- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » References in Research – Types, Examples and Writing Guide

References in Research – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

References in Research
Definition:
References in research are a list of sources that a researcher has consulted or cited while conducting their study. They are an essential component of any academic work, including research papers, theses, dissertations, and other scholarly publications.
Types of References
There are several types of references used in research, and the type of reference depends on the source of information being cited. The most common types of references include:
References to books typically include the author’s name, title of the book, publisher, publication date, and place of publication.
Example: Smith, J. (2018). The Art of Writing. Penguin Books.
Journal Articles
References to journal articles usually include the author’s name, title of the article, name of the journal, volume and issue number, page numbers, and publication date.
Example: Johnson, T. (2021). The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health. Journal of Psychology, 32(4), 87-94.
Web sources
References to web sources should include the author or organization responsible for the content, the title of the page, the URL, and the date accessed.
Example: World Health Organization. (2020). Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) advice for the public. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease/novel-coronavirus-2019/advice-for-public
Conference Proceedings
References to conference proceedings should include the author’s name, title of the paper, name of the conference, location of the conference, date of the conference, and page numbers.
Example: Chen, S., & Li, J. (2019). The Future of AI in Education. Proceedings of the International Conference on Educational Technology, Beijing, China, July 15-17, pp. 67-78.
References to reports typically include the author or organization responsible for the report, title of the report, publication date, and publisher.
Example: United Nations. (2020). The Sustainable Development Goals Report. United Nations.
Formats of References
Some common Formates of References with their examples are as follows:
APA (American Psychological Association) Style
The APA (American Psychological Association) Style has specific guidelines for formatting references used in academic papers, articles, and books. Here are the different reference formats in APA style with examples:
Author, A. A. (Year of publication). Title of book. Publisher.
Example : Smith, J. K. (2005). The psychology of social interaction. Wiley-Blackwell.
Journal Article
Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (Year of publication). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number(issue number), page numbers.
Example : Brown, L. M., Keating, J. G., & Jones, S. M. (2012). The role of social support in coping with stress among African American adolescents. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 22(1), 218-233.
Author, A. A. (Year of publication or last update). Title of page. Website name. URL.
Example : Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020, December 11). COVID-19: How to protect yourself and others. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html
Magazine article
Author, A. A. (Year, Month Day of publication). Title of article. Title of Magazine, volume number(issue number), page numbers.
Example : Smith, M. (2019, March 11). The power of positive thinking. Psychology Today, 52(3), 60-65.
Newspaper article:
Author, A. A. (Year, Month Day of publication). Title of article. Title of Newspaper, page numbers.
Example: Johnson, B. (2021, February 15). New study shows benefits of exercise on mental health. The New York Times, A8.
Edited book
Editor, E. E. (Ed.). (Year of publication). Title of book. Publisher.
Example : Thompson, J. P. (Ed.). (2014). Social work in the 21st century. Sage Publications.
Chapter in an edited book:
Author, A. A. (Year of publication). Title of chapter. In E. E. Editor (Ed.), Title of book (pp. page numbers). Publisher.
Example : Johnson, K. S. (2018). The future of social work: Challenges and opportunities. In J. P. Thompson (Ed.), Social work in the 21st century (pp. 105-118). Sage Publications.
MLA (Modern Language Association) Style
The MLA (Modern Language Association) Style is a widely used style for writing academic papers and essays in the humanities. Here are the different reference formats in MLA style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Book. Publisher, Publication year.
Example : Smith, John. The Psychology of Social Interaction. Wiley-Blackwell, 2005.
Journal article
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal, volume number, issue number, Publication year, page numbers.
Example : Brown, Laura M., et al. “The Role of Social Support in Coping with Stress among African American Adolescents.” Journal of Research on Adolescence, vol. 22, no. 1, 2012, pp. 218-233.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Webpage.” Website Name, Publication date, URL.
Example : Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “COVID-19: How to Protect Yourself and Others.” CDC, 11 Dec. 2020, https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Magazine, Publication date, page numbers.
Example : Smith, Mary. “The Power of Positive Thinking.” Psychology Today, Mar. 2019, pp. 60-65.
Newspaper article
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Newspaper, Publication date, page numbers.
Example : Johnson, Bob. “New Study Shows Benefits of Exercise on Mental Health.” The New York Times, 15 Feb. 2021, p. A8.
Editor’s Last name, First name, editor. Title of Book. Publisher, Publication year.
Example : Thompson, John P., editor. Social Work in the 21st Century. Sage Publications, 2014.
Chapter in an edited book
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Chapter.” Title of Book, edited by Editor’s First Name Last name, Publisher, Publication year, page numbers.
Example : Johnson, Karen S. “The Future of Social Work: Challenges and Opportunities.” Social Work in the 21st Century, edited by John P. Thompson, Sage Publications, 2014, pp. 105-118.
Chicago Manual of Style
The Chicago Manual of Style is a widely used style for writing academic papers, dissertations, and books in the humanities and social sciences. Here are the different reference formats in Chicago style:
Example : Smith, John K. The Psychology of Social Interaction. Wiley-Blackwell, 2005.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal volume number, no. issue number (Publication year): page numbers.
Example : Brown, Laura M., John G. Keating, and Sarah M. Jones. “The Role of Social Support in Coping with Stress among African American Adolescents.” Journal of Research on Adolescence 22, no. 1 (2012): 218-233.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Webpage.” Website Name. Publication date. URL.
Example : Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “COVID-19: How to Protect Yourself and Others.” CDC. December 11, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Magazine, Publication date.
Example : Smith, Mary. “The Power of Positive Thinking.” Psychology Today, March 2019.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Newspaper, Publication date.
Example : Johnson, Bob. “New Study Shows Benefits of Exercise on Mental Health.” The New York Times, February 15, 2021.
Example : Thompson, John P., ed. Social Work in the 21st Century. Sage Publications, 2014.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Chapter.” In Title of Book, edited by Editor’s First Name Last Name, page numbers. Publisher, Publication year.
Example : Johnson, Karen S. “The Future of Social Work: Challenges and Opportunities.” In Social Work in the 21st Century, edited by John P. Thompson, 105-118. Sage Publications, 2014.
Harvard Style
The Harvard Style, also known as the Author-Date System, is a widely used style for writing academic papers and essays in the social sciences. Here are the different reference formats in Harvard Style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of publication. Title of Book. Place of publication: Publisher.
Example : Smith, John. 2005. The Psychology of Social Interaction. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of publication. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal volume number (issue number): page numbers.
Example: Brown, Laura M., John G. Keating, and Sarah M. Jones. 2012. “The Role of Social Support in Coping with Stress among African American Adolescents.” Journal of Research on Adolescence 22 (1): 218-233.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of publication. “Title of Webpage.” Website Name. URL. Accessed date.
Example : Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2020. “COVID-19: How to Protect Yourself and Others.” CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html. Accessed April 1, 2023.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of publication. “Title of Article.” Title of Magazine, month and date of publication.
Example : Smith, Mary. 2019. “The Power of Positive Thinking.” Psychology Today, March 2019.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of publication. “Title of Article.” Title of Newspaper, month and date of publication.
Example : Johnson, Bob. 2021. “New Study Shows Benefits of Exercise on Mental Health.” The New York Times, February 15, 2021.
Editor’s Last name, First name, ed. Year of publication. Title of Book. Place of publication: Publisher.
Example : Thompson, John P., ed. 2014. Social Work in the 21st Century. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of publication. “Title of Chapter.” In Title of Book, edited by Editor’s First Name Last Name, page numbers. Place of publication: Publisher.
Example : Johnson, Karen S. 2014. “The Future of Social Work: Challenges and Opportunities.” In Social Work in the 21st Century, edited by John P. Thompson, 105-118. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Vancouver Style
The Vancouver Style, also known as the Uniform Requirements for Manuscripts Submitted to Biomedical Journals, is a widely used style for writing academic papers in the biomedical sciences. Here are the different reference formats in Vancouver Style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Book. Edition number. Place of publication: Publisher; Year of publication.
Example : Smith, John K. The Psychology of Social Interaction. 2nd ed. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell; 2005.
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Article. Abbreviated Journal Title. Year of publication; volume number(issue number):page numbers.
Example : Brown LM, Keating JG, Jones SM. The Role of Social Support in Coping with Stress among African American Adolescents. J Res Adolesc. 2012;22(1):218-233.
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Webpage. Website Name [Internet]. Publication date. [cited date]. Available from: URL.
Example : Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19: How to Protect Yourself and Others [Internet]. 2020 Dec 11. [cited 2023 Apr 1]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html.
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Article. Title of Magazine. Year of publication; month and day of publication:page numbers.
Example : Smith M. The Power of Positive Thinking. Psychology Today. 2019 Mar 1:32-35.
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Article. Title of Newspaper. Year of publication; month and day of publication:page numbers.
Example : Johnson B. New Study Shows Benefits of Exercise on Mental Health. The New York Times. 2021 Feb 15:A4.
Editor’s Last name, First name, editor. Title of Book. Edition number. Place of publication: Publisher; Year of publication.
Example: Thompson JP, editor. Social Work in the 21st Century. 1st ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications; 2014.
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Chapter. In: Editor’s Last name, First name, editor. Title of Book. Edition number. Place of publication: Publisher; Year of publication. page numbers.
Example : Johnson KS. The Future of Social Work: Challenges and Opportunities. In: Thompson JP, editor. Social Work in the 21st Century. 1st ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications; 2014. p. 105-118.
Turabian Style
Turabian style is a variation of the Chicago style used in academic writing, particularly in the fields of history and humanities. Here are the different reference formats in Turabian style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Book. Place of publication: Publisher, Year of publication.
Example : Smith, John K. The Psychology of Social Interaction. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell, 2005.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal volume number, no. issue number (Year of publication): page numbers.
Example : Brown, LM, Keating, JG, Jones, SM. “The Role of Social Support in Coping with Stress among African American Adolescents.” J Res Adolesc 22, no. 1 (2012): 218-233.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Webpage.” Name of Website. Publication date. Accessed date. URL.
Example : Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “COVID-19: How to Protect Yourself and Others.” CDC. December 11, 2020. Accessed April 1, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Magazine, Month Day, Year of publication, page numbers.
Example : Smith, M. “The Power of Positive Thinking.” Psychology Today, March 1, 2019, 32-35.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Title of Newspaper, Month Day, Year of publication.
Example : Johnson, B. “New Study Shows Benefits of Exercise on Mental Health.” The New York Times, February 15, 2021.
Editor’s Last name, First name, ed. Title of Book. Place of publication: Publisher, Year of publication.
Example : Thompson, JP, ed. Social Work in the 21st Century. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2014.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Chapter.” In Title of Book, edited by Editor’s Last name, First name, page numbers. Place of publication: Publisher, Year of publication.
Example : Johnson, KS. “The Future of Social Work: Challenges and Opportunities.” In Social Work in the 21st Century, edited by Thompson, JP, 105-118. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2014.
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) Style
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) style is commonly used in engineering, computer science, and other technical fields. Here are the different reference formats in IEEE style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Book Title. Place of Publication: Publisher, Year of publication.
Example : Oppenheim, A. V., & Schafer, R. W. Discrete-Time Signal Processing. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2010.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Article.” Abbreviated Journal Title, vol. number, no. issue number, pp. page numbers, Month year of publication.
Example: Shannon, C. E. “A Mathematical Theory of Communication.” Bell System Technical Journal, vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 379-423, July 1948.
Conference paper
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Paper.” In Title of Conference Proceedings, Place of Conference, Date of Conference, pp. page numbers, Year of publication.
Example: Gupta, S., & Kumar, P. “An Improved System of Linear Discriminant Analysis for Face Recognition.” In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Science and Network Technology, Harbin, China, Dec. 2011, pp. 144-147.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Webpage.” Name of Website. Date of publication or last update. Accessed date. URL.
Example : National Aeronautics and Space Administration. “Apollo 11.” NASA. July 20, 1969. Accessed April 1, 2023. https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/apollo/apollo11.html.
Technical report
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Report.” Name of Institution or Organization, Report number, Year of publication.
Example : Smith, J. R. “Development of a New Solar Panel Technology.” National Renewable Energy Laboratory, NREL/TP-6A20-51645, 2011.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Patent.” Patent number, Issue date.
Example : Suzuki, H. “Method of Producing Carbon Nanotubes.” US Patent 7,151,019, December 19, 2006.
Standard Title. Standard number, Publication date.
Example : IEEE Standard for Floating-Point Arithmetic. IEEE Std 754-2008, August 29, 2008
ACS (American Chemical Society) Style
ACS (American Chemical Society) style is commonly used in chemistry and related fields. Here are the different reference formats in ACS style:
Author’s Last name, First name; Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Article. Abbreviated Journal Title Year, Volume, Page Numbers.
Example : Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Cui, Y.; Ma, Y. Facile Preparation of Fe3O4/graphene Composites Using a Hydrothermal Method for High-Performance Lithium Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2715-2721.
Author’s Last name, First name. Book Title; Publisher: Place of Publication, Year of Publication.
Example : Carey, F. A. Organic Chemistry; McGraw-Hill: New York, 2008.
Author’s Last name, First name. Chapter Title. In Book Title; Editor’s Last name, First name, Ed.; Publisher: Place of Publication, Year of Publication; Volume number, Chapter number, Page Numbers.
Example : Grossman, R. B. Analytical Chemistry of Aerosols. In Aerosol Measurement: Principles, Techniques, and Applications; Baron, P. A.; Willeke, K., Eds.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, 2001; Chapter 10, pp 395-424.
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Webpage. Website Name, URL (accessed date).
Example : National Institute of Standards and Technology. Atomic Spectra Database. https://www.nist.gov/pml/atomic-spectra-database (accessed April 1, 2023).
Author’s Last name, First name. Patent Number. Patent Date.
Example : Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W. US Patent 9,999,999, December 31, 2022.
Author’s Last name, First name; Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Article. In Title of Conference Proceedings, Publisher: Place of Publication, Year of Publication; Volume Number, Page Numbers.
Example : Jia, H.; Xu, S.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Huang, X. Fast Adsorption of Organic Pollutants by Graphene Oxide. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, 2017; Volume 1, pp 223-228.
AMA (American Medical Association) Style
AMA (American Medical Association) style is commonly used in medical and scientific fields. Here are the different reference formats in AMA style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Article Title. Journal Abbreviation. Year; Volume(Issue):Page Numbers.
Example : Jones, R. A.; Smith, B. C. The Role of Vitamin D in Maintaining Bone Health. JAMA. 2019;321(17):1765-1773.
Author’s Last name, First name. Book Title. Edition number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year.
Example : Guyton, A. C.; Hall, J. E. Textbook of Medical Physiology. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 2015.
Author’s Last name, First name. Chapter Title. In: Editor’s Last name, First name, ed. Book Title. Edition number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year: Page Numbers.
