Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / How to Cite an Essay in MLA

How to Cite an Essay in MLA
The guidelines for citing an essay in MLA format are similar to those for citing a chapter in a book. Include the author of the essay, the title of the essay, the name of the collection if the essay belongs to one, the editor of the collection or other contributors, the publication information, and the page number(s).
Citing an Essay
Mla essay citation structure.
Last, First M. “Essay Title.” Collection Title, edited by First M. Last, Publisher, year published, page numbers. Website Title , URL (if applicable).
MLA Essay Citation Example
Gupta, Sanjay. “Balancing and Checking.” Essays on Modern Democracy, edited by Bob Towsky, Brook Stone Publishers, 1996, pp. 36-48. Essay Database, www . databaseforessays.org/modern/modern-democracy.
MLA Essay In-text Citation Structure
(Last Name Page #)
MLA Essay In-text Citation Example
Click here to cite an essay via an EasyBib citation form.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- Works Cited
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
To cite your sources in an essay in MLA style, you need to have basic information including the author’s name(s), chapter title, book title, editor(s), publication year, publisher, and page numbers. The templates for in-text citations and a works-cited-list entry for essay sources and some examples are given below:
In-text citation template and example:
For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the author on the first occurrence. For subsequent citations, use only the surname(s). In parenthetical citations, always use only the surname of the author(s).
Citation in prose:
First mention: Annette Wheeler Cafarelli
Subsequent occurrences: Wheeler Cafarelli
Parenthetical:
….(Wheeler Cafarelli).
Works-cited-list entry template and example:
The title of the chapter is enclosed in double quotation marks and uses title case. The book or collection title is given in italics and uses title case.
Surname, First Name. “Title of the Chapter.” Title of the Book , edited by Editor(s) Name, Publisher, Publication Year, page range.
Cafarelli, Annette Wheeler. “Rousseau and British Romanticism: Women and British Romanticism.” Cultural Interactions in the Romantic Age: Critical Essays in Comparative Literature , edited by Gregory Maertz. State U of New York P, 1998, pp. 125–56.
To cite an essay in MLA style, you need to have basic information including the author(s), the essay title, the book title, editor(s), publication year, publisher, and page numbers. The templates for citations in prose, parenthetical citations, and works-cited-list entries for an essay by multiple authors, and some examples, are given below:
For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the author (e.g., Mary Strine).
For sources with two authors, use both full author names in prose (e.g., Mary Strine and Beth Radick).
For sources with three or more authors, use the first name and surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues” (e.g., Mary Strine and others). In subsequent citations, use only the surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues” (e.g., Strine and others).
In parenthetical citations, use only the author’s surname. For sources with two authors, use two surnames (e.g., Strine and Radick). For sources with three or more author names, use the first author’s surname followed by “et al.”
First mention: Mary Strine…
Subsequent mention: Strine…
First mention: Mary Strine and Beth Radick…
Subsequent mention: Strine and Radick…
First mention: Mary Strine and colleagues …. or Mary Strine and others
Subsequent occurrences: Strine and colleagues …. or Strine and others
…. (Strine).
….(Strine and Radick).
….(Strine et al.).
The title of the essay is enclosed in double quotation marks and uses title case. The book or collection title is given in italics and uses title case.
Surname, First Name, et al. “Title of the Essay.” Title of the Book , edited by Editor(s) Name, Publisher, Publication Year, page range.
Strine, Mary M., et al. “Research in Interpretation and Performance Studies: Trends, Issues, Priorities.” Speech Communication: Essays to Commemorate the 75th Anniversary of the Speech Communication Association , edited by Gerald M. Phillips and Julia T. Wood, Southern Illinois UP, 1990, pp. 181–204.
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Referencing
A Quick Guide to Harvard Referencing | Citation Examples
Published on 14 February 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 15 September 2023.
Referencing is an important part of academic writing. It tells your readers what sources you’ve used and how to find them.
Harvard is the most common referencing style used in UK universities. In Harvard style, the author and year are cited in-text, and full details of the source are given in a reference list .
Harvard Reference Generator
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Harvard in-text citation, creating a harvard reference list, harvard referencing examples, referencing sources with no author or date, frequently asked questions about harvard referencing.
A Harvard in-text citation appears in brackets beside any quotation or paraphrase of a source. It gives the last name of the author(s) and the year of publication, as well as a page number or range locating the passage referenced, if applicable:
Note that ‘p.’ is used for a single page, ‘pp.’ for multiple pages (e.g. ‘pp. 1–5’).
An in-text citation usually appears immediately after the quotation or paraphrase in question. It may also appear at the end of the relevant sentence, as long as it’s clear what it refers to.
When your sentence already mentions the name of the author, it should not be repeated in the citation:
Sources with multiple authors
When you cite a source with up to three authors, cite all authors’ names. For four or more authors, list only the first name, followed by ‘ et al. ’:
Sources with no page numbers
Some sources, such as websites , often don’t have page numbers. If the source is a short text, you can simply leave out the page number. With longer sources, you can use an alternate locator such as a subheading or paragraph number if you need to specify where to find the quote:
Multiple citations at the same point
When you need multiple citations to appear at the same point in your text – for example, when you refer to several sources with one phrase – you can present them in the same set of brackets, separated by semicolons. List them in order of publication date:
Multiple sources with the same author and date
If you cite multiple sources by the same author which were published in the same year, it’s important to distinguish between them in your citations. To do this, insert an ‘a’ after the year in the first one you reference, a ‘b’ in the second, and so on:
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
A bibliography or reference list appears at the end of your text. It lists all your sources in alphabetical order by the author’s last name, giving complete information so that the reader can look them up if necessary.
The reference entry starts with the author’s last name followed by initial(s). Only the first word of the title is capitalised (as well as any proper nouns).

Sources with multiple authors in the reference list
As with in-text citations, up to three authors should be listed; when there are four or more, list only the first author followed by ‘ et al. ’:
Reference list entries vary according to source type, since different information is relevant for different sources. Formats and examples for the most commonly used source types are given below.
- Entire book
- Book chapter
- Translated book
- Edition of a book
Journal articles
- Print journal
- Online-only journal with DOI
- Online-only journal with no DOI
- General web page
- Online article or blog
- Social media post
Sometimes you won’t have all the information you need for a reference. This section covers what to do when a source lacks a publication date or named author.
No publication date
When a source doesn’t have a clear publication date – for example, a constantly updated reference source like Wikipedia or an obscure historical document which can’t be accurately dated – you can replace it with the words ‘no date’:
Note that when you do this with an online source, you should still include an access date, as in the example.
When a source lacks a clearly identified author, there’s often an appropriate corporate source – the organisation responsible for the source – whom you can credit as author instead, as in the Google and Wikipedia examples above.
When that’s not the case, you can just replace it with the title of the source in both the in-text citation and the reference list:
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Harvard referencing uses an author–date system. Sources are cited by the author’s last name and the publication year in brackets. Each Harvard in-text citation corresponds to an entry in the alphabetised reference list at the end of the paper.
Vancouver referencing uses a numerical system. Sources are cited by a number in parentheses or superscript. Each number corresponds to a full reference at the end of the paper.
A Harvard in-text citation should appear in brackets every time you quote, paraphrase, or refer to information from a source.
The citation can appear immediately after the quotation or paraphrase, or at the end of the sentence. If you’re quoting, place the citation outside of the quotation marks but before any other punctuation like a comma or full stop.
In Harvard referencing, up to three author names are included in an in-text citation or reference list entry. When there are four or more authors, include only the first, followed by ‘ et al. ’
Though the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, there is a difference in meaning:
- A reference list only includes sources cited in the text – every entry corresponds to an in-text citation .
- A bibliography also includes other sources which were consulted during the research but not cited.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, September 15). A Quick Guide to Harvard Referencing | Citation Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 1 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/referencing/harvard-style/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, harvard in-text citation | a complete guide & examples, harvard style bibliography | format & examples, referencing books in harvard style | templates & examples, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!

APA In-Text Citations and Sample Essay 7th Edition
This handout focuses on how to format in-text citations in APA.
Proper citation of sources is a two-part process . You must first cite each source in the body of your essay; these citations within the essay are called in-text citations . You MUST cite all quoted, paraphrased, or summarized words, ideas, and facts from sources. Without in-text citations, you are technically in danger of plagiarism, even if you have listed your sources at the end of the essay.
In-text citations point the reader to the sources’ information on the references page. The in-text citation typically includes the author's last name and the year of publication. If you use a direct quote, the page number is also provided.
More information can be found on p. 253 of the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association.
Citation Rules
Direct quotation with the author named in the text.
Heinze and Lu (2017) stated, “The NFL shifted its responses to institutional change around concussions significantly as the field itself evolved” (p. 509).
Note: The year of publication is listed in parenthesis after the names of the authors, and the page number is listed in parenthesis at the end of the quote.
Direct Quotation without the Author Named in the Text
As the NFL developed as an organization, it “shifted its responses to institutional change around concussions significantly” (Heinze & Lu, 2017, p. 509).
Note: At the end of the quote, the names of the authors, year of publication, and page number are listed in parenthesis.
Paraphrase with 1-2 Authors
As the NFL developed as an organization, its reactions toward concussions also transformed (Heinze & Lu, 2017).
Note: For paraphrases, page numbers are encouraged but not required.
Paraphrase with 3 or More Authors
To work toward solving the issue of violence in prisons begins with determining aspects that might connect with prisoners' violent conduct (Thomson et al., 2019).
Direct Quotation without an Author
The findings were astonishing "in a recent study of parent and adult child relationships" ("Parents and Their Children," 2007, p. 2).
Note: Since the author of the text is not stated, a shortened version of the title is used instead.
Secondary Sources
When using secondary sources, use the phrase "as cited in" and cite the secondary source on the References page.
In 1936, Keynes said, “governments should run deficits when the economy is slow to avoid unemployment” (as cited in Richardson, 2008, p. 257).
Long (Block) Quotations
When using direct quotations of 40 or more words, indent five spaces from the left margin without using quotation marks. The final period should come before the parenthetical citation.
At Meramec, an English department policy states:
To honor and protect their own work and that of others, all students must give credit to proprietary sources that are used for course work. It is assumed that any information that is not documented is either common knowledge in that field or the original work of that student. (St. Louis Community College, 2001, p. 1)
Website Citations
If citing a specific web document without a page number, include the name of the author, date, title of the section, and paragraph number in parentheses:
In America, “Two out of five deaths among U.S. teens are the result of a motor vehicle crash” (National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, 2004, Overview section, para. 1).
Here is a print-friendly version of this content.
Learn more about the APA References page by reviewing this handout .
For information on STLCC's academic integrity policy, check out this webpage .
For additional information on APA, check out STLCC's LibGuide on APA .
Sample Essay
A sample APA essay is available at this link .

