The Ultimate Guide to Project Cost Management with Templates
By Kate Eby | April 25, 2017
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Your organization’s projects are critical to its future. Sound cost management enables you to make optimal use of your resources (time, personnel, equipment, and materials), make data-driven decisions about projects and their risks, measure financial performance, and provide key metrics to senior management. This definitive guide to project cost management includes templates for key activities like cost estimating and creating a cost management plan. You’ll learn important terms, best practices, and subtle distinctions (such as the difference between cost management and strategic cost management), as well as how cost management works in specialized cases, like construction and IT projects.

What Is Project Cost Management?
Whether you are developing a new product, designing a facility, or changing a key process, it’s challenging to forecast and manage project costs effectively. In fact, the job is so challenging that half of all large IT projects massively blow their budgets , running on average 45 percent over budget and seven percent over time, according to consultants McKinsey & Co. and the University of Oxford. For projects in other sectors, the news is no better. The Project Management Institute (PMI) reported in 2016 that companies were completing only 53 percent of projects within their original budget. However, strong cost management helps you avoid that fate. So what exactly is cost management? Cost management refers to the activities concerning planning and controlling a project’s budget. Effective cost management ensures that a project is completed on budget and according to its planned scope. Since you assess the success of a project at least in part by its cost performance, cost management is a prime determinant of project outcome. Cost management activities are conducted throughout the project life cycle, from planning and budget allocation to controlling costs during project execution and assessing a project’s cost performance upon completion. Although cost management includes a whole ensemble of activities, it is sometimes referred to in terms of more specific functions, such as spend management, cost accounting, and cost transparency. Cost managers sometimes use these terms as loose synonyms for the broad cost management function.
Cost Management: Four Major Steps
The Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK), the bible of project management theory, says cost management is made up of four processes. These generally adhere to the sequence that follows — as a project goes from the planning board to reality.
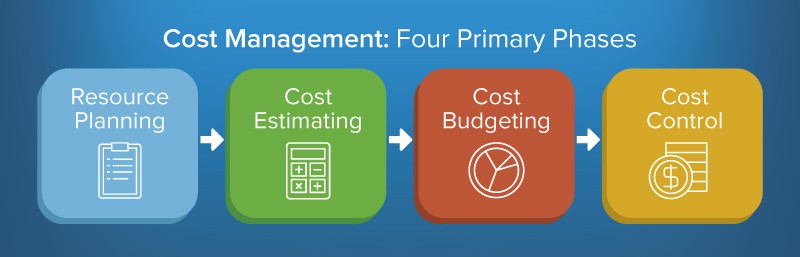
- Resource Planning: Part of the initiation stage of a project, resource planning uses a work breakdown structure — a hierarchical representation of all project deliverables and the work required to complete them — to calculate the full cost of resources needed to complete a project successfully. Managers typically determine required resources for each work breakdown structure component and then add them to create a total resource cost estimate for all project deliverables.
- Cost Estimating: Cost estimating is an iterative process that uses a variety of estimating techniques to determine the total cost of completing a project. Cost estimating techniques vary widely in their approaches to computing project costs, and stretch from conceptual techniques that draw mainly from historical experience and expert judgment to determinative techniques that estimate costs on a component-by-component basis. We will discuss these techniques in detail later, as they vary in their levels of accuracy. Determinative techniques are the most accurate; however, while the estimator’s job is always to create the most accurate estimate possible, determinative estimating techniques are only an option if you’ve reasonably finalized a project’s scope and deliverables. As such, you use the less accurate estimating techniques during the earliest stages of project planning, and then revise and update estimates as the project continues to be defined. To learn more about cost estimating, read The Ultimate Guide to Project Cost Estimating .
- Cost Budgeting: Once you’ve created satisfactory estimates, you can finalize and approve the project’s budget. Cost managers typically release budgeted amounts in stages according to the level of a project’s progress. These allocations include contingencies and reserves.
- Cost Control: Cost control is the practice of measuring a project’s cost performance according to cost and schedule baselines that provide points of comparison throughout the project life cycle. The specific requirements for effective cost control are set out in the project management plan. The individual in charge of cost management investigates the reasons for cost variations - if they deem cost variations unacceptable, corrective action is likely. Cost control also includes other related responsibilities, such as ensuring that updated project budgets reflect changes to a project’s scope.
Key Components of the Cost Management Plan
The cost management plan guides these four processes. Created during the project planning phase, the cost management plan is a document that defines how you manage, control, and communicate a project’s costs in order to complete the project on budget. Among other things, a cost management plan identifies the individual or group responsible for cost management, details how you will assess a project’s cost performance, and sets rules for how to communicate cost performance to project shareholders. It also establishes the methodologies by which you will control project cost variations. While you can customize a cost management plan to fit your organization’s needs, they generally follow a standard format. Sections often include the cost variance plan, the cost management approach, information on cost estimation, the cost baseline, cost control, and reporting processes, the change control process, the project budget, and approvals. You may also want to include the spending authority levels for key project personnel, specifying which roles can approve costs up to specific thresholds. Let’s look at the sections in greater depth:
- Cost Variance Plan: Cost variance is when the actual amount differs from the budgeted amount. In your cost management plan, you’ll need a section that details the actions you should take, including who is held responsible in the case of a cost variance. The size of the variance usually necessitates different action: a cost variance of less than five percent might result in an explanation of that variance, while a 95-percent-or-greater variance could force the project to be abandoned. To learn how to calculate cost variance, read Hacking the PMP: Studying Cost Variance . For a more detailed template on tracking schedule and budget variances, see this template:
- Cost Management Approach: This section outlines the approach a manager uses for cost management. The level of rigor can vary, but this describes how to establish a cost baseline and how to compare actual costs. You usually track and report costs through control accounts, where you roll up costs of subtasks. This often occurs at the third level of the work breakdown structure, a tool that breaks a project into small components or chunks of work to determine the resources needed to complete a job or project. However, the point at which you track and report depends on the scope of the project.
- Cost Estimation: Here you will define the methods used for estimating project costs, the levels of variation, and the expected precision, accuracy, and risk.
- Cost Baseline: This has a specialized meaning in project management and represents the authorized, time-phased spending plan against which you measure cost performance. It’s the sum of the estimated project cost and contingency reserves.
- Cost Control and Reporting Process: This section establishes how you measure costs and their key metrics during the project. We’ll provide greater detail on this later.
- Change Control Process: This describes the process for making changes to the cost baseline and how to approve those proposed changes.
- Project Budget: The budget builds on the cost baseline by totalling the cost of executing the project (including contingencies for possible risks). It also adds in management reserves, which is an amount to cover unanticipated risks or unidentified events that may arise. An organization will usually set a policy for this, and the amount is often five to 15 percent of the total budget.
Cost Management Activities: Essential Functions at Each Phase
Cost management includes a number of activities conducted at different phases during the project life cycle. It’s important to include the cost management function while developing project plans so that you build solid financial controls into the project structure. Here are some key terms and stages relevant to cost management: Planning: Using the work breakdown structure to determine the resources needed to complete a job or project. Estimating: The act of calculating or predicting the expected total cost of completing a project. Budgeting: The authorization of a budget based on a cost estimate to complete the project. You typically authorize budgets in tandem with schedules, so you can assess cost performance at specific points. Financing and Funding: The process of requesting, authorizing, and receiving money for a project. Cost Management: The general practice of overseeing project expenditures and making cost-related decisions throughout the project life cycle. Controlling: Addressing cost variations to avoid cost overruns. Job Control: Controlling project expenditure by comparing costs predicted by the cost estimate and costs actually being incurred. Scheduling: You can determine a project’s cost performance by using a schedule that compares the expected expenditure to the actual costs the project is incurring at any point in time. Accounting: The practice of recording expenditures and reconciling transactions.
How Accurate Project Cost Estimating Aids Cost Management Efforts
The first step towards robust cost management is having a clear idea of your project’s likely costs. However, it’s futile to track and control costs if you base your spending on unrealistic estimates. Project estimating considers several variables, including the method you use to create the estimate, the stage at which you build your estimate, and the types of cost you include. The first variable is the method you employ. You can produce cost estimates using a variety of estimating techniques, depending on the extent to which you define a project and the type of information you have access to. Here are some common estimation techniques:
Analogous Estimating: This uses historical data from similar past projects to create estimates for new projects. This method works if you have experience with projects of the same type.
Parametric Estimating: This method estimates time and cost by multiplying per unit or per task amounts by the total number expected in the project. The rates are often standard or publicly published rates and can be expressed in hours of work, amount of data entered, or the number of units of a product manufactured. This technique has a reputation for good reliability, but it’s less relevant when output isn’t uniform, such as when writing computer code. Some projects have widely varying or unprecedented tasks, so they do not lend themselves to this method.
Bottom-Up Estimating: This is a determinative estimating technique that estimates costs for work breakdown structure components and adds them together to create a cost estimate for an entire project. The project team members help create the estimate. Since the people who are going to be doing the work are engaged in estimating, professionals consider this method highly accurate, as well as a team commitment builder.
Three-Point Estimating: This is a PERT -related statistical method that uses the optimistic (lowest), pessimistic (highest), and most likely cost estimates to create expected values and standard deviations for project expenditures.
Software-Based Estimating: You can use software-based estimating techniques, such as Monte Carlo simulation, to model the effects of risk events on project costs. Another factor influencing the cost estimating is the stage at which you build your cost estimate. As a project progresses, you discover more variables and actual costs, so project estimates become more refined. You can classify cost estimates based on how well you define the project scope at the time of estimation and on the type of estimation technique you use - the latter generally determines the accuracy of an estimate. In order of accuracy, the main classes of cost estimates are: Order of Magnitude Estimates: These are very rough cost estimates based on expert judgment and on adjusting the costs of the current project to reflect the costs of similar, past projects. Created before fully defining projects, they are only used in high-level project screening. Preliminary Estimates: A preliminary estimate uses somewhat-detailed scope information to form estimates based on unit costs. These estimates are accurate enough to use as the basis for budgeting. Definitive Estimates: Created when you’ve fully defined a project’s scope, a definitive estimate uses deterministic estimating techniques, such as bottom-up estimating. Experts agree that definitive estimates are the most accurate and reliable. The final variable affecting project estimation is the type of cost included. Of course, your project budget must include all the relevant costs for labor and materials, but whether you include a portion of your organization’s indirect costs depends on the policies of your organization and the type of project. Here are the terms experts use to distinguish between various types of costs: Direct Costs: Direct costs are those which you can directly associate with a specific cost object. They are billable to specific projects.
Indirect Costs: You cannot associate indirect costs with a specific cost object, and you typically incur indirect costs by a number of projects at the same time. They are not billable to specific projects.
Fixed Costs: Fixed costs are costs you incur during manufacturing that are not associated with the volume of produced output.
Variable Costs: Variable costs are costs you incur during manufacturing that are directly associated with the volume of produced output.
Sunk Cost: A sunk cost is an expense you cannot recoup once it is incurred.
Opportunity Cost: When selecting a course of action, its opportunity cost is the loss of potential benefits from all alternative courses of action.
Costing Techniques Determine How to Account for Project Costs
A costing technique is the way in which you compute the total cost of producing a product or performing a task. Depending on the activity or activities being costed, you may use a variety of techniques. Here are some commons ones: Job Costing: Managers use job costing, also called job-order costing, to determine the cost of a product that is unique or dissimilar to other products. In industries such as construction, it’s extremely rare for two jobs to be identical. Job-order costing uses a unique job-cost record that compiles total labor and resource costs, as well as applicable overheads, for each task or activity completed as part of a task to determine total expenditures for the job. The job-cost record includes both direct and indirect costs. Process Costing: You use process costing to determine costs for products or tasks that are identical. Unlike job costing, it does not compute the total cost of a product by summing up the costs of all tasks and activities that go into creating the product. Instead, process costing looks at the processes included in the mass production that creates products. By dividing the total cost of a process by the number of units output, it is possible to determine the cost per unit of each process. After this, you may total the costs per unit of every process involved in the eventual manufacturing of the product. In this way, you compute the cost per unit of each product on a process-by-process basis. Activity-Based Costing: Activity-based costing (ABC) is an approach to assigning overhead costs to products. Since overhead cost allocation based simply on the number of machine hours needed may be misleading, this costing technique looks at the activities focused on creating a product — testing, machine setup, etc. — and then assigns portions of their costs to all products created using these activities. Products that were not created via these activities do not have shares of these activities’ costs added on. Direct Costing: Direct costing, also called contribution costing or variable costing, is a technique that only assigns variable manufacturing costs to the cost of a product. You do not add fixed manufacturing costs to the cost of creating a product but instead associate those costs with the time period during which you incur them. Life-Cycle Costing: Life-cycle costing is a comparative analysis technique that involves summing the total costs incurred during the life cycles of project options in order to choose the best option. Since starting capital costs may not be an accurate representation of how much a project will eventually cost, life-cycle costing includes all costs associated with ownership — including maintenance and disposal costs — to enable better decision making.
Measuring Project Performance With Cost Management KPIs
Once your budget is approved and your project is under way, you’ll want to benchmark your progress relative to your cost management plan. First, there are some key metrics and performance indicators to understand: Project Cost Performance: A project’s cost performance is an assessment of how actual expenditure on a project compares with planned expenditure as detailed in the project budget. The project manager communicates a project’s cost performance to the project stakeholders, and it may serve as the basis for preventative or corrective actions to avoid cost overruns. Earned Value: Earned value is a method of measuring project cost performance. It is based on the use of planned value (where you allot specific portions of a project’s budget to the project tasks), and earned value (where you measure progress in terms of the planned value that is earned upon completion of tasks). You may contrast the earned value with the actual cost - the expenditure you actually incur up to a certain point in the project schedule - to see how actual project costs compare to expected project costs. Cost Performance Index (CPI): This is a measurement of how earned value compares to actual cost. This ratio measures a project’s cost efficiency at a given point in time by expressing earned value in proportion to actual cost. To calculate CPI, divide earned value by actual cost. A result of 1 means the project is exactly on budget; a number above 1 means it is under budget.
To learn more about KPIs in project management, read All About KPI Dashboards .
How to Control Costs
Effective cost control means performing a number of related activities that all begin by monitoring costs — since you can’t know if costs are greater than planned unless you are tracking actual expenses. Then, project managers need to decide how to respond to cost variances. Here are some key steps and concepts that inform the cost control process: Monitoring Cost Performance: A project manager routinely monitors a project’s cost performance by creating performance reports that summarize current performance and forecast whether you will complete the project on budget. You provide project stakeholders with information about a project’s cost performance. Reviewing Changes: You must amend the cost baseline to reflect all cost-related changes, and you should inform the project shareholders about all changes. Actual Costs versus Budgeted Costs: Upon milestone and entire project completion, you examine the variances between actual costs and budgeted costs. Responses to the cost management plan will depend on the magnitude of the variance and the stage of the plan - this could range from a discussion to changes in the project scope that reduce costs. Reserve Analysis: Use reserve analyses to allocate contingency reserves to projects based on the likelihoods and magnitudes of risk. Cash-Flow Analysis: Used in financial reporting, cash-flow analyses detail cash inflows and outflows over a given period of time, and provide starting and ending balances. Learning-Curve Theory: The learning-curve theory applies to the relationship between the time spent producing a unit and the number of units produced. According to the theory, the time spent on each unit should decrease as workers gain experience and therefore produce units faster.
Cost Management vs. Strategic Cost Management
While cost management reduces expenses regardless of their cause or purpose, strategic cost management is a sub-discipline that strives to manage cost while also making the organization stronger. Robin Cooper, Professor of Management at Claremont’s Peter F. Drucker Graduate Management Center and Regine Slagmulder, Professor of Management Accounting at Tilberg University in the Netherlands, define strategic cost management as the “application of cost management techniques so that they simultaneously improve the strategic position of a firm and reduce costs.” Strategic cost management centers on the idea that cost reduction initiatives can affect an organization’s strategic position. Strategic cost management emphasizes considering the strategic and financial impact of cost management techniques. Cooper and Slagmulder classify cost management initiatives as one of three types based on how the initiative affects the organization: Strengthen: An example of an initiative that strengthens competitive positioning is a taxi service that replaces its phone booking system and team of booking agents with an app that allows people to book taxis using their mobile devices. An initiative like this both reduces costs and gives a company a strategic advantage, as it makes it easier to book taxis on short notice. No effect: An initiative that has no effect on competitiveness might concern a publishing house that outsources proofreading tasks to international freelancers who accept lower wages. While this increases the company’s profitability, it does not affect its strategic positioning. Weaken: Finally, an initiative that actively harms competitive positioning might involve the taxi company decreasing the frequency of regular vehicle maintenance, a move which, while saving costs initially, will result in cars breaking down more often. Strategic cost management also comprises a number of important strategies: Relevant Cost Strategies: Use relevant cost strategies to compare and decide between alternative courses of action. Relevant costs are costs you can reduce by adopting a particular course of action. They are different from sunk costs (which you cannot recoup once spent) and fixed overhead costs (which are the same for all potential courses of action). When you make decisions, a relevant costs strategy focuses only on costs that vary among options. Evaluating Opportunity Costs: Evaluating opportunity costs is a more holistic approach to decision making that considers not only all the monetary aspects of alternative courses of action, but also all the intangible aspects. For example, a company providing vehicle repair services might have to decide between two qualities of engine oil, taking into account both that one is more expensive than the other and that the more expensive engine oil also preserves engine health in the long term. Balanced Scorecard Strategy: A balanced scorecard strategy allows businesses to assess the impact of cost management initiatives across four key areas: financial results, customer impact, internal business processes, and employee growth and development. It provides a framework for thorough consideration of the impacts of cost management initiatives.
Getting Into the Details: Cost Accounting in Project Cost Management
Cost accounting involves the recording and classification of costs associated with a project. It is an internal practice that supports managerial decision making and is a primary discipline concerning cost management.
Cost accounting is different than general financial accounting. Financial accounting concerns reporting an organization’s past financial performance and does not delve into extensive detail. Since you carry out cost accounting for a specific area of activity within a company — such as a particular project or geographical region — it focuses on more granular aspects and may include projections of future costs. Cost accounting involves preparing reports for an organization’s management (these reports are not distributed externally). By contrast, financial accounting deals with standardized reports that may be distributed to a variety of stakeholders and regulators. As such, you typically perform cost accounting on an as-needed basis, such as during a strategic project, and it does not follow a mandated format. Financial accounting, on the other hand, is a mandated and regulated formal process, and you must create financial reports according to international financial reporting standards. There are a few commonly used cost accounting approaches: Standard Cost Accounting: This is based on the concept of efficiencies , or ratios that compare the time and resource costs of actually completing an activity with the costs of completing the activity under standard conditions. Variance analysis is a core element of standard cost accounting. However, since the idea of efficiencies is based on a paradigm in which labor costs contribute substantially to manufacturing — which is no longer the case — standard cost accounting is somewhat outdated. Activity-Based Costing: This is an approach to assigning overhead costs that examines activities that provide a service, execute a task, or create a product, and then assigns portions of their costs to output. Resource Consumption Accounting (RCA): This approach emerged around 2000, and assigns costs based on the consumption of resources. It uses a German cost management system known as GPK and activity-based costing, a cost allocation method. Throughput Accounting: This is an accounting approach that aims to maximize profitability by increasing the rate of production of goal units and minimizing operating expenses and investment costs. Life-Cycle Costing: This is a method of analyzing project alternatives that focuses on total costs of ownership and selecting the most cost-effective option based on more than simple capital costs. Environmental Accounting: Reporting the environmental costs incurred by a company or project’s activities. Target Costing: This uses a predetermined market price and preferred profit margin to determine how much money can be used to create a product or service. The target cost is the maximum amount you can spend on production without affecting the profit margin. Cost Coding: To make cost accounting easier, most organizations have adopted a method of identifying costs with a code, usually a number. The root of the code usually represents the type of expense, cost center, or business unit involved. This makes it easier to group and find related expenses in financial reports. Individual projects may be assigned their own code. A common structure in an enterprise or very large organization is a top-level, four-digit code that relates to the accounting entity (for example, a subsidiary company). The next numbers pertain to department, followed by a number for the cost, which can be a cost center, profit center, work-breakdown-structure element, fund, or internal order. This facilitates the cost management process by aligning the cost codes with the work breakdown structure, which makes it easier to calculate financial performance. In addition, costs in cost accounting may be classified by:
- Traceability: Direct and indirect costs
- Behavior: Fixed or variable costs
- Controllability: Controllable or uncontrollable costs
- Time Incurred: Historical or predetermined costs
- Normality: Normal or abnormal costs
- Functions: The organizational function by which you incur a cost
Cost accounts make it easy to identify cost overruns in specific sectors that might otherwise be lost in a budget overview. However, managing a large number of cost accounts — up to several hundred accounts and sub-accounts on larger projects — comes with its own challenges. It demands a higher degree of organization in accounting, for one, and classifying costs becomes more time consuming. In addition, the system of categorization you use for a project’s cost accounts may not match up with the system of categorization you use for an organization’s cost accounts. This complicates the creation of a project budget from a final cost estimate, and is likely to happen when you create cost accounts using a system of categorization different than the performing organization uses.
Aside from recording historical expenditure, project managers must also forecast expected activity costs to ensure that they remain under control. Managers can do this through the use of tables that classify costs for individual cost accounts and cost modeling techniques that indicate whether work associated with a particular activity is due to be completed on budget.
Software’s Role in Project Cost Management
Cost management software simplifies and expedites project cost management activities. This can ease the burden on project cost managers and make it easier to extract insights, such as the cost performance index. Some of the common functionalities include: Project-Tree Building: A visual representation of a work breakdown structure. This can be useful when employing deterministic estimating techniques.
Cost Estimation: Cost management software can provide powerful estimation capabilities such as using project trees to record activity costs, or running regression analyses to determine cost-estimate relationships in historical data. Project Cost Management Templates: For projects that are similar, cost management ]templates can expedite cost management activities. Budgeting: Cost management software can make it easier for project managers to conduct budget planning activities and allocate funding.
Keep Projects On-Budget Using a Cost Management Template
One tool that can help with project cost management is Smartsheet, a collaborative work management and automation platform. As a cloud-based platform, you can share and collaborate on your cost management activities with internal and external stakeholders, and access the information from anywhere, on any device.
Plus, with a pre-built, customizable template in Smartsheet, you can get started faster than ever. Track project and budget performance all in one sheet. Use symbols to quickly identify tasks that may be at risk of going over budget, and bring visibility to status of estimated versus actual labor, materials, and other costs. Set up alerts and reminders to notify you as costs change, and attach documents like invoices and purchase orders directly to tasks, to keep details in context.
Try one or all of the following templates to help ensure your next project stays on budget:
Project Budget Template
Download Project Budget Template
Excel | Smartsheet
Cost Management Plan Template

