Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
II. Getting Started

2.5 Writing Thesis Statements
Kathryn Crowther; Lauren Curtright; Nancy Gilbert; Barbara Hall; Tracienne Ravita; and Kirk Swenson
To be effective, all support in an essay must work together to convey a central point; otherwise, an essay can fall into the trap of being out of order and confusing. Just as a topic sentence focuses and unifies a single paragraph, the thesis statement focuses and unifies an entire essay. This statement is like a signpost that signals the essay’s destination; it tells the reader the point you want to make in your essay, while the essay itself supports that point.
Because writing is not a linear process, you may find that the best thesis statement develops near the end of your first draft. However, creating a draft or working thesis early in the writing project helps give the drafting process clear direction. You should form your thesis before you begin to organize an essay, but you may find that it needs revision as the essay develops.
A thesis is not just a topic, but rather the writer’s comment or interpretation of the question or subject. For whatever topic you select (for example, school uniforms, social networking), you must ask yourself, “What do I want to say about it?” Asking and then answering this question is vital to forming a thesis that is precise, forceful, and confident.
In the majority of essays, a thesis is one sentence long and appears toward the end of the introductory paragraph. It is specific and focuses on one to three points of a single idea—points that are able to be demonstrated in the body paragraphs. It forecasts the content of the essay and suggests how you will organize your information. Remember that a thesis statement does not summarize an issue but rather dissects it.
Working Thesis Statements
A strong thesis statement must have the following qualities:
- It must be arguable. A thesis statement must state a point of view or judgment about a topic. An established fact is not considered arguable.
- It must be supportable. The thesis statement must contain a point of view that can be supported with evidence (reasons, facts, examples).
- It must be specific. A thesis statement must be precise enough to allow for a coherent argument and remain focused on the topic.
Examples of Appropriate Thesis Statements
- Closing all American borders for a period of five years is one solution that will tackle illegal immigration.
- Compared to an absolute divorce, no-fault divorce is less expensive, promotes fairer settlements, and reflects a more realistic view of the causes for marital breakdown.
- Exposing children from an early age to the dangers of drug abuse is a sure method of preventing future drug addicts.
- In today’s crumbling job market, a high school diploma is not significant enough education to land a stable, lucrative job.
- The societal and personal struggles of Troy Maxson in the play Fences symbolize the challenges of black males who lived through segregation and integration in the United States.
Pitfalls to Avoid
A thesis is weak when it is simply a declaration of your subject or a description of what you will discuss in your essay.
Weak Thesis Statement Example
My paper will explain why imagination is more important than knowledge.
A thesis is weak when it makes an unreasonable or outrageous claim or insults the opposing side.
Religious radicals across America are trying to legislate their Puritanical beliefs by banning required high school books.
A thesis is weak when it contains an obvious fact or something that no one can disagree with or provides a dead end.
Advertising companies use sex to sell their products.
A thesis is weak when the statement is too broad.
The life of Abraham Lincoln was long and challenging.
Ways to Revise Your Thesis
Your thesis statement begins as a working thesis statement, an indefinite statement that you make about your topic early in the writing process for the purpose of planning and guiding your writing. Working thesis statements often become stronger as you gather information and develop new ideas and reasons for those ideas. Revision helps you strengthen your thesis so that it matches what you have expressed in the body of the paper.
You can cut down on irrelevant aspects and revise your thesis by taking the following steps:
- Pinpoint and replace all non specific words, such as people, everything, society, or life, with more precise words in order to reduce any vagueness.
Pinpoint and Replace Example
Working thesis: Young people have to work hard to succeed in life.
Revised thesis: Recent college graduates must have discipline and persistence in order to find and maintain a stable job in which they can use, and be appreciated for, their talents.
Explanation: The original includes too broad a range of people and does not define exactly what success entails. By replacing those general words like people and work hard , the writer can better focus their research and gain more direction in their writing. The revised thesis makes a more specific statement about success and what it means to work hard.
- Clarify ideas that need explanation by asking yourself questions that narrow your thesis.
Clarify Example
Working thesis: The welfare system is a joke.
Revised thesis: The welfare system keeps a socioeconomic class from gaining employment by alluring members of that class with unearned income, instead of programs to improve their education and skill sets.
Explanation: A joke means many things to many people. Readers bring all sorts of backgrounds and perspectives to the reading process and would need clarification for a word so vague. This expression may also be too informal for the selected audience. By asking questions, the writer can devise a more precise and appropriate explanation for joke and more accurately defines their stance, which will better guide the writing of the essay.
- Replace any linking verbs with action verbs. Linking verbs are forms of the verb to be , a verb that simply states that a situation exists.
Replace with Action Verbs Example
Working thesis: Kansas City school teachers are not paid enough.
Revised thesis: The Kansas City legislature cannot afford to pay its educators, resulting in job cuts and resignations in a district that sorely needs highly qualified and dedicated teachers.
Explanation: The linking verb in this working thesis statement is the word are . Linking verbs often make thesis statements weak because they do not express action. Rather, they connect words and phrases to the second half of the sentence. Readers might wonder, “Why are they not paid enough?” But this statement does not compel them to ask many more questions.
- Who is not paying the teachers enough?
- How much is considered “enough”?
- What is the problem?
- What are the results?
- Omit any general claims that are hard to support.
Omit General Claims Example
Working thesis: Today’s teenage girls are too sexualized.
Revised thesis: Teenage girls who are captivated by the sexual images on the internet and social media are conditioned to believe that a woman’s worth depends on her sensuality, a feeling that harms their self-esteem and behavior.
Explanation: It is true that some young women in today’s society are more sexualized than in the past, but that is not true for all girls. Many girls have strict parents, dress appropriately, and do not engage in sexual activity while in middle school and high school. The writer of this thesis should ask the following questions:
- Which teenage girls?
- What constitutes “too” sexualized?
- Why are they behaving that way?
- Where does this behavior show up?
- What are the repercussions?
This section contains material from:
Crowther, Kathryn, Lauren Curtright, Nancy Gilbert, Barbara Hall, Tracienne Ravita, and Kirk Swenson. Successful College Composition . 2nd ed. Book 8. Georgia: English Open Textbooks, 2016. http://oer.galileo.usg.edu/english-textbooks/8 . Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License .
Relating to lines; a way of explaining information logically and/or sequentially; can refer to the chronological relaying of information.
A brief and concise statement or series of statements that outlines the main point(s) of a longer work. To summarize is to create a brief and concise statement or series of statements that outlines the main point(s) of a longer work.
To analyze closely or minutely; to scrutinize every aspect. Unlike the fields of biology, anatomy, or medicine, in rhetoric and writing, dissect does not refer to the cutting apart of a physical body but to the taking apart the body of an argument or idea piece by piece to understand it better.
A logical, rational, lucid, or understandable expression of an idea, concept, or notion; consistent and harmonious explanation.
Assertion or announcement of belief, understanding, or knowledge; a formal statement or proclamation.
Without a defined number or limit; unlimited, infinite, or undetermined.
An altered version of a written work. Revising means to rewrite in order to improve and make corrections. Unlike editing, which involves minor changes, revisions include major and noticeable changes to a written work.
Not relevant; unimportant; beside the point; not relating to the matter at hand.
Attractive, tempting, or seductive; to have an appealing and charismatic quality.
To influence or convince; to produce a certain or specific result through the use of force.
2.5 Writing Thesis Statements Copyright © 2022 by Kathryn Crowther; Lauren Curtright; Nancy Gilbert; Barbara Hall; Tracienne Ravita; and Kirk Swenson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Thesis Statements
A thesis statement is the controlling idea in a medium of writing..
- Standardized testing may reduce learning because it discourages risk-taking.
- Reading Hamlet as "insane," and therefore as having hallucinated his father's ghost, completely redefines how we interpret the play's ultimate theme.
- Social media overuse may increase depression among users because social media, as a platform, immerses users into a comparative culture.
Statement of Purpose:
In this paper I will argue that standardized testing, used improperly, reduces learning. To do so I will show that an effective education requires 1). student buy-in, 2). real-world application, and 3). a sort of "educational risk-taking," i.e. a curriculum that encourages thinking outside the learning box rather than teaching to a standard.
Through a psychoanalytical reading of Hamlet as "insane," and therefore as having hallucinated his father's ghost, I posit that Shakespeare's classic play explores themes of 1). perception, 2). rational, 3). manipulation, and 4). consciousness.
- This paper will attempt two arguments. First, that a culture of comparison—in person or online—often leads to feelings of resentment and dissatisfaction. Second, that social media platforms like Instagram and Facebook are programmed to immerse users into such a culture, and should therefore be regulated, at least at the personal level.
Question thesis:
- What impact, if any, does "standardized testing" actually have on education? Is it merely a tool for assessment? Or does it become a detriment to learning?
- But what if we read Hamlet's character as neither rational nor sane? If Hamlet only hallucinated his father's ghost, how does that impact the way we read the rest of the play?
- In spite of its enormous popularity, what are some of the consequences of, say, social media use on teenage mental health? Is social media a 'new scourge,' as Jane Smith argues, or simply a tool for connecting grandma with her favorite grandchild?
Delayed Thesis:
Intro : What impact, if any, does "standardized testing" actually have on education? Is it merely a tool for assessment? Or does it become a detriment to learning?
Conclusion : Thus we see, standardized testing may reduce learning insofar as it discourages risk-taking.
Too Broad, Too Narrow
Here's an example of a broad and ineffective thesis:
- Julius Caesar had an important influence on history.
The concept of this thesis is obstructed by several generic words: important, influence, and history. Important influence could refer to how Caesar became a dictator and brought about a civil war, but it could just as likely describe how he solidified the Roman Republic, laying the groundwork for Rome to rise as an empire. The first step to clarifying this thesis is to figure out the main point it wants to bring out, which can often be accomplished by asking questions about your thesis
Returning to the phrase "important influence," what might that specifically mean? Let’s take the reference to Caesar becoming a dictator. What, exactly, about his process to becoming a dictator is important? And, how does it influence history?
By asking questions like these, intended to narrow the thesis, we come to this example below:
- Julius Caesar’s aggressive leadership at the Battle of Alesia led to his establishment as a dictator.
A strong thesis statement often employs concrete words, which reference explicit ideas. Words like Julius Caesar, aggressive, establishment, and dictator are specific enough to keep your reader from getting confused.
Keep in mind that, though pulling out specifics will solve most issues with vagueness, they might exacerbate issues when there’s a convoluted and complex thesis, especially when that thesis has a lot of qualifiers. Typically, an effective way to clarify a dense thesis is to identify the core idea and set it by itself. After identifying the main idea, identify all the qualifying information used to modify the thesis. How much of it is necessary to begin with? Can some of it be addressed later on?
Though not always an appropriate strategy, sometimes reducing initial complexity will increase clarity.
Are you ready to meet with a Writing Center Consultant? Here are some questions we can help you with:
- Does my thesis effectively explain my argument?
- Is there a disconnect between my thesis and the content of my paper?
- Could my thesis be more clear or concise?
- Should I adapt my thesis statement because of new research I’ve found?
- Thesis Statements Quick Reference- https://rwc.prod.brigham-young.psdops.com/00000188-e4bc-d222-a7ea-eefd82000000/thesis-statement-pdf
- Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements- https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/thesis_statement_tips.html
- Tips and Tools for Thesis Statements- https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/thesis-statements/

