
Professorship for Open-Source Software
Friedrich-Alexander University Erlangen-Nürnberg

Bachelor and Master Theses on Product Management
We currently have plenty of Bachelor and Master Thesis opportunities available that focus on product management. Specifically, these are case-writing theses. In such a thesis, you will work with an industry partner (and us) to analyse a specific situation that the industry partner once faced. Typically, that situation was about making a difficult decision. The industry partner provides the specifics of the situation and we help you with the underlying concepts needed to analyse the situation. The result of your work is a “case” that describes the situation and that we intend to use in future teaching. The case will be made available for free.
- We have explained the concept to industry partners before.
- We can also tell you about the expected results .
- Finally, you can take a look at specific cases available .
Please let us know if you are interested. Just send an email to Prof. Riehle. Also, a great way to get started or just get an impression is to take the Product Management seminar.
Share to your network!
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Category: 4.2 Thesis Opportunities

- USF Research
- USF Libraries
Digital Commons @ USF > Muma College of Business > Marketing > Theses and Dissertations
Marketing Theses and Dissertations
Theses/dissertations from 2023 2023.
How Feeling Like a Minority Affects Preferences for Autonomous Digital Interfaces , Ye Seul Kim
Theses/Dissertations from 2022 2022
Spillover Effects in Product Customization , Samuel Babu Sekar
Theses/Dissertations from 2021 2021
External and Internal Factors of Sports Sponsorship Selling Cycles in North American Professional Sports , Dan Kaufmann
Increasing Personal and Product Influence Through Background Auditory and Visual Cues , Zhihao Yu
Theses/Dissertations from 2020 2020
The Effects of Product Recalls on Competitors’ Market Value and Recalling Firm’s Reputation , Dong Liu
Corporate Brand Impact on Sales / Revenue Per Share , Brad A. Puckey
Competition in Upstream Humanitarian Supply Chain: Investigation of Food Banks , Iana Shaheen
Theses/Dissertations from 2019 2019
How Digital versus Non-Digital Modes of Food Ordering Influence Menu Healthfulness Perceptions and Food Choices , Annika Abell
Theses/Dissertations from 2018 2018
The Impact of Digital Marketing Decisions on Market Outcomes in Residential Real Estate , Denise Hunter Gravatt
Theses/Dissertations from 2017 2017
Hate is a Strong Word: The Influence of Hate-Acknowledging Advertising on Brand Outcomes , Lisa Monahan
The Effects of Loneliness on Consumers’ Digital Engagement with Social Media Ads , Yu Qin
Product Shadows and Ad Evaluations , Nazuk Sharma
Theses/Dissertations from 2016 2016
Understanding the Complexity of Product Returns Management: A Complex Adaptive Systems Theory Perspective , Jennifer Anne Espinosa
Branding Implications of Co-Created Social Responsibility , Alexander J. Kull
Theses/Dissertations from 2015 2015
How You Categorize Influences How Helpful You Are: The Effect of Categorization Mindset on Consumers’ Social Decisions , Hsiao-Ching Kuo
Theses/Dissertations from 2014 2014
Taken for Granted or Taken with Gratitude? An Examination of the Differential Effects of Donations of Time and Money on Consumers' Evaluation of Corporate Philanthropy , Ryan Langan
Essays on Consumer's Psychological and Behavioral Responses toward Social Coupons , Chinintorn Nakhata
Muscling Consumers to Optimal Option Differentiation: The Influence of Incidental Muscular Sensations on Option Differentiation , Courtney Szocs
Theses/Dissertations from 2012 2012
Essays on Mental Accounting and Consumers' Decision Making , Ali Besharat
Perceived Firm Transparency: Scale and Model Development , Jennifer Dapko
Theses/Dissertations from 2010 2010
Antecedents and Consequences of Channel Alienation: An Empirical Investigation within Franchised Channels of Distribution , Ivan Lapuka
Theses/Dissertations from 2009 2009
An Empirical Examination of the Dark Side of Relationship Marketing within a Business to Business Context , Brent L. Baker
Developing the Nomological Network of Perceived Corporate Affinity for Technology: A Three Essay Dissertation , David Earl Fleming
Theses/Dissertations from 2008 2008
Self-Directed Learning: Measures and Models for Salesperson Training and Development , Stefanie Leigh Boyer
Emotional Exhaustion and Its Role in Service Sabotage among Boundary Spanners , Diane R. Edmondson
Theses/Dissertations from 2007 2007
Essays on multiple identities and motivated consumption: Exploring the role of identity centrality on self-brand connections , Tracy R. Harmon
The impact of organizational climate variables of perceived organizational support, workplace isolation, and ethical climate on salesperson psychological and behavioral work outcomes , Robert J. Riggle
Theses/Dissertations from 2005 2005
The Effect of Perceived Entitativity on Implicit Image Transfer in Multiple Sponsorships , FrancoÌ?is Anthony Carrillat
Theses/Dissertations from 2004 2004
Relationship Advertising: Investigating the Strategic Appeal of Intimacy (Disclosure) in Services Marketing , Andrea Diahann Gaye Scott
Advanced Search
- Email Notifications and RSS
- All Collections
- USF Faculty Publications
- Open Access Journals
- Conferences and Events
- Theses and Dissertations
- Textbooks Collection
Useful Links
- Rights Information
- SelectedWorks
- Submit Research
Home | About | Help | My Account | Accessibility Statement | Language and Diversity Statements
Privacy Copyright
Main Content
Topic list for final theses.
On this page you will find suggested topics by the Research Group of Technology and Innovation Management for bachelor and master theses, subdivided into topic areas. If you want to write your thesis on a topic of your own choice or in a subject area not listed below, you are welcome to send us an unsolicited application (including an exposé on the proposed topic). The content of the application can be based on the topics covered in a lecture and the current research projects of the research group.
A. Strategic Management of Technology and Innovation
Inhalt ausklappen inhalt einklappen a3: corporate venture modes: a literature review of existing corporate venture typologies and their efficiency with regard to knowledge transfer, inhalt ausklappen inhalt einklappen a4: corporate venturing activities as a source of external knowledge: analysis of start-up/corporate relationship and knowledge transfer mechanisms, inhalt ausklappen inhalt einklappen a5: corporate venture program design: analyzing the rationale of corporate venture design across different industries, inhalt ausklappen inhalt einklappen a6: national culture and radical innovation: a cross-cultural comparison of organizational behavior.
Bachelor/Master (prefered)
B. Management and Economics of Intellectual Property
Inhalt ausklappen inhalt einklappen b2: "brand and patenting strategies of firms: are trademarks and patents substitute or complementary instruments to protect intellectual property an empirical investigation of thebrand and patent portfolios of firms in high-tech industries".
Literature recommendations:
Esch, F.-R. (2018): Strategie und Technik der Markenführung, 9. Vollständig überarbeitete und erweiterte Auflage, Verlag Franz Vahlen, München.
Grazzi, M./Piccardo, C./Vergari, C. (2020): Concordance and complementarity in IP instruments, in: Industry and Innovation, Vol. 27, No. 7, pp. 756-788, DOI: 10.1080/13662716.2020.1726728.
Llerena, P./Millot, V. (2020): Are two better than one? Modelling the complementarity between patents and trademarks across industries, in: Industry and Innovation, Vol 27, No. 1-2, pp. 52-79, DOI: 10.1080/13662716.2019.1688137.
Thoma, G. (2020): The valuation of patent-trademark pairing as IP strategy: evidence from the USPTO, in: Industry and Innovation, Vol. 27, No. 1-2, pp. 80-104, DOI: 10.1080/13662716.2019.1633281.
Inhalt ausklappen Inhalt einklappen B3: A Patent Landscape Analysis in the Field of Agricultural Biotechnology
Bachelor/Master
Literature recommendations:
Burr, W./Stephan, M. et al. (2007): Patentmanagement, Schaeffer-Poeschel Verlag, Stuttgart 2008.
Trippe, A. (2015): Guidelines for Preparing Patent Landscape Reports, WIPO Publication No. 946E. Geneva, World Intellectual Property Office.
Inhalt ausklappen Inhalt einklappen B5: A Case Study on Patents on Beer: A Multi-Stakeholder Perspective
Burr, W./Stephan, M. et al. (2007): Patentmanagement, Schaeffer-Poeschel Verlag, Stuttgart.
Stephan, M./Dietrich, A. (2020): IP Protection in Biotech, Chapter 8, IPM-Lecture WS 2019/20.
C. Innovation Culture and Entrepreneurship
Inhalt ausklappen inhalt einklappen c2: the micro-geography of corporate accelerator programs: facilitating explorative learning.
Literature recommendations: On request
Inhalt ausklappen Inhalt einklappen C3: Sports and the Entrepreneurial Cognition: An experimental approach on the influence of sport on the entrepreneurail process
Inhalt ausklappen inhalt einklappen.
Master Literature recommendations: On request
D. Service and Business Model Innovation
No topics offered at the moment
E. Industry and Company Specific Studies on Innovation Management
Inhalt ausklappen inhalt einklappen e1: organizing for open innovation.
Bachelor/ Master
a) A Comparative Analysis of the Telefonica and Telekom Case Studies b) A Comparative Analysis of the Bayer and Merck Case Studies
Literature recommendations: On request
Inhalt ausklappen Inhalt einklappen E2: Examining the Link between Market Structure and Innovation: An Analysis Based on the Corporate Landscape in the Seed Industry
Master/ Bachelor
Literature recommendation:
OECD (2018): Concentration in Seed Markets: Potential Effects and Policy Responses, OECD Publishing, Paris.
Final theses already completed
University of Fribourg
Department of Management
Topics for Bachelor and Master Theses in Management
You can find specific suggestions for Bachelor and Master theses, based on various thematic topics, on the websites of the different chairs . Please note that some chairs currently have waiting lists and therefore a proposal may not be accepted immediately. Those who wish to start their thesis without being placed on a waiting list may consult the list of general topics in the list below. Please contact the professors, or their assistants, directly by e-mail for further information.
Prof. Dr. Paul Dembinski (Master theses in English or French)
Here 3 propositions:
- Sustainable finance and risk
- An ethical approach of the discount rate
- Global value chains as a channel of social inclusion: case study in agriculture and propositions
Contact : Prof. Dembinski
Sujets pour des travaux de Master
Topics for Master Theses
Prof. Dr. Olivier Furrer (theses in English or French)
Here 4 propositions:
- Sustainable food marketing
- Cultural intelligence in services
- Co-creation of value and well-being for customers
- Customer satisfaction with "in-home" services
Contact : Prof. Furrer
Further topics for Bachelor and Master theses at the Chair of Marketing
Prof. Dr. Markus Gmür (theses in English, French or German)
Here 2 propositions:
- Social Entrepreneurship in selected sectors and/or countries
- The impact of digitalization of the nonprofit sector
The aim of the list here is to provide some ideas for current research topics at the VMI. It is based on requirements for master students. It is also possible to submit your own suggestions for topics related to NPO management (please also see the guidelines for writing papers and theses). Those interested are initially requested to contact Prof. Markus Gmür
Prof. Dr. Martin Wallmeier (theses in English or German)
Are capital protection products fairly priced?
Detecting earnings management – A critical analysis of the Jones model
Further information can be found on: https://www.unifr.ch/finance/en/teaching/theses.html
Other, own subjects are possible.
Requirements : sucessful attendance of a BA course (Bachelor theses) or MA course (Master theses) in the domain of Finance.
Please contact for preliminary discussion: Prof. Wallmeier
Job Offers see under News
Master en Mangement
Master in Marketing
Master in Accounting and Finance
Master in International and European Business

- General Information
- Tuition fees
Application & Admission
Language requirements, program features.
- List of Universities
2717 Study programs

Study Product Management in Germany: 29 Universities with 37 English Degree Programs
All important info for international students in germany (2024/2025).
The lifecycle of any product encompasses many stages. From the initial idea to the final product, the business process involves planning, developing, launching, etc. If you are interested in the nuances around these steps, Product Management might be your field. As a product manager, you learn how to connect products and services to their target customers and how to build sustainable and successful business strategies for the global market.
Study Programs in English
Universities
Universities in International Rankings
€ 0 (17 programs for EU citizens, 14 programs for Non-EU citizens)
€ 7,500 per semester (1 program for EU citizens/Non-EU)
Winter Semester
between April 30 and March 31
Summer Semester
between May 31 and September 01
Top-ranked German Universities in Product Management

public University
No. of Students: approx. 27,000 students
Program Fees: € 0 - € 1,500 (per semester)
Tuition Fees
3 english degree programs for product management in germany.
University of Tübingen Tübingen
Management and economics.

Leuphana University Lüneburg Lüneburg
Sustainable chemistry management.

HTW Berlin - University of Applied Sciences Berlin
Mba & engineering life science management.

Application Deadlines
Winter Semester 2024/2025
Summer Semester 2024
Winter Semester 2025/2026
Open Programs
31 programs
33 programs
Application Modes
Application process.
Technische Universität Berlin Berlin
Mba energy management.

MBA Sustainable Mobility Management

Pforzheim University Pforzheim
Business administration / international marketing.
TOEFL Scores
Cambridge Levels
5 (2 programs )
71 (2 programs )
B2 First (FCE) (11 programs )
7 (2 programs )
100 (1 program )
C2 Proficiency (CPE) (2 programs )
University of Europe for Applied Sciences Potsdam / Iserlohn
Visual & experience design.

ESB Business School Reutlingen University · Reutlingen
Mba international management full-time.

Deggendorf Institute of Technology Pfarrkirchen / Deggendorf
Industrial engineering.

2-7 semesters
→ View all programs with online courses
Master of Arts
Master of Business Administration
Master of Science
Bachelor of Arts
Bachelor of Engineering
Bachelor of Science
Winter intake
Summer intake
Winter & Summer intake
List of all German Universities offering English-taught Study Programs in Product Management
Ansbach University of Applied Sciences
Program Fees: € 0
M.A. (Master of Arts)
Aschaffenburg University of Applied Sciences
Berlin School of Popular Arts
Program Fees: € 4,740
B.A. (Bachelor of Arts)
Clausthal University of Technology
M.Sc. (Master of Science)
CODE University of Applied Sciences
Program Fees: € 6,900
← Prev page
Next Page →
News & Articles

Tuition-free Universities in Germany in English

Master's Requirements in Germany

Scholarships for international students (2022/23)

Uni-assist: A guide for international students (2024)

How Much Does it Cost to Live in Germany?

