- Program Design
- Peer Mentors
- Excelling in Graduate School
- Oral Communication
- Written communication
- About Climb

Creating a 10-15 Minute Scientific Presentation
In the course of your career as a scientist, you will be asked to give brief presentations -- to colleagues, lab groups, and in other venues. We have put together a series of short videos to help you organize and deliver a crisp 10-15 minute scientific presentation.
First is a two part set of videos that walks you through organizing a presentation.
Part 1 - Creating an Introduction for a 10-15 Minute Scientfic Presentation
Part 2 - Creating the Body of a 10-15 Minute Presentation: Design/Methods; Data Results, Conclusions
Two additional videos should prove useful:
Designing PowerPoint Slides for a Scientific Presentation walks you through the key principles in designing powerful, easy to read slides.
Delivering a Presentation provides tips and approaches to help you put your best foot forward when you stand up in front of a group.
Other resources include:
Quick Links
Northwestern bioscience programs.
- Biomedical Engineering (BME)
- Chemical and Biological Engineering (ChBE)
- Driskill Graduate Program in the Life Sciences (DGP)
- Interdepartmental Biological Sciences (IBiS)
- Northwestern University Interdepartmental Neuroscience (NUIN)
- Campus Emergency Information
- Contact Northwestern University
- Report an Accessibility Issue
- University Policies
- Northwestern Home
- Northwestern Calendar: PlanIt Purple
- Northwestern Search
Chicago: 420 East Superior Street, Rubloff 6-644, Chicago, IL 60611 312-503-8286
Reference management. Clean and simple.
5 tips for giving a good scientific presentation

What is a scientific presentation?
What is the objective of a scientific presentation, why is giving scientific presentations necessary, how to give a scientific presentation, tip 1: prepare during the days leading up to your talk, tip 2: deal with presentation nerves by practicing simple exercises, tip 3: deliver your talk with intention, tip 4: be adaptable and willing to adjust your presentation, tip 5: conclude your talk and manage questions confidently, concluding thoughts, other sources to help you give a good scientific presentation, frequently asked questions about giving scientific presentations, related articles.
You have made the slides for your scientific presentation. Now, you need to prepare to deliver your talk. But, giving an oral scientific presentation can be nerve-wracking. How do you ensure that you deliver your talk well, and leave a good impression on the audience?
Mastering the skill of giving a good scientific presentation will stand you in good stead for the rest of your career, as it may lead to new collaborations or even new employment opportunities.
In this guide, you’ll find everything you need to know to give a good oral scientific presentation, including
- Why giving scientific presentations is important for your career;
- How to prepare before giving a scientific presentation;
- How to keep the audience engaged and deliver your talk with confidence.
The following tips are a product of our research into the literature on giving scientific presentations as well as our own experiences as scientists in giving and attending talks. We advise on how to make a scientific presentation in another post.
A scientific presentation is a talk or poster where you describe the findings of your research to others. An oral presentation usually involves presenting slides to an audience. You may give an oral scientific presentation at a conference, give an invited seminar at another institution, or give a talk as part of an interview. A PhD thesis defense is one type of scientific presentation.
➡️ Read about how to prepare an excellent thesis defense
The objective of a scientific presentation is to communicate the science such that the audience:
- Learns something new;
- Leaves with a clear understanding of the key message of your research;
- Has confidence in you and your work;
- Remembers you afterward for the right reasons.

As a scientist, one of your responsibilities is disseminating your scientific knowledge by giving presentations. Communicating your research to others is an altruistic act, as it is an opportunity to teach others about your research findings, and the knowledge you have gained while researching your topic.
Giving scientific presentations confers many career benefits , such as:
- Having the opportunity to share your ideas and to have insightful conversations with other scientists. For example, a thoughtful question may create a new direction for your research.
- Gaining recognition for your work and generating excitement for your research program can help you to forge new collaborations and to obtain more citations of your papers. It's your chance to impress some of the biggest names in your field, build your reputation as a scientist, and get more people interested in your work.
- Improving your future employment prospects by getting presentation experience in high-stakes settings and by having talks listed on your academic CV.
➡️ Learn how to write an academic CV
You might have just 10 minutes for your talk. But those 10 minutes are your golden ticket. To make them shine, you'll need to put in some homework. You need to think about the story you want to tell , create engaging slides , and practice how you're going to deliver it.
Why all this effort? Because the rewards are potentially huge. Imagine speaking to the top names in your field, boosting your visibility, and getting more eyes on your work. It's more than just a talk; it's your chance to showcase who you are and what you do.
Here we share 5 tips for giving effective scientific presentations.
- Prepare adequately for your talk on the days leading up to it
- Deal with presentation nerves
- Deliver your talk with intention
- Be adaptable
- Conclude your talk with confidence
You should prepare for your talk with the seriousness it deserves and recognize the potential it holds for your career advancement. Here are our suggestions:
- Rehearse your talk multiple times to ensure smooth flow. Know the order of your slides and key transitions without memorizing every word. Practice your speech as though you are discussing with friendly and attentive listeners.
- Record your speech and listen back to yourself giving your talk while doing household chores or while going for a walk. This will help you remember the important points of your talk and feel more comfortable with the flow of it on the day.
- Anticipate potential questions that may arise during your talk, write down your responses to those questions, and practice them aloud.
- Back up your presentation in cloud storage and on a USB key. Bring your laptop with you on the day of your talk, if needed.
- Know the time and location of your talk. Familiarize yourself with the room, if you can. Introduce yourself to the moderator before the session begins.
- Giving a talk is a performance, so preparing yourself physically and mentally is essential. Prioritize good sleep and hydration, and eat healthy, nourishing food on the day of your talk. Plan your attire to be both professional and comfortable.
It’s natural to feel nervous before your talk, but you want to harness that energy to present your work with confidence. Here are some ways to manage your stress levels:
- Remember that your audience want to listen to you and learn from you. Believe that your audience will be kind, friendly, and interested, rather than bored and skeptical.
- Breathing slow and deep before your talk calms the mind and nervous system. Psychologist Amy Cuddy recommends practicing open, confident postures while sitting and standing to help you get into a positive frame of mind.
- Fight off impostor syndrome with positive affirmations. You’ve got this! Remember that you know more about your research than anyone else in the room and you are giving your talk to teach others about it.
Giving your talk with confidence is crucial for your credibility as a scientist. Focusing on your delivery helps ensure that your audience remembers and believes what you say. Here are some techniques to try:
- Before beginning, remember your professional goals and the benefits of giving your presentation. Start with a smile and exhale deeply.
- Memorize a simple opening. After the moderator introduces you, pause and take a breath. Welcome the audience, thank them for coming, and introduce yourself. You don’t need to read the title of your talk. But briefly, say something like, “today I’m going to talk to you about why [topic] is important and [what I hope you will learn from this talk]” in 1-2 sentences. Preparing your opening will settle your nerves and prevent you from starting your talk on a tangential topic, ensuring you stay on time.
- Project confidence outwardly, even if you feel nervous. Stand up tall with your shoulders back and make eye contact with individuals in the audience. Move your focus around the room, so everyone in the audience feels included.
- Maintain open body language and face the audience as much as possible, not your slides.
- Project your voice as much as you can so that people at the back of the room can hear you. Enunciate your words, avoid mumbling, and don’t trail off awkwardly.
- Varying your vocal delivery and intonation will make your talk more interesting and help the audience pay attention, particularly when you want to emphasize key points or transitions.
- Pausing for dramatic effect at crucial moments can help you relax and remember your message, as well as being an effective engagement device.
- A laser pointer can be off-putting for the audience if you are prone to having a shaky hand when nervous. Use a laser pointer only to emphasize information on the slide while providing an explanation. If you design your slides thoughtfully , you won’t need to use a laser pointer.
Not all parts of your talk may go according to plan. Here are some ways to adapt to hitches during your talk:
- Handle talk disruptions gracefully. If you make a mistake, or a technical issue occurs during your talk, remember that it’s okay to skip something and move on without apologizing.
- If you forget to mention something but the audience hasn’t noticed, don’t point it out! They don’t need to know.
- As you give your talk, be time-conscious, and watch the moderator for signals that the time is about to expire. If you realize you won’t have time to discuss all your slides, skip the less important ones. Adjust your presentation on the fly to finish on time, prioritizing content as needed.
- If you run out of time completely, just stop. You don’t have to give a conclusion, but you do need to stop on time! Practicing your talk should prevent this situation.
The ending of your talk is important for emphasizing your key message and ensuring the audience leave with a positive impression of you and your work. Here are some pointers.
- Conclude your talk with a memorized closing statement that summarizes the key take-home message of your research. After making your closing statement, end your talk with a simple “Thank you”. Then pause and wait for the applause. You don’t need to ask if the audience has questions because the moderator will call for questions on your behalf.
- When you receive a question, pause, then repeat the question. This ensures the whole audience understands the question and gives you time to calmly consider your answer.
- In a talk on attaining confidence in your scientific presentations, Michael Alley suggests that if you don’t know the answer to the question, then emphasize what you do know. Say something like, “Although I can’t fully answer your question, I can say [this about the topic].”
- Approach the Q&A with interest rather than anxiety by reframing it as an opportunity to further share your knowledge. Being curious, instead of feeling fearful, can help you shine during what might be the most stressful part of your presentation.
Communicating your research effectively is a key skill for early career scientists to learn. Taking ample time to prepare and practice your presentation is an investment in your scientific development.
But here's the good part: all that effort pays off. Think of your talk as not just a presentation, but as a way to show off what you and your research are all about. Giving a compelling scientific presentation will raise your professional profile as a scientist, lead to more citations of your work, and may even help you obtain a future academic job.
But most importantly of all, giving talks contributes to science, and sharing your knowledge is an act of generosity to the scientific community.
➡️ Questions to ask yourself before you make your talk
➡️ How to give a great scientific talk
1) Have a positive mindset. To help with nerves, breathe deeply and keep in mind that you are an authority on your topic. 2) Be prepared. Have a short list of points for each slide and know the key transition points of your talk. Practice your talk to ensure it flows smoothly. 3) Be well-rested before your talk and eat a light meal on the day of your presentation. A talk is a performance. 4) Project your voice and vary your vocal intonation and pitch to retain the interest of the audience. Take pauses at key moments, for emphasis. 5) Anticipate questions that audience members could ask, and prepare answers for them.
The goal of a scientific presentation is that the audience remembers the key outcomes of your research and that they leave with a good impression of you and your science.
Take a moment to exhale deeply and collect your thoughts after the moderator has introduced you. Don’t read your talk's title. Instead, introduce yourself, thank the audience for attending, and provide a warm welcome. Then say something along the lines of, "Today I'm going to talk to you about why [topic] is important and [what I hope you will learn from this presentation].” A rehearsed opening will ensure that you start your talk on a confident note.
Prepare a memorable closing statement that emphasizes the key message of your talk. Then end with a simple “Thank you”.
Preparation is key. Practice many times to familiarize yourself with the content of your presentation. Before giving your talk, breathe slowly and deeply, and remind yourself that you are the expert on your topic. When giving your talk, stand up tall and use open body language. Remember to project your voice, and make eye contact with members of the audience.
Get in touch
555-555-5555

Limited time offer: 20% off all templates ➞

Scientific Presentation Guide: How to Create an Engaging Research Talk
Creating an effective scientific presentation requires developing clear talking points and slide designs that highlight your most important research results..
Scientific presentations are detailed talks that showcase a research project or analysis results. This comprehensive guide reviews everything you need to know to give an engaging presentation for scientific conferences, lab meetings, and PhD thesis talks. From creating your presentation outline to designing effective slides, the tips in this article will give you the tools you need to impress your scientific peers and superiors.

Step 1. Create a Presentation Outline
The first step to giving a good scientific talk is to create a presentation outline that engages the audience at the start of the talk, highlights only 3-5 main points of your research, and then ends with a clear take-home message. Creating an outline ensures that the overall talk storyline is clear and will save you time when you start to design your slides.
Engage Your Audience
The first part of your presentation outline should contain slide ideas that will gain your audience's attention. Below are a few recommendations for slides that engage your audience at the start of the talk:
- Create a slide that makes connects your data or presentation information to a shared purpose, such as relevance to solving a medical problem or fundamental question in your field of research
- Create slides that ask and invite questions
- Use humor or entertainment

Identify Clear Main Points
After writing down your engagement ideas, the next step is to list the main points that will become the outline slide for your presentation. A great way to accomplish this is to set a timer for five minutes and write down all of the main points and results or your research that you want to discuss in the talk. When the time is up, review the points and select no more than three to five main points that create your talk outline. Limiting the amount of information you share goes a long way in maintaining audience engagement and understanding.