Download Project Cost Management Template
Activity Cost Estimate Template
Download Activity Cost Estimate Template
Smartsheet Project with Schedule & Budget Variance Template
Cost Management for IT Projects
IT project costs are notorious for going over budget, mainly because of development approaches that allow scope creep during the product development life cycle. There is also a tendency for IT cost estimates to be less fixed than those of hard projects in fields such as construction and engineering, where maturity in planning and estimating is higher. In Information Technology Project Management , Kathy Schwalbe suggests that the people creating cost estimates for IT projects lack experience compared to specialist cost surveyors who create cost estimates for construction projects. Furthermore, given how multifaceted these projects tend to be and how quickly IT evolves, IT projects often suffer from the “first-time, first-use penalty,” which means that it is hard to form accurate estimates when a project or project elements have not been attempted before. This makes documenting lessons learned crucial for IT projects. The U.S. research and advisory firm Gartner creates a research report for the project and portfolio management market that categorizes vendors into four categories based on their ability to understand market needs and to drive the acceptance of new technologies. These are graphed on axes labeled “completeness of vision” and “ability to execute,” respectively. The “magic quadrant” is the upper right of this graph in which leaders in both areas cluster.
Cost Management in Construction Projects
Construction project cost managers, or quantity surveyors, oversee cost estimation and cost control while maintaining a project’s profitability. They are responsible for ensuring that a project remains within budget while meeting its scope, quality, and performance requirements. Though the majority of construction projects are not subject to the “first-time, first-use penalty,” they are still highly complex. And as hard projects, their design, scope, and budgetary requirements must be planned before work begins. Experience and formal training are essential for quantity surveyors. The evaluation and recommendation of bids is one of the quantity surveyor’s primary responsibilities, though they may be engaged in a project from inception to conclusion. In fact, quantity surveyors get their name from the bill of quantities , a cost estimate prepared by the surveyor and by which contractors’ tenders are assessed.
To aid cost management for large, complex projects, quantity surveyors or project managers may use cost codes discussed earlier to set up multiple cost accounts. These accounts are essentially portions of budget marked for specific expenses such as labor, construction materials, architectural design, etc.
Home Construction Budget Template
Download Construction Budget Template
Excel | Smartsheet
Construction Estimator Template

