Home / Guides / Writing Guides / Parts of a Paper / How to Write an Essay Cover Page

How to Write an Essay Cover Page
What you include in your cover page depends slightly on which citation style you are using, but the rules are generally the same.
Guide Overview
- APA cover pages
- MLA cover pages
For APA cover pages:
Include the title of the paper, running head, the author’s name, institutional affiliation, and an author’s note.
Here is an example of a cover page in APA:
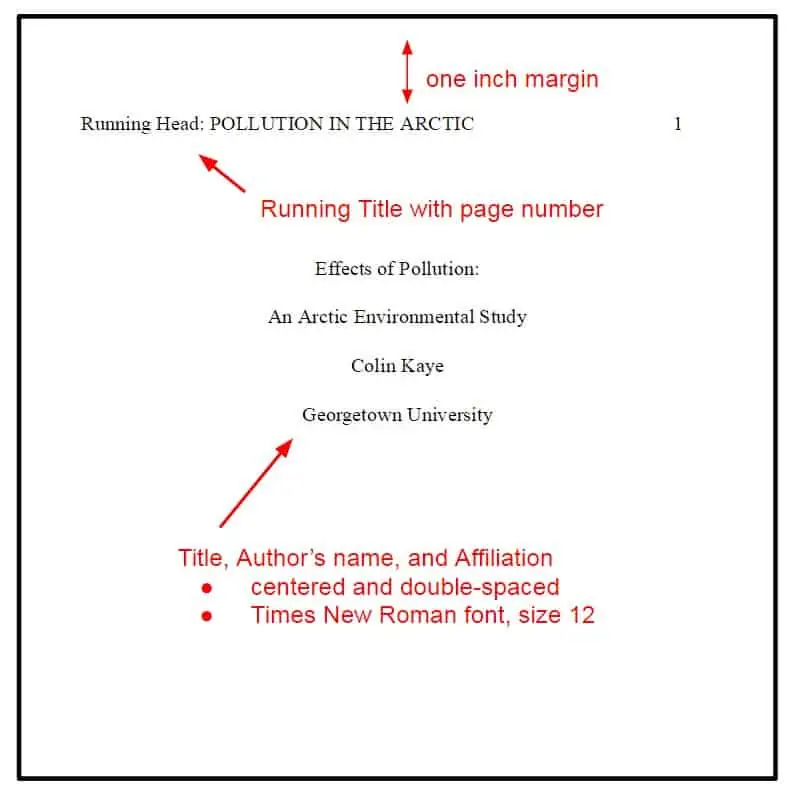
For MLA cover pages:
Cover pages are not as frequently used in MLA format, as the inclusion of headers is preferred.
A header looks like this:

Cover pages can include the name of your school, your paper title, your name, your course name, your teacher or professor’s name, and the due date of the paper. If you are unsure of what to include, check with your instructor.
Here is an example of a cover page in MLA format:

For more help making cover or title pages, visit our title page generator here.
EasyBib Writing Resources
Writing a paper.
- Academic Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- College Admissions Essay
- Expository Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Research Paper
- Thesis Statement
- Writing a Conclusion
- Writing an Introduction
- Writing an Outline
- Writing a Summary
EasyBib Plus Features
- Citation Generator
- Essay Checker
- Expert Check Proofreader
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tools
Plagiarism Checker
- Spell Checker
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Grammar and Plagiarism Checkers
Grammar Basics
Plagiarism Basics
Writing Basics
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
APA Title Page (Cover Page) Format, Example, & Templates
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
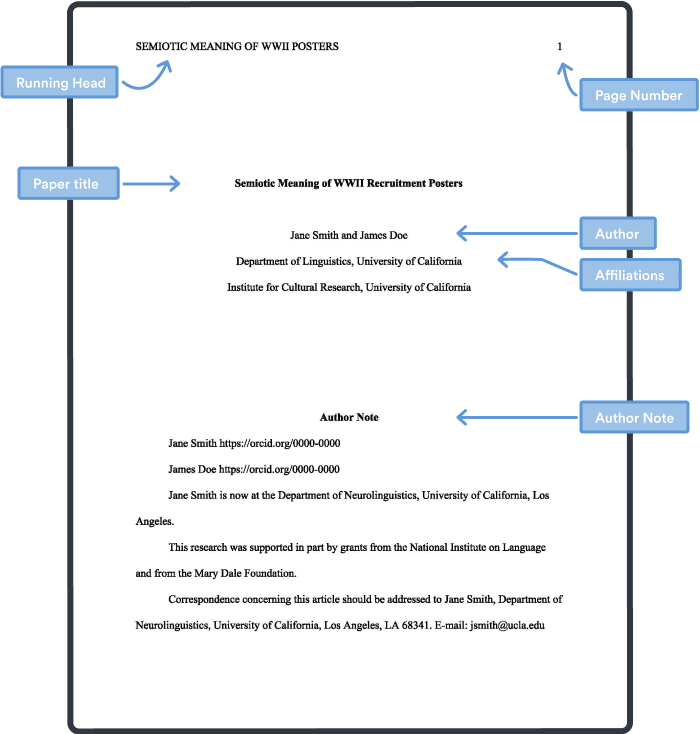
In APA Style (7th edition), the cover page, or title page, should include:
- A running head (professional papers only) and page number
- The title of the paper
- The name of the author(s)
- The institutional affiliation
- An author note; optional (professional papers only)
- A student paper should also include course information
Note : APA 7 provides slightly different directions for formatting the title pages of professional papers (e.g., those intended for scholarly publication) and student papers (e.g., those turned in for credit in a high school or college course).
Professional paper APA title page
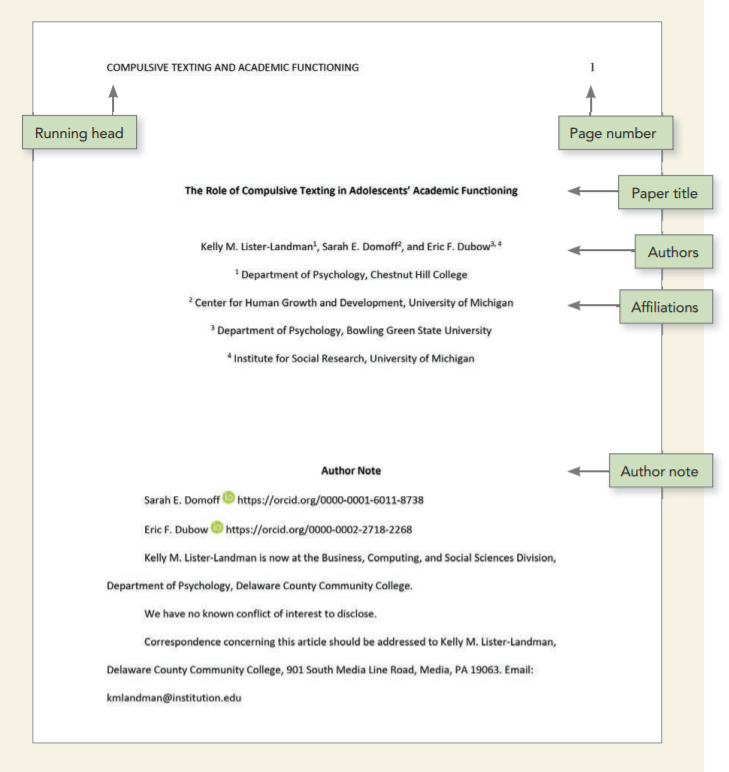
Student paper APA title page
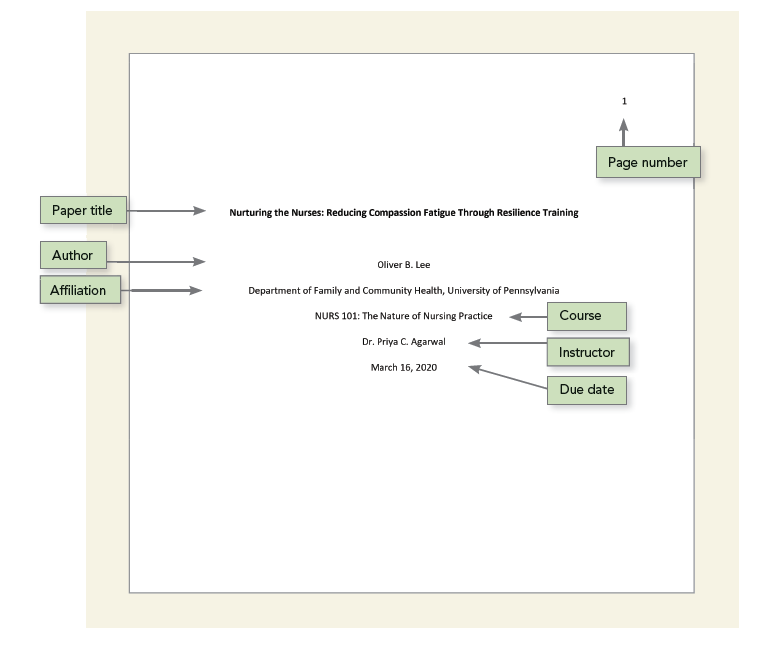
Formatting an APA title page
Note : All text on the title page should be double-spaced and typed in either 12-point, Times New Roman font. In the 7th edition, APA increaded the flexibility regarding font options: which now include Calibri 11, Arial 11, Lucida Sans Unicode 10, Times New Roman 12, or Georgia 11. All words should be centered, and capitalize the first letter of important words.
Running Head
In the 7th edition of the APA style manual, running heads are only required for professional papers that are being submitted for publication (student papers do not require a running head, but still need a page number).
Your title page should contain a running head that is flush left at the top of the page and a page number that is flush right at the top of the page.
Place the running head in the page’s header:
- The running head is the abbreviated title of the paper (IN UPPERCASE LETTERS) aligned left on the page header of all pages, including the title page. APA (7th edition) guidelines require that running heads be a maximum of 50 characters (spaces count as characters).
- The “Running head:” label used in the APA sixth edition is no longer used.
- Place the page number in this same header, but align right, beginning with page number 1 on the title page.
- This header should be 1 inch from the top. Some instructors allow for 1/2 inch, too, but the default is 1 inch.
Paper Title
Position the title of the paper in the upper half of the page. The title should be centered and written in boldface, and important words should be capitalized.
The APA recommends that your title should be a maximum of 12 words and should not contain abbreviations or words that serve no purpose.
Author Name(s)
Institutional affiliation.
Position the school or university’s name below the author(s) name, centered.
A student paper should also include the course number and name, instructor name, and assignment due date.
Further Information
- APA Student Title Page Guide
- APA Referencing
- How to Write a Lab Report
- Essay Writing Guide for Psychology Students
- APA Style Citations & References
- Example of an APA Formatted Paper
BibGuru Blog
Be more productive in school
- Citation Styles
APA cover (title) page: format and templates