Create a Take-Home Message
And finally, you should brainstorm a single take-home message that makes the most important main point stand out. This is the one idea that you want people to remember or to take action on after your talk. This can be your core research discovery or the next steps that will move the project forward.
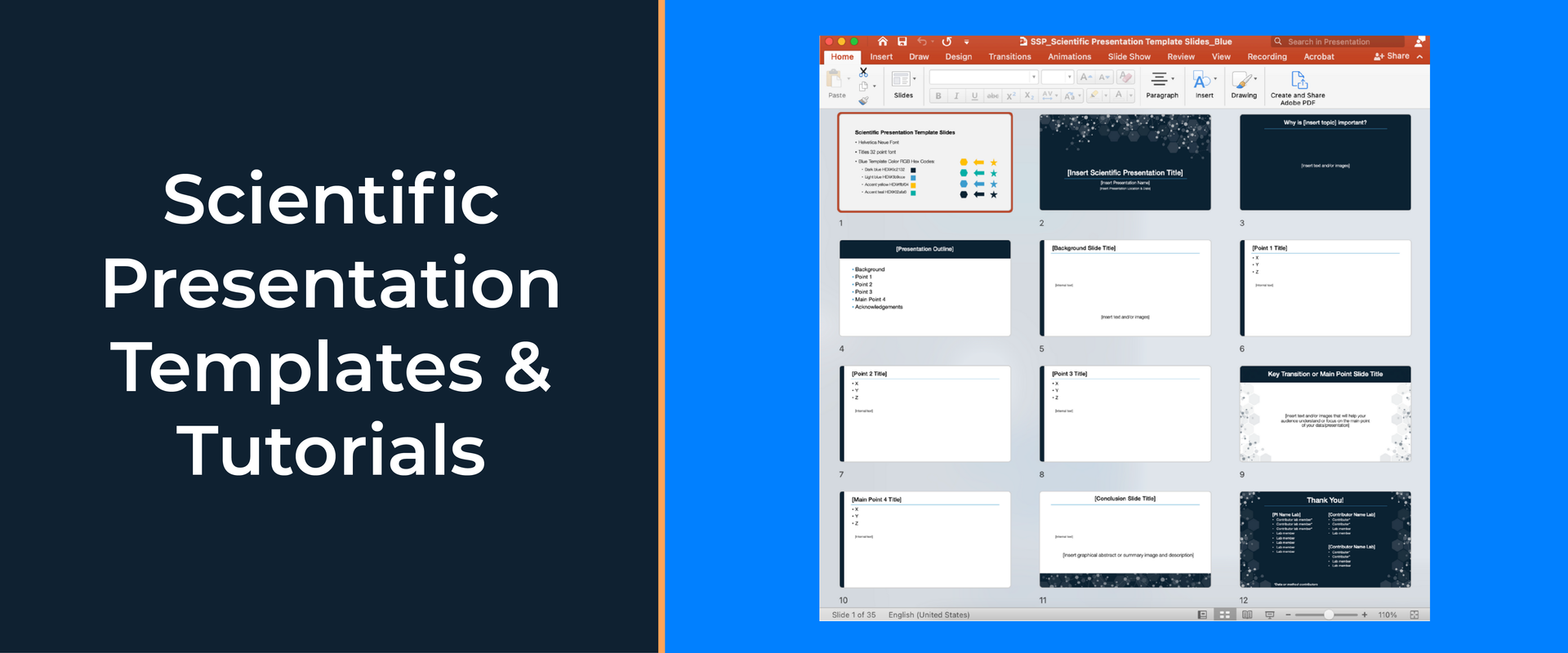
Step 2. Choose a Professional Slide Theme
After you have a good presentation outline, the next step is to choose your slide colors and create a theme. Good slide themes use between two to four main colors that are accessible to people with color vision deficiencies. Read this article to learn more about choosing the best scientific color palettes .
You can also choose templates that already have an accessible color scheme. However, be aware that many PowerPoint templates that are available online are too cheesy for a scientific audience. Below options to download professional scientific slide templates that are designed specifically for academic conferences, research talks, and graduate thesis defenses.
Step 3. Design Your Slides
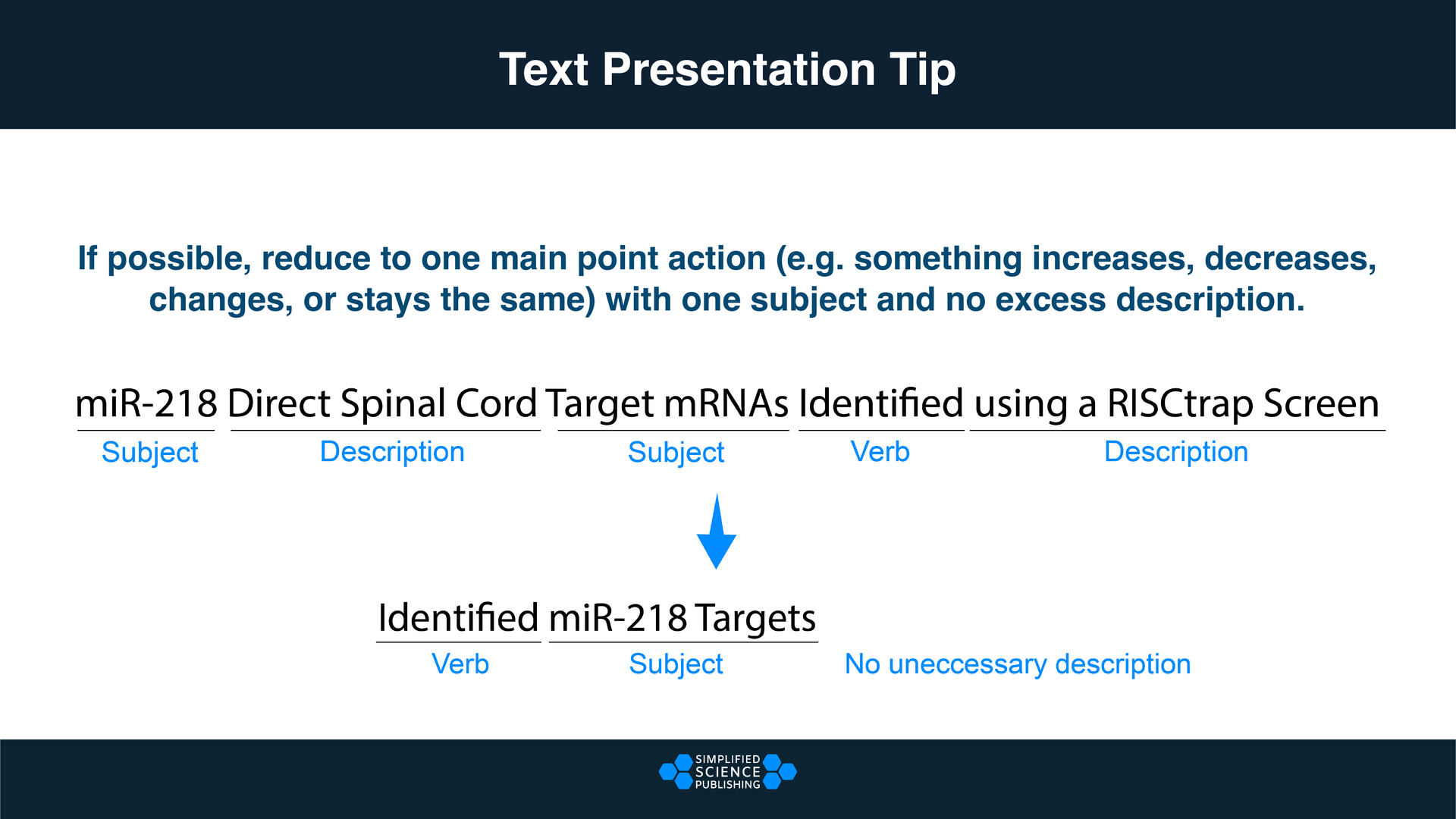
Designing good slides is essential to maintaining audience interest during your scientific talk. Follow these four best practices for designing your slides:
- Keep it simple: limit the amount of information you show on each slide
- Use images and illustrations that clearly show the main points with very little text.
- Read this article to see research slide example designs for inspiration
- When you are using text, try to reduce the scientific jargon that is unnecessary. Text on research talk slides needs to be much more simple than the text used in scientific publications (see example below).
- Use appear/disappear animations to break up the details into smaller digestible bites
- Sign up for the free presentation design course to learn PowerPoint animation tricks
Scientific Presentation Design Summary
All of the examples and tips described in this article will help you create impressive scientific presentations. Below is the summary of how to give an engaging talk that will earn respect from your scientific community.
Step 1. Draft Presentation Outline. Create a presentation outline that clearly highlights the main point of your research. Make sure to start your talk outline with ideas to engage your audience and end your talk with a clear take-home message.
Step 2. Choose Slide Theme. Use a slide template or theme that looks professional, best represents your data, and matches your audience's expectations. Do not use slides that are too plain or too cheesy.
Step 3. Design Engaging Slides. Effective presentation slide designs use clear data visualizations and limits the amount of information that is added to each slide.
And a final tip is to practice your presentation so that you can refine your talking points. This way you will also know how long it will take you to cover the most essential information on your slides. Thank you for choosing Simplified Science Publishing as your science communication resource and good luck with your presentations!
Interested in free design templates and training?
Explore scientific illustration templates and courses by creating a Simplified Science Publishing Log In. Whether you are new to data visualization design or have some experience, these resources will improve your ability to use both basic and advanced design tools.
Interested in reading more articles on scientific design? Learn more below:

