
Guide on How to Write a Reflection Paper with Free Tips and Example

A reflection paper is a very common type of paper among college students. Almost any subject you enroll in requires you to express your opinion on certain matters. In this article, we will explain how to write a reflection paper and provide examples and useful tips to make the essay writing process easier.
Reflection papers should have an academic tone yet be personal and subjective. In this paper, you should analyze and reflect upon how an experience, academic task, article, or lecture shaped your perception and thoughts on a subject.
Here is what you need to know about writing an effective critical reflection paper. Stick around until the end of our guide to get some useful writing tips from the writing team at EssayPro — a research paper writing service
What Is a Reflection Paper
A reflection paper is a type of paper that requires you to write your opinion on a topic, supporting it with your observations and personal experiences. As opposed to presenting your reader with the views of other academics and writers, in this essay, you get an opportunity to write your point of view—and the best part is that there is no wrong answer. It is YOUR opinion, and it is your job to express your thoughts in a manner that will be understandable and clear for all readers that will read your paper. The topic range is endless. Here are some examples: whether or not you think aliens exist, your favorite TV show, or your opinion on the outcome of WWII. You can write about pretty much anything.
There are three types of reflection paper; depending on which one you end up with, the tone you write with can be slightly different. The first type is the educational reflective paper. Here your job is to write feedback about a book, movie, or seminar you attended—in a manner that teaches the reader about it. The second is the professional paper. Usually, it is written by people who study or work in education or psychology. For example, it can be a reflection of someone’s behavior. And the last is the personal type, which explores your thoughts and feelings about an individual subject.
However, reflection paper writing will stop eventually with one very important final paper to write - your resume. This is where you will need to reflect on your entire life leading up to that moment. To learn how to list education on resume perfectly, follow the link on our dissertation writing services .
Unlock the potential of your thoughts with EssayPro . Order a reflection paper and explore a range of other academic services tailored to your needs. Dive deep into your experiences, analyze them with expert guidance, and turn your insights into an impactful reflection paper.

Free Reflection Paper Example
Now that we went over all of the essentials about a reflection paper and how to approach it, we would like to show you some examples that will definitely help you with getting started on your paper.
Reflection Paper Format
Reflection papers typically do not follow any specific format. Since it is your opinion, professors usually let you handle them in any comfortable way. It is best to write your thoughts freely, without guideline constraints. If a personal reflection paper was assigned to you, the format of your paper might depend on the criteria set by your professor. College reflection papers (also known as reflection essays) can typically range from about 400-800 words in length.
Here’s how we can suggest you format your reflection paper:

How to Start a Reflection Paper
The first thing to do when beginning to work on a reflection essay is to read your article thoroughly while taking notes. Whether you are reflecting on, for example, an activity, book/newspaper, or academic essay, you want to highlight key ideas and concepts.
You can start writing your reflection paper by summarizing the main concept of your notes to see if your essay includes all the information needed for your readers. It is helpful to add charts, diagrams, and lists to deliver your ideas to the audience in a better fashion.
After you have finished reading your article, it’s time to brainstorm. We’ve got a simple brainstorming technique for writing reflection papers. Just answer some of the basic questions below:
- How did the article affect you?
- How does this article catch the reader’s attention (or does it all)?
- Has the article changed your mind about something? If so, explain how.
- Has the article left you with any questions?
- Were there any unaddressed critical issues that didn’t appear in the article?
- Does the article relate to anything from your past reading experiences?
- Does the article agree with any of your past reading experiences?
Here are some reflection paper topic examples for you to keep in mind before preparing to write your own:
- How my views on rap music have changed over time
- My reflection and interpretation of Moby Dick by Herman Melville
- Why my theory about the size of the universe has changed over time
- How my observations for clinical psychological studies have developed in the last year
The result of your brainstorming should be a written outline of the contents of your future paper. Do not skip this step, as it will ensure that your essay will have a proper flow and appropriate organization.
Another good way to organize your ideas is to write them down in a 3-column chart or table.

Do you want your task look awesome?
If you would like your reflection paper to look professional, feel free to check out one of our articles on how to format MLA, APA or Chicago style
Writing a Reflection Paper Outline
Reflection paper should contain few key elements:
Introduction
Your introduction should specify what you’re reflecting upon. Make sure that your thesis informs your reader about your general position, or opinion, toward your subject.
- State what you are analyzing: a passage, a lecture, an academic article, an experience, etc...)
- Briefly summarize the work.
- Write a thesis statement stating how your subject has affected you.
One way you can start your thesis is to write:
Example: “After reading/experiencing (your chosen topic), I gained the knowledge of…”
Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs should examine your ideas and experiences in context to your topic. Make sure each new body paragraph starts with a topic sentence.
Your reflection may include quotes and passages if you are writing about a book or an academic paper. They give your reader a point of reference to fully understand your feedback. Feel free to describe what you saw, what you heard, and how you felt.
Example: “I saw many people participating in our weight experiment. The atmosphere felt nervous yet inspiring. I was amazed by the excitement of the event.”
As with any conclusion, you should summarize what you’ve learned from the experience. Next, tell the reader how your newfound knowledge has affected your understanding of the subject in general. Finally, describe the feeling and overall lesson you had from the reading or experience.
There are a few good ways to conclude a reflection paper:
- Tie all the ideas from your body paragraphs together, and generalize the major insights you’ve experienced.
- Restate your thesis and summarize the content of your paper.
We have a separate blog post dedicated to writing a great conclusion. Be sure to check it out for an in-depth look at how to make a good final impression on your reader.
Need a hand? Get help from our writers. Edit, proofread or buy essay .
How to Write a Reflection Paper: Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: create a main theme.
After you choose your topic, write a short summary about what you have learned about your experience with that topic. Then, let readers know how you feel about your case — and be honest. Chances are that your readers will likely be able to relate to your opinion or at least the way you form your perspective, which will help them better understand your reflection.
For example: After watching a TEDx episode on Wim Hof, I was able to reevaluate my preconceived notions about the negative effects of cold exposure.
Step 2: Brainstorm Ideas and Experiences You’ve Had Related to Your Topic
You can write down specific quotes, predispositions you have, things that influenced you, or anything memorable. Be personal and explain, in simple words, how you felt.
For example: • A lot of people think that even a small amount of carbohydrates will make people gain weight • A specific moment when I struggled with an excess weight where I avoided carbohydrates entirely • The consequences of my actions that gave rise to my research • The evidence and studies of nutritional science that claim carbohydrates alone are to blame for making people obese • My new experience with having a healthy diet with a well-balanced intake of nutrients • The influence of other people’s perceptions on the harm of carbohydrates, and the role their influence has had on me • New ideas I’ve created as a result of my shift in perspective
Step 3: Analyze How and Why These Ideas and Experiences Have Affected Your Interpretation of Your Theme
Pick an idea or experience you had from the last step, and analyze it further. Then, write your reasoning for agreeing or disagreeing with it.
For example, Idea: I was raised to think that carbohydrates make people gain weight.
Analysis: Most people think that if they eat any carbohydrates, such as bread, cereal, and sugar, they will gain weight. I believe in this misconception to such a great extent that I avoided carbohydrates entirely. As a result, my blood glucose levels were very low. I needed to do a lot of research to overcome my beliefs finally. Afterward, I adopted the philosophy of “everything in moderation” as a key to a healthy lifestyle.
For example: Idea: I was brought up to think that carbohydrates make people gain weight. Analysis: Most people think that if they eat any carbohydrates, such as bread, cereal, and sugar, they will gain weight. I believe in this misconception to such a great extent that I avoided carbohydrates entirely. As a result, my blood glucose levels were very low. I needed to do a lot of my own research to finally overcome my beliefs. After, I adopted the philosophy of “everything in moderation” as a key for having a healthy lifestyle.
Step 4: Make Connections Between Your Observations, Experiences, and Opinions
Try to connect your ideas and insights to form a cohesive picture for your theme. You can also try to recognize and break down your assumptions, which you may challenge in the future.
There are some subjects for reflection papers that are most commonly written about. They include:
- Book – Start by writing some information about the author’s biography and summarize the plot—without revealing the ending to keep your readers interested. Make sure to include the names of the characters, the main themes, and any issues mentioned in the book. Finally, express your thoughts and reflect on the book itself.
- Course – Including the course name and description is a good place to start. Then, you can write about the course flow, explain why you took this course, and tell readers what you learned from it. Since it is a reflection paper, express your opinion, supporting it with examples from the course.
- Project – The structure for a reflection paper about a project has identical guidelines to that of a course. One of the things you might want to add would be the pros and cons of the course. Also, mention some changes you might want to see, and evaluate how relevant the skills you acquired are to real life.
- Interview – First, introduce the person and briefly mention the discussion. Touch on the main points, controversies, and your opinion of that person.
Writing Tips
Everyone has their style of writing a reflective essay – and that's the beauty of it; you have plenty of leeway with this type of paper – but there are still a few tips everyone should incorporate.
Before you start your piece, read some examples of other papers; they will likely help you better understand what they are and how to approach yours. When picking your subject, try to write about something unusual and memorable — it is more likely to capture your readers' attention. Never write the whole essay at once. Space out the time slots when you work on your reflection paper to at least a day apart. This will allow your brain to generate new thoughts and reflections.
- Short and Sweet – Most reflection papers are between 250 and 750 words. Don't go off on tangents. Only include relevant information.
- Clear and Concise – Make your paper as clear and concise as possible. Use a strong thesis statement so your essay can follow it with the same strength.
- Maintain the Right Tone – Use a professional and academic tone—even though the writing is personal.
- Cite Your Sources – Try to cite authoritative sources and experts to back up your personal opinions.
- Proofreading – Not only should you proofread for spelling and grammatical errors, but you should proofread to focus on your organization as well. Answer the question presented in the introduction.
'If only someone could write my essay !' you may think. Ask for help our professional writers in case you need it.
Do You Need a Well-Written Reflection Paper?
Then send us your assignment requirements and we'll get it done in no time.
Related Articles
.webp)
How to Write a Reflection Paper in 5 Steps (plus Template and Sample Essay)
by Kaelyn Barron | 15 comments

If you’ve been assigned the task of writing a reflection paper on a book you’ve read, film you’ve seen, or an event you’ve attended, you may be wondering where to start.
After all, there are few rules when it comes to writing a reflection, since it’s basically just your reaction and thoughts on the material—and all that creative freedom can be intimidating at first! But even with this lack of structure, there are steps you can take to write a reflection paper that adds value to the discussion.
What Is a Reflection Paper?
A reflection paper is a type of essay that requires you to reflect, or give your thoughts and opinions, on a certain subject or material. This type of essay is often assigned to students after they’ve read a book or watched a film.
However, it can also be written in a professional setting, often by those who study education or psychology, to reflect on an individual’s behavior. Or, you can write a reflection paper for your own purposes, to work out your thoughts and feelings on a personal subject.
If you’re a student, in most cases, you’ll be given a prompt or question to guide your reflection. Often, these assignments are completed in class, so the reflections are generally under 1,000 words. The good news is that there are on wrong answers!
However, there are things you can do to write more effective reflections that will give you (and your teachers, if applicable) more insight to your views and thought processes.
How to Write a Reflection Paper

Use these 5 tips to write a thoughtful and insightful reflection paper.
1. Answer key questions.
To write a reflection paper, you need to be able to observe your own thoughts and reactions to the material you’ve been given. A good way to start is by answering a series of key questions.
For example:
- What was your first reaction to the material? Was it positive, negative, or neutral?
- Do you find the writer (or director, presenter, etc.) to be credible?
- Has the material changed your mind in some way?
- Which issues or questions does the material fail to address?
- What new or remaining questions do you have after reading/viewing the material?
- What have you learned from this material?
- Does it remind you of any personal experiences, or anything else you’ve seen or read?
Answering these questions will help you formulate your own opinions, draw conclusions, and write an insightful reflection.
2. Identify a theme.
Once you’ve answered a few basic questions, look at your responses and see if you can identify any common themes .
What’s the main takeaway? If you could summarize your thoughts on this piece in one sentence, what would you say?
Think about what you’ve learned, or how the material has affected you. Be honest about how you feel, especially if the material incites any strong opinions or reactions from you.
3. Summarize.
Your reflection paper should not be just a mere summary of the material you’ve read or studied. However, you should give a recap of the most important aspects, and offer specific examples when necessary to back up any assertions you make.
Include information about the author (if you’re writing about a book or article). If you’re writing about a work of fiction, very briefly and concisely summarize the plot. If writing about nonfiction, share the author’s thesis, or the main argument they’re trying to make.
Just be careful to not overdo the summary—you don’t want to reproduce or offer a play-by-play of the original work, but rather offer enough context so readers can appreciate your reflection and analysis.
4. Analyze.
Your reflection paper is a great place to practice your critical thinking skills , which include analysis. The questions in Step 1 will offer you a good start when it comes to thinking more analytically.
Once you’ve offered enough context for your readers by including a brief summary, analyze the
- the overall tone of the work
- the credibility of the writer (or producer of the content)
- potential biases
- the intended purpose of the material
If you’re writing a reflection paper on a work of fiction, be sure to check out our guide to writing a literary analysis.
5. Make connections.

