- Search Search Please fill out this field.

What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-14343635291-33bf053f368c43f6a792e94775285bbd.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

Manufacture
Omnichannel
Supply Chain
Employee database
Digital Transformation
Operations & Manufacturing
Sales, Marketing, Growth
Data Analytics
Human Resources
Strategy & Organization
Wholesale Distribution
Odoo Consulting
ABOUT IMPACT
Case Studies
LEARN & GET INSIGHT
Overview, benefits, key factors, and role of ERP
Learn each lean manufacturing activity in detail
Overview, the management, and the activities
Increase your warehouse operational, from inventory management to transportation management
Find important strategies in developing retail business, from planning to expanding
Overview, customer development, startup web, business model canvas
Bridging the branding gap, crafting buyer persona, achieve virality, syncing brand & culture
SEM, SEO, social media, and content marketing for business
Odoo user guide, installation & general setting, module configuration
News, ideas, and insights on business
BUSINESS DIRECTORY
Legal Consultant
Public Accountant
Tax Consultant
Creating a Solid Business Plan in 9 Simple Steps
- Posted: October 3, 2023
- Updated: October 9, 2023
IN THIS ARTICLE
In the previous chapter, we delved into the world of market research for your retail business, uncovering valuable insights and trends that could shape your venture’s success. As you embark on your entrepreneurial journey, it’s time to lay a solid foundation for your business with a crucial tool: the business plan.
So, what exactly is a business plan? It’s your roadmap, your blueprint, the compass that will guide you through the uncharted waters of business ownership. A well-structured business plan is your recipe for success.
Whether seeking investors, securing a loan, or simply charting your path forward, a well-crafted business plan is your ultimate tool for steering your business toward profitability and growth. In this chapter, we’ll walk you through the process of creating a tailor-made business plan in nine steps for your retail venture.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a comprehensive written document that outlines a business’s goals, strategies, and operational details. It serves as a roadmap for entrepreneurs and organizations, providing a clear and structured overview of how the company intends to operate, grow, and achieve its objectives. This document is not only used by small businesses and startups. Even well-established companies use business plans.
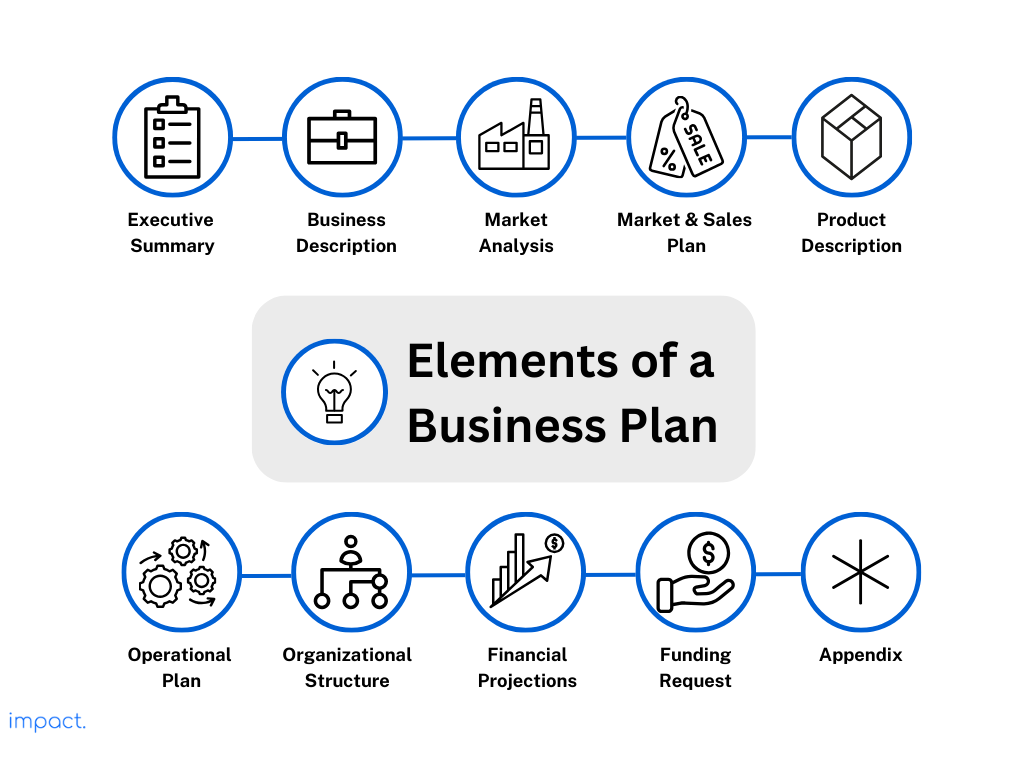
A business plan typically contains these elements:
- Executive Summary : A summary of the whole plan, highlighting the essential ideas.
- Business Description : Information about the business, what it’s all about, and what it wants to achieve.
- Market Analysis : Research regarding the industry the business is in, the customers, who the competition is, and what customers are like.
- Marketing and Sales Plan : Strategies on how the business plans to get and keep customers, how it’ll set prices, and where it’ll sell its products.
- Product or Service Description : Details about what the business sells, its uniqueness, and why people should buy it.
- Operational Plan : How the business will run day-to-day, where it’ll get the things it needs, and where it will operate.
- Management and Structure : Information about key figures and organization of the business.
- Financial Projections : Numbers that show how much money the business expects to make and spend, like profits and losses.
- Funding Request (if needed) : If a business requires external funding, it must specify the amount needed and the purpose for which it will be used.
- Appendix : Extra documentation and information like resumes, data about the market, and legal papers.
Business plans can be long, short, straightforward, or complex, depending on what kind of business it is and who will read it. They should be updated as the business changes and grows.
9 steps on how to write a business plan
Ensuring a well-organized business plan is in place for your company will help position it for success. Here are nine simple steps to write one, starting with the executive summary.
1. Write the executive summary
Start your business plan with a concise executive summary. This section is like the “quick start” button for your project. It gives readers a fast glimpse of your business, its purpose, and the most critical parts of your plan. Think of it like a trailer for an exciting movie — it should grab their attention and give them a taste of what’s coming next.
In the executive summary, focus on the key points. While making your business plan engaging and informative is essential, remember to include detailed information in other sections. This section is your chance to set the stage for the entire document. So, make it attention-grabbing, clear, and actionable. It’s the first thing your readers will see, so make it count.
2. Write the company description
Begin by painting a clear picture of your company. Provide a thorough description covering essential aspects such as your company’s history, its location, how it’s legally structured (like a sole proprietorship or LLC), and most importantly, the specific problem or need your business is here to solve.
This part is your chance to explain why your company stands out. What makes it unique? Highlight your strengths, expertise, or advantages that position your business for success.
3. List your business goals
When it comes to your business goals, make them crystal clear. Your goals should be specific so there’s no confusion about what you want to achieve. They should also be measurable, which means you can track your progress.
Ensure they’re attainable, meaning they’re realistic and doable. Keep them relevant to your business’s mission and direction. Lastly, add a time element – make them time-bound so you have a deadline for accomplishing them.
Your business plan should include both short-term and long-term goals. You aim to achieve short-term goals quickly, typically within a year. They include increasing monthly sales or launching a new product. Long-term goals are the more prominent, overarching objectives you’ve worked towards for several years. These could be expanding into new markets or becoming a leader in your industry.
4. Describe your products and services
Your products or services are central to your business plan. Let’s focus on a dedicated section to give readers all the vital information they need. Begin by offering a detailed description of what you’re offering. Describe what makes your products or services unique, highlighting their features and the benefits they bring to customers. Clearly show how they solve problems or fulfill the needs of your target audience.
If you have any upcoming products in the pipeline, mention them here. Additionally, if your business holds any intellectual property rights , like patents or trademarks, explain how they contribute to your competitive advantage and profitability.
5. Conduct your market analysis
To begin, conduct extensive research on your market. It involves profoundly understanding your industry, target audience, competition, and current trends. Collecting data and insights to demonstrate your knowledge of the market is crucial, including estimating the market size for your products, determining your business’s position in the market, and identifying your competitors.
One way of doing this is by conducting a SWOT Analysis . The SWOT analysis is a tool that helps you look at your business’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. You often see it as a grid or a visual chart. It lets your readers quickly see what could affect your business and where you might have an edge over your competition.
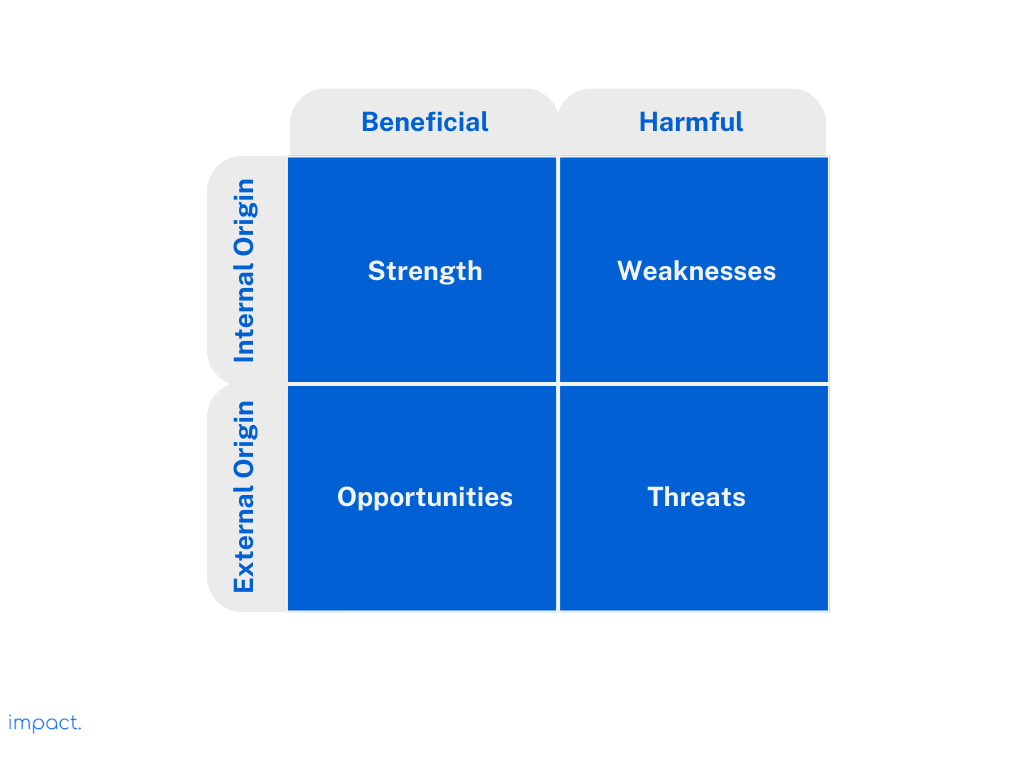
Having solid research to back up your conclusions is crucial. It helps convince investors that you know what you’re talking about and lets you double-check your assumptions as you put together your plan. Both lenders and investors will want to know what makes your product different from what’s already out there.
Read more: Market Research for Retail: 5 Reasons Why It’s Important
6. Outline your sales plan
Defining exactly how you’ll sell your products or services in your business plan is crucial. After analyzing your market, you can break down your sales strategy into clear steps.
Start by defining your pricing strategy — how much you’ll charge for what you offer. Next, outline your distribution channels, which are how you’ll get your products or services into customers’ hands. Then, describe your sales tactics, which are the methods and techniques you’ll use to make sales happen. Lastly, talk about your marketing efforts, which include how you’ll create awareness about your business.
Beyond this, clarify your approach to attracting and retaining customers. Outline your strategy for acquiring new customers through advertising, partnerships, or other means. Equally crucial is your plan for maintaining customers, which can boost revenue. Describe how you’ll offer excellent customer service, loyalty programs, or incentives to ensure repeat business.
7. Address operational needs
Now, let’s tackle your operational needs — these are the essential elements that make your business idea a reality.
When it comes to your team, clearly define the roles you must fill. Identify the key positions necessary for the smooth operation of your business. Explain the primary responsibilities of each team member. For instance, you might require sales representatives, customer support staff, or someone to manage your finances.
Consider what your business needs to function effectively. This section includes your physical workspace, whether an office, a storefront, or an online platform. List the equipment required, such as computers, machinery, or specialized tools. Additionally, consider the technology you’ll rely on, including software, websites, or digital systems to enhance operational efficiency.
This section demonstrates your grasp of the supply chain and contingency plans. Whether presenting this plan to others or using it as a guide for yourself, it’s crucial for making important decisions. For instance, it can help determine pricing strategies to cover estimated costs and establish when you anticipate breaking even on your initial investments.
8. Outline the structure of your organization
Explaining how your company is structured and who’s in charge of your business plan is essential. It means talking about the people in your management team, their qualifications, and what they do.
Clearly defining the reporting structure and responsibilities within your organization is essential. The explanation will help ensure everyone knows how things operate and who to approach for assistance or inquiries.