There are two types of title page required for APA style papers, a professional and a student version.
Student APA cover page
As long as students do not have any specific guidance from their instructors in regards to a cover page format, they should include the following elements on their cover page:
- Running head : only for APA 6th you write "Running head: TITLE" as a header. APA 7th does not require a running head.
- Title of the paper : three to four lines down from the top of the title page, centered and in bold for APA 7 (APA 6 does not have a title in bold).
- Name of author(s) : include a double-spaced blank line between the paper title and the author name(s).
- Affiliation for each author (the university attended, including department)
- Course number and name
- Name of instructor
- Due date of the assignment (date format used in your location)
- Page number (included on all pages), cover page is number 1.
- Times New Roman is the preferred font, 12-point .
- Double spacing
- 1 inch margins
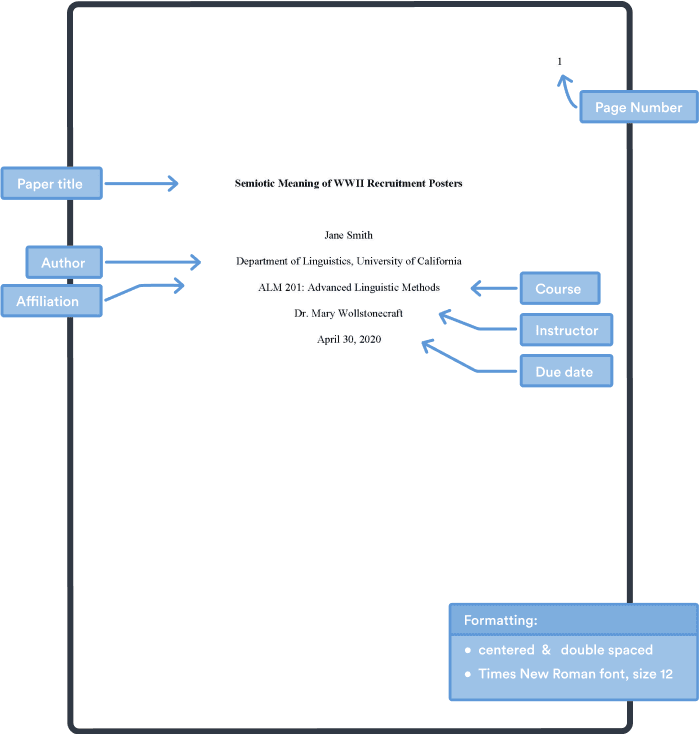
We created a a student APA cover page template of both 6th & 7th edition, which you can download:
Professional APA cover page
A professional APA cover page should include the following elements:
- Name of each author : include a double-spaced blank line between the paper title and the author names.
- Affiliation for each author: give the name of the institution at which the research was carried out.
- Author note : see the specific instructions below.
- Running head (included on all pages): for APA 6th you write "Running head: TITLE" and for APA 7th only the title in caps is required (omitting the phrase running head).
- Page number (included on all pages): page 1 is the cover page.
- Times New Roman is the preferred font, 12 -point.
Since there are a few slight differences between the professional cover page in APA 6th and 7th edition, we created a template for each version, which you can download.
APA cover page: Author note format
An author note in a professional paper can be found at the bottom of the cover page. It is usually composed of four paragraphs.
- In the first paragraph : for APA 6, give the name of the author and their affiliation. For APA 7, give the authors' ORCID iDs. Omit this part if the authors don't have ORCID iDs.
- Second paragraph : Specify any changes of affiliation (for both APA 6 & 7). Use the following format: “[Author’s name] is now at [affiliation].” This paragraph may also clarify the death of an author.
- Third paragraph : give any confidentiality disclosures and/or acknowledgments.
- Fourth paragraph : give the contact information of the author(s).
Format : start this section in the bottom half of the title page, below the affiliations. Leave a minimum of one blank line between the affiliation and the author note title. Center the title “Author Note” in bold. The first line of each paragraph should be indented and all aligned to the left.
Further reading
For more details not covered in this guide, take a look at the following sources:
📝 Student and Professional APA cover page (7th ed.)
🌐 APA 6th cover page tutorial
Frequently Asked Questions about APA cover (title) page
The title page of a student paper serves as a representation of the author. It is a mere formality, as it makes your paper appear more academic. As a student, the title page helps your instructor identify on a glance who wrote the paper, what the topic is, and for what course. In sum, a student should add a title page when indicated.
The title page of a professional paper serves as a representation of the author. For professionals, the function of a title page is to introduce the reader to the main facts of the paper, such as the author, the topic, the year of publication, and contact information. In sum, a professional should add a title page to comply with academic standards.
No. According to APA style, the title's font of a title page should not include any type of Word Art or "fun" fonts of any kind. APA style indicates titles should be written in the same font as the rest of the text, it should centered and in bold (for APA 7).
Yes, APA style's title page should be formated as page 1 of the paper, followed by the abstract page as page 2.
If you learn better by watching than by reading, here are two YouTube tutorials that will help you create a title page: APA Style 7th Edition: Student Paper Formatting and APA Style 7th Edition: Professional Paper Formatting by Samuel Forlenza, PhD.
Make your life easier with our productivity and writing resources.
For students and teachers.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Paper Title Page – Example and Making Guide
Research Paper Title Page – Example and Making Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper Title Page
Research Paper Title Page is the cover page of a research paper that provides basic information about the paper. It typically includes the title of the research paper, the author’s name, the date of submission, and the name of the institution or department where the research was conducted.
The title page of a research paper typically includes the following information:
- Title of the research paper
- Author(s) of the paper (including their name(s), affiliation(s), and contact information)
- Date of submission or publication
- Name of the academic institution or organization where the research was conducted (if applicable)
- Any acknowledgments or funding sources for the research
- Abstract of the research paper (usually a brief summary of the paper’s main findings or arguments)
Research Paper Title Page Example

Notes on formatting:
- The title of your research paper should be centered on the page, and should be written in title case (capitalizing the first letter of each major word).
- Your name should be written underneath the title, centered on the page.
- Your institutional affiliation (e.g. the name of your university or research institution) should be written underneath your name, centered on the page.
- The date of submission should be written underneath your institutional affiliation, centered on the page.
Research Paper Title Page Writing Guide
Here are some guidelines for writing a research paper title page:
- Title of the paper: The title should be concise and descriptive, reflecting the main idea or focus of the research paper. The title should be centered on the page and in title case (capitalize the first letter of each major word).
- Author’s name : The author’s name should be written below the title, also centered on the page. Use first name, middle initial, and last name.
- Institutional affiliation: The institutional affiliation is the name of the university, college, or organization where the research was conducted. It should be listed below the author’s name and centered on the page.
- Date of submission: The date of submission is the date when the research paper is being submitted for review or publication. It should be written below the institutional affiliation and centered on the page.
- Running head: A running head is a short version of the title that is used on subsequent pages of the paper. It should be written in all caps and flush left at the top of each page.
- Page number: The page number should be flush right at the top of each page.
- Font and spacing: Use a standard font such as Times New Roman or Arial in 12-point size. Double-space the entire title page.
Purpose of Research Paper Title Page
The purpose of the research paper title page is to:
- Identify the title of the research paper: The title page provides the title of the paper in a clear and concise manner so that readers can quickly understand the topic of the research.
- Indicate the author(s) of the paper: The title page should include the name(s) of the author(s) who conducted the research and wrote the paper. This information helps to establish credibility and accountability for the research.
- Provide information about the institutional affiliation: The title page should also include the name of the institution where the research was conducted. This information helps readers understand the context of the research and can be useful for citations and further research.
- Give the date of the research: The title page should include the date that the research was conducted or the paper was written. This information helps readers understand the currency of the research and can be useful for citing sources.
- Include other relevant information: Depending on the requirements of the research paper, the title page may also include other relevant information such as the course title, instructor’s name, or a brief abstract of the research.
- Establish a professional appearance : The title page provides an opportunity to present the research paper in a professional and organized manner. A well-designed title page with all necessary information can make a positive first impression on readers and demonstrate the author’s attention to detail.
- Facilitate easy referencing: A properly formatted title page can help readers locate the research paper easily in a database, library, or other sources. This is particularly important for academic and scientific research papers that may be referenced frequently by others.
- Comply with formatting guidelines : Many academic and scientific disciplines have specific formatting guidelines for research papers, including requirements for the title page. Adhering to these guidelines ensures that the research paper is presented in a consistent and standardized format that is familiar to readers in that field.
- Demonstrate compliance with ethical standards: Some academic institutions require that the title page include a statement of compliance with ethical standards for research, such as human subjects’ protection, data privacy, or animal welfare. This information ensures that the research was conducted in an ethical and responsible manner.
Advantages of Research Paper Title Page
There are several advantages to including a title page in a research paper, including:
- Professional Appearance: A title page provides a professional appearance to the research paper. It is the first thing that readers see, and it gives them an impression of the paper’s overall quality.
- Credibility : Including a title page with all the necessary information, such as the author’s name, institutional affiliation, and the date of submission, enhances the credibility of the research paper.
- Easy Identification: A title page makes it easier for readers to identify the research paper among other papers. It provides important information about the paper, such as the title, author’s name, and institutional affiliation.
- Easy Access: A title page provides a quick reference for readers who need to cite the research paper in their own work. The necessary information is all in one place and easily accessible.
- Compliance with Formatting Guidelines: Many academic institutions have specific formatting guidelines for research papers, including the use of a title page. Including a title page ensures compliance with these guidelines and helps avoid any confusion or penalties.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example

Research Paper Introduction – Writing Guide and...
Questions? Call us:
Email:
- How it works
- Testimonials
Essay Writing
- Essay service
- Essay writers
- College essay service
- Write my essay
- Pay for essay
- Essay topics
Term Paper Writing
- Term paper service
- Buy term papers
- Term paper help
- Term paper writers
- College term papers
- Write my term paper
- Pay for term paper
- Term paper topic
Research Paper Writing
- Research paper service
- Buy research paper
- Research paper help
- Research paper writers
- College research papers
- Write my research paper
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper topics
Dissertation Writing
- Dissertation service
- Buy dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Dissertation writers
- College thesis
- Write my dissertation
- Pay for dissertation
- Dissertation topics
Other Services
- Custom writing services
- Speech writing service
- Movie review writing
- Editing service
- Assignment writing
- Article writing service
- Book report writing
- Book review writing
Popular request:
Creating a captivating research paper title page – ultimate guide with examples.
August 29, 2019
A reader can become engaged or irritated after seeing your research paper title page. Th at is why you need to put in the effort to make sure that it is done properly, and it compels the reader to continue reading the content. Creating the title page for research paper is sometimes more difficult for students than writing a research paper.

How To Make A Title Page For Research Paper
The first thing you need to know is that there are primarily three formats for your title page – APA, Chicago style, and MLA. Your instructor will most likely tell you which format is ideal for the paper. The title page has to contain some precise information about the research in a few words. So, what should be contained in a research paper title page?
The front page of your research paper should contain your full name as it is stated on all your educational certificates. That should be on the same page where you put the topic.
Title Of The Research Paper
Make sure you come up with a good title for research paper and put it on the cover page along with your name. Make sure that the title is interesting. Also, it should not be misleading in any way but should provide a glimpse into the entire content. Typically, the title of the research paper title is expected to be written in capital letters and bold fonts.
Supervisor’s Name
Another important detail to add is the full name of the research supervisor. If you go through the research paper title page examples, you’ll see that adding the supervisor’s name is a must.
Course Information
You need to provide some information about the course, including the course code, academic year, and semester.
Now you know what your research paper title page is expected to contain, it’s time to dive into how to make a title page like a professional. Below are some useful tips for creating the perfect paper title page:
Use The Right Format
As stated earlier, there are three main research paper formats. The one you use will depend on what you’ve been instructed to use. However, you need to make sure you stick to one format from the title to the conclusion.

