

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 3 great narrative essay examples + tips for writing.
General Education

A narrative essay is one of the most intimidating assignments you can be handed at any level of your education. Where you've previously written argumentative essays that make a point or analytic essays that dissect meaning, a narrative essay asks you to write what is effectively a story .
But unlike a simple work of creative fiction, your narrative essay must have a clear and concrete motif —a recurring theme or idea that you’ll explore throughout. Narrative essays are less rigid, more creative in expression, and therefore pretty different from most other essays you’ll be writing.
But not to fear—in this article, we’ll be covering what a narrative essay is, how to write a good one, and also analyzing some personal narrative essay examples to show you what a great one looks like.
What Is a Narrative Essay?
At first glance, a narrative essay might sound like you’re just writing a story. Like the stories you're used to reading, a narrative essay is generally (but not always) chronological, following a clear throughline from beginning to end. Even if the story jumps around in time, all the details will come back to one specific theme, demonstrated through your choice in motifs.
Unlike many creative stories, however, your narrative essay should be based in fact. That doesn’t mean that every detail needs to be pure and untainted by imagination, but rather that you shouldn’t wholly invent the events of your narrative essay. There’s nothing wrong with inventing a person’s words if you can’t remember them exactly, but you shouldn’t say they said something they weren’t even close to saying.
Another big difference between narrative essays and creative fiction—as well as other kinds of essays—is that narrative essays are based on motifs. A motif is a dominant idea or theme, one that you establish before writing the essay. As you’re crafting the narrative, it’ll feed back into your motif to create a comprehensive picture of whatever that motif is.
For example, say you want to write a narrative essay about how your first day in high school helped you establish your identity. You might discuss events like trying to figure out where to sit in the cafeteria, having to describe yourself in five words as an icebreaker in your math class, or being unsure what to do during your lunch break because it’s no longer acceptable to go outside and play during lunch. All of those ideas feed back into the central motif of establishing your identity.
The important thing to remember is that while a narrative essay is typically told chronologically and intended to read like a story, it is not purely for entertainment value. A narrative essay delivers its theme by deliberately weaving the motifs through the events, scenes, and details. While a narrative essay may be entertaining, its primary purpose is to tell a complete story based on a central meaning.
Unlike other essay forms, it is totally okay—even expected—to use first-person narration in narrative essays. If you’re writing a story about yourself, it’s natural to refer to yourself within the essay. It’s also okay to use other perspectives, such as third- or even second-person, but that should only be done if it better serves your motif. Generally speaking, your narrative essay should be in first-person perspective.
Though your motif choices may feel at times like you’re making a point the way you would in an argumentative essay, a narrative essay’s goal is to tell a story, not convince the reader of anything. Your reader should be able to tell what your motif is from reading, but you don’t have to change their mind about anything. If they don’t understand the point you are making, you should consider strengthening the delivery of the events and descriptions that support your motif.
Narrative essays also share some features with analytical essays, in which you derive meaning from a book, film, or other media. But narrative essays work differently—you’re not trying to draw meaning from an existing text, but rather using an event you’ve experienced to convey meaning. In an analytical essay, you examine narrative, whereas in a narrative essay you create narrative.
The structure of a narrative essay is also a bit different than other essays. You’ll generally be getting your point across chronologically as opposed to grouping together specific arguments in paragraphs or sections. To return to the example of an essay discussing your first day of high school and how it impacted the shaping of your identity, it would be weird to put the events out of order, even if not knowing what to do after lunch feels like a stronger idea than choosing where to sit. Instead of organizing to deliver your information based on maximum impact, you’ll be telling your story as it happened, using concrete details to reinforce your theme.

3 Great Narrative Essay Examples
One of the best ways to learn how to write a narrative essay is to look at a great narrative essay sample. Let’s take a look at some truly stellar narrative essay examples and dive into what exactly makes them work so well.
A Ticket to the Fair by David Foster Wallace
Today is Press Day at the Illinois State Fair in Springfield, and I’m supposed to be at the fairgrounds by 9:00 A.M. to get my credentials. I imagine credentials to be a small white card in the band of a fedora. I’ve never been considered press before. My real interest in credentials is getting into rides and shows for free. I’m fresh in from the East Coast, for an East Coast magazine. Why exactly they’re interested in the Illinois State Fair remains unclear to me. I suspect that every so often editors at East Coast magazines slap their foreheads and remember that about 90 percent of the United States lies between the coasts, and figure they’ll engage somebody to do pith-helmeted anthropological reporting on something rural and heartlandish. I think they asked me to do this because I grew up here, just a couple hours’ drive from downstate Springfield. I never did go to the state fair, though—I pretty much topped out at the county fair level. Actually, I haven’t been back to Illinois for a long time, and I can’t say I’ve missed it.
Throughout this essay, David Foster Wallace recounts his experience as press at the Illinois State Fair. But it’s clear from this opening that he’s not just reporting on the events exactly as they happened—though that’s also true— but rather making a point about how the East Coast, where he lives and works, thinks about the Midwest.
In his opening paragraph, Wallace states that outright: “Why exactly they’re interested in the Illinois State Fair remains unclear to me. I suspect that every so often editors at East Coast magazines slap their foreheads and remember that about 90 percent of the United States lies between the coasts, and figure they’ll engage somebody to do pith-helmeted anthropological reporting on something rural and heartlandish.”
Not every motif needs to be stated this clearly , but in an essay as long as Wallace’s, particularly since the audience for such a piece may feel similarly and forget that such a large portion of the country exists, it’s important to make that point clear.
But Wallace doesn’t just rest on introducing his motif and telling the events exactly as they occurred from there. It’s clear that he selects events that remind us of that idea of East Coast cynicism , such as when he realizes that the Help Me Grow tent is standing on top of fake grass that is killing the real grass beneath, when he realizes the hypocrisy of craving a corn dog when faced with a real, suffering pig, when he’s upset for his friend even though he’s not the one being sexually harassed, and when he witnesses another East Coast person doing something he wouldn’t dare to do.
Wallace is literally telling the audience exactly what happened, complete with dates and timestamps for when each event occurred. But he’s also choosing those events with a purpose—he doesn’t focus on details that don’t serve his motif. That’s why he discusses the experiences of people, how the smells are unappealing to him, and how all the people he meets, in cowboy hats, overalls, or “black spandex that looks like cheesecake leotards,” feel almost alien to him.
All of these details feed back into the throughline of East Coast thinking that Wallace introduces in the first paragraph. He also refers back to it in the essay’s final paragraph, stating:
At last, an overarching theory blooms inside my head: megalopolitan East Coasters’ summer treats and breaks and literally ‘getaways,’ flights-from—from crowds, noise, heat, dirt, the stress of too many sensory choices….The East Coast existential treat is escape from confines and stimuli—quiet, rustic vistas that hold still, turn inward, turn away. Not so in the rural Midwest. Here you’re pretty much away all the time….Something in a Midwesterner sort of actuates , deep down, at a public event….The real spectacle that draws us here is us.
Throughout this journey, Wallace has tried to demonstrate how the East Coast thinks about the Midwest, ultimately concluding that they are captivated by the Midwest’s less stimuli-filled life, but that the real reason they are interested in events like the Illinois State Fair is that they are, in some ways, a means of looking at the East Coast in a new, estranging way.
The reason this works so well is that Wallace has carefully chosen his examples, outlined his motif and themes in the first paragraph, and eventually circled back to the original motif with a clearer understanding of his original point.
When outlining your own narrative essay, try to do the same. Start with a theme, build upon it with examples, and return to it in the end with an even deeper understanding of the original issue. You don’t need this much space to explore a theme, either—as we’ll see in the next example, a strong narrative essay can also be very short.
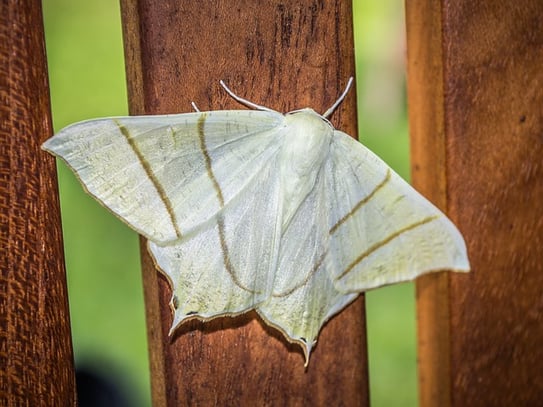

Death of a Moth by Virginia Woolf
After a time, tired by his dancing apparently, he settled on the window ledge in the sun, and, the queer spectacle being at an end, I forgot about him. Then, looking up, my eye was caught by him. He was trying to resume his dancing, but seemed either so stiff or so awkward that he could only flutter to the bottom of the window-pane; and when he tried to fly across it he failed. Being intent on other matters I watched these futile attempts for a time without thinking, unconsciously waiting for him to resume his flight, as one waits for a machine, that has stopped momentarily, to start again without considering the reason of its failure. After perhaps a seventh attempt he slipped from the wooden ledge and fell, fluttering his wings, on to his back on the window sill. The helplessness of his attitude roused me. It flashed upon me that he was in difficulties; he could no longer raise himself; his legs struggled vainly. But, as I stretched out a pencil, meaning to help him to right himself, it came over me that the failure and awkwardness were the approach of death. I laid the pencil down again.
In this essay, Virginia Woolf explains her encounter with a dying moth. On surface level, this essay is just a recounting of an afternoon in which she watched a moth die—it’s even established in the title. But there’s more to it than that. Though Woolf does not begin her essay with as clear a motif as Wallace, it’s not hard to pick out the evidence she uses to support her point, which is that the experience of this moth is also the human experience.
In the title, Woolf tells us this essay is about death. But in the first paragraph, she seems to mostly be discussing life—the moth is “content with life,” people are working in the fields, and birds are flying. However, she mentions that it is mid-September and that the fields were being plowed. It’s autumn and it’s time for the harvest; the time of year in which many things die.
In this short essay, she chronicles the experience of watching a moth seemingly embody life, then die. Though this essay is literally about a moth, it’s also about a whole lot more than that. After all, moths aren’t the only things that die—Woolf is also reflecting on her own mortality, as well as the mortality of everything around her.
At its core, the essay discusses the push and pull of life and death, not in a way that’s necessarily sad, but in a way that is accepting of both. Woolf begins by setting up the transitional fall season, often associated with things coming to an end, and raises the ideas of pleasure, vitality, and pity.
At one point, Woolf tries to help the dying moth, but reconsiders, as it would interfere with the natural order of the world. The moth’s death is part of the natural order of the world, just like fall, just like her own eventual death.
All these themes are set up in the beginning and explored throughout the essay’s narrative. Though Woolf doesn’t directly state her theme, she reinforces it by choosing a small, isolated event—watching a moth die—and illustrating her point through details.
With this essay, we can see that you don’t need a big, weird, exciting event to discuss an important meaning. Woolf is able to explore complicated ideas in a short essay by being deliberate about what details she includes, just as you can be in your own essays.
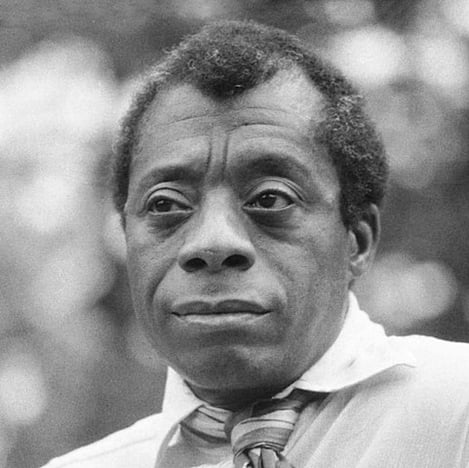

Notes of a Native Son by James Baldwin
On the twenty-ninth of July, in 1943, my father died. On the same day, a few hours later, his last child was born. Over a month before this, while all our energies were concentrated in waiting for these events, there had been, in Detroit, one of the bloodiest race riots of the century. A few hours after my father’s funeral, while he lay in state in the undertaker’s chapel, a race riot broke out in Harlem. On the morning of the third of August, we drove my father to the graveyard through a wilderness of smashed plate glass.
Like Woolf, Baldwin does not lay out his themes in concrete terms—unlike Wallace, there’s no clear sentence that explains what he’ll be talking about. However, you can see the motifs quite clearly: death, fatherhood, struggle, and race.
Throughout the narrative essay, Baldwin discusses the circumstances of his father’s death, including his complicated relationship with his father. By introducing those motifs in the first paragraph, the reader understands that everything discussed in the essay will come back to those core ideas. When Baldwin talks about his experience with a white teacher taking an interest in him and his father’s resistance to that, he is also talking about race and his father’s death. When he talks about his father’s death, he is also talking about his views on race. When he talks about his encounters with segregation and racism, he is talking, in part, about his father.
Because his father was a hard, uncompromising man, Baldwin struggles to reconcile the knowledge that his father was right about many things with his desire to not let that hardness consume him, as well.
Baldwin doesn’t explicitly state any of this, but his writing so often touches on the same motifs that it becomes clear he wants us to think about all these ideas in conversation with one another.
At the end of the essay, Baldwin makes it more clear:
This fight begins, however, in the heart and it had now been laid to my charge to keep my own heart free of hatred and despair. This intimation made my heart heavy and, now that my father was irrecoverable, I wished that he had been beside me so that I could have searched his face for the answers which only the future would give me now.
Here, Baldwin ties together the themes and motifs into one clear statement: that he must continue to fight and recognize injustice, especially racial injustice, just as his father did. But unlike his father, he must do it beginning with himself—he must not let himself be closed off to the world as his father was. And yet, he still wishes he had his father for guidance, even as he establishes that he hopes to be a different man than his father.
In this essay, Baldwin loads the front of the essay with his motifs, and, through his narrative, weaves them together into a theme. In the end, he comes to a conclusion that connects all of those things together and leaves the reader with a lasting impression of completion—though the elements may have been initially disparate, in the end everything makes sense.
You can replicate this tactic of introducing seemingly unattached ideas and weaving them together in your own essays. By introducing those motifs, developing them throughout, and bringing them together in the end, you can demonstrate to your reader how all of them are related. However, it’s especially important to be sure that your motifs and clear and consistent throughout your essay so that the conclusion feels earned and consistent—if not, readers may feel mislead.
5 Key Tips for Writing Narrative Essays
Narrative essays can be a lot of fun to write since they’re so heavily based on creativity. But that can also feel intimidating—sometimes it’s easier to have strict guidelines than to have to make it all up yourself. Here are a few tips to keep your narrative essay feeling strong and fresh.
Develop Strong Motifs
Motifs are the foundation of a narrative essay . What are you trying to say? How can you say that using specific symbols or events? Those are your motifs.
In the same way that an argumentative essay’s body should support its thesis, the body of your narrative essay should include motifs that support your theme.
Try to avoid cliches, as these will feel tired to your readers. Instead of roses to symbolize love, try succulents. Instead of the ocean representing some vast, unknowable truth, try the depths of your brother’s bedroom. Keep your language and motifs fresh and your essay will be even stronger!
Use First-Person Perspective
In many essays, you’re expected to remove yourself so that your points stand on their own. Not so in a narrative essay—in this case, you want to make use of your own perspective.
Sometimes a different perspective can make your point even stronger. If you want someone to identify with your point of view, it may be tempting to choose a second-person perspective. However, be sure you really understand the function of second-person; it’s very easy to put a reader off if the narration isn’t expertly deployed.
If you want a little bit of distance, third-person perspective may be okay. But be careful—too much distance and your reader may feel like the narrative lacks truth.
That’s why first-person perspective is the standard. It keeps you, the writer, close to the narrative, reminding the reader that it really happened. And because you really know what happened and how, you’re free to inject your own opinion into the story without it detracting from your point, as it would in a different type of essay.
Stick to the Truth
Your essay should be true. However, this is a creative essay, and it’s okay to embellish a little. Rarely in life do we experience anything with a clear, concrete meaning the way somebody in a book might. If you flub the details a little, it’s okay—just don’t make them up entirely.
Also, nobody expects you to perfectly recall details that may have happened years ago. You may have to reconstruct dialog from your memory and your imagination. That’s okay, again, as long as you aren’t making it up entirely and assigning made-up statements to somebody.
Dialog is a powerful tool. A good conversation can add flavor and interest to a story, as we saw demonstrated in David Foster Wallace’s essay. As previously mentioned, it’s okay to flub it a little, especially because you’re likely writing about an experience you had without knowing that you’d be writing about it later.
However, don’t rely too much on it. Your narrative essay shouldn’t be told through people explaining things to one another; the motif comes through in the details. Dialog can be one of those details, but it shouldn’t be the only one.
Use Sensory Descriptions
Because a narrative essay is a story, you can use sensory details to make your writing more interesting. If you’re describing a particular experience, you can go into detail about things like taste, smell, and hearing in a way that you probably wouldn’t do in any other essay style.
These details can tie into your overall motifs and further your point. Woolf describes in great detail what she sees while watching the moth, giving us the sense that we, too, are watching the moth. In Wallace’s essay, he discusses the sights, sounds, and smells of the Illinois State Fair to help emphasize his point about its strangeness. And in Baldwin’s essay, he describes shattered glass as a “wilderness,” and uses the feelings of his body to describe his mental state.
All these descriptions anchor us not only in the story, but in the motifs and themes as well. One of the tools of a writer is making the reader feel as you felt, and sensory details help you achieve that.
What’s Next?
Looking to brush up on your essay-writing capabilities before the ACT? This guide to ACT English will walk you through some of the best strategies and practice questions to get you prepared!
Part of practicing for the ACT is ensuring your word choice and diction are on point. Check out this guide to some of the most common errors on the ACT English section to be sure that you're not making these common mistakes!
A solid understanding of English principles will help you make an effective point in a narrative essay, and you can get that understanding through taking a rigorous assortment of high school English classes !
Need more help with this topic? Check out Tutorbase!
Our vetted tutor database includes a range of experienced educators who can help you polish an essay for English or explain how derivatives work for Calculus. You can use dozens of filters and search criteria to find the perfect person for your needs.

Melissa Brinks graduated from the University of Washington in 2014 with a Bachelor's in English with a creative writing emphasis. She has spent several years tutoring K-12 students in many subjects, including in SAT prep, to help them prepare for their college education.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Narrative Essay with Tips - a Detailed Guide

Defining What Is a Narrative Essay
We can explain a narrative essay definition as a piece of writing that tells a story. It's like a window into someone's life or a page torn from a diary. Similarly to a descriptive essay, a narrative essay tells a story, rather than make a claim and use evidence. It can be about anything – a personal experience, a childhood memory, a moment of triumph or defeat – as long as it's told in a way that captures the reader's imagination.
You might ask - 'which sentence most likely comes from a narrative essay?'. Let's take this for example: 'I could hear the waves crashing against the shore, their rhythm a soothing lullaby that carried me off to sleep.' You could even use such an opening for your essay when wondering how to start a narrative essay.
To further define a narrative essay, consider it storytelling with a purpose. The purpose of a narrative essay is not just to entertain but also to convey a message or lesson in first person. It's a way to share your experiences and insights with others and connect with your audience. Whether you're writing about your first love, a harrowing adventure, or a life-changing moment, your goal is to take the reader on a journey that will leave them feeling moved, inspired, or enlightened.
So if you're looking for a way to express yourself creatively and connect with others through your writing, try your hand at a narrative essay. Who knows – you might just discover a hidden talent for storytelling that you never knew you had!
Meanwhile, let's delve into the article to better understand this type of paper through our narrative essay examples, topic ideas, and tips on constructing a perfect essay.
Types of Narrative Essays
If you were wondering, 'what is a personal narrative essay?', know that narrative essays come in different forms, each with a unique structure and purpose. Regardless of the type of narrative essay, each aims to transport the reader to a different time and place and to create an emotional connection between the reader and the author's experiences. So, let's discuss each type in more detail:
- A personal narrative essay is based on one's unique experience or event. Personal narrative essay examples include a story about overcoming a fear or obstacle or reflecting on a particularly meaningful moment in one's life.
- A fictional narrative is a made-up story that still follows the basic elements of storytelling. Fictional narratives can take many forms, from science fiction to romance to historical fiction.
- A memoir is similar to personal narratives but focuses on a specific period or theme in a person's life. Memoirs might be centered around a particular relationship, a struggle with addiction, or a cultural identity. If you wish to describe your life in greater depth, you might look at how to write an autobiography .
- A literacy narrative essay explores the writer's experiences with literacy and how it has influenced their life. The essay typically tells a personal story about a significant moment or series of moments that impacted the writer's relationship with reading, writing, or communication.
You might also be interested in discovering 'HOW TO WRITE AN AUTOBIOGRAPHY'
Pros and Cons of Narrative Writing
Writing a narrative essay can be a powerful tool for self-expression and creative storytelling, but like any form of writing, it comes with its own set of pros and cons. Let's explore the pros and cons of narrative writing in more detail, helping you to decide whether it's the right writing style for your needs.
- It can be a powerful way to convey personal experiences and emotions.
- Allows for creative expression and unique voice
- Engages the reader through storytelling and vivid details
- It can be used to teach a lesson or convey a message.
- Offers an opportunity for self-reflection and growth
- It can be challenging to balance personal storytelling with the needs of the reader
- It may not be as effective for conveying factual information or arguments
- It may require vulnerability and sharing personal details that some writers may find uncomfortable
- It can be subjective, as the reader's interpretation of the narrative may vary
If sharing your personal stories is not your cup of tea, you can buy essays online from our expert writers, who will customize the paper to your particular writing style and tone.
20 Excellent Narrative Essay Topics and How to Choose One
Choosing a good topic among many narrative essay ideas can be challenging, but some tips can help you make the right choice. Here are some original and helpful tips on how to choose a good narrative essay topic:
- Consider your own experiences: One of the best sources of inspiration for a narrative essay is your own life experiences. Consider moments that have had a significant impact on you, whether they are positive or negative. For example, you could write about a memorable trip or a challenging experience you overcame.
- Choose a topic relevant to your audience: Consider your audience and their interests when choosing a narrative essay topic. If you're writing for a class, consider what topics might be relevant to the course material. If you're writing for a broader audience, consider what topics might be interesting or informative to them.
- Find inspiration in literature: Literature can be a great source of inspiration for a narrative essay. Consider the books or stories that have had an impact on you, and think about how you can incorporate elements of them into your own narrative. For example, you could start by using a title for narrative essay inspired by the themes of a favorite novel or short story.
- Focus on a specific moment or event: Most narrative essays tell a story, so it's important to focus on a specific moment or event. For example, you could write a short narrative essay about a conversation you had with a friend or a moment of realization while traveling.
- Experiment with different perspectives: Consider writing from different perspectives to add depth and complexity to your narrative. For example, you could write about the same event from multiple perspectives or explore the thoughts and feelings of a secondary character.
- Use writing prompts: Writing prompts can be a great source of inspiration if you struggle to develop a topic. Consider using a prompt related to a specific theme, such as love, loss, or growth.
- Choose a topic with rich sensory details: A good narrative essay should engage the senses and create a vivid picture in the reader's mind. Choose a topic with rich sensory details that you can use to create a vivid description. For example, you could write about a bustling city's sights, sounds, and smells.
- Choose a topic meaningful to you: Ultimately, the best narrative essays are meaningful to the writer. Choose a topic that resonates with you and that you feel passionate about. For example, you could write about a personal goal you achieved or a struggle you overcame.
Here are some good narrative essay topics for inspiration from our experts:
- A life-changing event that altered your perspective on the world
- The story of a personal accomplishment or achievement
- An experience that tested your resilience and strength
- A time when you faced a difficult decision and how you handled it
- A childhood memory that still holds meaning for you
- The impact of a significant person in your life
- A travel experience that taught you something new
- A story about a mistake or failure that ultimately led to growth and learning
- The first day of a new job or school
- The story of a family tradition or ritual that is meaningful to you
- A time when you had to confront a fear or phobia
- A memorable concert or music festival experience
- An experience that taught you the importance of communication or listening
- A story about a time when you had to stand up for what you believed in
- A time when you had to persevere through a challenging task or project
- A story about a significant cultural or societal event that impacted your life
- The impact of a book, movie, or other work of art on your life
- A time when you had to let go of something or someone important to you
- A memorable encounter with a stranger that left an impression on you
- The story of a personal hobby or interest that has enriched your life
Narrative Format and Structure
The narrative essay format and structure are essential elements of any good story. A well-structured narrative can engage readers, evoke emotions, and create lasting memories. Whether you're writing a personal essay or a work of fiction, the following guidelines on how to write a narrative essay can help you create a compelling paper:

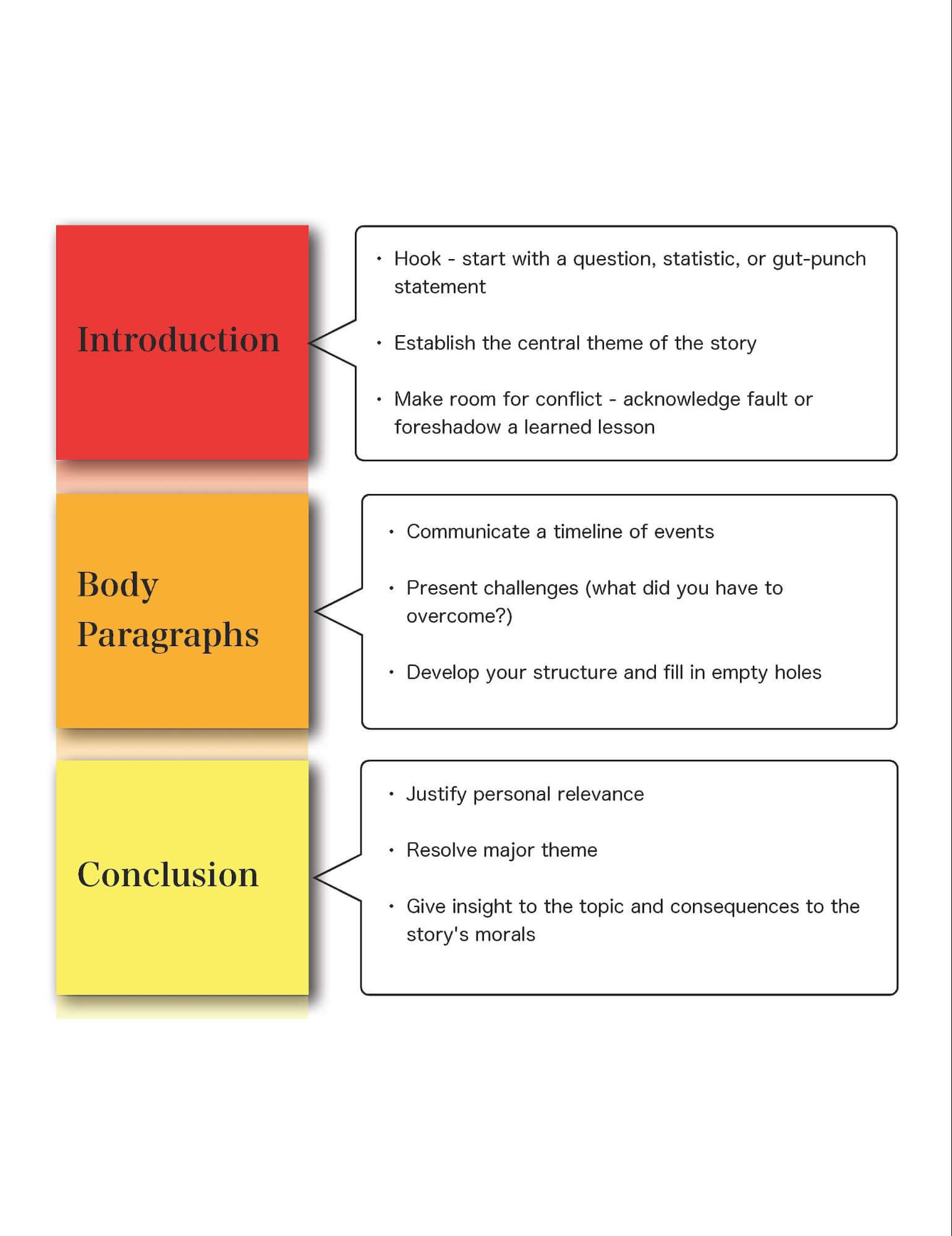
- Introduction : The introduction sets the scene for your story and introduces your main characters and setting. It should also provide a hook to capture your reader's attention and make them want to keep reading. When unsure how to begin a narrative essay, describe the setting vividly or an intriguing question that draws the reader in.
- Plot : The plot is the sequence of events that make up your story. It should have a clear beginning, middle, and end, with each part building on the previous one. The plot should also have a clear conflict or problem the protagonist must overcome.
- Characters : Characters are the people who drive the story. They should be well-developed and have distinct personalities and motivations. The protagonist should have a clear goal or desire, and the antagonist should provide a challenge or obstacle to overcome.
- Setting : The setting is the time and place the story takes place. It should be well-described and help to create a mood or atmosphere that supports the story's themes.
- Dialogue : Dialogue is the conversation between characters. It should be realistic and help to reveal the characters' personalities and motivations. It can also help to move the plot forward.
- Climax : The climax is the highest tension or conflict point in the story. It should be the turning point that leads to resolving the conflict.
- Resolution : The resolution is the end of the story. It should provide a satisfying conclusion to the conflict and tie up any loose ends.
Following these guidelines, you can create a narrative essay structure that engages readers and leaves a lasting impression. Remember, a well-structured story can take readers on a journey and make them feel part of the action.
Want to Be Like an Expert Writer?
Order now and let our narrative essay service turn your experiences into a captivating and unforgettable tale
Narrative Essay Outline
Here is a detailed narrative essay outline from our custom term paper writing :
Introduction
A. Hook: Start with an attention-grabbing statement, question, or anecdote that introduces the topic and draws the reader in. Example: 'The sun beat down on my skin as I stepped onto the stage, my heart pounding with nervous excitement.'
B. Background information: Provide context for the story, such as the setting or the characters involved. Example: 'I had been preparing for this moment for weeks, rehearsing my lines and perfecting my performance for the school play.'
C. Thesis statement: State the essay's main point and preview the events to come. Example: 'This experience taught me that taking risks and stepping outside my comfort zone can lead to unexpected rewards and personal growth.'
Body Paragraphs
A. First event: Describe the first event in the story, including details about the setting, characters, and actions. Example: 'As I delivered my first lines on stage, I felt a rush of adrenaline and a sense of pride in my hard work paying off.'
B. Second event: Describe the second event in the story, including how it builds on the first event and moves the story forward. Example: 'As the play progressed, I became more comfortable in my role and connecting with the other actors on stage.'
C. Turning point: Describe the turning point in the story, when something unexpected or significant changes the course of events. Example: 'In the final act, my character faced a difficult decision that required me to improvise and trust my instincts.'
D. Climax: Describe the story's climax, the highest tension or conflict point. Example: 'As the play reached its climax, I delivered my final lines with confidence and emotion, feeling a sense of accomplishment and fulfillment.'
A. Restate thesis: Summarize the essay's main point and how the events in the story support it. Example: 'Through this experience, I learned that taking risks and pushing past my comfort zone can lead to personal growth and unexpected rewards.'
B. Reflection: Reflect on the significance of the experience and what you learned from it. Example: 'Looking back, I realize that this experience not only taught me about acting and performance but also about the power of perseverance and self-belief.'
C. Call to action: if you're still wondering how to write an essay conclusion , consider ending it with a call to action or final thought that leaves the reader with something to consider or act on. Example: 'I encourage everyone to take risks and embrace new challenges because you never know what kind of amazing experiences and growth they may lead to.
You might also be interested in getting detailed info on 'HOW TO WRITE AN ESSAY CONCLUSION'
Narrative Essay Examples
Are you looking for inspiration for your next narrative essay? Look no further than our narrative essay example. Through vivid storytelling and personal reflections, this essay takes the reader on a journey of discovery and leaves them with a powerful lesson about the importance of compassion and empathy. Use this sample from our expert essay writer as a guide for crafting your own narrative essay, and let your unique voice and experiences shine through.
Narrative Essay Example for College
College professors search for the following qualities in their students:
- the ability to adapt to different situations,
- the ability to solve problems creatively,
- and the ability to learn from mistakes.
Your work must demonstrate these qualities, regardless of whether your narrative paper is a college application essay or a class assignment. Additionally, you want to demonstrate your character and creativity. Describe a situation where you have encountered a problem, tell the story of how you came up with a unique approach to solving it, and connect it to your field of interest. The narrative can be exciting and informative if you present it in such fashion.
Narrative Essay Example for High School
High school is all about showing that you can make mature choices. You accept the consequences of your actions and retrieve valuable life lessons. Think of an event in which you believe your actions were exemplary and made an adult choice. A personal narrative essay example will showcase the best of your abilities. Finally, use other sources to help you get the best results possible. Try searching for a sample narrative essay to see how others have approached it.
Final Words
So now that you know what is a narrative essay you might want to produce high-quality paper. For that let our team of experienced writers help. Our research paper writing service offers a range of professional writing services that cater to your unique needs and requirements, from narrative essays to medical personal statement , also offering dissertation help and more.
With our flexible pricing options and fast turnaround times, you can trust that you'll receive great value for your investment. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you succeed in your academic writing journey.
Unlock Your Potential with Our Essays!
Order now and take the first step towards achieving your academic goals
Related Articles
.webp)
BibGuru Blog
Be more productive in school
- Citation Styles
How to write a narrative essay [Updated 2023]

A narrative essay is an opportunity to flex your creative muscles and craft a compelling story. In this blog post, we define what a narrative essay is and provide strategies and examples for writing one.
What is a narrative essay?
Similarly to a descriptive essay or a reflective essay, a narrative essay asks you to tell a story, rather than make an argument and present evidence. Most narrative essays describe a real, personal experience from your own life (for example, the story of your first big success).
Alternately, your narrative essay might focus on an imagined experience (for example, how your life would be if you had been born into different circumstances). While you don’t need to present a thesis statement or scholarly evidence, a narrative essay still needs to be well-structured and clearly organized so that the reader can follow your story.
When you might be asked to write a narrative essay
Although less popular than argumentative essays or expository essays, narrative essays are relatively common in high school and college writing classes.
The same techniques that you would use to write a college essay as part of a college or scholarship application are applicable to narrative essays, as well. In fact, the Common App that many students use to apply to multiple colleges asks you to submit a narrative essay.
How to choose a topic for a narrative essay
When you are asked to write a narrative essay, a topic may be assigned to you or you may be able to choose your own. With an assigned topic, the prompt will likely fall into one of two categories: specific or open-ended.
Examples of specific prompts:
- Write about the last vacation you took.
- Write about your final year of middle school.
Examples of open-ended prompts:
- Write about a time when you felt all hope was lost.
- Write about a brief, seemingly insignificant event that ended up having a big impact on your life.
A narrative essay tells a story and all good stories are centered on a conflict of some sort. Experiences with unexpected obstacles, twists, or turns make for much more compelling essays and reveal more about your character and views on life.
If you’re writing a narrative essay as part of an admissions application, remember that the people reviewing your essay will be looking at it to gain a sense of not just your writing ability, but who you are as a person.
In these cases, it’s wise to choose a topic and experience from your life that demonstrates the qualities that the prompt is looking for, such as resilience, perseverance, the ability to stay calm under pressure, etc.
It’s also important to remember that your choice of topic is just a starting point. Many students find that they arrive at new ideas and insights as they write their first draft, so the final form of your essay may have a different focus than the one you started with.
How to outline and format a narrative essay
Even though you’re not advancing an argument or proving a point of view, a narrative essay still needs to have a coherent structure. Your reader has to be able to follow you as you tell the story and to figure out the larger point that you’re making.
You’ll be evaluated on is your handling of the topic and how you structure your essay. Even though a narrative essay doesn’t use the same structure as other essay types, you should still sketch out a loose outline so you can tell your story in a clear and compelling way.
To outline a narrative essay, you’ll want to determine:
- how your story will start
- what points or specifics that you want to cover
- how your story will end
- what pace and tone you will use
In the vast majority of cases, a narrative essay should be written in the first-person, using “I.” Also, most narrative essays will follow typical formatting guidelines, so you should choose a readable font like Times New Roman in size 11 or 12. Double-space your paragraphs and use 1” margins.
To get your creative wheels turning, consider how your story compares to archetypes and famous historical and literary figures both past and present. Weave these comparisons into your essay to improve the quality of your writing and connect your personal experience to a larger context.
How to write a narrative essay
Writing a narrative essay can sometimes be a challenge for students who typically write argumentative essays or research papers in a formal, objective style. To give you a better sense of how you can write a narrative essay, here is a short example of an essay in response to the prompt, “Write about an experience that challenged your view of yourself.”
Narrative essay example
Even as a child, I always had what people might call a reserved personality. It was sometimes framed as a positive (“Sarah is a good listener”) and at other times it was put in less-than-admiring terms (“Sarah is withdrawn and not very talkative”). It was the latter kind of comments that caused me to see my introverted nature as a drawback and as something I should work to eliminate. That is, until I joined my high school’s student council.
The first paragraph, or introduction, sets up the context, establishing the situation and introducing the meaningful event upon which the essay will focus.
The other four students making up the council were very outspoken and enthusiastic. I enjoyed being around them, and I often agreed with their ideas. However, when it came to overhauling our school’s recycling plan, we butted heads. When I spoke up and offered a different point of view, one of my fellow student council members launched into a speech, advocating for her point of view. As her voice filled the room, I couldn’t get a word in edgewise. I wondered if I should try to match her tone, volume, and assertiveness as a way to be heard. But I just couldn’t do it—it’s not my way, and it never has been. For a fleeting moment, I felt defeated. But then, something in me shifted.
In this paragraph, the writer goes into greater depth about how her existing thinking brought her to this point.
I reminded myself that my view was valid and deserved to be heard. So I waited. I let my fellow council member speak her piece and when she was finished, I deliberately waited a few moments before calmly stating my case. I chose my words well, and I spoke them succinctly. Just because I’m not a big talker doesn’t mean I’m not a big thinker. I thought of the quotation “still waters run deep” and I tried to embody that. The effect on the room was palpable. People listened. And I hadn’t had to shout my point to be heard.
This paragraph demonstrates the turn in the story, the moment when everything changed. The use of the quotation “still waters run deep” imbues the story with a dash of poetry and emotion.
We eventually reached a compromise on the matter and concluded the student council meeting. Our council supervisor came to me afterward and said: “You handled that so well, with such grace and poise. I was very impressed.” Her words in that moment changed me. I realized that a bombastic nature isn't necessarily a powerful one. There is power in quiet, too. This experience taught me to view my reserved personality not as a character flaw, but as a strength.
The final paragraph, or conclusion, closes with a statement about the significance of this event and how it ended up changing the writer in a meaningful way.
Narrative essay writing tips
1. pick a meaningful story that has a conflict and a clear “moral.”.
If you’re able to choose your own topic, pick a story that has meaning and that reveals how you became the person your are today. In other words, write a narrative with a clear “moral” that you can connect with your main points.
2. Use an outline to arrange the structure of your story and organize your main points.
Although a narrative essay is different from argumentative essays, it’s still beneficial to construct an outline so that your story is well-structured and organized. Note how you want to start and end your story, and what points you want to make to tie everything together.
3. Be clear, concise, concrete, and correct in your writing.
You should use descriptive writing in your narrative essay, but don’t overdo it. Use clear, concise, and correct language and grammar throughout. Additionally, make concrete points that reinforce the main idea of your narrative.
4. Ask a friend or family member to proofread your essay.
No matter what kind of writing you’re doing, you should always plan to proofread and revise. To ensure that your narrative essay is coherent and interesting, ask a friend or family member to read over your paper. This is especially important if your essay is responding to a prompt. It helps to have another person check to make sure that you’ve fully responded to the prompt or question.
Frequently Asked Questions about narrative essays
A narrative essay, like any essay, has three main parts: an introduction, a body and a conclusion. Structuring and outlining your essay before you start writing will help you write a clear story that your readers can follow.
The first paragraph of your essay, or introduction, sets up the context, establishing the situation and introducing the meaningful event upon which the essay will focus.
In the vast majority of cases, a narrative essay should be written in the first-person, using “I.”
The 4 main types of essays are the argumentative essay, narrative essay, exploratory essay, and expository essay. You may be asked to write different types of essays at different points in your education.
Most narrative essays will be around five paragraphs, or more, depending on the topic and requirements. Make sure to check in with your instructor about the guidelines for your essay. If you’re writing a narrative essay for a college application, pay close attention to word or page count requirements.

Make your life easier with our productivity and writing resources.
For students and teachers.

- Scriptwriting
What is a Narrative Essay — Examples, Format & Techniques
I was in the Amazon jungle the first time I wrote a narrative essay, enlightened and enraptured by the influence of ayahuasca. That’s not true. I’ve never been to South America nor have I ever taken ayahuasca. The purpose of that opening is to show how to craft a narrative essay intro — hook, line, and sinker. Narrative essays rely on hooking the reader, and enticing them to read on. But what is a narrative essay? We’re going to break down everything you need to know about these essays — definition, examples, tips and tricks included. By the end, you’ll be ready to craft your own narrative essay for school or for publication.
What’s a Narrative Essay?
First, let’s define narrative essay.
Narrative essays share a lot of similarities with personal essays, but whereas the former can be fictional or non-fictional, the latter are strictly non-fictional. The goal of the narrative essay is to use established storytelling techniques, like theme , conflict , and irony , in a uniquely personal way.
The responsibility of the narrative essayist is to make the reader feel connected to their story, regardless of the topic. This next video explores how writers can use structural elements and techniques to better engage their readers.
Personal Narrative Essay Examples With Essay Pro
Narrative essays rely on tried and true structure components, including:
- First-person POV
- Personal inspiration
- Focus on a central theme
By keeping these major tenets in mind, you’ll be better prepared to recognize weaknesses and strengths in your own works.
NARRATIVE ESSAY DEFINITION
What is a narrative essay.
A narrative essay is a prose-written story that’s focused on the commentary of a central theme. Narrative essays are generally written in the first-person POV, and are usually about a topic that’s personal to the writer. Everything in these essays should take place in an established timeline, with a clear beginning, middle, and end.
Famous Narrative Essay Examples
- Ticker to the Fair by David Foster Wallace
- After Life by Joan Didion
- Here is a Lesson in Creative Writing by Kurt Vonnegut
Narrative Writing Explained
How to start a narrative essay.
When you go to sleep at night, what do you think of? Flying squirrels? Lost loved ones? That time you called your teacher ‘mom’? Whatever it is, that’s what you need to write about. There’s a reason those ideas and moments have stuck with you over time. Your job is to figure out why.
Once you realize what makes a moment important to you, it’s your job to make it important to the reader too. In this next video, Academy Award-nominated filmmaker J. Christian Jensen explains the power of the personal narrative.
Narrative Writing and the Personal Narrative Essay • Video by TEDx Talks
Anything and everything can be the topic of your essay. It could be as benign as a walk to school or as grandiose as a trip to the moon — so long as that narrative exists within reality. Give your thoughts and opinions on the matter too — don’t be afraid to say “this is what I think” so long as it’s supported by storytelling techniques. Remember, never limit yourself as a writer, just keep in mind that certain topics will be harder to make engaging than others.
Narrative Essay Outline
How to write a narrative essay.
First step, game plan. You’re going to want to map out the story from beginning to end, then mark major story beats in your document.
Like all stories, your narrative essay needs a clear beginning, middle, and end. Each section should generally conform to a specifically outlined structure. For reference, check out the outline below.
Narrative Essay Format • How to Write a Narrative Essay Step by Step
Make sure to reference back to this outline throughout the writing process to make sure you have all your major beats covered.
Purpose of narrative essay writing
Narrative essays give writers the ability to freely express themselves within the structure of a traditional story. Nearly all universities ask applicants to submit a narrative essay with their formal application. This is done for two reasons: they allow institutions to judge the linguistic and grammar capabilities of its applicants, as well as their raw creative side.
If you’re considering studying creative writing in an undergraduate or graduate program, then you’re going to write A LOT of narrative style essays. This process may seem indomitable; How am I supposed to write hundreds of pages about… me? But by the end, you’ll be a better writer and you’ll have a better understanding of yourself.
One thing that all successful essayists have in common is that they make radical, often defiant statements on the world at large. Think Ralph Waldo Emerson, Virginia Woolf, and Langston Hughes for example.
Being a professional essayist isn’t easy, and it’s near-impossible to be one who makes a lot of money. Many essayists work as professors, editors, and curriculum designers as well.
This next video features the late, award-winning essayist Brian Doyle. He explains all the things you need to hear when thinking about writing a story.
Narrative Essay Examples “Lecture” via Boston University
We can learn a lot from the way Doyle “opens” his stories. My favorite is how he begins with the statement, “I met the Dalai Lama once.” How can we not be interested in learning more?
This brings us all the way back to the beginning. Start with a hook, rattle off the line, then reel in the sinker. If you entice the reader, develop a personal plot, and finish with a resolute ending, you’ll have a lot of success in essay writing.
Up Next
Narrative essay topics.
We've curated a collection of narrative essay topics that will spark your creativity and bring your experiences to life. Dive into the rich tapestry of your memories, explore the unique threads of your life, and let your narrative unfold.
Up Next: Narrative Essay Topics →
Write and produce your scripts all in one place..
Write and collaborate on your scripts FREE . Create script breakdowns, sides, schedules, storyboards, call sheets and more.
- Pricing & Plans
- Product Updates
- Featured On
- StudioBinder Partners
- The Ultimate Guide to Call Sheets (with FREE Call Sheet Template)
- How to Break Down a Script (with FREE Script Breakdown Sheet)
- The Only Shot List Template You Need — with Free Download
- Managing Your Film Budget Cashflow & PO Log (Free Template)
- A Better Film Crew List Template Booking Sheet
- Best Storyboard Softwares (with free Storyboard Templates)
- Movie Magic Scheduling
- Gorilla Software
- Storyboard That
A visual medium requires visual methods. Master the art of visual storytelling with our FREE video series on directing and filmmaking techniques.
We’re in a golden age of TV writing and development. More and more people are flocking to the small screen to find daily entertainment. So how can you break put from the pack and get your idea onto the small screen? We’re here to help.
- Making It: From Pre-Production to Screen
- What is Film Marketing — How to Sell Movies to an Audience
- What is Freytag's Pyramid — 5 Steps of Story Structure
- Titanic Script PDF Download — Plot, Quotes, and Analysis
- What is a Cross Fade Transition — Definitions & Examples
- What is a Demo Reel & How to Make One (& Why You Should)
- 1 Pinterest
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Academy FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Telling the Story of Yourself: 6 Steps to Writing Personal Narratives