Germany in University Rankings

DAAD Scholarships: Guide
Engineering Universities in Germany: A Guide (2022/23)
Google Custom Search
Wir verwenden Google für unsere Suche. Mit Klick auf „Suche aktivieren“ aktivieren Sie das Suchfeld und akzeptieren die Nutzungsbedingungen.
Hinweise zum Einsatz der Google Suche
- Chair of Operations Management
- TUM School of Management
- Technical University of Munich
Final Thesis
Topics for Bachelor's Theses should be related to our current research (see research fields ). The overview of completed theses gives a good impression of typical topics. The amount of theses supervised depends on our current capacity. The application process is described below.
Requirements
We prefer students who successfully took courses in the area of operations & supply chain management (OSCM). In addition, you need to hand-in the following documents:
- Transcript of Records
- Application Form ( Word , PDF )
- High School Diploma
We highly recommend to you take workshops on academic research and writing offered by the university library . The courses "Zitieren statt Plagiieren" and "Informationskompetenz 1 – Online-Medien suchen und finden" take place on a regular basis (also as Webinar and in English). In addition, there are several courses regarding the use of citation management software (Citavi/EndNote). Please be aware that we will prefer students who have successfully taken one of the courses in advance.
If you are interested in writing your thesis at our chair, please refrain from contacting us in advance and hand in a complete application instead. We are only able to decide about your application based on all of the listed documents.
Application Process
Every three months (February, May, August, November) students are able to register and start the work on their bachelor thesis at our chair. The application deadline is the 15th of the previous month (e.g. January 15th for a start in February). You may hand in your application earlier, but there will be no decision before the 21st of the previous month.
If you are considered for a certain period, there will be a mandatory meeting on the first Tuesday of the respective month. At this meeting we present topic proposals to the applicants. Afterwards you can prioritize the topics according to your preferences (pick at least five). A topic will be assigned to you by Friday night.
Most topics at our chair are quantitative and optimization-related. While we try to offer a diverse set of topics, knowledge of the techniques taught in course “Modeling, Optimization and Simulation in Operations Management” and/or proficiency in a programming language is highly recommended. We might not be able to offer enough topics for students without prior knowledge in these areas.
Please e-mail your application including all required documents as one PDF file named "Lastname_Firstname" to Christine Steinberger (subject: "Application Bachelor's Thesis").
Own Topic Proposals in Cooperation with a Company
If you would like to write your thesis in cooperation with a company, you need to prepare your own topic proposal. However, please check first which chair of the operations & supply chain management department fits your idea best.
Please prepare a one-page exposé after consulting with your partner company. The exposé should specify (1) your research question, (2) how this research question is relevant for ongoing research, and (3) how you plan to answer your research question.
Please e-mail the exposé in addition to the documents listed under the requirements section to Hendrik Weber. Be aware that you need to hand in your application at least four weeks prior to your desired start date.
Thesis Guidelines
Please review your "Fachprüfungs- und Studienordnung" (FPSO) for general guidelines.
You need to give an interim and final presentation of your (preliminary) results. Make sure to follow the guidelines of our chair:
Guidelines for how to write a thesis (Bachelor, Master) are available here . You are required to use the following LaTeX - or Word template.
Please make sure to check all formal requirements of the TUM School of Management with regard to writing, formatting and submitting your final theses. An information sheet can be found in the Downloads section of the School of Management.
Information sheet for submitting the final thesis can be found here .
Your thesis will be graded according to the following criteria:
- Description and classification of your research question by means of current literature.
- Selection and application of scientific methods.
- Structure and description of your results
- Compliance with our formal requirements
Open Theses
(No documents in this view)
Ongoing Theses
- Gelsinova, Lora: Optimization of the company-wide project portfolio by means of resource and capacity planning: An empirical study. Bachelor thesis, 2024 more… BibTeX
- Vogelsang, Davie: Optimizing seating charts for large events: A heuristic approach. Bachelor thesis, 2024 more… BibTeX
- List, Paul: The Vehicle Routing Problem with a Heterogeneous Fleet: a Literature Review. Bachelor thesis, 2024 more… BibTeX
- Awwad, Yazied: Analyse und Verbesserung eines Ansatzes zur Bewertung und Auswahl von Projekten in der Telekommunikationsbranche. Bachelor thesis, 2023 more… BibTeX
- Schneider Shugaev, Daniel: Optimizing Therapy and Rehabilitation Schedules: The Impact of a new Al-Driven Therapy App. Bachelor thesis, 2023 more… BibTeX
Completed Theses
- Verolini, Dante: A Comparative Analysis of Human Routing Strategies to Myopic Routing Heuristic Using Experimental Data. Bachelor thesis, 2023 more… BibTeX
- Xiao, Xuanqi: A Genetic Algorithm for Optimizing Schedules of Self-Employed Midwives: Insights from an Application at a German Hospital. Bachelor thesis, 2023 more… BibTeX
- Klauck, Julia: A Literature Review on Truck Platooning. Bachelor thesis, 2023 more… BibTeX
- Schott, Elias: Computational Analysis of Metaheuristics for the Resource-Constrained Project Scheduling Problem. Bachelor thesis, 2023 more… BibTeX
- Doan, Gia Bach: Data Analysis for Assessing the Effects of Demand and Supply Disruptions in Air Transport Networks. Bachelor thesis, 2023 more… BibTeX
- Shevtcov, Maksim: Data-Driven Optimization of Vertiport Locations to Introduce an Air Taxi Shuttle Network for Munich Airport. Bachelor thesis, 2023 more… BibTeX
- Schwarz, Kilian: Dynamic and Stochastic Vehicle Routing for Post-Disaster Relief Aid Distribution: A Case Study on the 2023 Turkish-Syrian Earthquake. Bachelor thesis, 2023 more… BibTeX
- Awwad, Yazied: Entwicklung eines Prozesses zur Projektbewertung und -auswahl bei einem Telekommunkationsunternehmen. Bachelor thesis, 2023 more… BibTeX
- Hitschfel Andreas: Planning an Air Taxi Network Using a p-Hub Location Approach with an Integrated Discrete Choice Model. Bachelor thesis, 2023 more… BibTeX
- Anduv, Gökay: Improving Airport Access: A Literature Review on Operational Aspects of Urban Air Mobility. Bachelor thesis, 2022 more… BibTeX
- Valentin Roth: Investigation of Machine Learning-Augmentation and End-to-End Learning for the Resource-Contrained Project Scheduling Problem. Bachelor thesis, 2022 more… BibTeX
- Selena Ofer: Project Portfolio Planning: Process Deninition and Portfolio Optimization for the IT-department of a Large Company. Bachelor thesis, 2022 more… BibTeX
- Pauni, Jonathan: Scheduling and Routing of Delivery Drones with Energy Consumption. Bachelor thesis, 2022 more… BibTeX
- Korbinian Biereder: Algorithmic Optimization of Runway Scheduling During Winter Operations. Bachelor thesis, 2022 more… BibTeX
- Milena Nguyen: Comparison of Mixes-Integer Programming Models for the Flexible Resource-Contrained Multi-Project Scheduling Problem. Bachelor thesis, 2022 more… BibTeX
- Dominik Mandel: Decarbonisation of Airport ground support: Optimal scheduling of electrical apron busses based on network flow model. Bachelor thesis, 2022 more… BibTeX
- Efe Doguer: Heuristic Approach for Improving Visual Attractiveness in Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problems. A Comparative Investigation. Bachelor thesis, 2022 more… BibTeX
- Niklas Bussert: Maximizing output of an insurance claims department: Stochastic optimization of work assignments under uncertain job durations and workforce skill levels. Bachelor thesis, 2022 more… BibTeX
- Cyrill Koch: 3D Printer Packing Problem. Bachelor thesis, 2021 more… BibTeX
- Felix Rottmeier: A Consistent Vehicle Routing Model for Optimizing Local Brewery Beverage Deliveries. Bachelor thesis, 2021 more… BibTeX
- Gonzalez Färber: Analyzing the Impact of Different Charging Strategies on the Battery Degradation of an Electric Bus Fleet. Bachelor thesis, 2021 more… BibTeX
- Benedikt Vollmann: Analyzing the potential of a lead-time based pricing approach to enhance the resilient sustainable supply chain management in the semiconductor industry. Bachelor thesis, 2021 more… BibTeX
- Leon Aramis Schug: Development and Implementation of an Emergency Medical Services Simulation Model to Optimize Amulance Facility Locations and Shifts. Bachelor thesis, 2021 more… BibTeX
- Julian Scharr: Evaluating the Benefit of Preprocessor Policies in Stochastic Resource-Constrained Project Scheduling. Bachelor thesis, 2021 more… BibTeX
- Jan Lucas Michels: How to Make Maximum Use of Scarce Spaces: Model Formulations and Solutions Approaches for Layout Planning Problems. Bachelor thesis, 2021 more… BibTeX
- Artem Kuznetsov: Improving Scheduling for Electric Taxicabs Using a Bidirectional Resource-Constrained Shortest-Path Formulation. Bachelor thesis, 2021 more… BibTeX
- Maximilian Wirth: Optimizing Pickup and Deliveries for the Distribution of Food Donations. Bachelor thesis, 2021 more… BibTeX
- Viktoria Harmel: The Time-Constrained Maximal Covering Routing Problem: Implementation and Evaluation Compared to Standard Route Planning Problems. Bachelor thesis, 2021 more… BibTeX
- Ömer Duman: Vehicle Routing with Synchronization: Challenges and Methods. Bachelor thesis, 2021 more… BibTeX
- Lorenz Friedrich: A Nudge-Based Approach to Human Solution Strategies for the Vehicle Routing Problem. Bachelor thesis, 2020 more… BibTeX
- Niklas Weller: Behavioral Investigation of a Two-Dimensional Packing Problem. Bachelor thesis, 2020 more… BibTeX
- Mohamed Benssassi: Design of Student Matching Algorithm for an International Exchange Program Considering Fairness. Bachelor thesis, 2020 more… BibTeX
- Felix Müller: Development and Implementation of an Adaptive Large Neighbourhood Search for a Vehicle Routing Problem with Synchronisation. Bachelor thesis, 2020 more… BibTeX
- Aziz Boushih: Experimental Investigation and Extension of a Two-Stage Stochastic Programming Model for the Resource-Constrained Project Scheduling Problem under Uncertainty. Bachelor thesis, 2020 more… BibTeX
- Nicolai Bittmann: Innovation in Project Management - Development of an Experimental Design. Bachelor thesis, 2020 more… BibTeX
- Philipp Hohmann: Metaheuristic for the Optimal Scheduling of Self-Employed Midwifes. Bachelor thesis, 2020 more… BibTeX
- Maximilian Janetschek: A Multiperiod Team Orienteering Approach to Technicion Routing: A Telecommunication Provider Case. Bachelor thesis, 2019 more… BibTeX
- Jan-Niklas Dörr: Column Geberations for the Flexible Resource, Project Scheduling in Continuous Time. Bachelor thesis, 2019 more… BibTeX
- Doiminik Rock: Design and Implementation of Evolutionary Algorithms for Airline Crew Scheduling. Bachelor thesis, 2019 more… BibTeX
- Max Rudat: The Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem: Implementation and Senditivity Analysis of a Genetic Algorithm. Bachelor thesis, 2019 more… BibTeX
- Kilian Filser: Artificial Intelligence Powered Ground Handling Steering Concept at Munich Airport. Bachelor thesis, 2019 more… BibTeX
- Veronika Eisgruber: Developing a Heuristic to Solve the Running Dinner Problem for a Large Number of Participants. Bachelor thesis, 2019 more… BibTeX
- Anete Gailite: Development of a Profitability Model for Flexible Operations of Biogas-Powered Cogeneration Plants. Bachelor thesis, 2019 more… BibTeX
- Dominik Haas: Entwicklung eines Referenzprozesses für den Projektmanagementprozess im Bereich der IT-Projekte am Beispiel der ESG Mobility. Bachelor thesis, 2019 more… BibTeX
- Sophie Christina Wieland: Information Asymmetry in Human-Al Collaboration: A Behavioral Analysis in the Context of Demand Forecasting. Bachelor thesis, 2019 more… BibTeX
- Kirsten Walter: Literature Review on Creativity Real-Effort Tasks. Bachelor thesis, 2019 more… BibTeX
- Jonas Grundler: Optimizing Demand Responsive Transport: The Telelous Case. Bachelor thesis, 2019 more… BibTeX
- Vollert Aileen: Resource-Constrained Project Scheduling: Investigation of Network Topologies an their Impact on Priority-Based Heuristics. Bachelor thesis, 2019 more… BibTeX
- Arzu Altintas: Explanation of a Neural Network Demand Forecast with an Expert System to Increase User Acceptance. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Niklas Tuma: A Performance Comparison of Pull Type Control Mechanisms for Serial Production Systems Using Petri Nets. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Julia Bühringer: Agile Project Management Method Scrum: An Explorative Analysis of the Implementation in Business Practice. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Lorenz Friedrich: Applicability and Effectiveness of Pruning Rules for the Runway Scheduling Problem. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Rebecca Griffel: Applicability of the Rolling Horizon Approach to a Runway Scheduling Problem. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Leon Arutyunov-Sincuk: Comparison of Optimal and Heuristic Solutions for the Runway Scheduling Problem in Winter. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Daniel Nientiedt: Design of an Algorithm for Planing and Assigning Guests in a Running Dinner Event While Minimizing Travel Distances. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Lukas Volpers: Effect of on-demand Parking on Emission and Travel-Time in Urban Areas - A Simulatory Approach. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Philipp Schlieker: Efficient Inventory Management for Process-Critical Tools with Volatile Demand. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Martin Krader: Efficient Methods for Solving the Resource Leveling Problem - Criteria for High Performing Heuristic Solution Methods. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Stefan Linnenbank: Einfluss von Clustering auf die Lösungsqualität eines Facility-Location-Problems und dessen Lösungsgeschwindigkeit. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Horst Urlberger: Einsatzmöglichkeiten von Predictive Analytics im Projektmanagement. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Tabea Richter: Emmission Reduction by Ride Sharing: A Case Study in the Region of Düsseldorf. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Sebastian Zett: Evaluating Heuristics for the Split Delivery Vehicle Routing Problem by the Example of FlixBus. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Johannes Rogowsky: From Toyota to Scumban - Kanban in Agile Project Management. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Johannes Lamprecht: Impact of Digitization on Key Performance Indicators of a German University Hospital's Surgical Emergency Department - A Discrete Event Simulation. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Maurice Löw: Implementation of an Order Lot-Sizing Optimization Model for the Material Supply Process of Lufthansa Technik AG. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Lana Mikolaschek: Integer Programming Model for a Hierarchical Workforce Scheduling Problem. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Alexander Georg: Optimizing Self-Employed Midwife Home Health Care Routing. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Bernhard Höcherl: Planning Group Performances of Artists. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Bernhard Höcherl: Scheduling a Performance at "Cirque du Soleil". Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Clemens Neumann: Simulation of E-Taxis in Munich to Evaluate Charging Station Network Layouts Using Simulation Software Anylogic. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Constanze Althammer: Use of Column Generation to Solve the Resource Leveling Problem in Realistic Problem Sizes: An Approach Motivated by the Strategic Planning of Vehicle Introductions in the Automotive Industry. Bachelor thesis, 2018 more… BibTeX
- Moritz Thiele: Development of a greedy algorithm for the multidimensional knapsack problem. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Timothy Hönig: A Clarke-and-Wright, Energy-Consumption-Based Heuristic for the Electric Vehicle Routing Problem. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Sophia Huber: Applying Agile Project Managment Methods for a Product Line at BMW Group. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Kai Kühnel: Battery Level Optimization of an Electrically-Operated Taxi under Requirement-Specialized Capacity Restruction in Urban Regions. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Trong Duc Nguyen: Charging Infrastructure for Electric Vehicles: Cost Model and Approximation Method for Charging Station Placement. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Markus Gaida: Complexity and Sensitiviy Analysis of an Optimization Model for Runway Scheduling during Winter Operations. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Ediz Erkmen: Die Einflüsse der Projektablaufplanung auf die Praxis des Projektmanagements. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Lorenz Hansbauer: Entwicklung eines Models zur Aufwandsschätzung für die Weiterentwicklung des Datenhaushalts eines Finanzdienstleistungsunternehmens. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Wen San: Identification of General Planning and Control Parameters for Two Part Families in Comparison for Two Overseas Plant within an Automotive Group. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Merith Berkay Sümer: Implemantation of an Appointment Scheduling System in Healthcare. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Christina Leinauer: Implementation of a Heuristic for the Flow-Refueling Location Model for the Case Hydrogen Refueling Infrastructure of the European Union. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Falk Herm: International Sourcing with Local Content Restrictions and Uncertainties - A Multi-Objective, Stochastic Modeling Approach. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Clemens Hauptmann: Investigating the Impact of Customer Changes on Tour Planning and Bus Procurement at FlixBus. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Linus Mohr: Meta Analysis of Data Envelopment Approaches in the Context of Football. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Theresa Klaus: Outpatient Scheduling in Theory and Practice. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Geuking Ralph: Pricing of Complex Purchasing Parts Using Multiple Regression Analysis. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Anna Maria Obermair: Project Management with Scrum. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Simon Bergmann: Scheduling the U.S. National Football League by Integer Programming. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Kilian Hieronymus: Workforce Planning Incorporating Skills: Overview with Sensitivity and Complexity Analysis. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Katharina Gegg: Zuweisung von Arbeitern zu Aufgaben mit flexiblen Pausen und Bestrafung von Verspätungen. Bachelor thesis, 2017 more… BibTeX
- Lucas Straub: Sustainable Airport Ground operations - Analyzing an Integrated Optimization Approach Based on Real World Data from Munich Airport. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Henrik Buck: Design Considerations for Terminal Layout Planning. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Antonia Wiggert: Robust Optimization of the International Sourcing Problem in the Automotive Industry. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Robert zur Bonsen: Analyse genetischer Algorithmen zur Lösung multidimensionaler Knapsack-Probleme. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Johannes Thanner: Analyzing and Optimizing Business Process Management According to the SCOR Model Focusing on Plan-Make Capabilities: An Innovative Approach Comparing Two High Tech Companies. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Lotta Opderbeck: Analyzing factors influencing the conversion rate in the bus charter market. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Björn Klages: Behavioral Aspects of Revenue Management and Pricing: A Literature Review. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Hannes Müller: Comparison and Evaluation of Arrival Flow Integration Techniques for Munich Aiport. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Florian Kuchler: Literature Overview of Selected Recent VRPMSs and Ground Handling Publications. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Dmitry Kerbelev: Challenges and Concepts of an Optimized Project Portfolio Managment. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Moritz Felber: Impacts of Machine Interruptions on Goal-Setting Processes at Bayer Grenzach. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Florian Burger: Implementierung und Evaluation von Optimierungsmodellen zur Gepäckabfertigung an Flughäfen. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Dominik Nitsch: Determining a demand-based markup model in the bus charter market using multiple regression. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Arminda Baez Fumero: An analysis of various algorithms to optimize the over-constrained airport baggage sorting station assignment problem. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Maximilian Arntz: Disruption Management for Flight Crew Scheduling. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Kilian Sagner: Measuring Efficiency of Football Teams playing in UEFA Champions League Using Data Envelopment Analysis. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Tiemo Morawitz-Bardenheuer: Quantitative Approaches in Jet Fuel Procurement. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Fabian Baur: Entwicklung einer Forecast-Methodik zur Prognose von Personalkosten für die Projektsteuerung bei der BMW AG. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Ahmet Cem Yamac: A Study on Mathematical Models to Optimize Scheduling of Medical Resident Training. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Friedrich Bürgin: Fair Centralized Allocation of Resource Limitations Among University Departments. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Matthias Aschenbrenner: Modeling and Optimizing the Disposition Management of Trams in a Storage Yard. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Malte Feucht: Scheduling Aircraft Landings: Identifiying, Implementing and Evaluating Different Optimization Models. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Manuel Freytag: Using Data Mining to Survey the Availability of Branded Busses for Customer Inquiries at FlixBus. Bachelor thesis, 2016 more… BibTeX
- Victoria Wahode: Usability, Acceptability and Extensions of an Healthcare Operations Management Application. Bachelor thesis, 2015 more… BibTeX
- Adriana Ullrich: Advanced Methods in Project Management: Scheduling Multiple Projects using Genetic Algorithms. Bachelor thesis, 2015 more… BibTeX
- Ramona Zauner: Anomaly Detection in Web Analytics - A Comparison of Algorithms. Bachelor thesis, 2015 more… BibTeX
- Sophie-Marie Barth: Behavioral Impact on Auction Mechanisms. Bachelor thesis, 2015 more… BibTeX
- Manuel Colberg: Behavioral Aspects in Supply Chain Management. Bachelor thesis, 2015 more… BibTeX
- Christopher Steinbacher: Evaluating Open Source Optimization Software for Operations Management. Bachelor thesis, 2015 more… BibTeX
- Christoph Schnitzenbaumer: Optimization models to improve the scheduling of surgical resident training. Bachelor thesis, 2015 more… BibTeX
- Anita Regler: Comparing and Evaluating Alternative Licences Software and a Commercial Software for Optimization in Operations Managment. Bachelor thesis, 2015 more… BibTeX
- Narei Rassuli: Routing Problems in Healthcare Operations Management: A Taxonomic Review. Bachelor thesis, 2015 more… BibTeX
- Oleksandra Tsyganok: Optimale Auslegung der Ladeinfrastuktur für elektrifizierte Flottenanwendungen. Bachelor thesis, 2015 more… BibTeX
- Jacqueline Schuster: Entwicklung eines Verfahrens zur Tourenplanung für einen Minibus-Share-Service. Bachelor thesis, 2015 more… BibTeX
- David Rudolph: The Pickup and Delivery Problem withTime Windows: A Survey of Construction and Improvement Heuristics. Bachelor thesis, 2015 more… BibTeX
- Melanie Baldinger: A Bee Colony Optimization Approach for the Flight Gate Assignment Problem based on Data from Munich Airport. Bachelor thesis, 2015 more… BibTeX
- Hoang Tung Le: Appointment Scheduling. Bachelor thesis, 2015 more… BibTeX
- Moritz Mergenthaler: Length of stay analytics and optimization - A review. Bachelor thesis, 2015 more… BibTeX
- Franz Hertenberger: Simulation der Gatezuweisung am Flughafen München. Bachelor thesis, 2015 more… BibTeX
- Dierauf, Steffen : Analyse und Konzepte zur Verbesserung der Produktionsplanung in einem Unternehmen der Einzel- und Kleinserienfertigung. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Marlene Pacheco: Practical Applications of the Location Routing Problem: An Overview. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Felix Grün: Implementation of a Rolling Horizon Approach for a General Resource-Constrained Project Scheduling Problem (RCPSP). Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX Full text (mediaTUM)
- Franziska Krenz: Behavioral Aspects of Sequential Decision Making. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Lutz, Myriam: Behavioral Issues in Portfolio Decision Analysis: Investigating Decision Maker Heuristics. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Eileen Zhang: Cyclic Staff Scheduling with Flexible Shift Parameters for Airport Ground Handling. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Nikolaus Witzgall: Economic Feasibility Study of Renewable Power Stations for Different Climatic Scenarios. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Julia Maihöfer: Review of Decision Support Systems for Project Portfolio Selection. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Beria Durdevic: Simulation and Analysis of Outbound Baggage Handling of a Mayor European Airport. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Arnold Dolderer: Developing and Analyzing a Multi-Agent-Based Simulation for Vehicle Routing Problems. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Chris Wengerter: Setting Targets for Process Improvement Initiatives with Ratio-Based Efficiency Analysis. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Flavius Zima: Resource Planning of Endoscopy Devices. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Christoph Meier: Implementation of a Decision Support System for Workforce Planning of Anesthetists. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Konstantin Römer: Implementation of a Tabu Search Algorithm for Markov Blanket Classification. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Stefan Schilcher: Efficiency Evaluation of Hospital IT-Services through Data Envelopment Analysis. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX Full text (mediaTUM)
- Martin Ly-Ky: Examination of the Ground Handling and Baggage Handling System Markets and Corresponding OR Software. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Anna Cäcilia Bierma: Modeling and Optimization of Cargo Transportation at Munich Airport. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Fabian Wurmer: Product Variety Management in Manufacturing Companies - a Review of Literature and Case Studies. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Michael Baur: Implementation and Benefit of a Quantitative Risk and Analysis on the Basis of the Time Schedule of an International Automotive Project. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Philipp Klautke: Modeling and Optimization of Cargo Transportation at Munich Airport. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Marcel Bischofberger: Key performance indicators for measuring productivity of development departments. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Gu, Yingtao: Implementing a Rolling Horizon Approach for General Resource-Constrained Project Scheduling Problems (RCPSP). Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX Full text (mediaTUM)
- Marina Pfann: Make-To-Order or Make-To-Stock: A Literature Study on Strategic Decisions and Approaches. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX Full text (mediaTUM)
- Markus Feuchtinger: Analysis of Practical Applications of Location-Routing Problems. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX Full text (mediaTUM)
- Inal Anil: Evaluierung der Anwendbarkeit von Standardsolvern zur Lösung von quadratischen Optimierungsproblemen. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX Full text (mediaTUM)
- Adrian Maier-Ring: Ein mathematisches Modell zur Optimierung der Insandsetzungsplanung und - steuerung von Mietmaterial der Firma PERI. Bachelor thesis, 2014 more… BibTeX
- Bierich, Eduard: Appointment Scheduling in Health Care. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Breiner, Marie-Luise: Mathematische Modellierung der Personaleinsatzplanung bei der Aeroground Flughafen München GmbH. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Schmel, Daniel: Erstellung eines Bewertungsmodells zur Fehlerpriorisierung in der Automobilindustrie. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Tisch, Andreas: Experimental Investigation of Behavioral Issues in Portfolio Decision Analysis. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Munz, Josef: Verfehlen von Projektzielen: Beispiele, Erfolgskriterien und Erfolgsfaktoren. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Klemm, Martin: Entwicklung eines simulationsgestützten Kennzahlensystems zur Bewertung der operationellen Stabilität des DLH HUB Systems MUC in der Flugplanungsphase. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Scheer, Franziska: Mathematische Modellierung der Personaleinsatzplanung bei der Aeroground Flughafen München GmbH. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Alexander Merkel: Optimierung der Schlepper-Flotte am Flughafen München. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Köster, Christoph: Investigation of Football Leagues using Data Envelopment Analysis. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Diebold, Tatjana: Investigation of Portfolio Decision Analysis Approaches for the Selection of Process Improvement Initiatives. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Vortmann, Matthias: Review and Categorization of Methods for Portfolio Decision Analysis. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Sikora, Malina: Review and Categorization of Problems in Portfolio Decision Analysis under Uncertainty. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Kufner, Andreas: Investigation of Multiple Seasons in the German Federal Football League using Data Envelopment Analysis. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Schell, Samira: Verfehlung von Zeit- und Kostenzielen am Beispiel des Projekts „Flughafen Berlin Brandenburg“. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Samira Schell: Verfehlung von Zeit- und Kostenzielen am Beispiel des Projekts "Flughafen Berlin Brandenburg". Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Hornung, Felix: Verhaltenswissenschaftliche Aspekte des Newsvendorproblems. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Forster, Anette: Modellierungsansätze für Erweiterungen des Tourenplanungsproblems. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Beninger, Helena: Entscheidungsverhalten im Revenue Management. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Bierich Eduard: Appointment Scheduling in Health Care. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Auchter, Hanna: Promotions meet Operations: Analyzing the Effect of Cross-Selling on Call Center Performance. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Bendeguz Antal Gati: An Economic Analysis of the Value of DRG-Information for Admission and Discharge Management in Hospitals. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Todorov, Ivailo: Development of Benchmark Instances for Behavioral Investigations of Portfolio Decision Making Problems. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Abberger Markus: Automatic Timetabling at the TUM School of Management. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Jochen Gold: Dantzig-Wolfe decomposition for the shift scheduling with flexible and cyclic work templates. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX Full text (mediaTUM)
- Dmitrij Doreziouk: Investigating Bounded Rationality in Behavioral Portfolio Decision Analysis. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Sonja Heins: Succsess factors for cross- and upselling- utilizing incoming calls at customer service centers. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Petra Hettenkofer: Optimization of the perceived waiting time in the emergency room of the county hospital Erding. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Steinau Andreas: Parkinson's Law and its Behavioral Implications for Project Management. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Christian Dörfel: Review of Mathematical Modeling Approaches for Portfolio Decision Analysis under Uncertainty. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX Full text (mediaTUM)
- Lagioia Jakob: Personel scheduling of cleaning workforces in hospitals. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Helm, Viktoria: Literature Survey in Portfolio Decision Analysis. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Büchner, Fabienne: Mathematical programming for patient scheduling in healthcare: A literature review. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Tobias Bölk: Waiting time management for patient admissions. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Mykyta Fedorovskiy: Implementation and Evaluation of a Robust Portfolio Modelling Approach for the Selection of Supply Chain Projects. Bachelor thesis, 2013 more… BibTeX
- Pröbstl, Martin: Sequencing cleaning jobs at hospital wards. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Harmel, Jan: Verhaltenswissenschaftliche Aspekte im Revenue Management. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Jieqing, Shi: Analyse von Projektplanungstools unter dem Gesichtspunkt der Ressourcenplanung. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Kommissari, Ines: Anwendungen der Data Envelopment Analysis im Projektportfolio-Management. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Pücher, Bettina: Investigation of Methods for Multi Criteria Decision Analysis. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Geier, Stephanie: Capacity planning in physical therapy. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Schaede, Maximilian: Untersuchung des Robust Portfolio Modeling Ansatzes im Projektportfoliomanagement. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Taralunga, Roxana: Wartezeitmanagement in der zentralen Patientenaufnahme. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Wirth, Johannes: Planungsprobleme im Bereich von Intensivstationen. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Bosler, Tim: Strategische Planung von Intensivstationskapazitäten. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Hernandez, Santiago: Operating Room Planning considering Downstream Units: A literature review. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Gruber, Carola: Wartezeitmanagement in der zentralen Patientenaufnahme. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Savvidis, Nikolas: Development of concepts and ideas to implement Revenue Management at Infineon Technologies AG. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Elsner, David: Analysis of product granularity suitable for inventory planning at Infineon Technologies AG. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Schädler, Fabian: Praktische Anwendung der flexiblen Schichtplanung am Beispiel von Anästhesisten. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Maier, Constantin: Optimierte Landeslotvergabe im Rahmen eines Ground Delay Programs unter Berücksichtigung von Crew- und Passagierverbindungen. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Plöckl, Teresa: Modellierung und Analyse der Pausenplanung bei der Personaleinsatzplanung an Check-in Schaltern. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Thürheimer, Karin: Modellierung und Optimierung der Flug-Gate-Zuweisung (FGZ) anhand von Passagierwegzeiten am Beispiel des Flughafen Münchens. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Schlechter, Lorenz: Push-Back von Flugzeugen am Flughafen München. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Bo, Lue: Investigation of the German Federal Football League using Data Envelopment Analysis. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Kläger, Lena: Investigation of Methods for Portfolio Decision Analysis under Fuzziness. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Kreuzer, Franz: Healthcare Operations Management: Prozesse und Herausforderungen in Krankenhäusern. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Stöhr, Tobias: Health Care Management: Empirical Investigations of Behavioral Issues in Operating Room Planning. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Schweiger, Richard: Ein modelltheoretischer Ansatz zur flexiblen Tages- und Schichtplanung in der Dienstleistungsindustrie. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Joß, Fabian: Taktische OP-Raumplanung. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Sutterer, Paul: Experimental Investigation of Scheduling Approaches for the Dynamic Stochastic Resource-Constrained Multi-Project Scheduling Problem. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Kalcheva, Desislava: Limitation of the Capacity Model ACG (Aggregated Capacity Group) at Infineon and the rollout of the new model based on moving bottlenecks. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Bahamon, Helmut: Investigation of Methods for Product Portfolio Planning under Uncertainty. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX
- Czaja, Roman: Experimentelle Studie zum Einsatz von Open Source Software für das Verweildauermanagement. Bachelor thesis, 2011 more… BibTeX
- Lambert, Gina: Optimierung der Treibstoffversorgung von Fluggesellschaften. Bachelor thesis, 2011 more… BibTeX
- Lauer, Anika: Flugzeugabfertigung an Flughäfen – Ein Literaturüberblick zu quantitativen Analyse- und Planungsmethoden. Bachelor thesis, 2011 more… BibTeX Full text (mediaTUM)
- Babanov, Boyan: Quantitative Methods for planning and scheduling multiple resources in hospitals. Bachelor thesis, 2011 more… BibTeX
- Falgas, Natalia: Study and simulation of the inbounds in baggage transport system at Munich Airport. Bachelor thesis, 2011 more… BibTeX
- Ecker, Monika: Finanztheoretische Methoden zur Projektbewertung. Bachelor thesis, 2011 more… BibTeX
- Castillo, Fabio: Research and optimization of the outbounds of the baggage handling system at Munich Airport. Bachelor thesis, 2011 more… BibTeX
- Ponkratz, Alexander: Modellierung und Analyse der medizinischen Kernprozesse einer radiologischen Praxis. Bachelor thesis, 2011 more… BibTeX
- Müller, Carolin : Passagierlogistik an Flughäfen – Ein Literaturüberblick zu quantitativen Analyse- und Planungsmethoden. Bachelor thesis, 2011 more… BibTeX
- Döge, Alexander: Flexible Personaleinsatzplanung in der Dienstleistungsbranche unter Berücksichtigung verschiedener Arbeitszeitregelungen. Bachelor thesis, 2011 more… BibTeX
- Conrad, Stephanie: Frachtumschlag an Flughäfen – Ein Literaturüberblick zu quantitativen Analyse- und Planungsmethoden. Bachelor thesis, 2011 more… BibTeX
- Fink, Maximilian: Das Newsvendor-Modell in der Operationsraumplanung. Bachelor thesis, 2011 more… BibTeX
- Lunow, Sascha: Evaluation of Different Inbound Logistics Concepts for the BMW Production Plant Munich. Bachelor thesis, 2011 more… BibTeX
- Meinhardt, Johannes: Integrierte Kapazitäts- und Terminplanung für Dienstleistungen mit fixer Kapazität und mehreren Kundenklassen. Bachelor thesis, 2010 more… BibTeX
- Scheungrab, Eva: Analyse eines stochastischen Dienstleistungsprozesses mit Methoden der Warteschlangentheorie am Beispiel der Prämedikationsambulanz eines Krankenhauses. Bachelor thesis, 2010 more… BibTeX
- Strobl, Edgar: Qualitätskriterien bei der Ressourcenallokation in der IT. Bachelor thesis, 2007 more… BibTeX
- Fürgut, Quirin: Heuristiken für kostenminimale Ressourcenallokation und Projektablaufplanung von IT-Projekten. Bachelor thesis, 2007 more… BibTeX
- Nathalie Steckenbiller: Das Verhalten von Patienten und Ärzten unter verschiedenen Terminvergabesystemen. Bachelor thesis, 2005 more… BibTeX
- Kraus, Martin: Identifikation und Implementierung entscheidungsrelevanter Kosten in Krankenhäusern in ein bestehendes Warteschlangenmodell. Bachelor thesis, 2005 more… BibTeX
- n.a.: Problemstellungen in der Operationsraumplanung. Bachelor thesis, more… BibTeX
Bachelor Thesis at the Chair of Service Operations Management
We offer different types of Bachelor thesis topics, related to literature review, empirical research, or quantitative analysis of a decision problem.
Example Topics:
- Approaches for Measuring Business Process Performance
- How to Measure and Manage Service Quality?
- Lean Management in Service Industries – Potential and Limitations
- Recent Approaches for Service Experience Design – A Literature Review
- “Green” Product Design
- The Impact of Delivery Lead Time on Demand (literature review or empirical analysis)
- Pricing of Magazine Advertisements – Current Practice and Recommendations for Improvement
- A Comparison of State-of-the-Art Optimization Solvers
- Dell's hybrid supply chain – make-to-stock vs. make-to-order
- Train Scheduling bei der Deutschen Bahn
- Theorie und Praxis hybrider Leistungsbündel
- Skill-based Project Management
- Delay management in railway systems
Techniques for visualizing service processes
- Revenue Management – The on-line booking problem
We try to consider student preferences when assigning topics.
The thesis can be written in English or German.
Topics in FSS23 for students “B.Sc. Betriebswirtschaftslehre”
- Bachelor Thesis Topics FSS 2023.pdf ( PDF , 398 KB )
Topics in FSS22 for students “B.Sc. Betriebswirtschaftslehre”
- Bachelor Thesis 2022 Topics.pdf ( PDF , 395 KB )
Topics in FSS21 for students “B.Sc. Betriebswirtschaftslehre”
Thema b01: home delivery with time windows.
In retail, the Corona crises accelerates a long-ongoing shift in customer preferences from purchase at physical stores to using e-commerce. While this change provides the opportunity for retailers to save on fixed costs for store locations in expensive city centers, the background processes such as delivery become more complex. Furthermore, e-commerce competes mainly via price putting all retailers under cost pressure. To stabilize the delivery process and fulfill customer expectations, assigning time slots for delivery becomes a viable option. On the other hand, popular time slots may even be “sold” following a Revenue Management approach.
The objectives of this thesis are to…
- introduce the home delivery problem and its foundation in the Operations Research literature,
- present and classify the literature (including assumptions, model characteristics & academical examples),
- discuss and / or improve one model in detail (optional),
- provide open research gaps and future trends.
Basic Literature:
Hernandez, F., Gendreau, M., & Potvin, J. Y. (2017). Heuristics for tactical time slot management: a periodic vehicle routing problem view. International transactions in operational research , 24 (6), 1233-1252.
Köhler, C., Ehmke, J. F., & Campbell, A. M. (2020). Flexible time window management for attended home deliveries. Omega , 91 , 102023.
Yang, X., & Strauss, A. K. (2017). An approximate dynamic programming approach to attended home delivery management. European Journal of Operational Research , 263 (3), 935–945.
Thema B02: Applications of Machine Learning in the Airline Scheduling Process
Airline Scheduling is one of the most complex problems in Operations resulting in a separation into four sequential steps. This separation helps to make the whole problem tractable but decreases the chance of finding an optimal solution for the whole process. As the schedule represents the product offering of an airline, suboptimal scheduling decisions have a large impact on the profitability of an airline. Machine Learning has recently gained importance for complex decision problems in various business applications where large datasets are analyzed in order to uncover patterns for better decision making. While machine learning might still not guarantee to find the globally best solution in scheduling decisions, it may be a building block for an improved scheduling process.
- introduce and compare different Machine Learning Approaches,
- summarize the problems of the Airline Scheduling & Recovery Process,
- identify and discuss applications of Machine Learning in the process & other practical applications,
Belobaba, P., Odoni, A., & Barnhart, C. (Eds.). (2015). The global airline industry . John Wiley & Sons.
Grosche, T. (2009). Airline Scheduling Process. In Computational Intelligence in Integrated Airline Scheduling (pp. 7–46). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Yaakoubi, Y., Soumis, F., & Lacoste-Julien, S. (2020). Machine learning in airline crew pairing to construct initial clusters for dynamic constraint aggregation. EURO Journal on Transportation and Logistics , 100020.
Thema B03: Integrated Models in the Airline Scheduling Process
Due to its complexity, the airline scheduling process is separated into four sequential steps of schedule design, aircraft assignment, maintenance routing and crew scheduling. These problems are solved sequentially and each former problem’s output serves as input for the following problem. While some of these steps do have different planning scales such as all aircraft fleets vs. only a single fleet; a complete integration is possible to model but not to solve with the currently available methods for realistic instances. To come closer to this ideal state of the process, some models have been integrating one or even more scheduling steps.
- introduce the Airline Scheduling Process and its sequential steps,
- summarize the literature of models covering multiple steps,
Sandhu, R., & Klabjan, D. (2007). Integrated airline fleeting and crew-pairing decisions. Operations Research , 55 (3), 439–456.
Shao, S., Sherali, H. D., & Haouari, M. (2017). A novel model and decomposition approach for the integrated airline fleet assignment, aircraft routing, and crew pairing problem. Transportation Science , 51 (1), 233–249.
Thema B04: Experiential Service Design – Empirical Evidence for Sequence Effects
Past researchers have found empirical evidence that customers consider the sequence of event utility when evaluating past and future service experiences. Dixon and Verma (2013) provide a thorough review of the psychology and behavioral economics literatures concerned with sequence effects and cite four main effects that emerge as relevant to sequencing service encounters: (1) the impact of the highest point, most intense, or highest utility part of an experience (Peak Effect); (2) the impact of the last point of an experience (End Effect); (2) the impact of the timing of the peak (Spread Effect); (4) and the overall trend of the experience over time (Trend Effect).
Because these sequence effects are used in optimization models (for example by Dixon & Thomson 2016), understanding empirical findings on these effects is very important for experiential service design.
- review current empirical knowledge on experiential service design with a focus on sequence effects (not limited to peak-, end-, trend-, and spread-effect);
- compare different empirical studies on sequence effects and discuss their limitations;
- discuss which findings could be generated in or adapted to services and give an outlook on future research opportunities in this field.
Bellos, I., & Kavadias, S. (2021). Service design for a holistic customer experience: A process framework. Management Science , 67(3), 1718-1736.
Dixon, M., & Verma, R. (2013). Sequence effects in service bundles: Implications for service design and scheduling. Journal of Operations Management , 31(3), 138–152.
Dixon, M. J., Victorino, L., Kwortnik, R. J., & Verma, R. (2017). Surprise, anticipation, and sequence effects in the design of experiential services. Production and Operations Management , 26(5), 945- 960.
Thema B05: Experiential Service Design – Empirical Evidence for Psychological Constructs
Customers evaluate past and future service experiences based on the sequence of events. The field of experiential service design uses this knowledge to develop optimization models increasing remembered utility – the utility that customers remember after the service has ended. Two perspectives have established: (1) Only a few defining utility values (highest utility or last utility value) or utility measures (trend over time, spread between peak and end) are used to calculate remembered utility (Dixon and Verma 2013). (2) All instant utilities at each service event are used to calculate remembered utility, thereby mapping the underlying mental processes in the consumer’s brain (Das Gupta et al. 2016). In recent years these psychological constructs are used in optimization models for experiential service design, demanding a deep understanding of empirical findings on these constructs.
- review current empirical knowledge on experiential service design with a focus on psychological constructs (not limited to memory decay or acclimation);
- compare different empirical studies on psychological constructs and discuss their limitations;
Bellos, I., & Kavadias, S. (2021). Service design for a holistic customer experience: A process framework. Management Science, 67(3), 1718-1736.
Das Gupta, A., Karmarkar, U. S., & Roels, G. (2016). The design of experiential services with accli- mation and memory decay: Optimal sequence and duration. Management Science , 62(5), 1278- 1296.
Roels, G. (2019). Optimal structure of experiential services: Review and extensions. Handbook of Service Science, Volume II , 105–146.
Thema B06: Digitization, Digitalization, and Digital Transformation – Creating a Research Landscape in an Emerging Field
Reviewing literature in both academic and business contexts, digital transformation can rapidly be identified as a trending topic in recent years. Besides of the term digital transformation itself, some authors also talk about digitization or digitalization. While the terms are often used interchangeably, they can also be defined individually and differentiated them from each other. Identifying similarities and differences between these terms is one focus of this thesis. The other focus is on digital transformation itself, referring to strategic business (model) changes taking advantage of digital progress. These changes have a fundamental impact for the respective company changing the way it operates in the market.
- define and differentiate the terms digitization, digitalization, and digital transformation;
- identify, cluster and analyze key research topics and questions in the field of digital transformation;
- discuss latest trends in this research field and highlight potential topics for future research.
Verhoef, P. C., Broekhuizen, T., Bart, Y., Bhattacharya, A., Dong, J. Q., Fabian, N., & Haenlein, M. (2021). Digital transformation: A multidisciplinary reflection and research agenda . Journal of Business Research, 122, 889–901.
Vial, G. (2019). Understanding digital transformation: A review and a research agenda. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems , 28(2), 118–144.
Thema B07: Digital Transformation as an Interdisciplinary Research Area
In both the academic world and the business world there is a growing interest in digital transformation in recent years. The term refers to strategic business (model) changes taking advantage of digital progress. These changes have a fundamental impact for the respective company changing the way it operates in the market. Due to this complexity, a variety of research disciplines works on topics of digital transformation – each contributing in a different way. While marketing might focus on identifying new customer needs in a more and more digital world, operations research can enable these new services with digital processes.
- review academic literature to introduce and define digital transformation and differentiate it from similar terms;
- discuss how different research areas like operations, marketing, information systems, and others contribute to digital transformation;
- focus on operations research and present research topics and trends in the context of digital transformation.
Li, F. (2020). Leading digital transformation: three emerging approaches for managing the transition. International Journal of Operations & Production Management.
Verhoef, P. C., Broekhuizen, T., Bart, Y., Bhattacharya, A., Dong, J. Q., Fabian, N., & Haenlein, M. (2021). Digital transformation: A multidisciplinary reflection and research agenda. Journal of Business Research , 122, 889–901.
Thema B08: Throwaway mentality and the environment – Are consumers responsible for the environmental damage?
Slade (2009) described that in North America over 100 million cell phones and 300 million personal computers were discarded each year in the beginning of the 20th century. Certainly, North America is not alone with such a development. The throwaway mentality is already in place in Europe and other regions.
Several factors have contributed to the emergence of this mentality. In particular, companies claim to be following consumer desires when creating new products. As a result, the policy of planned obsolescence – designing a product with an artificially limited useful life – is also justified by evolving consumer preferences.
- Review the development of throwaway mentality in the world;
- Identify main products and industries, this mentality occurs most in;
- Identify potential drivers of consumer throwaway mentality;
- Discuss whether consumers are responsible for the environmental damage;
- Discuss what future research in this field should focus on.
Echegaray, F. (2016). Consumers' reactions to product obsolescence in emerging markets: the case of Brazil. Journal of Cleaner Production , 134, 191–203.
Grewal, R., Mehta, R., & Kardes, F. R. (2004). The timing of repeat purchases of consumer durable goods: The role of functional bases of consumer attitudes. Journal of Marketing Research , 41(1), 101–115.
Slade, G. (2009). Made to break: Technology and obsolescence in America. Harvard University Press.
Thema B09: Planned obsolescence and environment – Are companies responsible for the environmental damage?
Planned obsolescence is a policy of designing a product with an artificially limited useful life, so it will become obsolete, i.e. no longer functional after a certain period of time. The rationale behind the strategy is to generate long-term sales volume by reducing the time between repeat purchases. Such a policy goes hand-in-hand with several side effects, in particular high impact on the environment in terms of resource use as well as waste disposal.
The impacts of this trend on the environment are manifold. First, natural resources become very scarce, since the increasing number of manufactured durables implies an increasing use of resources. Second, higher amounts of waste are created due to rising product disposals, which in turn increases the pressure for ex-post waste management. Third, impact on pollution and climate change stands out, since energy used in the manufacturing and distribution of durables is still strongly sourced from non-renewable fossil fuels.
- Review the literature for planned obsolescence and classify it;
- Identify potential drivers of planned obsolescence from the corporate perspective;
- Identify the implications of planned obsolescence from the triple bottom line perspective;
- Discuss whether companies are responsible for the environmental damage;
Agrawal, V. V., Kavadias, S., & Toktay, L. B. (2016). The limits of planned obsolescence for conspicuous durable goods. Manufacturing & Service Operations Management , 18(2), 216–226.
Guiltinan, J. (2009): Creative destruction and destructive creations: environmental ethics and planned obsolescence . Journal of business ethics 89(1), 19–28.
Thema B10: Comparison of Process Mining Tools for Academia and Industry
Process Mining combines process science and data science and provides many new forms of analysis in the area of business process management. For example, process discovery algorithms allow to derive process maps from the data collected during process execution, thereby creating a representation of the process as it is actually performed. For managers, these insights allow e.g. a comparison of the executed process model with the normative process model. Given the discovered process, further analyses can take place, such as the evaluation of process improvement possibilities. Using the output of the process mining’s discovery algorithm, a simulation model can be built in order to test different process variants and configurations.
Several process mining tools exist. As some of the offered functionalities are similar, other aspects as well as the respective target audiences of the tools differ. For example, the output of the tools, viz. the mined process models, can be compared as various algorithms for process discovery exist, allowing for potential differences in the output of two different tools. Hence, a comparison of the tools allows to specify the strengths and weaknesses on the basis of criteria defined through a previous literature review. A clear overview and recommendations for different user groups can be provided, offering valuable insights into the commonly used process mining tools in academia and industry.
- to provide an overview over the most commonly used process mining tools in academia and industry,
- to critically compare the process mining tools, including Celonis, ProM, Apromore and Disco, based on predefined criteria, and
- to give a recommendation concerning the tool selection based on different purposes.
Basic literature:
Mans R.S., Schonenberg M.H., Song M., van der Aalst W.M.P., Bakker P.J.M. (2008) : Application of Process Mining in Healthcare – A Case Study in a Dutch Hospital. In: Fred A., Filipe J., Gamboa H. (eds) Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies. BIOSTEC 2008. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 25. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Van Der Aalst, W. (2016): Process mining. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Van der Aalst, W., & Damiani, E. (2015): Processes meet big data: Connecting data science with process science. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing , 8(6), 810–819 .
Van der Aalst, W. M., & Weijters, A. J. (2004): Process mining: a research agenda. Computers in Industry, 53 (3), 231–244 .
Thema B11: Pricing strategies for digital product bundles
Price bundling is a strategy whereby a vendor sells many different goods/ items and offers the entire bundle at a single price. In the simplest case, the seller can offer only once and the customer can either accept or reject the offer. Research provides different facets of product price bundling. E.g. using personalized bundling, the seller receives a request for quote (RFQ) and determines a price based on the utility function of requested products. To solve this problem Xue (2016) uses a top-down and a bottom up approach. Other bundling problems use a customized bundle price scheme, where customers may select a fixed number of goods for a certain fixed price (Hitt, 2005). With current developments in the digital market, existing models can be assessed if they are applicable to digital products as well.
- review pricing strategies for product bundles,
- comment if those methods are applicable to digital product bundles given their characteristics,
- explain one model in detail, and
Xue, Z., Wang, Z., & Ettl, M. (2016). Pricing Personalized Bundles: A New Approach and An Empirical Study. Manufacturing & Service Operations Management , 18 (1), 51–68. doi.org/10.1287/msom.2015.0563
Hanson, W., & Martin, R. K. (1990). Optimal Bundle Pricing. Management Science , 36 (2), 155–174. doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.36.2.155
Hitt, L. M., & Chen, P. (2005). Bundling with Customer Self-Selection: A Simple Approach to Bundling Low-Marginal-Cost Goods. Management Science , 51 (10), 1481–1493. doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.1050.0403
Thema B12: Discrete choice for digital products and services
The choice between different software and service vendors can be characterized as a discrete choice situation, where the customer selects the best business partner. These decisions can be modelled with discrete choice models. One prominent functional specification is the multinomial choice model (MNL). An underlying assumption of the models is the possible decomposition of the product or service in attributes with different levels, where each attribute level is connected to a particular partial utility. While the model is well established for characteristics of transportation modes, little to no research has be done on digital products and services.
- introduce and compare the MNL and similar discrete choice models,
- provide an overview over empirical studies for drivers of software purchases,
- comment if and how a discreate choice model is applicable to digital products and services,
Gönsch, J., Klein, R., & Steinhardt, C. (2008): Discrete Choice Modelling (Teil I). WiSt Wirtschaftswissenschaftliches Studium , 37(7), 356–362.
Train, K., & Ebrary, Inc. (2009): Discrete choice methods with simulation (Second ed.). Cambridge University Press . New York Melbourne Madrid Cape Town Singapore São Paulo Delhi Mexico City
Kekre, S., Krishnan, M. S., & Srinivasan, K. (1995): Drivers of Customer Satisfaction for Software Products: Implications for Design and Service Support. Management Science , 41(9), 1456–1470. doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.41.9.1456
Thema B13: Optimal pricing model for software vendors
Product pricing is an important strategic part of a business. Due to the economic characteristics specific to the software industry, pricing concepts existing in other industries cannot be transferred without adaptation (Lehmann and Buxmann 2009). With the advancement of technology several new business models suit perfectly to digital products. As there is no universal pricing model for software providers, pricing can be divided into pricing parameters like price bundling or price discrimination. With the growth of cloud computing, SaaS products are offered mostly based on service contracts.
- review and systematically summarize the literature on pricing models for software vendors,
- compare and discuss the benefits and drawbacks of the different model categories,
- highlight one state-of-the-art pricing strategy and point out their benefits to comparable models,
- create a framework, which pricing model fits to what kind of digital product (optional).
Gurnani, H., & Karlapalem, K. (2001). Optimal pricing strategies for Internet-based software dissemination. Journal of the Operational Research Society , 52(1), 64–70. doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.jors.2601046
Lehmann, S., & Buxmann, P. (2009). Pricing Strategies of Software Vendors. Business & Information Systems Engineering , 1(6), 452–462. doi.org/10.1007/s12599-009-0075-y
Ojala, A. (2016). Adjusting software revenue and pricing strategies in the era of cloud computing. Journal of Systems and Software , 122, 40–51. doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2016.08.070
Rohitratana, J., & Altmann, J. (2012). Impact of pricing schemes on a market for Software-as-a-Service and perpetual software. Future Generation Computer Systems , 28(8), 1328–1339. doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2012.03.019
Thema B14: Effects of empirical estimates on product line design models
A key strategic decision for a firm is the product offering to maximize profit through customer satisfaction. The manufacturer can not only customize and optimize a single product, but they can design a product line which can capture the needs of different market segments. Product Line Design problems determines the products which should be offered and how to design them. The design decision takes different attributes (e.g. price, size, color) into account. The potential advantages for the vendor of an extensive product portfolio have to be weighed against the cost and possible substitution effects between products. To capture customer choice behavior conjoint or discrete choice analyses are often used.
In the scientific literature, the problem is known as the product line design or product line selection problem, respectively. It has become a pivotal research focus at the interface between quantitative marketing and operations research. In the past four decades several quantitative models for optimal product line design have been developed (see Belloni et al., 2008). Conjoint or discrete choice analysis is typically used to estimate functional relationships between attribute specifications and customer utility and/ or choice behavior.
- review and systematically summarize the literature on Product Line Design in regards to there assumed customer choice behavior,
- identify the affect of empirical estimates on problem formulation and solution methods,
- highlight one model and point out their benefits to comparable models.
Belloni, A., R. Freund, M. Selove, D. Simester , Optimizing product line designs: Efficient methods and comparisons, in: Management Science, Vol. 54 (2008), S. 1544-1552.
Bertsimas, D., & Mišić, V. V. (2019). Exact first-choice product line optimization. Operations Research, 67(3), 651–670.
Dobson, G., S. Kalish , Heuristics for Pricing and Positioning a Product-Line Using Conjoint and Cost Data, in: Management Science, Vol. 39 (1993), S. 160–175.
Topic B15: Consumer Preferences for Sustainable Product Attributes and Implications for Product and Supply Chain Design
Product design decisions are important decisions at the interface of marketing and operations that are very costly to implement and change, and are determinant for market success. In order to systematically support decision-making in this area, a number of predictive consumer behavior models (in particular based on conjoint and discrete choice analysis) and prescriptive mathematical programming models for optimal product (line) design based on customer preference data have been developed in the last decades (see e.g. Belloni et al. 2008). In these models, a product is considered to be a bundle of buyer relevant attributes and their levels, respectively. Sustainable products are “all kinds of products that have or aim at an improved environmental and social quality, which can be related back to the already mentioned implementation of environmental and social standards. The ultimate aim is to satisfy customers and gain a competitive advantage in the market.” (Seuring & Müller 2008). Typical product attributes that determine a product’s sustainability include the product’s CO2 footprint, its longevity, energy use during production, recyclability, whether it is regional, bio, fair traded (for food), its packaging and plastic content, etc. Various empirical studies show that sustainable attributes increase consumer willingness-to-pay and may pay off the efforts on the supply chain side if higher prices can be charged.
- briefly introduce conjoint analysis as a tool for measuring consumer preferences for certain attribute levels,
- review the empirical literature on consumer preferences for sustainable product features and provide a meaningful classification e.g. with regard to model assumptions, attributes, etc.,
- Is there any additional willingness-to-pay of customers for sustainable attributes? What evidence does the empirical literature provide for different sustainable attributes? What type of sustainable attributes are most preferable from a consumer’s and a designer’s perspective? How can empirical studies be classified?
- How does the seller’s cost structure change for producing “sustainable” attribute levels? What are the implications for optimal product and supply chain design?
Alriksson, S., & Öberg, T. (2008). Conjoint analysis for environmental evaluation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research , 15(3), 244–257.
