- Research Skills

50 Mini-Lessons For Teaching Students Research Skills
Please note, I am no longer blogging and this post hasn’t updated since April 2020.
For a number of years, Seth Godin has been talking about the need to “ connect the dots” rather than “collect the dots” . That is, rather than memorising information, students must be able to learn how to solve new problems, see patterns, and combine multiple perspectives.
Solid research skills underpin this. Having the fluency to find and use information successfully is an essential skill for life and work.
Today’s students have more information at their fingertips than ever before and this means the role of the teacher as a guide is more important than ever.
You might be wondering how you can fit teaching research skills into a busy curriculum? There aren’t enough hours in the day! The good news is, there are so many mini-lessons you can do to build students’ skills over time.
This post outlines 50 ideas for activities that could be done in just a few minutes (or stretched out to a longer lesson if you have the time!).
Learn More About The Research Process
I have a popular post called Teach Students How To Research Online In 5 Steps. It outlines a five-step approach to break down the research process into manageable chunks.

This post shares ideas for mini-lessons that could be carried out in the classroom throughout the year to help build students’ skills in the five areas of: clarify, search, delve, evaluate , and cite . It also includes ideas for learning about staying organised throughout the research process.
Notes about the 50 research activities:
- These ideas can be adapted for different age groups from middle primary/elementary to senior high school.
- Many of these ideas can be repeated throughout the year.
- Depending on the age of your students, you can decide whether the activity will be more teacher or student led. Some activities suggest coming up with a list of words, questions, or phrases. Teachers of younger students could generate these themselves.
- Depending on how much time you have, many of the activities can be either quickly modelled by the teacher, or extended to an hour-long lesson.
- Some of the activities could fit into more than one category.
- Looking for simple articles for younger students for some of the activities? Try DOGO News or Time for Kids . Newsela is also a great resource but you do need to sign up for free account.
- Why not try a few activities in a staff meeting? Everyone can always brush up on their own research skills!
- Choose a topic (e.g. koalas, basketball, Mount Everest) . Write as many questions as you can think of relating to that topic.
- Make a mindmap of a topic you’re currently learning about. This could be either on paper or using an online tool like Bubbl.us .
- Read a short book or article. Make a list of 5 words from the text that you don’t totally understand. Look up the meaning of the words in a dictionary (online or paper).
- Look at a printed or digital copy of a short article with the title removed. Come up with as many different titles as possible that would fit the article.
- Come up with a list of 5 different questions you could type into Google (e.g. Which country in Asia has the largest population?) Circle the keywords in each question.
- Write down 10 words to describe a person, place, or topic. Come up with synonyms for these words using a tool like Thesaurus.com .
- Write pairs of synonyms on post-it notes (this could be done by the teacher or students). Each student in the class has one post-it note and walks around the classroom to find the person with the synonym to their word.