Download Construction Estimator Template
Excel | Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Exploring Cost Management as a Career
Professional cost managers, sometimes called quantity surveyors, work on large projects (such as construction). But project managers also need an understanding of cost management strategies and techniques to perform their duties. Cost management requires creative problem-solving skills and a thorough understanding of the factors that affect project costs. As such, cost managers are in high demand and have opportunities to progress to lead project managers. One popular cost management profession is cost accounting, which is determining the costs focused on creating a product or providing a service. Cost accountants deal with budget preparation and profitability analysis, and their main responsibilities include collecting and communicating cost-related data to aid management decision-making and create financial transparency. Cost accountants typically study accounting or finance at the undergraduate level, and many pursue master’s degrees in business administration or finance with a specialization in accounting. They typically need a license to advance their careers, which can be obtained after meeting some combination of work and educational requirements.
How Smartsheet Can Help with Cost Management Across Your Projects
The best marketing teams know the importance of effective campaign management, consistent creative operations, and powerful event logistics -- and Smartsheet helps you deliver on all three so you can be more effective and achieve more.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Improve your marketing efforts and deliver best-in-class campaigns.
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Assign access to Cost Management data
- 4 contributors
For users with Azure Enterprise agreements, a combination of permissions granted in the Azure portal and the Enterprise (EA) portal define a user's level of access to Cost Management data. For users with other Azure account types, defining a user's level of access to Cost Management data is simpler by using Azure role-based access control (RBAC). This article walks you through assigning access to Cost Management data. After the combination of permissions is assigned, the user views data in Cost Management based on their access scope and on the scope that they select in the Azure portal.
The scope that a user selects is used throughout Cost Management to provide data consolidation and to control access to cost information. When scopes are used, users don't multi-select them. Instead, they select a larger scope that child scopes roll up to and then they filter-down to what they want to view. Data consolidation is important to understand because some people shouldn't access a parent scope that child scopes roll up to.
Watch the Cost Management controlling access video to learn about assigning access to view costs and charges with Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC). To watch other videos, visit the Cost Management YouTube channel .
Cost Management scopes
Cost management supports various Azure account types. To view the full list of supported account types, see Understand Cost Management data . The type of account determines available scopes.
Azure EA subscription scopes
To view cost data for Azure EA subscriptions, a user must have at least read access to one or more of the following scopes.
¹ The billing account is also referred to as the Enterprise Agreement or Enrollment.
² The enrollment account is also referred to as the account owner.
Enterprise administrators can assign the billing account, department, and enrollment account scope in the Azure portal . For more information, see Azure portal administration for direct Enterprise Agreements .
Other Azure account scopes
To view cost data for other Azure subscriptions, a user must have at least read access to one or more of the following scopes:
- Management group
- Subscription
- Resource group
Various scopes are available after partners onboard customers to a Microsoft Customer Agreement. Cloud solution providers (CSP) customers can then use Cost Management features when enabled by their CSP partner. For more information, see Get started with Cost Management for partners .
Enable access to costs in the Azure portal
The department scope requires the Department admins can view charges (DA view charges) option set to On . Configure the option in the Azure portal. All other scopes require the Account owners can view charges (Account owner (AO) view charges) option set to On .
To enable an option in the Azure portal:
- Sign in to the Azure portal with an enterprise administrator account.
- Select the Cost Management + Billing menu item.
- Select Billing scopes to view a list of available billing scopes and billing accounts.
- Select your Billing Account from the list of available billing accounts.

After the view charge options are enabled, most scopes also require Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC) permission configuration in the Azure portal.
Enterprise administrator role
By default, an enterprise administrator can access the billing account (Enterprise Agreement/enrollment) and all other scopes, which are child scopes. The enterprise administrator assigns access to scopes for other users. As a best practice for business continuity, you should always have two users with enterprise administrator access. The following sections are walk-through examples of the enterprise administrator assigning access to scopes for other users.
Assign billing account scope access
Access to the billing account scope requires enterprise administrator permission. The enterprise administrator can view costs across the entire EA enrollment or multiple enrollments. The enterprise administrator can assign access to the billing account scope to another user with read only access. For more information, see Add another enterprise administrator .
It might take up to 30 minutes before the user can access data in Cost Management.
Assign department scope access
Access to the department scope requires department administrator (DA view charges) access. The department administrator can view costs and usage data associated with a department or to multiple departments. Data for the department includes all subscriptions belonging to an enrollment account that are linked to the department.
Enterprise administrators can assign department administrator access. For more information, see Add a department administrator .
Assign enrollment account scope access
Access to the enrollment account scope requires account owner (AO view charges) access. The account owner can view costs and usage data associated with the subscriptions created from that enrollment account. Enterprise administrators can assign account owner access. For more information, see Add an account owner in the Azure portal .
Assign management group scope access
Access to view the management group scope requires at least the Cost Management Reader (or Reader) permission. You can configure permissions for a management group in the Azure portal. You must have at least the User Access Administrator (or Owner) permission for the management group to enable access for others. And for Azure EA accounts, you must also enable the AO view charges setting.
You can assign the Cost Management Reader (or reader) role to a user at the management group scope. For more information, see Assign Azure roles using the Azure portal .
Assign subscription scope access
Access to a subscription requires at least the Cost Management Reader (or Reader) permission. You can configure permissions to a subscription in the Azure portal. You must have at least the User Access Administrator (or Owner) permission for the subscription to enable access for others. And for Azure EA accounts, you must also enable the AO view charges setting.
You can assign the Cost Management Reader (or reader) role to a user at the subscription scope. For more information, see Assign Azure roles using the Azure portal .
Assign resource group scope access
Access to a resource group requires at least the Cost Management Reader (or Reader) permission. You can configure permissions to a resource group in the Azure portal. You must have at least the User Access Administrator (or Owner) permission for the resource group to enable access for others. And for Azure EA accounts, you must also enable the AO view charges setting.
You can assign the Cost Management Reader (or reader) role to a user at the resource group scope. For more information, see Assign Azure roles using the Azure portal .
Cross-tenant authentication issues
Currently, Cost Management provides limited support for cross-tenant authentication. In some circumstances when you try to authenticate across tenants, you may receive an Access denied error in cost analysis. This issue might occur if you configure Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC) to another tenant's subscription and then try to view cost data.
To work around the problem : After you configure cross-tenant Azure RBAC, wait an hour. Then, try to view costs in cost analysis or grant Cost Management access to users in both tenants.
- If you haven't read the first quickstart for Cost Management, read it at Start analyzing costs .
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback .
Submit and view feedback for
Additional resources
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Join us: Learn how to build a trusted AI strategy to support your company's intelligent transformation, featuring Forrester .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Register now .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Project planning |
- Project cost management: Definition, st ...
Project cost management: Definition, steps, and benefits

Cost management is the process of planning, budgeting, and reporting project spend in order to keep teams on budget and overall costs reasonable. In this article, we'll go over the four functions of cost management and explain exactly how to use them to improve your project's bottom line.
What is cost management?
Cost management is the process of estimating, budgeting, and controlling project costs. The cost management process begins during the planning phase and continues throughout the duration of the project as managers continuously review, monitor, and adjust expenditures to ensure the project doesn't go over the approved budget.
Why is cost management important?
Have you ever wondered what happens when a project goes significantly over budget? The consequences can be severe—from strained relationships with clients to financial losses. Let's consider an example:
A small software development team was tasked with creating a custom application for a client. Midway through, they realized the project was quickly exceeding the initial budget. They faced a common dilemma: continue as planned and absorb the extra costs or re-evaluate their approach.
By implementing rigorous cost management strategies, the team was able to identify areas where expenses were ballooning. They streamlined their project management processes, prioritized essential features, and renegotiated terms with subcontractors. This approach not only brought the project back within budget but also improved their working relationship with the client, who appreciated their transparency and commitment to delivering value.
This scenario highlights how effective cost management can transform a potentially disastrous situation into a success story.
How to create a cost management plan
Cost management is a continuous, fluid process. However, there are four main elements or functions that can be found in any cost management plan:
Resource planning
Cost estimating, cost budgeting, cost control.
Because new expenses can appear and project scope can be adjusted, cost managers need to be prepared to perform all four functions at any time throughout the project life cycle. Your workflow will vary according to the project’s needs.
Here, we'll break down each of the four elements in greater detail and explain what is required from the cost manager at each stage.
![cost management assignment [Inline Illustration] cost management (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/817309ee-ddc4-405a-90ce-3090369ac44d/inline-project-planning-cost-management-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
The very first step in any cost management process is resource planning, which is when the cost manager reviews the project's scope and specs to figure out what resources the project will require.
A resource is anything that helps you complete a project—including tools, money, time, equipment, and even team members. To create the most accurate resource plan possible, consult directly with team leads and stakeholders about what resources they will need during the project. People with hands-on experience in each project department will have a better understanding of what resources will be required.
For this step, you'll need:
Clearly defined project objectives
A high-level project roadmap or a work breakdown structure (WBS) , depending on the complexity of the project
A tentative resource management plan
A project scope statement
Once you have a list of necessary resources, the next step is to estimate what it will cost to procure them. The key to this step is to gather as much pricing information as possible so that you can make informed cost estimates.
For tangible resources like tools, supplies, and equipment, get real price quotes from sellers to inform your cost estimate. For labor costs, get multiple price quotes from potential contractors to help give you a realistic idea of what the work you require will actually cost. Keep in mind that some time may pass between when you make your estimate and when these items will be purchased, so you should build in some room in case prices rise.
In addition to building in a cushion for each individual cost, you'll also need to add a buffer of 5–10% to your cost total to account for unexpected expenses. If this is your first time working with this project team, find out if the previous cost manager generated budget reports at the end of past projects.
You can take a look at how much previous projects' final costs deviated from their initial estimates and use this cost data as a benchmark to estimate how much of a margin you need to build into your estimation report.
In the estimation stage , you'll need:
Project schedule or a PERT chart , depending on the complexity of the project
A list of your project deliverables
Clearly defined success metrics
Now that you have general estimates for your project needs and resource requirements, you can begin to work on your project budget . Your project budget is a detailed plan of how much you plan to spend during the project, for what, and by when.
Depending on the complexity of your project, the “when” may significantly influence your cost management strategy. For multi-year projects, you may want to specify cost allocations so that no more than 30% of your budget should be spent in the first year, etc. This can prevent cost overruns later down the road.
In this stage, you'll need:
A project budget document
A project stakeholder analysis
The bulk of the cost management process is made up of cost control . This is the process of recording and accounting costs as the project progresses, making adjustments, and alerting stakeholders to problems when they occur. The goal of the cost control step is to compare actual project costs with original budgets and estimates and take steps to make sure the project stays as close to plan as possible.
The frequency with which you review this will depend on your project. Sometimes you’ll want to review costs in real time. In other cases, you may check in monthly or even quarterly. Share cost updates as necessary through project status reports so the entire project team is on the same page.
Keep in mind that any changes to the project scope will impact the project budget and costs, so keep a close eye on scope creep. If the project cost deviates too much from what you budgeted, let your stakeholders know so you can proactively come up with an action plan.
Project management tool
Universal reporting tool
![cost management assignment [inline illustration] cost management (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/6f7dd800-aa58-4efe-bb4b-fad7043488c1/inline-project-planning-cost-management-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Post-project cost accounting
Once the project is over, it’s time to calculate cost variance and evaluate how far your project deviated from your original budget and estimates. What were the project’s total costs? How did your actual costs compare to your estimated costs?
A successful project ends close to (but under) the forecasted project budget. If you spent too much money, you either underestimated your project budget or had too many unforeseen expenses. If this happens, hold a project post-mortem meeting to evaluate why that happened and prevent it from happening in the future.
On the flip side, spending too little of your budget is also not ideal. You estimated these costs for a reason, and if you came in significantly under budget, your cost-budgeting process was inaccurate. Log this information as historical data and keep it in mind for future projects, so you can increase your accuracy during the cost estimation phase.
How to calculate project costs
To ensure that your project stays profitable and within budget, it is essential to have a solid understanding of how to calculate project costs.
Project managers have a variety of cost management methods to choose from, and picking the best one depends on the specific needs and scope of your project. Consider factors like project complexity, the predictability of tasks, client expectations, and the level of flexibility you'll need to achieve your cost-performance goals.
Calculating project costs on an hourly basis involves paying for the amount of work done, measured in hours. This method is particularly effective for projects where the scope is flexible or uncertain because it allows for adaptability as the project progresses.
For example, consider a software development project. The development team's cost is calculated based on the number of hours they spend on the project. If the team works 100 hours a month at a rate of $100 per hour, the project costing for that month would be $10,000. This method provides flexibility and can accommodate changes in the project's scope effectively.
A flat rate, or fixed price, approach involves agreeing on a total project cost upfront. This method is ideal for projects with a well-defined scope and deliverables. This gives both parties a clear understanding of the total cost.
Imagine a marketing campaign. The agency and the client agree on a fixed price of $20,000 for the entire campaign. This price covers all aspects of the project, from planning to execution. The advantage here is predictability in budgeting, as the client knows exactly how much the project will cost, irrespective of the time and resources utilized.
The cost-plus method involves charging the actual costs of the project plus a markup or additional fee. This approach is often used in long-term projects where the costs cannot be accurately estimated at the start. It ensures that all project costs are covered and includes a profit margin.
For instance, in a construction project, the contractor charges for the actual costs incurred (like materials and labor) plus a fixed percentage as profit. If the material and labor costs amount to $50,000 and the agreed markup is 20%, the total charge to the client would be $60,000. This cost management method aligns the interests of the client and the contractor, as both parties aim for optimal cost performance.
Value-based pricing
Value-based pricing focuses on the value or benefit the client receives rather than the cost of the project itself. This estimation method is ideal for projects where the outcome has a high perceived value, regardless of the actual cost of delivery.
Consider a scenario where a consulting firm is helping a client increase their annual revenue. If the consultant's strategies result in a $1 million revenue increase, the consultant may charge a fee based on a percentage of the revenue increase, say 10%, which would be $100,000. Value-based pricing ensures that the pricing reflects the value delivered.
Effective project cost management methods
One of the most persistent challenges faced by teams across various industries is controlling and preventing budget overruns. These overruns not only strain financial resources but can also lead to compromised project quality, delayed timelines, and even project failure.
Effective cost management is the key to tackling this challenge because it makes certain that projects are delivered within their allocated budgets while maintaining high standards of quality and efficiency.
Choosing the best cost-management method is key to addressing these financial challenges head-on. For further cost optimization, teams can leverage automation, management software, and dashboards that offer real-time cost analysis, cash flow, and future cost visualization. This will ultimately contribute to the success of your project.
Top-down estimating
Top-down estimating is a method where the overall project cost is estimated first, and then individual costs are deduced from this total. This approach is beneficial in the early stages of project planning, when detailed information is not yet available. It gives a quick and rough idea of how much the project will cost.
For example, in a new software development project, the project manager might estimate the total project cost at $200,000 based on previous similar projects. This total cost is then broken down into smaller segments like design, coding, testing, and deployment, each allocated a portion of the total budget. This method is effective for providing a preliminary cost framework and guiding early project decision-making.
Bottom-up estimating
Bottom-up estimating is the reverse of the top-down approach. It involves estimating individual tasks or components of the project first and then adding them up to get the total project cost. This estimation method is more accurate and reliable, especially for projects with a well-defined scope, as it considers detailed cost information.
Consider a construction project where each part of the project, such as foundation laying, framing, plumbing, and electrical work, is estimated individually based on detailed analysis. After estimating all these components, the costs are summed up to determine the overall project budget. Bottom-up estimating is ideal for teams that need precise control over each aspect of the project's costs.
Earned value management
Earned value management (EVM) is a sophisticated approach to cost management that combines measurements of project performance in terms of scope, schedule, and cost. EVM provides a comprehensive view of the project's progress and its alignment with the original project planning.
For instance, in a large infrastructure project, EVM would be used to track the following:
Budgeted cost of work scheduled (BCWS)
Actual cost of work performed (ACWP)
Budgeted cost of work performed (BCWP)
By comparing these figures, project managers can gauge the project's cost performance and take corrective action if necessary.
Three-point estimating
Three-point estimating is used to determine a more realistic estimate by considering three scenarios:
Most optimistic (best-case)
Most pessimistic (worst-case)
Most likely
This cost management method provides a range of possible outcomes, which can increase the predictability and cost performance of a project.
Take, for example, a new product development project. The project manager might estimate that the design phase could take 30 days (optimistic), 45 days (most likely), or 60 days (pessimistic). Using these three points, they calculate an average or weighted average duration, which helps in setting realistic timelines and budgets.
FAQ about cost management
What is the first step in project cost management.
The first step in project cost management is to define the baseline for your project's budget. This involves identifying all potential costs and inputs related to the project, including labor, materials, equipment, and any other expenses. Creating a baseline is essential because it provides the framework for monitoring and controlling expenses during the lifecycle of a project.
What are the 5 functions of cost management?
The five key functions of cost management are:
Cost estimation: Determining the total cost required for completing the project.
Cost budgeting: Allocating the overall cost estimate to individual work items to establish a baseline for measuring performance.
Cost control: Monitoring project expenses and implementing measures to keep costs within the approved budget.
Cash flow management : Ensuring there is adequate cash flow to meet project needs, which is critical for maintaining project momentum.
Procurement management: Managing the procurement of goods and services, ensuring that everything is obtained at the best possible cost and meets project needs.
What is cost management in project management?
Cost management in project management is the process of planning, estimating, budgeting, and controlling costs with the aim of completing the project within the approved budget. It involves a continuous process of measuring and monitoring project activities and expenses and implementing necessary adjustments to ensure that the project's financial resources are used effectively.
Improve your project performance with cost management
Cost management has a lot of moving parts. But as long as your team has visibility into project costs, you can prevent cost overruns and ensure you’re finishing your project under budget every time.
To keep track of all of your project’s information, use a work management platform like Asana. From project costing and kickoff to post-mortem, Asana helps you stay in sync with your project team members and stakeholders during the entire project process.
Related resources

