An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.60; Jan-Dec 2023
- PMC10265372

Impact of Nurse Leaders Behaviors on Nursing Staff Performance: A Systematic Review of Literature
Nourah alsadaan.
1 Jouf University, Sakaka, Saudi Arabia
Basma Salameh
2 Arab American University, Jenin, Palestine
Fadia Ahmed Abdelkader Elsaid Reshia
3 Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt
Reem F. Alruwaili
Majed alruwaili, shaimaa ahmed awad ali, abeer nuwayfi alruwaili, gehan refat hefnawy, maha suwailem s. alshammari, afrah ghazi rumayh alrumayh, alya olayan alruwaili, linda katherine jones.
4 Charles Sturt University, Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia
Nursing leadership is critical in facilitating and improving nurse performance, which is essential for providing quality care and ensuring patient safety. The aim of this study is to explore the relationship between nursing leadership and nurse performance by understanding the leadership behaviors and factors that motivate nurses to perform well. To study the factors that nurses believe motivate them to perform better, a systematic review was undertaken, correlating these factors to leadership behaviors/styles. The PRISMA guidelines were followed to identify relevant articles. After applying the selection criteria, 11 articles were included in the final analysis. Overall, 51 elements that influence nurses’ motivation to perform better were found and categorized into 6 categories, including autonomy, competencies, relatedness, individual nursing characteristics, relationships and support, and leadership styles/practices. It has been discovered that both direct and indirect nursing leadership behaviors affect nurses’ performance. A better understanding of the factors that motivate nurses to perform well and facilitating them in the work environment through leadership behaviors/styles can improve nurses’ performance. There is a need to increase research on nurse leadership and nurses’ performance in the current innovative and technologically integrated work environment to identify new factors of influence.
- What do we already know about this topic?
- Effective leadership in nursing can have a positive impact on nurse performance, job satisfaction, and patient outcomes.
- How does your research contribute to the field?
- It can provide new insights and understanding of how different leadership styles and practices impact nurse performance and patient outcomes
- What are your research’s implications toward theory, practice, or policy?
- To identify effective leadership practices that promote positive work environments, better nurse performance, and ultimately better patient outcomes, thus leading to improved patient contentment, safety, and care quality.
Introduction
Nurses are essential resources in hospitals as they spend more time with patients than any other healthcare personnel. Therefore, they play a significant role in ensuring quality care and patients’ safety by improving their performance. Despite accounting for 50% of the global healthcare workforce, 1 there is a severe shortage of nursing personnel in almost all countries. Developed countries such as the USA need an additional 275 000 nurses from 2020 to 2030. 2 According to the International Council of Nurses, there is a need for 13 million nurses globally to fill the shortage gap in the future. 3
The shortage of nurses has resulted in an increasing workload for existing nurses, significantly affecting their work life and performance, which can have a direct impact on the quality of care delivered. 4 Nursing performance is influenced by cognitive, physical, and organizational factors. 5 Various factors such as high workloads, lack of technological support, 6 skills and competencies (eg, problem-solving ability, nursing informatics competencies), 7 communication skills and confidence, 8 commitment, 9 quality of work life, 10 job stress, 11 and motivation 12 can significantly influence nursing performance. It is interesting to observe that most of these factors are a part of leadership management, focusing on providing training and support and addressing the issues affecting nurses.