Data Storytelling Techniques: How to Tell a Great Data Story in 4 Steps

Best Science PowerPoint Templates and Slide Design Examples

Free Research Poster Templates and Tutorials
Content is protected by Copyright license. Website visitors are welcome to share images and articles, however they must include the Simplified Science Publishing URL source link when shared. Thank you!
Online Courses
Stay up-to-date for new simplified science courses, subscribe to our newsletter.
Thank you for signing up!
You have been added to the emailing list and will only recieve updates when there are new courses or templates added to the website.
We use cookies on this site to enhance your user experience and we do not sell data. By using this website, you are giving your consent for us to set cookies: View Privacy Policy
Simplified Science Publishing, LLC
Ten Secrets to Giving a Good Scientific Talk
More people will probably listen to your scientific talk than will read the paper you may write. Thus the scientific talk has become one of the most important communication forums for the scientific community. As proof, we need only look at the rising attendance at and the proliferation of meetings. In many ways your research reputation will be enhanced (or diminished) by your scientific talk. The scientific talk, like the scientific paper, is part of the scientific communication process. The modern scientist must be able to deliver a well organized, well delivered scientific talk
I have compiled this personal list of "Secrets" from listening to effective and ineffective speakers. I don't pretend that this list is comprehensive - I am sure there are things I have left out. But, my list probably covers about 90% of what you need to know and do.
Most scientific presentations use visual aids - and almost all scientific presentations are casual and extemporaneous 1 . This "scientific style" places some additional burdens on the speaker because the speaker must both manipulate visual media, project the aura of being at ease with the material, and still have the presence to answer unanticipated questions. No one would argue with the fact that an unprepared, sloppy talk is a waste of both the speaker's and audience's time. I would go further. A poorly prepared talk makes a statement that the speaker does not care about the audience and perhaps does not care much about his subject.
So what are the secrets of a good talk? Here is my list of do's and don'ts.
The Introduction should not just be a statement of the problem - but it should indicate your motivation to solve the problem, and you must also motivate the audience to be interested in your problem. In other words, the speaker must try and convince the audience that the problem is important to them as well as the speaker.
The Method includes your approach and the caveats. To me , the Method becomes more interesting to the listener if this section is "story like" rather than "text book like". In other words "I did this and then I did that, but that didn't work so I did something else." This Rather than, "The final result was obtained using this approach." This adds the human element to your research which is always interesting.
The Results section is a brief summary of your main results. Try and be as clear as possible in explaining your results - include only the most salient details. Less salient details will emerge as people ask questions.
The Conclusion/Summary section should condense your results and implications. This should be brief - a bullet or outline form is especially helpful. Be sure to connect your results with the overview statements in the Introduction . Don't have too many points - three or four is usually the maximum.
These four items are the core of a good talk. Good speakers often broaden the Introduction to set the problem within a very wide context. Good speakers may also add fifth item: Future Research .
- Practice your talk . There is no excuse for this lack of preparation. The best way to familiarize yourself with the material and get the talk's timing right is to practice your talk. Many scientists believe that they are such good speakers, or so super-intelligent that practice is beneath them. This is an arrogant attitude. Practice never hurts and even a quick run through will produce a better talk. Even better, practice in front of a small audience.
- Don't put in too much material . Good speakers will have one or two central points and stick to that material. How many talks have you heard where the speaker squanders their time on unessential details and then runs out of time at the end? The point of a talk is to communicate scientific results, not to show people how smart you are (in case they can't figure it out for themselves). Less is better for a talk . Here is a good rule of thumb - each viewgraph takes about 1.5-2 minutes to show. Thus a 12-minute AGU talk should only have 6-8 viewgraphs. How many "viewgraph movies" have you seen at the AGU? How effective were those presentations? Furthermore, no one has ever complained if a talk finishes early. Finally, assume most of the audience will know very little about the subject, and will need a clear explanation of what you are doing not just details.
- Avoid equations . Show only very simple equations if you show any at all. Ask yourself - is showing the equation important? Is it central to my talk? The problem is that equations are a dense mathematical notation indicating quantitative relationships. People are used to studying equations, not seeing them flashed on the screen for 2 minutes. I have seen talks where giant equations are put up - and for no other purpose than to convince the audience that the speaker must be really smart. The fact is, equations are distracting. People stop listening and start studying the equation. If you have to show an equation - simplify it and talk to it very briefly.
- Have only a few conclusion points . People can't remember more than a couple things from a talk especially if they are hearing many talks at large meetings. If a colleague asks you about someone's talk you heard, how do you typically describe it? You say something like "So and so looked at such and such and they found out this and that." You don't say, "I remember all 6 conclusions points." The fact is, people will only remember one or two things from your talk - you might as well tell them what to remember rather than let them figure it out for themselves.
- Talk to the audience not to the screen . One of the most common problems I see is that the speaker will speak to the viewgraph screen. It is hard to hear the speaker in this case and without eye contact the audience loses interest. Frankly, this is difficult to avoid, but the speaker needs to consciously look at the object on the screen, point to it, and then turn back to the audience to discuss the feature. Here is another suggestion, don't start talking right away when you put up a viewgraph. Let people look at the viewgraph for a few moments - they usually can't concentrate on the material and listen to you at the same time. Speak loudly and slowly. . I like to pick out a few people in the audience and pointedly talk to them as though I were explaining something to them.
- Avoid making distracting sounds . Everyone gets nervous speaking in public. But sometimes the nervousness often comes out as annoying sounds or habits that can be really distracting. Try to avoid "Ummm" or "Ahhh" between sentences. If you put your hands in your pockets, take the keys and change out so you won't jingle them during your talk.
- Use large letters (no fonts smaller than 16 pts!!) To see how your graphics will appear to the audience, place the viewgraph on the floor - can you read it standing up? Special sore points with me are figure axis and captions - usually unreadable.
- Keep the graphic simple . Don't show graphs you won't need. If there are four graphs on the viewgraph and you only talk to one - cut the others out. Don't crowd the viewgraph, don't use different fonts or type styles - it makes your slide look like a ransom note. Make sure the graph is simple and clear. A little professional effort on graphics can really make a talk impressive. If someone in your group has some artistic talent (and you don't) ask for help or opinions.
- Use color . Color makes the graphic stand out, and it is not that expensive anymore. However avoid red in the text - red is difficult to see from a distance. Also, check your color viewgraph using the projector. Some color schemes look fine on paper, but project poorly.
- Use cartoons . I think some of the best talks use little cartoons which explain the science. It is much easier for someone to follow logic if they can see a little diagram of the procedure or thought process that is being described. A Rube-Goldberg sort of cartoon is great for explaining complex ideas.
- Use humor if possible . A joke or two in your presentation spices things up and relaxes the audience. It emphasizes the casual nature of the talk. I am always amazed how even a really lame joke will get a good laugh in a science talk.
- First, repeat the question. This gives you time to think, and the rest of the audience may not have heard the question. Also if you heard the question incorrectly, it presents an opportunity for clarification.
- If you don't know the answer then say "I don't know, I will have to look into that. " Don't try to invent an answer on the fly. Be honest and humble. You are only human and you can't have thought of everything.
- If the questioner disagrees with you and it looks like there will be an argument then defuse the situation. A good moderator will usually intervene for you, but if not then you will have to handle this yourself. e.g. "We clearly don't agree on this point, let's go on to other questions and you and I can talk about this later."
- Never insult the questioner. He/she may have friends, and you never need more enemies.
Miscellaneous Points
Thank you - It is always a good idea to acknowledge people who helped you, and thank the people who invited you to give a talk.
Dress up - People are there to hear your material, but when you dress up you send the message that you care enough about the audience to look nice for them.
Check your viewgraphs before you give the talk . Are they all there? Are they in order? This is especially important with slides. Try to bring them to the meeting in a tray, or at least check them to be sure they are not upside down or backwards when the projectionist gets them. It is especially annoying to watch people fumble to get a viewgraph right side up. Don't do this by looking at the screen. Just look at the viewgraph directly. If it is right side up to you, then it will project correctly on the screen assuming that you are facing the audience. Go over the slides or viewgraphs quickly before the talk. Some people attach little post-it notes to viewgraphs to remind them of points to make. This seems like a good idea to me. However, It is very annoying to watch people peel their viewgraphs from sheets of paper. It suggests that they have never looked at them before. It is faster, more permanent, and you are less likely to have a mixed up shuffle, if you put them into viewgraph holders which clip in to a three ring binder.
If you have an electronic presentation - check out the system well before the talk.
Mark Schoeberl and Brian Toon
1 Amazingly, in the field of literature or history the talks are not given extemporaneously but read from written text. Sometimes this is also done in science talks and it can be an interesting and different experience.
Department of Chemistry
Search form.
- Affiliated Faculty
- Administrators & Staff
- Research Faculty & Staff
- Research Associates
- Graduate Students
- Update/Submit Alumni Information
- Emeritus and Retired Faculty
- In Memoriam
- Research Facilities
- Centers & Programs
- Astrochemistry
- Bioanalytical
- Biophysical Chemistry
- Catalysis and Energy
- Chemical Biology
- Chemical Education Reserach
- Imaging and Sensing
- Inorganic and Organometallic Chemistry
- Nanosciences and Materials
- Organic Chemistry and Synthesis
- Surface Chemistry and Spectroscopy
- Theory and Computation
- Non-Thesis Master's Program (1 Year)
- PhD Program
- Applying to the PhD Program
- Information about Charlottesville
- Chemistry and Multidisciplinary Courses
- Graduate Handbook
- Professional and Career Development Opportunities
- Graduate Chemistry Program Clubs & Organizations
- Fellowships and Awards
- Graduate Program Calendar
- Graduate Student Forms
- 2023-24 Bi-weekly Payroll Calendar
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Initiatives
- Disability Accommodation Information
- Prospective and Transfer Students
- General Chemistry Options
- Undergraduate Advisors
- Process for declaring a major, minor, DMP, or ACS Certification
- B.A. in Chemistry
- B.S. Chemistry
- B.S. Specialization in Biochemistry
- B.S.Specialization in Chemical Education
- B.S. Specialization in Chemical Physics
- B.S. Specialization in Environmental Chemistry
- B.S. Specialization in Materials Science
- B.A./M.S. or B.S./M.S. in Chemistry ("3+1" Degree Option)
- American Chemical Society Poster Session
- Undergraduate Publications
- Undergraduate Research in a pandemic
- How to Prepare and Present a Scientific Poster
How to Prepare and Present a Scientific Talk
- Guidelines for Final Report
- Distinguished Majors
- Study Abroad
- First and Second Years
- Third and Fourth Years
- Graduation Information
- Undergraduate Resources
- Upcoming Seminars
- Seminar Archive
- Request Seminar Date
- Named Lectures
- Spring 2023 Newsletter
Ten Simple Rules for Making Good Oral Presentations
Philip E. Bourne
PLoS Comput Biol 3(4): e77. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030077
Rule 1: Talk to the Audience
We do not mean face the audience, although gaining eye contact with as many people as possible when you present is important since it adds a level of intimacy and comfort to the presentation. We mean prepare presentations that address the target audience. Be sure you know who your audience is—what are their backgrounds and knowledge level of the material you are presenting and what they are hoping to get out of the presentation? Off-topic presentations are usually boring and will not endear you to the audience. Deliver what the audience wants to hear.
Rule 2: Less is More
A common mistake of inexperienced presenters is to try to say too much. They feel the need to prove themselves by proving to the audience that they know a lot. As a result, the main message is often lost, and valuable question time is usually curtailed. Your knowledge of the subject is best expressed through a clear and concise presentation that is provocative and leads to a dialog during the question-and-answer session when the audience becomes active participants. At that point, your knowledge of the material will likely become clear. If you do not get any questions, then you have not been following the other rules. Most likely, your presentation was either incomprehensible or trite. A side effect of too much material is that you talk too quickly, another ingredient of a lost message.
Rule 3: Only Talk When You Have Something to Say
Do not be overzealous about what you think you will have available to present when the time comes. Research never goes as fast as you would like. Remember the audience’s time is precious and should not be abused by presentation of uninteresting preliminary material.
Rule 4: Make the Take-Home Message Persistent
A good rule of thumb would seem to be that if you ask a member of the audience a week later about your presentation, they should be able to remember three points. If these are the key points you were trying to get across, you have done a good job. If they can remember any three points, but not the key points, then your emphasis was wrong. It is obvious what it means if they cannot recall three points!
Rule 5: Be Logical
Think of the presentation as a story. There is a logical flow—a clear beginning, middle, and an end. You set the stage (beginning), you tell the story (middle), and you have a big finish (the end) where the take-home message is clearly understood.
Rule 6: Treat the Floor as a Stage
Presentations should be entertaining, but do not overdo it and do know your limits. If you are not humorous by nature, do not try and be humorous. If you are not good at telling anecdotes, do not try and tell anecdotes, and so on. A good entertainer will captivate the audience and increase the likelihood of obeying Rule 4.
Rule 7: Practice and Time Your Presentation
This is particularly important for inexperienced presenters. Even more important, when you give the presentation, stick to what you practice. It is common to deviate, and even worse to start presenting material that you know less about than the audience does. The more you practice, the less likely you will be to go off on tangents. Visual cues help here. The more presentations you give, the better you are going to get. In a scientific environment, take every opportunity to do journal club and become a teaching assistant if it allows you to present. An important talk should not be given for the first time to an audience of peers. You should have delivered it to your research collaborators who will be kinder and gentler but still point out obvious discrepancies. Laboratory group meetings are a fine forum for this.
Rule 8: Use Visuals Sparingly but Effectively
Presenters have different styles of presenting. Some can captivate the audience with no visuals (rare); others require visual cues and in addition, depending on the material, may not be able to present a particular topic well without the appropriate visuals such as graphs and charts. Preparing good visual materials will be the subject of a further Ten Simple Rules. Rule 7 will help you to define the right number of visuals for a particular presentation. A useful rule of thumb for us is if you have more than one visual for each minute you are talking, you have too many and you will run over time. Obviously some visuals are quick, others take time to get the message across; again Rule 7 will help. Avoid reading the visual unless you wish to emphasize the point explicitly, the audience can read, too! The visual should support what you are saying either for emphasis or with data to prove the verbal point. Finally, do not overload the visual. Make the points few and clear.
Rule 9: Review Audio and/or Video of Your Presentations
There is nothing more effective than listening to, or listening to and viewing, a presentation you have made. Violations of the other rules will become obvious. Seeing what is wrong is easy, correcting it the next time around is not. You will likely need to break bad habits that lead to the violation of the other rules. Work hard on breaking bad habits; it is important.
Rule 10: Provide Appropriate Acknowledgments
People love to be acknowledged for their contributions. Having many gratuitous acknowledgements degrades the people who actually contributed. If you defy Rule 7, then you will not be able to acknowledge people and organizations appropriately, as you will run out of time. It is often appropriate to acknowledge people at the beginning or at the point of their contribution so that their contributions are very clear.
As a final word of caution, we have found that even in following the Ten Simple Rules (or perhaps thinking we are following them), the outcome of a presentation is not always guaranteed. Audience–presenter dynamics are hard to predict even though the metric of depth and intensity of questions and off-line followup provide excellent indicators. Sometimes you are sure a presentation will go well, and afterward you feel it did not go well. Other times you dread what the audience will think, and you come away pleased as punch. Such is life. As always, we welcome your comments on these Ten Simple Rules by Reader Response.
Acknowledgments
The idea for this particular Ten Simple Rules was inspired by a conversation with Fiona Addison.
Also see the following guides:
Ten Secrets to Giving a Good Scientific Talk in Science and Society V1003 by Mark Schoeberl and Brian Toon
How to Give a Sensational Scientific Talk by Janet B. W. Williams, D.S.W.
How to Give a Talk by James Allan
Giving a Job Talk in the Sciences By Richard M. Reis
Spectacular Scientific Talks by Rachel A. Petkewich
Tips for Giving Clear Talks by IvyPanda
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Lippincott Open Access

How to deliver an oral presentation
Georgina wellstead.
a Lister Hospital, East and North Hertfordshire NHS Trust
Katharine Whitehurst
b Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital
Buket Gundogan
c University College London
d Guy's St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK
Delivering an oral presentation in conferences and meetings can seem daunting. However, if delivered effectively, it can be an invaluable opportunity to showcase your work in front of peers as well as receive feedback on your project. In this “How to” article, we demonstrate how one can plan and successfully deliver an engaging oral presentation.
Giving an oral presentation at a scientific conference is an almost inevitable task at some point during your medical career. The prospect of presenting your original work to colleagues and peers, however, may be intimidating, and it can be difficult to know how to approach it. Nonetheless, it is important to remember that although daunting, an oral presentation is one of the best ways to get your work out there, and so should be looked upon as an exciting and invaluable opportunity.
Slide content
Although things may vary slightly depending on the type of research you are presenting, the typical structure is as follows:
- Opening slide (title of study, authors, institutions, and date)
- Methodology
- Discussion (including strengths and weaknesses of the study)
Conclusions
Picking out only the most important findings to include in your presentation is key and will keep it concise and easy to follow. This in turn will keep your viewers engaged, and more likely to understand and remember your presentation.
Psychological analysis of PowerPoint presentations, finds that 8 psychological principles are often violated 1 . One of these was the limited capacity of working memory, which can hold 4 units of information at any 1 time in most circumstances. Hence, too many points or concepts on a slide could be detrimental to the presenter’s desire to give information.
You can also help keep your audience engaged with images, which you can talk around, rather than lots of text. Video can also be useful, for example, a surgical procedure. However, be warned that IT can let you down when you need it most and you need to have a backup plan if the video fails. It’s worth coming to the venue early and testing it and resolving issues beforehand with the AV support staff if speaking at a conference.
Slide design and layout
It is important not to clutter your slides with too much text or too many pictures. An easy way to do this is by using the 5×5 rule. This means using no more than 5 bullet points per slide, with no more than 5 words per bullet point. It is also good to break up the text-heavy slides with ones including diagrams or graphs. This can also help to convey your results in a more visual and easy-to-understand way.
It is best to keep the slide design simple, as busy backgrounds and loud color schemes are distracting. Ensure that you use a uniform font and stick to the same color scheme throughout. As a general rule, a light-colored background with dark-colored text is easier to read than light-colored text on a dark-colored background. If you can use an image instead of text, this is even better.
A systematic review study of expert opinion papers demonstrates several key recommendations on how to effectively deliver medical research presentations 2 . These include:
- Keeping your slides simple
- Knowing your audience (pitching to the right level)
- Making eye contact
- Rehearsing the presentation
- Do not read from the slides
- Limiting the number of lines per slide
- Sticking to the allotted time
You should practice your presentation before the conference, making sure that you stick to the allocated time given to you. Oral presentations are usually short (around 8–10 min maximum), and it is, therefore, easy to go under or over time if you have not rehearsed. Aiming to spend around 1 minute per slide is usually a good guide. It is useful to present to your colleagues and seniors, allowing them to ask you questions afterwards so that you can be prepared for the sort of questions you may get asked at the conference. Knowing your research inside out and reading around the subject is advisable, as there may be experts watching you at the conference with more challenging questions! Make sure you re-read your paper the day before, or on the day of the conference to refresh your memory.
It is useful to bring along handouts of your presentation for those who may be interested. Rather than printing out miniature versions of your power point slides, it is better to condense your findings into a brief word document. Not only will this be easier to read, but you will also save a lot of paper by doing this!
Delivering the presentation
Having rehearsed your presentation beforehand, the most important thing to do when you get to the conference is to keep calm and be confident. Remember that you know your own research better than anyone else in the room! Be sure to take some deep breaths and speak at an appropriate pace and volume, making good eye contact with your viewers. If there is a microphone, don’t keep turning away from it as the audience will get frustrated if your voice keeps cutting in and out. Gesturing and using pointers when appropriate can be a really useful tool, and will enable you to emphasize your important findings.
Presenting tips
- Do not hide behind the computer. Come out to the center or side and present there.
- Maintain eye contact with the audience, especially the judges.
- Remember to pause every so often.
- Don’t clutter your presentation with verbal noise such as “umm,” “like,” or “so.” You will look more slick if you avoid this.
- Rhetorical questions once in a while can be useful in maintaining the audience’s attention.
When reaching the end of your presentation, you should slow down in order to clearly convey your key points. Using phases such as “in summary” and “to conclude” often prompts those who have drifted off slightly during your presentation start paying attention again, so it is a critical time to make sure that your work is understood and remembered. Leaving up your conclusions/summary slide for a short while after stopping speaking will give the audience time to digest the information. Conclude by acknowledging any fellow authors or assistants before thanking the audience for their attention and inviting any questions (as long as you have left sufficient time).
If asked a question, firstly thank the audience member, then repeat what they have asked to the rest of the listeners in case they didn’t hear the first time. Keep your answers short and succinct, and if unsure say that the questioner has raised a good point and that you will have to look into it further. Having someone else in the audience write down the question is useful for this.
The key points to remember when preparing for an oral presentation are:
- Keep your slides simple and concise using the 5×5 rule and images.
- When appropriate; rehearse timings; prepare answers to questions; speak slowly and use gestures/ pointers where appropriate; make eye contact with the audience; emphasize your key points at the end; make acknowledgments and thank the audience; invite questions and be confident but not arrogant.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial conflict of interest with regard to the content of this report.
Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Published online 8 June 2017
Your browser is not supported
Sorry but it looks as if your browser is out of date. To get the best experience using our site we recommend that you upgrade or switch browsers.
Find a solution
- Skip to main content
- Skip to navigation
- hot-topics Extras
- Newsletters
- Reading room
Tell us what you think. Take part in our reader survey
Celebrating twenty years
- Back to parent navigation item
- Collections
- Water and the environment
- Chemical bonding
- Antimicrobial resistance
- Energy storage and batteries
- AI and automation
- Sustainability
- Research culture
- Nobel prize
- Food science and cookery
- Plastics and polymers
- Periodic table
- Coronavirus

- More from navigation items

Source: © Shutterstock
How to give a scientific presentation
By Manisha Lalloo 2017-09-20T13:27:00+01:00
Five tips to keep an audience engaged without using cat pictures
Whether lecturing, presenting results at a conference or applying for a research proposal, giving presentations are a way of life for any chemist. But what are the best ways to get your point across while keeping your audience interested?