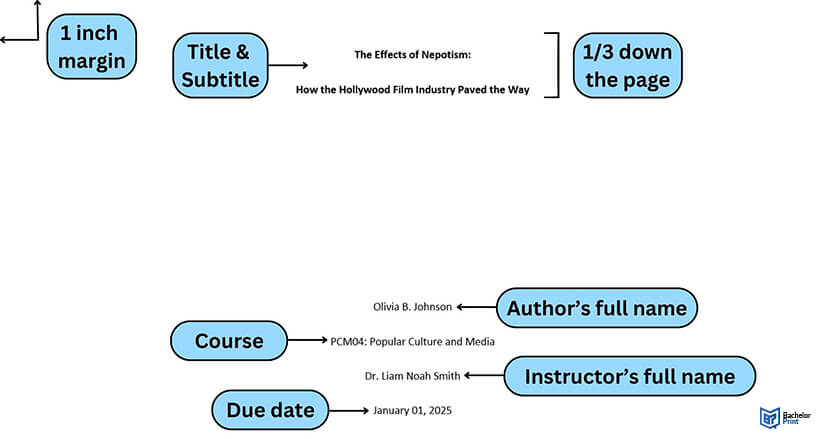
If you’ve been instructed to use the Chicago format, you have to make sure all the content on the cover page is aligned to the center. Your paper title should be halfway into the page. After the page title, write your full name followed by the name of your instructor and then the course title. There is no need to number the cover page when you’re using the Chicago style.

When you’re instructed to use the APA style, you have to number the title page at the top right corner. Use Times New Roman as your page font and keep one-inch margins on every side of the cover page. You may not need to write everything in capital letters.

For the MLA format, you need to start a third way into the paper, but it should not be as low as the Chicago style. You can add a subtitle to your original title. Just after that, add your name, the name of your school, the course title, your instructor’s name.
Writing A Research Paper – Quick Overview
After you’ve determined what you want your title page to look like, you need to find out how to start a research paper. It is important to note that each institution may have specific guidelines on how to write a research paper. So, make sure you read these guidelines thoroughly before you start. However, some general rules are as follows:
Don’t Joke With The Research
The research part of the research paper writing is crucial. Before you start writing anything, research the topic thoroughly, and get updated information about every fact you’re going to list. As soon as you understand the topic, you need to gather resources, formulate the idea, develop your thesis statement. Your research should be backed by empirical data. If possible, conduct first-hand research on the subject. Otherwise, look for reliable research on Google Scholar, government publications, encyclopedias, newspapers, and almanacs.
About Your Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement tells your reader what the main point of your essay is and what your supporting points are. It can be one or two sentences that prepare the minds of the readers for what is to come. Make sure that everything in the body of your paper is in line with the thesis statement, not opposite. Your thesis statement should appear at the end of your introduction and or should match the topic.
Work With An Outline
Your work would flow better if you use an outline from the beginning to the end. Your outline should be made up of all the points you intend to cover in the content. It can also include the research paper format. Make sure that you put down all the subheadings you intend to cover in the content as well as the details of the materials you want to use in each subheading.
Write A Draft First
To increase your chances of creating high-quality work, try writing a draft first. When you’ve completed the draft, you can start writing the content you will submit. Writing a draft first allows you to brainstorm ideas and find the perfect voice for the content.
Progress From Weakest To Strongest Point
For your content to have a logical flow, start with the weakest point, and slowly progress to the strongest. That doesn’t mean you need to start with a point that isn’t backed empirically. It just means the point you start with should not be your strongest. Each point should have a supporting argument as a backup. It makes your content better.
Restate Your Thesis Statement In Your Conclusion
When it’s time to conclude your paper after listing all the relevant points, you can restate your thesis statement as is common in research paper writing examples. That doesn’t mean you should copy and paste your thesis. Just find new words to say it and link all your points to it. Draw the reader’s attention to why all the points you’ve made support your thesis. That applies when you’re research is conclusive. If it is not, make sure you state that in the research is inconclusive.
Review Before Submission
So, you’ve completed your research paper successfully. That’s cool. However, you should not rush into submitting. Revise the work, make edits, and ask someone else to help you read it. Make sure that your work is as flawless as possible. There should be no inaccurate information, grammatical, or typographical errors. The last thing you want to do is submit a compelling research paper with bad grammar or typographical errors.
Let Our Writers Create Best Title Page For You
Writing a research paper, especially its title page, is like writing any other paper. However, it requires more precision and use of facts. Depending on the topic, make sure that everything you state is factual. These tips above will help when you’re creating a title page for your research paper and when you’re creating the paper. Also, should you feel stuck with crafting a research paper – feel free to hire our experts to help you get exciting results!

Take a break from writing.
Top academic experts are here for you.
- How To Write An Autobiography Guideline And Useful Advice
- 182 Best Classification Essay Topics To Learn And Write About
- How To Manage Stress In College: Top Practical Tips
- How To Write A Narrative Essay: Definition, Tips, And A Step-by-Step Guide
- How To Write Article Review Like Professional
- Great Problem Solution Essay Topics
- Creating Best Stanford Roommate Essay
- Costco Essay – Best Writing Guide
- How To Quote A Dialogue
- Wonderful Expository Essay Topics
- Research Paper Topics For 2020
- Interesting Persuasive Essay Topics

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Cover Page – APA, MLA & Chicago Style With Examples
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

In the academic and professional realms, the presentation of written work is nearly as crucial as the content itself. The most popular guidelines are the APA, MLA, and Chicago style. Each has its unique specifications and nuances, particularly when it comes to crafting the cover page , a pivotal aspect that provides the first impression of any document. This article delves into the distinct features and requirements with examples .
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Cover page in a nutshell
- 2 Definition: Cover page
- 3 When is a cover page used?
- 4 Essentials of a cover page
- 6 Cover page for students
Cover page in a nutshell
What is a cover page? A cover page is also called the title page and is the first page of an academic essay or other kinds of academic papers. It displays its title, the author’s name, and other relevant information, serving as an introduction or a preview of what’s inside. Think of it like the cover of a book, giving a glimpse of what the content is about.
Definition: Cover page
The cover page serves as a representation of the author. The format will differ based on the style you choose. It typically contains:
- Name of the author
- Name of the professor
- Name of the student’s educational establishment
- Due date of the paper
The topic of the paper and the course name are always included on the title page, regardless of the format used. As the name suggests, it is placed at the front of the paper and is the first thing your professor will see when they receive your paper. When writing an academic paper, you have to adhere to certain established standards. A cover page is required for many papers, as it introduces the professor to the project. In this article, we will look at the different types and their formats.

When is a cover page used?
A cover page is used in various academic, professional, and publishing contexts to provide a clear and organized introduction to a document. Its usage can vary based on the style guide in reference. Here’s a brief overview of when it is used in APA, MLA, and Chicago styles .
- APA style always requires a title page for both student papers and professional articles or studies. You can read more in our article about the APA format title pages.
- Title of the paper, author’s name, institutional affiliation, course name and number (for students), instructor’s name (for students), and due date
- MLA style does not typically require a title page for research papers , unless specifically requested by the instructor. Instead, essential details are usually placed in the top-left corner of the first page.
- Title, name of the author, instructor’s name, course, and date
Chicago style
- Its usage depends on specific publication or institutional requirements. For formal publications and individual assignments, a title page is typically preferred.
- Title, author’s name, often the specific class or course information, and date of submission
Essentials of a cover page
A cover page requires:
- A running head
- The title of your academic paper
- The name of your university
- The name of the author or authors
Besides these requirements, your professor may ask you to add extra information . As mentioned earlier, you should refer to the latest guidelines to see how the cover should be formatted. With APA style, you have to use 12-point Times New Roman font, double-spacing, and 1-inch margins.
The running head has to be left-aligned, and it should be capitalized. Besides the ‘running head,’ your header should have a maximum of 50 characters.
The title of your paper should also be properly formatted. It should be in the title case, meaning the first letters of every word is capitalized. The only words that should not be capitalized are small words like articles and prepositions . The title should be no more than 12 words in length. For the title, you should use whole words only. Avoid contractions and abbreviations.
The names of the authors should also be properly formatted. If multiple authors were involved in writing the paper, they should all be mentioned, along with the institutions they are affiliated with. Students with different affiliations should be listed separately.
The cover page should not be spruced up unnecessarily. Its only objective is to provide the reader or professor with essential information. Don’t use colored paper, colored text, or fancy images to make it look more attractive. That will only make you appear less professional.
There are as many kinds of cover pages as there are academic writing formats. The most commonly used cover page formats are MLA , APA , and Chicago . The difference lies in their format and content. Here is an overview of each of these types.
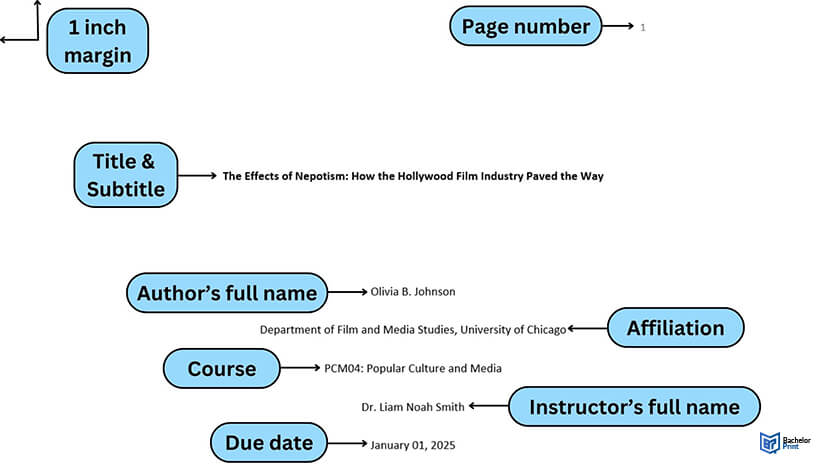
APA cover page
The APA format cover page should start with the running head, positioned at the top left of your paper. The page number is on the top right. Your paper title is to be in title case, in the upper half of the page. For the title, you simply respect the rules for capitalization in titles . APA recommends that your title should be 12 words in length or less, and it should not include any abbreviations or contractions. Words that serve no purpose should also be left out. The title can take up one or two lines.
The information for an APA format cover is below the title of your paper, then the names of the authors and their institutional affiliations are listed. The author’s name should include first name, middle initial(s), and last name. The titles of the author(s) and their educational qualifications should not be included in this part of the paper. The institutional affiliation is included under the author’s name, and it shows where the researcher carried out the research.
For more information, read our article about the APA cover page .
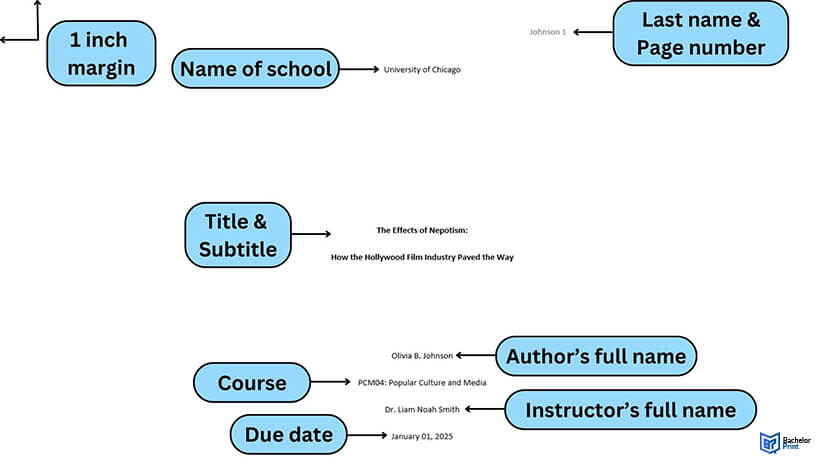
MLA cover page
When using an MLA format cover page, it is not required. Your instructor will let you know whether they require a cover. For some assignments, a cover can make your paper look more professional, so you should always consider adding one. For MLA, you will have to include:
- School or university name
- Title of your paper
- Name of the class
- Name of your professor
- Date of submission
Note: Different instructors may have different style requirements. You may need to add other details to the cover page.
Like in APA, the format cover page is double-spaced and the letters are centered on the page. The name of your university should be typed first, after which you can skip down to a third of the page and add the title of the research paper. From here, you can skip several lines and add the rest of the details. These details should be on the bottom half of the page.
Chicago style cover page
Usually, the Chicago style does not require a cover. However, they may be requested for individual assignments. In this case, the Chicago cover page includes the title of your page, the name of the author, the name of your teacher, the course title, and the due date. The title should be typed at about one-third of the way down the page. Some professors accept covers using 11 pt. Arial font, but the most widely used font is 12 pt. Times New Roman. You should generally avoid using fancy fonts or underlining the text. You can only use bold for the title and subtitle. The page should be double-spaced. The page number should not be included in a Chicago style cover page.
Cover page for students
Creating a student cover page involves considering the essential elements that offer a concise overview of the work, while also adhering to any style or formatting guidelines in place. Here’s a general outline of what should be included.
- Title of the document/paper Ideally placed at the center of the page Should be specific and concise, capturing the essence of the paper
- Student’s name Usually positioned under the title Full name is recommended unless specified otherwise
- Course name and code Essential for academic submissions to ensure the paper reaches the correct instructor or department
- Instructor/professor’s name Specify the honorific title (e.g., Dr., Prof.) if applicable
- Date of submission Can be written in different formats (e.g., September 21, 2023, or 21-09-2023) depending on institutional or style guide preferences
- Institution Name Name of the school, college, or university
- Class or section If applicable Especially useful for larger courses with multiple sections
- Assignment number or type Optional E.g., “Assignment 1”, “Final Project”, “Research Paper”, etc.
Formatting tips
Use a readable font like Times New Roman, Arial, or Calibri. Typically, a 12 pt. font size is recommended. Details on the cover are usually double-spaced for clarity. Ensure you have standard margins (typically 1 inch, so 2.54 cm, on all sides) unless specified otherwise by your institution or style guide. Most of the details are typically centered on the page, but some style guides might have different requirements. Always refer to specific institutional guidelines or the requested style guide (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago) as they may have distinct stipulations for page composition.
How do you write a title page for an essay?
The title page of your academic essay should be simple and straightforward, and it should only consist of text. For the cover page design, you should consult the latest manual of your institution. You may be required to use a certain style of formatting, such as APA, or MLA. The requirements for an APA title page differ from the requirements of an MLA title page .
Does the title page count as one page?
The title page will take up a whole page of your essay. However, it does not count as one page in terms of the page count for your essay . The table of contents and bibliography are also not included in the word/page count of your essay.
How do you format the names of multiple authors?
If more than one person was involved in writing the paper, all the names should be clearly indicated. The format used will depend on the affiliations of the authors and the institution that they’re working with. For an APA cover page, the authors should be listed below the title of the paper. List their first names, middle initials, and last names with any titles and qualifications.
Is a cover page always required?
The cover page is typically required when you use the APA citation style. With the MLA and Chicago formats, your instructor will advise you on whether you have to include a cover. However, more often than not, MLA formatting does not require a title page.
Will you be penalized for adding a cover page when it is not required?
No instructor will penalize you for including a cover page when it is not strictly required. You should consider adding one if you are uncertain whether it is required for your academic writing work. Nevertheless, you should check with your institution anyway to ensure that you’re fulfilling all requirements.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint
Create a research paper cover in minutes.
Make your own unique cover sheet in minutes with editable templates.