Quality leadership was identified to be one of the major factors for promoting behaviors among the nurses for exhibiting greater responsibility and physical activity. 13 Similarly, workplace incivility from supervisors was identified to be negatively related to nursing performance. 14 Nursing leadership behaviors play a crucial role in shaping nursing performance, thereby achieving the organizational goals of ensuring the delivery of quality care and achieving better patient outcomes. 15 - 17 Considering the nursing leadership theories, transformational and transactional leadership styles 18 , 19 and their impact on nurses’ satisfaction, burnout, and resilience have received lot of attention. 17 , 18 , 20 However, most of the studies investigated the leadership styles influence on the factors affecting the nursing performance, but very few studies have focused on the leadership factors influencing the nurses’ motivation to perform well. An attempt in this aspect was made in a study 21 through the systematic review, but it only included studies till 2006. However, major changes have been observed in the factors influencing nursing performance in the past decade. The use of the internet and telecommunication technologies have significantly changed the quality of work of nurses, and led to the new forms of remote practices such as telenursing. 22 Furthermore, advanced innovative technologies such as artificial intelligence, intelligent systems such as IoTs 23 , 24 have significantly contributed to the nursing practice. 25 , 26 Additionally, due to the sudden surge of patients caused by the recent Covid-19 pandemic, nurses have experienced heightened levels of burnout, 27 which has significantly affected nurses work-life balance and their performance. 28 , 29 Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has rendered the nursing shortage a critical issue on a global scale, according to the ICN study report 2023. 30 There are issues including understaffing and low job satisfaction, as well as an aging nursing workforce and a lack of young individuals entering the profession. The report highlighted that nurses’ shortage has grown significantly from 30.6 million in 2019 after the pandemic began. Furthermore, it identified that key research from surveys and reviews in the past 3 years, after the emergence of Covid-19 pandemic, there is a significant increase in nurses burn-out. This has resulted in burn-out nurses either leaving their employment or reducing their work hours, which has led to additional burden of work, increasing levels of stress among the resilient working nurses. 30 Therefore, significant changes in the factors that influence nurses’ motivation to perform well might have occurred. Considering these developments, it is necessary to extend the review conducted in Brady Germain and Cummings, 21 to identify the new developments in the research arena. For that, the purpose of this study is to conduct a systematic review for examining the factors related to nurses’ leadership and nurses’ performance. To achieve this objective, the following research questions are formulated.
- RQ1: What factors do nurses think affect their drive to excel in their work? The ambition and aptitude of the nurses to achieve their companies’ objectives of high-quality care and patient safety serve as the benchmarks for performance in this context.
- RQ2: Which leadership traits are associated with strong nurse performance? In this context, behaviors are described as the traits or tactics used by leaders to control nurses’ performance in order to accomplish organizational objectives, such as patient safety and high-quality care.
Materials and Methods
The protocol for this study is registered with PROSPERO (registration number: CRD42023387324), the registration date 15/01/2023.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines 33 was used for conducting the systematic review of recent literature and reporting the findings relating to nursing leadership attributes and nursing performance.
Search Methods
Various databases, including CINAHL, Cochrane, EMBASE, HealthSTAR, Medline, and PsychINFO, were utilized to search for relevant studies. The search terms “nursing performance,” “nurse motivation,” “nursing leadership,” and “nursing leadership behaviors” were combined using Boolean operators “AND” and “OR.” To improve search sensitivity, keywords from the identified studies were also used in the search process. Only studies published in English were considered. Additionally, studies published within the last 20 years were included to ensure the search was current and covered new literature since the previous study by 23. Therefore, those studies before 2003 are excluded. Inclusion and exclusion criteria, as presented in Table 1 , were applied for selecting studies. Figure 1 provides a detailed overview of the search strategy used to select studies.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria.

PRISMA flow diagram.
Quality Appraisal
Two methods were used to rate the methodological quality of the chosen studies. The PRISMA 31 methodological quality criterion, which contains 27 elements, was used to systematic reviews. TREND 32 was used to evaluate quasi-experimental studies. TREND 32 comprises 22 criteria. The last criterion received a “yes,” a “no,” or a “unclear” rating. The “yes” items were added up to create a total score for each study, which ranged from zero to the total number of items that were examined. Studies with low methodological quality were deemed to be omitted from the review if they received a score of less than or equal to 50% on the evaluated items. Studies were deemed to be of medium or high quality and included in the review if they scored more than 50% on the analyzed items.