Belloni, A., Freund, R., Selove, M., & Simester, D. (2008). Optimizing product line designs: Efficient methods and comparisons. Management Science , 54 (9), 1544-1552.
Hicks, R.L. (2012). Product Labeling, Consumer Willingness to Pay, and the Supply Chain. In: Boone, T., Jayaraman, V., & Ganeshan, R. (Eds.). (2013). Sustainable supply chains: Models, Methods, and Public Policy Implications. International Series in Operations Research & Management Science. Springer. https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-1-4419-6105-1
Seuring, S., & Müller, M. (2008). From a literature review to a conceptual framework for sustainable supply chain management. Journal of cleaner production , 16 (15), 1699-1710.
Topics in FSS21 for students “B.Sc. Wirtschaftspädagogik”
Thema b01: improving process performance through simulation analysis – a literature review.
Responsiveness is one important dimension of service quality, which is often operationalized as the flow time or flow rate of a process. In many situations, customers expect a fast service. Already in a pre-purchase phase, responsiveness can impact the purchase decision significantly. For example, in the loan application process, customers need to fill in an application form which is then check by the back-office. While the bank evaluates the credit worthiness of the applicant, the applicant has to wait until the contracts are sent. If multiple applications at different banks are filed, the customer might more likely choose the bank which answers fastest, as long as the interest costs are comparable. Banking is however only one of many sectors, which consider responsiveness as increasingly important factor. Generally, service providers should reduce unnecessary waiting time for the customers. Hence, the analysis of queuing systems can provide valuable insights into process improvements related to responsiveness.
Simulation studies are a suitable measure to compare the performance of different process variants while controlling for the differences. As such, a simulation allows to e.g. evaluate the performance of different process paths in terms of process speed and waiting time. Recommendations for process improvements could be based on a change of, for example, the capacity distribution or the order of activities.
The objectives of this thesis are
- to provide an overview of the current literature on simulation studies with focus on optimizing process speed and responsiveness with applications in selected service industries after 1995,
- to compare the methodological analysis of the identified simulation studies, and
- to give some recommendations when to apply the improvement measures proposed in different studies.
Watson, E. F., Chawda, P. P., McCarthy, B., Drevna, M. J., & Sadowski, R. P. (1998): A Simulation Metamodel for Response‐Time Planning. Decision Sciences, 29(1), 217–241.
Kim, H. W., & Kim, Y. G. (2001): Rationalizing the customer service process. Business Process Management Journal , 7(2), 139–156.
Madadi, N., Roudsari, A. H., Wong, K. Y., & Galankashi, M. R. (2013): Modeling and simulation of a bank queuing system. In 2013 Fifth International Conference on Computational Intelligence, Modelling and Simulation , 209–215, IEEE.
Thema B02: Identifizierung und Priorisierung relevanter Customer Journeys zur Optimierung der Customer Experience
Englischer Titel: Identification and Prioritization of Relevant Customer Journeys to Optimize the Overall Customer Experience
Das Kundenerlebnis (engl. „Customer Experience“) spielt für Unternehmen eine immer größere Rolle, um bestehende Kunden zu halten und neue Kunden zu gewinnen. Um die gesamte Customer Experience zu verbessern, gilt es, die „Reise“ eines Kunden entlang verschiedener Kontaktpunkte mit einem Produkt bzw. dessen Anbieter (engl. Customer Journey) und deren zugrundeliegende Wertschöpfungsprozesse zu optimieren. Die meisten Unternehmen bieten eine große Zahl an Dienstleistungen an, die wiederum unterschiedliche Customer Journeys je nach Segment, Kontext oder Phase des Kundenlebenszyklus aufweisen. Eine parallele Optimierung aller Customer Journeys ist entsprechend kaum möglich, so dass eine Priorisierung zwingend erforderlich ist. Da sowohl Unternehmens- als auch Kundeninteressen bei dieser Priorisierung eine wichtige Rolle spielen, gilt es, die Customer Journeys auszuwählen, die den größten Einfluss auf die übergreifende Customer Experience haben und deren Optimierung sich gleichzeitig in einem angemessenen Kostenrahmen bewegen.
Die Ziele dieser Arbeit sind es…
- die Begriffe Customer Experience Management und Service Process Design zu definieren;
- die Rolle verschiedener Forschungsgebiete wie Marketing, Service Research und Operations Research im Kontext der obigen Begriffe herauszuarbeiten;
- empirische Studien, Optimierungsmodelle oder theoretische Modelle zusammenzutragen, die aufzeigen, inwiefern einzelne Customer Journeys die gesamte Customer Experience beeinflussen.
Einstiegsliteratur:
Fließ, Sabine und Kleinaltenkamp, Michael (2004) . Blueprinting the service company: Managing service processes efficiently. Journal of Business Research 57 (4), 392–404.
Lemon, K. N., & Verhoef, P. C. (2016) . Understanding customer experience throughout the customer journey. Journal of marketing , 80(6), 69–96.
Stickdorn, Marc und Schneider, Jakob (2011) . This is service design thinking. Basics – tools – cases. Amsterdam.
Thema B03: Kompetenzorientiertes Training für Piloten
Die Luftfahrtindustrie legt trotz starkem Kostendruck einen sehr starken Fokus auf den Aspekt Sicherheit, was sich auch in der Aus- und Weiterbildung von Piloten wiederspiegelt. Ein wichtiger Bestandteil ist unter anderem das Simulator Training, in dem die richtige Reaktion auf und Abarbeitung von herausfordernden Zwischenfällen in einer realitätsnahen Umgebung getestet wird. Die Form des Trainings hatte sich seit den 1960er Jahren nicht weiterentwickelt, bis eine branchenübergreifende Initiative das Konzept des „Evidence-Based Trainings“ definiert und passende Regularien erarbeitet hat. Der Hauptunterschied ist der Wechsel von einem Methodenfokus zu einem Kompetenzfokus.
Aufgrund der weniger vorher festgelegten und mehr an Kompetenzen ausgerichteten Trainingsinhalte stellt sich für Instruktoren die Frage, welches Trainingsszenario sich am besten für die Teilnehmenden eignet. Dafür können Daten aus der operativen Flugtätigkeit herangezogen und zur Bewertung des vorliegenden Kompetenzstandes eines Piloten genutzt werden. Aus diesen Daten wird ein Profil gebildet, welches die Stärken und Schwächen in Bezug auf die Kompetenzen erläutert und somit die Entscheidungsgrundlage für eine manuelle oder automatisierte Auswahl der Trainingsinhalte bietet. Während die Luftfahrt bisher wenige Systeme zur Entscheidungsunterstützung für Trainingsinhalte hervorgebracht hat, haben dort andere Anwender wie das Militär oder die Spieleindustrie mehr Erfahrungen sammeln können.
Ziel der Bachelorarbeit ist es,
- Evidence-based Training inklusive der Kernkompetenzen vorzustellen,
- Best Practices aus vergleichbaren Anwendungen des beruflichen Trainings und weiteren Feldern des Trainings mit Fokus auf Auswahl der Trainingsszenarios aufzuführen,
- die benötigten Daten und der Entscheidung zugrundeliegende Hintergrundprozesse aus den Best Practices zu erläutern,
- offene Forschungsfelder und –lücken darzustellen.
Hörmann, H. J., Lehmann, O., & Schubert, E. (2007): Situationsbewusstsein und Fehlermanagement im Flugsimulator: Leistungsindikatoren von Flugzeugbesatzungen. Simulationsgestützte Systemgestaltung , 59–71
ICAO (2013): Manual of Evidence-Based Training. Doc 9995, AN/ 497. Montreal: International Civil Aviation
Kremer, H. H., & Zoyke, A. (2010): Kompetenzdiagnose als Basis individueller Förderung-Zum Geheimnis einer Black Box. Kompetenzermittlung für die Berufsbildung. Verfahren, Probleme und Perspektiven im nationalen, europäischen und internationalen Raum. Bielefeld: Bertelsmann , p. 145–160.
Zook, A., Lee-Urban, S., Riedl, M. O., Holden, H. K., Sottilare, R. A., & Brawner, K. W. (2012): Automated scenario generation: toward tailored and optimized military training in virtual environments. In Proceedings of the international conference on the foundations of digital games , p. 164–171
Topics in FSS20 for students “B.Sc. Betriebswirtschaftslehre”
Topic b01: product durability and planned obsolescence – empirical evidence.
The objective of the thesis is to provide a review on the topic of planned obsolescence from the marketing and operations management perspective. Focus should be placed on empirical research (incl. case examples) for products and industries, where this phenomenon occurs most.
- to review the literature for planned obsolescence and classify it, focus on empirical evidence and case examples;
- to discuss the pros and cons of planned obsolescence;
- to discuss practices and capabilities that are needed to move beyond unsustainable practices that may motivate companies to move beyond planned obsolescence; and
- to highlight the 5 most relevant contributions to the topic of planned obsolescence from your personal perspective (from the reviewed literature). Point out the facts that lead you to the selection of these contributions.
Echegaray, F. (2016): Consumers' reactions to product obsolescence in emerging markets: the case of Brazil. Journal of Cleaner Production 134, 191–203.
Guiltinan, J. (2009): Creative destruction and destructive creations: environmental ethics and planned obsolescence. Journal of business ethics 89(1), 19–28.
Satyro, W., Sacomano, J., Contador, J., Cardoso A., & Silva, E. (2017): Planned Obsolescence and Sustainability. Ten Years Workıng Together For a Sustaınable Future, Săo Paulo-Brazil-24 May To 26th.
Topic B02: Customer demand models – A review of state-of-the-art approaches
Understanding and predicting customer demand is a crucial task for any company. Since nearly all decisions – sales planning decisions, marketing decisions, production planning decisions, procurement decisions, HR planning decisions, etc. – within a company are based on demand predictions, the role of predicting demand as precisely as possible is a very important task.
Researchers have developed different demand models, ranging from non-causal models – where demand forecast is independent of the company’s actions – to causal (“demand-response”) models – where company’s decisions, such as the pricing strategy, influence the demand. The latter can be further sub-categorized, for example, into first-choice models, share-of-preference models or neural network models.
- to review and systematically summarize the literature on first-choice, share of-preference and neural network models;
- to compare and discuss the benefits and drawbacks of the different model categories (or individual models);
- to highlight the state-of-the-art approaches and point out their benefits as compared to the “older” models; and
- to select one of the reviewed models and implement a self-created example in Excel to explain how the model works (optional).
Bordoloi, S., Fitzsimmons, J. A., & Fitzsimmons, M. J. (2018). Service management: operations, strategy, information technology. McGraw-Hill Higher Education.
Denton, J. W. (1995). How good are neural networks for causal forecasting?. The Journal of Business Forecasting , 14(2), 17.
Train, K. E. (2009). Discrete choice methods with simulation. Cambridge university press.
Topic B03: Neural Networks in BPM – Application and Performance
The idea of Business Process Management (BPM) became popular in the 1980s. BPM academics discussed e.g. the need for cross-functional process flow through organizations or the BPM lifecycle, including designing, modelling, implementing, monitoring and improving business processes. Generally, BPM is defined as structured, comprehensive, and cross-functional approach for the development, ongoing management, analysis, and continuous improvement of business processes.
In recent years, research interests in BPM have risen again due to new technologies and their potential for process management. Neural networks, as just one example of these new technologies and machine learning approaches, promise great benefits and advantages as many constraints, which formerly restricted optimization models, can now be relieved. For example, process predictions on the next steps from neural networks allow to adequately manage the remaining process, to allocate resources accordingly, or to interfere if necessary. Success rates, remaining flow times, and resource requirements are further examples of such predictions.
- to briefly introduce neural networks for the BPM context,
- to identify studies which apply neural networks in BPM and to evaluate the performance, and
- to summarize the application cases and research questions addressed with neural networks.
Rehse, Jana-Rebecca; Dadashnia, Sharam; Fettke, Peter (2018): Business process management for Industry 4.0 – Three application cases in the DFKI-Smart-Lego-Factory. In it – Information Technology 60 (3), pp. 133–141. DOI: 10.1515/itit-2018-0006.
Evermann, Joerg; Rehse, Jana-Rebecca; Fettke, Peter (2017): Predicting process behaviour using deep learning. In Decision Support Systems 100, pp. 129–140. DOI: 10.1016/j.dss.2017.04.003.
Di Francescomarino C., Ghidini C., Maggi F.M., Milani F. (2018): Predictive Process Monitoring Methods: Which One Suits Me Best?. In: Weske M., Montali M., Weber I., vom Brocke J. (eds) Business Process Management. BPM 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 11080. Springer, Cham
Nolle, T., Luettgen, S., Seeliger, A. et al. (2018): Analyzing business process anomalies using autoencoders. Mach Learn 107, 1875–1893
Topic B04: Reliability in Business Processes – Recommendations on Process Design and Management
The quality of a service can include many factors. ServQual (Parasuraman et al, 1988), a popular approach to evaluate service quality, proposes five principal components of service quality: reliability, responsiveness, assurance, tangibles, and empathy. Reliability can be seen as the ability to perform the promised service dependably and accurately, despite the often heterogeneous customer participation. In many succeeding studies, reliability appears to have the highest relevance for service quality. This topic can be linked to Business Process Management (BPM) as a service can be seen as a process. Therefore, designing a reliable service equals designing a reliable process.
Further, reliable service operations and processes can create a competitive advantage. Some firms may thus compete on reliability, which means that reliability is a competitive priority. Yet, not every business model strives for reliability as most important competitive priority. Thus, two questions arise, which are the focus of this thesis: (1) which kind of business models/ value propositions focus mostly on reliability? and (2) how can reliability be operationalized?, in order to give recommendations on how services should be designed to be highly reliable.
- to review the literature in order to determine for which kind of value proposition or business model reliability is a major competitive priority,
- to identify approaches in the literature on the measurement and operationalization of reliability as operational capability, and
- to give recommendations on (service) process design and management to achieve reliability.
Parasuraman, A Parsu & Zeithaml, Valarie & Berry, Leonard. (1988): “SERVQUAL: A multiple- Item Scale for measuring consumer perceptions of service quality”, Journal of retailing , Vol. 64 No. 1, pp. 12–40.
Mehta, S. and Durvasula, S. (1998): “Relationships between SERVQUAL dimensions and organizational performance in the case of a business‐to‐business service”, Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, Vol. 13 No. 1, pp. 40–53.
Turner T.J., Bititci U.S. (1998): “Maintaining reliability of business processes using active monitoring techniques”, in: Bititci U.S., Carrie A.S. (eds) Strategic Management of the Manufacturing Value Chain. IFIP — The International Federation for Information Processing, vol 2. Springer, Boston, MA
Vergidis, K., Saxena, D., & Tiwari, A. (2012): “An evolutionary multi-objective framework for business process optimization”, Applied Soft Computing , 12 (8), 2638-2653.
Topic B05: Using Data Driven Analytics in Healthcare Industry
Data driven healthcare analytics is about making the computer learn from observational data collected in the process of delivering care. Data driven analytics-based approaches like machine learning, data mining and data visualization have been explored in recent research efforts to provide personalized decision support for care delivery and care management. The core idea is to enable learning from the collective experience of a care delivery network as recorded in the observational data, to iteratively improve care quality as care is being provided in a real-world setting.
- to review data driven analytics-based approaches used in the healthcare industry to improve the quality of care,
- to comment theoretically on the healthcare-specific performance measures for care quality improvements, and
- to discuss relevance of data driven analytics approaches in the service industry.
Hu, J., Perer, A., & Wang, F. (2016): Data driven analytics for personalized healthcare. In Healthcare Information Management Systems (pp. 529–554). Springer, Cham.
Topic B06: Impact of Covid-19 on Global Supply Chains and Managing Global Risk through Risk-mitigation Strategies
Reports based on the impact of Covid-19 outbreak on supply chains and disruptions in manufacturing operations around the world are making headlines on a daily basis. Haren and Simchi-Levi (2020) predict that the peak of the impact of Covid-19 on global supply chains will occur in mid-March, forcing thousands of companies to throttle down or temporarily shut assembly and manufacturing plants in the U.S. and Europe. The most vulnerable companies are those which rely heavily or solely on factories in China for parts and materials. The activity of Chinese manufacturing plants has fallen in the past month and is expected to remain depressed for months. For example, Fiat Chrysler Automobiles NV announced on 14 February that “it is temporarily halting production at a car factory in Serbia because it can’t get parts from China.” Similarly, Hyundai said that it “decided to suspend its production lines from operating at its plants in Korea due to disruptions in the supply of parts resulting from the coronavirus outbreak in China.”
- to review risks associated to global supply chain in face of disruptions caused by natural calamities e.g. earthquakes, pandemics;
- to discuss risk-mitigation strategies from the OR literature to manage such global risks; and
- to comment theoretically, how global risks can be managed by incorporating flexibility in system, process and product design.
Haren, P. and Simchi-Levi, D. (2020): How Coronavirus Could Impact the Global Supply Chain by Mid-March. HBS No. 603–068. Harvard Business Review . hbr.org/2020/02/how-coronavirus-could-impact-the-global-supply-chain-by-mid-march , accessed March 2020.
Simchi-Levi, D. (2010): Operations rules: delivering customer value through flexible operations., MIT Press , Cambridge, MA.
Topic B07: Service Network Design of Delivery Services using Location-Routing Models
Providers who deliver their products at the customer door-step have to incorporate several fundamental decisions related to network design to satisfy overall customer demand w.r.t. different objectives like maximizing market share or profit. Key decisions include where to locate the facilities, how to allocate customers to facilities, and how to route vehicles to serve customers. These facilities could be solid waste collection substations and distribution centers providing collection and/ or distribution functions in which demand is served by multiple drop off and/ or pickup routes. Such problems are studied under the literature stream of location-routing models.
- to review various variants of location-routing models in models,
- to tabulate important references in literature w.r.t. fundamental decisions (listed above) and applications therein, and
- to comment theoretically on using location-routing models for network design of delivery services e.g. Amazon, Lieferando.
Laporte, G. (1988): Location-routing problems. In: Golden, B.L., Assad, A.A. (Eds.), Vehicle Routing: Methods and Studies, North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp.163–198.
Current, J., Daskin, M., & Schilling, D. (2002): Discrete network location models. Facility location: Applications and theory , 1, pp.81–118.
Topic B08: Modeling Dynamics of Contagious Disease Spread Using Simulation
Since the beginning of 2020, Covid-19 is emerging as an epidemic disrupting global supply chains; and thus, hurting the economies worldwide. The 2002–2003 SARS epidemic and MERS-CoV are other examples of contagious disease spread globally. Using analytical modeling approaches like simulation, models mimicking the spread of such diseases can be developed and many important model outcomes like disease spread rate can be predicted. Such measures can be further translated in preparing the healthcare infrastructure in terms of number of care givers, preventive healthcare clinics network design and enhancing the quality of care.
- to review literature streams consisting of simulation-based models for contagious disease spread;
- to present a review of the existing models with the focus on objectives, model outcomes and methodologies; and
- to comment theoretically on how knowledge from the simulation models in the literature can be used for dealing with Covid-19.
Perez, L., & Dragicevic, S. (2009): An agent-based approach for modeling dynamics of contagious disease spread. International journal of health geographics , 8(1), 50.
Topic B09: Integrating Workforce Cross-training in Stochastic Location Models with Congestion
Network design and facility location are of great importance for a wide range of public and private firms e.g., in the health care industry. In location problems with congestion, customers generate streams of stochastic demand, and service times are uncertain. This combination may lead to congestion. Therefore, each facility in these models can be modeled as a queuing system. This bachelor thesis only focuses on immobile servers, i.e., the servers are fixed and customers have to visit the facility to use the services offered by the server. Retail stores (e.g. supermarkets, IKEA etc.), ATM machines, government offices and hospitals are examples of facilities with immobile servers. The main decisions involved in designing such a network is where to locate these facilities and what should be the capacities of the servers at these selected facility locations. Most of the literature assumes dedicated capacities at the services facilities. An important policy for decreasing operational cost of these networks is to consider a workforce mix of flexible and dedicated servers.
- to review literature streams which capture workforce cross-training at service facilities;
- to present a review of the existing models with the focus on objective function, queuing model, and decisions involved;
- to provide academic examples from the service industry where cross training is used; and
- to comment theoretically on benefits of cross-training in facility design.
Ahmadi-Javid, A., & Ramshe, N. (2020): A stochastic location model for designing primary healthcare networks integrated with workforce cross-training. Operations Research for Health Care, 24, 100226.
Topic B10: Customer Utility Functions in Airtravel
The choice between different transport modes for a trip can be characterized as a discrete choice situation, as the best travel option is selected by customers. These decisions can be modelled with discrete choice models; their most prominent functional specification is the multinomial choice model (MNL). An underlying assumption of the models is the possible decomposition of the product or service in attributes with different levels, where each attribute level is connected to a particular partial utility. As example, Coldren et al. (2003) identified itinerary service characteristics for flights connecting east & west coast of the United States as attributes and estimate the part worth utilities of the respective attribute levels. The emergence of online booking engines and data availability create a new possibility to analyze real-life data for parameter-estimation.
- to introduce and compare the MNL and similar discrete choice models;
- to provide an overview of empirical studies measuring the utility choice behavior of air travel and competing transport modes including attributes, their levels, and chosen segments;
- to identify and discuss the state-of-the-art approach in choice model estimation for air travel; and
- to provide open research gaps and future trends.
Adler, T., Falzarano, C. S., & Spitz, G. (2005): Modeling service trade-offs in air itinerary choices. Transportation Research Record , 1915(1), 20–26.
Coldren, G. M., Koppelman, F. S., Kasturirangan, K., & Mukherjee, A. (2003): Modeling aggregate air-travel itinerary shares: logit model development at a major US airline. Journal of Air Transport Management, 9(6), 361–369.
Train, K., & Ebrary, Inc. (2009): Discrete choice methods with simulation (Second ed.). Cambridge New York Melbourne Madrid Cape Town Singapore São Paulo Delhi Mexico City
Topic B11: Three Process Models of Alertness in the Airline Industry
Sleep is a complex phenomenon of human nature and hard to quantify and model. Nevertheless, a few facts about sleep are well known: Once per day, there is a sleeping period of multiple hours to recover. Also, the level of sleepiness feeling varies within a day. These findings have been included in the Three Process Models (TPM) of sleep; they provide a measure for the current sleepiness of a person, its “inner time zone”, and the expected time of falling asleep and waking up. These models can also be used in crew scheduling of airlines as Yildiz, Gzara and Elhedhli (2017) suggest.
- to introduce and compare the specifications of TPM,
- to present different model specifications available the literature,
- to discuss the applicability of TPM in crew scheduling, and
Ingre, M., Van Leeuwen, W., Klemets, T., Ullvetter, C., Hough, S., Kecklund, G., Karlsson, D. & Åkerstedt, T. (2014): Validating and extending the Three Process Model of alertness in airline operations. PloS one , 9 (10).
McCauley, P. J. (2009): Fatigue risk management: modeling the sleep/ wake-based dynamics of performance. Dissertation. The University of Montana
Yildiz, B. C., Gzara, F., & Elhedhli, S. (2017): Airline crew pairing with fatigue: Modeling and analysis. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies , 74 , 99–112.
Topic B12: Airline Schedule Design Models with Customer Choice Behavior
The task of the schedule design (SD) is to assign frequencies and departure times for specific routes by choosing from a set of proposed flights while aiming for the highest possible profit. Schön (2008) states that the schedule in combination with the fare conditions mainly determine passenger choice behavior; similarly, Barnhart and Cohn (2004) call it the “single most important product of an airline”. These arguments underline the large impact of the schedule on profitability and therefore suggest to include customer behavior in the modelling approach to account for the market side. All these influences make the subproblem so complex that Airlines are still challenged by using models for their schedule design and rely on a manual approach as Barnhart, Belobaba and Odoni (2016) suggest.
- to introduce choice-based SD models as well as other solution approaches and the underlying problem,
- to develop a classification for SD models regarding their characteristics,
- to explain one SD model in detail, and
Barnhart, C., & Cohn, A. (2004): Airline schedule planning: Accomplishments and opportunities. Manufacturing & service operations management , 6, 3–22.
Barnhart, C., & Vikrant, V. (2016): Airline Schedule Optimization, in: Belobaba, P., Odoni, A., & Barnhart, C. (Eds.). The global airline industry . John Wiley & Sons.
Schön, C. (2008): Integrated airline schedule design, fleet assignment and pricing. DSOR-Beiträge zur Wirtschaftsinformatik , 5, 73–88.
Wei, K., Vaze, V., & Jacquillat, A. (2019): Airline Timetable Development and Fleet Assignment Incorporating Passenger Choice. Transportation Science .
Topic B13: Scheduling in Sports Leagues
Schedules of professional sport leagues are a huge challenge due to many requirements, multiple parallel competitions (such as cup rounds, national team games, and sharing of infrastructure with other teams), and a huge public interest. Also, a fair assignment needs to be considered while fulfilling the sometimes-conflicting objectives from different stake holders such as players, clubs, fans, sponsors and the media. This problem may be tackled with Integer Programming techniques as Kendall et al. (2010) show.
- to introduce the scheduling problem for sports leagues including requirements and objectives from different stake holders,
- to provide an overview of recent models in the literature and explain one model in detail,
- to create an academical example (optional), and
Bartsch, T., Drexl, A., & Kröger, S. (2006): Scheduling the professional soccer leagues of Austria and Germany. Computers & Operations Research , 33 (7), 1907-1937.
Durán, G., Guajardo, M., & Sauré, D. (2017): Scheduling the South American Qualifiers to the 2018 FIFA World Cup by integer programming. European Journal of Operational Research , 262 (3), 1109-1115.
Kendall, G., Knust, S., Ribeiro, C. C., & Urrutia, S. (2010): Scheduling in sports: An annotated bibliography. Computers & Operations Research , 37 (1), 1–19.
Krumer, A. (2019): Testing the effect of kick-off time in the UEFA Europa League. European Sport Management Quarterly , 1–14.
Topic B14: Optimizing Market Entry Time for New Services – a Customers’ Perspective
Developing new products or services is a very intense project for any company in terms of both time and money. A major challenge in this context is to find the optimal point in time to launch a product, start a service or release an app. From a company’s perspective improved cashflows and early customer feedback motivate an early launch or go-live. From a customer’s perspective the decision for an early or late product launch is diverse: In case of an early launch the customer can benefit from the product or service earlier, but must expect minor quality, more errors or other problems. In case of a later launch, a customer needs to wait longer for the product’s benefits, but receives a well-engineered product with for example higher usability and less defects. A prominent example is software development especially in gaming, which encountered a shift in recent years. More and more companies sell products on a beta test level and thus prepone the software launch and simultaneously the time they receive first cash inflows.
- to provide an overview of empirical studies on finding the optimal market entry time – first with a broad perspective across products and services; second, with a special focus on digital products or services;
- to present articles that try to optimize (at least certain aspects of) the market entry decision; and
- to develop an overview, which aspects such an optimization model should have – focus explicitly on the trade-offs that a customer is facing in this context.
August, T., and Niculescu, M. F. (2013) . The influence of software process maturity and customer error reporting on software release and pricing. Management Science , 59(12), 2702-2726.
Kalish, S., and Lilien, G. L. (1986). A market entry timing model for new technologies. Management Science , 32(2), 194–205.
Zachary, M. A., Gianiodis, P. T., Payne, G. T., and Markman, G. D. (2015). Entry timing: Enduring lessons and future directions. Journal of Management 41(5), 1388-1415.
Topic B15: An Overview of the Research Landscape in Service Process Mapping
In contrast to products services are intangible both for customers and the company offering the services. Nevertheless, a clear understanding of its own services is highly important for any company in order to offer high service quality and to continuously improve its services. Process mapping can help companies to achieve such an understanding of its own processes. Today, there is a variety of interesting tools like service blueprinting, process chain network analysis or customer journey mapping. Although most of these tools are very established and used for several years or even decades, research on these tools is still conducted leading to more insights and further improvements.
- to provide an overview of tools for service process mapping including (but not restricted to) the tools mentioned above,
- to identify the three most interesting tools from your perspective and analyze the research that has been done on these tools during the last ten years (2010–2019), and
- to cluster the research articles to derive a high-level overview of the research landscape on service process mapping in the last decade.
Kazemzadeh, Yahya; Milton, Simon K. and Johnson, Lester W. (2015) . An explication of three service business process modelling approaches. Australian Journal of Business and Economic Studies 1 (2), 40–53.
Sampson, Scott E. (2012). Visualizing Service Operations. Journal of Service Research 15 (2), 182–198.
Topic B16: Optimizing the Sequence of Events in Service Companies
Following the attribute-based utility theory, the overall utility of a product or service can be calculated by adding up the part-worth utilities for every attribute and attribute level of the product or service. As an alternative approach in recent years, research in the field of incident-based utility measurement has strongly increased. This new perspective is focused on services and interprets them as a series of events. Research in this context provides insights on how to order the events to maximize the customers utility or more precisely the customers’ retrospective global evaluation of a service experience. This so called remembered utility can be calculated in two different ways: First, calculated directly using psychological constructs like memory decay and acclimation and second, estimated using sequence effects like peak-effect or end-effect. While research publications in this field increased during the last decade, companies rarely use the insights derived in research.
- to introduce sequence effects and psychological constructs,
- to present an overview of managerial implications derived in research papers on these constructs, and
- to provide own ideas on where and how to use the optimization of the sequence of events in service companies.
Das Gupta, A., Karmarkar, U. S., and Roels, G. (2015) : The design of experiential services with acclimation and memory decay: Optimal sequence and duration. Management Science 62(5), 1278-1296.
Dixon, M. J., and Victorino, L. (2019) : The Sequence of Service: An Affect Perspective to Service Scheduling. In Handbook of Service Science, Volume II, p. 49–76.
Topics in FSS20 for students “B.Sc. Wirtschaftspädagogik”
Thema B01: Einführung eines Customer Journey Mappings in einem digitalen Dienstleistungsunternehmen
Englischer Titel: Introducing Customer Journey Mapping in a Digital Service Company
Im Gegensatz zu physischen Produkten sind Dienstleistungen sowohl für den Kunden als auch für das Unternehmen selbst nicht direkt greifbar. Gerade unternehmensseitig ist ein klares Verständnis der eigenen Dienstleistungen aber elementar wichtig, um eine konsistente Qualität der Dienstleistung bieten und darüber hinaus Verbesserungen vornehmen zu können. Die Möglichkeiten der Darstellung des Dienstleistungsprozesses sind mittlerweile vielfältig und reichen vom Service Blueprinting, über das klassische Customer Journey Mapping bis hin zur PCN-Analyse. Unternehmen stehen entsprechend vor der Aufgabe, ein für ihre Bedürfnisse und Anforderungen adäquates Tool zu wählen und dieses im zweiten Schritt einheitlich über das gesamte Unternehmen an den relevanten Stellen auszurollen.
- aufzuzeigen, welche Möglichkeiten des Customer Journey Mappings es gibt und was ggf. sinnvolle Alternativen sind,
- darzustellen, an welchen Stellen im Unternehmen man Customer Journey Maps sinnvoll einsetzen kann,
- zu analysieren, welche Vor- und Nachteile die einzelnen Alternativen im Kontext der verschiedenen Anwendungsgebiete haben,
- und abschließend zu erläutern, was bei der Einführung eines Customer Journey Mappings in einem digitalen Dienstleistungsunternehmen zu beachten ist.
Thema B02: Measurement of Process Capabilities
The literature agrees on the importance of capabilities possessed by a firm, e.g. for achieving a competitive advantage. Yet, there is some dissent on the best measurement approach, as capabilities are intangible and tacit in nature. In the field of business process management, process capabilities are needed for effective operations. They are thus closely linked to the strategic alignment of operations and value proposition. To assess this strategic fit, process capabilities ought to be measured, which can often only be done indirectly. How can capabilities in general and process capability specifically be measured?
The aim of this bachelor thesis should be:
- to identify approaches given by the existing literature for the measurement of process capabilities and capabilities in general
- to discuss and compare the most relevant approaches
Peng, David Xiaosong; Schroeder, Roger G.; Shah, Rachna (2008): Linking routines to operations capabilities: A new perspective. In Journal of Operations Management 26 (6), pp. 730–748. DOI: 10.1016/j.jom.2007.11.001.
Houy, Constantin; Reiter, Markus; Fettke, Peter; Loos, Peter; Hoesch-Klohe, Konstantin; Ghose, Aditya (2012): Advancing Business Process Technology for Humanity: Opportunities and Challenges of Green BPM for Sustainable Business Activities. In Jan Vom Brocke, Stefan Seidel, Jan Recker (Eds.): Green business process management. Towards the sustainable enterprise, vol. 25. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg (Progress in IS), pp. 75–92.
Wu, Sarah Jinhui; Melnyk, Steven A.; Flynn, Barbara B. (2010): Operational Capabilities: The Secret Ingredient. In Decision Sciences 41 (4), pp. 721–754. DOI: 10.1111/j.1540-5915.2010.00294.x.
Thema B03: Product durability – Expert interviews and online evaluations
A product’s durability is a central decision component in product development stage. While decades ago long durability was a key determinant of quality and thus an essential part of product attractiveness, the strategy of planned obsolescence has become very popular in recent years (Guiltinan 2009, Slade 2009).
The objective of the thesis is to conduct expert interviews (e.g., with personnel in electronic markets, fashion markets, etc.) and to statistically evaluate online evaluations (e.g., on Amazon website) of different products with regard to their durability decades ago and nowadays.
The objectives of this thesis are to:
- Conduct expert interviews and statistically evaluate online evaluations of different products
- Derive products (or product categories) that are most affected vs. those that are least affected by planned obsolescence
- If applicable: Derive different business strategies of different companies for the same product (or product category)
- Discuss whether the adopted strategies of planned obsolescence are beneficial based on triple bottom line analysis (see, for example, Elkington 2013)
Elkington, J. (2013). Enter the triple bottom line. In The triple bottom line (pp. 23–38). Routledge.
Slade, G. (2009): Made to break: Technology and obsolescence in America. Harvard University Press.
Thema B04: Kompetenzorientiertes Training für Piloten
Obwohl in der Luftfahrtindustrie ein starker Kostendruck herrscht, legt sie einen sehr starken Fokus auf den Aspekt Sicherheit. Ein Unfall kann nicht nur eine dreistellige Anzahl an Opfern fordern, sondern auch das Vertrauen in einzelne Airlines oder das Fliegen an sich zerstören. Daher werden zahlreiche Systeme mit dem Ziel höchstmöglich Sicherheit geschaffen, sei es in der reinen Luftfahrzeugtechnik, in der Wartung oder auch in der täglichen „Operations“. Auch die Aus- und Weiterbildung von Piloten und anderem Personal ist mit dem Fokus auf größtmögliche Sicherheit gestaltet. Ein wichtiger Bestandteil ist unter anderem das Simulator Training, in dem die richtige Reaktion und Abarbeitung von herausfordernden Zwischenfällen in einer Realitätsnahen Umgebung getestet wird.
Die Form des Trainings hatte sich seit den 1960er Jahren nicht weiterentwickelt, bis sich ICAO, die IATA im Namen der Luftfahrtindustrie und die Pilotenverbände sich zusammengetan haben, um das Konzept des „Evidence-Based Trainings“ für die Industrie zu definieren und Regularien zu erarbeiten. Der Hauptunterschied ist der Wechsel von einem Methodenfokus zu einem Kompetenzfokus, bspw. würden beim Üben von Landungen mit unerwarteten Turbulenzen kurz vor der Landung weniger die isolierte Fähigkeit „Durchstarten bei gefährlichen Landungen“ anstatt den Kompetenzen „Problemlösung und Entscheidungsfindung“ oder „manuelles Verfolgen eines Flugpfades“ geübt werden. Diese Kompetenzen sind dann auch auf andere Herausforderungen, die geringe Gemeinsamkeiten mit den geübten Fähigkeiten haben (hier z.B. eine unverzügliche Landung wegen eines medizinischen Notfalls), übertragbar. Außerdem wird nun auf die individuelle Leistung, Stärken und Schwächen von Piloten eingegangen.
- das Konzept des Kompetenzorientierten Lernens vorzustellen und die Entwicklung von einem Methodenorientierten Ansatz auf einen Kompetenzorientierten Ansatz im beruflichen Lernumfeld sowie dessen Vor- und Nachteile zu erläutern,
- Evidence-based Training inklusive der Kernkompetenzen und benötigten Prozesse für die Umsetzung vorzustellen,
- einen Überblick über Möglichkeiten zur Erfolgsmessung von verschiedenen Trainingskonzepten zu geben und Industriespezifische Vor- und Nachteile zur erarbeiten,
- ein Pilot oder ein Mitglied aus dem Sicherheitsteam einer Fluggesellschaft zu den eigenen Erfahrungen zu interviewen (optional),
Klotz, V. K. (2015): Diagnostik beruflicher Kompetenzentwicklung: Eine wirtschaftsdidaktische Modellierung für die kaufmännische Domäne . Springer-Verlag .
Topics in FSS19 for students “B.Sc. Betreibswirtschaftslehre”
Flight Schedule Design under customer choice
The task of the schedule design (SD) is to assign frequencies and departure times for specific routes by choosing from a set of proposed flights while aiming for the highest possible profit. Schön (2008) states that the schedule in combination with the fare conditions is the main criterion for passengers to choose an airline; similarly, Barnhart and Cohn (2004) call it the “single most important product of an airline”. These arguments underline on one hand the large impact of the schedule on profitability but on the other hand, suggest to include customer behavior in the modelling approach to account for the market side. All these influences make the subproblem so complex that Airlines are still challenged by using models for their schedule design and rely on a manual approach as Barnhart, Belobaba and Odoni (2016) suggest.
Aim of the bachelor thesis should be to,
- introduce schedule design models and compare the most important models,
- to discuss a specific model in detail,
- to create an academical example in Excel (optional),
- to provide open research gaps and future trends.
Fleet Assignment in the Airline Scheduling Process
For the fleet assignment (FA) the chosen flight legs from schedule design are assigned to a particular fleet of an airline in order to manage the tradeoff between lost revenue from spill of customers and higher operational costs for larger aircraft. The decisions are not taken in isolation for each leg and route, rather, the fixed fleet mix requires an efficient allocation of resources over the whole flight network as Barnhart and Cohn (2004) point out. Usually, the problem is modelled as a multicommodity network flow problem with side constraints and an underlying time-line network. Barnhart, Belobaba and Odoni (2016) suggest that the problem size under this setting is much smaller and it can be solved faster in comparison with other alternative settings.
- introduce fleet assignment models and compare the most important models,
- to create an academical example (optional),
Maintenance Routing
In Maintenance Routing (MR) all assigned flight legs of a particular fleet have to be assigned to specific aircrafts on each day. As the aircraft type is fixed, MR is done for each fleet individually. Following Barnhart and Cohn (2004) as well as Gopalan and Talluri (1998), MR is modelled as a network circulation problem with side constraints and it is only solved for feasibility as different routings do not result in different costs. Others, e.g. Gabteni and Grönkvist (2009), model it as extended Set Partitioning problem. While the assignment of flight legs to aircraft should be feasible due to the fleet assignment, the challenge is to include all required maintenance events for each individual aircraft. These maintenance events can only be undertaken at specific airports; furthermore, it is beneficial to let aircrafts fly to maintenance airports regularly because when a non-critical component breaks it can be fixed quickly.
- introduce MR models and compare the most important models,
Crew Scheduling for Railways
In all transportation industries several scheduling steps are required to assign available resources to the given demand as the Railway Planning Process by Lusby et al. (2011) shows; somewhat similar steps can be found in the airline industry. The last step is usually crew scheduling which assigns to each trip or flight a human resource (train conductor or pilot, respectively) to operate it. Research has so far focused on the airline industry because airline crews represent one of the biggest cost factors in their business model; for railways there have been fewer models and approaches. While the underlying assumptions and constraints may be different, both model types share the same objective of cost minimization.
- introduce and compare crew scheduling models from railways and airlines,
- to discuss a specific railway crew scheduling model in detail,
Allocation of Customer demand to Service Facilities in Inventory Location Models
In inventory location models, the service providers decide on locations of facilities subject to stochastic demand and the amount of inventory to be held at each facility. Another essential aspect of the location models is the mechanism by which customer demand is allocated to facilities. Directed Assignment (DA) and Customer Choice (CC) are the two mechanisms used widely in location literature. In DA, the customers are assigned to facilities by a central decision maker such that overall system performance is optimized. On the contrary in CC, customers self-select facilities maximizing their own utilities based on their choice preferences associated to service offerings at the facility.
The objectives of this thesis are to
- review closely the objectives and decisions in Inventory-location models
- compare DA and CC
- comment theoretically, on the relevance of each DA (or CC) to various service facility settings.
- Provide academic examples from the service industry to support the findings of the thesis.
Integration of Customer Behavioral Models in Operations Research
The vast majority of OR models in the literature are inclined towards the “supply” side of the problem. The “demand” side is often neglected, assumed as a known parameter and modeled using simplifying assumptions. These assumptions are often not justified for real-world applications. Therefore, policy makers encounter huge uncertainties associated to customer demand while planning for their systems. To bridge the demand and supply gap, it is crucial to understand customer patronization behavior and preferences associated to service offerings. These preferences are formalized with discrete choice models. The mathematical models associated to planning problems (e.g. design and system configurations) are often Mixed-Integer Linear Programming (MILP) models.
- review OR models, in which demand and supply interact closely and where integration of customer behavioral models might result in better decisions from policy maker’s perspective
- discuss methods, to integrate discrete choice models in MILP and resulting complexity of the mathematical models.
Choice-based Revenue Management: Theory and methods
Revenue Management (RM) as a discipline has its roots soaked in the Airline Industry. At present RM is used widely across many industries, ranging from transportation to broadcasting and advertising. In previous literature, demand is often assumed to be independent. In other words, it was assumed that customers would never substitute one product for another, but instead would consider the purchase of a specific product only and, if this was not available, not to purchase at all. However, in case of airlines, by the early 21st century, the independent demand assumption turned out to be problematic due to the increased competition and visibility of different fares.
- review the design and estimation of discrete choice models for RM
- comment theoretically on, how to control demand via product availability over a finite period of time while accounting for customer’s choice behavior
Service Network Design in Face of Stochastic demand and Congestion
Network design and facility location are of great importance for a wide range of public and private firms (eg, in the health care industry). In location problems with congestion, customers generate streams of stochastic demand, and service times are uncertain. This combination leads to congestion. Therefore, each facility in these models can be modeled as a queuing system. This bachelor thesis only focuses on immobile servers i.e. server is fixed and customers has to visit the facility to use the services offered by the server. Retail stores (e.g. supermarkets, IKEA etc.), ATM machines, government offices and hospitals are examples of immobile servers. The main decisions involved in designing such a network is where to locate these facilities and what should be the capacities of the servers at these selected facility locations. Most of the literature assumes that the waiting rooms at the services facilities are infinite. Also, the existing location models with congested immobile facilities focus on the expected waiting time and pays less attention towards other performance measures percentage of blocked or delayed customers.
- review literature streams which capture finiteness of the waiting rooms at service facilities
- present a review of the existing models with the focus on objective function, queuing model and decisions involved
- comment theoretically, on how service performance measures other than expected waiting time can be integrated into location models subject to congestion
Public Sector Facility Location Planning
Facility location planning in the public sector is different from private sector in terms of the objective functions considered by the planners. The objective functions considered in public sectors are often social cost minimization, access, efficiency, and equity. Facility location planning in the public sector has a wide range of applications: Bike sharing systems, simultaneous bus scheduling and depot location planning, electric vehicle charging station planning, healthcare facility location planning, and school location planning.
- review the academic literature on the public sector facility location planning with focus on objective functions considered, approaches to include more and more relevant planning decision factors
- suggest directions for future research
- Provide academic examples from the public sector applications to support the findings of the thesis
Revenue Management in Railway Companies
Revenue Management (RM) for Railway Companies is a small but active research field. Railway business can be divided in passenger and cargo traffic, i.e. transporting people in regional or long-distance trains and transporting freight in cargo trains. Although both branches are dealing with railway traffic, they have significant differences in their business model and revenue management models have to be adapted on these special properties.
Since a working paper of Armstrong, Meissner (2010) is currently the only paper that gives an overview of RM in the rail industry, the objective is to do a literature review for railway RM with a focus on recent contributions in renowned journals. The literature review should include explanations of the different approaches in research and compare/ distinguish them among each other.
The relationship between income and happiness
Sustainability in general terms is about maximizing social well-being in the world, from today to infinite future. Well-being can be well characterized by happiness of people. While for long income was assumed to improve happiness, doubts have risen in (recent) past. The research on happiness topics thus experienced a major attention. For example, the aspiration-based theory was developed, claiming that income only leads to short-term but not to long-term happiness. The goal of this thesis is thus to examine the “income-happiness” relationship from different perspectives.
Aim of the bachelor thesis should be to
- Present a brief historical development of the “income-happiness” beliefs in scientific world
- Differentiate between qualitative and quantitative literature and classify quantitative literature according to Bertrand and Fransoo (2002)
- Identify the latest status of scientific view on the “income-happiness” relation
- Conclude with ideas for future research in this field
- Discuss, how a good prescriptive model for the relationship between income and happiness could look like
- Highlight the 5 most relevant contributions to this field of research from your personal perspective. Point out the facts that lead you to the selection of these contributionsto discuss a specific model in detail,
Does human dynamism and thrust for new truly drive growth?
Sustainability in general terms is about maximizing social well-being in the world, from today to infinite future. Economic growth was for long believed to be the main (and sometimes the only) driver of well-being increase. Economic growth of course directly translates to growth of the corporate sector in the industrialized world. One of the main claims is as follows: “Growth and profitability on corporate level are driven by two factors: 1) The human self-interest and dynamism in terms of innovativeness and thrust for the new; 2) The human desire of increasing power compared to their peers”
The goal of this thesis is to examine the above-mentioned claims and develop an own qualitative model of growth drivers.
- Review the literature for drivers of growth and profitability on corporate level
- Identify potential corporate concepts and approaches in pursuit for growth
- If applicable: Has the perspective or the focus changed over time?
- Identify the latest status of scientific view on the growth drivers
- Develop an own qualitative model on the interplay between human dynamism, human desires, growth and other factors
- Highlight the 5 most relevant contributions to this field of research from your personal perspective. Point out the facts that lead you to the selection of these contributions
The throwaway mentality in the developed world and the influence of planned obsolescence
Slade (2009) described that in North America over 100 million cell phones and 300 million personal computers were discarded each year in the beginning of the 20 th century. Certainly, North America is not alone with such a development. The throwaway mentality is already in place in Europe and other regions. Planned obsolescence is a policy of designing a product with an artificially limited useful life, so it will become obsolete, i.e. no longer functional after a certain period of time. The rationale behind the strategy is to generate long-term sales volume by reducing the time between repeat purchases.
The objective of the thesis is to provide a review on the topic of throwaway mentality, its drivers, development over time and impact on environment and humans. A guiding question is to identify the main products and industries, this phenomenon occurs most in and the reasons for this observation.
- Review the development of throwaway mentality in the world
- Identify main products and industries, this phenomenon occurs most in
- Highlight statistical development of throwaway mentality in different regions of the world and identify the regions where this mentality is most advanced
- Identify empirical evidence regarding consumer attitudes driving this phenomenon
- Implications of this phenomenon on environment and humans
- Potential strategies that can help to mitigate this phenomenon and its harmful effects
- What future research in this field should focus on
- Optional: Highlight the 5 most relevant contributions to this field of research from your personal perspective. Point out the facts that lead you to the selection of these contributionsto provide open research gaps and future trends.
Literature review on transportation planning process aiming for environmental impact reduction
The transportation industry plays an important role in today’s world. Not only does it transport products and goods, it also connects people and nations. A downside of the growing transportation practice is the impact on environment, in terms of emissions. Belobaba, Odoni and Barnhart (2016) describe the Airline planning process (Chapter 7), which can be generalized to the transportation industry. It aims at planning all relevant processes. Operations research typically focuses on the four-step Scheduling Process (Chapter 8) and Barnhart and Cohn (2004) argue that the schedule is the main product.
The objective of the thesis is to critically review and classify the literature regarding the route planning and schedule design and approaches to manage emissions, present the state-of-the-art, and assess the potential to achieve environmental improvements. Focus should be placed on quantitative Operations Management or Operations Research models.
- Review the importance of transportation industry (focus on aviation) for GHG emissions
- Describe the Planning Process and point out the importance of Route planning and Schedule Design with respect to the environmental impact
- Review the different approaches of incorporating two objectives (economic and environmental) into the same model
- Optional: Highlight the 5 most relevant contributions to this field of research from your personal perspective. Point out the facts that lead you to the selection of these
The Potential of leasing/ servicizing as a sustainable business model
Sustainability in general terms is about maximizing social well-being in the world, from today to infinite future. Economic growth was for long believed to be the main (and sometimes the only) driver of well-being increase. However, the increasing number of products manufactured and sold increases the impact of the economy on the environment. Leasing or servicization is a business strategy to sell the functionality of a product rather than the product it-self. It has been argued that leasing/ servicizing business models are environmentally friendly as they encourage manufacturers to take more responsibility for their products and to offer products with higher efficiency. Motivated by these arguments, an increasing number of papers investigate the economic and environmental potential of leasing/ servicizing business models.
The objective of the Thesis is to critically review and synthesize the scientific literature, assess the potential of leasing/ servicizing as a sustainable business model, and identify open questions as future research opportunities.
- Review and classify the literature for leasing/ servicizing business models and identify key characteristics of these business models
- Highlight the links of such business models to sustainability and assess their potential as sustainable business models
- Develop an own qualitative model on the interplay between business model, economic success and environmental impact
- Identify open questions as future research opportunities
- Optional: Highlight the 5 most relevant contributions to this field of research from your personal perspective. Point out the facts that lead you to the selection of these contributions
Finding the best sequence of events – theory and applications
The sequence of events plays a crucial role for the customers’ evaluation of a service experience. With the optimal sequence, both repurchase and positive word-of-mouth can be maximized. Companies can alter the sequence of their service events in order to influence the retrospective global evaluation of their service experience. This remembered utility is either directly calculated using psychological constructs like memory decay and acclimation or estimated using sequence effects like peak-effect or end-effect.
This bachelor thesis should review both of these approaches and explain the diverse ways of calculating remembered utility. A simple application example might illustrate the differences of the approaches and make them more transparent. In a last step, the thesis should derive guidelines on how companies should schedule their service events.
A methodological overview on measuring schedule preferences
To further improve customers’ likelihood to (re)purchase, a company can focus on the utility of its products or services. For products, utility is usually measured through conjoint analysis, a popular technique in the field of multi-attribute utility theory. According to this theory, every product can be described through different attributes and the respective attribute levels. The same logic can also be applied to services with some limitations. Alternatively, there is also an incident-based approach that is especially designed for services. Every service is here interpreted as a series of events and the goal is to find the right order and time of events to maximize the utility of the schedule.
The objective of this thesis is to provide a review on both fundamental and most recent literature on attribute-based and incident-based utility measurement. The focus should be on finding, explaining and evaluating empirical studies that try to measure customers’ utility for a schedule or series of events. A broad focus should be set without restrictions to service design or scheduling.
Service design as an interdisciplinary research discipline
Services play a significant role in our economy in terms of number of employees, sales volumes and market size. Any company competing for these goals should set high priorities on designing and optimizing its services. Traditional methods of product design can only be adapted to some extent – leading to the establishment of service design as a research field. Researchers working in this field usually just focus and problems and research questions within their respective research discipline. Nevertheless, only by analyzing service design decisions integratively new holistic approaches can be derived.
This bachelor thesis should first provide an overview of the research disciplines working on questions of service design and present their key interest in that topic. Based on that the focus should be set on the interface of marketing and operations research by presenting current research papers linking tools and techniques from both areas. In a final step, the importance and strength of such an integrated perspective should be discussed and future research opportunities should be presented.
Topics in FSS19 for students “B.Sc. Wirtschaftspädagogik”
Industry 4.0 and the Circular Economy for Sustainable Operations
What is the circular economy (CE) and how can Industry 4.0 and Digitization help to manage in line with CE principles and make operations more sustainable? The objective of the thesis is to critically review and classify the empirical and normative literature, present the state-of-the-art, and assess the potential of Industry 4.0 to achieve sustainable operations.
Planned Obsolescence in Product Design – Critical Review and Servicizing Opportunities
Planned obsolescence is a policy of designing a product with an artificially limited useful life, so it will become obsolete, i.e. no longer functional after a certain period of time. The rationale behind the strategy is to generate long-term sales volume by reducing the time between repeat purchases. The objective of the thesis is to provide a literature review on the topic and thereby, answer the following question: which products/ industries typically apply the policy of planned obsolescence? What is the economic rationale for planned obsolescence? What are the pitfalls and critical assumptions underlying the planned obsolescence rationale? What empirical evidence of consumer attitudes to product obsolescence do we have? What other strategies such as service differentiation could help to mitigate product obsolescence?
Methoden zur Präferenzmessung von Zeitplänen
Der Nutzen eines Produktes oder einer Dienstleistung stellt ein wichtiges Konstrukt für jedes Unternehmen dar und hat direkte Auswirkungen auf die (Wieder-) Kaufwahrscheinlichkeit der Kunden und somit auch auf Absatz und Gewinn des Unternehmens. Bei Produkten wird dieser Nutzen mit Hilfe der Conjoint-Analyse gemessen, die einen weitverbreiteten Ansatz im Bereich der multiattributiven Nutzentheorie darstellt. Demnach lässt sich jedes Produkt durch verschiedene Attribute beschreiben, die jeweils wiederum unterschiedliche Ausprägungen annehmen können. Auch wenn sich die Methodik mit einigen Einschränkungen auch auf Dienstleistungen anwenden lässt, gibt es mit der ereignisbasierten Nutzenmodellierung einen speziell für Dienstleistungen entwickelten Ansatz. Demnach wird jede Dienstleistung im Sinne eines Zeitplans als Serie von einzelnen Ereignissen interpretiert, die dann zur Maximierung des Nutzens in die richtige Reihenfolge gebracht und zum richtigen Zeitpunkt terminiert werden. Trotz der Vorteile dieses neuen Ansatzes stellt gerade die immense Anzahl an alternativen Zeitplänen / Dienstleistungskonfigurationen eine große Schwierigkeit dar.
Im Rahmen der Bachelorarbeit sollte zunächst die grundlegende und aktuellste Literatur zur ereignisbasierten Nutzenmodellierung zusammengetragen werden. Darauf aufbauend gilt es, empirische Studien vorzustellen, die den Kundennutzen von Zeitplänen versuchen zu messen. Inhaltlich sollte die Suche einen breiten Fokus haben und nicht zwingend auf das Gebiet der Dienstleistungsgestaltung begrenzt sein. Abschließend sollte die Eignung der verschiedenen Lösungsansätze zur Reduzierung der oben dargestellten Komplexität diskutiert und nach Möglichkeit verglichen werden.
Dienstleistungsgestaltung an der Schnittstelle zwischen Marketing und Operations
In unserer Wirtschaft, in der der tertiäre Sektor eine maßgebliche Rolle in Bezug auf Mitarbeiterzahlen, Absatzvolumen und Marktausdehnung einnimmt, ist die Gestaltung und Optimierung von Dienstleistungen von großer Bedeutung. Klassische Methoden der Produktgestaltung lassen sich nicht oder nur eingeschränkt übertragen, so dass sich ein eigenes Forschungsfeld – das Service Design – entwickelt hat. Wissenschaftler verschiedener Disziplinen haben sich dem Thema angenommen und beantworten Fragestellungen, die sich meist auf ihr jeweiliges Forschungsgebiet fokussieren. Gerade aber durch die Verknüpfung verschiedener Bereich können ganzheitlichere Ansätze entwickelt werden.
Diese Bachelorarbeit sollte zunächst eine grundlegende Einführung in das Service Design geben und die verschiedenen Disziplinen aufzeigen, die sich dem Thema annehmen. Anschließend sollte der Fokus jedoch ausschließlich auf die Schnittstelle zwischen Marketing und Operations Management gelegt werden. Hier gilt es, aktuelle Studien und Forschungsbeiträge zusammenzutragen, die beide Sichtweisen miteinander verknüpfen und so integrierte Lösungsansätze aufzeigen. Abschließend sollten die Bedeutung der ganzheitlichen Betrachtungsweise bewertet und zukünftige Forschungsfelder an der Schnittstelle diskutiert werden.
Modelle im Störungsmanagement von Airlines
In der Airline Industrie gibt es vier Planungsschritte, um den Flugplan, die Routen für einzelne Flotten sowie die Einteilung der einzelnen Flugzeuge und Crewmitglieder festzulegen – alle mit dem Ziel, den Gewinn zu maximieren bzw. die Kosten zu minimieren. Diese Pläne sind optimal für den Fall, dass die Umweltzustände wie erwartet eintreten und keine Störungen durch Wetter, Defekte, Staus oder Streiks auftreten. Wenn Störungen auftreten, ist es wahrscheinlich, dass durch die vielen operativen Regeln der ursprünglich optimale Plan nicht mehr zulässig ist und umgeplant werden muss. Dies betrifft sowohl die Flüge als auch Flugzeuge, Crews und Passagiere. Hierfür wurden schon zahlreiche Optimierungsmodelle aufgestellt, die sich entweder auf einzelne Planungsschritte fokussieren oder mehrere ineinander integrieren. Außerdem liegt der Fokus auf der schnellen Lösung der Probleme, weil sofort eine Entscheidung getroffen werden muss.