Scholarly Writing & Citing: Citation Examples & Resources
- Scholarly Writing Resources
- Citation Examples & Resources
Essential Citation Elements
No matter the style you are using (APA, AMA, NLM, etc.), these are the essential pieces of information you must cite from each source you use to ensure they are properly attributed:

Style Guides
Citation Manager Software
- EndNote EndNote is a software program for PC or MAC that works with Microsoft Word to automatically format in-text citations and end-of-paper bibliography lists for your manuscripts with your chosen style (APA, NIH, Vancouver, etc). EndNote can also be used as a personal database to gather and store citation records from a variety of information sources.
- Zotero Zotero is a free bibliographic citation manager. It is used to: gather citations from several sources including databases, store them locally and online, organize them in collections, share them in online groups, and place them in Word documents as in-text citations and bibliographies.
- Periodicals
- Figures & Tables
AMA Style is published by the American Medical Association, JAMA (Journal of the American Medical Association), and Oxford University Press. AMA Style is used by scientists in many research disciplines.
AMA Style uses numerical superscripts in-text to reference a reference list at the end of the document.
The basic elements of AMA Style citations are as follows:

Examples come from amamanualofstyle.com
AMA Style Blog
Journal Article
Journal titles should be abbreviated. See this list for examples.
Physical Book
Sacks O. Hallucinations . Alfred A Knopf; 2012.
Guyatt G, Rennie D, Meade MO, Cook DJ. Users’ Guides to the Medical Literature: A Manual for Evidence-Based Clinical Practice. 3rd ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2015. Accessed August 15, 2016. https://jamaevidence.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookID=847
Chapter From A Book With Editors
Boushey CJ. Application of research paradigms to nutrition practice. In: Coulston AM, Boushey CJ, Ferruzzi MG, eds. Nutrition in the Prevention and Treatment of Disease . 3rd ed. Academic Press; 2013:99-105.
In citing data from a website, include the following elements, if available, in the order shown:
■ Authors’ surnames and initials, if given (the names of all authors should be given unless there are more than 6, in which case the names of the first 3 authors are used, followed by “et al”), or name of the group
■ Title of the specific item cited (if none is given, use the name of the organization responsible for the site)
■ Name of the website
■ [Date published]
■ Updated [date]
■ Accessed [date]
■ URL (verify that the link still works as close as possible to publication)
Zika travel information. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. January 26, 2016. Updated August 11, 2016. Accessed June 18, 2019. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/page/zika-travel-information
A figure is any graphic that is not a table - photos, drawings, graphs, charts, and maps are all figures.
"The original source should be acknowledged in the legend. If the original source in which the illustration has been published is included in the reference list, the reference may be cited in the legend, with the citation number for the reference corresponding to its first appearance in the text, tables, or figures. Permission should be obtained to reproduce the material in print, online, and in all licensed versions (eg, reprints)." AMA 4.2.9
Reprinted with permission from the American Academy of Pediatrics. 5
Government Reports
(1) name of author (if given); (2) title of bulletin; (3) name of issuing bureau, agency, department, or other governmental division (note that in this position, Department should be abbreviated Dept; also note that if the US Government Printing Office is supplied as the publisher, it would be preferable to obtain the name of the issuing bureau, agency, or department); (4) date of publication; (5) page numbers (if specified); (6) publication number (if any); (7) series number (if given); (8) online accessed date (if applicable); and (9) web address (if applicable)
National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Questions and Answers About Sprains and Strains . National Institutes of Health; 2015. NIH publication 15-5328. Accessed January 28, 2016. http://www.niams.nih.gov/Health_Info/Sprains_Strains/default.asp
Conference Presentations
Morales M, Zhou X. Health practices of immigrant women: indigenous knowledge in an urban environment. Paper presented at: 78th Association for Information Science and Technology Annual Meeting; November 6-10, 2015; St Louis, MO. Accessed March 15, 2016. https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/2857070.2857108
Dissertations/Theses
Ghanbari S. Integration of the Arts in STEM: A Collective Case Study of Two Interdisciplinary University Programs . Dissertation. University of California; 2014. Accessed October 14, 2016. http://escholarship.org/uc/item/9wp9x8sj
Stata 14 . Version 14. StataCorp; 2015. Accessed March 14, 2016. http://www.stata.com/
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM). Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine; 2016. Updated March 13, 2016. Accessed March 14, 2016. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim
US Federal Statutes
Citations of statutes include the official name of the act, the title number (similar to a chapter number), the abbreviation of the code cited, the section number (designated by §), and the date of the code edition cited.
Female Genital Mutilation, 18 USC §116 (2012). Accessed March 18, 2016. https://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/granule/USCODE-2011-title18/USCODE-2011-title18-partI-chap7-sec116
See more legal examples here: https://www.amamanualofstyle.com/view/10.1093/jama/9780190246556.001.0001/med-9780190246556-chapter-3-div2-127
APA Style is a popular academic style guide produced by the American Psychological Association. APA Style is used across many disciplines beyond psychology.
APA Style uses in-text citations to refer to larger reference lists at the end of the document.
The 2 basic elements of an APA Style in-text citation are: (Author, Date)
The 4 basic elements of an APA Style reference are: Author. (Date). Title. Source .
Examples come from apastyle.apa.org unless otherwise noted.
- APA Style Blog
- APA Style Official Website
- Clinical Practice Reference Examples
In-Text: (Grady et al., 2019)
Reference List: Grady, J. S., Her, M., Moreno, G., Perez, C., & Yelinek, J. (2019). Emotions in storybooks: A comparison of storybooks that represent ethnic and racial groups in the United States. Psychology of Popular Media Culture , 8 (3), 207–217. https://doi.org/10.1037/ppm0000185
UpToDate Article
(Bordeaux & Lieberman, 2020)
Bordeaux, B., & Lieberman, H. R. (2020). Benefits and risks of caffeine and caffeinated beverages. UpToDate . Retrieved February 26, 2020, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/benefits-and-risks-of-caffeine-and-caffeinated-beverages
In-Text: (Jackson, 2019)
Reference List: Jackson, L. M. (2019). The psychology of prejudice: From attitudes to social action (2nd ed.). American Psychological Association. https://doi.org/10.1037/0000168-000
Book With Editors
(Torino et al., 2019)
Torino, G. C., Rivera, D. P., Capodilupo, C. M., Nadal, K. L., & Sue, D. W. (Eds.). (2019). Microaggression theory: Influence and implications . John Wiley & Sons. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119466642
(Aron et al., 2019)
Aron, L., Botella, M., & Lubart, T. (2019). Culinary arts: Talent and their development. In R. F. Subotnik, P. Olszewski-Kubilius, & F. C. Worrell (Eds.), The psychology of high performance: Developing human potential into domain-specific talent (pp. 345–359). American Psychological Association. https://doi.org/10.1037/0000120-016
In-Text: (National Institute of Mental Health, 2018)
Reference List: National Institute of Mental Health. (2018, July). Anxiety disorders . U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/anxiety-disorders/index.shtml
(World Health Organization, 2019)
World Health Organization. (2019). 2A85.5 Mantle cell lymphoma. In International statistical classification of diseases and related health problems (11th ed.). https://icd.who.int/browse11/l-m/en#/http://id.who.int/icd/entity/1804127841
Figure With Attribution Required (Copyright)

Reference list:
Denali National Park and Preserve. (2013). Lava [Photograph]. Flickr. https://www.flickr.com/photos/denalinps/8639280606/
Figure With No Attribution Required (Creative Commons, etc.)

No reference list entry required.

Williams, C. L. (1992). The glass escalator: Hidden advantages for men in the "female" professions. Social Problems , 39 (3), 253-267. https://doi.org/10.2307/3096961
(This example comes from: https://www.lib.sfu.ca/help/cite-write/citation-style-guides/apa/tables-figures#examples-for-citing-tables )
National Cancer Institute. (2019). Taking time: Support for people with cancer (NIH Publication No. 18-2059). U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health. https://www.cancer.gov/publications/patient-education/takingtime.pdf
Evans, A. C., Jr., Garbarino, J., Bocanegra, E., Kinscherff, R. T., & Márquez-Greene, N. (2019, August 8–11). Gun violence: An event on the power of community [Conference presentation]. APA 2019 Convention, Chicago, IL, United States. https://convention.apa.org/2019-video
Dissertations
Kabir, J. M. (2016). Factors influencing customer satisfaction at a fast food hamburger chain: The relationship between customer satisfaction and customer loyalty (Publication No. 10169573) [Doctoral dissertation, Wilmington University]. ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global.
O’Donohue, W. (2017). Content analysis of undergraduate psychology textbooks (ICPSR 21600; Version V1) [Data set]. ICPSR. https://doi.org/10.3886/ICPSR36966.v1
The National Library of Medicine has produced a document called Citing Medicine: The NLM Style Guide for Authors, Editors, and Publishers. This style guide is one of the recommended texts used in the AMA Style Guide, and serves as its own complete style as well.
The NLM Style Guide includes information and examples for three different types of in-text citations:
citation-sequence system: numerical superscripts that are listed in the reference list in the order they appear in the text (similar to AMA)
citation-name system: numerical superscripts that are listed in the reference list in alphabetical order, regardless of what order they appear in the text
name-year system: author and year of publication are used in-text as (Author Year) to reference to alphabetical reference list (similar to APA)
Examples come from Citing Medicine .
Journal titles should be abbreviated. For abbreviations visit: https://www.issn.org/services/online-services/access-to-the-ltwa/
Petitti DB, Crooks VC, Buckwalter JG, Chiu V. Blood pressure levels before dementia. Arch Neurol. 2005 Jan;62(1):112-6.
See many more examples here: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK7282/#A32680
Jenkins PF. Making sense of the chest x-ray: a hands-on guide. New York: Oxford University Press; 2005. 194 p.
Izzo JL Jr, Black HR, editors. Hypertension primer: the essentials of high blood pressure. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; c2003. 532 p.
Whiteside TL, Heberman RB. Effectors of immunity and rationale for immunotherapy. In: Kufe DW, Pollock RE, Weichselbaum RR, Bast RC Jr, Gansler TS, Holland JF, Frei E 3rd, editors. Cancer medicine 6. Hamilton (ON): BC Decker Inc; 2003. p. 221-8.