Data Extraction
Quantitative studies were the source of data, which encompassed details such as the author, publication year, research aim, sample size, methodology employed, independent and dependent variables, measurement criteria, reliability and validity of the measures, analytical techniques, and findings. The number of studies examined and the key conclusions were retrieved for systematic reviews.
Search Outcomes
Initially, 1632 articles were identified from different electronic databases, and 16 articles were identified through manual searching of journals, resulting in a total of 1648 articles. After removing 587 duplicates, 1061 articles were screened for titles and abstracts. Out of these, 984 articles were excluded based on title and abstract assessment, and 77 articles were selected for full-text reviews. After reviewing the full-text articles, 64 articles did not meet the inclusion criteria and were excluded. Finally, 13 articles were deemed eligible for quality assessment. Two articles did not meet quality criteria and were excluded resulting in 11 articles that are included in this review (See Figure 1 ).
Study Characteristics
Table 2 exhibits the attributes of the studies that were incorporated in this review. It can be observed that 6 studies were published recently (1 study in 2020, 3 studies in 2021, and 2 studies in 2022). Majority of the participants in most of the studies were females and were aged above 30 years with high work experience.
Summary of Study Characteristics Included in This Review.
Focusing on the leadership styles, 3 studies considered the effect of different leadership styles on nursing performance, 2 studies exclusively focused on transformational leadership, one each on sustainable leadership, entrepreneurial leadership, and servant leadership. There were 10 studies that have adopted quantitative approach of survey in data collection, and different analysis techniques were utilized in these studies. Only one systematic review was included that focused on the leadership attributes and nursing performance.
Theoretical Framework
Theories in research provides a rationale for developing hypothesis and testing the relationship between the variables, 44 and therefore it is important that the research studies should be guided by theoretical framework or a model that either confirmation of existing theory or generating new theories. Ten out of the 11 studies in this review were guided by a theoretical framework or a model. Six studies 33 - 37 ,45 in this review adopted leadership theories or developed a model for testing the leadership attributes on nursing performance. Social exchange theory and self-determination theories were used in Kül and Sönmez, 38 supporting the role of servant leadership in developing the innovative behavior of nurses (guided by social exchange) and motivating them in improving their performance by developing autonomy, competence and relatedness (self-determination theory: extrinsic motivation from leaders leading to intrinsic motivation among nurses). 39 Another study conducted by Salanova et al 40 emphasized the significance of social interactions in the work environment in improving self-efficacy by adopting social cognitive theory, where self-efficacy is considered as the primary personal resource, and transformational leadership as contextual resource for motivating nurses. In extending the leadership theories, another study 41 linked it with Innovative work behavior theory.
This theory contends that while functional competences give entrepreneurial nursing leaders the ability to inspire nurses to take innovative action while providing care, personal competencies enable them to establish an innovative vision. This builds confidence and commitment to adopting new ideas. 42 , 43 Wang et al 37 argued that leadership is a position that can be achieved by gaining skills, which contradicts leadership theories that suggest some people are born leaders. This also contradicts psychological theory that women have low aggressiveness and avoid leadership positions 46 , 47 However, recent studies focus on theories relevant to changes in the nursing industry, including the introduction of innovative technologies and new business models such as gig economy and eHealth. Many frameworks continue to focus on leadership styles such as transformational and transactional styles and relevant attributes that have been extensively researched over the past few decades. 21 However, new leadership attributes such as nursing informatics leadership, in light of growing influence of technology and industry policies in the quality care sector, have been neglected.
Measures of Nurse Performance
Twenty-two distinct measurement instruments were employed to evaluate the various factors that influence nursing performance in relationship with nursing leadership attributes. Five studies used questionnaires developed by authors for measuring nurses’ performance in relation to different aspects such as motivation, engagement, self-efficacy, performance, problem solving skills, and job satisfaction. Multifactor leadership questionnaires or its components were used in 3 studies focusing on different leadership styles and their impact on nursing performance as a part of the study model designed by respective authors. 34 , 35 , 40 Other major instruments used for measuring nurses’ performance related attributes include Caring Efficacy Scale, nurses’ activity scale, 45 Nurses performance evaluation checklist, 34 , 38 Innovative work behavior scale, 38 generic job satisfaction scale, 35 and innovative work behavior questionnaire. 41
Factors Influencing Nurses’ Performances
A total of 51 different factors that affected the nurses’ performance were identified from the studies included in the review ( Table 3 ). These factors were grouped into 6 categories including autonomy, competencies, relatedness, individual nurse characteristics, relationships and support, and leadership practices.