Jennifer Xue

Table of Contents
Why do we write personal narratives, 6 guidelines for writing personal narrative essays, inspiring personal narratives, examples of personal narrative essays, tell your story.
First off, you might be wondering: what is a personal narrative? In short, personal narratives are stories we tell about ourselves that focus on our growth, lessons learned, and reflections on our experiences.
From stories about inspirational figures we heard as children to any essay, article, or exercise where we're asked to express opinions on a situation, thing, or individual—personal narratives are everywhere.
According to Psychology Today, personal narratives allow authors to feel and release pains, while savouring moments of strength and resilience. Such emotions provide an avenue for both authors and readers to connect while supporting healing in the process.
That all sounds great. But when it comes to putting the words down on paper, we often end up with a list of experiences and no real structure to tie them together.
In this article, we'll discuss what a personal narrative essay is further, learn the 6 steps to writing one, and look at some examples of great personal narratives.
As readers, we're fascinated by memoirs, autobiographies, and long-form personal narrative articles, as they provide a glimpse into the authors' thought processes, ideas, and feelings. But you don't have to be writing your whole life story to create a personal narrative.
You might be a student writing an admissions essay , or be trying to tell your professional story in a cover letter. Regardless of your purpose, your narrative will focus on personal growth, reflections, and lessons.
Personal narratives help us connect with other people's stories due to their easy-to-digest format and because humans are empathising creatures.
We can better understand how others feel and think when we were told stories that allow us to see the world from their perspectives. The author's "I think" and "I feel" instantaneously become ours, as the brain doesn't know whether what we read is real or imaginary.
In her best-selling book Wired for Story, Lisa Cron explains that the human brain craves tales as it's hard-wired through evolution to learn what happens next. Since the brain doesn't know whether what you are reading is actual or not, we can register the moral of the story cognitively and affectively.
In academia, a narrative essay tells a story which is experiential, anecdotal, or personal. It allows the author to creatively express their thoughts, feelings, ideas, and opinions. Its length can be anywhere from a few paragraphs to hundreds of pages.
Outside of academia, personal narratives are known as a form of journalism or non-fiction works called "narrative journalism." Even highly prestigious publications like the New York Times and Time magazine have sections dedicated to personal narratives. The New Yorke is a magazine dedicated solely to this genre.
The New York Times holds personal narrative essay contests. The winners are selected because they:
had a clear narrative arc with a conflict and a main character who changed in some way. They artfully balanced the action of the story with reflection on what it meant to the writer. They took risks, like including dialogue or playing with punctuation, sentence structure and word choice to develop a strong voice. And, perhaps most important, they focused on a specific moment or theme – a conversation, a trip to the mall, a speech tournament, a hospital visit – instead of trying to sum up the writer’s life in 600 words.
In a nutshell, a personal narrative can cover any reflective and contemplative subject with a strong voice and a unique perspective, including uncommon private values. It's written in first person and the story encompasses a specific moment in time worthy of a discussion.
Writing a personal narrative essay involves both objectivity and subjectivity. You'll need to be objective enough to recognise the importance of an event or a situation to explore and write about. On the other hand, you must be subjective enough to inject private thoughts and feelings to make your point.
With personal narratives, you are both the muse and the creator – you have control over how your story is told. However, like any other type of writing, it comes with guidelines.
1. Write Your Personal Narrative as a Story
As a story, it must include an introduction, characters, plot, setting, climax, anti-climax (if any), and conclusion. Another way to approach it is by structuring it with an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should set the tone, while the body should focus on the key point(s) you want to get across. The conclusion can tell the reader what lessons you have learned from the story you've just told.
2. Give Your Personal Narrative a Clear Purpose
Your narrative essay should reflect your unique perspective on life. This is a lot harder than it sounds. You need to establish your perspective, the key things you want your reader to take away, and your tone of voice. It's a good idea to have a set purpose in mind for the narrative before you start writing.
Let's say you want to write about how you manage depression without taking any medicine. This could go in any number of ways, but isolating a purpose will help you focus your writing and choose which stories to tell. Are you advocating for a holistic approach, or do you want to describe your emotional experience for people thinking of trying it?
Having this focus will allow you to put your own unique take on what you did (and didn't do, if applicable), what changed you, and the lessons learned along the way.
3. Show, Don't Tell
It's a narration, so the narrative should show readers what happened, instead of telling them. As well as being a storyteller, the author should take part as one of the characters. Keep this in mind when writing, as the way you shape your perspective can have a big impact on how your reader sees your overarching plot. Don't slip into just explaining everything that happened because it happened to you. Show your reader with action.
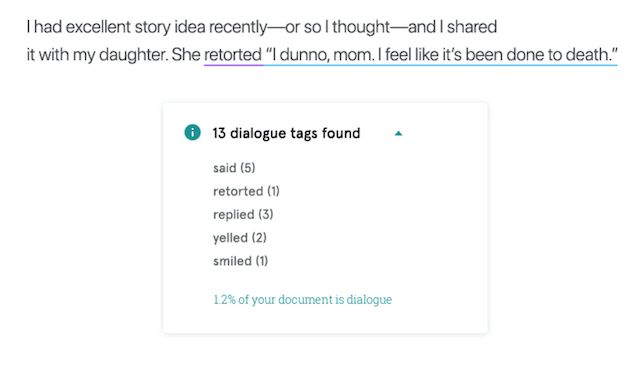
You can check for instances of telling rather than showing with ProWritingAid. For example, instead of:
"You never let me do anything!" I cried disdainfully.
"You never let me do anything!" To this day, my mother swears that the glare I levelled at her as I spat those words out could have soured milk.
Using ProWritingAid will help you find these instances in your manuscript and edit them without spending hours trawling through your work yourself.
4. Use "I," But Don't Overuse It
You, the author, take ownership of the story, so the first person pronoun "I" is used throughout. However, you shouldn't overuse it, as it'd make it sound too self-centred and redundant.
ProWritingAid can also help you here – the Style Report will tell you if you've started too many sentences with "I", and show you how to introduce more variation in your writing.
5. Pay Attention to Tenses
Tense is key to understanding. Personal narratives mostly tell the story of events that happened in the past, so many authors choose to use the past tense. This helps separate out your current, narrating voice and your past self who you are narrating. If you're writing in the present tense, make sure that you keep it consistent throughout.

6. Make Your Conclusion Satisfying
Satisfy your readers by giving them an unforgettable closing scene. The body of the narration should build up the plot to climax. This doesn't have to be something incredible or shocking, just something that helps give an interesting take on your story.
The takeaways or the lessons learned should be written without lecturing. Whenever possible, continue to show rather than tell. Don't say what you learned, narrate what you do differently now. This will help the moral of your story shine through without being too preachy.
GoodReads is a great starting point for selecting read-worthy personal narrative books. Here are five of my favourites.
Owl Moon by Jane Yolen
Jane Yolen, the author of 386 books, wrote this poetic story about a daughter and her father who went owling. Instead of learning about owls, Yolen invites readers to contemplate the meaning of gentleness and hope.
Night by Elie Wiesel
Elie Wiesel was a teenager when he and his family were sent to Auschwitz concentration camp in 1944. This Holocaust memoir has a strong message that such horrific events should never be repeated.
The Diary of a Young Girl by Anne Frank
This classic is a must-read by young and old alike. It's a remarkable diary by a 13-year-old Jewish girl who hid inside a secret annexe of an old building during the Nazi occupation of the Netherlands in 1942.
The Year of Magical Thinking by Joan Didion
This is a personal narrative written by a brave author renowned for her clarity, passion, and honesty. Didion shares how in December 2003, she lost her husband of 40 years to a massive heart attack and dealt with the acute illness of her only daughter. She speaks about grief, memories, illness, and hope.
Educated by Tara Westover
Author Tara Westover was raised by survivalist parents. She didn't go to school until 17 years of age, which later took her to Harvard and Cambridge. It's a story about the struggle for quest for knowledge and self-reinvention.
Narrative and personal narrative journalism are gaining more popularity these days. You can find distinguished personal narratives all over the web.
Curating the best of the best of personal narratives and narrative essays from all over the web. Some are award-winning articles.
Narratively
Long-form writing to celebrate humanity through storytelling. It publishes personal narrative essays written to provoke, inspire, and reflect, touching lesser-known and overlooked subjects.
Narrative Magazine
It publishes non,fiction narratives, poetry, and fiction. Among its contributors is Frank Conroy, the author of Stop-Time , a memoir that has never been out of print since 1967.
Thought Catalog
Aimed at Generation Z, it publishes personal narrative essays on self-improvement, family, friendship, romance, and others.
Personal narratives will continue to be popular as our brains are wired for stories. We love reading about others and telling stories of ourselves, as they bring satisfaction and a better understanding of the world around us.
Personal narratives make us better humans. Enjoy telling yours!

Write like a bestselling author
Love writing? ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of your stories.
Jennifer Xue is an award-winning e-book author with 2,500+ articles and 100+ e-books/reports published under her belt. She also taught 50+ college-level essay and paper writing classes. Her byline has appeared in Forbes, Fortune, Cosmopolitan, Esquire, Business.com, Business2Community, Addicted2Success, Good Men Project, and others. Her blog is JenniferXue.com. Follow her on Twitter @jenxuewrites].
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
Narrative Essay
Narrative Essay Examples
10+ Interesting Narrative Essay Examples Plus Writing Tips!
Published on: Jun 23, 2018
Last updated on: Nov 30, 2023

People also read
Share this article
Many students struggle with crafting engaging and impactful narrative essays. They often find it challenging to weave their personal experiences into coherent and compelling stories.
If you’re having a hard time, don't worry!
We’ve compiled a range of narrative essay examples that will serve as helpful tools for you to get started. These examples will provide a clear path for crafting engaging and powerful narrative essays.
So, keep reading and find our expertly written examples!
- 1. Narrative Essay Definition
- 2. Narrative Essay Examples
- 3. Narrative Essay Examples for Students
- 4. Narrative Essay Topics
- 5. Narrative Essay Writing Tips
Narrative Essay Definition
Writing a narrative essay is a unique form of storytelling that revolves around personal experiences, aiming to immerse the reader in the author's world. It's a piece of writing that delves into the depths of thoughts and feelings.
In a narrative essay, life experiences take center stage, serving as the main substance of the story. It's a powerful tool for writers to convey a personal journey, turning experiences into a captivating tale. This form of storytelling is an artful display of emotions intended to engage readers, leaving the reader feeling like they are a part of the story.
By focusing on a specific theme, event, emotions, and reflections, a narrative essay weaves a storyline that leads the reader through the author's experiences.
The Essentials of Narrative Essays
Let's start with the basics. The four types of essays are argumentative essays , descriptive essays , expository essays , and narrative essays.
The goal of a narrative essay is to tell a compelling tale from one person's perspective. A narrative essay uses all components you’d find in a typical story, such as a beginning, middle, and conclusion, as well as plot, characters, setting, and climax.
The narrative essay's goal is the plot, which should be detailed enough to reach a climax. Here's how it works:
- It's usually presented in chronological order.
- It has a function. This is typically evident in the thesis statement's opening paragraph.
- It may include speech.
- It's told with sensory details and vivid language, drawing the reader in. All of these elements are connected to the writer's major argument in some way.
Before writing your essay, make sure you go through a sufficient number of narrative essay examples. These examples will help you in knowing the dos and don’ts of a good narrative essay.
It is always a better option to have some sense of direction before you start anything. Below, you can find important details and a bunch of narrative essay examples. These examples will also help you build your content according to the format.
Here is a how to start a narrative essay example:
Sample Narrative Essay
The examples inform the readers about the writing style and structure of the narration. The essay below will help you understand how to create a story and build this type of essay in no time.
Here is another narrative essay examples 500 words:
Narrative Essay Examples for Students
Narrative essays offer students a platform to express their experiences and creativity. These examples show how to effectively structure and present personal stories for education.
Here are some helpful narrative essay examples:
Narrative Essay Examples Middle School
Narrative Essay Examples for Grade 7
Narrative Essay Examples for Grade 8
Grade 11 Narrative Essay Examples
Narrative Essay Example For High School
Narrative Essay Example For College
Personal Narrative Essay Example
Descriptive Narrative Essay Example
3rd Person Narrative Essay Example
Narrative Essay Topics
Here are some narrative essay topics to help you get started with your narrative essay writing.
- When I got my first bunny
- When I moved to Canada
- I haven’t experienced this freezing temperature ever before
- The moment I won the basketball finale
- A memorable day at the museum
- How I talk to my parrot
- The day I saw the death
- When I finally rebelled against my professor
Need more topics? Check out these extensive narrative essay topics to get creative ideas!
Narrative Essay Writing Tips
Narrative essays give you the freedom to be creative, but it can be tough to make yours special. Use these tips to make your story interesting:
- Share your story from a personal viewpoint, engaging the reader with your experiences.
- Use vivid descriptions to paint a clear picture of the setting, characters, and emotions involved.
- Organize events in chronological order for a smooth and understandable narrative.
- Bring characters to life through their actions, dialogue, and personalities.
- Employ dialogue sparingly to add realism and progression to the narrative.
- Engage readers by evoking emotions through your storytelling.
- End with reflection or a lesson learned from the experience, providing insight.
Now you have essay examples and tips to help you get started, you have a solid starting point for crafting compelling narrative essays.
However, if storytelling isn't your forte, you can always turn to our essay writing service for help.
Our writers are specialists that can tackle any type of essay with great skill. With their experience, you get a top-quality, 100% plagiarism free essay everytime.
So, let our narrative essay writing service make sure your narrative essay stands out. Order now!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading
Writing a Personal Narrative Essay: Everything You Need to Know
Best Narrative Essay Topics 2023 for Students
Crafting a Winning Narrative Essay Outline: A Step-by-Step Guide


Narrative Writing: A Complete Guide for Teachers and Students
MASTERING THE CRAFT OF NARRATIVE WRITING
Narratives build on and encourage the development of the fundamentals of writing. They also require developing an additional skill set: the ability to tell a good yarn, and storytelling is as old as humanity.
We see and hear stories everywhere and daily, from having good gossip on the doorstep with a neighbor in the morning to the dramas that fill our screens in the evening.
Good narrative writing skills are hard-won by students even though it is an area of writing that most enjoy due to the creativity and freedom it offers.
Here we will explore some of the main elements of a good story: plot, setting, characters, conflict, climax, and resolution . And we will look too at how best we can help our students understand these elements, both in isolation and how they mesh together as a whole.

WHAT IS A NARRATIVE?

A narrative is a story that shares a sequence of events , characters, and themes. It expresses experiences, ideas, and perspectives that should aspire to engage and inspire an audience.
A narrative can spark emotion, encourage reflection, and convey meaning when done well.
Narratives are a popular genre for students and teachers as they allow the writer to share their imagination, creativity, skill, and understanding of nearly all elements of writing. We occasionally refer to a narrative as ‘creative writing’ or story writing.
The purpose of a narrative is simple, to tell the audience a story. It can be written to motivate, educate, or entertain and can be fact or fiction.
A COMPLETE UNIT ON TEACHING NARRATIVE WRITING

Teach your students to become skilled story writers with this HUGE NARRATIVE & CREATIVE STORY WRITING UNIT . Offering a COMPLETE SOLUTION to teaching students how to craft CREATIVE CHARACTERS, SUPERB SETTINGS, and PERFECT PLOTS .
Over 192 PAGES of materials, including:
TYPES OF NARRATIVE WRITING
There are many narrative writing genres and sub-genres such as these.
We have a complete guide to writing a personal narrative that differs from the traditional story-based narrative covered in this guide. It includes personal narrative writing prompts, resources, and examples and can be found here.

As we can see, narratives are an open-ended form of writing that allows you to showcase creativity in many directions. However, all narratives share a common set of features and structure known as “Story Elements”, which are briefly covered in this guide.
Don’t overlook the importance of understanding story elements and the value this adds to you as a writer who can dissect and create grand narratives. We also have an in-depth guide to understanding story elements here .
CHARACTERISTICS OF NARRATIVE WRITING
Narrative structure.
ORIENTATION (BEGINNING) Set the scene by introducing your characters, setting and time of the story. Establish your who, when and where in this part of your narrative
COMPLICATION AND EVENTS (MIDDLE) In this section activities and events involving your main characters are expanded upon. These events are written in a cohesive and fluent sequence.
RESOLUTION (ENDING) Your complication is resolved in this section. It does not have to be a happy outcome, however.
EXTRAS: Whilst orientation, complication and resolution are the agreed norms for a narrative, there are numerous examples of popular texts that did not explicitly follow this path exactly.
NARRATIVE FEATURES
LANGUAGE: Use descriptive and figurative language to paint images inside your audience’s minds as they read.
PERSPECTIVE Narratives can be written from any perspective but are most commonly written in first or third person.
DIALOGUE Narratives frequently switch from narrator to first-person dialogue. Always use speech marks when writing dialogue.
TENSE If you change tense, make it perfectly clear to your audience what is happening. Flashbacks might work well in your mind but make sure they translate to your audience.
THE PLOT MAP
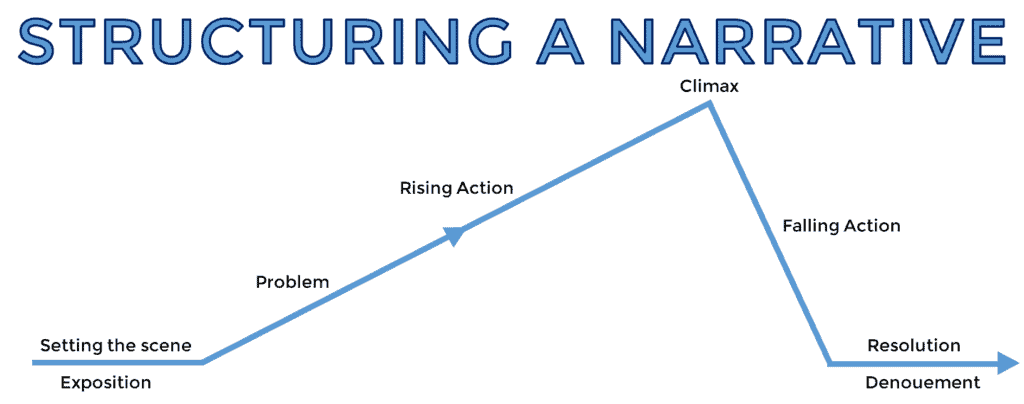
This graphic is known as a plot map, and nearly all narratives fit this structure in one way or another, whether romance novels, science fiction or otherwise.
It is a simple tool that helps you understand and organise a story’s events. Think of it as a roadmap that outlines the journey of your characters and the events that unfold. It outlines the different stops along the way, such as the introduction, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution, that help you to see how the story builds and develops.
Using a plot map, you can see how each event fits into the larger picture and how the different parts of the story work together to create meaning. It’s a great way to visualize and analyze a story.
Be sure to refer to a plot map when planning a story, as it has all the essential elements of a great story.
THE 5 KEY STORY ELEMENTS OF A GREAT NARRATIVE (6-MINUTE TUTORIAL VIDEO)
This video we created provides an excellent overview of these elements and demonstrates them in action in stories we all know and love.

HOW TO WRITE A NARRATIVE

Now that we understand the story elements and how they come together to form stories, it’s time to start planning and writing your narrative.
In many cases, the template and guide below will provide enough details on how to craft a great story. However, if you still need assistance with the fundamentals of writing, such as sentence structure, paragraphs and using correct grammar, we have some excellent guides on those here.
USE YOUR WRITING TIME EFFECTIVELY: Maximize your narrative writing sessions by spending approximately 20 per cent of your time planning and preparing. This ensures greater productivity during your writing time and keeps you focused and on task.
Use tools such as graphic organizers to logically sequence your narrative if you are not a confident story writer. If you are working with reluctant writers, try using narrative writing prompts to get their creative juices flowing.
Spend most of your writing hour on the task at hand, don’t get too side-tracked editing during this time and leave some time for editing. When editing a narrative, examine it for these three elements.
- Spelling and grammar ( Is it readable?)
- Story structure and continuity ( Does it make sense, and does it flow? )
- Character and plot analysis. (Are your characters engaging? Does your problem/resolution work? )
1. SETTING THE SCENE: THE WHERE AND THE WHEN

The story’s setting often answers two of the central questions in the story, namely, the where and the when. The answers to these two crucial questions will often be informed by the type of story the student is writing.
The story’s setting can be chosen to quickly orient the reader to the type of story they are reading. For example, a fictional narrative writing piece such as a horror story will often begin with a description of a haunted house on a hill or an abandoned asylum in the middle of the woods. If we start our story on a rocket ship hurtling through the cosmos on its space voyage to the Alpha Centauri star system, we can be reasonably sure that the story we are embarking on is a work of science fiction.
Such conventions are well-worn clichés true, but they can be helpful starting points for our novice novelists to make a start.
Having students choose an appropriate setting for the type of story they wish to write is an excellent exercise for our younger students. It leads naturally onto the next stage of story writing, which is creating suitable characters to populate this fictional world they have created. However, older or more advanced students may wish to play with the expectations of appropriate settings for their story. They may wish to do this for comic effect or in the interest of creating a more original story. For example, opening a story with a children’s birthday party does not usually set up the expectation of a horror story. Indeed, it may even lure the reader into a happy reverie as they remember their own happy birthday parties. This leaves them more vulnerable to the surprise element of the shocking action that lies ahead.
Once the students have chosen a setting for their story, they need to start writing. Little can be more terrifying to English students than the blank page and its bare whiteness stretching before them on the table like a merciless desert they must cross. Give them the kick-start they need by offering support through word banks or writing prompts. If the class is all writing a story based on the same theme, you may wish to compile a common word bank on the whiteboard as a prewriting activity. Write the central theme or genre in the middle of the board. Have students suggest words or phrases related to the theme and list them on the board.
You may wish to provide students with a copy of various writing prompts to get them started. While this may mean that many students’ stories will have the same beginning, they will most likely arrive at dramatically different endings via dramatically different routes.