9. Present your financial projections
The financial section of your business plan is crucial. Regardless of how great your business idea is, its success ultimately hinges on its economic well-being. People want assurance that your business is financially stable for the long run.
In this part of your business plan, you should explain how your business will make enough money to repay loans or provide investors with a satisfactory return. The level of detail required depends on your audience and goals. Still, generally, you should include three main financial views: an income statement, a balance sheet, and a cash flow statement.
It’s also a good idea to include financial data and projections. Accuracy is vital, so thoroughly review your past financial statements before making projections. Your goals should be ambitious yet attainable.
Why do you need a business plan?
Benjamin Franklin wisely stated , “If you don’t make a plan, you’re setting yourself up to fail.” Franklin’s quote means that success usually doesn’t happen by luck alone but by carefully thinking and organizing your actions.
Some entrepreneurs might think they don’t need a business plan. Still, Franklin’s words remind us that having a plan, setting goals, and thinking about possible challenges can significantly boost your chances of reaching your goals. Even the best business ideas won’t succeed without a well-thought-out strategy to make them a reality.
Here are some reasons why business owners should use a business plan:
To secure funding
A strong business plan is crucial for attracting funding from investors or lenders. Research from Palo Alto Software demonstrates its significance.
They studied 2,877 entrepreneurs, revealing that those with business plans had twice the chance of securing funding. Among the 995 entrepreneurs with business plans, 30% secured loans, 28% secured investment capital, and 50% grew their businesses. In contrast, of the 1,882 entrepreneurs without plans, only 12% secured loans, 12% secured investment capital, and 27% increased their businesses.
The point is this: A good plan isn’t just about explaining your business to investors and showing them your vision. It’s also about proving that you’ve thought deeply about your business, its challenges, and the nuts and bolts of how it will make money. Just talking about your idea isn’t enough; a solid business plan shows your dedication and a clear strategy for success.
To guide decision-making
Many small businesses don’t make it past five years , but a good business plan can help change that. Think of a business plan as your business’s roadmap. It’s like having a guide that enables you to make wise choices when dealing with decisions or problems.
A business plan is essential for entrepreneurs. It’s not just about money. It’s also about running your business, working with your team, using technology, and keeping your customers happy. When you have a business plan, you can think ahead and solve problems before they become significant. It keeps your business on track with your goals.
Business plans are also helpful when you start working with new partners. A potential partner may want to see your business plan. Partnering takes time and money. A good outline can attract the right partners for your new business.
To secure better talent
Bringing in talented people and partners is crucial to make your business successful. A business plan plays a significant role in attracting talent at the right time. People who might work for your company want to know your goals, how you plan to achieve them, and how they can help.
Whether you need experienced leaders or skilled workers, a strong business plan can help you get the best people. It can also keep them motivated and committed to your business for a long time. Within it, you’ll introduce your leadership team and list the jobs you need to fill now and in the future.
To be more adaptable
Business changes quickly. Product features evolve, new competitors show up, and the economy can shift. That’s why a business plan should be flexible. Having a plan makes adapting to market changes, customer needs, and industry trends easier.
To keep your plan flexible, you can include a risk assessment . Many big companies do this, but it’s crucial for new businesses too. You don’t have to cover every single possibility. Instead, show that you can handle changes as they come. Also, have regular check-ins to ensure your business is still going in the direction you originally planned.
To communicate better
A business plan is a unique tool that helps you talk to your team about your business dreams and plans. It ensures everyone in your group understands what you want to achieve and keeps everyone focused on the same goals. This way, everyone works together towards the same targets, making your business more robust and thriving.
Furthermore, your team can rely on the business plan as a guide . It is designed to assist your team in your absence or when they require assistance. Ensure your staff understands that if they ever feel unsure, they can turn to the business plan to figure out what to do next, especially if they can’t reach you for an immediate answer.
The many different types of business plans
Now that we’ve discussed the importance of having a business plan and its various purposes let’s delve into the diverse types of business plans you can use. These different types cater to specific needs and situations, allowing you to tailor your planning approach to suit your business goals and circumstances. Let’s explore these variations to determine which fits your unique business scenario.
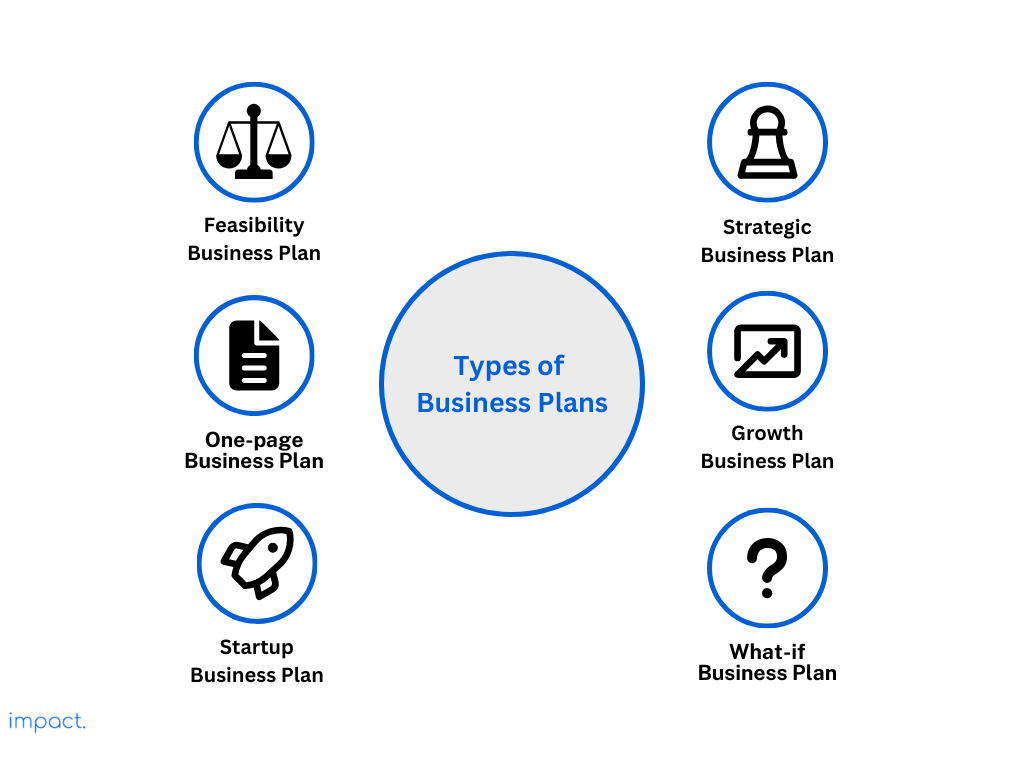
One-page business plan
You’ve got your detailed business plan, but sometimes, you need a shorter version to share with key stakeholders. That’s where the one-page business plan comes in. It’s a condensed version of your regular business plan, but it fits on just one page. It’s quick to read and gives the main info about your business idea and strategy.
Think of it as a mix between a business plan and a quick elevator pitch. Even though it’s short, it should still cover all the essential information from your entire business plan.
Here are some specific scenarios where a one-page business plan can be beneficial:
- Startup pitch to investors
- Business idea validation
- Internal planning
- Networking events
- Initial business planning
- Quick updates on the business
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is like a detailed roadmap for your new business idea. It does two main things:
1. Inside Help: It guides you and your team on how to start the business and get results from day one.
2. Outside Help: It shows banks and investors that your business idea is solid.
These plans can be pretty long, and that’s a good thing for investors — they like to see all the details. This type is popular in the tech industry. It focuses on getting a minimum viable product (MVP) first and then growing from there.
Here are the specific needs and situations where a startup business plan is applicable:
- Securing funding
- Business Validation
- Business development
- Team alignment
- Strategic planning
- Exit strategy
- Communication tool
Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a detailed document that maps out what your organization aims to achieve long-term and how it plans to get there. It acts as your roadmap, guiding your company’s decisions and actions for the next three to five years.
You’ll use this plan to ensure everyone in your organization, including your employees and internal teams, understand your company’s mission, vision, and future objectives. Your strategic plan should balance giving you a broad view of where your business will go and providing enough specifics to help you reach your goals effectively.
Here are the specific needs and situations where this business plan is applicable:
- Long term planning
- Goal alignment
- Growth and expansion
- Decision-making
- Performance measurement
Feasibility business plan
A feasibility business plan is like a decision-making guide. It helps you figure out if your business idea will work or not. These plans are usually used within a company and aim to answer two simple questions: Is there a market for your vision, and can you make money from it?
Unlike startup business plans, feasibility plans are shorter and more to the point. You don’t need to include big-picture ideas about your company. Instead, you concentrate on checking if your idea is doable and profitable.
- When going to a new venture
- New product or service launch
- Business expansion
Growth business plan
A growth business plan, or an expansion plan, is a roadmap for established companies to increase their market presence, revenue, and profitability over a specific period. It outlines the steps to achieve this growth, including the resources needed, such as funding, materials, staff, or additional facilities.
Unlike a startup plan, a growth plan is tailored for existing businesses looking to capitalize on opportunities and enhance their operations. However, similar to a startup plan, a growth business plan should be comprehensive, especially when the readers may not be familiar with your company.
- Increased market share
- Diversification
- Acquisitions
- Scaling operations
- Exit planning
What-if business plan
A “What-If” business plan is a tool for preparing your business for unexpected situations. Instead of sticking to a single strategy, it looks at different “what-if” scenarios and how your business would handle them.
For example, if you run a restaurant, you can create a plan to see how your business would deal with a public health emergency like the COVID-19 pandemic. The plan helps you come up with strategies to minimize the impact.
You can use this plan within your team to get everyone ready and share it with banks and partners to show them that your business is ready for tough times. It’s a way to be better prepared and more resilient.
- Expansion to a new market
- Product diversification
- Market fluctuations
- Regulatory changes
- Technology advancements
Read more: Business Model Canvas: 9 Components to Map Startup Success
Creating a solid business plan is essential to your entrepreneurial journey, whether launching a new retail venture or aiming to take your existing business to the next level. Your business plan acts as your guiding compass, helping you navigate the complexities of the business world with clarity and purpose.
From defining your company’s goals and market analysis to detailing your financial projections, each step contributes to your enterprise’s overall success and sustainability.
The next chapter will explore another critical aspect of setting up your store location. Choosing the right site can significantly impact your retail business’s visibility, foot traffic, and overall success.