Diaz-Cruz ES, Shapiro CL, Brueggemeier RW. Cyclooxygenase inhibitors suppress aromatase expression and activity in breast cancer cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005 May;90(5):2563-70. Table 2, Aromatase activity and expression in cell lines; p. 2565.
Mitchell GF, Pfeffer MA. Evaluation and management of patients with uncontrolled systolic hypertension: is another new paradigm really needed? Am Heart J. 2005 May;149(5):776-84. Figure 3, Regional pressure wave forms in the normal arterial system; p. 780.
National High Blood Pressure Education Program (US). The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Rev. ed. Bethesda (MD): National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (US); 2005. 48 p. (NIH publication; no. 05-5267).
Hu X, Gao Z, Xu F, Liu N. A novel approach to harvesting lymphatic endothelial cells from human foreskin dermis. Paper presented at: 8th TESI Annual Meeting; 2005 Oct 22-25; Shanghai, China.
Jones DL. The role of physical activity on the need for revision total knee arthroplasty in individuals with osteoarthritis of the knee [dissertation]. [Pittsburgh (PA)]: University of Pittsburgh; 2001. 436 p.
RxNorm [dataset on the Internet]. Release META2011AA Full Update 2011_07_05. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US); 2011 Jul 5 [cited 2011 Jul 14]. Available from: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/rxnorm/docs/rxnormfiles.html
Federal Statutes
Veterans Hearing Loss Compensation Act of 2002, Pub. L. No. 107-9, 115 Stat. 11 (May 24, 2001).
See more legal citation examples in The Bluebook .
A Note on Plagiarism
Properly citing your sources is the number one way to prevent claims of plagiarism against your work.
The Library does not promote or subscribe to any tools offering plagiarism checking for manuscripts. There are many websites offering "free" plagiarism checking services online, but note that many of these services limit word count/databases searched/searches per month etc. Plagiarism checkers recommended by other libraries include:
- << Previous: Scholarly Writing Resources
- Last Updated: Feb 22, 2024 2:47 PM
- URL: https://libguides.wakehealth.edu/citations
Carpenter Library | Atrium Health/Wake Forest University School of Medicine | Contact Us
APA Citation Style
Citation examples.
- Paper Format
- Style and Grammar Guidelines
- Citation Management Tools
- What's New in the 7th Edition?
- APA Style References Guidelines from the American Psychological Association
- APA Style (OWL - Online Writing Lab, Purdue University)
- Common Reference Examples Handout
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Edited Book Chapter
- Dictionary Entry
- Government Report
- YouTube Video
- Facebook Post
- Webpage on a Website
- Supplemental Reference Examples
- Archival Documents and Collections
Parenthetical citations: (Grady et al., 2019; Jerrentrup et al., 2018)
Narrative citations: Grady et al. (2019) and Jerrentrup et al. (2018)
- If a journal article has a DOI, include the DOI in the reference.
- If the journal article does not have a DOI and is from an academic research database, end the reference after the page range (for an explanation of why, see the database information page). The reference in this case is the same as for a print journal article.
- Do not include database information in the reference unless the journal article comes from a database that publishes original, proprietary content, such as UpToDate (see an example on the database information page).
- If the journal article does not have a DOI but does have a URL that will resolve for readers (e.g., it is from an online journal that is not part of a database), include the URL of the article at the end of the reference.
- If the journal article has an article number instead of a page range, include the article number instead of the page range (as shown in the Jerrentrup et al. example).
Parenthetical citations: (Rabinowitz, 2019; Sapolsky, 2017)
Narrative citations: Rabinowitz (2019) and Sapolsky (2017)
- If the book includes a DOI, include the DOI in the reference after the publisher name.
- Do not include the publisher location.
- If the book does not have a DOI and comes from an academic research database, end the book reference after the publisher name. Do not include database information in the reference. The reference in this case is the same as for a print book.
Parenthetical citations: (Schaefer & Shapiro, 2019; Schulman, 2019)
Narrative citations: Schaefer and Shapiro (2019) and Schulman (2019)
- If a magazine article has a DOI, include the DOI in the reference.
- If the magazine article does not have a DOI and is from an academic research database, end the reference after the page range. Do not include database information in the reference. The reference in this case is the same as for a print magazine article.
- If the magazine article does not have a DOI but does have a URL that will resolve for readers (e.g., it is from an online magazine that is not part of a database), include the URL of the article at the end of the reference.
- If the magazine article does not have volume, issue, and/or page numbers (e.g., because it is from an online magazine), omit the missing elements from the reference (as in the Schulman example).
Parenthetical citation: (Carey, 2019)
Narrative citation: Carey (2019)
- If the newspaper article is from an academic research database, end the reference after the page range. Do not include database information in the reference. The reference in this case is the same as for a print newspaper article.
- If the newspaper article has a URL that will resolve for readers (e.g., it is from an online newspaper), include the URL of the article at the end of the reference.
- If the newspaper article does not have volume, issue, and/or page numbers (e.g., because it is from an online newspaper), omit the missing elements from the reference, as shown in the example.
- If the article is from a news website (e.g., CNN, HuffPost)—one that does not have an associated daily or weekly newspaper—use the format for a webpage on a website instead.
Parenthetical citation: (Aron et al., 2019)
Narrative citation: Aron et al. (2019)
- If the edited book chapter includes a DOI, include the chapter DOI in the reference after the publisher name.
- If the edited book chapter does not have a DOI and comes from an academic research database, end the edited book chapter reference after the publisher name. Do not include database information in the reference. The reference in this case is the same as for a print edited book chapter.
- Do not create references for chapters of authored books. Instead, write a reference for the whole book and cite the chapter in the text if desired (e.g., Kumar, 2017, Chapter 2).
Parenthetical citation: (Merriam-Webster, n.d.)
Narrative citation: Merriam-Webster (n.d.)
- Because entries in Merriam-Webster’s Dictionary are updated over time and are not archived, include a retrieval date in the reference.
- Merriam-Webster is both the author and the publisher, so the name appears in the author element only to avoid repetition.
- To quote a dictionary definition, view the pages on quotations and how to quote works without page numbers for guidance. Additionally, here is an example: Culture refers to the “customary beliefs, social forms, and material traits of a racial, religious, or social group” (Merriam-Webster, n.d., Definition 1a).
Parenthetical citation: (National Cancer Institute, 2019)
Narrative citation: National Cancer Institute (2019)
The specific agency responsible for the report appears as the author. The names of parent agencies not present in the group author name appear in the source element as the publisher. This creates concise in-text citations and complete reference list entries.
Parenthetical citation: (Harvard University, 2019)
Narrative citation: Harvard University (2019)
- Use the name of the account that uploaded the video as the author.
- If the account did not actually create the work, explain this in the text if it is important for readers to know. However, if that would mean citing a source that appears unauthoritative, you might also look for the author’s YouTube channel, official website, or other social media to see whether the same video is available elsewhere.
Parenthetical citations: (APA Databases, 2019; Gates, 2019)
Narrative citations: APA Databases (2019) and Gates (2019)
- Present the name of the individual or group author the same as you would for any other reference. Then provide the Twitter handle (beginning with the @ sign) in square brackets, followed by a period.
- Provide the first 20 words of the tweet as the title. Count a URL, a hashtag, or an emoji as one word each, and include them in the reference if they fall within the first 20 words.
- If the tweet includes an image, a video, a poll, or a thumbnail image with a link, indicate that in brackets after the title: [Image attached], [Video attached], [Thumbnail with link attached].
- The same format used for Twitter is also used for Instagram.
Parenthetical citation: (News From Science, 2019)
Narrative citation: News From Science (2019)
- Provide the first 20 words of the Facebook post as the title. Count a URL or other link, a hashtag, or an emoji as one word each, and include them in the reference if they fall within the first 20 words.
- If a status update includes images, videos, thumbnail links to outside sources, or content from another Facebook post (such as when sharing a link), indicate that in square brackets.
Parenthetical citations: (Fagan, 2019; National Institute of Mental Health, 2018; Woodyatt, 2019; World Health Organization, 2018)
Narrative citations: Fagan (2019), National Institute of Mental Health (2018), Woodyatt (2019), and World Health Organization (2018)
- Provide as specific a date as is available on the webpage. This might be a year only; a year and month; or a year, month, and day.
- Italicize the title of a webpage.
- When the author of the webpage and the publisher of the website are the same, omit the publisher name to avoid repetition (as in the World Health Organization example).
- When contents of a page are meant to be updated over time but are not archived, include a retrieval date in the reference (as in the Fagan example).
- Use the webpage on a website format for articles from news websites such as CNN and HuffPost (these sites do not have associated daily or weekly newspapers). Use the newspaper article category for articles from newspaper websites such as The New York Times or The Washington Post .
- Create a reference to an open educational resources (OER) page only when the materials are available for download directly (i.e., the materials are on the page and/or can be downloaded as PDFs or other files). If you are directed to another website, create a reference to the specific webpage on that website where the materials can be retrieved. Use this format for material in any OER repository, such as OER Commons, OASIS, or MERLOT.
- Do not create a reference or in-text citation for a whole website. To mention a website in general, and not any particular information on that site, provide the name of the website in the text and include the URL in parentheses. For example, you might mention that you used a website to create a survey.
The following supplemental example references are mention in the Publication Manual:
- retracted journal or magazine article
- edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM)
- edition of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD)
- religious work
- annotated religious work
Archival document and collections are not presented in the APA Publication Manual, Seventh Edition . This content is available only on the APA Style website . This guidance has been expanded from the 6th edition.
Archival sources include letters, unpublished manuscripts, limited-circulation brochures and pamphlets, in-house institutional and corporate documents, clippings, and other documents, as well as such nontextual materials as photographs and apparatus, that are in the personal possession of an author, form part of an institutional collection, or are stored in an archive such as the Archives of the History of American Psychology at the University of Akron or the APA Archives. For any documents like these that are available on the open web or via a database (subscription or nonsubscription), follow the reference templates shown in Chapter 10 of the Publication Manual.
The general format for the reference for an archival work includes the author, date, title, and source. The reference examples shown on this page may be modified for collections requiring more or less specific information to locate materials, for different types of collections, or for additional descriptive information (e.g., a translation of a letter). Authors may choose to list correspondence from their own personal collections, but correspondence from other private collections should be listed only with the permission of the collector.
Keep in mind the following principles when creating references to archival documents and collections:
- As with any reference, the purpose is to direct readers to the source, despite the fact that only a single copy of the document may be available and readers may have some difficulty actually seeing a copy.
- Include as much information as is needed to help locate the item with reasonable ease within the repository. For items from collections with detailed finding aids, the name of the collection may be sufficient; for items from collections without finding aids, more information (e.g., call number, box number, file name or number) may be necessary to help locate the item.
- If several letters are cited from the same collection, list the collection as a reference and provide specific identifying information (author, recipient, and date) for each letter in the in-text citations (see Example 3).
- Use square brackets to indicate information that does not appear on the document.
- Use “ca.” (circa) to indicate an estimated date (see Example 5).
- Use italics for titles of archival documents and collections; if the work does not have a title, provide a description in square brackets without italics.
- Separate elements of the source (e.g., the name of a repository, library, university or archive, and the location of the university or archive) with commas. End the source with a period.
- If a publication of limited circulation is available in libraries, the reference may be formatted as usual for published material, without the archival source.
- Note that private letters (vs. those in an archive or repository) are considered personal communications and cited in the text only.
1. Letter from a repository
Frank, L. K. (1935, February 4). [Letter to Robert M. Ogden]. Rockefeller Archive Center (GEB Series 1.3, Box 371, Folder 3877), Tarrytown, NY, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: (Frank, 1935)
- Narrative citation: Frank (1935)
- Because the letter does not have a title, provide a description in square brackets.
2. Letter from a private collection
Zacharius, G. P. (1953, August 15). [Letter to William Rickel (W. Rickel, Trans.)]. Copy in possession of Hendrika Vande Kemp.
- Parenthetical citation: (Zacharius, 1953)
- Narrative citation: Zacharius (1953)
- In this example, Hendrika Vande Kemp is either the author of the paper or the author of the paper has received permission from Hendrika Vande Kemp to cite a letter in Vande Kemp’s private collection in this way. Otherwise, cite a private letter as a personal communication .
3. Collection of letters from an archive
Allport, G. W. (1930–1967). Correspondence. Gordon W. Allport Papers (HUG 4118.10), Harvard University Archives, Cambridge, MA, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: (Allport, 1930–1967)
- Narrative citation: Allport (1930–1967)
To cite specific letters in the text, provide the author and range of years as shown in the reference list entry, plus details about who wrote the specific letter to whom and when the specific letter was written.
- Parenthetical citation: (Allport, 1930–1967, G. Boring to Allport, December 26, 1937)
- Narrative citation: Allport (1930–1967, Allport to G. Boring, March 1, 1939)
- Use the parenthetical citation format to cite a letter that E. G. Boring wrote to Allport because Allport is the author in the reference. Use either the parenthetical or narrative citation format to cite letters that Allport wrote.
4. Unpublished papers, lectures from an archive or personal collection
Berliner, A. (1959). Notes for a lecture on reminiscences of Wundt and Leipzig. Anna Berliner Memoirs (Box M50), Archives of the History of American Psychology, University of Akron, Akron, OH, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: (Berliner, 1959)
- Narrative citation: Berliner (1959)
5. Archival/historical source for which the author and/or date is known or is reasonably certain but not stated on the document
Allport, A. (presumed). (ca. 1937). Marion Taylor today—by the biographer [Unpublished manuscript]. Marion Taylor Papers, Schlesinger Library, Radcliffe College, Cambridge, MA, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: (Allport, ca. 1937)
- Narrative citation: Allport (ca. 1937)
- Because the author is reasonably certain but not stated on the document, place the word “presumed” in parentheses after the name, followed by a period.
- Because the date is reasonably certain but not stated on the document, the abbreviation “ca.” (which stands for “circa”) appears before the year in parentheses.
6. Archival source with group author
Subcommittee on Mental Hygiene Personnel in School Programs. (1949, November 5–6). Meeting of Subcommittee on Mental Hygiene Personnel in School Programs. David Shakow Papers (M1360), Archives of the History of American Psychology, University of Akron, Akron, OH, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: (Subcommittee on Mental Hygiene Personnel in School Programs, 1949)
- Narrative citation: Subcommittee on Mental Hygiene Personnel in School Programs (1949)
7. Interview recorded and available in an archive
Smith, M. B. (1989, August 12). Interview by C. A. Kiesler [Tape recording]. President’s Oral History Project, American Psychological Association, APA Archives, Washington, DC, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: (Smith, 1989)
- Narrative citation: Smith (1989)
- For interviews and oral histories recorded in an archive, list the interviewee as the author. Include the interviewer’s name in the description.
8. Transcription of a recorded interview, no recording available
Sparkman, C. F. (1973). An oral history with Dr. Colley F. Sparkman/Interviewer: Orley B. Caudill. Mississippi Oral History Program (Vol. 289), University of Southern Mississippi, Hattiesburg, MS, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: (Sparkman, 1973)
- Narrative citation: Sparkman (1973)