- Explore how to search Google using your voice (i.e. click/tap on the microphone in the Google search box or on your phone/tablet keyboard) . List the pros and cons of using voice and text to search.
- Open two different search engines in your browser such as Google and Bing. Type in a query and compare the results. Do all search engines work exactly the same?
- Have students work in pairs to try out a different search engine (there are 11 listed here ). Report back to the class on the pros and cons.
- Think of something you’re curious about, (e.g. What endangered animals live in the Amazon Rainforest?). Open Google in two tabs. In one search, type in one or two keywords ( e.g. Amazon Rainforest) . In the other search type in multiple relevant keywords (e.g. endangered animals Amazon rainforest). Compare the results. Discuss the importance of being specific.
- Similar to above, try two different searches where one phrase is in quotation marks and the other is not. For example, Origin of “raining cats and dogs” and Origin of raining cats and dogs . Discuss the difference that using quotation marks makes (It tells Google to search for the precise keywords in order.)
- Try writing a question in Google with a few minor spelling mistakes. What happens? What happens if you add or leave out punctuation ?
- Try the AGoogleADay.com daily search challenges from Google. The questions help older students learn about choosing keywords, deconstructing questions, and altering keywords.
- Explore how Google uses autocomplete to suggest searches quickly. Try it out by typing in various queries (e.g. How to draw… or What is the tallest…). Discuss how these suggestions come about, how to use them, and whether they’re usually helpful.
- Watch this video from Code.org to learn more about how search works .
- Take a look at 20 Instant Google Searches your Students Need to Know by Eric Curts to learn about “ instant searches ”. Try one to try out. Perhaps each student could be assigned one to try and share with the class.
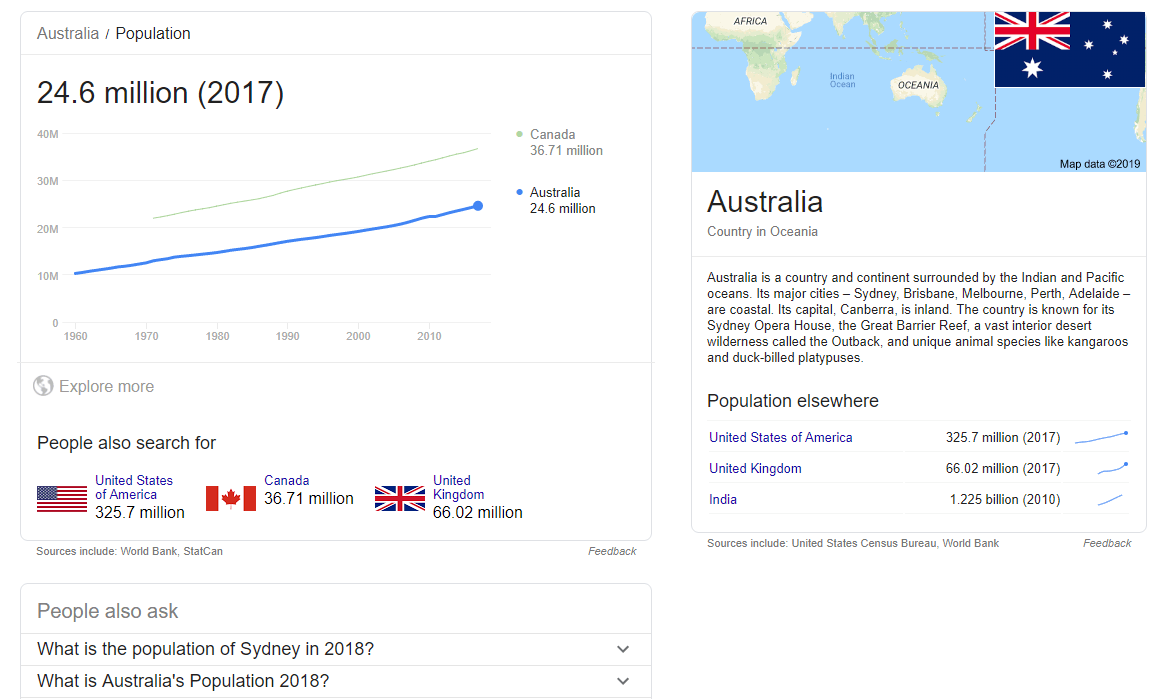
- Experiment with typing some questions into Google that have a clear answer (e.g. “What is a parallelogram?” or “What is the highest mountain in the world?” or “What is the population of Australia?”). Look at the different ways the answers are displayed instantly within the search results — dictionary definitions, image cards, graphs etc.
- Watch the video How Does Google Know Everything About Me? by Scientific American. Discuss the PageRank algorithm and how Google uses your data to customise search results.
- Brainstorm a list of popular domains (e.g. .com, .com.au, or your country’s domain) . Discuss if any domains might be more reliable than others and why (e.g. .gov or .edu) .
- Discuss (or research) ways to open Google search results in a new tab to save your original search results (i.e. right-click > open link in new tab or press control/command and click the link).
- Try out a few Google searches (perhaps start with things like “car service” “cat food” or “fresh flowers”). A re there advertisements within the results? Discuss where these appear and how to spot them.
- Look at ways to filter search results by using the tabs at the top of the page in Google (i.e. news, images, shopping, maps, videos etc.). Do the same filters appear for all Google searches? Try out a few different searches and see.
- Type a question into Google and look for the “People also ask” and “Searches related to…” sections. Discuss how these could be useful. When should you use them or ignore them so you don’t go off on an irrelevant tangent? Is the information in the drop-down section under “People also ask” always the best?
- Often, more current search results are more useful. Click on “tools” under the Google search box and then “any time” and your time frame of choice such as “Past month” or “Past year”.
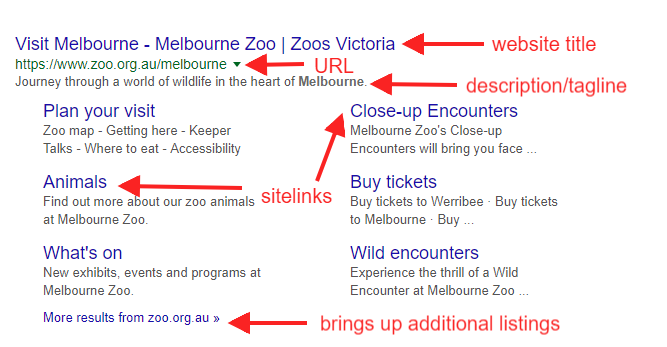
- Have students annotate their own “anatomy of a search result” example like the one I made below. Explore the different ways search results display; some have more details like sitelinks and some do not.
- Find two articles on a news topic from different publications. Or find a news article and an opinion piece on the same topic. Make a Venn diagram comparing the similarities and differences.
- Choose a graph, map, or chart from The New York Times’ What’s Going On In This Graph series . Have a whole class or small group discussion about the data.
- Look at images stripped of their captions on What’s Going On In This Picture? by The New York Times. Discuss the images in pairs or small groups. What can you tell?
- Explore a website together as a class or in pairs — perhaps a news website. Identify all the advertisements .
- Have a look at a fake website either as a whole class or in pairs/small groups. See if students can spot that these sites are not real. Discuss the fact that you can’t believe everything that’s online. Get started with these four examples of fake websites from Eric Curts.
- Give students a copy of my website evaluation flowchart to analyse and then discuss as a class. Read more about the flowchart in this post.
- As a class, look at a prompt from Mike Caulfield’s Four Moves . Either together or in small groups, have students fact check the prompts on the site. This resource explains more about the fact checking process. Note: some of these prompts are not suitable for younger students.
- Practice skim reading — give students one minute to read a short article. Ask them to discuss what stood out to them. Headings? Bold words? Quotes? Then give students ten minutes to read the same article and discuss deep reading.