OASIS: Writing Center
Writing a paper: thesis statements, basics of thesis statements.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper. Specific means the thesis deals with a narrow and focused topic, appropriate to the paper's length. Arguable means that a scholar in your field could disagree (or perhaps already has!).
Strong thesis statements address specific intellectual questions, have clear positions, and use a structure that reflects the overall structure of the paper. Read on to learn more about constructing a strong thesis statement.
Being Specific
This thesis statement has no specific argument:
Needs Improvement: In this essay, I will examine two scholarly articles to find similarities and differences.
This statement is concise, but it is neither specific nor arguable—a reader might wonder, "Which scholarly articles? What is the topic of this paper? What field is the author writing in?" Additionally, the purpose of the paper—to "examine…to find similarities and differences" is not of a scholarly level. Identifying similarities and differences is a good first step, but strong academic argument goes further, analyzing what those similarities and differences might mean or imply.
Better: In this essay, I will argue that Bowler's (2003) autocratic management style, when coupled with Smith's (2007) theory of social cognition, can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover.
The new revision here is still concise, as well as specific and arguable. We can see that it is specific because the writer is mentioning (a) concrete ideas and (b) exact authors. We can also gather the field (business) and the topic (management and employee turnover). The statement is arguable because the student goes beyond merely comparing; he or she draws conclusions from that comparison ("can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover").
Making a Unique Argument
This thesis draft repeats the language of the writing prompt without making a unique argument:
Needs Improvement: The purpose of this essay is to monitor, assess, and evaluate an educational program for its strengths and weaknesses. Then, I will provide suggestions for improvement.
You can see here that the student has simply stated the paper's assignment, without articulating specifically how he or she will address it. The student can correct this error simply by phrasing the thesis statement as a specific answer to the assignment prompt.
Better: Through a series of student interviews, I found that Kennedy High School's antibullying program was ineffective. In order to address issues of conflict between students, I argue that Kennedy High School should embrace policies outlined by the California Department of Education (2010).
Words like "ineffective" and "argue" show here that the student has clearly thought through the assignment and analyzed the material; he or she is putting forth a specific and debatable position. The concrete information ("student interviews," "antibullying") further prepares the reader for the body of the paper and demonstrates how the student has addressed the assignment prompt without just restating that language.
Creating a Debate
This thesis statement includes only obvious fact or plot summary instead of argument:
Needs Improvement: Leadership is an important quality in nurse educators.
A good strategy to determine if your thesis statement is too broad (and therefore, not arguable) is to ask yourself, "Would a scholar in my field disagree with this point?" Here, we can see easily that no scholar is likely to argue that leadership is an unimportant quality in nurse educators. The student needs to come up with a more arguable claim, and probably a narrower one; remember that a short paper needs a more focused topic than a dissertation.
Better: Roderick's (2009) theory of participatory leadership is particularly appropriate to nurse educators working within the emergency medicine field, where students benefit most from collegial and kinesthetic learning.
Here, the student has identified a particular type of leadership ("participatory leadership"), narrowing the topic, and has made an arguable claim (this type of leadership is "appropriate" to a specific type of nurse educator). Conceivably, a scholar in the nursing field might disagree with this approach. The student's paper can now proceed, providing specific pieces of evidence to support the arguable central claim.
Choosing the Right Words
This thesis statement uses large or scholarly-sounding words that have no real substance:
Needs Improvement: Scholars should work to seize metacognitive outcomes by harnessing discipline-based networks to empower collaborative infrastructures.
There are many words in this sentence that may be buzzwords in the student's field or key terms taken from other texts, but together they do not communicate a clear, specific meaning. Sometimes students think scholarly writing means constructing complex sentences using special language, but actually it's usually a stronger choice to write clear, simple sentences. When in doubt, remember that your ideas should be complex, not your sentence structure.
Better: Ecologists should work to educate the U.S. public on conservation methods by making use of local and national green organizations to create a widespread communication plan.
Notice in the revision that the field is now clear (ecology), and the language has been made much more field-specific ("conservation methods," "green organizations"), so the reader is able to see concretely the ideas the student is communicating.
Leaving Room for Discussion
This thesis statement is not capable of development or advancement in the paper:
Needs Improvement: There are always alternatives to illegal drug use.
This sample thesis statement makes a claim, but it is not a claim that will sustain extended discussion. This claim is the type of claim that might be appropriate for the conclusion of a paper, but in the beginning of the paper, the student is left with nowhere to go. What further points can be made? If there are "always alternatives" to the problem the student is identifying, then why bother developing a paper around that claim? Ideally, a thesis statement should be complex enough to explore over the length of the entire paper.
Better: The most effective treatment plan for methamphetamine addiction may be a combination of pharmacological and cognitive therapy, as argued by Baker (2008), Smith (2009), and Xavier (2011).
In the revised thesis, you can see the student make a specific, debatable claim that has the potential to generate several pages' worth of discussion. When drafting a thesis statement, think about the questions your thesis statement will generate: What follow-up inquiries might a reader have? In the first example, there are almost no additional questions implied, but the revised example allows for a good deal more exploration.
Thesis Mad Libs
If you are having trouble getting started, try using the models below to generate a rough model of a thesis statement! These models are intended for drafting purposes only and should not appear in your final work.
- In this essay, I argue ____, using ______ to assert _____.
- While scholars have often argued ______, I argue______, because_______.
- Through an analysis of ______, I argue ______, which is important because_______.
Words to Avoid and to Embrace
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize , and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing.
Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question , and interrogate . These more analytical words may help you begin strongly, by articulating a specific, critical, scholarly position.
Read Kayla's blog post for tips on taking a stand in a well-crafted thesis statement.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Search our website or email us .
Read our website accessibility and accommodation statement .
- Previous Page: Introductions
- Next Page: Conclusions
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2.5: Identifying Thesis Statements
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 5269
- Lumen Learning
Learning Objectives
- Identify explicit thesis statements in texts
- Identify implicit thesis statements in texts
- Identify strategies for using thesis statements to predict content of texts
Being able to identify the purpose and thesis of a text, as you’re reading it, takes practice. This section will offer you that practice.
One fun strategy for developing a deeper understanding the material you’re reading is to make a visual “map” of the ideas. Mind maps, whether hand-drawn or done through computer programs, can be fun to make, and help put all the ideas of an essay you’re reading in one easy-to-read format.
Your understanding of what the “central” element of the mind map is might change as you read and re-read. Developing the central idea of your mind map is a great way to help you determine the reading’s thesis.
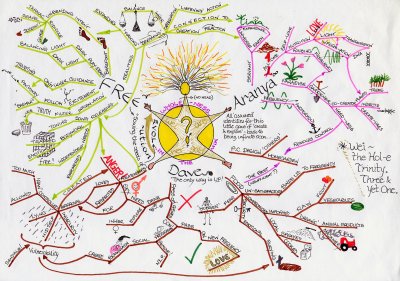
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) - Hand-drawn Mind Map
Locating Explicit and Implicit Thesis Statements
In academic writing, the thesis is often explicit : it is included as a sentence as part of the text. It might be near the beginning of the work, but not always–some types of academic writing leave the thesis until the conclusion.
Journalism and reporting also rely on explicit thesis statements that appear very early in the piece–the first paragraph or even the first sentence.
Works of literature, on the other hand, usually do not contain a specific sentence that sums up the core concept of the writing. However, readers should finish the piece with a good understanding of what the work was trying to convey. This is what’s called an implicit thesis statement: the primary point of the reading is conveyed indirectly, in multiple locations throughout the work. (In literature, this is also referred to as the theme of the work.)
Academic writing sometimes relies on implicit thesis statements, as well.
This video offers excellent guidance in identifying the thesis statement of a work, no matter if it’s explicit or implicit.
Topic Sentences
We’ve learned that a thesis statement conveys the primary message of an entire piece of text. Now, let’s look at the next level of important sentences in a piece of text: topic sentences in each paragraph.
A useful metaphor would be to think of the thesis statement of a text as a general: it controls all the major decisions of the writing. There is only one thesis statement in a text. Topic sentences, in this relationship, serve as captains: they organize and sub-divide the overall goals of a writing into individual components. Each paragraph will have a topic sentence.
Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)
It might be helpful to think of a topic sentence as working in two directions simultaneously. It relates the paragraph to the essay’s thesis, and thereby acts as a signpost for the argument of the paper as a whole, but it also defines the scope of the paragraph itself. For example, consider the following topic sentence:
Many characters in Lorraine Hansberry’s play A Raisin in the Sun have one particular dream in which they are following, though the character Walter pursues his most aggressively.
If this sentence controls the paragraph that follows, then all sentences in the paragraph must relate in some way to Walter and the pursuit of his dream.
Topic sentences often act like tiny thesis statements. Like a thesis statement, a topic sentence makes a claim of some sort. As the thesis statement is the unifying force in the essay, so the topic sentence must be the unifying force in the paragraph. Further, as is the case with the thesis statement, when the topic sentence makes a claim, the paragraph which follows must expand, describe, or prove it in some way. Topic sentences make a point and give reasons or examples to support it.
The topic sentence is often, though not always, the first sentence of a paragraph.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Developing Strong Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
These OWL resources will help you develop and refine the arguments in your writing.
The thesis statement or main claim must be debatable
An argumentative or persuasive piece of writing must begin with a debatable thesis or claim. In other words, the thesis must be something that people could reasonably have differing opinions on. If your thesis is something that is generally agreed upon or accepted as fact then there is no reason to try to persuade people.
Example of a non-debatable thesis statement:
This thesis statement is not debatable. First, the word pollution implies that something is bad or negative in some way. Furthermore, all studies agree that pollution is a problem; they simply disagree on the impact it will have or the scope of the problem. No one could reasonably argue that pollution is unambiguously good.
Example of a debatable thesis statement:
This is an example of a debatable thesis because reasonable people could disagree with it. Some people might think that this is how we should spend the nation's money. Others might feel that we should be spending more money on education. Still others could argue that corporations, not the government, should be paying to limit pollution.
Another example of a debatable thesis statement:
In this example there is also room for disagreement between rational individuals. Some citizens might think focusing on recycling programs rather than private automobiles is the most effective strategy.
The thesis needs to be narrow
Although the scope of your paper might seem overwhelming at the start, generally the narrower the thesis the more effective your argument will be. Your thesis or claim must be supported by evidence. The broader your claim is, the more evidence you will need to convince readers that your position is right.
Example of a thesis that is too broad:
There are several reasons this statement is too broad to argue. First, what is included in the category "drugs"? Is the author talking about illegal drug use, recreational drug use (which might include alcohol and cigarettes), or all uses of medication in general? Second, in what ways are drugs detrimental? Is drug use causing deaths (and is the author equating deaths from overdoses and deaths from drug related violence)? Is drug use changing the moral climate or causing the economy to decline? Finally, what does the author mean by "society"? Is the author referring only to America or to the global population? Does the author make any distinction between the effects on children and adults? There are just too many questions that the claim leaves open. The author could not cover all of the topics listed above, yet the generality of the claim leaves all of these possibilities open to debate.
Example of a narrow or focused thesis:
In this example the topic of drugs has been narrowed down to illegal drugs and the detriment has been narrowed down to gang violence. This is a much more manageable topic.
We could narrow each debatable thesis from the previous examples in the following way:
Narrowed debatable thesis 1:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just the amount of money used but also how the money could actually help to control pollution.
Narrowed debatable thesis 2:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just what the focus of a national anti-pollution campaign should be but also why this is the appropriate focus.
Qualifiers such as " typically ," " generally ," " usually ," or " on average " also help to limit the scope of your claim by allowing for the almost inevitable exception to the rule.
Types of claims
Claims typically fall into one of four categories. Thinking about how you want to approach your topic, or, in other words, what type of claim you want to make, is one way to focus your thesis on one particular aspect of your broader topic.
Claims of fact or definition: These claims argue about what the definition of something is or whether something is a settled fact. Example:
Claims of cause and effect: These claims argue that one person, thing, or event caused another thing or event to occur. Example:
Claims about value: These are claims made of what something is worth, whether we value it or not, how we would rate or categorize something. Example:
Claims about solutions or policies: These are claims that argue for or against a certain solution or policy approach to a problem. Example:
Which type of claim is right for your argument? Which type of thesis or claim you use for your argument will depend on your position and knowledge of the topic, your audience, and the context of your paper. You might want to think about where you imagine your audience to be on this topic and pinpoint where you think the biggest difference in viewpoints might be. Even if you start with one type of claim you probably will be using several within the paper. Regardless of the type of claim you choose to utilize it is key to identify the controversy or debate you are addressing and to define your position early on in the paper.
Developing a Thesis Statement
Many papers you write require developing a thesis statement. In this section you’ll learn what a thesis statement is and how to write one.
Keep in mind that not all papers require thesis statements . If in doubt, please consult your instructor for assistance.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement . . .
- Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic.
- Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper.
- Is focused and specific enough to be “proven” within the boundaries of your paper.
- Is generally located near the end of the introduction ; sometimes, in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or in an entire paragraph.
- Identifies the relationships between the pieces of evidence that you are using to support your argument.
Not all papers require thesis statements! Ask your instructor if you’re in doubt whether you need one.
Identify a topic
Your topic is the subject about which you will write. Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic; or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper.
Consider what your assignment asks you to do
Inform yourself about your topic, focus on one aspect of your topic, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts, generate a topic from an assignment.
Below are some possible topics based on sample assignments.
Sample assignment 1
Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II.
Identified topic
Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis
This topic avoids generalities such as “Spain” and “World War II,” addressing instead on Franco’s role (a specific aspect of “Spain”) and the diplomatic relations between the Allies and Axis (a specific aspect of World War II).
Sample assignment 2
Analyze one of Homer’s epic similes in the Iliad.
The relationship between the portrayal of warfare and the epic simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64.
This topic focuses on a single simile and relates it to a single aspect of the Iliad ( warfare being a major theme in that work).
Developing a Thesis Statement–Additional information
Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic, or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper. You’ll want to read your assignment carefully, looking for key terms that you can use to focus your topic.
Sample assignment: Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II Key terms: analyze, Spain’s neutrality, World War II
After you’ve identified the key words in your topic, the next step is to read about them in several sources, or generate as much information as possible through an analysis of your topic. Obviously, the more material or knowledge you have, the more possibilities will be available for a strong argument. For the sample assignment above, you’ll want to look at books and articles on World War II in general, and Spain’s neutrality in particular.
As you consider your options, you must decide to focus on one aspect of your topic. This means that you cannot include everything you’ve learned about your topic, nor should you go off in several directions. If you end up covering too many different aspects of a topic, your paper will sprawl and be unconvincing in its argument, and it most likely will not fulfull the assignment requirements.
For the sample assignment above, both Spain’s neutrality and World War II are topics far too broad to explore in a paper. You may instead decide to focus on Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis , which narrows down what aspects of Spain’s neutrality and World War II you want to discuss, as well as establishes a specific link between those two aspects.
Before you go too far, however, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts. Try to avoid topics that already have too much written about them (i.e., “eating disorders and body image among adolescent women”) or that simply are not important (i.e. “why I like ice cream”). These topics may lead to a thesis that is either dry fact or a weird claim that cannot be supported. A good thesis falls somewhere between the two extremes. To arrive at this point, ask yourself what is new, interesting, contestable, or controversial about your topic.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times . Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Derive a main point from topic