9. Newspaper article clipping, historical, in personal collection
Psychoanalysis institute to open. (1948, September 18). [Clipping from an unidentified Dayton, OH, United States, newspaper]. Copy in possession of author.
- Parenthetical citation: (“Psychoanalysis Institute to Open,” 1948)
- Narrative citation: “Psychoanalysis Institute to Open” (1948)
- Use this format only if you are the person who is in possession of the newspaper clipping.
10. Historical publication of limited circulation
Sci-Art Publishers. (1935). Sci-Art publications [Brochure]. Roback Papers (HUGFP 104.50, Box 2, Folder “Miscellaneous Psychological Materials”), Harvard University Archives, Cambridge, MA, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: (Sci-Art Publishers, 1935)
- Narrative citation: Sci-Art Publishers (1935)
11. Archived photographs, no author and no title
[Photographs of Robert M. Yerkes]. (ca. 1917–1954). Robert Mearns Yerkes Papers (Box 137, Folder 2292), Manuscripts and Archives, Yale University Library, New Haven, CT, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: ([Photographs of Robert M. Yerkes], ca. 1917–1954)
- Narrative citation: [Photographs of Robert M. Yerkes] (ca. 1917–1954)
- Because the archived photographs do not have a title, provide a bracketed description instead.
- Because the archived photographs do not have an author, move the bracketed description to the author position of the reference.
12. Microfilm
U.S. Census Bureau. (1880). 1880 U.S. census: Defective, dependent, and delinquent classes schedule: Virginia [Microfilm]. NARA Microfilm Publication T1132 (Rolls 33–34), National Archives and Records Administration, Washington, DC, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: (U.S. Census Bureau, 1880)
- Narrative citation: U.S. Census Bureau (1880)
Read the full APA guidelines on citing ChatGPT
OpenAI. (2023). ChatGPT (Mar 14 version) [Large language model]. https://chat.openai.com/chat
- Parenthetical citation: (OpenAI, 2023)
- Narrative citation: OpenAI (2023)
Author: The author of the model is OpenAI.
Date: The date is the year of the version you used. Following the template in Section 10.10, you need to include only the year, not the exact date. The version number provides the specific date information a reader might need.
Title: The name of the model is “ChatGPT,” so that serves as the title and is italicized in your reference, as shown in the template. Although OpenAI labels unique iterations (i.e., ChatGPT-3, ChatGPT-4), they are using “ChatGPT” as the general name of the model, with updates identified with version numbers.
The version number is included after the title in parentheses. The format for the version number in ChatGPT references includes the date because that is how OpenAI is labeling the versions. Different large language models or software might use different version numbering; use the version number in the format the author or publisher provides, which may be a numbering system (e.g., Version 2.0) or other methods.
Bracketed text is used in references for additional descriptions when they are needed to help a reader understand what’s being cited. References for a number of common sources, such as journal articles and books, do not include bracketed descriptions, but things outside of the typical peer-reviewed system often do. In the case of a reference for ChatGPT, provide the descriptor “Large language model” in square brackets. OpenAI describes ChatGPT-4 as a “large multimodal model,” so that description may be provided instead if you are using ChatGPT-4. Later versions and software or models from other companies may need different descriptions, based on how the publishers describe the model. The goal of the bracketed text is to briefly describe the kind of model to your reader.
Source: When the publisher name and the author name are the same, do not repeat the publisher name in the source element of the reference, and move directly to the URL. This is the case for ChatGPT. The URL for ChatGPT is https://chat.openai.com/chat . For other models or products for which you may create a reference, use the URL that links as directly as possible to the source (i.e., the page where you can access the model, not the publisher’s homepage).
What to include and what to exclude
Works included in a reference list.
The reference list provides a reliable way for readers to identify and locate the works cited in a paper. APA Style papers generally include reference lists, not bibliographies.
In general, each work cited in the text must appear in the reference list, and each work in the reference list must be cited in the text. Check your work carefully before submitting your manuscript or course assignment to ensure no works cited in the text are missing from the reference list and vice versa, with only the following exceptions.
Works Excluded From a Reference List
There are a few kinds of works that are not included in a reference list. Usually a work is not included because readers cannot recover it or because the mention is so broad that readers do not need a reference list entry to understand the use.
Information on works included in a reference list is covered in Sections 2.12 and 8.4 of the APA Publication Manual, Seventh Edition
*This guidance has been expanded from the 6th edition.*
- Personal communications such as emails, phone calls, or text messages are cited in the text only, not in the reference list, because readers cannot retrieve personal communications.
- General mentions of whole websites, whole periodicals, and common software and apps in the text do not require in-text citations or reference list entries because the use is broad and the source is familiar.
- The source of an epigraph does not usually appear in the reference list unless the work is a scholarly book or journal. For example, if you open the paper with an inspirational quotation by a famous person, the source of the quotation does not appear in the reference list because the quotation is meant to set the stage for the work, not substantiate a key point.
- Quotations from research participants in a study you conducted can be presented and discussed in the text but do not need citations or reference list entries. Citations and reference list entries are not necessary because the quotations are part of your original research. They could also compromise participants’ confidentiality, which is an ethical violation.
- References included in a meta-analysis, which are marked with an asterisk in the reference list, may be cited in the text (or not) at the author’s discretion. This exception is relevant only to authors who are conducting a meta-analysis.
DOIs and URLs
The DOI or URL is the final component of a reference list entry. Because so much scholarship is available and/or retrieved online, most reference list entries end with either a DOI or a URL.
- A DOI is a unique alphanumeric string that identifies content and provides a persistent link to its location on the internet. DOIs can be found in database records and the reference lists of published works.
- A URL specifies the location of digital information on the internet and can be found in the address bar of your internet browser. URLs in references should link directly to the cited work when possible.
Follow these guidelines for including DOIs and URLs in references:
- Include a DOI for all works that have a DOI, regardless of whether you used the online version or the print version.
- If a print work does not have a DOI, do not include any DOI or URL in the reference.
- If an online work has both a DOI and a URL, include only the DOI.
- For works without DOIs from websites (not including academic research databases), provide a URL in the reference (as long as the URL will work for readers).
- For works without DOIs from most academic research databases , do not include a URL or database information in the reference because these works are widely available. The reference should be the same as the reference for a print version of the work.
- For works from databases that publish original, proprietary material available only in that database (such as the UpToDate database) or for works of limited circulation in databases (such as monographs in the ERIC database), include the name of the database or archive and the URL of the work. If the URL requires a login or is session-specific (meaning it will not resolve for readers), provide the URL of the database or archive home page or login page instead of the URL for the work. See the page on including database information in references for more information.
- If the URL is no longer working or no longer provides readers access to the content you intend to cite, follow the guidance for works with no source .
- Other alphanumeric identifiers such as the International Standard Book Number (ISBN) and the International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) are not included in APA Style references.
Follow these guidelines to format DOIs and URLs:
- Present both DOIs and URLs as hyperlinks (i.e., beginning with “http:” or “https:”).
- Because a hyperlink leads readers directly to the content, it is not necessary to include the words “Retrieved from” or “Accessed from” before a DOI or URL.
- It is acceptable to use either the default display settings for hyperlinks in your word-processing program (e.g., usually blue font, underlined) or plain text that is not underlined.
- Leave links live if the work is to be published or read online.
- Follow the current recommendations of the International DOI Foundation to format DOIs in the reference list, which as of this publication is as follows:
https://doi.org/ xxxxx
- The string “https://doi.org/” is a way of presenting a DOI as a link, and “xxxxx” refers to the DOI number.
- The preferred format of the DOI has changed over time. Although older works use previous formats (e.g., “http:/dx.doi.org/” or “doi:” or “DOI:” before the DOI number), in your reference list, standardize DOIs into the current preferred format for all entries. For example, use https://doi.org/10.1037/a0040251 in your reference even though that article, published in 2016, presented the number in an older format.
- Copy and paste the DOI or URL from your web browser directly into your reference list to avoid transcription errors. Do not change the capitalization or punctuation of the DOI or URL. Do not add line breaks manually to the hyperlink; it is acceptable if your word-processing program automatically adds a break or moves the hyperlink to its own line.
- Do not add a period after the DOI or URL because this may interfere with link functionality.
When a DOI or URL is long or complex, you may use shortDOIs or shortened URLs if desired.
- Use the shortDOI service provided by the International DOI Foundation to create shortDOIs. A work can have only one DOI and only one shortDOI; the shortDOI service will either produce a new shortDOI for a work that has never had one or retrieve an existing shortDOI.
- Some websites provide their own branded shortened URLs, and independent URL shortening services are available as well. Any shortened URL is acceptable in a reference as long as you check the link to ensure that it takes you to the correct location.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Paper Format >>
- Last Updated: Jan 24, 2024 12:02 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.udel.edu/apa
Sample Essays: Writing with MLA Style
Congratulations to the students whose essays were selected for the 2023 edition of Writing with MLA Style! Essays were selected as examples of excellent student writing that use MLA style for citing sources. Essays have been lightly edited.
If your institution subscribes to MLA Handbook Plus , you can access annotated versions of the essays selected in 2022 and 2023.
Writing with MLA Style: 2023 Edition
The following essays were selected for the 2023 edition of Writing with MLA Style. The 2023 selection committee was composed of Ellen C. Carillo, University of Connecticut (chair); Rachel Ihara, Kingsborough Community College, City University of New York; and Tarshia L. Stanley, Wagner College.
Caroline Anderson (Pepperdine University)
“ L’Appel du Vide : Making Spaces for Sinful Exploration in The Strange Case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde ”
Hunter Daniels (University of South Carolina, Aiken)
“Biblical Legalism and Cultural Misogyny in The Tragedy of Mariam ”
Aspen English (Southern Utah University)
“Putting the ‘Comm’ in Comics: A Communication-Theory-Informed Reading of Graphic Narratives”
Raul Martin (Lamar University)
“The Book-Object Binary: Access and Sustainability in the Academic Library”
Grace Quasebarth (Salve Regina University)
“Finding a Voice: The Loss of Machismo Criticisms through Translation in Isabel Allende’s The House of the Spirits ”
Writing with MLA Style: 2022 Edition
The following essays were selected for the 2022 edition of Writing with MLA Style. The 2022 selection committee was composed of Ellen C. Carillo, University of Connecticut; Jessica Edwards, University of Delaware (chair); and Deborah H. Holdstein, Columbia College Chicago.
Kaile Chu (New York University, Shanghai)
“Miles Apart: An Investigation into Dedicated Online Communities’ Impact on Cultural Bias”
Sietse Hagen (University of Groningen)
“The Significance of Fiction in the Debate on Dehumanizing Media Portrayals of Refugees”
Klara Ismail (University of Exeter)
“Queering the Duchess: Exploring the Body of the Female Homosexual in John Webster’s The Duchess of Malfi ”
Yasmin Mendoza (Whittier College)
“Banning without Bans”
Niki Nassiri (Stony Brook University)
“Modern-Day US Institutions and Slavery in the Twenty-First Century”
Samantha Wilber (Palm Beach Atlantic University)
“‘Pero, tu no eres facil’: The Poet X as Multicultural Bildungsroman”
Writing with MLA Style: 2019 Edition
The following essays were selected for the 2019 edition of Writing with MLA Style. The 2019 selection committee was composed of Jessica Edwards, University of Delaware; Deborah H. Holdstein, Columbia College Chicago (chair); and Liana Silva, César E. Chavez High School, Houston, Texas.
Catherine Charlton (University of King’s College, Nova Scotia)
“‘Coal Is in My Blood’: Public and Private Representations of Community Identity in Springhill, Nova Scotia”
Alyiah Gonzales (California Polytechnic State University)
“Disrupting White Normativity in Langston Hughes’s ‘I, Too’ and Toni Morrison’s ‘Recitatif’”
Meg Matthias (Miami University, Ohio)
“Prescriptions of (Living) Historical Happiness: Gendered Performance and Racial Comfort in Reenactment”
Jennifer Nguyen (Chaminade University of Honolulu)
“The Vietnam War, the American War: Literature, Film, and Popular Memory”
Emily Schlepp (Northwest University)
“A Force of Love: A Deconstructionist Reading of Characters in Dickens’s Great Expectations ”
- Free Tools for Students
- MLA Citation Generator
Free MLA Citation Generator
Generate accurate citations in MLA format automatically, with MyBib!