Factors Affecting Nurses’ Performance.
Three studies 33 , 38 , 45 examined the influence of autonomy related factors on nurses’ performance. Manojlovich 45 identified that strong nursing leadership behavior can contribute to the empowerment and self-efficacy on practice behaviors of the nurses, indicating that nursing leaders should provide more access to structural empowerment factors for nurses and exhibit unit-level nursing leadership. Kim and Sim 33 suggest that utilizing action-oriented and self-reward strategies, along with constructive thinking, can improve self-efficacy and empower individuals, leading to a significant improvement in their performance.
However, it is also observed that nursing performance can be affected by their communication abilities, indicating that in developing autonomy, communication skills play a significant role. Kül and Sönmez 38 identified that servant leadership attributes, such as being humanistic, empathetic, mutually beneficial, and service-oriented, can empower nurses to develop innovative behavior, which can improve their job performance. Innovative behaviors reflect an autonomy in nurses’ attitudes, where they autonomously take decisions in developing new ideas and new ways of delivering care, thereby improving the performance.
Competencies
Four studies 37 , 36 , 41 , 48 examined the influence of competencies related factors on the nurses’ performance. Few of these studies reflected new approaches in leadership and their impact on new areas of performance. For instance, Bagheri and Akbari 41 found that entrepreneurial leadership has positively influenced nurses’ innovation work behavior such as ideas exploration, generation, implementation, and championing, which can improve the overall performances and can support the achievement of organizational goals such as sustainability. Similarly, by creating a positive work environment and effectively managing resources and transformational leadership practices, nurse managers can significantly improve sustainability of nursing leadership. Moreover, Fing et al 36 found that competencies such as treating employees like family members, guiding them, and letting them make independent decisions have led to improvements in several areas that can impact nurses’ performance. These improvements include decision-making, the ability to accept criticism and suggestions. 36 Wang et al 48 found that leaders’ skills, such as idealized influence and intellectual stimulation, have a significant positive impact on nurses’ self-efficacy and work engagement.
Relatedness
Relatedness reflects how the nurse managers relate them to nurses and vice versa, which is reflected in their behavior toward each other. The study conducted by El-Azim et al 34 was the only study that did not find a significant statistical relationship between nursing leadership styles and nurses’ performance.
Individual Nurse Characteristics
Two studies have identified individual nursing characteristics related to nurses’ performance. The interest of nurses’ in taking up extra roles in addition to the existing roles supported by the nurse managers supported by transformational leadership practices through increased work engagement. 40 The findings of this study indicated that through supportive leadership practices, extra-role performance can be enhanced which in turn increases hospital efficacy. Wang et al 48 identified that psychological safety (a belief that nurses won’t be punished or humiliated for sharing ideas, concerns, and issues) could effectively improve nurses’ performance.
Relationships and Support
Wang et al 37 assessed the impact of nursing performance on nursing leadership along with other variables. They found that a caring and supportive work environment can positively affect nurses’ behavior and performance, and in turn, nursing leadership. This emphasizes the need for support from nursing leaders. 37
Leadership Styes/Practices
Although leadership practices were considered in most of the studies, significant approaches can be analyzed from 3 studies. Firstly, as discussed in the autonomy section, servant leadership approaches, such as humanistic, empathic, mutual benefit, and service-oriented approaches, can improve nurses’ competencies and skills, especially their ability to express themselves, communicate, and apply innovative ideas. Secondly, both transformational and transactional approaches, such as motivation, support, contingent rewards, and intellectual stimulation, can improve nurses’ satisfaction levels and job performance. 35 Thirdly, paternalistic leadership practices, such as treating nurses as family members, and laissez-faire practices, such as enabling nurses to make independent decisions, were identified as improving nurses’ performance. However, paternalistic approaches were found to be more influential than laissez-faire approaches. Fourthly, entrepreneurial leadership practices, such as driving innovation, risk-taking, and passion for work, were identified as promoting innovative behavior among nurses, which can improve their performance.