Example: Rajakumar, K. Vitamin D and Bone Health. In: Holick, M. F., ed. Vitamin D: Physiology, Molecular Biology, and Clinical Applications. 2nd ed. New York, NY: Springer; 2010:211-222.
Author’s Last name, First name. Webpage Title. Website Name. URL. Published date. Updated date. Accessed date.
Example : National Cancer Institute. Breast Cancer Prevention (PDQ®)–Patient Version. National Cancer Institute. https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/breast-prevention-pdq. Published October 11, 2022. Accessed April 1, 2023.
Author’s Last name, First name. Conference presentation title. In: Conference Title; Conference Date; Place of Conference.
Example : Smith, J. R. Vitamin D and Bone Health: A Meta-Analysis. In: Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research; September 20-23, 2022; San Diego, CA.
Thesis or dissertation
Author’s Last name, First name. Title of Thesis or Dissertation. Degree level [Doctoral dissertation or Master’s thesis]. University Name; Year.
Example : Wilson, S. A. The Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on Bone Health in Postmenopausal Women [Doctoral dissertation]. University of California, Los Angeles; 2018.
ASCE (American Society of Civil Engineers) Style
The ASCE (American Society of Civil Engineers) style is commonly used in civil engineering fields. Here are the different reference formats in ASCE style:
Author’s Last name, First name. “Article Title.” Journal Title, volume number, issue number (year): page numbers. DOI or URL (if available).
Example : Smith, J. R. “Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Sustainable Drainage Systems in Urban Areas.” Journal of Environmental Engineering, vol. 146, no. 3 (2020): 04020010. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0001668.
Example : McCuen, R. H. Hydrologic Analysis and Design. 4th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education; 2013.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Chapter Title.” In: Editor’s Last name, First name, ed. Book Title. Edition number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year: page numbers.
Example : Maidment, D. R. “Floodplain Management in the United States.” In: Shroder, J. F., ed. Treatise on Geomorphology. San Diego, CA: Academic Press; 2013: 447-460.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Paper Title.” In: Conference Title; Conference Date; Location. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year: page numbers.
Example: Smith, J. R. “Sustainable Drainage Systems for Urban Areas.” In: Proceedings of the ASCE International Conference on Sustainable Infrastructure; November 6-9, 2019; Los Angeles, CA. Reston, VA: American Society of Civil Engineers; 2019: 156-163.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Report Title.” Report number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year.
Example : U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. “Hurricane Sandy Coastal Risk Reduction Program, New York and New Jersey.” Report No. P-15-001. Washington, DC: U.S. Army Corps of Engineers; 2015.
CSE (Council of Science Editors) Style
The CSE (Council of Science Editors) style is commonly used in the scientific and medical fields. Here are the different reference formats in CSE style:
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. “Article Title.” Journal Title. Year;Volume(Issue):Page numbers.
Example : Smith, J.R. “Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Sustainable Drainage Systems in Urban Areas.” Journal of Environmental Engineering. 2020;146(3):04020010.
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. Book Title. Edition number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year.
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. “Chapter Title.” In: Editor’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial., ed. Book Title. Edition number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year:Page numbers.
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. “Paper Title.” In: Conference Title; Conference Date; Location. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year.
Example : Smith, J.R. “Sustainable Drainage Systems for Urban Areas.” In: Proceedings of the ASCE International Conference on Sustainable Infrastructure; November 6-9, 2019; Los Angeles, CA. Reston, VA: American Society of Civil Engineers; 2019.
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. “Report Title.” Report number. Place of Publication: Publisher; Year.
Bluebook Style
The Bluebook style is commonly used in the legal field for citing legal documents and sources. Here are the different reference formats in Bluebook style:
Case citation
Case name, volume source page (Court year).
Example : Brown v. Board of Education, 347 U.S. 483 (1954).
Statute citation
Name of Act, volume source § section number (year).
Example : Clean Air Act, 42 U.S.C. § 7401 (1963).
Regulation citation
Name of regulation, volume source § section number (year).
Example: Clean Air Act, 40 C.F.R. § 52.01 (2019).
Book citation
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. Book Title. Edition number (if applicable). Place of Publication: Publisher; Year.
Example: Smith, J.R. Legal Writing and Analysis. 3rd ed. New York, NY: Aspen Publishers; 2015.
Journal article citation
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. “Article Title.” Journal Title. Volume number (year): first page-last page.
Example: Garcia, C. “The Right to Counsel: An International Comparison.” International Journal of Legal Information. 43 (2015): 63-94.
Website citation
Author’s Last name, First Initial. Middle Initial. “Page Title.” Website Title. URL (accessed month day, year).
Example : United Nations. “Universal Declaration of Human Rights.” United Nations. https://www.un.org/en/universal-declaration-human-rights/ (accessed January 3, 2023).
Oxford Style
The Oxford style, also known as the Oxford referencing system or the documentary-note citation system, is commonly used in the humanities, including literature, history, and philosophy. Here are the different reference formats in Oxford style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Book Title. Place of Publication: Publisher, Year of Publication.
Example : Smith, John. The Art of Writing. New York: Penguin, 2020.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Article Title.” Journal Title volume, no. issue (year): page range.
Example: Garcia, Carlos. “The Role of Ethics in Philosophy.” Philosophy Today 67, no. 3 (2019): 53-68.
Chapter in an edited book citation
Author’s Last name, First name. “Chapter Title.” In Book Title, edited by Editor’s Name, page range. Place of Publication: Publisher, Year of Publication.
Example : Lee, Mary. “Feminism in the 21st Century.” In The Oxford Handbook of Feminism, edited by Jane Smith, 51-69. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2018.
Author’s Last name, First name. “Page Title.” Website Title. URL (accessed day month year).
Example : Jones, David. “The Importance of Learning Languages.” Oxford Language Center. https://www.oxfordlanguagecenter.com/importance-of-learning-languages/ (accessed 3 January 2023).
Dissertation or thesis citation
Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of Dissertation/Thesis.” PhD diss., University Name, Year of Publication.
Example : Brown, Susan. “The Art of Storytelling in American Literature.” PhD diss., University of Oxford, 2020.
Newspaper article citation
Author’s Last name, First name. “Article Title.” Newspaper Title, Month Day, Year.
Example : Robinson, Andrew. “New Developments in Climate Change Research.” The Guardian, September 15, 2022.
AAA (American Anthropological Association) Style
The American Anthropological Association (AAA) style is commonly used in anthropology research papers and journals. Here are the different reference formats in AAA style:
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. Book Title. Place of Publication: Publisher.
Example : Smith, John. 2019. The Anthropology of Food. New York: Routledge.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. “Article Title.” Journal Title volume, no. issue: page range.
Example : Garcia, Carlos. 2021. “The Role of Ethics in Anthropology.” American Anthropologist 123, no. 2: 237-251.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. “Chapter Title.” In Book Title, edited by Editor’s Name, page range. Place of Publication: Publisher.
Example: Lee, Mary. 2018. “Feminism in Anthropology.” In The Oxford Handbook of Feminism, edited by Jane Smith, 51-69. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. “Page Title.” Website Title. URL (accessed day month year).
Example : Jones, David. 2020. “The Importance of Learning Languages.” Oxford Language Center. https://www.oxfordlanguagecenter.com/importance-of-learning-languages/ (accessed January 3, 2023).
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. “Title of Dissertation/Thesis.” PhD diss., University Name.
Example : Brown, Susan. 2022. “The Art of Storytelling in Anthropology.” PhD diss., University of California, Berkeley.
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. “Article Title.” Newspaper Title, Month Day.
Example : Robinson, Andrew. 2021. “New Developments in Anthropology Research.” The Guardian, September 15.
AIP (American Institute of Physics) Style
The American Institute of Physics (AIP) style is commonly used in physics research papers and journals. Here are the different reference formats in AIP style:
Example : Johnson, S. D. 2021. “Quantum Computing and Information.” Journal of Applied Physics 129, no. 4: 043102.
Example : Feynman, Richard. 2018. The Feynman Lectures on Physics. New York: Basic Books.
Example : Jones, David. 2020. “The Future of Quantum Computing.” In The Handbook of Physics, edited by John Smith, 125-136. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Conference proceedings citation
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. “Title of Paper.” Proceedings of Conference Name, date and location: page range. Place of Publication: Publisher.
Example : Chen, Wei. 2019. “The Applications of Nanotechnology in Solar Cells.” Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Nanotechnology, July 15-17, Tokyo, Japan: 224-229. New York: AIP Publishing.
Example : American Institute of Physics. 2022. “About AIP Publishing.” AIP Publishing. https://publishing.aip.org/about-aip-publishing/ (accessed January 3, 2023).
Patent citation
Author’s Last name, First name. Year of Publication. Patent Number.
Example : Smith, John. 2018. US Patent 9,873,644.
References Writing Guide
Here are some general guidelines for writing references:
- Follow the citation style guidelines: Different disciplines and journals may require different citation styles (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). It is important to follow the specific guidelines for the citation style required.
- Include all necessary information : Each citation should include enough information for readers to locate the source. For example, a journal article citation should include the author(s), title of the article, journal title, volume number, issue number, page numbers, and publication year.
- Use proper formatting: Citation styles typically have specific formatting requirements for different types of sources. Make sure to follow the proper formatting for each citation.
- Order citations alphabetically: If listing multiple sources, they should be listed alphabetically by the author’s last name.
- Be consistent: Use the same citation style throughout the entire paper or project.
- Check for accuracy: Double-check all citations to ensure accuracy, including correct spelling of author names and publication information.
- Use reputable sources: When selecting sources to cite, choose reputable and authoritative sources. Avoid sources that are biased or unreliable.
- Include all sources: Make sure to include all sources used in the research, including those that were not directly quoted but still informed the work.
- Use online tools : There are online tools available (e.g., citation generators) that can help with formatting and organizing references.
Purpose of References in Research
References in research serve several purposes:
- To give credit to the original authors or sources of information used in the research. It is important to acknowledge the work of others and avoid plagiarism.
- To provide evidence for the claims made in the research. References can support the arguments, hypotheses, or conclusions presented in the research by citing relevant studies, data, or theories.
- To allow readers to find and verify the sources used in the research. References provide the necessary information for readers to locate and access the sources cited in the research, which allows them to evaluate the quality and reliability of the information presented.
- To situate the research within the broader context of the field. References can show how the research builds on or contributes to the existing body of knowledge, and can help readers to identify gaps in the literature that the research seeks to address.
Importance of References in Research
References play an important role in research for several reasons:
- Credibility : By citing authoritative sources, references lend credibility to the research and its claims. They provide evidence that the research is based on a sound foundation of knowledge and has been carefully researched.
- Avoidance of Plagiarism : References help researchers avoid plagiarism by giving credit to the original authors or sources of information. This is important for ethical reasons and also to avoid legal repercussions.
- Reproducibility : References allow others to reproduce the research by providing detailed information on the sources used. This is important for verification of the research and for others to build on the work.
- Context : References provide context for the research by situating it within the broader body of knowledge in the field. They help researchers to understand where their work fits in and how it builds on or contributes to existing knowledge.
- Evaluation : References provide a means for others to evaluate the research by allowing them to assess the quality and reliability of the sources used.
Advantages of References in Research
There are several advantages of including references in research:
- Acknowledgment of Sources: Including references gives credit to the authors or sources of information used in the research. This is important to acknowledge the original work and avoid plagiarism.
- Evidence and Support : References can provide evidence to support the arguments, hypotheses, or conclusions presented in the research. This can add credibility and strength to the research.
- Reproducibility : References provide the necessary information for others to reproduce the research. This is important for the verification of the research and for others to build on the work.
- Context : References can help to situate the research within the broader body of knowledge in the field. This helps researchers to understand where their work fits in and how it builds on or contributes to existing knowledge.
- Evaluation : Including references allows others to evaluate the research by providing a means to assess the quality and reliability of the sources used.
- Ongoing Conversation: References allow researchers to engage in ongoing conversations and debates within their fields. They can show how the research builds on or contributes to the existing body of knowledge.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...

CMAT6820: Action Research: Citing in APA format (7th edition)
- Introduction
- Finding Books and Media
- Finding Articles
- When the article isn't available...
- Citing in APA format (7th edition)
- Writing your Paper
Buy one of these!
Sample citations
The attached document shows sample citations in APA (7th). The second page shows the layout for a reference list. Please note the spacing.
- APA Citation -7th ed.
Before you turn in your paper!
Before you turn in your paper compare the Reference List with the content of the paper.
- Make sure that ALL the items in the Reference list are cited in the paper, and
- ALL the items cited in the paper are in the Reference list.
All citations in the text and the Reference list should match.
General format for APA citations
Author's name: Last name, first initial, e.g. Banks, J. A.
Date of publication: Usually just the year in parentheses, followed by a period, e.g. (2008). When including additional information for newspapers, etc., start with the year, e.g. (2009, July 16). If no date is available, use (n.d.).
Title of article: Capitalize first word of title and subtitle. Period at the end, e.g. Conjuring cut scores: How it distorts our picture of student achievement.
Title of book: Italicize and capitalize first word of title and subtitle. Period at the end, e.g. Improving multicultural education: Lessons from the intergroup education movement.
Journal information: Italicize and capitalize all important words in the title. Italicize volume number. Issue number goes in parentheses (not italicized). Include beginning and ending page numbers of journal article, e.g. Journal of Research in Reading , 31 (4), 20-28 .
With the exception of web site information or DOI's (Digital Object Identifier) all citations should end with a period.
Double space all citations in Reference list. Do not increase spacing between citations. Indent second line of citation to show separation.
Why and how to cite
A good scholar cites the source of information whenever using another person's ideas, opinion or theory. A good scholar also provides citations for any facts, statistics, graphs, or drawings that are obtained from another source. Quotations of another person's actual spoken or written word, and paraphrases of another person's spoken or written words should also be cited.
For additional information about citing sources and avoiding plagiarism, try any or all of the following:
- Basics of APA Style Created by APA--26 brief lessons, each less than two minutes long. Choose the lessons you need.
- Cheng Library's APA handout: Almost all you need to know in two pages!
- APA Citation Style -- Color Coded Guide Sample citations and other APA formatting information, developed by IVY TECH Community College, Central Indiana.
- APA Exposed This PDF of a popular APA tutorial from Harvard Graduate School of Education introduces viewers to the basics of APA style. While the tutorial is no longer available to non-Harvard students, this PDF provides help for learning APA conventions.
Education Librarian

- << Previous: When the article isn't available...
- Next: Writing your Paper >>
- Last Updated: Jan 24, 2024 5:56 PM
- URL: https://guides.wpunj.edu/cmat6820
education, community-building and change
What is action research and how do we do it?
In this article, we explore the development of some different traditions of action research and provide an introductory guide to the literature.
Contents : what is action research · origins · the decline and rediscovery of action research · undertaking action research · conclusion · further reading · how to cite this article . see, also: research for practice ., what is action research.