😕 What is an MLA Citation Generator?
An MLA citation generator is a software tool designed to automatically create academic citations in the Modern Language Association (MLA) citation format. The generator will take information such as document titles, author, and URLs as in input, and output fully formatted citations that can be inserted into the Works Cited page of an MLA-compliant academic paper.
The citations on a Works Cited page show the external sources that were used to write the main body of the academic paper, either directly as references and quotes, or indirectly as ideas.
👩🎓 Who uses an MLA Citation Generator?
MLA style is most often used by middle school and high school students in preparation for transition to college and further education. Ironically, MLA style is not actually used all that often beyond middle and high school, with APA (American Psychological Association) style being the favored style at colleges across the country.
It is also important at this level to learn why it's critical to cite sources, not just how to cite them.
🙌 Why should I use a Citation Generator?
Writing citations manually is time consuming and error prone. Automating this process with a citation generator is easy, straightforward, and gives accurate results. It's also easier to keep citations organized and in the correct order.
The Works Cited page contributes to the overall grade of a paper, so it is important to produce accurately formatted citations that follow the guidelines in the official MLA Handbook .
⚙️ How do I use MyBib's MLA Citation Generator?
It's super easy to create MLA style citations with our MLA Citation Generator. Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form.
The generator will produce a formatted MLA citation that can be copied and pasted directly into your document, or saved to MyBib as part of your overall Works Cited page (which can be downloaded fully later!).
MyBib supports the following for MLA style:

Daniel is a qualified librarian, former teacher, and citation expert. He has been contributing to MyBib since 2018.
Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — Discrimination — Essay On The Purpose Of Government
Essay on The Purpose of Government
- Categories: Discrimination
About this sample

Words: 629 |
Published: Mar 14, 2024
Words: 629 | Page: 1 | 4 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof. Kifaru
Verified writer
- Expert in: Social Issues