Does the material remind you of any personal experiences you’ve had, or other books or films you’ve encountered? Can you connect it to any current events or real-world examples?
Then, zoom out and try to see the bigger picture. What do these connections have in common? Can you point out a larger, more universal theme?
The more of these connections you can tie in to your reflection to create a cohesive picture, the better.
Reflection Paper Template
Reflection papers don’t really require a rigid structure—the most important thing is that you communicate your ideas clearly and effectively. (Of course, if you received specific guidelines from your instructor, you should stick to those.)
The following is a loose outline that you can use to guide you through your reflection paper:
- Include: Title, Author Name (or Director, Photographer, etc.).
- Briefly summarize the work and its main themes.
- Write a thesis that states the work’s overall impact on you.
- When relevant, include specific quotes or examples to support your claims.
- Explore your main reactions and thoughts after reviewing the material.
- Build connections to personal experiences and other works you’ve encountered.
- Show how the ideas from your body paragraphs tie together to support your thesis.
- Summarize the overall effect the material had on you.
Reflection Paper Example
The following is an example of a reflection paper I wrote for a university course in response to an academic article on conflict resolution, found in the book Managing Conflict in a World Adrift :
In “Understanding the Gendered Nature of Power,” Oudraat and Kuehnast explain how peace theorists have fallen short in their analyses of the role of gender (and of women especially). Because gender roles are a reflection of power dynamics within societies, they can also serve as valuable indicators of dynamics within conflicts and post-conflict processes.
The authors emphasize the importance of using international intervention wisely. Although postconflict reconstruction might seem like an opportunity to rethink gender norms and roles, it seems that postconflict programs tend more often to reproduce gender norms that “no longer contribute productive approaches to society and escalate social tensions.” While I think we should always strive to bring more opportunities to women and eradicate gender biases, I agree with the authors that international actors must “be attentive to the gendered nature of the societies in which they intervene.” We have seen many cases where international intervention, although well-meaning, can end up hurting a community even more by meddling without truly knowing the conditions of a local situation.
One example of such misguided help is the campaign for “clean stoves” in African villages, based on the idea that women are assaulted when they look for fuel and water outside their camps. Providing clean stoves does nothing to address the root of the problem (sexual violence), and in fact further confines women to their homes, while many studies show that times of collecting water or other supplies are often critical opportunities for women to communicate, socialize, exchange ideas, and so on. In many cases it is the only time they will leave the home or village that day. The solution proposed by the clean stoves campaign reminds me of the culture surrounding sexual violence in the United States, where rather than working to attack the root causes of such crimes, we instead teach women that it is unsafe to go out late, or to dress in a certain way.
In order to make any progress, I agree with the authors when they suggest we need qualitative data that capture the changing nature of societies coming out of war. We must first identify the information we lack in order to move forward wisely and effectively.
Writing a Reflective Essay
Whether you’ve been assigned a reflection paper for school or simply want to write one for your own exercise, these tips will help you get the most from the experience.
Remember that when you’re consuming any type of media, it’s good practice to reflect on what you’ve absorbed and ask critical questions so you can draw your own conclusions.
Did you find this post helpful? Let us know in the comments below!
If you enjoyed this post, then you might also like:
- 19 Books That Make You Think: A List of Thought-Provoking Reads
- Why You Should Keep a Reading Journal: Tips for More Reflective Reading
- How to Write a Literary Analysis: 6 Tips for the Perfect Essay
- How to Summarize a Novel: 4 Steps to Writing a Great Summary
As a blog writer for TCK Publishing, Kaelyn loves crafting fun and helpful content for writers, readers, and creative minds alike. She has a degree in International Affairs with a minor in Italian Studies, but her true passion has always been writing. Working remotely allows her to do even more of the things she loves, like traveling, cooking, and spending time with her family.
15 Comments
Very helpful, thanks a lot!
Thankful for this! Thanks to you!
we’re glad you found the post helpful! :)
In my understanding, this post helped me to guide my students while I was teaching them how to write effective reflection paper. In addition to this, I had time to correct my past through this post. Thanks a lot!!!
I’m so glad you found this post helpful for your students! :)
I believe I understood the steps and instructions on how to write a reflection paper and it makes lots of sense to me now than before . What I was really hoping for was that you could give us an example of a text or an article written followed by a reflection that was done on that article . Maybe I`m asking too much. Thank you though!!!!
Hi Larry, I’m glad the article was helpful for your reflection paper! I tried to provide an example of one of my own papers, but I couldn’t find the full text of the article I wrote on (it was from a textbook). I’ll try to find another example though :)
am very empress with this information. it really helps me to write an effective reflection papers
thanks Benjamin, we’re so glad you found it helpful! :)
This is very helpful as I am preparing for my portfolio defense. Many thanks Mark
I’m so glad you found it helpful, Mark!
Very informative.
Thanks Sara, I’m glad you found the post helpful! :)
Many thanks for this information,,very needed today for my final exam.
You’re very welcome Lyn, I hope it helped for your exam! :)

Learn More About
- Fiction (223)
- Nonfiction (71)
- Blogging (46)
- Book Promotion (28)
- How to Get Reviews (9)
- Audiobooks (17)
- Book Design (11)
- Ebook Publishing (13)
- Hybrid Publishing (8)
- Print Publishing (9)
- Self Publishing (70)
- Traditional Publishing (53)
- How to Find an Editor (11)
- Fitness (4)
- Mindfulness and Meditation (7)
- Miscellaneous (116)
- New Releases (17)
- Career Development (73)
- Online Courses (46)
- Productivity (45)
- Personal Finance (21)
- Podcast (179)
- Poetry Awards Contest (2)
- Publishing News (8)
- Readers Choice Awards (5)
- Reading Tips (145)
- Software (17)
- Technology (15)
- Contests (4)
- Grammar (59)
- Word Choice (64)
- Writing a Book (62)
- Writing Fiction (195)
- Writing Nonfiction (68)
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Don't Miss a Post! Subscribe
- Guest Posts

- Educational AI
- Edtech Tools
- Edtech Apps
- Teacher Resources
- Special Education
- Edtech for Kids
- Buying Guides for Teachers

Educators Technology
Innovative EdTech for teachers, educators, parents, and students
80 Learning Reflection Questions for Students
By Med Kharbach, PhD | Last Update: March 23, 2024

Reflection questions are an important way to boost students’ engagement and enhance their learning. By encouraging learners to ponder their experiences, understandings, and feelings about what they’ve learned, we open a gateway to deeper comprehension and personal growth.
This process not only solidifies their grasp on the material but also cultivates critical thinking and self-awareness. Throughout this post, I’ll share the insights and techniques I’ve gained from my years in the classroom, with a focus on the power and purpose of reflection questions in fostering deep learning.
5. Facilitates Continuous Improvement
What are reflection questions.
Before we define reflective questions, let’s first discuss what reflection is. Citing ASCD, Purdue defines reflection as “a process where students describe their learning, how it changed, and how it might relate to future learning experiences”.
Based on this definition, reflection questions, are tools that prompt introspection and critical thinking. They empower students to questions their acquired knowledge and transform their experiences into meaningful understandings and personal growth. But this isn’t just based on my personal experience – research supports the idea that reflection plays a critical role in the learning process.
Studies show that when students pause to reflect on their learning journey—assessing their understanding, evaluating their performance, setting future goals, and analyzing their group work—it leads to increased self-awareness , responsibility for learning, and improved academic performance.
Over the years, I’ve integrated these reflection techniques into my teaching practice and have witnessed first-hand the profound impact they can have. It’s always a joy to see my students evolve from passive recipients of information to active, engaged learners who take ownership of their educational journey.
In this post, we’ll dive deeper into how teachers can incorporate reflection questions into their teaching strategies , the best times to use these questions, and a list of reflection question examples for different scenarios. So whether you’re a fellow teacher looking for inspiration or an interested parent wanting to support your child’s learning, read on.
To provide even more value, we’ve taken the time to create a highly-engaging, visually-appealing PDF version of this blog post. This PDF not only includes the original material, but it also features informative visuals to illustrate the concepts better, making it a more comprehensive resource.
We want to offer this PDF exclusively to our valued members of the Educators Technology community.
So if you’re not yet part of our community, we strongly encourage you to subscribe:
Importance of Reflection Questions in Learning
Reflection is an integral part of the learning process, and its importance for students cannot be overstated. It acts as a bridge between experiences and learning, transforming information into meaningful knowledge.
However, as Bailey and Rehman reported in the Harvard Business Review, to reap the benefits of reflection, one needs to make the act of reflecting a habit. You need to incorporate it in your daily practice and use both forms reflection in action (while being engaged in doing the action) and reflection on action (after the action has taken place).
The following are some of the benefits of integrating reflection questions in learning:
1. Boosts Self-Awareness
Reflection encourages students to think deeply about their own learning process. It prompts them to ask themselves questions about what they’ve learned, how they’ve learned it, and what it means to them.
This practice cultivates self-awareness, making students more conscious of their learning strengths, weaknesses, styles, and preferences. As students better understand their unique learning journey, they become more equipped to tailor their learning strategies in ways that work best for them.
2. Fosters Responsibility for Learning
When students reflect on their learning, they are actively involved in the process of their own education. This involvement fosters a sense of ownership and r esponsibility . It transforms students from passive recipients of knowledge to active participants in their learning journey. They start to recognize that the onus of learning lies with them, making them more committed and proactive learners.
3. Promotes Personal Growth
Reflection is not only about academic growth; it’s also about personal and professional development . When students reflect, they evaluate their actions, decisions, and behaviors, along with their learning.
This helps them identify not only what they need to learn but also what they need to do differently. They gain insights into their personal growth, such as improving their time management, being more collaborative, or handling stress better. This promotes the development of life skills that are crucial for their future.
4. Enhances Critical Thinking
Reflection also enhances critical thinking skills. When students reflect, they analyze their learning experiences, break them down, compare them, and draw conclusions. This practice of critical analysis helps them embrace a questioning attitude and therefore fosters the development of their critical thinking abilities.
Reflection is a self-regulatory practice that helps students identify areas of improvement. By reflecting on what worked, what didn’t, and why, students can pinpoint the areas they need to focus on. This paves the way for continuous improvement , helping them to become lifelong learners.
Tips to Incorporate reflection questions in your teaching
As teachers and educators, you can use reflection questions to deepen student understanding and promote active engagement with the learning material. Here are few tips to help you integrate reflection questions in your teaching:

1. Incorporating Reflection Questions into Lessons
- Introduce at the End of a Lesson: One of the most common times to use reflection questions is at the end of a lesson. This helps students to review and consolidate the key concepts they have just learned. For example, you might ask, “What was the most important thing you learned today?” or “What questions do you still have about the topic?”
- Use in Class Discussions: You can also incorporate reflection questions into your classroom discussions to foster a deeper understanding of the topics at hand. These questions can push students to think beyond the surface level and engage with the material in a more meaningful way.
- Incorporate in Assignments: Reflection questions can be included as part of homework assignments or projects. For instance, after a group project, you could ask, “How did your team work together?” or “What role did you play in the group, and how did it contribute to the final outcome?”
2. Choosing the Right Time to Use Reflection Questions
- After Lessons: As mentioned above, reflection questions can be highly effective when used immediately after a lesson. This is when the information is still fresh in students’ minds, and they can easily connect the concepts they’ve learned.
- End of the School Day: At the end of the school day, reflection questions can help students recall what they’ve learned across different subjects. This can help in connecting concepts across disciplines and promote broader understanding.
- After a Project or Unit: When a project, assignment, or unit is completed, reflection questions can help students consider their performance, what they learned, what challenges they faced, and how they overcame those challenges. It’s an opportunity for them to recognize their growth over time and understand how they can improve in the future.
- During Parent-Teacher Conferences: Reflection questions can also be useful during parent-teacher conferences. Teachers can share these reflections with parents to provide them with insights into their child’s learning process, strengths, and areas of improvement.
Keep in mind that the goal of these questions is not to judge or grade students but to promote introspection, self-awareness, and active participation in their own learning journey. The responses to reflection questions should be valued for the thought process they reveal and the learning they represent, not just the final answer.
Reflection Questions for Understanding Concepts
These reflection questions aim to prompt students to think deeply about the content of the lesson, ensuring they truly grasp the material rather than just memorizing facts. Effective reflection requires an environment where students feel comfortable expressing their thoughts, doubts, and feelings, so it’s important to create a supportive and non-judgmental classroom culture.
Below are ten examples of reflection questions that can help students evaluate their understanding of key concepts or lessons:
- What was the most important thing you learned in today’s lesson?
- Can you summarize the main idea or theme of the lesson in your own words?
- Was there anything you found confusing or difficult to understand? If so, what?
- How does this concept relate to what we learned previously? Can you draw connections?
- How would you explain this concept to a friend who missed the lesson?
- What were the key points or steps in today’s lesson that helped you understand the concept?
- If you could ask the teacher one question about today’s lesson, what would it be?
- Can you provide an example of how this concept applies in real life?
- Did today’s lesson change your perspective or understanding about the topic? If so, how?
- What strategies or methods did you find helpful in understanding today’s lesson?
Reflection Questions for Self-Assessment
These questions encourage students to look inward and evaluate their performance, behaviors, and strategies. They provide valuable insights that can guide students in setting goals for improvement and taking responsibility for their learning. The goal of these questions is not to make students feel criticized, but to empower them to become more proactive, effective learners.
Here are ten examples of self-assessment reflection questions:
- What was the most challenging part of the lesson/project for you, and how did you overcome that challenge?
- What are some strengths you utilized in today’s lesson/project?
- Are there any areas you think you could have done better in? What are they?
- Did you meet your learning goals for today’s lesson/project? Why or why not?
- What is something you’re proud of in your work today?
- What learning strategies did you use today, and how effective were they?
- If you were to do this lesson/project again, what would you do differently?
- What steps did you take to stay organized and manage your time effectively during the lesson/project?
- How well did you collaborate with others (if applicable) in today’s lesson/project?
- On a scale of 1-10, how would you rate your effort on this lesson/project, and why?
Reflection Questions for Group Work and Collaboration
These questions prompt students to reflect on their collaborative skills, from communication and decision-making to conflict resolution and leadership. The insights gained can guide students to improve their future collaborative efforts, enhancing not only their learning but also their teamwork skills, which are vital for their future careers.
Here are ten reflection questions designed to help students evaluate their performance and experience within a group setting:
- What role did you play in your group, and how did it contribute to the project’s outcome?
- What were the strengths of your group? How did these strengths contribute to the completion of the project?
- Were there any challenges your group faced? How were they resolved?
- What did you learn from your group members during this project?
- If you could change one thing about the way your group worked together, what would it be and why?
- How did your group make decisions? Was this method effective?
- What was the most valuable contribution you made to the group project?
- What is one thing you would do differently in future group work?
- Did everyone in your group contribute equally? If not, how did this impact the group dynamics and the final product?
- What skills did you use during group work, and how can you further improve these skills for future collaboration?
Reflection Questions for Goal Setting
- Based on your recent performance, what is one learning goal you would like to set for the next lesson/unit/project?
- What specific steps will you take to achieve this goal?
- What resources or support do you think you will need to reach your goal?
- How will you know when you have achieved this goal? What will success look like?
- What is one thing you could improve in the next lesson/unit/project?
- What skills would you like to improve or develop in the next term?
- What learning strategies do you plan to use in future lessons to help you understand the material better?
- How do you plan to improve your collaboration with others (if applicable) in future projects or group tasks?
- How can you better manage your time or stay organized in future lessons/projects?
- How can you apply what you’ve learned in this lesson/unit/project to future lessons or real-world situations?
Reflection Questions for Students After a Project
- What part of this project did you enjoy the most, and why?
- What challenges did you face during this project, and how did you overcome them?
- If you were to do this project again, what would you do differently?
- What skills did you utilize for this project?
- How does this project connect to what you’ve previously learned?
Reflection Questions for Students About Behavior
- How do you feel your behavior affects your learning?
- Can you identify a time when your behavior positively impacted others?
- How can you improve your behavior in the next term?
- What triggers certain behaviors, and how can you manage these triggers?
- How do you plan to exhibit positive behavior in the future?