All students can benefit from learning about plagiarism, copyright, how to write information in their own words, and how to acknowledge the source. However, the formality of this process will depend on your students’ age and your curriculum guidelines.
- Watch the video Citation for Beginners for an introduction to citation. Discuss the key points to remember.
- Look up the definition of plagiarism using a variety of sources (dictionary, video, Wikipedia etc.). Create a definition as a class.
- Find an interesting video on YouTube (perhaps a “life hack” video) and write a brief summary in your own words.
- Have students pair up and tell each other about their weekend. Then have the listener try to verbalise or write their friend’s recount in their own words. Discuss how accurate this was.
- Read the class a copy of a well known fairy tale. Have them write a short summary in their own words. Compare the versions that different students come up with.
- Try out MyBib — a handy free online tool without ads that helps you create citations quickly and easily.
- Give primary/elementary students a copy of Kathy Schrock’s Guide to Citation that matches their grade level (the guide covers grades 1 to 6). Choose one form of citation and create some examples as a class (e.g. a website or a book).
- Make a list of things that are okay and not okay to do when researching, e.g. copy text from a website, use any image from Google images, paraphrase in your own words and cite your source, add a short quote and cite the source.
- Have students read a short article and then come up with a summary that would be considered plagiarism and one that would not be considered plagiarism. These could be shared with the class and the students asked to decide which one shows an example of plagiarism .
- Older students could investigate the difference between paraphrasing and summarising . They could create a Venn diagram that compares the two.
- Write a list of statements on the board that might be true or false ( e.g. The 1956 Olympics were held in Melbourne, Australia. The rhinoceros is the largest land animal in the world. The current marathon world record is 2 hours, 7 minutes). Have students research these statements and decide whether they’re true or false by sharing their citations.
Staying Organised

- Make a list of different ways you can take notes while researching — Google Docs, Google Keep, pen and paper etc. Discuss the pros and cons of each method.
- Learn the keyboard shortcuts to help manage tabs (e.g. open new tab, reopen closed tab, go to next tab etc.). Perhaps students could all try out the shortcuts and share their favourite one with the class.
- Find a collection of resources on a topic and add them to a Wakelet .
- Listen to a short podcast or watch a brief video on a certain topic and sketchnote ideas. Sylvia Duckworth has some great tips about live sketchnoting
- Learn how to use split screen to have one window open with your research, and another open with your notes (e.g. a Google spreadsheet, Google Doc, Microsoft Word or OneNote etc.) .
All teachers know it’s important to teach students to research well. Investing time in this process will also pay off throughout the year and the years to come. Students will be able to focus on analysing and synthesizing information, rather than the mechanics of the research process.
By trying out as many of these mini-lessons as possible throughout the year, you’ll be really helping your students to thrive in all areas of school, work, and life.
Also remember to model your own searches explicitly during class time. Talk out loud as you look things up and ask students for input. Learning together is the way to go!
You Might Also Enjoy Reading:
How To Evaluate Websites: A Guide For Teachers And Students
Five Tips for Teaching Students How to Research and Filter Information
Typing Tips: The How and Why of Teaching Students Keyboarding Skills
8 Ways Teachers And Schools Can Communicate With Parents