Research paper covers

Discover more categories in the app.
Student Business Cards
Class Schedules
Presentations
Infographics
Make a research paper cover sheet with Adobe Express.
Wow your professors and keep your research paper or thesis looking sharp with a fully customizable research cover page. Choose from thousands of professional-looking, editable templates to start with, then click and drag your favorite fonts, icons, and images to make it your own. When you’re finished, download and share it electronically or print it out.
Template IDs
(To pull in manually curated templates if needed)
Orientation
(Horizontal/Vertical)
( Full, Std, sixcols )
(number of templates to load each pagination. Min. 5)
Most Viewed
Rare & Original
Newest to Oldest
Oldest to Newest
(true, false, all) true or false will limit to premium only or free only.

How to make a research paper cover.

Impress your professors and classmates.
Whether you’re creating a research paper cover sheet or searching for some inspiration to draft up a master's thesis defense presentation, we’ve got you covered with thousands of customizable templates. Drag and drop your favorite icons and graphics or get recommended fonts and color palettes curated just for your design. Discover how fast it is to create impressive cover sheets and presentations with Adobe Express.

Let Adobe Express be your go-to app for cover pages.
The cover page is the first step in letting your readers know what your research is about and who wrote it. Adobe Express lets you make a great first impression on professors, teachers, and peers with easy-to-use editing tools and the ability to simultaneously produce print and electronic versions of your work. You can print out your full-color page in any size or download it as a PDF, JPEG, or PNG.
Frequently asked questions.
Looking for adobe express for education.

Use Adobe Express in your classroom.
FOR TEACHER
- Set up an Adobe Express classroom account.
- Create and manage classrooms.
- Securely invite students with a class code.
Available for teachers in the US who have a Google Workspace for Education (Google) account and supported domains. Need help? View the Getting Started Guide
Get started now

Deploy Adobe Express for schools and school districts.
FOR ADMINISTRATORS
- Enable school or district-wide access for licensed users.
- Set up through the Adobe Admin Console.
- Manage users and groups.
Available for licensed educational institutions and nonprofit educational organizations. Call for more info. Questions? View the Deployment Guide.
Call for more info. United States: US schools request access | United Kingdom: UK schools request access Australia: 18-0091-0584 | Japan: Japan schools request access

Are you a student interested in Adobe Express?
FOR STUDENTS
- Design stunning presentations, images, and animations.
- Create attention-grabbing web pages.
- Make captivating videos.
Adobe Express offers everything students need to make graphics, photos, presentations, web pages, and videos to express themselves inside and outside the classroom.
K-12 Students
Higher Education
Let’s grow together with professional learning.


- Email the Library
- 701.401.4229
CIS 170: Intro to Computer Information Systems
- Your Assignment
- APA Formatting Basics
About Cover Pages
Step by step guide, apa sample papers.
- How to Format Your Abstract
- Online Government Resources for Career Information & Data
- Sources for Career Predictions Research
- Advanced Search: How-to and Tips
- How to Format Your Reference Page and APA Citations
- Additional Helpful Information
What is a Cover Page?
The cover page is the first page of a paper. It provides important information about the paper, including its title, author, and publication date. For a student paper, the following information is required:
- Title of the paper
- Author's name
- Department and University the paper was written for
- Course number, section (if applicable), and name
- Professor's name
How is a Cover Page Formatted?
- The title page should be double-spaced, with all information centered.
- The paper's title should start 3-4 lines from the top of the page and should have all important words capitalized.
- Each piece of information goes on a new line.
- Names should be written First Name, Middle Initial, Last Name.
- Ensure that your cursor is at the very beginning of your document.
- Click the insert tab on the top of your document.
- Choose pages, then blank page to insert a blank page above your content.
- Go back to the home tab, then go to the paragraphs section and center your text.
- Type your title capitalizing most of the words; do not capitalize words like the, of, in, or and.
- Add your first name, middle initial if applicable, and last name.
- Write out your university affiliation, which will be Department of Computer Systems and Software Engineering, Valley City State University.
- Type the course number, section, and name, making sure to add a colon (:) between the section and the name.
- Add the first and last name of your professor, making sure to include Dr. before their name if applicable.
- Add the due date for the assignment.
- Select all of your text, then go to line spacing and set everything to be double-spaced.
- Put your cursor at the beginning of your title page, then hit enter or return 4 times to move the text down.
- under Insert, click page number, and add page number to the top right-hand side of the page.
- Put your cursor directly in front of the new page number, then type a shortened version of your title in all capital letters. If your title is less than 50 characters long, you can use the full title as your running head.
- Hit your tab key twice to position the running head at the left of the header.
- Purdue OWL's APA Sample Paper A fully formatted sample paper in APA style. See page 9 for a sample reference list in APA style.
- Sample Paper Formatting for CIS 170 This word document is formatted to APA standards and is set up to look like your assignment will.
- << Previous: APA Formatting Basics
- Next: How to Format Your Abstract >>
- Last Updated: Feb 28, 2024 2:54 PM
- URL: https://libguides.library.vcsu.edu/cis170
- How to setup your software
- Sample MLA Paper – normal paper
- Sample MLA Paper – has cover page
- Sample APA Paper
- Sample Chicago Paper
- Sample CSE Paper
- APA Format Guidelines
- MLA Format Cover Page
The Modern Language Association (MLA) does not require you to create a cover page when you complete your research paper, but some instructors may require it.
If your instructor requires your paper to have a cover page, here is how to make it (very easy). This cover page should include: your school name, your research paper title, your name, your class, your professor name and your paper due date.
How to Format Your MLA Cover Page:
- This page is double spaced and the letters are centered.
- Font: Times New Roman
- Font size: 12
- The first letter of each word should be capitalized with the exception of very short words such as: the, and, of, or, a, an, in, to, for. Note: the first letter of the first word should be capitalized, regardless of what kind of word it is.
- Type the name of your university or college.
- Skip to about one-third of the page and type your research paper title, include a subtitle if you have.
- Skip several lines down and type your name, your course name and number, your instructor name and your paper’s due date.
Sample MLA Format Cover Page:

Sample MLA Format Cover Page
Alternate First Page:
If your instructor requires a cover page, you would omit the main heading on your first page. Here is an example of the first page if a cover page is used. You still need your last name and page number on the first page and every other page.

