Best 10 BCG Matrix Examples for Students
Discover more helpful information.
BCG Matrix is an apparatus utilized to incorporate methodology to break down specialty units or product offerings dependent on two factors: relative piece of the overall industry and the market development rate. By joining these two factors into a matrix, an organization can plot their specialty units as needs are and figure out where to dispense extra (financial) assets, where to money out, and where to strip.
The primary reason for the BCG Matrix is accordingly to settle on speculation choices on a corporate level. Contingent upon how well the unit and the business are doing, four different classification names can be credited to every group:
- Question Marks
This article covers every classification and how to utilize the BCG Matrix appropriately.

10 Examples of BCG Matrix (of famous companies)
The BCG Model depends on items as opposed to administrations, be that as it may, it applies to both. You could utilize this if checking on a scope of items, particularly before growing new ones. Here are the example list:
1. BCG Matrix of Coca-Cola
A world-driving ready-to-drink refreshment company, Coca-Cola Company has more than 500 soda pop brands, from Fuse Tea to Oasis to Lilt to Powerade. Yet, none of them is anyplace near the coke brand in terms of mindfulness, income, and benefit.
Stage 1. Choose the Product/Firm/Brand
We pick the firm Coca-Cola for investigation. Also, you need to identify the market, as the picked market is beverages, diet cokes, and mineral water.
Stage 2. Calculate Relative Market Share & Find out the Market Growth Rate
By and tremendous Growth rate in Coke is that it is no: in more than 200 countries.
Stage 3. Draw the Circles on a Matrix

2. BCG Matrix of Samsung
Stage 1. choose the product/firm/brand.
We pick the firm Samsung for investigation.
The picked market is the consumer electronics industry which incorporates smartphones, computers, tablets, etc.
Stage 3. Calculate Relative Market Share
By and tremendous Growth rate in Samsung home appliances by making 60% of the sales.
Stage 4. Draw the circles on a matrix

3. BCG Matrix of L'Oréal
We pick the firm L'Oréal for investigation.
Stage 2. Identify Market
The picked market is the Cosmetics Industry, which essentially incorporates Skincare, Makeup, Haircare, Hair shading, and Fragrances.
Stage 4. Find out the Market Growth rate
By and tremendous Growth rate in Cosmetics Industry (starting at 2018) = 4.8%
Stage 5. Draw the circles on a matrix
Note: Just follow the above pattern with every example and BCG matrix you will be making for your class.

4. BCG Matrix of PepsiCo

5. BCG Matrix of Apple

6. BCG Matrix of Nestle

7. BCG Matrix of Unilever

8. BCG Matrix of McDonalds

9. BCG Matrix of KFC

10. BCG Matrix of Amazon

What is BCG Matrix?
The Boston Consulting Group's item portfolio matrix ( BCG matrix ), otherwise called the Growth/Share Matrix, is a vital arranging device that enables a business to consider development openings by inspecting its arrangement of items to choose where to contribute to suspend or create things. It's otherwise called the Growth/Share Matrix. The Matrix is separated into four quadrants dependent on an investigation of market development and the relative peace of the overall industry.
It depends on the mix of market development and the overall industry comparative with the following best contender.
High Growth, High Market Share
Star units are pioneers in the classification. Items situated in this quadrant are appealing as they are located in a hearty class, and these items are exceptionally serious in the classification.
2. Question Marks
High Growth, Low Market Share
Like the name proposes, the future capability of these items is dubious. Since the development rate is high here, with the correct systems and ventures, they can become Cash cows and, at last, Stars if they have a flat piece of the overall industry so that off-base ventures can downsize them to Dogs significantly after loads of speculation.
3. Cash Cows
Low Growth, High Market Share
In the long run, if you are working for quite a while working in the business, advertising development may decay, and incomes deteriorate. At this stage, your Stars are probably going to change into Cash Cows. Since they despise everything that has a substantial relative piece of the overall industry in a deteriorating (developed) market, benefits and cash streams are relied upon to be high. As a result of the lower development rate, ventures required ought to likewise below. Along these lines, cash cows ordinarily produce cash in an overabundance of the measure of money expected to keep up the business. This 'overabundance cash' should be 'drained' from the Cash Cow for interests in different specialty units (Stars and Question Marks). Cash Cows eventually carry parity and security to a portfolio.
Low Growth, Low Market Share
Dogs hold a flat piece of the overall industry contrasted with contenders. Neither do they create cash, nor do they require huge cash. As a rule, the resources are not worth putting into because they create low or negative cash returns and may need enormous entireties of money to help. Because of the flat piece of the pie, these items face cost inconveniences.
How to Make a BCG Matrix Diagram?
So far, we realize products are ordered in four sorts. Presently we will see on what premise and how that order is done. We will comprehend the five procedures of improving a BCG matrix by making one for L'Oréal in the areas to follow.
Stage 1. Choose the Product
BCG matrix can be utilized to operate Business Units, separate brands, products, or firms as a unit itself. The decision of the group impacts the entire investigation. Along these lines, characterizing the unit is essential.
Stage 2. Define the Market
A mistakenly characterized market can prompt a weak characterization of products. For instance, if we investigate Daimler's Mercedes-Benz vehicle brand in the traveler vehicle market, it would wind up as a dog (it holds under 20% relative market share). However, it would be a cash cow in the extravagant vehicle market. Characterizing the market is a significant pre-imperative for a better understanding of the portfolio position.
Stage 3. Calculate the Relative Market Share
Market share is the level of the entire market taken into account by your company, estimated either in income terms or unit volume terms.
We utilize Relative Market Share in a BCG matrix, contrasting our product deals and the main adversary's sales for a similar product.
Relative Market Share = Product's business this year/Leading opponent's business this year
For instance, if your rival's market share in the vehicle business was 25% and your association's image market share was 10% around the same time, your relative market share would be just 0.4. The relative market share is given on the x-axis.
Stage 4. Find out the Market Development Rate
The business development rate can be effortlessly found through free online sources. It can likewise be determined by deciding the healthy income development of the leading firms. The market development rate is estimated in rate terms.
Market development rate was typically given side-effects (business this year – Product's business a year ago)/Product's business a year ago.
Markets with high development are ones where the total market share accessible is growing, so there are a lot of chances for all organizations to bring in cash.
Stage 5. Draw the Circles on a Matrix
Having determined the above measures, you have to plot the brands on the Matrix simply on EdrawMind desktop version. It has the premade templates for BCG. All you have to do is put up the data just like we did with every example.
The x-axis shows the relative market share, and the they-pivot shows the business development rate. You can plan a hover for every unit/brand/product, the size of which ought to relate to the extent of income created by it in a perfect world.
Taken these variables together, you can attract the perfect way to follow the BCG Matrix, from start-up to market pioneer. Question Marks and Stars should be financed with ventures produced with Cash Cows. What's more, Dogs should be stripped or exchanged to let loose cash with minimal potential and use it somewhere else. At long last, you will require a reasonable arrangement of Question Marks, Stars, and Cash Cows to guarantee positive cash streams later on.

[2023] Story Summary Examples

7 Types of Organizational Charts (With Examples)

Sunburst Chart: Explained with Examples & Templates

Story Outline Examples

To-Do List Mind Map Template

B2U – Business-to-you.com
THE place that brings real life business, management and strategy to you
BCG Matrix: Portfolio Analysis in Corporate Strategy
BCG Matrix (also known as the Boston Consulting Group analysis, the Growth-Share matrix, the Boston Box or Product Portfolio matrix) is a tool used in corporate strategy to analyse business units or product lines based on two variables: relative market share and the market growth rate. By combining these two variables into a matrix, a corporation can plot their business units accordingly and determine where to allocate extra (financial) resources, where to cash out and where to divest. The main purpose of the BCG Matrix is therefore to make investment decisions on a corporate level. Depending on how well the unit and the industry is doing, four different category labels can be attributed to each unit: Dogs, Question Marks, Cash Cows and Stars. This article will cover each of these categories and how to properly use the BCG Matrix yourself.
Figure 1: BCG Matrix
BCG Matrix Example: Samsung’s Product Portfolio
Samsung is a conglomerate consisting of multiple strategic business units (SBUs) with a diverse set of products. Samsung sells phones, cameras, TVs, microwaves, refrigerators, laundry machines, and even chemicals and insurances. This is a smart corporate strategy to have because it spreads risk among a large variety of business units. In case something might happen to the camera industry for instance, Samsung is still likely to have positive cash flows from other business units in other product categories. This helps Samsung to cope with the financial setback elsewhere. However even in a well balanced product portfolio, corporate strategists will have to make decisions on allocating money to and distributing money across all of those business units. Where do you put most of the money and where should you perhaps divest? The BCG Matrix uses Relative Market Share and the Market Growth Rate to determine that.

BCG Matrix Video Tutorial
Relative Market Share
The creator of the BCG Matrix used this variable to actually measure a company’s competitiveness . The exact measure for Relative Market Share is the focal company’s share relative to its largest competitor. So if Samsung has a 20 percent market share in the mobile phone industry and Apple (its largest competitor) has 60 percent so to speak, the ratio would be 1:3 (0.33) implying that Samsung has a relatively weak position. If Apple only had a share of 10 percent, the ratio would be 2:1 (2.0), implying that Samsung is in a relatively strong position, which might be reflected in above average profits and cash flows. The cut-off point here is 1.0, meaning that the focal company should at least have a similar market share as its largest competitor in order to have a high relative market share. The assumption in this framework is that an increase in relative market share will result in an increase in the generation of cash , since the focal company benefits from economies of scales and thus gains a cost advantage relative to its competitors.
Market Growth Rate
The second variable is the Market Growth Rate , which is used to measure the market attractiveness . Rapidly growing markets are what organizations usually strive for, since they are promising for interesting returns on investments in the long term. The drawback however is that companies in growing markets are likely to be in need for investments in order to make growth possible. The investments are for example needed to fund marketing campaigns or to increase capacity. High or low growth rates can vary from industry to industry, but the cut-off point in general is usually chosen around 10 percent per annum. This means that if Samsung would be operating in an industry where the market is growing 12 percent a year on average, the market growth rate would be considered high.
Question Marks
Ventures or start-ups usually start off as Question Marks . Question Marks (or Problem Children) are businesses operating with a low market share in a high growth market. They have the potential to gain market share and become Stars (market leaders) eventually. If managed well, Question Marks will grow rapidly and thus consume a large amount of cash investments. If Question Marks do not succeed in becoming a market leader, they might degenerate into Dogs when market growth declines after years of cash consumption. Question marks must therefore be analyzed carefully in order to determine whether they are worth the investment required to grow market share.
Stars are business units with a high market share (potentially market leaders) in a fast-growing industry. Stars generate large amounts of cash due to their high relative market share but also require large investments to fight competitors and maintain their growth rate. Successfully diversified companies should always have some Stars in their portfolio in order to ensure future cash flows in the long term. Apart from the assurance that Stars give for the future, they are also very good to have for your corporate’s image.
Eventually after years of operating in the industry, market growth might decline and revenues stagnate. At this stage, your Stars are likely to transform into Cash Cows . Because they still have a large relative market share in a stagnating (mature) market, profits and cash flows are expected to be high. Because of the lower growth rate, investments needed should also be low. Cash cows therefore typically generate cash in excess of the amount of cash needed to maintain the business. This ‘excess cash’ is supposed to be ‘milked’ from the Cash Cow for investments in other business units (Stars and Question Marks). Cash Cows ultimately bring balance and stability to a portfolio.
Business units in a slow-growth or declining market with a small relative market share are considered Dogs. These units typically break even (they neither create nor consume a large amount of cash) and generate barely enough cash to maintain the business’s market share. These businesses are therefore not so interesting for investors. Since there is still money involved in these business units that could be used in units with more potential, Dogs are likely to be divested or liquidated.
Figure 2: Cash Flows and Desired Movement in BCG Matrix
BCG Matrix and the Product Life Cycle
The BCG matrix has a strong connection with the Product Life Cycle . The Question Marks represent products or SBU’s that are in the introduction phase. This is when new products are being launched in the market. Stars are SBU’s or products in their growth phase. This is when sales are increasing at their fastest rate. Cash Cows are in the maturity phase: when sales are near their highest, but the rate of growth is slowing down due to saturation in the market. And Dogs are in the decline phase: the final stage of the cycle, when sales begin to fall.
Figure 3: BCG Matrix and Product Life Cycle
BCG Matrix In Sum
Taken all of these factors together, you can draw the ideal path to follow in the BCG Matrix, from start-up to market leader. Question Marks and Stars are supposed to be funded with investments generated by Cash Cows. And Dogs need to be divested or liquidated to free up cash with little potential and use it elsewhere. In the end, you will need a balanced portfolio of Question Marks, Stars and Cash Cows to assure positive cash flows in the future. If you want to know more about HOW to spend these investments in order to grow a business unit, you might want to read more about the Ansoff Matrix . Besides the BCG Matrix, there are other portfolio management frameworks you might want to have a look at such as the GE McKinsey Nine Box Matrix .
Further Reading:
- Henderson, B. (1970). Growth-Share Matrix. BCG Perspectives.
- https://www.bcgperspectives.com/content/articles/corporate_strategy_portfolio_management_strategic_planning_growth_share_matrix_bcg_classics_revisited/
- https://www.bcg.com/publications/1970/strategy-the-product-portfolio.aspx
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window)
- ← Marketing Funnel: Visualizing the Customer Journey
- Value Chain Analysis: An Internal Assessment of Competitive Advantage →
10 thoughts on “ BCG Matrix: Portfolio Analysis in Corporate Strategy ”
Simple, easy to follow and moreover Clear and Perfect presentation Sir.
impressing thank you so much……well articulated easily understandable tutorial/lecture.
Thank you, all the videos have helped me with my studies and progress in my MBA
Great videos, really helps
Great video it was really easy to follow!!
From ILOVEADIAN
This is a great video. Explained BCG matrix succinctly
Fantastic breakdown of the BCG matrix. greatly simplified!
What a powerful presantation of the BCG Matrix. You are simply the best.
Great website. It helps to add further clarity and more context to my textbook.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- BCG Growth-Share Matrix
- How It Works
- Limitations
The Bottom Line
- Corporate Finance
- Corporate Finance Basics
Understanding the BCG Growth Share Matrix and How to Use It
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
Investopedia / Laura Porter
What Is a BCG Growth-Share Matrix?
The Boston Consulting Group (BCG) growth-share matrix is a planning tool that uses graphical representations of a company’s products and services in an effort to help the company decide what it should keep, sell, or invest more in.
The matrix plots a company’s offerings in a four-square matrix, with the y-axis representing the rate of market growth and the x-axis representing market share. It was introduced by the Boston Consulting Group in 1970.
Key Takeaways
- The BCG growth-share matrix is a tool used internally by management to assess the current state of value of a firm's units or product lines.
- BCG stands for the Boston Consulting Group, a well-respected management consulting firm.
- The growth-share matrix aids the company in deciding which products or units to either keep, sell, or invest more in.
- The BCG growth-share matrix contains four distinct categories: dogs, cash cows, stars, and question marks.
- The matrix helps companies decide how to prioritize their various business activities.
Understanding a BCG Growth-Share Matrix
The BCG growth-share matrix breaks down products into four categories, known simply as dogs, cash cows, stars, and question marks. Each category quadrant has its own set of unique characteristics.
Dogs (or Pets)
If a company’s product has a low market share and is at a low rate of growth, it is considered a dog and should be sold, liquidated, or repositioned. Dogs , found in the lower right quadrant of the grid, don't generate much cash for the company since they have a low market share and little to no growth. Because of this, dogs can turn out to be cash traps, tying up company funds for long periods of time. For this reason, they are prime candidates for divestiture .
Products that are in low-growth areas but for which the company has a relatively large market share are considered cash cows, and the company should thus milk the cash cow for as long as it can. Cash cows, seen in the lower left quadrant, are typically leading products in markets that are mature .
These products generally generate returns that are higher than the market's growth rate and sustain itself from a cash flow perspective. These products should be taken advantage of for as long as possible. The value of cash cows can be easily calculated since their cash flow patterns are highly predictable. In effect, low-growth, high-share cash cows should be milked for cash to reinvest in high-growth, high-share stars with high future potential .
The matrix is not a predictive tool; it takes into account neither new, disruptive products entering the market nor rapid shifts in consumer demand.
Products that are in high-growth markets and that make up a sizable portion of that market are considered stars and should be invested in more. In the upper left quadrant are stars, which generate high income but also consume large amounts of company cash. If a star can remain a market leader, it eventually becomes a cash cow when the market's overall growth rate declines.
Question Marks
Questionable opportunities are those in high growth rate markets but in which the company does not maintain a large market share. Question marks or "problem children" are in the upper right portion of the grid. They typically grow fast but consume large amounts of company resources. Products in this quadrant should be analyzed frequently and closely to see if they are worth maintaining.
Limitations of the Matrix
One thing to note is that the matrix is a decision-making tool. This means that it does not necessarily take into account all the factors that a business ultimately must face. For example, increasing market share may be more expensive than the additional revenue gained from new sales. Because product development may take years, businesses must plan for contingencies carefully.
Since the matrix only classifies businesses as low and high, it does leave mid-sized businesses out of the mix. These types of companies often make up a big part of the market, so leaving them out means that the business environment isn't truly reflected.
The BCG matrix assumes that all businesses operate independently of one another. But that isn't always necessarily true. Certain players in the market, such as dogs, may end up giving others a boost—sometimes unintentionally.
Bruce Henderson, who founded BCG, created the concept of the growth matrix in 1970.
Example of a BCG Growth Matrix
There are many companies that we can apply the growth matrix to in the real world. Apple ( AAPL ) is a great candidate. Let's take a look at the products Apple has on the market according to the matrix categories:
- Star: iPhone
- Cash Cow: Macbook
- Question Mark: Apple TV
In 2022, the company earned $394.33 billion in net sales , out of which almost $316.2 billion was attributed to its products section. The remaining $78.13 billion came from its services division:
- There's no doubt that the majority of Apple's sales come from its most popular product. The iPhone brought in $205.49 billion in sales for the year. In this case, it's considered the company's star.
- The cash cow for the company is its Mac products—notably the Macbook laptop, which is one of the most popular in this group. Sales for Mac products came in at $40.18 billion for the fiscal year (FY) .
- One of the question marks for Apple is its Apple TV streaming service, which falls under the Services category. The competition in the streaming world is intense, with traditional services like Netflix , Hulu, Disney+ dominating the market. But others like YouTube and Vimeo are also eating away at market share. In 2022, Apple's Services division earned $78.13 billion in sales.
- Once a darling of the company, the iPad is now considered a dog. Apple's tablet continues to show low growth, as sales continue to decline. Sales for the year came in at $29.29 billion, compared to $31.86 billion in 2021.
What Are the 4 Quadrants of the BCG Matrix?
The BCG Growth-Share Matrix uses a 2x2 grid with growth on one axis and market share on the other. Each of the four quadrants represents a specific combination of relative market share and growth:
- Low Growth, High Share: Companies should milk these cash cows for cash to reinvest elsewhere.
- High Growth, High Share: Companies should significantly invest in these stars as they have high future potential.
- High Growth, Low Share: Companies should invest in or discard these question marks, depending on their chances of becoming stars.
- Low Share, Low Growth: Companies should liquidate, divest, or reposition these pets .
How Does the BCG Matrix Work?
The BCG Growth-Share Matrix considers a company's growth prospects and available market share via a 2x2 grid. By assigning each business to one of these four categories, executives can then decide where to focus their resources and capital to generate the most value, as well as where to cut their losses.
Is the BCG Matrix Used in the Real World?
According to BCG, at the height of its success, the growth share matrix was used by about half of all Fortune 500 companies; today, it is still central in business school teachings on business strategy.
The BCG Growth-Share Matrix is a business management tool that allows companies to identify the aspects of their business that should be prioritized and which might be jettisoned. By constructing a 2x2 table along the dimensions of growth and market share, a company's businesses can be categorized into one of four classifications: stars, pets, cash cows, and question marks.
Boston Consulting Group. " BCG Classics Revisited: The Growth Share Matrix ."
Boston Consulting Group. " What Is the Growth Share Matrix? "
Apple. " CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS (Unaudited) ," Page 1.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/investing17-5bfc2b8fc9e77c00519aa64c.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
New User? Start here.
Business Studies 101: Inside the BCG Matrix

Table of Contents
The BCG Matrix is a growth-share matrix developed by the Boston Consulting Group in 1968. The BCG matrix is an exceptionally effective tool for interpreting a company’s growth share. The design of the growth-share matrix was a collaborative effort by Alan Zakon, BCG’s first CEO and his colleagues. The popularity of the BCG growth matrix rose through the roof after BCG founder Bruce Henderson wrote about its usage and usefulness in an essay in 1970.
The BCG Matrix has been and is still used by nearly every major corporation across industries. Nearly every Fortune 500 company implements improved business portfolio & resource management.
So, what makes the BCG matrix so useful? What are its features & how to interpret one? This article answers all such questions and more with clear explanations & examples.
What is the BCG Matrix?
The BCG matrix, by definition, is a powerful framework for business portfolio management. The matrix helps businesses understand what is working and what is not. They can thus re-prioritise and make better decisions about different investments & subsidiaries. BCG matrices provide vital info about brand/product performance and competition, thereby, aiding in better resource allocation, strategies, and ROI.
Here is what a typical BCG matrix looks like.

As can be seen, the entire matrix is divided into four quadrants and has two referential axes. The horizontal axis is the market share, and the vertical axis denotes growth.
- Businesses with low growth and high market share are called cash cows. The Boston Consulting Group suggests companies ‘ milk these cash cows’ for money.
- Business portfolios with high growth and high market share are the According to BCG, these have huge potential and are the company’s flagships.
- The subsidiaries with high growth and low market share are the question marks. There is no surety how they might perform soon. The low market share, and high competition, can eat away at the high growth. BCG analysts leave it to the company heads to invest further or discard the question marks.
- Finally, businesses with low growth and low market share are called These businesses eat up resources without bringing much of a return. Boston Consulting Group advises divestment, repositioning, or liquidation.
Let us dig in a bit deeper.
Understanding The Components of a BCG Matrix
The original BCG Matrix of 1968 defines four different product categories. Each of these possesses unique features.
- Question marks are products or services in markets that are growing fast. However, these are not market leaders and do not even have a large portion of the share.
With the right strategies, there is a chance to overcome competitors and grab a large share. But to do that, a company must invest resources heavily.
Question marks are the wild cards. A company must decide whether to take advantage of the high growth or discard it. If a company decides to invest further, it is aim should be to make the best use of high growth and capture major market share.
A good BCG matrix question mark example can be Apple’s Apple TV or Google’s Drive and Workspace.
- Pets are products that are neither growing nor above the competition. They do not generate much money and, if not taken care of, can tie up resources without giving much return. Pets should be let go as quickly as possible since they can lead to losses.
Low market share and growth mean lower profits. This usually reflects poor quality, marketing, and high prices.
- Stars are flagship products that enjoy a large market share and swift growth. If these can maintain a high market share, they become cash cows when growth slows. Staying ahead of the competition in every sense is key and requires heavy investments.
These are the rising market leader due to high demand and increasing popularity. Stars can make large profits but require heavy investments due to high market growth. Growing markets means more demand and more competition. To rise above the competition, stars need solid support and major resources.
When growth slows, rising stars that have maintained market superiority become cash cows.
- Cash cows enjoy a large market share, but their markets have saturated. These products have left behind the competition and produced large cash flows. Though their market has slowed, cash cows control most of it and thus generate solid returns.
They are kings of a market and, thus, produce money in excess. Their markets are stable; thus, cash cows do not need major investments. Profit margins are high, and cash flows are strong. However, innovation is necessary to maintain a major market share.
Do note that the BCG matrix can only prescribe, not predict. It tells companies what decisions to make, where to invest & divest, etc. but does not tell anything about what might happen. The matrix also does not consider any rapid market changes or major disruptions.
To go through different BCG matrices based on company examples, look at the examples section of this guide.
Once created, it is important to understand exactly what the matrix shows.