Think about your audience and remember that they want you to succeed
Jacquie Robson, is an associate professor of teaching at Durham University, UK, while Paul Bader is creative director at Screenhouse, an organisation which regularly trains scientists on how to develop better presentation skills. Here are their top tips.
Think about your audience
Whether presenting to colleagues or the general public, remember not everyone in your audience will be specialists. A common mistake scientists make is to assume others know as much as them when – more often than not – they are the expert in the room.
Even if your audience is well versed in the topic – for example, if you are presenting to a funding committee – do not start off with complex details. ‘If one person on the panel is outside the field, then you’ve lost them at the beginning,’ says Bader. Remember to give the big picture: it’s a good way in and a great way to make an impact.
Tell a story
‘Stories are easy to listen to and easy to tell,’ says Bader, who believes one of the most common mistakes is to cram too much information into just one talk. Structuring your talk in this way will help you to be selective.
Robson and Bader advise against learning a script by rote or reading a sheet of prose aloud. Written text is often more formal than convoluted than speech and sounds unnatural. Instead, have a set of key points on cue cards or use your slides as aide-mémoires. With a strong narrative, one point will lead to the next, making your talk more logical to follow and simpler to remember.
Robson also suggests telling your audience what you are going to speak about at the beginning of your talk and finishing off with a summary. That way your audience hears your main points three times – at the beginning, middle and end.
Visual aids are key
While PowerPoint is almost a given in today’s scientific presentations, try not to rely on it too much. ‘Slides should be clear, uncluttered and readable,’ says Robson. ‘Use diagrams rather than text.’
Slides should be used to highlight key points, not replicate your talk in written form. And remember never to turn your back on the audience – otherwise will be giving your presentation to the screen instead.
Don’t forget body language
‘Think about how you present yourself,’ says Robson. Have an open stance, smile, maintain eye contact, speak to the back of the room and at a good volume. ‘If you act confidently, they won’t know you’re feeling nervous.’
One of Robson’s pet peeves is a speaker who distracts the audience, for example by chewing gum or overusing laser pointers. Try to identify any habits you have while speaking that might take your audience’s attention away from your talk.
If you are feeling anxious, Robson advises against holding pieces of paper, which might shake in your hands. Bader suggests taking a moment to breathe. And both say the best technique is to ignore your nerves. The audience doesn’t want you to fail, and often won’t notice slip-ups. If you do make a big mistake, just correct yourself and carry on.
Practice, practice, practice
Perhaps the most important tip is to go through your presentation out loud before delivering it on the day.
‘People spend a lot of time writing their presentation or working on their slides but often the first time in public is the first time [they] do it,’ says Bader. By practising in advance and timing your run-throughs, you can discover if your talk is too long or too complicated.
There are many ways to practice, and it’s important to find the technique that works for you: you could video yourself on a phone and play it back, speak to yourself in front of a mirror or get somebody to listen to a rehearsal. According to Bader, the best way is to deliver your talk to a colleague or friend as you can see which parts they are engaged with (or not). ‘[But] any of the above is better than doing nothing,’ he adds.
And what about the dreaded questions at the end? ‘You can’t prepare for questions, so don’t fret,’ says Robson. ‘It’s not a spot exam, it’s a discussion. Make it into a conversation and don’t be afraid of saying “I don’t know the answer”.’
- Careers advice
- conferences
Related articles

A sustainable career in sustainability
2024-03-28T14:28:00Z
By Julia Robinson

Universities in the UK beat national average on gender pay gap but large discrepancies remain
2024-03-22T14:30:00Z

Making science communication persuasive and engaging
2024-03-21T09:30:00Z
By Philipp Gramlich

Losing a job can make you question who you are
2024-03-07T14:30:00Z
By Emma Pewsey

The community of colleagues supporting each other through redundancy
2024-03-07T09:31:00Z

How to deal with being made redundant
2024-03-07T09:30:00Z
1 Reader's comment
Only registered users can comment on this article., more from careers.

Seven musicians who you might not know are chemists
2024-02-16T14:20:00Z

When should you declare your feelings for a colleague?
2024-02-13T11:20:00Z


How to write a PhD thesis
2024-02-01T14:30:00Z
By Zahra Khan
Visionary chemistry is making labs accessible to blind students and researchers
2024-01-12T14:37:00Z
By Rebecca Trager

Should you pay for career advice?
2024-01-09T09:30:00Z
By Fawzi Abou-Chahine

Helping others is hard to incentivise, but an important part of work
2023-12-19T14:27:00Z
- Contributors
- Terms of use
- Accessibility
- Permissions
- This website collects cookies to deliver a better user experience. See how this site uses cookies .
- This website collects cookies to deliver a better user experience. Do not sell my personal data .
- Este site coleta cookies para oferecer uma melhor experiência ao usuário. Veja como este site usa cookies .
Site powered by Webvision Cloud
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER COLUMN
- 15 May 2019
Ways to give an effective seminar about your research project
- Ananya Sen 0
Ananya Sen is a PhD student in microbiology at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
In my first year of graduate school, I was terrified of giving presentations. I would put too much information on my slides, talk too fast and constantly forget or trip over certain words. Unsuprisingly, the reception was lukewarm at best.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-019-01574-z
This is an article from the Nature Careers Community, a place for Nature readers to share their professional experiences and advice. Guest posts are encouraged. You can get in touch with the editor at [email protected].
Related Articles

- Communication
- Conferences and meetings

Tweeting your research paper boosts engagement but not citations
News 27 MAR 24

Divas, captains, ghosts, ants and bumble-bees: collaborator attitudes explained
Career Column 15 MAR 24

Three actions PhD-holders should take to land their next job
Career Column 13 MAR 24

China promises more money for science in 2024
News 08 MAR 24

One-third of Indian STEM conferences have no women
News 15 NOV 23

How remote conferencing broadened my horizons and opened career paths
Career Column 04 AUG 23

Overcoming low vision to prove my abilities under pressure
Career Q&A 28 MAR 24

How a spreadsheet helped me to land my dream job
Career Column 28 MAR 24

Maple-scented cacti and pom-pom cats: how pranking at work can lift lab spirits
Career Feature 27 MAR 24
Tenure-track Assistant Professor in Ecological and Evolutionary Modeling
Tenure-track Assistant Professor in Ecosystem Ecology linked to IceLab’s Center for modeling adaptive mechanisms in living systems under stress
Umeå, Sweden
Umeå University
Faculty Positions in Westlake University
Founded in 2018, Westlake University is a new type of non-profit research-oriented university in Hangzhou, China, supported by public a...
Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Westlake University
Postdoctoral Fellowships-Metabolic control of cell growth and senescence
Postdoctoral positions in the team Cell growth control by nutrients at Inst. Necker, Université Paris Cité, Inserm, Paris, France.
Paris, Ile-de-France (FR)
Inserm DR IDF Paris Centre Nord
Zhejiang Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine on Open Recruitment of Medical Talents and Postdocs
Director of Clinical Department, Professor, Researcher, Post-doctor
The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University
Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Warmly Welcomes Talents Abroad
“Qiushi” Distinguished Scholar, Zhejiang University, including Professor and Physician
No. 3, Qingchun East Road, Hangzhou, Zhejiang (CN)
Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital Affiliated with Zhejiang University School of Medicine
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
This service is more advanced with JavaScript available
How to Deliver Great Scientific Presentations A Guide for Scientists and Engineers
- Jean-Philippe Dionne
Continuing in
How to Deliver Great Scientific Presentations
This is a preview of subscription content
Your browser needs to be JavaScript capable to view this video
Try reloading this page, or reviewing your browser settings
You're watching a preview of subscription content. Log in to check access
- View contents
- Details Details
- Transcript Transcript
- Contents Table of contents
This video provides concise and effective tips spanning all relevant areas to deliver engaging scientific presentations. You will strengthen your skills in preparing, practicing and delivering presentations at both physical and virtual conferences and seminars. Best practices for structuring presentations and elements to include and those to exclude such as detailed sections on the use of videos, animations and tables are included. Common errors often seen in scientific presentations are highlighted along with tips on how to interact with audiences and keep them engaged. This will be a valuable resource for scientists in all areas of chemistry and materials science as well as engineers who wish to elevate their scientific presentations.
Introduction
A straight to the point video providing concise and effective tips spanning all relevant areas to delivering engaging scientific presentations.
About The Author

Jean-Philippe Dionne, Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering (McGill University, Canada) has authored a number of scientific publications (conference proceedings, journal or magazine articles) in the field of personal protective equipment during his 20-year career in the industry. He has spent countless hours preparing and delivering presentations for scientific conferences and other events in various forms throughout his career.
About this video
Related content, presentation skills for scientists and engineers the slide master.
- Dr. Jean-Philippe Dionne
Video Transcript
[MUSIC PLAYING]
It strikes me every time I attend scientific conferences to realize that most presenters definitely stars in their respective domains of research. There are representations that are either boring, way too complex, or both. It’s great to spend 10 years of one’s life at University to get some prestigious degree, but why isn’t any time spent on learning how to give effective presentations?
Great speakers are entertaining and instill confidence. But despite their speaking skills, their message might not get across properly if they rely on poor visual backup. On the brighter side, even a poor public speaker with a shaky mastery of the language can deliver a great and well-structured talk if backed up by the appropriate visual.
Towards that goal, the following video segments are filled with many tricks and tips provided in a very concise manner. The main sections to be covered are some basics to get us started, animations, images and videos, graphs– they rarely get the attention they deserve– tables, maths in equations– always intimidating– structure of your talk, interactions, practice tricks, planning, and delivery– the few terrifying minutes on the stage.
My name is Jean-Philippe Dionne– PhD in mechanical engineering, working in industry with more than 20 years experience delivering scientific presentation, as well as an acute observer of other people’s presentations. I’m confident that all those following the advice provided here, whether young undergrads or seasoned scientists, are likely to benefit from these videos. Let’s proceed.

There is unequivocal evidence that Earth is warming at an unprecedented rate. Human activity is the principal cause.

- While Earth’s climate has changed throughout its history , the current warming is happening at a rate not seen in the past 10,000 years.
- According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change ( IPCC ), "Since systematic scientific assessments began in the 1970s, the influence of human activity on the warming of the climate system has evolved from theory to established fact." 1
- Scientific information taken from natural sources (such as ice cores, rocks, and tree rings) and from modern equipment (like satellites and instruments) all show the signs of a changing climate.
- From global temperature rise to melting ice sheets, the evidence of a warming planet abounds.
The rate of change since the mid-20th century is unprecedented over millennia.
Earth's climate has changed throughout history. Just in the last 800,000 years, there have been eight cycles of ice ages and warmer periods, with the end of the last ice age about 11,700 years ago marking the beginning of the modern climate era — and of human civilization. Most of these climate changes are attributed to very small variations in Earth’s orbit that change the amount of solar energy our planet receives.
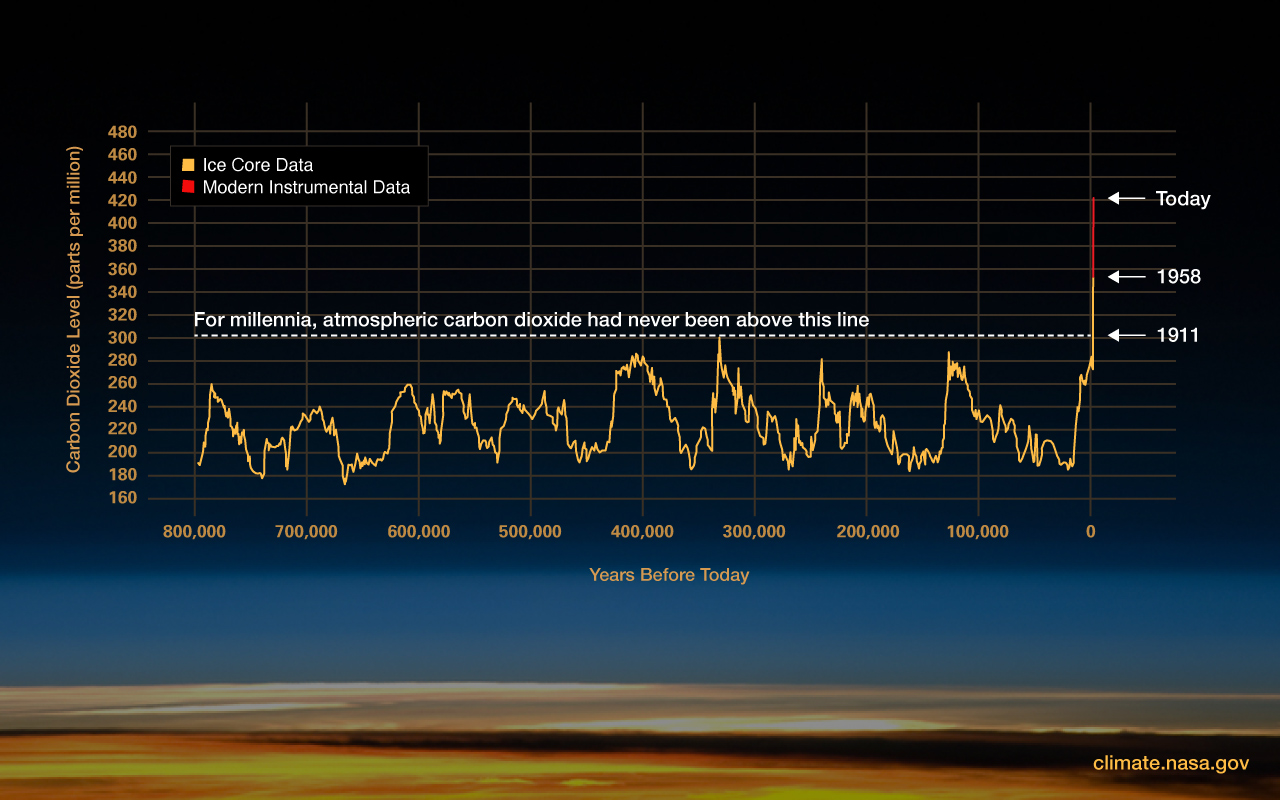
The current warming trend is different because it is clearly the result of human activities since the mid-1800s, and is proceeding at a rate not seen over many recent millennia. 1 It is undeniable that human activities have produced the atmospheric gases that have trapped more of the Sun’s energy in the Earth system. This extra energy has warmed the atmosphere, ocean, and land, and widespread and rapid changes in the atmosphere, ocean, cryosphere, and biosphere have occurred.
Earth-orbiting satellites and new technologies have helped scientists see the big picture, collecting many different types of information about our planet and its climate all over the world. These data, collected over many years, reveal the signs and patterns of a changing climate.
Scientists demonstrated the heat-trapping nature of carbon dioxide and other gases in the mid-19th century. 2 Many of the science instruments NASA uses to study our climate focus on how these gases affect the movement of infrared radiation through the atmosphere. From the measured impacts of increases in these gases, there is no question that increased greenhouse gas levels warm Earth in response.
Scientific evidence for warming of the climate system is unequivocal.

Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
Ice cores drawn from Greenland, Antarctica, and tropical mountain glaciers show that Earth’s climate responds to changes in greenhouse gas levels. Ancient evidence can also be found in tree rings, ocean sediments, coral reefs, and layers of sedimentary rocks. This ancient, or paleoclimate, evidence reveals that current warming is occurring roughly 10 times faster than the average rate of warming after an ice age. Carbon dioxide from human activities is increasing about 250 times faster than it did from natural sources after the last Ice Age. 3
The Evidence for Rapid Climate Change Is Compelling:
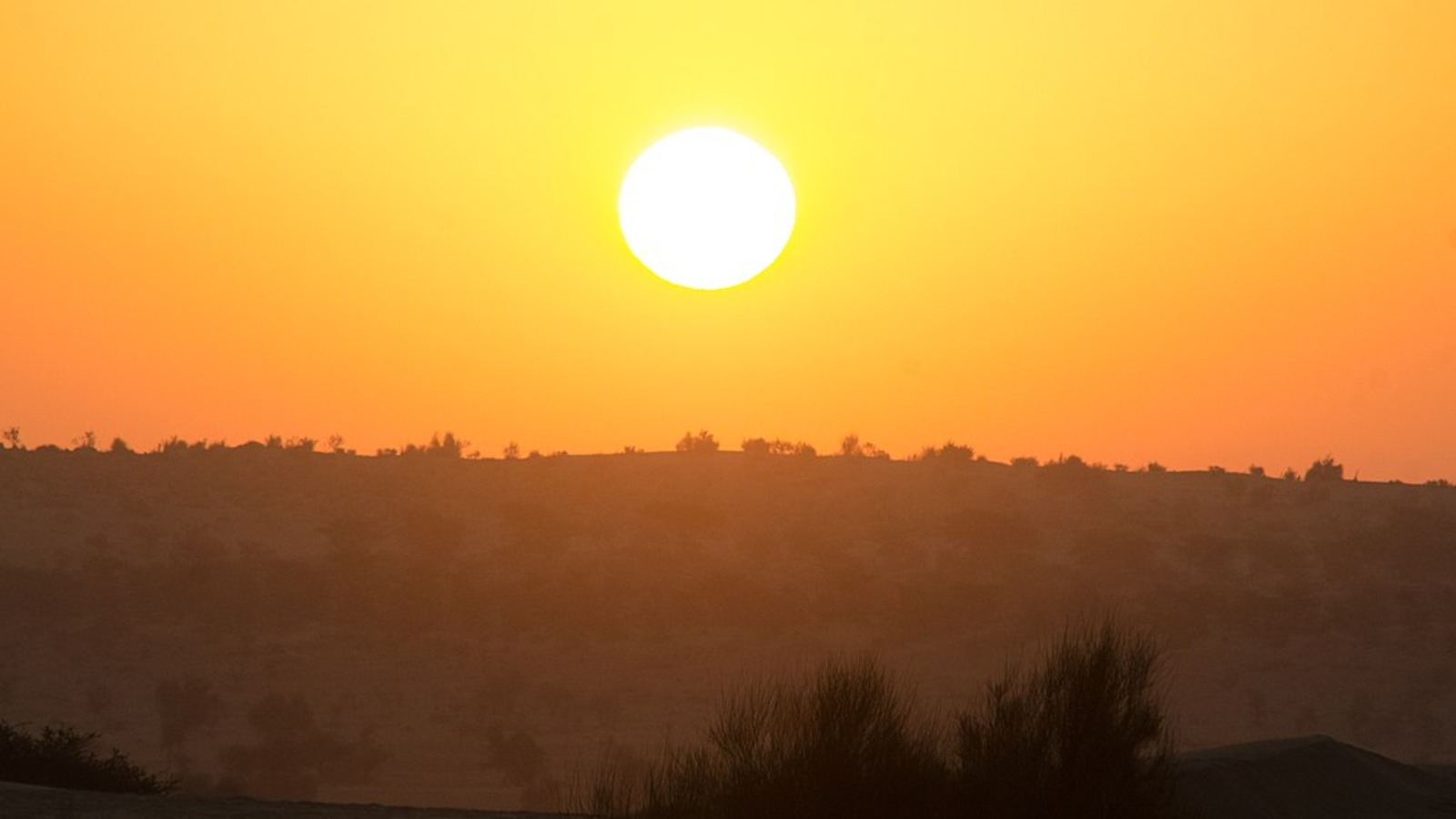

Global Temperature Is Rising
The planet's average surface temperature has risen about 2 degrees Fahrenheit (1 degrees Celsius) since the late 19th century, a change driven largely by increased carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere and other human activities. 4 Most of the warming occurred in the past 40 years, with the seven most recent years being the warmest. The years 2016 and 2020 are tied for the warmest year on record. 5 Image credit: Ashwin Kumar, Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 Generic.

The Ocean Is Getting Warmer
The ocean has absorbed much of this increased heat, with the top 100 meters (about 328 feet) of ocean showing warming of 0.67 degrees Fahrenheit (0.33 degrees Celsius) since 1969. 6 Earth stores 90% of the extra energy in the ocean. Image credit: Kelsey Roberts/USGS
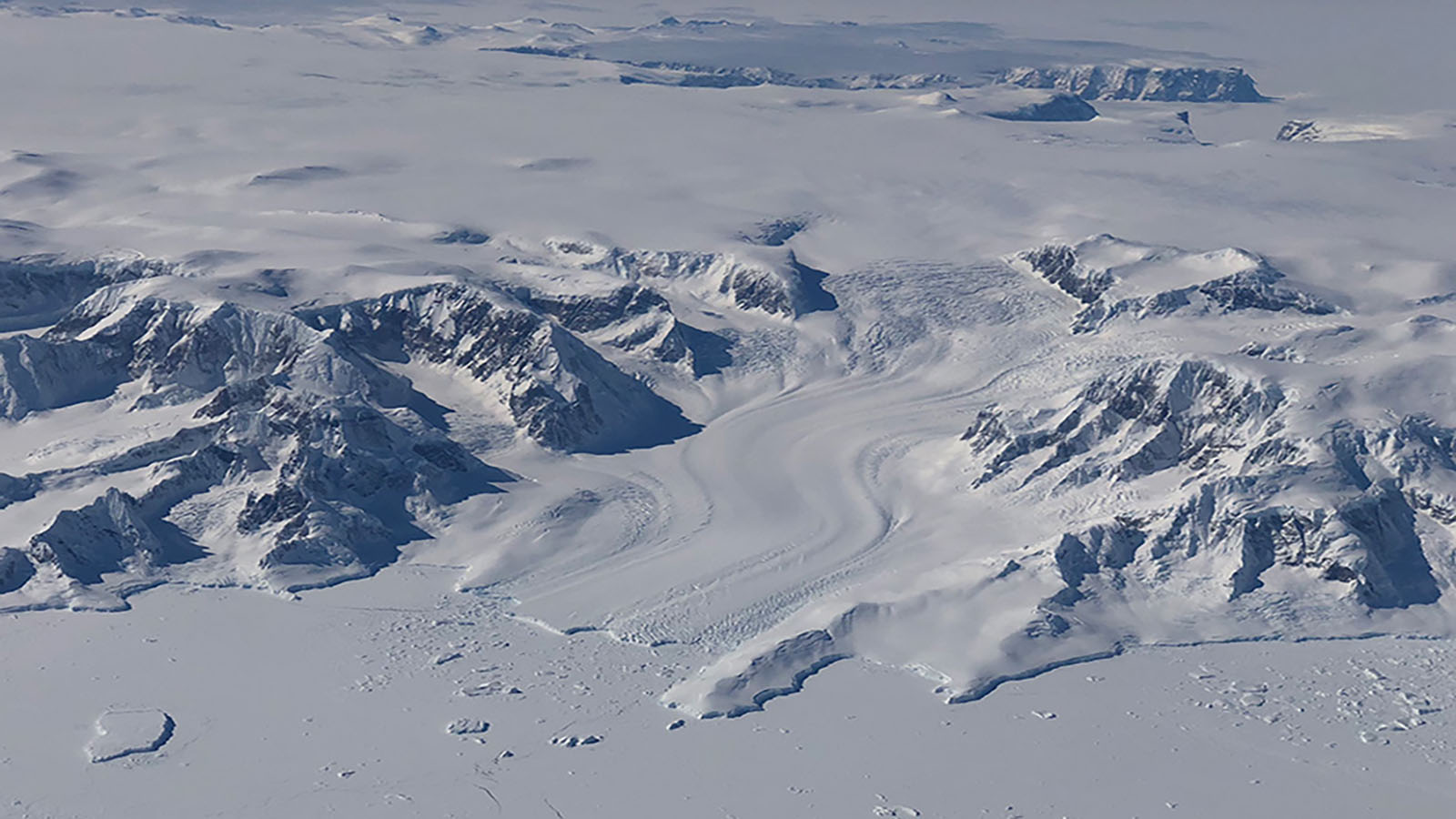

The Ice Sheets Are Shrinking
The Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets have decreased in mass. Data from NASA's Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment show Greenland lost an average of 279 billion tons of ice per year between 1993 and 2019, while Antarctica lost about 148 billion tons of ice per year. 7 Image: The Antarctic Peninsula, Credit: NASA
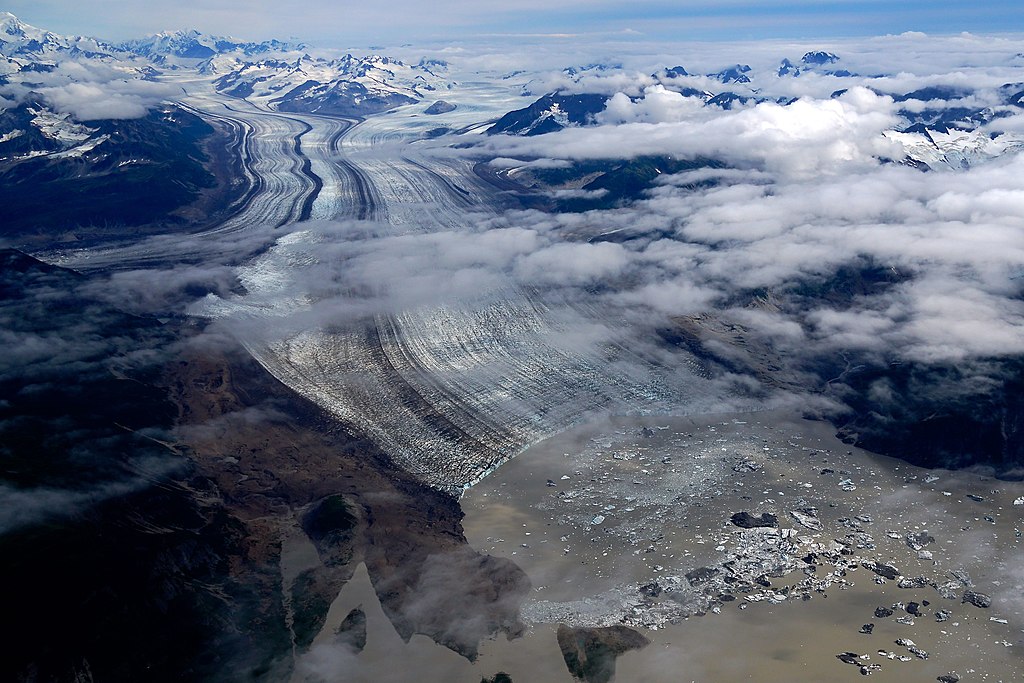

Glaciers Are Retreating
Glaciers are retreating almost everywhere around the world — including in the Alps, Himalayas, Andes, Rockies, Alaska, and Africa. 8 Image: Miles Glacier, Alaska Image credit: NASA

Snow Cover Is Decreasing
Satellite observations reveal that the amount of spring snow cover in the Northern Hemisphere has decreased over the past five decades and the snow is melting earlier. 9 Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech

Sea Level Is Rising
Global sea level rose about 8 inches (20 centimeters) in the last century. The rate in the last two decades, however, is nearly double that of the last century and accelerating slightly every year. 10 Image credit: U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Norfolk District

Arctic Sea Ice Is Declining
Both the extent and thickness of Arctic sea ice has declined rapidly over the last several decades. 11 Credit: NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio

Extreme Events Are Increasing in Frequency
The number of record high temperature events in the United States has been increasing, while the number of record low temperature events has been decreasing, since 1950. The U.S. has also witnessed increasing numbers of intense rainfall events. 12 Image credit: Régine Fabri, CC BY-SA 4.0 , via Wikimedia Commons