Sample MLA Format First Page with Cover Page

Sample MLA Paper:
Visit here for a sample paper with the cover page. The cover page can vary slightly. This paper also has the outline page for your sample.
If you find this website useful, please share with a friend:
How do I get the header on the second page on down? I tried editing it but then it takes the header away from all the pages.
In word select the header then go to: Header & Footer>Page Number>Format Page Numbers>Page Numbering>Start at page>Set to 0
How do I get the header on the second page on down? I tried editing it but then it takes the header away from all the pages. I am using windows. Also, the page numbers are not working for me either. Please help me.
How should I start the page after my cover page?
https://mlaformat.org/mla-format-heading/
Thank you so much Stephen !!! Helped a lot in my written assignments 🙂
Great site ! Thank you so much. Just returned to school to complete my bachelors and needed a little refreshing. Has all the information I needed !
Thanks so much for all of the great information! I have not used MLA before and was a little panic stricken. I have found all of my answers here. This is now saved to my favorites so I can use it regularly. Thanks again!
Should the lines on the cover page be double spaced?
Thanks so much for the picture of the cover page it has helped a lot. But, I was wondering do I still need to put my Title at the top of every page after the header?
Hello Lydia. You do not.
After your cover page, your next page’s heading should look like the “Alternate First Page” above.
After the “Alternate First Page” => your next pages should have “The Inner Pages” heading: https://mlaformat.org/mla-format-heading/
Sample paper: https://mlaformat.org/mla-format-sample-paper-with-cover-page-and-outline/
hey Lydia you don’t need to but if you want to you can
Thank you so so much. I love the simplicity of the website, very easy to understand. I finally have a cover page for my paper!!
I love this website!! It helped so many times with all my essays. I’m working on a college one and this was very useful. Thank you soo much. And thanks for the examples im a visual person I needed that 🙂
Hi Kaylin, I am glad you find this site useful. Take care!
By the way (sorry i forgot!) for the coverpage, would the text font be 12 times new roman???
You can set everything 12, Times New Roman. Or you can set the Title a little larger than 12, that should work too.
In the example above, I have the title larger than 12.
Here is an example with everything set at 12.
Thank you so much for your help on this useful website! I found it very organized and I’m very glad that I came across this particular article. Thanks!!!!!!!:)
I have a question regarding the cover page and the following pages. If I have a cover page as the example provided, do I still need the heading on the next page? And should the pages after that contain my last name on the top left as the header does on the on the previous pages? or do I not need the header at all if I have the cover page and just my name?
Excellence question, Stella! I have updated this article with information on the first page if a cover page is used. Please see “Alternate First Page” above.
You can omit the main heading but you still need your last name and page number on the first page and all subsequent pages. Take care!
Leave a Comment
Current ye ignore me @r *
Leave this field empty
Next post: MLA Format Heading
Previous post: MLA Format Websites
- The Format of the Research Paper
- MLA Format Headings
- MLA Citations
- MLA Format Works Cited
- MLA Format FAQs
- MLA Format Sample Paper
- MLA Sample Paper w/ Cover and Outline Pages
HOW TO SETUP YOUR SOFTWARE
- MLA Format using Google Docs
- MLA Format Microsoft Word 2016
- MLA Format using Pages on Mac
Copyright © 2011–2024 • MLA Format • All rights reserved. Currently, MLA is at its 8th edition. This website has no official relationship with the Modern Language Association and is not endorsed by the MLA.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
13.1 Formatting a Research Paper
Learning objectives.
- Identify the major components of a research paper written using American Psychological Association (APA) style.
- Apply general APA style and formatting conventions in a research paper.
In this chapter, you will learn how to use APA style , the documentation and formatting style followed by the American Psychological Association, as well as MLA style , from the Modern Language Association. There are a few major formatting styles used in academic texts, including AMA, Chicago, and Turabian:
- AMA (American Medical Association) for medicine, health, and biological sciences
- APA (American Psychological Association) for education, psychology, and the social sciences
- Chicago—a common style used in everyday publications like magazines, newspapers, and books
- MLA (Modern Language Association) for English, literature, arts, and humanities
- Turabian—another common style designed for its universal application across all subjects and disciplines
While all the formatting and citation styles have their own use and applications, in this chapter we focus our attention on the two styles you are most likely to use in your academic studies: APA and MLA.
If you find that the rules of proper source documentation are difficult to keep straight, you are not alone. Writing a good research paper is, in and of itself, a major intellectual challenge. Having to follow detailed citation and formatting guidelines as well may seem like just one more task to add to an already-too-long list of requirements.
Following these guidelines, however, serves several important purposes. First, it signals to your readers that your paper should be taken seriously as a student’s contribution to a given academic or professional field; it is the literary equivalent of wearing a tailored suit to a job interview. Second, it shows that you respect other people’s work enough to give them proper credit for it. Finally, it helps your reader find additional materials if he or she wishes to learn more about your topic.
Furthermore, producing a letter-perfect APA-style paper need not be burdensome. Yes, it requires careful attention to detail. However, you can simplify the process if you keep these broad guidelines in mind:
- Work ahead whenever you can. Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” includes tips for keeping track of your sources early in the research process, which will save time later on.
- Get it right the first time. Apply APA guidelines as you write, so you will not have much to correct during the editing stage. Again, putting in a little extra time early on can save time later.
- Use the resources available to you. In addition to the guidelines provided in this chapter, you may wish to consult the APA website at http://www.apa.org or the Purdue University Online Writing lab at http://owl.english.purdue.edu , which regularly updates its online style guidelines.
General Formatting Guidelines
This chapter provides detailed guidelines for using the citation and formatting conventions developed by the American Psychological Association, or APA. Writers in disciplines as diverse as astrophysics, biology, psychology, and education follow APA style. The major components of a paper written in APA style are listed in the following box.
These are the major components of an APA-style paper:
Body, which includes the following:
- Headings and, if necessary, subheadings to organize the content
- In-text citations of research sources
- References page
All these components must be saved in one document, not as separate documents.
The title page of your paper includes the following information:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Name of the institution with which the author is affiliated
- Header at the top of the page with the paper title (in capital letters) and the page number (If the title is lengthy, you may use a shortened form of it in the header.)
List the first three elements in the order given in the previous list, centered about one third of the way down from the top of the page. Use the headers and footers tool of your word-processing program to add the header, with the title text at the left and the page number in the upper-right corner. Your title page should look like the following example.

The next page of your paper provides an abstract , or brief summary of your findings. An abstract does not need to be provided in every paper, but an abstract should be used in papers that include a hypothesis. A good abstract is concise—about one hundred fifty to two hundred fifty words—and is written in an objective, impersonal style. Your writing voice will not be as apparent here as in the body of your paper. When writing the abstract, take a just-the-facts approach, and summarize your research question and your findings in a few sentences.
In Chapter 12 “Writing a Research Paper” , you read a paper written by a student named Jorge, who researched the effectiveness of low-carbohydrate diets. Read Jorge’s abstract. Note how it sums up the major ideas in his paper without going into excessive detail.

Write an abstract summarizing your paper. Briefly introduce the topic, state your findings, and sum up what conclusions you can draw from your research. Use the word count feature of your word-processing program to make sure your abstract does not exceed one hundred fifty words.
Depending on your field of study, you may sometimes write research papers that present extensive primary research, such as your own experiment or survey. In your abstract, summarize your research question and your findings, and briefly indicate how your study relates to prior research in the field.
Margins, Pagination, and Headings
APA style requirements also address specific formatting concerns, such as margins, pagination, and heading styles, within the body of the paper. Review the following APA guidelines.
Use these general guidelines to format the paper:
- Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch.
- Use double-spaced text throughout your paper.
- Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point).
- Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section. Page numbers appear flush right within your header.
- Section headings and subsection headings within the body of your paper use different types of formatting depending on the level of information you are presenting. Additional details from Jorge’s paper are provided.

Begin formatting the final draft of your paper according to APA guidelines. You may work with an existing document or set up a new document if you choose. Include the following:
- Your title page
- The abstract you created in Note 13.8 “Exercise 1”
- Correct headers and page numbers for your title page and abstract
APA style uses section headings to organize information, making it easy for the reader to follow the writer’s train of thought and to know immediately what major topics are covered. Depending on the length and complexity of the paper, its major sections may also be divided into subsections, sub-subsections, and so on. These smaller sections, in turn, use different heading styles to indicate different levels of information. In essence, you are using headings to create a hierarchy of information.
The following heading styles used in APA formatting are listed in order of greatest to least importance:
- Section headings use centered, boldface type. Headings use title case, with important words in the heading capitalized.
- Subsection headings use left-aligned, boldface type. Headings use title case.
- The third level uses left-aligned, indented, boldface type. Headings use a capital letter only for the first word, and they end in a period.
- The fourth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are boldfaced and italicized.
- The fifth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are italicized and not boldfaced.
Visually, the hierarchy of information is organized as indicated in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” .
Table 13.1 Section Headings
A college research paper may not use all the heading levels shown in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” , but you are likely to encounter them in academic journal articles that use APA style. For a brief paper, you may find that level 1 headings suffice. Longer or more complex papers may need level 2 headings or other lower-level headings to organize information clearly. Use your outline to craft your major section headings and determine whether any subtopics are substantial enough to require additional levels of headings.
Working with the document you developed in Note 13.11 “Exercise 2” , begin setting up the heading structure of the final draft of your research paper according to APA guidelines. Include your title and at least two to three major section headings, and follow the formatting guidelines provided above. If your major sections should be broken into subsections, add those headings as well. Use your outline to help you.
Because Jorge used only level 1 headings, his Exercise 3 would look like the following:
Citation Guidelines
In-text citations.
Throughout the body of your paper, include a citation whenever you quote or paraphrase material from your research sources. As you learned in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , the purpose of citations is twofold: to give credit to others for their ideas and to allow your reader to follow up and learn more about the topic if desired. Your in-text citations provide basic information about your source; each source you cite will have a longer entry in the references section that provides more detailed information.
In-text citations must provide the name of the author or authors and the year the source was published. (When a given source does not list an individual author, you may provide the source title or the name of the organization that published the material instead.) When directly quoting a source, it is also required that you include the page number where the quote appears in your citation.
This information may be included within the sentence or in a parenthetical reference at the end of the sentence, as in these examples.
Epstein (2010) points out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Here, the writer names the source author when introducing the quote and provides the publication date in parentheses after the author’s name. The page number appears in parentheses after the closing quotation marks and before the period that ends the sentence.
Addiction researchers caution that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (Epstein, 2010, p. 137).
Here, the writer provides a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence that includes the author’s name, the year of publication, and the page number separated by commas. Again, the parenthetical citation is placed after the closing quotation marks and before the period at the end of the sentence.
As noted in the book Junk Food, Junk Science (Epstein, 2010, p. 137), “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive.”
Here, the writer chose to mention the source title in the sentence (an optional piece of information to include) and followed the title with a parenthetical citation. Note that the parenthetical citation is placed before the comma that signals the end of the introductory phrase.
David Epstein’s book Junk Food, Junk Science (2010) pointed out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Another variation is to introduce the author and the source title in your sentence and include the publication date and page number in parentheses within the sentence or at the end of the sentence. As long as you have included the essential information, you can choose the option that works best for that particular sentence and source.
Citing a book with a single author is usually a straightforward task. Of course, your research may require that you cite many other types of sources, such as books or articles with more than one author or sources with no individual author listed. You may also need to cite sources available in both print and online and nonprint sources, such as websites and personal interviews. Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.2 “Citing and Referencing Techniques” and Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provide extensive guidelines for citing a variety of source types.
Writing at Work
APA is just one of several different styles with its own guidelines for documentation, formatting, and language usage. Depending on your field of interest, you may be exposed to additional styles, such as the following:
- MLA style. Determined by the Modern Languages Association and used for papers in literature, languages, and other disciplines in the humanities.
- Chicago style. Outlined in the Chicago Manual of Style and sometimes used for papers in the humanities and the sciences; many professional organizations use this style for publications as well.
- Associated Press (AP) style. Used by professional journalists.
References List
The brief citations included in the body of your paper correspond to the more detailed citations provided at the end of the paper in the references section. In-text citations provide basic information—the author’s name, the publication date, and the page number if necessary—while the references section provides more extensive bibliographical information. Again, this information allows your reader to follow up on the sources you cited and do additional reading about the topic if desired.
The specific format of entries in the list of references varies slightly for different source types, but the entries generally include the following information:
- The name(s) of the author(s) or institution that wrote the source
- The year of publication and, where applicable, the exact date of publication
- The full title of the source
- For books, the city of publication
- For articles or essays, the name of the periodical or book in which the article or essay appears
- For magazine and journal articles, the volume number, issue number, and pages where the article appears
- For sources on the web, the URL where the source is located
The references page is double spaced and lists entries in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. If an entry continues for more than one line, the second line and each subsequent line are indented five spaces. Review the following example. ( Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provides extensive guidelines for formatting reference entries for different types of sources.)