A bargain is at the centre of the relationship between the writer and the reader. That bargain is that the reader promises to suspend their disbelief as long as the writer creates a consistent and convincing fictional reality. Creating a believable world for the fictional characters to inhabit requires the student to draw on convincing details. The best way of doing this is through writing that appeals to the senses. Have your student reflect deeply on the world that they are creating. What does it look like? Sound like? What does the food taste like there? How does it feel like to walk those imaginary streets, and what aromas beguile the nose as the main character winds their way through that conjured market?
Also, Consider the when; or the time period. Is it a future world where things are cleaner and more antiseptic? Or is it an overcrowded 16th-century London with human waste stinking up the streets? If students can create a multi-sensory installation in the reader’s mind, then they have done this part of their job well.
Popular Settings from Children’s Literature and Storytelling
- Fairytale Kingdom
- Magical Forest
- Village/town
- Underwater world
- Space/Alien planet
2. CASTING THE CHARACTERS: THE WHO
Now that your student has created a believable world, it is time to populate it with believable characters.
In short stories, these worlds mustn’t be overpopulated beyond what the student’s skill level can manage. Short stories usually only require one main character and a few secondary ones. Think of the short story more as a small-scale dramatic production in an intimate local theater than a Hollywood blockbuster on a grand scale. Too many characters will only confuse and become unwieldy with a canvas this size. Keep it simple!
Creating believable characters is often one of the most challenging aspects of narrative writing for students. Fortunately, we can do a few things to help students here. Sometimes it is helpful for students to model their characters on actual people they know. This can make things a little less daunting and taxing on the imagination. However, whether or not this is the case, writing brief background bios or descriptions of characters’ physical personality characteristics can be a beneficial prewriting activity. Students should give some in-depth consideration to the details of who their character is: How do they walk? What do they look like? Do they have any distinguishing features? A crooked nose? A limp? Bad breath? Small details such as these bring life and, therefore, believability to characters. Students can even cut pictures from magazines to put a face to their character and allow their imaginations to fill in the rest of the details.
Younger students will often dictate to the reader the nature of their characters. To improve their writing craft, students must know when to switch from story-telling mode to story-showing mode. This is particularly true when it comes to character. Encourage students to reveal their character’s personality through what they do rather than merely by lecturing the reader on the faults and virtues of the character’s personality. It might be a small relayed detail in the way they walk that reveals a core characteristic. For example, a character who walks with their head hanging low and shoulders hunched while avoiding eye contact has been revealed to be timid without the word once being mentioned. This is a much more artistic and well-crafted way of doing things and is less irritating for the reader. A character who sits down at the family dinner table immediately snatches up his fork and starts stuffing roast potatoes into his mouth before anyone else has even managed to sit down has revealed a tendency towards greed or gluttony.
Understanding Character Traits
Again, there is room here for some fun and profitable prewriting activities. Give students a list of character traits and have them describe a character doing something that reveals that trait without ever employing the word itself.
It is also essential to avoid adjective stuffing here. When looking at students’ early drafts, adjective stuffing is often apparent. To train the student out of this habit, choose an adjective and have the student rewrite the sentence to express this adjective through action rather than telling.
When writing a story, it is vital to consider the character’s traits and how they will impact the story’s events. For example, a character with a strong trait of determination may be more likely to overcome obstacles and persevere. In contrast, a character with a tendency towards laziness may struggle to achieve their goals. In short, character traits add realism, depth, and meaning to a story, making it more engaging and memorable for the reader.
Popular Character Traits in Children’s Stories
- Determination
- Imagination
- Perseverance
- Responsibility
We have an in-depth guide to creating great characters here , but most students should be fine to move on to planning their conflict and resolution.
3. NO PROBLEM? NO STORY! HOW CONFLICT DRIVES A NARRATIVE

This is often the area apprentice writers have the most difficulty with. Students must understand that without a problem or conflict, there is no story. The problem is the driving force of the action. Usually, in a short story, the problem will center around what the primary character wants to happen or, indeed, wants not to happen. It is the hurdle that must be overcome. It is in the struggle to overcome this hurdle that events happen.
Often when a student understands the need for a problem in a story, their completed work will still not be successful. This is because, often in life, problems remain unsolved. Hurdles are not always successfully overcome. Students pick up on this.
We often discuss problems with friends that will never be satisfactorily resolved one way or the other, and we accept this as a part of life. This is not usually the case with writing a story. Whether a character successfully overcomes his or her problem or is decidedly crushed in the process of trying is not as important as the fact that it will finally be resolved one way or the other.
A good practical exercise for students to get to grips with this is to provide copies of stories and have them identify the central problem or conflict in each through discussion. Familiar fables or fairy tales such as Three Little Pigs, The Boy Who Cried Wolf, Cinderella, etc., are great for this.
While it is true that stories often have more than one problem or that the hero or heroine is unsuccessful in their first attempt to solve a central problem, for beginning students and intermediate students, it is best to focus on a single problem, especially given the scope of story writing at this level. Over time students will develop their abilities to handle more complex plots and write accordingly.
Popular Conflicts found in Children’s Storytelling.
- Good vs evil
- Individual vs society
- Nature vs nurture
- Self vs others
- Man vs self
- Man vs nature
- Man vs technology
- Individual vs fate
- Self vs destiny
Conflict is the heart and soul of any good story. It’s what makes a story compelling and drives the plot forward. Without conflict, there is no story. Every great story has a struggle or a problem that needs to be solved, and that’s where conflict comes in. Conflict is what makes a story exciting and keeps the reader engaged. It creates tension and suspense and makes the reader care about the outcome.
Like in real life, conflict in a story is an opportunity for a character’s growth and transformation. It’s a chance for them to learn and evolve, making a story great. So next time stories are written in the classroom, remember that conflict is an essential ingredient, and without it, your story will lack the energy, excitement, and meaning that makes it truly memorable.
4. THE NARRATIVE CLIMAX: HOW THINGS COME TO A HEAD!

The climax of the story is the dramatic high point of the action. It is also when the struggles kicked off by the problem come to a head. The climax will ultimately decide whether the story will have a happy or tragic ending. In the climax, two opposing forces duke things out until the bitter (or sweet!) end. One force ultimately emerges triumphant. As the action builds throughout the story, suspense increases as the reader wonders which of these forces will win out. The climax is the release of this suspense.
Much of the success of the climax depends on how well the other elements of the story have been achieved. If the student has created a well-drawn and believable character that the reader can identify with and feel for, then the climax will be more powerful.
The nature of the problem is also essential as it determines what’s at stake in the climax. The problem must matter dearly to the main character if it matters at all to the reader.
Have students engage in discussions about their favorite movies and books. Have them think about the storyline and decide the most exciting parts. What was at stake at these moments? What happened in your body as you read or watched? Did you breathe faster? Or grip the cushion hard? Did your heart rate increase, or did you start to sweat? This is what a good climax does and what our students should strive to do in their stories.
The climax puts it all on the line and rolls the dice. Let the chips fall where the writer may…
Popular Climax themes in Children’s Stories
- A battle between good and evil
- The character’s bravery saves the day
- Character faces their fears and overcomes them
- The character solves a mystery or puzzle.
- The character stands up for what is right.
- Character reaches their goal or dream.
- The character learns a valuable lesson.
- The character makes a selfless sacrifice.
- The character makes a difficult decision.
- The character reunites with loved ones or finds true friendship.
5. RESOLUTION: TYING UP LOOSE ENDS
After the climactic action, a few questions will often remain unresolved for the reader, even if all the conflict has been resolved. The resolution is where those lingering questions will be answered. The resolution in a short story may only be a brief paragraph or two. But, in most cases, it will still be necessary to include an ending immediately after the climax can feel too abrupt and leave the reader feeling unfulfilled.
An easy way to explain resolution to students struggling to grasp the concept is to point to the traditional resolution of fairy tales, the “And they all lived happily ever after” ending. This weather forecast for the future allows the reader to take their leave. Have the student consider the emotions they want to leave the reader with when crafting their resolution.
While the action is usually complete by the end of the climax, it is in the resolution that if there is a twist to be found, it will appear – think of movies such as The Usual Suspects. Pulling this off convincingly usually requires considerable skill from a student writer. Still, it may well form a challenging extension exercise for those more gifted storytellers among your students.
Popular Resolutions in Children’s Stories
- Our hero achieves their goal
- The character learns a valuable lesson
- A character finds happiness or inner peace.
- The character reunites with loved ones.
- Character restores balance to the world.
- The character discovers their true identity.
- Character changes for the better.
- The character gains wisdom or understanding.
- Character makes amends with others.
- The character learns to appreciate what they have.
Once students have completed their story, they can edit for grammar, vocabulary choice, spelling, etc., but not before!
As mentioned, there is a craft to storytelling, as well as an art. When accurate grammar, perfect spelling, and immaculate sentence structures are pushed at the outset, they can cause storytelling paralysis. For this reason, it is essential that when we encourage the students to write a story, we give them license to make mechanical mistakes in their use of language that they can work on and fix later.
Good narrative writing is a very complex skill to develop and will take the student years to become competent. It challenges not only the student’s technical abilities with language but also her creative faculties. Writing frames, word banks, mind maps, and visual prompts can all give valuable support as students develop the wide-ranging and challenging skills required to produce a successful narrative writing piece. But, at the end of it all, as with any craft, practice and more practice is at the heart of the matter.
TIPS FOR WRITING A GREAT NARRATIVE
- Start your story with a clear purpose: If you can determine the theme or message you want to convey in your narrative before starting it will make the writing process so much simpler.
- Choose a compelling storyline and sell it through great characters, setting and plot: Consider a unique or interesting story that captures the reader’s attention, then build the world and characters around it.
- Develop vivid characters that are not all the same: Make your characters relatable and memorable by giving them distinct personalities and traits you can draw upon in the plot.
- Use descriptive language to hook your audience into your story: Use sensory language to paint vivid images and sequences in the reader’s mind.
- Show, don’t tell your audience: Use actions, thoughts, and dialogue to reveal character motivations and emotions through storytelling.
- Create a vivid setting that is clear to your audience before getting too far into the plot: Describe the time and place of your story to immerse the reader fully.
- Build tension: Refer to the story map earlier in this article and use conflict, obstacles, and suspense to keep the audience engaged and invested in your narrative.
- Use figurative language such as metaphors, similes, and other literary devices to add depth and meaning to your narrative.
- Edit, revise, and refine: Take the time to refine and polish your writing for clarity and impact.
- Stay true to your voice: Maintain your unique perspective and style in your writing to make it your own.
NARRATIVE WRITING EXAMPLES (Student Writing Samples)
Below are a collection of student writing samples of narratives. Click on the image to enlarge and explore them in greater detail. Please take a moment to read these creative stories in detail and the teacher and student guides which highlight some of the critical elements of narratives to consider before writing.
Please understand these student writing samples are not intended to be perfect examples for each age or grade level but a piece of writing for students and teachers to explore together to critically analyze to improve student writing skills and deepen their understanding of story writing.
We recommend reading the example either a year above or below, as well as the grade you are currently working with, to gain a broader appreciation of this text type.
NARRATIVE WRITING PROMPTS (Journal Prompts)
When students have a great journal prompt, it can help them focus on the task at hand, so be sure to view our vast collection of visual writing prompts for various text types here or use some of these.
- On a recent European trip, you find your travel group booked into the stunning and mysterious Castle Frankenfurter for a single night… As night falls, the massive castle of over one hundred rooms seems to creak and groan as a series of unexplained events begin to make you wonder who or what else is spending the evening with you. Write a narrative that tells the story of your evening.
- You are a famous adventurer who has discovered new lands; keep a travel log over a period of time in which you encounter new and exciting adventures and challenges to overcome. Ensure your travel journal tells a story and has a definite introduction, conflict and resolution.
- You create an incredible piece of technology that has the capacity to change the world. As you sit back and marvel at your innovation and the endless possibilities ahead of you, it becomes apparent there are a few problems you didn’t really consider. You might not even be able to control them. Write a narrative in which you ride the highs and lows of your world-changing creation with a clear introduction, conflict and resolution.
- As the final door shuts on the Megamall, you realise you have done it… You and your best friend have managed to sneak into the largest shopping centre in town and have the entire place to yourselves until 7 am tomorrow. There is literally everything and anything a child would dream of entertaining themselves for the next 12 hours. What amazing adventures await you? What might go wrong? And how will you get out of there scot-free?
- A stranger walks into town… Whilst appearing similar to almost all those around you, you get a sense that this person is from another time, space or dimension… Are they friends or foes? What makes you sense something very strange is going on? Suddenly they stand up and walk toward you with purpose extending their hand… It’s almost as if they were reading your mind.
NARRATIVE WRITING VIDEO TUTORIAL

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
When teaching narrative writing, it is essential that you have a range of tools, strategies and resources at your disposal to ensure you get the most out of your writing time. You can find some examples below, which are free and paid premium resources you can use instantly without any preparation.
FREE Narrative Graphic Organizer
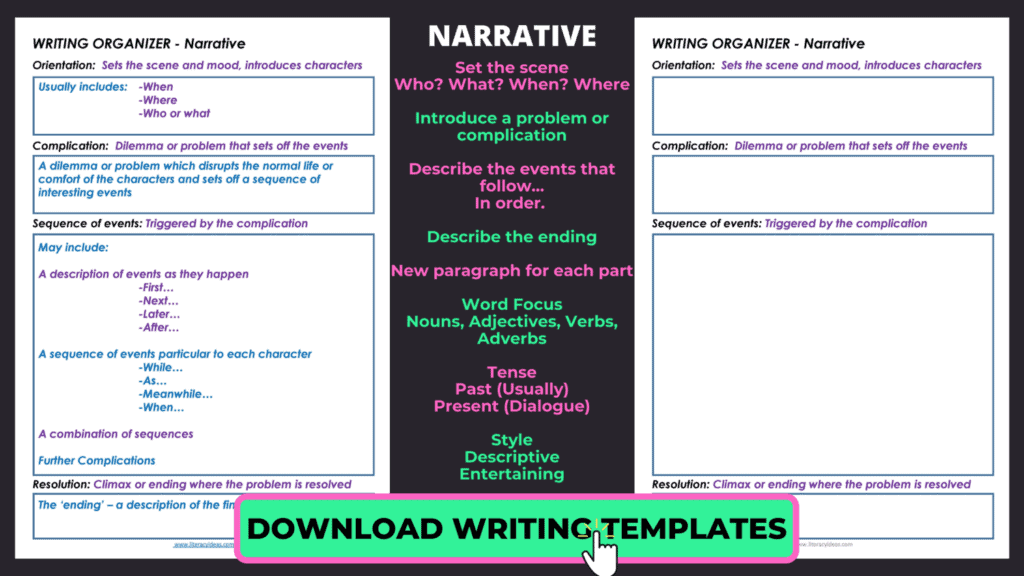
THE STORY TELLERS BUNDLE OF TEACHING RESOURCES

A MASSIVE COLLECTION of resources for narratives and story writing in the classroom covering all elements of crafting amazing stories. MONTHS WORTH OF WRITING LESSONS AND RESOURCES, including:
NARRATIVE WRITING CHECKLIST BUNDLE

OTHER GREAT ARTICLES ABOUT NARRATIVE WRITING

Narrative Writing for Kids: Essential Skills and Strategies

7 Great Narrative Lesson Plans Students and Teachers Love

Top 7 Narrative Writing Exercises for Students

How to Write a Scary Story
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- The four main types of essay | Quick guide with examples
The Four Main Types of Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
Published on September 4, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays.
Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and descriptive essays are about exercising creativity and writing in an interesting way. At university level, argumentative essays are the most common type.
In high school and college, you will also often have to write textual analysis essays, which test your skills in close reading and interpretation.

Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Argumentative essays, expository essays, narrative essays, descriptive essays, textual analysis essays, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about types of essays.
An argumentative essay presents an extended, evidence-based argument. It requires a strong thesis statement —a clearly defined stance on your topic. Your aim is to convince the reader of your thesis using evidence (such as quotations ) and analysis.
Argumentative essays test your ability to research and present your own position on a topic. This is the most common type of essay at college level—most papers you write will involve some kind of argumentation.
The essay is divided into an introduction, body, and conclusion:
- The introduction provides your topic and thesis statement
- The body presents your evidence and arguments
- The conclusion summarizes your argument and emphasizes its importance
The example below is a paragraph from the body of an argumentative essay about the effects of the internet on education. Mouse over it to learn more.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
An expository essay provides a clear, focused explanation of a topic. It doesn’t require an original argument, just a balanced and well-organized view of the topic.
Expository essays test your familiarity with a topic and your ability to organize and convey information. They are commonly assigned at high school or in exam questions at college level.
The introduction of an expository essay states your topic and provides some general background, the body presents the details, and the conclusion summarizes the information presented.
A typical body paragraph from an expository essay about the invention of the printing press is shown below. Mouse over it to learn more.
The invention of the printing press in 1440 changed this situation dramatically. Johannes Gutenberg, who had worked as a goldsmith, used his knowledge of metals in the design of the press. He made his type from an alloy of lead, tin, and antimony, whose durability allowed for the reliable production of high-quality books. This new technology allowed texts to be reproduced and disseminated on a much larger scale than was previously possible. The Gutenberg Bible appeared in the 1450s, and a large number of printing presses sprang up across the continent in the following decades. Gutenberg’s invention rapidly transformed cultural production in Europe; among other things, it would lead to the Protestant Reformation.
A narrative essay is one that tells a story. This is usually a story about a personal experience you had, but it may also be an imaginative exploration of something you have not experienced.
Narrative essays test your ability to build up a narrative in an engaging, well-structured way. They are much more personal and creative than other kinds of academic writing . Writing a personal statement for an application requires the same skills as a narrative essay.
A narrative essay isn’t strictly divided into introduction, body, and conclusion, but it should still begin by setting up the narrative and finish by expressing the point of the story—what you learned from your experience, or why it made an impression on you.
Mouse over the example below, a short narrative essay responding to the prompt “Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself,” to explore its structure.
Since elementary school, I have always favored subjects like science and math over the humanities. My instinct was always to think of these subjects as more solid and serious than classes like English. If there was no right answer, I thought, why bother? But recently I had an experience that taught me my academic interests are more flexible than I had thought: I took my first philosophy class.
Before I entered the classroom, I was skeptical. I waited outside with the other students and wondered what exactly philosophy would involve—I really had no idea. I imagined something pretty abstract: long, stilted conversations pondering the meaning of life. But what I got was something quite different.
A young man in jeans, Mr. Jones—“but you can call me Rob”—was far from the white-haired, buttoned-up old man I had half-expected. And rather than pulling us into pedantic arguments about obscure philosophical points, Rob engaged us on our level. To talk free will, we looked at our own choices. To talk ethics, we looked at dilemmas we had faced ourselves. By the end of class, I’d discovered that questions with no right answer can turn out to be the most interesting ones.
The experience has taught me to look at things a little more “philosophically”—and not just because it was a philosophy class! I learned that if I let go of my preconceptions, I can actually get a lot out of subjects I was previously dismissive of. The class taught me—in more ways than one—to look at things with an open mind.
A descriptive essay provides a detailed sensory description of something. Like narrative essays, they allow you to be more creative than most academic writing, but they are more tightly focused than narrative essays. You might describe a specific place or object, rather than telling a whole story.
Descriptive essays test your ability to use language creatively, making striking word choices to convey a memorable picture of what you’re describing.
A descriptive essay can be quite loosely structured, though it should usually begin by introducing the object of your description and end by drawing an overall picture of it. The important thing is to use careful word choices and figurative language to create an original description of your object.
Mouse over the example below, a response to the prompt “Describe a place you love to spend time in,” to learn more about descriptive essays.
On Sunday afternoons I like to spend my time in the garden behind my house. The garden is narrow but long, a corridor of green extending from the back of the house, and I sit on a lawn chair at the far end to read and relax. I am in my small peaceful paradise: the shade of the tree, the feel of the grass on my feet, the gentle activity of the fish in the pond beside me.
My cat crosses the garden nimbly and leaps onto the fence to survey it from above. From his perch he can watch over his little kingdom and keep an eye on the neighbours. He does this until the barking of next door’s dog scares him from his post and he bolts for the cat flap to govern from the safety of the kitchen.
With that, I am left alone with the fish, whose whole world is the pond by my feet. The fish explore the pond every day as if for the first time, prodding and inspecting every stone. I sometimes feel the same about sitting here in the garden; I know the place better than anyone, but whenever I return I still feel compelled to pay attention to all its details and novelties—a new bird perched in the tree, the growth of the grass, and the movement of the insects it shelters…
Sitting out in the garden, I feel serene. I feel at home. And yet I always feel there is more to discover. The bounds of my garden may be small, but there is a whole world contained within it, and it is one I will never get tired of inhabiting.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Though every essay type tests your writing skills, some essays also test your ability to read carefully and critically. In a textual analysis essay, you don’t just present information on a topic, but closely analyze a text to explain how it achieves certain effects.
Rhetorical analysis
A rhetorical analysis looks at a persuasive text (e.g. a speech, an essay, a political cartoon) in terms of the rhetorical devices it uses, and evaluates their effectiveness.
The goal is not to state whether you agree with the author’s argument but to look at how they have constructed it.
The introduction of a rhetorical analysis presents the text, some background information, and your thesis statement; the body comprises the analysis itself; and the conclusion wraps up your analysis of the text, emphasizing its relevance to broader concerns.
The example below is from a rhetorical analysis of Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech . Mouse over it to learn more.
King’s speech is infused with prophetic language throughout. Even before the famous “dream” part of the speech, King’s language consistently strikes a prophetic tone. He refers to the Lincoln Memorial as a “hallowed spot” and speaks of rising “from the dark and desolate valley of segregation” to “make justice a reality for all of God’s children.” The assumption of this prophetic voice constitutes the text’s strongest ethical appeal; after linking himself with political figures like Lincoln and the Founding Fathers, King’s ethos adopts a distinctly religious tone, recalling Biblical prophets and preachers of change from across history. This adds significant force to his words; standing before an audience of hundreds of thousands, he states not just what the future should be, but what it will be: “The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.” This warning is almost apocalyptic in tone, though it concludes with the positive image of the “bright day of justice.” The power of King’s rhetoric thus stems not only from the pathos of his vision of a brighter future, but from the ethos of the prophetic voice he adopts in expressing this vision.
Literary analysis
A literary analysis essay presents a close reading of a work of literature—e.g. a poem or novel—to explore the choices made by the author and how they help to convey the text’s theme. It is not simply a book report or a review, but an in-depth interpretation of the text.
Literary analysis looks at things like setting, characters, themes, and figurative language. The goal is to closely analyze what the author conveys and how.
The introduction of a literary analysis essay presents the text and background, and provides your thesis statement; the body consists of close readings of the text with quotations and analysis in support of your argument; and the conclusion emphasizes what your approach tells us about the text.
Mouse over the example below, the introduction to a literary analysis essay on Frankenstein , to learn more.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, protagonist Victor Frankenstein is a stable representation of the callous ambition of modern science throughout the novel. This essay, however, argues that far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as. This essay begins by exploring the positive portrayal of Frankenstein in the first volume, then moves on to the creature’s perception of him, and finally discusses the third volume’s narrative shift toward viewing Frankenstein as the creature views him.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
At high school and in composition classes at university, you’ll often be told to write a specific type of essay , but you might also just be given prompts.
Look for keywords in these prompts that suggest a certain approach: The word “explain” suggests you should write an expository essay , while the word “describe” implies a descriptive essay . An argumentative essay might be prompted with the word “assess” or “argue.”
The vast majority of essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Almost all academic writing involves building up an argument, though other types of essay might be assigned in composition classes.
Essays can present arguments about all kinds of different topics. For example:
- In a literary analysis essay, you might make an argument for a specific interpretation of a text
- In a history essay, you might present an argument for the importance of a particular event
- In a politics essay, you might argue for the validity of a certain political theory
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
The key difference is that a narrative essay is designed to tell a complete story, while a descriptive essay is meant to convey an intense description of a particular place, object, or concept.
Narrative and descriptive essays both allow you to write more personally and creatively than other kinds of essays , and similar writing skills can apply to both.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). The Four Main Types of Essay | Quick Guide with Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 13, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/essay-types/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, how to write an expository essay, how to write an essay outline | guidelines & examples, what is your plagiarism score.