Ziel der Bachelorarbeit ist es,
- neue wichtige Quellen nach Clausen et al. (2010) zu finden und aktuelle Trends aufzuzeigen,
- das Modell von Barnhart und Vaze (2016, Seite 274) zu diskutieren,
- ein akademisches Beispiel aufzusetzen (optional),
- offene Forschungsfelder und –lücken darzustellen.
Topics in FSS18 for students “B.Sc. Betriebswirtschaftslehre”
Franchise Distribution Systems: International Service Network Expansion
In the 1950s, the setting stone of modern day business format franchising was laid with the foundation of the two fast-food restaurant franchises, well-known today and growing till date: Burger King and McDonald’s (Rajiv2014 JMC). The profit-driven, Franchise Distribution Systems (FDS), benefit in terms of increasing sales; primarily by adding superior locations to their service network. This is evident from the current expansion trends of the veteran brands (Ikea, Subway, KFC) to the US-based restaurant franchise, Sweetgreen, blowout hair salon franchise Drybar and many more upcoming franchises.
The objectives of this thesis are: a) to review closely the objectives and decision making process of FDS, when expanding internationally and b) comment theoretically, on the importance to strike balance between maximizing system revenue and minimizing the cannibalization of sales of existing outlets, when a firm expands its FDS. Provide academic examples from the franchise industry to support the findings of the thesis.
Convenience in Service Industry
In highly competitive businesses, offering similar services or products, the service provider needs to strengthen its position in the market with respect to its competitors; by offering a unique and convenient service experience. In order to attract a new market segment, or gain a competitive advantage in serving an existing segment, service providers often focus on delivering the ultimate convenient product or service. For example, a pizza delivery service can offer convenience to its customer at different steps of its service process: ordering (phone and online), payment (cash, credit/ debit card, online payment (e.g. paypal)) and delivery (pleasant wait times).
With the increase in number of dual-worker families, the service industry has witnessed a rise in convenience consumption. The desire to save, or at least to manage time better, is an important factor in convenience consumption.
The objectives of this thesis are: a) to review how the definition of convenience has evolved in the convenience literature and b) discuss measures/ methods, adopted by service providers, to offer and improve service convenience. Provide academic examples from the service industry to support the findings of the thesis.
Customer’s Purchasing Behavior, when Wait-times Infer Quality
Customers encounter queues in everyday life, whether queuing up virtually for ordering food online or physically while withdrawing cash at ATM. Due to demand and service time uncertainty at a service station, queues are unavoidable. Therefore, it becomes important for the service provider to understand a customer’s threshold (or satisfaction) in terms of waiting time.
In case of service facilities, e.g. supermarket, wait times at checkout are perceived negatively. Huge volume of OR/ OM literature focuses on strategies and technology used by service providers to minimize wait times. On the other hand, long shipping delays of Apple’s iPad is associated with high demand and superior quality. Also, tourists while selecting a restaurant are more confident about the restaurant in terms of quality, if it has longer wait times.
The objective of the thesis is to review observational learning literature, to derive relations between wait times and customer purchasing behavior, along with academic examples from service industry.
Competitive Stochastic Location Models with Congestion
Stochastic location models are facility location models where consumers generate streams of stochastic demands for service and service times are stochastic. This combination leads to congestion. Therefore, each facility in these models can be modeled as a queuing system. This bachelor thesis only focuses on immobile servers i.e. server is fixed and customers has to visit the facility to use the services offered by the server. Retail stores (e.g. supermarkets, IKEA etc.), ATM machines, government offices and hospitals are examples of immobile servers. The main decisions involved in designing such a network is where to locate these facilities and what should be the capacities of the servers at these selected facility locations. Some of the models in literature do not consider the competition due to the existing facilities in the region of interest.
The aim of thesis is to review literature streams which capture competition due to existing facilities in stochastic location models with congestion. The thesis should present a review of the existing models with the focus on objective function, queuing model and decisions involved.
Assortment Planning in Retail Industry
The physical distribution channel stores in the retail category sell products ranging from specialty retail industry, like electronic goods, automotive, home furnishing, and apparel to products of daily usage at convenience stores.
A retailer’s assortment is the set of products carried in each store at each point in time. The objective of assortment planning is to specify an assortment that maximizes sales or gross margin subject to various constraints, such as a limited budget for purchase of products, limited shelf space for displaying products, and a variety of miscellaneous constraints such as a desire to have at least two vendors for each type of product.
The objective of this thesis is to review the academic literature on assortment planning, to overview the approaches to assortment planning used by several retailers and to suggest directions for future research.
Modelling Remembered Utility Using Psychological Constructs
The utility of its products or services is very important for any company. It directly affects consumers’ likelihood to buy a product and thus has a crucial impact on economic success. Considering the process characteristic of services event-based utility modelling is a new approach to better align customer preferences and services. According to this perspective, a service can be described as a series of events, each generating instant utility to the customer. In order to derive an aggregate measure of service utility, a remembered utility value needs to be calculated as a function of these instant utilities. In this formulation different psychological constructs like acclimation or memory decay might play a role.
The first goal of this thesis is to come up with a short introduction to sequence-based service design. In a second step, the thesis should present a broad range of psychological constructs and their impact on the remembered utility. The pros and cons of these constructs might add additional value to the thesis.
Menu-based Conjoint-Analysis as a Tool for Service Design
One way of increasing the attractiveness of products or services is to maximize the respective utility from a customer’s point of view. According to the attribute-based utility modelling concept every product or service can be described with a list of determinant attributes and their levels. In order to derive utility values for each attribute level, conjoint analysis (CA) is an established tool in theory and practice. During the past decades a variety of different CA techniques like conjoint value analysis (CVA) or choice-based conjoint (CBC) has emerged. One technique that best reflects the menu-type of choice situation of different services or products is menu-based conjoint analysis.
In a first step of this bachelor thesis, an introduction to the concept and different forms of conjoint analysis should be presented. Afterwards, a deep-dive into the technique of menu-based conjoint analysis is required. In a last step, current and future areas of application of this approach should be analyzed and discussed – with a strong focus on the strengths and weaknesses compared to other related techniques.
Current State and Future Research of Service Bundling
A service bundle can be defined as a combination of several different services, which are sold in one single package. Examples are widespread and range from telecommunication providers offering phone, mobile and TV solutions to season subscriptions for sports events. The concept of bundling is already well established in a product or goods context with several years of research in this area.
The goal of this bachelor thesis is to provide and introduction to the topic of bundling in general and to compare similarities and differences between the bundling of goods and services. Beside of key concepts and important quantitative models in this field, the thesis should also collect and present ideas for future research.
Revenue Management for Ski Resorts
During the last years, ski resorts started to use revenue management techniques. With different prices for their tickets (dependent on booking time, validity etc.) they try to attract customers and therefore increase revenues. The goal of this thesis is to analyze the current situation in the ski resort market, analyze the business model of ski resorts and describe how/ why revenue management can be applied. Furthermore, a concept for a fictional ski resort should be developed and explained. Optionally the thesis can include a survey/ interviews with ski resort representatives to get deeper insights and describe the topic from a practical perspective.
Revenue Management for Small Enterprises
Revenue Management (RM) techniques are typically applied in medium or large sized companies. Still RM could also be beneficial for smaller companies like a family-run hotel, local concert hall or a small car rental company. The thesis should analyze if and how RM techniques can be used in small enterprises. This includes the analysis of selected business models (e.g. hotel, ticket office), analysis of necessary data for RM models and interviews with owners of such companies. The goal is to develop a blueprint for RM in small companies.
Airline Crew Scheduling: Current state of research
The Airline Crew Scheduling problem is one of the most complex crew scheduling problems in transportation due to various reasons: Airlines often have a large number of flights to be covered and many operational requirements due to union agreements, regulatory agencies and the flight network infrastructure which all impose constraints in the problem. As Kasirzadeh, Saddoune and Soumis (2017) point out, the two major techniques to solve the Airline Crew Scheduling problem are the Set Covering Problem and the Set Partitioning Problem. Furthermore, they point out that the whole Airline Crew Scheduling Problem is split in two subproblems: The Crew pairing problem creates pairings by deciding which flights are combined to become a work schedule of several days for a crew while in the crew assignment problem these pairings are assigned to particular crew members for a planning period such as a month. E.g. a bidding approach, where each crew member bids on vacation times and particular flights, is used.
Task of the thesis is to compare the different current approaches in the Airline Crew Scheduling Problem and to provide current research gaps as well as trends in research. Optionally, a small academical example of a crew pairing problem may be modelled.
Behavioral Scheduling: Current state of research
The Airline Crew Scheduling problem helps to decide which pilot is assigned to which flight and vice versa. It is one of the most complex crew scheduling problems in transportation due to various reasons: Airlines often have a large number of flights to be covered and many operational requirements due to union agreements, regulatory agencies and the flight network infrastructure which all impose constraints in the problem. While the basic problem is well discussed and solved by various contributions, Yildiz, Gzara, and Elhedhli’s (2017) provided a new aspect by including behavioral factors such as sleepiness into a model. The aim of their model is to avoid assigning duties which are especially tiring for pilots in order to decrease the risk of accidents in the airline industry; therefore they go beyond the single objective of only minimizing cost.
Task of the thesis is to recap Yildiz, Gzara, and Elhedhli’s (2017) model with focus on the scheduling part and to compare it to other scheduling models from the Airline Crew Scheduling Problem or other scheduling problems. These models should include sleeping and/ or other behavioral factors. Optionally, a small academical example of a crew pairing problem may be modelled.
Railway Rescheduling – Using Passenger Feedback for Dispatching Decisions
The main goal of railway rescheduling is to take dispatching decisions if the actual timetable is no longer feasible, e.g. after disruptions. But to determine what the best decision is, depends from case to case and even from passenger to passenger. Therefore it could be very helpful to have further information about the passengers’ travel plans. In Stelzer et al. (2016) the exchange of information between passengers and transportation companies is analyzed. The thesis should describe how they can use the customer feedback for dispatching decisions and to improve the service quality.
Delay Propagation in Railway Networks
Punctuality is an important topic in railway scheduling. Delays cause a lot of problems for railway companies and inconvenience for passengers. Several models exist to cope with delays, e.g. taking wait-depart decisions, creating robust timetables, etc. But to improve solution models or timetables it is helpful to understand the propagation of delays in networks. The goal of the thesis is to explain how the delay propagation can be quantified and included in delay management models.
Buffer Allocation for Robust Railway Timetables
Timetables for railways are often periodic so they can be easily kept in mind. But this is not always the best structure to cope with unforeseen events like disruptions. In literature several approaches exist to create robust timetables or to make a timetable more robust against disruptions. This can be done e.g. by adding buffer times in the schedule. The thesis should contain an overview of buffer allocation methods for timetables and a comparison of them.
Railway Timetable Adaptions by Optimizing Stopping Patterns
Railway operators create timetables for customer needs and in regard to the infrastructure of train lines. Sometimes these timetables have to be adapted due to unforeseen events. In the case of e.g. insufficient capacity of a train it might be necessary to pass a station without stopping. In literature several works exist that analyze train stopping patterns. The goal of the thesis is to explain the different patterns and their use for timetable adaptions.
Topics in FSS18 for students “B.Sc. Wirtschaftspädagogik”
Key Performance Indicators (KPI) in Revenue Management
To measure the performance of a company, typically predetermined KPIs are used. As these KPIs are also very interesting for financial investors/ stockholders, companies started to publish them in their annual reports. In companies that use revenue management techniques (e.g. airlines, hotels) the Yield or RASK are popular KPIs.
The thesis should 1. present, explain and discuss possible KPIs in RM context, 2. study annual reports and press releases of companies that typically use Revenue Management techniques and present the findings to give an overview of used KPIs in practice. 3. Analyze if there is a relationship between financial performance of the company and the amount/ relevance of Revenue Management content in the annual report.
Attribut-basierte Nutzenmodellierung im Dienstleistungsbereich
Ein elementares Mittel, um Güter oder Dienstleistungen attraktiv für den Kunden zu gestalten und das entsprechende Absatzpotenzial zu entfalten, ist die Maximierung des Nutzens aus Kundensicht. Je größer der Kundennutzen ist, desto höher sind Kaufwahrscheinlichkeit und Zahlungsbereitschaft der Kunden. Um diesen Nutzen zu erfassen, kann die Attribut-basierte Nutzenmodellierung als ein mögliches Konzept herangezogen werden. Güter oder Dienstleistungen werden demnach durch mehrere Attribute beschrieben, wobei jedes dieser Attribute verschiedene Ausprägungen annehmen kann. Unterschiedliche Ausprägungen können entsprechend unterschiedlich große Nutzen für den Kunden entfalten. Die dem Modell zugrundeliegende Datenerhebung erfolgt dabei meist mithilfe einer Conjoint-Analyse.
Die vorliegende Arbeit sollte zunächst eine kurze theoretische Einführung sowohl in die Grundlagen der Attribut-basierten Nutzenmodellierung, als auch in die Empirie der Conjoint-Analyse geben. Darauf aufbauend gilt es, Anwendungsbeispiele im Dienstleistungsbereich zu sammeln und strukturiert darzustellen. Abschließend sollten dann Stärken und Schwächen der Modellierung im Dienstleistungskontext gerade auch im Hinblick auf den Prozess-Charakter von Dienstleistungen aufgezeigt werden.
Ereignis-basierte Nutzenmodellierung – Grundlagen der Psychologie und ihre Anwendbarkeit auf Dienstleistungen
Der Nutzen von Gütern oder Dienstleistungen ist ein zentrales Entscheidungskriterium in jedem Unternehmen. Er bestimmt, wie gut das Angebot vom Kunden angenommen wird und ist entsprechend ein Wegbereiter für den wirtschaftlichen Erfolg eines Unternehmens. Während im Allgemeinen zur Modellierung des Kundennutzens meist Attribut-basierte Modelle und Erhebungsmethoden wie die Conjoint-Analyse eingesetzt wurden, hat sich speziell im Bereich der Dienstleistungen eine neue Herangehensweise etabliert. In dieser Ereignis-basierten Perspektive wird eine Dienstleistung als Prozess gesehen, der sich über mehrere Ereignisse hinweg abspielt. Jedes dieser Ereignisse generiert einen bestimmten direkt messbaren Nutzen beim Kunden. Um übergeordnet für die Dienstleistung einen Gesamtnutzen zu ermitteln, braucht es jedoch Regeln, die über die rein additive Modellierung hinausgehen.
Das Ziel dieser Arbeit ist es entsprechend im ersten Schritt, die unterschiedlichen Formen des Nutzens (erwarteter, unmittelbarer und erinnerter Nutzen) zu definieren. Im Speziellen soll dann ein Fokus auf den erinnerten Nutzen gelegt werden. Hierzu gilt es, die unterschiedlichen Regeln zusammenzutragen, mit denen sich der retrospektive Nutzen modellieren lässt. Der Fokus sollte dabei möglichst breit gewählt und auch Studien fernab des Dienstleistungsbereiches untersucht werden. Interessante Ansätze lassen sich dabei u.a. in Studien aus dem Umfeld der Psychologie bzw. Medizin finden.
The main goal of railway rescheduling is to take dispatching decisions if the actual timetable is no longer feasible, e.g. after disruptions. But to determine what the best decision is, depends from case to case and even from passenger to passenger. Therefore it could be very helpful to have further information about the passengers travel plans. In Stelzer et al. (2016) the exchange of information between passengers and transportation companies is analyzed. The thesis should describe how they can use the customer feedback for dispatching decisions and to improve the service quality.
Topics in FSS17 for students “B.Sc. Betriebswirtschaftslehre”
Bridging the Gap between Facility Location Models and Supply Chain Management
Given a set of customer demand nodes and potential facility locations, the location of new facilities and allocating customer demand to newly located facilities are main decisions of facility location models. Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the process of planning, implementing and controlling the operations of the supply chain; spanning from the point-of-origin to the point-of-consumption in an efficient way. Researchers in (service) system design often discuss the design of distribution systems without taking into account the whole supply chain. The output of the facility location problem is strategic input for supply chain network design. Therefore, it is important to study features and decisions most important for supply chain planning; and need to be captured in facility location models.
The aim of thesis is to review role of facility location models in SCM, with academic examples from various application industries. The thesis should point out drawbacks of existing facility location models with respect to the decision-making process in integrated supply chain planning.
Stochastic Location Models with Congestion for mobile servers
Stochastic location models are facility location models where consumers generate streams of stochastic demands for service and service times are stochastic. This combination leads to congestion. This bachelor thesis only focuses on mobile servers i.e. server travels to customer’s location to provide service. Delivery services (food, grocery, online purchased goods etc.), emergency medical and firefighting services are examples of mobile servers.
The aim of thesis is to review stochastic location models for mobile facilities subject to congestion. The review should classify different existing mathematical models based on the objective function, involved decision variables, congestion modeling (explicit or implicit) and solution procedures (exact or heuristic).
Response Time in Public Services
In day to day life, in cases of natural calamities, criminal encounter, medical emergency, and fire, responsiveness of the concerned public service provider plays a vital role in deciding the fate of human life at risk. In other public (or formerly public) services like telephone, electricity, and consumer gas supply, maintenance of water supply and sewage disposal systems responsiveness of service provider is a competitive priority and hence an important element for creating value for the customer.
Responsiveness being a measure of delivery performance can be measured in terms of the average response time to a random call for service. In Operations Research terminology, this problem can be rephrased as estimating average response time for spatially distributed networks of demand nodes serviced by mobile servers. The demand nodes can be thought of as representing city neighborhoods connected by roads. Each node represents demands for service originating from that neighborhood. The demands are generated stochastically and the service units, stationed in service centers, go and service these calls according to a preselected policy.
The aim of thesis is to review mathematical formulations related to response time approximations for public services.
Service Process Improvement: the Customer’s Waiting Experience
Promptness of service and the customer’s perceived waiting experience (e.g. at checkout) or related service attributes can have a significant impact on value-to-the-customer. Therefore, service process improvement should include proactively managing the customer’s wait in a better way to improve customer’s perception of wait times and hence strengthen the competitive position of service provider.
The objective of thesis is to review strategies and technology used by service providers to make customer’s waiting experience a pleasant one.
Modern Trends in Revenue Management
The increasing availability of data in businesses like e-commerce, online advertising, retailing etc. made it possible to apply new methods for price optimization (like Google’s way of selling advertising space or grocery stores with electronic shelf labels). This thesis should identify and analyze these new approaches and compare it to traditional revenue management techniques to derive implications for the field of revenue management.
Customer Choice Behavior in Revenue Management
Traditional Revenue Management models typically assume that customer’s buying decision only depends on the price of the sold product. During the past years, customer choice behavior (i.e. applying additional criteria like quality of the product compared to other products) was integrated in many RM-models to capture the effects of a more complex buying decision. This thesis should review and explain current approaches of customer choice behavior in Revenue Management and identify differences compared to traditional RM models.
Overbooking in Revenue Management
One important aspect in many Revenue Management models is to determine the optimal number of overbookings (i.e. number of sold tickets beyond the available fixed capacity). For example it is quite common in the airline industry to sell a number of tickets that exceeds the available seat capacity on the airplane. This thesis should explain the idea of overbooking in Revenue Management and give an overview about current approaches in literature. In addition it should be briefly discussed how these approaches could be applied in different industries.
Network Revenue Management
Companies with a complex structure of products (Lufthansa or Deutsche Bahn with many flights/ connections in the network) face the problem that multiple products use the same capacity. For example, the Lufthansa flights from Hamburg to Bangkok (via FRA) and from Düsseldorf to Bangkok (via FRA) both use the Lufthansa flight from Frankfurt to Bangkok. A Network Revenue Management model addresses this sharing of capacity and finds optimal prices for both connecting flights.
This thesis should explain the idea of Network Revenue Management in more detail and give an overview of current Network Revenue Management models in literature.
Conjoint Analysis with Experiential Attributes – A Literature Review
Conjoint analysis is a well-established tool to evaluate customers’ attitude towards a product or service. The disciplines of application are widespread – ranging from engineering and architecture to medicine and business. Using verbal representations, 2D or 3D models as well as prototypes each discipline takes advantage of this technique differently. Studying these applications raises two questions with high importance for business in general and service design in specific: 1) Are new procedures of conjoint analysis superior to classical forms? And if so, 2) how can a service process alternatively be described instead of a verbal representation? Advances in technology might improve realism of the hypothetical situation and help to better capture process attributes. Virtual reality techniques may be of interest in this context putting the customer in an active role instead of a passive observer.
Thus, the thesis should elaborate on the following questions and tasks: What forms of representations of a product or service with experiential attributes have been used in conjoint analysis independent of a specific research area? Did these studies prove a benefit of a certain technique over the other? How can virtual reality help to better capture process attributes and which studies did already apply it? Which implications can be drawn with regard to the research design? Are there any methodological changes beyond the interviewing technique itself?
On the Concepts of Outcome and Process Utility
The health care sector plays an important role in service research and is often an excellent area of application for general models and methods of service design. One such example is a study conducted by Ryan (1999). With a conjoint analysis based approach the author tries to find an empirical evidence for both outcome and process utility. The underlying idea is that any service might not only be evaluated based on the outcome itself, but additionally on the process executed to achieve the outcome.
The goal of this thesis is to analyze the constructs of outcome and process utility, while the literature to be analyzed does not necessarily need to be related to a service context. In specific the questions are: What studies have been conducted to analyze and measure these constructs? Are there any other constructs related to this topic and need to be considered for further analysis? What implications could be derived from these studies and which future research is needed to advance this field?
Sequence Effects in Service Design – Background, Importance and Implications
The sequence of events plays an important role in a customer’s evaluation of an overall service experience. Different sequences of positive and negative experiences during a service encounter can have different influences on the overall evaluation. The peak-end-rule for example suggests that incidents that occurred at the end of an encounter have a much stronger effect on the overall evaluation than the incidents during the rest of the experience.
The goal of this thesis is to analyze these sequence effects with a strong focus on the psychological aspects. The literature to be analyzed does not necessarily need to be related to a service context. Detailed questions are: What experimental, quantitative studies have been conducted to analyze these sequence effects? How did those studies measure the occurrence and implications of this phenomenon? How do consumers combine memories of a sequence of pleasant and unpleasant moments to form an evaluation of the experience as a whole?
Rerouting Railways versus Rerouting Aircrafts – A Comparison
In case of disruptions, scheduled flight resp. railway trips are sometimes no longer feasible. Due to missing capacities it can be necessary to use other routes. In the literature exist rerouting models for aircraft as well as for railways. The goal of the thesis is to compare both streams. Illustrate similarities and differences concerning the contents. Which industry is further developed?
Railway Scheduling – Capacity Analysis
A railway network underlies several restrictions. To yield a feasible model, considering capacities, such as capacities of stations, lines, etc. is necessary. In Abril et al. (2008) a capacity analysis for railway networks is done. The thesis should provide an overview of the different kinds of capacity. Furthermore, influence factors on capacities should be analyzed and methods for evaluation be explained.
Demand Oriented Timetables for Railways
A basis for running a railway system among a network of tracks is a timetable. Creating railway timetables can be subject to several objectives, e.g. minimal trip times or cyclicity. Some models in the literature try to focus on demand for railways. The goal of the thesis is to explain how passenger demand is measured in Canca et al. 2014 and to compare their method with further examples from literature.
Topics in FSS17 for students “B.Sc. Wirtschaftspädagogik”
Revenue Management für den Schienenpersonenfernverkehr
Das Themengebiet Revenue Management (RM) ist in bestimmten Industrien (Luftverkehr, Hotels, Mietwagen) bereits seit Jahren etabliert. Auch im Schienenverkehr werden Revenue Management Methoden genutzt, um die Kapazität der Züge möglichst umsatzmaximierend zu verkaufen. Jedoch wurde dieser Industrie vor allem in der Forschung bisher deutlich weniger Aufmerksamkeit geschenkt. Ziel ist es, neben einem Literaturüberblick zu Revenue Management (im Allgemeinen sowie im speziellen Fall des Schienenverkehrs), zu analysieren, welche aktuellen RM-Ansätze sich aus anderen Industrien auf den Schienenpersonenfernverkehr übertragen lassen.
On the Importance and Impact of Customers’ Experiencing and Remembering Self
When analyzing customer experiences, one important criterion is the point in time of the evaluation. Every event can be assessed either in real time or retrospectively, reflecting the actual experienced utility and the way it is summarized afterwards, respectively. Each event is associated with a stream of affective states that may vary in intensity from moment to moment within a single episode. A summary evaluation is attached to events in past experiences: customers may remember them as more or less good or bad, and are accordingly prone to seek or avoid repeated encounters, or to recommend or not recommend the experience to others.
This bachelor thesis should present the current state of research with a strong focus on the psychological aspects of the problem mentioned above. Key questions are: What experimental, quantitative studies have been conducted to analyze the impact of the time of evaluation? How did those studies measure the occurrence and implications of this phenomenon? How does the evaluation during the experience differ from the overall evaluation after the experience? What are reasons and implications?
Dynamic Impact Factors on the Customer – Service-Provider – Relationship
A customer-company-relationship is rather a dynamic process than a static construct. Different parameters like customer satisfaction or experiences from former service encounters may have an impact on length and strength of such a relationship.
This seminar thesis should first review the empirical literature on dynamic relationship modeling. It should clearly describe the influencing factors and the studies performed to gain these research insights. In a second step, the thesis should discuss how service designers may take advantage of these finding to increase retention and profitability in the long-run. The thesis should conclude by deriving implications for future research.
A review on railway crew scheduling
One topic of the tactical level of railway planning problems is crew scheduling. Each train running in a network needs an appropriate crew to operate it. After disruptions it can be possible to reschedule plans of action. In the literature, several works about crew scheduling respectively crew rescheduling already exist. The topic of this thesis is to survey the literature about crew scheduling and to summarize the respective contents.
Railway rescheduling – minimizing passengers’ discomfort
Rescheduling trains in case of disruptions has to be done with regard to a feasible solution for the infrastructure. But other topics, e.g. solution quality or minimizing waiting times for passengers, play also important roles. In the paper of Corman et al. (2015), the model aims at minimizing passengers’ discomfort, more precisely the quality of service perceived by passengers after rescheduling decisions. The thesis should describe this model and explain the heuristics used to find solutions as well as the associated numerical study.
Topics in FSS16 for students “B.Sc. Betriebswirtschaftslehre”
Exact Solution Procedures for Stochastic Location Models with Congestion
Stochastic location models are facility location models where consumers generate streams of stochastic demands for service and service times are stochastic. This combination leads to congestion. Therefore, each facility in these models can be modeled as a queuing system. This bachelor thesis only focuses on immobile servers i.e. server is fixed and customers has to visit the facility to use the services offered by the server. Retail stores (e.g. Supermarkets, IKEA etc.), ATM machines, government offices and hospitals are examples of immobile servers. The literature streams based on stochastic location models with immobile facilities and congestion (SLMIFC) can be divided into two types of models on the basis of solution procedures: exact and heuristic.
The aim of thesis is to study exact solution procedures for SLMIFC. The thesis should present a review of the exact solution procedures in the literature with focus on methodology, parameters, decisions, maximum size of the problem solved and computational times.
Heuristic Solution Procedures for Stochastic Location Models with Congestion
The aim of thesis is to study heuristic solution procedures for SLMIFC. The thesis should present a review of the heuristic solution procedures in the literature with the focus on methodology, parameters, decisions, maximum size of the problem solved, nearness to optimality and computational times.
Stochastic Location Models with Congestion modeled using G/ G/1
Stochastic location models are facility location models where consumers generate streams of stochastic demands for service and service times are stochastic. This combination leads to congestion. Therefore, each facility in these models can be modeled as a queuing system. This bachelor thesis only focuses on immobile servers i.e. server is fixed and customers has to visit the facility to use the services offered by the server. Retail stores (e.g. Supermarkets, IKEA etc.), ATM machines, government offices and hospitals are examples of immobile servers. The literature streams based on stochastic location models with immobile facilities and congestion (SLMIFC) comprises of different types of models, modeled assuming different queuing systems.
The aim of thesis is to study SLMIFC modeled using G/ G/k (k is the number of servers) queuing systems. The thesis should present a review of SLMIFC modeled using G/ G/k in the literature. The thesis should also review how the performance measures related to G/ G/k queuing system are modeled in the existing mathematical models from the literature. These performance measures could be the expected waiting time in queues or expected number of entities waiting in the queue.
Preventive Healthcare Facility Network Design with Congestion
Preventive Healthcare Facility Network Design (PHFND) models with congestion are a special case of Stochastic Location models with Congestion (SLC). SLC are facility location models where consumers generate streams of stochastic demands for service and service times are stochastic. This combination leads to congestion. Therefore, each facility in these models can be modeled as a queuing system. The servers could be categorized as mobile servers and immobile servers. Immobile servers are those in which server is fixed and customers has to visit the facility to use the services offered by the server. Retail stores (e.g. Supermarkets, IKEA etc.), ATM machines, government offices and hospitals are examples of immobile servers. This seminar thesis only focuses on PHFND with congestion at immobile servers.
Preventive healthcare is much needed for early detection of life-threatening diseases like breast cancer in women. The aim of the thesis is to review PHFND models with congestion.
Stochastic location models are facility location models where consumers generate streams of stochastic demands for service and service times are stochastic. This combination leads to congestion. Therefore, each facility in these models can be modeled as a queuing system. This bachelor thesis only focuses on immobile servers i.e. server is fixed and customers has to visit the facility to use the services offered by the server. Retail stores (e.g. Supermarkets, IKEA etc.), ATM machines, government offices and hospitals are examples of immobile servers. The main decisions involved in designing such a network is where to locate these facilities and what should be the capacities of the servers at these selected facility locations. Some of the models in literature do not consider the competition due to the existing facilities in the region of interest.
On the impact of behavioral aspects on operations research
The term operations research describes a discipline using mathematical models to support company decision making. Since its emergence at the beginning of the 20 th century most formal analytical models have assumed that participants in a process behave fully rationale. The new stream of behavioral operations is challenging this perspective by incorporating more realistic behavioral attributes into analytical models.
This bachelor thesis should provide a structured overview of the concept of behavioral operations . Key questions to be answered are: How can behavioral operations be defined? What are the origins and in which specified areas can this new research stream be subdivided? What is the current state of research in these areas and what are potentials topics for future research? Throughout the whole thesis the major focus should be on service operations.
Customer-Oriented Service Design – Fundamentals and Methods
Designing services is a key success factor in every modern business. The final design must effectively meet the needs and desires of the targeted customer groups. At the same time, it must be aligned with the internal company perspective and its processes. To achieve these goals both qualitative (e.g. QFD) and quantitative (e.g. optimization) approaches can be used. Each class of tools has its own strengths and weaknesses, which should be analyzed in this bachelor thesis. The analysis should be based on a profound overview of tools for service design from both categories. In the second step each tool should be evaluated according to the extend that it integrates the customer perspective.
Simulating Service Processes
Simulation is a powerful tool to analyze complex problems from all scientific fields. Even in business, the areas of application are widespread ranging from production, through logistics to services. Depending on the context and goal of the respective simulation, different approaches might be used. Beside discrete-event simulation and the system-dynamic approach, agent-based modelling accounts for the latest development. This bachelor thesis is intended to provide a service-focused overview of simulation applications. Key questions are: In which industries and for which scenarios has simulation already been applied in services? Which simulation techniques are most common in service simulation? Based on the answers, the root causes for these trends should be analyzed. The thesis will conclude with an outlook on the future of simulation in service research.
Multilevel Service Design (MSD) – Minor progress or groundbreaking evolution?
In order to design services, people in both research and business have a variety of tools at hand – service blueprinting, PCN-Analysis, QFD, conjoint analysis, and optimization are just a few to mention. Each tool has its own strengths and weaknesses that the user has to consider before and during the application. The most promising approach is often a sophisticated combination of several techniques. One such integrated approach was presented in 2011 by Patrício et al. and is called Multilevel Service Design (MSD). Instead of designing all service aspects simultaneously, the authors suggest a three-step-approach. In each of the three hierarchical layers the level of detail increases from a general conceptual perspective to the detailed design of the service encounter.
This bachelor thesis should critically assess the Multilevel Service Design technique. Key questions might be: What are the strengths and weaknesses of this technique? What tools have been integrated into MSD and would there have been other alternatives to achieve the respective goals? For which services or industries is the tool best suited? What is the future of MSD and how can it be further improved?
Railway Delay Management: Online vs. Offline Solutions
In der klassischen Optimierung wird davon ausgegangen, dass Daten, die zum Lösen eines Problems benötigt werden, vollständig vorliegen. Aufbauend auf diesem vollständigen Wissen wird dann die optimale (oder approximative) Lösung berechnet. Durch diese Art der Optimierung werden Situationen aus der Praxis oft jedoch die nur ungenügend modelliert. Zahlreiche Problemstellungen erfordern Entscheidungen, die unmittelbar und ohne Wissen zukünftiger Ereignisse getroffen werden müssen. Die Daten zum Lösen eines Problems liegen also nicht vollständig vor. Im Rahmen dieser Arbeit soll das Railway Delay Management Problem diesbezüglich untersucht werden. Beispielsweise wird die Entscheidung ob ein verspäteter Zug warten soll (oder nicht) häufig unmittelbar getroffen. Die Frage, unter welchen Annahmen das Problem in der Literatur gelöst wird, ist in Form eines Literaturüberblicks zu beantworten. Bestehende Literatur soll basierend auf den Annahmen zur Datenverfügbarkeit ( online vs. offline ) untersucht und klassifiziert werden.
The Concept of Lookahead in Railway Delay Management
In the Online Delay Management Problem the number of delayed passengers who want to board the train is not known beforehand but revealed in an online fashion once the train arrives at the corresponding station. The goal is to decide at which station a train should wait in order to minimize the total delay of all passengers. In this thesis two approaches of Bender, M.; Büttner, S. & Krumke, S. (2013) that overcome the often criticized pessimism of standard competitive analysis, namely lookahead and comparative analysis, should be presented and illustrated by an example. These approaches extend the classical worst-case approach of competitive analysis in different aspects.
Average-case Analysis in Railway Delay Management
In the Online Delay Management Problem the number of delayed passengers who want to board the train is not known beforehand but revealed in an online fashion once the train arrives at the corresponding station. The goal is to decide at which station a train should wait in order to minimize the total delay of all passengers. In this thesis the average-case analysis approach of Bender, M.; Büttner, S. & Krumke, S. (2013) to overcome the often criticized pessimism of standard competitive should be presented and illustrated by an example. This method extends the classical worst-case approach of competitive analysis in different aspects.
Uncertain multi-product newsboy problem
In the uncertain multi-product newsboy problem demands for the products are estimated by experts and assumed to be independent uncertain variables. Uncertainty theory, which is a new mathematical tool to deal with human uncertainty, is employed to model demand distributions. A fixed setup cost and a linear ordering cost are incurred if products are ordered. The focus of this thesis is to present and illustrate the methodology of Ding, S. & Gao, Y. (2014) for determining an optimal ordering policy. A two-product example should be provided to show how to design an optimal policy in a realistic situation.
A portfolio approach to the multi-product newsboy problem
When solving the multi-product newsboy problem via a portfolio approach, a procurement strategy for each newsboy product is designed as portfolio contract. A portfolio contract consists of a fixed-price contract and an option contract. In this thesis the portfolio solution procedure with budget constraint of Zhang, B. & Hua, Z. (2010) should be illustrated and compared to three different existing procurement contracts: fixed-price contract, option contract, and portfolio contract. Additionally, an illustrative example should be provided to show the practical applicability in a realistic situation.
Iterative optimization of railway delay management
Railway companies are often confronted with delayed trains that can cause a disarranged timetable. If the connecting train waits for a delayed feeder train, delays get transferred, else passenger miss their connection. Delay management models try to answer the question if connections should be maintained in case of delays. Dollevoet et al. 2014 present an iterative optimization model including macroscopic and microscopic points of view. How this model works should be explained in the thesis.
Robust timetable optimization for railways
Railways are often confronted with disturbances that cause delays which make it impossible to keep the original timetable. Therefore more robust timetables need to be planned to cope with several delays. In the literature exist some approaches to create robust timetables by using stochastic respectively dynamic optimization models. These approaches should be explained and compared in the thesis.
Models for passenger’s choice of railway services
For service companies such as Deutsche Bahn it is important to find out what passengers’ needs are. With the information obtained it is possible to create more passenger oriented timetables. Therefore exist so called choice models to demonstrate passenger’s behavior for e.g. service type, run and class. The goal of the thesis is to describe these choice models and to compare them.
Topics in FSS16 for students “B.Sc. Wirtschaftspädagogik”
In der klassischen Optimierung wird davon ausgegangen, dass Daten, die zum Lösen eines Problems benötigt werden, vollständig vorliegen. Aufbauend auf diesem vollständigen Wissen wird dann die optimale (oder approximative) Lösung berechnet. Durch diese Art der Optimierung werden Situationen aus der Praxis oft jedoch die nur ungenügend modelliert. Zahlreiche Problemstellungen erfordern Entscheidungen, die unmittelbar und ohne Wissen zukünftiger Ereignisse getroffen werden müssen. Die Daten zum Lösen eines Problems liegen also nicht vollständig vor. Im Rahmen dieser Arbeit soll das Railway Delay Management Problem diesbezüglich untersucht werden. Beispielsweise wird die Entscheidung ob ein verspäteter Zug warten soll (oder nicht) häufig unmittelbar getroffen. Die Frage, unter welchen Annahmen das Problem in der Literatur gelöst wird, ist in Form eines Literaturüberblicks zu beantworten. Bestehende Literatur soll basierend auf den Annahmen zur Datenverfügbarkeit ( online vs. offline nature ) untersucht und klassifiziert werden.
Agent-based modelling as a tool for behavioral operations
At the beginning of the 21 st century a new stream called behavioral operations has emerged from classic operations management. Instead of assuming rational behavior among all participants in a system, it integrates more realistic actions among all. Due to its broad perspective areas of interest are widespread. To get enable a detailed analysis this thesis should focus on one specific area – the simulation of (service) processes. While classical forms like discrete-event simulation neglect the distinctiveness of any individual, agent-based modelling is challenging this perspective since its development ten years ago.
The following bachelor thesis should evaluate to what extend agent-based modelling can be seen as a tool for behavioral operations . Besides performing a profound literature review in both fields of interest, the application of agent-based modelling to a simplified service process might offer additional insights for this thesis.
Macroscopic vs. microscopic dispatching analysis for railways
Railways are often confronted with delay problems. In the literature, many different approaches to deal with delays are known. They can be divided into macroscopic and microscopic models. Some models compute solutions for the whole railway network, other models decide what to do just for the current station. The thesis should explain the difference between macroscopic and microscopic dispatching. Furthermore, examples for both approaches should be illustrated.
Service design for railways
One challenge for railway companies is the design of services that fit customer needs. Different methods exist in order to find out which preferences customers have. One method is the so called conjoint analysis. Attributes can be defined and ranked for services or customers can choose a service with a certain bundle of attributes. The thesis should describe the conjoint analysis and how it has been used in the literature with focus on railways.
Topics in FSS15 for students “B.Sc. Betriebswirtschaftslehre”
Quality Function Deployment for Customer-Oriented Service Design – Method and Case Study
The challenge of service design begins with design. It must effectively meet the needs and desires of the targeted customer groups. Quality Function Deployment (QFD) is a systematic planning methodology for product and service development that translates customer needs into technical specifications and business process activities. In this thesis, the general method should be presented and applied to a real-world case study, in particular to the development of ideas for the potential redesign of an MBA program.
Robust Airline Fleet Composition
Recently, researchers have developed advanced decision support models to assist airlines in strategic airline fleet planning and dynamic capacity allocation. The approach explicitly accounts for the stochastic nature of passenger demand in the fleet composition problem, e.g. through scenario analysis. The thesis should give an overview of the recent literature and provide insights into the basic idea by presenting the underlying mathematical model and developing an academic example.
Price and shelf-space dependent demand models in decision modeling
The demand models use certain types of functional forms, such as linear, power/ iso-elastic, multinomial logit, and multiplicative competitive interaction. The aim of the thesis is to survey the functional forms of price and shelf-space dependent demand models and compare their advantages and disadvantages. The second objective is to investigate qualitatively the optimal shelf-space allocation problem in Martín-Herrán, Taboubi, and Zaccour (2006) with a more realistic space-dependent demand model that is sensitive to both space and price.
Pricing models in Revenue Management
Consider the problem faced by a seller who owns a fixed and perishable set of resources that are sold to a price sensitive population of buyers. In this framework, where capacity is fixed, the seller is mainly interested in finding an optimal pricing strategy that maximizes the revenue collected over the selling horizon. Price manipulation is an important variable to encourage or discourage demand. The objective of the thesis is to review the pricing models in RM and new potential directions of research.
Dynamic Pricing and Learning
Dynamic pricing is the study of determining optimal selling prices of products or services, in a setting where prices can easily and frequently be adjusted. This class of problem captures trade-off between learning and instant optimization. The aim of the thesis is to survey these literature streams and provide an in-depth overview of the available literature on dynamic pricing and learning and identify the gaps for future research.
Revenue Management in a dynamic network environment
In situations like sequential reservations for an airline network, hotel or car rental service; the allocation of scarce inventory to stochastic demand for multiple fare classes is an interesting problem from the researcher’s point of view. The aim of the thesis is to explore dynamic policies to allocate demand to customers and maximize revenue through an algorithmic approach based on approximate dynamic programming. The functionality of the algorithm should be depicted through a small example.
Dynamic Bid Prices in Revenue Management
Bid-price control policies are used by many airlines for decisions like when to open and close customer fare classes for sale. The aim of the thesis is to explore a tractable model for computing a time trajectory of bid prices and to compare the model with standard deterministic linear program for bid-price control. The second objective is to qualitatively analyze the relationship between bid prices in revenue management and dynamic programming.
Train Scheduling – delay resistant railway timetables
Train timetables are scheduled in a cyclic manner to be kept in mind easily, for example, every 60 minutes. On their route, passengers often have to change their trains. If their current train is late, it could be that passengers have to wait nearly one hour. But if the connecting train waits, delays are transferred. In this thesis, the concept of a delay resistant timetable should be presented. An example should additionally be developed to demonstrate how the approach can be applied in practice.
Delay management in railway syste m s
Delayed trains can disarrange the timetable. If a connecting train waits, the passengers who have to change trains will be glad. But then the delay is transferred to the next train. In the other case, passengers probably have to wait a long time for their connecting train. A so called wait-depart decision must be made. In the Literature, an integer program formulation is often used to model this problem. In this thesis, this classical solution should be analyzed. Additionally, a short example how the integer program works should be given.
Railway Scheduling – Optimization Models
In the last decades, a great variety of scheduling models for the dispatching of trains were published. The underlying paper for this thesis is a survey about optimization models in train scheduling and train routing. The goal of the thesis is to expand the existing survey in one of the given scheduling fields. A short insight into the new papers should be delivered.
Railway Scheduling – Minimizing the total travel time
One of the goals in Railway scheduling is to find an optimal distribution of the railroad line capacity. Especially on single line tracks, an exact meet and pass plan for trains is needed to avoid deviations from the timetable. In this thesis, the underlying algorithm for an effective travel advance strategy should be explained and compared to the previous algorithm. Furthermore, a short example how the algorithm works should be given.
Multi-market Newsvendor with Interval Demand Data
When the newsvendor setting is applied to manufacturing the objective is to determine production planning and procurement decisions. Lin and Ng (2011) provide a solution to the multimarket newsvendor problem where demands are only known to be bounded within some given interval. Besides finding the optimal order quantity the authors assume that the newsvendor has to decide on the market, i.e., the customers it will serve. In this thesis, the concept of hybrid objectives in the context of inventory management should be presented. Furthermore, an example should be developed to demonstrate how the approach can be applied to take optimal decisions.
Optimal Capacity Allocation under Interval Uncertainty
The field of revenue management originates in the airline industry as a way to efficiently allocate fixed capacity to different classes of customers. Traditional models assume that future demand is unknown but can be described by a stochastic process or a probability distribution. Contrary, Perakis and Roels (2010) characterize demand only with three points, namely average-case, worst-case, and best-case scenarios, which naturally leads to an interval representation of demand uncertainty. In this thesis, the concept of interval uncertainty in the context of airline revenue management should be presented. Furthermore, an example should be developed to demonstrate how the approach can be used to solve the capacity allocation problem.
Newsvendors Models under Biased Demand Information
Commonly, newsvendor models under limited information assume that the demand structure is known a-priori with certainty. Zhang and Xu (2009) analyze the newsvendor problem under the assumption that the information on the demand structure might be bound to errors. In this thesis, the concept of uncertain or biased demand information in the context of inventory management should be presented. Furthermore, an example should be developed to demonstrate how the quality of information affects optimal decisions.
Service Blueprints, BPMN or PCN-analysis are just three of many tools for visualizing and analyzing service processes. During the last decades researchers and practitioners have developed new tools or advanced existing ones. The aim of this thesis is to provide a comprehensive overview of the existing visualization techniques with a focus on service processes. Nevertheless, further concepts or ideas from other disciplines could strongly enhance the value of this thesis.
Service Blueprints – Current state of the art of an established tool for service design
The concept of service blueprinting has been introduced by Lynn G. Shostack back in 1982. Since then it has been recognized as one of the most suitable and powerful tools to visualize and analyze service processes. Besides this tremendous success in the business world, the tool has also been in focus of the scientific community. The objective of this bachelor thesis is to bring research on this topic up to date by providing an overview of the most relevant articles published during the last three decades. Based on this analysis ideas for future research on this topic should be gathered.
Petri nets as a tool for service process design?
The concept of petri nets has been developed by Carl Adam Petri during his dissertation in the field of mathematics in the early 1960s. While it started as a tool in information systems to model and analyze computer systems and processes it has also been applied to business processes later on. The idea of this bachelor thesis is to present to original concept of petri nets, to highlight its development during the last decades and to provide insights on how to use petri nets in a business setting, especcially with regard to the service industry.
PCN-Analysis – Potentials and limitations of a new technique
PNC-Analysis has been introduced by Scott Sampson in 2012. As a new tool for visualizing processes especially in the field of services, this technique tries to overcome different pitfalls of previous tools. The purpose of this thesis is to present the idea and concept of PCN-analysis, to review the literature on this new technique and to present its benefits and challenges as well as potentials and limitations. Concluding from the main findings, a plan for future research in this field should be developed.
Topics in FSS15 for students “B.Sc. Wirtschaftspädagogik”
Design von Kundenerfahrungen mit Hilfe der PCN Analyse am Beispiel des Schienenpersonenfernverkehrs
Anders als beim Design physischer Produkte fehlt es bei der Gestaltung von prozessorientierten Dienstleistungen leider noch immer an systematischen Design Tools. Die PCN (Process Chain Network) Analyse ist ein einfaches aber mächtiges Instrument zur Visualisierung, Bewertung und wertorientierten Verbesserung von Dienstleistungen und den zugrundliegenden Prozessen der Leistungserbringung. Mit Hilfe der PCN Analyse lässt sich systematisch untersuchen, an welchen Stellen im Prozess Wert durch eine strategische Repositionierung einzelner Prozesselemente generiert werden kann. Ziel der Arbeit ist es, eine kurze Einführung in die Methodik der PCN-Analyse zugeben und sie auf ein Beispiel im Schienenpersonenfernverkehr anzuwenden und zu diskutieren. Genauer betrachtet werden soll hierbei der Prozess von der Online Reservierung eines Zuges durch den Kunden bis hin zu seiner Ankunft am Zielort.
Verteilungsfreie Verfahren zum Bestandsmanagement
Wie wird der Bestellzeitpunkt anhand der Merkmale eines Artikels ausgewählt und die optimale Bestellmenge ermittelt? Im Rahmen dieser Thesis soll ein Literaturüberblick zum sogenannten “Online Inventory Management Problem” erstellt werden. Im Gegensatz zu klassischen Modellen ist dieser Ansatz zum Bestandsmanagement verteilungsfrei. Existierende Verfahren zur Bestands- und Beschaffungsplanung sollen untersucht werden. Hierbei stellt sich beispielsweise die Frage nach dem optimalen Sicherheitsbestand oder der optimalen Bestellpolitik vor dem Hintergrund ungewisser Nachfrage- und/ oder Preisprozesse.
Verteilungsfreie Revenue Management Verfahren
Wer zuerst kommt, bekommt den billigsten noch verfügbaren Tarif – nach außen sieht es so aus, als würden die Preise für Flugtickets mit der Zeit steigen. Im Rahmen dieser Thesis soll ein Literaturüberblick zum sogenannten “Online Revenue Management Problem” erstellt werden. Im Gegensatz zu klassischen Modellen ist dieser Ansatz zur Preis- und Kapazitätssteuerung verteilungsfrei. Existierende Verfahren zur Preisdifferenzierung und Kontingentierung sollen untersucht werden. Hierbei stellt sich beispielsweise die Frage nach optimalen Ticketkontingenten, denn ist ein Kontingent aufgebraucht, ist der zugehörige Tarif nicht mehr verfügbar.
Planungsprobleme von Eisenbahnunternehmen mit verschiedenen Zeithorizonten
Das Betreiben eines Eisenbahnunternehmens erfordert komplexe Planungsentscheidungen hinsichtlich Liniennetz, Fahrplan, Zügen, etc. Dabei lassen sich die unterschiedlichen Planungsprobleme in kurz-, mittel-und langfristige Probleme kategorisieren. Ziel der Arbeit ist es, eine Klassifizierung der verschiedenen Planungsprobleme nach Zeithorizonten auszuarbeiten. Außerdem soll ein Überblick diverser Methoden, die zur Entscheidungsfindung in den einzelnen Kategorien dienen, erstellt werden.
Service design – gegenwärtige und zukünftige Forschungsfelder
In der heutigen Wirtschaft spielen Dienstleistungen eine bedeutende Rolle und machen einen Großteil der wirtschaftlichen Aktivitäten aus. Nur die Unternehmen mit den besten Dienstleistungen werden den Wettstreit um Kunden und Abschlüsse für sich entscheiden können. Zum Erreichen dieses Ziels nutzen Unternehmen Service Design, um neue Dienstleistungen zu entwickeln oder bestehende zu verbessern. Das Ziel dieser Arbeit ist es, einen umfassenden Überblick über die verschiedenen Schritte von und Perspektiven auf Service Design zu erarbeiten, aktuelle Literatur zu diesem Thema zu sichten und vielversprechende Ansätze für zukünftige Forschungsarbeiten abzuleiten.
Topics in FSS14 for students “B.Sc. Betriebswirtschaftslehre”
Innovations in Quality Management for Service Firms
Innovation is a necessary process in an enterprise´s life. Especially quality management offers a great variety of possible innovations. The aim of this thesis is to point out how innovations in quality management support and promote service firms. Three studies from the literature with reference to service enterprises should be given as an example.
DMAIC method – an improvement procedure of Six Sigma
Six Sigma helps to improve the strategic process of organizations and its services. DMAIC – Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control – is a procedure to improve the Six Sigma method by showing strengths and weaknesses in companies’ transactions. This thesis should give an introduction to Six Sigma with focus on DMAIC. Furthermore, the limitations of Six Sigma in services should be presented.
New JIT – a novel approach of Toyota's management strategy
Toyota is known for its lean management process. A new approach – New JIT – consists of three core elements of Toyota`s management principles (TMS, TDS and TPS) in connection with a software system (TQM-S). The goals of New JIT are a revised global production and to ensure a high quality level. This thesis should describe the implementation of this approach, especially in the service area (TMS).
Revenue Management – The Adwords Problem
How do search engine companies, such as Google, Yahoo or MSN, decide what ads to display with each query so as to maximize their revenue? The key problem is to find the correct trade-off between the bid and unspent budget of the advertiser. In this thesis, three algorithms solving the adwords problem should be presented. In addition, examples should be given to demonstrate the algorithms’ functionality and practical relevance.
Revenue Management – The On-line Booking Problem
Which booking policy guarantees the largest possible percentage of the optimum revenue, for any demands and request sequence? In this thesis, revenue management policies should be presented from the perspective of on-line algorithms. Furthermore, an example should be developed to demonstrate how the approach can be applied to find an optimal booking policy.
Inventory Management – The On-line Problem
What is the optimal point of time to replenish and how much raw materials to buy? The key problem is to find a strategy to fill the inventory to capacity at minimum cost without any knowledge of future prices, i.e., decisions must be taken in an on-line fashion. In this thesis, the concept of on-line algorithms in the context of inventory management should be presented. Furthermore, an example should be developed to demonstrate how the approach can be applied to take optimal decisions.
Green products: sustainable society and network design
The growing volume of transportation has consequences upon the environment. Countries and companies are faced with strict targets in order to reduce the level of pollution and emissions. Besides, scholars argue that to be a sustainable society developed countries need to consume less. The objective of this thesis is to give a review on the existing literature on green supply chain network design and servicizing (change of business focus from selling products to providing services): Which factors should be considered in order to optimize a network design and to reduce the level of pollution, emissions and consumption.
Queuing-theory: balking and reneging
Companies pay attention on positive customer experiences. Customers don't want to spend too much time waiting. If customers are faced with intolerable delays they will balk (leave without joining the queue) or renege (departs queue without being – fully – served). Why do customers balk or renerge? It is known that it is more costly to win a new customer than holding a loyal customer. What empirical evidence do we have regarding customer balking and reneging behaviour and what is the current state-of-the-art in analytical queuing models considering balking and reneging? Where do analytical models fall short of capturing the behavioral realities? How could future research close this gap?
Tracking cookies are currently allowed.
Tracking cookies are currently not allowed.
- Job subscription
- Career Website

