge. She adds a third, intermediate incarnation of the couple, crowding the stage with replicants and pushing the 27-year-old Allie (Joy Woods) into the star spot because someone has to be there. (The 29-year-old Noah is played by Ryan Vasquez.) And instead of the cliché geese, Brunstetter gives us … sea turtles?
No, I don’t get that one either.
In any case, the de-slicking was a mistake; it turns out that the Hollywood varnish was the only thing holding the picture together. In its place, the musical makes few convincing arguments for a separate existence.
Certainly Michaelson’s relentlessly mid-tempo songs do not; they are pretty but flyaway, as insubstantial as blue smoke. Except for a number in which teenager Allie and Noah (Jordan Tyson and John Cardoza) first see each other undressed, the lyrics are vague and humorless, often budding with clichés the book is trying to prune. “I wanna know that my old heart can grow like spring again,” sings Older Noah (Dorian Harewood) — an alarming thought, really, for a 72-year-old or for his cardiologist. Older Allie (the great Maryann Plunkett) barely sings at all, a great loss.
When songs provide so little information, barely differentiating the characters let alone advancing the plot, a musical tends to sag. And when a musical has gone to some trouble to accommodate those songs — the movie of “The Notebook” runs two hours, the show hardly 20 minutes more — the trade-offs are of the nose-versus-face variety.
So Brunstetter, hacking through the story with a scythe to make room, has left bald stumps everywhere. Allie’s meddling, disapproving parents are demoted to mere nasties, their motivations discarded with their back story. Her fiancé is a nonentity. What Noah and Allie do between their late teens (when they meet and separate) and their late 20s (when they are rapturously rejoined) is reduced to a throwaway: “Let’s see — heartbreak, graduation, many many Tuesdays, Thanksgivings, a war.” Flip lines like that break whatever spell the material, usually earnest to a fault, is trying to cast.
The staging is consistently more engaging. Unlike the movie, which keeps its focus on one couple at a time, here we often get all three together, in color-coded costumes (by Paloma Young) that clarify their connections. (The Noahs wear blue and brown, the Allies blue and white.) And though the switching among them sometimes feels mechanical, as the lights (by Ben Stanton) dim on Older Noah reading the notebook and rise on the younger characters enacting its story, the process creates a kind of time-lapse exposure that feels natively theatrical and thus occasionally effective.
On Allie’s side of the equation especially, the time-lapse provides information the movie did not. Because all three ages exist simultaneously, her impetuousness as a teenager is connected to her indecisiveness 10 years later and, perhaps less credibly, to her eventual dementia. In all periods, her relationship to home — “Home” is the title of the Act I finale — is usefully forefronted: the home she leaves, the home she dreams of, the home Noah builds her, the home she cannot get back to.
But only in this last stage does “The Notebook” achieve any real pathos, thanks to Plunkett’s uncompromising naturalism and the lifetime of stage savvy she inevitably brings with her. Her locked-down Allie, banging frantically on the doors of her memory, is an unexpectedly terrifying character to meet in an otherwise bland musical.
It doesn’t hurt that, for those who have followed Plunkett over the years, she is also banging down the doors of our memory. Her troubled Agnes in “Agnes of God” (her Broadway debut, in 1982), her insouciant Sally in “Me and My Girl,” for which she won a Tony Award, and her series of anxious dinner-table Americans in all 12 plays of Richard Nelson’s “Rhinebeck Panorama” help turn a barely there character into a moving one.
Whether that is sufficient to make me cry for a would-be weepie is a different matter. That the “Notebook”-themed tissues are so teeny says it all.
The Notebook At the Gerald Schoenfeld Theater, Manhattan; notebookmusical.com . Running time: 2 hours 20 minutes.
Jesse Green is the chief theater critic for The Times. He writes reviews of Broadway, Off Broadway, Off Off Broadway, regional and sometimes international productions. More about Jesse Green

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Definition of Pathos With Examples. The power of emotion can be overwhelmingly compelling even when it runs up against our sense of logic or reason. Pathos is a term used to describe an appeal to emotion in persuasive rhetoric or other forms of writing. Understanding what pathos is and how to employ it effectively is an essential tool for any ...
Here's a quick and simple definition: Pathos, along with logos and ethos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Pathos is an argument that appeals to an audience's emotions. When a speaker tells a personal story, presents an audience with a powerful visual image, or appeals to an ...
Pathos Definition. Pathos is a tool of persuasion that is used to appeal to readers' emotions by arousing positive or negative feelings. It can be used in rhetoric, literature, film, and other forms of expression. While pathos is used to draw an emotional response, the other rhetorical appeals—ethos and logos—appeal to credibility and ...
Definition of Pathos. Pathos is a literary device that is designed to inspire emotions from readers. Pathos, Greek for "suffering" or "experience," originated as a conceptual mode of persuasion by the Greek philosopher, Aristotle. Aristotle believed that utilizing pathos as a means of stirring people's emotions is effective in turning their opinion towards the speaker.