This study mainly focused on examining the link between nursing leadership and nurses’ performance by assessing the factors that nurses believed had an impact on their motivation to perform well; and the leadership behaviors that correlate with nurses’ performance. There has been a significant rise in the identification of number of factors that nurses perceive to be influencing their performance in the recent literature. This study has identified 51 such factors from research studies published since 2005, compared to a study conducted by Ronquillo et al 23 which included studies from 1995 to 2006, identifying 25 factors. This development indicates that significant progress can be observed in the research related to nurses’ leadership and nurses’ performance. One of the interesting findings in the review is that most of the studies (10 out of 11) were quantitative and adopted survey strategy for data collection; and only one study adopted systematic review approach, indicating the gaps in adoption of different methodological approaches in the research, which can contribute to diverse findings.
Most of the previous studies adopted social theories and the self-determination theory in assessing the relationship between nursing leadership and nurses’ performance. As a result, few studies mainly focused on the nurses’ approaches in providing quality care through social interaction, rather than on their personal attributes such as satisfaction, quality of life, and motivation. However, some studies attempted to develop theoretical models, 34 , 35 , 40 indicating the emergence of various constructs and relations between nursing leadership and nurses’ performance. One of the effective qualities of leaders is promoting autonomy among the team and making them self-reliant by developing skills and competencies to improve overall processes. Accordingly, from the findings ( Table 3 ), it was observed that the majority of the factors identified were in relation to leadership practices that focused on promoting autonomy and competencies among nurses
In the past few years, significant developments can be observed in the adoption of Industry technologies such as the Internet of Things, Artificial Intelligence, Cloud computing, block chain technology etc., 49 - 52 giving rise to new form of leadership such as nursing informatics leadership. 53 , 54 These developments can influence various factors within hospital settings, including organizational culture, workload, motivation, values in hospital settings that can directly or indirectly influence nursing performance. However, no studies were identified in this review which considered these developments in identifying the factors that influence nurses’ performance. Studies reviewed indicated that nursing leadership can influence autonomy, 33 , 38 , 45 relatedness, 34 competencies, 36 , 37 , 41 , 48 individual characteristics, 40 , 48 and relationships and support, 37 as perceived by nurses influencing their motivation to perform well. In addition, leadership practices were identified to be nurses’ abilities to perform well. Furthermore, leadership behaviors that support autonomy, inclusivity, transformation (improving skills, innovation abilities, and competencies), and staff prioritization (caring, paternalistic behavior, empathy) can result in high nursing performance. 33 , 38 , 45 It is important that nurse leaders share organizational goals to encourage staff, offer suggestions, and receive feedback on innovative practices for achieving goals in a cooperative and supportive work culture. The studies reviewed suggest leadership plays a crucial role in influencing nurses’ performance in various areas, such as innovation, decision-making, and work engagement. 36 , 37 , 41 , 48 Furthermore, new approaches to leadership, such as entrepreneurial leadership and transformational leadership practices, can positively impact nurses’ performance and support the achievement of organizational goals such as sustainability. 41 Therefore, it is important for nurse managers to continuously develop their leadership skills and create a positive work environment that supports nurses’ ability to perform well. 36 By doing so, nurse managers can help to create practice environments that promote nurses’ ability to perform their roles effectively, thus enhancing overall nursing performance.