Ocean Acidification Is Increasing
Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, the acidity of surface ocean waters has increased by about 30%. 13 , 14 This increase is due to humans emitting more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere and hence more being absorbed into the ocean. The ocean has absorbed between 20% and 30% of total anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions in recent decades (7.2 to 10.8 billion metric tons per year). 1 5 , 16 Image credit: NOAA
1. IPCC Sixth Assessment Report, WGI, Technical Summary . B.D. Santer et.al., “A search for human influences on the thermal structure of the atmosphere.” Nature 382 (04 July 1996): 39-46. https://doi.org/10.1038/382039a0. Gabriele C. Hegerl et al., “Detecting Greenhouse-Gas-Induced Climate Change with an Optimal Fingerprint Method.” Journal of Climate 9 (October 1996): 2281-2306. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1996)009<2281:DGGICC>2.0.CO;2. V. Ramaswamy, et al., “Anthropogenic and Natural Influences in the Evolution of Lower Stratospheric Cooling.” Science 311 (24 February 2006): 1138-1141. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1122587. B.D. Santer et al., “Contributions of Anthropogenic and Natural Forcing to Recent Tropopause Height Changes.” Science 301 (25 July 2003): 479-483. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1084123. T. Westerhold et al., "An astronomically dated record of Earth’s climate and its predictability over the last 66 million years." Science 369 (11 Sept. 2020): 1383-1387. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1094123
2. In 1824, Joseph Fourier calculated that an Earth-sized planet, at our distance from the Sun, ought to be much colder. He suggested something in the atmosphere must be acting like an insulating blanket. In 1856, Eunice Foote discovered that blanket, showing that carbon dioxide and water vapor in Earth's atmosphere trap escaping infrared (heat) radiation. In the 1860s, physicist John Tyndall recognized Earth's natural greenhouse effect and suggested that slight changes in the atmospheric composition could bring about climatic variations. In 1896, a seminal paper by Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius first predicted that changes in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels could substantially alter the surface temperature through the greenhouse effect. In 1938, Guy Callendar connected carbon dioxide increases in Earth’s atmosphere to global warming. In 1941, Milutin Milankovic linked ice ages to Earth’s orbital characteristics. Gilbert Plass formulated the Carbon Dioxide Theory of Climate Change in 1956.
3. IPCC Sixth Assessment Report, WG1, Chapter 2 Vostok ice core data; NOAA Mauna Loa CO2 record O. Gaffney, W. Steffen, "The Anthropocene Equation." The Anthropocene Review 4, issue 1 (April 2017): 53-61. https://doi.org/abs/10.1177/2053019616688022.
4. https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/monitoring https://crudata.uea.ac.uk/cru/data/temperature/ http://data.giss.nasa.gov/gistemp
5. https://www.giss.nasa.gov/research/news/20170118/
6. S. Levitus, J. Antonov, T. Boyer, O Baranova, H. Garcia, R. Locarnini, A. Mishonov, J. Reagan, D. Seidov, E. Yarosh, M. Zweng, " NCEI ocean heat content, temperature anomalies, salinity anomalies, thermosteric sea level anomalies, halosteric sea level anomalies, and total steric sea level anomalies from 1955 to present calculated from in situ oceanographic subsurface profile data (NCEI Accession 0164586), Version 4.4. (2017) NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. https://www.nodc.noaa.gov/OC5/3M_HEAT_CONTENT/index3.html K. von Schuckmann, L. Cheng, L,. D. Palmer, J. Hansen, C. Tassone, V. Aich, S. Adusumilli, H. Beltrami, H., T. Boyer, F. Cuesta-Valero, D. Desbruyeres, C. Domingues, A. Garcia-Garcia, P. Gentine, J. Gilson, M. Gorfer, L. Haimberger, M. Ishii, M., G. Johnson, R. Killick, B. King, G. Kirchengast, N. Kolodziejczyk, J. Lyman, B. Marzeion, M. Mayer, M. Monier, D. Monselesan, S. Purkey, D. Roemmich, A. Schweiger, S. Seneviratne, A. Shepherd, D. Slater, A. Steiner, F. Straneo, M.L. Timmermans, S. Wijffels. "Heat stored in the Earth system: where does the energy go?" Earth System Science Data 12, Issue 3 (07 September 2020): 2013-2041. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-12-2013-2020.
7. I. Velicogna, Yara Mohajerani, A. Geruo, F. Landerer, J. Mouginot, B. Noel, E. Rignot, T. Sutterly, M. van den Broeke, M. Wessem, D. Wiese, "Continuity of Ice Sheet Mass Loss in Greenland and Antarctica From the GRACE and GRACE Follow-On Missions." Geophysical Research Letters 47, Issue 8 (28 April 2020): e2020GL087291. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020GL087291.
8. National Snow and Ice Data Center World Glacier Monitoring Service
9. National Snow and Ice Data Center D.A. Robinson, D. K. Hall, and T. L. Mote, "MEaSUREs Northern Hemisphere Terrestrial Snow Cover Extent Daily 25km EASE-Grid 2.0, Version 1 (2017). Boulder, Colorado USA. NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center. doi: https://doi.org/10.5067/MEASURES/CRYOSPHERE/nsidc-0530.001 . http://nsidc.org/cryosphere/sotc/snow_extent.html Rutgers University Global Snow Lab. Data History
10. R.S. Nerem, B.D. Beckley, J. T. Fasullo, B.D. Hamlington, D. Masters, and G.T. Mitchum, "Climate-change–driven accelerated sea-level rise detected in the altimeter era." PNAS 15, no. 9 (12 Feb. 2018): 2022-2025. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1717312115.
11. https://nsidc.org/cryosphere/sotc/sea_ice.html Pan-Arctic Ice Ocean Modeling and Assimilation System (PIOMAS, Zhang and Rothrock, 2003) http://psc.apl.washington.edu/research/projects/arctic-sea-ice-volume-anomaly/ http://psc.apl.uw.edu/research/projects/projections-of-an-ice-diminished-arctic-ocean/
12. USGCRP, 2017: Climate Science Special Report: Fourth National Climate Assessment, Volume I [Wuebbles, D.J., D.W. Fahey, K.A. Hibbard, D.J. Dokken, B.C. Stewart, and T.K. Maycock (eds.)]. U.S. Global Change Research Program, Washington, DC, USA, 470 pp, https://doi.org/10.7930/j0j964j6 .
13. http://www.pmel.noaa.gov/co2/story/What+is+Ocean+Acidification%3F
14. http://www.pmel.noaa.gov/co2/story/Ocean+Acidification
15. C.L. Sabine, et al., “The Oceanic Sink for Anthropogenic CO2.” Science 305 (16 July 2004): 367-371. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1097403.
16. Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate , Technical Summary, Chapter TS.5, Changing Ocean, Marine Ecosystems, and Dependent Communities, Section 5.2.2.3. https://www.ipcc.ch/srocc/chapter/technical-summary/
Header image shows clouds imitating mountains as the sun sets after midnight as seen from Denali's backcountry Unit 13 on June 14, 2019. Credit: NPS/Emily Mesner Image credit in list of evidence: Ashwin Kumar, Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 Generic.
Discover More Topics From NASA
Explore Earth Science

Earth Science in Action

Earth Science Data
Facts About Earth

Home Blog Design How to Design a Winning Poster Presentation: Quick Guide with Examples & Templates
How to Design a Winning Poster Presentation: Quick Guide with Examples & Templates

How are research posters like High School science fair projects? Quite similar, in fact.
Both are visual representations of a research project shared with peers, colleagues and academic faculty. But there’s a big difference: it’s all in professionalism and attention to detail. You can be sure that the students that thrived in science fairs are now creating fantastic research posters, but what is that extra element most people miss when designing a poster presentation?
This guide will teach tips and tricks for creating poster presentations for conferences, symposia, and more. Learn in-depth poster structure and design techniques to help create academic posters that have a lasting impact.
Let’s get started.
Table of Contents
- What is a Research Poster?
Why are Poster Presentations important?
Overall dimensions and orientation, separation into columns and sections, scientific, academic, or something else, a handout with supplemental and contact information, cohesiveness, design and readability, storytelling.
- Font Characteristics
- Color Pairing
- Data Visualization Dimensions
- Alignment, Margins, and White Space
Scientific/Academic Conference Poster Presentation
Digital research poster presentations, slidemodel poster presentation templates, how to make a research poster presentation step-by-step, considerations for printing poster presentations, how to present a research poster presentation, final words, what is a research poster .
Research posters are visual overviews of the most relevant information extracted from a research paper or analysis. They are essential communication formats for sharing findings with peers and interested people in the field. Research posters can also effectively present material for other areas besides the sciences and STEM—for example, business and law.
You’ll be creating research posters regularly as an academic researcher, scientist, or grad student. You’ll have to present them at numerous functions and events. For example:
- Conference presentations
- Informational events
- Community centers
The research poster presentation is a comprehensive way to share data, information, and research results. Before the pandemic, the majority of research events were in person. During lockdown and beyond, virtual conferences and summits became the norm. Many researchers now create poster presentations that work in printed and digital formats.