Unmanaged business goals don’t work. Here’s what does.
How Asana uses work management to drive product development

How Asana uses work management to streamline project intake processes

How Asana uses work management for smoother creative production

What is Cost Assignment?
Share This...
Cost assignment.
Cost assignment is the process of associating costs with cost objects, such as products, services, departments, or projects. It encompasses the identification, measurement, and allocation of both direct and indirect costs to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the resources consumed by various cost objects within an organization. Cost assignment is a crucial aspect of cost accounting and management accounting, as it helps organizations make informed decisions about pricing, resource allocation, budgeting, and performance evaluation.
There are two main components of cost assignment:
- Direct cost assignment: Direct costs are those costs that can be specifically traced or identified with a particular cost object. Examples of direct costs include direct materials, such as raw materials used in manufacturing a product, and direct labor, such as the wages paid to workers directly involved in producing a product or providing a service. Direct cost assignment involves linking these costs directly to the relevant cost objects, typically through invoices, timesheets, or other documentation.
- Indirect cost assignment (Cost allocation): Indirect costs, also known as overhead or shared costs, are those costs that cannot be directly traced to a specific cost object or are not economically feasible to trace directly. Examples of indirect costs include rent, utilities, depreciation, insurance, and administrative expenses. Since indirect costs cannot be assigned directly to cost objects, organizations use various cost allocation methods to distribute these costs in a systematic and rational manner. Some common cost allocation methods include direct allocation, step-down allocation, reciprocal allocation, and activity-based costing (ABC).
In summary, cost assignment is the process of associating both direct and indirect costs with cost objects, such as products, services, departments, or projects. It plays a critical role in cost accounting and management accounting by providing organizations with the necessary information to make informed decisions about pricing, resource allocation, budgeting, and performance evaluation.
Example of Cost Assignment
Let’s consider an example of cost assignment at a bakery called “BreadHeaven” that produces two types of bread: white bread and whole wheat bread.
BreadHeaven incurs various direct and indirect costs to produce the bread. Here’s how the company would assign these costs to the two types of bread:
- Direct cost assignment:
Direct costs can be specifically traced to each type of bread. In this case, the direct costs include:
- Direct materials: BreadHeaven purchases flour, yeast, salt, and other ingredients required to make the bread. The cost of these ingredients can be directly traced to each type of bread.
- Direct labor: BreadHeaven employs bakers who are directly involved in making the bread. The wages paid to these bakers can be directly traced to each type of bread based on the time spent working on each bread type.
For example, if BreadHeaven spent $2,000 on direct materials and $1,500 on direct labor for white bread, and $3,000 on direct materials and $2,500 on direct labor for whole wheat bread, these costs would be directly assigned to each bread type.
- Indirect cost assignment (Cost allocation):
Indirect costs, such as rent, utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses, cannot be directly traced to each type of bread. BreadHeaven uses a cost allocation method to assign these costs to the two types of bread.
Suppose the total indirect costs for the month are $6,000. BreadHeaven decides to use the number of loaves produced as the allocation base , as it believes that indirect costs are driven by the production volume. During the month, the bakery produces 3,000 loaves of white bread and 2,000 loaves of whole wheat bread, totaling 5,000 loaves.
The allocation rate per loaf is:
Allocation Rate = Total Indirect Costs / Total Loaves Allocation Rate = $6,000 / 5,000 loaves = $1.20 per loaf
BreadHeaven allocates the indirect costs to each type of bread using the allocation rate and the number of loaves produced:
- White bread: 3,000 loaves × $1.20 per loaf = $3,600
- Whole wheat bread: 2,000 loaves × $1.20 per loaf = $2,400
After completing the cost assignment, BreadHeaven can determine the total costs for each type of bread:
- White bread: $2,000 (direct materials) + $1,500 (direct labor) + $3,600 (indirect costs) = $7,100
- Whole wheat bread: $3,000 (direct materials) + $2,500 (direct labor) + $2,400 (indirect costs) = $7,900
By assigning both direct and indirect costs to each type of bread, BreadHeaven gains a better understanding of the full cost of producing each bread type, which can inform pricing decisions, resource allocation, and performance evaluation.
Other Posts You'll Like...

Most Common Errors When Preparing Consolidated Financial Statements

How are Joint Ventures Treated in Consolidated Financial Statements?

How to Treat Foreign Subsidiaries in Consolidated Financial Statements?

How Is Goodwill Treated in a Business Combination?

Equity Method vs Acquisition Method in Business Combinations


REG CPA Practice Questions Explained: How to Deduct Charitable Contributions
Helpful links.
- Learn to Study "Strategically"
- How to Pass a Failed CPA Exam
- Samples of SFCPA Study Tools
- SuperfastCPA Podcast

Helicopter Pilot to CPA: How Chase Passed His CPA Exams

How Josh Passed His CPA Exams Using Shorter Study Sessions

The Changes That Helped Marc Pass His CPA Exams After Failing 6 Times

The CPA Study Tweaks Gabi Used to Pass Her CPA Exams

How Skylar Went From a Psychology Major to Becoming a CPA

How Dalton Is Passing Exams by Making His CPA Study a Lifestyle
Want to pass as fast as possible, ( and avoid failing sections ), watch one of our free "study hacks" trainings for a free walkthrough of the superfastcpa study methods that have helped so many candidates pass their sections faster and avoid failing scores....

Make Your Study Process Easier and more effective with SuperfastCPA
Take Your CPA Exams with Confidence
- Free "Study Hacks" Training
- SuperfastCPA PRO Course
- SuperfastCPA Review Notes
- SuperfastCPA Audio Notes
- SuperfastCPA Quizzes
Get Started
- Free "Study Hacks Training"
- Read Reviews of SuperfastCPA
- Busy Candidate's Guide to Passing
- Subscribe to the Podcast
- Purchase Now
- Nate's Story
- Interviews with SFCPA Customers
- Our Study Methods
- SuperfastCPA Reviews
- CPA Score Release Dates
- The "Best" CPA Review Course
- Do You Really Need the CPA License?
- 7 Habits of Successful Candidates
- "Deep Work" & CPA Study
Module 7: Costing Methods
Introduction to cost management, what you’ll learn to do: discuss the importance of cost management.

Managing the costs in a business are crucial to success. There are many different ways to classify costs, which will be discussed in this module. When we discuss costs from a managerial accounting standpoint, the same cost may be classified differently depending on what information is needed.
Being aware of the different cost classifications and ways to look at costs will be an important skill as a manager. It will give you the skills to budget and plan effectively for your department or company.
Contribute!
Improve this page Learn More
- Introduction to Cost Management. Authored by : Freedom Learning Group. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- laptops, notes, meeting. Authored by : Helloquence. Provided by : Unsplash. Located at : https://unsplash.com/photos/5fNmWej4tAA . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved

- Contact sales
Start free trial
Project Cost Management Basics

Table of Contents
What is project cost management, how to manage project costs in 4 steps, what is a cost management plan, cost management plan outline.
- Why Is Cost Management Important?
Cost Management Tips
Projectmanager is your cost management software, free cost management templates.
Cost management is the process of planning and managing the budget of a business or project. In the case of a project, it helps the project manager estimate what the project will cost and set controls to reduce the chances of the project going over budget.
Cost management is one of the most important responsibilities of a project manager; projects always need resources such as materials, labor and equipment, which generate costs. Those costs must be estimated and controlled throughout the project life cycle to complete the project.
Get your free
Project Estimate Template
Use this free Project Estimate Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
The four steps below outline how the cost management process works in project management.
1. Resource Planning
Resource planning is the process of forecasting future resource requirements for a business, project or scope of work. To create a resource plan, you need to start by defining the project scope , a document that details the project activities that will be done.
Once the project activities have been defined, project managers usually rely on historical data, expert opinions, and resource planning tools such as a resource breakdown structure (RBS) to estimate the resources that will be needed.
2. Cost Estimating
Cost estimating consists of assigning costs to the resources you need to execute your projects, such as labor, materials and equipment. Cost estimating is one of the most important steps in the cost management process because it lays out the base for your project budget. There are several project cost estimating techniques you can use depending on the characteristics of your project.
3. Cost Budgeting
Based on your cost estimates, you can now create a project budget , which is simply the sum of all your project costs. Make sure to include all types of project costs, including direct, indirect, fixed and variable costs. A project budget should also include contingency reserves in case there’s work that needs to be redone, or a risk has struck the project and risk mitigation strategies need to be taken.
Once the project starts, the project budget is a baseline that’s used to compare actual costs vs. estimated costs. Therefore, project budgets allow project managers to quickly understand if their costs are too high and if there’s a risk of cost overrun .
4. Cost Control
Cost control refers to all the activities, guidelines and procedures taken to minimize and track project costs. Poor cost control can affect the profitability of a project, but luckily project management software can help you to easily keep track of costs with tools such as timesheets, workload planners and project dashboards.
The outputs of these 4 steps can be documented in a cost management plan, a critical component of the project plan.
Effective cost management requires the right software. ProjectManager is the perfect tool to track project costs, resources and workload. Our Gantt charts, project calendars and timesheets allow you to manage costs, time and tasks in one place. Get started for free.
A cost management plan sounds simple. It’s an outline of the cost estimation for the project—but that includes all allocation and how the project manager will control those costs to bring the project in as budgeted.
A cost management plan must take into account the resources that impact the project budget, whether materials or people. There are also fixed, variable and overhead costs. All these must be calculated to know what your financial commitment to the project will be.
Last but not least is the stakeholder, who has a vested interest in keeping costs down. Cost overrun is a problem many projects experience, but not one that stakeholders will tolerate well. Keep the stakeholder in mind when formulating your cost management plan. They need to stay in the loop and get reports throughout the project.
Here are some key elements that must be included in a cost management plan:
- Estimation Methods: Explain which cost estimation method was employed, such as parametric, bottom-up, three-point, etc.
- Units of Measure: To measure costs accurately, it’s important to establish units of measure for your labor, materials and equipment. Some examples of measurement units can be staff hours, square feet, tons, kilograms, etc.
- Cost Baseline: Based on your cost estimates, you must define a cost baseline that marks the spending limit for your project.
- Cost Control Thresholds: Establishing thresholds to monitor cost performance is important. This simply means that when cost variation reaches a certain percentage, the project team will take cost management actions.
- Performance Measurement Methods: Establish how the cost performance will be measured to see if you’re meeting the goals and expectations of the project. To do so, you’ll need a cost tracking system and earned value management (EVM) techniques.
- Reporting Guidelines: You need to have a format and communication channels to report your findings as you monitor the project’s progress and present this data to your stakeholders.
Why Is Cost Management Important In Project Management?
The main reason why cost management is so important in project management is that your cost management plan includes the guidelines and procedures needed to stay on budget. This is critical because otherwise, the organization could lose money as costs exceed profits.
The cost management process begins in the planning phase of the project , where costs are estimated and then a project budget is defined. Then, when the project is executed, the expenses are carefully monitored and recorded to make sure that they’re aligned with the budget.
When you have a project budget, it sets a baseline for project costs. That means it governs the decisions and directions you take when managing costs on your project. This helps you keep the project on track without overspending.
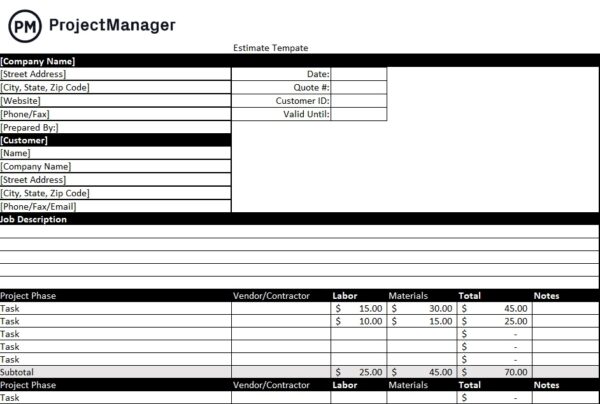
Project Cost Estimate Template
This free project cost estimate template for Excel lets you list down all the costs related to your project resources such as labor, materials and equipment rental. Once you’ve accurately estimated these costs, you can create a project budget.
The following are some tips to keep in mind as you’re working on managing your project costs.
- Plan for Inflation: Pricing is not set in stone, and any good budget is going to take this into account by allowing for a range of costs.
- Account for Natural Disasters or Potential Events: Expect the unexpected might sound silly, but you must have room in your budget for a weather event, personal issue or another unknown that will delay the project.
- Other Unexpected Costs: Not all unexpected costs are random. There can be legal issues, penalties associated with the project or unexpected labor costs, all of which you can’t budget for, but can inform your budget.
- Track in Real-Time: Having software to monitor the budget as you execute the project is key for managing costs. However, if you’re looking at data that isn’t current, you won’t be able to act swiftly enough to resolve issues. Therefore, you want to have software with real-time data tracking .
- Respond Promptly: Regardless of how you discover a discrepancy in your project cost, you must act immediately. The longer you wait, the more money is wasted.
- Size Accordingly: Some people think smaller projects don’t need project cost management. But small or large, you’ll want to manage costs.
In order to best manage project costs, you have to know your project inside and out. The best way to do that is at the start of the project by creating a thorough project charter .
ProjectManager is online software with the tools you need for cost management planning across all phases of your project. Because our software is cloud-based, project data is delivered in real time so you can immediately gauge the accuracy of your cost estimates against the actual expenditure.
Our resource management feature helps you keep your workload balanced, which reigns in costs. We also have easy-to-use timesheets, where team members can submit with one click and project managers can approve with one click. But, our most powerful feature for cost management is our project dashboard, which tracks project costs in real time so you can keep a close eye on your budget.
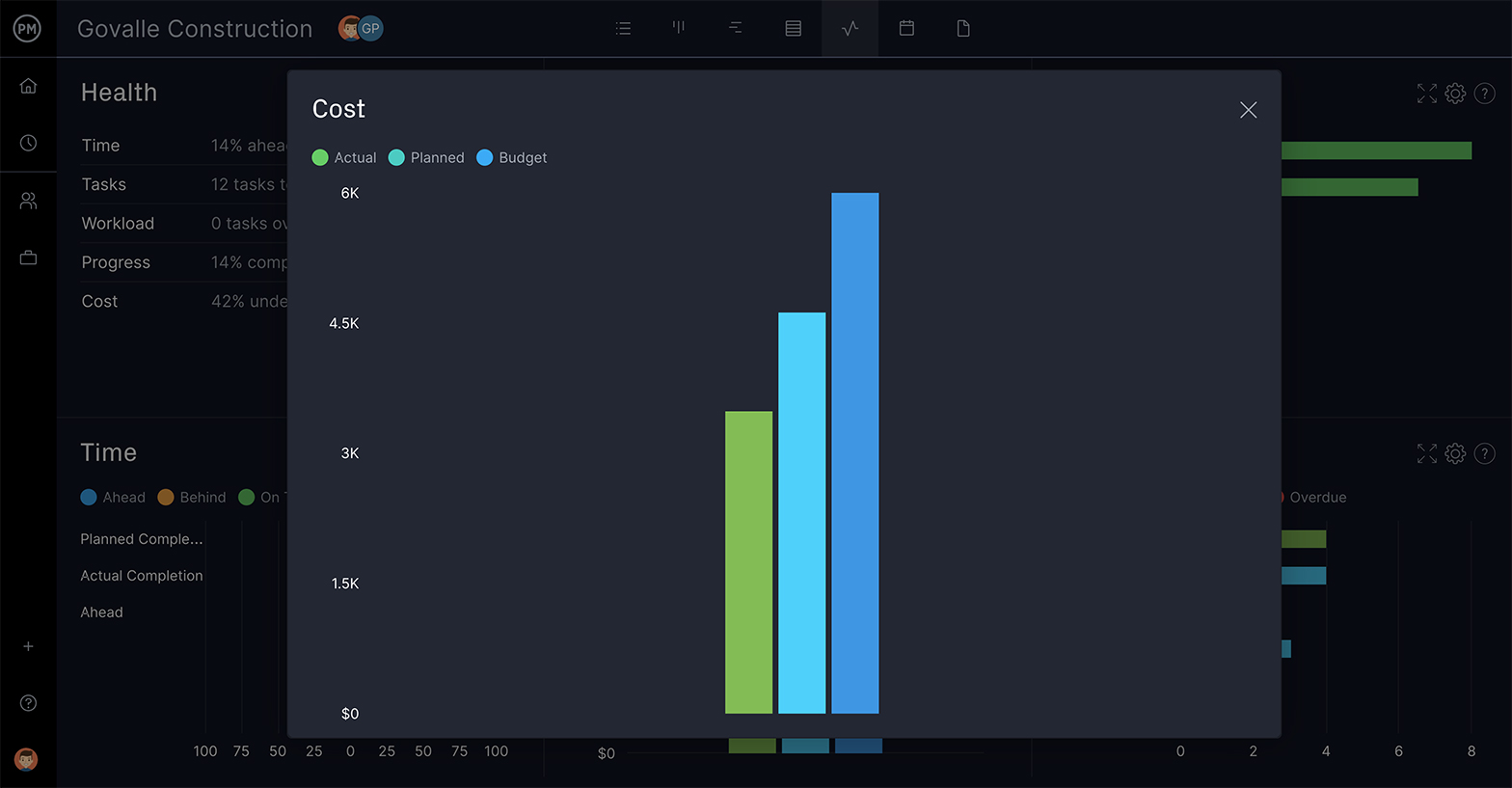
We offer dozens of project management templates to help you manage your projects. Here are some templates to assist you as you go through the cost management process.
Project Budget Template
Our project budget template is ideal to document all your costs and set a baseline for your projects. It can be easily customized to meet the needs of your organization.
Resource Plan Template
You can’t manage costs without solid resource planning. Our resource plan template is the perfect tool to keep track of all the different resources that you’ll need to execute your projects.
Cost Benefit Analysis Template
Projects must be profitable, otherwise, it’s not a good idea to execute them. Before you start a project, make sure you do a cost-benefit analysis beforehand. Our cost-benefit analysis template is a great place to start.
Related Content
- Cost Benefit Analysis
- How to Track Project Expenses
- How to Calculate Cost Variance
- Tips for Better Cost Control
Learn More About Managing Project Cost
When you’re working on cost management, you’re establishing policies and procedures to manage and control your project costs. Jennifer Bridges, PMP, speaks to the core knowledge you need to know in order to understand cost management on any project in this short tutorial video.
Here’s a thumbnail for your reference.
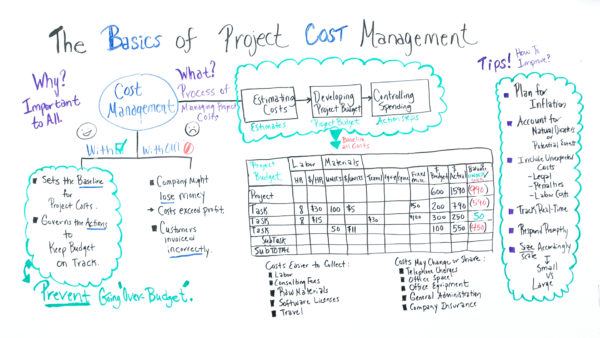
Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Cost Accounting?
Understanding cost accounting.
- Cost vs. Financial Accounting
- Cost Accounting FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Corporate Finance
Cost Accounting: Definition and Types With Examples
Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Her expertise is in personal finance and investing, and real estate.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/YariletPerez-d2289cb01c3c4f2aabf79ce6057e5078.jpg)
Cost accounting is a form of managerial accounting that aims to capture a company's total cost of production by assessing the variable costs of each step of production as well as fixed costs, such as a lease expense.
Cost accounting is not GAAP-compliant , and can only be used for internal purposes.
Key Takeaways
- Cost accounting is used internally by management in order to make fully informed business decisions.
- Unlike financial accounting, which provides information to external financial statement users, cost accounting is not required to adhere to set standards and can be flexible to meet the particular needs of management.
- As such, cost accounting cannot be used on official financial statements and is not GAAP-compliant.
- Cost accounting considers all input costs associated with production, including both variable and fixed costs.
- Types of cost accounting include standard costing, activity-based costing, lean accounting, and marginal costing.
Investopedia / Theresa Chiechi
Cost accounting is used by a company's internal management team to identify all variable and fixed costs associated with the production process. It will first measure and record these costs individually, then compare input costs to output results to aid in measuring financial performance and making future business decisions. There are many types of costs involved in cost accounting , each performing its own function for the accountant.
Types of Costs
- Fixed costs are costs that don't vary depending on the level of production. These are usually things like the mortgage or lease payment on a building or a piece of equipment that is depreciated at a fixed monthly rate. An increase or decrease in production levels would cause no change in these costs.
- Variable costs are costs tied to a company's level of production. For example, a floral shop ramping up its floral arrangement inventory for Valentine's Day will incur higher costs when it purchases an increased number of flowers from the local nursery or garden center.
- Operating costs are costs associated with the day-to-day operations of a business. These costs can be either fixed or variable depending on the unique situation.
- Direct costs are costs specifically related to producing a product. If a coffee roaster spends five hours roasting coffee, the direct costs of the finished product include the labor hours of the roaster and the cost of the coffee beans.
- Indirect costs are costs that cannot be directly linked to a product. In the coffee roaster example, the energy cost to heat the roaster would be indirect because it is inexact and difficult to trace to individual products.
Cost Accounting vs. Financial Accounting
While cost accounting is often used by management within a company to aid in decision-making, financial accounting is what outside investors or creditors typically see. Financial accounting presents a company's financial position and performance to external sources through financial statements , which include information about its revenues , expenses , assets , and liabilities . Cost accounting can be most beneficial as a tool for management in budgeting and in setting up cost-control programs, which can improve net margins for the company in the future.
One key difference between cost accounting and financial accounting is that, while in financial accounting the cost is classified depending on the type of transaction, cost accounting classifies costs according to the information needs of the management. Cost accounting, because it is used as an internal tool by management, does not have to meet any specific standard such as generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and, as a result, varies in use from company to company or department to department.
Cost-accounting methods are typically not useful for figuring out tax liabilities, which means that cost accounting cannot provide a complete analysis of a company's true costs.
Types of Cost Accounting
Standard costing.
Standard costing assigns "standard" costs, rather than actual costs, to its cost of goods sold (COGS) and inventory. The standard costs are based on the efficient use of labor and materials to produce the good or service under standard operating conditions, and they are essentially the budgeted amount. Even though standard costs are assigned to the goods, the company still has to pay actual costs. Assessing the difference between the standard (efficient) cost and the actual cost incurred is called variance analysis.
If the variance analysis determines that actual costs are higher than expected, the variance is unfavorable. If it determines the actual costs are lower than expected, the variance is favorable. Two factors can contribute to a favorable or unfavorable variance. There is the cost of the input, such as the cost of labor and materials. This is considered to be a rate variance.
Additionally, there is the efficiency or quantity of the input used. This is considered to be a volume variance. If, for example, XYZ company expected to produce 400 widgets in a period but ended up producing 500 widgets, the cost of materials would be higher due to the total quantity produced.
Activity-Based Costing
Activity-based costing (ABC) identifies overhead costs from each department and assigns them to specific cost objects, such as goods or services. The ABC system of cost accounting is based on activities, which refer to any event, unit of work, or task with a specific goal, such as setting up machines for production, designing products, distributing finished goods, or operating machines. These activities are also considered to be cost drivers , and they are the measures used as the basis for allocating overhead costs .
Traditionally, overhead costs are assigned based on one generic measure, such as machine hours. Under ABC, an activity analysis is performed where appropriate measures are identified as the cost drivers. As a result, ABC tends to be much more accurate and helpful when it comes to managers reviewing the cost and profitability of their company's specific services or products.