In the literature, discussion of action research tends to fall into two distinctive camps. The British tradition – especially that linked to education – tends to view action research as research-oriented toward the enhancement of direct practice. For example, Carr and Kemmis provide a classic definition:
Action research is simply a form of self-reflective enquiry undertaken by participants in social situations in order to improve the rationality and justice of their own practices, their understanding of these practices, and the situations in which the practices are carried out (Carr and Kemmis 1986: 162).
Many people are drawn to this understanding of action research because it is firmly located in the realm of the practitioner – it is tied to self-reflection. As a way of working it is very close to the notion of reflective practice coined by Donald Schön (1983).
The second tradition, perhaps more widely approached within the social welfare field – and most certainly the broader understanding in the USA is of action research as ‘the systematic collection of information that is designed to bring about social change’ (Bogdan and Biklen 1992: 223). Bogdan and Biklen continue by saying that its practitioners marshal evidence or data to expose unjust practices or environmental dangers and recommend actions for change. In many respects, for them, it is linked into traditions of citizen’s action and community organizing. The practitioner is actively involved in the cause for which the research is conducted. For others, it is such commitment is a necessary part of being a practitioner or member of a community of practice. Thus, various projects designed to enhance practice within youth work, for example, such as the detached work reported on by Goetschius and Tash (1967) could be talked of as action research.
Kurt Lewin is generally credited as the person who coined the term ‘action research’:
The research needed for social practice can best be characterized as research for social management or social engineering. It is a type of action-research, a comparative research on the conditions and effects of various forms of social action, and research leading to social action. Research that produces nothing but books will not suffice (Lewin 1946, reproduced in Lewin 1948: 202-3)
His approach involves a spiral of steps, ‘each of which is composed of a circle of planning, action and fact-finding about the result of the action’ ( ibid. : 206). The basic cycle involves the following:
This is how Lewin describes the initial cycle:
The first step then is to examine the idea carefully in the light of the means available. Frequently more fact-finding about the situation is required. If this first period of planning is successful, two items emerge: namely, “an overall plan” of how to reach the objective and secondly, a decision in regard to the first step of action. Usually this planning has also somewhat modified the original idea. ( ibid. : 205)
The next step is ‘composed of a circle of planning, executing, and reconnaissance or fact-finding for the purpose of evaluating the results of the second step, and preparing the rational basis for planning the third step, and for perhaps modifying again the overall plan’ ( ibid. : 206). What we can see here is an approach to research that is oriented to problem-solving in social and organizational settings, and that has a form that parallels Dewey’s conception of learning from experience.
The approach, as presented, does take a fairly sequential form – and it is open to a literal interpretation. Following it can lead to practice that is ‘correct’ rather than ‘good’ – as we will see. It can also be argued that the model itself places insufficient emphasis on analysis at key points. Elliott (1991: 70), for example, believed that the basic model allows those who use it to assume that the ‘general idea’ can be fixed in advance, ‘that “reconnaissance” is merely fact-finding, and that “implementation” is a fairly straightforward process’. As might be expected there was some questioning as to whether this was ‘real’ research. There were questions around action research’s partisan nature – the fact that it served particular causes.
The decline and rediscovery of action research
Action research did suffer a decline in favour during the 1960s because of its association with radical political activism (Stringer 2007: 9). There were, and are, questions concerning its rigour, and the training of those undertaking it. However, as Bogdan and Biklen (1992: 223) point out, research is a frame of mind – ‘a perspective that people take toward objects and activities’. Once we have satisfied ourselves that the collection of information is systematic and that any interpretations made have a proper regard for satisfying truth claims, then much of the critique aimed at action research disappears. In some of Lewin’s earlier work on action research (e.g. Lewin and Grabbe 1945), there was a tension between providing a rational basis for change through research, and the recognition that individuals are constrained in their ability to change by their cultural and social perceptions, and the systems of which they are a part. Having ‘correct knowledge’ does not of itself lead to change, attention also needs to be paid to the ‘matrix of cultural and psychic forces’ through which the subject is constituted (Winter 1987: 48).
Subsequently, action research has gained a significant foothold both within the realm of community-based, and participatory action research; and as a form of practice-oriented to the improvement of educative encounters (e.g. Carr and Kemmis 1986).
Exhibit 1: Stringer on community-based action research
A fundamental premise of community-based action research is that it commences with an interest in the problems of a group, a community, or an organization. Its purpose is to assist people in extending their understanding of their situation and thus resolving problems that confront them….
Community-based action research is always enacted through an explicit set of social values. In modern, democratic social contexts, it is seen as a process of inquiry that has the following characteristics:
• It is democratic , enabling the participation of all people.
• It is equitable , acknowledging people’s equality of worth.
• It is liberating , providing freedom from oppressive, debilitating conditions.
• It is life enhancing , enabling the expression of people’s full human potential.
(Stringer 1999: 9-10)
Undertaking action research
As Thomas (2017: 154) put it, the central aim is change, ‘and the emphasis is on problem-solving in whatever way is appropriate’. It can be seen as a conversation rather more than a technique (McNiff et. al. ). It is about people ‘thinking for themselves and making their own choices, asking themselves what they should do and accepting the consequences of their own actions’ (Thomas 2009: 113).
The action research process works through three basic phases:
Look -building a picture and gathering information. When evaluating we define and describe the problem to be investigated and the context in which it is set. We also describe what all the participants (educators, group members, managers etc.) have been doing.
Think – interpreting and explaining. When evaluating we analyse and interpret the situation. We reflect on what participants have been doing. We look at areas of success and any deficiencies, issues or problems.
Act – resolving issues and problems. In evaluation we judge the worth, effectiveness, appropriateness, and outcomes of those activities. We act to formulate solutions to any problems. (Stringer 1999: 18; 43-44;160)
The use of action research to deepen and develop classroom practice has grown into a strong tradition of practice (one of the first examples being the work of Stephen Corey in 1949). For some, there is an insistence that action research must be collaborative and entail groupwork.
Action research is a form of collective self-reflective enquiry undertaken by participants in social situations in order to improve the rationality and justice of their own social or educational practices, as well as their understanding of those practices and the situations in which the practices are carried out… The approach is only action research when it is collaborative, though it is important to realise that action research of the group is achieved through the critically examined action of individual group members. (Kemmis and McTaggart 1988: 5-6)
Just why it must be collective is open to some question and debate (Webb 1996), but there is an important point here concerning the commitments and orientations of those involved in action research.
One of the legacies Kurt Lewin left us is the ‘action research spiral’ – and with it there is the danger that action research becomes little more than a procedure. It is a mistake, according to McTaggart (1996: 248) to think that following the action research spiral constitutes ‘doing action research’. He continues, ‘Action research is not a ‘method’ or a ‘procedure’ for research but a series of commitments to observe and problematize through practice a series of principles for conducting social enquiry’. It is his argument that Lewin has been misunderstood or, rather, misused. When set in historical context, while Lewin does talk about action research as a method, he is stressing a contrast between this form of interpretative practice and more traditional empirical-analytic research. The notion of a spiral may be a useful teaching device – but it is all too easy to slip into using it as the template for practice (McTaggart 1996: 249).
Further reading
This select, annotated bibliography has been designed to give a flavour of the possibilities of action research and includes some useful guides to practice. As ever, if you have suggestions about areas or specific texts for inclusion, I’d like to hear from you.
Explorations of action research
Atweh, B., Kemmis, S. and Weeks, P. (eds.) (1998) Action Research in Practice: Partnership for Social Justice in Education, London: Routledge. Presents a collection of stories from action research projects in schools and a university. The book begins with theme chapters discussing action research, social justice and partnerships in research. The case study chapters cover topics such as: school environment – how to make a school a healthier place to be; parents – how to involve them more in decision-making; students as action researchers; gender – how to promote gender equity in schools; writing up action research projects.
Carr, W. and Kemmis, S. (1986) Becoming Critical. Education, knowledge and action research , Lewes: Falmer. Influential book that provides a good account of ‘action research’ in education. Chapters on teachers, researchers and curriculum; the natural scientific view of educational theory and practice; the interpretative view of educational theory and practice; theory and practice – redefining the problem; a critical approach to theory and practice; towards a critical educational science; action research as critical education science; educational research, educational reform and the role of the profession.
Carson, T. R. and Sumara, D. J. (ed.) (1997) Action Research as a Living Practice , New York: Peter Lang. 140 pages. Book draws on a wide range of sources to develop an understanding of action research. Explores action research as a lived practice, ‘that asks the researcher to not only investigate the subject at hand but, as well, to provide some account of the way in which the investigation both shapes and is shaped by the investigator.
Dadds, M. (1995) Passionate Enquiry and School Development. A story about action research , London: Falmer. 192 + ix pages. Examines three action research studies undertaken by a teacher and how they related to work in school – how she did the research, the problems she experienced, her feelings, the impact on her feelings and ideas, and some of the outcomes. In his introduction, John Elliot comments that the book is ‘the most readable, thoughtful, and detailed study of the potential of action-research in professional education that I have read’.
Ghaye, T. and Wakefield, P. (eds.) CARN Critical Conversations. Book one: the role of the self in action , Bournemouth: Hyde Publications. 146 + xiii pages. Collection of five pieces from the Classroom Action Research Network. Chapters on: dialectical forms; graduate medical education – research’s outer limits; democratic education; managing action research; writing up.
McNiff, J. (1993) Teaching as Learning: An Action Research Approach , London: Routledge. Argues that educational knowledge is created by individual teachers as they attempt to express their own values in their professional lives. Sets out familiar action research model: identifying a problem, devising, implementing and evaluating a solution and modifying practice. Includes advice on how working in this way can aid the professional development of action researcher and practitioner.
Quigley, B. A. and Kuhne, G. W. (eds.) (1997) Creating Practical Knowledge Through Action Research, San Fransisco: Jossey Bass. Guide to action research that outlines the action research process, provides a project planner, and presents examples to show how action research can yield improvements in six different settings, including a hospital, a university and a literacy education program.
Plummer, G. and Edwards, G. (eds.) CARN Critical Conversations. Book two: dimensions of action research – people, practice and power , Bournemouth: Hyde Publications. 142 + xvii pages. Collection of five pieces from the Classroom Action Research Network. Chapters on: exchanging letters and collaborative research; diary writing; personal and professional learning – on teaching and self-knowledge; anti-racist approaches; psychodynamic group theory in action research.
Whyte, W. F. (ed.) (1991) Participatory Action Research , Newbury Park: Sage. 247 pages. Chapters explore the development of participatory action research and its relation with action science and examine its usages in various agricultural and industrial settings
Zuber-Skerritt, O. (ed.) (1996) New Directions in Action Research , London; Falmer Press. 266 + xii pages. A useful collection that explores principles and procedures for critical action research; problems and suggested solutions; and postmodernism and critical action research.
Action research guides
Coghlan, D. and Brannick, D. (2000) Doing Action Research in your own Organization, London: Sage. 128 pages. Popular introduction. Part one covers the basics of action research including the action research cycle, the role of the ‘insider’ action researcher and the complexities of undertaking action research within your own organisation. Part two looks at the implementation of the action research project (including managing internal politics and the ethics and politics of action research). New edition due late 2004.
Elliot, J. (1991) Action Research for Educational Change , Buckingham: Open University Press. 163 + x pages Collection of various articles written by Elliot in which he develops his own particular interpretation of action research as a form of teacher professional development. In some ways close to a form of ‘reflective practice’. Chapter 6, ‘A practical guide to action research’ – builds a staged model on Lewin’s work and on developments by writers such as Kemmis.
Johnson, A. P. (2007) A short guide to action research 3e. Allyn and Bacon. Popular step by step guide for master’s work.
Macintyre, C. (2002) The Art of the Action Research in the Classroom , London: David Fulton. 138 pages. Includes sections on action research, the role of literature, formulating a research question, gathering data, analysing data and writing a dissertation. Useful and readable guide for students.
McNiff, J., Whitehead, J., Lomax, P. (2003) You and Your Action Research Project , London: Routledge. Practical guidance on doing an action research project.Takes the practitioner-researcher through the various stages of a project. Each section of the book is supported by case studies
Stringer, E. T. (2007) Action Research: A handbook for practitioners 3e , Newbury Park, ca.: Sage. 304 pages. Sets community-based action research in context and develops a model. Chapters on information gathering, interpretation, resolving issues; legitimacy etc. See, also Stringer’s (2003) Action Research in Education , Prentice-Hall.
Winter, R. (1989) Learning From Experience. Principles and practice in action research , Lewes: Falmer Press. 200 + 10 pages. Introduces the idea of action research; the basic process; theoretical issues; and provides six principles for the conduct of action research. Includes examples of action research. Further chapters on from principles to practice; the learner’s experience; and research topics and personal interests.
Action research in informal education
Usher, R., Bryant, I. and Johnston, R. (1997) Adult Education and the Postmodern Challenge. Learning beyond the limits , London: Routledge. 248 + xvi pages. Has some interesting chapters that relate to action research: on reflective practice; changing paradigms and traditions of research; new approaches to research; writing and learning about research.
Other references
Bogdan, R. and Biklen, S. K. (1992) Qualitative Research For Education , Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Goetschius, G. and Tash, J. (1967) Working with the Unattached , London: Routledge and Kegan Paul.
McTaggart, R. (1996) ‘Issues for participatory action researchers’ in O. Zuber-Skerritt (ed.) New Directions in Action Research , London: Falmer Press.
McNiff, J., Lomax, P. and Whitehead, J. (2003) You and Your Action Research Project 2e. London: Routledge.
Thomas, G. (2017). How to do your Research Project. A guide for students in education and applied social sciences . 3e. London: Sage.
Acknowledgements : spiral by Michèle C. | flickr ccbyncnd2 licence
How to cite this article : Smith, M. K. (1996; 2001, 2007, 2017) What is action research and how do we do it?’, The encyclopedia of pedagogy and informal education. [ https://infed.org/mobi/action-research/ . Retrieved: insert date] .
© Mark K. Smith 1996; 2001, 2007, 2017
Last Updated on December 7, 2020 by infed.org

The Palgrave Encyclopedia of the Possible pp 9–16 Cite as
Action Research
- David Coghlan 2
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 01 January 2023
385 Accesses
Action research is an approach to research which aims at both taking action and creating knowledge or theory about that action as the action unfolds. It starts with everyday experience and is concerned with the development of living knowledge. Its characteristics are that it generates practical knowledge in the pursuit of worthwhile purposes; it is participative and democratic as its participants work together in the present tense in defining the questions they wish to explore, the methodology for that exploration, and its application through cycles of action and reflection. In this vein they are agents of change and coresearchers in knowledge generation and not merely passive subjects as in traditional research. In this vein, action research can be understood as a social science of the possible as the collective action is focused on creating a desired future in whatever context the action research is located.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Banks, S., & Brydon-Miller, M. (2018). Ethics in participatory research for health and social well-being . Abingdon: Routledge.