Reflection Questions for Students After Watching a Video
- What is the main message or idea of the video?
- How does the content of the video relate to what we’re learning?
- What part of the video stood out to you the most, and why?
- What questions do you have after watching the video?
- Can you apply the lessons from the video to real-world scenarios?
Reflection Questions for Students at the End of the Year
- What is the most significant thing you’ve learned this year?
- Which areas have you seen the most growth in?
- What was the most challenging part of the year for you, and how did you overcome it?
- What are your learning goals for the next school year?
- How have you changed as a learner over this school year?
Reflection Questions for Students After a Test
- How well do you feel you prepared for the test?
- What part of the test did you find most challenging and why?
- Based on your performance, what areas do you need to focus on for future tests?
- How did you handle the stress or pressure of the test?
- What will you do differently to prepare for the next test?
Reflection Questions for Students After a Unit
- What was the most important concept you learned in this unit?
- How can you apply the knowledge from this unit to other subjects or real-life situations?
- Were there any concepts in this unit you found confusing or difficult?
- How does this unit connect to the overall course objectives?
- What strategies helped you learn the material in this unit?
Reflection Questions for Students After Reading
- What is the main idea or theme of the text?
- How do the characters or events in the text relate to your own experiences?
- What questions do you have after reading the text?
- How has this reading changed your perspective on the topic?
- What part of the text resonated with you the most, and why?
Reflection Questions for Students After a Semester
- What are three significant things you’ve learned this semester?
- What strategies did you use to stay organized and manage your time effectively?
- How have you grown personally and academically this semester?
- What challenges did you face this semester, and how did you overcome them?
- What are your goals for the next semester?
Final thoughts
Circling back to the heart of this post, reflection questions are undeniably a potent catalyst for meaningful learning. They are more than just queries thrown at the end of a lesson; they are introspective prompts that nudge learners to weave together the tapestry of their educational journey with threads of self-awareness, critical analysis, and personal growth. It’s through these questions that students can reflect on their academic canvas and begin to paint a picture of who they are and who they aspire to be in this ever-evolving world of knowledge.
References and Further Readings
Sources cited in the post:
- Driving Continuous Improvement through Reflective Practice, stireducation.org
- Practice-based and Reflective Learning, https://libguides.reading.ac.uk/
- Don’t underestimate the Power of Self-reflection, https://hbr.org/
- Reflective Practice, https://le.unimelb.edu.au/
- Reflection in Learning, https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1210944.pdf
- The purpose of Reflection, https://www.cla.purdue.edu/
- Self-reflection and Academic Performance: Is There A Relationship, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
- Reflection and Self-awareness, https://academic.oup.com/
Further Readings
A. Books on reflective learning
- Brockbank, A., & McGill, I. (2007). “ Facilitating Reflective Learning in Higher Education “. McGraw-Hill Education.
- Dewey, J. (1933). “ How We Think “.
- Moon, J. A. (2013). Reflection in Learning and Professional Development .
- Schön, D. A. (1983). “ The Reflective Practitioner: How Professionals Think in Action “. Basic Books.
- Gibbs, G. (1988). “ Learning by Doing: A Guide to Teaching and Learning Methods “. FEU.
- Boud, D., Keogh, R., & Walker, D. (1985). “Promoting Reflection in Learning: A Model”. In Reflection: Turning Experience into Learning . Kogan Page.
- Kolb, D. A. (1984). “ Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development “. Prentice-Hall.
- Rolheiser, C., Bower, B., & Stevahn, L. (2000). “ The Portfolio Organizer: Succeeding with Portfolios in Your Classroom “. Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development.
B. Peer-reviewed journal articles
- Rusche, S. N., & Jason, K. (2011). “You Have to Absorb Yourself in It”: Using Inquiry and Reflection to Promote Student Learning and Self-knowledge. Teaching Sociology, 39(4), 338–353. http://www.jstor.org/stable/41308965
- Ciardiello, A. V. (1993). Training Students to Ask Reflective Questions. The Clearing House, 66(5), 312–314. http://www.jstor.org/stable/30188906
- Lee, Y., & Kinzie, M. B. (2012). Teacher question and student response with regard to cognition and language use. Instructional Science, 40(6), 857–874. http://www.jstor.org/stable/43575388
- Gunderson, A. (2017). The Well-Crafted Question: Inspiring Students To Connect, Create And Think Critically. American Music Teacher, 66(5), 14–18. https://www.jstor.org/stable/26387562
- Grossman, R. (2009). STRUCTURES FOR FACILITATING STUDENT REFLECTION. College Teaching, 57(1), 15–22. http://www.jstor.org/stable/25763356
- Holden, R., Lawless, A., & Rae, J. (2016). From reflective learning to reflective practice: assessing transfer. Studies in Higher Education, 43(7), pages 1172-1183. Jacobs, Steven MN, MA Ed, RN. Reflective learning, reflective practice. Nursing 46(5):p 62-64, May 2016. | DOI: 10.1097/01.NURSE.0000482278.79660.f2
- Thompson, G, Pilgrim, A., Oliver, K. (2006). Self-assessment and Reflective Learning for First-year University Geography Students: A Simple Guide or Simply Misguided?. Journal of Geography in Higher Education, Pages 403-420. https://doi.org/10.1080/03098260500290959
- Kember, D., McKay, J., Sinclair, K., & Kam, F. Y. (2008). “A Four-Category Scheme for Coding and Assessing the Level of Reflection in Written Work”. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education.

Join our mailing list
Never miss an EdTech beat! Subscribe now for exclusive insights and resources .

Meet Med Kharbach, PhD
Dr. Med Kharbach is an influential voice in the global educational technology landscape, with an extensive background in educational studies and a decade-long experience as a K-12 teacher. Holding a Ph.D. from Mount Saint Vincent University in Halifax, Canada, he brings a unique perspective to the educational world by integrating his profound academic knowledge with his hands-on teaching experience. Dr. Kharbach's academic pursuits encompass curriculum studies, discourse analysis, language learning/teaching, language and identity, emerging literacies, educational technology, and research methodologies. His work has been presented at numerous national and international conferences and published in various esteemed academic journals.

Join our email list for exclusive EdTech content.