Impact Insight Team
Impact Insights Team is a group of professionals comprising individuals with expertise and experience in various aspects of business. Together, we are committed to providing in-depth insights and valuable understanding on a variety of business-related topics & industry trends to help companies achieve their goals.

Subscribe to our blogs
Stay up-to-date with our daily blog posts. Subscribe now and join our community of avid learners and experts!
Related Articles
Get more insights

Developing a Successful YouTube Marketing Strategy in 2024
Overview YouTube is where creators and businesses thrive, reaching audiences worldwide through captivating videos, the…
Sean Thobias

Using Instagram Marketing to Boost Brand Performance in 2024
Overview In today’s digital world, social media is critical for marketers. Among these platforms, Instagram…

Using LinkedIn Marketing to Maximize Your Reach in 2024
Overview In our last piece, we discussed how to market well on Facebook, sharing tips…
Have a chat with us!
Contact us to get complete ERP features comparison of top 7 ERP systems in Indonesia.

How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated March 18, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information you need to cover in a business plan sometimes isn’t quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
If you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template to get you started, download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

6 Min. Read
How to Get and Show Initial Traction for Your Business
How to Write Your Business Plan Cover Page + Template

8 Min. Read
How to Forecast Personnel Costs in 3 Steps

5 Min. Read
How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Accessibility Quick Links
- Skip to Online Banking
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Navigation
Are you sure you want to delete this saved card number?
- CIBC Advice Centre
- Smart Business Advice
- The Dos and Don’ts of Writing a Solid Business Plan
Business Plans 201: The dos and don’ts of writing a solid business plan

We get it. That new business or venture that you’ve been dreaming about can be nerve-racking, but it’s possible.
Starting a new business starts with an idea which comes to life with a strong business plan. Your business plan is more than a piece of paper or a writing exercise. It’s a roadmap that will keep you focused and give you a baseline for measuring success and achieving your goals.
It isn’t a fixed or final artifact. Instead, think of it as a living document that you’ll revisit, learn from and adjust as your business grows.
Writing your plan at first may take a lot of effort and it’s normal to go through several drafts. Consult your advisory team as they can support your plan’s development. And your plan will develop as you get new ideas, make new decisions and learn about changing business developments.
Your plan is also key to unlocking funding. Whether you finance your business or solicit investors, either party will want to learn more about your plan before they invest. Effective language is key to communicating your business plan successfully to potential investors.
Follow these guidelines to start writing a solid business plan that communicates your vision and speaks to your audience.
The “dos” for writing a solid business plan
Be professional yet simple.
Writing with a professional tone allows investors to appreciate your vision and understand your short- and long-term goals. At the same time, it’s best to write in a simple manner. Aim for your plan to be understood by a non-expert. Replace jargon with active verbs. You can always get your final draft edited by a professional.
Refer to your business in third person
Writing in third person allows objectivity which can be more convincing and accepted by audiences like banks and investors. Avoid using “we” or “I” throughout your business plan. Writing in first person may come across as too personal. Remember to keep it business, not personal.
Be direct throughout your plan. Avoid ambiguous or vague language. Being direct allows you to be convincing about the steps you’ll take to bring your idea to life.
Supply evidence
Do your research and present data to support your case. Showing statistics about your business, competitors, customers and industry allows investors to get a bigger picture of the survival and growth of your business.
Be realistic
Avoid adding assumptions in your business plan. Instead of over-promising, show solid data backed up by research on how your business can be successful.
Practice makes perfect
Read your business plan out loud. Ask yourself these questions: Does it sound effective? Does it have the tone of confidence? Is it easily understood by your audience? What are the strengths and opportunities to tackle in your plan? Have a friend read your plan and summarize it back to you .
Be optimistic
The language of your business plan should be assertive, yet optimistic. Allow your passion to shine through in your business plan and show your advisor that you’re serious about bringing your vision to life.
The “don’ts ” of writing your business plan
Avoid acronyms and abbreviations.
Use industry specific abbreviations and acronyms only if necessary and if they’re part of your business operations.
Don’t assume the reader knows your industry
Investors and advisors are here to support you. Allow them to understand what industry your business lives in. Provide in-depth knowledge of your industry so they can understand your business functions.
Don’t turn it into an essay
When writing your business plan and conducting industry research, sometimes it’s easy to get sidetracked and turn your plan into an essay. Make sure your business plan has a solid focus and includes all the required information.
Avoid extensive research
Use only credible sources and findings for your research and analysis. It’s a great practice to use government-issued statistics and data. Use this data in your own language for business projections and goals. Simplicity is key.
Don’t be repetitive
Avoid repeating yourself throughout the plan. You can do this by reading your plan out loud and removing duplicate ideas. Include the key points and messages you need to relay.
Don’t forget about it
Be proactive and don’t forget to follow up with your advisor within the right time frame. Communicate with your advisory team and take advantage of your relationships with your investors, business partners and CIBC business advisor.
Updating your business plan on a quarterly basis is a great practice for staying on track of your business growth. Our team is here to support you as you develop your plan and assemble your team.
To create a tailored plan for your business needs and help you achieve your goals, meet with us opens in a new window. . We’re here to help. Talk to a CIBC Business Advisor today by calling 1-866-992-7223 . Opens your phone app.

Written By Lauren Rabindranath
Lauren Rabindranath is a copywriter and communications consultant based in Toronto, Ontario, who works with clients across industries. Working with CIBC Business Banking, Lauren supports content development for online platforms, relating her personal experience as an entrepreneur to CIBC’s tailored services.
Connect with a business banking expert on your schedule or in your community.
Telephone Banking: 1-800-465-2422 Opens your phone app. | Contact us Opens in a new window.
- English United States English. Opens in a new window.
Please note: Multilanguage sites do not provide full access to all content on CIBC.com. The full CIBC website is available in English and French.
Plan Smarter, Grow Faster:
25% Off Annual Plans! Save Now

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
What Is a Business Plan? Definition and Planning Essentials Explained
Posted february 21, 2022 by kody wirth.