Book Google Scholar
Bradbury, H. (2015). The Sage handbook of action research (3rd ed.). Sage: London.
Bradbury, H., Mirvis, P., Neilsen, E., & Pasmore, W. (2008). Action research at work: Creating the future following the path from Lewin. In P. Reason & H. Bradbury (Eds.), The Sage handbook of action research (2nd ed., pp. 77–92). London: Sage.
Chapter Google Scholar
Bradbury, H., Roth, J., & Gearty, M. (2015). The practice of learning history: Local and open approaches. In H. Bradbury (Ed.), The Sage handbook of action research (3rd ed., pp. 17–30). London: Sage.
Brydon-Miller, M., Greenwood, D., & Maguire, P. (2003). Why action research? Action Research, 1 (1), 9–28.034201[1476–7503(200307)1:1].
Article Google Scholar
Chevalier, J. M., & Buckles, D. J. (2019). Participatory action research. Theory and methods for engaged inquiry (2nd ed.). Abingdon: Routledge.
Coghlan, D. (2010). Seeking common ground in the diversity and diffusion of action research and collaborative management research action modalities: Toward a general empirical method. In W.A. Pasmore, A.B.. (Rami) Shani and R.W. Woodman (Eds.), Research in organizational change and development (vol 18, pp. 149–181). Bingley: Emerald.
Google Scholar
Coghlan, D. (2016). Retrieving the philosophy of practical knowing for action research. International Journal of Action Research, 12 , 84–107. https://doi.org/10.1688/IJAR-2016-01 .
Coghlan, D. (2019). Doing action research in your own organization (5th ed.). London: Sage.
Coghlan, D., & Brydon-Miller, M. (2014). The Sage encyclopedia of action research . London: Sage.
Coghlan, D., & Shani, A.B.. (Rami). (2017). Inquiring in the present tense: The dynamic mechanism of action research. Journal of Change Management , 17, 121–137. https://doi.org/10.1080/14697017.2017.1301045 .
Coghlan, D., Shani, A.B.. (Rami), & Hay, G.W. (2019). Toward a social science philosophy of organization development and change. In D.A. Noumair & A.B.. (Rami) Shani (eds.). Research in organizational change and development (Vol. 27, pp. 1–29). Bingley: Emerald.
Gearty, M., & Coghlan, D. (2018). The first-, second- and third-person dynamics of learning history. Systemic Practice & Action Research., 31 , 463–478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11213-017-9436-5 .
Greenwood, D., & Levin, M. (2007). Introduction to action research (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Heron, J., & Reason, P. (1997). A participatory inquiry paradigm. Qualitative Inquiry, 3 , 274–294.
Heron, J., & Reason, P. (2008). Extending epistemology within a cooperative inquiry. In P. Reason & H. Bradbury (Eds.), The Sage handbook of action research (2nd ed., pp. 366–380). London: Sage.
Huxham, C. (2003). Actionresearch as a methodology for theory development. Policy and Politics, 31 (2), 239–248. https://doi.org/10.1332/030557303765371726 .
Koshy, E., Koshy, V., & Waterman, H. (2011). Action research in healthcare . London: Sage.
Lonergan, B. J. (2005). Dimensions of meaning. In B. J. Lonergan (Ed.), The collected work of Bernard Lonergan (Vol. 4, pp. 232–244). Toronto: Toronto University Press.
Marshall, J. (2016). First person action research: Living life as inquiry . London: Sage.
Owen, R., Bessant, J., & Heintz, M. (2013). Responsible innovation: Managing the responsible emergence of science and innovation in society . London: Wiley.
Pasmore, W. A. (2001). Action research in the workplace: The socio-technical perspective. In P. Reason & H. Bradbury (Eds.), The handbook of action research (pp. 38–47). London: Sage.
Revans, R. W. (1971). Developing effective managers . London: Longmans.
Revans, R. (1998). ABC of action learning . London: Lemos& Crane.
Schein, E. H. (2013). Humble inquiry: The gentle art of asking instead of telling . Oakland: Berrett-Kohler.
Shani, A.B.. (Rami), & Coghlan, D. (2019). Action research in business and management: A reflective review. Action Research . https://doi.org/10.1177/1476750319852147 .
Susman, G. I., & Evered, R. D. (1978). An assessment of the scientific merits of action research. Administrative Science Quarterly, 23 , 582–601. https://doi.org/10.2307/2392581 .
Torbert, W. R., & Associates. (2004). Action inquiry . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Whitney, D., & Trosten-Bloom, A. (2010). The power of appreciative inquiry: A practical guide to positive change . Oakland: Berrett-Kohler.
Williamson, G., & Bellman, L. (2012). Action research in nursing and healthcare . London: Sage.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Trinity Business School, University of Dublin Trinity College, Dublin, Ireland
David Coghlan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to David Coghlan .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Dublin City University, Dublin, Ireland
Vlad Petre Glăveanu
Section Editor information
Webster University Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland
Richard Randell
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Coghlan, D. (2022). Action Research. In: Glăveanu, V.P. (eds) The Palgrave Encyclopedia of the Possible. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90913-0_180
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90913-0_180
Published : 26 January 2023
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-90912-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-90913-0
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science and Psychology Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
References on Action Research
This is a list of references on action research. After a brief introduction which suggests those works which are essential reading for newcomers to the field, the list is organized into two parts: the first part lists some important citations related to the approach in other disciplines (including the source disciplines), the second lists citations related to the approach in Information Systems. You can use the E dit F ind command in Netscape to look for a specific citation.
Please send additional references and/or short abstracts of items on this page (maximum 50 words) to the Section Editor at: [email protected]
[ Introduction ] [ Citations in Other Disciplines ] [ Citations in Information Systems ]
Introduction
A brief introduction to the action research method is the article by Susman and Evered (1978) . For a more in-depth look at the method, the collection of articles by Kemmis and McTaggart (1988) is very useful, as is the Human Relations Special Issue which was devoted to action research (see Elden and Chisholm, 1994) . In Information Systems, a good place to start would be the articles by Baskerville and Wood-Harper (1996) , and Checkland (1991) .
Citations in Other Disciplines
Argyris, C., Putnam, R. and Smith, D. Action Science , Jossey-Bass, San Francisco, 1985. Argyris, C. and Schön, D. Organizational Learning: A Theory of Action Perspective . Addison-Wesley, Reading, 1978. Baburoglu, O.N. and Ravn, I. "Normative Action Research." Organization Studies (13:1), 1992, pp. 19-34. Blum, F. "Action research - a scientific approach?" Philosophy of Science 22 (January), 1955, pp. 1-7. Brown, L.D. and Tandon, R. "Ideology and Political Economy in Inquiry: Action Research and Participatory Research," Journal of Applied Behavioural Science (19), 1983, pp. 277-285. Carr, W. and Kemmis, S. Becoming Critical: Education, Knowledge and Action Research , Falmer Press, London, 1986. Chisholm, R.F. and Elden, M. "Features of Emerging Action Research," Human Relations (46:2), 1993, pp. 275-298. Clark, P.A. Action Research and Organizational Change , Harper and Row, London, 1972. Cunningham, B. "Action Research: Toward a Procedural Model," Human Relations (29:3), 1976, pp. 215-238. Elden, M. and Chisholm , R.F. "Emerging Varieties of Action Research: Introduction to the Special Issue," Human Relations (46:2), 1993, pp. 121-142. Greenwood, D.J., Whyte, W.W. and Harkavy, I. "Participatory Action Research as a Process and as a Goal," Human Relations (46:2), 1993, pp. 175-192. Gustavsen, B. "Action Research and the Generation of Knowledge," Human Relations (46:10), 1993, pp. 1361-1365. Harris, R.T. "Improving Patient Satisfaction Through Action Research," Journal of Applied Behavioral Science (14:3), 1978, pp. 382-399. Heller, F. "Another Look at Action Research," Human Relations (46:10), 1993, pp. 1235-1242. Hindle, T., Checkland, P., Mumford, M. and Worthington, D. "Developing a Methodology for Multidisciplinary Action Research: A Case Study," Journal of the Operational Research Society (46:4), 1995, pp. 453-464. Hult, M. and Lennung, S-A. "Towards a Definition of Action Research: A Note and Bibliography," Journal of Management Studies , May 1980, pp. 241-250. Johnston, S. and Proudford, C. "Action Research: Who Owns the Process?," Educational Review (46:1), 1994, pp. 3-14. Karlsen, J.I. "Action Research as a Method," in Participatory Action Research , W.F. Whyte (ed.), Sage Publications, New York, 1991. Kemmis, S. and McTaggart, R. The Action Research Reader . Third edition. Deakin University Press, Victoria, 1988. Ledford, G.E.Jr. and Mohrman, S.A. "Self-Design for High Involvement: A Large-Scale Organizational Change," Human Relations (46:1), 1993, pp. 143-173. Lewin, K. "Frontiers in Group Dynamics: II. Channels of Group Life; Social Planning and Action Research," Human Relations (1:2), pp. 143-153. Lippit, G. and Lippit, R. The Consulting Process in Action. University Associates, San Diego, CA, 1978. McTaggart, R. Action Research: A Short Modern History , Deakin University Press, Geelong, 1991. Nosek, J.T. and Yaverbaum, G. "Overcoming Obstacles to University and industry Synergy in Information System Education: Lessons from Action Research," Education for Information , (9), 1991, pp. 3-19. Peters, M. and Robinson, V. "The Origins and Status of Action Research," Journal of Applied Behavioral Science (20:2), 1984, pp. 113-124. Rapoport, R.N. "Three Dilemmas in Action Research," Human Relations , (23:4), 1970, pp. 499-513. Robinson, V.M.J. "Current Controversies in Action Research," Public Administration Quarterly (17:3), 1993, pp. 263-290. Susman, G.I. "Action Research: A Sociotechnical systems perspective," in Beyond Method: Strategies for Social Science Research , G. Morgan (ed.), Sage Publications, London, 1983. Susman, G.I. and Evered, R.D. "An Assessment of the Scientific Merits of Action Research," Administrative Science Quarterly , (23) 1978, pp. 582-603. Trist, E. "Engaging with large-scale systems," in Experimenting with Organizational Life: The Action Research Approach , A. Clark (ed.), Plenum, New York, 1976, pp. 43-75. Whyte, W.F. (ed.). Participatory Action Research , Sage Publications, New York, 1991.

Citations in Information Systems
Baskerville, R.L. and Wood-Harper, A.T. "A Critical Perspective on Action Research as a Method for Information Systems Research," Journal of Information Technology (11), 1996, pp. 235-246. Checkland, P. "From framework through experience to learning: the essential nature of action research," in Information Systems Research: Contemporary Approaches and Emergent Traditions , H-E. Nissen, H.K. Klein, R.A. Hirschheim (eds.), North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1991, pp. 397-403. Jonsson, S. "Action Research," in Information Systems Research: Contemporary Approaches and Emergent Traditions , H-E. Nissen, H.K. Klein and R.A. Hirschheim (eds.), North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1991. Lee, A.S., Baskerville, R.L. and Davies, L. "A Workshop on Two Techniques for Qualitative Data Analysis: Action Research and Ethnography," Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Information Systems , 1992, p. 305-306. Lee, A.S., Baskerville, R.L., Liebenau, J. and Myers, M.D. "Judging Qualitative Research in Information Systems: Criteria for Accepting and Rejecting Manuscripts," Proceedings of the Sixteenth International Conference on Information Systems, 1995. Levin, M. "Action Research and Critical Systems Thinking: Two Icons Carved Out of the Same Log?", Systems Practice (7:1), 1994, pp. 25-41. Mansell, G. "Action research in information systems development," Journal of Information Systems (1), 1991, pp. 29-40. Warmington, A. "Action Research: Its Methods and its Implications," Journal of Applied Systems Analysis (7), 1980, pp. 23-39. Wood-Harper, A.T. "Research Methods in Information Systems: Using Action Research," in Research Methods in Information Systems , E. Mumford, R.A. Hirschheim, G. Fitzgerald and A.T. Wood-Harper (eds.), North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1985. Wood-Harper, A.T. "Viewpoint: Action Research," Journal of Information Systems (2), 1992, pp. 235-236.
ISWorld Net Navigation Map
Revised: february 05, 2004.
This work was published in MISQ Discovery on May 20, 1997. This is the original archival version. It is currently maintained by Michael D. Myers . Corrections, clarifications, and suggested modifications should be directed to him at [email protected] . Serious problems should be referred to the Editor-in-Chief .
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples
What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples
Published on 27 January 2023 by Tegan George . Revised on 21 April 2023.
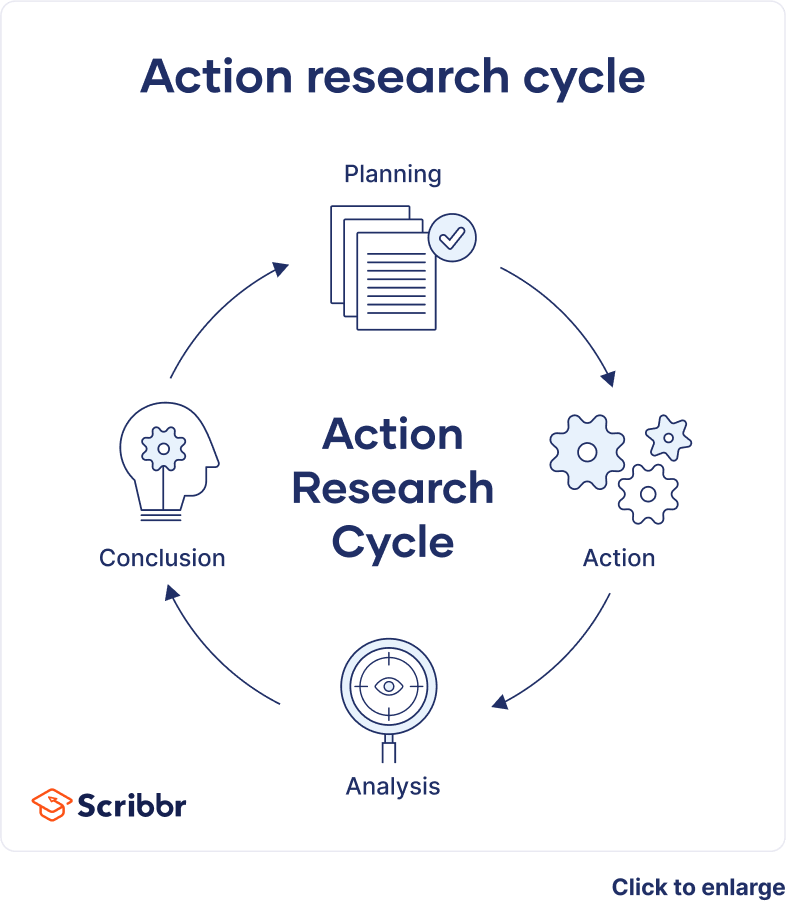
Table of contents
Types of action research, action research models, examples of action research, action research vs. traditional research, advantages and disadvantages of action research, frequently asked questions about action research.