Once you have a topic, you will have to decide what the main point of your paper will be. This point, the “controlling idea,” becomes the core of your argument (thesis statement) and it is the unifying idea to which you will relate all your sub-theses. You can then turn this “controlling idea” into a purpose statement about what you intend to do in your paper.
Look for patterns in your evidence
Compose a purpose statement.
Consult the examples below for suggestions on how to look for patterns in your evidence and construct a purpose statement.
- Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis
- Franco turned to the Allies when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from the Axis
Possible conclusion:
Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: Franco’s desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power.
Purpose statement
This paper will analyze Franco’s diplomacy during World War II to see how it contributed to Spain’s neutrality.
- The simile compares Simoisius to a tree, which is a peaceful, natural image.
- The tree in the simile is chopped down to make wheels for a chariot, which is an object used in warfare.
At first, the simile seems to take the reader away from the world of warfare, but we end up back in that world by the end.
This paper will analyze the way the simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64 moves in and out of the world of warfare.
Derive purpose statement from topic
To find out what your “controlling idea” is, you have to examine and evaluate your evidence . As you consider your evidence, you may notice patterns emerging, data repeated in more than one source, or facts that favor one view more than another. These patterns or data may then lead you to some conclusions about your topic and suggest that you can successfully argue for one idea better than another.
For instance, you might find out that Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis, but when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from them, he turned to the Allies. As you read more about Franco’s decisions, you may conclude that Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: his desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power. Based on this conclusion, you can then write a trial thesis statement to help you decide what material belongs in your paper.
Sometimes you won’t be able to find a focus or identify your “spin” or specific argument immediately. Like some writers, you might begin with a purpose statement just to get yourself going. A purpose statement is one or more sentences that announce your topic and indicate the structure of the paper but do not state the conclusions you have drawn . Thus, you might begin with something like this:
- This paper will look at modern language to see if it reflects male dominance or female oppression.
- I plan to analyze anger and derision in offensive language to see if they represent a challenge of society’s authority.
At some point, you can turn a purpose statement into a thesis statement. As you think and write about your topic, you can restrict, clarify, and refine your argument, crafting your thesis statement to reflect your thinking.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Compose a draft thesis statement
If you are writing a paper that will have an argumentative thesis and are having trouble getting started, the techniques in the table below may help you develop a temporary or “working” thesis statement.
Begin with a purpose statement that you will later turn into a thesis statement.
Assignment: Discuss the history of the Reform Party and explain its influence on the 1990 presidential and Congressional election.
Purpose Statement: This paper briefly sketches the history of the grassroots, conservative, Perot-led Reform Party and analyzes how it influenced the economic and social ideologies of the two mainstream parties.
Question-to-Assertion
If your assignment asks a specific question(s), turn the question(s) into an assertion and give reasons why it is true or reasons for your opinion.
Assignment : What do Aylmer and Rappaccini have to be proud of? Why aren’t they satisfied with these things? How does pride, as demonstrated in “The Birthmark” and “Rappaccini’s Daughter,” lead to unexpected problems?
Beginning thesis statement: Alymer and Rappaccinni are proud of their great knowledge; however, they are also very greedy and are driven to use their knowledge to alter some aspect of nature as a test of their ability. Evil results when they try to “play God.”
Write a sentence that summarizes the main idea of the essay you plan to write.
Main idea: The reason some toys succeed in the market is that they appeal to the consumers’ sense of the ridiculous and their basic desire to laugh at themselves.
Make a list of the ideas that you want to include; consider the ideas and try to group them.
- nature = peaceful
- war matériel = violent (competes with 1?)
- need for time and space to mourn the dead
- war is inescapable (competes with 3?)
Use a formula to arrive at a working thesis statement (you will revise this later).
- although most readers of _______ have argued that _______, closer examination shows that _______.
- _______ uses _______ and _____ to prove that ________.
- phenomenon x is a result of the combination of __________, __________, and _________.
What to keep in mind as you draft an initial thesis statement
Beginning statements obtained through the methods illustrated above can serve as a framework for planning or drafting your paper, but remember they’re not yet the specific, argumentative thesis you want for the final version of your paper. In fact, in its first stages, a thesis statement usually is ill-formed or rough and serves only as a planning tool.
As you write, you may discover evidence that does not fit your temporary or “working” thesis. Or you may reach deeper insights about your topic as you do more research, and you will find that your thesis statement has to be more complicated to match the evidence that you want to use.
You must be willing to reject or omit some evidence in order to keep your paper cohesive and your reader focused. Or you may have to revise your thesis to match the evidence and insights that you want to discuss. Read your draft carefully, noting the conclusions you have drawn and the major ideas which support or prove those conclusions. These will be the elements of your final thesis statement.
Sometimes you will not be able to identify these elements in your early drafts, but as you consider how your argument is developing and how your evidence supports your main idea, ask yourself, “ What is the main point that I want to prove/discuss? ” and “ How will I convince the reader that this is true? ” When you can answer these questions, then you can begin to refine the thesis statement.
Refine and polish the thesis statement
To get to your final thesis, you’ll need to refine your draft thesis so that it’s specific and arguable.
- Ask if your draft thesis addresses the assignment
- Question each part of your draft thesis
- Clarify vague phrases and assertions
- Investigate alternatives to your draft thesis
Consult the example below for suggestions on how to refine your draft thesis statement.
Sample Assignment
Choose an activity and define it as a symbol of American culture. Your essay should cause the reader to think critically about the society which produces and enjoys that activity.
- Ask The phenomenon of drive-in facilities is an interesting symbol of american culture, and these facilities demonstrate significant characteristics of our society.This statement does not fulfill the assignment because it does not require the reader to think critically about society.
Drive-ins are an interesting symbol of American culture because they represent Americans’ significant creativity and business ingenuity.
Among the types of drive-in facilities familiar during the twentieth century, drive-in movie theaters best represent American creativity, not merely because they were the forerunner of later drive-ins and drive-throughs, but because of their impact on our culture: they changed our relationship to the automobile, changed the way people experienced movies, and changed movie-going into a family activity.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast-food establishments, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize America’s economic ingenuity, they also have affected our personal standards.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast- food restaurants, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize (1) Americans’ business ingenuity, they also have contributed (2) to an increasing homogenization of our culture, (3) a willingness to depersonalize relationships with others, and (4) a tendency to sacrifice quality for convenience.
This statement is now specific and fulfills all parts of the assignment. This version, like any good thesis, is not self-evident; its points, 1-4, will have to be proven with evidence in the body of the paper. The numbers in this statement indicate the order in which the points will be presented. Depending on the length of the paper, there could be one paragraph for each numbered item or there could be blocks of paragraph for even pages for each one.
Complete the final thesis statement
The bottom line.
As you move through the process of crafting a thesis, you’ll need to remember four things:
- Context matters! Think about your course materials and lectures. Try to relate your thesis to the ideas your instructor is discussing.
- As you go through the process described in this section, always keep your assignment in mind . You will be more successful when your thesis (and paper) responds to the assignment than if it argues a semi-related idea.
- Your thesis statement should be precise, focused, and contestable ; it should predict the sub-theses or blocks of information that you will use to prove your argument.
- Make sure that you keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Change your thesis as your paper evolves, because you do not want your thesis to promise more than your paper actually delivers.
In the beginning, the thesis statement was a tool to help you sharpen your focus, limit material and establish the paper’s purpose. When your paper is finished, however, the thesis statement becomes a tool for your reader. It tells the reader what you have learned about your topic and what evidence led you to your conclusion. It keeps the reader on track–well able to understand and appreciate your argument.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects

Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing
Identifying the Thesis Statement
Learning objectives.
- identify explicit thesis statements in texts
- identify implicit thesis statements in texts
You’ll remember that the first step of the reading process, previewing , allows you to get a big-picture view of the document you’re reading. This way, you can begin to understand the structure of the overall text. The most important step in getting a good understanding of an essay or book is to find the thesis statement.
A thesis consists of a specific topic and a position statement on the topic. All of the other ideas in the text support and develop the thesis. The thesis statement is often found in the introduction, sometimes after an initial “hook” or interesting story; sometimes, however, the thesis is not explicitly stated until the end of an essay, and sometimes it is not stated at all. In those instances, there is an implied thesis statement, in which you can generally extract the thesis statement by looking for a few key sentences and ideas.
According to author Pavel Zemliansky,
Arguments then, can be explicit and implicit, or implied. Explicit arguments contain noticeable and definable thesis statements and lots of specific proofs. Implicit arguments, on the other hand, work by weaving together facts and narratives, logic and emotion, personal experiences and statistics. Unlike explicit arguments, implicit ones do not have a one-sentence thesis statement. Instead, authors of implicit arguments use evidence of many different kinds in effective and creative ways to build and convey their point of view to their audience. Research is essential for creative effective arguments of both kinds.
Even if what you’re reading is an informative text, rather than an argumentative one, it might still rely on an implicit thesis statement. It might ask you to piece together the overall purpose of the text based on a series of content along the way.
Most readers expect to see the point of your argument (the thesis statement) within the first few paragraphs. This does not mean that you have to place it there every time. Some writers place it at the very end, slowly building up to it throughout their work, to explain a point after the fact. Others don’t bother with one at all, but feel that their thesis is “implied” anyway. Beginning writers, however, should avoid the implied thesis unless certain of the audience. Almost every professor will expect to see a clearly discernible thesis sentence in the introduction.
Thesis statements vary based on the rhetorical strategy of the essay, but thesis statements typically share the following characteristics:
- Presents the main idea
- Most often is one sentence
- Tells the reader what to expect
- Is a summary of the essay topic
- Usually worded to have an argumentative edge
- Written in the third person
In academic writing, the thesis is often explicit : it is included as a sentence as part of the text. It might be near the beginning of the work, but not always–some types of academic writing leave the thesis until the conclusion.
Journalism and reporting also rely on explicit thesis statements that appear very early in the piece–the first paragraph or even the first sentence.
Works of literature, on the other hand, usually do not contain a specific sentence that sums up the core concept of the writing. However, readers should finish the piece with a good understanding of what the work was trying to convey. This is what’s called an implicit thesis statement: the primary point of the reading is conveyed indirectly, in multiple locations throughout the work. (In literature, this is also referred to as the theme of the work.)
Academic writing sometimes relies on implicit thesis statements, as well.
This video offers excellent guidance in identifying the thesis statement of a work, no matter if it’s explicit or implicit. As the video below argues, every piece of writing has a thesis statement.
Click here to download a transcript for this video
- Identify the Thesis Statement. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Checklist for a Thesis Statement. Provided by : Excelsior OWL. Located at : https://owl.excelsior.edu/esl-wow/getting-ready-to-write/developing-a-thesis/esl-checklist-for-a-thesis-statement/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Research Writing and Argument. Authored by : Pavel Zemliansky. Located at : https://learn.saylor.org/mod/page/view.php?id=7163 . Project : Methods of Discovery: A Guide to Research Writing. License : CC BY: Attribution
- How to Identify the Thesis Statement. Authored by : Martha Ann Kennedy. Located at : https://youtu.be/di1cQgc1akg . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License