The short story is a fiction writer’s laboratory: here is where you can experiment with characters, plots, and ideas without the heavy lifting of writing a novel. Learning how to write a short story is essential to mastering the art of storytelling . With far fewer words to worry about, storytellers can make many more mistakes—and strokes of genius!—through experimentation and the fun of fiction writing.
Nonetheless, the art of writing short stories is not easy to master. How do you tell a complete story in so few words? What does a story need to have in order to be successful? Whether you’re struggling with how to write a short story outline, or how to fully develop a character in so few words, this guide is your starting point.
Famous authors like Virginia Woolf, Haruki Murakami, and Agatha Christie have used the short story form to play with ideas before turning those stories into novels. Whether you want to master the elements of fiction, experiment with novel ideas, or simply have fun with storytelling, here’s everything you need on how to write a short story step by step.
The Core Elements of a Short Story
There’s no secret formula to writing a short story. However, a good short story will have most or all of the following elements:
- A protagonist with a certain desire or need. It is essential for the protagonist to want something they don’t have, otherwise they will not drive the story forward.
- A clear dilemma. We don’t need much backstory to see how the dilemma started; we’re primarily concerned with how the protagonist resolves it.
- A decision. What does the protagonist do to resolve their dilemma?
- A climax. In Freytag’s Pyramid , the climax of a story is when the tension reaches its peak, and the reader discovers the outcome of the protagonist’s decision(s).
- An outcome. How does the climax change the protagonist? Are they a different person? Do they have a different philosophy or outlook on life?
Of course, short stories also utilize the elements of fiction , such as a setting , plot , and point of view . It helps to study these elements and to understand their intricacies. But, when it comes to laying down the skeleton of a short story, the above elements are what you need to get started.
Note: a short story rarely, if ever, has subplots. The focus should be entirely on a single, central storyline. Subplots will either pull focus away from the main story, or else push the story into the territory of novellas and novels.
The shorter the story is, the fewer of these elements are essentials. If you’re interested in writing short-short stories, check out our guide on how to write flash fiction .
How to Write a Short Story Outline
Some writers are “pantsers”—they “write by the seat of their pants,” making things up on the go with little more than an idea for a story. Other writers are “plotters,” meaning they decide the story’s structure in advance of writing it.
You don’t need a short story outline to write a good short story. But, if you’d like to give yourself some scaffolding before putting words on the page, this article answers the question of how to write a short story outline:
https://writers.com/how-to-write-a-story-outline
How to Write a Short Story Step by Step
There are many ways to approach the short story craft, but this method is tried-and-tested for writers of all levels. Here’s how to write a short story step by step.
1. Start With an Idea
Often, generating an idea is the hardest part. You want to write, but what will you write about?
What’s more, it’s easy to start coming up with ideas and then dismissing them. You want to tell an authentic, original story, but everything you come up with has already been written, it seems.
Here are a few tips:
- Originality presents itself in your storytelling, not in your ideas. For example, the premise of both Shakespeare’s A Midsummer Night’s Dream and Ostrovsky’s The Snow Maiden are very similar: two men and two women, in intertwining love triangles, sort out their feelings for each other amidst mischievous forest spirits, love potions, and friendship drama. The way each story is written makes them very distinct from one another, to the point where, unless it’s pointed out to you, you might not even notice the similarities.
- An idea is not a final draft. You will find that exploring the possibilities of your story will generate something far different than the idea you started out with. This is a good thing—it means you made the story your own!
- Experiment with genres and tropes. Even if you want to write literary fiction , pay attention to the narrative structures that drive genre stories, and practice your storytelling using those structures. Again, you will naturally make the story your own simply by playing with ideas.
If you’re struggling simply to find ideas, try out this prompt generator , or pull prompts from this Twitter .
2. Outline, OR Conceive Your Characters
If you plan to outline, do so once you’ve generated an idea. You can learn about how to write a short story outline earlier in this article.
If you don’t plan to outline, you should at least start with a character or characters. Certainly, you need a protagonist, but you should also think about any characters that aid or inhibit your protagonist’s journey.
When thinking about character development, ask the following questions:
- What is my character’s background? Where do they come from, how did they get here, where do they want to be?
- What does your character desire the most? This can be both material or conceptual, like “fitting in” or “being loved.”
- What is your character’s fatal flaw? In other words, what limitation prevents the protagonist from achieving their desire? Often, this flaw is a blind spot that directly counters their desire. For example, self hatred stands in the way of a protagonist searching for love.
- How does your character think and speak? Think of examples, both fictional and in the real world, who might resemble your character.
In short stories, there are rarely more characters than a protagonist, an antagonist (if relevant), and a small group of supporting characters. The more characters you include, the longer your story will be. Focus on making only one or two characters complex: it is absolutely okay to have the rest of the cast be flat characters that move the story along.
Learn more about character development here:
https://writers.com/character-development-definition
3. Write Scenes Around Conflict
Once you have an outline or some characters, start building scenes around conflict. Every part of your story, including the opening sentence, should in some way relate to the protagonist’s conflict.
Conflict is the lifeblood of storytelling: without it, the reader doesn’t have a clear reason to keep reading. Loveable characters are not enough, as the story has to give the reader something to root for.
Take, for example, Edgar Allan Poe’s classic short story The Cask of Amontillado . We start at the conflict: the narrator has been slighted by Fortunato, and plans to exact revenge. Every scene in the story builds tension and follows the protagonist as he exacts this revenge.
In your story, start writing scenes around conflict, and make sure each paragraph and piece of dialogue relates, in some way, to your protagonist’s unmet desires.
4. Write Your First Draft
The scenes you build around conflict will eventually be stitched into a complete story. Make sure as the story progresses that each scene heightens the story’s tension, and that this tension remains unbroken until the climax resolves whether or not your protagonist meets their desires.
Don’t stress too hard on writing a perfect story. Rather, take Anne Lamott’s advice, and “write a shitty first draft.” The goal is not to pen a complete story at first draft; rather, it’s to set ideas down on paper. You are simply, as Shannon Hale suggests, “shoveling sand into a box so that later [you] can build castles.”
5. Step Away, Breathe, Revise
Whenever Stephen King finishes a novel, he puts it in a drawer and doesn’t think about it for 6 weeks. With short stories, you probably don’t need to take as long of a break. But, the idea itself is true: when you’ve finished your first draft, set it aside for a while. Let yourself come back to the story with fresh eyes, so that you can confidently revise, revise, revise .
In revision, you want to make sure each word has an essential place in the story, that each scene ramps up tension, and that each character is clearly defined. The culmination of these elements allows a story to explore complex themes and ideas, giving the reader something to think about after the story has ended.
6. Compare Against Our Short Story Checklist
Does your story have everything it needs to succeed? Compare it against this short story checklist, as written by our instructor Rosemary Tantra Bensko.
Below is a collection of practical short story writing tips by Writers.com instructor Rosemary Tantra Bensko . Each paragraph is its own checklist item: a core element of short story writing advice to follow unless you have clear reasons to the contrary. We hope it’s a helpful resource in your own writing.
Update 9/1/2020: We’ve now made a summary of Rosemary’s short story checklist available as a PDF download . Enjoy!

Click to download
How to Write a Short Story: Length and Setting
Your short story is 1000 to 7500 words in length.
The story takes place in one time period, not spread out or with gaps other than to drive someplace, sleep, etc. If there are those gaps, there is a space between the paragraphs, the new paragraph beginning flush left, to indicate a new scene.
Each scene takes place in one location, or in continual transit, such as driving a truck or flying in a plane.
How to Write a Short Story: Point of View
Unless it’s a very lengthy Romance story, in which there may be two Point of View (POV) characters, there is one POV character. If we are told what any character secretly thinks, it will only be the POV character. The degree to which we are privy to the unexpressed thoughts, memories and hopes of the POV character remains consistent throughout the story.
You avoid head-hopping by only having one POV character per scene, even in a Romance. You avoid straying into even brief moments of telling us what other characters think other than the POV character. You use words like “apparently,” “obviously,” or “supposedly” to suggest how non-POV-characters think rather than stating it.
How to Write a Short Story: Protagonist, Antagonist, Motivation
Your short story has one clear protagonist who is usually the character changing most.
Your story has a clear antagonist, who generally makes the protagonist change by thwarting his goals.
(Possible exception to the two short story writing tips above: In some types of Mystery and Action stories, particularly in a series, etc., the protagonist doesn’t necessarily grow personally, but instead his change relates to understanding the antagonist enough to arrest or kill him.)
The protagonist changes with an Arc arising out of how he is stuck in his Flaw at the beginning of the story, which makes the reader bond with him as a human, and feel the pain of his problems he causes himself. (Or if it’s the non-personal growth type plot: he’s presented at the beginning of the story with a high-stakes problem that requires him to prevent or punish a crime.)
The protagonist usually is shown to Want something, because that’s what people normally do, defining their personalities and behavior patterns, pushing them onward from day to day. This may be obvious from the beginning of the story, though it may not become heightened until the Inciting Incident , which happens near the beginning of Act 1. The Want is usually something the reader sort of wants the character to succeed in, while at the same time, knows the Want is not in his authentic best interests. This mixed feeling in the reader creates tension.
The protagonist is usually shown to Need something valid and beneficial, but at first, he doesn’t recognize it, admit it, honor it, integrate it with his Want, or let the Want go so he can achieve the Need instead. Ideally, the Want and Need can be combined in a satisfying way toward the end for the sake of continuity of forward momentum of victoriously achieving the goals set out from the beginning. It’s the encounters with the antagonist that forcibly teach the protagonist to prioritize his Needs correctly and overcome his Flaw so he can defeat the obstacles put in his path.
The protagonist in a personal growth plot needs to change his Flaw/Want but like most people, doesn’t automatically do that when faced with the problem. He tries the easy way, which doesn’t work. Only when the Crisis takes him to a low point does he boldly change enough to become victorious over himself and the external situation. What he learns becomes the Theme.
Each scene shows its main character’s goal at its beginning, which aligns in a significant way with the protagonist’s overall goal for the story. The scene has a “charge,” showing either progress toward the goal or regression away from the goal by the ending. Most scenes end with a negative charge, because a story is about not obtaining one’s goals easily, until the end, in which the scene/s end with a positive charge.
The protagonist’s goal of the story becomes triggered until the Inciting Incident near the beginning, when something happens to shake up his life. This is the only major thing in the story that is allowed to be a random event that occurs to him.
How to Write a Short Story: Characters
Your characters speak differently from one another, and their dialogue suggests subtext, what they are really thinking but not saying: subtle passive-aggressive jibes, their underlying emotions, etc.
Your characters are not illustrative of ideas and beliefs you are pushing for, but come across as real people.
How to Write a Short Story: Prose
Your language is succinct, fresh and exciting, specific, colorful, avoiding clichés and platitudes. Sentence structures vary. In Genre stories, the language is simple, the symbolism is direct, and words are well-known, and sentences are relatively short. In Literary stories, you are freer to use more sophisticated ideas, words, sentence structures and underlying metaphors and implied motifs.
How to Write a Short Story: Story Structure
Your plot elements occur in the proper places according to classical Act Structure so the reader feels he has vicariously gone through a harrowing trial with the protagonist and won, raising his sense of hope and possibility. Literary short stories may be more subtle, with lower stakes, experimenting beyond classical structures like the Hero’s Journey. They can be more like vignettes sometimes, or even slice-of-life, though these types are hard to place in publications.
In Genre stories, all the questions are answered, threads are tied up, problems are solved, though the results of carnage may be spread over the landscape. In Literary short stories, you are free to explore uncertainty, ambiguity, and inchoate, realistic endings that suggest multiple interpretations, and unresolved issues.
Some Literary stories may be nonrealistic, such as with Surrealism, Absurdism, New Wave Fabulism, Weird and Magical Realism . If this is what you write, they still need their own internal logic and they should not be bewildering as to the what the reader is meant to experience, whether it’s a nuanced, unnameable mood or a trip into the subconscious.
Literary stories may also go beyond any label other than Experimental. For example, a story could be a list of To Do items on a paper held by a magnet to a refrigerator for the housemate to read. The person writing the list may grow more passive-aggressive and manipulative as the list grows, and we learn about the relationship between the housemates through the implied threats and cajoling.
How to Write a Short Story: Capturing Reader Interest
Your short story is suspenseful, meaning readers hope the protagonist will achieve his best goal, his Need, by the Climax battle against the antagonist.
Your story entertains. This is especially necessary for Genre short stories.
The story captivates readers at the very beginning with a Hook, which can be a puzzling mystery to solve, an amazing character’s or narrator’s Voice, an astounding location, humor, a startling image, or a world the reader wants to become immersed in.
Expository prose (telling, like an essay) takes up very, very little space in your short story, and it does not appear near the beginning. The story is in Narrative format instead, in which one action follows the next. You’ve removed every unnecessary instance of Expository prose and replaced it with showing Narrative. Distancing words like “used to,” “he would often,” “over the years, he,” “each morning, he” indicate that you are reporting on a lengthy time period, summing it up, rather than sticking to Narrative format, in which immediacy makes the story engaging.
You’ve earned the right to include Expository Backstory by making the reader yearn for knowing what happened in the past to solve a mystery. This can’t possibly happen at the beginning, obviously. Expository Backstory does not take place in the first pages of your story.
Your reader cares what happens and there are high stakes (especially important in Genre stories). Your reader worries until the end, when the protagonist survives, succeeds in his quest to help the community, gets the girl, solves or prevents the crime, achieves new scientific developments, takes over rule of his realm, etc.
Every sentence is compelling enough to urge the reader to read the next one—because he really, really wants to—instead of doing something else he could be doing. Your story is not going to be assigned to people to analyze in school like the ones you studied, so you have found a way from the beginning to intrigue strangers to want to spend their time with your words.
Where to Read and Submit Short Stories
Whether you’re looking for inspiration or want to publish your own stories, you’ll find great literary journals for writers of all backgrounds at this article:
https://writers.com/short-story-submissions
Learn How to Write a Short Story at Writers.com
The short story takes an hour to learn and a lifetime to master. Learn how to write a short story with Writers.com. Our upcoming fiction courses will give you the ropes to tell authentic, original short stories that captivate and entrance your readers.
Rosemary – Is there any chance you could add a little something to your checklist? I’d love to know the best places to submit our short stories for publication. Thanks so much.
Hi, Kim Hanson,
Some good places to find publications specific to your story are NewPages, Poets and Writers, Duotrope, and The Submission Grinder.
“ In Genre stories, all the questions are answered, threads are tied up, problems are solved, though the results of carnage may be spread over the landscape.”
Not just no but NO.
See for example the work of MacArthur Fellow Kelly Link.
[…] How to Write a Short Story: The Short Story Checklist […]
Thank you for these directions and tips. It’s very encouraging to someone like me, just NOW taking up writing.
[…] Writers.com. A great intro to writing. https://writers.com/how-to-write-a-short-story […]
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
100 Writing Practice Lessons & Exercises
by Joe Bunting | 50 comments
Want to become a better writer? Perhaps you want to write novels, or maybe you just want to get better grades in your essay writing assignments , or maybe you'd like to start a popular blog .
If you want to write better, you need practice. But what does a writing practice actually look like? In this post, I'm going to give you everything you need to kick off your writing practice and become a better writer faster.

What Is Writing Practice?
Writing practice is a method of becoming a better writer that usually involves reading lessons about the writing process, using writing prompts, doing creative writing exercises , or finishing writing pieces, like essays, short stories , novels , or books . The best writing practice is deliberate, timed, and involves feedback.
How Do You Practice Writing?
This was the question I had when I first started The Write Practice in 2011. I knew how to practice a sport and how to practice playing an instrument. But for some reason, even after studying it in college, I wasn't sure how to practice writing.
I set out to create the best writing practice I could. The Write Practice is the result.
I found that the best writing practice has three aspects:
Deliberate . Writing whatever you feel like may be cathartic, but it's not an effective way to become a better writer or build your writing skills. You'll get better faster by practicing a specific technique or aspect of the writing process each time you sit down to write.
This is why we have a new lesson about the writing process each day on The Write Practice, followed by a practice prompt at the end so you can put what you learned to use immediately.
Timed . It's no secret writers struggle with focus. There are just too many interesting distractions—Facebook, email, Kim Kardashian's Instagram feed (just kidding about that last one, sort of)—and writing is just too hard sometimes.
Setting a timer, even for just fifteen minutes, is an easy and effective way to stay focused on what's important.
This is why in our writing practice prompt at the end of each post we have a time limit, usually with a link to an online tool egg timer , so you can focus on deliberate practice without getting distracted.
Feedback . Getting feedback is one of the requirements to deliberately practice writing or any other craft. Feedback can look like listening to the reactions of your readers or asking for constructive criticism from editors and other writers.
This is why we ask you to post your writing practice after each lesson, so that you can get feedback from other writers in The Write Practice community. It's also why we set up The Write Practice Pro community , to provide critique groups for writers to get feedback on each finished piece of writing.

Our 100+ Best Creative Writing Practice Exercises and Lessons
Now that you know how we practice writing at The Write Practice, here are our best writing practice lessons to jumpstart your writing skills with some daily writing exercises, for beginner writers to even the most expert writers:
All-Time, Top 10 Writing Lessons and Exercises
These ten posts are our most viewed articles to boost your writing practice:
1. What is Plot? The 6 Elements of Plot and How to Use Them . Great stories use similar elements in wildly different ways to build page-turning stories. Click here to read what they are and learn how to start using them !
2. Top 100 Short Story Ideas . Here are over a hundred writing prompts in a variety of genres. If you need ideas for your next story, check this out!
3. How To Use Neither, Nor, Or, and Nor Correctly . Even good writers struggle figuring out when to use neither/nor and either/or. In this post, our copy-queen Liz Bureman settles the confusion once and for all. Click to continue to the writing exercise
4. Ten Secrets To Write Better Stories . How does Pixar manage to create such great stories, year after year? And how do you write a good story? In this post, I distill everything I've learned about how to write a good story into ten tips. Click to continue to the writing exercise
5. 35 Questions To Ask Your Characters From Marcel Proust . To get to know my characters better, I use a list of questions known as the Proust Questionnaire, made famous by French author, Marcel Proust. Click to continue to the writing exercise
6. How a Scene List Can Change Your Novel-Writing Life . Creating a scene list changed my novel-writing life, and doing the same will change yours too. Includes examples of the scene lists from famous authors. Click to continue to the writing exercise
7. Why You Need to be Using the Oxford Comma . Most people I've met have no idea what the Oxford comma is, but it's probably something that you have used frequently in your writing. Click to continue to the writing exercise
8. Six Surprising Ways to Write Better Interview Questions. The interview is the most-used tool in a journalist's bag. But that doesn't mean novelists, bloggers, and even students can't and don't interview people. Here's how to conduct a great interview. Click to continue to the writing exercise
9. Why You Should Try Writing in Second Person . You've probably used first person and third person point-of-view already. But what about second person? This post explains three reasons why you should try writing from this point-of-view. Click to continue to the writing exercise
10. The Secret to Show, Don't Tell . You've heard the classic writing rule, “Show. Don't Tell.” Every writing blog ever has talked about it, and for good reason. Showing, for some reason, is really difficult. Click to continue to the writing exercise.