There are 2 common types of action research: participatory action research and practical action research.
- Participatory action research emphasises that participants should be members of the community being studied, empowering those directly affected by outcomes of said research. In this method, participants are effectively co-researchers, with their lived experiences considered formative to the research process.
- Practical action research focuses more on how research is conducted and is designed to address and solve specific issues.
Both types of action research are more focused on increasing the capacity and ability of future practitioners than contributing to a theoretical body of knowledge.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Action research is often reflected in 3 action research models: operational (sometimes called technical), collaboration, and critical reflection.
- Operational (or technical) action research is usually visualised like a spiral following a series of steps, such as “planning → acting → observing → reflecting.”
- Collaboration action research is more community-based, focused on building a network of similar individuals (e.g., college professors in a given geographic area) and compiling learnings from iterated feedback cycles.
- Critical reflection action research serves to contextualise systemic processes that are already ongoing (e.g., working retroactively to analyse existing school systems by questioning why certain practices were put into place and developed the way they did).
Action research is often used in fields like education because of its iterative and flexible style.
After the information was collected, the students were asked where they thought ramps or other accessibility measures would be best utilised, and the suggestions were sent to school administrators. Example: Practical action research Science teachers at your city’s high school have been witnessing a year-over-year decline in standardised test scores in chemistry. In seeking the source of this issue, they studied how concepts are taught in depth, focusing on the methods, tools, and approaches used by each teacher.
Action research differs sharply from other types of research in that it seeks to produce actionable processes over the course of the research rather than contributing to existing knowledge or drawing conclusions from datasets. In this way, action research is formative , not summative , and is conducted in an ongoing, iterative way.
As such, action research is different in purpose, context, and significance and is a good fit for those seeking to implement systemic change.
Action research comes with advantages and disadvantages.
- Action research is highly adaptable , allowing researchers to mould their analysis to their individual needs and implement practical individual-level changes.
- Action research provides an immediate and actionable path forward for solving entrenched issues, rather than suggesting complicated, longer-term solutions rooted in complex data.
- Done correctly, action research can be very empowering , informing social change and allowing participants to effect that change in ways meaningful to their communities.
Disadvantages
- Due to their flexibility, action research studies are plagued by very limited generalisability and are very difficult to replicate . They are often not considered theoretically rigorous due to the power the researcher holds in drawing conclusions.
- Action research can be complicated to structure in an ethical manner . Participants may feel pressured to participate or to participate in a certain way.
- Action research is at high risk for research biases such as selection bias , social desirability bias , or other types of cognitive biases .
Action research is conducted in order to solve a particular issue immediately, while case studies are often conducted over a longer period of time and focus more on observing and analyzing a particular ongoing phenomenon.
Action research is focused on solving a problem or informing individual and community-based knowledge in a way that impacts teaching, learning, and other related processes. It is less focused on contributing theoretical input, instead producing actionable input.
Action research is particularly popular with educators as a form of systematic inquiry because it prioritizes reflection and bridges the gap between theory and practice. Educators are able to simultaneously investigate an issue as they solve it, and the method is very iterative and flexible.
A cycle of inquiry is another name for action research . It is usually visualized in a spiral shape following a series of steps, such as “planning → acting → observing → reflecting.”
Sources for this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
George, T. (2023, April 21). What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 15 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/action-research-cycle/
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2017). Research methods in education (8th edition). Routledge.
Naughton, G. M. (2001). Action research (1st edition). Routledge.
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, primary research | definition, types, & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, what is an observational study | guide & examples.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
7 Let it Be Known! Sharing your Results
ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS
- What are the best ways to share my findings?
- Why should I share my work at a conference?
- What are the key components of a report detailing your findings?
Many action researchers are not expected to share their findings or produce written reports, yet it is a useful endeavor for not only the educator-researcher, but also for colleagues in their related fields. For those who are compelled or required to share their findings, Hopkins (2003, 140) provides some guidance, asserting that all action researchers need to share their data and share it in a way that:
- the study could be replicated in another context;
- the evidence used to generate claims or action is clearly documented;
- the action taken as a result of the research is tracked;
- the findings are accessible to the consumer and relatable to their practice.
I personally believe it is important to formally share your work one way or another, or at least prepare it to be shared. This process helps you think deeply and concisely about what you have researched, what your findings were, and what the significance is for you and your colleagues. When you prepare your work for public consumption, you add another layer of scrutiny and validity to your thinking and editing process.
Action researchers can share their findings in several ways that colleagues and other consumers of research will be able to engage with their work. The three following ways are the most common paths for educator-researchers to share their work:
- Develop a report for personal documentation or to be shared with colleagues.
- Write an article summarizing your research and its significance to the field.
- Local, State, Regional, National, or International Conference
- District or School-Wide Professional Learning Session or Workshop
- Research Symposium
- Personal Website
Writing a Report or Article
Regardless of the purposes for writing your report or article, there are a few factors to consider as you begin to write. Remember, the purpose of action research is to improve your practice and/or implement change, based on the findings of your research, as part of professional learning and development as an educator. As mentioned in previous chapters, your goal as an action researcher is not to make generalizable claims, but to share your research with other educators who want to learn from it, develop a similar study, or use your findings to improve their own teaching in a similar context. Whether it is a report that you share on your own, or an article accepted, edited, and published by a journal or magazine, the important part is to share your findings and contribute to the knowledge base.
Before you begin, the primary task is to consider the audience you are addressing and the requirements and the purpose of your report or article. An article usually has a specific audience and purpose. For example, if I submit an article to the Elementary Social Studies Journal , then I am trying to inform elementary teachers about my findings in social studies and I am providing pedagogical insights to them. However, reports can have several purposes depending on the intent and audience. Reports can be for the purpose of:
- Reporting to Grant or External Funding Agency;
- Completing a thesis or dissertation;
- Contributing to a Pedagogical or Educational Database;
- Documenting for Personal, Administrative, or District-Level Record.
Regardless of the purpose, it is important to demonstrate a clear and consistent understanding of the issues you have researched. With the exception of reports to some grant or external funding agencies (as they may require formal writing or templates), when reporting on your action research, the quality of your writing can be enhanced by writing in an authentic and personal style. I have always felt that reporting action research is often powerful for one’s own professional learning and development because of the personal nature of the writing. It may be useful to think about it as you are reporting your own story, based on your experiences and collaborations with other people.
When writing a report or article you will want to have representations of the following sections:
- Problematization of your Topic (Why is your topic important to you or the field?)
- Literature Review and Underlying Theories (What do we know and not know?)
- Methodology (How was your study structured, what data was collected, and how was data analyzed?)
- Summary of Findings (What were the predominant themes, codes, patterns, or meaningful consequences of the study?)
- Discussion of Findings’ Significance (How do your findings compare to the literature?)
- Implications of Findings for Practice (How will your findings impact your practice?)
These sections will help you think about the important aspects of your study, as well as the aspects that will be of interest to potential readers.
Imagine the Reader
As an educator-researcher you can imagine many of your colleagues as potential readers of your work. Imagining potential readers is a useful strategy to utilize as you write your report. In this vein, and as you think about the aforementioned sections, the following considerations provide further guidance in the writing process:
- Always provide the background to your study, your context, and your positionality as an educator-researcher. Readers will potentially relate to your study and more easily apply the findings to their own context.
- Clearly present your aims, intentions, and purposes to situate your study and present your findings within the context of what you have set out to achieve.
- Do not be afraid to describe the process, success and challenges, as readers appreciate realism and honesty.
- Write clearly and concisely so others may be able to replicate the study.
- Write in first person if it feels more natural and accurate to the study.
- Readers may not be knowledgeable about your topic. Be concise and explain all aspects of your study in clear, simple language, and explain any educational jargon to be clear about its meaning.
- It is easier to read text with subheadings. Use subheadings when possible.
Since your study will likely be an inquiry into your own practice, remember our discussions from other chapters related to subjectivity:
- Acknowledge your own beliefs, prior assumptions, and values as part of your positionality or bias statement.
- Acknowledge any experiences that will relate directly to the study and your interpretations of the data.
- Discuss any ethical issues and how you addressed them.
Presentations of Action Research
There are many ways for educator researchers to present their findings. Some educator researchers present their research findings to colleagues and others at discipline-specific conferences before writing their final reports, as they believed that the preparation for the presentation helped to bring their thoughts together. Many others present their research findings after they have written out their reports, and still, many other researchers do not write a formal report, but instead disseminate their research through various presentations in other ways. These different methods of presentations all serve the purpose of bringing their ideas together and reflecting on them before sharing their work with colleagues and others. Here are some examples of presentations.
Conference presentations
A primary way for academic researchers to disseminate their research is through conference presentations at either the local, state, regional, national, or international level. I encourage educator-researchers to do the same, as these are some of the best ways to share your research with engaged and captivated audiences who attended the conference specifically to find out about new research. Similar to writing an article for a specific journal, many conferences will have a disciplinary or developmental level focus that will allow you to present your work to the most interested audience.
District or school-wide professional learning session or workshop
As an educator in a school context, your districts and schools will undoubtedly offer professional learning opportunities or workshops. Educators in the district or school are often encouraged to present at these events, especially if you are researching a new initiative implemented by the district or school.
Research symposium
If you and some other colleagues have all done action research studies, or maybe a group of colleagues researched the same topic, it would be appropriate to create a research symposium to share your work. These can be formal or informal, but they are a way to have a conference-like setting focused on a specific topic and for specific audience.
Web-Based Contributions
Many educator researchers are simply and effectively sharing their research online. There are many ways to share your research online, including some ways that would be in combination with writing an article, report, or sharing at a conference on an organization’s website. However, the most common ways for individual educator researchers to share their work is through providing a webinar, contributing to a blog, or uploading to a personal website. These online formats all provide a way for educator researchers to present their work and reflect on it with the potential to receive feedback from others. Below are some journals specifically focused on publishing education-based action research:
Action Research Publications
- Action Research – a print-based, international, interdisciplinary, peer reviewed, quarterly published refereed journal which is a forum for the development of the theory and practice of action research https://journals.sagepub.com/home/arj
- Educational Action Research – Supported by Collaborative Action Research Network (CARN) a print-based peer reviewed journal. https://www.tandfonline.com/toc/reac20/current
- Journal of Teacher Action Research – an open-access, online, international journal that publishes peer-reviewed articles and lesson plans written by teachers and researchers to inform classroom practice. http://www.practicalteacherresearch.com/
- Inquiry in Education – a online, peer reviewed international journal of action research in education and related fields. https://digitalcommons.nl.edu/ie/
- Networks: An Online Journal for Teacher Research – offers a place for sharing reports of action research, in which teachers at all levels, kindergarten to postgraduate, are reflecting on classroom practice through research ventures. https://newprairiepress.org/networks/
Concluding Thoughts
As we discussed in Chapter 1 of this book, Action Research is a cycle—the process is ongoing, and for many teachers, once you engage in Action Research, it becomes difficult to stop pursuing new and interesting questions in your classroom. As you answer one question, new ideas and issues emerge, prompting a new modification, and so on. Action Research, as such, is not finite. For teacher action researchers, disseminating your work is an important step in this cycle, as it offers you an opportunity to contribute your new knowledge to the field at-large, and it can open the door to new learning opportunities for both you and your colleagues. Please do not get stressed out about the dissemination portion of this cycle. Simply find the best way for you to share your hard work and accomplish your intended goals. The important part is to share your work and share in a way that allows you to deeply reflect, celebrate your progress, get feedback, and contemplate your next steps or project. The best teachers are lifelong learners, and Action Research allows you the space to continue the deep learning that is necessary in education. Hopefully, this book has provided a vehicle to engage in a cycle of research in your classroom.
The following supplemental chapter contains a full-length vignette from a high school English teacher. The vignette details the steps to an action research project using a real-life example from her classroom. While every project will look different, the vignette serves as an outline for how action research can develop from your classroom wonderings, and it includes the detailed steps the teacher took to fulfill all the parts of action research as outlined in this book.
Action Research Copyright © by J. Spencer Clark; Suzanne Porath; Julie Thiele; and Morgan Jobe is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Linking Research to Action: A Simple Guide to Writing an Action Research Report
What Is Action Research, and Why Do We Do It?
Action research is any research into practice undertaken by those involved in that practice, with the primary goal of encouraging continued reflection and making improvement. It can be done in any professional field, including medicine, nursing, social work, psychology, and education. Action research is particularly popular in the field of education. When it comes to teaching, practitioners may be interested in trying out different teaching methods in the classroom, but are unsure of their effectiveness. Action research provides an opportunity to explore the effectiveness of a particular teaching practice, the development of a curriculum, or your students’ learning, hence making continual improvement possible. In other words, the use of an interactive action-and-research process enables practitioners to get an idea of what they and their learners really do inside of the classroom, not merely what they think they can do. By doing this, it is hoped that both the teaching and the learning occurring in the classroom can be better tailored to fit the learners’ needs.
You may be wondering how action research differs from traditional research. The term itself already suggests that it is concerned with both “action” and “research,” as well as the association between the two. Kurt Lewin (1890-1947), a famous psychologist who coined this term, believed that there was “no action without research; no research without action” (Marrow, 1969, p.163). It is certainly possible, and perhaps commonplace, for people to try to have one without the other, but the unique combination of the two is what distinguishes action research from most other forms of enquiry. Traditional research emphasizes the review of prior research, rigorous control of the research design, and generalizable and preferably statistically significant results, all of which help examine the theoretical significance of the issue. Action research, with its emphasis on the insider’s perspective and the practical significance of a current issue, may instead allow less representative sampling, looser procedures, and the presentation of raw data and statistically insignificant results.
What Should We Include in an Action Research Report?
The components put into an action research report largely coincide with the steps used in the action research process. This process usually starts with a question or an observation about a current problem. After identifying the problem area and narrowing it down to make it more manageable for research, the development process continues as you devise an action plan to investigate your question. This will involve gathering data and evidence to support your solution. Common data collection methods include observation of individual or group behavior, taking audio or video recordings, distributing questionnaires or surveys, conducting interviews, asking for peer observations and comments, taking field notes, writing journals, and studying the work samples of your own and your target participants. You may choose to use more than one of these data collection methods. After you have selected your method and are analyzing the data you have collected, you will also reflect upon your entire process of action research. You may have a better solution to your question now, due to the increase of your available evidence. You may also think about the steps you will try next, or decide that the practice needs to be observed again with modifications. If so, the whole action research process starts all over again.