10 Replies to “50 Mini-Lessons For Teaching Students Research Skills”
Loving these ideas, thank you
This list is amazing. Thank you so much!
So glad it’s helpful, Alex! 🙂
Hi I am a student who really needed some help on how to reasearch thanks for the help.
So glad it helped! 🙂
seriously seriously grateful for your post. 🙂
So glad it’s helpful! Makes my day 🙂
How do you get the 50 mini lessons. I got the free one but am interested in the full version.
Hi Tracey, The link to the PDF with the 50 mini lessons is in the post. Here it is . Check out this post if you need more advice on teaching students how to research online. Hope that helps! Kathleen
Best wishes to you as you face your health battler. Hoping you’ve come out stronger and healthier from it. Your website is so helpful.
Comments are closed.
Join my VIP teacher email club!

If you are struggling with teaching the research report process, you are not alone. Seriously, we’ve all been there!
I spent several years avoiding research reports in my classroom or depending on the Library-Media Specialist to teach the research process.
One year, I decided to take the plunge and teach my students how to research a topic and write a research report.
The process was clunky at first, but I learned a lot about how students approach research and how to guide them from choosing a topic to completing their final copies.
Before we discuss the HOW , let’s talk about the WHY .

Why should you assign research reports to 5th and 6th grade students?
I have three main reasons for assigning research reports to my students.
First, the skill involved in finding reliable sources and citing sources is valuable.
Beginning in 5th grade, and possibly even before, students need to be able to discern the reliability of a source . They should be able to spot propaganda and distinguish between reputable sources and phony ones.
Teaching the procedure for citing sources is important because my 5th grade students need to grasp the reality of plagiarism and how to avoid it.
By providing information about the sources they used, students are consciously avoiding copying the work of authors and learning to give credit where credit is due.
Second, by taking notes and organizing their notes into an outline, students are exercising their ability to find main ideas and corresponding details.
Being able to organize ideas is crucial for young writers.
Third, when writing research reports, students are internalizing the writing process, including organizing, writing a rough draft, proofreading/editing, and writing a final draft.
When students write research reports about topics of interest, they are fine-tuning their reading and writing skills.

How to Teach Research Reports in Grades 5 & 6
As a veteran upper elementary teacher, I know exactly what is going to happen when I tell my students that we are going to start research reports.
There will be a resounding groan followed by students voicing their displeasure. (It goes something like this…. “Mrs Bazzit! That’s too haaaaaaard!” or “Ugh. That’s boring!” *Sigh* I’ve heard it all, lol.)
This is when I put on my (somewhat fictional) excited teacher hat and help them to realize that the research report process will be fun and interesting.

Step 1: Choose a Topic and Cite Sources
Students definitely get excited when they find out they may choose their own research topic. Providing choice leads to higher engagement and interest.
It’s best practice to provide a list of possible research topics to students, but also allow them to choose a different topic.
Be sure to make your research topics narrow to help students focus on sources. If students choose broad topics, the sources they find will overwhelm them with information.
Too Broad: American Revolution
Just Right: The Battle of Yorktown
Too Broad: Ocean Life
Just Right: Great White Shark
Too Broad: Important Women in History
Just Right: The Life of Martha Washington
Be sure to discuss appropriate, reliable sources with students.
I suggest projecting several examples of internet sources on your technology board. Ask students to decide if the sources look reliable or unreliable.
While teaching students about citing sources, it’s a great time to discuss plagiarism and ways to avoid it.
Students should never copy the words of an author unless they are properly quoting the text.
In fact, I usually discourage students from quoting their sources in their research reports. In my experience, students will try to quote a great deal of text and will border on plagiarism.
I prefer to see students paraphrase from their sources because this skill helps them to refine their summarization skills.
Citing sources is not as hard as it sounds! I find that my students generally use books and internet sources, so those are the two types of citations that I focus on.
How to cite a book:
Author’s last name, First name. Title of Book. City of Publication: Publisher, Date.
How to cite an internet article:
Author’s last name, First name (if available). “Title of Article or Page.” Full http address, Date of access.
If you continue reading to the bottom of this post, I have created one free screencast for each of the five steps of the research process!