For example, cost accountants using ABC might pass out a survey to production-line employees who will then account for the amount of time they spend on different tasks. The costs of these specific activities are only assigned to the goods or services that used the activity. This gives management a better idea of where exactly the time and money are being spent.
To illustrate this, assume a company produces both trinkets and widgets. The trinkets are very labor-intensive and require quite a bit of hands-on effort from the production staff. The production of widgets is automated, and it mostly consists of putting the raw material in a machine and waiting many hours for the finished good. It would not make sense to use machine hours to allocate overhead to both items because the trinkets hardly used any machine hours. Under ABC, the trinkets are assigned more overhead related to labor and the widgets are assigned more overhead related to machine use.
Lean Accounting
The main goal of lean accounting is to improve financial management practices within an organization. Lean accounting is an extension of the philosophy of lean manufacturing and production, which has the stated intention of minimizing waste while optimizing productivity. For example, if an accounting department is able to cut down on wasted time, employees can focus that saved time more productively on value-added tasks.
When using lean accounting, traditional costing methods are replaced by value-based pricing and lean-focused performance measurements. Financial decision-making is based on the impact on the company's total value stream profitability. Value streams are the profit centers of a company, which is any branch or division that directly adds to its bottom-line profitability.
Marginal Costing
Marginal costing (sometimes called cost-volume-profit analysis ) is the impact on the cost of a product by adding one additional unit into production. It is useful for short-term economic decisions. Marginal costing can help management identify the impact of varying levels of costs and volume on operating profit. This type of analysis can be used by management to gain insight into potentially profitable new products, sales prices to establish for existing products, and the impact of marketing campaigns.
The break-even point —which is the production level where total revenue for a product equals total expense —is calculated as the total fixed costs of a company divided by its contribution margin. The contribution margin , calculated as the sales revenue minus variable costs, can also be calculated on a per-unit basis in order to determine the extent to which a specific product contributes to the overall profit of the company.
History of Cost Accounting
Scholars believe that cost accounting was first developed during the industrial revolution when the emerging economics of industrial supply and demand forced manufacturers to start tracking their fixed and variable expenses in order to optimize their production processes.
Cost accounting allowed railroad and steel companies to control costs and become more efficient. By the beginning of the 20th century, cost accounting had become a widely covered topic in the literature on business management.
How Does Cost Accounting Differ From Traditional Accounting Methods?
In contrast to general accounting or financial accounting, the cost-accounting method is an internally focused, firm-specific system used to implement cost controls . Cost accounting can be much more flexible and specific, particularly when it comes to the subdivision of costs and inventory valuation. Cost-accounting methods and techniques will vary from firm to firm and can become quite complex.
Why Is Cost Accounting Used?
Cost accounting is helpful because it can identify where a company is spending its money, how much it earns, and where money is being lost. Cost accounting aims to report, analyze, and lead to the improvement of internal cost controls and efficiency. Even though companies cannot use cost-accounting figures in their financial statements or for tax purposes, they are crucial for internal controls.
Which Types of Costs Go Into Cost Accounting?
These will vary from industry to industry and firm to firm, however certain cost categories will typically be included (some of which may overlap), such as direct costs, indirect costs, variable costs, fixed costs, and operating costs.
What Are Some Advantages of Cost Accounting?
Since cost-accounting methods are developed by and tailored to a specific firm, they are highly customizable and adaptable. Managers appreciate cost accounting because it can be adapted, tinkered with, and implemented according to the changing needs of the business. Unlike the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)-driven financial accounting, cost accounting need only concern itself with insider eyes and internal purposes. Management can analyze information based on criteria that it specifically values, which guides how prices are set, resources are distributed, capital is raised, and risks are assumed.
What Are Some Drawbacks of Cost Accounting?
Cost-accounting systems ,and the techniques that are used with them, can have a high start-up cost to develop and implement. Training accounting staff and managers on esoteric and often complex systems takes time and effort, and mistakes may be made early on. Higher-skilled accountants and auditors are likely to charge more for their services when evaluating a cost-accounting system than a standardized one like GAAP.
Cost accounting is an informal set of flexible tools that a company's managers can use to estimate how well the business is running. Cost accounting looks to assess the different costs of a business and how they impact operations, costs, efficiency, and profits. Individually assessing a company's cost structure allows management to improve the way it runs its business and therefore improve the value of the firm. These are meant to be internal metrics and figures only. Since they are not GAAP-compliant, cost accounting cannot be used for a company's audited financial statements released to the public.
Fleischman, Richard K., and Thomas N. Tyson. "The Economic History Review: Cost Accounting During the Industrial Revolution: The Present State of Historical Knowledge." Economic History Review , vol. 46, no. 3, 1993, pp. 503-517.
- Accounting Explained With Brief History and Modern Job Requirements 1 of 51
- What Is the Accounting Equation, and How Do You Calculate It? 2 of 51
- What Is an Asset? Definition, Types, and Examples 3 of 51
- Liability: Definition, Types, Example, and Assets vs. Liabilities 4 of 51
- Equity Definition: What it is, How It Works and How to Calculate It 5 of 51
- Revenue Definition, Formula, Calculation, and Examples 6 of 51
- Expense: Definition, Types, and How Expenses Are Recorded 7 of 51
- Current Assets vs. Noncurrent Assets: What's the Difference? 8 of 51
- What Is Accounting Theory in Financial Reporting? 9 of 51
- Accounting Principles Explained: How They Work, GAAP, IFRS 10 of 51
- Accounting Standard Definition: How It Works 11 of 51
- Accounting Convention: Definition, Methods, and Applications 12 of 51
- What Are Accounting Policies and How Are They Used? With Examples 13 of 51
- How Are Principles-Based and Rules-Based Accounting Different? 14 of 51
- What Are Accounting Methods? Definition, Types, and Example 15 of 51
- What Is Accrual Accounting, and How Does It Work? 16 of 51
- Cash Accounting Definition, Example & Limitations 17 of 51
- Accrual Accounting vs. Cash Basis Accounting: What's the Difference? 18 of 51
- Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB): Definition and How It Works 19 of 51
- Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP): Definition, Standards and Rules 20 of 51
- What Are International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)? 21 of 51
- IFRS vs. GAAP: What's the Difference? 22 of 51
- How Does US Accounting Differ From International Accounting? 23 of 51
- Cash Flow Statement: What It Is and Examples 24 of 51
- Breaking Down The Balance Sheet 25 of 51
- Income Statement: How to Read and Use It 26 of 51
- What Does an Accountant Do? 27 of 51
- Financial Accounting Meaning, Principles, and Why It Matters 28 of 51
- How Does Financial Accounting Help Decision-Making? 29 of 51
- Corporate Finance Definition and Activities 30 of 51
- How Financial Accounting Differs From Managerial Accounting 31 of 51
- Cost Accounting: Definition and Types With Examples 32 of 51
- Certified Public Accountant: What the CPA Credential Means 33 of 51
- What Is a Chartered Accountant (CA) and What Do They Do? 34 of 51
- Accountant vs. Financial Planner: What's the Difference? 35 of 51
- Auditor: What It Is, 4 Types, and Qualifications 36 of 51
- Audit: What It Means in Finance and Accounting, and 3 Main Types 37 of 51
- Tax Accounting: Definition, Types, vs. Financial Accounting 38 of 51
- Forensic Accounting: What It Is, How It's Used 39 of 51
- Chart of Accounts (COA) Definition, How It Works, and Example 40 of 51
- What Is a Journal in Accounting, Investing, and Trading? 41 of 51
- Double Entry: What It Means in Accounting and How It's Used 42 of 51
- Debit: Definition and Relationship to Credit 43 of 51
- Credit: What It Is and How It Works 44 of 51
- Closing Entry 45 of 51
- What Is an Invoice? It's Parts and Why They Are Important 46 of 51
- 6 Components of an Accounting Information System (AIS) 47 of 51
- Inventory Accounting: Definition, How It Works, Advantages 48 of 51
- Last In, First Out (LIFO): The Inventory Cost Method Explained 49 of 51
- The FIFO Method: First In, First Out 50 of 51
- Average Cost Method: Definition and Formula with Example 51 of 51
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-982493310-8309982cf401480aba022056d8934f07.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Cost Assignment at Production Enterprises
- Published: 19 April 2022
- Volume 42 , pages 426–429, ( 2022 )
Cite this article
- A. N. Genova 1
57 Accesses
2 Citations
Explore all metrics
An approach to calculating production costs is outlined. The specifics of calculation are considered for costs of different type. Methods of cost assignment are described.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Smart manufacturing systems for Industry 4.0: Conceptual framework, scenarios, and future perspectives
Pai Zheng, Honghui wang, … Xun Xu
Machine learning applied in production planning and control: a state-of-the-art in the era of industry 4.0
Juan Pablo Usuga Cadavid, Samir Lamouri, … Arnaud Fortin
Designing and developing smart production planning and control systems in the industry 4.0 era: a methodology and case study
Olumide Emmanuel Oluyisola, Swapnil Bhalla, … Jan Ola Strandhagen
Chaika, N.K., Formation of development strategy for industrial enterprise quality, J. Manage. Syst ., 2021, vol. 22, no. 180, pp. 20–26.
Google Scholar
Danilina, M.V., Trifonov, P.V., Surkova, E.V., et al., Managing business in the regions of Russia: Threats’ analysis, Int. J. Econ. Res ., 2017, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 55–67.
Drury, C., Management and Cost Accounting , Cengage Learning, 2012, 8th ed.
Kulikova, A.N., Building a management accounting system at industrial enterprises, Vseross. Zh. Nauchn. Publ ., 2012, no. 2 (12), pp. 29–31.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Moscow Aviation Institute, Moscow, Russia
A. N. Genova
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to A. N. Genova .
Additional information
Translated by B. Gilbert
About this article
Genova, A.N. Cost Assignment at Production Enterprises. Russ. Engin. Res. 42 , 426–429 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068798X22040074
Download citation
Received : 01 October 2021
Revised : 01 October 2021
Accepted : 01 October 2021
Published : 19 April 2022
Issue Date : April 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068798X22040074
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- production costs
- cost calculation
- cost assignment
- cost management
- corporate governance
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Understanding Global Assignment Costs
By LaQuita Morrison, GMS
Confidence in the U.S. economy is rising, and with it, the number of companies seeking to establish, strengthen or expand their global positions is increasing. Often, this involves expatriating talent to fill key positions in other countries. Some companies will also provide global assignment opportunities to expand their employees’ knowledge and skills.
Whether your company is well versed or new to managing global assignments, the cost of them can be daunting. However, when appropriately managed, global assignments can positively impact a company’s global business goals.
Sending an employee and a family of three on a three-year global assignment could cost in excess of USD $1 million. So, it’s not surprising that many global companies believe traditional overseas assignments are cost-prohibitive. Some companies have reduced, frozen or even eliminated their global assignment programs. However, to remain competitive, companies still need to place the best talent at the appropriate locations, and often that talent isn’t available without a global transfer. This is when the proper management and oversight of relocation costs becomes imperative.
Understanding the Costs
If you’re planning global assignments, there are ways to scale back costs without compromising operations or impacting employee productivity. Finding that balance between employee support and cost management to successfully oversee global assignments is a challenge, but it can be done. Below is a list of some of the expenses associated with a global assignment:
- Candidate Assessment – Conducted by the company to determine if the employee is the right candidate for the global assignment.
- Pre-Decision Assessment – Aligns the individual needs of the employee and the employee’s family with the business goals of the assignment.
- Immigration – Obtaining the appropriate documentation for the assignment. The reason for the assignment will dictate the appropriate visa type.
- Tax Implications – Determining the tax implications of the assignment and responsibilities of both the company and the employee.
- Tax Assistance – Providing the employee with tax assistance, which could include consultation; preparation (for both home and host countries); filing (for both home and host countries); tax equalization.
- Host Country Housing – Providing reasonable and customary rent and utility costs for the employee’s housing in the host country according to regional guidelines based on family size and location.
- Cost-of-Living Allowance (COLA) – An allowance or differential paid to the employee for similar goods and services in the host location that they have in the home location based on family size and salary. Intended to cover costs to purchase host country goods and services over those from the home country.
- Transportation – An allowance for a car for the duration of the assignment, the amount of which may vary by location and family size.
- Hardship – An allowance paid in addition to salary and COLA for assignments in locations designated as a hardship for the employee based on factors that include potential violence, incidence of disease, medical care quality, geographic isolation and availability of goods and services.
- Miscellaneous Expense Allowance – One-time payment made, separate from base salary, intended to cover expenses not expressly covered in the Letter of Understanding, like renter’s insurance, obtaining a new driver’s license, immunizations, taxis, etc.
- Cultural/Language Training – Provided to the employee and the family to assist in understanding the host country culture and language.
- Home Finding and Destination Services – Locating housing in the host country, as well as registering with local authorities and setting up accounts.
- Departure Services – Home sale, property management, lease termination, etc.
- Global Household Goods – Transporting (via land, air and/or sea) or storing household goods and personal effects.
- Temporary Living – Fully furnished housing at the destination location.
- Repatriation – Return of the employee to the home country following assignment completion.
To learn more about managing global assignment costs, download our free guide.
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share with Email
Insights + Resources
What is an executive relocation package, how to build an effective hr communication strategy, should your relocation package include hardship allowances, 8 benefits of outsourcing your relocation program.