- Peterborough

How to Write a Reflection Paper
Why reflective writing, experiential reflection, reading reflection.
- A note on mechanics
Reflection offers you the opportunity to consider how your personal experiences and observations shape your thinking and your acceptance of new ideas. Professors often ask students to write reading reflections. They do this to encourage you to explore your own ideas about a text, to express your opinion rather than summarize the opinions of others. Reflective writing can help you to improve your analytical skills because it requires you to express what you think, and more significantly, how and why you think that way. In addition, reflective analysis asks you to acknowledge that your thoughts are shaped by your assumptions and preconceived ideas; in doing so, you can appreciate the ideas of others, notice how their assumptions and preconceived ideas may have shaped their thoughts, and perhaps recognize how your ideas support or oppose what you read.
Types of Reflective Writing
Popular in professional programs, like business, nursing, social work, forensics and education, reflection is an important part of making connections between theory and practice. When you are asked to reflect upon experience in a placement, you do not only describe your experience, but you evaluate it based on ideas from class. You can assess a theory or approach based on your observations and practice and evaluate your own knowledge and skills within your professional field. This opportunity to take the time to think about your choices, your actions, your successes and your failures is best done within a specific framework, like course themes or work placement objectives. Abstract concepts can become concrete and real to you when considered within your own experiences, and reflection on your experiences allows you to make plans for improvement.
To encourage thoughtful and balanced assessment of readings, many interdisciplinary courses may ask you to submit a reading reflection. Often instructors will indicate to students what they expect of a reflection, but the general purpose is to elicit your informed opinions about ideas presented in the text and to consider how they affect your interpretation. Reading reflections offer an opportunity to recognize – and perhaps break down – your assumptions which may be challenged by the text(s).
Approaches to Reflective Inquiry
You may wonder how your professors assess your reflective writing. What are they looking for? How can my experiences or ideas be right or wrong? Your instructors expect you to critically engage with concepts from your course by making connections between your observations, experiences, and opinions. They expect you to explain and analyse these concepts from your own point of view, eliciting original ideas and encouraging active interest in the course material.
It can be difficult to know where to begin when writing a critical reflection. First, know that – like any other academic piece of writing – a reflection requires a narrow focus and strong analysis. The best approach for identifying a focus and for reflective analysis is interrogation. The following offers suggestions for your line of inquiry when developing a reflective response.
It is best to discuss your experiences in a work placement or practicum within the context of personal or organizational goals; doing so provides important insights and perspective for your own growth in the profession. For reflective writing, it is important to balance reporting or descriptive writing with critical reflection and analysis.
Consider these questions:
- Contextualize your reflection: What are your learning goals? What are the objectives of the organization? How do these goals fit with the themes or concepts from the course?
- Provide important information: What is the name of the host organization? What is their mission? Who do they serve? What was your role? What did you do?
- Analytical Reflection: What did you learn from this experience? About yourself? About working in the field? About society?
- Lessons from reflection: Did your experience fit with the goals or concepts of the course or organization? Why or why not? What are your lessons for the future? What was successful? Why? What would you do differently? Why? How will you prepare for a future experience in the field?
Consider the purpose of reflection: to demonstrate your learning in the course. It is important to actively and directly connect concepts from class to your personal or experiential reflection. The following example shows how a student’s observations from a classroom can be analysed using a theoretical concept and how the experience can help a student to evaluate this concept.
For Example My observations from the classroom demonstrate that the hierarchical structure of Bloom’s Taxonomy is problematic, a concept also explored by Paul (1993). The students often combined activities like application and synthesis or analysis and evaluation to build their knowledge and comprehension of unfamiliar concepts. This challenges my understanding of traditional teaching methods where knowledge is the basis for inquiry. Perhaps higher-order learning strategies like inquiry and evaluation can also be the basis for knowledge and comprehension, which are classified as lower-order skills in Bloom’s Taxonomy.
Critical reflection requires thoughtful and persistent inquiry. Although basic questions like “what is the thesis?” and “what is the evidence?” are important to demonstrate your understanding, you need to interrogate your own assumptions and knowledge to deepen your analysis and focus your assessment of the text.
Assess the text(s):
- What is the main point? How is it developed? Identify the purpose, impact and/or theoretical framework of the text.
- What ideas stood out to me? Why? Were they new or in opposition to existing scholarship?
Develop your ideas:
- What do I know about this topic? Where does my existing knowledge come from? What are the observations or experiences that shape my understanding?
- Do I agree or disagree with this argument? Why?
Make connections:
- How does this text reinforce my existing ideas or assumptions? How does this text challenge my existing ideas or assumptions?
- How does this text help me to better understand this topic or explore this field of study/discipline?
A Note on Mechanics
As with all written assignments or reports, it is important to have a clear focus for your writing. You do not need to discuss every experience or element of your placement. Pick a few that you can explore within the context of your learning. For reflective responses, identify the main arguments or important elements of the text to develop a stronger analysis which integrates relevant ideas from course materials.
Furthermore, your writing must be organized. Introduce your topic and the point you plan to make about your experience and learning. Develop your point through body paragraph(s), and conclude your paper by exploring the meaning you derive from your reflection. You may find the questions listed above can help you to develop an outline before you write your paper.
You should maintain a formal tone, but it is acceptable to write in the first person and to use personal pronouns. Note, however, that it is important that you maintain confidentiality and anonymity of clients, patients or students from work or volunteer placements by using pseudonyms and masking identifying factors.
The value of reflection: Critical reflection is a meaningful exercise which can require as much time and work as traditional essays and reports because it asks students to be purposeful and engaged participants, readers, and thinkers.
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
Reflective writing is a process of identifying, questioning, and critically evaluating course-based learning opportunities, integrated with your own observations, experiences, impressions, beliefs, assumptions, or biases, and which describes how this process stimulated new or creative understanding about the content of the course.
A reflective paper describes and explains in an introspective, first person narrative, your reactions and feelings about either a specific element of the class [e.g., a required reading; a film shown in class] or more generally how you experienced learning throughout the course. Reflective writing assignments can be in the form of a single paper, essays, portfolios, journals, diaries, or blogs. In some cases, your professor may include a reflective writing assignment as a way to obtain student feedback that helps improve the course, either in the moment or for when the class is taught again.
How to Write a Reflection Paper . Academic Skills, Trent University; Writing a Reflection Paper . Writing Center, Lewis University; Critical Reflection . Writing and Communication Centre, University of Waterloo; Tsingos-Lucas et al. "Using Reflective Writing as a Predictor of Academic Success in Different Assessment Formats." American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education 81 (2017): Article 8.
Benefits of Reflective Writing Assignments
As the term implies, a reflective paper involves looking inward at oneself in contemplating and bringing meaning to the relationship between course content and the acquisition of new knowledge . Educational research [Bolton, 2010; Ryan, 2011; Tsingos-Lucas et al., 2017] demonstrates that assigning reflective writing tasks enhances learning because it challenges students to confront their own assumptions, biases, and belief systems around what is being taught in class and, in so doing, stimulate student’s decisions, actions, attitudes, and understanding about themselves as learners and in relation to having mastery over their learning. Reflection assignments are also an opportunity to write in a first person narrative about elements of the course, such as the required readings, separate from the exegetic and analytical prose of academic research papers.
Reflection writing often serves multiple purposes simultaneously. In no particular order, here are some of reasons why professors assign reflection papers:
- Enhances learning from previous knowledge and experience in order to improve future decision-making and reasoning in practice . Reflective writing in the applied social sciences enhances decision-making skills and academic performance in ways that can inform professional practice. The act of reflective writing creates self-awareness and understanding of others. This is particularly important in clinical and service-oriented professional settings.
- Allows students to make sense of classroom content and overall learning experiences in relation to oneself, others, and the conditions that shaped the content and classroom experiences . Reflective writing places you within the course content in ways that can deepen your understanding of the material. Because reflective thinking can help reveal hidden biases, it can help you critically interrogate moments when you do not like or agree with discussions, readings, or other aspects of the course.
- Increases awareness of one’s cognitive abilities and the evidence for these attributes . Reflective writing can break down personal doubts about yourself as a learner and highlight specific abilities that may have been hidden or suppressed due to prior assumptions about the strength of your academic abilities [e.g., reading comprehension; problem-solving skills]. Reflective writing, therefore, can have a positive affective [i.e., emotional] impact on your sense of self-worth.
- Applying theoretical knowledge and frameworks to real experiences . Reflective writing can help build a bridge of relevancy between theoretical knowledge and the real world. In so doing, this form of writing can lead to a better understanding of underlying theories and their analytical properties applied to professional practice.
- Reveals shortcomings that the reader will identify . Evidence suggests that reflective writing can uncover your own shortcomings as a learner, thereby, creating opportunities to anticipate the responses of your professor may have about the quality of your coursework. This can be particularly productive if the reflective paper is written before final submission of an assignment.
- Helps students identify their tacit [a.k.a., implicit] knowledge and possible gaps in that knowledge . Tacit knowledge refers to ways of knowing rooted in lived experience, insight, and intuition rather than formal, codified, categorical, or explicit knowledge. In so doing, reflective writing can stimulate students to question their beliefs about a research problem or an element of the course content beyond positivist modes of understanding and representation.
- Encourages students to actively monitor their learning processes over a period of time . On-going reflective writing in journals or blogs, for example, can help you maintain or adapt learning strategies in other contexts. The regular, purposeful act of reflection can facilitate continuous deep thinking about the course content as it evolves and changes throughout the term. This, in turn, can increase your overall confidence as a learner.
- Relates a student’s personal experience to a wider perspective . Reflection papers can help you see the big picture associated with the content of a course by forcing you to think about the connections between scholarly content and your lived experiences outside of school. It can provide a macro-level understanding of one’s own experiences in relation to the specifics of what is being taught.
- If reflective writing is shared, students can exchange stories about their learning experiences, thereby, creating an opportunity to reevaluate their original assumptions or perspectives . In most cases, reflective writing is only viewed by your professor in order to ensure candid feedback from students. However, occasionally, reflective writing is shared and openly discussed in class. During these discussions, new or different perspectives and alternative approaches to solving problems can be generated that would otherwise be hidden. Sharing student's reflections can also reveal collective patterns of thought and emotions about a particular element of the course.
Bolton, Gillie. Reflective Practice: Writing and Professional Development . London: Sage, 2010; Chang, Bo. "Reflection in Learning." Online Learning 23 (2019), 95-110; Cavilla, Derek. "The Effects of Student Reflection on Academic Performance and Motivation." Sage Open 7 (July-September 2017): 1–13; Culbert, Patrick. “Better Teaching? You Can Write On It “ Liberal Education (February 2022); McCabe, Gavin and Tobias Thejll-Madsen. The Reflection Toolkit . University of Edinburgh; The Purpose of Reflection . Introductory Composition at Purdue University; Practice-based and Reflective Learning . Study Advice Study Guides, University of Reading; Ryan, Mary. "Improving Reflective Writing in Higher Education: A Social Semiotic Perspective." Teaching in Higher Education 16 (2011): 99-111; Tsingos-Lucas et al. "Using Reflective Writing as a Predictor of Academic Success in Different Assessment Formats." American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education 81 (2017): Article 8; What Benefits Might Reflective Writing Have for My Students? Writing Across the Curriculum Clearinghouse; Rykkje, Linda. "The Tacit Care Knowledge in Reflective Writing: A Practical Wisdom." International Practice Development Journal 7 (September 2017): Article 5; Using Reflective Writing to Deepen Student Learning . Center for Writing, University of Minnesota.