In brief, action research is more like a cyclical process, with the reflection upon your action and research findings affecting changes in your practice, which may lead to extended questions and further action. This brings us back to the essential steps of action research: identifying the problem, devising an action plan, implementing the plan, and finally, observing and reflecting upon the process. Your action research report should comprise all of these essential steps. Feldman and Weiss (n.d.) summarized them as five structural elements, which do not have to be written in a particular order. Your report should:
- Describe the context where the action research takes place. This could be, for example, the school in which you teach. Both features of the school and the population associated with it (e.g., students and parents) would be illustrated as well.
- Contain a statement of your research focus. This would explain where your research questions come from, the problem you intend to investigate, and the goals you want to achieve. You may also mention prior research studies you have read that are related to your action research study.
- Detail the method(s) used. This part includes the procedures you used to collect data, types of data in your report, and justification of your used strategies.
- Highlight the research findings. This is the part in which you observe and reflect upon your practice. By analyzing the evidence you have gathered, you will come to understand whether the initial problem has been solved or not, and what research you have yet to accomplish.
- Suggest implications. You may discuss how the findings of your research will affect your future practice, or explain any new research plans you have that have been inspired by this report’s action research.
The overall structure of your paper will actually look more or less the same as what we commonly see in traditional research papers.
What Else Do We Need to Pay Attention to?
We discussed the major differences between action research and traditional research in the beginning of this article. Due to the difference in the focus of an action research report, the language style used may not be the same as what we normally see or use in a standard research report. Although both kinds of research, both action and traditional, can be published in academic journals, action research may also be published and delivered in brief reports or on websites for a broader, non-academic audience. Instead of using the formal style of scientific research, you may find it more suitable to write in the first person and use a narrative style while documenting your details of the research process.
However, this does not forbid using an academic writing style, which undeniably enhances the credibility of a report. According to Johnson (2002), even though personal thoughts and observations are valued and recorded along the way, an action research report should not be written in a highly subjective manner. A personal, reflective writing style does not necessarily mean that descriptions are unfair or dishonest, but statements with value judgments, highly charged language, and emotional buzzwords are best avoided.
Furthermore, documenting every detail used in the process of research does not necessitate writing a lengthy report. The purpose of giving sufficient details is to let other practitioners trace your train of thought, learn from your examples, and possibly be able to duplicate your steps of research. This is why writing a clear report that does not bore or confuse your readers is essential.
Lastly, You May Ask, Why Do We Bother to Even Write an Action Research Report?
It sounds paradoxical that while practitioners tend to have a great deal of knowledge at their disposal, often they do not communicate their insights to others. Take education as an example: It is both regrettable and regressive if every teacher, no matter how professional he or she might be, only teaches in the way they were taught and fails to understand what their peer teachers know about their practice. Writing an action research report provides you with the chance to reflect upon your own practice, make substantiated claims linking research to action, and document action and ideas as they take place. The results can then be kept, both for the sake of your own future reference, and to also make the most of your insights through the act of sharing with your professional peers.
Feldman, A., & Weiss, T. (n.d.). Suggestions for writing the action research report . Retrieved from http://people.umass.edu/~afeldman/ARreadingmaterials/WritingARReport.html
Johnson, A. P. (2002). A short guide to action research . Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Marrow, A. J. (1969). The practical theorist: The life and work of Kurt Lewin . New York, NY: Basic Books.
Tiffany Ip is a lecturer at Hong Kong Baptist University. She gained a PhD in neurolinguistics after completing her Bachelor’s degree in psychology and linguistics. She strives to utilize her knowledge to translate brain research findings into practical classroom instruction.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Citing sources
How to Cite Sources | Citation Generator & Quick Guide
Citing your sources is essential in academic writing . Whenever you quote or paraphrase a source (such as a book, article, or webpage), you have to include a citation crediting the original author.
Failing to properly cite your sources counts as plagiarism , since you’re presenting someone else’s ideas as if they were your own.
The most commonly used citation styles are APA and MLA. The free Scribbr Citation Generator is the quickest way to cite sources in these styles. Simply enter the URL, DOI, or title, and we’ll generate an accurate, correctly formatted citation.
Generate accurate citations with Scribbr
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text.
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When do you need to cite sources, which citation style should you use, in-text citations, reference lists and bibliographies.
Scribbr Citation Generator
Other useful citation tools
Citation examples and full guides, frequently asked questions about citing sources.
Citations are required in all types of academic texts. They are needed for several reasons:
- To avoid plagiarism by indicating when you’re taking information from another source
- To give proper credit to the author of that source
- To allow the reader to consult your sources for themselves
A citation is needed whenever you integrate a source into your writing. This usually means quoting or paraphrasing:
- To quote a source , copy a short piece of text word for word and put it inside quotation marks .
- To paraphrase a source , put the text into your own words. It’s important that the paraphrase is not too close to the original wording. You can use the paraphrasing tool if you don’t want to do this manually.
Citations are needed whether you quote or paraphrase, and whatever type of source you use. As well as citing scholarly sources like books and journal articles, don’t forget to include citations for any other sources you use for ideas, examples, or evidence. That includes websites, YouTube videos , and lectures .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
Usually, your institution (or the journal you’re submitting to) will require you to follow a specific citation style, so check your guidelines or ask your instructor.
In some cases, you may have to choose a citation style for yourself. Make sure to pick one style and use it consistently:
- APA Style is widely used in the social sciences and beyond.
- MLA style is common in the humanities.
- Chicago notes and bibliography , common in the humanities
- Chicago author-date , used in the (social) sciences
- There are many other citation styles for different disciplines.
If in doubt, check with your instructor or read other papers from your field of study to see what style they follow.
In most styles, your citations consist of:
- Brief in-text citations at the relevant points in the text
- A reference list or bibliography containing full information on all the sources you’ve cited
In-text citations most commonly take the form of parenthetical citations featuring the last name of the source’s author and its year of publication (aka author-date citations).
An alternative to this type of in-text citation is the system used in numerical citation styles , where a number is inserted into the text, corresponding to an entry in a numbered reference list.
There are also note citation styles , where you place your citations in either footnotes or endnotes . Since they’re not embedded in the text itself, these citations can provide more detail and sometimes aren’t accompanied by a full reference list or bibliography.
A reference list (aka “Bibliography” or “Works Cited,” depending on the style) is where you provide full information on each of the sources you’ve cited in the text. It appears at the end of your paper, usually with a hanging indent applied to each entry.
The information included in reference entries is broadly similar, whatever citation style you’re using. For each source, you’ll typically include the:
- Author name
- Publication date
- Container (e.g., the book an essay was published in, the journal an article appeared in)
- Location (e.g., a URL or DOI , or sometimes a physical location)
The exact information included varies depending on the source type and the citation style. The order in which the information appears, and how you format it (e.g., capitalization, use of italics) also varies.
Most commonly, the entries in your reference list are alphabetized by author name. This allows the reader to easily find the relevant entry based on the author name in your in-text citation.
In numerical citation styles, the entries in your reference list are numbered, usually based on the order in which you cite them. The reader finds the right entry based on the number that appears in the text.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Because each style has many small differences regarding things like italicization, capitalization , and punctuation , it can be difficult to get every detail right. Using a citation generator can save you a lot of time and effort.
Scribbr offers citation generators for both APA and MLA style. Both are quick, easy to use, and 100% free, with no ads and no registration required.
Just input a URL or DOI or add the source details manually, and the generator will automatically produce an in-text citation and reference entry in the correct format. You can save your reference list as you go and download it when you’re done, and even add annotations for an annotated bibliography .
Once you’ve prepared your citations, you might still be unsure if they’re correct and if you’ve used them appropriately in your text. This is where Scribbr’s other citation tools and services may come in handy:
Plagiarism Checker
Citation Checker
Citation Editing
Plagiarism means passing off someone else’s words or ideas as your own. It’s a serious offense in academia. Universities use plagiarism checking software to scan your paper and identify any similarities to other texts.
When you’re dealing with a lot of sources, it’s easy to make mistakes that could constitute accidental plagiarism. For example, you might forget to add a citation after a quote, or paraphrase a source in a way that’s too close to the original text.
Using a plagiarism checker yourself before you submit your work can help you spot these mistakes before they get you in trouble. Based on the results, you can add any missing citations and rephrase your text where necessary.
Try out the Scribbr Plagiarism Checker for free, or check out our detailed comparison of the best plagiarism checkers available online.
Scribbr Plagiarism Checker
Scribbr’s Citation Checker is a unique AI-powered tool that automatically detects stylistic errors and inconsistencies in your in-text citations. It also suggests a correction for every mistake.
Currently available for APA Style, this is the fastest and easiest way to make sure you’ve formatted your citations correctly. You can try out the tool for free below.
If you need extra help with your reference list, we also offer a more in-depth Citation Editing Service.
Our experts cross-check your in-text citations and reference entries, make sure you’ve included the correct information for each source, and improve the formatting of your reference page.
If you want to handle your citations yourself, Scribbr’s free Knowledge Base provides clear, accurate guidance on every aspect of citation. You can see citation examples for a variety of common source types below:
And you can check out our comprehensive guides to the most popular citation styles:
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
The abbreviation “ et al. ” (Latin for “and others”) is used to shorten citations of sources with multiple authors.
“Et al.” is used in APA in-text citations of sources with 3+ authors, e.g. (Smith et al., 2019). It is not used in APA reference entries .
Use “et al.” for 3+ authors in MLA in-text citations and Works Cited entries.
Use “et al.” for 4+ authors in a Chicago in-text citation , and for 10+ authors in a Chicago bibliography entry.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .
APA format is widely used by professionals, researchers, and students in the social and behavioral sciences, including fields like education, psychology, and business.
Be sure to check the guidelines of your university or the journal you want to be published in to double-check which style you should be using.
MLA Style is the second most used citation style (after APA ). It is mainly used by students and researchers in humanities fields such as literature, languages, and philosophy.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- Citation Styles Guide | Examples for All Major Styles
- APA vs. MLA | The Key Differences in Format & Citation
- The Basics of In-Text Citation | APA & MLA Examples
More interesting articles
- Citation examples for common sources types
- Et Al. | Meaning & Use in APA, MLA & Chicago
- Hanging Indent | Word & Google Docs Instructions
- How to Cite a Book | APA, MLA, & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Journal Article | APA, MLA, & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Lecture | APA, MLA & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Newspaper Article | MLA, APA & Chicago
- How to Cite a Website | MLA, APA & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Wikipedia Article | APA, MLA & Chicago
- How to Cite a YouTube Video | MLA, APA & Chicago
- How to Cite an Image | Photographs, Figures, Diagrams
- How to Cite an Interview | APA, MLA & Chicago Style
- Parenthetical Citation | APA, MLA & Chicago Examples
- What Are Endnotes? | Guide with Examples
- What Are Footnotes? | Guide with Word Instructions
- What Does Ibid. Mean? | Definition & Examples
- What is a DOI? | Finding and Using Digital Object Identifiers
- What Is an Annotated Bibliography? | Examples & Format
Scribbr APA Citation Checker
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!


Archer Library
Action research: literature review .
- Archer Library This link opens in a new window
- EDFN 504 • Action Research Handout This link opens in a new window
- Locating Books
- ebook Collections This link opens in a new window
- A to Z Database List This link opens in a new window
- Research & Statistics
- Literature Review Resources
- Citation & Reference
Exploring the literature review
Literature review model: 6 steps.

Adapted from The Literature Review , Machi & McEvoy (2009, p. 13).
Your Literature Review
Step 2: search, boolean search strategies, search limiters, ★ ebsco & google drive.

1. Select a Topic
"All research begins with curiosity" (Machi & McEvoy, 2009, p. 14)
Selection of a topic, and fully defined research interest and question, is supervised (and approved) by your professor. Tips for crafting your topic include:
- Be specific. Take time to define your interest.
- Topic Focus. Fully describe and sufficiently narrow the focus for research.
- Academic Discipline. Learn more about your area of research & refine the scope.
- Avoid Bias. Be aware of bias that you (as a researcher) may have.
- Document your research. Use Google Docs to track your research process.
- Research apps. Consider using Evernote or Zotero to track your research.
Consider Purpose
What will your topic and research address?
In The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students , Ridley presents that literature reviews serve several purposes (2008, p. 16-17). Included are the following points:
- Historical background for the research;
- Overview of current field provided by "contemporary debates, issues, and questions;"
- Theories and concepts related to your research;
- Introduce "relevant terminology" - or academic language - being used it the field;
- Connect to existing research - does your work "extend or challenge [this] or address a gap;"
- Provide "supporting evidence for a practical problem or issue" that your research addresses.
★ Schedule a research appointment
At this point in your literature review, take time to meet with a librarian. Why? Understanding the subject terminology used in databases can be challenging. Archer Librarians can help you structure a search, preparing you for step two. How? Contact a librarian directly or use the online form to schedule an appointment. Details are provided in the adjacent Schedule an Appointment box.
2. Search the Literature
Collect & Select Data: Preview, select, and organize
AU Library is your go-to resource for this step in your literature review process. The literature search will include books and ebooks, scholarly and practitioner journals, theses and dissertations, and indexes. You may also choose to include web sites, blogs, open access resources, and newspapers. This library guide provides access to resources needed to complete a literature review.
Books & eBooks: Archer Library & OhioLINK
Databases: scholarly & practitioner journals.
Review the Library Databases tab on this library guide, it provides links to recommended databases for Education & Psychology, Business, and General & Social Sciences.
Expand your journal search; a complete listing of available AU Library and OhioLINK databases is available on the Databases A to Z list . Search the database by subject, type, name, or do use the search box for a general title search. The A to Z list also includes open access resources and select internet sites.
Databases: Theses & Dissertations
Review the Library Databases tab on this guide, it includes Theses & Dissertation resources. AU library also has AU student authored theses and dissertations available in print, search the library catalog for these titles.
Did you know? If you are looking for particular chapters within a dissertation that is not fully available online, it is possible to submit an ILL article request . Do this instead of requesting the entire dissertation.
Newspapers: Databases & Internet
Consider current literature in your academic field. AU Library's database collection includes The Chronicle of Higher Education and The Wall Street Journal . The Internet Resources tab in this guide provides links to newspapers and online journals such as Inside Higher Ed , COABE Journal , and Education Week .
Search Strategies & Boolean Operators
There are three basic boolean operators: AND, OR, and NOT.
Used with your search terms, boolean operators will either expand or limit results. What purpose do they serve? They help to define the relationship between your search terms. For example, using the operator AND will combine the terms expanding the search. When searching some databases, and Google, the operator AND may be implied.
Overview of boolean terms
About the example: Boolean searches were conducted on November 4, 2019; result numbers may vary at a later date. No additional database limiters were set to further narrow search returns.
Database Search Limiters
Database strategies for targeted search results.