Let’s look at why it’s crucial to spend time creating poster presentations for your research projects, research, analysis, and study papers.
Research posters represent you and your sponsor’s research
Research papers and accompanying poster presentations are potent tools for representation and communication in your field of study. Well-performing poster presentations help scientists, researchers, and analysts grow their careers through grants and sponsorships.
When presenting a poster presentation for a sponsored research project, you’re representing the company that sponsored you. Your professionalism, demeanor, and capacity for creating impactful poster presentations call attention to other interested sponsors, spreading your impact in the field.
Research posters demonstrate expertise and growth
Presenting research posters at conferences, summits, and graduate grading events shows your expertise and knowledge in your field of study. The way your poster presentation looks and delivers, plus your performance while presenting the work, is judged by your viewers regardless of whether it’s an officially judged panel.
Recurring visitors to research conferences and symposia will see you and your poster presentations evolve. Improve your impact by creating a great poster presentation every time by paying attention to detail in the poster design and in your oral presentation. Practice your public speaking skills alongside the design techniques for even more impact.
Poster presentations create and maintain collaborations
Every time you participate in a research poster conference, you create meaningful connections with people in your field, industry or community. Not only do research posters showcase information about current data in different areas, but they also bring people together with similar interests. Countless collaboration projects between different research teams started after discussing poster details during coffee breaks.
An effective research poster template deepens your peer’s understanding of a topic by highlighting research, data, and conclusions. This information can help other researchers and analysts with their work. As a research poster presenter, you’re given the opportunity for both teaching and learning while sharing ideas with peers and colleagues.
Anatomy of a Winning Poster Presentation
Do you want your research poster to perform well? Following the standard layout and adding a few personal touches will help attendees know how to read your poster and get the most out of your information.
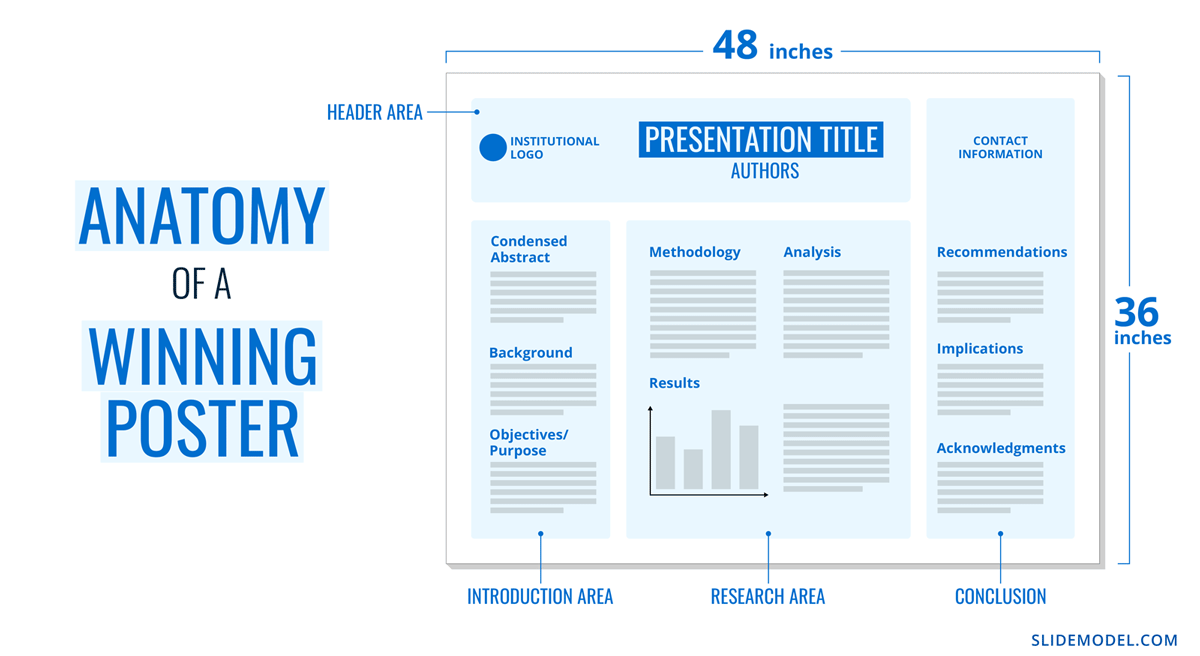
The overall size of your research poster ultimately depends on the dimensions of the provided space at the conference or research poster gallery. The poster orientation can be horizontal or vertical, with horizontal being the most common. In general, research posters measure 48 x 36 inches or are an A0 paper size.
A virtual poster can be the same proportions as the printed research poster, but you have more leeway regarding the dimensions. Virtual research posters should fit on a screen with no need to scroll, with 1080p resolution as a standard these days. A horizontal presentation size is ideal for that.
A research poster presentation has a standard layout of 2–5 columns with 2–3 sections each. Typical structures say to separate the content into four sections; 1. A horizontal header 2. Introduction column, 3. Research/Work/Data column, and 4. Conclusion column. Each unit includes topics that relate to your poster’s objective. Here’s a generalized outline for a poster presentation:
- Condensed Abstract
- Objectives/Purpose
- Methodology
- Recommendations
- Implications
- Acknowledgments
- Contact Information
The overview content you include in the units depends on your poster presentations’ theme, topic, industry, or field of research. A scientific or academic poster will include sections like hypothesis, methodology, and materials. A marketing analysis poster will include performance metrics and competitor analysis results.
There’s no way a poster can hold all the information included in your research paper or analysis report. The poster is an overview that invites the audience to want to find out more. That’s where supplement material comes in. Create a printed PDF handout or card with a QR code (created using a QR code generator ). Send the audience to the best online location for reading or downloading the complete paper.
What Makes a Poster Presentation Good and Effective?
For your poster presentation to be effective and well-received, it needs to cover all the bases and be inviting to find out more. Stick to the standard layout suggestions and give it a unique look and feel. We’ve put together some of the most critical research poster-creation tips in the list below. Your poster presentation will perform as long as you check all the boxes.
The information you choose to include in the sections of your poster presentation needs to be cohesive. Train your editing eye and do a few revisions before presenting. The best way to look at it is to think of The Big Picture. Don’t get stuck on the details; your attendees won’t always know the background behind your research topic or why it’s important.
Be cohesive in how you word the titles, the length of the sections, the highlighting of the most important data, and how your oral presentation complements the printed—or virtual—poster.
The most important characteristic of your poster presentation is its readability and clarity. You need a poster presentation with a balanced design that’s easy to read at a distance of 1.5 meters or 4 feet. The font size and spacing must be clear and neat. All the content must suggest a visual flow for the viewer to follow.
That said, you don’t need to be a designer to add something special to your poster presentation. Once you have the standard—and recognized—columns and sections, add your special touch. These can be anything from colorful boxes for the section titles to an interesting but subtle background, images that catch the eye, and charts that inspire a more extended look.
Storytelling is a presenting technique involving writing techniques to make information flow. Firstly, storytelling helps give your poster presentation a great introduction and an impactful conclusion.
Think of storytelling as the invitation to listen or read more, as the glue that connects sections, making them flow from one to another. Storytelling is using stories in the oral presentation, for example, what your lab partner said when you discovered something interesting. If it makes your audience smile and nod, you’ve hit the mark. Storytelling is like giving a research presentation a dose of your personality, and it can help turning your data into opening stories .
Design Tips For Creating an Effective Research Poster Presentation
The section above briefly mentioned how important design is to your poster presentation’s effectiveness. We’ll look deeper into what you need to know when designing a poster presentation.
1. Font Characteristics
The typeface and size you choose are of great importance. Not only does the text need to be readable from two meters away, but it also needs to look and sit well on the poster. Stay away from calligraphic script typefaces, novelty typefaces, or typefaces with uniquely shaped letters.
Stick to the classics like a sans serif Helvetica, Lato, Open Sans, or Verdana. Avoid serif typefaces as they can be difficult to read from far away. Here are some standard text sizes to have on hand.
- Title: 85 pt
- Authors: 65 pt
- Headings: 36 pt
- Body Text: 24 pt
- Captions: 18 pt
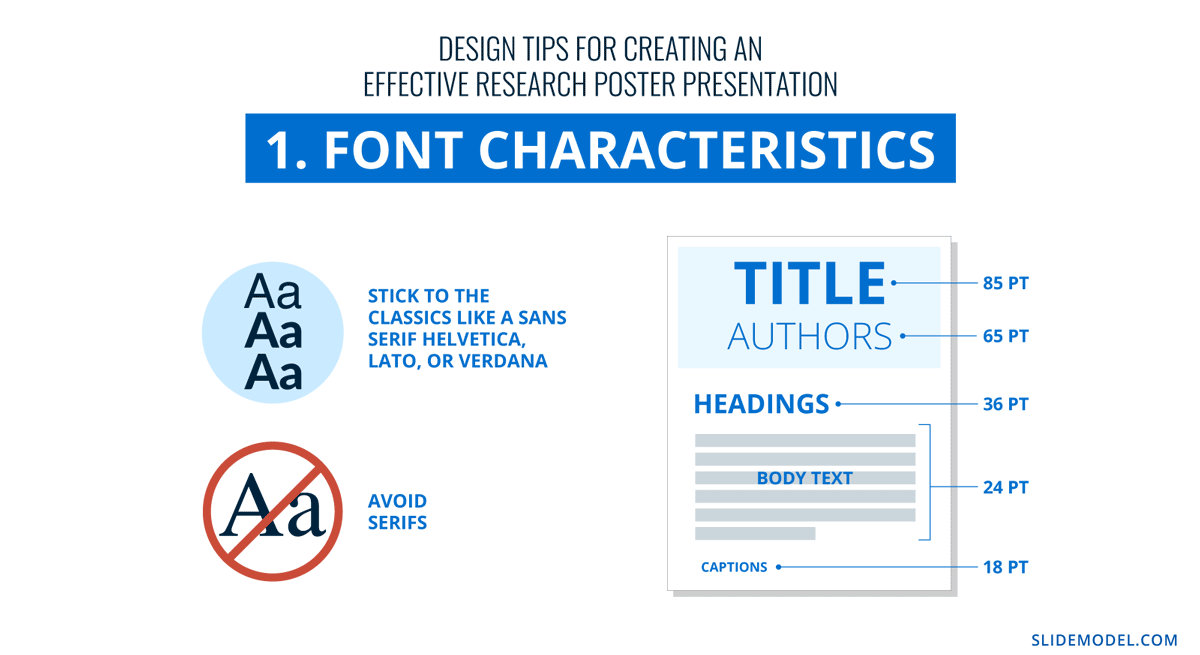
If you feel too prone to use serif typefaces, work with a font pairing tool that helps you find a suitable solution – and intend those serif fonts for heading sections only. As a rule, never use more than 3 different typefaces in your design. To make it more dynamic, you can work with the same font using light, bold, and italic weights to put emphasis on the required areas.
2. Color Pairing
Using colors in your poster presentation design is a great way to grab the viewer’s attention. A color’s purpose is to help the viewer follow the data flow in your presentation, not distract. Don’t let the color take more importance than the information on your poster.
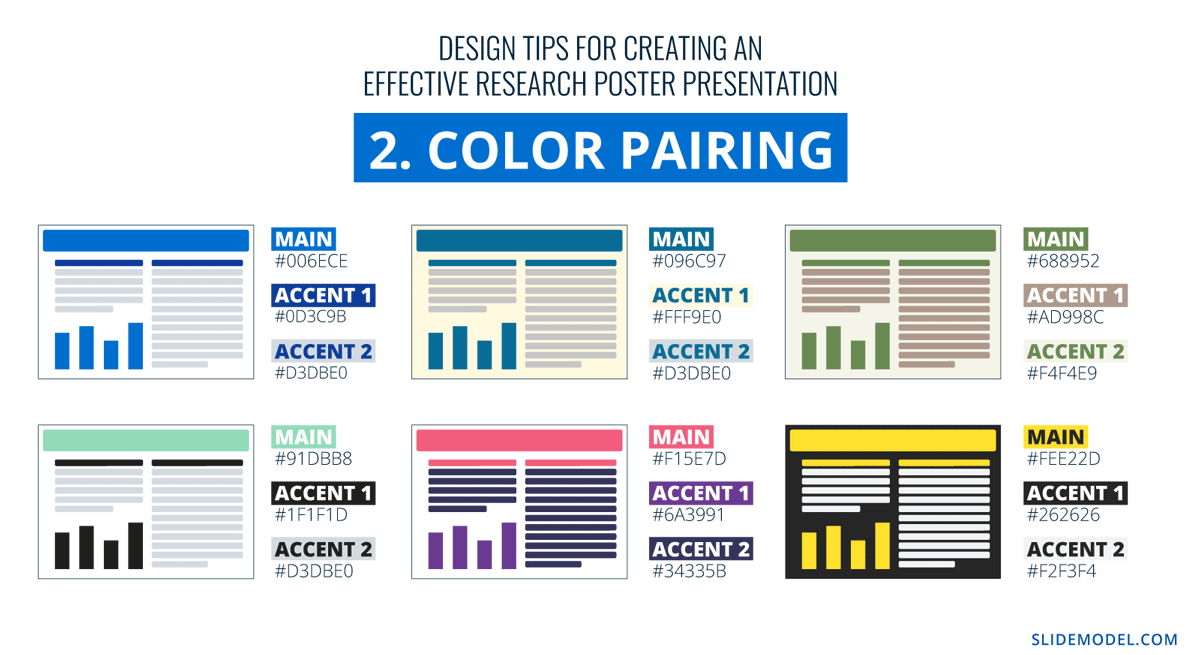
Choose one main color for the title and headlines and a similar color for the data visualizations. If you want to use more than one color, don’t create too much contrast between them. Try different tonalities of the same color and keep things balanced visually. Your color palette should have at most one main color and two accent colors.
Black text over a white background is standard practice for printed poster presentations, but for virtual presentations, try a very light gray instead of white and a very dark gray instead of black. Additionally, use variations of light color backgrounds and dark color text. Make sure it’s easy to read from two meters away or on a screen, depending on the context. We recommend ditching full white or full black tone usage as it hurts eyesight in the long term due to its intense contrast difference with the light ambiance.
3. Data Visualization Dimensions
Just like the text, your charts, graphs, and data visualizations must be easy to read and understand. Generally, if a person is interested in your research and has already read some of the text from two meters away, they’ll come closer to look at the charts and graphs.
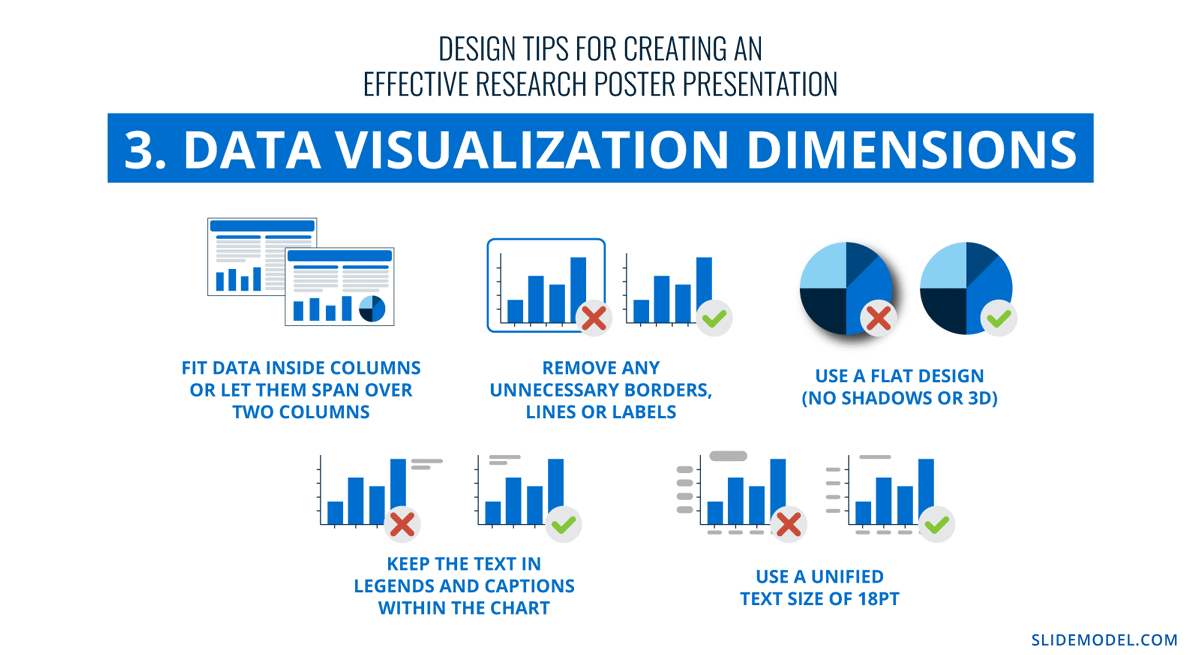
Fit data visualizations inside columns or let them span over two columns. Remove any unnecessary borders, lines, or labels to make them easier to read at a glance. Use a flat design without shadows or 3D characteristics. The text in legends and captions should stay within the chart size and not overflow into the margins. Use a unified text size of 18px for all your data visualizations.
4. Alignment, Margins, and White Space
Finally, the last design tip for creating an impressive and memorable poster presentation is to be mindful of the layout’s alignment, margins, and white space. Create text boxes to help keep everything aligned. They allow you to resize, adapt, and align the content along a margin or grid.
Take advantage of the white space created by borders and margins between sections. Don’t crowd them with a busy background or unattractive color.
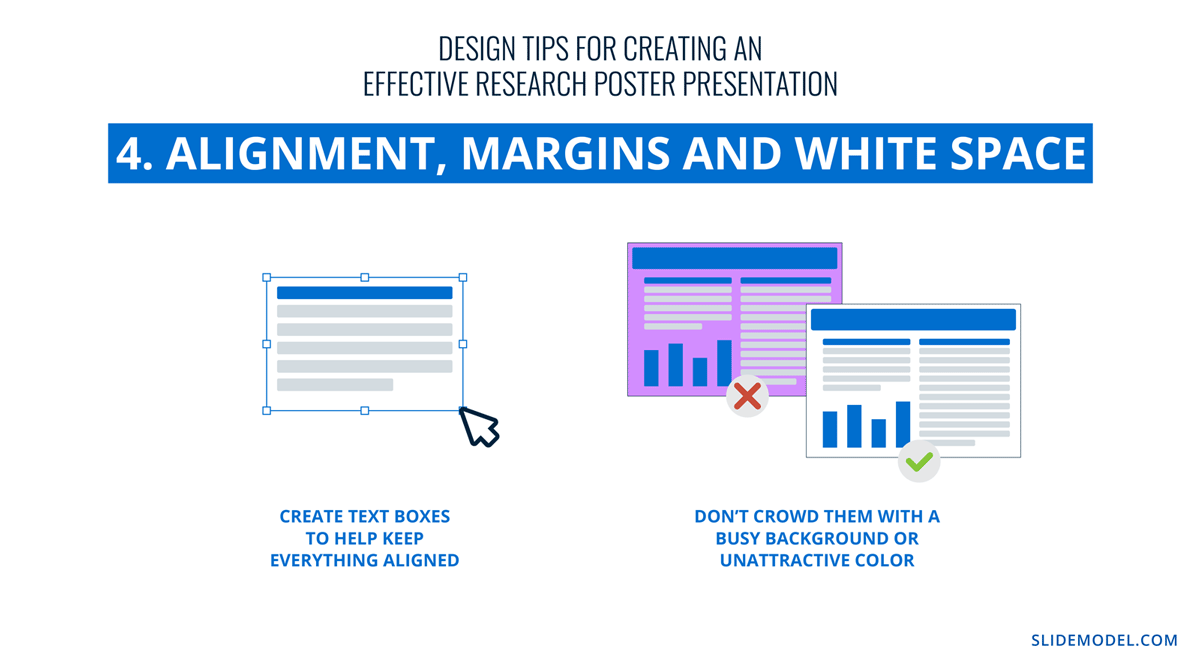
Calculate margins considering a print format. It is a good practice in case the poster presentation ends up becoming in physical format, as you won’t need to downscale your entire design (affecting text readability in the process) to preserve information.
There are different tools that you can use to make a poster presentation. Presenters who are familiar with Microsoft Office prefer to use PowerPoint. You can learn how to make a poster in PowerPoint here.
Poster Presentation Examples
Before you start creating a poster presentation, look at some examples of real research posters. Get inspired and get creative.
Research poster presentations printed and mounted on a board look like the one in the image below. The presenter stands to the side, ready to share the information with visitors as they walk up to the panels.
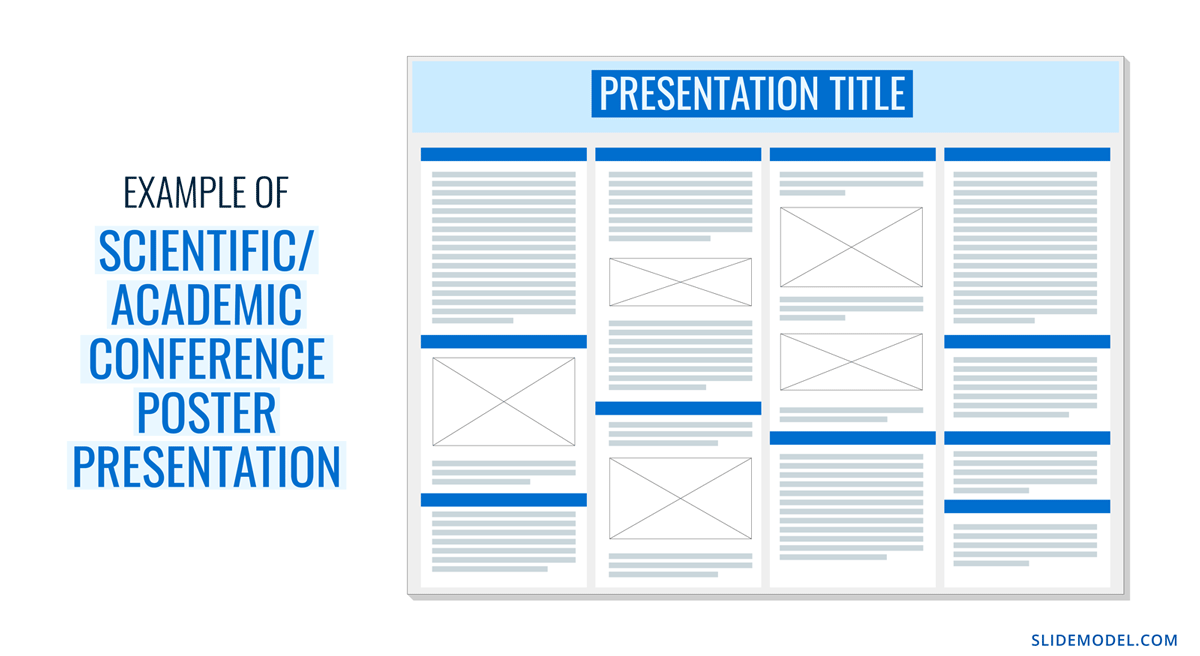
With more and more conferences staying virtual or hybrid, the digital poster presentation is here to stay. Take a look at examples from a poster session at the OHSU School of Medicine .
Use SlideModel templates to help you create a winning poster presentation with PowerPoint and Google Slides. These poster PPT templates will get you off on the right foot. Mix and match tables and data visualizations from other poster slide templates to create your ideal layout according to the standard guidelines.
If you need a quick method to create a presentation deck to talk about your research poster at conferences, check out our Slides AI presentation maker. A tool in which you add the topic, curate the outline, select a design, and let AI do the work for you.
1. One-pager Scientific Poster Template for PowerPoint