Step 2: Take Notes
During this step, students will use their sources to take notes.
I do provide instruction and examples during this step because from experience, I know that students will think every piece of information from each source is important and they will copy long passages from each source.
I teach students that taking notes is an exercise in main idea and details. They should read the source, write down the main idea, and list several details to support the main idea.
I encourage my students NOT to copy information from the source but instead to put the information in their own words. They will be less likely to plagiarize if their notes already contain their own words.
Additionally, during this step, I ask students to write a one-sentence thesis statement. I teach students that a thesis statement tells the main point of their research reports.
Their entire research report will support the thesis statement, so the thesis statement is actually a great way to help students maintain a laser focus on their research topic.

Step 3: Make an Outline
Making an outline can be intimidating for students, especially if they’ve never used this organization format.
However, this valuable step will teach students to organize their notes into the order that will be used to write the rough draft of their reports.
Because making an outline is usually a new concept for my 5th graders, we do 2-3 examples together before I allow students to make their outlines for their research reports.
I recommend copying an outline template for students to have at their fingertips while creating their first outline.
Be sure to look over students’ outlines for organization, order, and accuracy before allowing them to move on to the next step (writing rough drafts).

Step 4: Write a Draft
During this step, each student will write a rough draft of his/her research report.
If they completed their outlines correctly, this step will be fairly simple.
Students will write their research reports in paragraph form.
One problem that is common among my students is that instead of writing in paragraphs, they write their sentences in list format.
I find that it’s helpful to write a paragraph in front of and with students to remind them that when writing a paragraph, the next sentence begins immediately after the prior sentence.
Once students’ rough drafts are completed, it’s time to proofread/edit!
To begin, I ask my students to read their drafts aloud to listen for their own mistakes.
Next, I ask my students to have two individuals look over their draft and suggest changes.

Step 5: Final Draft
It’s finally time to write final drafts!
After students have completed their rough drafts and made edits, I ask them to write final drafts.
Students’ final drafts should be as close to perfect as possible.
I prefer a typed final draft because students will have access to a spellchecker and other features that will make it easier to create their final draft.
Think of a creative way to display the finished product, because they will be SO proud of their research reports after all the hard work that went into creating them!
When grading the reports, use a rubric similar to the one shown in the image at the beginning of this section.
A detailed rubric will help students to clearly see their successes and areas of needed improvement.
Once students have completed their first research projects, I find that they have a much easier time with the other research topics assigned throughout the remainder of the school year.
If you are interested in a no-prep, step-by-step research report instructional unit, please click here to visit my Research Report Instructional Unit for 5th Grade and 6th Grade.

This instructional unit will guide students step-by-step through the research process, including locating reliable sources, taking notes, creating an outline, writing a report, and making a “works cited” page.
I’d like to share a very special free resource with you. I created five screencast videos, one for each step of the research report process. These screencasts pair perfectly with my Research Report Instructional Unit for 5th Grade and 6th Grade!
Research Report Step 1 Screencast
Research Report Step 2 Screencast
Research Report Step 3 Screencast
Research Report Step 4 Screencast
Research Report Step 5 Screencast
Hi, If i purchase your complete package on grade 5/6 writing does it come with your wonderful recordings on how to teach them? Thanks
Hi Gail! The recordings on this blog post can be used by anyone and I will leave them up 🙂 The writing bundle doesn’t come with any recordings but I did include step-by-step instructions for teachers. I hope this helps!
Thank you for sharing your information with everyone. I know how to write (I think, haha), but I wanted to really set my students up for success with their research and writing. Your directions and guides are just what I needed to jar my memory and help my students become original writers. Be blessed.
You are very welcome, Andrea! Thank you for this comment 🙂
Hi Andrea, I am a veteran teacher who has taught nothing but primary for 25 years. However, this is my first year in 5th. I’m so excited to have found your post. Can you direct me to how I can purchase your entire bundle for writing a 5-paragraph essay. Thanks, Sue
Sure, Susan, I can help with that! Here is the link for the 5th Grade Writing Bundle: https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Product/5th-Grade-Writing-Bundle-3611643
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
You may also enjoy...