Bachelor Thesis - Product Management - REF55157W
For the area of product management at the Villingen-Schwenningen site, we are offering an opportunity for a bachelor's student (m/f/diverse) to write their mandatory thesis with Continental starting in September 2024. The working-hours will be mainly on-site in Villingen-Schwenningen. Remote work is possible according to prior agreement.
The Bachelor Thesis will explore the topic of integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) into fleet management software (VDO Fleet). This project aims to enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve decision-making processes within fleet operations. The student (m/f/diverse) will support in researching, developing, and proposing innovative AI solutions that can be integrated into our existing fleet management systems.
Get on board, become a part of Continental and also benefit from our Villingen Internship Program (VIP). Key tasks:
- Conduct research on current AI technologies and their application in fleet management
- Analyze existing fleet management processes to identify areas for improvement through AI integration
- Develop a detailed proposal outlining the scope, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes of the thesis. This should include a plan for how AI can be integrated into specific aspects of fleet management software, e.g. in vehicle tracking, maintenance scheduling, and fuel consumption optimization.
- Work closely with the product management and development teams to understand the technical architecture of our fleet management software. Propose and prototype AI-driven features or modules that align with the project's goals
- Design and conduct tests to evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed AI integrations. This includes setting up benchmarks, analyzing data, and gathering feedback from stakeholders
- Document all research findings, development processes, test results, and analysis in a comprehensive thesis. Prepare and deliver a presentation to company stakeholders, showcasing the project, its findings, and potential impact on the business.
Your profile
- Bachelor Students (m/f/diverse) in the field of Information Technology, Business Informatics, Artificial Intelligence / Machine Learning or similar courses of study
- Know-how in the field of Artificial intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
- Knowledge of Cloud Applications, Jira / Confluence, Python, Java, R or similar experience
- Advanced handling of MS Office-applications
- Fluent English skills (C1), written and spoken, for daily communication within the international team
- Good German skills (B1) are a plus
- Distinct communication skills
- Analytic thinking, result-oriented work style, customer orientation, self-dependence
- Creativity & flexibility
Please remember to upload your current enrollment certificate and overview of grades as well as the conditions of study related to mandatory internship, as these are absolutely necessary for the processing of your application! If required, please submit your valid residence permit as well as your work permit including the additional sheet.
Applications from severely handicapped people are welcome. Diversity drives our engine and gives us the essential boost to develop groundbreaking ideas, new products and business models.
What we offer:
- An exciting and varied area of responsibility in a motivated team with flat hierarchies
- Hybrid working (occasional working from home possible)
- Flexible working hours
- A modern working environment based on New Work principles
- Performance-related compensation for your internship with us
- The opportunity to apply theoretical knowledge in practice by encouraging personal responsibility and commitment
- An open working atmosphere: with a hands-on mentality, you will be a valuable member of the team.
- Villingen Internship Programm (VIP): Special events and team activites for students (m/f/diverse)
- Benefit from a variety of discounts and reductions through our corporate benefits and local providers
- Health courses and sports programmes
- Working in a motivated and experienced team
- Challenging and varied area of responsibility
- Internship compensation by standard of the Continental group
Sie wollen mit uns Gas geben? Starten Sie durch und bewerben Sie sich jetzt!
Continental develops pioneering technologies and services for sustainable and connected mobility of people and their goods. Founded in 1871, the technology company offers safe, efficient, intelligent and affordable solutions for vehicles, machines, traffic and transportation. In 2022, Continental generated sales of €39.4 billion and currently employs around 200,000 people in 57 countries and markets.
The Automotive group sector comprises technologies for passive safety, brake, chassis, motion and motion control systems. Innovative solutions for assisted and automated driving, display and operating technologies, as well as audio and camera solutions for the vehicle interior, are also part of the portfolio, as is intelligent information and communication technology for the mobility services of fleet operators and commercial vehicle manufacturers. Comprehensive activities relating to connectivity technologies, vehicle electronics and high-performance computers round off the range of products and services.
Related Jobs
Pflichtpraktikum - Product Management / IoT & Cloud-Applications - REF55140D
Facility Management & ESH Projektkoordinator (CBS Lighthouse) (m/w/d) - befristet bis 31.12.2025 - REF35883P
Pflichtpraktikum - Kundenprojektmanagement für den Bereich Tachographen & Sensorik / ADAS - REF54118F
Pflichtpraktikum - Projekt- & Qualitätsmanagement für Digitale Tachographen - REF54383A
All search results