The word pathos is derived from the Greek word páthos, which means "experience," "suffering," or "emotion.". The Greek philosopher Aristotle introduced the concept of pathos in his written work Rhetoric, in which he also introduced the three other modes of persuasion: ethos, logos, and kairos. Although appealing to an audience's ...
Simply put, logos, ethos and pathos are three powerful tools that you can use to persuade an audience of your argument. At the most basic level, logos appeals to logic and reason, while pathos appeals to emotions and ethos emphasises credibility or authority. Naturally, a combination of all three rhetorical appeals packs the biggest punch, but ...
Conclusion. Ethos, logos, and pathos are powerful tools for persuasive speech and writing. By establishing credibility, using logical arguments, and appealing to emotion, speakers and writers can influence the beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors of their audiences. When used effectively, these elements can help to create meaningful and lasting ...
Ethos, Pathos, and Logos are three strategies commonly employed when attempting to persuade a reader. Pathos, or the appeal to emotion, means to persuade an audience by purposely evoking certain emotions to make them feel the way the author wants them to feel. Authors make deliberate word choices, use meaningful language, and use examples and ...
Pathos offers a way for the audience to relate to the subject through commonly held emotions. However, it is important to determine when pathos will be useful and when it will only serve to muddy the argumentative waters. Take, for instance, a student who is writing an essay on human trafficking.
How to use pathos in an essay transcends mere technique; it's an exploration of humanity's shared emotional experiences. The ability to touch readers' hearts and minds through emotion-infused writing is a skill that can transform an ordinary essay into a compelling narrative. By strategically incorporating personal stories, imagery, values, and ...
Aristotle developed the concept of "ethos," "logos," and "pathos.". Ethos, logos, and pathos are elements of writing that make it more effective and persuasive. While ethos establishes the writer's credibility, logos appeals to the audience's reason, and pathos appeals to their emotions. These three concepts, also known as the ...
So, when writing a persuasive essay, make sure to incorporate pathos effectively by using emotionally compelling language, personal anecdotes, and real-life examples. By appealing to the emotions of your audience, you can establish a stronger connection and make your arguments more persuasive. Remember to balance pathos with logos and ethos ...
The goal of argumentative writing is to persuade your audience that your ideas are convincing. Basically, there are three ways of doing this: You can convince your reader that your authority is indisputable (ethos) You can convince your reader by appealing to his emotions (pathos) You can convince your reader by appealing to his sense of logic ...
For academic essays, pathos may be useful in introductory sections, concluding sections, or as ways to link various parts of the paper together. However, if your argument is based solely or primarily upon emotional appeals, it will be viewed as weak in an academic setting, especially when data or ethical sources can disprove your claims.
1. Appeals to the Reader's Emotions. Most obviously, pathos appeals to a reader's emotions. An effective argument from pathos will draw upon one specific emotion and target it to get a response from the listener. You may find that pathos commonly plays on darker emotions, like sadness, guilt, or anger.
Pathos. Appealing to pathos is about appealing to your audience's emotions. Because people can be easily moved by their emotions, pathos is a powerful mode of persuasion. When you think about appealing to pathos, you should consider all of the potential emotions people experience. While we often see or hear arguments that appeal to sympathy ...
Make sure your argument is persuasive by learning the three modes of persuasion—ethos, pathos, and logos—and how to effectively use them in communication.
This essay will delve into the concept of pathos in the rhetorical argument, exploring its significance and impact on the audience. By examining various examples and scholarly insights, we will uncover the power of pathos in persuasive writing and its role in shaping our perceptions and decisions.
Incorporating appeals to pathos into persuasive writing increases a writer's chances of achieving his or her purpose. Read "Pathos" to define and understand pathos and methods for appealing to it. The following brief article discusses examples of these appeals in persuasive writing. An important key to incorporating pathos into your persuasive writing effectively is appealing to your ...
Revised on July 23, 2023. A rhetorical analysis is a type of essay that looks at a text in terms of rhetoric. This means it is less concerned with what the author is saying than with how they say it: their goals, techniques, and appeals to the audience. A rhetorical analysis is structured similarly to other essays: an introduction presenting ...
Example 1: Advertising. Pathos is an especially common persuasion tool in advertising. Since emotions influence people's decision-making, pathos is well-suited to the task of persuading customers to buy products (Ho & Siu, 2012). For example, advertising is to appeal to empathy, which would be part of pathos.
Get custom essay. In conclusion, Antony's speech in "Julius Caesar" exemplifies the theme of pathos. Through the strategic use of rhetorical techniques and emotional language, Antony successfully captivates the crowd and drives them towards his desired outcome. By tapping into their emotions, Antony manipulates public opinion, showcasing the ...
Essay On Pathos. Authors use pathos when they want to make an appeal based on readers' emotion. Through the provision of emotional enrichment of reasoning, by influencing the audience's emotional, vivid vision to attract the audience. This rhetoric is often used to induce specific emotional reactions, such as anger, sadness, happiness, desire ...
Performances in N.Y.C. Advertisement Supported by The 2004 weepie comes to Broadway with songs by Ingrid Michaelson and a $5 box of tissues. By Jesse Green Romantic musicals are as personal as ...