Ben Franklin’s Fire Brigade – Free Lesson

Five Paragraph Essays – How to Teach & Grade

Tips for Teaching the Constitution in Upper Elementary

American Revolution Cloze Passages

Consistency for Upper Elementary Teachers


My Favorite “Student-Led” Open House Activity
What can i help you teach, find it here, let's connect, i'd love to connect with you.
Enter your first name and email address to join my exclusive VIP email club.
Copyright © 2020 | Thrive in Grade Five | All Rights Reserved
Quick Links
Elementary Librarian
Library lesson plans and ideas for the school librarian. Lessons incorporate Common Core and AASL standards.
Sixth Grade Library Lesson Plans

Sixth grade is a challenging time for students. Many have transitioned to middle school. They are adjusting to the more advanced curriculum. They also have extended responsibilities.
Along with those responsibilities, sixth grade students should be encouraged to delve deeper into texts. They will be asked to compare/contrast and classify information. They must also evaluate different types of texts. In addition, they will use context clues to decode increasingly difficult vocabulary words.
Download a sample sixth grade lesson plan Word || PDF || ZIP
Want access to all of the sixth grade lesson plans? Subscribe to Elementary Librarian. If you are an Elementary Subscriber, access the sixth grade lessons here .
Looking for more sixth grade language arts worksheets and resources? Visit our friends at Help Teaching .
Worth more than I paid!
All the work is done for me, my students are engaged, my principal was impressed.

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.

Research Writing (Grades 4-6)
Our Research Writing lesson plan for grades 4-6 teaches students how to write a thoroughly researched and factually accurate five paragraph essay. Students write an essay based on research they conduct in order to practice this type of writing.
Description
Additional information.
Our Research Writing Lesson Plan for grades 4-6 teaches students about the importance of researching and reporting findings accurately and effectively. Being able to clearly and accurately inform and communicate findings through writing is a valuable skill that students will need in many areas of their lives. Gathering and summarizing key information will also be a powerful tool for academic reading and writing throughout upper grades and higher education. In this lesson, students are asked to use the information they have learned to research and write a research paper from start to finish, including brainstorming and outlining.
At the end of the lesson, students will have written an essay based on a topic of their choosing with sources cited.
Thank you for submitting a review!
Your input is very much appreciated. Share it with your friends so they can enjoy it too!
Great Resource
Awesome! I was encouraged to find this as I develop my own writing curriculum for my homeschooled middle schoolers.

Nice resource
I haven't used this resource yet, but at first glance it looks helpful!
Research Writing
I have not started this with my child yet, but I have looked over the information. I am really looking forward to using this. Very informative.
I absolutely love the blended
I absolutely love the blended lesson plan structure that accommodates for all types of learners. you all ROCK!!!
Excellent curriculum
Lots of subjects and ways to teach kids. Love the packets
Related products

Meriwether Lewis and William Clark

Man o’ Wars
Make your life easier with our lesson plans, stay up-to-date with new lessons.

- Lesson Plans
- For Teachers
© 2024 Learn Bright. All rights reserved. Terms and Conditions. Privacy Policy.
- Sign Up for Free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
It outlines a five-step approach to break down the research process into manageable chunks. This post shares ideas for mini-lessons that could be carried out in the classroom throughout the year to help build students’ skills in the five areas of: clarify, search, delve, evaluate, and cite. It also includes ideas for learning about staying ...
Step 1: Choose a Topic and Cite Sources. Students definitely get excited when they find out they may choose their own research topic. Providing choice leads to higher engagement and interest. It’s best practice to provide a list of possible research topics to students, but also allow them to choose a different topic.
Olivia Franklin. Engage students with interesting research topics, teach them skills to become adept independent researchers, and help them craft their end-of-unit research papers. CommonLit 360 is a comprehensive ELA curriculum for grades 6-12. Our standards-aligned units are highly engaging and develop core reading and writing skills.
Help students find out with this research strategies lesson plan! Designed for a sixth-grade curriculum, this lesson provides learners with essential guidance and practice in assessing the credibility of sources. Students will use a checklist with guiding questions to explore examples and non-examples of quality resources for research.
Sixth Grade Library Lesson Plans. Sixth grade is a challenging time for students. Many have transitioned to middle school. They are adjusting to the more advanced curriculum. They also have extended responsibilities. Along with those responsibilities, sixth grade students should be encouraged to delve deeper into texts.
Our Research Writing lesson plan for grades 4-6 teaches students how to write a thoroughly researched and factually accurate five paragraph essay. Students write an essay based on research they conduct in order to practice this type of writing. Categories: Downloadable, Language Arts Tags: 4th Grade, 5th Grade, 6th Grade.