In APA style, book and article titles are formatted in sentence case, not title case. Sentence case means that only the first word is capitalized, along with any proper nouns.
Key Takeaways
- Following proper citation and formatting guidelines helps writers ensure that their work will be taken seriously, give proper credit to other authors for their work, and provide valuable information to readers.
- Working ahead and taking care to cite sources correctly the first time are ways writers can save time during the editing stage of writing a research paper.
- APA papers usually include an abstract that concisely summarizes the paper.
- APA papers use a specific headings structure to provide a clear hierarchy of information.
- In APA papers, in-text citations usually include the name(s) of the author(s) and the year of publication.
- In-text citations correspond to entries in the references section, which provide detailed bibliographical information about a source.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
APA Sample Paper

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resource for the older APA 6 style can be found here .
Media Files: APA Sample Student Paper , APA Sample Professional Paper
This resource is enhanced by Acrobat PDF files. Download the free Acrobat Reader
Note: The APA Publication Manual, 7 th Edition specifies different formatting conventions for student and professional papers (i.e., papers written for credit in a course and papers intended for scholarly publication). These differences mostly extend to the title page and running head. Crucially, citation practices do not differ between the two styles of paper.
However, for your convenience, we have provided two versions of our APA 7 sample paper below: one in student style and one in professional style.
Note: For accessibility purposes, we have used "Track Changes" to make comments along the margins of these samples. Those authored by [AF] denote explanations of formatting and [AWC] denote directions for writing and citing in APA 7.
APA 7 Student Paper:
Apa 7 professional paper:.
- How To Setup Your Software
- Motivational Stories
- Funny Jokes
- Memory Techniques
- MLA Format Cover Page
The Modern Language Association (MLA) does not require you to create a cover page when you complete your research paper, but some instructors may require it.
If your instructor requires your paper to have a cover page, here is how to make it (very easy). This cover page should include: your school name, your research paper title, your name, your class, your professor name and your paper due date.
How to Format Your MLA Cover Page:
- This page is double spaced and the letters are centered.
- Font: Times New Roman
- Font size: 12
- The first letter of each word should be capitalized with the exception of very short words such as: the, and, of, or, a, an, in, to, for. Note: the first letter of the first word should be capitalized, regardless of what kind of word it is.
- Type the name of your university, college or high school.
- Skip to about one-third of the page and type your research paper title, include a subtitle if you have.
- Skip several lines down and type your name, your course name and number, your instructor name and your paper due date.
Sample MLA Format Cover Page:

Sample MLA Format Cover Page
Alternate First Page (Important):
If your instructor requires a cover page, you would omit the main heading on your first page.
Here is an example of the first page if a cover page is used. You still need your last name and page number on the first page and every other page.

Sample MLA Format First Page with Cover Page


Sample MLA Paper:
Visit here for a sample paper with the cover page. The cover page can vary slightly. This paper also has the outline page for your sample.
For some reason, it warms my heart to see people saying “thanks” in this era — despite how old this guide is. OP is here saving lives in the year 2024 o7
ty ty ty ty
thank you sir
thank you so much for this amazing guide
thanks a lot!
this was very helpful thank you mrs. silvey
yeah thanks mrs. story
Thank you for the example of the cover page.
thank mrs story
Thank You Ms. K! (¬‿¬)
Leave a Comment
Current ye ignore me @r *
Leave this field empty
Next post: MLA Format Headings
- How to Format the Research Paper
- MLA Format Headings
- MLA Citations
- MLA Format Works Cited
- MLA Format Sample Paper
- MLA Sample Paper w/ Cover & Outline Pages
- MLA Format FAQs
- General Format of the APA Paper
- APA Format Title Page
- APA Format Abstract Page
- APA Headings
- APA Format Citations
- APA Reference Page
- APA Sample Paper
AcademicTips.org 1999–2024 • MLA Format • Privacy • Back to top ↑
10+ Free Cover Page Templates for Research Papers in MS Word – (Pro Formats)
#1 – general design.

#2 – For Analytical Research Paper

#3 – Format for Argumentative Research Paper

#4 – Best for Case and Effect Research

#5 – Compare and Contrast Format

#6 – Design for Definition Research Paper

#7 – Experimental Research Paper Design

#8 – Interpretative Research Paper Format

#9 – Best Format for Problem/Solution Research Paper

#10 – Template for Survey Research Paper

- Name of student
- Name of university
- The title of research done
- Name of professor
- Due date of the paper.
Essentials of a research cover paper
Importance of good research paper cover page.
← Previous Article
Next Article →
You may also like

- Doctor Prescription Pad Formats
- Printable ID Cards
- Creative Resume Formats for Freshers
- Modern Resume Templates
- Best Cover Page Formats
- Printable Report Cards
- Business Proposal Templates
- 22 Raffle Ticket Templates
- Free Certificate Templates
Search the database of 10,000+ templates, designs & formats for Microsoft Office.
- Make Your Mark: Free Printable Dog Name Tags for Every Tail-Wagger!
- 7+ Free Stunning Easter Templates for Joyful Celebrations
- 9+ Free Admit-One Ticket Templates: Flexible and Easy to Edit
- Get Cooking with Style: 8+ Free Customizable Recipe Card Templates
- 11+ Free Mortgage Flyer Templates to Elevate Your Marketing
- Enhance Your Events with 20+ Unique and Free Ticket Voucher Templates
- Relaxation Redefined: Explore Free 8+ Spa Voucher Templates
- 24+ Free Employment Verification Letter Templates
- Free 5+ Best Christmas Wishlist Templates for Joyful Giving
- 5+ Best FREE Wedding Timeline Templates for a Magical Celebration
- 6+ Free Checklist Templates to Simplify Your Inspection Process
- Honoring Educators: 6+ Free Teacher Certificate Templates
- Certificates
- Cover Pages
- Educational
- Event Templates
- Invoices & Receipts
- Letterheads
- Office Related
- Personal Use
- 137+ Professional Reports – MS Word & Excel
- 70+ Printable & Editable ID Card Designs
- 59+ Proposal Formats
- 31+ Best Flyer Designs & Formats
- 100+ Cover Page Templates
- 22+ Free Letterhead Designs and Formats
- 24+ Free Resume Designs & for Freshers and Professionals
- 136+ Printable Certificate Templates
- 55+ Quotations & Invoices
- Create FREE PDF Calendar Online
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
How to Write a Research Paper | A Beginner's Guide
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research.
Research papers are similar to academic essays , but they are usually longer and more detailed assignments, designed to assess not only your writing skills but also your skills in scholarly research. Writing a research paper requires you to demonstrate a strong knowledge of your topic, engage with a variety of sources, and make an original contribution to the debate.
This step-by-step guide takes you through the entire writing process, from understanding your assignment to proofreading your final draft.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Understand the assignment, choose a research paper topic, conduct preliminary research, develop a thesis statement, create a research paper outline, write a first draft of the research paper, write the introduction, write a compelling body of text, write the conclusion, the second draft, the revision process, research paper checklist, free lecture slides.
Completing a research paper successfully means accomplishing the specific tasks set out for you. Before you start, make sure you thoroughly understanding the assignment task sheet:
- Read it carefully, looking for anything confusing you might need to clarify with your professor.
- Identify the assignment goal, deadline, length specifications, formatting, and submission method.
- Make a bulleted list of the key points, then go back and cross completed items off as you’re writing.
Carefully consider your timeframe and word limit: be realistic, and plan enough time to research, write, and edit.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