What is a business plan? It’s the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you’ll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance.
A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. It’s more than just a stack of paper and can be one of your most effective tools as a business owner.
Let’s explore the basics of business planning, the structure of a traditional plan, your planning options, and how you can use your plan to succeed.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that explains how your business operates. It summarizes your business structure, objectives, milestones, and financial performance. Again, it’s a guide that helps you, and anyone else, better understand how your business will succeed.
Why do you need a business plan?
The primary purpose of a business plan is to help you understand the direction of your business and the steps it will take to get there. Having a solid business plan can help you grow up to 30% faster and according to our own 2021 Small Business research working on a business plan increases confidence regarding business health—even in the midst of a crisis.
These benefits are directly connected to how writing a business plan makes you more informed and better prepares you for entrepreneurship. It helps you reduce risk and avoid pursuing potentially poor ideas. You’ll also be able to more easily uncover your business’s potential. By regularly returning to your plan you can understand what parts of your strategy are working and those that are not.
That just scratches the surface for why having a plan is valuable. Check out our full write-up for fifteen more reasons why you need a business plan .
What can you do with your plan?
So what can you do with a business plan once you’ve created it? It can be all too easy to write a plan and just let it be. Here are just a few ways you can leverage your plan to benefit your business.
Test an idea
Writing a plan isn’t just for those that are ready to start a business. It’s just as valuable for those that have an idea and want to determine if it’s actually possible or not. By writing a plan to explore the validity of an idea, you are working through the process of understanding what it would take to be successful.
The market and competitive research alone can tell you a lot about your idea. Is the marketplace too crowded? Is the solution you have in mind not really needed? Add in the exploration of milestones, potential expenses, and the sales needed to attain profitability and you can paint a pretty clear picture of the potential of your business.
Document your strategy and goals
For those starting or managing a business understanding where you’re going and how you’re going to get there are vital. Writing your plan helps you do that. It ensures that you are considering all aspects of your business, know what milestones you need to hit, and can effectively make adjustments if that doesn’t happen.
With a plan in place, you’ll have an idea of where you want your business to go as well as how you’ve performed in the past. This alone better prepares you to take on challenges, review what you’ve done before, and make the right adjustments.
Pursue funding
Even if you do not intend to pursue funding right away, having a business plan will prepare you for it. It will ensure that you have all of the information necessary to submit a loan application and pitch to investors. So, rather than scrambling to gather documentation and write a cohesive plan once it’s relevant, you can instead keep your plan up-to-date and attempt to attain funding. Just add a use of funds report to your financial plan and you’ll be ready to go.
The benefits of having a plan don’t stop there. You can then use your business plan to help you manage the funding you receive. You’ll not only be able to easily track and forecast how you’ll use your funds but easily report on how it’s been used.
Better manage your business
A solid business plan isn’t meant to be something you do once and forget about. Instead, it should be a useful tool that you can regularly use to analyze performance, make strategic decisions, and anticipate future scenarios. It’s a document that you should regularly update and adjust as you go to better fit the actual state of your business.
Doing so makes it easier to understand what’s working and what’s not. It helps you understand if you’re truly reaching your goals or if you need to make further adjustments. Having your plan in place makes that process quicker, more informative, and leaves you with far more time to actually spend running your business.
What should your business plan include?
The content and structure of your business plan should include anything that will help you use it effectively. That being said, there are some key elements that you should cover and that investors will expect to see.
Executive summary
The executive summary is a simple overview of your business and your overall plan. It should serve as a standalone document that provides enough detail for anyone—including yourself, team members, or investors—to fully understand your business strategy. Make sure to cover the problem you’re solving, a description of your product or service, your target market, organizational structure, a financial summary, and any necessary funding requirements.
This will be the first part of your plan but it’s easiest to write it after you’ve created your full plan.
Products & Services
When describing your products or services, you need to start by outlining the problem you’re solving and why what you offer is valuable. This is where you’ll also address current competition in the market and any competitive advantages your products or services bring to the table. Lastly, be sure to outline the steps or milestones that you’ll need to hit to successfully launch your business. If you’ve already hit some initial milestones, like taking pre-orders or early funding, be sure to include it here to further prove the validity of your business.
Market analysis
A market analysis is a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current market you’re entering or competing in. It helps you understand the overall state and potential of the industry, who your ideal customers are, the positioning of your competition, and how you intend to position your own business. This helps you better explore the long-term trends of the market, what challenges to expect, and how you will need to initially introduce and even price your products or services.
Check out our full guide for how to conduct a market analysis in just four easy steps .
Marketing & sales
Here you detail how you intend to reach your target market. This includes your sales activities, general pricing plan, and the beginnings of your marketing strategy. If you have any branding elements, sample marketing campaigns, or messaging available—this is the place to add it.
Additionally, it may be wise to include a SWOT analysis that demonstrates your business or specific product/service position. This will showcase how you intend to leverage sales and marketing channels to deal with competitive threats and take advantage of any opportunities.
Check out our full write-up to learn how to create a cohesive marketing strategy for your business.
Organization & management
This section addresses the legal structure of your business, your current team, and any gaps that need to be filled. Depending on your business type and longevity, you’ll also need to include your location, ownership information, and business history. Basically, add any information that helps explain your organizational structure and how you operate. This section is particularly important for pitching to investors but should be included even if attempted funding is not in your immediate future.
Financial projections
Possibly the most important piece of your plan, your financials section is vital for showcasing the viability of your business. It also helps you establish a baseline to measure against and makes it easier to make ongoing strategic decisions as your business grows. This may seem complex on the surface, but it can be far easier than you think.
Focus on building solid forecasts, keep your categories simple, and lean on assumptions. You can always return to this section to add more details and refine your financial statements as you operate.
Here are the statements you should include in your financial plan:
- Sales and revenue projections
- Profit and loss statement
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
The appendix is where you add additional detail, documentation, or extended notes that support the other sections of your plan. Don’t worry about adding this section at first and only add documentation that you think will be beneficial for anyone reading your plan.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. So, to get the most out of your plan, it’s best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you’ll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. We recommend only starting with this business plan format if you plan to immediately pursue funding and already have a solid handle on your business information.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear structure in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It’s faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations. This is really best for those exploring their business idea for the first time, but keep in mind that it can be difficult to actually validate your idea this way as well as adapt it into a full plan.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan. This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. It basically serves as a beefed-up pitch document and can be finished as quickly as the business model canvas.
By starting with a one-page plan, you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan. This plan type is useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Now, the option that we here at LivePlan recommend is the Lean Plan . This is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27-minutes . However, it’s even easier to convert into a full plan thanks to how heavily it’s tied to your financials. The overall goal of Lean Planning isn’t to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the Lean Planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and stable through times of crisis.
It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Try the LivePlan Method for Lean Business Planning
Now that you know the basics of business planning, it’s time to get started. Again we recommend leveraging a Lean Plan for a faster, easier, and far more useful planning process.
To get familiar with the Lean Plan format, you can download our free Lean Plan template . However, if you want to elevate your ability to create and use your lean plan even further, you may want to explore LivePlan.
It features step-by-step guidance that ensures you cover everything necessary while reducing the time spent on formatting and presenting. You’ll also gain access to financial forecasting tools that propel you through the process. Finally, it will transform your plan into a management tool that will help you easily compare your forecasts to your actual results.
Check out how LivePlan streamlines Lean Planning by downloading our Kickstart Your Business ebook .
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Posted in Business Plan Writing
Join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
- Auto Insurance Best Car Insurance Cheapest Car Insurance Compare Car Insurance Quotes Best Car Insurance For Young Drivers Best Auto & Home Bundles Cheapest Cars To Insure
- Home Insurance Best Home Insurance Best Renters Insurance Cheapest Homeowners Insurance Types Of Homeowners Insurance
- Life Insurance Best Life Insurance Best Term Life Insurance Best Senior Life Insurance Best Whole Life Insurance Best No Exam Life Insurance
- Pet Insurance Best Pet Insurance Cheap Pet Insurance Pet Insurance Costs Compare Pet Insurance Quotes
- Travel Insurance Best Travel Insurance Cancel For Any Reason Travel Insurance Best Cruise Travel Insurance Best Senior Travel Insurance
- Health Insurance Best Health Insurance Plans Best Affordable Health Insurance Best Dental Insurance Best Vision Insurance Best Disability Insurance
- Credit Cards Best Credit Cards 2024 Best Balance Transfer Credit Cards Best Rewards Credit Cards Best Cash Back Credit Cards Best Travel Rewards Credit Cards Best 0% APR Credit Cards Best Business Credit Cards Best Credit Cards for Startups Best Credit Cards For Bad Credit Best Cards for Students without Credit
- Credit Card Reviews Chase Sapphire Preferred Wells Fargo Active Cash® Chase Sapphire Reserve Citi Double Cash Citi Diamond Preferred Chase Ink Business Unlimited American Express Blue Business Plus
- Credit Card by Issuer Best Chase Credit Cards Best American Express Credit Cards Best Bank of America Credit Cards Best Visa Credit Cards
- Credit Score Best Credit Monitoring Services Best Identity Theft Protection
- CDs Best CD Rates Best No Penalty CDs Best Jumbo CD Rates Best 3 Month CD Rates Best 6 Month CD Rates Best 9 Month CD Rates Best 1 Year CD Rates Best 2 Year CD Rates Best 5 Year CD Rates
- Checking Best High-Yield Checking Accounts Best Checking Accounts Best No Fee Checking Accounts Best Teen Checking Accounts Best Student Checking Accounts Best Joint Checking Accounts Best Business Checking Accounts Best Free Checking Accounts
- Savings Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Best Free No-Fee Savings Accounts Simple Savings Calculator Monthly Budget Calculator: 50/30/20
- Mortgages Best Mortgage Lenders Best Online Mortgage Lenders Current Mortgage Rates Best HELOC Rates Best Mortgage Refinance Lenders Best Home Equity Loan Lenders Best VA Mortgage Lenders Mortgage Refinance Rates Mortgage Interest Rate Forecast
- Personal Loans Best Personal Loans Best Debt Consolidation Loans Best Emergency Loans Best Home Improvement Loans Best Bad Credit Loans Best Installment Loans For Bad Credit Best Personal Loans For Fair Credit Best Low Interest Personal Loans
- Student Loans Best Student Loans Best Student Loan Refinance Best Student Loans for Bad or No Credit Best Low-Interest Student Loans
- Business Loans Best Business Loans Best Business Lines of Credit Apply For A Business Loan Business Loan vs. Business Line Of Credit What Is An SBA Loan?
- Investing Best Online Brokers Top 10 Cryptocurrencies Best Low-Risk Investments Best Cheap Stocks To Buy Now Best S&P 500 Index Funds Best Stocks For Beginners How To Make Money From Investing In Stocks
- Retirement Best Gold IRAs Best Investments for a Roth IRA Best Bitcoin IRAs Protecting Your 401(k) In a Recession Types of IRAs Roth vs Traditional IRA How To Open A Roth IRA
- Business Formation Best LLC Services Best Registered Agent Services How To Start An LLC How To Start A Business
- Web Design & Hosting Best Website Builders Best E-commerce Platforms Best Domain Registrar
- HR & Payroll Best Payroll Software Best HR Software Best HRIS Systems Best Recruiting Software Best Applicant Tracking Systems
- Payment Processing Best Credit Card Processing Companies Best POS Systems Best Merchant Services Best Credit Card Readers How To Accept Credit Cards
- More Business Solutions Best VPNs Best VoIP Services Best Project Management Software Best CRM Software Best Accounting Software
- Manage Topics
- Investigations
- Visual Explainers
- Newsletters
- Abortion news
- Coronavirus
- Climate Change
- Vertical Storytelling
- Corrections Policy
- College Football
- High School Sports
- H.S. Sports Awards
- Sports Betting
- College Basketball (M)
- College Basketball (W)
- For The Win
- Sports Pulse
- Weekly Pulse
- Buy Tickets
- Sports Seriously
- Sports+ States
- Celebrities
- Entertainment This!
- Celebrity Deaths
- American Influencer Awards
- Women of the Century
- Problem Solved
- Personal Finance
- Small Business
- Consumer Recalls
- Video Games
- Product Reviews
- Destinations
- Airline News
- Experience America
- Today's Debate
- Suzette Hackney
- Policing the USA
- Meet the Editorial Board
- How to Submit Content
- Hidden Common Ground
- Race in America
Personal Loans
Best Personal Loans
Auto Insurance
Best Auto Insurance
Best High-Yields Savings Accounts
CREDIT CARDS
Best Credit Cards
Advertiser Disclosure
Blueprint is an independent, advertising-supported comparison service focused on helping readers make smarter decisions. We receive compensation from the companies that advertise on Blueprint which may impact how and where products appear on this site. The compensation we receive from advertisers does not influence the recommendations or advice our editorial team provides in our articles or otherwise impact any of the editorial content on Blueprint. Blueprint does not include all companies, products or offers that may be available to you within the market. A list of selected affiliate partners is available here .
How to write a business plan in 9 steps
Robert Bruce

Bryce Colburn
“Verified by an expert” means that this article has been thoroughly reviewed and evaluated for accuracy.
Published 7:54 a.m. UTC Jan. 2, 2024
- path]:fill-[#49619B]" alt="Facebook" width="18" height="18" viewBox="0 0 18 18" fill="none" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
- path]:fill-[#202020]" alt="Email" width="19" height="14" viewBox="0 0 19 14" fill="none" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
Editorial Note: Blueprint may earn a commission from affiliate partner links featured here on our site. This commission does not influence our editors' opinions or evaluations. Please view our full advertiser disclosure policy .

andresr, Getty Images
Starting a business is a risky venture.
Even the smartest of entrepreneurs have many questions to consider as they develop and execute their business idea. One of the best outlets for creating a successful company is having a business plan in place before you launch on day one.
A solid business plan will provide a game plan for your company, both now and in the future. It should guide all of your decisions and allow you to navigate difficult times by providing a resource by which you operate and strategize.
A business plan is a vital part of any successful company.
Featured registered agent service offers
Zenbusiness.

Via ZenBusiness’ website
$199 annually
Same-day document delivery
Phone support

Via LegalZoom’s website
Northwest Registered Agent

Via Northwest Registered Agent’s website
What is a business plan?
A business plan is simply an outline of a company’s future goals and how it plans to achieve those goals. A solid business plan will guide a company’s strategy and decision-making and help it navigate through any unforeseen obstacles.
Companies of all sizes can benefit from a business plan. Smaller-sized companies can use this plan to develop a strategy for growth, development and investor strategy. Larger, more established companies can use a business plan to expand, explore other profit possibilities and stay on track with its original vision.
Business plans are also important when it comes to funding, as many investors will want to see your plan before funding your project or company.
How to write a business plan
One of the most important parts of writing a business plan is the realization you need one in the first place. If that’s you, congratulations on overcoming that initial obstacle.
Now that you understand why a business plan is important let’s take a look at the steps you’ll need to follow to create a successful one.
1. Write an executive summary
Think of your executive summary as a Cliffs Notes for your business plan. This summary will condense the entire business plan that follows into one easy-to-follow package. It should contain all the highlights while giving a solid overview of the entire plan.
The plan should also briefly offer key company information, such as business goals and vision, product descriptions, marketing strategy and current financials — as well as other relevant information like leadership, employees and location.
In addition to offering a brief overview of your business strategy, the executive summary is a useful tool to give to potential investors who might not have the time to read the entire plan.
2. Draft a company description
This section simply covers the basics of your company — what you do, how you separate yourself in your industry, what makes the services and/or products you provide worthwhile and why your company would be a smart investment.
You should also include information like your business’s mission statement, its structure, short- and long-term goals, business history and other similar facts. This is also a good place to list your company’s core values.
A lot of these issues should be well thought out before you draft a company description or business plan. By this point, you should be able to easily articulate all of this. If not, take a breath and meet with your team to go back through this to make sure you have all your bases covered.
3. Include a description of your products and services
This is where you outline what you sell and why your target market should care. You should outline key specs like price, size and material quality. If you provide a service, you should offer information about availability, quality and durability.
Give a brief overview of the multiple products you offer, as well as those that are a part of your future plans.