A PowerPoint template tailored to make your poster presentations an easy-to-craft process. Meet our One-Pager Scientific Poster Slide Template, entirely editable to your preferences and with ample room to accommodate graphs, data charts, and much more.
Use This Template
2. Eisenhower Matrix Slides Template for PowerPoint

An Eisenhower Matrix is a powerful tool to represent priorities, classifying work according to urgency and importance. Presenters can use this 2×2 matrix in poster presentations to expose the effort required for the research process, as it also helps to communicate strategy planning.
3. OSMG Framework PowerPoint Template
Finally, we recommend presenters check our OSMG Framework PowerPoint template, as it is an ideal tool for representing a business plan: its goals, strategies, and measures for success. Expose complex processes in a simplified manner by adding this template to your poster presentation.
Remember these three words when making your research poster presentation: develop, design, and present. These are the three main actions toward a successful poster presentation.
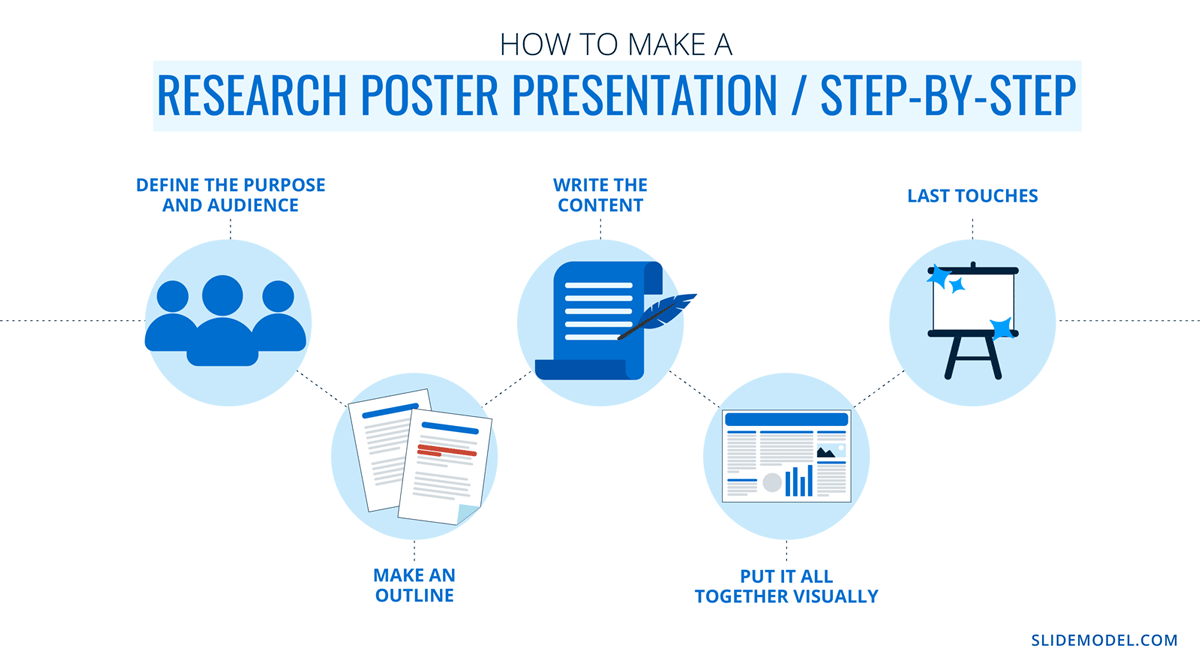
The section below will take you on a step-by-step journey to create your next poster presentation.
Step 1: Define the purpose and audience of your poster presentation
Before making a poster presentation design, you’ll need to plan first. Here are some questions to answer at this point:
- Are they in your field?
- Do they know about your research topic?
- What can they get from your research?
- Will you print it?
- Is it for a virtual conference?
Step 2: Make an outline
With a clear purpose and strategy, it’s time to collect the most important information from your research paper, analysis, or documentation. Make a content dump and then select the most interesting information. Use the content to draft an outline.
Outlines help formulate the overall structure better than going straight into designing the poster. Mimic the standard poster structure in your outline using section headlines as separators. Go further and separate the content into the columns they’ll be placed in.
Step 3: Write the content
Write or rewrite the content for the sections in your poster presentation. Use the text in your research paper as a base, but summarize it to be more succinct in what you share.
Don’t forget to write a catchy title that presents the problem and your findings in a clear way. Likewise, craft the headlines for the sections in a similar tone as the title, creating consistency in the message. Include subtle transitions between sections to help follow the flow of information in order.
Avoid copying/pasting entire sections of the research paper on which the poster is based. Opt for the storytelling approach, so the delivered message results are interesting for your audience.
Step 4: Put it all together visually
This entire guide on how to design a research poster presentation is the perfect resource to help you with this step. Follow all the tips and guidelines and have an unforgettable poster presentation.
Moving on, here’s how to design a research poster presentation with PowerPoint Templates . Open a new project and size it to the standard 48 x 36 inches. Using the outline, map out the sections on the empty canvas. Add a text box for each title, headline, and body text. Piece by piece, add the content into their corresponding text box.
Transform the text information visually, make bullet points, and place the content in tables and timelines. Make your text visual to avoid chunky text blocks that no one will have time to read. Make sure all text sizes are coherent for all headings, body texts, image captions, etc. Double-check for spacing and text box formatting.
Next, add or create data visualizations, images, or diagrams. Align everything into columns and sections, making sure there’s no overflow. Add captions and legends to the visualizations, and check the color contrast with colleagues and friends. Ask for feedback and progress to the last step.
Step 5: Last touches
Time to check the final touches on your poster presentation design. Here’s a checklist to help finalize your research poster before sending it to printers or the virtual summit rep.
- Check the resolution of all visual elements in your poster design. Zoom to 100 or 200% to see if the images pixelate. Avoid this problem by using vector design elements and high-resolution images.
- Ensure that charts and graphs are easy to read and don’t look crowded.
- Analyze the visual hierarchy. Is there a visual flow through the title, introduction, data, and conclusion?
- Take a step back and check if it’s legible from a distance. Is there enough white space for the content to breathe?
- Does the design look inviting and interesting?
An often neglected topic arises when we need to print our designs for any exhibition purpose. Since A0 is a hard-to-manage format for most printers, these poster presentations result in heftier charges for the user. Instead, you can opt to work your design in two A1 sheets, which also becomes more manageable for transportation. Create seamless borders for the section on which the poster sheets should meet, or work with a white background.
Paper weight options should be over 200 gsm to avoid unwanted damage during the printing process due to heavy ink usage. If possible, laminate your print or stick it to photographic paper – this shall protect your work from spills.
Finally, always run a test print. Gray tints may not be printed as clearly as you see them on screen (this is due to the RGB to CMYK conversion process). Other differences can be appreciated when working with ink jet plotters vs. laser printers. Give yourself enough room to maneuver last-minute design changes.
Presenting a research poster is a big step in the poster presentation cycle. Your poster presentation might or might not be judged by faculty or peers. But knowing what judges look for will help you prepare for the design and oral presentation, regardless of whether you receive a grade for your work or if it’s business related. Likewise, the same principles apply when presenting at an in-person or virtual summit.
The opening statement
Part of presenting a research poster is welcoming the viewer to your small personal area in the sea of poster presentations. You’ll need an opening statement to pitch your research poster and get the viewers’ attention.
Draft a 2 to 3-sentence pitch that covers the most important points:
- What the research is
- Why was it conducted
- What the results say
From that opening statement, you’re ready to continue with the oral presentation for the benefit of your attendees.
The oral presentation
During the oral presentation, share the information on the poster while conversing with the interested public. Practice many times before the event. Structure the oral presentation as conversation points, and use the poster’s visual flow as support. Make eye contact with your audience as you speak, but don’t make them uncomfortable.
Pro Tip: In a conference or summit, if people show up to your poster area after you’ve started presenting it to another group, finish and then address the new visitors.
QA Sessions
When you’ve finished the oral presentation, offer the audience a chance to ask questions. You can tell them before starting the presentation that you’ll be holding a QA session at the end. Doing so will prevent interruptions as you’re speaking.
If presenting to one or two people, be flexible and answer questions as you review all the sections on your poster.
Supplemental Material
If your audience is interested in learning more, you can offer another content type, further imprinting the information in their minds. Some ideas include; printed copies of your research paper, links to a website, a digital experience of your poster, a thesis PDF, or data spreadsheets.
Your audience will want to contact you for further conversations; include contact details in your supplemental material. If you don’t offer anything else, at least have business cards.
Even though conferences have changed, the research poster’s importance hasn’t diminished. Now, instead of simply creating a printed poster presentation, you can also make it for digital platforms. The final output will depend on the conference and its requirements.
This guide covered all the essential information you need to know for creating impactful poster presentations, from design, structure and layout tips to oral presentation techniques to engage your audience better .
Before your next poster session, bookmark and review this guide to help you design a winning poster presentation every time.

Like this article? Please share
Cool Presentation Ideas, Design, Design Inspiration Filed under Design
Related Articles

Filed under Design • January 11th, 2024
How to Use Figma for Presentations
The powerful UI/UX prototyping software can also help us to craft high-end presentation slides. Learn how to use Figma as a presentation software here!

Filed under Design • December 28th, 2023
Multimedia Presentation: Insights & Techniques to Maximize Engagement
Harnessing the power of multimedia presentation is vital for speakers nowadays. Join us to discover how you can utilize these strategies in your work.

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • December 15th, 2023
How to Delete a Text Box in Google Slides
Discover how to delete a text box in Google Slides in just a couple of clicks. Step-by-step guide with images.
Leave a Reply

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
First is a two part set of videos that walks you through organizing a presentation. Part 1 - Creating an Introduction for a 10-15 Minute Scientfic Presentation. Part 2 - Creating the Body of a 10-15 Minute Presentation: Design/Methods; Data Results, Conclusions. Two additional videos should prove useful: Designing PowerPoint Slides for a ...
Related Articles. This guide provides a 4-step process for making a good scientific presentation: outlining the scientific narrative, preparing slide outlines, constructing slides, and practicing the talk. We give advice on how to make effective slides, including tips for text, graphics, and equations, and how to use rehearsals of your talk to ...
7 Appearance: if you look good, you'll feel good, which will help you give a great speech. 8 Pauses: they give the audience time to think, and help them engage. 9 Body language: use ...
Here are 10 tips to help you present your scientific work and leave the audience wanting more. 1. Set the stage. Get your equipment ready and run through your slides if possible (use the "speaker ready" room if one is available). If you've never been in the venue, try getting there early and walk the room.
Tip 3: Deliver your talk with intention. Tip 4: Be adaptable and willing to adjust your presentation. Tip 5: Conclude your talk and manage questions confidently. Concluding thoughts. Other sources to help you give a good scientific presentation. Frequently Asked Questions about giving scientific presentations.
Below is the summary of how to give an engaging talk that will earn respect from your scientific community. Step 1. Draft Presentation Outline. Create a presentation outline that clearly highlights the main point of your research. Make sure to start your talk outline with ideas to engage your audience and end your talk with a clear take-home ...
Delivery. It is important to dress appropriately, stand up straight, and project your voice towards the back of the room. Practise using a microphone, or any other presentation aids, in advance. If you don't have your own presenting style, think of the style of inspirational scientific speakers you have seen and imitate it.
A Rube-Goldberg sort of cartoon is great for explaining complex ideas. Use humor if possible. A joke or two in your presentation spices things up and relaxes the audience. It emphasizes the casual nature of the talk. I am always amazed how even a really lame joke will get a good laugh in a science talk. Be personable in taking questions ...
Rule 3: Only Talk When You Have Something to Say. Do not be overzealous about what you think you will have available to present when the time comes. Research never goes as fast as you would like. Remember the audience's time is precious and should not be abused by presentation of uninteresting preliminary material.
The result highlighted in your title will help you to focus your talk so that the solutions you present lead to this overarching result. Here is the general pattern: 1. Present the first part of ...
They want to get something out of it. The thing about an audience is that you are there for them, and not the other way around. 2. Practice, practice, practice. To make your ideas stand out and stick, you do need to practice and experiment with both the content of your presentation and your delivery.
An easy way to do this is by using the 5×5 rule. This means using no more than 5 bullet points per slide, with no more than 5 words per bullet point. It is also good to break up the text-heavy slides with ones including diagrams or graphs. This can also help to convey your results in a more visual and easy-to-understand way.
Are you giving a presentation at an upcoming conference, but not sure where to begin? Julian Rayner from the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, UK, has plenty ...
Step 1: Understand the Goal of Your Talk. Many speakers assume that giving a seminar is about simply presenting your data to an audience. It's not! Your job is to give the audience information and make sure that they understand your message. This is not the same as just standing up and talking.
Tip No. 2: Get the details right. Once you've settled on a broad theme, the next step is homing in on the precise details that are necessary for your audience to understand your main points. As Grice recommends: Present nothing more and nothing less. Figuring this out—again—boils down to thinking carefully about who you're communicating ...
Below we propose a quick framework for creating a compelling scientific presentation in PowerPoint (+ some helpful templates!). 1. Open with a Research Question. Here's how to start a scientific presentation with ease: share your research question. On the first slide, briefly recap how your thought process went.
peers, expanding your science program. But all these benefits hinge on giving good presentations. Giving bad presentations is worse than being invisible. I, along with everyone else in the audience, want you to inform and entertain us. However, a good talk is not easy to deliver, and it is rare to see a talk that could not be improved.
Practice, practice, practice. Perhaps the most important tip is to go through your presentation out loud before delivering it on the day. 'People spend a lot of time writing their presentation ...
Guidelines for Scientific Presentations Know Your Audience There are many different contexts in which you might be asked to give a scientific presentation: department colloquium, conference presentation, outreach at a public library or school, for a funding agency (to name a few). The content and tone of your presentation will significantly
Ways to give an effective seminar about your research project. Grab your audience's attention by using slides as a roadmap and focusing on your role as a presenter, recommends Ananya Sen. By ...
This video provides concise and effective tips spanning all relevant areas to deliver engaging scientific presentations. You will strengthen your skills in preparing, practicing and delivering presentations at both physical and virtual conferences and seminars. Best practices for structuring presentations and elements to include and those to ...
scientific knowledge. Remember that most of the people in your audience will know less than you about your subject. PARTS OF A PRESENTATION Your presentation will be far more interesting and appreciated if you consider the following instructions: YOUR SLIDES o Give a short general introduction for those who are not exactly from your field of ...
A sommelier, a costume designer, and a marathon runner offer their best advice for giving a great presentation.
The current warming trend is different because it is clearly the result of human activities since the mid-1800s, and is proceeding at a rate not seen over many recent millennia. 1 It is undeniable that human activities have produced the atmospheric gases that have trapped more of the Sun's energy in the Earth system. This extra energy has warmed the atmosphere, ocean, and land, and ...
Scientific/Academic Conference Poster Presentation. Research poster presentations printed and mounted on a board look like the one in the image below. The presenter stands to the side, ready to share the information with visitors as they walk up to the panels. Example of Scientific / Academic Conference Poster Presentation