Please log in to save materials. Log in
- Thesis Statement
Thesis Statements: How to Identify and Write Them

Students read about and watch videos about how to identify and write thesis statements.
Then, students complete two exercises where they identify and write thesis statements.
*Conditions of Use: While the content on each page is licensed under an Attribution Non-Commercial Share Alike license, some pages contain content and/or references with other types of licenses or copyrights. Please look at the bottom of each page to view this information.
Learning Objectives
By the end of these readings and exercises, students will be able to:
- define the term thesis statement
- read about two recommended thesis statement models
- practice identifying thesis statements in other texts
- write your own effective thesis statements

Attributions:
- The banner image is licensed under Adobe Stock .
- The untitled image of a detective by Peggy_Marco is licensed under Pixabay .
What is a thesis statement?
The thesis statement is the key to most academic writing. The purpose of academic writing is to offer your own insights, analyses, and ideas—to show not only that you understand the concepts you’re studying, but also that you have thought about those concepts in your own way and agreed or disagreed, or developed your own unique ideas as a result of your analysis. The thesis statement is the one sentence that encapsulates the result of your thinking, as it offers your main insight or argument in condensed form.
We often use the word “argument” in English courses, but we do not mean it in the traditional sense of a verbal fight with someone else. Instead, you “argue” by taking a position on an issue and supporting it with evidence. Because you’ve taken a position about your topic, someone else may be in a position to disagree (or argue) with the stance you have taken. Think about how a lawyer presents an argument or states their case in a courtroom—similarly, you want to build a case around the main idea of your essay. For example, in 1848, when Elizabeth Cady Stanton drafted “The Declaration of Sentiments,” she was thinking about how to convince New York State policymakers to change the laws to allow women to vote. Stanton was making an argument.
Some consider all writing a form of argument—or at least of persuasion. After all, even if you’re writing a letter or an informative essay, you’re implicitly trying to persuade your audience to care about what you’re saying. Your thesis statement represents the main idea—or point—about a topic or issue that you make in an argument. For example, let’s say that your topic is social media. A thesis statement about social media could look like one of the following sentences:
- Social media harms the self-esteem of American pre-teen girls.
- Social media can help connect researchers when they use hashtags to curate their work.
- Social media tools are not tools for social movements, they are marketing tools.
Please take a look at this video which explains the basic definition of a thesis statement further (we will be building upon these ideas through the rest of the readings and exercises):
Attributions:
- The content about thesis statements has been modified from English Composition 1 by Lumen Learning and Audrey Fisch et al. and appears under an Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license.
- The video "Purdue OWL: Thesis Statements" by the Purdue University Online Writing Lab appears under a YouTube license .
The Two-Story Model (basic)
First, we will cover the two-story thesis statement model. This is the most basic model, but that doesn't mean it's bad or that you shouldn't use it. If you have a hard time with thesis statements or if you just want to keep things simple, this model is perfect for you. Think of it like a two-story building with two layers.
A basic thesis sentence has two main parts:
- Topic: What you’re writing about
- Angle: What your main idea is about that topic, or your claim
Examples:
When you read all of the thesis statement examples, can you see areas where the writer could be more specific with their angle? The more specific you are with your topic and your claims, the more focused your essay will be for your reader.
Thesis: A regular exercise regime leads to multiple benefits, both physical and emotional.
- Topic: Regular exercise regime
- Angle: Leads to multiple benefits
Thesis: Adult college students have different experiences than typical, younger college students.
- Topic: Adult college students
- Angle: Have different experiences
Thesis: The economics of television have made the viewing experience challenging for many viewers because shows are not offered regularly, similar programming occurs at the same time, and commercials are rampant.
- Topic: Television viewing
- Angle: Challenging because shows shifted, similar programming, and commercials
Please watch how Dr. Cielle Amundson demonstrates the two-story thesis statement model in this video:
- The video "Thesis Statement Definition" by Dr. Cielle Amundson appears under a YouTube license .
The Three-Story Model (advanced)
Now, it's time to challenge yourself. The three-story model is like a building with three stories. Adding multiple levels to your thesis statement makes it more specific and sophisticated. Though you'll be trying your hand with this model in the activity later on, throughout our course, you are free to choose either the two-story or three-story thesis statement model. Still, it's good to know what the three-story model entails.
A thesis statement can have three parts:
- Relevance : Why your argument is meaningful
Conceptualizing the Three-Story Model:
A helpful metaphor based on this passage by Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr.:
There are one-story intellects, two-story intellects, and three-story intellects with skylights. All fact collectors who have no aim beyond their facts are one-story men. Two-story men compare, reason, generalize using the labor of fact collectors as their own. Three-story men idealize, imagine, predict—their best illumination comes from above the skylight.
One-story theses state inarguable facts. Two-story theses bring in an arguable (interpretive or analytical) point. Three-story theses nest that point within its larger, compelling implications.
The biggest benefit of the three-story metaphor is that it describes a process for building a thesis. To build the first story, you first have to get familiar with the complex, relevant facts surrounding the problem or question. You have to be able to describe the situation thoroughly and accurately. Then, with that first story built, you can layer on the second story by formulating the insightful, arguable point that animates the analysis. That’s often the most effortful part: brainstorming, elaborating and comparing alternative ideas, finalizing your point. With that specified, you can frame up the third story by articulating why the point you make matters beyond its particular topic or case.
Though the three-story thesis statement model appears a little bit differently in this video, you can still see how it follows the patterns mentioned within this section:
- The content about thesis statements has been modified from Writing in College by Amy Guptill from Milne Publishing and appears under an Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) license.
- The video "How to Write a STRONG Thesis Statement" by Scribbr appears under a YouTube license .
Identifying Thesis Statements
You’ll remember that the first step of the reading process, previewing , allows you to get a big-picture view of the document you’re reading. This way, you can begin to understand the structure of the overall text. The most important step of understanding an essay or a book is to find the thesis statement.
Pinpointing a Thesis Statement
A thesis consists of a specific topic and an angle on the topic. All of the other ideas in the text support and develop the thesis. The thesis statement is often found in the introduction, sometimes after an initial “hook” or interesting story; sometimes, however, the thesis is not explicitly stated until the end of an essay. Sometimes it is not stated at all. In those instances, there is an implied thesis statement. You can generally extract the thesis statement by looking for a few key sentences and ideas.
Most readers expect to see the point of your argument (the thesis statement) within the first few paragraphs. This does not mean that it has to be placed there every time. Some writers place it at the very end, slowly building up to it throughout their work, to explain a point after the fact. Others don’t bother with one at all but feel that their thesis is “implied” anyway. Beginning writers, however, should avoid the implied thesis unless certain of the audience. Almost every professor will expect to see a clearly discernible thesis sentence in the introduction.
Shared Characteristics of Thesis Statements:
- present the main idea
- are one sentence
- tell the reader what to expect
- summarize the essay topic
- present an argument
- are written in the third person (does not include the “I” pronoun)
The following “How to Identify a Thesis Statement” video offers advice for locating a text’s thesis statement. It asks you to write one or two sentences that summarize the text. When you write that summary, without looking at the text itself, you’ve most likely paraphrased the thesis statement.
You can view the transcript for “How to Identify the Thesis Statement” here (download).
Try it!
Try to check your thesis statement identification skills with this interactive exercise from the Excelsior University Online Writing Lab.
- The video "How to Identidy the Thesis Statement" by Martha Ann Kennedy appears under a YouTube license .
- The "Judging Thesis Statements" exercise from the Purdue University Online Writing Lab appears under an Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license.
Writing Your Own Thesis Statements
A thesis statement is a single sentence (or sometimes two) that provides the answers to these questions clearly and concisely. Ask yourself, “What is my paper about, exactly?” Answering this question will help you develop a precise and directed thesis, not only for your reader, but for you as well.
Key Elements of an Effective Thesis Statement:
- A good thesis is non-obvious. High school teachers needed to make sure that you and all your classmates mastered the basic form of the academic essay. Thus, they were mostly concerned that you had a clear and consistent thesis, even if it was something obvious like “sustainability is important.” A thesis statement like that has a wide-enough scope to incorporate several supporting points and concurring evidence, enabling the writer to demonstrate his or her mastery of the five-paragraph form. Good enough! When they can, high school teachers nudge students to develop arguments that are less obvious and more engaging. College instructors, though, fully expect you to produce something more developed.
- A good thesis is arguable . In everyday life, “arguable” is often used as a synonym for “doubtful.” For a thesis, though, “arguable” means that it’s worth arguing: it’s something with which a reasonable person might disagree. This arguability criterion dovetails with the non-obvious one: it shows that the author has deeply explored a problem and arrived at an argument that legitimately needs 3, 5, 10, or 20 pages to explain and justify. In that way, a good thesis sets an ambitious agenda for a paper. A thesis like “sustainability is important” isn’t at all difficult to argue for, and the reader would have little intrinsic motivation to read the rest of the paper. However, an arguable thesis like “sustainability policies will inevitably fail if they do not incorporate social justice,” brings up some healthy skepticism. Thus, the arguable thesis makes the reader want to keep reading.
- A good thesis is well specified. Some student writers fear that they’re giving away the game if they specify their thesis up front; they think that a purposefully vague thesis might be more intriguing to the reader. However, consider movie trailers: they always include the most exciting and poignant moments from the film to attract an audience. In academic papers, too, a well specified thesis indicates that the author has thought rigorously about an issue and done thorough research, which makes the reader want to keep reading. Don’t just say that a particular policy is effective or fair; say what makes it is so. If you want to argue that a particular claim is dubious or incomplete, say why in your thesis.
- A good thesis includes implications. Suppose your assignment is to write a paper about some aspect of the history of linen production and trade, a topic that may seem exceedingly arcane. And suppose you have constructed a well supported and creative argument that linen was so widely traded in the ancient Mediterranean that it actually served as a kind of currency. 2 That’s a strong, insightful, arguable, well specified thesis. But which of these thesis statements do you find more engaging?
How Can You Write Your Thesis Statements?
A good basic structure for a thesis statement is “they say, I say.” What is the prevailing view, and how does your position differ from it? However, avoid limiting the scope of your writing with an either/or thesis under the assumption that your view must be strictly contrary to their view.
- focus on one, interesting idea
- choose the two-story or three-story model
- be as specific as possible
- write clearly
- have evidence to support it (for later on)
Thesis Statement Examples:
- Although many readers believe Romeo and Juliet to be a tale about the ill fate of two star-crossed lovers, it can also be read as an allegory concerning a playwright and his audience.
- The “War on Drugs” has not only failed to reduce the frequency of drug-related crimes in America but actually enhanced the popular image of dope peddlers by romanticizing them as desperate rebels fighting for a cause.
- The bulk of modern copyright law was conceived in the age of commercial printing, long before the Internet made it so easy for the public to compose and distribute its own texts. Therefore, these laws should be reviewed and revised to better accommodate modern readers and writers.
- The usual moral justification for capital punishment is that it deters crime by frightening would-be criminals. However, the statistics tell a different story.
- If students really want to improve their writing, they must read often, practice writing, and receive quality feedback from their peers.
- Plato’s dialectical method has much to offer those engaged in online writing, which is far more conversational in nature than print.
You can gather more thesis statement tips and tricks from this video titled "How to Create a Thesis Statement" from the Florida SouthWestern State College Academic Support Centers:
- The video "How to Create a Thesis Statement" by the Florida SouthWestern State College Academic Support Centers appears under a YouTube license .
Additional, Optional Resources

If you feel like you might need more support with thesis statements, please check out these helpful resources for some extra, optional instruction:
- "Checklist for a Thesis Statement" from the Excelsior University Online Writing Lab which appears under an Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license.
- "Developing Your Thesis" from Hamiliton College which appears under a copyright.
- "Parts of a Thesis Sentence and Common Problems" from the Excelsior University Online Writing Lab which appears under an Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license.
- "Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements" from the Purdue University Writing Lab which appears under a copyright.
- "Writing Thesis Statements & Hypotheses" by Hope Matis from Clarkson University which appears under a copyright.
- The content about these resources has been modified from English Composition 1 by Lumen Learning and Audrey Fisch et al. and appears under an Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license.
- The content about these resources has been modified from Writing in College by Amy Guptill from Milne Publishing and appears under an Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) license.
- The untitled image of the books by OpenClipart-Vectors is licensed under Pixabay .
Exercise #1: Identify Thesis Statements
Throughout the readings, we have been learning what an effective thesis statement is and what it is not. Before we even get to writing our own thesis statements, let's look for real-world examples. It's your turn to locate and identify thesis statements!