4. Consider your company goals and objectives
You’ve already briefly mentioned your goals and objectives in prior sections, but this section allows you to go a little more in-depth.
Here, expand on your mission statement and why it’s important to your company. You might talk about the thought process behind the statement and how it came to be. Who was involved in crafting it, and what were the important elements they wanted to include?
Then, begin going more in-depth on your specific business goals — both short-term and long-term. What are some of your priorities for the next year? Five years? Decade? Listing out these objectives shows you not only have a good grasp of your company’s current situation but also of where it is headed.
5. Perform market research and competitor analysis
Performing market research and competitive analysis is an extremely important part of your business plan. Getting familiar with other businesses in your market will help you see what works and what doesn’t.
You should be able to list out the size of your market and who might be interested in your products or services, how you fit into that market and what other competitors are doing. Along those lines, what is your brand’s differentiation with that market — what sets you apart?
Knowing your market and how you approach it strategically can make or break your business.
6. Create a marketing plan
Who is your ideal customer? And, strategically, how do you plan on reaching them? This is the foundation of your marketing plan.
How much money and effort do you plan on putting into marketing, or will you rely more heavily on sales? With your marketing, this is where you’ll outline the platforms you plan on using to reach your audience — whether that’s through social media, online ads, television or radio commercials.
Ultimately, this section will provide the details on your product or service, how much it will cost, how you plan to promote it and where you plan on selling it.
7. Define your operating procedures
This section explains the framework of your organization and how you operate.
You’ll outline your leadership structure with an organizational chart if you have one. Explain some of the key members of your team and how they make your business run successfully. You might consider including resumes or CVs.
This is where you’ll lay out the legal structure of your company as well. Do you plan on incorporating, or are you a limited liability company (LLC) or sole proprietor ?
In terms of operations, outline who your suppliers will be, how your production process will work, which facilities and equipment you’ll use to develop your products, how you plan on shipping and the amount of inventory you’ll keep on hand.
8. Create a financial plan
Obviously, your financials are the backbone of your business. With a solid financial plan, your company will thrive. Without one, it may whither. The basics of your financial plan will include a balance sheet, income statement and cash-flow statement.
The balance sheet shows your total assets and liabilities. The income statement will show your revenue and expenses — the two main factors that ultimately reveal your business’s profit or loss. The cash-flow statement shows how much cash your business will have available at any given time — based on when you pay your bills and deposit revenue.
9. Set a timeline for progress and goals
In this section, you’ll set the timeline for your company’s progress. You’ll break down different milestones and when you expect to reach them, as well as what progress will look like for your business.
Be specific. List out the exact amount of profit you hope to have over a certain time frame. This should be as detailed as possible. So when writing out your goals, don’t use generalized phrases like “increase revenue.” Instead, go into the specifics of those goals.
Additional business planning resources
In addition to a business plan, you definitely want to make sure you have other aspects of your business covered. Some business planning topics to think about include:
- Business structures: Starting out, will you form your business structure as a limited liability company (LLC), which protects you from your company’s debts and liabilities in the event of a lawsuit? Or are you forming a partnership or sole proprietorship ?
- Business licenses: Most businesses will require a business license , which may be needed at the county, state and federal level, depending on the type of business you operate.
- Business taxes: The type of business you have will dictate how you pay taxes. You may be required to pay income tax, payroll tax, self-employment tax, employment taxes and excise tax.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
You don’t necessarily need a business plan to start your business, but creating one will put you at a great advantage.
A business plan communicates your vision and mission to your company as well as potential investors. It also allows you to get buy-in from your current employees and how you plan to build your business into the future.
A solid business plan will include the following:
- Executive summary: A quick overview of the entire business plan.
- Company description: A description of your company and what it does.
- Products and services description: A description of the products and services your company offers.
- Company goals and objectives: An outline of your company’s future goals.
- Market research: Who are your competitors and how do you fit into the industry?
- Marketing plan: Details about how you plan to reach your ideal customer.
- Operating procedures: Outline the framework of your organization and how it operates.
- Financial plan: Provide details about your balance sheet, income statement and cash-flow statement.
- Progress and goals: A breakdown of company milestones and your timeline for reaching them.
A business plan allows you to precisely define the basic information and values of your company, as well as its viability, vision, mission, marketing strategy and future goals. A solid plan will outline all the above while explaining, in detail, how you plan to make these ideas a reality.
Blueprint is an independent publisher and comparison service, not an investment advisor. The information provided is for educational purposes only and we encourage you to seek personalized advice from qualified professionals regarding specific financial decisions. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
Blueprint has an advertiser disclosure policy . The opinions, analyses, reviews or recommendations expressed in this article are those of the Blueprint editorial staff alone. Blueprint adheres to strict editorial integrity standards. The information is accurate as of the publish date, but always check the provider’s website for the most current information.

Robert Bruce has been a full-time writer for nearly 20 years. His work has been featured in US News & World Report, Yahoo Finance, The Penny Hoarder, The Money Manual, WGN Chicago, Nashville Lifestyles Magazine, among others.
Bryce Colburn is a USA TODAY Blueprint small business editor with a history of helping startups and small firms nationwide grow their business. He has worked as a freelance writer, digital marketing professional and business-to-business (B2B) editor at U.S. News and World Report, gaining a strong understanding of the challenges businesses face. Bryce is enthusiastic about helping businesses make the best decisions for their company and specializes in reviewing business software and services. His expertise includes topics such as credit card processing companies, payroll software, company formation services and virtual private networks (VPNs).

How to start a small business: A step-by-step guide
Business Eric Rosenberg
- Entrepreneurship

The Ultimate Guide to Developing a Solid Business Plan
Starting a business can be a daunting task, but developing a solid business plan can help you navigate the process with confidence. A business plan is essentially a roadmap that outlines your business goals, strategies, and financial projections. It’s a crucial document that can help you secure funding, attract investors, and stay on track as you grow your business. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the process of developing a solid business plan, step-by-step.
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is the first section of your business plan and is often considered the most important. This section should provide a brief overview of your business, including its mission, products/services, target market, and financial projections. It should also highlight what makes your business unique and why it’s likely to succeed.
In this section, you should also include a summary of your management team and any key personnel, as well as information about your funding needs and how you plan to use the funds. Be sure to keep this section concise and engaging, as it’s often the first thing potential investors will read.
2. Company Description
The company description section provides a more detailed overview of your business and its history. This section should cover your company’s legal structure, location, and any key milestones you’ve achieved thus far.
You should also include information about your target market, including demographics, psychographics, and any relevant trends or market research. This section should also cover your products or services and how they meet the needs of your target market.
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should provide a detailed analysis of your industry and competitors. This section should cover the size of your industry, any relevant trends, and your target market’s needs and preferences.
You should also provide an overview of your competitors, including their strengths and weaknesses. This section should also detail any barriers to entry and potential threats to your business.
4. Products and Services
The products and services section should provide a detailed overview of what your business offers. This section should cover the features and benefits of your products or services, as well as any unique selling points.
You should also include information about your pricing strategy and how it compares to your competitors. Be sure to highlight any intellectual property or proprietary technology that sets your products or services apart.
5. Marketing and Sales Strategies
The marketing and sales strategies section should detail how you plan to reach and attract customers. This section should cover your advertising and promotional strategies, as well as your sales channels and tactics.
You should also include information about your sales team and any relevant training or support. Be sure to highlight any partnerships or collaborations that could help you reach your target market.
6. Management and Personnel
The management and personnel section should provide an overview of your team and their roles and responsibilities. This section should cover your management structure, any key personnel, and any relevant experience or qualifications.
You should also include information about your hiring and training processes, as well as any relevant policies or procedures. Be sure to highlight any key partnerships or collaborations that could help you attract and retain top talent.
7. Financial Projections
The financial projections section should provide a detailed overview of your business’s financials. This section should cover your revenue projections, expenses, and any relevant financial metrics.
You should also include information about your funding needs and how you plan to use the funds. Be sure to provide a detailed breakdown of your costs and revenue streams, as well as any potential risks or challenges.
8. Funding Needs
The funding needs section should provide a detailed overview of your funding needs and how you plan to secure funding. This section should cover your current funding sources, as well as any future funding needs.
You should also include information about any grants, loans, or other funding opportunities that may be available to your business. Be sure to highlight any key partnerships or collaborations that could help you secure funding.
9. Risk Assessment
The risk assessment section should detail any potential risks or challenges that your business may face. This section should cover both internal and external risks, including market trends, competition, and regulatory changes.
You should also include information about any contingency plans or risk mitigation strategies that you have in place. Be sure to highlight any key partnerships or collaborations that could help you mitigate risk.
10. Conclusion
The conclusion section should provide a summary of your business plan and reiterate your key points. This section should also provide a call to action, encouraging potential investors or partners to take action.
Be sure to highlight any key benefits or advantages of your business, as well as any potential challenges or risks. Finally, be sure to thank your readers for their time and consideration.
In conclusion, developing a solid business plan is a critical step in starting and growing a successful business. By following these steps and including relevant information in each section, you can create a professional and engaging business plan that can help you secure funding, attract investors, and stay on track as you grow your business.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is a business plan important.
A business plan is important because it helps you to define your business idea, identify your target market, understand your competition, and determine your financial projections. It is a roadmap that guides you towards success and helps you make informed decisions.
In addition, having a solid business plan can also help you secure funding from investors or lenders. It shows that you have a clear vision for your business and have thought through the potential challenges and opportunities.
What are the key components of a business plan?
The key components of a business plan include an executive summary, company description, market analysis, organization and management, products and services, marketing and sales, and financial projections.
The executive summary is a brief overview of the entire plan, while the company description provides more detailed information about the company’s history, mission, and objectives. The market analysis helps you to understand your target market and competition, while the organization and management section outlines the structure of your company and the roles and responsibilities of team members. The products and services section describes what you will offer, while the marketing and sales section outlines your strategies for reaching and selling to your target market. Finally, the financial projections provide an estimate of your revenue, expenses, and profitability.
How do I create financial projections for my business plan?
Creating financial projections for your business plan involves estimating your revenue, expenses, and profitability over a specific period of time.
Start by researching similar businesses and industry trends to get a sense of what is realistic for your business. Then, estimate your revenue based on your pricing strategy and sales projections. Next, estimate your expenses, including fixed costs (such as rent and salaries) and variable costs (such as materials and inventory). Finally, calculate your profitability by subtracting your expenses from your revenue.
It is important to be realistic and conservative in your projections, as investors and lenders will want to see that you have thought through the potential risks and challenges.
How often should I update my business plan?
Your business plan should be a living document that is updated regularly to reflect changes in your business and industry.
At a minimum, you should update your business plan annually to ensure that it is current and relevant. However, you may need to update it more frequently if you experience significant changes in your business, such as entering a new market or introducing a new product or service.
Updating your business plan can help you stay on track and adjust your strategies as needed to achieve your goals.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when developing a business plan?
Some common mistakes to avoid when developing a business plan include failing to research your market and competition, being overly optimistic in your financial projections, and not having a clear understanding of your target market.
Other mistakes include not having a solid marketing and sales strategy, underestimating the importance of team and organizational structure, and not being realistic about the potential challenges and risks.
To avoid these mistakes, take the time to thoroughly research your market and competition, seek feedback from others, and be realistic in your projections and expectations.
The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Solid Business Plan: Navigating Business Days and More
Remember, a successful business plan requires careful research, analysis, and attention to detail. It’s important to conduct market research, identify your target audience, and develop a clear marketing strategy. By doing so, you can position your business for growth and profitability.
So, whether you’re starting a new business or looking to take your existing business to the next level, a solid business plan is the foundation for success. By investing the time and effort into developing a comprehensive plan, you’ll be well on your way to achieving your goals and building a thriving business.
RELATED ARTICLES
What is sampling in marketing research, how much does it cost to do market research, how important is marketing for small business, what is the difference between market and marketing research, is a business with high cash flow good or bad, do employees hired by the federal gov, how to do marketing for your business, 10 benefits of investing in money market instruments for businesses, 10 common business goals and how to set them, 10 common financial risks faced by businesses and how to manage them, 10 common types of bonds for business financing and investments, 10 customer retention techniques to foster long-term loyalty, how can trust be gained between the business and development, software startup ideas, the dummies guide to starting your own business, how to find new businesses before they open, what must an entrepreneur assume when starting a business, editor’s choice, how to start a dairy products business, what factors can influence stock prices, how to keep your kids busy on a budget, how does an increase in productivity affect business, is a limited partnership a body corporate, stay in touch.
To be updated with all the latest news, offers and special announcements.
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use