12 Exercises and Lessons To Become a Better Writer
How do you become a better writer? These posts share our best advice:
- Want to Be a Better Writer? Cut These 7 Words
- What I Mean When I Say I Am A Writer
- How to Become a Writer: 3 Simple Steps
- 72% of Writers Struggle With THIS
- 7 Lies About Becoming a Writer That You Probably Believe
- 10 Questions to Find Your Unique Writing Voice
- The Best Writing Book I’ve Ever Read
- The Best Way to Become a Better Writer
- The Creative Writer’s Toolkit: 6 Tools You Can’t Write Without
- Should You Write More or Write Better: Quantity vs Quality
- How to Become a Better Writer in One, Simple Step
- 11 Writing Tips That Will Change Your Life
6 Lessons and Exercises from Great Writers
If you want to be a writer, learn from the great writers who have gone before you:
- 23 Essential Quotes from Ernest Hemingway About Writing
- 29 Quotes that Explain How to Become a Better Writer
- 10 Lessons Dr. Seuss Can Teach Writers
- 10 Writing Tips from Ursula Le Guin
- Once Upon a Time: Pixar Prompt
- All the Pretty Words: Writing In the Style of Cormac McCarthy
12 Genre and Format Specific Writing Lessons and Exercises
Here are our best writing lessons for specific types of writing, including essays, screenplays, memoir, short stories, children's books, and humor writing:
- Writing an Essay? Here Are 10 Effective Tips
- How To Write a Screenplay: The 5 Step Process
- How to Write a Great Memoir: a Complete Guide
- How to Write a Short Story from Start to Finish
- How to Write a Thriller Novel
- How to Write a Children's Book
- How to Write a Love Story
- How to Write a Coming of Age Story or Book
- How to Write an Adventure Book
- 5 Key Elements for Successful Short Stories
- 4 Tips to Write a Novel That Will Be Adapted Into a Movie
- Humor Writing for People Who Aren’t Funny
14 Characterization Lessons and Exercises
Good characters are the foundation of good fiction. Here are our best lessons to create better characters:
- Character Development: How to Create Characters Audiences Will Love
- Writing Villains: 9 Evil Examples of the Villain Archetype
- How NOT to Introduce a New Character
- The Strongest Form of Characterization
- The Most Important Character Archetype
- How Do You Build A Strong Character In Your Writing?
- 75+ Antihero Examples and How to Use Them
- How to Explore Your Characters’ Motivations
- 8 Tips for Naming Characters
- The Protagonist: How to Center Your Story
- Heroes vs. Anti-Heroes: Which Is Right For Your Story?
- The Weakest Form of Characterization
- How to Write With an Accent
- How To Create a Character Sketch Using Scrivener
15 Grammar Lessons and Exercises
I talk to so many writers, some of whom are published authors, who struggle with grammar. Here are our best writing lessons on grammar:
- Is It Okay To End A Sentence With A Preposition?
- Contractions List: When To Use and When To Avoid
- Good vs. Well
- Connotation vs. Denotation
- Per Se vs. Per Say
- When You SHOULD Use Passive Voice
- When Do You Use “Quotation Marks”
- Polysyndeton and Asyndeton: Definition and Examples
- The Case Against Twilight
- Affect Versus Effect
- Stop Saying “Literally”
- What Is a Comma Splice? And Why Do Editors Hate Them?
- Intra vs. Inter: Why No One Plays Intermural Sports
- Alright and Alot: Words That Are Not Words
- The Poor, Misunderstood Semicolon
4 Journalism Lessons and Exercises
Want to be a journalist? Or even use techniques from journalism to improve your novel, essay, or screenplay? Here are our best writing lessons on journalism:
- Six Ways to Ask Better Questions In Interviews
- How Should You Interview Someone? Over Email? In Person?
- What If They Don’t Want to Talk to You?
- Eleven Habits of a Highly Effective Interviewers
16 Plot and Structure Lessons and Exercises
Want to write a good story? Our top plot and structure lessons will help:
- The Ten Types of Story and How to Master Them
- Points of a Story: 6 Plot Points Every Story Needs
- How to Shape a Story: The 6 Arcs
- 7 Keys To Write the Perfect First Line of a Novel
- The Secret to Creating Conflict
- 4 Tips to Avoid Having Your Short Story Rejected by a Literary Magazine
- 7 Steps to Creating Suspense
- 5 Elements of Storytelling
- 3 Important Rules for Writing Endings
- A Writer’s Cheatsheet to Plot and Structure
- Overcoming the Monster
- How to Satisfy Your Reader With a Great Ending
- Pow! Boom! Ka-Pow! 5 Tips to Write Fight Scenes
- The Dramatic Question and Suspense in Fiction
- How to Write a Memorable Beginning and Ending
- How to Write the Perfect First Page
6 Lessons and Exercises to Beat Writer's Block
Writer's block is real, and it can completely derail your writing. Here are six lessons to get writing again:
- How To Write Whether You Feel Like it Or Not
- This Fun Creative Writing Exercise Will Change Your Life
- When You Should Be Writing But Can't…
- What to do When Your Word Count is Too Low
- 7 Tricks to Write More with Less Willpower
- When You Don’t Know What to Write, Write About Your Insecurities
7 Literary Technique Lessons and Exercises
These writing and storytelling techniques will teach you a few tricks of the trade you may not have discovered before:
- 3 Tips to “Show, Don’t Tell” Emotions and Moods
- 3 Reasons to Write Stream of Consciousness Narrative
- 16 Observations About Real Dialogue
- Intertextuality As A Literary Device
- Why You Should Use Symbolism In Your Writing
- 6 Ways to Evoke Emotion in Poetry and Prose
- 3 Tips To Write Modern Allegorical Novels
- Symbol vs. Motif: What’s the Difference
3 Inspirational Writing Lessons and Exercises
Need some inspiration? Here are three of our most inspiring posts:
- Why We Write: Four Reasons
- You Must Remember Every Scar
- 17 Reasons to Write Something NOW
3 Publishing Blogging Lessons and Exercises
If you want to get published, these three lessons will help:
- The Secret to Writing On Your Blog Every Day
- How to Publish Your Book and Sell Your First 1,000 Copies
- How to Get Published in Literary Magazines
11 Writing Prompts
Need inspiration or just a kick in the pants to write. Try one of our top writing prompts :
- Grandfathers [writing prompt]
- Out of Place [writing prompt]
- Sleepless [writing prompt]
- Longing [writing prompt]
- Write About Yourself [writing prompt]
- 3 Reasons You Should Write Ghost Stories
- Road Trip [writing prompt]
- Morning [writing prompt]
- The Beach [writing prompt]
- Fall [writing prompt]
- How to Use Six-Word Stories As Writing Prompts
Is It Time To Begin Your Writing Practice?
It's clear that if you want to become a writer, you need to practice writing. We've created a proven process to practice your writing at The Write Practice, but even if you don't join our community, I hope you'll start practicing in some way today.
Personally, I waited far too long to start practicing and it set my writing back years.
How about you? Do you think practicing writing is important? Let me know in the comments section .
Choose one of the writing practice posts above. Then, read the lesson and participate in the writing exercise, posting your work in the Pro Practice Workshop . And if you post, please give feedback to your fellow writers who also posted their practices.
Have fun and happy practicing!
Joe Bunting
Joe Bunting is an author and the leader of The Write Practice community. He is also the author of the new book Crowdsourcing Paris , a real life adventure story set in France. It was a #1 New Release on Amazon. Follow him on Instagram (@jhbunting).
Want best-seller coaching? Book Joe here.

Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

Now, Take Your Idea and Write a Book!
Enter your email to get a free 3-step worksheet and start writing your book in just a few minutes.
You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Connect on Whatsapp : +1 206 673 2541 , Get Homework Help 24x7, 100% Confidential. Connect Now
Free Short Story Essay Examples and Topics

The term, short story essay , is a combination of the two genres, “short story” and “essay.” Short stories are meant to be an engaging experience for the audience. The author should tell a compelling narrative in order to captivate their audience. There are many different ways in which you can write this type of essay including: brainstorming ideas, researching your topic, outlining your plot points, making notes about important details that need to be included in your story, writing out dialogue between characters or describing scenes where major events occurred. This article will discuss how you can write a short story essay with examples from other students’ work.
How to write a short story essay
Writing a short story requires the writer to work with many aspects of fiction writing. A person must have imagination, creativity and discipline.
Short story essay vary in length such as:
- 3-5 paragraph short story essay
- 2 Page Short story essay (500-600 words)
- 3 page short story essay (750-900 Words
- 5 Page short story essay (1250-1500 Words)
To guide you in your efforts here are six (6) steps to follow when writing a short story essay:
- Start with an idea
Every good piece of writing starts with an idea, so start by considering what sort of idea you would like to write about. Try brainstorming some ideas that are personal or unique to you. Once you decide on your subject it is time to develop it into a full blown concept for your short story.
- Build the characters
Next consider who will be involved in your story and what roles they play in the narrative. The best stories are those which have strong, dynamic characters. Characters which the readers can relate to and empathise with. Think of your characters as people, real or imagined, who have a certain type of personality which affects how they behave in different situations. In this way you can inspire your readers to have a better understanding about themselves and their own personality traits.
- Incorporate descriptive details
The setting is an important element in any story so be sure that it is properly described. Do not just tell us that a character woke up early one morning but describe the feeling of waking up on a cold winter morning when the sun has not risen yet and everything is silent except for the birds chirping outside our window. All those senses are engaged by those few simple words “silent except for the birds chirping outside our window”.
- Keep a record of ideas and inspirations
A writer needs to be open to inspiration in order to create a good story. If you find an interesting object or spot, make sure that you take note of it because this could later provide you with motivation when writing your short story essay. For example, if while taking a walk in the park you see two people looking at each other from across a gap between the trees, these characters may serve as an inspiration for your short story.
- Create momentum
The best stories are action-packed so try and incorporate actions into your narrative. The best way to do this is by giving your protagonist(s) problems to solve or tasks to achieve, then making it increasingly difficult for them to do so. This will provoke conflict and tension which is what keeps your readers interested in the story.
- The conclusion
The conclusion of the short story must provide conclusions about your characters, their actions and conclusions about life in general. You can leave some thoughts with your readers by adding an element of mystery, something that makes them think back on the entire narrative. A “what if” statement can be useful here: “ What if my grandmother had seen him across the park? Would she have run after him?” These are the kind of questions that arise in our minds when reading a good short story essay.
Comparison Essay on Two (2) Short Stories
Comparison essay is an essential part of academic writing. A fair amount of comparison essay is that it requires students to read two texts, identify similarities and differences between them, create a thesis statement on which are the main differences, back it up with evidence from both stories/texts/books etc., arrange all points in clear paragraphs, learn how to write a conclusion paragraph where you summarize all your ideas again so that the reader will have no difficulty understanding your point even after several days have passed since reading your text.
When teachers require students to write comparison essays on two short stories they give specific instructions on what topics to choose for discussion with their examples, but most often these examples are not enough for students who do not know what exactly should be discussed in their texts.
If you are writing a comparison essay on two short stories, there is no point of discussing different topics as it is not possible within such a paper. The same ideas should be written over and over again but from different perspectives. If you think “I don’t want to write the same thing again and again” you are wrong because that’s the only way to show how similar or different two texts are.
If your teacher wants you to compare/contrast two short stories, he/she expects you to follow certain rules. Here are a few steps you can follow to get better at writing short stories.
Steps to Follow when Writing a Comparison Essay:
- You need to start with a thesis statement which clearly shows what main elements of the texts are being compared and what the focus of your essay is going on about.
- The next paragraphs should be dedicated to comparison of point by point, so there should be several sentences devoted one by one to describe similarities and differences between stories under discussion; please make sure that these points or facts don’t seem too obvious for your reader as they already know them
- Make sure you use correct examples from both texts for comparison so that they are really alike in their right perspective
- Your paragraphs should be organized according to how important certain elements are. You can’t write all your ideas in one paragraph unless the point is very small and unimportant.
- Another tip on ordering of sentences in your essay: if two points are similar, they should be written in one sentence; if they differ, then you need to divide them into several sentences.
- There has to be a clear structure in every paper you write even if it’s just a comparison essay on two short stories! This means correct organization of thoughts with the help of topic sentences (which show what will be discussed next). Point of view should also be clear and easy to understand for the reader.
- Do not forget to write a conclusion paragraph where you summarize your main ideas again using different words, phrases or sentences than those that were used in your essay; this will emphasize their importance.
- You need to read your paper several times checking all kinds of errors (grammar/punctuation/spelling etc.) as even one mistake can ruin your final grade!
How do you Cite (address) a short story in an essay?
When citing or referencing a short story in an essay or other written work, you must include all relevant information about the author and title of the story as well as identifying any additional information specific to your usage. Whether you’re creating an MLA , APA, Chicago/abian or any other type of formatting style, it’s important that your short story citation matches the format and standards outlined in your assignment.
The Basics: Author and Title of Story
As with any work you’re citing, the title and author of the story must be included in your reference entry. The title should include all words from the original publication; for example, if there were quotation marks around the title when originally published, then they should remain on any references. Similarly, underline or italicize titles just as they appeared on a book or magazine cover or publication you found them in.
Cite a short story by its full name along with an abbreviation for state/city/publication information if included at all. If more than one author is listed, use the word “and” between their names as you would for any other citation. If a publication is included, include publisher name and year of publication in parentheses immediately following the title.
When you are finished, your entry should have the author’s last name followed by any relevant title information in italics before the full-stop. Following this should be the city, state abbreviation and publisher of where the short story was originally published. All publication information goes after a forward slash – reference books will often include page numbers for you to use as well.
For Example:
Chavez, Jennifer L., and Monica R. Hand. “The Baby Pharma Industry—Exploiting Expectant Mothers.” Mothering 43 (1999): 38+. ProQuest Central. Web. 15 July 2015 <Link>.
Crowley, Dennis J., et al. “Exercise-Induced Bronchospasm among Young Soldiers.” Military Medicine 158 (1983): 363-67. ProQuest Central. Web. 15 July 2015 <Link>.
These examples are both in MLA format; however, remember that you should never copy and paste your information directly from a document as it is very easy for another person to steal the information and pretend as though they were the original author. Instead, use these examples as a guide to create your own short story citation in whatever format you choose.
Additional Information: Paraphrase or Quote
If you’re directly quoting from a short story under fair-use policy (refer to your assignment on this) then be sure that first and foremost quote marks are properly placed around any text that was originally said by another individual.
Include parenthetical documentation after any quoted text specifying which page number the quotation can be found on if applicable; if not included, place quotations directly after the author’s name without parentheses. If paraphrased words or ideas from a short story are included in your work, simply include a reference entry at the end before works cited.
Short Story Essay Topics and Prompts
Writing a short story essay is a complex task. Readers’ thoughts and ideas are influenced by the words that writers use in their stories. This makes it difficult to write an original, unique opinion about a topic from which many people have written before.
However, there are still some topics that every good writer should consider when writing a literary analysis of a short story- no matter how boring or insignificant they may seem at first glance.
Most of shorty story writing prompts revolve around the following subjects:
- The Beginning of the Story
- The ending of the story
- Character Analysis
- Point Of View [POV]/ Tense
- Style/ Literary devices used
- Setting/ Theme/ Mood Themes within the Story / Writer’s Intentions Annotated Texts [using quotes from the story]
The Beginning of a Story
- One of the most important elements of a short story is its hook . “A good storyteller has to have something that will entice his audience from the very beginning.” [1] In other words, he must be able to capture and keep their attention, and make them want to read on and find out what happens next. Therefore, choosing an interesting topic to write about in regards to a story’s beginning can be quite difficult. Nevertheless, there are several topics that students should consider when writing their literary analysis essay:
- How did the protagonist get into his current situation? (ex: How did Emma ever end up with such awful parents?) Why does the protagonist feel like things need to change? (ex: Why does Emma feel like she can’t continue living with her awful parents?) What happens that makes the protagonist realize/realize that things need to change?
- What are some possible obstacles that must be faced before the protagonist reaches his goal? What other problems might he encounter along the way? How does the protagonist overcome these difficulties and solve his problem(s)?
- How does the first paragraph of a story set up its theme or mood? Does it give you any clues as to what might happen next? How does it prepare you for what is to come in this particular story?
- Are there any foreshadowing techniques used in the beginning of this story that make you think about how things will end or affect your interpretation of the story’s events?
The Ending of a Story
- In general, the ending of a short story is what gives meaning to everything that came before it. If the beginning hooked readers in, then the end must leave them satisfied and fulfilled. In addition to discussing how well or badly a story ends, students might consider writing about some of these possible topics:
- How does the ending reinforce what was already said/written about in this particular piece? What connections can you make between certain parts of this work and its conclusion? How do they fit together?
- What kind of final impression did this work leave on you- either positive or negative?
- Was the ending realistic? Why or why not?
- Was the ending “happy” or “sad”? What evidence does the writer give to support this claim?
- Do you agree with how things ended up, and would you have made a different choice if you had been in charge of writing the conclusion to this particular story?
- What types of events led up to the final moment of resolution/clarity within this piece? Does it make sense that these specific scenarios unfolded as they did, given what you know about each character’s personality and background from earlier parts of the text? In other words, were any coincidences too convenient for your liking, or do certain events seem far-fetched based on their context within story as a whole? How would you have ended this story if you were the writer?
- What impact does the ending have on your overall impressions of the work as a whole? What type of final impression did this story leave with you- positive or negative?
Character Analysis/Development
- What is the main differences between the two characters in the shorty story “A cup of tea”
- One common topic for short story essays is to consider how well or badly a character has been developed. Depending on what kind of feedback students are looking for, some quick questions they might ask themselves include:
- How important was it for this particular character to be convincing and realistic within this setting? Were they interesting enough to carry the story forward by themselves, even if the same events had played out altogether differently? How convincing were they in light of their own history (and everything that led up to the point in which the story took place)?
- Are any of these characters based on real people? If so, how does this influence your interpretation of the character’s actions and motivations throughout the story? For example, some critics have claimed that several aspects of “Catcher in the Rye” are autobiographical. In what ways is Holden similar to Salinger himself? In what ways do you think he differs from his creator?
- How did the author go about developing their backstory? How might this help us better understand why they behave as they do in certain situations within this particular short story or novel? Are there any details that didn’t seem important enough to include, but which could have helped us better understand the character as a whole?
- How does this person change or learn from the events that occur throughout the course of this narrative (if at all)? How would you describe their reactions to various circumstances- particularly those which might elicit surprise, anger, confusion, and/or fear within you as a reader? Is there anything about these changes in behavior that makes them believable and realistic to you?
- What types of details characterize this character’s actions and feelings throughout the work- either directly or indirectly? How well do these match up with your impressions of who they were “supposed” to be based on what was already revealed about them earlier on in the story? Does seeing this specific event change your views about how they might act in the future? Why or why not?
- How would you describe this character’s personality, based on what little we know about them in comparison to the other characters in this work? Are there any significantly different aspects of their backstory which make them stand out compared to others within the same setting (in terms of physical description, socioeconomic status, age-related issues, etc.)? How do these differences influence your interpretation of their behavior throughout the course of this short story or novel?
- What types of evidence does the writer use to develop this person beyond stereotypes and assumptions that might be obvious at first glance? For example, if one reads “The Things They Carried” by Tim O’Brien, much can already be inferred about each character based on their age and physical appearance alone. That said, how well do we get to know the characters as a whole? And in what ways might this understanding of them change depending on whether you read the short story or novel version (or both)?
- How effectively does the setting contribute to your interpretation of this character’s actions and motivations? Do they seem out-of-place within their own world, or is every detail just right given their role in this narrative? Does knowing more about their backstory influence your overall reading experience, positively or negatively?
Attitudes/Opinions
Another common topic for short stories relates to a writer’s point of view about certain issues. For example:
- Do you agree with the author’s opinions on the following subjects? Why or why not?
- How did you identify with this character’s attitudes and opinions throughout the narrative, if at all? Were there certain situations in which their views seemed to change for better or worse? If so, what were some of the factors that influenced these changes within them (i.e., other characters, settings, etc.)?
- Did anything about this person’s behavior irritate you throughout the course of the short story or novel (for example: self-righteousness)? At times, do you think they might have been right when others around them disagreed with them on specific points? Or was it more likely that others held a stronger grasp on reality than they did? What type of information is revealed within the plot to convince you that this character was right in what they said/did, if at all?
- What kinds of details support their points-of-view throughout the course of this narrative? Are there any decisions or actions which seemed out-of-character based on your understanding of their personality and personal history? How do these incongruences make you feel about them as a whole (positively or negatively)?
- How much did their views tend to change throughout the work, especially when it came to issues that were particularly relevant for them personally? For example, take a look at “Miss Brill” by Katherine Mansfield. In the beginning, Miss Brill is seen engaging in her usual pastime while eventually coming to realize how little she appears to have in common with the people surrounding her. But do their opinions really matter when it comes to how she perceives herself? How would you describe this character’s personality, based on what little we know about them in comparison to the other characters in this work? Are there any significantly different aspects of their backstory which make them stand out compared to others within the same setting (in terms of physical description, socioeconomic status , age-related issues, etc.)? How do these differences influence your interpretation of their behavior throughout the course of this short story or novel?
- Can they be seen as a universal archetype for people living within a specific era, place, or situation? What kinds of details support this interpretation throughout the course of the narrative? Do any events stand out as being particularly significant within this setting, even if they only lasted briefly? How does this information change your view of them as a human being compared to those around them who are influenced by similar factors but end up reacting in different ways?
- Which characters do you see as having the most in common with this person, and might there be any significant moral implications for these similarities? Do you feel that their opinions are justified on issues where people of their age, gender, social standing, etc., might not have had equal rights or access to certain types of information? How would their lives have been different if they’d taken a more proactive approach to topics concerning politics, race relations by other groups, etc.?
- What is your opinion about the treatment of women within the setting(s) explored throughout this piece? Is there anything which author seems particularly critical about how women are expected to behave or interact with others who present themselves as being progressive on certain issues (i.e. feminism or gender equality)? Is this treatment applied to all women, regardless of their background in comparison to the majority of people within this specific time period?
- How much can you understand about them based on either your personal experiences with these topics or what you’ve learned about people who shared similar views during historical or current events? Do any characters stand out as being significantly more open-minded when it comes to certain issues which are often seen as controversial even today (i.e. LGBT rights, premarital sex, etc.)? How would they have responded if they were exposed to someone who held beliefs that were at odds with their own values and sense of self-identity?
- What major decisions did they make throughout their life that made an impact on other people, or even this person themselves? What kind of changes can be traced back to these events and what evidence is there that they would not have occurred if it hadn’t been for the influence of the protagonist(s)? How does this information supplement your understanding of their personality and general character arc? What do you think might’ve happened if they’d made a different choice at any point in time (even one which seems like an insignificant detail when read from a modern perspective)?
- Does their personal philosophy differ significantly from those around them based on the context provided by the narrative? Is there anything about this character’s way of thinking which stands out as being particularly unusual within such a setting, even if only lasts briefly (such as during a specific scene or chapter)? What can be inferred about this person’s personal values, even if they only make a brief appearance in the story? Are they significantly different from those around them, and if so is that difference justified by events within the story?
- In what ways does the style of narration change throughout the course of this piece? In what ways might it have influenced how you perceive certain details as being more relevant than others, especially when compared to other genres or works of fiction which rely on a similar technique to tell their stories? How significant do you consider each character’s perspectives to be within this narrative and why were certain events described from a particular viewpoint instead of generalizing it based on who was taking part in these scenes?
- What types of emotions does this work evoke in the reader and why do you think they were emphasized so strongly? Do these techniques contribute to how we perceive each character’s internal thought process throughout their interactions with others, or how we understand their position within the group as a whole? How might different choices have been made if you assume that other types of emotional reactions were minimized or excluded entirely?
- Many people would consider this book to be one of the most significant pieces of literature ever published, for both its historical value and what it helped to inspire during periods such as the Harlem Renaissance. However, not everyone will agree about whether it should be categorized as fine art because of its purposeful ambiguity concerning certain details (such as which characters are meant to represent real-life historical figures and whether or not they were actually based on specific individuals). How might the overall tone of the story change if you assume that all of its characters, events, etc. are meant to be understood as being factual? Would it still have made just as much of an impact if it’d been written in a more straightforward manner instead of using symbols and techniques which don’t need to be deciphered in order for the narrative to be coherent?
- What kinds of conclusions can you make about this collection once you’ve reached the end? Have any major revelations been presented within its pages which will have a significant impact on how you interpret each individual piece afterwards? Were these details revealed gradually throughout the work instead of being clustered at the conclusion where they could provide a better sense of closure?
- Why is it significant that the author chose to include such a wide range of topics within this anthology, and how does each contribute to the story as a whole? Do certain emotions or themes become more strongly emphasized depending on which specific piece you’re reading and why do you think these elements remain consistent with earlier selections in terms of tone and style? How would your response to each individual story differ if they were written by multiple authors instead of just one person (and if so, how might this affect your overall appreciation for both the texts and narrative progression)?
- In what ways is this text intended to be interpreted from an allegorical perspective? What types of events are meant to symbolize other conflicts taking place at the same time, and are their meanings meant to be understood in literal terms or within the broader context of the story as a whole? How might this information change your perception of various characters’ roles within each scene, especially if you assume that they are meant to represent something else entirely outside of what’s explicitly stated?
- What elements about this piece make it effective at portraying its theme in particular ways? Are there any sequences which could have been used more effectively to demonstrate these ideas instead of just hinting them without enough elaboration? Could specific techniques have been employed in order to avoid making certain moments feel either too forced or underwhelming compared to other parts which successfully convey similar themes?
Style/ Literary Devices Used:
- How does the author’s style contribute to the story’s overall tone and atmosphere? Is this choice of writing consistent throughout or does it change at any point, and if so, does this have a significant impact on how you perceive each character’s personality? Do you notice any elements which could be considered postmodern in nature (such as nonlinear plot structure and self-reflexivity)? What types of messages do these convey about the work itself and what might they imply about its focus when compared with similar texts? Are there certain techniques used multiple times throughout which help strengthen this connection between events we’ve seen before and things yet to come?
- Does the text include any specific commentary on human nature, especially when contrasting different characters’ actions against one another? Are there certain moments when the environment or backstory are more significant than which of the people inhabiting it, and if so, what kinds of emotional responses can you expect to experience while reading these scenes? Is the narrative ever intended to be confusing in any way (in terms of its structure or by presenting symbolism within otherwise normal circumstances)?
- How would this short story’s tone change if you assumed that all of its characters are meant to be understood as being factual? Would it still have made just as much of an impact if it’d been written in a more straightforward manner instead of using symbols and techniques which don’t need to be deciphered in order for the narrative to be coherent?
- What kinds of conclusions can you make about this collection of stories as a whole? Is there any specific common element between each piece (in terms of genre, time period, setting, etc.)? How would they vary if they had been written by someone who isn’t the same person who created this compilation and how might it change your overall appreciation for both the text and its author?
- Why is this anthology classified as science fiction in particular and what needs to be included in order for an individual story to fit within that category? Are there elements about it which could put off some readers from making certain connections or having certain reactions when reading it? What makes this selection different compared to similar texts with extremely similar content (such as “The Veldt” by Ray Bradbury) and why didn’t you find those as appealing?
- How do the changes in tone and atmosphere presented within the stories affect your overall impression of each one? For instance, if a darker piece were to follow a more whimsical story about an otherwise innocent protagonist, would this have a negative impact on your interpretation of how the characters within that first work had been portrayed by the author? What about vice versa – would lighter stories be more enjoyable if they came after something which had been intended for mature audiences only due to its dark nature and violence toward its characters?
- What makes these particular pieces especially effective at portraying their themes without feeling excessively preachy or forced down your throat from beginning to end? How do the different emotions evoked by each entry help create a balance between enjoyment and genuine appreciation for the text itself? Does this collection ever take on any unexpected levels of depth or does it present everything in-between its covers clearly and concisely, while still making you think about them for hours after finishing each one?
- Did the stories presented within “The Illustrated Man” have a noticeable impact on other works released near the same time period (such as The Twilight Zone television episode “The Long Morrow”) or can you identify elements which were likely to have been directly influence by Bradbury’s work instead (such as Superman)? Do any aspects of this anthology help to date it compared with similar books from around that era and would it be more or less enjoyable depending on your familiarity with 20th Century culture?
- Are there specific characters who are common to more than one story in the anthology? What are the circumstances surrounding their first appearance and what makes them stand out among Bradbury’s other characters which weren’t featured as frequently throughout this book? Is there any difference between how these central individuals appear within each separate narrative or do they seem like copies of each other without any significant differences, no matter where you encounter them?
- How would your perspective on “The Illustrated Man” change if it was labeled as horror instead of science fiction? Would that have an impact on its appeal or general tone depending on who you are or how familiar you are with either genre? What about its overall structure – is it ever meant to be read linearly from beginning through end, or should people skip around whenever they feel like doing so?
- What makes the writing style in particular stand out compared to other entries you’ve read throughout your life? Does it ever seem too wordy or overly complicated even when the subject matter is complex to begin with? Do any elements of Bradbury’s prose help you become more invested in what he has presented as a result and do any changes present between each piece come across as improvements instead of hindrances?
- Do any aspects of this book still surprise you after having read it multiple times already, whether due to its length or content itself? Is there anything which was likely going through your head while reading certain parts which you never expected to find at all beforehand – including things related directly the plot and characters themselves as well as small details which you wouldn’t normally think to be included for certain reasons?
- If the stories within “The Illustrated Man” were to be adapted into a movie, would they fit in with modern tastes and expectations or would it feel like something from the past which belonged at its time of creation? Is there anything about this book which could easily be updated with special effects such as space travel and other such technologies, while leaving everything else exactly the same no matter how many decades pass by during your lifetime?
- Would any of the stories be more effective if they were read out loud instead of silently flipping between pages throughout an average-sized book? Do you think Bradbury ever intended for anything written here to be presented outside of its original medium to begin with, by either recording each story in an audio format or branching the film rights out into separate spin-offs?
Setting/ Theme/ Mood within the Story / Writer’s Intentions
- What are some of the different elements that have been included in order to create a specific tone/ mood throughout this piece? Which of these are most significant and why? How do all of these contribute toward establishing an overall theme for the entire text as well as its individual components?
- Why are all of these characters behaving differently than usual, or why are they engaging with one another in ways which seemed unlikely during the first few chapters? Are there any clues (either subtle or obvious) which can be used to accurately infer what happened or why it has led to their current situation?
- What are the main differences between how each character sees themselves, and how do other people in their life see them instead? How might their perception of reality change over time if they’re able to be more objective about these observations?
- Given the setting of the story, have any assumptions you’d previously made about certain characters been proven wrong by this point in the narrative? Why does the author choose to include so many different perspectives when telling this particular story, and is there any reason behind presenting multiple perspectives that don’t necessarily agree with one another whenever possible ?
- Is this piece written from anyone’s perspective but that of an outsider? Is there any specific reason why the author would choose to follow a more detached approach to their storytelling, or does this fact help establish an overall theme of alienation that remains consistent throughout the entire text?
- What are some of the various points of view which have been included in this story, and how do their individual viewpoints differ from one another? Does anyone receive special treatment within its pages, or is everyone represented as being flawed at best/ reprehensible at worst ?
- How does conflict affect the progression of events during each scene? Can you identify certain moments where it might have been able to be diffused before longtime rivalries become irreconcilable grievances, or are these violent exchanges apparently inevitable despite certain characters’ efforts toward reconciliation?
- How do the actions of one character affect another’s choices within this piece, and vice versa? What is the overall significance of their relationship with one another, and does it remain consistent during each scene or evolve into something different over time?
- Why does the author choose to include certain dialogue exchanges (and more importantly, details regarding how these individuals behave in private)? What are some of the various aspects which make up a person’s personality, and why would an author attempt to capture these idiosyncrasies on paper?
- To what extent is the setting an integral part of this story; why does the author choose to set it at this specific place/ time instead of another location/ era? Does it help establish an overall theme of nostalgia, regret, or instead a false sense of security?
- How does the setting help enhance the events and moods which take place during this piece (in other words, can you identify certain environmental factors which make it easier for these individuals to become more accepting of one another after an extended amount of time)? Are any of these moments seemingly insignificant; perhaps explained away as part of everyday life- such as enjoying a cup of coffee on the front porch- why might they be included in spite of seeming like ordinary activities?
- How do all of these texts seem to relate with one another? Why is there so much emphasis placed upon family ties and their role within society as a whole during each work? What larger message might the author be trying to convey by incorporating these similarities into each story?
- Which aspect of family has been most emphasized within this text (is it biological relationships, or is it the connection between friends?)? What does this particular theme indicate about how people are supposed to relate with one another throughout their lives, and why would an author choose to give so much prominence to any specific element within their work of fiction ?
- If you were able to narrate this piece (either in its entirety or only certain scenes), what would you want your audience to know/ understand better after reading your account of events? How do you think they’ll be affected by everything that takes place within each scene, and how has their understanding changed as a result of reading about these characters’ experiences?
- How has your overall appreciation for this story changed as a result of completing the various questions found above? Do you have anything else to add regarding its significance, or do you believe it is self-explanatory without any additional commentary?
Short Story Essay Examples
- Short story essay on childhood memories
Sample Short Story Essay On Childhood Memories
- Short story essay about friendship
Sample Short Story Essay About Friendship (pdf)
- Short story essay about accident
Sample Short Story Essay About An Accident (pdf)
Sample comparison essay on two short stories
Get Help in Short Story Writing
Are you struggling to write your short story essay and getting tired of writing and rewriting? Have you run out of time and don’t know what to do? If the answer to either question is yes, then we can help. Writing a high-quality essay for your short story class takes an immense amount of effort and we understand that at times it feels like too much. Not only does one need extensive knowledge of the subject material but it also requires creativity, proper research skills, ability to convey information clearly and coherently as well as academic standards such as grammar and formatting. This is why many students decide to pay someone or a professional essay writing service their short stories essays. The good news is that there are legitimate custom writing services offering first-rate work for money by professional writers.
WhatsApp us