Objectives/Goals
By completeting this exercise students will be able to:
- identify the main ideas within a text
- summarize the main ideas within a text
- choose one sentence from the text which you believe is the thesis statement
- argue why you believe that's the true thesis statement of the text
Instructions
- Any print or online text (probably something around a page in length) will be fine for this exercise.
- If you have trouble finding a text, I recommend looking at this collection from 88 Open Essays – A Reader for Students of Composition & Rhetoric by Sarah Wangler and Tina Ulrich.
- Write the title of the text that you selected and the full name(s) of the author (this is called the full citation).
- Provide a hyperlink for that text.
- Write one paragraph (5+ sentences) summarizing the main points of the text.
- Write one more argumentative paragraph (5+ sentences) where you discuss which sentence (make sure it appears within quotation marks, but don't worry about in-text citations for now) you think is the author's thesis statement and why.
Submitting the Assignment
You will be submitting Exercise #1: Identify Thesis Statements within Canvas in our weekly module.
Please check the assignment page for deadlines and Canvas Guides to help you in case you have trouble submitting your document.
- "88 Open Essays - A Reader for Students of Composition & Rhetoric" by Sarah Wangler and Tina Ulrich from LibreTexts appears under an Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-SA 4.0) license.
Exercise #2: Write Your Own Thesis Statements
Now that you've had some practice with locating and identifying thesis statements, you are ready to write some practice thesis statements yourself.

- write a two-story thesis statement
- write a three-story thesis statement
- reflect on your thesis statement skills
- Using the same text from Exercise #1, write a two-story thesis statement in response to that text.
- Using the same text from Exercise #1, write a three-story thesis statement in response to that text.
- Is it easy for you to identify thesis statements in other texts? Why or why not?
- What methods do you use to identify/locate thesis statements?
- In the past, how have you felt when you needed to write a thesis statement?
- How did you feel about writing your own thesis statements in Exercise #2?
- Which thesis statement writing strategies were the most beneficial to you? Why?
- What challenges did you face when you were writing you thesis statement for Exercise #2?
You will be submitting Exercise #2: Write Your Own Thesis Statements within Canvas in our weekly module.
- The untitled image of the writing supplies by ptra is licensed under Pixabay .
Version History
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

Everything You Need to Know About Thesis Statement

Table of Contents

Persuasion is a skill that every human leverages to achieve their goals. For example, you persuade your friends to join you on some trip, your parents to purchase you an automobile, and your committee or audience to provide you approval for your research proposal.
Likewise, every scholarly task is aimed to persuade your readers or audience for certain goals. And the end goal is to incline the readers towards your perspective (facts and evidence-based). So, the act of convincing readers of your viewpoints via research work is often termed academic argument, and it follows a predetermined pattern of guidelines-based writing. After providing a comprehensive introduction to the research topic, you are supposed to state your perspective on the topic in a sentence or two, known as Thesis Statement . It summarizes the argument you will make throughout the paper.
Also, the Thesis Statement often serves as an answer to your research question. Thus, the thesis statement is a must for every research paper and scholarly work.
What is Thesis Statement?

A Thesis Statement:
- Describes how you interpret the subject matter's cause, significance, and results.
- Is a guideline for the paper. In other words, it provides an understanding of the research topic.
- Directly answers the question you are asked. The thesis is not the question itself but an interpretation of it. For example, a thesis can be about World War II, and it should also provide a way to understand the war.
- Claims that other people might disagree with.
- Is a single sentence at the beginning of your paper or near the end of the first para (where you present your argument to the reader). The body of the essay is the rest of the paper. It gathers and organizes evidence to support your argument.
A thesis statement should be concise and easily understandable. Use it as a magnet to attract your readers to keep them reading your paper till the end.
What is the purpose or the goal of the thesis statement?
The real purpose of the thesis statement is:
- To establish a gateway through which your readers can make an entrance into your research paper.
- To bring the entire research paper together to an epicenter of various arguments provided throughout the paper.
Simply put, the goal of writing a strong thesis statement is to make your research paper appear interesting enough for the readers to understand it and prove your arguments right completely.
Additionally, the goal of the thesis statement varies from the kind of research you are presenting. If your thesis provides some claims, justifications, or study, you should present an argumentative thesis statement . However, if your thesis is based on analysis, interpretation, demonstration of cause and effect, comparisons, and contrast, you should develop a persuasive thesis statement.
What is the length of an Ideal Thesis Statement?
You should write your thesis statement in 1-2 sentences. Ideally, it should not be more than 50 words in total.
Also, you should try inserting the thesis statement at the end of the topic introduction or just before the background information.
While writing your thesis statement, be mindful that a thesis statement is never meant to be factual. Your thesis statement is one of the most important elements of your thesis that will help your audience understand what you discuss throughout your paper. So, ensure that your thesis statement must appear like an arguable statement, not a factual one.
Many early researchers or young scholars choose to write factual statements as thesis statements as they are easy to prove. However, resorting to factual statements instead of arguable ones will overshadow your analytical and critical thinking skills, which readers anticipate in your paper.
How to Start a Thesis Statement?

The thesis statement is an outline of your research topic in one sentence. Therefore, you must write it in a concise and catchy style. So, here are a few quick tips that help you understand how to start a thesis statement for a research paper:
Discover Your Research Question
Once the subject matter is finalized for writing a research paper, the next requirement is to figure out the research question. While formulating your research question, make sure that it shows the gaps in the current field of study and should serve as a primary interrogation point for your research.
Figure out the answer and develop your argument
Carry out intensive research to determine the perfect answer for your research question. Your answer should further guide you to structure your entire research paper and its content flow.
For example, if you write an argumentative paper, craft your opinion and create an argument. Then, develop your claim against the topics you want to cover and justify it through various data & facts.
Establish back-up for your Answer with Evidence
The more you research, the more you will learn about the variations in the research answer that you were trying to formulate. Similarly, with various sources and newer evidence coming up, you should be able to make an answer that should stand coherently, correctly, relevant, and justified enough. The answer should enhance the reader’s understanding of your paper from beginning to end.
How to determine if my thesis statement is strong?

Make a self-evaluation of your thesis statement and check if it stands the following interrogation:
- Does it answer the question?
Re-read to understand the question prompt to ensure that your answer or the thesis statement itself doesn't skip the focus of the question. Try rephrasing it if you feel that the question prompt is not structured or appropriately discussed.
- Does my thesis statement appear like an argument (for or against)?
Suppose you have chosen to present the facts and rationality behind it in the best way possible and assume that no one would or could ever disagree with it. It indicates that you've presented a summary instead of presenting an argument. So, always pick an opinion from the topic and justify your arguments backed with various evidence.
- Is the Thesis Statement explicit and specific?
It may lack a strong argument if you have written a very general statement or vaguely crafted a thesis statement. Your audience will figure it out instantly.
Therefore, if you have used words like “good’’ or “bad,” try to put it more specifically by answering and figuring out “Why something is good”? Or ''What makes something good or bad”?
- Does it clear the “So What” test?
After reading any research paper, the prompt question that pops up from a reader's mind is, "So What?". Now, if your thesis statement urges the reader with such questions, you need to develop a strong argument or relationship that bridges your research topic to a more significant real-world problem.
- Does it go beyond the “How” and “Why” assessments?
After going through your thesis statement, if the readers come up with questions like "How" and 'Why," it indicates that your statement failed to provide the reader with the critical insights to understand your thesis statement and is too open-ended. So, you must provide your readers with the best statement explaining the introduction's real significance and the impending need for further research.
Thesis Statement Examples
Follow through with some interesting and creative thesis statements to clarify your doubts and better understand the concept.
Example 1: Social Media affects public awareness both positively and negatively
Yeah, it does answer the question. However, the answer is pretty vague and generic as it shows the effects both positively and negatively.
Not accurately. The statement can be argued only with the people having opinions either on positive or the negative aspect. Therefore, it fails to address every section of the audience.
- Is the Thesis statement specific enough?
Not exactly. This thesis statement doesn't provide any details on positive and negative impacts.
No, not at all. The thesis statement stated above provides no clarifications over how the positive or negative impacts build up or the factors that build up such impacts.
Again, No. It fails to justify why anyone should bother about the impacts, be it positive or negative.
A stronger and alternate version for the above thesis statement can be:
Since not every piece of information provided on social media is credible and reliable enough, users have become avid consumers of critical information and, therefore, more informed.
Even though the above thesis statement is lengthy, it answers every question and provides details over cause, effect, and critical aspects that readers can easily challenge.
Example 2: Analytical Thesis Statement
- Water is extremely important for human survival, but consuming contaminated water poses many health risks.
- The hibernation period is one of the most important periods in animals for healthy well-being. Still, it renders them in a state of weakness and exposed to external and environmental threats.
Example 3: Argumentative Thesis Statement
- At the end of the nineteenth century, French women lawyers experienced misogynist attacks from male lawyers when they attempted to enter the legal profession because male lawyers wanted to keep women out of judgeships.
- High levels of alcohol consumption have detrimental effects on your health, such as weight gain, heart disease, and liver complications.
Tips for writing a Strong Thesis Statement