Business Planning 101: How to Create a Solid Business Plan for Your Startup
Entrepreneurship.
- Innovation & Digital Transformation
- Sustainability
- Education & Training
- Culture & Creativity
- Social Inclusion & Human Rights
- Health & Wellbeing

Business planning is the process of creating and documenting a strategy designed to cultivate growth for your company. Most business planning techniques revolve around three primary objectives: maximizing profit, mitigating risks, and communicating a strategy to secure funding. Although there are different aspects of business planning, in most cases, business planning is centred on creating one specific document: the business plan.
No matter what industry you’re in or what products or services you’re selling, it would help if you had a business plan to guide you . Whether you’re launching an online digital marketing agency or opening a local coffee shop, your business plan is the foundation for your growth efforts. Ultimately, the time and effort you put into your business plan development can significantly impact the success or failure of your venture.
But why is a business plan so important? Couldn’t you use a website builder to launch a site within minutes or have a minimum viable product within a few days? While starting something is simple, solidifying it is not.
Startup founders don’t always see the value of a business plan, particularly when they don’t plan to raise money right away and are silk working out the cracks and kinks of their product. But regardless, think of a business plan as the bedrock for your company.
This detailed document is much more than a description of what your business does and how it does it. It can be used to secure loans and other forms of funding, solidify your milestones, help you better understand your market and competition, and outline your financial needs and feasibility. In short, it can prevent you from walking down a dead end.
Business Planning Tools
A myriad of tools and services exist to help entrepreneurs develop business plans of their own. Many companies offer their own version of a small business plan template to guide business owners through the process. However, numerous services are dedicated to helping business owners build out certain portions of their business plans. For example, business owners could outsource micro and macroeconomic research, financial planning and forecasting, and marketing agencies. Additionally, they can work alongside business plan writers to help them create a document that’s most likely to appeal to investors and lenders.
Business Plan Table of Contents
Understanding the benefits of a business plan is one thing, but writing it is entirely another. Start by checking out different industry-specific templates for inspiration. From there, follow the tried-and-true format using this table of contents.
Each section provides valuable insight into how you plan to build your business, both from a high-level overview and a detailed perspective. It’s important to note that business plans aren’t just for lenders and investors—it’s also for you. Many business owners have found that their business plans help foster accountability and guidance. With that in mind, here’s what you need to include in a winning business plan:
1. Executive Summary
2. Company Details
3. Market Analysis
4. Customer Analysis
5. Competitor Analysis
6. Marketing Plan
7. Operations & Logistics Plan
8. Management Team
9. Financial Plan
10. Appendix
Executive Summary
Your executive summary is an overview of your startup. This section provides the reader with a quick synopsis of the overall business plan. The executive summary should be written last to properly convey and summarize the contents in the rest of the document.
For example, once you’ve written a thorough analysis of your target market, it’ll better equip you to include a short synopsis of it in your summary. This section highlights the key points you’ll cover in your business plan by defining your mission and strategy.
Your executive summary should:
- Include a captivating introduction to your business
- Describe the problem your business is trying to solve
- Explain how your company offers a solution to a problem
- Describe products and services you offer
- Address how you plan on reaching your customers with your marketing efforts
- Include your projected revenue
- Introduce the team
Company Description
The Company Description section of your business plan covers three key components: who you are, what you do, and why you do it. Begin by creating an elevator pitch and then expound upon it.
For example, let’s say you’re trying to raise money for your package delivery startup, ParcelPass. Your elevator pitch might be: “Think of ParcelPass as an Uber for package deliveries. When you need something delivered locally, request a GPS-enabled vehicle through the app. ParcelPass arrives, picks it up, and hand-delivers it to its recipient.”
Remember, the company description is designed to sell. Not only does it help readers understand your mission and unique value proposition, but it can also help you practice pitching your company to others, both verbally and written.
Your company description should:
- Share your origin story
- Offer basic company history, such as location and start date
- Explain how you developed the business concept
- Include relevant industry information
- Describe your team in detail (including qualifications and background)
- Include a mission statement and vision statement
Here’s an example of a “Company Overview” introduction from Cady’s Cookies, a fictional cookie company developed by Planbuildr:

Market Analysis
Your market analysis is one of (if not the ) most important parts of your business plan because it tells the reader that you have a verifiable market. How your business performs in your industry depends on the market, and it’s crucial for you to present proof that the current (and foreseeable) market leans in your favour.
Your market/industry analysis shows how comparable businesses in your industry perform and highlights market demand. You can find plenty of free market research resources that offer relevant market data, or you can hire a market research firm to spearhead this section for you. In short, your market analysis will provide quantitative and qualitative assessments for your industry.
Your market analysis should:
- Describe customer segments in your market
- Highlight favourable buying patterns
- Explain how you intend to build brand loyalty and acquire repeat customers
- Provide an analysis of your competition
- Identify historical trends that have shaped your industry
- Include relevant statistics, including market size, market growth, and future growth estimates
Customer Analysis
Who are your customers? This is the question that the Customer Analysis section of your business plan aims to answer. This section dives deeper into your target market and addresses how you plan to solve their pain points.
These “pain points” can be versatile and multi-faceted. For example, if you own a long-distance moving company, a potential customer pain point might be finding a business that knows how to handle the fragile or expensive property. Another pain point might be finding vetted drivers with outstanding long-haul driving records.
As you write your customer analysis, consider buyer personas or ideal customers. Use this persona as a model for your written description. Describe their demographics, personality traits, buying patterns, income and education level, and hobbies.
Your customer analysis should:
- Offer a holistic overview of your ideal customer
- Describe your customers’ pain points
- Explain how you can solve your customers’ issues
- Assess customer buying patterns
- Acknowledge your proximity to your customers and how you plan to reach them
Competitor Analysis
Your competitive analysis should answer the question, “Why is my business better than other businesses that offer similar services and products?” This is where you’ll communicate how you plan to outperform your competition.
Competitor research is crucial because it explains what makes you different, helps you understand why they’re succeeding, and identifies gaps that you can leverage to build a better business .
Your competitor analysis should:
- Explain how your business differentiates itself from the competition
- Describe strengths your company offers that your competitors don’t
- Highlight key advantages in management or operations
- Illustrate issues your current competitors are having and explain how you plan to address them
Marketing Plan

Your marketing plan should explain how you intend to reach your target market. It should be determined by the specific needs of your target market, as described in your customer analysis. Overall, your marketing plan reveals how you intend to reach potential customers, build brand awareness, and educate your market.
Your marketing plan should include four key sections:
1. Products. What products or services do you offer, and what makes them better than similar offerings? Are there any particular features or benefits?
2. Promotions. How do you plan to promote your organization ? How will you spread the word and attract customers? Your promotion plan should include a detailed description of how you intend to position yourself in front of buyers. This could consist of advertising, product giveaways, influencer marketing , content, or content marketing.
3. Price. What’s the cost of your products? Justify higher prices when necessary and leverage lower prices if possible.
4. Place/Distribution. This section describes where you sell your products and how you sell them. Are you selling your product online, in a retail shop, or both? What are the benefits? If you plan to sell wholesale and direct, describe these channels as well.
Operations & Logistics Plan
Your Operations and Logistics section describes the workflows and processes you’ll implement to make your business plan come to life. Your operational objective covers several factors, including how each of your departments supports different operational goals. This section will also outline strong contingency plans in the event of unexpected circumstances. In this area, make it clear to the reader that you have a strong understanding of your supply chain.
Your operations and logistics analysis should:
- Describe who your suppliers are
- What your production process will look like
- Define key metrics and milestones
- List the necessary equipment and technology to keep your business running
- Describes your shipping and fulfilment needs
- Explain quality control measures
Management Team
The people behind your business can make or break its success. This section of your business plan describes the team in detail and explains why their qualifications and experience make them well-suited for success.
Investors aren’t just putting their dollars into products and services but the people building the brand. The calibre of your team plays a significant role in helping readers understand your business’s willingness and readiness. Lastly, this is where you’ll explain how each team member’s skill set contributes to the company’s bottom line.
Your management team section should:
- Provide biographies for key team members
- Highlight educational achievements, experience, and accomplishments
- Describe how your business ownership is structured
- List any external management resources, such as an advisory board
Financial Plan
No matter how much hard work you’ve put into growing an idea into a business, its financial welfare will be the ultimate determination of success. Your financial plan is designed to help financial investors understand what to expect now and in the foreseeable future. In short, it explains how you’ll generate income. It would be best to work with an accountant , bookkeeper , or third-party financial planner to shape this section of the business plan.
The financial plan is typically broken down into three parts:
1. Income statement. Income statements show revenue sources and expenses over a given period.
2. Balance sheet. A balance sheet reveals the equity you have in your business, considering the assets you own and the liabilities you owe.
3. Cash flow statement. The cash flow statement is what’s left when expenses are paid, and revenue is collected.
The Appendix closes out your business plan and provides supporting materials or documentation for previous sections, such as balance sheets and income statements. Essentially, this is where you put all the essential details that you didn’t include in prior areas. The appendix exists to keep the business plan concise early on so as not to bulk up the portions of the business plan where content matters most.
Your appendix should include:
- Detailed financial forecasts
- Business credit history if available
- Applicable patents or trademarks
- Management team resumes
- Market research
Writing a winning business plan is no walk in the park, but it’s important to put proper time and effort into building it out. Many great businesses fail to get funding because they miss the mark in terms of their business plan and fail to convey the viability of their company.
As you create your business plan, reference templates and actual, archived business plans. Use these as inspiration and guidance, but don’t forget to customize your plan as much as possible. You don’t want your business plan to be a copycat of everyone else’s template at the end of the day. Be original and thorough, and your plan will speak for itself.
Do you want to write for us? Read our guest post guidelines here !
VIEW ALL POSTS
7 tips to manage a high-performing and effective virtual team, disability and covid-19: a threat or benefit for disabled youth, subscribe to our mail list.
Receive our newsletter to stay on top of iEDs latest posts.
Related Posts
What is ied.