The Role of Environmental NGOs: Russian Challenges, American Lessons: Proceedings of a Workshop (2001)
Chapter: 14 problems of waste management in the moscow region, problems of waste management in the moscow region.
Department of Natural Resources of the Central Region of Russia
The scientific and technological revolution of the twentieth century has turned the world over, transformed it, and presented humankind with new knowledge and innovative technologies that previously seemed to be fantasies. Man, made in the Creator’s own image, has indeed become in many respects similar to the Creator. Primitive thinking and consumerism as to nature and natural resources seem to be in contrast to this background. Drastic deterioration of the environment has become the other side of the coin that gave the possibility, so pleasant for the average person, to buy practically everything that is needed.
A vivid example of man’s impact as “a geological force” (as Academician V. I. Vernadsky described contemporary mankind) is poisoning of the soil, surface and underground waters, and atmosphere with floods of waste that threaten to sweep over the Earth. Ecosystems of our planet are no longer capable of “digesting” ever-increasing volumes of waste and new synthetic chemicals alien to nature.
One of the most important principles in achieving sustainable development is to limit the appetite of public consumption. A logical corollary of this principle suggests that the notion “waste” or “refuse” should be excluded not only from professional terminology, but also from the minds of people, with “secondary material resources” as a substitute concept for them. In my presentation I would like to dwell on a number of aspects of waste disposal. It is an ecological, economic, and social problem for the Moscow megalopolis in present-day conditions.
PRESENT SITUATION WITH WASTE IN MOSCOW
Tens of thousand of enterprises and research organizations of practically all branches of the economy are amassed over the territory of 100,000 hectares: facilities of energy, chemistry and petrochemistry; metallurgical and machine-building works; and light industrial and food processing plants. Moscow is occupying one of the leading places in the Russian Federation for the level of industrial production. The city is the greatest traffic center and bears a heavy load in a broad spectrum of responsibilities as capital of the State. The burden of technogenesis on the environment of the city of Moscow and the Moscow region is very considerable, and it is caused by all those factors mentioned above. One of the most acute problems is the adverse effect of the huge volumes of industrial and consumer wastes. Industrial waste has a great variety of chemical components.
For the last ten years we witnessed mainly negative trends in industrial production in Moscow due to the economic crisis in the country. In Moscow the largest industrial works came practically to a standstill, and production of manufactured goods declined sharply. At the same time, a comparative analysis in 1998–99 of the indexes of goods and services output and of resource potential showed that the coefficient of the practical use of natural resources per unit of product, which had been by all means rather low in previous years, proceeded gradually to decrease further. At present we have only 25 percent of the industrial output that we had in 1990, but the volume of water intake remains at the same level. Fuel consumption has come down only by 18 percent, and the amassed production waste diminished by only 50 percent. These figures indicate the growing indexes of resource consumption and increases in wastes from industrial production.
Every year about 13 million tons of different kinds of waste are accumulated in Moscow: 42 percent from water preparation and sewage treatment, 25 percent from industry, 13 percent from the construction sector, and 20 percent from the municipal economy.
The main problem of waste management in Moscow city comes from the existing situation whereby a number of sites for recycling and disposal of certain types of industrial waste and facilities for storage of inert industrial and building wastes are situated outside the city in Moscow Region, which is subject to other laws of the Russian Federation. Management of inert industrial and building wastes, which make up the largest part of the general volume of wastes and of solid domestic wastes (SDW), simply means in everyday practice their disposal at 46 sites (polygons) in Moscow Region and at 200 disposal locations that are completely unsuitable from the ecological point of view.
The volume of recycled waste is less than 10–15 percent of the volume that is needed. Only 8 percent of solid domestic refuse is destroyed (by incineration). If we group industrial waste according to risk factor classes, refuse that is not
dangerous makes up 80 percent of the total volume, 4th class low-hazard wastes 14 percent, and 1st-3rd classes of dangerous wastes amount to 3.5 percent. The largest part of the waste is not dangerous—up to 32 percent. Construction refuse, iron and steel scrap, and non-ferrous metal scrap are 15 percent. Paper is 12 percent, and scrap lumber is 4 percent. Metal scrap under the 4th class of risk factor makes up 37 percent; wood, paper, and polymers more than 8 percent; and all-rubber scrap 15 percent. So, most refuse can be successfully recycled and brought back into manufacturing.
This is related to SDW too. The morphological composition of SDW in Moscow is characterized by a high proportion of utilizable waste: 37.6 percent in paper refuse, 35.2 percent in food waste, 10 percent in polymeric materials, 7 percent in glass scrap, and about 5 percent in iron, steel, and non-ferrous metal scrap. The paper portion in commercial wastes amounts to 70 percent of the SDW volume.
A number of programs initiated by the Government of Moscow are underway for the collection and utilization of refuse and for neutralization of industrial and domestic waste. A waste-recycling industry is being developed in the city of Moscow, mostly for manufacturing recycled products and goods. One of the most important ecological problems is the establishment in the region of ecologically safe facilities for the disposal of dangerous wastes of 1st and 2nd class risk factors.
Pre-planned industrial capacities for thermal neutralization of SDW will be able to take 30 percent of domestic waste and dangerous industrial waste. Construction of rubbish-burning works according to the old traditional approach is not worthwhile and should come to an end. Waste-handling stations have been under construction in the city for the last five years. In two years there will be six such stations which will make it possible to reduce the number of garbage trucks from 1,156 to 379 and to reduce the amount of atmospheric pollution they produce. In addition the switch to building stations with capacity of briquetting one ton of waste into a cubic meter will decrease the burden on waste disposal sites and prolong their life span by 4–5 fold. Trash hauling enterprises will also make profit because of lower transportation costs.
Putting into operation waste-segregation complexes (10–12 sites) would reduce volumes of refuse to disposal sites by 40 percent—that is 1,200,000 tons per year. The total volume of burned or recycled SDW would reach 2,770,000 tons a year. A total of 210,000 tons of waste per year would be buried. So, in the course of a five year period, full industrial recycling of SDW could be achieved in practice.
Collection of segregated waste is one of the important elements in effective disposal and utilization of SDW. It facilitates recycling of waste and return of secondary material into the manufacturing process. Future trends in segregation and collection of SDW will demand wide popularization and improvement of the ecological culture and everyday behavior of people.
In recent years the high increase in the number of cars in Moscow has brought about not only higher pollution of the atmosphere, but also an avalanche-like accumulation of refuse from vehicles. Besides littering residential and recreation areas, cars represent a source for toxic pollution of land and reservoirs. At the same time, automobile wastes are a good source for recycled products. In the short-term outlook, Moscow has to resolve the problem of collection and utilization of decommissioned vehicles and automobile wastes with particular emphasis on activities of the private sector. Setting up a system for collection and utilization of bulky domestic waste and electronic equipment refuse is also on the priority list.
In 1999 in Moscow the following volumes of secondary raw materials were produced or used in the city or were recycled: 300,000 tons of construction waste, 296,000 tons of metal scrap, 265 tons of car battery lead, 21,000 tons of glass, 62,500 tons of paper waste, 4,328 tons of oil-bearing waste, and 306 tons of refuse from galvanizing plants.
Such traditional secondary materials as metal scrap and paper waste are not recycled in Moscow but are shipped to other regions of Russia.
The worldwide practice of sorting and recycling industrial and domestic wastes demands the establishment of an industry for secondary recycling. Otherwise segregation of waste becomes ineffective.
There are restraining factors for the development of an effective system of assorted selection, segregation, and use of secondary raw resources, namely lack of sufficient manufacturing capacities and of suitable technologies for secondary recycling.
The problem of utilization of wastes is closely linked with the problem of modernization and sometimes even demands fundamental restructuring of industries. The practical use of equipment for less energy consumption and a smaller volume of wastes and a transition to the use of alternative raw materials are needed. Large enterprises—the main producers of dangerous wastes—are in a difficult financial situation now, which is an impediment for proceeding along these lines.
Private and medium-size enterprises are becoming gradually aware of the economic profitability in rational use of waste. For example, the firm Satory started as a transportation organization specialized in removal of scrap from demolished buildings and those undergoing reconstruction. It now benefits from recycling of waste, having developed an appropriate technology for the dismantling of buildings with segregation of building waste. So, as it has been already mentioned above, the first task for Moscow is to establish a basis for waste recycling.
HOW TO CHANGE THE SITUATION WITH WASTE
Transition to modern technologies in the utilization of wastes requires either sufficient investments or a considerable increase in repayment for waste on the part of the population. Obviously, these two approaches are not likely to be realized in the near future.
The recovery of one ton of SDW with the use of ecologically acceptable technology requires not less than $70–100.
Given the average per capita income in 1999 and the likely increase up to the year of 2005, in 2005 it will be possible to receive from a citizen not more than $14 per year. This means that the cost of technology should not exceed $40 per ton of recycled waste. Unfortunately, this requirement can fit only unsegregated waste disposal at the polygons (taking into account an increase in transportation costs by the year 2005).
Such being the case, it looks like there is only one acceptable solution for Russia to solve the problem of waste in an up-to-date manner: to introduce trade-in value on packaging and on some manufactured articles.
In recent years domestic waste includes more and more beverage containers. Plastic and glass bottles, aluminium cans, and packs like Tetrapak stockpiled at disposal sites will soon reach the same volumes as in western countries. In Canada, for example, this kind of waste amounts to one-third of all domestic waste.
A characteristic feature of this kind of waste is that the packaging for beverages is extremely durable and expensive. Manufactured from polyethylene terephthalate (PTA) and aluminum, it is sometimes more expensive than the beverage it contains.
What are the ways for solving the problem? Practically all of them are well-known, but most will not work in Russia in present conditions. The first problem relates to collection of segregated waste in the urban sector and in the services sector. A number of reasons make this system unrealistic, specifically in large cities. Sorting of waste at waste-briquetting sites and at polygons is possible. But if we take into account the present cost of secondary resources, this system turns out to be economically unprofitable and cannot be widely introduced.
The introduction of deposits on containers for beverages is at present the most acceptable option for Russia. This system turned out to be most effective in a number of countries that have much in common with Russia. In fact this option is not at all new for us. Surely, all people remember the price of beer or kefir bottles. A system of deposit for glass bottles was in operation in the USSR, and waste sites were free from hundreds of millions of glass bottles and jars. We simply need to reinstate this system at present in the new economic conditions according to new types and modes of packaging. Deposits could be introduced also on glass bottles and jars, PTA and other plastic bottles, aluminium cans, and Tetrapak packing.
Let us investigate several non-ecological aspects of this problem, because the ecological impact of secondary recycling of billions of bottles, cans, and packs is quite obvious.
Most of the population in Russia lives below the poverty line. When people buy bottles of vodka, beer, or soft drinks, they will have to pay a deposit value (10–20 kopeks for a bottle). The poorest people will carry the bottles to receiving points. A system of collection of packaging will function by itself. Only receiving points are needed. Millions of rubles that are collected will be redistributed among the poorest people for their benefit, and a social problem of the poor will be solved to a certain extent not by charity, but with normal economic means.
A second point is also well-known. In a market economy one of the most important problems is that of employment. What happens when the trade-in value is introduced?
Thousands of new jobs are created at receiving points and at enterprises that recycle glass, plastics, etc. And we don’t need a single penny from the state budget. More than that, these enterprises will pay taxes and consume products of other branches of industry, thus yielding a return to the budget, not to mention income tax from new jobs.
There is another aspect of the matter. Considerable funding is needed from budgets of local governments, including communal repayments for waste collection and disposal at polygons and incinerators. Reduction of expenses for utilization of waste can be significant support for housing and communal reform in general.
It is practically impossible to evaluate in general an ecological effect when thousands of tons of waste will cease to occupy plots of land near cities as long-term disposal sites. Operation costs of receiving points and transportation costs could be covered by funds obtained from manufacturers and from returned packaging. Besides, when a waste recycling industry develops and becomes profitable, recycling factories will be able to render partial support to receiving points.
Trade-in value can be introduced on all types of packaging except milk products and products for children. It could amount to 15 or 30 kopecks per container, depending on its size. If all plastic bottles with water and beer are sold with trade-in value only in Moscow, the total sum will reach 450 million rubles a year. If we include glass bottles, aluminum cans, and packets, the sum will be one billion rubles. This sum will be redistributed at receiving points among people with scanty means when they receive the money for used packaging and jobs at receiving points and at recycling factories.
The bottleneck of the problem now is the absence in Russia of high technology industries for waste recycling. It can be resolved rather easily. At the first stage, used packaging can be sold as raw material for enterprises, including those overseas. There is unrestricted demand for PTA and aluminum on the part
of foreign firms. When waste collection mechanisms are established, there will be limited investments in this branch of industry.
With regard to the inexhaustible source of free raw material, this recycling industry will become one of the most reliable from the point of view of recoupment of investments. The Government, regional authorities, the population, and of course ecologists should all be interested in having such a law.
The same should be done with sales of cars, tires, and car batteries. Prices of every tire or battery should be higher by 30–50 rubles. These sums of money should be returned back to a buyer or credited when he buys a new tire or a new battery. For sure, such being the case we will not find used batteries thrown about the city dumps. In this case the task is even simpler because there are already a number of facilities for the recycling of tires and batteries.