A strong thesis statement is the foremost requirement of academic writing, and it holds greater importance when written for research papers. However, it becomes more crucial when you want your readers to get convinced of your opinions or perspective of the subject matter.
Below are some pro-tips that can help you crack the code of how to write a strong thesis statement, especially for research papers, thesis, and dissertations:
Keep it specific
Readers often get disappointed and confused when you present a weak argument based on a generic thesis statement. To develop a strong thesis statement, focus on one key aspect and develop it further.
Keep it simple and clear
The essence of your entire research paper is dependent on your thesis statement. Also, a strong thesis statement stays hinged over the clarity it provides. Therefore, don't disrupt the meaning or clarity of your research paper by using some jargonish words or complexing it by combining different concepts.
Ingrain your opinions
Your thesis statement should explicitly display your opinion or position for the subject matter under discussion. Your reader wants to understand your position in detail and the factors you will justify with evidence and facts.
Make it unique and Original
Your audience or the readers have gone through the subject matter several times in their careers. Hence, you must present your thesis statement in a unique and completely original form. Never use generic statements; grow some risk-taking capability and surprise your readers.
Keep it Concise and Coherent
Your thesis statement can be considered good only if it is concise yet informational. Don’t make it wordy in any case, and never go beyond more than 50 words.
Additionally, your research paper will discuss many aspects of a topic. Still, in the end, every single aspect should come together to form a coherent whole, addressing, explaining, and justifying the research question.
Conclusion: How to write a Thesis Statement?
A strong thesis statement is the one of the most important elements of your research paper. The thesis statement always serves as a pillar that carries the entire load of a research paper and it’s several sections.
Whether your research paper is worthy of your audience time or not, entirely hinges upon your thesis statement. A thesis statement always depicts the plan for the research but a good thesis statement reflects your opinions, viewpoints and of course the trajectory that it sets for the entire paper.
So, always try to write a good thesis statement by carefully following its structure, about which we have already discussed.
Before you go: In view of your interest in simplifying research workflows, we suggest you take a look at SciSpace . In a single portal, you can complete all your research writing tasks, including literature searches.

SciSpace provides researchers, universities, and publishers with all the tools they need. Our comprehensive research repository features more than 200 million research papers from multiple disciplines with SEO-optimized abstracts, a publicly visible profile to highlight your expertise, a specially-built collaborative text editor, 20,000+ journal templates, and more.

Hope the article has explained everything that you needed to know about the thesis statement. In case you have any questions or doubts, join our SciSpace (Formerly Typeset) community platform and put your questions there. We will make sure that you get your answers at the earliest.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The thesis (primary argument) is as follows: "Pet ownership is highly beneficial for children." Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like The subject/ essay map approach is helpful for all types of essays., The essay map provides a preview of your main points., The subject/ essay map approach is usually helpful for ...
WEAK THESIS: Slavery in the United States damaged many lives. This is a weak thesis statement for two reasons. First, slavery can't be discussed thoroughly in a short essay. Second, damaged is vague and many lives is very general. You should be able to identify specific causes and effects.
It must be arguable. A thesis statement must state a point of view or judgment about a topic. An established fact is not considered arguable. It must be supportable. The thesis statement must contain a point of view that can be supported with evidence (reasons, facts, examples). It must be specific. A thesis statement must be precise enough to ...
Thesis statements vary based on the rhetorical strategy of the essay, but thesis statements typically share the following characteristics: Presents the main idea; Most often is one sentence; Tells the reader what to expect; Is a summary of the essay topic; Usually worded to have an argumentative edge; Written in the third person
The thesis statement focuses the essay by stating the main idea of the paper and limiting the topic. A thesis is often only one sentence in length, though it may be longer for some assignments. Most readers expect to find your thesis at the end of the introduction, where it gains emphasis.
Most writers, in time, find that choosing clear, precise words when writing a thesis will make it easier to identify and understand. Here's an example of a broad and ineffective thesis: Julius Caesar had an important influence on history. The concept of this thesis is obstructed by several generic words: important, influence, and history.
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize, and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing. Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question, and interrogate.
Each paragraph will have a topic sentence. Figure 2.5.2 2.5. 2. It might be helpful to think of a topic sentence as working in two directions simultaneously. It relates the paragraph to the essay's thesis, and thereby acts as a signpost for the argument of the paper as a whole, but it also defines the scope of the paragraph itself.
Narrowed debatable thesis 1: At least 25 percent of the federal budget should be spent on helping upgrade business to clean technologies, researching renewable energy sources, and planting more trees in order to control or eliminate pollution. This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just the amount of money used but also ...
The Components of an Effective Thesis Statement. You can't just pluck a thesis out of thin air. Even if you have a terrific insight concerning a topic, it won't be worth much unless you can logically and persuasively support it in the body of your essay. A thesis is the evolutionary result of a thinking process, not a miraculous creation.
identify strategies for using thesis statements to predict content of texts. Being able to identify the purpose and thesis of a text, as you're reading it, takes practice. This section will offer you that practice. One fun strategy for developing a deeper understanding the material you're reading is to make a visual "map" of the ideas.
A thesis statement . . . Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic. Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper. Is focused and specific enough to be "proven" within the boundaries of your paper. Is generally located near the end ...
Thesis Statements. A thesis is the main claim you are making in an argument, similar to the hypothesis in a scientific experiment. It is what you are trying to prove or persuade your audience to believe or do. It's helpful to develop a working thesis to guide your composition process. "Working" is the operative word here; your ideas are ...
The thesis is the author's reason for writing. The word thesis is a Greek word meaning position. The thesis statement is the controlling idea. It is the point the writer wants to make. It is not necessarily in the beginning of an essay. It is not even necessarily physically present. It might be implied.
A. Identify and correct sentences which are too broad or too narrow using (TB/TN) B. identify and correct sentences which announce the topic using (A). C. Identify and correct incomplete ideas using (INC) D. Identify the thesis statements that are fine as they are using (OK). For screen reader users, blanks are indicated by *. 1.
A thesis statement is a sentence in a paper or essay (in the opening paragraph) that introduces the main topic to the reader. As one of the first things your reader sees, your thesis statement is one of the most important sentences in your entire paper—but also one of the hardest to write! In this article, we explain how to write a thesis ...
The thesis statement is the key to most academic writing. The purpose of academic writing is to offer your own insights, analyses, and ideas—to show not only that you understand the concepts you're studying, but also that you have thought about those concepts in your own way and agreed or disagreed, or developed your own unique ideas as a result of your analysis.
The thesis statement tells your reader about the paper's focus. This resource will describe characteristics of two general types of thesis statements: 1. The "Point-of-View" or Argumentative thesis: presents an argument or case to be made. 2. The "Scope" or Explanatory thesis: outlines the scope of the paper. However, what different ...
A Thesis Statement: Describes how you interpret the subject matter's cause, significance, and results. Is a guideline for the paper. In other words, it provides an understanding of the research topic. Directly answers the question you are asked. The thesis is not the question itself but an interpretation of it.
identify strategies for using thesis statements to predict content of texts. Being able to identify the purpose and thesis of a text, as you're reading it, takes practice. This section will offer you that practice. One fun strategy for developing a deeper understanding the material you're reading is to make a visual "map" of the ideas.
The thesis statement that is most restricted from your options is 'Beethoven's 5th Symphony has inspired many rock musicians'. This statement is most restricted because it is specific and focused on a particular piece of classical music (Beethoven's 5th Symphony), and its influence on a defined group of people (rock musicians). The other ...
A thesis statement is usually included at the end of the introductory paragraph and summarizes the central theme of the paper. The original thesis statement is "Classical music is the basis for most rock music". This thesis statement is unrestricted because it is too broad and can lead to a long essay that covers a lot of aspects.