Privacy Overview

Build Your Business: Management
6 ways to create a solid business plan for 2021.
By James Andres , Contributing Writer

A good business plan serves as a critical roadmap to your destination of having a successful 2021. “Start focusing on getting the first quarter of 2021 right,” says business coach Marshall Atkinson, owner of Atkinson Consulting . “We need to head into this next year with clarity of purpose, strategic plans for the future, and the willingness to do what it takes to succeed.”
To start your year off right, you need a solid plan that you’ll refer to often. There’s an old adage that states, “Those who fail to plan, plan to fail.” There’s a lot of truth to this statement, especially after a year where it’s been difficult for shops to keep running through the chaos, much less keep running as usual.
Here’s how to create a solid business plan for the year ahead 1. Realize you need a plan. The first step in any process is knowing you have to take a step forward. This past year has probably taught you that you need a plan for what could possibly happen. While there’s no way to know what all of 2021 will bring, it’s important to have multiple contingencies in place. For example, we still don’t know how COVID-19 will continue to affect the economy, and the way people live, work and shop. Thinking through various scenarios will not only help your anxiety levels because you know you have something at the ready, but it’ll spell out actionable steps toward meeting your goals for the year and beyond.
2. Set your 2021 goals. Next, you need to set your clear, SMART goals for your business in the coming year. This means that your goals should be:
● Specific: Don’t be vague like, “I want to increase sales.” Instead, get more detailed, such as, “I want to increase sales by adding direct-to-garment (DTG) and heat-press services.” This is much more specific and beneficial to you and your team.
● Measurable: Your goal should have a finite number that you can attach to it. For instance, “I want to increase sales by 20% by adding DTG and heat-press services.” That’s a measurable goal you can aim for. “What matters most in your shop?” Atkinson says. “There’s no sense measuring something if you aren’t going to do anything with the data. The key performance Indicators you select for your shop are actually about the ‘key’ things that you need to know.”
● Achievable: This is a goal that you can reach. For example, you can purchase a DTG printer and train an operator to use it. You can market the new service to your current customers to start. The achievable part goes hand-in-hand with the next point of a SMART goal.
● Realistic: Be sure you can realistically achieve your goal. It probably doesn’t make sense to say, “I want to increase sales by 1,000% by this time next year.” Setting unrealistic goals also can hurt your team’s morale when it becomes obvious that they won’t be able to achieve it.
● Time-based: Finally, you want a goal marked by a specific time measurement. Ideally, your goal should have regular “checkpoints” to ensure you’re making progress along the way. This might mean, “I plan to increase sales by at least 5% each quarter.” With this goal, you’re building in time-sensitive checkpoints so that if you don’t reach a goal, you can work harder to make up the difference by the next one. You’ll need to regularly review your SMART goals. Schedule time every quarter to determine if your plan is moving you toward your goals and if it’s addressing the current needs of your business and customers. Also, take a close look at any other complications or issues, which may have cropped up during that time, that you didn’t anticipate. That should help you plan how you’ll tackle those potential roadblocks in the future, it also will help you recognize any warning signs you can look out for next time.
3. Get clear on your market and niche. Your next step should be to figure out exactly who you should focus your marketing efforts on to score new business. When you know who you want to serve (and how), you can target your marketing sales efforts on them. Here are some questions to ask to clearly define this:
● What’s your Unique Selling Point (USP)? ● What are your core values? ● Who do you need to employ? ● Are you thinking of introducing new decorating services or products in the future? ● What markets are you going to sell into? Expand into? ● What ways do you have to sell should lockdowns happen again? (This is especially important since we have no way of knowing what will happen with COVID-19 in the coming year.) ● Are there companies you can partner with or subcontract to? ● What’s the personality of your business and what are you trying to portray? In other words, what do you hope people will think of when they see your shop name? Value for their money? Fast turnaround? Amazing artwork and spot-on decoration? High-end products? Eco-friendly? Fun? Friendly? Trustworthy? ● What sort of things do you want your customers or social media to be saying about your business?
4. Complete an analysis of your competitors. Look closely at your nearest competitors, so you can see what they’re doing well and what weaknesses they may have for you to capitalize on. This will ensure you’re on par or better than these other companies. You want to be able to offer similar (or better) experiences, while also giving your customers uniquely decorated products and marketing strategies. Here’s how to do your own competitive analysis.
5. Plan to be flexible. After 2020, there’s not a lot more we can say other than this: Anything can happen. Build a resiliency plan into your goals for 2021. This way, you protect your employees and assets in the event that something major happens. For example, after COVID-19 hit, many businesses realized that they needed online systems so employees could work from home. Many decorators saw that robust ecommerce platforms to make ordering easy were now a must, not a maybe.
The reality? There’s a lot we can’t control, but we can plan ahead to deal with those scenarios. Your plan should be flexible enough to allow you to make changes if something happens. To this end, review your business plan at least every quarter so you can adjust as needed.
6. Look out for your employees. You’re only as strong as your employees, and 2020 has shown how important it is to protect this valuable asset. You need a strategy in place that addresses how you’ll look after those who look after your business. Your employees want to work and you need them to keep your business running. That’s why it’s a good idea to put a plan in place that allows you to keep your people, their families and your customers healthy and safe. This also is a good time to look at compensation plans, benefits and time off, along with the small perks you use along the way to recognize and motivate great team members.
Now that you’ve got some ideas on how to make plans for the new year, it’s time to start achieving those goals, so you can look back on 2021 as a resounding success.
James Andres is the content manager for S&S Activewear. You can reach him at [email protected] .
More Build Your Business
Making your decorated-apparel shop more sustainable.
If you’re a print shop owner who’s curious about the benefits of sustainable practices, now is a great time to start on the path toward a greener, cleaner and more profitable future for your decorated-apparel business.

Decorated-Apparel Business FUNdamentals—why FUN?
Successful screen-printing, heat-press and embroidery entrepreneurs don’t just go into business to make money, but for the satisfaction of a life well lived and a job well done.

Ask the Experts: Ninja Transfers and Direct-to-Film Custom Decorating
As part of his “Ask the Experts” series, Impressions Content Director, Adam Cort, discusses the state of direct-to-film (DTF) technology with “Ninja Mike,” founder and CEO of custom heat-transfer specialist Ninja Transfers.

5 Steps to Developing a Solid Business Plan
You have a great business idea and want to jump right in. The one thing holding you back may be lack of a clear business plan . While some would say having a business plan is an absolute must, others would argue that you can get started and be successful without one.
I think the answer lies in how confident you are in your idea and how organized you are in terms of executing it. If you already have a clear plan in your head along with the steps you need to take and the means to take them, you may not see the need to create a 20-page business plan.
On the flip side, if your idea lacks clarity and you are considering seeking out funding from others sources, it would be best if you came up with a solid business plan. The good news, is that you can sit down and create a business plan in under a day. It doesn’t have to be super extensive so long as you hit all your main points and follow stick to outlining these steps.
Table of Contents
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is the first part of your business plan. This is where you capture the reader’s attention be explaining the specifics of your business. What is the name? What will you be doing? What is the mission of your business and what are your goals?
Be sure to include what makes your business unique and summarize why you feel it will succeed.
2. Market Analysis
Next you want to analyze the market in order to prove that there is a need and target audience for your business. This is a great way to validate your business idea as well. If you can’t narrow down your target market or find that they aren’t interested in what you are offering, that could be a huge red flag.
Be sure to clarify who you wish to serve along with some detailed statistics that describe them, their interests, what products and services they buy, along with and their needs and wants.
3. Financial Projections
The financial projections section is where you get to have some fun with numbers. Map out the financial progress you plan to make with your business over the next 3-5 years. Include revenue goals and you might want to specify how much you’d need from an investor or a loan to bring those goals to fruition.
This is also a great place to mention various different start-up costs you’ll have so investors can know why you need money to support your business.
4. Organizational Structure
Have you ever thought about how your business will operate and be structured? Will you act as the CEO? Will you have a team or hire interns ? Will you eventually need to work with accounting, sales, and marketing experts? Or will you be more of a solopreneur.
This is a great section to answer all of those questions and map out how you might expect your business to grow in the future and which roles you’ll have and need.
5. Products or Services
Finally, in step 5 you want to go into more detail about your products and services. Most people start with this step (especially if they don’t consider making a business plan) but it’s best to end here after you’ve covered your bases in the previous steps.
Discuss what makes your product or service unique and how you plan to execute it in a competitive marketplace. If you’re going to be selling products include descriptions and images along with whether you’d need to trademark anything.
A business plan can be a crucial tool to help you get organized and perform neccessary research before moving forward with your new venture. If you’re considering asking for funding or financial assistance, a solid business plan is usually a requirement.
Even so, it’s a great way to get crystal clear on your goals and intentions so you can focus in on carrying out your plans and being successful.
Choncé Maddox
Due makes it easier to retire on your terms. We give you a realistic view on exactly where you’re at financially so when you retire you know how much money you’ll get each month. Get started today.
Top Trending Posts

Samuel Bankman-Fried to serve 25 years for misleading investors

Man found guilty of Selling $3.5M in Counterfeit and Deficient Electronics to Department of Defense

Decoding Buddha’s Concept of Enlightenment

Embracing the unknown: understanding faith

Trump Media Stock’s impact on finance

Mortgage Refinancing: How Does It Work?

Due Fact-Checking Standards and Processes
To ensure we’re putting out the highest content standards, we sought out the help of certified financial experts and accredited individuals to verify our advice. We also rely on them for the most up to date information and data to make sure our in-depth research has the facts right, for today… Not yesterday. Our financial expert review board allows our readers to not only trust the information they are reading but to act on it as well. Most of our authors are CFP (Certified Financial Planners) or CRPC (Chartered Retirement Planning Counselor) certified and all have college degrees. Learn more about annuities, retirement advice and take the correct steps towards financial freedom and knowing exactly where you stand today. Learn everything about our top-notch financial expert reviews below… Learn More

- Agile & Development
- Prioritization
- Product Management
- Product Marketing & Growth
- Product Metrics
- Product Strategy
Home » What Is Business Plan and How To Write It? [Template]
What Is Business Plan and How To Write It? [Template]
July 20, 2021 max 7min read.