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 672 words
3 pages / 1171 words
3 pages / 1462 words
3 pages / 1552 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Discrimination
In today's competitive job market, companies often prioritize the appearance and image of their employees as a part of their brand strategy. This practice, commonly known as "going for the look," involves hiring individuals [...]
Discrimination in health care is a distressing reality that persists in modern societies, casting a shadow over the principles of fairness and equality that should govern medical practices. Health care is a fundamental human [...]
Skin discrimination is a deeply entrenched form of bias that persists in many societies, perpetuating social inequalities and hindering progress towards a more inclusive world. This essay delves into the complexities of skin [...]
The question of whether healthcare is a right or a luxury is a contentious and complex issue that lies at the intersection of social, economic, and ethical considerations. Access to quality healthcare is a fundamental [...]
Discrimination is a disgusting practice that has been around for many years. The culture and bad teaching have kept this unfair act of exclusionary favor of one group over another alive by means of unchanging learned behaviors, [...]
The dictionary defines microaggression as an utterance, or incident regarded as an instance of indirect, or unintentional discrimination against members of a marginalized group. Professor Derald Sue attempts to define [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Open Letters: Our New Opinion-Writing Contest
We invite students to write public-facing letters to people or groups about issues that matter to them. Contest dates: March 13 to May 1.
By The Learning Network
What’s bothering you? Who could do something about it? What could you say to them that would persuade them to care, or to make change?
And … what if we all read your letter? How could you make us care too?
These are some of the questions we’re asking you to ponder for our new Open Letter Contest. An open letter is a published letter of protest or appeal usually addressed to an individual, group or institution but intended for the general public. Think of the many “Dear Taylor Swift” open letters you can find online and on social media: Sure, they’re addressed to Ms. Swift, but they’re really a way for the writer to share opinions and feelings on feminism, or ticket sales, or the music industry, or … the list goes on.
As you might already know if you’ve read Martin Luther King’s famous Letter From Birmingham Jail , an open letter is a literary device. Though it seems on the surface to be intended for just one individual or group, and therefore usually reads like a personal letter (and can make readers feel they are somehow “listening in” on private thoughts), it is really a persuasive essay addressed to the public. This recent letter signed by over 1,000 tech leaders about the dangers of A.I. , this funny 2020 letter addressed to Harry and Meghan , and this video letter from young Asian Americans to their families about Black Lives Matter are all examples of the tradition.
Now we’re inviting you to try it yourself. Write your own open letter, to anyone you like on any issue you care about, as long as it is also appropriate and meaningful for a general Times audience.
Whom should you write to? What should you say? How do open letters work?
The rules and FAQ below, along with our Student Opinion forum and related how-to guide , can walk you through ways to get started.
This is a new contest and we expect questions. Please ask any you have in the comments and we’ll answer you there, or write to us at [email protected]. And, consider hanging this PDF one-page announcement on your class bulletin board.
Here’s what you need to know:
The challenge, a few rules, resources for students and teachers, frequently asked questions, submission form.
Write an open letter to a specific audience that calls attention to an issue or problem and prompts reflection or action on it.
Whether you choose to write to your parents, teachers, school board members or mayor; a member of Congress; the head of a corporation; an artist or entertainer; or a metonym like “Silicon Valley” or “The Kremlin,” ask yourself, What do I care about? Who can make changes, big or small, local or global, to address my issue or problem? What specifically do I want my audience to understand or do? And how can I write this as an “open letter,” compelling not just to me and the recipient, but to the general audience who will be reading my words?
The Times has published numerous open letters over the years, to both famous and ordinary people. You can find a long list of free examples in our related guide .
This contest invites students to express themselves and imagine that their words can lead to real change.
Your open letter MUST:
Focus on an issue you care about and with which you have some experience. You can write about almost anything you like, whether it’s a serious issue like bullying , or something more lighthearted like why bugs deserve respect , but we have found over the years that the most interesting student writing grows out of personal experience. Our related Student Opinion forum and how-to guide can help you come up with ideas.
Address a specific audience relevant to the issue. Choose an individual, group, organization or institution who is in a position to make change or promote understanding about your topic.
Call for action, whether the change you seek is something tangible , like asking Congress to enact a law or demanding a company stop a harmful practice, or something more abstract, like inviting your audience to reflect on something they may have never considered.
Be suitable and compelling for a wide general audience . An open letter simultaneously addresses an explicit recipient — whether Joe Biden or your gym teacher — as well as us, the general public, your implicit audience. Though your letter might seem to be meant just for one person, it is really trying to persuade all readers. Make sure you write it in such a way that it is relevant, understandable, appropriate and meaningful for anyone who might come across it in The New York Times. (Again, our related guide can help.)
Be written as a letter, in a voice and tone that is appropriate for both your audience and purpose. Are you simply taking an argumentative essay you’ve written for school already and slapping a “Dear X” on top of it and a “Sincerely, Y” on the bottom? No. A letter — even an open letter — is different from a formal essay, and your writing should reflect that. Can you be informal? Funny? If that makes sense for your purpose and audience, then yes, please.
Our related guide, and the many examples we link to, can help you think about this, but we hope the format of a letter will let you loosen up a bit and express yourself in your natural voice. (For example, you’ll be writing as “I” or “we,” and addressing your letter’s recipient as “you.”)
Also attempt to persuade a general audience. Though it is written in the form of a letter, it is an opinion piece, and you are trying to make a case and support it with evidence, as you would any argument. Remember that you are trying to change hearts and minds, so you’ll be drawing on the same rhetorical strategies as you might have for our long-running editorial contest . (Again, more on this in the related guide .)
Make your case in 460 words or fewer. Your title and sources are not part of the word count.
Inform with evidence from at least two sources, including one from The Times and one from outside The Times. We hope this contest encourages you to deepen your understanding of your topic by using multiple sources, ideally ones that offer a range of perspectives. Just make sure those sources are trustworthy .
Because this is a letter, not a formal essay, we are not asking you to provide in-text citations, but we will be asking you to list the sources you used — as many as you like — in a separate field that does not contribute to your word count. Keep in mind, however, that if you include evidence from those sources, our readers (and judges) should always be able to tell where it came from. Be careful to put quotations around any direct quotes you use, and cite the source of anything you paraphrase.
In addition to the guidelines above, here are a few more details:
You must be a student ages 13 to 19 in middle school or high school to participate , and all students must have parent or guardian permission to enter. Please see the F.A.Q. section for additional eligibility details.
The writing you submit should be fundamentally your own — it should not be plagiarized, created by someone else or generated by artificial intelligence.
Your open letter should be original for this contest. That means it should not already have been published at the time of submission, whether in a school newspaper, for another contest or anywhere else.
Keep in mind that the work you send in should be appropriate for a Times audience — that is, something that could be published in a family newspaper (so, please, no curse words).
You may work alone or in groups , but students should submit only one entry each.
You must also submit a short, informal “artist’s statement” as part of your submission, that describes your writing and research process. These statements, which will not be used to choose finalists, help us to design and refine our contests. See the F.A.Q. to learn more.
All entries must be submitted by May 1, at 11:59 p.m. Pacific time using the electronic form at the bottom of this page.
Use these resources to help you write your open letter:
Our step-by-step guide : To be used by students or teachers, this guide walks you through the process of writing an open letter.
A list of free examples of open letters published both in and outside The New York Times, which you can find in our step-by-step guide .
A writing prompt: To Whom Would You Write an Open Letter? This prompt offers students a “rehearsal space” for thinking about to whom they’d like to write, the reason they’re writing and why they think that issue is important — not only for the recipient but also for a wider audience.
Argumentative writing prompts: We publish new argumentative writing prompts for students each week in our Student Opinion and Picture Prompt columns. You can find them all, as they publish, here , or many of them, organized by topic, in our new collection of over 300 prompts .
Argumentative writing unit: This unit includes writing prompts, lesson plans, webinars and mentor texts. While it was originally written to support our Student Editorial Contest , the resources can help students make compelling arguments, cite reliable evidence and use rhetorical strategies for their open letters as well.
Our contest rubric : This is the rubric judges will use as they read submissions to this contest.
Below are answers to your questions about writing, judging, the rules and teaching with this contest. Please read these thoroughly and, if you still can’t find what you’re looking for, post your query in the comments or write to us at [email protected].
Questions About Writing
How is this contest different from your long-running Editorial Contest? Can we still use those materials?
For a decade we ran an editorial contest , and the students who participated wrote passionately about all kinds of things — A.I. , fast fashion , race , trans rights , college admissions , parental incarceration , fan fiction , snow days , memes , being messy and so much more . You can still write about the issues and ideas that fire you up — it’s just that this time around you’ll be framing your work as a letter to a person who has the power to make change on or bring understanding to that issue.
Our related guide has more about the differences between a traditional opinion essay and an open letter, but the many materials we developed for that earlier contest are also woven into the guide, as concepts like ethos, logos and pathos are still very much relevant to this challenge.
I have no idea what to write about. Where should I start?
Our Student Opinion forum can help via its many questions that encourage you to brainstorm both the audience you might write to and the topics you’d like to address.
Can I actually send my open letter?
You can! Just wait until after you have submitted your work to us to do so. (As always for our contests, you retain the copyright to the piece you submit, and can do whatever you like with it.)
Questions About Judging
How will my open letter be judged?
Your work will be read by New York Times journalists, as well as by Learning Network staff members and educators from around the United States. We will use this rubric to judge entries.
What’s the “prize”?
Having your work published on The Learning Network and being eligible to have your work published in the print New York Times.
When will the winners be announced?
About 8-10 weeks after the contest has closed.
My piece wasn’t selected as a winner. Can you tell me why?
We typically receive thousands of entries for our contests, so unfortunately, our team does not have the capacity to provide individual feedback on each student’s work.
QUESTIONS ABOUT THE RULES
Who is eligible to participate in this contest?
This contest is open to students ages 13 to 19 who are in middle school or high school around the world. College students cannot submit an entry. However, high school students (including high school postgraduate students) who are taking one or more college classes can participate. Students attending their first year of a two-year CEGEP in Quebec Province can also participate. In addition, students age 19 or under who have completed high school but are taking a gap year or are otherwise not enrolled in college can participate.
The children and stepchildren of New York Times employees are not eligible to enter this contest. Nor are students who live in the same household as those employees.
Can I have someone else check my work?
We understand that students will often revise their work based on feedback from teachers and peers. That is allowed for this contest. However, be sure that the final submission reflects the ideas, voice and writing ability of the student, not someone else.
Do I need a Works Cited page?
Yes. We provide you with a separate field to list the sources you used to inform or write your open letter. You’re allowed to format your list however you want; we will not judge your entry based on formatting in this section. Internal citations in your letter are not necessary.
Why are you asking for an Artist’s Statement about our process? What will you do with it?
All of us who work on The Learning Network are former teachers. One of the many things we miss, now that we work in a newsroom rather than a classroom, is being able to see how students are reacting to our “assignments” in real time — and to offer help, or tweaks, to make those assignments better. We’re asking you to reflect on what you did and why, and what was hard or easy about it, in large part so that we can improve our contests and the curriculum we create to support them. This is especially important for new contests, like this one.
Another reason? We have heard from many teachers that writing these statements is immensely helpful to students. Stepping back from a piece and trying to put into words what you wanted to express, and why and how you made artistic choices to do that, can help you see your piece anew and figure out how to make it stronger. For our staff, they offer important context that help us understand individual students and submissions, and learn more about the conditions under which students around the world create.
Whom can I contact if I have questions about this contest or am having issues submitting my entry?
Leave a comment on this post or write to us at [email protected].
QUESTIONS ABOUT TEACHING WITH THIS CONTEST
Do my students need a New York Times subscription to access these resources?
No. All of the resources on The Learning Network are free.
If your students don’t have a subscription to The New York Times, they can also get access to Times pieces through The Learning Network . All the activities for students on our site, including mentor texts and writing prompts, plus the Times articles they link to, are free. Students can search for articles using the search tool on our home page.
How do my students prove to me that they entered this contest?
After they press “Submit” on the form below, they will see a “Thank you for your submission.” line appear. They can take a screenshot of this message. Please note: Our system does not currently send confirmation emails.
Please read the following carefully before you submit:
Students who are 13 and older in the United States or the United Kingdom, or 16 and older elsewhere in the world, can submit their own entries. Those who are 13 to 15 and live outside the United States or the United Kingdom must have an adult submit on their behalf.
All students who are under 18 must provide a parent or guardian’s permission to enter.
You will not receive email confirmation of your submission. After you submit, you will see the message “Thank you for your submission.” That means we received your entry. If you need proof of entry for your teacher, please screenshot that message.
If you have questions about your submission, please write to us at [email protected] and provide the email address you used for submission.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Citing sources
How to Cite Sources | Citation Generator & Quick Guide
Citing your sources is essential in academic writing . Whenever you quote or paraphrase a source (such as a book, article, or webpage), you have to include a citation crediting the original author.
Failing to properly cite your sources counts as plagiarism , since you’re presenting someone else’s ideas as if they were your own.
The most commonly used citation styles are APA and MLA. The free Scribbr Citation Generator is the quickest way to cite sources in these styles. Simply enter the URL, DOI, or title, and we’ll generate an accurate, correctly formatted citation.
Generate accurate citations with Scribbr
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text.
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When do you need to cite sources, which citation style should you use, in-text citations, reference lists and bibliographies.
Scribbr Citation Generator
Other useful citation tools
Citation examples and full guides, frequently asked questions about citing sources.
Citations are required in all types of academic texts. They are needed for several reasons:
- To avoid plagiarism by indicating when you’re taking information from another source
- To give proper credit to the author of that source
- To allow the reader to consult your sources for themselves
A citation is needed whenever you integrate a source into your writing. This usually means quoting or paraphrasing:
- To quote a source , copy a short piece of text word for word and put it inside quotation marks .
- To paraphrase a source , put the text into your own words. It’s important that the paraphrase is not too close to the original wording. You can use the paraphrasing tool if you don’t want to do this manually.
Citations are needed whether you quote or paraphrase, and whatever type of source you use. As well as citing scholarly sources like books and journal articles, don’t forget to include citations for any other sources you use for ideas, examples, or evidence. That includes websites, YouTube videos , and lectures .
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Usually, your institution (or the journal you’re submitting to) will require you to follow a specific citation style, so check your guidelines or ask your instructor.
In some cases, you may have to choose a citation style for yourself. Make sure to pick one style and use it consistently:
- APA Style is widely used in the social sciences and beyond.
- MLA style is common in the humanities.
- Chicago notes and bibliography , common in the humanities
- Chicago author-date , used in the (social) sciences
- There are many other citation styles for different disciplines.
If in doubt, check with your instructor or read other papers from your field of study to see what style they follow.
In most styles, your citations consist of:
- Brief in-text citations at the relevant points in the text
- A reference list or bibliography containing full information on all the sources you’ve cited
In-text citations most commonly take the form of parenthetical citations featuring the last name of the source’s author and its year of publication (aka author-date citations).
An alternative to this type of in-text citation is the system used in numerical citation styles , where a number is inserted into the text, corresponding to an entry in a numbered reference list.
There are also note citation styles , where you place your citations in either footnotes or endnotes . Since they’re not embedded in the text itself, these citations can provide more detail and sometimes aren’t accompanied by a full reference list or bibliography.
A reference list (aka “Bibliography” or “Works Cited,” depending on the style) is where you provide full information on each of the sources you’ve cited in the text. It appears at the end of your paper, usually with a hanging indent applied to each entry.
The information included in reference entries is broadly similar, whatever citation style you’re using. For each source, you’ll typically include the:
- Author name
- Publication date
- Container (e.g., the book an essay was published in, the journal an article appeared in)
- Location (e.g., a URL or DOI , or sometimes a physical location)
The exact information included varies depending on the source type and the citation style. The order in which the information appears, and how you format it (e.g., capitalization, use of italics) also varies.
Most commonly, the entries in your reference list are alphabetized by author name. This allows the reader to easily find the relevant entry based on the author name in your in-text citation.
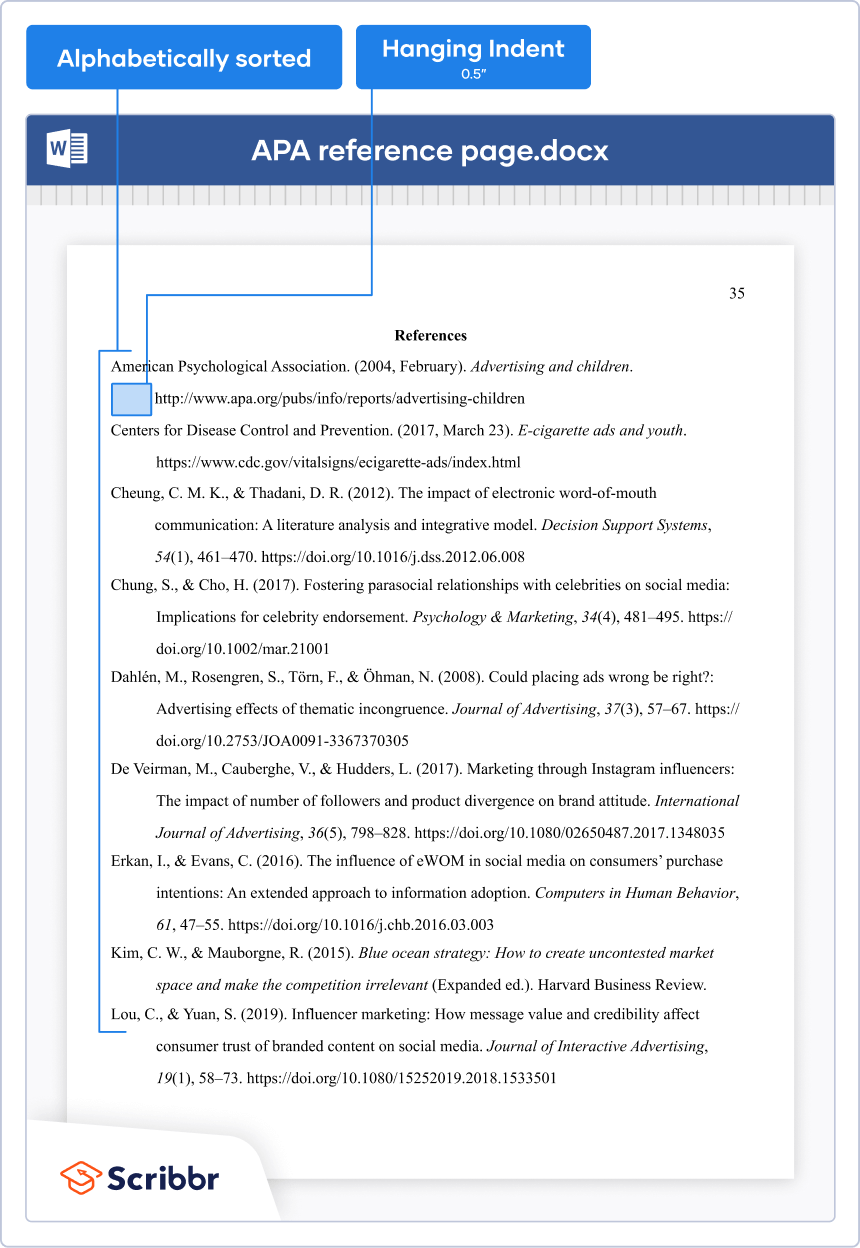
In numerical citation styles, the entries in your reference list are numbered, usually based on the order in which you cite them. The reader finds the right entry based on the number that appears in the text.
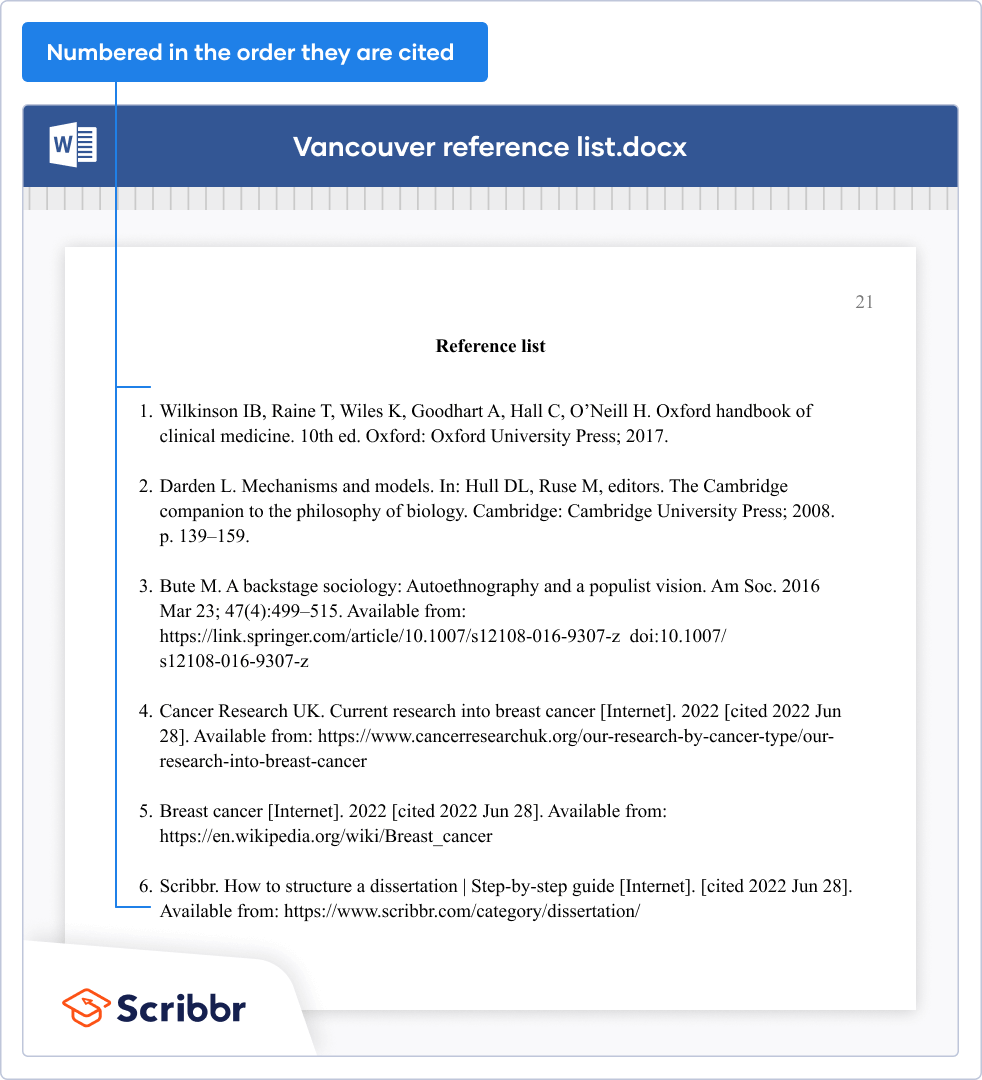
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