How to Approach Writing a Reflection Paper
Thinking About Reflective Thinking
Educational theorists have developed numerous models of reflective thinking that your professor may use to frame a reflective writing assignment. These models can help you systematically interpret your learning experiences, thereby ensuring that you ask the right questions and have a clear understanding of what should be covered. A model can also represent the overall structure of a reflective paper. Each model establishes a different approach to reflection and will require you to think about your writing differently. If you are unclear how to fit your writing within a particular reflective model, seek clarification from your professor. There are generally two types of reflective writing assignments, each approached in slightly different ways.
1. Reflective Thinking about Course Readings
This type of reflective writing focuses on thoughtfully thinking about the course readings that underpin how most students acquire new knowledge and understanding about the subject of a course. Reflecting on course readings is often assigned in freshmen-level, interdisciplinary courses where the required readings examine topics viewed from multiple perspectives and, as such, provide different ways of analyzing a topic, issue, event, or phenomenon. The purpose of reflective thinking about course readings in the social and behavioral sciences is to elicit your opinions, beliefs, and feelings about the research and its significance. This type of writing can provide an opportunity to break down key assumptions you may have and, in so doing, reveal potential biases in how you interpret the scholarship.
If you are assigned to reflect on course readings, consider the following methods of analysis as prompts that can help you get started :
- Examine carefully the main introductory elements of the reading, including the purpose of the study, the theoretical framework being used to test assumptions, and the research questions being addressed. Think about what ideas stood out to you. Why did they? Were these ideas new to you or familiar in some way based on your own lived experiences or prior knowledge?
- Develop your ideas around the readings by asking yourself, what do I know about this topic? Where does my existing knowledge about this topic come from? What are the observations or experiences in my life that influence my understanding of the topic? Do I agree or disagree with the main arguments, recommended course of actions, or conclusions made by the author(s)? Why do I feel this way and what is the basis of these feelings?
- Make connections between the text and your own beliefs, opinions, or feelings by considering questions like, how do the readings reinforce my existing ideas or assumptions? How the readings challenge these ideas or assumptions? How does this text help me to better understand this topic or research in ways that motivate me to learn more about this area of study?
2. Reflective Thinking about Course Experiences
This type of reflective writing asks you to critically reflect on locating yourself at the conceptual intersection of theory and practice. The purpose of experiential reflection is to evaluate theories or disciplinary-based analytical models based on your introspective assessment of the relationship between hypothetical thinking and practical reality; it offers a way to consider how your own knowledge and skills fit within professional practice. This type of writing also provides an opportunity to evaluate your decisions and actions, as well as how you managed your subsequent successes and failures, within a specific theoretical framework. As a result, abstract concepts can crystallize and become more relevant to you when considered within your own experiences. This can help you formulate plans for self-improvement as you learn.
If you are assigned to reflect on your experiences, consider the following questions as prompts to help you get started :
- Contextualize your reflection in relation to the overarching purpose of the course by asking yourself, what did you hope to learn from this course? What were the learning objectives for the course and how did I fit within each of them? How did these goals relate to the main themes or concepts of the course?
- Analyze how you experienced the course by asking yourself, what did I learn from this experience? What did I learn about myself? About working in this area of research and study? About how the course relates to my place in society? What assumptions about the course were supported or refuted?
- Think introspectively about the ways you experienced learning during the course by asking yourself, did your learning experiences align with the goals or concepts of the course? Why or why do you not feel this way? What was successful and why do you believe this? What would you do differently and why is this important? How will you prepare for a future experience in this area of study?
NOTE: If you are assigned to write a journal or other type of on-going reflection exercise, a helpful approach is to reflect on your reflections by re-reading what you have already written. In other words, review your previous entries as a way to contextualize your feelings, opinions, or beliefs regarding your overall learning experiences. Over time, this can also help reveal hidden patterns or themes related to how you processed your learning experiences. Consider concluding your reflective journal with a summary of how you felt about your learning experiences at critical junctures throughout the course, then use these to write about how you grew as a student learner and how the act of reflecting helped you gain new understanding about the subject of the course and its content.
ANOTHER NOTE: Regardless of whether you write a reflection paper or a journal, do not focus your writing on the past. The act of reflection is intended to think introspectively about previous learning experiences. However, reflective thinking should document the ways in which you progressed in obtaining new insights and understandings about your growth as a learner that can be carried forward in subsequent coursework or in future professional practice. Your writing should reflect a furtherance of increasing personal autonomy and confidence gained from understanding more about yourself as a learner.
Structure and Writing Style
There are no strict academic rules for writing a reflective paper. Reflective writing may be assigned in any class taught in the social and behavioral sciences and, therefore, requirements for the assignment can vary depending on disciplinary-based models of inquiry and learning. The organization of content can also depend on what your professor wants you to write about or based on the type of reflective model used to frame the writing assignment. Despite these possible variations, below is a basic approach to organizing and writing a good reflective paper, followed by a list of problems to avoid.
Pre-flection
In most cases, it's helpful to begin by thinking about your learning experiences and outline what you want to focus on before you begin to write the paper. This can help you organize your thoughts around what was most important to you and what experiences [good or bad] had the most impact on your learning. As described by the University of Waterloo Writing and Communication Centre, preparing to write a reflective paper involves a process of self-analysis that can help organize your thoughts around significant moments of in-class knowledge discovery.
- Using a thesis statement as a guide, note what experiences or course content stood out to you , then place these within the context of your observations, reactions, feelings, and opinions. This will help you develop a rough outline of key moments during the course that reflect your growth as a learner. To identify these moments, pose these questions to yourself: What happened? What was my reaction? What were my expectations and how were they different from what transpired? What did I learn?
- Critically think about your learning experiences and the course content . This will help you develop a deeper, more nuanced understanding about why these moments were significant or relevant to you. Use the ideas you formulated during the first stage of reflecting to help you think through these moments from both an academic and personal perspective. From an academic perspective, contemplate how the experience enhanced your understanding of a concept, theory, or skill. Ask yourself, did the experience confirm my previous understanding or challenge it in some way. As a result, did this highlight strengths or gaps in your current knowledge? From a personal perspective, think introspectively about why these experiences mattered, if previous expectations or assumptions were confirmed or refuted, and if this surprised, confused, or unnerved you in some way.
- Analyze how these experiences and your reactions to them will shape your future thinking and behavior . Reflection implies looking back, but the most important act of reflective writing is considering how beliefs, assumptions, opinions, and feelings were transformed in ways that better prepare you as a learner in the future. Note how this reflective analysis can lead to actions you will take as a result of your experiences, what you will do differently, and how you will apply what you learned in other courses or in professional practice.
Basic Structure and Writing Style
Reflective Background and Context
The first part of your reflection paper should briefly provide background and context in relation to the content or experiences that stood out to you. Highlight the settings, summarize the key readings, or narrate the experiences in relation to the course objectives. Provide background that sets the stage for your reflection. You do not need to go into great detail, but you should provide enough information for the reader to understand what sources of learning you are writing about [e.g., course readings, field experience, guest lecture, class discussions] and why they were important. This section should end with an explanatory thesis statement that expresses the central ideas of your paper and what you want the readers to know, believe, or understand after they finish reading your paper.
Reflective Interpretation
Drawing from your reflective analysis, this is where you can be personal, critical, and creative in expressing how you felt about the course content and learning experiences and how they influenced or altered your feelings, beliefs, assumptions, or biases about the subject of the course. This section is also where you explore the meaning of these experiences in the context of the course and how you gained an awareness of the connections between these moments and your own prior knowledge.
Guided by your thesis statement, a helpful approach is to interpret your learning throughout the course with a series of specific examples drawn from the course content and your learning experiences. These examples should be arranged in sequential order that illustrate your growth as a learner. Reflecting on each example can be done by: 1) introducing a theme or moment that was meaningful to you, 2) describing your previous position about the learning moment and what you thought about it, 3) explaining how your perspective was challenged and/or changed and why, and 4) introspectively stating your current or new feelings, opinions, or beliefs about that experience in class.
It is important to include specific examples drawn from the course and placed within the context of your assumptions, thoughts, opinions, and feelings. A reflective narrative without specific examples does not provide an effective way for the reader to understand the relationship between the course content and how you grew as a learner.
Reflective Conclusions
The conclusion of your reflective paper should provide a summary of your thoughts, feelings, or opinions regarding what you learned about yourself as a result of taking the course. Here are several ways you can frame your conclusions based on the examples you interpreted and reflected on what they meant to you. Each example would need to be tied to the basic theme [thesis statement] of your reflective background section.
- Your reflective conclusions can be described in relation to any expectations you had before taking the class [e.g., “I expected the readings to not be relevant to my own experiences growing up in a rural community, but the research actually helped me see that the challenges of developing my identity as a child of immigrants was not that unusual...”].
- Your reflective conclusions can explain how what you learned about yourself will change your actions in the future [e.g., “During a discussion in class about the challenges of helping homeless people, I realized that many of these people hate living on the street but lack the ability to see a way out. This made me realize that I wanted to take more classes in psychology...”].
- Your reflective conclusions can describe major insights you experienced a critical junctures during the course and how these moments enhanced how you see yourself as a student learner [e.g., "The guest speaker from the Head Start program made me realize why I wanted to pursue a career in elementary education..."].
- Your reflective conclusions can reconfigure or reframe how you will approach professional practice and your understanding of your future career aspirations [e.g.,, "The course changed my perceptions about seeking a career in business finance because it made me realize I want to be more engaged in customer service..."]
- Your reflective conclusions can explore any learning you derived from the act of reflecting itself [e.g., “Reflecting on the course readings that described how minority students perceive campus activities helped me identify my own biases about the benefits of those activities in acclimating to campus life...”].
NOTE: The length of a reflective paper in the social sciences is usually less than a traditional research paper. However, don’t assume that writing a reflective paper is easier than writing a research paper. A well-conceived critical reflection paper often requires as much time and effort as a research paper because you must purposeful engage in thinking about your learning in ways that you may not be comfortable with or used to. This is particular true while preparing to write because reflective papers are not as structured as a traditional research paper and, therefore, you have to think deliberately about how you want to organize the paper and what elements of the course you want to reflect upon.
ANOTHER NOTE: Do not limit yourself to using only text in reflecting on your learning. If you believe it would be helpful, consider using creative modes of thought or expression such as, illustrations, photographs, or material objects that reflects an experience related to the subject of the course that was important to you [e.g., like a ticket stub to a renowned speaker on campus]. Whatever non-textual element you include, be sure to describe the object's relevance to your personal relationship to the course content.
Problems to Avoid
A reflective paper is not a “mind dump” . Reflective papers document your personal and emotional experiences and, therefore, they do not conform to rigid structures, or schema, to organize information. However, the paper should not be a disjointed, stream-of-consciousness narrative. Reflective papers are still academic pieces of writing that require organized thought, that use academic language and tone , and that apply intellectually-driven critical thinking to the course content and your learning experiences and their significance.
A reflective paper is not a research paper . If you are asked to reflect on a course reading, the reflection will obviously include some description of the research. However, the goal of reflective writing is not to present extraneous ideas to the reader or to "educate" them about the course. The goal is to share a story about your relationship with the learning objectives of the course. Therefore, unlike research papers, you are expected to write from a first person point of view which includes an introspective examination of your own opinions, feelings, and personal assumptions.
A reflection paper is not a book review . Descriptions of the course readings using your own words is not a reflective paper. Reflective writing should focus on how you understood the implications of and were challenged by the course in relation to your own lived experiences or personal assumptions, combined with explanations of how you grew as a student learner based on this internal dialogue. Remember that you are the central object of the paper, not the research materials.
A reflective paper is not an all-inclusive meditation. Do not try to cover everything. The scope of your paper should be well-defined and limited to your specific opinions, feelings, and beliefs about what you determine to be the most significant content of the course and in relation to the learning that took place. Reflections should be detailed enough to covey what you think is important, but your thoughts should be expressed concisely and coherently [as is true for any academic writing assignment].
Critical Reflection . Writing and Communication Centre, University of Waterloo; Critical Reflection: Journals, Opinions, & Reactions . University Writing Center, Texas A&M University; Connor-Greene, Patricia A. “Making Connections: Evaluating the Effectiveness of Journal Writing in Enhancing Student Learning.” Teaching of Psychology 27 (2000): 44-46; Good vs. Bad Reflection Papers , Franklin University; Dyment, Janet E. and Timothy S. O’Connell. "The Quality of Reflection in Student Journals: A Review of Limiting and Enabling Factors." Innovative Higher Education 35 (2010): 233-244: How to Write a Reflection Paper . Academic Skills, Trent University; Amelia TaraJane House. Reflection Paper . Cordia Harrington Center for Excellence, University of Arkansas; Ramlal, Alana, and Désirée S. Augustin. “Engaging Students in Reflective Writing: An Action Research Project.” Educational Action Research 28 (2020): 518-533; Writing a Reflection Paper . Writing Center, Lewis University; McGuire, Lisa, Kathy Lay, and Jon Peters. “Pedagogy of Reflective Writing in Professional Education.” Journal of the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning (2009): 93-107; Critical Reflection . Writing and Communication Centre, University of Waterloo; How Do I Write Reflectively? Academic Skills Toolkit, University of New South Wales Sydney; Reflective Writing . Skills@Library. University of Leeds; Walling, Anne, Johanna Shapiro, and Terry Ast. “What Makes a Good Reflective Paper?” Family Medicine 45 (2013): 7-12; Williams, Kate, Mary Woolliams, and Jane Spiro. Reflective Writing . 2nd edition. London: Red Globe Press, 2020; Yeh, Hui-Chin, Shih-hsien Yang, Jo Shan Fu, and Yen-Chen Shih. “Developing College Students’ Critical Thinking through Reflective Writing.” Higher Education Research and Development (2022): 1-16.
Writing Tip
Focus on Reflecting, Not on Describing
Minimal time and effort should be spent describing the course content you are asked to reflect upon. The purpose of a reflection assignment is to introspectively contemplate your reactions to and feeling about an element of the course. D eflecting the focus away from your own feelings by concentrating on describing the course content can happen particularly if "talking about yourself" [i.e., reflecting] makes you uncomfortable or it is intimidating. However, the intent of reflective writing is to overcome these inhibitions so as to maximize the benefits of introspectively assessing your learning experiences. Keep in mind that, if it is relevant, your feelings of discomfort could be a part of how you critically reflect on any challenges you had during the course [e.g., you realize this discomfort inhibited your willingness to ask questions during class, it fed into your propensity to procrastinate, or it made it difficult participating in groups].
Writing a Reflection Paper . Writing Center, Lewis University; Reflection Paper . Cordia Harrington Center for Excellence, University of Arkansas.
Another Writing Tip
Helpful Videos about Reflective Writing
These two short videos succinctly describe how to approach a reflective writing assignment. They are produced by the Academic Skills department at the University of Melbourne and the Skills Team of the University of Hull, respectively.
- << Previous: Writing a Policy Memo
- Next: Writing a Research Proposal >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 1:00 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
- Jump to menu
- Student Home
- Accept your offer
- How to enrol
- Student ID card
- Set up your IT
- Orientation Week
- Fees & payment
- Academic calendar
- Special consideration
- Transcripts
- The Nucleus: Student Hub
- Referencing
- Essay writing
- Learning abroad & exchange
- Professional development & UNSW Advantage
- Employability
- Financial assistance
- International students
- Equitable learning
- Postgraduate research
- Health Service
- Events & activities
- Emergencies
- Volunteering
- Clubs and societies
- Accommodation
- Health services
- Sport and gym
- Arc student organisation
- Security on campus
- Maps of campus
- Careers portal
- Change password
Examples of Reflective Writing
Types of reflective writing assignments.
A journal requires you to write weekly entries throughout a semester. May require you to base your reflection on course content.
A learning diary is similar to a journal, but may require group participation. The diary then becomes a place for you to communicate in writing with other group members.
A logbook is often used in disciplines based on experimental work, such as science. You note down or 'log' what you have done. A log gives you an accurate record of a process and helps you reflect on past actions and make better decisions for future actions.
A reflective note is often used in law. A reflective note encourages you to think about your personal reaction to a legal issue raised in a course.
An essay diary can take the form of an annotated bibliography (where you examine sources of evidence you might include in your essay) and a critique (where you reflect on your own writing and research processes).
a peer review usually involves students showing their work to their peers for feedback.
A self-assessment task requires you to comment on your own work.
Some examples of reflective writing
Social science fieldwork report (methods section), engineering design report, learning journal (weekly reflection).
Brookfield, S 1987, Developing critical thinkers: challenging adults to explore alternative ways of thinking and acting , Open University Press, Milton Keynes.
Mezirow, J 1990, Fostering critical reflection in adulthood: a guide to transformative and emancipatory learning , Jossey-Bass, San Francisco.
Schön, DA 1987, Educating the reflective practitioner , Jossey-Bass. San Francisco.
We thank the students who permitted us to feature examples of their writing.
Prepared by Academic Skills, UNSW. This guide may be distributed or adapted for educational purposes. Full and proper acknowledgement is required.
Essay and assignment writing guide
- Essay writing basics
- Essay and assignment planning
- Answering assignment questions
- Editing checklist
- Writing a critical review
- Annotated bibliography
- How do I write reflectively?
- Examples of reflective writing
- ^ More support
Study Hacks Workshops | All the hacks you need! 7 Feb – 10 Apr 2024

- Schools & departments

Structure of academic reflections
Guidance on the structure of academic reflections.
Academic reflections or reflective writing completed for assessment often require a clear structure. Contrary to some people’s belief, reflection is not just a personal diary talking about your day and your feelings.
Both the language and the structure are important for academic reflective writing. For the structure you want to mirror an academic essay closely. You want an introduction, a main body, and a conclusion.
Academic reflection will require you to both describe the context, analyse it, and make conclusions. However, there is not one set of rules for the proportion of your reflection that should be spent describing the context, and what proportion should be spent on analysing and concluding. That being said, as learning tends to happen when analysing and synthesising rather than describing, a good rule of thumb is to describe just enough such that the reader understands your context.
Example structure for academic reflections
Below is an example of how you might structure an academic reflection if you were given no other guidance and what each section might contain. Remember this is only a suggestion and you must consider what is appropriate for the task at hand and for you yourself.
Introduction
Identifies and introduces your experience or learning
- This can be a critical incident
- This can be the reflective prompt you were given
- A particular learning you have gained
When structuring your academic reflections it might make sense to start with what you have learned and then use the main body to evidence that learning, using specific experiences and events. Alternatively, start with the event and build up your argument. This is a question of personal preference – if you aren’t given explicit guidance you can ask the assessor if they have a preference, however both can work.
Highlights why it was important
- This can be suggesting why this event was important for the learning you gained
- This can be why the learning you gained will benefit you or why you appreciate it in your context
You might find that it is not natural to highlight the importance of an event before you have developed your argument for what you gained from it. It can be okay not to explicitly state the importance in the introduction, but leave it to develop throughout your reflection.
Outline key themes that will appear in the reflection (optional – but particularly relevant when answering a reflective prompt or essay)
- This can be an introduction to your argument, introducing the elements that you will explore, or that builds to the learning you have already gained.
This might not make sense if you are reflecting on a particular experience, but is extremely valuable if you are answering a reflective prompt or writing an essay that includes multiple learning points. A type of prompt or question that could particularly benefit from this would be ‘Reflect on how the skills and theory within this course have helped you meet the benchmark statements of your degree’
It can be helpful to explore one theme/learning per paragraph.
Explore experiences
- You should highlight and explore the experience you introduced in the introduction
- If you are building toward answering a reflective prompt, explore each relevant experience.
As reflection is centred around an individual’s personal experience, it is very important to make experiences a main component of reflection. This does not mean that the majority of the reflective piece should be on describing an event – in fact you should only describe enough such that the reader can follow your analysis.
Analyse and synthesise
- You should analyse each of your experiences and from them synthesise new learning
Depending on the requirements of the assessment, you may need to use theoretical literature in your analysis. Theoretical literature is a part of perspective taking which is relevant for reflection, and will happen as a part of your analysis.
Restate or state your learning
- Make a conclusion based on your analysis and synthesis.
- If you have many themes in your reflection, it can be helpful to restate them here.
Plan for the future
- Highlight and discuss how your new-found learnings will influence your future practice
Answer the question or prompt (if applicable)
- If you are answering an essay question or reflective prompt, make sure that your conclusion provides a succinct response using your main body as evidence.
Using a reflective model to structure academic reflections
You might recognise that most reflective models mirror this structure; that is why a lot of the reflective models can be really useful to structure reflective assignments. Models are naturally structured to focus on a single experience – if the assignment requires you to focus on multiple experiences, it can be helpful to simply repeat each step of a model for each experience.
One difference between the structure of reflective writing and the structure of models is that sometimes you may choose to present your learning in the introduction of a piece of writing, whereas models (given that they support working through the reflective process) will have learning appearing at later stages.
However, generally structuring a piece of academic writing around a reflective model will ensure that it involves the correct components, reads coherently and logically, as well as having an appropriate structure.
Reflective journals/diaries/blogs and other pieces of assessed reflection
The example structure above works particularly well for formal assignments such as reflective essays and reports. Reflective journal/blogs and other pieces of assessed reflections tend to be less formal both in language and structure, however you can easily adapt the structure for journals and other reflective assignments if you find that helpful.
That is, if you are asked to produce a reflective journal with multiple entries it will most often (always check with the person who issued the assignment) be a successful journal if each entry mirrors the structure above and the language highlighted in the section on academic language. However, often you can be less concerned with form when producing reflective journals/diaries.
When producing reflective journals, it is often okay to include your original reflection as long as you are comfortable with sharing the content with others, and that the information included is not too personal for an assessor to read.
Developed from:
Ryan, M., 2011. Improving reflective writing in higher education: a social semiotic perspective. Teaching in Higher Education, 16(1), 99-111.
University of Portsmouth, Department for Curriculum and Quality Enhancement (date unavailable). Reflective Writing: a basic introduction [online]. Portsmouth: University of Portsmouth.
Queen Margaret University, Effective Learning Service (date unavailable). Reflection. [online]. Edinburgh: Queen Margaret University.
Module: Reflection
Process of reflective writing, learning objectives.
- Recognize possible structures for reflective writing
- Recognize component skills of reflective writing
Reflective writing is a balancing act with many factors at play: description, analysis, interpretation, evaluation, and future application. Reflective writers must weave their personal perspectives with evidence of deep, critical thought as they make connections between theory, practice, and learning. The steps below should help you find the appropriate balance among all these factors.