Interpreting The BCG Matrix
The idea and logic behind the matrix are simple – businesses that lead a market rake in bigger bucks. They gain a cost advantage over rivals and, thus, enjoy a huge market share. This automatically leads to high growth potential.
Relative market share and the growth rate are two key indicators that reveal two of the most important investment factors – competitiveness and market attractiveness .
- Market attractiveness is the extent to which a market offers opportunities for a business to turn a profit and sustain itself. This factor is considered concerning the total market size, growth rate, and competition.
- Competitiveness or business competitiveness is the ability of a business to generate better profits than its market rivals.
Products or businesses that grab a large market share before growth slows down become cash cows. To do so, it must provide higher quality-to-cost ratios than its rivals. If it can grab the lion’s market share before growth slows down, it can become a cash cow.
Realistically, growth in any business sector is bound to slow down as the market saturates. Businesses should aim to turn their stars and question marks into cash cows. Cash cows provide the money to turn question marks into stars &, eventually, into newer cash cows.
It is time we looked at how to create a BCG matrix.
Make Strategic Planning Easy with Accurate BCG Matrix Samples at Your Fingertips
Studying business or management can often be challenging. And the difficulty increases even more when you have to write flawless papers on the BCG matrix. No worries. Refer to our clearly illustrated BCG matrix examples to enhance your understanding and solve complicated problems accurately.
Check This BCG Matrix Example
How To Create A BCG Matrix?
To create a BCG Growth-Share matrix, a company needs to do careful market research and analyses all its products, services, subsidiaries, etc. How is a product performing? How does it compare to the competition? What is the consumer perception?
Armed with all such information, a company should start working on the framework using the following steps. Below is an example of a BCG matrix process.
- Step 1: Choosing A Product
Pick the product or service to be checked.
- Step 2: Understand the Market Deeply
The major rivals, the factors affecting the growth rate, the trends, market size, market features, the nature of consumers, the economics, etc. – all these market aspects are vital. In-depth market analysis is THE MOST crucial part of this process. Wrongly defined markets will lead to grossly incorrect results.
Detailed market research and analysis are the only to make accurate decisions.
- Step 3: Determine the Relative Market Share
Market analyses will reveal how much a product’s share compares to others. There’s a formula that shows market share relative to the largest competitor
Relative Market Share = (Product Market Share Percentage / Largest Rival Market Share Percentage) * 100
To find out the product market share percentage, the formula is
Product Market Share Percentage = (Product Revenue for a Business / Total Market Revenue) *100
- Step 4: Work Out the Market Growth Rate
The growth rate of a market is given by the following equation
((Current total market sales – Total market sales in the previous year) / Total sales in the previous year) *100
- Step 5: Use Data to Place the Product/Service in the BCG Matrix
Use any BCG matrix template with an example, such as the ones at MyAssignmenthelp.com, to classify & place products.
Well, that was the gist of how to develop a BCG matrix. Now, let’s look at how businesses use this tool in real-life scenarios.
Real World Applications
As may be intuitive, BCG matrices come in handy when a company needs to take stock & rejig its business structure. Complete market research & analyses of every offering reveal where each stands with respect to the other and the competitors. The BCG matrix then helps to segregate, prioritise, and make better decisions.
Here’s how Fortune 500 companies like Apple, Coca-Cola, Pepsi, and Google use BCG matrices.
- When focused on innovating and diversifying, companies increase investments in stars and question marks. This can increase market share, help grab new growth opportunities, and leave rivals in the dust.
- During cash crunches, cash cows come to the rescue. Cash cows require less effort to maintain, but complacency is a major no-no. Major disruptions and sudden trend changes can appear at any time.
Companies reduce investments if a product has been doing well for years and has become the market leader. Examples are Apple’s iPhone and Coca-Cola’s primary soft drink.
- Divesting money from pets and using it elsewhere is another useful strategy during cash crunches.
- Question marks become the focus if a company is hopeful about a product and sees good opportunities. Investing in these products leads to more R & D and marketing expenses, new tactics & strategies, heavy resource usage & direct costs, etc.
- Focusing on stars can boost cash flow and capture greater market share. However, heavy investments and innovation are necessary to defeat rivals.
- BCG matrices suggest the best way to invest and divert. They can help companies save time, money, and resources. In these uncertain and competitive times, these tools can be very handy.
Markets are ever-changing. And so are consumer preferences. For the best results, a company must routinely conduct thorough market analyses and revise their BCG matrices. Though effective, BCG matrices do have drawbacks.
Advantages and Limitations of the BCG Matrix
- Simple and intuitive
- Allows quick screening of the best investment opportunities
- Helps understand the biggest and smallest cash flow sources
- A system for effective resource allocation
- Enables comparative portfolio analysis
- Classifies only based on relative market share and market growth rate
- Does not account for costs
- Does not consider market changes and disruptions
- Cannot tell anything about profitability or success
- Ignores brand synergy and relations
- Does not consider small but rapidly-growing competitors
We wrap things up with our expert BCG matrix analysis of Apple and Alphabet(Google), two of the richest companies in 2023.
Two Examples: BCG Growth Matrices of Apple & Google
Here are two examples of BCG matrix on these two tech giants.
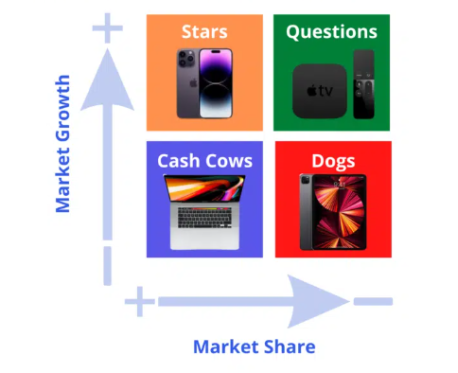
Star iPhone is undoubtedly the rising star, the flagship product. The demand is high among the rich & elite, and honestly, there’s no consistent competition for the iPhone in its category. Yet, the luxury phone segment is quite a niche, and Samsung is always coming up with something to challenge Apple.
Cash Cows The Appel MacBook, the successor of the hugely successful Apple Computer, is widely recognised and sells. It is a leader in the laptop market.
Question Marks Digital television is a fast-expanding domain but has major competitors. The Apple TV is not a market leader, sells low, and has stiff competition from Amazon Fire Stick and Google Chromecast.
Pets The iPad, the once popular tablet, raked in lower amounts in fiscal year 2022 than in 2021. The tablet market itself has been in a steady decline even before the 2020 Covid-19 pandemic.
Alphabet/Google
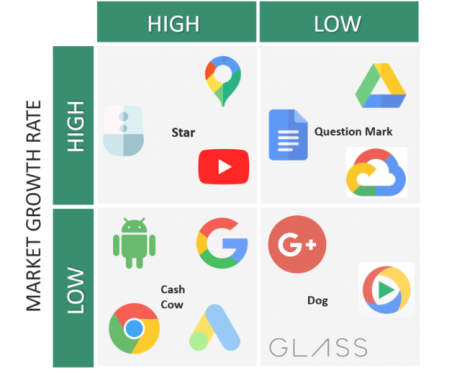
Cash Cows Google Search, Android OS, Google Chrome, and Google Advertising dominate their respective markets. These alone have consumed most of the market share and driven it to saturation. If all else fails, Google Search will still keep Alphabet as one of the tech giants.
Stars YouTube was already a cash cow and a leader in the online streaming market. The rise of streaming services like NetFlix, Amazon Prime, Disney+, etc. rejuvenated the market and increased opportunities. Competition increased, but YouTube is still the winner in streaming content.
Google Assistant is going toe-to-toe with the like of Amazon’s Alexa, Apple’s Siri, and Microsoft’s Cortana.
Question Marks Google Drive and Workspace reap the benefits of a growing market for digital workspace. But, Microsoft 365, Slack, Dropbox, and Zoom hold major portions of the market share.
Pets Google Plus, Google Glass, and the age-old Google Video Player never took off. Google + was Google’s answer to Facebook; it raised more questions about Google’s ideas & strategies for social networking & a behemoth like Facebook.
And that finally brings us to the end of this write-up. Here’s hoping this was an interesting and informative read for everyone.
Go through the well-researched BCG matrix on Starbucks, Coca-Cola, Microsoft, General Motors, Amazon, Hyundai, etc., here at MyAssignmenthelp.com. And, if you need some expert help while working on the BCG matrix assignment, connect with us anytime!
Call, mail, or drop a message at our live chat portal.
Most Frequently Asked Questions:
What is the bcg matrix an example of.
Ans: The BCG matrix is an example of a business planning and prescriptive portfolio management tool.
What are the 4 categories of the Boston Matrix?
Ans: The four categories are Stars, Cash Cows, Question Marks, and Pets .
What is the BCG matrix for startups?
Ans: The BCG matrix is a great way for investors to determine where and how to invest.
What is the full form of BCG company?
Ans: BCG is an acronym for Boston Consulting Group Inc., one of the USA’s oldest global management consulting firms.
What is the BCG matrix used for?
Ans: The matrix requires companies to do deep market research & analysis. It then helps companies conduct a comparative analysis of their product portfolios, judging market growth & determining market share concerning the biggest competitors.
What is a cash cow in the BCG matrix?
Ans: Cash cows are established market leaders that generate continual, heavy cash flows. They act as continual sources of steady cash flow for a company and do not consume many resources.
How do you write a BCG matrix?
Ans: The steps to write a BCG matrix are as follows:
- Identify a product to classify
- Do a detailed market analysis on it.
- Calculate its relative market share.
- Calculate its market growth rate.
- Use market share and growth data to place the product in the correct BCG matrix segment.
What is the market growth rate in the BCG matrix?
Ans: The market growth rate is the percentage by which a market has grown in a specific time period

Lucy Wilson
Hi, my name is Lucy Wilson. I am 26, a successful digital marketer, lifestyle blogger, and a Literature writing expert based in Melbourne. I have loved social media and writing since my teenage days. I am a certified digital marketer with a Masters degree in Literature. Sounds quite wierd? Well, that’s because I can’t be less or more enthusiastic about either of my passions. Additionally, I work part-time as a writing expert for myassignmenthelp.com. When I am not working, I am probably partying with my friends or listening to my kind of music or simply lazing around.
Related Post

Writing Get your essay and assignment written from scratch by PhD expert
Rewriting: Paraphrase or rewrite your friend's essay with similar meaning at reduced cost
Editing: Proofread your work by experts and improve grade at Lowest cost
Enter phone no. to receive critical updates and urgent messages !
Please upload all relevant files for quick & complete assistance.
Get original papers written according to your instructions and save time for what matters most.
What is a BCG Matrix and how to get the most out of it?

Trying to make high-level decisions about the future of your company can feel overwhelming. Trust us — we know first-hand what that feels like here at Miro. Companies often set up special committees that take months — or even years — and dozens of meetings before committing to a path.
But in the 21st century, the first mover’s advantage is more crucial than ever. You need to prioritize fast without letting biases affect how you invest your capital and effort.
That’s where the BCG (Boston Consulting Group) Matrix comes in. It’s a portfolio management tool that helps your company prioritize different businesses or products to get the best long-term results.
Let’s dive into everything you need to know about a BCG Matrix.
Try Miro’s BCG Matrix Template
- BCG Matrix definition: What is a Growth Share Matrix?
The Growth Share Matrix, also known as the BCG Matrix, is a portfolio management framework developed by the Boston Consulting Group’s founder in 1968.
It divides a company’s business units into categories based on their respective market shares and market sizes. To help you roughly estimate the profitability of a business, the matrix uses the two metrics of relative market share and market growth rate.
- Relative market share: Your share of the market compared to your largest competitor.
- Market growth rate: The rate at which a certain market grows in revenues compared to the previous year.
Based on these two metrics, you divide your company’s businesses or products into four categories:
- Stars: High market share in a high-growth market.
- Cash cow: High market share in a mature market.
- Dogs (or pets): Low market share in a market with a slow growth rate.
- Question marks: Currently low market share in a fast-growing market.
The different categories help you simplify complex decision-making about investment and business focus. Companies use the framework to decide which businesses or products to invest in to maximize growth potential and profitability.
While first created to manage product lines for manufacturing companies in the ‘60s and ‘70s, it’s equally relevant for tech startups that offer a variety of digital services. Just because you deal in pixels doesn’t mean you’re immune to regular business mistakes like overspending on a product with little potential.
The BCG Matrix can help you make sense of your portfolio of products and make smarter decisions about future investments in both R&D and marketing. If you’re struggling to visualize it, don’t worry. Below, we’ll cover a real example and showcase how the different categories work.
- BCG Matrix example
The table below shows a fictitious company’s product line, including necessary metrics for using the BCG Matrix.
It includes the revenues, the largest competitor’s market share — the local market leader — the product’s market share, and the market growth rate.
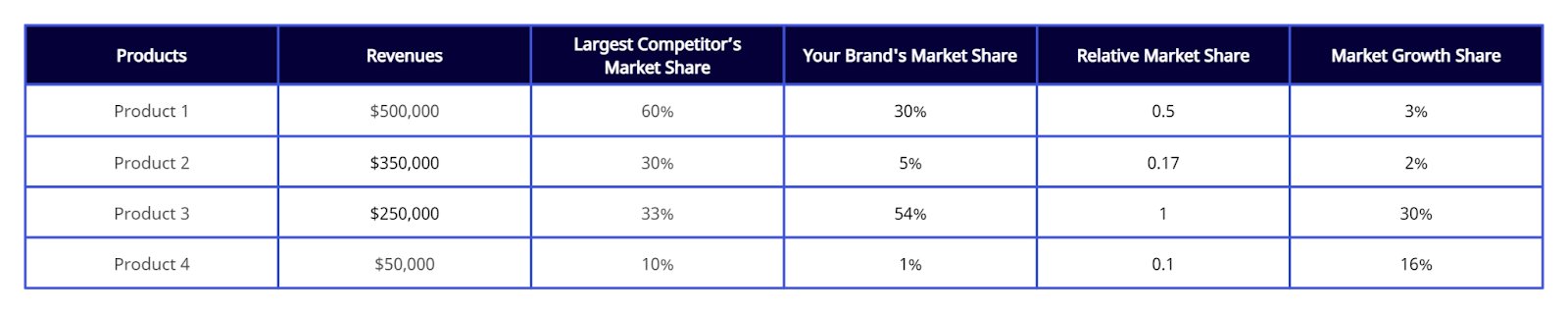
If we put these products through the BCG Matrix, #1 is a dog, #2 a cash cow, #3 a star, and #4 a question mark.
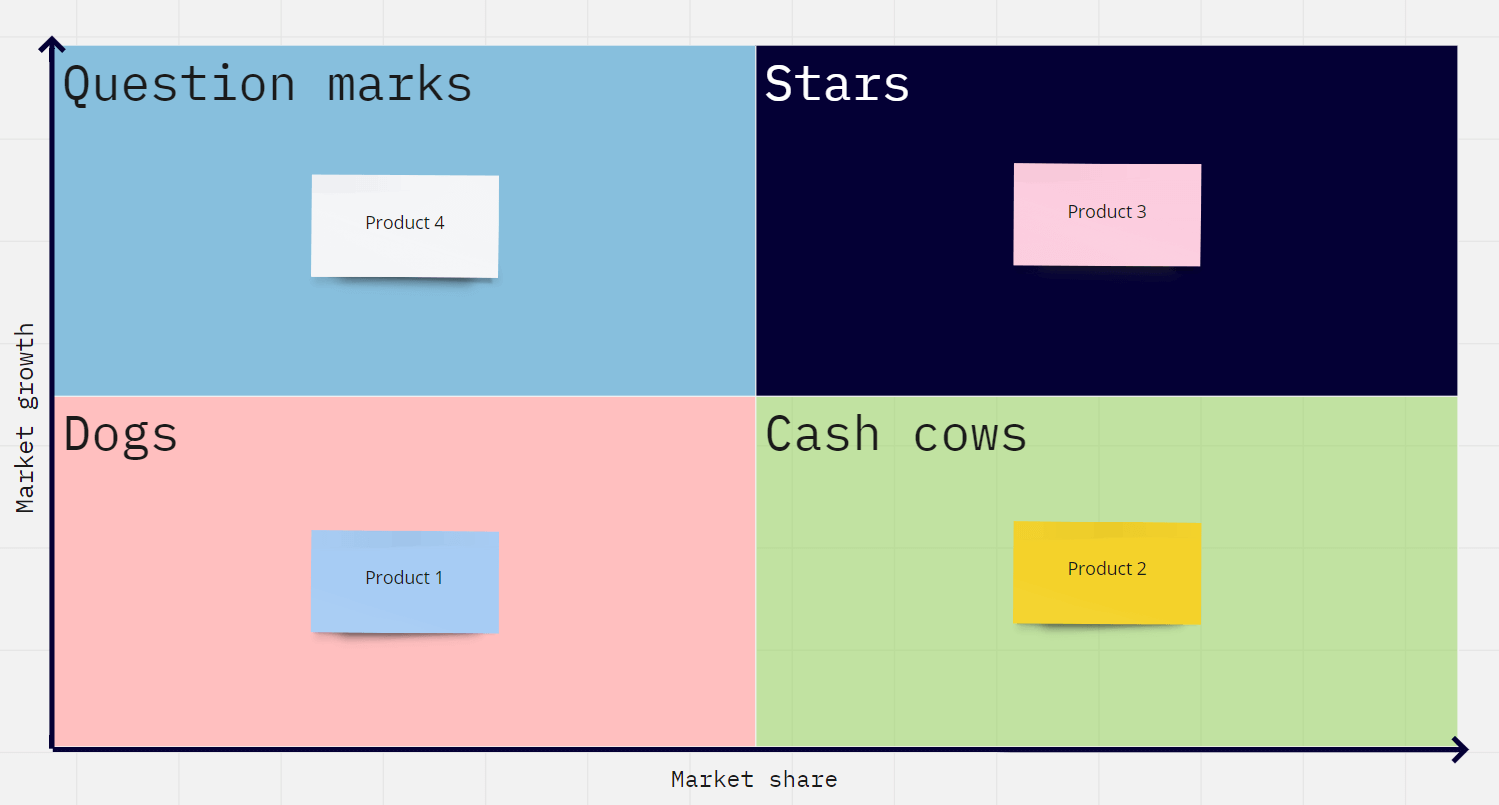
As you can see, the quadrants have nothing to do with the objective revenue numbers. It’s all about where the market is going and how your product’s doing within that market.
But before you dive in and create your own, you should understand the benefits and your ultimate goal for creating a BCG Matrix in the first place.
Why you should use a BCG Matrix — key benefits
You should use a BCG Matrix because it helps you prioritize business and products, cut waste, and create a robust portfolio.
Let’s break down these benefits.
Prioritize the right business or product quickly to establish a first-mover advantage
Instead of focusing on dying products or cash cows that sustain themselves without much effort, your company can focus on creating new winning products and businesses.
For example, your star product has the lion’s share of the market in a marketplace that’s growing at a rapid pace. Focusing on this business unit would be the smart move going forward.
Eliminate wasteful spending by cutting your losses
A dog product or product line can weigh down your company’s capital and manpower when you’d be better off selling it off and focusing on your winners.
By identifying a business as a dog — something with limited growth potential — you can cut your losses by selling the business or even, if it’s not profitable, simply closing it down.
For example, realizing that its TV business was a dog, Phillips decided to sell off its TV business unit in 2012. The company was coming off record deficits in 2011 and decided to cut its losses.
Since that decision, the company has refocused on other areas and regained healthy profitability.
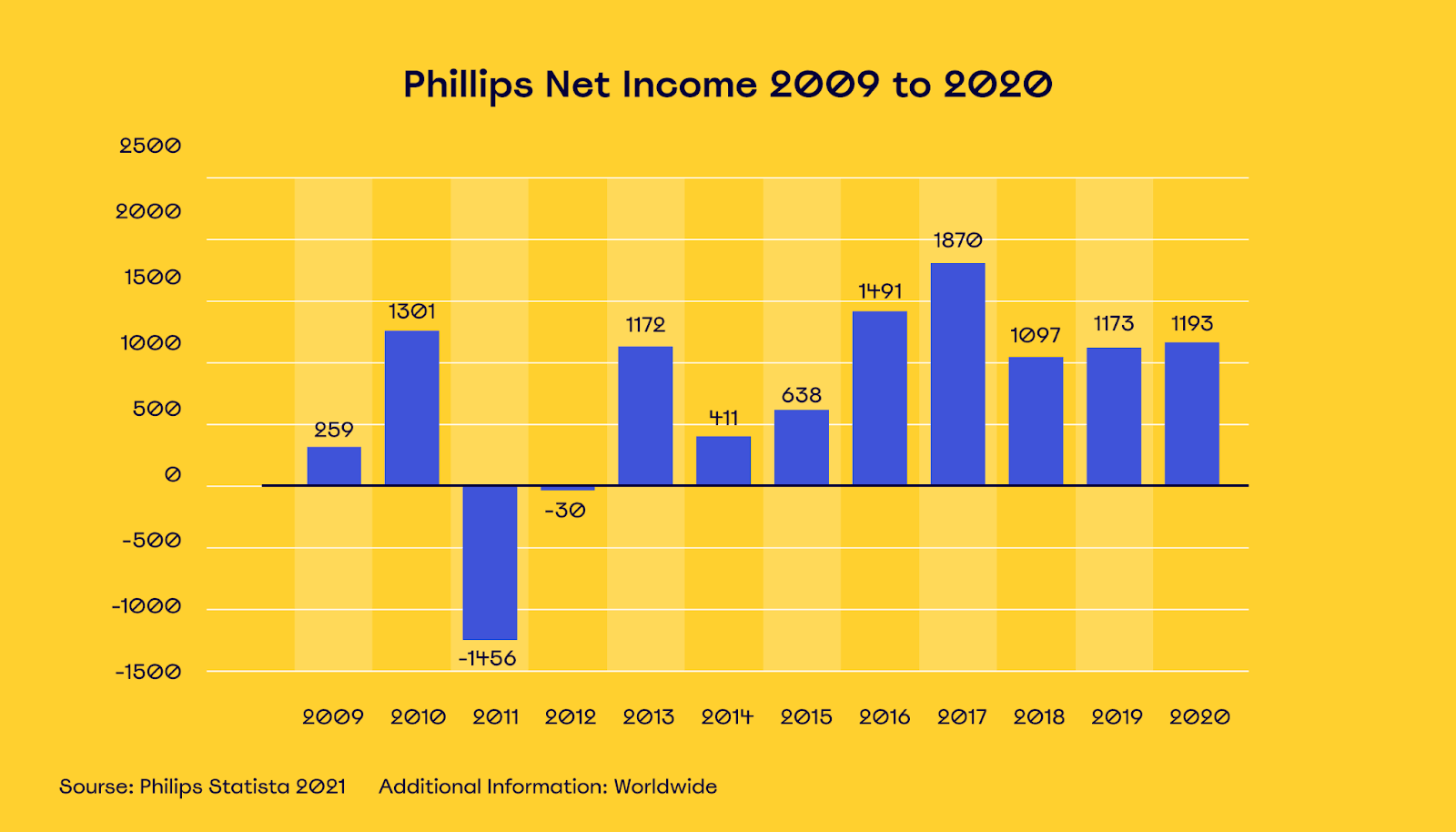
It is one of the most iconic success stories of selling off and divesting from a “dog” product line in modern history.
Create a more robust and balanced portfolio
Ultimately, the goal isn’t to succeed in one area but to better balance your company’s investment of capital and effort across your entire portfolio. By placing bets on high-growth markets while maintaining healthy cash cows, you can future-proof your company.
If you’re looking for a similar tool to help you plan the journey of a single product, you could try impact mapping .
- What are the four quadrants of the BCG Matrix?
The four quadrants of the BCG Matrix are stars, dogs, cash cows, and question marks.
While we’ve roughly covered them above, let’s explore each category a bit closer, using real product examples.
A cash cow is a well-established business with stable brands in a mature market.
An example of a cash cow business is the domestic soft drink business in the U.S. for Coca-Cola, where the company maintains a 44% share of all revenue.
The market has long since matured and is growing at a fairly slow rate at about 5.1% , which is currently lower than the U.S. rate of inflation.
So, it’s a low-growth market with little potential for future growth, but the business is a winner — AKA a cash cow.
An example of a star is Amazon’s Amazon Web Services business that provides cloud services to B2B customers. The company has a 32% market share, and the public cloud industry is growing rapidly, forecasted to grow 21% in 2021 alone.
This type of market-leading product in an industry that’s virtually exploding is what we call a star .
Phillips’ television business — which we covered earlier — is an example of a dog, where the company had a low market share in a mature marketplace.
Question mark
Kia’s electric vehicle business is a good example of a question mark. Although it currently has a small market share of around 2.1% , the EV market is rapidly growing globally, at an expected average rate of 24.3% in the U.S. until 2028.
Because of the rapid growth of the market, there’s plenty of opportunity for new players to establish themselves.
- How to calculate relative market share in the BCG Matrix
Before you can categorize your businesses, you need real data to see where they stand in the marketplace. The relative market share is one of the key metrics you use in the BCG Matrix.
Let’s break down how to calculate it.
Find a reliable source for up-to-date marketplace data
There are a plethora of market research firms that sell industry data of varying levels of accuracy online.
Either find a firm that specializes in your industry and locations and offers the most accurate data, or establish your own in-house research team.
The important thing is to find a reliable source of the latest, up-to-date market information. Without accurate data, your product portfolio decisions are going to be more luck than judgment.
Identify your largest competitor’s market share
Examine the marketplace data and find your largest competitor for the specific product you’re researching.
Try to find its latest revenue numbers. The company may release revenue data by sector or even product in its quarterly reports. Get as specific as possible to use accurate numbers on the actual business area you want to compare.
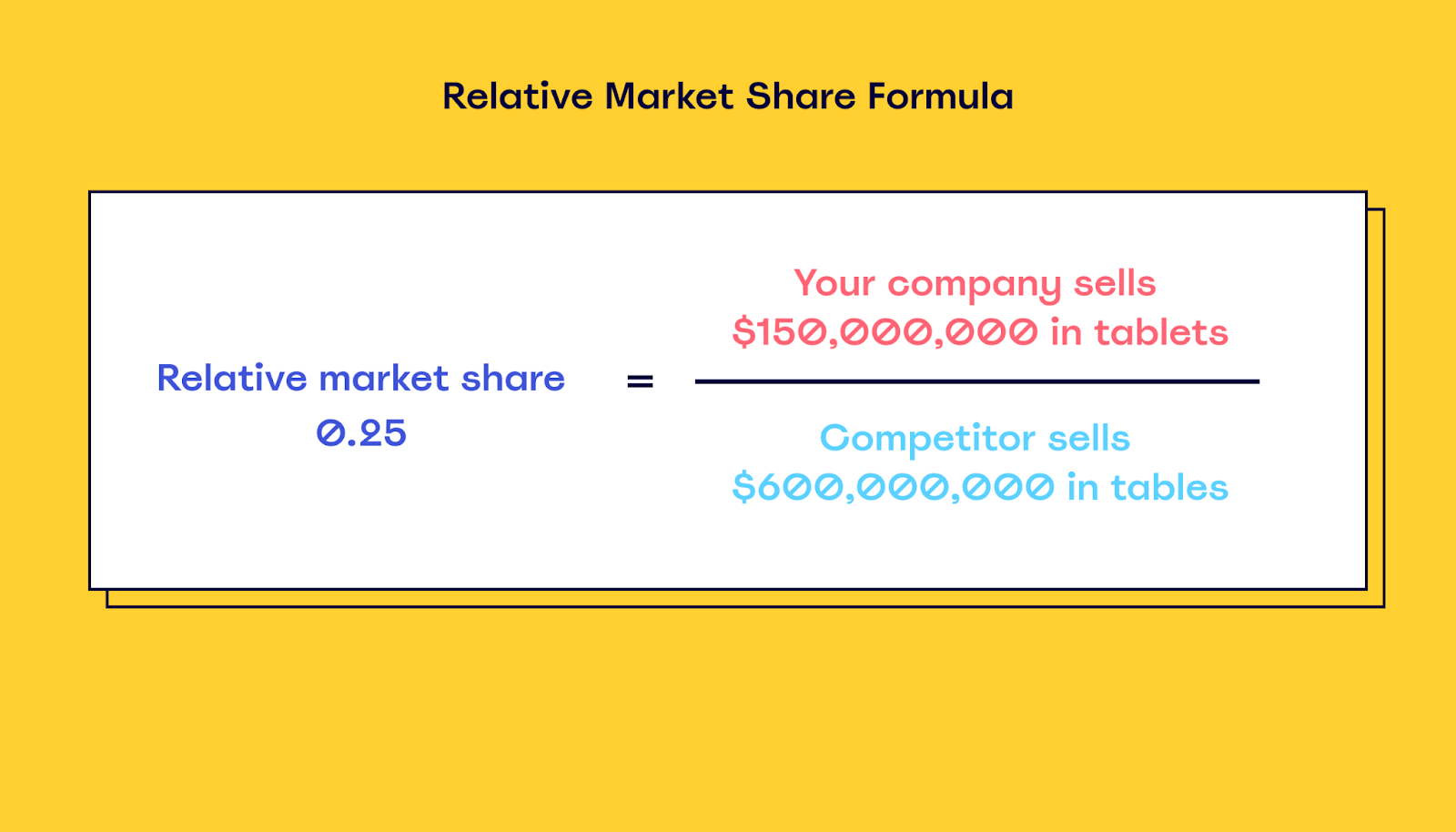
Divide your market share by the largest competitor’s market share
The formula to find your relative market share is super simple — just divide your market share (or revenues) by that of your largest competitor.
For example, if your main competitor sells $600,000,000 in tablets and you sell $150,000,000 worth of tablets per year, your relative market share is 0.25.
The relative market share focuses on the importance of “owning” a market, which typically means stable income even without large marketing efforts.
- The role of the BCG Matrix in strategic management
Strategic management is the process of using objectives, procedures, and initiatives to make a company more competitive.
Instead of vague guesswork and thinking, you use formalized processes and real data to come up with objectives and strategies.
For example, this could be investing in researching competitors to explore where your products stand in the marketplace.
The BCG Matrix in itself isn’t the end-all-be-all of strategic management. It’s only a single tool in a larger process.
Start with a planning workshop and creating a big-picture strategy
Don’t try to create a BCG Matrix in a vacuum. Before your company will get anything of value out of it, you need the big picture figured out.
You wouldn’t try to build a house without setting up a robust foundation. So first, you should come up with a vision and strategic objectives for your company based on real data like market research.
A practical way to do this is to arrange a planning workshop with executives and key stakeholders involved with your entire portfolio.
Using a framework like OKR (Objective & Key Results) makes it easier to avoid wild guessing and personal biases.
Combine with strategic objectives to prioritize investments
If your objective is to focus on innovation, double down on stars and question mark businesses in rapidly growing markets, and move some of the marketing and R&D budgets away from stable cash cows.
If it’s to expand globally, focus on the market expansion of an existing cash cow product.
Revise and adapt as circumstances change
It’s important to understand that you’re not going to perfectly predict the path to bombastic success for your company in a single planning workshop and your first BCG Matrix.
As markets and competitors change, you need to adapt your plan and revise your BCG Matrix and priorities.
For example, as market growth peters off, a previous question mark could quickly become a dog, with no real prospects of becoming a winning product for your company.
- How to use the BCG Matrix to improve your marketing strategy
The BCG Matrix can also help you optimize your marketing strategy and grow your business with better promotions.
Let’s look at how.
Re-adjust budgets based on the growth Matrix quadrants
The first step is to use the BCG Matrix to recalibrate your marketing budget.
Ideally, you’d do this in a live meeting with every key stakeholder on board. Of course, if everyone doesn’t work in the same office, which is often the case, this can be difficult. But with our BCG Matrix Template , your team can remotely collaborate on a virtual board in real-time.