There are many ways to generate an idea for a research paper, from brainstorming with pen and paper to talking it through with a fellow student or professor.
You can try free writing, which involves taking a broad topic and writing continuously for two or three minutes to identify absolutely anything relevant that could be interesting.
You can also gain inspiration from other research. The discussion or recommendations sections of research papers often include ideas for other specific topics that require further examination.
Once you have a broad subject area, narrow it down to choose a topic that interests you, m eets the criteria of your assignment, and i s possible to research. Aim for ideas that are both original and specific:
- A paper following the chronology of World War II would not be original or specific enough.
- A paper on the experience of Danish citizens living close to the German border during World War II would be specific and could be original enough.
Note any discussions that seem important to the topic, and try to find an issue that you can focus your paper around. Use a variety of sources , including journals, books, and reliable websites, to ensure you do not miss anything glaring.
Do not only verify the ideas you have in mind, but look for sources that contradict your point of view.
- Is there anything people seem to overlook in the sources you research?
- Are there any heated debates you can address?
- Do you have a unique take on your topic?
- Have there been some recent developments that build on the extant research?
In this stage, you might find it helpful to formulate some research questions to help guide you. To write research questions, try to finish the following sentence: “I want to know how/what/why…”
A thesis statement is a statement of your central argument — it establishes the purpose and position of your paper. If you started with a research question, the thesis statement should answer it. It should also show what evidence and reasoning you’ll use to support that answer.
The thesis statement should be concise, contentious, and coherent. That means it should briefly summarize your argument in a sentence or two, make a claim that requires further evidence or analysis, and make a coherent point that relates to every part of the paper.
You will probably revise and refine the thesis statement as you do more research, but it can serve as a guide throughout the writing process. Every paragraph should aim to support and develop this central claim.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
A research paper outline is essentially a list of the key topics, arguments, and evidence you want to include, divided into sections with headings so that you know roughly what the paper will look like before you start writing.
A structure outline can help make the writing process much more efficient, so it’s worth dedicating some time to create one.
Your first draft won’t be perfect — you can polish later on. Your priorities at this stage are as follows:
- Maintaining forward momentum — write now, perfect later.
- Paying attention to clear organization and logical ordering of paragraphs and sentences, which will help when you come to the second draft.
- Expressing your ideas as clearly as possible, so you know what you were trying to say when you come back to the text.
You do not need to start by writing the introduction. Begin where it feels most natural for you — some prefer to finish the most difficult sections first, while others choose to start with the easiest part. If you created an outline, use it as a map while you work.
Do not delete large sections of text. If you begin to dislike something you have written or find it doesn’t quite fit, move it to a different document, but don’t lose it completely — you never know if it might come in useful later.
Paragraph structure
Paragraphs are the basic building blocks of research papers. Each one should focus on a single claim or idea that helps to establish the overall argument or purpose of the paper.
Example paragraph
George Orwell’s 1946 essay “Politics and the English Language” has had an enduring impact on thought about the relationship between politics and language. This impact is particularly obvious in light of the various critical review articles that have recently referenced the essay. For example, consider Mark Falcoff’s 2009 article in The National Review Online, “The Perversion of Language; or, Orwell Revisited,” in which he analyzes several common words (“activist,” “civil-rights leader,” “diversity,” and more). Falcoff’s close analysis of the ambiguity built into political language intentionally mirrors Orwell’s own point-by-point analysis of the political language of his day. Even 63 years after its publication, Orwell’s essay is emulated by contemporary thinkers.
Citing sources
It’s also important to keep track of citations at this stage to avoid accidental plagiarism . Each time you use a source, make sure to take note of where the information came from.
You can use our free citation generators to automatically create citations and save your reference list as you go.
APA Citation Generator MLA Citation Generator
The research paper introduction should address three questions: What, why, and how? After finishing the introduction, the reader should know what the paper is about, why it is worth reading, and how you’ll build your arguments.
What? Be specific about the topic of the paper, introduce the background, and define key terms or concepts.
Why? This is the most important, but also the most difficult, part of the introduction. Try to provide brief answers to the following questions: What new material or insight are you offering? What important issues does your essay help define or answer?
How? To let the reader know what to expect from the rest of the paper, the introduction should include a “map” of what will be discussed, briefly presenting the key elements of the paper in chronological order.
The major struggle faced by most writers is how to organize the information presented in the paper, which is one reason an outline is so useful. However, remember that the outline is only a guide and, when writing, you can be flexible with the order in which the information and arguments are presented.
One way to stay on track is to use your thesis statement and topic sentences . Check:
- topic sentences against the thesis statement;
- topic sentences against each other, for similarities and logical ordering;
- and each sentence against the topic sentence of that paragraph.
Be aware of paragraphs that seem to cover the same things. If two paragraphs discuss something similar, they must approach that topic in different ways. Aim to create smooth transitions between sentences, paragraphs, and sections.
The research paper conclusion is designed to help your reader out of the paper’s argument, giving them a sense of finality.
Trace the course of the paper, emphasizing how it all comes together to prove your thesis statement. Give the paper a sense of finality by making sure the reader understands how you’ve settled the issues raised in the introduction.
You might also discuss the more general consequences of the argument, outline what the paper offers to future students of the topic, and suggest any questions the paper’s argument raises but cannot or does not try to answer.
You should not :
- Offer new arguments or essential information
- Take up any more space than necessary
- Begin with stock phrases that signal you are ending the paper (e.g. “In conclusion”)
There are four main considerations when it comes to the second draft.
- Check how your vision of the paper lines up with the first draft and, more importantly, that your paper still answers the assignment.
- Identify any assumptions that might require (more substantial) justification, keeping your reader’s perspective foremost in mind. Remove these points if you cannot substantiate them further.
- Be open to rearranging your ideas. Check whether any sections feel out of place and whether your ideas could be better organized.
- If you find that old ideas do not fit as well as you anticipated, you should cut them out or condense them. You might also find that new and well-suited ideas occurred to you during the writing of the first draft — now is the time to make them part of the paper.
The goal during the revision and proofreading process is to ensure you have completed all the necessary tasks and that the paper is as well-articulated as possible. You can speed up the proofreading process by using the AI proofreader .
Global concerns
- Confirm that your paper completes every task specified in your assignment sheet.
- Check for logical organization and flow of paragraphs.
- Check paragraphs against the introduction and thesis statement.
Fine-grained details
Check the content of each paragraph, making sure that:
- each sentence helps support the topic sentence.
- no unnecessary or irrelevant information is present.
- all technical terms your audience might not know are identified.
Next, think about sentence structure , grammatical errors, and formatting . Check that you have correctly used transition words and phrases to show the connections between your ideas. Look for typos, cut unnecessary words, and check for consistency in aspects such as heading formatting and spellings .
Finally, you need to make sure your paper is correctly formatted according to the rules of the citation style you are using. For example, you might need to include an MLA heading or create an APA title page .
Scribbr’s professional editors can help with the revision process with our award-winning proofreading services.
Discover our paper editing service
Checklist: Research paper
I have followed all instructions in the assignment sheet.
My introduction presents my topic in an engaging way and provides necessary background information.
My introduction presents a clear, focused research problem and/or thesis statement .
My paper is logically organized using paragraphs and (if relevant) section headings .
Each paragraph is clearly focused on one central idea, expressed in a clear topic sentence .
Each paragraph is relevant to my research problem or thesis statement.
I have used appropriate transitions to clarify the connections between sections, paragraphs, and sentences.
My conclusion provides a concise answer to the research question or emphasizes how the thesis has been supported.
My conclusion shows how my research has contributed to knowledge or understanding of my topic.
My conclusion does not present any new points or information essential to my argument.
I have provided an in-text citation every time I refer to ideas or information from a source.
I have included a reference list at the end of my paper, consistently formatted according to a specific citation style .
I have thoroughly revised my paper and addressed any feedback from my professor or supervisor.
I have followed all formatting guidelines (page numbers, headers, spacing, etc.).
You've written a great paper. Make sure it's perfect with the help of a Scribbr editor!
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide
- Writing a Research Paper Conclusion | Step-by-Step Guide
- Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
More interesting articles
- Academic Paragraph Structure | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- Checklist: Writing a Great Research Paper
- How to Create a Structured Research Paper Outline | Example
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- How to Write Topic Sentences | 4 Steps, Examples & Purpose
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Research Paper Damage Control | Managing a Broken Argument
- What Is a Theoretical Framework? | Guide to Organizing
What is your plagiarism score?
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Volume 627 Issue 8005, 28 March 2024
Qubit quota.
The accumulation of errors hampers the use of quantum computers. Although there are ways to design circuits so they detect and correct errors, this typically requires a substantial number of additional qubits. In this week’s issue, researchers at IBM present a protocol for low-overhead error correction in quantum computers. The researchers use low-density parity-check codes, which correct errors by monitoring several symmetries each supported on only a small set of qubits. This code performed as well as established error-correction protocols but crucially needed only about one-tenth of the qubits. This could make error-corrected quantum computers substantially smaller machines than previously assumed. The cover image offers an artistic rendering of the qubit connectivity required for the new protocol in which each qubit needs to interact with six others. Qubits are linked as if they were placed onto the surface of a torus.
Cover image: IBM
Nature is committed to diversifying its journalistic sources
The latest data are in on the diversity of people interviewed for the journal’s News, Features and Careers articles, and audio and video content.
Advertisement
Deep-sea mining plans should not be rushed
Why are companies and governments determined to start commercial-scale mining for rare metals, when so little is known about its wider impacts?
‘Exhausted and insulted’: how harsh visa-application policies are hobbling global research
Institutions and individuals from low- and middle-income countries are wasting time, effort and money trying to get visas for research travel, only to be rejected. A new approach is needed.
- Sandra Owusu-Gyamfi
Research Highlights
How the body’s cholesterol factory avoids producing too much.
Scientists identify a molecule that halts cholesterol production in the liver when dietary consumption is high.
A view of wind turbines drives down home values — but only briefly
House prices drop by 1% if wind turbines are close and visible, but they rebound quickly.
A supercollider glimpses a gathering of three particles never seen together before
Data from billions of proton collisions reveal that subatomic particles called W + and W − bosons keep company with a photon.
Squeeze, freeze, bake: how to make 3D-printed wood that mimics the real thing
Scientists turn waste wood into an ‘ink’ that can be printed into a variety of structures.
News in Focus
Cutting-edge car-t cancer therapy is now made in india — at one-tenth the cost.
The treatment, called NexCAR19, raises hopes that this transformative class of medicine will become more readily available in low- and middle-income countries.
- Smriti Mallapaty
Collection:
- Cancer at Nature Portfolio
First pig liver transplanted into a person lasts for 10 days
Pig organs could provide temporary detox for people whose livers need time to recover or who are awaiting human donors.
Ketamine is in the spotlight thanks to Elon Musk — but is it the right treatment for depression?
The entrepreneur endorses the drug, but researchers caution that it’s not to be taken lightly.
What Putin’s next term means for science
Researchers in Russia expect growing isolation as Vladimir Putin embarks on six more years as president.
- Olga Dobrovidova
Mathematician who tamed randomness wins Abel Prize
Michel Talagrand laid mathematical groundwork that has allowed others to tackle problems involving random processes.
- Davide Castelvecchi
China’s giant underground neutrino lab prepares to probe cosmic mysteries
Due to come online this year, the JUNO facility will help to determine which type of neutrino has the highest mass — one of the biggest mysteries in physics.
- Gemma Conroy
The ‘Mother Tree’ idea is everywhere — but how much of it is real?
A popular theory about how trees cooperate has enchanted the public and raised the profile of forest conservation. But some ecologists think its scientific basis has been oversold.
- Aisling Irwin
AI image generators often give racist and sexist results: can they be fixed?
Researchers are tracing sources of racial and gender bias in images generated by artificial intelligence, and making efforts to fix them.
Books & Arts
How did the big bang get its name here’s the real story.
Astronomer Fred Hoyle supposedly coined the catchy term to ridicule the theory of the Universe’s origins — 75 years on, it’s time to set the record straight.
- Helge Kragh
Anthony Epstein (1921–2024), discoverer of virus causing cancer in humans
Pathologist whose finding that viruses can trigger tumours in humans transformed medical research.
- Alan Rickinson
How a tree-hugging protest transformed Indian environmentalism
Fifty years ago, a group of women from the villages of the Western Himalayas sparked Chipko, a green movement that remains relevant in the age of climate change.
- Seema Mundoli
How to achieve safe water access for all: work with local communities
Four scientists reflect on how to foster a more sustainable relationship between water and society amid complex and wide-ranging challenges.
- Farhana Sultana
- Tara McAllister
- Michael D. Blackstock
Correspondence
The ‘anthropocene’ is here to stay — and it’s better not as a geological epoch.
- Thomas P. Roland
- Graeme T. Swindles
- Alastair Ruffell
Superconductivity case shows the need for zero tolerance of toxic lab culture
- Juan Pablo Fuenzalida Werner
Cuts to postgraduate funding threaten Brazilian science — again
- Marcus F. Oliveira
- Adriane R. Todeschini
Don’t underestimate the rising threat of groundwater to coastal cities
- Daniel J. Rozell
What’s the sign for ‘centrifuge’? How we added scientific terms to Indian Sign Language