Most databases include limiters, or additional parameters, you may use to strategically focus search results. EBSCO databases, such as Education Research Complete & Academic Search Complete provide options to:
- Limit results to full text;
- Limit results to scholarly journals, and reference available;
- Select results source type to journals, magazines, conference papers, reviews, and newspapers
- Publication date
Keep in mind that these tools are defined as limiters for a reason; adding them to a search will limit the number of results returned. This can be a double-edged sword. How?
- If limiting results to full-text only, you may miss an important piece of research that could change the direction of your research. Interlibrary loan is available to students, free of charge. Request articles that are not available in full-text; they will be sent to you via email.
- If narrowing publication date, you may eliminate significant historical - or recent - research conducted on your topic.
- Limiting resource type to a specific type of material may cause bias in the research results.
Use limiters with care. When starting a search, consider opting out of limiters until the initial literature screening is complete. The second or third time through your research may be the ideal time to focus on specific time periods or material (scholarly vs newspaper).
★ Truncating Search Terms
Expanding your search term at the root.
Truncating is often referred to as 'wildcard' searching. Databases may have their own specific wildcard elements however, the most commonly used are the asterisk (*) or question mark (?). When used within your search. they will expand returned results.
Asterisk (*) Wildcard
Using the asterisk wildcard will return varied spellings of the truncated word. In the following example, the search term education was truncated after the letter "t."
Explore these database help pages for additional information on crafting search terms.
- EBSCO Connect: Searching with Wildcards and Truncation Symbols
- EBSCO Connect: Searching with Boolean Operators
- EBSCO Connect: EBSCOhost Search Tips
- EBSCO Connect: Basic Searching with EBSCO
- ProQuest Help: Search Tips
- ERIC: How does ERIC search work?
★ EBSCO Databases & Google Drive
Tips for saving research directly to Google drive.
Researching in an EBSCO database?
It is possible to save articles (PDF and HTML) and abstracts in EBSCOhost databases directly to Google drive. Select the Google Drive icon, authenticate using a Google account, and an EBSCO folder will be created in your account. This is a great option for managing your research. If documenting your research in a Google Doc, consider linking the information to actual articles saved in drive.
EBSCO Databases & Google Drive
EBSCOHost Databases & Google Drive: Managing your Research
This video features an overview of how to use Google Drive with EBSCO databases to help manage your research. It presents information for connecting an active Google account to EBSCO and steps needed to provide permission for EBSCO to manage a folder in Drive.
About the Video: Closed captioning is available, select CC from the video menu. If you need to review a specific area on the video, view on YouTube and expand the video description for access to topic time stamps. A video transcript is provided below.
- EBSCOhost Databases & Google Scholar
Defining Literature Review
What is a literature review.
A definition from the Online Dictionary for Library and Information Sciences .
A literature review is "a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works" (Reitz, 2014).
A systemic review is "a literature review focused on a specific research question, which uses explicit methods to minimize bias in the identification, appraisal, selection, and synthesis of all the high-quality evidence pertinent to the question" (Reitz, 2014).
Recommended Reading
About this page
EBSCO Connect [Discovery and Search]. (2022). Searching with boolean operators. Retrieved May, 3, 2022 from https://connect.ebsco.com/s/?language=en_US
EBSCO Connect [Discover and Search]. (2022). Searching with wildcards and truncation symbols. Retrieved May 3, 2022; https://connect.ebsco.com/s/?language=en_US
Machi, L.A. & McEvoy, B.T. (2009). The literature review . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press:
Reitz, J.M. (2014). Online dictionary for library and information science. ABC-CLIO, Libraries Unlimited . Retrieved from https://www.abc-clio.com/ODLIS/odlis_A.aspx
Ridley, D. (2008). The literature review: A step-by-step guide for students . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, Inc.
Archer Librarians
Schedule an appointment.
Contact a librarian directly (email), or submit a request form. If you have worked with someone before, you can request them on the form.
- ★ Archer Library Help • Online Reqest Form
- Carrie Halquist • Reference & Instruction
- Jessica Byers • Reference & Curation
- Don Reams • Corrections Education & Reference
- Diane Schrecker • Education & Head of the IRC
- Tanaya Silcox • Technical Services & Business
- Sarah Thomas • Acquisitions & ATS Librarian
- << Previous: Research & Statistics
- Next: Literature Review Resources >>
- Last Updated: Nov 17, 2023 7:46 AM
- URL: https://libguides.ashland.edu/action-research
Archer Library • Ashland University © Copyright 2023. An Equal Opportunity/Equal Access Institution.
Educational Action Research Referencing Guide (updated Apr 2024)
This is the citationsy guide to educational action research citations, reference lists, in-text citations, and bibliographies. the complete, comprehensive guide shows you how easy citing any source can be. referencing books, youtube videos, websites, articles, journals, podcasts, images, videos, or music in educational action research..

How do you cite a book in the Educational Action Research referencing style? (2024 Guide)
How to reference a journal article in the educational action research citation style, how do you cite scientific papers in educational action research format.
References on Action Research
Qualitative research in information systems: references on action research.
Section Editor: Michael D. Myers
This is a list of references on action research. After a brief introduction which suggests those works which are essential reading for newcomers to the field, the list is organized into two parts: the first part lists citations related to the approach in Information Systems, the second lists citations related to the approach in other disciplines. Please note that this list contains a few suggestions only and is not intended to be comprehensive. I encourage you to search Google Scholar, the AIS e-library and/or some other bibliographic database for a more complete and up-to-date list.
[ Introduction ] [ Citations in Information Systems ] [ Citations in Other Disciplines ] [ Back to Qualitative Research in Information Systems ]
Introduction
A brief introduction to the action research method is the article by Susman and Evered (1978) . For a more in-depth look at the method, the collection of articles by Kemmis and McTaggart (1988) is very useful, as is the Human Relations Special Issue which was devoted to action research (see Elden and Chisholm, 1994) . In Information Systems, a good place to start would be the articles by Baskerville and Wood-Harper (1996) , and Checkland (1991) . From there, I suggest you look at the collection of articles published in the MIS Quarterly Special Issue on Action Research ( Baskerville and Myers, 2004 ). All the articles from that issue are listed below (MISQ Volume 28 Number 3).
Citations in Information Systems
Avison, D.E., Baskerville, R. and Myers, M.D. “Controlling action research projects,” Information Technology & People (14:1), 2001, pp. 28-45. Avison, David, Francis Lau, Michael D. Myers and Peter Axel Nielson. “Action Research,” Communications of the ACM, Vol. 42, No. 1, January 1999, pp. 94-97. Baskerville, R. “Investigating Information Systems with Action Research,” Communications of the AIS (2:19) 1999, AIS E-library. Baskerville, R., and Myers, M.D. “Special Issue on Action Research in Information Systems: Making IS Research Relevant to Practice-Foreword,” MIS Quarterly (28:3) 2004, pp 329-335. Baskerville, R. and Pries-Heje, J. “Grounded action research: a method for understanding IT in practice,” Accounting, Management and Information Technologies (9:1), 1999, pp. 1-23. Baskerville, R.L. and Wood-Harper, A.T. “A Critical Perspective on Action Research as a Method for Information Systems Research,” Journal of Information Technology (11), 1996, pp. 235-246. Baskerville, R.L. and Wood-Harper, A.T. “Diversity in information systems action research methods,” European Journal of Information Systems (7), 1998, pp. 90-107. Braa, J., Monteiro, E., and Sahay, S. “Networks Of Action: Sustainable Health Information Systems Across Developing Countries,” MIS Quarterly (28:3) 2004, pp 337-362. Checkland, P. “From framework through experience to learning: the essential nature of action research,” in Information Systems Research: Contemporary Approaches and Emergent Traditions , H-E. Nissen, H.K. Klein, R.A. Hirschheim (eds.), North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1991, pp. 397-403. Davison, R.M. “An Action Research Perspective of Group Support Systems: How to Improve Meetings in Hong Kong,” Unpublished PhD thesis, City University of Hong Kong, 1998. A web version of Davison’s PhD thesis is available .
Davison, R.M. “GSS and Action Research in the Hong Kong Police Force,” Information Technology and People (14:1), 2001, pp. 60-77.
Davison, R.M., Martinsons, M.G., and Kock, N. “Principles of canonical action research,” Information Systems Journal (14), 2004, pp. 65-86.
Davison, R.M., Martinsons, M.G. and Malaurent, J. Improving Action Research by Integrating Methods, Journal of the AIS (22:3), 2021, pp. 851-873.
Davison, R.M., Martinsons, M.G. and Ou, C.X.J. (2012) The Roles of Theory in Canonical Action Research, Management Information Systems Quarterly (36:3), 2021, pp. 763-786.
Davison, R.M. and Vogel, D.R. “Group Support Systems in Hong Kong: An Action Research Project,” Information Systems Journal (10:1), 2000, pp. 3-20.
Henfridsson, O., and Lindgren, R. “Multi-Contextuality in Ubiquitous Computing: Investigating the Car Case through Action Research,” Information and Organization (15:2), 2005, pp. 95-124.
Iversen, J.H., Mathiassen, L., and Nielsen, P.A. “Managing Risk In Software Process Improvement: An Action Research Approach,” MIS Quarterly (28:3) 2004, pp 395-433.
Jonsson, S. “Action Research,” in Information Systems Research: Contemporary Approaches and Emergent Traditions , H-E. Nissen, H.K. Klein and R.A. Hirschheim (eds.), North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1991.
Kock, N.F. Jr. The Effects of Asynchronous Groupware on Business Process Improvement . Unpublished PhD thesis, University of Waikato, New Zealand, 1997.
This research investigates the effects of asynchronous groupware on group-based business process improvement efforts. Thirty-eight business process improvement groups were facilitated in three organisations over four iterations of the action research cycle proposed by Susman and Evered. The asynchronous groupware tool used to support these groups was an e-mail conferencing system.
Kock, N. “Action research: Lessons learned from a multi-iteration study of computer-mediated communication in groups,” IEEE Transactions on Professional Communication , (46), 2003, pp. 105-128.
Kock, N.F., Jr., McQueen, R.J. and Scott, J.L. “Can Action Research be Made More Rigorous in a Positivist Sense? The Contribution of an Iterative Approach,” Journal of Systems and Information Technology , (1:1), 1997, pp. 1-24.
Kohli, R., and Kettinger, W.J. “Informating The Clan: Controlling Physicians’ Costs And Outcomes,” MIS Quarterly (28:3) 2004, pp 363-394.
Lau, F. “A Review on the Use of Action Research in Information Systems Studies,” in Information Systems and Qualitative Research , A.S. Lee, J. Liebenau and J.I. DeGross (eds.), Chapman and Hall, London, 1997, pp. 31-68.
Lee, A.S., Baskerville, R.L. and Davies, L. “A Workshop on Two Techniques for Qualitative Data Analysis: Action Research and Ethnography,” Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Information Systems , 1992, p. 305-306.
Lee, A.S., Baskerville, R.L., Liebenau, J. and Myers, M.D. “Judging Qualitative Research in Information Systems: Criteria for Accepting and Rejecting Manuscripts,” Proceedings of the Sixteenth International Conference on Information Systems, 1995.
Levin, M. “Action Research and Critical Systems Thinking: Two Icons Carved Out of the Same Log?”, Systems Practice (7:1), 1994, pp. 25-41.
Lindgren, R., Henfridsson, O., and Schultze, U. “Design Principles For Competence Management Systems: A Synthesis Of An Action Research Study,” MIS Quarterly (28:3) 2004, pp 435-472.
Mansell, G. “Action research in information systems development,” Journal of Information Systems (1), 1991, pp. 29-40.
Markus, M.L., Majchrzak, A., and Gasser, L. “A Design Theory for Systems that Support Emergent Knowledge Processes,” MIS Quarterly (26:3), 2002, pp. 179-212.
Mårtensson, P., and Lee, A.S. “Dialogical Action Research At Omega Corporation,” MIS Quarterly (28:3) 2004, pp 507-536.
Mathiasen, L. “Collaborative practice research,” Information Technology & People (14:4), 2002, pp. 321-345.
Reports from a systems development research tradition in which emphasis is put on relating research activities to practice and on establishing fruitful collaboration between groups of researchers and practitioners. Describes and evaluates a specific research project in which a large group of researchers and practitioners worked together to understand, support, and improve systems development practices in four organisations over a period of three years. Uses the case to reflect on the research goals, approaches, and results involved in this tradition for researching systems development practice. Proposes collaborative practice research as a way to organise and conduct research into systems development practice based on close collaboration between researchers and practitioners. Exemplifies the use of pluralist research methodology by combining action research with experiments and conventional practice studies. Argues that collaborative practice research offers one practical way to strike a useful balance between relevance and rigour. Concludes with a discussion of the implications for the relation between research and practice within the systems development discipline and with lessons on how to design research efforts as collaborations between researchers and practitioners.
Sein, M., Henfridsson, O., Purao, S., Rossi, M., and Lindgren, R. 2011. “Action Design Research,” MIS Quarterly (35:2), pp. 37-56.
Street, C.T., and Meister, D.B. “Small Business Growth And Internal Transparency: The Role Of Information Systems,” MIS Quarterly (28:3) 2004, pp 473-506.
Warmington, A. “Action Research: Its Methods and its Implications,” Journal of Applied Systems Analysis (7), 1980, pp. 23-39.
Wood-Harper, A.T. “Research Methods in Information Systems: Using Action Research,” in Research Methods in Information Systems , E. Mumford, R.A. Hirschheim, G. Fitzgerald and A.T. Wood-Harper (eds.), North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1985.
Wood-Harper, A.T. “Viewpoint: Action Research,” Journal of Information Systems (2), 1992, pp.235-236.
Ytterstad, P., Akselsen, S., Svendsen, G. and Watson, R.T. “Teledemocracy: Using Information Technology to Enhance Political Work,” MISQ Discovery (1), 1996.