Prioritization Methods and Techniques – Part 2: MoSCoW Method
In my previous article, Prioritization Methods and Techniques - Part 1: Why Prioritize and the Kano Model , I talked about the need to prioritize and the Kano model as a prioritization method. In this second article in the series on prioritization methods and techniques, I will discuss the MoSCoW method.
The MoSCoW method is a highly widespread prioritization method which was popularized by Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM). The term MoSCoW has nothing to do with the capital of Russia. It is an acronym derived from the first letter of each of four prioritization categories – Must have, Should have, Could have and Won’t have.[1] The two “O” are added to make the word pronounceable.
Must have: This category contains requirements or features that are absolutely mandatory. Those are fundamental to the system (being a product or a service). If any of them are neglected, the system will certainly not work or will have no value for the customer.
Should have: These features are important, ideally, we should have them for the system to work correctly. If they are not there, a workaround may be possible, but it can be costly or cumbersome. Yet, they are not mandatory and therefore do not have the highest priority. Simply put, they don’t have much impact on delivery success right now, though they must be implemented soon enough (after the “must-haves”).
Could have: These are useful additions (often small-scale improvements) that add tangible value. These are “nice-to-have” requests. In general, they do not take considerable resources, but they are not essential to implement either. Their absence won’t affect almost anything, or at least wouldn’t impact the release negatively.
Won’t have (sometimes also known as “would like to have, but not this time”): These items are not worth the investment (of time, money, energy) and are unlikely to make the cut (at least not in the near future). These requirements are of the lowest importance and can be easily omitted (definitely considered out of scope for the first release) or rescheduled for future releases.
When prioritizing requirements in a project, DSDM recommends no more than 60% effort for “must-haves” requirements and a sensible pool of “could-haves”, usually around 20% effort (see Figure 1 below). Anything that is higher than 60% effort for the “must-haves” poses a risk to the success and predictability of the project, unless the environment and the used technology are well understood, there are minimal external risks/dependencies and the team is experienced and well established. Note that we are talking about a balance based on estimated effort of requirements (i.e. the expected time it takes to implement the prioritized features) and not total number of requirements. When calculating effort for a specific timeframe (e.g. first release), “won’t haves” are excluded, as they are considered out of scope for this timeframe.[2]
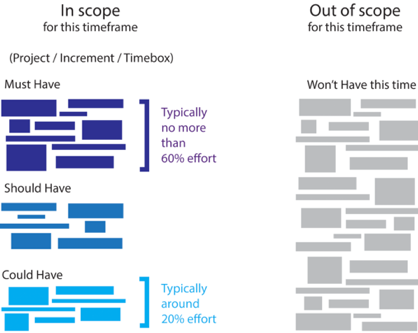
Figure 1: Balancing priorities using the MoSCoW prioritization technique (recommendation by DSDM[2])

Practical example
Let’s take a simple practical example. How can you categorize the features required to manufacture a child’s bicycle?
Must have: two wheels ; a frame
Should have: brakes for safe stopping; pedals; ability to adjust the saddle to accommodate growth; safety cover for the chain; stabilizers or the ability to fit them when needed (the last two features can also be classified as “could-haves” depending how essential they are for the child/parents)
Could have: bell or horn to alert others in proximity; attractive color of the bike; front suspension; Presta valves for inflating tires
Won’t have: valve caps to cover the tires valve; Bluetooth bike speaker
Even though it may seem strange not to have the pedals and the brakes in the “must have” category, in reality they are not mandatory for a child’s bike. By definition a bike is two-wheeled transportation device, so it must certainly have two wheels and a frame to link the wheels together, but everything else is subject to discussion and negotiation. For example, small kids can learn to ride a bike by simply using their feet, so no pedals and brakes are really needed. This simple example also shows that there is often a disconnect between expectations and requirements. People often have high level of expectations, but high expectations are different from must-have requirements which are mandatory and non-negotiable.
Let’s now look at the advantages and disadvantages of the MoSCoW method.
Pros of MoSCoW
- Simplicity. The MoSCoW method is one of the simplest prioritization techniques. It does not require searching for detailed data or making complicated calculations. So, it is easy to master and use because it is based on simple principles. Using this prioritization scheme in a product management context promotes mutual understanding between product people (product managers and product owners) and stakeholders. It is also a great method to resolve conflicts and to bring stakeholders to consensus. Prioritizing work using MoSCoW is fast and transparent.
- Agility for flexible scheduling and implementation. Since this prioritization method has no strict time limits for the implementation, except for the “must-have” category (items there should always go first and be implemented as soon as possible), it allows for flexible implementation timeframes per feature. Therefore, a team can easily adjust feature deliveries or releases on favorable terms based on agreement with customers/stakeholders.
Cons of MoSCoW
The MoSCoW technique is very simple, but such simplicity comes with some pitfalls.
- The technique lacks a clear consistency of implementation and lacks specific planning per feature. Even though priorities can be easily and quickly set, the MoSCoW method prioritizes the backlog items in four categories (in a similar fashion to the Kano model, covered in my previous article, which also prioritizes features in different categories), so it does not introduce any sequencing of features/backlog items and lacks specific planning. This makes it quite challenging for product people to decide on the exact priority of a feature compared to another one within the same category. At the end of the day, this drawback might put the entire release at risk.
- MoSCoW classification rules can be subjective and this creates imbalance between the absolutely required (must have or mandatory) and slightly desirable. Often, the blurred lines between categories make it hard to decide in which category a feature should go into, specifically when we talk about “must-have” and “should-have” lists. But it is sometimes also the case between “should-haves” and could-haves”. This happens due to the subjectivity of requirements. Therefore, features or stories allocated to the different categories should be approached with great thought and care and the chosen categorization should be agreed with (or well explained to) all stakeholders.
When to use the MoSCoW method
The MoSCoW method is probably the simplest and most widespread prioritization scheme for new product development, and more specifically for small products. But as we saw above, this technique also has its disadvantages and is not always effective. For instance, if you have a complicated backlog with many time-sensitive releases, consider choosing other prioritization method or complementing MoSCoW with another more accurate or comprehensive technique.
On the other hand, it is quite reasonable to use MoSCoW when prioritizing work for small (and not too complex) products, which does not have many technical limitations. The MoSCoW requirements help product people and teams take a strategic, orderly approach to prioritization. This method is great for avoiding wasted time, arguments and misdirection.
In my next article I will talk about the Eisenhower matrix. Meanwhile, if you want to know more about prioritizing using the MoSCoW method, please feel free to contact me.
About this article or just curious about working at BlinkLane? Contact Martin or take a look at our open vacancy .
References:
[1] Griffiths, M. (2012). PMI-ACP Exam Prep (2nd ed.). RMC Publications Inc.
[2] Agile Business Consoritum (n.d.). Chapter 10: MoSCoW Prioritisation. Retrieved from https://www.agilebusiness.org/page/ProjectFramework_10_MoSCoWPrioritisation
You are using an old version of Internet Explorer. We recommend updating your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Close ×