While one study included in the review did not find any significant statistical association between nursing leadership styles and nurses’ performance, it suggested that further research is needed to better analyze the relationship between nursing leadership and nurses’ performance by adopting relatedness factors in the areas of advanced leadership approaches and providing performance appraisal. 34 This highlights the importance of considering relatedness factors in nursing leadership to support nurses’ performance and promote positive relationships between nurse managers and nurses.
The results of Salanova et al 40 study highlight the significance of nurse managers adopting transformational leadership practices to increase nurses’ interest in taking up extra roles, which can lead to improved hospital efficacy. Additionally, promoting psychological safety in the workplace can create a supportive work environment that encourages open communication and enhances nurses’ performance. 48 This indicates the nurses should have enough freedom with nurse managers for sharing their opinions without any hesitation or fear, which may benefit both of them.
Therefore, nursing leadership has a significant impact on nurses’ perceptions of the factors that influence their motivation to perform. This impact can be both direct and indirect. Therefore, it is essential to have competent nursing leaders to create practice settings that can foster nurses’ capacity to succeed. In other words, the link between nursing leadership and nurses’ success is critical, and it is necessary to prioritize leadership development in the nursing profession to achieve optimal patient outcomes.
As observed from the recent report by ICN, 30 the lack of strategic and systematic approach by the employers and policymakers is one of the key challenges associated with rising nursing problems. In this context, it may be implied that effective leadership approaches coupled with systematic management of nursing resources could be one of the effective ways to improve nursing performance, retention, and reduced burn-out rates. Accordingly, apart from the patient-related aspects, personal, co-worker, organizational, and societal related factors were identified to be the significantly contributing factors of nurses’ burn-out during the pandemic, 55 highlighting the issues with nurses’ leadership and organizational/employer approaches. In this context, a systematic review on interventions to reduce occupational stress and burn-out, 56 observed that the interventions were effective when they focus at individual level and organization directed, implying the strategic and systematic approach adopted by the employers and led by nursing leaders, with an individualized focus, signifying the relevance of transformational, motivational, and supportive leadership styles. For instance, spiritual intelligence among nursing leaders was identified to be influencing nursing managers’ competencies in managing stress and burn-out, 57 and similar strategies could be directed by employers to effectively manage nursing resources. Such streamlined approaches may be effective in not only improving nurses’ performance, but also in addressing the challenges such as nurses’ burn-out, retention, and increasing stress in the post-pandemic era.
Implications for Nurse Researchers
The findings from this review supports a theoretical model ( Figure 2 ) on factors that influences nurses’ motivation to perform well, which may be tested and evaluated in future research. Analyzing published research till date in this review has suggested that leadership practices that support autonomy, competencies, and relatedness through inclusive approaches reflect that nurses’ contributions are valued and this process resulted in increased motivation of nurses to perform well. In addition, leadership practices that support innovation (entrepreneurial), and cooperative culture (transformational) were identified to be more influencing in improving nurses’ motivation to perform better. Although, different leadership practices and their relationship with nurses’ performance were investigated, significant changes have been observed in the nursing work environment in the past few years. The introduction of innovative technologies and business models, such as the gig economy and online health services, is among the many changes. These changes can lead to new leadership practices and new factors that influences nurses’ performance, such as informatics competencies and skills, remote work culture. These are some areas that future researchers can investigate to identify new leadership practices and the factors that influence nurses’ performance. Furthermore, sustainability has become a core component of all organizations, including healthcare. Therefore, it is important to examine leadership behaviors that can have an impact on nurses’ abilities to help achieve sustainable organizational goals. Furthermore, unexpected disasters such as the recent Covid-19 pandemic has significantly increased the burden on nursing care. Leadership practices in such a highly demanding workload environment and their impact on nurses’ abilities to provide quality care and achieve better patient outcomes could be examined. Finally, it is evident from the review that most of the studies have adopted quantitative methods. Diverse methodological framework adoption can contribute to the quality of research. Therefore, future researchers should focus on adopting other frameworks such as qualitative, and mixed methods in conducting the research.

Proposed theoretical model.