Citations in Other Disciplines
Argyris, C., Putnam, R. and Smith, D. Action Science , Jossey-Bass, San Francisco, 1985. Argyris, C. and Schön, D. Organizational Learning: A Theory of Action Perspective . Addison-Wesley, Reading, 1978. Argyris, Chris, and Donald A. Schön. “Participatory Action Research and Action Science Compared: A Commentary”, in: William Foote Whyte (ed.), Participatory Action Research , Sage, Newbury Park, CA, 1991, pp. 85-98. Baburoglu, O.N. and Ravn, I. “Normative Action Research.” Organization Studies (13:1), 1992, pp. 19-34. Blum, F. “Action research – a scientific approach?” Philosophy of Science 22 (January), 1955, pp. 1-7. Brown, L.D. and Tandon, R. “Ideology and Political Economy in Inquiry: Action Research and Participatory Research,” Journal of Applied Behavioural Science (19), 1983, pp. 277-285. Carr, W. and Kemmis, S. Becoming Critical: Education, Knowledge and Action Research , Falmer Press, London, 1986. Chisholm, R.F. and Elden, M. “Features of Emerging Action Research,” Human Relations (46:2), 1993, pp. 275-298. Clark, P.A. Action Research and Organizational Change , Harper and Row, London, 1972. Cunningham, B. “Action Research: Toward a Procedural Model,” Human Relations (29:3), 1976, pp. 215-238. Elden, M. and Chisholm, R.F. “Emerging Varieties of Action Research: Introduction to the Special Issue,” Human Relations (46:2), 1993, pp. 121-142. Eden, Colin, and Chris Huxham. “Action Research for Management Research”, British Journal of Management , (7), 1991, pp. 75-86. Greenwood, D.J., Whyte, W.W. and Harkavy, I. “Participatory Action Research as a Process and as a Goal,” Human Relations (46:2), 1993, pp. 175-192. Gustavsen, B. “Action Research and the Generation of Knowledge,” Human Relations (46:10), 1993, pp. 1361-1365. Harris, R.T. “Improving Patient Satisfaction Through Action Research,” Journal of Applied Behavioral Science (14:3), 1978, pp. 382-399. Heller, F. “Another Look at Action Research,” Human Relations (46:10), 1993, pp. 1235-1242. Hindle, T., Checkland, P., Mumford, M. and Worthington, D. “Developing a Methodology for Multidisciplinary Action Research: A Case Study,” Journal of the Operational Research Society (46:4), 1995, pp. 453-464. Hult, M. and Lennung, S-A. “Towards a Definition of Action Research: A Note and Bibliography,” Journal of Management Studies , May 1980, pp. 241-250. Johnston, S. and Proudford, C. “Action Research: Who Owns the Process?,” Educational Review (46:1), 1994, pp. 3-14. Karlsen, J.I. “Action Research as a Method,” in Participatory Action Research , W.F. Whyte (ed.), Sage Publications, New York, 1991. Kemmis, S. and McTaggart, R. The Action Research Reader . Third edition. Deakin University Press, Victoria, 1988. Ledford, G.E.Jr. and Mohrman, S.A. “Self-Design for High Involvement: A Large-Scale Organizational Change,” Human Relations (46:1), 1993, pp. 143-173. Lewin, K. “Frontiers in Group Dynamics: II. Channels of Group Life; Social Planning and Action Research,” Human Relations (1:2), pp. 143-153. Lippit, G. and Lippit, R. The Consulting Process in Action. University Associates, San Diego, CA, 1978. McTaggart, R. Action Research: A Short Modern History , Deakin University Press, Geelong, 1991. Nosek, J.T. and Yaverbaum, G. “Overcoming Obstacles to University and industry Synergy in Information System Education: Lessons from Action Research,” Education for Information , (9), 1991, pp. 3-19. Peters, M. and Robinson, V. “The Origins and Status of Action Research,” Journal of Applied Behavioral Science (20:2), 1984, pp. 113-124. Rapoport, R.N. “Three Dilemmas in Action Research,” Human Relations ,, (23:6), 1970, pp. 499-513. Robinson, V.M.J. “Current Controversies in Action Research,” em>Public Administration Quarterly (17:3), 1993, pp. 263-290. Susman, G.I. “Action Research: A Sociotechnical systems perspective,” in Beyond Method: Strategies for Social Science Research , G. Morgan (ed.), Sage Publications, London, 1983. Susman, G.I. and Evered, R.D. “An Assessment of the Scientific Merits of Action Research,” Administrative Science Quarterly , (23) 1978, pp. 582-603. Trist, E. “Engaging with large-scale systems,” in Experimenting with Organizational Life: The Action Research Approach , A. Clark (ed.), Plenum, New York, 1976, pp. 43-75. Whyte, W.F. (ed.). Participatory Action Research , Sage Publications, New York, 1991.
[ Back to Qualitative Research in Information Systems ]
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to format your references using the Educational Action Research citation style
This is a short guide how to format citations and the bibliography in a manuscript for Educational Action Research. For a complete guide how to prepare your manuscript refer to the journal's instructions to authors .
- Using reference management software
Typically you don't format your citations and bibliography by hand. The easiest way is to use a reference manager:
- Journal articles
Those examples are references to articles in scholarly journals and how they are supposed to appear in your bibliography.
Not all journals organize their published articles in volumes and issues, so these fields are optional. Some electronic journals do not provide a page range, but instead list an article identifier. In a case like this it's safe to use the article identifier instead of the page range.
- Books and book chapters
Here are examples of references for authored and edited books as well as book chapters.
Sometimes references to web sites should appear directly in the text rather than in the bibliography. Refer to the Instructions to authors for Educational Action Research .
This example shows the general structure used for government reports, technical reports, and scientific reports. If you can't locate the report number then it might be better to cite the report as a book. For reports it is usually not individual people that are credited as authors, but a governmental department or agency like "U. S. Food and Drug Administration" or "National Cancer Institute".
- Theses and dissertations
Theses including Ph.D. dissertations, Master's theses or Bachelor theses follow the basic format outlined below.
- News paper articles
Unlike scholarly journals, news papers do not usually have a volume and issue number. Instead, the full date and page number is required for a correct reference.
- In-text citations
References should be cited in the text by name and year in parentheses :
Here are examples of in-text citations with multiple authors:
- Two authors: (Bekerman and Einav 2015)
- Three authors: (Nam, Park, and Ko 2012)
- 4 or more authors: (Stone et al. 2007)
- About the journal
- Other styles
- Current Opinion in Microbiology
- Chemosphere
- Computational Cognitive Science
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
6 Common Leadership Styles — and How to Decide Which to Use When
- Rebecca Knight

Being a great leader means recognizing that different circumstances call for different approaches.
Research suggests that the most effective leaders adapt their style to different circumstances — be it a change in setting, a shift in organizational dynamics, or a turn in the business cycle. But what if you feel like you’re not equipped to take on a new and different leadership style — let alone more than one? In this article, the author outlines the six leadership styles Daniel Goleman first introduced in his 2000 HBR article, “Leadership That Gets Results,” and explains when to use each one. The good news is that personality is not destiny. Even if you’re naturally introverted or you tend to be driven by data and analysis rather than emotion, you can still learn how to adapt different leadership styles to organize, motivate, and direct your team.
Much has been written about common leadership styles and how to identify the right style for you, whether it’s transactional or transformational, bureaucratic or laissez-faire. But according to Daniel Goleman, a psychologist best known for his work on emotional intelligence, “Being a great leader means recognizing that different circumstances may call for different approaches.”
- RK Rebecca Knight is a journalist who writes about all things related to the changing nature of careers and the workplace. Her essays and reported stories have been featured in The Boston Globe, Business Insider, The New York Times, BBC, and The Christian Science Monitor. She was shortlisted as a Reuters Institute Fellow at Oxford University in 2023. Earlier in her career, she spent a decade as an editor and reporter at the Financial Times in New York, London, and Boston.
Partner Center
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Reference List: Textual Sources

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Basic Format for Books
Edited book, no author, edited book with an author or authors, a translation.
Note : When you cite a republished work, like the one above, in your text, it should appear with both dates: Plato (385-378/1989)
Edition Other Than the First
Article or chapter in an edited book.
Note : When you list the pages of the chapter or essay in parentheses after the book title, use "pp." before the numbers: (pp. 1-21). This abbreviation, however, does not appear before the page numbers in periodical references, except for newspapers. List any edition number in the same set of parentheses as the page numbers, separated by a comma: (2nd ed., pp. 66-72).
Multivolume Work
Articles in periodicals.
APA style dictates that authors are named with their last name followed by their initials; publication year goes between parentheses, followed by a period. The title of the article is in sentence-case, meaning only the first word and proper nouns in the title are capitalized. The periodical title is run in title case, and is followed by the volume number which, with the title, is also italicized. If a DOI has been assigned to the article that you are using, you should include this after the page numbers for the article. If no DOI has been assigned and you are accessing the periodical online, use the URL of the website from which you are retrieving the periodical.
Article in Print Journal
Note: APA 7 advises writers to include a DOI (if available), even when using the print source. The example above assumes no DOI is available.
Article in Electronic Journal
Note : This content also appears on Reference List: Online Media .
As noted above, when citing an article in an electronic journal, include a DOI if one is associated with the article.
DOIs may not always be available. In these cases, use a URL. Many academic journals provide stable URLs that function similarly to DOIs. These are preferable to ordinary URLs copied and pasted from the browser's address bar.
Article in a Magazine
Article in a newspaper.
The Federal Register
The daily journal of the united states government, request access.
Due to aggressive automated scraping of FederalRegister.gov and eCFR.gov, programmatic access to these sites is limited to access to our extensive developer APIs.
If you are human user receiving this message, we can add your IP address to a set of IPs that can access FederalRegister.gov & eCFR.gov; complete the CAPTCHA (bot test) below and click "Request Access". This process will be necessary for each IP address you wish to access the site from, requests are valid for approximately one quarter (three months) after which the process may need to be repeated.
An official website of the United States government.
If you want to request a wider IP range, first request access for your current IP, and then use the "Site Feedback" button found in the lower left-hand side to make the request.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
References. Barton, K. C. (2015). Elicitation techniques: getting people to talk about ideas they don't usually talk about. Theory & Research in Social Education , 43 (2), 179-205. Bassey, M. (1998). Action research for improving educational practice.
Journal Articles. References to journal articles usually include the author's name, title of the article, name of the journal, volume and issue number, page numbers, and publication date. Example: Johnson, T. (2021). The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health. Journal of Psychology, 32 (4), 87-94.
This paper analyzed the action research reports (ARRs) in terms of objectives, methodologies, citations and references, structures, areas covered in the problem, and lengths purposively selecting ...
Action research is a research method that aims to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue. In other words, as its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time. It was first coined as a term in 1944 by MIT professor Kurt Lewin.A highly interactive method, action research is often used in the social ...
Before you turn in your paper compare the Reference List with the content of the paper. Make sure that ALL the items in the Reference list are cited in the paper, and; ALL the items cited in the paper are in the Reference list. All citations in the text and the Reference list should match.
APA in-text citations The basics. In-text citations are brief references in the running text that direct readers to the reference entry at the end of the paper. You include them every time you quote or paraphrase someone else's ideas or words to avoid plagiarism.. An APA in-text citation consists of the author's last name and the year of publication (also known as the author-date system).
Action research is simply a form of self-reflective enquiry undertaken by participants in social situations in order to improve the rationality and justice of their own practices, their understanding of these practices, and the situations in which the practices are carried out (Carr and Kemmis 1986: 162).
Chicago Style. A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, & Dissertations. LB2369 .T8 2018. Library use only copies are available in Reference and Reserves. Additional copies are available at the ATS library. The Chicago Manual of Style Online. Chicago Manual of Style: Video Tutorials.
Definition. Action research is a form of enquiry that integrates theory and action to address real life problems. It enables practitioners to systematically evaluate and improve their practice. The number of types of action researches has multiplied over the last 50 years (Fourali 2016 ) or so and, accordingly, so did the number of definitions ...
As the name suggests, action research is an approach to research which aims at both taking action and creating knowledge or theory about that action as the action unfolds. It rejects the notion that research must be value free in order to be credible, in favor an explicitly socially engaged and democratic practice (Brydon-Miller et al. 2003 ).
References on Action Research. This is a list of references on action research. After a brief introduction which suggests those works which are essential reading for newcomers to the field, the list is organized into two parts: the first part lists some important citations related to the approach in other disciplines (including the source disciplines), the second lists citations related to the ...
Action research is a research method that aims to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue. In other words, as its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time. It was first coined as a term in 1944 by MIT professor Kurt Lewin. A highly interactive method, action research is often used in the social ...
Action researchers can share their findings in several ways that colleagues and other consumers of research will be able to engage with their work. The three following ways are the most common paths for educator-researchers to share their work: Written Report or Article. Develop a report for personal documentation or to be shared with ...
Thus, action research is often a cyclical process. The action research report that you write is based on this process. Typically, an action research report is written in the same way as you would write an original research article. However, you need to ensure that your report has the following components: The context or background.
This brings us back to the essential steps of action research: identifying the problem, devising an action plan, implementing the plan, and finally, observing and reflecting upon the process. Your action research report should comprise all of these essential steps. Feldman and Weiss (n.d.) summarized them as five structural elements, which do ...
To quote a source, copy a short piece of text word for word and put it inside quotation marks. To paraphrase a source, put the text into your own words. It's important that the paraphrase is not too close to the original wording. You can use the paraphrasing tool if you don't want to do this manually.
How to write references in research papers. If the citations follow the Harvard system, references in a research papers are sorted alphabetically by the last name of the first author; if the citations follow the Vancouver system, the references are arranged by numbers: the reference corresponding to the first numbered citation is numbered 1 ...
In The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students, Ridley presents that literature reviews serve several purposes (2008, p. 16-17). Included are the following points: Historical background for the research; Overview of current field provided by "contemporary debates, issues, and questions;" Theories and concepts related to your research;
This is the Citationsy guide to Educational Action Research citations, reference lists, in-text citations, and bibliographies. The complete, comprehensive guide shows you how easy citing any source can be. Referencing books, youtube videos, websites, articles, journals, podcasts, images, videos, or music in Educational Action Research. ...
1.3 Writing your paper. ... Action Research adheres to the APA reference style. View the APA guidelines to ensure your manuscript conforms to this reference style. 4.5 English language editing services. Authors seeking assistance with English language editing, translation, or figure and manuscript formatting to fit the journal's ...
Qualitative Research in Information Systems: References on Action Research. Section Editor: Michael D. Myers This is a list of references on action research. After a brief introduction which suggests those works which are essential reading for newcomers to the field, the list is organized into two parts: the first part lists citations related to the approach in Information Systems, the second ...
The easiest way is to use a reference manager: Paperpile. The citation style is built in and you can choose it in Settings > Citation Style or Paperpile > Citation Style in Google Docs. EndNote. Download the output style file. Mendeley, Zotero, Papers, and others. The style is either built in or you can download a CSL file that is supported by ...
366 Belenky, M.F. (1996). "Public homeplaces: nurturing the development of people, families, and communities". In: Goldberger, N., Tarule, J., Clinchy, B. and
Denny, H., Nordlof, J., & Salem, L. (2018). "Tell me exactly what it was that I was doing that was so bad": Understanding the needs and expectations of working-class students in writing centers.
Much has been written about common leadership styles and how to identify the right style for you, whether it's transactional or transformational, bureaucratic or laissez-faire. But according to ...
Writing your journal article in twelve weeks: A guide to academic publishing success ... does not appear before the page numbers in periodical references, except for newspapers. List any edition number in the same set of parentheses as the page numbers, separated by a comma: (2nd ed., pp. 66-72). ... Data and experience design: Negotiating ...
The R&D Plan will act as an organizing national document, providing guidance for government investments in spectrum-related research and offering valuable insights. The Plan will identify key innovation areas for spectrum research and development and will include a process to refine and enhance these areas on an ongoing basis. Workshop Objectives.