Because each style has many small differences regarding things like italicization, capitalization , and punctuation , it can be difficult to get every detail right. Using a citation generator can save you a lot of time and effort.
Scribbr offers citation generators for both APA and MLA style. Both are quick, easy to use, and 100% free, with no ads and no registration required.
Just input a URL or DOI or add the source details manually, and the generator will automatically produce an in-text citation and reference entry in the correct format. You can save your reference list as you go and download it when you’re done, and even add annotations for an annotated bibliography .
Once you’ve prepared your citations, you might still be unsure if they’re correct and if you’ve used them appropriately in your text. This is where Scribbr’s other citation tools and services may come in handy:
Plagiarism Checker
Citation Checker
Citation Editing
Plagiarism means passing off someone else’s words or ideas as your own. It’s a serious offense in academia. Universities use plagiarism checking software to scan your paper and identify any similarities to other texts.
When you’re dealing with a lot of sources, it’s easy to make mistakes that could constitute accidental plagiarism. For example, you might forget to add a citation after a quote, or paraphrase a source in a way that’s too close to the original text.
Using a plagiarism checker yourself before you submit your work can help you spot these mistakes before they get you in trouble. Based on the results, you can add any missing citations and rephrase your text where necessary.
Try out the Scribbr Plagiarism Checker for free, or check out our detailed comparison of the best plagiarism checkers available online.
Scribbr Plagiarism Checker
Scribbr’s Citation Checker is a unique AI-powered tool that automatically detects stylistic errors and inconsistencies in your in-text citations. It also suggests a correction for every mistake.
Currently available for APA Style, this is the fastest and easiest way to make sure you’ve formatted your citations correctly. You can try out the tool for free below.
If you need extra help with your reference list, we also offer a more in-depth Citation Editing Service.
Our experts cross-check your in-text citations and reference entries, make sure you’ve included the correct information for each source, and improve the formatting of your reference page.
If you want to handle your citations yourself, Scribbr’s free Knowledge Base provides clear, accurate guidance on every aspect of citation. You can see citation examples for a variety of common source types below:
And you can check out our comprehensive guides to the most popular citation styles:
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
The abbreviation “ et al. ” (Latin for “and others”) is used to shorten citations of sources with multiple authors.
“Et al.” is used in APA in-text citations of sources with 3+ authors, e.g. (Smith et al., 2019). It is not used in APA reference entries .
Use “et al.” for 3+ authors in MLA in-text citations and Works Cited entries.
Use “et al.” for 4+ authors in a Chicago in-text citation , and for 10+ authors in a Chicago bibliography entry.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .
APA format is widely used by professionals, researchers, and students in the social and behavioral sciences, including fields like education, psychology, and business.
Be sure to check the guidelines of your university or the journal you want to be published in to double-check which style you should be using.
MLA Style is the second most used citation style (after APA ). It is mainly used by students and researchers in humanities fields such as literature, languages, and philosophy.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- Citation Styles Guide | Examples for All Major Styles
- APA vs. MLA | The Key Differences in Format & Citation
- The Basics of In-Text Citation | APA & MLA Examples
More interesting articles
- Citation examples for common sources types
- Et Al. | Meaning & Use in APA, MLA & Chicago
- Hanging Indent | Word & Google Docs Instructions
- How to Cite a Book | APA, MLA, & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Journal Article | APA, MLA, & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Lecture | APA, MLA & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Newspaper Article | MLA, APA & Chicago
- How to Cite a Website | MLA, APA & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Wikipedia Article | APA, MLA & Chicago
- How to Cite a YouTube Video | MLA, APA & Chicago
- How to Cite an Image | Photographs, Figures, Diagrams
- How to Cite an Interview | APA, MLA & Chicago Style
- Parenthetical Citation | APA, MLA & Chicago Examples
- What Are Endnotes? | Guide with Examples
- What Are Footnotes? | Guide with Word Instructions
- What Does Ibid. Mean? | Definition & Examples
- What is a DOI? | Finding and Using Digital Object Identifiers
- What Is an Annotated Bibliography? | Examples & Format
What is your plagiarism score?
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA General Format