Implications for Nurse Leaders
Nursing performance is a key factor influencing the sustainability of nursing leadership. 37 Therefore, nurse leaders must adopt various leadership practices and behaviors that improve nursing performance, especially those that increase nurses’ motivation to perform better. Leadership practices that encourage employees’ motivation can influence organizational practices and goals. 58 As nurse leaders carry huge workloads, their work effectiveness can be affected, 59 which create barriers and challenges in achieving optimal nursing performance and ultimately providing high-quality care. Addressing nurse leaders’ workload is therefore necessary to enhance their ability to influence nurses and improve overall nursing performance.
Limitations
This review has a few potential limitations. It can be observed that 10 out of the 11 studies reviewed adopted quantitative methods, reflecting the limitation of including diverse methodological studies. Furthermore, reporting bias may exist as published studies tend to over-report positive findings. Many studies used self-designed scales to measure nurses’ performance, and others used different tools, limiting the validity and generalizability of findings. Most of the studies in this review are cross-sectional correlation studies and may be prone to bias 44, but they are helpful in examining the relationship between nursing leadership practices, behaviors, and nurses’ performance, which is the main purpose of this study.
Conclusions
Providing quality care and ensuring patients’ safety are fundamental goals for all healthcare organizations. Since nurses are the primary healthcare providers who spend a significant amount of time with patients delivering care and services, they have a crucial role in achieving these objectives. Nurse leaders who manage the nursing resources are the key personnel who are responsible for overseeing the quality of care and patients’ safety, and therefore they need to encourage nurses’ in better understanding the patients’ needs and values. Strong nurse leaders are effective in implementing evidence-based practices to ensure that these objectives are achieved, as research showed that nursing leadership can both directly and indirectly influence nurses’ performance. The present review has identified 51 factors that nurses categorize under 6 domains, which they believe motivate them to perform effectively. These included autonomy, relatedness, competencies, individual nurse characteristics, relationships and support, and leadership practices/styles. Comprehending these actors is essential and necessary for nurse leaders to promote quality of care and to achieve organizational goals such as sustainability, growth and innovativeness. Therefore, nurse leaders should strive to understand and identify the factors that motivate nurses to perform well and accordingly should address/facilitate these factors through their behavior or leadership styles.
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding: The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethical Approval: Our study did not require an ethical board approval because systematic reviews generally do not need ethics committee or institutional review board approval,

The essentials of nursing leadership: A systematic review of factors and educational interventions influencing nursing leadership
Affiliations.
- 1 Faculty of Nursing, Edmonton Clinic Health Academy, University of Alberta, 11405 87 Ave NW, Edmonton, AB T6G 1C9, Canada. Electronic address: [email protected].
- 2 Department of Nutrition, Dietetics and Food, School of Clinical Sciences at Monash Health, Monash University, Level 1, 264 Ferntree Gully Rd, Notting Hill, VIC 3168, Australia.
- 3 Faculty of Nursing, Edmonton Clinic Health Academy, University of Alberta, 11405 87 Ave NW, Edmonton, AB T6G 1C9, Canada.
- 4 Faculty of Nursing, Edmonton Clinic Health Academy, University of Alberta, 11405 87 Ave NW, Edmonton, AB T6G 1C9, Canada; Technical High School of Campinas, State University of Campinas (UNICAMP), Barão Geraldo, Campinas - São Paulo 13083-970, Brazil.
- PMID: 33383271
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2020.103842
Background: Nursing leadership plays a vital role in shaping outcomes for healthcare organizations, personnel and patients. With much of the leadership workforce set to retire in the near future, identifying factors that positively contribute to the development of leadership in nurses is of utmost importance.
Objectives: To identify determining factors of nursing leadership, and the effectiveness of interventions to enhance leadership in nurses.
Design: We conducted a systematic review, including a total of nine electronic databases.
Data sources: Databases included: Medline, Academic Search Premier, Embase, PsychInfo, Sociological Abstracts, ABI, CINAHL, ERIC, and Cochrane.