Department of Management and Entrepreneurship
Bachelor thesis, available bachelor thesis topics spring semester 2024.
If you want to write a Bachelor thesis at the Institute of Marketing and Management, Entrepreneurship Department, or are already writing one, you should know about the assignment of topics, design guidelines, the type of supervision, as well as requirements. Therefore, we have compiled tips and information that should make it easier for you to write your thesis.
Preconditions
To apply for a bachelor thesis at our department, students must have completed a ‘proseminar’ (preferably the “Proseminar in Management”).
Application Procedure
If you intend to write a thesis in management or entrepreneurship, take a look at the list of our currently available thesis topics. Read the relevant core literature, if indicated, to find a topic that is of interest to you.
The application window for the bachelor theses for the Spring Semester 2024 is open from Wednesday , December 20th, 2023 until Friday, February 9th, 2024.
While the topics will only be assigned after the application period has ended, we will inform you within 5 working days of your submission whether you will be able to complete your thesis with our institute or not.
Application Form
The online application form can be found here .
In your application form you will have to upload as a ZIP file:
- Your course achievements (Studienblatt) of bachelor studies
- Evaluation of equivalence of the Strategic Management course and/or Proseminar, if you did not attend these courses at the university of Bern
Spectrum of theses
Each year, the Department of Management oversees about 25-30 bachelor and master theses dealing with management or entrepreneurship matters. Literature studies about scientifically relevant topics, as well as empirical studies, and 'consulting–papers' relevant to practitioners can be composed. The institute proposes a list of topics. In agreement with the department, the treatment of one's own topic is also possible.
We encourage teamwork!
What selection criteria do you have?
Our selection criteria vary from semester to semester depending on the number of applicants, as well as on their individual track-record(s). Generally, we give preference to the students of higher semesters who have completed the courses “Proseminar in Management” and “Strategic Management”.
Do you assign topics on the first come – first serve basis?
No. The exact time of the application is not considered. The assignment of the topics is carried out after the application period ends.
Can I apply for a bachelor thesis at your Department if I have not attended “Proseminar in Management” or “Strategic Management” (yet)?
Yes. We invite students to apply even if they do not have all prerequisites. See also the question on selection criteria.
Can I attend “Proseminar in Management” and/or “Strategic Management” parallel to writing my bachelor thesis?
Yes. However, your chances of getting accepted for writing a bachelor thesis at our department are higher if you have already attended both courses. Also, if you are accepted your chances of succeeding are higher if you have already attended the “Proseminar in Management” and the course “Strategic Management”.
Can I offer my own topic?
Yes. In addition to your regular application (Application form plus uploads) you have to submit a short proposal of two pages where you present your topic, your motivation and at least five relevant literature references (as an orientation: see the description of writing a proposal in the guidelines on top of this site). You may put this short proposal into your ZIP file together with the other demanded attachments and upload it in the application form. Please note that we do not guarantee acceptance of your own topic and generally supervise theses, which lie within our own research interests.
Product Management
Dive into the world of making cool stuff with a Master's in Product Management ! Ever wondered how your favourite apps or gadgets came to be? With a master's in product management, you'll pick up the skills needed to conceptualise, develop and launch amazing products .
Rated 5 stars for our online learning, among the best in the world
WES Canada U.S. recognised: our grads can work/study in both countries
Globally recognised for our quality-assured digital education
Enhanced research opportunities help IU provide the very best to you
Our teaching and faculty meet European educational standards
Academically top ranked in Germany with 6 out of 25 categories won
Reaccredited until 2026 for our competency in teaching and research
Build the career you’ve always dreamt of
Apply by April 25th to secure your spot!*
Don’t let anything stand between you and your goals. Earn a career-centric, globally recognised degree, 100% online – and build the skills you need to succeed.
*You can start anytime.
Build the career of your dreams
Apply by 25th April and secure your spot !
Study on campus at IU and kickstart your career path in Germany . Network with students and experts to build your professional network, all while you earn your international degree!
Unfortunately your form could not be sent. Please try again.
Hang tight… We’re preparing your brochure and you’ll receive it in your email inbox soon.
We’re excited to help you make the right choice for your future. The brochure will give you more information on our study models and degree programmes, how to apply at IU, scholarship information, and more.
While you’re waiting, don’t forget to sign up for our free webinars and get your questions answered in real time by our Study Advisors.
Please enter just a few more details to complete your application today.
You can reach out to our Student Advisors simply by e-mail.
We will also be glad to help you on WhatsApp
You can reach our Student Advisory Service for free
Start your Master's in Product Management now
If you have a bachelor’s in product management, business administration, management, or a related business-related field and want to further your education in this field, our consecutive 120-ETCS master's in product management is a good fit for you.
How your studies are moving you forward:
- You will gain thorough knowledge of product management and its techniques, as well as expertise in management and leadership, marketing, and performance and strategy, so that you can comprehend product management as a whole.
- To specialize in areas like Digital Transformation and Product Management, Creative and Agile Methods, or Social Media Models, you take two elective modules.
- You are qualified for key specialist and management positions, such as product manager, product owner, product marketing manager, or product and business developer.
Your online campus degree summed up
Study at your own pace from anywhere in the world
According to our latest alumni survey
enrolled in Germany’s largest university
Overview of your Master's in Product Management
With a Master's in Product Management, you'll learn about the conception, development, and launch of innovative products. Pick up a comprehensive skill set to navigate the challenges of today's digital age. Hone your management skills, master market research techniques, and establish valuable industry connections. This program empowers graduates to take on pivotal roles in product development, marketing, and strategic planning - all of which are in high-demand and offer competitive salaries. Along with sustainability, you will also discuss issues like digitalisation, ethics, and internationality. Explore subjects such as product strategy, user experience design, and data-driven decision-making, all geared toward shaping product managers capable of creating impactful products .
Electives overview
In your 3th semester, you'll need to choose an elective module, which you can choose from one of the following modules:
Module guide
Online course schedule
Course schedule
Enhance your learning with AI
Work with AI
The AI revolution is here. We’ll help you lead it.
This programme offers an AI prompt engineering elective course, so you can:
- Develop the best practices for working with AI
- Explore the strengths and limits of current technology
- Build confidence in your ability to work with AI tools
Learn with AI
Enhance your learning with Syntea : an AI tutor at your service.
Ask any question related to your studies, and get answers based on the study contents, 24/7.
- Answers are routinely verified by human tutors
- Build personal study plan s based on Syntea’s feedback
- Coming soon - learn through dialogue: Socratic Teaching
Transform with AI
You don’t need to navigate the world of AI on your own. We’re here to guide you.
Develop your ability to work with AI in a positive, experienced setting.
- Study plans created by AI experts
- Benefit from being an early adopter of a revolutionary technology
- Graduate with skills that fit tomorrow’s job market
Each course in this study programme has a live teaching session
At IU, we want you to feel supported, and to give you the best learning experience possible.
In keeping with our mission, we now offer two-hour, monthly intensive live sessions in every course. The live events are recorded , so you can access them whenever you want. Each monthly session will cover all the course contents , so you only need to attend or watch it once.
Entry requirements
The admissions documents must be provided in English or German. If they were not issued in one of these two languages, a translation is required. If you need to translate your documents, we can help refer you to our trusted translation partners. You can find more details here .
General admission requirements
- Completed, undergraduate degree with 180 ECTS credits in Product Management, Business Administration, Management, Innovation Management, Entrepreneurship, Intrapreneurship, or other business related degree programs.
- Your degree must be from a state or state-recognised higher education institution/university
- You must have achieved a final grade of at least “satisfactory” or Grade C equivalent in your previous undergraduate degree
Further admission opportunities
Is your undergraduate degree not in the required subject field for this programme's 120 ECTS credits variation admission requirements? You can still apply! You'll have to take 2 specific courses at the start of your studies, and pass them successfully in order to continue with your studies. That way, you don't have to take an entrance examination, and can prove your skills while earning ECTS credits as part of your studies.
Scholarship programme
Apply for the scholarship programme and receive a discount on your tuition fees.
Please get in touch with our Study Advisory Team for more details.
English language skills
Depending on your personal circumstances, you might be required to provide proof of your English language proficiency. Your skills would need to match the B2 level of the Common European Framework (CEF).
We accept the following English language skills certificates*:
- TOEFL (minimum 80 points)* or
- IELTS (minimum Level 6)* or
- Duolingo English Test (minimum 95 points)*
- PTE Academics (minimum 59 points)* or
- Cambridge Certificate (minimum Grade B)*
Is English your native language, or have you graduated from an English-speaking school or university? Then you do not need to prove your English language proficiency.
Get in touch with our study advisors for more details.
*Proof must be provided before the start of the study and must not be older than five years.
Your Product Management career outlook
You can anticipate having a successful career across all industries as a product management professional with rewarding opportunities for moving up to a management position. Following graduation, you might work, for instance, as a...
Strategic Product Manager
You develop strategies and visions for cutting-edge products in your capacity as a strategic product manager. You lead interdisciplinary teams and collaborate closely with your stakeholders. Additionally, you will be in charge of portfolio management, the launch of new products, and budget planning.
Product Owner for Data-Driven Products
Product managers for data-driven products collaborate with data scientists and developers to implement innovative product concepts. If this is your chosen career path, you can anticipate an innovative workplace where agile methods are in demand. The use of customer and market data analysis will also be one of your tasks.
Technical Product Manager
Are you devoted to data science, cloud computing, blockchain, and other related fields? You should then begin your career as a technical product manager! In this role, you will create technical concepts in accordance with user-oriented standards. By doing this, you will be working at the intersection of the market, technology, and consumers.
This is what our students say
Vikrant Lokhande
MBA , India
Tokyo Ndela
MBA , South Africa
Nirupam Sakar
Online Study models & fees for your Master degree in Product Management
On campus study model and fees for your master degree in product management.
Depending on your personal or professional circumstances, you may wish to complete your studies as quickly as possible, or you may prefer a more flexible study programme that is less time-consuming. That’s why we offer part-time options for all our study programmes. This allows you to study alongside professional or personal commitments. We adjust your study fees based on your chosen time model.
Are you unable to finish your programme within the given time? No problem! If you realise that you need more time, you can simply switch to another time model with one months’ notice before the end of the month.
No registration or administration fees are charged when you apply for studying – you’ll only be charged once your studies have started. If you won’t be admitted to a programme because you do not meet the admission requirements, no fees will be charged.
At IU, we believe in full transparency – so there are no hidden fees . You only pay for your tuition and the one-time campus registration fee of €1,500.
No registration or administration fees are charged when you apply for studying – you'll only be charged once your studies have started. If you won't be admitted to a programme because you do not meet the admission requirements, no fees will be charged .
Duration 24 Months
Perfect for those who want to hit the ground running and learn at the fastest pace possible. Starting from:
Part-Time I
Duration 36 Months
Great for all-round talents who want to go full throttle in their studies but also keep up with other commitments. Starting from:
Part-Time II
Duration 48 Months
Ideal for students with a lot of work or family commitments. This plan also reduces monthly study costs. Starting from:
All our study programmes include the following benefits
- Teaching and study material
- Marking of your end-of-module exams
- Monthly live and recorded tutorials
- Use of the online campus
- Individual study coaching
- Online exams
- Career coaching
- Learn English for free
- Money back guarantee during 1st month
- On-campus tutorials, 2-3x week
- Access to all on-campus services
Recognition of previous achievements
Have you already completed a training course, studied at a university or gained work experience? Have you completed a course or a learning path through IU LinkedIn Learning , and earned a certificate? Then you have the opportunity to get your previous achievements recognised, and complete your studies at IU sooner.
- Save time: Skip individual modules or whole semesters!
Even before you apply for a study programme, we’ll gladly check whether we can take your previous achievements into account: 100% online, no strings attached. Simply fill in our recognition application form, which you can find under the content section of each study programme's webpage, and upload it via our upload section. You can also e-mail it to us, or send it via post.
Send an email to [email protected] to find out which previous achievements you can get recognised. You can get your previous achievements recognised during your studies.
Recognition files
Guide to recognition
Individual application for recognition
Why IU International University of Applied Sciences is the best choice
Schedule when you want to learn and study 100% online. At IU you have the possibility to complete your degree fully from home, whether full-time or part-time. You can even take your exams online whenever it suits you.
IU is accredited and certified with a seal of approval from the German Accreditation Council. All IU study programmes, materials, and services meet high internal and external quality standards, which are regularly reviewed and updated. We can also provide you with an official Europass Diploma Supplement once you graduate, to ensure that your degree is recognised anywhere in the EU.
We provide you with innovative learning tools, digital study material, tutorial videos, live teaching sessions, student advice and support. You also have 24/7 access to our large online library. Your tutors are always available to answer your questions. Our study coaches are also available to help at any time.
Our programmes provide you with essential theoretical knowledge and focus, above all, on practice-oriented studies designed to best prepare you for your future career. Thanks to our great variety of electives you can specialise in the specific areas that match your personal goals.
By combining in-person tutorials 2-3 times per week with 24/7 access to online study materials, you get to benefit from a more flexible study schedule. This allows you to work alongside your studies, or combine other activities, with relative ease.
We provide you with innovative learning tools, intimate campuses, easy access to lecturers, live teaching sessions, student advice services, and career support. You also have 24/7 access to our large online library. Your tutors are always available to answer your questions – and so are our study coaches.
Which masters degree makes me a product manager?
Our masters in product management is specifically designed to prepare you for roles in product management! In this programme, you'll learn the necessary skills and knowledge to excel in the product management field, and can apply for roles in areas ranging from engineering and marketing to business and innovation.
What is the qualification for masters in product management?
For this ms in product management programme, you will need to have completed an undergraduate degree from a recognised higher education institution or university.
Do product managers need a masters degree?
Product manager is a highly sought after position! So while having a master's degree may not be mandatory, it definitely gives you an upper hand. This degree can significantly enhance your management skills, market research abilities and not to mention provide you with industry connections through university community networking.
What is a master's in product management?
A masters in product management is an advanced degree programme focused on developing skills to create products successfully in the digital age. You'll learn a plethora of skills ranging from market research, business analytics, managerial skills, leadership skills, design strategy, marketing, product design and more. This degree prepares you for a role as a product manager.
You might also be interested in these study programmes
Master project management, master digital product management, master digital innovation & intrapreneurship, master management + majors, master international management, master engineering management.
Unfortunately, our services are not available in your country. For more information, please contact us via: [email protected]
Unfortunately, your search did not return any results
Try another search term, check the spelling or get in touch with our Study Advisory Team

- Aviation and Astronautical Sciences
- Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence and Data Science
- Construction and Facilities
- Critical Infrastructure
- Cyber & Information Security
- Cyberpsychology
- Engineering
- Engineering Technologies
- Intelligence and Global Security Studies
- Management of Technology
- Occupational Safety and Health
- Uncrewed Systems
- Doctoral Degrees
- Master's Degrees
- Bachelor's Degrees
- Online Programs
- Associate Degrees
- Certificates
- Minor Degrees
- Summer Programs
- STEM Events
- Webinars and Podcasts
- Master's
- Undergraduate
- Transfer Students
- Military and Veterans
- International Students
- Admissions Counselor
- Capitol Connections
- Accepted Students
- Project Lead the Way
- Builder Culture
- Campus Life
- Clubs and Organizations
- Centers and Labs
- Online Classes
- The Capitol Commitment
- Top Employers
- Co-ops and Internships
- Professional Education
- Find a Mentor
- Career Services
- Capitol Online Job Board
- Recruiters and Employers
- Why Capitol Tech
- At a Glance
- Mission, Vision and Goals
- Diversity, Equity and Inclusion
- Washington, D.C.
- Capitol History
- Capitol Partners
- News and Events
- Visitors/Campus
- Accreditation
- Recognitions & Awards
- Current Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Alumni & Giving
- News & Events
- Capitology Blog
- Maps / Directions

- Degrees and Programs
Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Product Management
- Request Information
Earn a doctorate in Product Management, meet the industry demand for technological expertise
Product Management has undergone a tremendous transformation from its original application and practice as a particular company’s management of the marketplace appeal of a single, commercial brand. Now, at its highest levels, Product Management has expanded to include the application of new technology, not as an option, but as an imperative to remain competitive and viable.
Capitol Technology University’s online PhD in Product Management will prepare you, the business professional, to meet the challenges and maximize the opportunities presented by these sweeping changes. Through this research-based, online doctorate, students engage quickly in research and publishing without the limitations inherent in traditional coursework models. Graduates will be prepared for a variety of leadership roles in business management.
Your expertise will be in high demand among companies seeking to introduce new technologies while mitigating the risk that can accompany such transformations. You’ll be able to deliver solutions that can lower costs, streamline processes, and ensure the highest quality as your organization competes in the global marketplace. Through this uniquely designed doctoral program, you can undertake research that is specific to your professional needs and complete your degree while maintaining your career.
As a doctoral student in Product Management, you’ll enter the program with a research idea and at least a committee chair. After enrollment, you’ll work with your chair and research committee to further develop your research proposal. You’ll then work independently to produce a meaningful body of original research of publishable quality. In the process, you’ll also gain valuable insight into the legal, political, ethical, and social dimensions of your field of study.
This is a research based doctorate PhD degree where you will be assigned an academic supervisor almost immediately to guide you through your program and is based on mostly independent study through the entire program. It typically takes a minimum of two years but typically three years to complete if a student works closely with their assigned academic advisor. Under the guidance of your academic supervisor, you will conduct unique research in your chosen field before submitting a Thesis or being published in three academic journals agreed to by the academic supervisor. If by publication route it will require original contribution to knowledge or understanding in the field you are investigating.
As your PhD progresses, you move through a series of progression points and review stages by your academic supervisor. This ensures that you are engaged in a process of research that will lead to the production of a high-quality Thesis and/or publications and that you are on track to complete this in the time available. Following submission of your PhD Thesis or accepted three academic journal articles, you have an oral presentation assessed by an external expert in your field.
Why Capitol?
Learn around your busy schedule
Program is 100% online, with no on-campus classes or residencies required, allowing you the flexibility needed to balance your studies and career.
Proven academic excellence
Study at a university that specializes in industry-focused education in technology fields, with a faculty that includes many industrial and academic experts.
Expert guidance in doctoral research
Capitol’s doctoral programs are supervised by faculty with extensive experience in chairing doctoral dissertations and mentoring students as they launch their academic careers. You’ll receive the guidance you need to successfully complete your doctoral research project and build credentials in the field.
Key Faculty

Dissertation Chair/Adjunct Professor
Career Opportunities
Market demand for product management
Those who earn a Doctor of Philosophy in Product Management pursue careers such as:
- Senior Vice President, Product Management
- Product Management Senior Scientist
- Vice President, Channel and Product Management
- Managing Director, Product Line
- Corporate Product Management Officer
- Product Management Senior Strategist
- Business Development Consultant
Degree Details
This program may be completed with a minimum of 60 credit hours, but may require additional credit hours, depending on the time required to complete the dissertation/publication research. Students who are not prepared to defend after completion of the 60 credits will be required to enroll in RSC-899, a one-credit, eight-week continuation course. Students are required to be continuously enrolled/registered in the RSC-899 course until they successfully complete their dissertation defense/exegesis.
The PhD program offers two degree completion requirement options.
- Dissertation Option: the student will produce, present, and defend a doctoral dissertation after receiving the required approvals from the student’s Committee and the PhD Review Boards.
- Publication Option: the student will produce, present, and defend doctoral research that is published as articles (3 required) in peer reviewed journals identified by the university and the student’s Committee. Students must receive the required approvals from the student’s Committee and the PhD Review Board prior to publication.
PhD in Product Management - 60 credits
Educational Objectives:
- Students will integrate and synthesize alternate, divergent, or contradictory perspectives or ideas fully within the field of Product Management.
- Prepare students to critically analyze existing theories in Product Management to draw data supported conclusions to move the field forward and support the attainment of desired outcomes.
- Prepare students to conceptualize, apply and integrate effective qualitative and quantitative research strategies in Product Management and to develop new information effectively.
- Prepare students to take a leadership role in a field of Product Management while employing the highest levels of ethics, analytics, decision analysis, and data visualization.
- Students will present scholarly work on Product Management via appropriate communication channels.
- Students will demonstrate advanced knowledge and competencies in Product Management.
- Students will execute a plan to complete a significant piece of scholarly research in Product Management.
- Students will evaluate how Product Management affects target populations in local and extended communities.
- Students will address the need for sustainability and Green products.
Learning Outcomes:
Upon graduation:
- Graduates will evaluate the legal, social, economic, environmental, and ethical impact of actions within Product Management and demonstrate advanced knowledge and competency to integrate the results in the leadership decision-making process.
- Graduates will demonstrate a mastery of an area of Product Management research, ethics of research, the stages of the research process, conceptualization and operationalization of research questions, data collection techniques, analytics, qualitative and quantitative methods, measurement, program evaluation research, and research proposal development.
- Graduates will demonstrate the highest mastery of traditional and technological techniques of communicating ideas effectively and persuasively within Product Management.
- Graduates will evaluate complex problems, synthesize divergent/alternative/contradictory perspectives and ideas fully, and develop advanced solutions to Product Management challenges.
- Graduates will contribute to the body of knowledge in the study of Product Management.
- Graduates will assess the impact of modern Product Management nationally and globally.
- Graduates will demonstrate a mastery of the concepts of probability, common distributions, statistical methods, data analysis, analysis of contingency tables, generalized linear models, linking logit and log-linear methods with generalized linear model, analysis of discrete data using state-of-the-art programming languages, and data visualization techniques within Product Management.
Tuition & Fees
Tuition rates are subject to change.
The following rates are in effect for the 2024-2025 academic year, beginning in Fall 2024 and continuing through Summer 2025:
- The application fee is $100
- The per-credit charge for doctorate courses is $950. This is the same for in-state and out-of-state students.
- Retired military receive a $50 per credit hour tuition discount
- Active duty military receive a $100 per credit hour tuition discount for doctorate level coursework.
- Information technology fee $40 per credit hour.
- High School and Community College full-time faculty and full-time staff receive a 20% discount on tuition for doctoral programs.
Find additional information for 2024-2025 doctorate tuition and fees.
Need more info, or ready to apply?
Explore your training options in 10 minutes Get Started
- Graduate Stories
- Partner Spotlights
- Bootcamp Prep
- Bootcamp Admissions
- University Bootcamps
- Coding Tools
- Software Engineering
- Web Development
- Data Science
- Tech Guides
- Tech Resources
- Career Advice
- Online Learning
- Internships
- Apprenticeships
- Tech Salaries
- Associate Degree
- Bachelor's Degree
- Master's Degree
- University Admissions
- Best Schools
- Certifications
- Bootcamp Financing
- Higher Ed Financing
- Scholarships
- Financial Aid
- Best Coding Bootcamps
- Best Online Bootcamps
- Best Web Design Bootcamps
- Best Data Science Bootcamps
- Best Technology Sales Bootcamps
- Best Data Analytics Bootcamps
- Best Cybersecurity Bootcamps
- Best Digital Marketing Bootcamps
- Los Angeles
- San Francisco
- Browse All Locations
- Digital Marketing
- Machine Learning
- See All Subjects
- Bootcamps 101
- Full-Stack Development
- Career Changes
- View all Career Discussions
- Mobile App Development
- Cybersecurity
- Product Management
- UX/UI Design
- What is a Coding Bootcamp?
- Are Coding Bootcamps Worth It?
- How to Choose a Coding Bootcamp
- Best Online Coding Bootcamps and Courses
- Best Free Bootcamps and Coding Training
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Community College
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Self-Learning
- Bootcamps vs. Certifications: Compared
- What Is a Coding Bootcamp Job Guarantee?
- How to Pay for Coding Bootcamp
- Ultimate Guide to Coding Bootcamp Loans
- Best Coding Bootcamp Scholarships and Grants
- Education Stipends for Coding Bootcamps
- Get Your Coding Bootcamp Sponsored by Your Employer
- GI Bill and Coding Bootcamps
- Tech Intevriews
- Our Enterprise Solution
- Connect With Us
- Publication
- Reskill America
- Partner With Us
- Resource Center
- Bachelor’s Degree
- Master’s Degree
Best Doctorates in Product Management: Top PhD Programs, Career Paths, and Salaries
The demand for professionals skilled in product management has grown rapidly in recent years. Companies have realized that the creation of a successful product is an investment that requires skillful leadership and management. Having a PhD in Product Management gives you an advantage when pursuing desirable, high-paying product management jobs.
A product management PhD can lead to a career as an industry expert. It can also open the door to higher salaries. This guide offers a look at the best PhDs in Product Management as well as what you can expect for a PhD in Product Management salary.
Find your bootcamp match
The best doctorates in product management will help students earn an excellent salary following graduation and become great product managers in their chosen fields or enter the world of academia as skilled teachers and researchers.
What Is a PhD in Product Management?
A PhD in Product Management is a postgraduate degree that prepares students to become experts at managing products, usually in retail environments. Students will be required to complete advanced courses in product management before graduating as well as conduct original research in the field and produce and defend a thesis.
How to Get Into a Product Management PhD Program: Admission Requirements
The main requirement to get into a product management PhD program is a bachelor’s or master’s degree from an accredited institution. You would need to prove completion of the degree program and provide transcripts from each institution you previously attended. You will also likely have to present letters of recommendation.
In addition, the majority of PhD in Product Management programs require prospective students to take a standardized test such as the Graduate Record Examinations (GRE) or Graduate Management Admission Test (GMAT). Some graduate schools require students to have work experience so you must provide a resume. International students will also have to submit English proficiency test scores.
PhD in Product Management Admission Requirements
- Bachelor’s or master’s degree from an accredited university or college
- Transcripts from each post-secondary institution attended
- GMAT/GRE scores
- Letters of recommendation
- Resume detailing educational and professional experience
- English proficiency exam scores
Product Management PhD Acceptance Rates: How Hard Is It to Get Into a PhD Program in Product Management?
It is hard to get into a PhD program in product management, especially the ones at prestigious universities. Many well-known and accredited schools have rigid admissions for PhD applicants and are highly selective. Excelling in your undergraduate or master’s degree may give you a better chance of gaining acceptance.
How to Get Into the Best Universities
[query_class_embed] how-to-get-into-*school
Best PhDs in Product Management: In Brief
Best universities for product management phds: where to get a phd in product management.
The best universities for product management PhDs have been accredited by a recognized accrediting body. Since PhD programs rely heavily on research and teaching work, the best universities in product management also focus on research. Below are 10 of the top universities to consider if you want to pursue a PhD in Product Management.
Arizona State University (ASU) is one of the country’s top universities offering high-quality degree programs. It features over 450 graduate degree programs and certificates and is home to some of the country’s best researchers in various fields of study. ASU is also one of the fastest-growing research institutions in the United States.
PhD in Business Administration with a Concentration in Management
Arizona State University’s PhD program in business administration with a concentration in management will give students a chance to gain current and relevant knowledge on organizational behavior and strategic management. It is offered under ASU’s W.P. Carey School of Business and places emphasis on research and teaching.
PhD in Business Administration with a Concentration in Management Overview
- Program Length: 5 years
- Acceptance Rate: N/A
- Tuition and Fees: $6,457/semester (in state); $12,699/semester (out of state); $15,575/ semester (international)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Federal financial aid, fellowships and awards, teaching and research assistantships, loans
PhD in Business Administration with a Concentration in Management Admission Requirements
- Bachelor's or master's degree from a regionally accredited institution
- Minimum cumulative GPA of 3.00
- Graduate admission application and application fee
- GMAT scores
- Official transcripts from previously attended schools
- 3 letters of recommendation
- Personal statement
- Resume with an employment summary
- Proof of English proficiency (international students)
Carnegie Mellon University is a private research university with a student body of over 14,500. It offers outstanding graduate and undergraduate education and research via seven schools and colleges. The university has a strong focus on interdisciplinary work, as many of its courses combine multiple disciplines.
PhD in Operations Management
The PhD in Operations Management from Carnegie Mellon University is designed to provide students with the tools they need to develop scientific solutions to the problems currently faced by operations managers. You will be dealing with a broad range of topics, such as supply chain management, new product development, inventory control, and others.
PhD in Operations Management Overview
- Program Length: 2-5 years
- Acceptance Rate: 3-5%
- Tuition: $47,000/year
- PhD Funding Opportunities: The program is fully funded by the university through the William Larimer Mellon Fellowship, except for the annual activity and transportation fees; other fellowship programs and scholarships
PhD in Operations Management Admission Requirements
- Scanned copies of all transcripts from previous institutions attended
- 3 completed Tepper School of Business evaluation forms
- Application fee of $90
- TOEFL, DET, or IELTS (non-native English speakers)
Located in New York City, Columbia University is one of the most distinguished research universities in the US. This Ivy League university has three undergraduate schools, 13 graduate and professional schools, and more than 100 research centers and institutes.
PhD in Management
Columbia University’s PhD in Management is offered at the Columbia Business School and focuses on basic social science knowledge and research. Doctoral students are trained for academic research careers and select one of three subfields: organizational behavior, organizational theory, and strategy.
PhD in Management Overview
- Program Length: 5-6 years
- Acceptance Rate: Less than 5%
- Tuition and Fees: $38,688/semester (full residence of more than 6 points)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Doctoral candidates are fully funded for their first four years; merit-based fellowships, assistantships, tuition exemption, research grants
PhD in Management Admission Requirements
- Online application
- Official transcripts
- Application fee of $100
- 2-5 letters of recommendation
- Enrollment commitment deposit
- TOEFL/IELTS (international applicants)
Duke University is a private research university in North Carolina. It is home to 16,780 students, including 6,789 undergraduates and 9,991 graduate and professional students. In the Fall of 2021, Duke University conferred 4,007 graduate and professional degrees.
Duke University’s PhD in Operations Management is offered via the Fuqua School of Business. It focuses on training doctoral students to produce original research in the field. The doctoral program aims to provide the skills and tools necessary to prepare students for academic careers or work as consultant product managers.
- Program Length: 4-5 years
- Acceptance Rate: 2-8%
- Tuition and Fees: $69,775/year (years 1-3); $17,775/year (years 4-6)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: The graduate school covers the tuition and fees for students’ first five years; full or partial scholarships, fellowship stipends, training programs, and research, graduate, and teaching assistantships
- Bachelor’s degree from an accredited institution
- Transcripts from each undergraduate and graduate institution attended
- 3 letters of recommendation
- Statement of purpose
- Undergraduate GPA
- English language proficiency test (nonnative English speakers)
Georgia Institute of Technology started as a trade school. When the school began to focus on advanced technological and scientific research, it changed its name to reflect these efforts to solve real-world problems. Today, Georgia Tech is one of the largest industrial and engineering research agencies in the South, with more than 100 interdisciplinary research units.
The PhD in Operations Management at Georgia Tech is offered through the Scheller College of Business. It is a research-oriented program that trains students for radical innovation and emphasizes learning outside the classroom. You will be using a wide variety of research methods, including modeling, empirical, and behavioral laboratory experiments.
- Acceptance Rate: 21%
- Tuition: $586/credit (in state); $1,215/credit (out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Research assistantships, teaching assistantships, fellowships, outside sponsorships, veteran benefits, tuition waivers
- Undergraduate (and, if applicable, graduate) overall GPA
- Essay
- Transcripts from previous institutions attended
Harvard University is an Ivy League research university established in 1636. It is one of the oldest institutions of higher learning in the United States and one of the world's most prestigious universities. There are 35,276 students studying at the school but getting into Harvard can be difficult.
PhD in Technology and Operations Management
Harvard Business School's PhD in Technology and Operations Management offers students the opportunity to pursue their interests in various disciplinary areas. The program is designed to help students develop valuable skills for organizations across various industries. Students are trained in multiple disciplines, including operations research, operations management, and economics.
PhD in Technology and Operations Management Overview
- Acceptance Rate: 4%
- Tuition and Fees: $46,200/year
- PhD Funding Opportunities: The program is fully funded for five years
PhD in Technology and Operations Management Admission Requirements
- Online application form
- Resume
- Statement of purpose
- Transcripts
- $105 application fee
- Writing sample (optional, not more than 10 pages)
- TOEFL/IELTS scores (non-native English speakers)
Founded in 1831, New York University is one of the most prominent research universities in the world. NYU is home to more than 65,000 students and undertakes nearly $1 billion in research every year. In 2021, it had 18,300 graduate and professional students enrolled in its degree programs.
New York University’s PhD in Operations Management is offered through the Leonard N. Stern School of Business. Doctoral students will have sufficient training in operations management and operations research and take core courses in optimization theory, stochastic processes, and data science.
- Tuition and Fees: Fully funded, except for a small portion of registration fees (currently $275/semester)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: NYU Stern PhD programs are fully funded, The Fred Renwick Doctoral Fellowship Program
- Essay (optional)
- Letters of recommendation
- GRE (preferred)/GMAT scores
- Official transcripts for the institutions included in your online application
- Application fee of $100
Northwestern University is a research university that is home to more than 50 university research centers and 90 school-based centers. It has a total of $893 million in annual research awards in various areas such as neuroscience, nanotechnology, biotechnology, and drug discovery.
The PhD in Operations Management at Northwestern University is offered through the Kellogg School of Management. Students will be trained to evaluate strategic issues when it comes to operations design and the tactical problems of executing processes so that they can be successful in both business and engineering.
- Program Length: Approximately 5.5 years
- Acceptance Rate: 13%
- Tuition: $18,689/quarter
- PhD Funding Opportunities: The PhD program is fully funded for five years, teaching and research assistantships, tuition scholarships
- Bachelor’s degree from a regionally accredited institution
- Transcripts from each school you attended
- “Courses Taken” form
- GRE/GMAT scores
- Application fee of $95
Founded in 1801, the University of South Carolina is an innovative, inclusive public institution that continues to be recognized as one of the finest research universities in the nation. In 2021, it had 35,388 students enrolled, with 6,726 graduate students and 1,881 professional students. It is recognized by the Carnegie Foundation as an R1 “very high research activity” institution.