With a visual representation of where the products are in their market, it’s easier to accurately distribute the budget.
If you want to be more aggressive, you can focus on question marks and star products with growth potential rather than the safe and steady cash cows.
Adjust your marketing message based on the state of the market and your brand
If you’re pushing an up-and-coming product, you can’t use the same message as you use for markets where you’re already the go-to brand.
You need to adjust based on your place in the market. For example, Avis had a legendary marketing campaign where the company pointed out that it wasn’t the market leader.
By making the argument that “we work harder since we’re second,” Avis experienced rapid growth and established itself as a strong contender to Hertz in the rental car market.
The average consumer tends to default to familiar products and market leaders because it’s a “safe choice.” Find a unique angle to turn your underdog status into a perceived benefit, not a risk.
- Disadvantages of using the BCG Matrix
Just because you can use the BCG Matrix in various areas of your business doesn’t mean you should trust it blindly.
This framework has a number of limitations and issues that make it an imperfect tool for strategic planning.
A high market share doesn’t equal profitability
Just because your product has a high market share doesn’t mean it’s a profitable business. It could be a cut-throat market with high costs, leaving you with bad margins and poor cash generation.
Depending on variations in market size and product type, dogs can actually earn more than cash cows.
It doesn’t account for external factors
The BCG Matrix doesn’t leave room to account for crucial external factors outside the market. For example, the Covid-19 pandemic decimated the tourism sector as a whole, with over one trillion dollars in lost revenue in 2020.
If your company had a plan to expand your tour bus offerings, it’s probably a good idea to put that on hold, even if you could win market share.
Lack of middle ground — only classified low or high
The BCG Matrix tends to deal in extremes — a product either has a low market share or high, with no in-between.
But that’s an overly simplistic outlook on marketplace dynamics. For example, could you truly describe PepsiCo’s share of the U.S. beverage market as low? That’s what you’d have to do if you followed the BCG Matrix formula.
The model is simply too simple
Market growth rates and your relative market shares are important metrics, sure. But on their own, that’s not enough data to make a solid investment or other business decisions.
To make a truly educated decision about your company’s future, you must also consider overall market size, profit margins, operating costs, cash flow, and much more.
So for best results, use it in combination with other frameworks and data when planning budgets and marketing campaigns.
- Use the BCG Matrix as a starting point to make better long-term strategic decisions
The BCG Matrix alone isn’t a complete framework that will help you predict the future and always make the right business decisions.
But it’s a great starting point to help you live up to your strategic objectives over the long term.
It forces you to dig up data on your competition and put your products into context, which can help you identify new marketing opportunities.
It’s not a solution on its own, but it can become a valuable tool in your strategic management toolbox.
Are you ready to build your own BCG Matrix?
Use our bcg matrix template to get started., miro is your team's visual platform to connect, collaborate, and create — together..
Join millions of users that collaborate from all over the planet using Miro.
- Why you should use a BCG Matrix — key benefits
Keep reading
How to streamline processes to make your org more efficient.
From chaos to clarity: How project workflows lead to success

Your guide to understanding (and improving) organizational efficiency
BCG Matrix: Definition, Chart, Explanation With Examples
BCG stands for Boston Consulting Group; also called ‘Growth/Share Matrix/ BCG Matrix’; developed by Boston Consulting Group, a world-renowned management consulting firm located in the USA. It is a useful tool for analyzing a diversified company’s business portfolio.
In the BCG matrix, SBU(Strategic Business Unit) is a unit of the company that has a separate mission and objectives that can be planned independently from other company businesses. Diversified companies having several SBUs (Strategic Business Units) use the BCG Matrix. These SBUs form the ‘business portfolio’ of the company. Companies use the BCG matrix is as a portfolio planning tool.
This matrix has four steps:
- Dividing the business-organization. into several (at least two) SBUs
- Determining the prospects of each SBU of the organization
- Comparing each SBU against other SBUs with the help of a matrix (two-dimensional)
- Setting strategic objectives for each SBU.
What is the Strategic Business Unit (SBU)?
In the BCG matrix, SBU(Strategic Business Unit) is a company that has a separate mission and objectives and can be planned independently from other company businesses.
For example, a company division, a product line within a division, or sometimes a single product or brand.
A strategic business unit (SBU) is a relatively autonomous unit of a firm. In a diversified company, each business unit is an SBU. A division of a company may also be treated as Strategic Business Units (SBUs).
According to Pearce and Robinson, Strategic Business Units (SBUs) must have certain characteristics:
- A unique business mission
- An identifiable set of competitors
- The SBU strategic manager can make or implement a strategic decision relatively independent of other SBUs
- Crucial operating decisions can be made within the SBU.
An SBU is responsible for its products, services ‘and markets and, therefore, it is also responsible for developing its strategy. Generally, an SBU rs independent in business operations has its managerial resources and has all its assets under its control.
For example, PNG has 21 business units for the production of textile products, ceramics, pharmaceutical products, etc. Each of these units is treated as an SBU.
They, however, work under the Tesla corporate management. In a diversified company, all the business-units constitute its business portfolio. Each business unit or SBU is treated as a standalone profit center.
A business portfolio approach is commonly followed in a diversified company for corporate strategic analysis .
A corporate strategy for each SBU is set in such a way that it becomes consistent with the resource capabilities of the overall company.
Each unit is assessed as a separate entity after a portfolio approach is followed.
As remarked by Hili and Jones, the portfolio approach is a visual way of identifying and evaluating alternative strategies for the generation and allocation of corporate resources.
One of the most widely used portfolio approaches is the Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrix.
How to Use the BCG Matrix in Practice?

To use this matrix, the SBUs of the company are plotted on a two- dimensional chart.
One dimension of the chart (vertical dimension or Y-axis) represents future market growth (growth rate of SBU’s industry ), and the other dimension (horizontal dimension or X-axis) represents an SBU’s relative market share.
The growth rate is measured concerning the economy of the country. The growth rate of an SBUs industry may be faster or slower than the economy’s growth rate.
As postulated by BCG Matrix, a favorable competitive environment exists in an industry when the growth rate is faster in the industry. On the other hand, relative market share is ‘the ratio of an SBU’s market share to the market, the share held by the largest rival company in its industry.
If SBU X has a market share of 10 percent and its largest rival has a market share of 30 percent, SBU X’s relative market share is 10/30 or 0.3.
If an SBU is a market leader in its industry, it will have a relative market share greater than 1.0.
For example, if SBU Y has a market share of 40 percent and its largest rival has a market share of 10 percent, then SBU Y’s relative market shareis40/l0 or 4 0.
When an SBU’s relative market share is greater than you can assume that it has a significant cost advantage over its competitors.
In the Figure, you will find that the market growth rate is placed on the left-hand side (Y-axis), and the relative market share is placed at the bottom (X-axis), below the horizontal line.
The chart is divided into 4 Quadrants.
- quadrant 1 shows the star SBUs,
- quadrant 2 shows the ‘question mark’ SBUs,
- quadrant 3 shows’ cash cow’ SBUs, and
- quadrant 4 shows’ dogs’ SBUs.
Two pieces of information are required to plot and SBU in the matrix
- an estimate of the future rate of growth in the market and
- An estimate of the relative market share of the business unit.
Any business that is to the left of the dark violet is dominant in the market.
Any business to the right of the start point is nondominant.
Separate high growth from low growth markets common cut point is GDP + 3%. Markets growing faster than these are considered high growth; markets going slower than these are considered slow growth.
Both cut points are somewhat arbitrary.
For example, a business with its share of 1.01 may be the leader, but it is scarcely in a commanding position compared to the next largest competitor.
Using the classic Boston Consulting Group (BCG) approach, a company classifies all its SBUs according to the growth-share matrix, as shown in Figure.
On the vertical axis, the market growth rate provides a measure of market attractiveness.
On the horizontal axis, relative market share serves as a measure of company strength in the market. The growth-share matrix defines 4 types of SBUs.
4 Strategic Business Units (SBUs) of BCG Matrix
Using the Boston Consulting Group (BCG) approach, a company classifies all its SBUs according to the growth-share matrix.
On the vertical axis, the market growth rate provides a measure of market attractiveness. On the horizontal axis, relative market share serves as a measure of company strength in the market.
By dividing the growth-share matrix as indicated, 4 types of SBUs of BCG Matrix are;
- Question Marks,
Stars: High Growth, High Share Businesses
Stars are high-growth, high-share businesses or products. They often need heavy investments to finance their rapid growth. Eventually, their growth will slow down, and they will turn into cash cows.
An SBU with high market growth and a high relative market share is considered as a star business-unit. It is a profitable business. It has attractive long-term profit opportunities.
Stars are in the high growth rate and, therefore, highly competitive markets. They have the potential to be the cash cows only if they can consolidate their competitive position.
They generate as well as consume revenue. Their net contribution to the kitty of the organization is not very substantive.
Cash Cows: Low-Growth, High-Share Businesses
From the matrix, it is clear that these businesses operate in the industries which are in the maturity stage and hold a very strong competitive position in their respective industry.
They generate far more cash than they consume. The surplus cash can be used to nurture those businesses that are in the star quadrant or the question mark quadrant.
Cash cows are low-growth, high-share businesses or products. These established and successful Strategic Business Units (SBUs) need less investment to hold its market share.
Thus, they produce a lot of the cash that the company uses to pay its bills and support other Strategic Business Units (SBUs) that need investment.
A Strategic Business Unit (SBU) is considered a question mark when it has high market growth and low market share.
It is relatively weak in competitive terms. A question mark business-unit is risky due to the inherent uncertainty in a high-growth market and weak market share position.
However, such a unit is considered to have a future. It may offer-opportunities for long-term profit. If more cash is poured down into this SBU and properly nurtured, it may become a star Strategic Business Unit (SBU).
Question Marks: Low-Share Business Units in High-Growth Markets
Question marks are low-share business units in high-growth markets. They require a lot of cash to hold their share, let alone increase it.
Management has to think hard about which question marks it should try to build into stars and which should be phased out.
An SBU is considered as a cash cow when it has low market growth and high market share.
It is a highly profitable firm and generates a substantial amount of cash. Since this Strategic Business Unit (SBU) has a lack of opportunity for future expansion, more cash should not be injected.
Question marks lie in the high business growth rate segment with a weak competitive position.
This means that the organization has to develop some competencies to make the best use of high growth rates. To sustain these business resources, the organization has to be committed to developing them in the select areas.
Dogs: Low-Growth, Low-Share Businesses
Dogs are low-growth, lo,w-share businesses, and products. They may generate enough cash to maintain themselves but do not promise to be large sources of cash.
An SBU with low market growth and low market share is treated like a dog. It has a weak competitive position in a low-growth industry. It cannot generate cash, and also, it has a dim prospect.
The corporate head office has to decide about its future. It may be divested or liquidated or turned around if there are sufficient reasons for its revival.
Dogs are in the low attractiveness, low competitiveness (low relative market share) quadrant. They are not generating revenue, nor does it make sense to develop them as their competitive position would remain weak. It is best to divest these businesses.
Understanding BCG Matrix
The chart below shows the ten circles in the growth-share matrix represent a company’s ten current SBUs. The company has two stars, two cash cows, three question marks, and three dogs.

The areas of the circles are proportional to the SBU’s dollar sales. This company is in fair shape, although not in good shape. It wants to invest in the more promising question marks to make them stars and maintain the stars to become cash cows as their markets mature.
Fortunately, it has two good-sized cash cows whose income helps finance the company’s question marks, stars, and dogs. The company should take some decisive action concerning its dogs and its question marks. The picture would be worse if the company had no stars, if it had too many dogs, or if it had only one weak cash cow.8
Once it has classified its SBUs, the company must determine what role each will play in the future.
One of the four strategies can be pursued for each SBU. The company can invest more in the business unit to build its share. Or it can invest just enough to hold the SBU’s share at the current level.
It can harvest the SBU, milking its short-term cash flow regardless of the long-term effect. Finally, the company can divest the SBU by selling it or phasing it out and using the resources elsewhere.9
As time passes, SBUs change their positions in the growth-share matrix. Each SBU has a life cycle. Many SBUs start as question marks and move into the star category if they succeed. They later become cash cows as market growth falls, then finally die off or turn into dogs toward the end of their life cycle. The company needs to add new products and units continuously so that some of them will become stars and, eventually, cash cows that will help finance other SBUs.
BCG recommends several things based on the grid;
- The stars should be nurtured with the surplus cash flows from the cash cows. The long-term objective should be to consolidate the star SBU’s position.
- The question marks should be provided supports from the surplus of the cash cows. However, if a question mark SBU’s long-term prospect is uncertain, it should be divested.
- To make a diversified company’s business- portfolio more attractive, the corporate head office should have an objective of turning the favored question mark SBUs into stars.
- The company should seriously think about getting rid of dog SBUs.
- The corporate management should consider making the company an organization of a balanced portfolio with enough number of stars, question marks, and cash cows.
Strategic Considerations of BCG Matrix
The portfolio matrix gives the company an idea about the health of its businesses. If there are too many dogs or question marks or too few cash cows and starts, the company’s portfolio can be called an imbalanced one.
After getting the portfolio’s picture, the company should then decide on each SBU’s objective, strategy, and budget . With regards to this, it can pursue one of the following strategies:
The building strategy is designed to improve market positions in spite of possible short-run damage to profitability. Building strategies are most appropriate when a firm wants to move question marks into the star category. A building approach can also be used to convert small stars into bigger stars. To ensure success, both of these building strategies require significant commitments of company resources.
A holding strategy, on the other hand, is a defensive strategy designed to preserve market positions. Holding is most commonly used to keep cash cows productive.
Cash cows are often vulnerable to newer competitors, and marketing programs need to promote new versions and applications to maintain customer interest.
Harvesting strategies are aimed at making as much money off a product as possible . The idea is to cut promotion and production costs to the bone and mine the product for its cash flow.
This approach focuses on extracting cash from a project at the expense of the business’s long-run survival. Harvesting is a ruthless strategy that is best suited to weakening cash cows, dogs, and some question marks.
A strategy of divestment attempts to sell or liquidate businesses to generate cash so it can be better used in other areas. Divestment is employed on question marks and dogs that the firm cannot finance into better growth positions.
Candidates for divestment include businesses that have little room for cost savings and those that just break-even or operate at a loss. Sometimes divestment can work to the advantage of both the seller and the buyer.
The market share/growth matrix implies a preference for high market growth and the need to maintain a firm’s cash balance. Neither the theoretical nor the empirical work exists to support such a preference conclusively.
Moreover, the feasibility of a strategy is dependent on more factors than simply share and market growth. You should appreciate that SBUs change their positions in the growth-share matrix with the elapse of time.
Like a product, SBUs have a life cycle starting with question marks, becoming stars, turning to cash cows, and end up as dogs. That is why companies should examine the businesses’ future positions side by side with the current position analysis.
Limitations of BCG Matrix
BCG matrix has certain flaws. Because of these flaws, it should be used cautiously.
- BCG matrix is criticized as a very simplistic model. An ABU is affected not only by market share and growth rate. Many other relevant factors, such as product differentiation^niche market possibility, etc. affect the business operations of the SBU BCG matrix and do not take into account all these factors.
- BCG matrix suggests a straight-forward Hnkage relative market Share’ and cost savings. In reality, cost advantage may not accrue to an SBU simply due to high maShaS Depending on the industry, an SBU with low simple, low-cost technology.
- Cash cow SBUs are supposed to generate substantial cash Sows because of their high market share. It may not always be in some businesses; the capital investments needed to remain competitive are so high that an SBU classified as a cash cow may find it very difficult to yield substantial cash flows.
Resource Allocation with BCG Matrix
In a multi-business, different businesses have different resource requirements. Some businesses are net resource generators, and some are resource consumers.
To construct a visual depiction of its various businesses, the organization uses the Portfolio matrices.
The portfolio matrix plots the different businesses on two axes: one that shows the attractiveness of the industry the business is into the strength of the business based on a chosen indicator such as relative market share (in case of the BCG matrix as shown above and Business Strengths in the nine-cell GE Matrix).
The decision-maker must assess the resource requirement of the different businesses plotted on the matrix to allocate resources.
The portfolio has to be balanced in terms of those businesses that generate revenue and are likely to generate revenue versus their resource consumption.
The use of the BCG Matrix lies in estimating which businesses are the net cash generators and which are the net cash consumers. The businesses that are the cash consumers must also exhibit the potential to be the leaders in their business with a highly competitive position so that they can contribute enough cash to nurture future businesses in the future.
Strategic choices are concerned with resource allocation among businesses so that the ones with potential are nurtured and the ones without are divested. The decisions to retain and divest are top management decisions.
What should an ideal portfolio of business be like? An ideal business portfolio developed using the GE nine-cell matrix with industry attractiveness and business strengths as the two measures.
In reality, an organization may have a portfolio where there are too many profit producers, which means no cash users (young businesses that in the future will be profit earners), or too many losers (low possibility of growth/profits), or too many developers (demand too much cash leading to unstable growth).
In such situations, the organization has to balance its portfolio. Those in a strong position and are growing need cash to be harvested from those in a weak industry position.
You will notice that it is recommended to avoid being in those quadrants where the business strength and industry attractiveness are low.
In the Figure below, businesses B, C, F, G, and H. A, D, E, and I could be winners in large markets or have a very dominant position in smaller markets. Notice that businesses are concentrated in the upper left-hand quadrant of the Figure.