10 quick tips to improve essay writing skills
M any students struggle to hone their writing skills for years if not decades. While it might seem straightforward, the reality is that many learners fail because it’s demanding. However, there’s no cause for alarm. Writing hardly comes naturally even to the most gifted authors. It takes hard work, practice, and dedication. In this article, we’ll share with you a few secrets to improve essay writing skills in college. Read on to understand.
The importance of essay writing skills
If you didn’t know it, essay-writing skills are vital for academic and professional success. Their potential to open doors of opportunities is almost unmatched. Below are some benefits of honing your writing skills:
- Enhances critical thinking
- Improves communication skills
- Develop researching skills
- Inspires and enhances creativity
- Boosts your analytical skills
- Makes you a better planner
- Improves academic performance
- Improves your chances of career success
- Promotes lifelong learning
Tools and resources to improve writing skills
Undeniably, technology has completely revolutionized our education system. Whether we like it or not, it’s here to stay and we must embrace it or risk being left behind. Today, there are numerous Edtech programs to help students write essays better. We believe each college student should consider the following three resources. First, if you struggle with brainstorming, use Evernote to capture ideas and notes for writing inspiration. Secondly, try online help if you’re overwhelmed with work, education, and family responsibilities. A same day essay writing service like FastEssay has a team of highly qualified individuals providing quick essay writing services for students like you. They can help you with both business and academic writing services. Lastly, try Textero, an AI platform that can assist you in generating texts in minutes!
From mediocre to masterful: 10 tips to get better at writing essays
Learn to plan.
Failing to plan is planning to fail – nothing could be truer. If you want to master a skill, you must develop a clear plan for learning, practicing, and conquering it. Writing isn’t any different. Many students fail to hone their writing skills because of poor preparation. We’d advise you to develop a flexible practice schedule to help you master new words and phrases. Most importantly, you must recognize that learning doesn’t happen overnight. Therefore, follow your plan with patience and discipline.
Read widely
Just as an iron sharpens another, you’ll learn a lot from accomplished authors in your area of interest. It’s improbable to become a great writer if you’re a lazy reader. You must be willing to read widely and pick a few tips along the way. You can learn new phrases, vocabularies, idioms, and expressions from simple newspaper cutting, magazines, books, or blog articles. Moreover, it’s not just about the positives, you’ll also learn what to avoid in your own articles. For example, if the material you’re reading has a flat and uninspiring introduction, you can learn to make yours catchy to improve readership and engagement.
Understand the process
Essay writing is a process. It’s structured. You can’t write winning essays haphazardly. It’s critical to understand this basic concept. Otherwise, it would be impossible to accord the process the respect it deserves. Too many students crafting an essay can take any direction and shape. In some cases, it’s the case of putting the cart before the horse. Employing such tactics often proves counterproductive. However, if you want to improve your essay writing skills, you must recognize the stages involved, i.e., brainstorming, drafting, revising, and editing, and follow them. Understand that they’re all critical to a winning paper.
Use the right structure
The structure of your essay is just as important as the writing process. It’s unsurprising, therefore, that most educators emphasize it in their teachings. While a typical essay has three parts, introduction, body, and conclusion, each of them demands different skills and organization. For example, you must understand that the introduction will require a special touch with a solid thesis statement. In addition, your body paragraphs must flow logically and provide irrefutable evidence. Most importantly, your conclusion should come last and highlight all your major arguments. Ignoring any of these parts could lead to a failing grade.
Choose the right topics
Even though some lecturers insist on select topics, many allow students to choose subjects that interest them. Therefore, if you have the freedom, please focus on your interests. Writing about subjects, ideas, and topics that pique your curiosity is likely to unlock your creative genius, making the process seamless and enjoyable. The reverse is true for issues that hardly interest you. Remember that your keen interest in a subject will make you dedicate more of your time to it, research deeply, and explore its controversies, which can only spice up your work.
Incorporate evidence
Writing an essay is like drawing on an empty canvas. You can model it the way you want, creating a masterpiece or trash. However, with each stroke, you make permanent marks that expose your thought pattern and mental state. So, avoid babbling, and instead craft a logical paper by incorporating supporting arguments. Don’t take your audience on a guessing trip, wondering if your claims are factual or mere hearsay. Instead, support every claim with evidence from reliable and credible sources. To become better at writing, you must be accountable to your audience.
Embrace simplicity
Sometimes we try too hard to impress our audiences. In fact, many students try too hard to capture their teachers’ attention. While this isn’t a crime, they run the risk of crossing the line. This shouldn’t happen if you intend to improve your writing skills. Be simple in your approach. Avoid using complex vocabulary and phrases. Additionally, be wary of incorporating ideas that are beyond your scope. For example, when writing an English essay about the disadvantages of smoking, don’t change it into a medical opinion piece, digging deeply into the complex interlink between tobacco and cancer. Keep it simple.
Follow instructions
The simple things are often the hardest to adhere to. This partly explains why teachers occasionally include trick questions in their exam papers. It doesn’t matter how well-structured and polished your essay is if you don’t follow your lecturers’ instructions. For instance, if your teacher wants a 500-word paper, don’t surprise them with a 1000-word article. Otherwise, they’ll be more likely to mark you down, reject your submission, or fail you than praise you.
Editing and proofreading your essay
No one is perfect. If it would help, you should know that even the most accomplished authors make mistakes. However, writing better papers demands that you work on your errors constantly until they no longer define you. Don’t be the writer known for structural, stylistic, or grammar issues. Once you’re done with your first draft, let it settle for a few hours, then proofread and edit it to eliminate all errors. This is the surest way to get better at writing essays.
Maintain timeliness
You’ll be surprised to learn the number of students who’ve failed their courses for late submissions. The introduction of the Education Management Information System has made it impossible for learners to submit their papers after the deadline by automatically locking the submission pane. It doesn’t matter how great your essay is if you can’t submit it for marking. The best strategy is to start working on your paper early and complete it with days to spare.
Read widely and excel in essay writing!
As captured in the short article above, there are numerous strategies for improving your essay writing skills. While these aren’t the only ways to write better essays, they can surely set you on the right path to honing your skills. With the right attitude, adherence to all instructions, timeliness, and simplicity, you can conquer most hurdles on your way and become an accomplished writer. But most importantly, READ!
More From Forbes
5+ Generative AI Writing Tools Everyone Should Know About
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
One of the most popular use cases for generative AI is writing. This is thanks to the ability of tools like ChatGPT and Gemini to create any kind of text, from poetry and fiction to technical documents.
Their ability to understand context and mimic any human writing style in order to create comprehensive content on any subject is probably their most impressive ability right now.
It's worth remembering, however, that these large language model (LLM) tools are, for the most part, limited to constructing text based on their training data. This means it isn't necessarily great at communicating new ideas or writing in a way that will grip the attention of a human audience.
But when it comes to brainstorming, drafting, structuring, researching and fact-checking, it can be a powerful tool that can save time and effort for anyone who needs to create written content.
It can also speed up all manner of routine, day-to-day writing, such as drafting emails or creating product descriptions for e-commerce businesses.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024, five of my favorite generative ai writing tools.
The most well-known generative AI tools are all capable of creating written text. But here, I'm focusing on those that specifically provide features and functions designed to assist with writing. These are some of the most useful and interesting players on the field right now:
Jasper was one of the first specialist generative AI writing tools, positioning itself as a solution for marketers needing to create copy in a hurry. It provides templates that speed up the process of generating blogs, social media posts or product listings.
This gives it an advantage over more general-purpose genAI tools that often start you off on a blank page and require careful prompting if you want them to follow a process to create multiple pieces of writing. It also adapts to its user's style and voice over time.
Another advantage over general-purpose tools (like ChatGPT) is that Jasper doesn't rely on any one language model. While its output is powered by OpenAI’s models, including GPT-4, it is also reported to use models created by Google, Anthropic and more. Jasper isn’t the cheapest option on the market, but it stands out by providing a tailored set of solutions for marketing-focused writers.
One thing that sets Sudowrite apart is that it is tailored specifically for fiction writers. So, if you’re looking for an AI that might help you write the next Game Of Thrones, it could be the right choice for you!
Sudowrite is built around tools that can help fiction authors, such as brainstorming aids, restructuring sentences to make them more readable or exciting, and providing detailed feedback on their own writing. It is designed to understand concepts such as audiences and genres, as well as what makes a piece of writing engaging for an audience to read. Not sure where your story’s going? Simply hit the Write button and have it continue the tale, giving you options to choose from and mimicking your own tone and voice!
Anyword is focused on what it calls "performance content," content designed to sell, generate clicks or encourage audiences to take some other form of action.
It includes a “predicted performance” stat that attempts to forecast how well your piece of content will go down with your audience. The aim is to automate the data analytics that marketers use when creating and publishing content at the point of writing in order to encourage greater engagement.
Unlike some of the other options here, this is marketed firmly as a business solution and isn't the best choice for hobby writers or those starting a small business marketing strategy from scratch. It’s accessed via an API rather than a friendly chatbot web interface.
But for established companies who have plenty of data and an established content pipeline that want to start leveraging AI-driven analytics, it’s a good option.
Canva Magic Write
Okay, so this one isn't a standalone writing tool. It’s the writing element of the versatile cloud-based design platform Canva that has recently added a ton of AI functionality under the heading Magic.
As you might expect, this one is mostly geared toward writing as an element of design rather than creating plain, long-form text. This means it's optimized for creating marketing emails, social media ads and advertising copy. I particularly like the way it lets you adjust the tone of your text. This is stuff that you’d need to dive into prompt engineering in order to do if you’re relying on something like ChatGPT or Gemini to write marketing copy. One of the differences when using a specialized platform is that this kind of use case-specific function is built into the user interface, so it's always at your fingertips.
Grammarly has been around for a long time and has always been marketed as an AI typing assistant. But a major overhaul last year saw the introduction of Grammarly GO, its generative AI-augmented service. Currently still in beta but available to most users, GO uses large language algorithms to provide content suggestions and synonyms and to suggest better ways of saying what you want to say.
It isn’t a standalone tool that will churn out long-form content on its own, but rather a plugin that can be integrated into software from word processors to web browsers – anywhere you might want to write text. It also scores your text for readability, detects plagiarism and gives automated guidance on word choice and sentence structure. It may not get mentioned in so many news reports as newer players like ChatGPT or Google Gemini, but as an all-around writing assistant for the sort of writing that most people do every day, it's hard to beat.
Other Great Generative AI Writing Tools
There are many other apps, tools and platforms that also specialize in writing, so here’s a quick overview of the rest!
Writes content like blog posts while citing its sources to help overcome issues of AI hallucination.
Chibi aims to give users deeper control over the AI writing process, creating personalized workflows rather than relying on templates.
Content At Scale
Geared for creating human-like written content for marketing purposes.
Content creation tool aimed at businesses and enterprises, with built-in templates for common jobs.
AI copywriting tool that specializes in website copy, blogs and social media posts for businesses or hobbyists.
Copysmith’s Describely tool is a very useful application optimized for using AI to write product descriptions for e-commerce.
This one provides feedback on grammar and clarity of your writing, and also optimizes copy for SEO purposes.
A collaborative writing assistant focused on simplifying content production with tools for brainstorming as well as templates.
Designed to help writers create clear, concise and to-the-point writing in an active voice, much like Hemmingway himself.
Writing assistant with a comprehensive toolbox of AI features to help tackle a variety of writing tasks.
Auto-generate SEO-optimized content to improve ranking in search engines.
An AI co-pilot for writers offering AI feedback on your work and tools for finding the right words or expressions or generating ideas.
Create more long-form content that differentiates by promising zero hallucinations.
Designed to help would-be novelists get their ideas out of their heads and onto the page.
Another extension-based assistant that plugs into your favorite software and offers in-line automated assistance as you work.
ProWritingAid
A writing mentor for professionals, offering in-depth analysis of style and readability with the aim of creating elegant prose.
Quillbot bills itself as a paraphraser tool to help writers find a better way of phrasing something.
Generates blogs, emails, social media posts, SEO headlines and ads.
Automates the creation of documentation, step-by-step and how-to guides.
This one focuses on streamlining and automating SEO-related tasks, cutting down the need for manual keyword research.
Textmetrics
Provides feedback on grammar, style and clarity in order to improve the user’s writing.
Textio is an AI writing assistant specifically designed for HR writing, automating the process of creating performance feedback and assessments.
Generative writing assistant aimed at professionals.
This one uses an open-source LLM that has only been trained on freely distributable writing data in order to avoid copyright infringement issues.
Geared towards creating SEO content and traffic-boosting copy.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

NH is pausing its use of AI to grade standardized test essays — but just temporarily

For the first time in at least five years, New Hampshire elementary and middle school students who take the state’s writing tests will have their essays scored by humans, rather than computers.
Cambium , the company that administers the statewide assessment, typically uses automated scoring — basically, artificial intelligence — to grade most students’ essays. A portion of the essays, usually between 15 and 25%, are routed to human scoring due to unusual responses or other reasons.
This hybrid approach, using a mix of automated and manual scoring, is becoming more common for standardized tests nationwide; the idea is that it’s cheaper, faster and as accurate as relying entirely on human scorers.
But this year, the Department of Education says it’s returning old-fashioned human grading. The reason? There’s a batch of new writing prompts, which were developed in consultation with New Hampshire teachers, and Cambium’s AI isn’t yet trained to score these.

Cambium directed questions about its scoring process to the New Hampshire Department of Education. State officials who are in charge of assessments say they’ve relied on computer-assisted essay scoring for at least the last five years. Tests are expected to be scored by hand just this year, and this year’s manual scoring process will be used to train the new automated scoring system for future years.
During the writing assessments, each student receives a randomly selected essay prompt. The new prompts are meant to include more variety, including a focus on testing different kinds of writing — for example, asking students to write a narrative piece instead of a persuasive one. The state encourages schools to require students to complete the essays in a single sitting, though it’s not mandatory.
Schools must administer the writing tests for grades three through eight by March 15.

Top stories of the day, 3X a week - subscribe today!

You make NHPR possible.
NHPR is nonprofit and independent. We rely on readers like you to support the local, national, and international coverage on this website. Your support makes this news available to everyone.
Give today. A monthly donation of $5 makes a real difference.
Search our catalog, articles, website and more.
Today's hours, victor sholl recipient of 2024 mary hatch marshall essay award.
March 12, 2024, 9 a.m.