"Career Karma entered my life when I needed it most and quickly helped me match with a bootcamp. Two months after graduating, I found my dream job that aligned with my values and goals in life!"
Venus, Software Engineer at Rockbot
PhD in Production/Operations Management
The PhD in Production/Operations Management at the University of South Carolina prepares students for careers in university teaching and research. It is offered through the Darla Moore School of Business and is designed for students or product managers who want to pursue an academic career in research, business, and government.
PhD in Production/Operations Management Overview
- Tuition and Fees: $6,867/semester (full time, in state), $572.25/credit (part time, in state); $14,880/semester (full time, out of state), $1,240/credit (part time, out of state)
- PhD Funding Opportunities: 100% tuition coverage for all courses approved on the student’s Program of Study, plus graduate assistantships, PhD Scholars Program, UofSC Rising Star Fellowship program
PhD in Production/Operations Management Admission Requirements
- GMAT/GRE scores
- TOEFL/IELTS/PTEA
- At least 2 letters of recommendation
The University of Texas at Austin is home to over 52,000 students and 3,000 teaching faculty. It offers programs across its 18 colleges and schools. The university has continuously proved itself as a vital component of the state through its leading research, which attracts more than $650 million in funding annually.
PhD in Information, Risk, and Operations Management
The University of Texas at Austin’s PhD in Information, Risk, and Operations Management under the McCombs School of Business focuses on business applications. Students can choose to specialize in data science, information systems, operations management, or statistics. Students in operations management are trained to use analytical and empirical methods for strategic operational issues.
PhD in Information, Risk, and Operations Management Overview
- Program Length: 4-6 years
- Tuition and Fees: See school’s tuition tables
- PhD Funding Opportunities: Teaching assistantships, research assistantships, fellowships, special grants, assistant instructor appointment, federal loans
PhD in Information, Risk, and Operations Management Admission Requirements
- GRE/GMAT test scores
- Bachelor’s degree
- 3.0 GPA
- Letters of reference
- Personal statements
- Application fee of $65 (US residents)/$90 (International)
- Department application form
- TOEFL/IELTS (non-native English speakers)
Can You Get a PhD in Product Management Online?
Yes, you can get a PhD in Product Management online. Various schools offer this doctoral degree online, such as Capitol Technology University, Indiana State University, Walden University, Sullivan University, and Bellevue University.
Best Online PhD Programs in Product Management
How long does it take to get a phd in product management.
In general, it takes four to five years to complete a PhD in Product Management. However, this can vary based on the program you choose and whether it is a full-time or part-time program. Your specific school and program may also have requirements regarding how long it takes to complete your degree.
Most people who complete a PhD in Product Management program choose to do so through full-time study over four years, but it is possible to do it part-time over six years. This includes time spent completing coursework, conducting research, writing papers, and preparing for your qualifying exam and dissertation defense.
Is a PhD in Product Management Hard?
Yes, a PhD in Product Management is hard. The requirements for admission to the program are numerous and include a bachelor’s degree from an accredited university, letters of recommendation, a statement of purpose, and standardized test scores. Schools offering PhD programs in product management are very selective and only accept a handful of students.
The program itself requires rigorous training and a significant commitment from students. Students will have to complete unique research on a topic related to their field of study, which requires a lot of focus and time because conducting experiments and analyzing data sets is required.
How Much Does It Cost to Get a PhD in Product Management?
It costs an average of $19,314 per year in tuition and fees to get a PhD in Product Management , according to the National Center for Education Statistics. However, this number will depend on the grad school you attend. A PhD in Product Management offered by public schools typically costs $12,171 per year, while private institutions’ annual tuition and fees average $25,929.
How to Pay for a PhD in Product Management: PhD Funding Options
The PhD funding options that students can use to pay for a PhD in Product Management include teaching and research assistantships, tuition scholarships, fellowship programs, or loans. Many universities offer full tuition and fees funding for part or all of the PhD program, and sometimes even cover students’ housing costs.
Best Online Master’s Degrees
[query_class_embed] online-*subject-masters-degrees
What Is the Difference Between a Product Management Master’s Degree and PhD?
The difference between a product management master’s degree and a PhD is the education offered and the career options available for students after graduation. Graduates of both programs will have the opportunity for a successful career in product management in the corporate world, with additional opportunities in academia for PhD holders.
A Master’s Degree in Product Management is intended for those seeking a career outside of academia. Graduates can become product managers and will have a considerable advantage in the job market.
A PhD in Product Management does not necessarily prepare students for a product manager role. It focuses on the experimental methods for the product development process, managing innovative products, and other strategic operations. The program will prepare you for a research or teaching career through independent study.
Master’s vs PhD in Product Management Job Outlook
Master’s Degrees and PhDs in Product Management will help you gain a competitive edge in the job market. Those with a master’s degree can find jobs as product managers, economists, and instructional coordinators in different industries.
Those with a PhD in Product Management can land top executive roles, such as business managers, in which they will develop strategies and oversee budgets. However, most PhD graduates in product management have positions in the academic world as professors. You can also become a researcher for various industries and organizations.
Difference in Salary for Product Management Master’s vs PhD
A doctorate holder in product management can expect to earn about $121,000 annually , according to PayScale. Jobs for these graduates include chief executive officer, vice president of operations, and director of a department or team. Meanwhile, students who graduate with a product development master’s degree earn an average of $94,000 a year and work in positions such as senior manager or program manager.
Related Product Management Degrees
[query_class_embed] https://careerkarma.com/blog/online-product-management-courses/ https://careerkarma.com/blog/best-product-management-masters-degrees/ https://careerkarma.com/blog/best-schools-for-product-management/
Why You Should Get a PhD in Product Management
You should get a PhD in Product Management because you will gain a competitive edge to become a leader in the field of product management. This advanced degree will help your career, especially if you want to switch from the corporate world to the academic world. Below are five reasons why you should get a PhD in Product Management.
Reasons for Getting a PhD in Product Management
- Develop your critical thinking capabilities. The vast amount of research involved in earning a PhD in Product Management will help you think independently and intensively. A PhD encourages active learning so that you can apply new and exciting methods and solutions for organizations.
- Hone your skills and expertise. A PhD in Product Management will teach you new skills and strategies for managing and developing products. This includes new and advanced statistical methods for analyzing relevant factors such as consumer behavior in order to build strong market strategies.
- Become a scholar-practitioner. A PhD will help give you the authority and confidence to become a leader in your field. This may happen through writing a doctoral dissertation and other research-based articles and getting them published in academic journals and being invited to present at academic conferences.
- Access higher salaries. Becoming more skilled and knowledgeable in your field will bring you more opportunities for a higher salary. Many businesses do not hesitate to pay higher wages to individuals with postgraduate degrees, and you can be confident in asking for better compensation too.
Getting a PhD in Product Management: Product Management PhD Coursework

Getting a PhD in Product Management requires rigorous training and coursework. Doctoral degree programs require that students take advanced core courses and electives. Aside from this, some schools will require you to attend doctoral seminars and conferences. Below are some of the more common requirements when pursuing a PhD in Product Management.
Research Writing
For many students, their thesis or dissertation will be the most taxing, complex piece of writing they ever undertake. Through a focus on the mechanics of writing, with tips for research-based papers, this course helps students turn months’ or even years’ worth of research into a compelling piece of writing ready for publication.
Stochastic Foundations
This course teaches stochastic foundations and processes for application in the business field. Students learn about various modeling concepts for financial investments. They are trained in completing competitive analyses of queuing systems and other analysis processes to help business stakeholders make sound decisions.
Advanced Optimization
The advanced optimization course will help students gain an extensive array of optimization techniques for complex decision-making and problem-solving. Students will be using modeling concepts and applications of linear, nonlinear, and dynamic programming models.
Economics or Microeconomics
Economics or microeconomics will help product managers analyze the relationship between businesses and the markets with which they interact. This course trains PhD students in consumer psychology and psychological processes so that businesses and internal stakeholders can make informed decisions regarding the innovation of their products or services.
Dynamic Programming
This course teaches PhD students how to simplify decision-making regarding complex problems by turning them into a series of smaller, simpler problems. Students will study examples that follow a general optimization framework and then think creatively to apply that framework to other problems affecting businesses.
Best Master’s Degrees
[query_class_embed] *subject-masters-degrees
How to Get a PhD in Product Management: Doctoral Program Requirements
In order to get a PhD in Product Management, you have to satisfy all of the doctoral program requirements. Many PhD programs are fully funded but require you to maintain good academic standing. You will also be required to complete advanced coursework, teach at the undergraduate level, take a comprehensive exam, conduct original research, and write and defend a thesis.
Doctoral students are expected to maintain a minimum grade point average in order to remain in good academic standing and receive program funding. You also have to complete all coursework, both courses core and electives, and other degree requirements by the deadlines provided.
Doctoral students are often required to serve as teaching or research assistants while pursuing their PhD in Product Management. Most postgraduate students are preparing for an academic career, and this requirement provides great training to help them learn the teaching skills they will need.
Students will be required to take a comprehensive exam once they have completed the core coursework in product management. The exam will focus on course content and will measure students’ overall knowledge of the field.
Some programs, like the one at Northwestern University, require the submission of a research paper before the dissertation. You will be responsible for consulting with an advisor throughout the process who will also approve the paper. This will help prepare you to write your dissertation.
You will be required to present a thesis or dissertation proposal usually by the end of your third year. This is the first step to publishing an original and significant piece of research, which is one of the most important requirements of a PhD program in product management.
The most important requirement in order to get a PhD in Product Management is a thesis or dissertation. This is a publishable research paper that requires the approval of the department. You will have to successfully defend your thesis in an oral exam.
Potential Careers With a Product Management Degree
[query_class_embed] how-to-become-a-*profession
PhD in Product Management Salary and Job Outlook
With a PhD in Product Management you have a good chance of making a six-figure salary shortly after graduating. The degree also gives you access to the highest-ranking jobs in a company, like CEO, with an average salary of $179,520, according to PayScale. The job outlook is also good for doctoral degree holders in this field, with higher-than-average growth expected for most positions.
What Can You Do With a PhD in Product Management?
With a PhD in Product Management, you can have a successful career in the academic world or in business. You can become a scholar or professor or a product manager or top executive in various industries. Below are the best jobs for those with a PhD in Product Management.
Best Jobs with a PhD in Product Management
- Chief Executive Officer
- Finance Manager
What Is the Average Salary for a PhD in Product Management?
The average salary for a PhD in Product Management is $121,000, according to PayScale. You can work as a professor or researcher in the academic world, or you can pursue high-paying jobs in the industry like chief executive officer, economist, or financial manager.
Highest-Paying Product Management Jobs for PhD Grads
Best product management jobs with a doctorate.
The best product management jobs with a doctorate are high paying. While some of these jobs do not necessarily demand that someone have a PhD, getting one will open many more doors of opportunity. Below are five of the highest-paying jobs in product management and related fields.
The chief executive officer (CEO) of a company is the highest-ranking executive in the organization. The CEO is responsible for managing company operations and serves as a spokesperson for the company. They represent the interests of stakeholders to outside parties such as investors and customers.
- Salary with a Product Management PhD: $179,520
- Job Outlook: 8% job growth from 2020 to 2030
- Number of Jobs: 247,100
- Highest-Paying States: District of Columbia, Hawaii, Washington, South Dakota, Massachusetts
Financial managers control the finances of a business or organization. They are responsible for analyzing data and advising senior managers on certain company decisions such as ways to maximize profits. They are often known as advisors to top executives, who rely on them for advice on how to spend company funds.
- Salary with a Product Management PhD: $131,710
- Job Outlook: 17% job growth from 2020 to 2030
- Number of Jobs: 64,200
- Highest-Paying States: New York, Delaware, New Jersey, Colorado, District of Columbia
Economists study and analyze the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Economists research economic issues for businesses, governments, and individuals. They may also be called upon to conduct surveys and collect data, analyze data using mathematical models, statistical techniques, and software, and make policy recommendations.
- Salary with a Product Management PhD: $105,630
- Job Outlook: 13% job growth from 2020 to 2030
- Number of Jobs: 1,600
- Highest-Paying States: New York, District of Columbia, California, New Hampshire, Illinois
Social scientists can work for a variety of different companies and educational or governmental institutions. The goal of their work is to discover new information about the way humans behave. They analyze data using software and summarize it using tables, graphs, and factsheets.
- Salary with a Product Management PhD: $80,890
- Job Outlook: 4% job growth from 2020 to 2030
- Number of Jobs: 1,200
- Highest-Paying States: District of Columbia, Maryland, New York, Idaho, Iowa
Professors are typically employed by colleges, universities, and other institutions of higher education. They instruct students in a variety of academic subjects beyond high school, and they may also conduct research and publish papers based on their findings.
- Salary with a Product Management PhD: $79,640
- Job Outlook: 12% job growth from 2020 to 2030
- Number of Jobs: 139,600
- Highest-Paying States: California, Rhode Island, New Hampshire, New York, Maryland
Is a PhD in Product Management Worth It?
Yes, a PhD in Product Management is worth it. A Doctoral Degree in Product Management is a great investment for professionals who want to become product managers . You will learn and practice new skills, which will help you get ahead in your field. In addition, having a PhD can help open the door to careers in research or in teaching at the postsecondary level.
Pursuing this degree requires a lot of hard work and dedication on your part, which means that by the time you finish, you will be prepared to take on leadership roles in product management within your company or organization.
A PhD in Product Management will also give you more opportunities for employment than someone without one. You will likely be able to earn more money with this advanced degree because employers will be willing to pay more for someone with such extensive experience and knowledge in their field.
Additional Reading About Product Management
[query_class_embed] https://careerkarma.com/careers/product-management/ https://careerkarma.com/blog/how-to-get-a-job-in-product-management/ https://careerkarma.com/blog/how-to-become-a-product-manager/
PhD in Product Management FAQ
No, it is not necessary to get a master’s degree before pursuing a PhD in Product Management. However, earning a master’s degree first could give you a chance to finish the PhD faster if the school allows you to apply some of the credits you earned during your master’s program toward the PhD.
Many product managers work in tech companies. Some of the top companies hiring product managers are Google, Adobe, Microsoft, and Cisco Systems.
Yes, product management is a good career path. According to Glassdoor, product manager is one of the top 10 jobs for 2022 . It scores a four-out-of-five job satisfaction rate, which makes it a very rewarding career.
Earning a PhD will help you gain effective problem-solving skills along with very extensive research skills. You will also become familiar with advanced marketing and finance skills and knowledge, which is beneficial if you wish to become a product owner or do other product management for a business organization.
About us: Career Karma is a platform designed to help job seekers find, research, and connect with job training programs to advance their careers. Learn about the CK publication .
What's Next?
Get matched with top bootcamps
Ask a question to our community, take our careers quiz.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *


MoSCoW prioritization of the product backlog
Moscow backlog prioritization.
Prioritization is probably the most discussed part of development processes. Product backlogs are often quite complex with hundreds of requirements. How to find user stories in your story map which you should start developing first?
Traditional approach
The approach of traditional processes is simple. You have high, medium, low priorities. Ok, for some organizations it is still not enough so they have priorities on the scale of 0 to 10.
But do such priorities help deliver the most important and most valuable thing at the same time?
In agile, we want to support the pull principle. We want to let our developers pull the next requirement, develop it, deliver it. Then continue to the next one. So, in Agile we need a line of requirements. Agile processes and frameworks focus on the delivery of valuable stuff first. This is fine; however, there is a necessity to consider other perspectives as well. There are two kinds of companies.
If you want to prioritize and be agile, you can’t be just one of the types. You have to be company following both of them and even more .
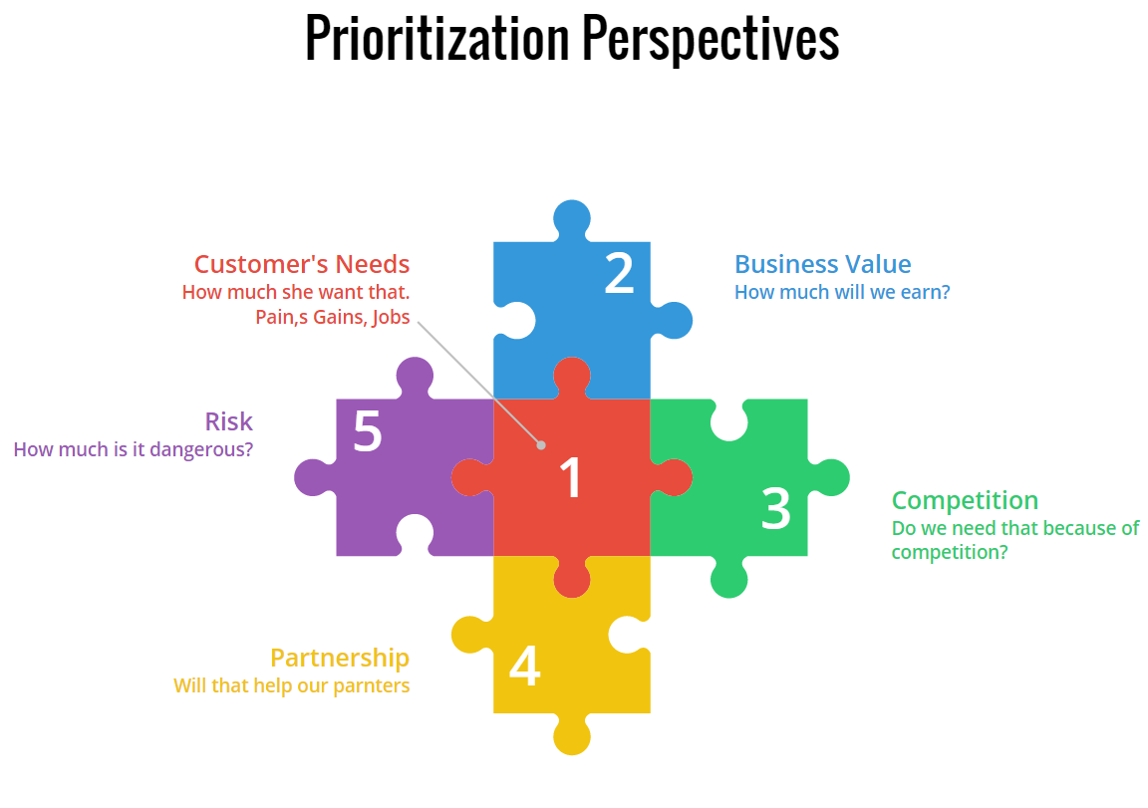
Customers’ perspective
In ScrumDesk we prefer to consider the customer’s perspective first. The idea is that a satisfied customer is a driver of further changes and success of the product itself . A satisfied customer is willing to improve the product not just by social marketing, by new ideas, but in our case even by the development of the product itself.
As the product owner, the first thing you have to understand is who your customer/user is. You need to understand and describe her space, her context, her jobs, the pains or gains she is looking for.
The best part is just coming. Based on a more than 10 years old survey done by Scot Ambler, 45% of functionalities are NEVER, NOT ONCE, used. Only 7% are used always. Plus 13% very often.
So, why develop something that customers will not use? You just spent the life of your colleagues! Common! The answer is NO! Now MoSCoW prioritization comes to help.

Based on that you should be able to decide if a feature is:
- Must – a heart is a “must”. Without it, there is no live organism. What is a must in your application?
- Should – a hand is “should”. Without it is hard. But you can survive even without a hand. Well, in most cases.
- Could – hair is “could”. It is fine to have them, you even look nicer, but you will definitely survive without them
- Won’t – unnecessary waste. Btw, is there anything “won’t” in a body?
How to estimate MoSCoW values in 7 steps?
- As a Product Owner, try to be in the skin of your customer. There might be multiple types of them, so choose one, or some group of them.
- If you were him, will the feature be a must, should, could, or won’t?
- Forget about the time of development, forget about effort. It is just about customer and feature.
- What if this feature was not a must, but should? Would the customer realize that?
- What if the feature was could and not should? Would the customer realize that?
- Try to make it less “must”. Remember 7% features used always.
- Compare requirements to each other. Repeat a couple of times.
Let’s say your backlog looks like this:
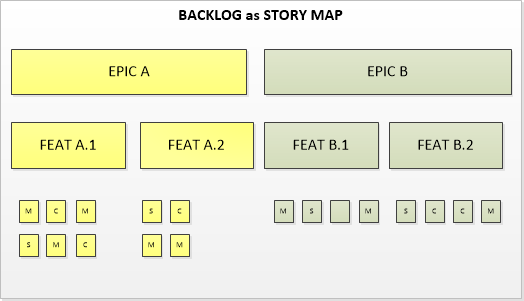
After MoSCoW prioritization you should have a line of requirements ordered by MUST, SHOULD, COULD values. This might be done in ScrumDesk PLAN view
How to manage MoSCoW in ScrumDesk ?
To set the value to backlog item you need just click it (in any view, either STORY MAP , BACKLOG , PLAN or WORK ) to access details in the side view. Prioritization fields are displayed below the title of the backlog item. The first one is MoSCoW.
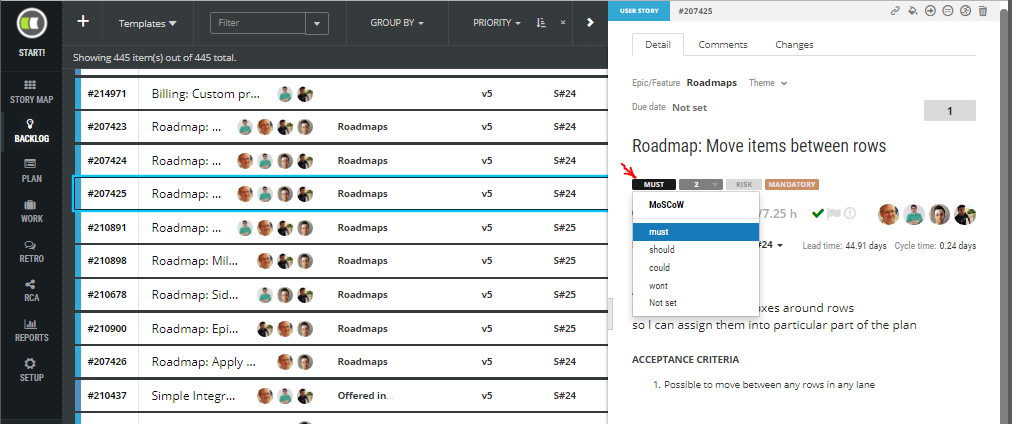
Value can be visible on cards in STORY MAP.
Once the value is entered, you can filter and group items based on it all ScrumDesk views, i.e. in the product backlog.
However, you are not done with prioritization in this step. What about business value? More to follow…
< Print physical cards | Content | Agile prioritization based on Business value >

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Suggestions about bachelor thesis about product management. Hello, I am a student in a Information Technolgoy program in my university and I will be writing my bachelors thesis this summer. My current plan is to start working as web developer / programmer in the next fall.
2012-02-05. We currently have plenty of Bachelor and Master Thesis opportunities available that focus on product management. Specifically, these are case-writing theses. In such a thesis, you will work with an industry partner (and us) to analyse a specific situation that the industry partner once faced. Typically, that situation was about ...
This thesis has found that product management is understood on two main levels and that the practice comprises both consistency and inconsistency on an inter-organisational level. Findings suggest that shared identity, strong commitment, cues, metaphors and expectations have influenced consistent ...
product is finally launched (Annacchino, 2003; Trott, 2008). New or upgraded products are launched into the market on a daily basis, but successful new product introduction is hard to achieve and the failure rate is significantly high (Crawford, 1977). New product performance is measured by financial objectives, market share
Theses/Dissertations from 2020. PDF. The Effects of Product Recalls on Competitors' Market Value and Recalling Firm's Reputation, Dong Liu. PDF. Corporate Brand Impact on Sales / Revenue Per Share, Brad A. Puckey. PDF. Competition in Upstream Humanitarian Supply Chain: Investigation of Food Banks, Iana Shaheen.
On this page you will find suggested topics by the Research Group of Technology and Innovation Management for bachelor and master theses, subdivided into topic areas. If you want to write your thesis on a topic of your own choice or in a subject area not listed below, you are welcome to send us an unsolicited application (including an exposé ...
Here 4 propositions: Sustainable food marketing. Cultural intelligence in services. Co-creation of value and well-being for customers. Customer satisfaction with "in-home" services. Contact : Prof. Furrer. Further topics for Bachelor and Master theses at the Chair of Marketing.
2.4 Submission of the bachelor thesis . You submit the bachelor thesis at the examination office and stick to the officially assigned deadline. 2.4.1 Length of the bachelor thesis . The length of the bachelor thesis should be approximately . 12.000 words (+/- 10%) with some flexibility for empirical work that can have about 10 .000 words (+/- 10%).
Top-ranked German Universities in Product Management. Top 100 Worldwide. Top 250 Worldwide. National Ranking. #89 Times Higher Education Ranking. University of Tübingen. public University. No. of Students: approx. 27,000 students. Program Fees: € 0 - € 1,500 (per semester)
For the area of product management at the Villingen-Schwenningen site, we are offering an opportunity for a bachelor's student (m/f/diverse) to write their mandatory thesis with Continental starting inSeptember 2024.The working-hours will be mainly on-site in Villingen-Schwenningen. Remote work is possible according to prior agreement.
We suppose that the product and service quality management in the agro-industrial sector is currently one of the few practice-oriented tools, the effectiveness of which has been proved by time and demand patterns. This thesis is also confirmed by the results of previous studies (in particular, the analysis of trends in the agro-industrial
Bachelor Thesis Product Management - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX; Kalcheva, Desislava: Limitation of the Capacity Model ACG (Aggregated Capacity Group) at Infineon and the rollout of the new model based on moving bottlenecks. Bachelor thesis, 2012 more… BibTeX; Bahamon, Helmut: Investigation of Methods for Product Portfolio Planning under Uncertainty. Bachelor thesis ...
Theorie und Praxis hybrider Leistungsbündel. Skill-based Project Management. Delay management in railway systems. Techniques for visualizing service processes. Revenue Management - The on-line booking problem. We try to consider student preferences when assigning topics. The thesis can be written in English or German.
For the area of product management at the Villingen-Schwenningen site, we are offering an opportunity for a bachelor's student (m/f/diverse) to write their mandatory thesis with Continental starting in September 2024. The working-hours will be mainly on-site in Villingen-Schwenningen.Remote work is possible according to prior agreement.
In this second article in the series on prioritization methods and techniques, I will discuss the MoSCoW method. The MoSCoW method is a highly widespread prioritization method which was popularized by Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM). The term MoSCoW has nothing to do with the capital of Russia. It is an acronym derived from the first ...
Each year, the Department of Management oversees about 25-30 bachelor and master theses dealing with management or entrepreneurship matters. Literature studies about scientifically relevant topics, as well as empirical studies, and 'consulting-papers' relevant to practitioners can be composed. The institute proposes a list of topics.
If you have a bachelor's in product management, business administration, management, or a related business-related field and want to further your education in this field, our consecutive 120-ETCS master's in product management is a good fit for you. ... Master Thesis. 30. Electives overview. Elective A. In your 3th semester, you'll need to ...
Product Management has undergone a tremendous transformation from its original application and practice as a particular company's management of the marketplace appeal of a single, commercial brand. Now, at its highest levels, Product Management has expanded to include the application of new technology, not as an option, but as an imperative ...
The main requirement to get into a product management PhD program is a bachelor's or master's degree from an accredited institution. You would need to prove completion of the degree program and provide transcripts from each institution you previously attended. ... For many students, their thesis or dissertation will be the most taxing ...
To set the value to backlog item you need just click it (in any view, either STORY MAP, BACKLOG, PLAN or WORK) to access details in the side view. Prioritization fields are displayed below the title of the backlog item. The first one is MoSCoW. Value can be visible on cards in STORY MAP. Once the value is entered, you can filter and group items ...
Dorie Clark. Dorie Clark is an adjunct professor at Duke University's Fuqua School of Business and a professional speaker. She is the author of Entrepreneurial You (Harvard Business Review Press), which was named one of the Top 10 Business Books of 2017 by Forbes. Her previous books include Reinventing You and Stand Out, which Inc. magazine declared the #1 Leadership Book of 2015, and was a ...