An organization may not have an ideal portfolio. The Figure indicates the direction in which the corporate strategies must be fashioned to shift the portfolio towards the left hand upper two quadrants.
According to Hofer and Schendel (1977), the portfolio analysis should yield a statement of the firm’s current portfolio position as well as a forecast of its future position under the existing strategy.
To develop a portfolio analysis, an organization may follow the following steps;
- Choose the matrix to plot its position.
- Assess the relative attractiveness of industries that determines the long-run performance of the business.
- Assess the organization’s competitive position in each industry. Can it derive benefits from the industry?
- Assess the unique opportunity and threats the organization faces in each industry.
- Assess the unique resources of the organization to match the opportunities/threat. This may alter the competitive position assessment.
- Plot the organization’s current portfolio.
- Plot a future performance portfolio.
- Assess what results in the business will attain with the current situation.
- Assess the gaps and make decisions to either change some businesses’ competitive strategies or remove some businesses from the portfolio or add some businesses to the portfolio or reduce the performance targets.
- Prune/strengthen/consolidate businesses as required.
Having allocated the resources, the organization must also ensure that the corporate parent removes any problems that may have been caused or are likely to be caused by inadequacy or shortfall in managerial skills , foresight, and capabilities by sharing of skills, the transference of learning and meditation.
In multi-business companies, corporate parenting enables the headquarters to focus on core competencies and tries to create value among various business units by establishing relationships and a good fit between needs and opportunities of units and resources and capabilities within the firm.
Incorporate parenting, and the corporate headquarters tries to achieve synergy among business units by allocating resources, transferring critical skills and capabilities among various units, and coordinating shared units’ activities to attain economies of scope.
Developing a corporate parenting strategy involves three analytical steps.
- Assess the critical success factors, which are the basis of the unit’s competitive advantage .
- Are there any areas that need improvement? Can the parent contribute?
- What is the fit between the parent’s capability and that of the unit’s? To what extent can they complement?
The parent’s role is not to interfere but to develop. Therefore, corporate parenting requires restraint, the exercise of mature leadership , and discretion retrenchment and combination. Within each of these options are various sub-options.
Further, the organization can develop a functional strategy to support its options and sub-options.
This explains how different organizations can follow widely differing strategies leading to varying profitability in the same industry, other conditions being equal. There is no fixed manner in which an organization decides upon strategies. There are only indicative recommendations.
The process of strategic choice also entails the commitment of financial and other resources through portfolio analysis and access to the corporate parent’s cumulative knowledge and learning through corporate parenting.
Overall, as is the case with other strategic management aspects, a strategic choice is an analytical process backed by managerial foresight, commitment, and vision .
Problems with BCG Matrix Approaches
The BCG and other formal methods revolutionized strategic planning . However, such approaches have limitations. They can be difficult, time-consuming, and costly to implement. Management may find it difficult to define SBUs and measure market share and growth.
In addition, these approaches focus on classifying current businesses but provide little advice for future planning. Management must still rely on its own judgment to set each SBU’s business objectives, determine what resources each will be given, and figure out which new businesses should be added.
Formal planning approaches can also lead the company to place too much emphasis on market-share growth or growth through entry into attractive new markets. Many companies plunged into unrelated and new high-growth businesses using these approaches that they did not know how to manage—with very bad results.
At the same time, these companies were often too quick to abandon, sell, or milk to death their healthy mature businesses.
As a result, many companies that diversified too broadly in the past now are narrowing their focus and getting back to the basics of serving one or a few industries that they know best.
Despite such problems, and although many companies have dropped formal matrix methods in favor of more customized approaches that are better suited to their situations, most companies remain firmly committed to strategic planning .
During the 1970s, many companies embraced high-level corporate strategy planning as a kind of magical path to growth and profits. By the 1980s, however, such strategic planning took a backseat to cost and efficiency concerns, as companies struggled to become more competitive through improved quality, restructuring, downsizing, and reengineering.
Recently, strategic planning has made a strong comeback.
However, unlike former strategic-planning efforts, which rested mostly in senior managers’ hands, today’s strategic planning has been decentralized.
Companies are increasingly moving responsibility for strategic planning out of company headquarters and placing it in the hands of cross-functional teams of line and staff managers who are close to their markets. Some teams even include customers and suppliers in their strategic-planning processes.
Such analysis is no cure-all for finding the best strategy.
But it can help management understand the company’s overall situation, see how each business or product contributes, assign resources to its businesses, and orient the company for future success. When used properly, strategic planning is just one important aspect of overall strategic management , a way of thinking about how to manage a business.
Now that you have a clear idea about BCG matrix. Take a deep dive in studying with our full guideline on strategic management , principles of marketing and marketing management .
- Cut Back Strategies
- Harvest Strategy: Maximizing Profits with Minimum Investment
- Offensive Strategy: 5 Steps to Successful Offensive Strategy
- Best Cost Strategy: Definition, Examples
- Business Process Reengineering
- Outsourcing Strategy: Streamline Business Activities With Outsourcing
- New Venture Strategy
- Stability Strategy: Definition, Adopting, Pathways to Stability Strategy
- Strategic Control: 3 Types of Strategic Control
- Mission Meaning: Ideal Contents of a Mission Statement
- Strategic Action Plan: Vision, Mission, Objectives, & Strategies
- Combination Strategy: Align Businesses Strategically For Explosive Growth
- Internal Check: Definition, Objectives, Principles, Characteristics
- Vertical Integration Strategy: Advantages, Disadvantages, Types
- 4 Levels of Strategy: Types of Strategic Alternatives
- Brand: Meaning, Objective, Benefit, Importance, Strategies
- Design a Competitive Intelligence System: 4 Steps
- Marketing Communication
- Value Delivery Process
- Price: Meaning, Role, Steps of Price Setting Process
- 5 Types of Adopters: Innovators, Early Adopters, Early Majority, Late Majority, Laggards
- Price Changes: Initiation & Reactions of Price Changes
- Market Oriented Strategic Planning
- Marketing Information: Sources, Need for Marketing Information
- 5 Core Customer and Marketplace Concepts
- Market Leader Strategies
- Product Differentiation Strategies To Stand Out in the Market
- Steps in Customer Value Analysis
- Individual Product Decisions
- 4 Characteristics of Service: Intangibility, Inseparability, Variability, Perishability
- 7Ps of Marketing: Boost Your Marketing Strategy
- Logistics Management: Nature, Goals, Functions
- Market Segmentation: Meaning, Bases, Types, Levels, Importance
- 4Cs of Marketing
- Business Market Segmentation: Strategies for B2B Success
- Marketing Environment: Macro and Micro Marketing Environment
- 💰How To Build a Sales Force: Mastering Structure & Strategy
- 7 Goals of Marketing
- 7 Methods of Forecasting Future Market Demands
- Factors Affecting Price Decisions
- Freudian Motivation Theory: A Comprehensive Guide
- 4 Types of Market Segmentation: Bases of Consumer Market Segmentation
What Is BCG Matrix? – Examples & How-To Guide

For a company with a big portfolio, it’s important to assess its product lines regularly to see which product is profitable, which is making losses, and which ones need some work. This practice helps the company to allocate its resources accordingly in order to function more efficiently.
While many practices and tools are available to the company to accomplish this mission, the BCG matrix, developed by the Boston Consulting Group, is considered a gold standard for finding the cash cows, the stars, the question marks, and the dogs.
But what is the BCG matrix, and what do these terms mean?
What Is BCG Matrix?
BCG matrix (also called Growth-Share Matrix ) is a portfolio planning model used to analyse the products in the business’s portfolio according to their growth and relative market share.
The model is based on the observation that a company’s business units can be classified into four categories:
Question Marks

It is based on the combination of market growth and market share relative to the next best competitor.
High Growth, High Market Share
Star units are leaders in the category. These products have –
- A significant market share, hence they bring the most cash to the business.
- A high growth potential that can be used to increase further cash inflow.
With time, when the market matures, these stars become cash cows that hold huge market shares in a low-growth market. Such cows are milked to fund other innovative products to develop new stars.
Low Growth, High Market Share
Cash cows are products with significant ROI but operating in a matured market which lacks innovation and growth. These products generate more cash than it consumes.
Usually, these products finance other activities in progress (including stars and question marks).
Low Growth, Low Market Share
Dogs hold a low market share and operate in a market with a low growth rate. Neither do they generate cash, nor do they require huge cash. In general, they are not worth investing in because they generate low or negative cash returns and may require large sums of money to support. Due to low market share, these products face cost disadvantages.
High Growth, Low Market Share
Question marks have high growth potential but a low market share which makes their future potential to be doubtful.
Since the growth rate is high here, with the right strategies and investments, they can become cash cows and ultimately stars. But they have a low market share so wrong investments can downgrade them to Dogs even after lots of investment.
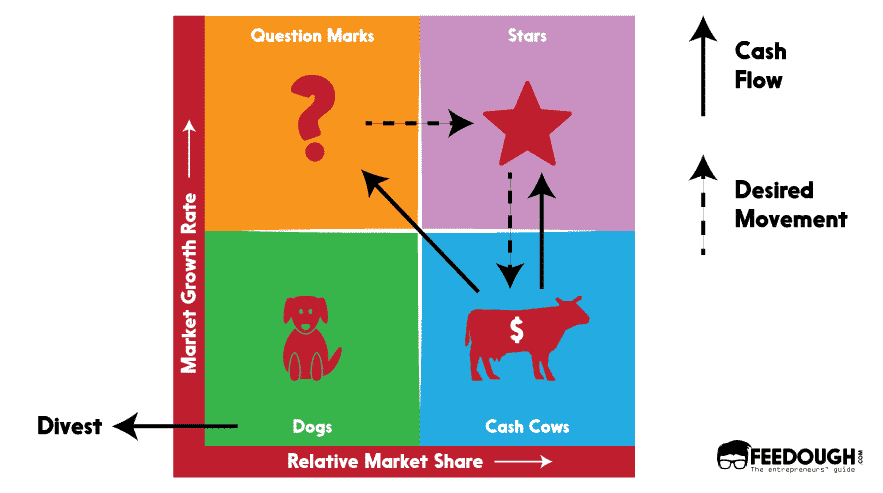
A perfect example to demonstrate the BCG matrix could be the BCG matrix of Pepsico. The company has perfected its product mix over the years according to what’s working and what’s not.
Here are the four quadrants of Pepsico’s growth-share matrix:
- Cash Cows – With a US market share of 58.8% , Frito Lay is the biggest cash cow for Pepsico.
- Stars – Even though Pepsi’s share in the market has been reduced to 8.4%, it’s still the star for Pepsico because of its brand equity. Other stars are Aquafina (the biggest selling mineral water brand in the USA), Tropicana, Gatorade, and Mountain Dew.
- Question Marks – Since it’s a mystery whether the diet food and soda industry will boom in the future and will Pepsico’s products will find their place or not, Diet Pepsi, Pepsi Max, Quaker, etc. fall in the question marks section of the Pepsico’s BCG matrix.
- Dogs – As of now, there isn’t any product line that falls in the dogs section of Pepsico’s BCG matrix. However, seasonal and experimental products like Pepsi Real Sugar, and Mtn Merry Mash-up can be inserted in this section.


How To Make A BCG matrix?
So far, we know products are classified into four types. Now we will see on what basis and how that classification is done.
We shall understand the five processes of making a BCG matrix better by making one for L’Oréal in the following sections.
Step 1: Choose the product
BCG matrix can be used to analyse Business Units, separate brands, products or a firm as a unit itself. The choice of the unit impacts the whole analysis. Therefore, defining the unit is necessary.
Step 2: Define the market
An incorrectly defined market can lead to a poor classification of products. For example, if we would analyse Daimler’s Mercedes-Benz car brand in the passenger vehicle market, it would end up as a dog (it holds less than 20% relative market share), but it would be a cash cow in the luxury car market. Therefore, defining the market accurately is an important prerequisite for better understanding the portfolio position.
Step 3: Calculate the relative market share
Market share is the percentage of your company’s total market that is being catered to, measured either in revenue terms or unit volume terms.
We use Relative Market Share in a BCG matrix, comparing our product sales with the leading rival’s sales for the same product.
Relative Market Share = Product’s sales this year/Leading rival’s sales this year
For example, if your competitor’s market share in the automobile industry was 25% and your firm’s brand market share was 10% in the same year, your relative market share would be only 0.4. Relative market share is given on the x-axis.
Step 4: Find out the market growth rate
The industry growth rate can be easily found through free online sources. It can also be calculated by determining the average revenue growth of the leading firms. The market growth rate is measured in percentage terms.
Market growth rate is usually given by: (Product’s sales this year – Product’s sales last year)/Product’s sales last year
Markets with high growth are ones where the total market share available is expanding, so there are a lot of opportunities for all companies to make money.
Step 5: Draw the circles on a matrix
Having calculated the above measures, now you need to just plot the brands on the matrix. The x-axis shows the relative market share, and the y-axis shows the industry growth rate. You can plot a circle for each unit/brand/product, the size of which should ideally correspond to the proportion of revenue generated by it.
BCG Matrix Example
Let us consider the BCG matrix of L’Oréal, for example.
For a simpler understanding, we look at L’Oreal’s business segments and overall growth.
Step 1: Choose the product/firm/brand
We choose the firm L’Oreal for analysis.

Step 2: Identify Market
The chosen market is the Cosmetics Industry which includes primarily- Skincare, Makeup, Haircare, Hair colour and Fragrances.
Step 3: Calculate Relative Market Share
Tabulated below:
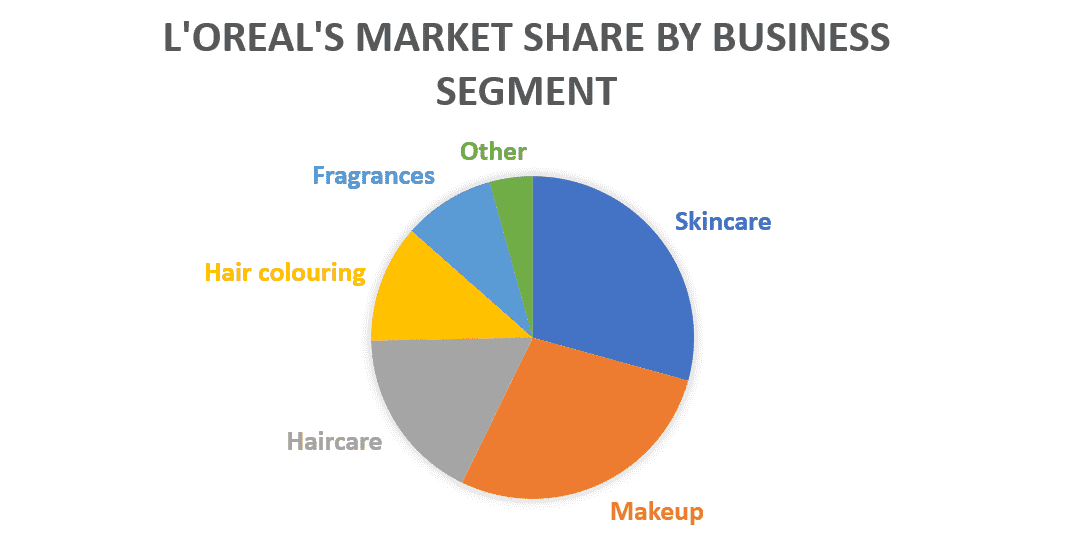
Step 4: Find out Market Growth rate
The overall growth rate in the Cosmetics Industry (as of 2018) = 4.8%
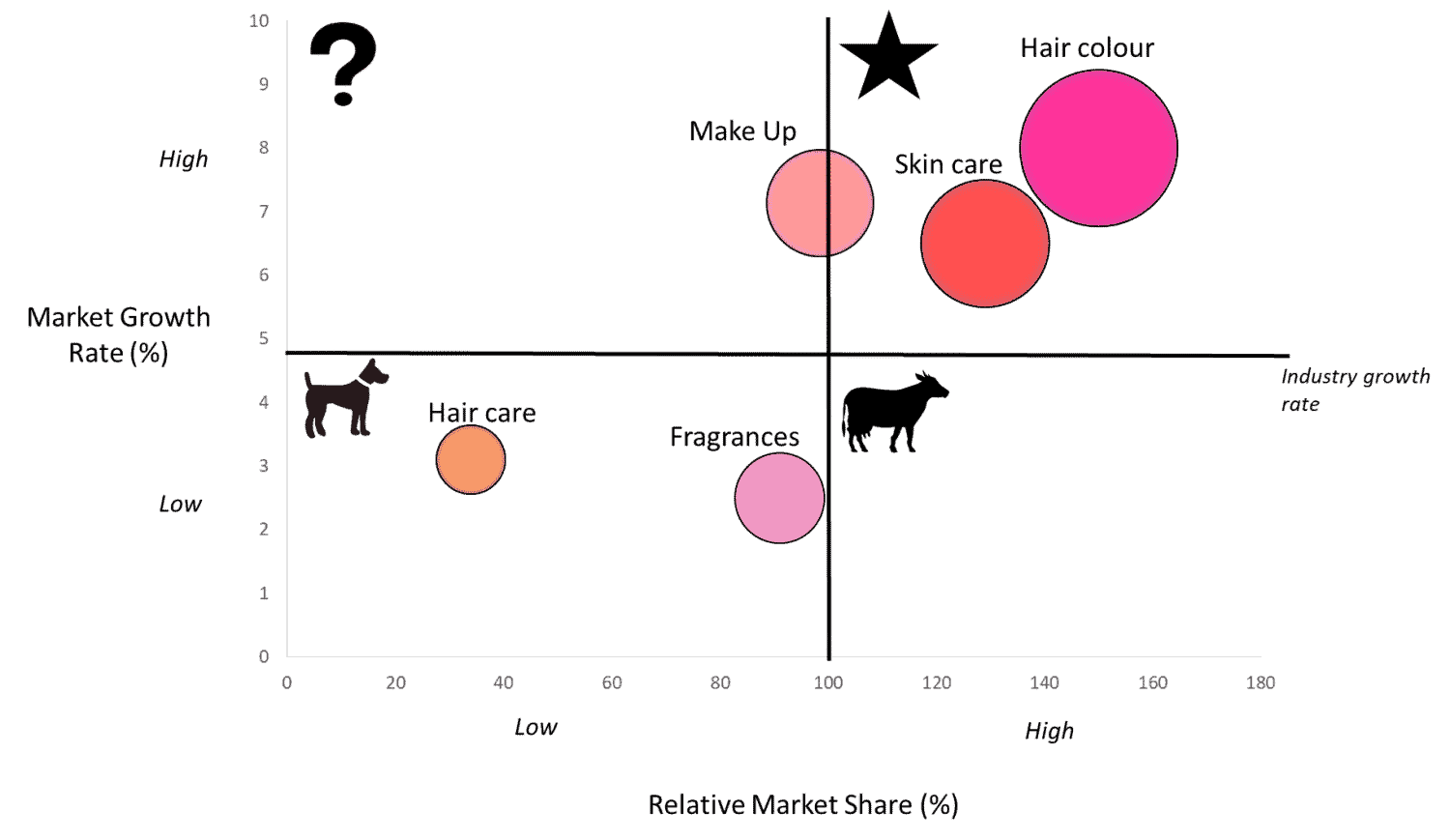
How To Use A BCG Matrix?
Now that we have segregated the brands under four categories, let us see what strategies the company should use for each:
Products located in this quadrant are attractive as they are located in a robust category, and these products are highly competitive in the category. There is huge potential for high revenue growth since they have a high market share and a high growth rate. They may have been expensive to develop but are worth spending money on for promotion given the long extent of their product life cycle . If successful, a star will become a cash cow when the category matures (assuming they maintain its relative market share). Yet, not all stars become cash flows. This happens mainly in continuously changing industries, where even innovative products can be displaced by new technological advancements, so a star becomes a dog instead of a cash cow.
Strategic choices : Vertical integration, horizontal integration, market penetration , market development, product development
Most businesses start off as question marks. These require huge investments to capture or protect market share. Question marks have the potential to become stars and eventually cash cows but can also become dogs or exit. Investments should be high for question marks otherwise may produce negative cash flow.
Like stars, Question marks too may not always succeed, and if even after a large investment, they aren’t able to gain market share, they become dogs. Hence, careful consideration is required before investing in this category.
Strategic choices: Market penetration, market development, product development , divestiture.
They generate profits by investing as little cash as possible in low-cost support and need to be managed for continued profits & cash flow. These are large corporates or SBUs that are efficient in innovation and have the potential to become stars. Cash cows need to maintain a strong market position and defend their market share. The company should take advantage of sales volume and leverage the size of its operations. Cash cows can also be used to support other businesses.
Strategic choices: Product development, diversification
Due to low market share, these products face cost disadvantages so they may generate enough cash to break even , but they are rarely, if ever, worth investing in. Unless a dog has some other strategic aim, it should be liquidated if there are fewer prospects for it to gain market share (there is a low scale of economies: so difficult to make a profit). These are situated at a declining stage of the product life cycle. Therefore, the number of dogs in the company should be minimized. A company should optimize its current operations. It should get rid of all non-value-added activities and features. It must then reposition the offering to generate positive cash flow or sell this business.
Strategic choices: Retrenchment, divestiture, liquidation
Let us now see some advantages and limitations of using the BCG Matrix:
Advantages of BCG Matrix
- It is simple and easy to understand.
- It helps you to quickly and simply screen the opportunities open to you and helps you think about how you can make the most of them.
- It is used to identify how corporate cash resources can best be used to maximize a company’s future growth and profitability.
- The BCG Matrix produces a framework for allocating resources among different products and makes it possible to compare the product portfolio at a glance.
Limitations of BCG Matrix
- BCG Matrix uses only two dimensions, relative market share and market growth rate. These are not the only indicators of profitability, attractiveness or success.
- It neglects the effects of synergy between brands.
- Businesses with a low market share can be profitable too.
- High market share does not always lead to high profits since a high cost goes into getting a high market share.
- At times, dogs may help the business or other products gain a competitive advantage .
- The model neglects small competitors that have fast-growing market shares.
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on BCG Matrix in the comments section.
An MBA graduate and an idiosyncratic bibliophile with an experience in sales, marketing, and economics.
Related Posts:

- How to Apply BCG Matrix to Your Company
Featured in:

© Shutterstock.com | stockphotoatinat
In this article, we will look at 1) what is the BCG Matrix , 2) understanding the BCG Matrix , 3) how to apply BCG Matrix to your company , and 4) some examples .
WHAT IS THE BCG MATRIX?
The BCG matrix was created by Bruce D. Henderson for the Boston Consulting Group in 1970. This chart was created with the purpose of helping companies analyze their different business units or product lines. The analysis helps these companies to allocate resources where they are most appropriate as well as to use the results in brand marketing, product management, strategic management, and portfolio analyses.
The chart is a graphical planning tool, where the company’s products and services can be plotted to help make key business decisions. These decisions include whether to keep a particular business unit, sell it or to invest more in it. The y-axis of the graph represents rate of market growth while the x-axis represents market share.
The matrix helps add input to the decision making process but does not take into account all possible factors that a company may face. The tool is not predictive and also doesn’t take into account any new or disruptive products that may enter and change the market, nor does it account for shifts in consumer demand.
UNDERSTANDING THE MATRIX
The chart or graph is divided into four categories. These are the cows, the dogs, the stars and the unknowns. A product line of a business unit is plotted based on its relative market share and rate of growth in the market and falls within one of these categories.
1) The Cash Cows
The product lines that fall within this category enjoy a large share of the market in a slow-growing industry. This means that they are able to generate revenues in greater amounts than the investment required to maintain their business. The product line may be considered boring and settled in a mature market, with the company holding it to continue to generate revenues. The company will attempt to milk these as much as possible with as little investment as possible.
2) The Dogs
The dogs are those product lines or business units that have a smaller market share in a mature and slow-growing industry. Usually, these product lines manage to earn what is put into them, breaking-even and maintaining the market share. Generally this unit is largely worthless to the company in terms of earning potential but may afford other benefits to the company such as the creation of jobs as well as synergies that assist other business units. These benefits may be enough for the company to keep this business unit active despite its less than exciting position. However, dogs can negatively affect how investors judge the management of a company and it is suggested that these product lines be sold off.
3) The Stars
As the name makes clear, stars are those business units that have a large market share in a fast-growing industry. These product lines have a clearly visible market or niche leading path and require large amounts of funding to ensure that they can fight of competitors and maintain their growth rate. Companies aim to turn stars into their next cash cows with the inevitable decline in the growth of the industry. This can happen potentially if they are able to maintain their position as a market leader. If this does not happen, then stars can turn into dogs.
4) The Unknowns
The unknowns (also called question marks or problem children) are those business units that have a smaller market share in a high-growth market. This is where most businesses will start from and at this point the business unit has the potential to grow market share and turn into a star or lose further marker share and turn into dogs when the growth of the market itself declines. Careful study and analysis is required for business units in this category to assess their potential and worth. If any potential is seen then further investment can be made into them.
The natural cycle for most products in that they begin their life as question marks and turn into stars as their position clarifies. When the market growth slows down, they turn into cash cows and at the end of the cycle, the cash cow turns into a dog. According to the Boston Consulting Group, a diversified company with a balanced portfolio is in the ideal position to use its strengths to capitalize on its growth opportunities and potential. A balanced portfolio is one which has:
- Stars to assure future success
- Cash cows to bring in funds for future growth
- Question marks that can be turned into the next stars with some attention and investment
On either side of the grid is an indicator marked on the axis. The idea that prompted this grid as a while was the need to manage cash flows. The model assumes that one of the main indicators for cash generation is relative market share and the one for cash usage was the market growth rate.
- Relative Market Share – A higher market share means higher cash return. The reason behind the selection of this metric is based on its relationship with the experience curve. The belief is that when the company produces more products, it benefits from higher economies of scale and the experience curve which in turn result in higher profits. The market share is measured relative to its largest competitor. Another reason for the selection is that this indicator carries more information than just cash flows as is the case in profits. It shows the brand’s position in relation to major competitors and a likely indication for the future.
- Market Growth Rate – A higher market growth rate means more earnings and often profits. On the other hand, it also means a higher consumption of cash as investment to stimulate future growth. This investment is made into those products which show a good potential for continued growth and success and are expected to provide a return on investment. This matrix assumes that a higher growth rate is an indicator of accompanying demands for investment. The market growth rate provides more information about the brand position than just the cash flow and is a good indicator of the strength of the market and its future potential as well as attractiveness to more competitors.
The BCG Matrix is named after the Boston Consulting Group, a global management consulting firm. The company has 81 offices in 45 countries and is one of the Big Three management consulting firms. The company was founded by Bruce D Henderson, an alumnus of Vanderbilt University and Harvard Business School. He was recruited by McKinsey and it is here that he founded the Boston Consulting Group. Henderson developed the famous BCG matrix in 1968. According to the BCG, Henderson told clients the following:
“The payoff for leadership [in market share] is very high indeed, if it is achieved early and maintained until growth slows. Investment in market share during the growth phase can be very attractive, if you have the cash. Growth in market is compounded by growth in share. Increases in share increase the profit margin. The return in investment is enormous. “
Limitations
There are some limitations to the use of this popular matrix as well. These limitations mean a decline in the once extensive use of this tool. These include:
- Market growth is one of many factors that determine industry attractiveness and relative market share is only one of many factors that determine competitive advantage. This matrix does not take into account any other factors that may have a bearing on both industry attractiveness and competitive advantage.
- There is an underlying assumption that the business units are operating in isolation in relation to each other. In reality, a dog may be helping another unit gain a competitive advantage for example.
- The definition of a market is taken in the broad sense. This fails to take into account different situations such as a business unit that is dominating a niche but is overall less dominant in the larger industry. The way a market is defined in such an instance may change its definition from a dog to a cash cow.
HOW TO APPLY BCG MATRIX TO YOUR BUSINESS
“To be successful, a company should have a portfolio of products with different growth rates and different market shares. The portfolio composition is a function of the balance between cash flows. High growth products require cash inputs to grow. Low growth products should generate excess cash. Both kinds are needed simultaneously.” – Bruce Henderson
Practical Use Tips
The BCG matrix can be useful to companies if applied using the following general steps.
Step 1 – Choose the Unit. Strategic Business Units, individual brands, product lines or the firm as a whole are all areas that can be analyzed using the BCG matrix. The chosen unit drives the entire analysis and key definitions. The market, industry, competitors and position will all be based on the chosen unit.
Step 2 – Define the Market. Following the choice of the unit or area to be analyzed, the most important stage for the rest of the matrix is the definition of the market. An incorrectly defined market will lead to an incorrect classification of the unit. A Mercedes-Benz analyzed in a passenger vehicle market will be a dog with a small market share. However, analyzed within a luxury car market, it will be a cash cow.
Step 3 – Calculate Relative Market Share. At this stage, the relative market share for the chosen unit needs to be calculated. This can be done in terms or revenues or marker share. The formula used here us a division of the selected brand’s market share or revenues by the market share or revenues of the biggest competitor in the industry. The result in plotted on the x-axis.
Step 4 – Calculate Market Growth Rate. Online industry reports can be used to find the rate of growth for the industry. If this is not possible, then it can be estimated by looking at the average revenue growth of the leading firms in the industry. This measurement is a percentage and is plotted on the y-axis.
Step 5 – Draw Circles on the Matrix. Once all the measures are calculated, they can be put onto the matrix. This can be done by drawing a circle for each brand within a unit, or all the brands in a company. The size of each circle should correspond to business revenue generated by the brand.
According to an analysis posted here , the BCG matrix analysis for Nestle reveals some interesting perspectives. A global multinational in the food and beverage industry, the Swiss company is the 69 th highest revenue producer in the world. Over 8000 brands fall within its umbrella and are as widespread as bottled water and pet food. The company announced plans to sell off under-performing brands which were consistently showing poor sales. This analysis used the 2002 annual report for its figures which can be found here .
- Question Marks – Here, the question marks have a low market share within a high growth market. The product mentioned here requires an influx of investment to capitalize on potential segments. This investment is however, not likely to yield too much return investment.
- Stars – These brands have a high share in a high growth market. Nestle’s varied mineral water is in this quadrant. The brands in this are require investment to maintain their position and differentiation in both mature and emerging markets.
- Dogs – The Nestle products in this category have a lower market share in a low growth market. An example of this is a lean cuisine unit and weight loss management brands which did not take off outside the US. A sports performance and nutrition brand called PowerBar is also confirmed to be divested by the company most likely due to poor sales in a saturated market. These products generate enough revenue to sustain themselves but are not exciting not major sources of revenues.
- Cash Cows – These brands are important because of their cash generating potential. This means that they have a higher market share in a slow-growth industry. Very little investment is needed by these brands and funds generated from them are used to fuel Stars or Question Marks.

Comments are closed.
Related posts
How to Create an Effective Peer Review System
When you’re a member of an organization or a similar setup, evaluations are, for lack of a better …
Reputation.com | Interview with its Founder & Executive Chairman – Michael Fertik
In Redwood City (CA), we meet Founder & Executive Chairman of Reputation.com, Michael Fertik. …
The Basics of Branding For Building A Loyal and Profitable Customer Base
The face of your brand must be in the minds of your customers every time an opportunity to purchase …
408,000 + job opportunities

Not yet a member? Sign Up
join cleverism
Find your dream job. Get on promotion fasstrack and increase tour lifetime salary.
Post your jobs & get access to millions of ambitious, well-educated talents that are going the extra mile.
First name*
Company name*
Company Website*
E-mail (work)*
Login or Register
Password reset instructions will be sent to your E-mail.