1st Step: Review the assignment
As with any writing situation, the first step in writing a reflective piece is to clarify the task. Reflective assignments can take many forms, so you need to understand exactly what your instructor is asking you to do. Some reflective assignments are short, just a paragraph or two of unpolished writing. Usually the purpose of these reflective pieces is to capture your immediate impressions or perceptions. For example, your instructor might ask you at the end of a class to write quickly about a concept from that day’s lesson. That type of reflection helps you and your instructor gauge your understanding of the concept.
Other reflections are academic essays that can range in length from several paragraphs to several pages. The purpose of these essays is to critically reflect on and support an original claim(s) about a larger experience, such as an event you attended, a project you worked on, or your writing development. These essays require polished writing that conforms to academic conventions, such as articulation of a thesis and substantive revision. They might address a larger audience than you and your instructor, including, for example, your classmates, your family, a scholarship committee, etc.
It’s important, before you begin writing, that you can identify the assignment’s purpose, audience, intended message or content, and requirements. If you can’t, ask your instructor for clarification.
2nd Step: Generate ideas for content
Refer to the Borton, DIEL, and DIEP models as you generate ideas for your writing. To meet the tasks identified in those models you might consider things like:
- Recollections of an experience, assignment, or course
- Ideas or observations made during that event
- Questions, challenges, or areas of doubt
- Strategies employed to solve problems
- A-ha moments linking theory to practice or learning something new
- Connections between this learning and prior learning
- New questions that arise as a result of the learning or experience
- New actions taken as a result of the learning or experience
3rd Step: Organize content
The Borton, DEAL, and DIEP frameworks can help you consider how to organize your content. Remember that your reflection will generally include descriptive writing, followed by analysis and interpretation, followed by consideration of significance for future action. That pattern might be developed once throughout a short piece or repeated several times in an academic reflective essay.
When writing an academic reflection essay (as opposed to a short reflection), you’ll need to devise and support a thesis. That thesis should be an interpretive or evaluative claim, or series of claims, that moves beyond obvious statements (such as, “I really enjoyed this project”) and demonstrates you have come to a deeper understanding of what you have learned and how you will use that learning. For example, the thesis below appeared in an end-of-semester reflection essay, written in response to an assignment asking students to consider their writing progress. Notice that the student makes a focused, interpretive claim that can be supported throughout her essay with evidence from her own writing.
Throughout this class, I’ve learned that a skilled writer writes with a central focus in mind. Writing with a central focus results in a greater emphasis on the writer’s message and brings about specificity and clarity within the writing piece.
A word about thesis placement: Because a reflection essay combines personal perception with academic convention, the thesis does not necessarily appear in the introduction. Many writers build to the thesis in the conclusion of their essays. You should place the thesis where it is most effective based on the essay’s structure.
And speaking of structure, there is no one-size-fits-all organization pattern for an academic reflection essay. Some writers introduce the subject, follow the introduction with a series of reflections, and then move to an interpretive close. Others establish a chronology of events, weaving the implications of those events throughout. Still others articulate a series of major points, supporting those points with evidence. You should craft an organizational structure that best fits your distinctive ideas and observations.
However you choose to organize an academic reflection essay, you’ll need to support your claims with evidence. Evidence is defined broadly in an academic reflection, so it might include such things as anecdotes, examples, relevant material from a course or outside sources, explanations of logic or decision-making, definitions, speculations, details, and other forms of non-traditional evidence. In the example below, notice how the writer uses her decision to limit the scope of a project as evidence to support her claim.
Keeping a central focus in mind applies to multimodal compositions as well as written essays. A prime example of this was in my remix. When storyboarding for the video, I wanted to appeal to all college students in general. Within my compressed time limit of three minutes, I had planned to showcase numerous large points. It was too much. I decided to limit the scope of the topic to emphasize how digitally “addicted” Ole Miss college students are and that really changed the project in significant ways.
4th Step: Draft, Revise, Edit, Repeat
A single, unpolished draft may suffice for short, in-the-moment reflections. Longer academic reflection essays will require significant drafting, revising, and editing. Whatever the length of the assignment, keep this reflective cycle in mind:
- briefly describe the event or action;
- analyze and interpret events and actions, using evidence for support;
- demonstrate relevance in the present and the future.
Contribute!
Improve this page Learn More
- Process of Reflective Writing. Authored by : Karen Forgette. Provided by : University of Mississippi. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Meme: Ask not what balance can do for you. License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Fair Use

How to Reveal the Creative Process Through Reflection

For many visual art teachers, time with students is precious and fleeting. Sometimes you have less than an hour with students before they’re gone and a new crop of students come through the door. There’s barely enough time to finish a project, let alone stop and reflect on the work.
However, as educators and as artists, we know just how valuable it is to take time to reflect on and to make revisions to our work.
So how do we build reflection time into our classroom routines? And how do we use that time to help our students better understand the creative process? Let’s find out.

Why is it essential for students to recognize the value of process?
Our society values products and outcomes, but often ignores how we get there. But artists grasp the value of the process, which comes from the research, planning, and execution of a piece of work. An understanding of the process not only allows for growth and learning but also for a more authentic presentation of work and self. It’s how artists can push boundaries and move beyond the simple reproduction of an object and into the creation of new works of art.
Additionally, understanding how they’ve gotten from point A to point B helps our students build cognitive functions and processing. The development of an iterative process that looks at where you’ve been, where you are, and where you want to go, holds immense value. Pausing to reflect helps to guide this journey.
Recording the Creative Process
One way I’ve found to help students reflect on the creative process is to have them record it. While that may sound daunting, I assure you it can be done.
At my school, the 6th-grade students work with the drama teacher, the dance teacher, and me on a rotating basis, spending eight sessions with each teacher before moving on to the next. After the students have worked with each teacher, we bring them back together and work as one large group on an interdisciplinary collaborative project. It’s a creative format that allows for experimentation and flexibility, but it also moves quickly!
It was through this project we figured out how we could have students document their process through daily reflections. Our goal was to allow them to look back on their work and see how they’d incorporated projects and concepts from all three disciplines.
The daily reflections were so successful; I’m considering doing them with all of my classes.

If you’d like to try something similar, here’s what to do:
1. At the end of each class, set aside five to seven minutes for students to reflect on the day’s activities.
2. Have students snap a quick photo of their work. This can be done on an iPad or with a digital camera or another device. If you don’t have the technology available in your classroom, you can also have students do a quick thumbnail sketch.
3. Have students respond to one or two prompts in writing.
You might consider asking things like:
- What was your inspiration for the project/work you completed today?
- What was the biggest challenge you encountered on the project?
- How does this project tie together previous exercises and concepts from the class?
- What was your favorite part of class today?
At my school, we can to do this type of reflection using a discussion thread (private to the individual student and teachers) on our school’s learning platform called Schoology . This platform makes the whole process extremely easy. After the students make their entries, we can respond with clarifying questions, informal feedback, critique, and positive affirmations.
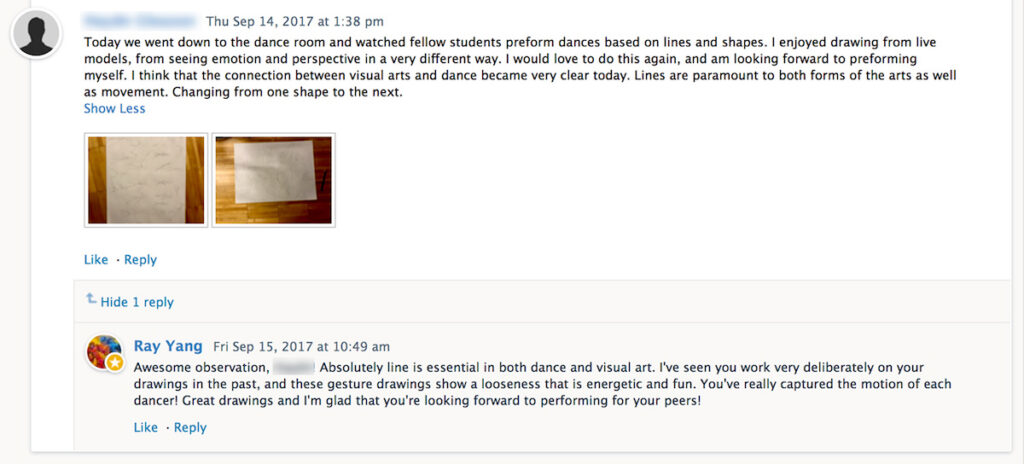
The value of these reflections and individual journals has been extremely beneficial to us, as teachers.
Creating this back and forth dialogue with the students has allowed us to:
- See which students are connecting with which concepts and which students seem lost or unengaged
- Direct students to refer to earlier work and connect threads between the different disciplines
- Create dialogue around student work and process as we respond to their entries
- Get to know the students better
- Look back on student work while writing comments and grades
- Provide evidence to administrators of the creative process our students have gone through and the ways our classes are building student thinking and analysis skills
If your school doesn’t have a learning management system that supports this type of back and forth dialogue, you can set up something similar through a private classroom blog or even through a set of sketchbooks. Anything where students are writing and recording can provide valuable documentation.
An Alternate Approach: Cutting Back
For my other classes, my schedule is more traditional, as I see my students on a consistent basis. Even so, I feel a rush to get through project after project during the course. After seeing how formal reflection positively informed my teaching, I worked on making shifts with my Art Foundations class, a survey class for 7th and 8th-grade students.
One of the first things I did was to make a conscious choice to let go of some of the projects in my curriculum.
Even though there are lots of fun projects I want to do with students, the extra space to breathe is more important. I wanted to create room to build in reflection and journaling but was worried about kids not taking the reflections seriously, or giving little thought to them.
If you’re having similar thoughts, I would encourage you to start with exit slips . In my experience, these can serve several purposes. First, they allow you to gauge how much the students are enjoying particular projects. Second, they give students a chance to have a voice and participate in the structure of your work. Finally, and most importantly, they provide a moment for students to pause and reflect on their work.
When starting out, simple prompts work best. You might want to try things like:
- A particular challenge for me was…
- An awesome success for me was…
Once students are comfortable with simple feedback forms like this, you can move onto more extensive reflections. For example, you can post things like essential questions and enduring understandings on the board throughout a project. In this way, you can remind students what they should be thinking about while working. This method helps keep students in the mode of process and reflection, rather than just creation.

The most important piece of this, ultimately, is building the artistic skill of reflection artists use as part of the larger creative process. Tangible documentation of the process allows students to see their progress and understand their, and others’, thinking. Seeing the process reinforces that progress is being made and solidifies understandings of technique and skill. There are many methods of reflection, and while the ones I’ve shared have worked for me, I am always considering how to expand on them.
How is the creative process revealed in your classroom?
What ways do your students reflect on their work?
Magazine articles and podcasts are opinions of professional education contributors and do not necessarily represent the position of the Art of Education University (AOEU) or its academic offerings. Contributors use terms in the way they are most often talked about in the scope of their educational experiences.

Raymond Yang
Ray Yang is the Director of Equity, Diversity and Inclusion of NAEA and a former AOEU Writer. They believe the arts can change the world.
7 Ways to Process Artistic Growth With Your Elementary Students

10 Unique End-of-Year Portfolio Assessments for Secondary Art Students

How to Help Your Students Learn to Talk to Each Other Again

6 Activities to Get Your Students Excited to Talk About Art
Support Student Reflection, Critique, and Revision in Project-Based Learning
Let’s go deeper into the key elements of project-based learning and explore strategies to support student reflection, critique, and revision.