Molecular biologist Alka Rao brought together her research group and sign-language specialists to broaden access to science for deaf students in India.
- Deepa Padmanaban
- Disability and ableism in science careers
Adding scientific signs to Indian Sign Language will create a more inclusive field for deaf students
Digvijay Singh, a deaf sign-language educator, works with biology researchers and sign-language specialists to add to the scientific lexicon for deaf students in India.
Communication barriers for a Deaf PhD student meant risking burnout
Megan Majocha is gearing up to complete her PhD. But developing a sign-language lexicon to help her succeed took an immense toll during her scientific research.
- Jyoti Madhusoodanan
Where I Work
I peer into volcanoes to see when they’ll blow.
Mariton Antonia Bornas runs a Filipino volcano research and response organization.
- Margaret Simons
News & Views
Electrons flip a switch on optical communications.
Clever manipulation of electrons has enabled scientists to change a key property of light emitted by a device using electrically controlled magnetization. The method could lead to stable and energy-efficient information transfer.
- Satoshi Hiura
The 50th anniversary of a key paper on how bird flight evolved
For a century, scientists pondered whether bird flight evolved by animals gliding down from trees or by creatures running and flapping from the ground up. A landmark 1974 paper reset the debate to focus on the evolution of the flight stroke instead.
- Kevin Padian
The surprising history of the Southern Ocean’s super current
Reconstructions of the strength of a powerful current that circles the South Pole reveal that it has undergone no long-term change in the past five million years, even though Earth cooled substantially over that time.
- Natalie J. Burls
Powerful microscopy reveals blood-cell production in bone marrow
A method for imaging the production of blood cells in the bones of mice has revealed the organization of cell lineages, both in a steady state and in response to stressors, such as bleeding and infection.
- M. Carolina Florian
Well-matched vibrations cool electronic hot spots
Diamond layers can help to dissipate the heat generated by high-power semiconductor devices. This effect has now been enhanced by adding layers of materials and engineering their crystal-lattice vibrations to be compatible at the interfaces.
Astrocyte cells in the brain have immune memory
The central nervous system’s astrocyte cells respond to injury and disease. The finding that they form molecular memories of certain responses, and that these modify inflammatory signalling, sheds light on autommunity.
- Michael V. Sofroniew
A figure of merit for efficiency roll-off in TADF-based organic LEDs
Efficiency roll-off in a wide range of TADF OLEDs is analysed and a figure of merit proposed for materials design to improve efficiency at high brightness, potentially expanding the range of applications of TADF materials.
- I. D. W. Samuel
A shock flash breaking out of a dusty red supergiant
A type II supernova (SN 2023ixf) was observed in the galaxy M101 at a distance of 6.85 ± 0.15 Mpc, at about 1.0 h after the explosion.
- Eliot Herman
The complex circumstellar environment of supernova 2023ixf
Using ultraviolet data as well as a comprehensive set of further multiwavelength observations of the supernova 2023ixf, a reliable bolometric light curve is derived that indicates the heating nature of the early emission.
- E. A. Zimmerman
Thermonuclear explosions on neutron stars reveal the speed of their jets
Relativistic jets observed from transient neutron stars throughout the Universe produce bright flares for minutes after each X-ray burst, helping to determine the role individual system properties have on the speed and revealing the dominant launching mechanism.
- Thomas D. Russell
- Nathalie Degenaar
- Melania Del Santo
Optomechanical realization of the bosonic Kitaev chain
We report the experimental realization of a bosonic Kitaev chain in a nano-optomechanical network.
- Jesse J. Slim
- Clara C. Wanjura
- Ewold Verhagen
High-fidelity spin qubit operation and algorithmic initialization above 1 K
Initialization and operation of spin qubits in silicon above 1 K reach fidelities sufficient for fault-tolerant operations at these temperatures.
- Jonathan Y. Huang
- Rocky Y. Su
- Chih Hwan Yang
High-threshold and low-overhead fault-tolerant quantum memory
An end-to-end quantum error correction protocol that implements fault-tolerant memory on the basis of a family of low-density parity-check codes shows the possibility of low-overhead fault-tolerant quantum memory within the reach of near-term quantum processors.
- Sergey Bravyi
- Andrew W. Cross
- Theodore J. Yoder
Controlling the helicity of light by electrical magnetization switching
The helicity of light from a light-emitting diode can be electrically controlled by spin–orbit torque effects, enabling a seamless integration of magnetization dynamics with photonics.
- Pambiang Abel Dainone
- Nicholas Figueiredo Prestes
Five million years of Antarctic Circumpolar Current strength variability
The strength of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, as traced in sediment cores from the Pacific Southern Ocean, shows no linear long-term trend over the past 5.3 Myr; instead, the strongest flow occurs consistently in warmer-than-present intervals.
- Gisela Winckler
- Xiangyu Zhao
Global supply chains amplify economic costs of future extreme heat risk
A global high-resolution disaster footprint analytical model is developed to show substantial socioeconomic impacts from climatic change-driven heat stress through the global supply chain by 2060 due to direct and indirect effects on health and labour productivity.
- Shupeng Zhu
East-to-west human dispersal into Europe 1.4 million years ago
Burial-dating methods using cosmogenic nuclides indicate that the oldest stone tools at Korolevo archaeological site in western Ukraine date to around 1.4 million years ago, providing evidence of early human dispersal into Europe from the east.
- J. D. Jansen
The hagfish genome and the evolution of vertebrates
A chromosome-scale genome assembly for the hagfish Eptatretus atami , combined with a series of phylogenetic analyses, sheds light on ancient polyploidization events that had a key role in the early evolution of vertebrates.
- Ferdinand Marlétaz
- Nataliya Timoshevskaya
- Daniel S. Rokhsar
Subicular neurons encode concave and convex geometries
Longitudinal calcium imaging reveals the ability of corner cells to synchronize their activity with the environment, with the results implying the potential of the subiculum to contain the information required to reconstruct spatial environments.
- Douglas A. Nitz
- Lisa M. Giocomo
A vagal reflex evoked by airway closure
A specific neural reflex of the vagus nerve is identified that induces gasping in response to airway closure.
- Michael S. Schappe
- Philip A. Brinn
- Stephen D. Liberles
Resilient anatomy and local plasticity of naive and stress haematopoiesis
This study develops a method for spatially resolving multipotent haematopoiesis, erythropoiesis and lymphopoiesis in mice and uncovers heterogeneous haematopoietic stress responses in different bones.
- Qingqing Wu
- Jizhou Zhang
- Daniel Lucas
Substrate-induced condensation activates plant TIR domain proteins
Binding of the substrates NAD + and ATP to the plant Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain proteins induces phase separation and, thereby, activation of TIR enzymatic and immune signalling activity.
Spatially organized cellular communities form the developing human heart
Combining single-cell RNA-sequencing with high-resolution multiplexed error-robust fluorescence in situ hybridization reveals in detail the cellular interactions and specialization of cardiac cell types that form and remodel the human heart.
- Elie N. Farah
- Robert K. Hu
- Neil C. Chi
Disease-associated astrocyte epigenetic memory promotes CNS pathology
In an experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model in mice, a subset of astrocytes retains an epigenetically regulated memory of past inflammation, causing exacerbated inflammation upon subsequent rechallenge.
- Hong-Gyun Lee
- Joseph M. Rone
- Francisco J. Quintana
The CRL5–SPSB3 ubiquitin ligase targets nuclear cGAS for degradation
The ubiquitin proteasomal system degrades nuclear cGAS in cycling cells.
- Pengbiao Xu
- Andrea Ablasser
Evolutionary trajectories of small cell lung cancer under therapy
We uncover key processes of the genomic evolution of small cell lung cancer under therapy, identify the common ancestor as the source of clonal diversity at relapse and show central genomic patterns associated with drug response.
- Julie George
- Roman K. Thomas
Parental histone transfer caught at the replication fork
Structures of the yeast replisome associated with the FACT complex and an evicted histone hexamer offer insights into the mechanism of replication-coupled histone recycling for maintaining epigenetic inheritance.
- Ningning Li
- Yuanliang Zhai
Blueprinting extendable nanomaterials with standardized protein blocks
A study describes an approach using designed building blocks that are far more regular in geometry than natural proteins to construct modular multicomponent protein assemblies.
- Timothy F. Huddy
- David Baker
The structure and physical properties of a packaged bacteriophage particle
Multiresolution computational simulations generate all-atom models of a complete packaged virus particle.
- Kush Coshic
- Christopher Maffeo
- Aleksei Aksimentiev
Anoxygenic phototroph of the Chloroflexota uses a type I reaction centre
Cultivation of a new anoxygenic phototrophic bacterium from Boreal Shield lake water—representing a transition form in the evolution of photosynthesis—offers insights into how the major modes of phototrophy diversified.
- J. M. Tsuji
- J. D. Neufeld
Amendments & Corrections
Publisher correction: anti-tigit antibody improves pd-l1 blockade through myeloid and t reg cells.
- Xiangnan Guan
- Namrata S. Patil
Publisher Correction: Nuclear export of circular RNA
- Linh H. Ngo
- Andrew G. Bert
- Vihandha O. Wickramasinghe
Publisher Correction: Durable CO 2 conversion in the proton-exchange membrane system
- Wensheng Fang
Nature Outline
Cancer vaccines.
The use of vaccines not to prevent illness but as treatments, rallying the immune system to attack existing tumours, has the potential to revolutionize cancer therapy.
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Cover pages can include the name of your school, your paper title, your name, your course name, your teacher or professor's name, and the due date of the paper. If you are unsure of what to include, check with your instructor. Here is an example of a cover page in MLA format: For more help making cover or title pages, visit our title page ...
The student version of the APA title page should include the following information (double spaced and centered): Paper title. Author name. Department and university name. Course number and name. Instructor name. Due date of the assignment. The professional title page also includes an author note (flushed left), but not a course name, instructor ...
The title page (or cover page) of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper should contain all the key information about your document. It usually includes: Dissertation or thesis title. Your name. The type of document (e.g., dissertation, research paper) The department and institution. The degree program (e.g., Master of Arts)
If the cover page template for your research paper doesn't come with a featured visual, select "Elements" on the left-hand side of the editing deck, then type "Frames" in the search box. Drag and drop your frame of choice onto the layout, and arrange its size and position. Then, insert your image of choice in it.
In APA Style (7th edition), the cover page, or title page, should include: A running head (professional papers only) and page number. The title of the paper. The name of the author (s) The institutional affiliation. An author note; optional (professional papers only) A student paper should also include course information.
Title of the paper: three to four lines down from the top of the title page, centered and in bold for APA 7 (APA 6 does not have a title in bold). Name of each author: include a double-spaced blank line between the paper title and the author names. Affiliation for each author: give the name of the institution at which the research was carried out.
Follow the guidelines described next to format each element of the student title page. Place the title three to four lines down from the top of the title page. Center it and type it in bold font. Capitalize major words of the title. Place the main title and any subtitle on separate double-spaced lines if desired.
Indent the first line of every paragraph of text 0.5 in. using the tab key or the paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program. Page numbers: Put a page number in the top right corner of every page, including the title page or cover page, which is page 1. Student papers do not require a running head on any page.
Research Paper Title Page is the cover page of a research paper that provides basic information about the paper. It typically includes the title of the research paper, the author's name, the date of submission, and the name of the institution or department where the research was conducted.
The front page of your research paper should contain your full name as it is stated on all your educational certificates. That should be on the same page where you put the topic. Title Of The Research Paper. Make sure you come up with a good title for research paper and put it on the cover page along with your name.
APA cover page. The APA format cover page should start with the running head, positioned at the top left of your paper.The page number is on the top right. Your paper title is to be in title case, in the upper half of the page. For the title, you simply respect the rules for capitalization in titles.APA recommends that your title should be 12 words in length or less, and it should not include ...
A title page is not mandatory; if you haven't been told to include one, you can just center your title at the top of the first page. These are the key guidelines for creating a title page in Turabian style: Title and subtitle appear ⅓ of the way down the page. Other information (e.g., your name, the date, class information) appears ⅔ down ...
Make a research paper cover sheet with Adobe Express. Wow your professors and keep your research paper or thesis looking sharp with a fully customizable research cover page. Choose from thousands of professional-looking, editable templates to start with, then click and drag your favorite fonts, icons, and images to make it your own.
What is a Cover Page? The cover page is the first page of a paper. It provides important information about the paper, including its title, author, and publication date. For a student paper, the following information is required: Title of the paper; Author's name; Department and University the paper was written for
This cover page should include: your school name, your research paper title, your name, your class, your professor name and your paper due date. How to Format Your MLA Cover Page: This page is double spaced and the letters are centered.
Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch. Use double-spaced text throughout your paper. Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point). Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section.
An APA title page must include: A running head (including page number) The title of your paper (one or two lines long) The full name of the author (s) Your university or institution. Additional information, such as a course number or an author's note, should be placed on a separate line below the institution. APA title page template.
Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resource for the older APA 6 style can be found here. Media Files: APA Sample Student Paper , APA Sample Professional Paper This resource is enhanced by Acrobat PDF files. Download the free Acrobat Reader
This cover page should include: your school name, your research paper title, your name, your class, your professor name and your paper due date. How to Format Your MLA Cover Page: This page is double spaced and the letters are centered.
619.70 KB. This is the front page of research work widely known as the thesis. It is written by a student who is undergoing any degree program and duly submitted to the teacher after completion. This covers the following areas: Name of student. Name of university. The title of research done. Name of professor. Due date of the paper.
Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist.
Cover image: IBM. Subscribe. Table of Contents. ... effort and money trying to get visas for research travel, only to be rejected. ... A landmark 1974 paper reset the debate to focus on the ...
The aim of the paper is to introduce appropriate tools for quantifying the changes occurred at edge level when analyzing land cover changes. The research is conducted in two directions. Firstly, the binary change index at edge level is introduced and its relationship to the already existing binary change edge (computed at pixel level) is studied. It is proved that a certain inequality between ...