Best 15 BCG Matrix Examples for Students

Published on Jul 12, 2023, updated on Mar 15, 2024
What is the BCG matrix?
The Boston Consulting Group Matrix (BCG Matrix) is also called Growth/Share Matrix. As the name suggests, it is a framework for portfolio management used to prioritize different products. It was developed by the Boston Consulting Group in the 1970s and is widely used for strategic planning and decision-making regarding investment in competitiveness and market attractiveness.
The BCG matrix categorizes products or business units into four quadrants based on their market growth and relative market share. These quadrants are: Stars, Cash Cows, Question Marks (or Problem Children), and Dogs.
1) Stars -- High Growth, High Market Share
Stars units are leaders in the category. They have the potential to generate substantial returns and are considered strategic assets for the organization.
2) Cash Cows -- Low Growth, High Market Share
While Cash Cows operates in a matured market and may not have significant growth prospects, they generate stable and positive cash flow, contributing to the financial stability of the organization. Usually, these products finance other activities in progress (including stars and question marks).
3) Question Marks (or Problem Children) -- High Growth, Low Market Share
Since the development rate is high here, with the correct strategies and ventures, they can turn into Cash Cows and even Stars in the end. However, the low market share means that wrong investments can downsize them to Dogs significantly after loads of speculation.
4) Dogs -- Low Growth, Low Market Share
Dogs do not have strong prospects for growth or profitability and may drain resources from the organization. Businesses may consider divesting or discontinuing dogs if they are not strategically valuable.
How to Make a BCG Matrix Diagram?
The following shows the six basic processes of creating a BCG matrix diagram:
Step 1: Identify your products or business units
BCG matrix can be used to analyze Business Units, separate brands, products, or a firm as a unit itself. The choice of the unit impacts the whole analysis. So be careful to determine the products or business units that you want to analyze and classify.
Step 2: Define the market
An incorrectly defined market can lead to a poor classification of products. For example, Daimler’s Mercedes-Benz car brand would be considered a Dog if analyzed in the passenger vehicle market, but it would be a cash cow in the luxury car market.
Step 3: Calculate the relative market share
This can be calculated by dividing the company’s market share by the market share of the largest competitor in that particular market. Categorize them as high, medium, or low market share.
Relative Market Share = Product’s sales this year/Leading rival’s sales this year
Step 4: Find out the market growth rate
This can be done by analyzing industry data, market research, or internal sales data. It can also be calculated by determining the average revenue growth of the leading firms. The market growth rate is usually given by:
(Product sales this year – Product sales last year)/Product sales last year
Step 5: Draw the circles on a matrix
Having calculated the above measures, now you need to just plot the brands on the matrix. The x-axis shows the relative market share, and the y-axis shows the industry growth rate. You can plot a circle for each unit/brand/product, the size of which should ideally correspond to the proportion of revenue generated by it.
Step 6: Analyze and regularly update
Analyze the positioning of each product or business unit on the matrix. Develop appropriate strategies for each quadrant. Also, remember to regularly update and review the matrix to reflect changes in market conditions, performance, and strategies.
15 BCG Matrix Examples
Bcg matrix for coca-cola.
1) Stars: Kinley and Dasani
Bottled water brands Kinley and Dasani are Stars because they dominate the market in Europe and the US and show no signs of slowing down.
2) Question marks: Diet Coke, Minute Maid, Honest Tea, Sparkling water
With an aim to cater to the changing needs of consumers for zero calories and no-sugar drinks, the Coca-cola company has launched a number of products/brands to cater to the same. However, some products/brands are still in the initial/development phase of the product lifecycle and have a huge potential to grow. Diet Coke, Minute Maid, Honest Tea, and Sparkling Water are the few Question Mark products, as they appeal to a modest audience but still have room for growth.
3) Cash Cows: Coke
Coke for years has been a market leader in the carbonated soft drink segment and a major cash generator for the company. However, demand for carbonated soft drinks is declining, fueling a growing demand for healthier options or low-calorie drinks like Diet Coke.
4) Dogs: Coke
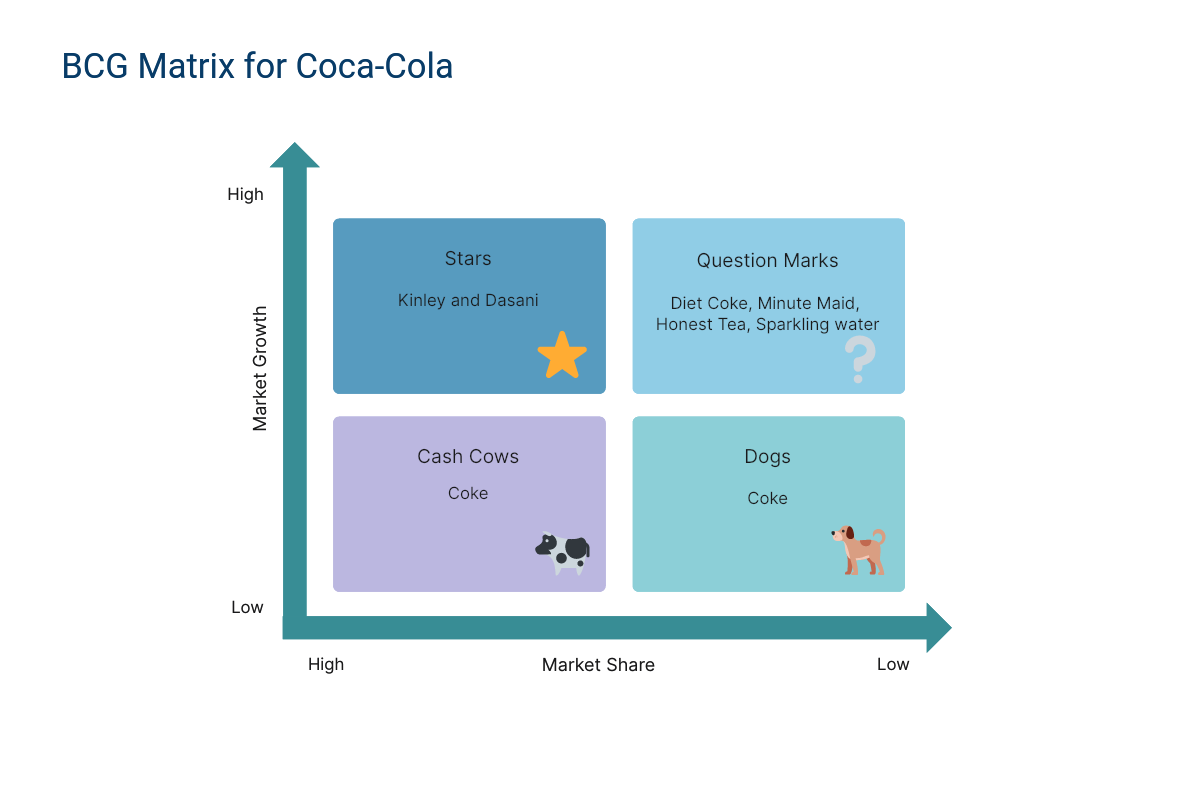
BCG Matrix for Apple
1) Stars: iPhones
Apple’s iPhones continue to generate excess profits, and the company dominates the growing smartphone market. Apple iPhones have a high stature because of their unique design and advanced technology. Also, the iPhone enjoys a loyal customer base that makes it beat all the competition in the booming mobile phone market.
2) Question marks: AirPods and Apple Smart TVs
Apple’s AirPods are growing extremely quickly but have yet to dominate the market. Likewise, Apple Smart TVs makes a little money but is still far from its true potential, and it can become a star if Apple can fix a few ecosystem issues.
3) Cash Cows: Apple iTunes, Apple MacBook, and iMacs
Once an innovative product, some products like Apple’s laptops are no longer in a fast-growing industry but generate healthy profits for the company. Over the years, these products have retained their market share and have increased cash flows for the company. Apple has a strong, loyal customer base that prefers Apple products exclusively.
4) Dogs: iPods
Apple’s iPods are considered dogs because they have lost their attraction due to high competition and low customer demand. They have now been cannibalized by its iPhones and should no longer receive further heavy investment.
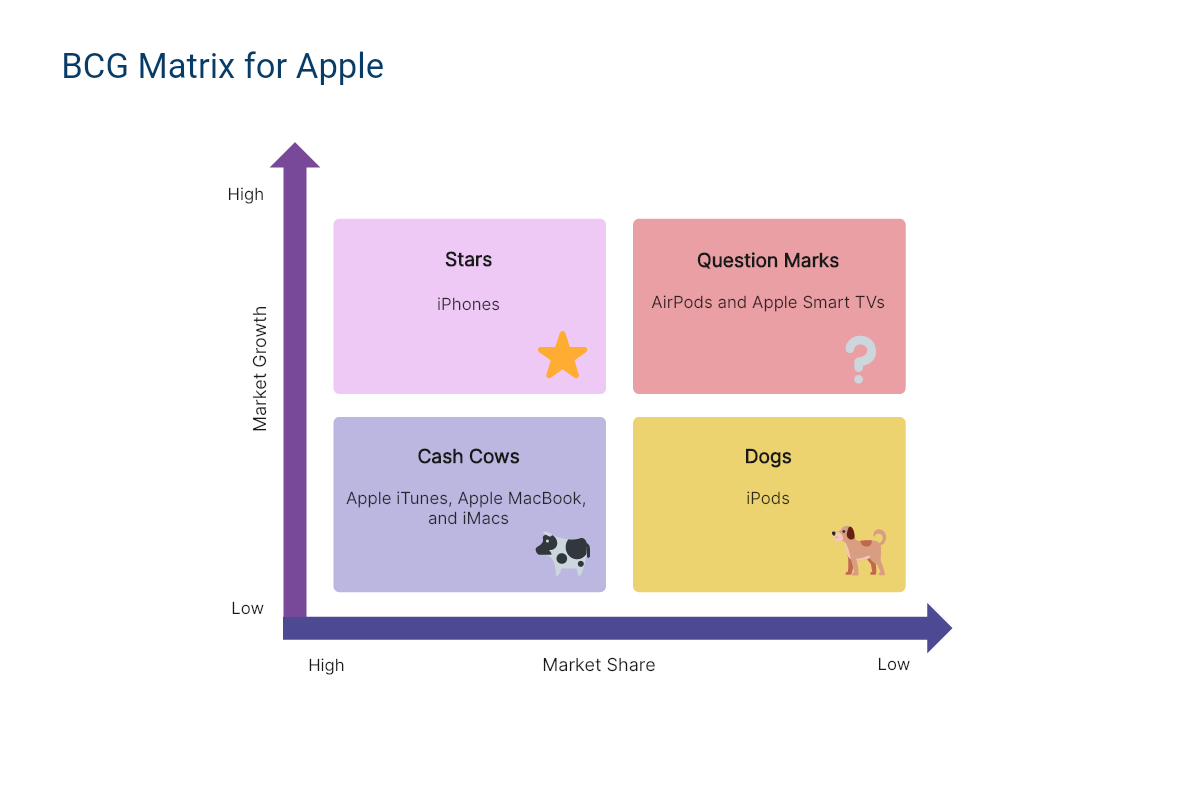
BCG Matrix for Amazon
1) Stars: online store, AWS, and cloud segment
Amazon’s claim to fame is definitely its online store called Amazon.com. It continues to generate great ROI with a high growth rate. Amazon’s AWS and cloud segment is also showing growth potential, and the market is also becoming attractive.
2) Question marks: Amazon Live and video on demand
In the Amazon BCG matrix, video on demand and Amazon Live can become a question mark because of limited growth. However, they still have promising growth potential.
3) Cash Cows: E-books, audiobooks, and movies on demand
The E-books division is a lucrative cash cow for the company. Amazon has its native e-book reader called Kindle, and it has generated substantial ROI. Audiobooks and movies on demand also generate potential revenue and are in high demand from consumers.
4) Dogs: Alexa and physical stores
Amazon’s physical stores are the least competitive in terms of market share. They represent only about 0.015% of the market share, which is almost negligible. Besides, Amazon Alexa can also be categorized as a dog in the Amazon BCG matrix because its market is shrinking and showing negative market growth.
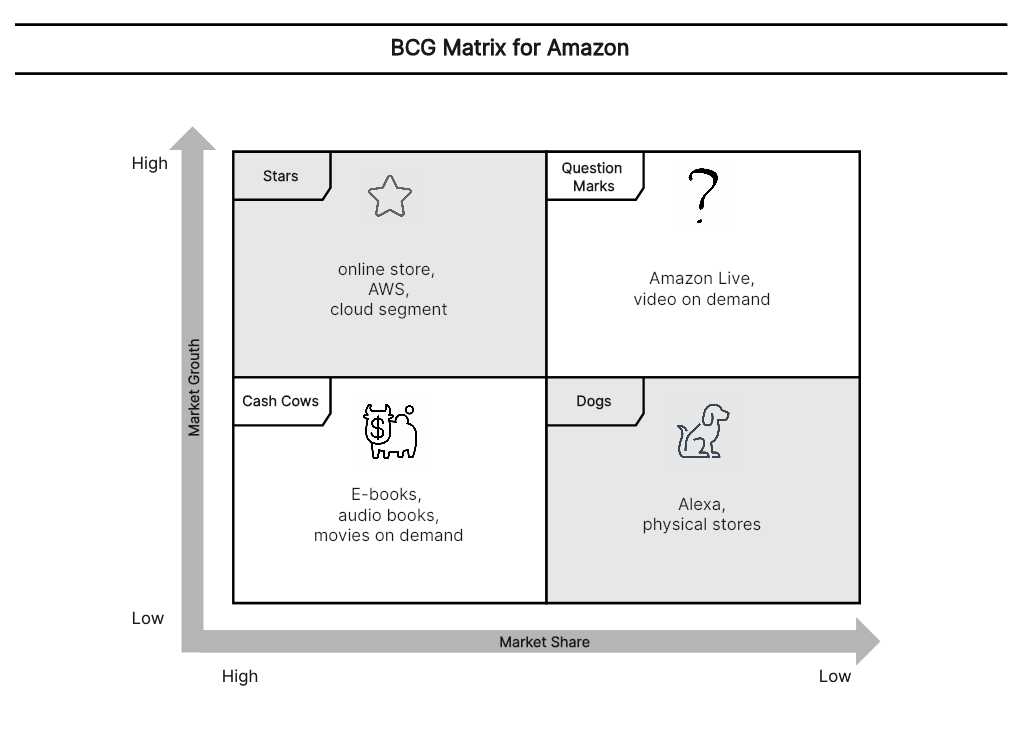
Reference: https://www.edrawmax.com/article/amazon-bcg-matrix-analysis.html
BCG Matrix for Samsung
1) Stars: Samsung smart TVs
Samsung smart TVs are quite competitive in this industry, continuing to gain traction as consumers demand more smart products. Mobile phones from Samsung also fall into this quadrant because the industry is still evolving. It is an industry developing fast with newer advancements in mobile computing devices.
2) Question marks: Samsung laptops
Samsung laptops fall in the question mark quadrant, owing to a poor reputation for unreliable battery life and basic design among their counterparts.
3) Cash Cows: Samsung home appliances, refrigerators, and washing machines
Samsung home appliances, refrigerators, and washing machines are the cash cows in its BCG matrix analysis, for they contribute to a significant share of the company’s revenue.
4) Dogs: Samsung printers
Samsung printers is a business that Samsung tried to push but has failed. The printers business was finally transferred to HP, which is a good choice because HP is one of the well-known printer brands.
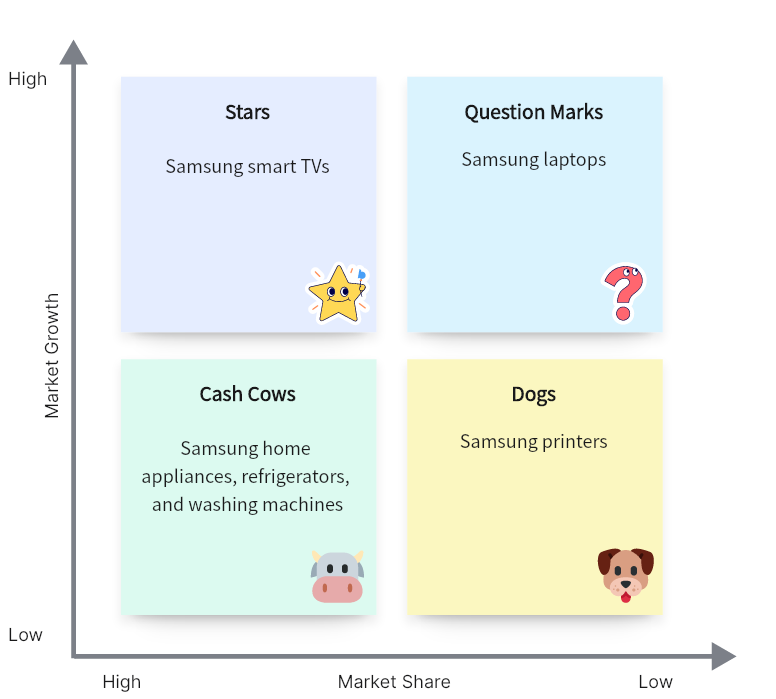
Reference: https://www.financefied.com/education/bcg-matrix-example/
BCG Matrix for Microsoft
1) Stars: Azure Cloud Platform, Microsoft Teams
Azure is Microsoft’s cloud computing platform that offers a wide range of services, which has experienced significant growth and has a strong market position.
Microsoft Teams is a collaboration and communication platform that has gained significant traction, especially with the rise of remote work and virtual meetings. Its high growth potential has made it a central product in Microsoft’s portfolio.
2) Cash Cows: Windows operating system, Microsoft Office Suite
Windows is Microsoft’s flagship operating system that powers a vast majority of personal computers worldwide. While the growth of the PC market has slowed down, it continues to generate substantial revenue and profit as a mature and established product.
The Office Suite is widely used in business, education, and personal settings. As a dominant and well-established product, it generates steady cash flow for Microsoft.
3) Question Marks: Surface hardware, Xbox gaming console
While the Surface lineup (laptops, tablets, and hybrid devices) has gained recognition for its design and innovation, it faces strong competition in the hardware market. These products have the potential for growth but require further investment and market share expansion.
Xbox is Microsoft’s gaming console brand. Born in the highly competitive gaming console market, Xbox faces challenges from competitors such as Sony’s PlayStation, which has restricted its growth potential.
4) Dogs: Windows Phone (discontinued)
Microsoft discontinued its mobile hardware efforts, and the Windows Phone platform no longer receives active development or support.
BCG Matrix for Toyota
1) Stars: Toyota Prius (hybrid cars), Toyota Camry (midsize sedans)
The Prius, known for its fuel efficiency and environmentally friendly features, has enjoyed significant market growth and has established a strong market share in the hybrid car segment. Toyota Camry, a popular midsize sedan known for its reliability, comfort, and fuel efficiency, has consistently performed well in the market.
2) Cash Cows: Toyota Corolla (compact cars), Toyota RAV4 (compact SUVs)
The Corolla is one of the best-selling compact cars globally, while Toyota RAV4 is a compact SUV that has gained popularity for its versatility, practicality, and fuel efficiency. They both enjoy a well-established market share and generate substantial cash flow for Toyota.
3) Question Marks: Toyota Mirai (hydrogen fuel cell vehicles), Toyota C-HR (compact crossover)
While Toyota Mirai is a technologically advanced and environmentally friendly option, the market for hydrogen fuel cell vehicles is still in its early stages. Besides, Toyota C-HR has shown promise with a distinctive design. Still, it is not impressive enough in the highly competitive compact crossover segment.
4) Dogs: Scion brand (discontinued)
Scion was a brand owned by Toyota that targeted younger demographics with compact and sporty vehicles. However, due to various reasons, Toyota has abolished the Scion brand. It represents a low-growth, low-market-share product that no longer exists in Toyota’s portfolio.
BCG Matrix for Nike
1) Stars: Nike shoes (Nike Air Max etc.), sportswear
Certainly, the leader of the Nike product portfolio is Nike shoes. However, due to the pandemic period, sportswear has become a star of the portfolio because there have been changes in the lifestyle of consumers.
2) Cash Cows: equipment and accessories
The equipment and accessories are Cash Cows for the Nike company. They generate cash to turn questioned products (dilemmas) into dairy cows.
3) Question Marks: Nike Converse
The Nike Converse product category can be found in the dilemmas. If Nike adopts effective and specific strategies, this product can be converted into a Cash Cows.
4) Dogs: Nike Skateboarding
Nike Skateboarding products fall in the dogs quadrant since these offerings are not very popular among the skateboarding community. However, the company continues to produce skateboarding shoes and clothing despite a large number of competitors.
Reference: https://awware.co/blog/bcg-matrix/
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/BCG-Matrix-for-Nikes-Portfolio_fig2_351123152
BCG Matrix for Procter & Gamble (P&G)
1) Stars: Gillette, Oral-B
Gillette is a well-established brand known for its shaving products, while Oral-B is a leading brand in the oral care market, specializing in toothbrushes and other dental products. They have experienced strong growth and have a significant market share.
2) Cash Cows: Tide, Pampers
Tide is one of P&G’s most successful brands, offering a wide range of laundry detergent products. Pampers is a leading brand in the baby care market, particularly known for its diapers. They enjoy a well-established market share and generate consistent cash flow for P&G.
3) Question Marks: Olay, Head & Shoulders
Olay is a skincare brand offering a variety of products, and Head & Shoulders is a popular brand in the hair care industry. While they have a strong presence, they face challenges in a competitive market.
4) Dogs: Duracell
Duracell is a battery brand that has a relatively low growth rate and market share compared to P&G’s other brands.
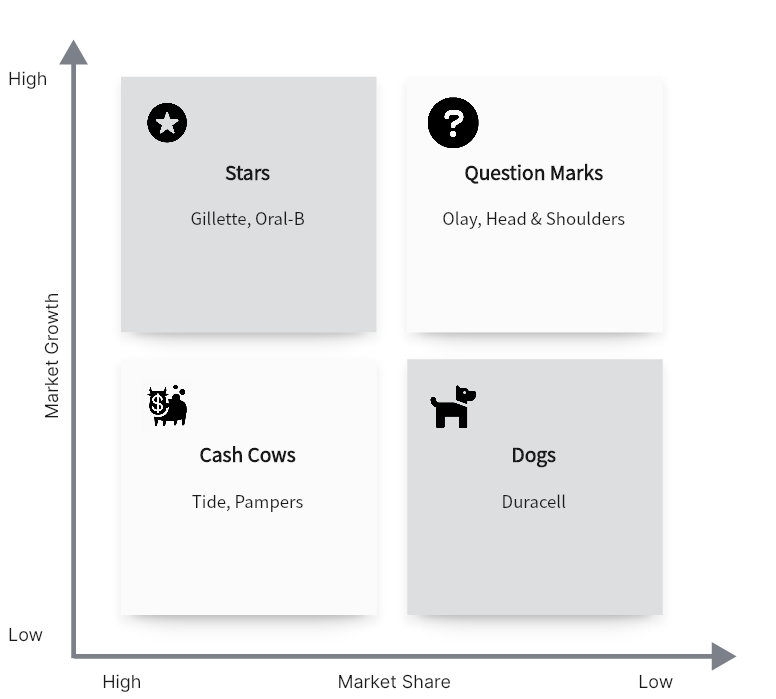
BCG Matrix for Nestlé
1) Stars: Mineral Water, Nescafe Coffee
Nestle’s Mineral Water and Nescafe Coffee (like Nescafe Latte) fall in the Star quadrant of the BCG Matrix of Nestle. With the growing number of health-conscious customers, these products have the potential to produce greater ROI later. Even though it might take heavy investment to make Nestle brand visible in that market, they may turn to cash cows in the short run.
2) Cash Cows: Nestle’s Maggi Noddles
With a market share of 80-85 %, Maggi Noddles holds a very strong hold in the market and have high customer loyalty. This product requires very less investment to maintain its market share and fight off any competition.
3) Question Marks: Milk products and Nutrition
Nestle Everyday, Nestlé Slim, and Nestlé Milk Maid are some of the milk and milk-based products from the house of Nestlé. Being in the phase of development, this domain needs a higher investment. And there is a high-risk decision to invest in them too.
4) Dogs: Nestle’s Milo
Nestle’s Milo was launched as chocolate and malt powder for milk and water; however, the product failed to create any significant impact on the business.
References: https://heartofcodes.com/bcg-matrix-of-nestle/
https://www.superheuristics.com/bcg-matrix-of-nestle-detailed/
BCG Matrix for PepsiCo
1) Stars: Aquafina, Gatorade, and Powerade
Aquafina holds 15% of the bottled water market share and is second to Bisleri. The trend for carbonated drinks has decreased significantly as consumers move away from sugar-laden sodas. Gatorade is now the market leader in sports drinks, with 77% share of the market, up from 63% a year ago. Powerade has a 20% share of the market. With rising health trends and emerging markets, the brand is investing huge amounts of money into healthier foods and beverages, making a bigger dent in the soft drink category.
2) Cash Cows: Frito Lay
Frito-Lay has a dominant 72.4% market share in the chip segment, but its main competitors are Doritos with 7% and Tostitos with 8.7%. The product requires a little investment to maintain its market share, as its sales don’t fluctuate significantly with new products.
3) Question Marks: Diet soda
Not many people associate the term “Diet soda” with PepsiCo. The company launched Diet Pepsi to take back a portion of the market share it had lost to Coca-Cola and recapture the consumers’ attention. In its initial launch, Diet Pepsi captured just 5 percent of the market, but soon after, it began losing market share to Coca-Cola’s diet version.
4) Dogs: Pepsi
The present and future trends suggest that Pepsi will shift from Star to the Dog quadrant. The segment share of Pepsi has dropped from 10.3% to 8.4% due to increasing demand for low-calorie and healthy beverages and snacks.
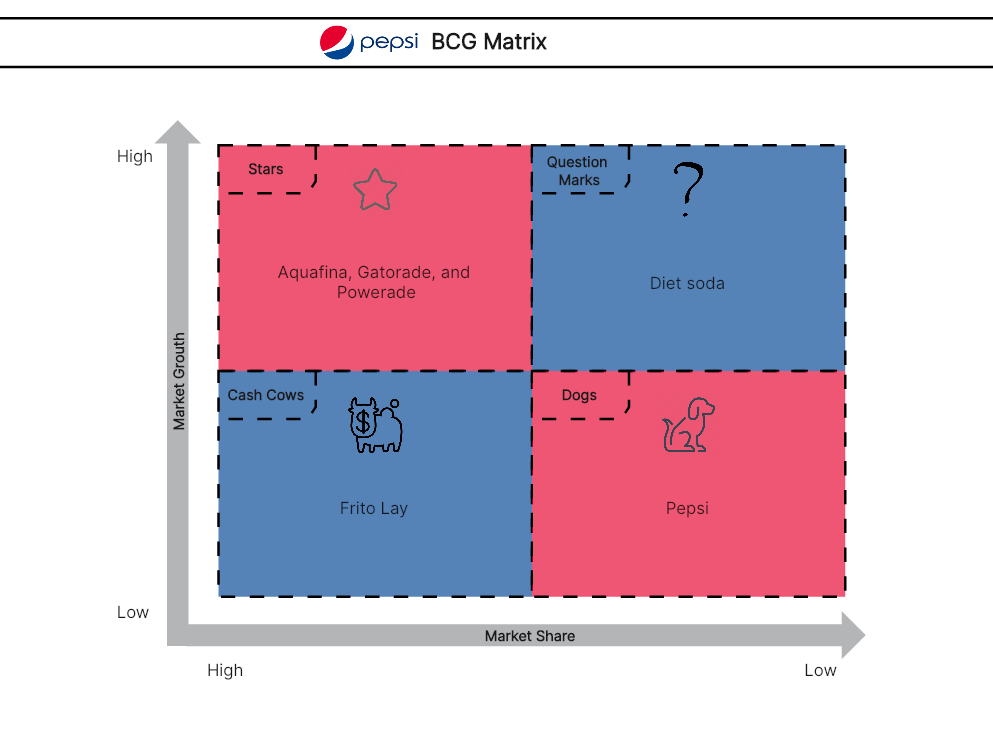
Reference: https://www.edrawmax.com/article/pepsi-bgc-matrix.html
BCG Matrix for Google
1) Stars: Google search engine
For Google, its star product would be its search engine, which is the company’s flagship product and has a dominant market position in the search engine industry.
2) Cash Cows: Advertising business
For Google, its cash cow product would be its advertising business, which is a major source of revenue for the company. The advertising business generates high revenue for the company but does not require much investment to maintain its market position.
3) Question Marks: Google Glass, Google Home, and Google Stadia
The newer ventures such as Google Glass, Google Home, and Google Stadia may be counted as Google’s question mark products. They are new products and services that require significant investment to improve their market position but have the potential to become stars or cash cows for the company in the future.
4) Dogs: Google Video Player, Google Glass, and Google Plus
The popularity of YouTube is part of the reason why Google video player failed to get income. Another example, Google Glass was a product whose “target problem” wasn’t chalked out properly. Also, Google Plus was another example of such failure that couldn’t keep up with the competition.
Reference: https://heartofcodes.com/bcg-matrix-of-google/
BCG Matrix for General Electric (GE)
1) Stars: Renewable Energy, Healthcare
This business unit encompasses GE’s offerings in the renewable energy sector. With the increasing focus on clean energy and sustainability, this segment has experienced significant market growth and has established a strong market share. GE’s healthcare division includes medical equipment and solutions. Likewise, this segment has seen substantial growth due to the growing demand for advanced healthcare technologies and equipment.
2) Cash Cows: Aviation, Power
GE’s aviation business is known for its jet engines and related services. The aviation industry has a consistent demand for aircraft engines and maintenance services. The power division focuses on gas turbines and related products for power generation. This segment also has a strong market position and generates substantial cash flow for the company.
3) Question Marks: Digital Solutions, Transportation
GE’s digital solutions and transportation division have the potential for growth, while at the same time, they also face challenges in the competitive market.
4) Dogs: Lighting (discontinued)
GE had a lighting division that was involved in manufacturing and selling lighting products. However, the company decided to exit this business, and it is no longer a part of GE’s portfolio.
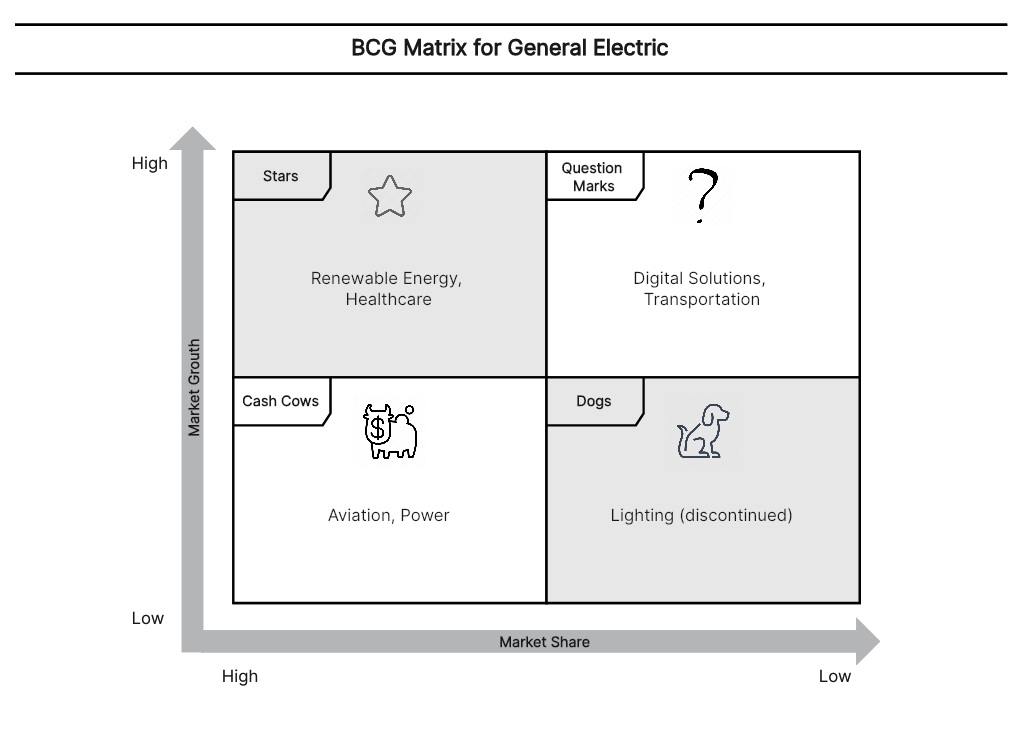
BCG Matrix for Tesla
1) Stars: electric vehicles, cleaner energy
Tesla is indeed a leader in the sustainability industry, and all of its products and services are focused on a healthier environment. The three series is the latest vehicle that has been released and has proven to be the most popular with consumers.
2) Cash Cows: Powerwall
This is the case for all other vehicle models, which require little investment. The Powerwall also falls into this category. This battery can be used in domestic settings.
3) Question Marks: miscellaneous accessories, energy storage, and solar power
The dilemmas faced by the company include miscellaneous accessories, energy storage, and solar power. Competition in these markets is very high, so it is difficult to differentiate yourself over the long term. Ecology remains a niche market in today’s world that interests more and more players. These services require larger investments to be profitable.
4) Dogs: certain models
It is possible to highlight the manufacturing complication of certain models, which can largely compromise consumer orders, especially since the competition is becoming increasingly fierce.
Reference: https://www.oboolo.com/blog/our-tips/tesla-bcg-matrix-02-03-2022.html
BCG Matrix for Adidas
1) Stars: Reebok, Adidas
For the Adidas group, Reebok and Adidas are the stars, as both have the stronger market share, despite of the tough competition they are facing in the fitness and sports industry, mainly its shoes.
2) Cash Cows: Clothing and apparels
For Adidas, its clothing and apparels are the cash cow items, and it is necessary for Adidas to consider this point, and position itself well in customers’ minds by targeting different geographic markets
3) Question Marks: Taylor Made, Rockport
Taylor Made and Rockport are the question marks for Adidas, as both have very low market shares but still possess the potential to grow more in the competitive market. Adidas needs to revise its strategies for turning potential into benefits for the strategic objective of the Group.
4) Dogs: Hats, sunglasses
The hats and sunglasses of Adidas are categorized in this quadrant because these are the least-selling items of the company, and many people are not interested in spending their money on them, as they have better options in this category.
Reference: https://bcgmatrixanalysis.com/bcg-matrix-of-adidas/
BCG Matrix for IBM
1) Stars: IBM Cloud, IBM Watson
IBM’s cloud computing services have shown significant market growth and have established a strong position in the cloud market. In addition, IBM’s Watson AI platform has demonstrated rapid growth and has become a prominent player in the field of artificial intelligence.
2) Cash Cows: IBM Software, IBM Global Business Services
IBM offers various software solutions, such as enterprise software and analytics, which generate steady cash flow for the company. Besides, IBM’s consulting services have a well-established market share and provide consistent revenue and profitability for the company.
3) Question Marks: IBM Quantum, IBM Blockchain
The company is actively involved in quantum computing research and development, representing a high-potential but uncertain market segment. Also, its blockchain technology has potential growth opportunities, although the market is still evolving, and its long-term potential is uncertain.
4) Dogs: IBM Systems
IBM’s hardware division, including servers and mainframes, represents a low-growth, low-market-share product category in comparison to their other offerings.
What is Cognition Labs' Devin? Explore 5 More AI Tools That Disrupt Industries
10 Conversational AI Platforms for 2024: Transforming Industries with Intelligent Interaction
Customer Journey Map Example: Understanding User Interactions Effectively