Victor Sholl, a doctoral candidate in the Department of Philosophy in the College of Arts and Sciences (A&S), was selected as the 2024 winner of the prestigious Mary Hatch Marshall Essay Award for his piece titled “Writing the story of the world: the case for World Narrativism.” A&S and the Syracuse University Library Associates will host a virtual award event and author reading on Wednesday, April 10 at 1 p.m. (EST). Anyone interested in attending can register by emailing [email protected] by April 3.
Sholl, this year’s recipient, will receive a $1000 prize. His article introduces and argues for a view he calls World Narrativism: that narrative features affect the quality of trajectories the world can take, thus becoming relevant when we decide which course of the world we should promote. Though the idea that the history of the world has narrative features has been defended before, views of this kind typically do not involve an explicit claim that individuals should promote a better story of the world. The common assumption is that whatever is the story of the world, it is something governed by factors beyond the control of individuals. He argues that World Narrativism is original in this respect.
His essay was chosen from those submitted by A&S graduate students currently enrolled in African American studies; English; art and music histories; languages, literatures and linguistics; philosophy; religion; and writing studies, rhetoric, and composition.
Sholl received his master’s in philosophy from the University of São Paulo in 2022. His research interests include well-being, normative reasons, explanations, consequentialism, and artificial intelligence and art.
Professor Mary Hatch Marshall was a founding member of the Library Associates and holds a distinguished place in the College’s history. In 1952, she became the Jesse Truesdell Peck Professor of English Literature —the first woman appointed a full professor in the College— after having joined the faculty four years earlier. Library Associates established the annual Mary Hatch Marshall Award to honor and help perpetuate her scholarly standards and the generous spirit that characterized her inspirational teaching career, which lasted through her retirement in 1993. Members of Library Associates, Marshall’s friends and family, the Gladys Krieble Delmas Foundation and the Central New York Community Foundation all contributed to the endowment, established in 2004, that funds the award.
Library Associates are a group of dedicated SU Libraries supporters who help to raise funds and accessibility for the Libraries' special collections, rare books, and manuscripts through opportunities like the Faculty Fellows program. Those wishing to join the Library Associates or make a gift to the Mary Hatch Marshall Award Endowment can contact Ron Thiele, assistant dean for advancement for the Libraries, at [email protected] or 315.560.9419.

Victor Sholl To Receive 2024 Mary Hatch Marshall Essay Award
Victor Sholl, a doctoral candidate in the Department of Philosophy in the College of Arts and Sciences (A&S), was selected as the 2024 winner of the prestigious Mary Hatch Marshall Essay Award for his piece titled “Writing the story of the world: the case for World Narrativism.” A&S and the Syracuse University Library Associates will host a virtual award event and author reading on Wednesday, April 10 at 1 p.m. (EDT). Anyone interested in attending can register by emailing [email protected] by April 3.

Victor Sholl
Sholl will receive a $1,000 prize. His article introduces and argues for a view he calls World Narrativism: that narrative features affect the quality of trajectories the world can take, thus becoming relevant when we decide which course of the world we should promote. Though the idea that the history of the world has narrative features has been defended before, views of this kind typically do not involve an explicit claim that individuals should promote a better story of the world. The common assumption is that whatever is the story of the world, it is something governed by factors beyond the control of individuals. He argues that World Narrativism is original in this respect.
His essay was chosen from those submitted by A&S graduate students currently enrolled in African American studies; English; art and music histories; languages, literatures and linguistics; philosophy; religion; and writing studies, rhetoric and composition.
Sholl received his master’s in philosophy from the University of São Paulo in 2022. His research interests include well-being, normative reasons, explanations, consequentialism, and artificial intelligence and art.
Professor Mary Hatch Marshall was a founding member of the Library Associates and holds a distinguished place in the history of A&S. In 1952, she became the Jesse Truesdell Peck Professor of English Literature—the first woman appointed a full professor in the college—after having joined the faculty four years earlier. Library Associates established the annual Mary Hatch Marshall Award to honor and help perpetuate her scholarly standards and the generous spirit that characterized her inspirational teaching career, which lasted through her retirement in 1993. Members of Library Associates, Marshall’s friends and family, the Gladys Krieble Delmas Foundation and the Central New York Community Foundation all contributed to the endowment, established in 2004, that funds the award.
Library Associates is a group of dedicated SU Libraries supporters who help to raise funds and accessibility for the Libraries’ special collections, rare books and manuscripts through opportunities like the Faculty Fellows program. Those wishing to join the Library Associates or make a gift to the Mary Hatch Marshall Award Endowment can contact Ron Thiele, assistant dean for advancement for the Libraries, at [email protected] or 315.560.9419.
Cristina Hatem
- In Memoriam: Life Trustee the Reverend Vernon L. Lee Jr. ’54 Wednesday, March 13, 2024, By Eileen Korey
- Crucial Influence Course for Leaders/Supervisors Begins March 27 Wednesday, March 13, 2024, By News Staff
- School of Education Spring 2024 Ganders Lecture Invites You to ‘Notice Noise” Tuesday, March 12, 2024, By Martin Walls
- Victor Sholl To Receive 2024 Mary Hatch Marshall Essay Award Tuesday, March 12, 2024, By Cristina Hatem
- Highlights from the Light Work Collection: Dawoud Bey Monday, March 11, 2024, By News Staff
More In Campus & Community
In memoriam: life trustee the reverend vernon l. lee jr. ’54.
It’s a love story that began at Hendricks Chapel, where Vernon L. Lee Jr. first met Marcia L. Heath. Both undergraduates, they raised their voices in song together, worshipped together and, six days after they both graduated from Syracuse University…
Crucial Influence Course for Leaders/Supervisors Begins March 27
The Office of Human Resources is offering a series of Crucial Influence workshops to help supervisors build skills in leading behavior change within their team or organization. Through this program, supervisors, managers and leaders will learn how to influence other’s…
Community Police Academy Graduates Largest Ever Class
On March 6, 33 members of the campus community graduated from the Department of Public Safety’s (DPS) Community Police Academy (CPA). The 33 graduates are nearly double the 17 that graduated from the Fall 2023 CPA. The CPA is a…
Jeff Rubin ’95, G’98 Named Syracuse University’s First Chief Digital Officer
Chancellor Kent Syverud today announced that Jeff Rubin, an innovative leader, accomplished entrepreneur and longtime member of the Orange community, has been named the University’s inaugural senior vice president for digital transformation and chief digital officer. Rubin, who first arrived…
School of Education Spring 2024 Ganders Lecture Invites You to ‘Notice Noise”
Busy cafeterias, hushed auditoriums, quiet libraries—learning spaces have familiar soundscapes, but how often do we notice the noise, or lack of it? Join University of Michigan’s Jon M. Wargo for the spring 2024 School of Education Ganders Lecture as he…
Subscribe to SU Today
If you need help with your subscription, contact [email protected] .
Connect With Us
For the media.

Santa Clarita Valley's #1 Local News Source
How long does it take to write 3000 words essay, sponsored post.
- March 12, 2024
What Constitutes a 3000-Word Essay?
Time should be the least of your worries when writing a 3 000 word essay. However, you still need to plan and organize your task to make it perfect. Thus, in a way, time is still a factor. Before you can estimate the time it takes to complete such an assignment, you must understand the process of writing a great essay. Academic writing begins with a prompt from your professor or the examining body with instructions and a strict guideline. You may also have access to the grading rubric. With these details, you can plan your essay and organize the writing process.
Initial preparations for essay writing help you clarify the instructions and plan your time effectively. Give this initiative a day or two. This way, you will have a better grasp of the task ahead and organize your time to meet all the expectations. This is usually the best point to engage an essay writer to help create a topic, a thesis, and an outline. You must also seek clarification from your instructor, which demonstrates seriousness and commitment. You need only write a message or two with specific questions and your professor will respond with suggestions.

Factors Influencing Writing Time
Writing speed .
Your writing experience is a critical determinant of the speed and efficiency of your writing. While most people are good in typing, a 3 000 word essay requires slightly more than keyboard skills. You must understand sentence structures and word choices. You must also incorporate multiple sources and integrate evidence from verifiable articles. These factors determine your speed of writing. The faster you are at mastering them, the faster you can complete a 3000-word essay.
Research and Analysis
The amount of research required for the specific 3000-word essay will also affect your timelines. In some cases, you might only need to compile some evidence from readily available sources. However, in most cases, a 3 000 word essay requires in-depth research from multiple databases. You should also set some time for analyzing the evidence using tables, figures, and charts. In such cases, writing a 3000-word essay will take slightly longer.
Essay Type and Complexity
The paper type also affects writing speed and time spent researching and structuring the document. If you are working on a dissertation chapter, you are more likely to spend more time finding supporting evidence and analyzing sources. When working on an argumentative essay, you’ll spend the time developing your argument and counterarguments. Complexity varies with paper type and discipline, affecting how long it takes to write a 3 000 word essay.
Individual Differences
Writing a good 3 000 word essay should take a maximum of eight hours for a professional writer and four days for an ordinary student. If you have a longer deadline, you can take time to perfect your essay and make it more compelling. You can also use the time to engage your peers and enjoy some criticism. If you are working on a short deadline, consider hiring a professional writer. Some expert writers can complete a 3000-word essay in four hours. Note that even the best writers need sufficient time to produce a perfect document.
Tips and Tricks
Create a detailed outline .
Creating a good outline can also be challenging for inexperienced writers. You need basic writing skills to generate a useful skeleton for a 3 000 word essay. If you are not confident enough at this point, you may experience a few hiccups when you get to the actual paper. However, with the necessary help, this step shouldn’t take more than an hour. Ensure you understand the instructions and use the grading rubric to generate a comprehensive outline. Countercheck the structure with your thesis statement highlighting all the major arguments and topic sentences. Use headings and subheadings to organize your essay.
Set Mini Deadlines
Subdivide the 3 0000 word essay into smaller tasks with defined timelines. Ensure each segment has a definite deadline in line with your smart objectives. Create a task organizer or a checklist to track your progress. Mini deadlines help create a sense of achievement and boost your energy. Avoid procrastination as delays in the smaller tasks will affect your overall productivity.
Use a Timer for Focused Writing Sessions
A timer can help you enforce the strict deadlines. You can incorporate a reward system in your deadlines to encourage your progress systematically. For instance, you can reward yourself with a stroll after every task or watch a favorite show between major sessions. A 3 000 word essay should have several smaller tasks, creating multiple opportunities for rewards. Use negative reinforcements where necessary like setting restrictions to your social media platforms between sessions.
Eliminate Distractions
Writing a 3 000 word essay can be daunting to inexperienced writers. Due to the complexity and length of the task, you can experience bouts of distractions between sessions. Find a suitable location for your writing away from common distractors like your phone and noise. Take breaks between tasks to avoid burnout and increase your concentration span.
Leverage AI Writing Tools Wisely
Capitalize on the most efficient technological development of the 21st century. How long is a 3 000 word essay going to take you without writing from scratch? The best AI writing tool will save you at least two days of research. The programs can generate human-like content within seconds. You can use this information to familiarize yourself with the topic and context of writing. You can even generate templates and sample thesis statements. However, you should not copy the content from an AI tool. Instead, use the program as a guide for writing.
Strategies for Efficient Writing
Planning and outlining .
At this stage, your biggest concern should be understanding the prompt and any requirements. You want to clarify any ambiguous instructions before commencing the work. You also need to understand your professor’s expectations and any other requirements from your institution. Identify the writing style required and the implied academic writing languages. Review your institution’s writing guide and recommendations. If you must choose your own topic, request your professor’s approval and advice soon enough. If possible, review the topic with peers or the instructor to conceptualize the scope of your assignment. Identify the possible challenges you might face when looking for information.
Time Management and Prioritization
How long is a 3 000 word essay? The answer to this question lies in your time management ability. With a proper outline and enough initial research, you can organize your time effectively. Allocate sufficient time to the most important tasks. Identify possible challenges, especially when finding reliable sources and seek alternatives. Plan for failure and unforeseeable events and give yourself a buffer. Incorporate slack time and scope creep. Allocate the number of words needed for each section and the time you might take to complete it. Planning your time can be time-consuming as most of the allocations are based on assumptions. However, this exercise shouldn’t take more than an hour with the right information.
Active Research and Note-Taking
Once you’ve understood the task and its scope, you can now start investigating your topic. The initial research for a 3 000 word essay helps you evaluate the prevailing ideas about the issue you are investigating. You will also encounter arguments from other researchers in research papers, books, and periodicals. Sometimes a simple web search about the topic is sufficient. In other cases, you may need a deeper understanding of the topic before you can generate a reasonable argument. If the topic is straightforward, you only need to take a side and argue for it. Allocate a day for this task if the assignment is not urgent. It will take you less than an hour if you are an experienced writer.
Utilizing AI Writing Tools
AI has revolutionized the writing industry with unprecedented levels of efficiency and accuracy. This technology makes writers more effective and helps them write faster. Utilizing these tools in writing saves you lots of time for initial research. You can also produce a sample 3 000 word essay for comparison and guidelines. For security reasons, use only verifiable AI tools and avoid sharing personal details on any online platform.
Writing Process and Revision Cycles
Start your 3 000 word essay by developing a strong thesis statement to communicate your main argument. The thesis statement is the equivalent of the whole assignment in a sentence or two. You may want to engage a professional to help with this part if you are not familiar with thesis statements. You can also use AI tools to generate possible theses for your assignment depending on the level of importance and urgency. For a professional writer, this task should take less than half an hour. A good AI tool will generate multiple thesis states in seconds. Revise and edit at the proofreading stage to save more time for writing, research, and analysis.
What is the average time required to write a 3000-word essay?
The average time for writing a 3 000 word essay depends on the paper type and complexity. It also depends on the writer’s experience and writing speed. An experienced writer can take less that less than eight hours to complete an urgent 3000-word essay. An ordinary student may need up to four days to achieve the same milestone.
What factors influence the writing time for a 3000-word essay?
Writing a 3000-word essay depends on the writer’s abilities and other individual differences. Your writing speed will determine how best you can convert your thoughts into written work. Similarly, your research and analysis capabilities will influence evidence collection and integration in your paper. Most importantly, the time taken to complete a 3000-word essay will depend on the paper type and complexity of the instructions.
Can the writing time be reduced by using AI writing assistants?
Leveraging AI technology can help you scale down the writing time significantly. These tools are fast and efficient, helping writers with research and content generation. Experienced writers use AI tools to conduct initial research and compile sufficient details for their documents. Some even use the technology to generate thesis statements and outlines.
What are effective strategies for planning a 3000-word essay?
The most effective strategy to tackle any time management problem is planning and prioritizing. Organize your work in mini tasks with mini-deadlines and complete the segments independently. Eliminate all distractors by finding a comfortable working space away from your phone and noise. Leverage the power of AI and conduct active research while taking notes. Start your document with the body and finish with proofreading.
Related To This Story
Controversy surrounds justin sun’s htx wallet revelation: a deep dive into the allegations and implications, is a crypto bull market happening right now, what is bitcoin halving and why does it matter , the coinbase catastrophe: a $100 billion bitcoin debacle, floki inu’s ascent: a new challenger in the cryptocurrency arena , enhancing blockchain interoperability: ripple and axelar’s strategic partnership , latest news.

Car hits Canyon Country building

Schiavo introduces bill to address nursing shortage

City Council members to get slight pay raises

Garcia calls for Chiquita landfill closure

Charges still pending in year-old fatal hit-and-run
Sign up for the, morning rundown.
Filled with the top stories to start your day, and emergency news alerts.

25060 Avenue Stanford, St. 141
Valencia, CA, 91355
Main Desk: 661-259-1234
Newsroom: 661-255-1234
Advertising: 661-287-5564
Have a news tip? Let us know!
News Sections
- Coronavirus
- Environment
- Politics & Government
More Sections
- Video + Podcasts
- Sunday Signal
- Subscribe to Print
- Classified Ads
- Event Calendar

COMMENTS
oConsideration of counterarguments (what Sandel might say in response to this section of your argument) Each argument you will make in an essay will be different, but this strategy will often be a useful first step in figuring out the path of your argument. Strategy #2: Use subheadings, even if you remove themlater.
The key difference is that a narrative essay is designed to tell a complete story, while a descriptive essay is meant to convey an intense description of a particular place, object, or concept. Narrative and descriptive essays both allow you to write more personally and creatively than other kinds of essays , and similar writing skills can ...
A narrative essay is one of the most intimidating assignments you can be handed at any level of your education. Where you've previously written argumentative essays that make a point or analytic essays that dissect meaning, a narrative essay asks you to write what is effectively a story.. But unlike a simple work of creative fiction, your narrative essay must have a clear and concrete motif ...
A narrative essay is an essay that tells a story. Typically, it's nonfiction but may include some enhanced language to clarify or heighten the dramatic effect. What are the steps to writing a narrative essay? 1 Choose a topic and generate ideas for your essay. 2 Write an outline. 3 Write a first draft. 4 Edit the draft.
Updated on August 4, 2021 Writing Tips. Narrative writing is, essentially, story writing. A narrative can be fiction or nonfiction, and it can also occupy the space between these as a semi-autobiographical story, historical fiction, or a dramatized retelling of actual events. As long as a piece tells a story through a narrative structure, it ...
The narrative essay format and structure are essential elements of any good story. A well-structured narrative can engage readers, evoke emotions, and create lasting memories. Whether you're writing a personal essay or a work of fiction, the following guidelines on how to write a narrative essay can help you create a compelling paper:
How to write a story in 5 steps. The story writing process is similar but not identical to the writing process you use for other kinds of writing. With a story, you need to make sure the five elements we listed above are present. Here's how to write a short story: 1 Find inspiration. The first step in writing a story is coming up with an idea.
1. Pick a meaningful story that has a conflict and a clear "moral.". If you're able to choose your own topic, pick a story that has meaning and that reveals how you became the person your are today. In other words, write a narrative with a clear "moral" that you can connect with your main points. 2.
The goal of the narrative essay is to use established storytelling techniques, like theme, conflict, and irony, in a uniquely personal way. The responsibility of the narrative essayist is to make the reader feel connected to their story, regardless of the topic. This next video explores how writers can use structural elements and techniques to ...
1. Generating Narrative Essay Ideas. If you're not sure what to write about, you'll want to generate some narrative essay ideas. One way to do this is to look for writing prompts online: Reedsy adds new prompts to their site every week, and we also post writing prompts every Wednesday to our Facebook group.
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
It's written in first person and the story encompasses a specific moment in time worthy of a discussion. 6 Guidelines for Writing Personal Narrative Essays. Writing a personal narrative essay involves both objectivity and subjectivity. You'll need to be objective enough to recognise the importance of an event or a situation to explore and write ...
Narrative Essay Definition. Writing a narrative essay is a unique form of storytelling that revolves around personal experiences, aiming to immerse the reader in the author's world. It's a piece of writing that delves into the depths of thoughts and feelings. In a narrative essay, life experiences take center stage, serving as the main substance of the story. It's a powerful tool for writers ...
A short story essay is a blended type of short writing that consolidates an essay's components and a short story. The word tally of a short story paper is generally between 1000 to 5000 words. This kind of article is not quite the same as a short story or simply a five-section exposition.
Top 10 Story Ideas. Tell the story of a scar. A group of children discover a dead body. A young prodigy becomes orphaned. A middle-aged woman discovers a ghost. A woman who is deeply in love is crushed when her fiancé breaks up with her. A talented young man's deepest fear is holding his life back.
A narrative can spark emotion, encourage reflection, and convey meaning when done well. Narratives are a popular genre for students and teachers as they allow the writer to share their imagination, creativity, skill, and understanding of nearly all elements of writing. We occasionally refer to a narrative as 'creative writing' or story writing.
The key difference is that a narrative essay is designed to tell a complete story, while a descriptive essay is meant to convey an intense description of a particular place, object, or concept. Narrative and descriptive essays both allow you to write more personally and creatively than other kinds of essays , and similar writing skills can ...
In your story, start writing scenes around conflict, and make sure each paragraph and piece of dialogue relates, in some way, to your protagonist's unmet desires. 4. Write Your First Draft. The scenes you build around conflict will eventually be stitched into a complete story.
Writing practice is a method of becoming a better writer that usually involves reading lessons about the writing process, using writing prompts, doing creative writing exercises, or finishing writing pieces, like essays, short stories, novels, or books. The best writing practice is deliberate, timed, and involves feedback.
The basic steps for how to write an essay are: Generate ideas and pick a type of essay to write. Outline your essay paragraph by paragraph. Write a rough first draft without worrying about details like word choice or grammar. Edit your rough draft, and revise and fix the details. Review your essay for typos, mistakes, and any other problems.
3-5 paragraph short story essay. 2 Page Short story essay (500-600 words) 3 page short story essay (750-900 Words. 5 Page short story essay (1250-1500 Words) To guide you in your efforts here are six (6) steps to follow when writing a short story essay: Start with an idea. Every good piece of writing starts with an idea, so start by considering ...
Others work in pieces they arrange later, while others work from sentence to sentence. Whether you're writing a novel, novella, short story, or flash fiction, don't be afraid to try out different voices, and styles. Experiment with different story writing techniques, story ideas, and story structures. Keep what works for you and discard the ...
Employing such tactics often proves counterproductive. However, if you want to improve your essay writing skills, you must recognize the stages involved, i.e., brainstorming, drafting, revising ...
Share to Linkedin. 5+ Generative AI Writing Tools Everyone Should Know About. Adobe Stock. One of the most popular use cases for generative AI is writing. This is thanks to the ability of tools ...
The new prompts are meant to include more variety, including a focus on testing different kinds of writing — for example, asking students to write a narrative piece instead of a persuasive one ...
Short stories are to novels what TV episodes are to movies. Short stories are a form of narrative writing that has all the same elements as novels—plot, character development, point of view, story structure, theme—but are delivered in fewer words. For many writers, short stories are a less daunting way to dive into creative writing than attempting to write a novel.
Victor Sholl, a doctoral candidate in the Department of Philosophy in the College of Arts and Sciences (A&S), was selected as the 2024 winner of the prestigious Mary Hatch Marshall Essay Award for his piece titled "Writing the story of the world: the case for World Narrativism." A&S and the Syracuse University Library Associates will host a virtual award event and author reading on ...
Victor Sholl, a doctoral candidate in the Department of Philosophy in the College of Arts and Sciences (A&S), was selected as the 2024 winner of the prestigious Mary Hatch Marshall Essay Award for his piece titled "Writing the story of the world: the case for World Narrativism.". A&S and the Syracuse University Library Associates will host ...
Individual Differences. Writing a good 3 000 word essay should take a maximum of eight hours for a professional writer and four days for an ordinary student. If you have a longer deadline, you can ...
6 likes, 1 comments - writebytheseakq on March 13, 2024: "Our Writing competition is open until Friday 21st June 2024. Do you have a personal essay or mem..." Write by the Sea on Instagram: "Our Writing competition is open until Friday 21st June 2024.