Have you ever spent hours of time reflecting on student work? Have you critiqued an assignment or assessment and provided feedback that some students perhaps ultimately never looked at, internalized, or used to make revisions to their work? When students only reflect and receive feedback at the end of a project, this is exactly what happens. Why would students go back and revise anything when the grade is already in and the changes don’t seem to matter? Why reflect on something if the reflection doesn’t result in some type of change?
Project-based learning (PBL) provides an authentic reason for students to actively reflect on what they are doing, seek and provide critique and feedback, and then use that information to revise and change their project in order to improve it. In PBL, reflections, critique, and revisions are not just between a single student and the teacher at the end of the project; students are working together in groups and creating a public product, not just something for themselves. Reflection, critique, and revision are key components of PBL that should be utilized throughout the process, not just at the end.
In PBL, reflection is not just done at the end of a project. We should reflect on where we started, where we ended, and everything in between. In other words, reflection should be ongoing and done throughout the entirety of the project. There are many reasons why reflection is so important in PBL. Below are just a few of the ways in which reflection allows for deeper understanding for students.
- Reflection in PBL allows for deeper understanding. Reflection can happen authentically and multiple times in project-based learning because students have the opportunity to work on answering a driving question over a long period of time. Students are allowed multiple opportunities to reflect, critique, and revise their thinking and work. This allows for much deeper reflection because all of the smaller components relate to the bigger picture or driving question.
- Reflection provides students an authentic opportunity to analyze information, problem-solve, and make decisions. In other words, the reflection matters and will be used to critique and then make revisions. This skill helps prepare students for their careers and future.
- Students are able to identify and explain why they are doing what they are doing and how it is supporting their final project, how they need to change their path so that they are able to achieve their final product, or how they may need to modify their final project. Once again, the reflection leads to critique and revision.
- Students are able to make personal connections to the work they are engaged in, making it more authentic and increasing student ownership and engagement. When students are reflecting on their own work and the work of their group around a public project they are creating, they develop a personal connection to the work and will almost always be more engaged in the project.
- When students reflect on how they were able to persevere and solve a problem that at first seemed so large and complex, they develop perseverance and skills, strategies, and confidence to tackle large (and small) problems. Students have to figure out how to break apart problems into more manageable pieces, ask the right questions to solve the problem, and then design and execute a plan to gather credible information to answer the questions or solve the problem. For more ideas on how to support students searching and seeking information, consider reading the AVID Open Access article, Search and Seek Credible Information: Step 3 of the Searching for ANSWERS Inquiry Process .
When planning out PBL, you should always allow and encourage reflection after any significant learning or creation of work. You can try and preplan these opportunities as much as possible, but remember to also be flexible in creating and encouraging reflection opportunities when appropriate. You and your students might use a project assessment map to identify points of reflection. Consider creating and allowing students to practice specific reflection processes. Below are several ideas that you might consider using with your students.
- Google Docs
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft OneNote
- Google Slides
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Google Sites ( Tips )
- Seesaw ( Tips )
- Seesaw Blogs
- Give students an opportunity to reflect on what they used to think as well as how their thinking has changed as a result of inquiry. They can capture this thinking in their learning journal or blog, or they can share their thinking with a partner or small group.
- Use Google Forms , Microsoft Forms , or SurveyMonkey to gather student reflections or have students use one of these programs to gather and organize their own reflections.
- The teacher presents a topic or question, and each student in turn shares something that they have learned about that topic or question.
- In pairs or groups, one student pretends that the others have no idea about a topic and shares or explains what they have learned.
- The teacher asks a reflection question and gives 1 minute for students to think of a response. Then, students are given time to write down what they are thinking. Lastly, students share their thinking in partner pairs or small groups.
Critique and Revision
Reflection becomes more meaningful when it leads to action, and critique and revision are the action portions of the reflection process. However, students need to be taught how to critique work and how to receive feedback, before then using that feedback to revise their work. Teachers need to provide multiple opportunities for students to engage in this work in a safe environment, so they are able to engage in the process effectively on their own once they are in college and working in their careers. Teachers might think about providing an opportunity for students to engage in a low-stakes critique before having them critique each other’s work. For example, ask students to create the classroom layout, and then model how you might use the critique that students provide to revise the classroom layout.
Provide students with a clear understanding of what feedback looks like and sounds like. Feedback should be specific, helpful, and thoughtful. If students make a claim, they need to provide evidence to support their claim. For example, if a student provides feedback saying that something is not very appealing, require them to explain why and offer suggestions to help improve it. Below are several strategies and tools to support critique and revision in PBL.
- When giving feedback, students provide the recipient of the feedback with two stars (positive feedback) and a wish (something they wish would be different or changed). You can share this Two Stars and a Wish poster, which includes sentence stems, when engaged in this protocol:

- Students can either share work or present work to a peer or group of students. The students providing feedback can use the Pluses and Wishes template and are given 1–3 minutes to fill in the Pluses column of the worksheet with positive comments and feedback. Students are then given 1–3 minutes to fill in the Wishes column of the worksheet with things that they think there should be more of or less of, or things they think should be changed.
- Analog and digital Gallery Tours allow students to be both givers and receivers of feedback. Consider using this article from PBLWorks to guide you through using Gallery Tours or variations with your students.
- Tuning Protocol: Overview (National School Reform Faculty)
- Tuning Protocol Overview Video (PBLWorks)
- Students Use Tuning Protocol for Critique and Revision in PBL (PBLWorks)
- There are many tools that can support students with critique and revision. Shared documents in Google Workspace (Google Docs, Google Slides, Google Sheets, etc.) and Microsoft 365 (Microsoft Word, Microsoft PowerPoint, Microsoft Excel, etc.) allow multiple people to access, edit, and/or comment on the same document and even at the same time.
- Discussion tools can help manage the sharing of ideas and feedback in virtual conversation threads. Most learning management systems (Canvas, Schoology, Google Classroom, etc.) offer discussion tools with text, audio, and video response options. Some platforms, like Flip ( Tips ), are specifically designed to be video-based. Another example is VoiceThread , where ideas are presented in a slideshow-style format, and participants can respond with audio, text, or video comments.
- Padlet ( Tips )
Throughout the reflection, critique, and revision process in PBL, create opportunities to celebrate students who intentionally reflect on their work, provide good feedback to themselves and others, and use feedback to revise their thinking and make changes to their project. As teachers, we also need to reflect, critique, and revise. We can model reflection, critique, and revision in our work for students and model how we never stop learning and growing. Make sure and provide opportunities for students to provide feedback on different aspects of the PBL process. Ask for feedback on what is going well and what needs to be changed and why. Once you receive feedback, use it to revise your project and future projects. We can continually make PBL better for ourselves and our students if we practice what we teach. For more ideas on how to support students with reflection, critique, and revision, consider reading the AVID Open Access articles or listening to the podcast episodes below:
- Structure Student Reflection Activities Effectively for Remote Learning (article)
- Support Student Reflection With Live Virtual Strategies and Tools (article)
- Support Student Reflection With Self-Paced Virtual Strategies and Tools (article)
- Develop Your Students’ Digital Organization Skills: eFiles, eBinders, and ePortfolios (article)
- Develop Your Students’ Time Management Skills (article)
- Learn and Manage Your Digital Learning Environment (article)
- Establish a Feedback System to Keep Everyone Informed (article collection)
- Collect, Reflect, and Recollect: The Power of eBinders and ePortfolios (podcast episode)
- Engage Students with Project-Based Learning (podcast episode)
- Teacher Insights with Annie Tremonte (podcast episode)
Extend Your Learning
- Critique Protocols Strategy Guide (PBLWorks; sign up to receive this free resource)
- Best Student-Collaboration Tools (Common Sense Education)
- Tools for Project-Based Learning (Common Sense Education)
- Critique and Revision of Student Work in Remote PBL (PBLWorks)
Topic Collections
This course is part of the following collections:.
Did you find this resource useful?
Your rating helps us continue providing useful content in relevant subject areas.
- System Status
- Rest Assured Policy
Select from the list below to add to one of your Journeys, or create a new one.
You haven't created a Journey yet.
Stay in the Know!
Sign up for our weekly newsletter and be the first to receive access to best practice teaching strategies, grab-and-go lessons, and downloadable templates for grades K-12.
Student Reflection & Self-Assessment
4 ideas for building self-evaluation into the learning process

Project-based learning is a student-centered approach to learning, so it is natural to make student self-evaluation an integral part of the process.
Providing time for students to reflect on their work, helps them make connections to previous learning and experience. As Rachel Showalter observes, “students cannot truly improve their product without understanding the content.” Combining this opportunity to deepen learning through reflection with time to self-correct and improve, is an essential step towards meeting standards.
Many educators implementing a PBL or STEM approach use a design process that includes a specific Improve phase that asks students to stop, reflect, and evaluate their work with the intent of returning to the ideation phase to improve upon it.
Asking students to evaluate their strengths, weaknesses, progress, and growth, helps them more deeply understand the causes of their successes and failures and become aware of their learning. This also helps them see more clearly where to focus their energy to have the greatest impact. As they grow their metacognitive skills, students are better able to meet the challenges and thrive in directing their own learning.
Make sure students are clear on standards, learning, and project goals
Before you begin integrating reflection and self-assessment, make sure students have a clear definition or picture of what success looks like. A rubric or checklist can help provide students with criteria they can use to evaluate the success of their work and progress toward academic, personal, and social goals. Successful rubrics and checklists include criteria that provide specific actions students can take to improve their work.
Build in reflection time and procedures for self-assessment
Reflection and student self-assessment require time and are most successful when you add specific procedures for them during the learning process. Work in time for reflection, as well as time to improve their work based on the evaluation.
Here are a few ideas to help you integrate reflection and student self-assessment throughout the process of learning.
Daily Reflection Journals
One of the easiest ways to begin implementing reflection into your classroom is to have students keep a project journal or work log. Provide reflection prompts, or questions, like:
- What new content knowledge did you learn today?
- How did your effort contribute to your success?
- What should you focus on next?
Reflection journals provide artifacts both you and your students can use to see and evaluate growth and progress.

Download a sample Project Reflection page
If journaling seems like it will take too much classroom time, use the last 2 minutes of class for a 3-2-1 exit ticket .
Summative Self-Assessments
In addition to daily journaling, have students complete a summative self-assessment that asks them to reflect on the strengths and weaknesses of their product or performance and evaluate their efforts during the development process. You might ask them to reflect on:
- content knowledge gained.
- project management, leadership, and other skills acquired.
- obstacles and how they overcame them.
- conflicts within a team and their resolution.
- personal insights gained from product and process.
Written self-assessments are a natural part of the reflection process after students complete a project or performance. However, providing time to evaluate their work before it is complete, allows students to improve their work and honors that learning is an iterative process.
Peer Review and Feedback
While peer review may not seem like a form of self-evaluation, reviewing the work of others often helps students more clearly see errors and areas for improvement in their own work. Peer reviews that focus on effective writing, design, and communication provide a useful place to start.
Simply have students “turn-and-talk” with a classmate and complete a “warm and cool” form to direct their feedback.

Download a Warm and Cool Feedback sheet page
If students are presenting their work to a small group, provide reviewers with sentence starters to promote critical review and feedback:
- You do a great job of …
- I would love to see more …
- Can you explain …
- What if …
Employing peer reviews during the process with time after for editing, creates a learning culture of growth where students reflect on their work and the work of others and then do the work necessary to improve.
Digital Portfolios
If you want to get serious about integrating student reflection and self-assessment, asking students to craft portfolios of their learning throughout a school year is a must. A learning portfolio is a purposeful collection of student work, combined with reflections about the learning artifacts, that demonstrates student learning and growth over time.

For a portfolio to be a success, students need to be in charge of choosing the work they will include and tasked with explaining via text, audio, or video why it demonstrates growth.
Once again, providing a rubric or similar evaluation criteria will help students choose artifacts of learning and performances that correlate to learning goals, as well as provide a structure for their reflections.
In Conclusion
Reflecting helps students process and organize their learning. As they reflect, students observe how successful they have been during an activity. Then, they work to identify what they learned from their experience.
Combining your formative and summative assessments along with student’s self-reflections and peer reviews can help you paint a clearer picture of student growth and progress.

by Melinda Kolk
Melinda Kolk ( @melindak ) is the Editor of Creative Educator and the author of Teaching with Clay Animation . She has been helping educators implement project-based learning and creative technologies like clay animation into classroom teaching and learning for the past 15 years.

Project-based Learning Professional Development
Creative Educator can help you bring project-based learning to your school.
- What is PBL and why do it?
- Make It Matter! Move it from projects to project-based learning
- Developing the questions for project-based learning
- Write a Great Authentic Task
- It's the Process, Not the Product
- Assessing Project Work
- Formative assessment during project-based learning
- Collaboration
- PBL and Presentations of Learning

Bring project-based learning to your school

Five habits of great classroom coaches

Get the most out of collaboration during student project work

The glorious, wonderful, empty page

Make It Matter! Move from projects to project-based learning

More sites to help you find success in your classroom

Share your ideas, imagination, and understanding through writing, art, voice, and video.

Rubric Maker
Create custom rubrics for your classroom.

Pics4Learning
A curated, copyright-friendly image library that is safe and free for education.

Write, record, and illustrate a sentence.