- The Investment Banker Micro-degree
- The Project Financier Micro-degree
- The Private Equity Associate Micro-degree
- The Research Analyst Micro-degree
- The Portfolio Manager Micro-degree
- The Restructurer Micro-degree
- Fundamental Series
- Asset Management
- Markets and Products
- Corporate Finance
- Mergers & Acquisitions
- Financial Statement Analysis
- Private Equity
- Financial Modeling
- Try for free
- Pricing Full access for individuals and teams
- View all plans
- Public Courses
- Investment Banking
- Investment Research
- Equity Research
- Professional Development for Finance
- Commercial Banking
- Data Analysis
- Team Training
- Felix Continued education, eLearning, and financial data analysis all in one subscription
- Learn more about felix
- Publications
- My Store Account
- Learning with Financial Edge
- Certification
- Masters in Investment Banking MSc
- Student Discount
- Find out more
- Diversity and Inclusion
- The Investment banker
- The Private Equity
- The Portfolio manager
- The real estate analyst
- The credit analyst
- Felix: Learn online
- Masters Degree
- Public courses
By Oliver Sealey |
Reviewed By Rebecca Baldridge |
May 17, 2022
What is the BCG Matrix?
The Boston Consulting Group (BCG) designed its four-celled matrix, the BCG Matrix, to aid in long-term strategic planning. The matrix is used to assess the growth opportunities of different products/brands that an organization has in its portfolio based on relative market share and market growth rates across industries/sectors.
The matrix makes it possible to examine the business potential and market environment of different products and brands, which enables the company to decide where to invest, divest, or develop new products.
For credit analysts, the matrix can be a helpful framework for analyzing business risk, an essential part of deciding the credit-worthiness of a company.
In this article we’ll examine how the matrix categorizes products, giving examples. We’ll then see what actions companies can take having decided on the categories. Finally we’ll look at some of the limitations of the matrix.
Key Learning Points
- The BCG matrix is divided into four quadrants and is based on two parameters, relative market share and market growth rate
- The BCG Matrix includes four categories: stars, cash cows, question marks, and dogs
- To calculate the relative market share of a product, divide its market share by the market share of the product’s largest competitor
- This matrix can help businesses make good choices around their portfolio. For example, it can help companies decide which products should be their focus and which should be discontinued
- Care should be exercised around the use of the matrix. It can over-simplify concepts due to its two axis nature
- “High” and “low” market share and market growth determine which category a product ends up in, but deciding what “high” is can be difficult
- Defining the market can also be difficult. Deciding define the market broadly or more narrowly will make a big difference to the matrix and the categories it suggests for a company’s products.
BCG Matrix – Key Terminologies
The BCG matrix is divided into four quadrants and is based on two parameters – relative market share and the market growth rate. The horizontal axis of this matrix represents relative market share, while the vertical axis represents the market growth rate. The four cells of this matrix are designated stars, cash cows, question marks, and dogs. There are general actions associated with the 4 different types, but in the real world companies may of course decide to do something completely different if it suits their plans!
“High” and “Low”
The axes are categorized by “high” and “low”, which means there may be some difficult choices. When analyzing market growth, 10% is often used to decide a market is “high” growth. This can seem arbitrary. Imagine two markets, one with 10.1% growth, and another with 9.9% growth. Some judgement may be needed to decide what “high” and “low” mean in BCG market growth.
Market share is somewhat easier to analyze. The market share of all players in the market are compared. If the market share of the company being analyzed is greater than its next biggest rival, it’s deemed “high” (we’ll look at how that works in more detail later in this article).
Four Quadrants of the BCG Matrix
The four quadrants of the BCG Matrix are:

Exhibit high growth and command a high market share. A company should invest more in stars, as they are well-established products or brands in high-growth markets. Stars are leading brands in exciting markets. The Apple Watch in 2022 is a star. It’s selling around a third of smartwatches worldwide and has more than three times the market share of its nearest rival, Huawei. The market is predicted to grow by around 28% every year at this point, making it a very high-growth market. Despite being the market leader Apple will have to hold its position. This means it will have to spend a great deal on marketing, and making sure its product stays competitive. Because of this, as of 2022 the Apple watch probably isn’t the most cash-positive product in Apple’s portfolio. If Apple keep spending and making good choices, the watch market may mature and the Apple watch may become a cash cow. This would be the best outcome according to the BCG matrix.
Exhibit low market growth but command high market share. These are the ideal products to have, according to the BCG matrix. They are leading brands, in slower markets. It may seem counterintuitive that slower market growth would be seen as positive, but cash cows require little investment. The brand is dominant, and the fewer new buyers to the market will naturally gravitate to the brand. The market is less frenetic than before, and the company doesn’t have to spend as much cash winning the hearts and minds of all that growth!
The cash these products generate can be invested elsewhere. This is an important part of BCG, not immediately obvious from the diagram. The portfolio of a company should be a pipeline, with cash-positive products (primarily the cash cow) paying for the development of question marks and stars.
Coca-Cola has been a cash cow product for the Coca-Cola company for a long time. As of 2023, it holds around 46% of the soft drink market sales, far beyond its nearest rival. The market growth is modest, around 3.2% per year at this point. Coca-Cola has created excellent positive cashflows for the company, which they can use for other ventures such as their less mature food business. The part of Coca-Cola that doesn’t fit as well is the marketing spend. You’re probably aware of Coca-Cola adverts. A better BCG fit would have Coca-Cola not feeling the need to spend so much on marketing. Again, the real world means not everything fits nicely into a matrix.
Question Marks
Show high growth but command low market share. Question marks require significant investment to maintain or increase market share, but are excellent prospects for the company.
Question marks are usually recently introduced products with sound commercial prospects. With sufficient investment, they have the potential to become stars. If neglected, they may become dogs. Wise companies will know if they can’t build a question mark into a star. They’ll divest despite the exciting market.
It’s easy to think of examples of successful question marks, just think of any star or cash cow and rewind some years. It’s more interesting to think of a failed question mark. You could argue that Google Glass was a question mark that went wrong. Their wearable smart glasses were introduced around 2013. At that point, their market share of wearable tech was small, as not many wearable glasses were being sold compared to e.g. watches (this does rely on us putting glasses in with the broader “wearables” market, highlighting one issue of BCG: defining the market). But, the market was growing. It was arguably a case of “too early”, which is fairly common in tech. Google found the technology wasn’t quite good enough, and presumably was having to spend colossal amounts of money behind the scenes to develop, market and distribute the glasses. They ended up halting the production of the glasses in 2015.
Have both low growth and low market share. The bad performance may be due to high costs, inferior quality, or a lack of effective marketing.
Unless there is some hope of gaining market share, a company is wise to dispose of these products if they are a drain on cash. Dogs are often, but don’t have to be, cash negative.
Imagine you are the undisputed market leader in producing vinyl records in the 1990s. You probably have a great cash cow, but the years to come will reduce that to a dog. CDs and streaming will make your position obsolete and turn your product into a dog. It may be tempting to divest all dogs, but they may still be cash-generative. Vinyl now commands a premium price, so although they represent a slim minority of music sales it is still probably worth being in the market.
BCG Matrix – Advantages and Lim itations
The BCG matrix is very useful for manufacturing companies since an understanding of a product’s market position is imperative to understanding its growth potential. The BCG matrix can also be used to assess the market share of a product relative to competing products. The matrix offers a useful framework for allocating resources to particular products.
However, the matrix does have certain limitations. First, markets may be less clearly defined than the matrix suggests. Moreover, it doesn’t offer information about what the competition is doing. Second, the market growth rate and relative market share are not the only indicators of profitability. Third, this four-quadrant approach may be overly simplistic considering the dynamic nature of markets and industries/sectors. Finally, a high market share does not always result in strong profits given that high costs may also be involved in maintaining that market share.
BCG Matrix – How to use the BCG Matrix
Using five parameters – the definition of the market, relative market share, market growth rate, cash generation, and usage of cash – a company should allocate its products to the relevant quadrant. Based on this allocation, the company can determine which products to invest in and which to discontinue.
It might be noted that defining the market is the most important step. If a market is incorrectly defined, the product could be incorrectly classified. The relative market share is calculated by dividing the selected product’s market share (or revenue) by the market share or revenue of the largest competitor in the sector. Moreover, it’s also necessary to calculate the market growth rate. This can be estimated by assessing the average revenue growth of the leading companies within the product sector.
BCG Matrix – Advantages and Limitations
The BCG matrix is very useful for companies since an understanding of a product’s market position is useful for understanding its growth potential. The BCG matrix can also be used to assess the market share of a product relative to competing products. The matrix offers a useful framework for allocating resources to particular products and building a healthy pipeline in a product portfolio.
However, the matrix does have certain limitations. First, markets may be less clearly defined than the matrix suggests. We’ve seen in the examples that you could narrowly define the vinyl market, or put it as part of the wider music market.
Market growth rate and relative market share are not the only indicators of profitability. We saw that vinyl still has good cashflows for some companies, and question marks may not always be the best to build if it is a pointless drain on company resources with no future.
Finally, we need to be mindful that categorizing by “high” and “low” may lead to some products that are very similar being given different categories. Our earlier example of a 9.9 and 10.1% market growth is relevant here. Some judgment and discussion would be needed to get the most out of the matrix in this case.
Calculating Relative Market Share
The relative market share is used to compare a company’s brand market share with the market share of its largest competitor in the industry. When we calculate relative market share, the market leader’s market share is used as the benchmark.
Relative Market Share Formula:
Relative Market Share = % market share of the company’s product divided by the market share of the largest competing product.
Below we’ve calculated the hypothetical relative market shares of two products from one company using the market share of the largest competitor in that industry. If you’d like to practice this yourself, please see the download attached to this article. This attachment has more products to practice on beyond what’s in the graphic below.

Brand B appears to be dominant in its market, far beyond the share of its nearest rival, rival 1. It is a star or cash cow, depending on the market growth.
Brand A is lagging. It operates in a different market to brand B, and can’t compete on share with its rival 1. It will be a question mark or dog.
The BCG matrix can be a helpful tool for thinking about a company’s portfolio. It creates clear categories and can create great discussions about the balance of products, their cashflows, and their future. It can also suggest sensible actions to create that balance. However, it should be treated with care. It is arguably too simple, reducing the world to two axes. It’s also important to think carefully about what the market is before starting the analysis.
For credit analysts, BCG can create a clear set of categories and language when putting together presentations on a company’s business risk.
If you’re interested in learning more about the world of business, you may be interested in our Investment Banking course . This course gives you the same training as new hires in the top investment banks and covers a wide range of subjects.
Additional resources
Porters Five Forces
Credit Risk
Financial Modeling Course
Share this article
Bcg matrix workout example.
Sign up to access your free download and get new article notifications, exclusive offers and more.
Recommended Course
BCG Matrix (2024): Meaning and Example [+ Template]
Home » BCG Matrix | 🕑
Gust de Backer
November 3, 2023, 10 reacties.
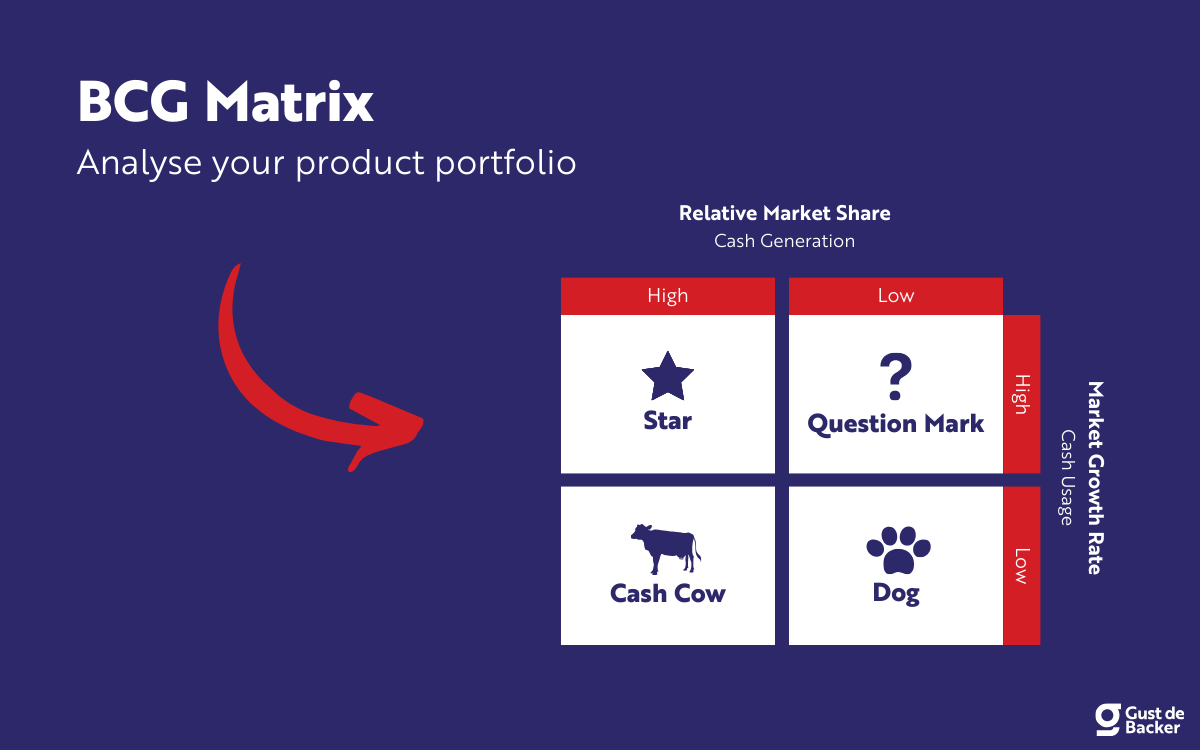
The BCG Matrix also known as the Boston Consulting Group Growth-Share Matrix is a strategic marketing model for assessing product lines for relative market growth and sales volume.
Do you have several products or services that you want to know what their performance is relative to each other and what’s left in terms of market?
Instead of guessing which products to focus on, you can map them out in an orderly fashion and decide which product lines are better stopped and which are worth investing in.
I’m going to show you:
- What the BCG Matrix is
- How to fill in the BCG Matrix
- What you ultimately do with the results of the BCG Matrix
Let’s get started
Table of Contents
What is the BCG Matrix?
The BCG Matrix is a strategic marketing model invented by the Boston Consulting Group .
Companies use the BCG Matrix (portfolio analysis) to compare different products or services against each other to determine whether companies should:
- Continue producing
- Stop producing
- Or invest in it
The BCG Matrix helps companies allocate resources in a way that maximizes the following:
- Market share and market growth
- Company growth
- Long-term profitability for each product line
By understanding where products fall in the BCG Matrix, companies can more effectively determine how to allocate resources.
Four quadrants of the BCG Matrix
The BCG Matrix has four quadrants into which products can fall:

In this, it is notable that you often see that products have a certain Product Lifecycle :

1. Question Marks – Construction
Low market share and high market growth.
The “Question Marks” are a product group in which there is a low market share, but where the market is actually showing high growth.
These products are not necessarily very profitable at this time, but have potential to gain market share with the right investments .
It is therefore possible to build a ‘Question Mark’ into a ‘Star’.
If you introduce a new smartwatch to the market, it will be difficult to gain ground, despite the fact that the market is growing rapidly.
This is because large companies already have strong differentiation combined with large market budgets.
2. Stars – Holding
High market share and high market growth.
The ‘Stars’ are a product group with a high market share and a fast growing market.
These products are profitable and it is worthwhile to continue investing in this product group so that they at least maintain their market share and perhaps even continue to grow.
The Apple Smartwatch is an example of a product where Apple has a high market share and the smartwatch market is experiencing strong growth.
3. Cash Cows – Harvesting
High market share and low market growth.
The ‘Cash Cows’ are a product group with a high market share and a market with hardly any growth.
These products are already profitable with little growth potential in the market. The desired strategy here is to invest as little as possible and still maintain the market position.
The revenue generated from a Cash Cow can be invested in Stars or Question Marks.
Rocket ice creams are an example of OLA, a market with relatively low growth where OLA has a large market share.
The money OLA earns from its rocket ice creams they can invest in, for example, alcoholic ice creams in which there is still a lot of market potential.
4. Dogs – Divestment
Low market share and low market growth.
The Dogs are a product group with a low market share and a market that will hardly grow.
These products are loss-making and have no potential to become profitable.
You want to stop investing in a ‘Dog’, because there is nothing more to be gained from it.
Suppose that a new pharmaceutical company starts developing a corona vaccine in 2023, they will find themselves in a market in which they have virtually no market share and there is no market growth to gain that share.
Points of criticism of the BCG Matrix
Besides being a good model for mapping the (potential) performance of your various product lines, the BCG Matrix also has some criticisms:
- Market share does not guarantee profitability.
- Market growth can be influenced by the company (by boosting).
- The matrix leaves out competition.
- Some products are very interdependent in practice.
- Declining / collapsing markets are not taken into account.
- Both axes are assigned the same prioritization, in practice this need not be so and depends on the business strategy.
The model is easy to use, but needs context to ultimately base decisions on it.
BCG Matrix example
Download the BCG Matrix here:

Good choice! Check your e-mail for the resources...
How do you complete the BCG Matrix?
Start by identifying your own products or services. Which products do you want to include in the portfolio analysis?
To determine your own market share and the market share of your biggest competitor you will need to know how big the total market is.
Based on the size of the total market, calculate your own market share.
Based on the total size of the market, calculate the market share of your competitor so that the relative market share can be calculated.
Determine how much the market is going to grow in the coming period.
To fill in the size of the circles you need to indicate how much sales you do per product category.
Taking Apple as an example…
If we enter that into the BCG Matrix we get the following visualization:

Getting started…
If all goes well, you are now armed with enough knowledge to formulate your portfolio strategy….
Now I want to know from you, what do you think is the most effective method of measuring product performance?
Let me know in a comment.
P.S. should you want additional help please let me know at [email protected]
Frequently Asked Questions
The BCG Matrix, also known as the Boston Consulting Group Growth-Share Matrix, is a model that helps organizations analyze their product portfolios and make resource allocation decisions. The matrix plots strategic business units (SBUs) on a graph to help organizations assess their competitive position in the marketplace and identify potential opportunities.
A BCG portfolio analysis is a way to measure how well a company is performing by looking at its various activities and products. It can help a company decide where to invest its money and which products to stop with.
Market growth is calculated by determining the percentage increase in sales from one year to the next. This figure is then multiplied by the total value of sales from the previous year to determine the market value.
A cash cow is a product or service that generates a large amount of stable, ongoing revenue. A cash cow is usually not the most innovative product or service, but it is reliable and profitable.
The BCG matrix is a strategic marketing model used to help a company decide where to allocate its resources. The matrix is divided into four quadrants: -Stars: high market share and high growth -Questrels: high market share but low growth -Cash Cows: low market share but high growth -Dogs: low market share and low growth. An example of how the BCG matrix can be used would be two companies competing in the same industry. Company A has a large market share but is not growing as fast as Company B. Company B has a small market share but is growing fast. In this case, Company A is considered a cash cow and Company B is considered a star.
I try to help business surpass their growth ceiling with my content.
Sounds interesting?
Let’s connect on LinkedIn!
BCG Matrix | Business Strategy | Customer Development Process | Market Research | Marketing and Sales | Marketing Strategy | Product-market Fit | Value Proposition Canvas
Gust’s Must-Reads 👇🏼
- TAM SAM SOM
- Value Proposition
- Brainstorming
- Decision Making Unit
- Product-Market Fit
- North Star Metric
- Market Research
- Customer Development
- Growth Hacking
- Brand Identity
- Customer Journey
- Account-Based Marketing
![bcg matrix assignment OGSM Model (2024): How-to & Examples [+ Template]](https://gustdebacker.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/OGSM-Model.png)
OGSM Model (2024): How-to & Examples [+ Template]
OGSM Model: a solution that helps with strategic planning and goal setting. You know where you want to go, but you don't have a clear picture of how you're going to get there. Ideas and goals are often not realized because there is no clear planning associated with...
Rapid Experimentation: The Road To Innovation (Complete Guide)
You read it left and right, companies that owe much of their success to experimentation.... Of course, experimentation can be understood in a hugely broad way, so in this article I'm going to get you started with: Understanding why experimentation is important...
![bcg matrix assignment Cognitive Biases (2024): Complete List of 151 Biases [Psychology]](https://gustdebacker.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/151-Cognitive-Biases.png)
Cognitive Biases (2024): Complete List of 151 Biases [Psychology]
Cognitive biases, there are so many of them... Decisions we make based on emotion, cognitive biases are irrational 'errors' that are programmed into people's brains and affect the decision-making process. Plenty of different articles have been written and an entire...
10 Comments
This is very good explanation. May Allah increase your knowledge.
Thank you, Kiran!
the example given by your explanation is wrong as you have mentioned as the company A would become the question or questol and the Company B shall become the cash cow
Thank you for the comment! I have adjusted it.
Cash Cows are units with high market share and low market growth, not the other way round.
Thanks for the comment Babatola! Where do you see this mistake?
I really find this helpful
Thank you, Alinafe!
Thank for helping me ,I have really understood the matrix
Thank you, Deborah!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
You have Successfully Subscribed!

Text for Mobile
What is the BCG Matrix? Definition, Example, Template and Guide

How to Use the BCG Matrix Model for Your Organization or Business?
The ‘Boston Consulting group’s ‘abbreviation is the BCG matrix. This BCG matrix is designed to help long-term strategic planning for the benefit of the business and its growth opportunities by means of a review of its product portfolio to decide on the most suitable investment to obtain maximum Return on Investment. This also determines about discontinuing as well as developing products. It is also named the Growth Share Matrix.

How Do You Prepare a BCG Matrix?
BCG matrix is prepared by executing the following steps:
Step 1: Selection of the Product:
BCG matrix is utilised for this purpose by:
- Analysis of Business Units,
- Separation of brands, products or considering an organisation as a unit
Step 2: By defining and market study
Step 3: By comparison and by calculation of the relative market share
Step 4: a study of the market growth rate.
Step 5: Draw the circles on a matrix.
What Are the Four Categories of BCG MATRIX?
It is primarily based on planning in a portfolio-dependent study and observation. So, a company’s business units can be classified into four categories:
- Question Marks
It is necessary to conceptualise better the above four processes related to the BCG matrix by making one for L’Oréal in the following sections.
How Do You Find a BCG MATRIX?
By following the steps indicated below, you can find a BCG matrix.
Step 1: Induction of BCG Matrix.
Step 2: Reach the Ribbon > Insert > Other Charts and click Bubble Chart.
Step 3: Change X-axis values.
Step 4: Click Edit to change the source of data.
Step 5: Change series X values.
Step 6: Selection of Relative Market Share values.
Step 7: Your BCG Matrix chart is a bit changed.

How to Find Market Growth Rate?
The growth rate of industries can be easily estimated using free online resources. Alternatively, it can be calculated by counting the reputed companies’ average growth rate of revenue. Usually, the Market growth rate is represented in percentage terms.
The market growth rate is usually estimated by the formula stated below:
(Product’s sales in the current year – Product’s sales of the previous year)/Product sales last year
High growth-rated markets are the ones where the total market share gained is expanding; this results in many advantages for all companies in gaining monetary profit.

Step 5: Drawing the Circles over a Matrix
After the above calculation, it needs only to plot the brands on the matrix. The x-axis represents or shows the relative market share, and the y-axis indicates the company’s growth rate. A similar circle can be plotted for each unit, brand, and Product, and the size of which must correspond ideally to the company’s revenue.
What do the Question Marks Signify In the BCG Matrix?
The feature of question marks represents a business to have high growth prospects but a low share in the market. They consume a significant amount of cash but with little return. Ultimately, ‘question marks ‘lose money. However, as these business units increase, they have the potentiality to upgrade into stars by entering a higher growth-oriented market.
How to Use a BCG Matrix?
After defining four categories of the BCG market, we can review the strategies of the company by using each category as discussed below:

Stars: The location of the products in this quadrant is highly attractive as they are located in a robust category, and these products are highly competitive. A huge potential has been found in this category for high revenue growth. This is due to its high market share and high growth rate. It is expensive to develop but is worth investment for promotion to the long extent of its Product Life Cycle. In the event of its success, a star may be a cash cow in the event of maturity, assuming they keep the same market share unchanged.
Strategic Choices, As Indicated Below:
- Vertical Integration,
- Horizontal Integration,
- Market Penetration,
- Market Development, And
- Product Development

Question Marks: Most businesses start as question marks. Huge investments are necessary to achieve or protect market share. The question mark sector has the potential to become stars category and ultimately c ash cows but can also become dogs or exits. It requires high Investments for question marks; otherwise, this categor y may result in negative cash flow.
Like stars, the category of Question also does not always succeed; if, after a large investment, they cannot fetch profit and gain market share, they become the dog category. Therefore, careful observation and review are necessary before investing in this category.
Strategic Choices Are The Follows:
- Market Development,
- Product Development,
- Process of Investment.