This article covers:
What Is a Business Plan?
Who is in charge of writing a business plan.
- How To Write a Business Plan?
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Writing a Business Plan?
- What Is the Skeleton of a Business Plan?
Business Plan Definition
A business plan is a document that outlines the strategies and objectives that a startup or organization wants to achieve and how they plan to achieve them.
A business plan is like a map for starting or growing your company. It lays out the essential details of your business and how you plan to succeed.
Simply put, a business plan is a written copy of the business idea, what financial model it will adopt, the product or service, who will be the target audience, their marketing strategies, etc. It is conducive in the initial stages of establishing your enterprise.
The business plan is essential for the investment process. A detailed plan is crucial to attract stakeholders , venture capitalists, and investors or angel investors to pitch your business idea. In such a case, your business plan becomes your way of convincing them to invest their resources in your plan because it is worth it.
The core of a good plan tells the story of your business idea – what problem you’re solving and for whom. Are you hoping to start a bakery downtown? Create a new software tool? The plan explains who your potential customers are and why they’ll love what you offer.
It also includes specifics like who’s on your team, what you’re selling or the service you provide, and how you’ll spread the word (marketing). You’ll want to estimate sales projections and costs so folks understand how you’ll make money. This shows profits down the road.
A big part is differentiating from the competition. What makes your approach unique? Why pick you over similar options? The plan convinces potential backers or partners that you’ve thought it through and have a clear path to profits.
Overall, taking time to craft a solid plan is super helpful in the long term. It guides you through launch and growth. Review it yearly to check if your assumptions are still tracked, or if changes are needed. A plan keeps momentum on your side.
Starting or developing a business plan isn’t a science or learned through a degree. Some companies develop through trial and error, while others are drafted from head to toe.
Hence, the answer is No if we are talking about a particular person responsible for writing a business plan. Similarly, there is no need for an extended, lengthy business plan to be written with each plan elaborated.
Irrespective of all this, there are still some conditions in which a business increases its chances of becoming successful by drafting a business plan. Such conditions are as follows:
- For tech startups, a business plan can be a medium to gain long-term funding, especially with no trading history.
- When the market is new, untested, or volatile, a business plan can come in handy and serve as a document to fall back upon, mainly to tackle uncertainties and unclarity.
- If you have an excellent business idea and haven’t given it much thought or put it on paper, drafting a business plan can be a good option. Writing a business plan can help you carefully structure and evaluate your thoughts from different angles to spot risks.
How To Write a Business Plan?
First and foremost, when writing a business plan, you need to identify the problem your business will aim to solve and the purpose your business serves.
Once that is sorted, you need to consider who you are trying to attract with it, what kind of customers, and why. Following are some additional key points to consider while drafting your business plan:
- Note how you plan to secure your funding through private investors, bank loans, etc.
- Write about your business history, the concept, and what products or services you are trying to sell.
- Ensure you are transparent with your investors and do not keep any information from them. Do not exaggerate or bluff about your experience and skills. Gaining trust is crucial.
- Explain the details about your product or service in layperson’s terms. Avoid jargon as much as possible to avoid confusing the reader.
- Focus on the business’s strengths, the problem it aims to solve, and the evidence you have to prove the same.
- Understanding the market you are penetrating is crucial, as is conducting competitor analysis, knowing who your competitors are, learning about your competitive advantage , and finding your unique selling proposition (USP) .
- Last but not least, ensure your business plan is brief. Instead, keep it as short and precise as possible. Your aim through the business plan is to deliver crucial information so the reader can decide.
It’s quite easier to write a business plan if you consider the given points. However, it’s still not a walk in the park. If you still have trouble drafting your plan, consider hiring a writer—an affordable business plan writer who can help you put the first version of your plan on paper.
If you are still trying to decide whether or not you should dedicate your time to making a business plan, here are a few advantages and disadvantages of a business plan to help you make this decision.
Advantages of a Business Plan
- A business plan can be your golden document to secure funding for your business . Initially, funding is crucial, especially for tech and SaaS startups.
- The strategic focus of your business is preserved after the first stage. You can read about scope creep and understand how a company occasionally diverges from its goal, which could lead to stagnancy. In such a case, it is essential to understand the success factors in a business and plan exactly to serve the purpose.
- Having a business plan on paper invites other passionate people on board . When you have a trading history, it is easier to get people on board. However, if you have a plan, it convinces potential investors that you are sure about what you are doing.
Disadvantages of a Business Plan
- A business plan can hamper you from looking forward. This means you may depend too much on your plan without considering other external factors such as market conditions, trends, etc. Such a dependency can lead you to make mistakes and miss potential golden opportunities just because they were not in the plan.
- Analyzing performance can become time-consuming. A business plan can make you dwell on your past mistakes by focusing on the goals and objectives you could not achieve. Analyzing past performance could save time and resources by focusing on moving forward with strength.
- Constant change makes a business plan outdated as soon as it’s written. We know that the world is changing quickly, so your business plan will likely lose its relevance by the time you are ready to launch. A great alternative to the business plan is a strategic project roadmap . This is because a business plan has a lot of essential details, such as the mission statement , which are less likely to change either way. Moreover, a roadmap can help pave the most adaptable and actionable path.
What Is the Skeleton of a Business Plan?
Since you are still reading, I am sure you’ll want to know what the skeleton of a business plan looks like.
Remember that it can be frustrating because critical thinking is involved, and there is no hard-fast rule for a business plan. However, the best approach is to look at other business plan templates and write yours in a way that makes sense to any layman.
Here is what a Business plan constitutes of:
- Overview: In this section, you summarize your business concept and its execution.
- Detailed Description: In this section, you will describe the kind of product or service you are offering, what the unique selling point is, and how valuable your business is.
- Target audience: In this section, you will explain your market segmentation , the target market , their essential traits, etc., backed up by user research .
- Marketing strategy: Once you know your target audience well, you must document how you will reach them through a marketing strategy. A marketing strategy is often defined within the marketing plan , where primary establishment and engagement strategies are explained in detail. However, as a subsection in a business plan, it need not be as detailed as a market plan.
- Core team: This section will discuss your people and the team behind the development process. If you don’t have a team yet, you must discuss how team members will be selected, what candidates suit you, and the timeline. This section is critical to procure external investments such as passion and enthusiasm.
- Financial Predictions: Remember that investors are mainly concerned about finances because no one wants to invest in a loss-making company. Hence, your financial sedition is going to be scrutinized a lot more than anything else. Therefore, it is crucial to be thorough with the same. Make sure you talk about how much money you need to get started and how you plan to keep the money rolling in. Ensure that your cash flow forecast is realistic and achievable, which will help keep your business floating for the first few years.
More like this:
- What is Product Marketing? (Strategies and Examples)
- Product Marketing Manager: Everything You Need To Know
- How to Align Your Product Roadmap with Business Goals
- How to Create Effective Product Release Plans
- What Is an Execution Plan? Definition and Overview
A business plan consists of the overview of your business idea, detailed descriptions of your product or service and its unique selling proposition, your target audience, your marketing strategy, the core team and how to hire it, and the financial model or predictions.
A business plan helps you pitch your business idea to potential investors and secure funding. When your business is on the brink of losing focus after a few initial years, a business plan helps you to stay on track. Lastly, it invites other potential employees, partners, or investors to invest their resources in your business.
A business plan expires fast because of our constantly evolving world. It is not dependable in the long run because of its ignorance towards changing marketing conditions. It can obstruct you from looking forward to external factors and golden opportunities since it compels you to focus on the plan, creating dependency.
Crafting great product requires great tools. Try Chisel today, it's free forever.
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit in the current market or are ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform. Business plans are a required tool for all entrepreneurs, business owners, and business acquirers. Learn what a business plan is and why you need one.
It is a foundational document that I think of as the constitution of your business. It tells you everything you need to know about your idea, your goals, your strategy, and the financial picture of a business. Here at Masterplans, we strongly believe that entrepreneurs need to understand that a business plan is not a one-time use product, like ...
Ensuring a well-organized business plan is in place for your company will help position it for success. Here are nine simple steps to write one, starting with the executive summary. 1. Write the executive summary. Start your business plan with a concise executive summary. This section is like the "quick start" button for your project.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Follow these guidelines to start writing a solid business plan that communicates your vision and speaks to your audience. The "dos" for writing a solid business plan. Be professional yet simple. Writing with a professional tone allows investors to appreciate your vision and understand your short- and long-term goals. At the same time, it ...
1. Investors Are Short On Time. If your chief goal is using your business plan to secure funding, then it means you intend on getting it in front of an investor. And if there's one thing investors are, it's busy. So keep this in mind throughout writing a business plan.
Describe your company, its mission, and vision. Identifying the "why" of your business is a crucial step in learning how to write a business plan. There are two ways of articulating that "why.". One is your company's mission statement — a brief explanation of what you hope to achieve by starting or growing your business.
It's the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you'll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance. A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and ...
A solid business plan will include the following: Executive summary: A quick overview of the entire business plan. Company description: A description of your company and what it does. Products and ...
If you're an entrepreneur or aspiring business owner, you know that developing a solid business plan is crucial for success. But where do you even start? This ultimate guide will take you step-by-step…
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
Identify your goals and methods. The main function of a business plan is to clarify the center purpose of your business and how you are going to run it. It will also cover issues such as your products, target markets and promotional strategies. Raise capital. You definitely need a business plan if you plan to raise money or get a loan.
Include a captivating introduction to your business. Describe the problem your business is trying to solve. Explain how your company offers a solution to a problem. Describe products and services you offer. Address how you plan on reaching your customers with your marketing efforts. Include your projected revenue.
Here's how to create a solid business plan for the year ahead. 1. Realize you need a plan. The first step in any process is knowing you have to take a step forward. This past year has probably taught you that you need a plan for what could possibly happen. While there's no way to know what all of 2021 will bring, it's important to have ...
Be sure to include what makes your business unique and summarize why you feel it will succeed. 2. Market Analysis. Next you want to analyze the market in order to prove that there is a need and target audience for your business. This is a great way to validate your business idea as well.
Lending naturally involves risk, and a great business plan can help lenders understand and quantity that risk, increasing your chances for approval. 2. Potential partners and investors. Where ...
2 Do your research. The next step is to do your research. You need to gather information about your industry, market, customers, and competitors. You need to understand the trends, opportunities ...
A business plan is a document that outlines the strategies and objectives that a startup or organization wants to achieve and how they plan to achieve them. A business plan is like a map for starting or growing your company. It lays out the essential details of your business and how you plan to succeed. Simply put, a business plan is a written ...
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
closer plan. n. cohesive plan. n. concrete scheme. continuous plan. n. Another way to say Solid Plan? Synonyms for Solid Plan (other words and phrases for Solid Plan).