Interactive digital worksheets for grades K-8 to use in Brightspace or Canvas.
Professional Learning

Digital Storytelling
21st Century Classrooms
Project-based Learning
Teaching and Learning
Informational Text
English Language Aquisition
Language Arts
Social Studies
Visual Arts
© 2024 Tech4Learning, Inc | All Rights Reserved | Privacy Policy
© 2024 Tech4Learning, Inc | All Rights Reserved | https://www.thecreativeeducator.com
- Toggle navigation
Project Reflection: Assignment 1
To guide your first project reflection, I have created five categories for questions below. Please compose answers to these questions in a document that you can upload to Canvas. Your task is to engage thoroughly in the task of assessing your project; you may structure this in whatever way works best for you. My goal is to share video feedback on your first assignment by the end of the day Friday (9/13). I recommend you start on this reflection before you’ve watched that video. This reflection is your chance to evaluate yourself, so thinking about this on your own before getting my feedback can help establish that this is your reflection about your work.
I asked you to prepare for this assignment through the following homework and in-class activities. How many of these activities did you do and how did they help you think through your work? Did you do anything outside of this assigned work to help your project come together? To answer this question with specifics, please read through your doc and our doc and select examples of specific things you did. If there are activities you didn’t do, please explain what interfered with you completing the work and/or anything you did on your own to make progress on the assignment. Your goal here is to assess your process with this assignment so you can establish specific goals for future work.
In your document, I asked you to annotate the syllabus
In our document, I asked you to share what you’d written about communities you belong to and problems they encounter
Before class, I asked you to annotate the prompt for assignment 1
In class, I demonstrated how to start using Zotero. In our document, I asked you to share sources you were finding about the community/problem you were exploring.
In your document, I asked you to continue finding sources to build your project
In class, I asked for volunteers to share sources found so we could all test their reliability together.
over the weekend, you had a draft due
In our document, I asked you to: share the bits of your draft that you felt comfortable sharing and invited students to workshop their drafts
Before class, I asked you to keep refining your first project
In class, I demonstrated the process for using grantforward and PND. In our document, I asked you to share what you were finding in those two databases.
How did you get feedback on your rough draft for this project? Did you ask for direct feedback from Dr. Isbell or anyone else? Did you get feedback in person, via zoom, or through text comments? Kaizena was not working; did that stop you from reaching out again to get feedback? What kind of feedback do you ideally want to seek for your next project?
How would you assess the quality of the work you produced? How clearly does it describe the organization you plan to help with grant funding? How clearly does it establish your role in that organization? Does it make it clear which aspects of the project are true and which are fictionalized? Are reliable sources included to support claims made? Are there things you wish were different that you’re not sure how to change?
Given your assessment of the work you put into this project and the quality of the bio you produced, what grade do you give yourself on this project?
What is your plan for success on our next project? Are there things you want to make sure to continue doing? Are there new things you’d like to try?
Welcome to OpenLab at the University of New Haven!
Read our mission statement at our About page to learn more about how we hope you'll take advantage of this platform.
Send an email to [email protected]
Powered by:
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Book Bracket Template. For March and Beyond!
45 Awesome Must-Use Questions to Encourage Student Reflection and Growth
Reflection questions for before, during, and after a project or lesson.

Teaching our students the importance of reflecting upon their knowledge, work, effort, and learning is super important, but it’s not always that easy.
Reflection questions allow students to think about their thinking.
This kind of questioning allows students to better understand how they are working or learning so they can make changes and adjustments from there. Reflection takes time, and often students think that once their work is complete, they should be finished. Often, the younger the student, the more difficult it can be to get them to reflect on what they’ve done.
Here are a few of our favorite reflection questions to use in your instruction. Adjust or edit these questions to meet your students’ needs.
Before students begin their work:
- What do I know about this topic or subject?
- What would I like to learn about this topic or subject?
- Where will I find the information I need for this assignment?
- What kinds of research do I need to do?
- Do I fully understand the question or prompt?
- How can I break down the assignment into smaller parts?
- Did I give myself ample time to really think about this assignment and brainstorm possible solutions?
- Who can help me get what I need to complete this work?
- What tools or supplies should I use for this assignment?
- How will I be assessed for this project?
- Do I understand all parts of the rubric or scoring guide?
- What are my goals for this assignment?
- What do I need to do in order to meet those goals?
- How will this assignment be turned in to my teacher?
- Do I know the due date for this project, and am I able to meet it?
[contextly_auto_sidebar]
While students are working:
- What have I learned so far?
- What else do I need to know in order to finish this task?
- Can I make a few predictions about what will happen next?
- How well am I using my time?
- Am I answering all parts of the questions completely?
- Which parts of this assignment are easy for me?
- Which parts of this assignment are challenging for me?
- Does my work reflect my effort thus far?
- Am I putting forth my best effort in my work?
- Are the sources I am using reliable?
- Am I citing my sources properly?
- How close am I to achieving my original goals with this assignment?
- Are the goals I set before I began this assignment still reasonable? Do I need to readjust them?
- If possible, can I ask my teacher or a classmate for feedback on my current progress on this assignment?
- Am I learning interesting information as I work on this project?
After students finish their work or assignment:
- What new information have I learned from this assignment?
- What surprised me about what I learned?
- How quickly was I able to finish this work?
- Where were my roadblocks?
- How did I move through roadblocks or challenges?
- Is my work adapted for the correct, appropriate audience?
- How closely did I follow the parameters of the assignment?
- Using the grade rubric, how would I score my own work?
- What would the teacher say about my work?
- If given the opportunity, one thing I would change about this assignment is …
- How does my work compare to what my classmates did on this assignment?
- Does my work truly reflect my effort?
- Have I achieved the goal I set for myself with this assignment?
- What would I do differently next time, if given the chance?
- Am I proud of my work?
Do you want a short one-page printable of all of these questions to guide your instruction?

Grab the printable version here.
What other questions would you add to this list? Come and share in our WeAreTeachers Chat group on Facebook.
Plus, check out our big list of critical thinking questions and growth mindset posters.

You Might Also Like

Doing Student-Led Conferences the Right Way
Set it up for success, stand back, and reap the rewards. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Table of Contents
Collaboration, information literacy, writing process, final course reflection.
The Final Course Reflection assignment
- asks students to reflect about their coursework in Professional Writing from the perspective of research and theory.
The Final Course Reflection aims to help students
- demonstrate their understanding of 21st century literacies;
- demonstrate declarative knowledge about writing processes , workplace genres (memos, proposals, progress reports, and technical writing conventions (particularly information design and document-design principles).
- analyze their past writing, presentations, and collaborative work to demonstrate they are
The National Academies of Sciences defines 21st Century Literacies as an amalgam of three interdependent competencies: cognitive, intrapersonal, and interpersonal:
- “Cognitive competencies involve thinking, reasoning, and related skills.
- Intrapersonal competencies involve self-management and the ability to regulate one’s behavior and emotions to reach goals.
- Interpersonal competencies involve expressing information to others.” ( Education for Life and Work 2012)
Each year NACE (National Association of Colleges and Employers) surveys employees in the U.S. regarding job readiness in relation to 21st Century literacies. Invariably, written communication skills are identified by employers as critical to success in the workplace. Problem-solving, collaboration, leadership, work ethic, analytical/quantitative skills, initiative–these highly desired competencies have been identified by NACE as the most desired competencies sought by employers, as depicted below. All of these qualities are clustered around the larger competency of communication.
Metacognition , the ability to reflect on how you have mastered these 21st Century, empowers self-development and writing improvement.
Instructions
Write a two-page memo to your a prospective employer that provides evidence you have mastered 21st century literacies and are well positioned to be a productive member of the team. Here you can invent the nature of the job you are applying for.
Suggestions for Drafting this Assignment
Take a moment to conduct an inventory of the writing you completed for Workplace Writing :
- Rhetorical Analysis Memo
- Problem-Definition Heuristic
- Revise, Redesign, Edit: Tailoring Documents for Audiences
- Client Proposal
- Team Charter
- Project Management Portfolio + Bibliography Template
- Group Research Proposal
- Research Notes + Executive Summary
- Progress Report Assignment
- Recommendation Report Assignment
- Evaluation Memo
- Infographic
- Final Reflection
As a result of the writing you have completed for this course, can you identify evidence that demonstrates you have robust cognitive, intrapersonal, and interpersonal competencies?
Recommended Schedule
Submission guidelines.
- Upload Final Course Reflection to the course management system.
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority – How to Establish Credibility in Speech & Writing

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Your reflection may include quotes and passages if you are writing about a book or an academic paper. They give your reader a point of reference to fully understand your feedback. Feel free to describe what you saw, what you heard, and how you felt. Example: "I saw many people participating in our weight experiment.
Using reflective assignments can be a great way of synthesising learning and challenging the status quo. This page outlines some of the things to keep in mind when posing reflective assignments. Overview. In higher education or professional develop initiatives it is very common to have some sort of assignment. These are typically written but ...
Use these 5 tips to write a thoughtful and insightful reflection paper. 1. Answer key questions. To write a reflection paper, you need to be able to observe your own thoughts and reactions to the material you've been given. A good way to start is by answering a series of key questions. For example:
After a Project or Unit: When a project, assignment, or unit is completed, reflection questions can help students consider their performance, what they learned, what challenges they faced, and how they overcame those challenges. It's an opportunity for them to recognize their growth over time and understand how they can improve in the future.
Develop your point through body paragraph (s), and conclude your paper by exploring the meaning you derive from your reflection. You may find the questions listed above can help you to develop an outline before you write your paper. You should maintain a formal tone, but it is acceptable to write in the first person and to use personal pronouns.
Reflection assignments are also an opportunity to write in a first person narrative about elements of the course, such as the required readings, separate from the exegetic and analytical prose of academic research papers. ... Ramlal, Alana, and Désirée S. Augustin. "Engaging Students in Reflective Writing: An Action Research Project ...
Types of reflective writing assignments. A journal requires you to write weekly entries throughout a semester.May require you to base your reflection on course content. A learning diary is similar to a journal, but may require group participation. The diary then becomes a place for you to communicate in writing with other group members.
Both the language and the structure are important for academic reflective writing. For the structure you want to mirror an academic essay closely. You want an introduction, a main body, and a conclusion. Academic reflection will require you to both describe the context, analyse it, and make conclusions. However, there is not one set of rules ...
1st Step: Review the assignment. As with any writing situation, the first step in writing a reflective piece is to clarify the task. Reflective assignments can take many forms, so you need to understand exactly what your instructor is asking you to do. Some reflective assignments are short, just a paragraph or two of unpolished writing.
For my other classes, my schedule is more traditional, as I see my students on a consistent basis. Even so, I feel a rush to get through project after project during the course. After seeing how formal reflection positively informed my teaching, I worked on making shifts with my Art Foundations class, a survey class for 7th and 8th-grade students.
Throughout the reflection, critique, and revision process in PBL, create opportunities to celebrate students who intentionally reflect on their work, provide good feedback to themselves and others, and use feedback to revise their thinking and make changes to their project. As teachers, we also need to reflect, critique, and revise.
Here are a few ideas to help you integrate reflection and student self-assessment throughout the process of learning. Daily Reflection Journals. One of the easiest ways to begin implementing reflection into your classroom is to have students keep a project journal or work log. Provide reflection prompts, or questions, like:
Project Reflection 3 Choosing to plan the Floryance wedding was the project of my choice because I love planning and I love weddings. I get so excited for planning someone's wedding and designing ideas, colors, dresses, and much more. Although I don't get to see the wedding, I can still picture how their perfect day would have gone. Making other dreams come true only gets me more excited to ...
Self-Reflection. When you complete this project, reflect on the process by answering the statements below: What I did: (explain what you or your group did to finish your project.) What I enjoyed: (write about what you liked most about the project) What I found difficult: (write about any part of the project you found hard to do.) What really ...
Project Reflection: Assignment 1. To guide your first project reflection, I have created five categories for questions below. Please compose answers to these questions in a document that you can upload to Canvas. Your task is to engage thoroughly in the task of assessing your project; you may structure this in whatever way works best for you.
8-2 Project Two Feedback and Revision Reflection; 2-5 Assignment - "Caring for Your Introvert: The Habits and Needs of a Little-Understood Group""Caring ... Preview text. 1. English 122: 8-2 Project Two: Feedback and Revision Reflection Carolyn Kolb English Department, Southern New Hampshire University ENG-122, English Composition 1 Dr. Susan ...
45 Awesome Must-Use Questions to Encourage Student Reflection and Growth. Reflection questions for before, during, and after a project or lesson. Cute pupil writing at desk in classroom at the elementary school. Student girl doing test in primary school. Children writing notes in classroom. African schoolgirl writing on notebook during the lesson.
English 1223: 8-3 Project Three - Reflection Emily Miller Southern New Hampshire University ENG-123-22EW Mary Peterson April 24, 2022. Emily Miller Mary Peterson ENG 123 April 24, 2022 ENG 123: 8-3 Project Three: Reflection I chose to incorporate specific feedback into my essay to help strengthen my writing skills and ultimately strengthen my persuasion.
8-2 Project Two: Feedback and Revision Reflection The approaches to revision that I understood the most throughout this course are both the large-scale and small-scale revision processes. However, the method that works best for me is small-scale revision, as it simplifies the details of the work that I have written.
The Final Course Reflection assignment asks students to reflect about their coursework in Professional Writing from the perspective of research and theory. The Final Course Reflection aims to help students demonstrate their understanding of 21st century literacies;demonstrate declarative knowledge about writing processes, workplace genres (memos, proposals, progress reports, and technical ...
A minimum of 3 main body paragraphs. (around 75-80% of the total word count) Each paragraph will explore one of your key points (an exploration of the way in which the person/experience / event / text / movie / music affected you in this case). Your reflection can include quotes, extracts, etc. A conclusion. (around 10-15% of the total word count)
8 - 3 PROJECT THREE: REFLECTION 2. Throughout the writing process external review is critical for providing valuable feedback from additional perspectives. These perspectives offer insight into the ability for others to comprehend the information presented and offer opportunity to modify phrasing or content to be easier understood.