Cash Cows: In this category, cash generates profits by investing as little cash as possible. It needs low-cost support and needs to be managed for continued profits & cash flow. Large corporate or SBUs are considered efficient and innovative and should have the potential to become stars. It requires maintaining a healthy market status and should defend the market share of the business house or investors. The company should take advantage of sales volume and leverage the size of its operations. It can support other businesses too.
Strategic Choices: Product Development, Diversification

Dogs: Low market share makes it a face of cost disadvantages, so they need enough cash to reach break-even, but they are rarely, if ever, worth investing. This Dog sector should be liquidated if there are fewer prospects for gaining market share. This is at a declining stage of the Product Life Cycle, requiring a minimum number of dogs in the company.
Advantages of BCG Matrix
- It is simple and easily understood.
- It can quickly and merely show the opportunities open to you,
- This can identify how corporate cash resources can be invested suitably to maximize a company’s growth and profitability.
- BCG Matrix can prepare a framework for allocating resources among different products
Limitations of BCG Matrix
This type of matrix has two-dimensional applications as given below:
- Relative market share and
- Market growth rate
Limitations are indicated below:
- BCG matrix is not the only indicator of the profitability of a business, attractiveness or success.
- It does not care for the effects of synergy from brand to brand.
- A company which has a minimum market share can become profitable as well.
- It has been observed that a High market share does not always produce high profits since there is also a high cost in obtaining a high market share.
- It has been observed that dogs may benefit the business or other products in achieving and gaining a competitive advantage.
- It does not care for small competitors with a fast-growing market share component.

Get Instant Help with your BCG Matrix Assignment
If you are a marketing student and given assignment writing tasks , say on (BCG) Boston matrix, then you can seek Boston matrix assignment help from the Assignment provider of Casestudyhelp.com.
Casestudyhelp.com provides 24×7 live support and online chat, as well as solves direct inquiries of the students of Business Law, Contractual Law and BCG Matrix Business case studies which help them in their BCG Matrix Assignment Help .
Why Choose Us?
We hope this writing by our Casestudyhelp.com will help students write on the BCG market and related studies. We can improve your writing skill. Our quality of work benefits us in maintaining a crowd of loyal customers. They provide us with excellent client perception.
- Our Product is 100 % Original–and is free of plagiarism. We use Free ‘Turnitin’ software for checking.
- We provide free Rework –we give all Rework and modifications free.
- 24/7 Customer Assistance–we provide round-the-clock customer assistance by our experts free of cost.
If you require any writing assignment help, please get in touch with us early.
Understanding the significance of the BCG matrix in business studies

- Uncategorized
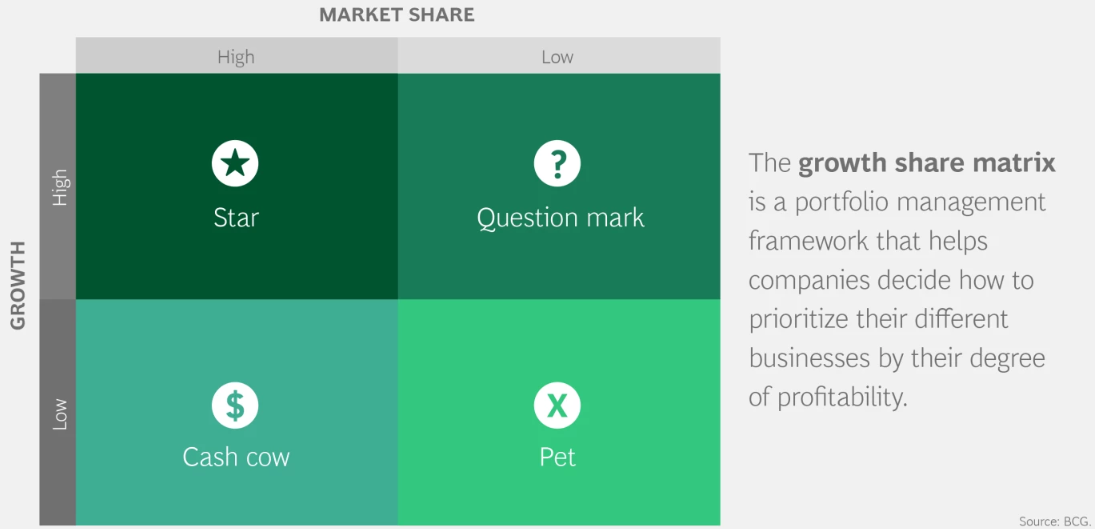
The Boston Consulting Group in 1968 developed the BCG matrix to understand the growth-share matrix. The BCG matrix is an extremely successful tool for explaining an organization’s growth share. Allan Zakon, BCG’s CEO, and his colleagues designed the growth-share matrix. The founder of BCG addressed the effectiveness of the matrix and its usefulness, Bruce Henderson, in an essay in 1970, which led to its popularity.
Nearly all big organizations across different industries use the BCG matrix, and it is found that nearly all top 500 companies listed on the Fortune implement this matrix for business portfolio and resource management.
Do you know what makes the BCG matrix so effective? How to interpret it, and what are its characteristics? The blog will answer all your queries with detailed explanations and organizational examples.
Explaining BCG matrix
By definition, the BCG matrix is a high-powered framework for business portfolio management. Businesses can utilize the matrix to determine what is working and what is going against them. The things going against them can be reprioritized by making better decisions through investments and subsidiaries. One can gain crucial information by applying the BCG matrix about an investment, product/service, performance in the market, competitive position, etc. Basis the information, individuals can make better resource allocation, ROI, and strategies. The image below is a representation of the BCG matrix.
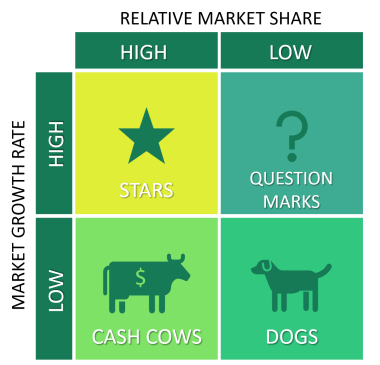
It can be seen that the matrix is split into four quadrants and has two referential axes. Market share is represented on the horizontal axis, and growth is indicated on the vertical axis.
- Cash cows indicate businesses with low growth and high market share. It is suggested by the Boston Consulting Group that businesses must milk these cash cows for money.
- Stars indicate business portfolios with high growth and high market share. According to the Group, these have immense prospects and are the business’s flagships.
- Question marks indicate subsidiaries with high growth rates and low market share. Their performance is not guaranteed, and the low market share and high competition can damage their growth. It is up to the business management to invest further or leave the question marks.
- Dogs indicate businesses with low market share and low growth. Such businesses deplete resources with no added returns. As per the BCG matrix, the businesses must divest, reposition, or liquidate such investments.
Elements of BCG matrix
We have already provided an overview of the quadrants of the BCG matrix; now, let us explain in detail each of them. Each has unique features, which will be discussed in this section.
Question marks: Products or services growing fast in the market are represented as question marks. But they are neither market leaders nor possess a large share. Application of correct strategies can help get over the competitors and hold a large share of the market. To do that, the business must invest greatly in its resources. Question marks are identical to wild cards; the business may determine whether to exploit or reject the high growth. In case the business chooses to invest, it must aim to take advantage of the high growth and seize major market share. Apple’s Apple TV and Google’s Drive and Workspace are good examples of this quadrant.
Pets: Products neither growing nor above the competition fall into the pet quadrant. They do not bring about much money, and if not looked after, can finish off resources without giving much return. They can lead to losses, so they must be given up quickly. Reduced market share and growth indicate lower profits, which reflects poor quality, high prices, and poor marketing.
Stars: Flagship products with large market share and continuous growth fall into the star quadrant. If the high market share is not maintained, it can become cash cows once the growth slows. Advancing through the competition in all aspects is vital and requires huge investments. Due to the high demand and rising popularity, the flagship product manufacturers have become market leaders. Maximum profits can be generated in this position, but it also requires heavy investments. To remain ahead of the competition, stars need strong support and resources.
Cash cows: Products with a large market share but a saturated market fall into the cash cows quadrant. The products have gone past the competition and delivered huge cash flows. Having a slow market, cash cows handle the most of it and create strong returns. They produce money in bulk as they become the kings of the market. Having a stable market, no major investments are required in this position. Cash flows are strong as profit margins are high. But, innovation is vital to continue huge market share.
Remember that the BCG matrix can only prescribe, not foretell. It informs businesses of the decisions to be taken, where to invest, divest, etc. However, it does not inform them about what might occur. The matrix is inconsiderate towards any swift market changes or major disruptions.
Interpretation of the BCG matrix
The concept and logic behind the matrix are clear: businesses that are market leaders have more returns. They enjoy huge market share and have a competitive advantage over their rivals, leading to high growth potential. The two key indicators of competitiveness and market attractiveness are relative market share and the growth rate.
Competitiveness: Business competitiveness is the capability of a business to produce more profits compared to its arch-rivals in the market.
Market attractiveness: It is the extent to which a market provides chances for a business to generate profit and maintain itself. The factor is considered contingent on total market share, competition, and growth rate.
Businesses or products that hold huge market share before slowing growth turn into cash cows. To achieve this, it must give higher quality-to-cost rations than its competitors. It can change into a cash cow if it can hold a bigger market share before slowing down.
Practically, growth in any sector will certainly slow down if the market saturates. Companies should set their sights on turning their questions and stars into cash cows. Cash cows’ money can change the question marks into stars and, thus, newer cash cows.
Steps to make a BCG matrix
To produce an accurate BCG matrix to ascertain the growth and share in the market, a company needs to conduct careful market research and analyze its products, services, subsidiaries, etc. What is the performance of the product? How is it positioned in the competition? How does the consumer perceive it?
By getting answers to all such questions, the company can begin the work on using the matrix in the following steps.
- Select a product: Select the product or service to be examined.
- Comprehend the market minutely: The biggest competitors, the factors impacting the growth, market size, trends, nature of consumers, economics, market features, etc., all these market features are crucial. Deep market analysis is extremely crucial to work out the BCG matrix. If the markets are incorrectly defined, it may lead to incorrect results.
- Discover the relative market share: A company needs to conduct a market analysis if it wants to know a product’s share compared to rivals. Market share relative to the biggest competitor can be represented through a formula.

- Compute the market growth rate: The equation below can determine a company’s growth rate.

- Utilize data to put the product/service in the matrix: Many free online BCG matrix templates can be used to classify and place the products. A few of them can be found at TotalAssignment.com.
Applying the BCG matrix in the real world
BCG matrix is handy for a company that wants to take stock and reorganize its business structure. Thorough market research and evaluation of each item discloses the position of each related to others and rivals. The matrix helps to divide, prioritize, and make the best decisions. Look at the BCG matrix application by company giants Apple, Coca-Cola, Google, and Pepsi.
- When innovation and diversification are the focus, companies enhance investments in question marks and stars. It can grow the market share, assist new opportunities, and defeat competitors.
- At the time of a cash crisis, cash cows can provide rescue. Less effort is required to maintain the cash cows, but arrogance is a huge no-no. Any disruption and instant changes in the trend can emerge at any period.
Companies minimize investments in products that have been performing well for many years and have become market leaders. Examples of such companies are the primary soft drinks of Coca-Cola and the iPhone of Apple.
- Divesting money from pets and utilizing it at different places is a perfect strategy during a cash crisis.
- A company focuses on question marks if it is confident about a product and its opportunities. Putting money into such products leads to new tactics and strategies, more resources and development and marketing expenses, direct costs, heavy resource usage, etc.
- Concentrating on stars can increase cash flow and seize huge market share. However, increased investments and innovations are required to defeat competitors.
- BCG matrix recommends a better method to invest and divert. It can aid businesses in saving time, resources, and money. In these competitive and unstable times, the tool can be used differently for different businesses.
The dynamic nature of the markets and ever-changing consumer preferences make companies apply the BCG matrix. A company must conduct deep market research and revise its BCG matrices regularly.
Advantages and disadvantages of the matrix
Advantages:
- Simple and instinctive
- Permits swift screening of the ideal investment opportunities
- Assists in comprehending the largest and smallest sources of cash flow
- Determines comparative portfolio analysis
- A system of effective resource allocation
Disadvantages:
- Costs are not accounted
- Categories only based on market growth rate and relative market share
- Do not think about disruptions and market changes
- Incapable of telling about success or profitability
- Disregard relations and brand synergy
- Only considers fast-growing competitors and leaves the smaller one
Considering tech giants Apple and Google to determine their growth with the aid of the BCG matrix
In this blog section, we have considered two tech giants, Apple and Google, to understand their usage of the BCG matrix.
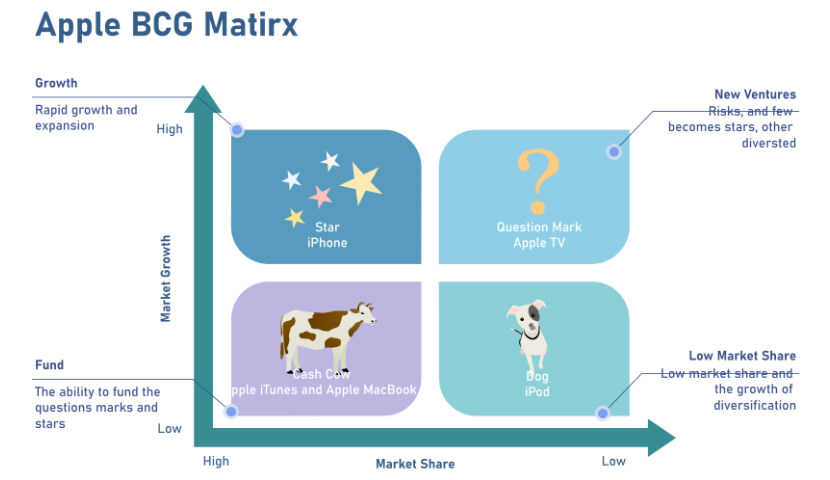
Star: The flagship of Apple is its iPhone, a rising star. The demand for the product is high among the elite and the rich, and there is no competition for the iPhone in this category. However, the luxury phone category is quite specific, and Samsung regularly develops its products to compete with Apple.
Cash cows: The successor of the Apple Computer, the Apple MacBook is widely recognized and has great sales. In the laptop market, it is considered a leader.
Question marks: There are major competitors in the digital appliances field, including the television. The Apple TV is not recognized as a market leader; it has fewer buyers, and Google Chromecast and Amazon’s Fire Stick are quite competitive in this area.
Pets: In the fiscal year 2022, the iPad, once a popular device, ranked lower compared to 2021. The tablet industry has steadily declined even before the advent of coronavirus in 2020.
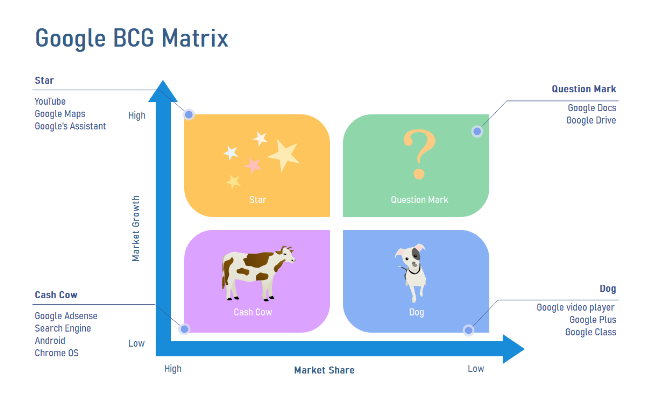
Cash cows: Android OS, Google Search, Google Advertising, and Google Chrome control their specific markets. Most of the market share has been consumed by these products of Google, which has driven them to a saturation point. If the products fail, Google Search will keep it as one of the top tech companies.
Stars: YouTube was so far a cash cow and a leader in the online streaming market; however, the advent of Netflix, Disney+, Amazon Prime, etc., increased competition and opportunities for such services. Though the competition has increased, YouTube remains the leader in this industry. Google Assistant is trying to compete with Amazon’s Alexa, Microsoft’s Cortana, and Apple’s Siri.
Question marks: In the digital workspace, Google Drive and Workspace enjoy the growing market’s benefits. However, Slack, Zoom, Dropbox, and Microsoft 365 hold a major market share.
Pets: Google introduced certain new products that did not take off, like Google Plus, Google Video Player, and Google Glass. To give competition to Facebook, Google + was developed, but it led to many questioning the strategies of the tech company.
Wrapping up
We hope that the blog was informative and interesting at the same time for our users who are quite new to the framework of the BCG matrix. You can check our sample BCG matrix for other big companies, such as Coca-Cola, Starbucks, Hyundai, General Motors, etc., on our website. The samples can be read and used for free, and in case you are looking for additional help, you can contact our subject matter experts.
Frequently asked questions
What does the BCG matrix represent?
BCG matrix represents business planning and prescriptive portfolio management techniques.
How does the BCG matrix help startups?
The matrix can help the investors of the startups to ascertain the areas for investment and disinvestment.
What is the market growth rate in the BCG matrix?
The market growth rate showcases the percentage of market growth in a particular period.
Total Assignment Help
Incase, you are looking for an opportunity to work from home and earn big money. TotalAssignmenthelp Affiliate program is the best choice for you.
Do visit : https://www.totalassignment.com/affiliate-program for more details
Total Assignment help is an assignment help Online service available in 9 countries. Our local operations span across Australia, US, UK, South east Asia and the Middle East. With extensive experience in academic writing, Total assignment help has a strong track record delivering quality writing at a nominal price that meet the unique needs of students in our local markets.
We have specialized network of highly trained writers, who can provide best possible assignment help solution for all your needs. Next time you are looking for assignment help, make sure to give us a try.
Related posts
Understanding the difference between basic vs applied research with the aid of examples.

Examining How To Write The Perfect Hook For Your Assignment

Get Expert Advice On How To Develop Yourself As A Human Resource Practitioner
Comments are closed.
- Study Guides
- Homework Questions
- Information Systems

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The BCG Matrix is one of the most popular portfolio analysis methods. It classifies a firm's product and/or services into a two-by-two matrix. Each quadrant is classified as low or high performance, depending on the relative market share and market growth rate. Learn more about strategy in CFI's Business Strategy Course.
Here are the example list: 01 BCG Matrix of Coca-Cola. 02 BCG Matrix of Samsung. 03 BCG Matrix of L'Oréal. 04 BCG Matrix of PepsiCo. 05 BCG Matrix of Apple. 06 BCG Matrix of Nestle. 07 BCG Matrix of Unilever. 08 BCG Matrix of McDonalds.
BCG Matrix Video Tutorial. Relative Market Share. The creator of the BCG Matrix used this variable to actually measure a company's competitiveness.The exact measure for Relative Market Share is the focal company's share relative to its largest competitor. So if Samsung has a 20 percent market share in the mobile phone industry and Apple (its largest competitor) has 60 percent so to speak ...
Step 5: Draw the Circles on a Matrix. Once you have determined each product or business unit's market share and growth rate, the next step is to draw the circles on a matrix. The BCG matrix is a simple two-by-two grid with a market share on the x-axis and a growth rate on the y-axis.
BCG Growth Share Matrix: The Boston Consulting Group (BGC) growth share matrix is a planning tool that uses graphical representations of a company's products and services in an effort to help ...
The BCG Matrix is a growth-share matrix developed by the Boston Consulting Group in 1968. The BCG matrix is an exceptionally effective tool for interpreting a company's growth share. The design of the growth-share matrix was a collaborative effort by Alan Zakon, BCG's first CEO and his colleagues. The popularity of the BCG growth matrix ...
For a company with a big portfolio, it's important to assess its product lines regularly to see which product is profitable, which is making losses, and wh...
4 Components of the BCG Matrix. On a BCG matrix graph, the vertical axis considers the growth rate from low to high, whereas the horizontal axis considers the relative market share from high to low. The axes help divide the matrix into four different quadrants: Dogs, Question Marks, Cash Cows, and Stars. Let's discuss each quadrant one by one.
The Growth Share Matrix, also known as the BCG Matrix, is a portfolio management framework developed by the Boston Consulting Group's founder in 1968. It divides a company's business units into categories based on their respective market shares and market sizes. To help you roughly estimate the profitability of a business, the matrix uses ...
The Boston Consulting group's product portfolio matrix (BCG matrix) is designed to help with long-term strategic planning, to help a business consider growth opportunities by reviewing its portfolio of products to decide where to invest, to discontinue, or develop products. It's also known as the Growth/Share Matrix.
BCG stands for Boston Consulting Group; also called 'Growth/Share Matrix/ BCG Matrix'; developed by Boston Consulting Group, a world-renowned management consulting firm located in the USA. It is a useful tool for analyzing a diversified company's business portfolio. In the BCG matrix, SBU (Strategic Business Unit) is a unit of the company ...
BCG matrix (also called Growth-Share Matrix) is a portfolio planning model used to analyse the products in the business's portfolio according to their growth and relative market share. The model is based on the observation that a company's business units can be classified into four categories: Cash Cows. Stars. Question Marks.
BCG matrix is a strategic decision-making framework that helps in resource allocation among different strategic business units (SBUs) by categorizing them based on their ability to generate cash inflows against cash outflows. The matrix classifies business portfolio into four categories based on industry attractiveness (growth rate of that ...
The BCG matrix can be useful to companies if applied using the following general steps. Step 1 - Choose the Unit. Strategic Business Units, individual brands, product lines or the firm as a whole are all areas that can be analyzed using the BCG matrix. The chosen unit drives the entire analysis and key definitions.
The BCG matrix, also known as a growth/share matrix, is a business tool that you can use to help you create strategic, long-term plans regarding investment in competitiveness and market attractiveness. It is a framework for portfolio management that allows you to prioritize different products. You can write a BCG matrix as a table that is ...
15 BCG Matrix Examples. BCG Matrix for Coca-Cola. 1) Stars: Kinley and Dasani. Bottled water brands Kinley and Dasani are Stars because they dominate the market in Europe and the US and show no signs of slowing down. 2) Question marks: Diet Coke, Minute Maid, Honest Tea, Sparkling water.
The BCG matrix is divided into four quadrants and is based on two parameters, relative market share and market growth rate. The BCG Matrix includes four categories: stars, cash cows, question marks, and dogs. To calculate the relative market share of a product, divide its market share by the market share of the product's largest competitor.
The BCG matrix is a strategic marketing model used to help a company decide where to allocate its resources. The matrix is divided into four quadrants: -Stars: high market share and high growth. -Questrels: high market share but low growth. -Cash Cows: low market share but high growth. -Dogs: low market share and low growth.
The 'Boston Consulting group's 'abbreviation is the BCG matrix. This BCG matrix is designed to help long-term strategic planning for the benefit of the business and its growth opportunities by means of a review of its product portfolio to decide on the most ... Get Instant Help with your BCG Matrix Assignment. If you are a marketing student and ...
The Best Assignment Help Service Blog helps you build your insight on assignment quality parameters, thus helping you select the best assignment writing service. ... The Boston Consulting Group in 1968 developed the BCG matrix to understand the growth-share matrix. The BCG matrix is an extremely successful tool for explaining an organization ...
BCG Matrix Assignment 1 - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
1). What is BCG Matrix an Which area does it help to analyze in the business environment? The BCG Matrix is a tool used by companies to analyze their business units or products based on two factors: market growth rate and market share relative to the largest competitor. It is divided into four quadrants: Stars, Cash Cows, Dogs, and Question Marks.
BCG Matrix - Assignment. Marketing. Course. Marketing Management (BA(BBA)-401) 14 Documents. Students shared 14 documents in this course. University University of Karachi. Academic year: 2023/2024. Uploaded by: Anonymous Student. This document has been uploaded by a student, just like you, who decided to remain anonymous.
Illustrate how IBM company uses BCG matrix in business decisions As of my last update in September 2021, I can illustrate how IBM, a global technology company, may use the BCG matrix in business decisions. The BCG (Boston Consulting Group) matrix is a strategic tool that helps companies analyze their product portfolio and make informed decisions about resource allocation and growth strategies.