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
MLA Style specifies guidelines for formatting manuscripts and citing research in writing. MLA Style also provides writers with a system for referencing their sources through parenthetical citation in their essays and Works Cited pages.
Writers who properly use MLA also build their credibility by demonstrating accountability to their source material. Most importantly, the use of MLA style can protect writers from accusations of plagiarism, which is the purposeful or accidental uncredited use of source material produced by other writers.
If you are asked to use MLA format, be sure to consult the MLA Handbook (9th edition). Publishing scholars and graduate students should also consult the MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing (3rd edition). The MLA Handbook is available in most writing centers and reference libraries. It is also widely available in bookstores, libraries, and at the MLA web site. See the Additional Resources section of this page for a list of helpful books and sites about using MLA Style.
Paper Format
The preparation of papers and manuscripts in MLA Style is covered in part four of the MLA Style Manual . Below are some basic guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA Style :
General Guidelines
- Type your paper on a computer and print it out on standard, white 8.5 x 11-inch paper.
- Double-space the text of your paper and use a legible font (e.g. Times New Roman). Whatever font you choose, MLA recommends that the regular and italics type styles contrast enough that they are each distinct from one another. The font size should be 12 pt.
- Leave only one space after periods or other punctuation marks (unless otherwise prompted by your instructor).
- Set the margins of your document to 1 inch on all sides.
- Indent the first line of each paragraph one half-inch from the left margin. MLA recommends that you use the “Tab” key as opposed to pushing the space bar five times.
- Create a header that numbers all pages consecutively in the upper right-hand corner, one-half inch from the top and flush with the right margin. (Note: Your instructor may ask that you omit the number on your first page. Always follow your instructor's guidelines.)
- Use italics throughout your essay to indicate the titles of longer works and, only when absolutely necessary, provide emphasis.
- If you have any endnotes, include them on a separate page before your Works Cited page. Entitle the section Notes (centered, unformatted).
Formatting the First Page of Your Paper
- Do not make a title page for your paper unless specifically requested or the paper is assigned as a group project. In the case of a group project, list all names of the contributors, giving each name its own line in the header, followed by the remaining MLA header requirements as described below. Format the remainder of the page as requested by the instructor.
- In the upper left-hand corner of the first page, list your name, your instructor's name, the course, and the date. Again, be sure to use double-spaced text.
- Double space again and center the title. Do not underline, italicize, or place your title in quotation marks. Write the title in Title Case (standard capitalization), not in all capital letters.
- Use quotation marks and/or italics when referring to other works in your title, just as you would in your text. For example: Fear and Loathing in Las Vegas as Morality Play; Human Weariness in "After Apple Picking"
- Double space between the title and the first line of the text.
- Create a header in the upper right-hand corner that includes your last name, followed by a space with a page number. Number all pages consecutively with Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, 4, etc.), one-half inch from the top and flush with the right margin. (Note: Your instructor or other readers may ask that you omit the last name/page number header on your first page. Always follow instructor guidelines.)
Here is a sample of the first page of a paper in MLA style:

The First Page of an MLA Paper
Section Headings
Writers sometimes use section headings to improve a document’s readability. These sections may include individual chapters or other named parts of a book or essay.
MLA recommends that when dividing an essay into sections you number those sections with an Arabic number and a period followed by a space and the section name.
MLA does not have a prescribed system of headings for books (for more information on headings, please see page 146 in the MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing , 3rd edition). If you are only using one level of headings, meaning that all of the sections are distinct and parallel and have no additional sections that fit within them, MLA recommends that these sections resemble one another grammatically. For instance, if your headings are typically short phrases, make all of the headings short phrases (and not, for example, full sentences). Otherwise, the formatting is up to you. It should, however, be consistent throughout the document.
If you employ multiple levels of headings (some of your sections have sections within sections), you may want to provide a key of your chosen level headings and their formatting to your instructor or editor.
Sample Section Headings
The following sample headings are meant to be used only as a reference. You may employ whatever system of formatting that works best for you so long as it remains consistent throughout the document.
Formatted, unnumbered:
Level 1 Heading: bold, flush left
Level 2 Heading: italics, flush left
Level 3 Heading: centered, bold
Level 4 Heading: centered, italics
Level 5 Heading: underlined, flush left

Conditional Formatting in classic Outlook for Windows
Conditional formatting in classic Outlook for Windows allows you to automatically change incoming message colors and fonts based on sender, subject, or recipients. Conditional formatting in classic Outlook for Windows is a way to make the incoming messages that meet defined conditions stand out in the message list by using color, fonts, and styles. You specify conditions that an incoming message should meet, such as a sender’s name or email address, and then conditional formatting is applied only to those messages.
For example, a conditional rule can specify that all messages sent from your manager appear in red text in the message list. If you want to make further changes to the body of your email messages, change the default font or text color for email messages .
Note: Beginning with Microsoft Outlook 2010, the Organize feature that enabled you to create conditional text formatting rules for email messages was removed. Conditional text formatting is now accessed in the Advanced View Settings dialog box.
In this article
Create a conditional formatting rule in classic outlook for windows, example conditional formatting rules in classic outlook for windows, make all messages from john kane appear in red, make all messages that contain the word contoso in the subject appear green, make all messages that contain the word holiday in the subject or message body appear blue.
In Outlook for Windows, click View .
In the Current View group, click View Settings .
In the Advanced View Settings dialog box, click Conditional Formatting .

A set of default rules appears. This includes the Unread messages rule. This rule makes unread messages appear bold in the message list. In addition, any conditional formatting rules that you created in the Organize pane with an earlier version of Outlook appear.
Do any of the following:
To delete a rule, click the rule, and then click Delete .
To temporarily turn off a rule, clear the check box for that rule.
To change the criteria for a rule, click the rule, and then click Condition .
To change the text formatting, click the rule, and then click Font .
To add a new conditional formatting rule, click Add , in the Name box, type a name, click Font to specify the formatting, and then click Condition to specify the criteria for this rule.
Following are some examples of conditional formatting rules that you can create in Outlook.
Click Add .
Enter a name for the rule.
Click Font .
Under Color , click Red .
Click Condition .
In the From box, type John Kane.
Note: The name must exactly match the full name that appears on messages that you receive.
In the Filter , Conditional Formatting , and Advanced View Settings dialog boxes, click OK .
Under Color , click Green .
In the Search for the word(s) box, type Contoso.
Under Color , click Blue .
In the Search for the word(s) box, type holiday.
Top of Page

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Create manual citation. The guidelines for citing an essay in MLA format are similar to those for citing a chapter in a book. Include the author of the essay, the title of the essay, the name of the collection if the essay belongs to one, the editor of the collection or other contributors, the publication information, and the page number (s).
Citation Examples | Books, Articles, Websites & More. Published on April 9, 2021 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on January 17, 2024. The most common citation styles are APA and MLA. To cite a source in these styles, you need a brief in-text citation and a full reference. Use the interactive tool to understand how a citation is structured and see ...
Throughout your paper, you need to apply the following APA format guidelines: Set page margins to 1 inch on all sides. Double-space all text, including headings. Indent the first line of every paragraph 0.5 inches. Use an accessible font (e.g., Times New Roman 12pt., Arial 11pt., or Georgia 11pt.).
The Bluebook: A Uniform System of Citation is the main style guide for legal citations in the US. It's widely used in law, and also when legal materials need to be cited in other disciplines. Bluebook footnote citation. 1 David E. Pozen, Freedom of Information Beyond the Freedom of Information Act, 165, U. P🇦 .
When you cite a work that appears inside a larger source (for instance, an article in a periodical or an essay in a collection), cite the author of the internal source (i.e., the article or essay). For example, to cite Albert Einstein's article "A Brief Outline of the Theory of Relativity," which was published in Nature in 1921, you might write ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Crucially, citation practices do not differ between the two styles of paper. However, for your convenience, we have provided two versions of our APA 7 sample paper below: one in student style and one in professional style. Note: For accessibility purposes, we have used "Track Changes" to make comments along the margins of these samples.
More than 100 reference examples and their corresponding in-text citations are presented in the seventh edition Publication Manual.Examples of the most common works that writers cite are provided on this page; additional examples are available in the Publication Manual.. To find the reference example you need, first select a category (e.g., periodicals) and then choose the appropriate type of ...
When you cite a source with up to three authors, cite all authors' names. For four or more authors, list only the first name, followed by ' et al. ': Number of authors. In-text citation example. 1 author. (Davis, 2019) 2 authors. (Davis and Barrett, 2019) 3 authors.
In-text citations point the reader to the sources' information on the references page. The in-text citation typically includes the author's last name and the year of publication. If you use a direct quote, the page number is also provided. More information can be found on p. 253 of the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American ...
Start by applying these MLA format guidelines to your document: Times New Roman 12. 1″ page margins. Double line spacing. ½" indent for new paragraphs. Title case capitalization for headings. For accurate citations, you can use our free MLA Citation Generator. Download Word template Open Google Docs template.
APA Style uses in-text citations to refer to larger reference lists at the end of the document. The 2 basic elements of an APA Style in-text citation are: (Author, Date) The 4 basic elements of an APA Style reference are: Author. (Date). Title. Source. Examples come from apastyle.apa.org unless otherwise noted.
Works Included in a Reference List. The reference list provides a reliable way for readers to identify and locate the works cited in a paper. APA Style papers generally include reference lists, not bibliographies. In general, each work cited in the text must appear in the reference list, and each work in the reference list must be cited in the ...
When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, like, for example, (Jones, 1998). One complete reference for each source should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
Congratulations to the students whose essays were selected for the 2023 edition of Writing with MLA Style! Essays were selected as examples of excellent student writing that use MLA style for citing sources. Essays have been lightly edited. If your institution subscribes to MLA Handbook Plus, you can access annotated versions of the essays selected …
Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form. The generator will produce a formatted MLA ...
The tone used in professional, scientific, and scholarly writing is different from the style used in creative or less formal writing. For example, in APA Style writing, do not use creative writing techniques such as suddenly shifting the topic or tense. Also, avoid an informal writing style such as using contractions, colloquialisms, and slang.
Quotes should always be cited (and indicated with quotation marks), and you should include a page number indicating where in the source the quote can be found. Example: Quote with APA Style in-text citation. Evolution is a gradual process that "can act only by very short and slow steps" (Darwin, 1859, p. 510).
The protection of individual rights is a fundamental aspect of government's role in promoting the common good and ensuring the well-being of society. This is only a sample. Get a custom paper now from our expert writers. In conclusion, the purpose of government is multifaceted, encompassing the maintenance of order, the provision of essential ...
Summary: MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
A gerund is a noun that is derived from a verb, using the "-ing" ending (e.g., "swimming," cooking").. A gerund phrase is a group of words that begins with a gerund and includes any of its modifiers or objects (e.g., "swimming in the ocean," "cooking dinner every night for my friends").. Both gerunds and gerund phrases act as nouns in sentences and can be subjects, direct ...
These are some of the questions we're asking you to ponder for our new Open Letter Contest. An open letter is a published letter of protest or appeal usually addressed to an individual, group or ...
Scribbr offers citation generators for both APA and MLA style. Both are quick, easy to use, and 100% free, with no ads and no registration required. Just input a URL or DOI or add the source details manually, and the generator will automatically produce an in-text citation and reference entry in the correct format.
MLA General Format. MLA Style specifies guidelines for formatting manuscripts and citing research in writing. MLA Style also provides writers with a system for referencing their sources through parenthetical citation in their essays and Works Cited pages. Writers who properly use MLA also build their credibility by demonstrating accountability ...
Make all messages that contain the word Contoso in the subject appear green. Click Add. Enter a name for the rule. Click Font. Under Color, click Green. Click OK. Click Condition. In the Search for the word (s) box, type Contoso. In the Filter, Conditional Formatting, and Advanced View Settings dialog boxes, click OK.