In fact, a law of trade-in value can change the situation with waste in Russia in a fundamental way. Russian legislation has already been prepared, and the concept of an ecological tax has been introduced in the new Internal Revenue Code. Now it needs to be competently introduced. The outlay for waste recycling has to become a type of ecological tax. To realize this task much work has to be done among the deputies and with the Government. Public ecological organizations, including international ones, should play a leading role.
ACTIVITY OF PUBLIC ORGANIZATIONS IN THE SPHERE OF WASTE MANAGEMENT IN THE MOSCOW REGION
We know examples of the ever increasing role of the general public in the solution of the problem of waste utilization, first of all in those countries that have well-developed democratic institutions. “Fight Against Waste” is one of the popular slogans of public organizations abroad. Public opinion has brought about measures of sanitary cleaning in cities, secured better work by municipal services, shut down hazardous industries, and restricted and prohibited incineration facilities. Nevertheless, the struggle against wastes in the economically developed countries, being a manifestation of an advanced attitude towards the environment, has in the long run brought about a paradoxical result. Transfer of hazardous industries to countries with lower environmental standards and inadequate public support—Russia, as an example—has made the world even more dangerous from the ecological point of view.
Russia has just embarked on the path of formation of environmental public movements by the establishment of nongovernmental organizations. Representatives of nongovernmental organizations from Russia took part in the international gathering in Bonn in March 2000 of nongovernmental organizations that are members of the International Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) Elimination Network. A declaration against incineration was adopted in
Bonn by nongovernmental organizations, which called for elaboration of effective alternative technologies for utilization of waste and safe technologies for elimination of existing stockpiles of POP.
Quite a number of environmental organizations are operating now in Moscow. First to be mentioned is the All-Russia Society for the Conservation of Nature, which was established in Soviet times. There are other nongovernmental organizations: Ecosoglasiye, Ecolain, Ecological Union, and the Russian branches of Green Cross and Greenpeace. All these organizations collect and popularize environmental information and organize protest actions against policies of the Government or local administrations on ecological matters. A new political party—Russia’s Movement of the Greens—is being formed.
Laws currently in force in the Russian Federation (“On Protection of the Environment,” “On State Ecological Examination by Experts,” “On Production and Consumption of Waste”) declare the right of the public to participate in environmental examination of projects that are to be implemented, including those on the establishment of facilities for elimination and disposition of waste. Public examinations can be organized by the initiative of citizens and public associations. For example, under the law of Moscow “On Protection of the Rights of Citizens while Implementing Decisions on Construction Projects in Moscow,” public hearings are organized by the city’s boards. Decisions taken by local authorities, at referenda and public meetings, may be the very reason for carrying out public examinations. Such examinations are conducted mainly by commissions, collectives, or ad hoc groups of experts. Members of public examination panels are responsible for the accuracy and validity of their expert evaluations in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation. A decision of a public environmental panel has an informative nature as a recommendation, but it becomes legally mandatory after its approval by the appropriate body of the State. Besides, the opinion of the public is taken into account when a project submitted for state environmental review has undergone public examinations and there are supporting materials.
Public environmental examination is supposed to draw the attention of state bodies to a definite site or facility and to disseminate well-grounded information about potential ecological risks. This important facet of public environmental organizations in Moscow and in Russia is very weak. To a large extent, it can be explained by an insufficient level of specific and general knowledge of ecology even on the part of the environmentalists themselves. Lack of knowledge on the part of ordinary citizens and public groups and inadequate information (for various reasons) produce alarm-motivated behavior by those who harm the organization of environmental activity in general and waste management in particular.
There are nevertheless positive examples of public participation in designing policies of local authorities in the waste management sphere.
Speaking about the Moscow region we can point to the very productive work of the Public Ecological Commission attached to the Council of Deputies in Pushchino, in Moscow Oblast.
The population of Pushchino is 21,000. The polygon for solid biological wastes (SBW) has practically exhausted its capacities. In 1996, in order to find a way out, the Administration of the town showed an interest in a proposal made by the Austrian firm FMW to support financially the construction of an electric power station in the vicinity of the town that would operate using both fuel briquettes and SBW of the town. The briquettes would be manufactured in Turkey and would contain 70 percent Austrian industrial waste with added oil sludge. It was also envisaged that during the construction period of the electric power station, 300,000 tons of briquettes would be shipped and stockpiled. The original positive decision was annulled due to an independent evaluation of the project organized by the Public Ecological Commission.
The general public of Puschino put forward a counter proposal before the Administration in order to reduce volumes of SBW disposal at the polygon and to prolong its operation—segregation of SBW (food waste, paper refuse, fabrics, metal, glass, used car batteries). As a result, a new scheme for sanitary measures in the town was worked out in 1998, which on the basis of segregation of waste provided for a considerable decrease in refuse flow to the polygon. Unfortunately, for lack of finances in the town budget, the scheme has not been introduced to the full extent. But in spite of severe shortages of special containers for segregated wastes, a network of receiving points for secondary materials was set up.
One of the pressing tasks for greater public activity is wide popularization of environmental knowledge on waste management, especially among the young generation. There is a very important role for public organizations to play in this domain when enlightenment and education are becoming a primary concern of nongovernmental organizations. Referring again to the example of the Public Ecological Commission in Pushchino, I have to underline that this organization is taking an active part in the enlightenment of the population through organizing exhibitions, placing publications in the press, and spurring school children into action to encourage cleaning of the town by means of environmental contests, seminars, and conferences. Children help the Commission organize mobile receiving points for secondary material. They even prepare announcements and post them around the town calling on the citizens to take valuable amounts of domestic wastes and car batteries to receiving points.
There are other examples of a growing influence of public organizations on the policy of administration in the sphere of waste management in the Moscow region. The Moscow Children’s Ecological Center has worked out the Program “You, He, She and I—All Together Make Moscow Clean,” which is being introduced with the support of the Moscow Government. In the framework of this program, children collect waste paper at schools, and they are taught how to
be careful about the environment and material resources. The storage facilities agreed to support the initiative. They buy waste paper at a special price for school children. Then, the schools spend the earned money for excursions, laboratory equipment, books, and plant greenery.
Another example of an enlightened activity is a project realized in 1999 by the firm Ecoconcord on producing video-clips for TV about the adverse effects of waste incineration and the illegality of unauthorized storage of waste.
The name Ecoconcord speaks for the main purpose of this organization—to achieve mutual understanding between the general public and governmental organizations, to encourage public involvement in decision-making, and to promote the formation of policy bodies that would not let public opinion be ignored.
Proceeding from the global task of integrating the activities of interested parties in lessening adverse waste pollution, public organizations have to cooperate with authorities and not stand against them. Cooperation and consensus between governmental and nongovernmental organizations in working out strategies and tactics in waste management should become a prerequisite in successful realization of state policy in this sphere in the Russian Federation.
An NRC committee was established to work with a Russian counterpart group in conducting a workshop in Moscow on the effectiveness of Russian environmental NGOs in environmental decision-making and prepared proceedings of this workshop, highlighting the successes and difficulties faced by NGOs in Russia and the United States.
READ FREE ONLINE
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
Switch between the Original Pages , where you can read the report as it appeared in print, and Text Pages for the web version, where you can highlight and search the text.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Financing and Funding: The process of requesting, authorizing, and receiving money for a project. Cost Management: The general practice of overseeing project expenditures and making cost-related decisions throughout the project life cycle. Controlling: Addressing cost variations to avoid cost overruns.
What is Cost Assignment? Cost assignment is the allocation of costs to the activities or objects that triggered the incurrence of the costs. The concept is heavily used in activity-based costing, where overhead costs are traced back to the actions causing the overhead to be incurred. The cost assignment is based on one or more cost drivers.. Example of a Cost Assignment
Select the Cost Management + Billing menu item. Select Billing scopes to view a list of available billing scopes and billing accounts. Select your Billing Account from the list of available billing accounts. Under Settings, select the Policies menu item and then configure the setting.
Cost management is the process of estimating, budgeting, and controlling project costs. The cost management process begins during the planning phase and continues throughout the duration of the project as managers continuously review, monitor, and adjust expenditures to ensure the project doesn't go over the approved budget.
In summary, cost assignment is the process of associating both direct and indirect costs with cost objects, such as products, services, departments, or projects. It plays a critical role in cost accounting and management accounting by providing organizations with the necessary information to make informed decisions about pricing, resource ...
Managing the costs in a business are crucial to success. There are many different ways to classify costs, which will be discussed in this module. When we discuss costs from a managerial accounting standpoint, the same cost may be classified differently depending on what information is needed. Being aware of the different cost classifications ...
It is typically made up of four steps: resource planning, cost estimation, budgeting and cost control. It's strongly recommended that you use project planning software to assist you in the process of creating a cost management plan, as there will be many tasks, costs and resources to track. 1.
Cost Allocation or cost assignment is the process of identifying and assigning costs to the various cost objects. These cost objects could be those for which the company needs to find out the cost separately. A few examples of cost objects can be a product, customer, project, department, and so on. The need for cost allocation arises because ...
Cost management is the process of planning and controlling the budget of a business. Having a good cost management system in place makes it easier for an organization to estimate and allocate its budget. Cost management is a form of management accounting that helps a business reduce the chance of going over budget with more accurate forecasts ...
Cost allocation provides the management with important data about cost utilization that they can use in making decisions. It shows the cost objects that take up most of the costs and helps determine if the departments or products are profitable enough to justify the costs allocated. For unprofitable cost objects, the company's management can ...
In an effort to take the cost management practices beyond initial deployment activities, DASA-CE has developed a multi-tier cost management course plan. ... The difference between cost capturing, allocations, and assignments Lesson 1: Cost Assignments Overview (Slide 199) Lesson 2: Capture Output Costs (Slide 208) Lesson 3: Summary/Key Take ...
Effective cost management requires the right software. ProjectManager is the perfect tool to track project costs, resources and workload. Our Gantt charts, project calendars and timesheets allow you to manage costs, time and tasks in one place. Get started for free. Keep project costs under control with ProjectManager's dashboards.
The important topics covered include cost management planning, cost estimation, budget determination, and cost control. Compared with available texts on project management, the perspective of this ...
Cost accounting is an accounting method that aims to capture a company's costs of production by assessing the input costs of each step of production as well as fixed costs, such as depreciation of ...
This course satisfies 3 credit hours at Arizona State University. It is strongly encouraged that you consult with your institution of choice to determine how these credits will be applied. In order to receive academic credit for this course, you must earn a grade of "C" or better. You have one year to add the course to your transcript.
Let us review what you will learn in the GFEBS Cost Management process. In this module, we will discuss the following topics: The Cost Management Process. Cost Planning. Cost Accounting. Interfaces. Cost Analysis. ERP Central Component (ECC) vs. Business Intelligence (BI) Cost Controlling.
The Growing Importance of Data Analytics within Cost Management. A Framework for Understanding the Role of Data Analytics in Cost Management; Data Analytic Types and Cost Management Analyses; Cost Assignment: Direct Tracing, Driver Tracing, and Allocation. Cost Objects; Accuracy of Cost Assignments; Product and Service Costs
for costs of different type. Methods of cost assignment are described. Keywords: production costs, cost calculation, cost assignment, cost management, corporate governance DOI: 10.3103/S1068798X22040074 Because markets are oversaturated and highly competitive today, we must constantly improve man-agement methods and consequently systems for calcu-
between employee support and cost management to successfully oversee global assignments is a challenge, but it can be done. Below is a list of some of the expenses associated with a global assignment: Candidate Assessment - Conducted by the company to determine if the employee is the right candidate for the global assignment.
Besides, analytics and data-driven management provided by the unified system resulted in 88% administrative cost savings. Noteworthy is the fact that the average weight of pupil's backpack fell ...
Walking tour around Moscow-City.Thanks for watching!MY GEAR THAT I USEMinimalist Handheld SetupiPhone 11 128GB https://amzn.to/3zfqbboMic for Street https://...
Modified: Mar 26, 2020. By AMA Staff. Moscow has replaced Tokyo as the world's most expensive city, according to the latest Cost of Living Survey from Mercer Human Resource Consulting. Seoul is in second place, climbing three places since last year. Tokyo moves down two positions in the rankings to take third place, followed by Hong Kong.
Management of inert industrial and building wastes, which make up the largest part of the general volume of wastes and of solid domestic wastes (SDW), simply means in everyday practice their disposal at 46 sites (polygons) in Moscow Region and at 200 disposal locations that are completely unsuitable from the ecological point of view.