Review methods: Studies were included if they quantitatively examined factors contributing to nursing leadership or educational interventions implemented with the intention of developing leadership practices in nurses. Two research team members independently reviewed each article to determine inclusion. All included studies underwent quality assessment, data extraction and content analysis.
Results: 49,502 titles/abstracts were screened resulting in 100 included manuscripts reporting on 93 studies (n=44 correlational studies and n=49 intervention studies). One hundred and five factors examined in correlational studies were categorized into 5 groups experience and education, individuals' traits and characteristics, relationship with work, role in the practice setting, and organizational context. Correlational studies revealed mixed results with some studies finding positive correlations and other non-significant relationships with leadership. Participation in leadership interventions had a positive impact on the development of a variety of leadership styles in 44 of 49 intervention studies, with relational leadership styles being the most common target of interventions.
Conclusions: The findings of this review make it clear that targeted educational interventions are an effective method of leadership development in nurses. However, due to equivocal results reported in many included studies and heterogeneity of leadership measurement tools, few conclusions can be drawn regarding which specific nurse characteristics and organizational factors most effectively contribute to the development of nursing leadership. Contextual and confounding factors that may mediate the relationships between nursing characteristics, development of leadership and enhancement of leadership development programs also require further examination. Targeted development of nursing leadership will help ensure that nurses of the future are well equipped to tackle the challenges of a burdened health-care system.
Keywords: Interventions; Leadership; Nursing workforce; Systematic Review.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Publication types
- Systematic Review
- Delivery of Health Care*
- Leadership*
This website is intended for healthcare professionals

- { $refs.search.focus(); })" aria-controls="searchpanel" :aria-expanded="open" class="hidden lg:inline-flex justify-end text-gray-800 hover:text-primary py-2 px-4 lg:px-0 items-center text-base font-medium"> Search
Search menu
Anderson C. Exploring the role of advanced nurse practitioners in leadership. Nurs Stand. 2018; 33:(2)29-33 https://doi.org/10.7748/ns.2018.e11044
Bass B. The Bass handbook of leadership: Theory, research, and managerial applications.New York (NY): Simon and Schuster; 2010
Cummings G. The call for leadership to influence patient outcomes. Nurs Leadersh (Tor Ont). 2011; 24:(2)22-5 https://doi.org/10.12927/cjnl.2011.22459
Collaborative leadership: new perspectives in leadership development. 2011. https://tinyurl.com/2usp5yve (accessed 24 February 2021)
Dover N, Lee GA, Raleigh M A rapid review of educational preparedness of advanced clinical practitioners. J Adv Nurs. 2019; 75:(12)3210-3218 https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.14105
Edwards A. Being an expert professional practitioner. The relational turn in expertise.London: Springer Verlag; 2010
Evans C, Pearce R, Greaves S, Blake H. Advanced clinical practitioners in primary care in the UK: a qualitative study of workforce transformation. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020; 17:(12) https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124500
Hamric A, Hanson C, Tracy M, O'Grady E. Advanced practice nursing. An integrative approach.Philadelphia (PA): Elsevier Saunders; 2014
Health Education England. Advanced practice. 2021. https://www.hee.nhs.uk/our-work/advanced-clinical-practice (accessed 24 February 2021)
Heinen M, van Oostveen C, Peters J, Vermeulen H, Huis A. An integrative review of leadership competencies and attributes in advanced nursing practice. J Adv Nurs. 2019; 75:(11)2378-2392 https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.14092
Kotter JP. Leading change.Boston (MA): Harvard Business Review Press; 1996
Kramer M, Maguire P, Schmalenberg CE. Excellence through evidence: the what, when, and where of clinical autonomy. J Nurs Adm. 2006; 36:(10)479-491 https://doi.org/10.1097/00005110-200610000-00009
Lamb A, Martin-Misener R, Bryant-Lukosius D, Latimer M. Describing the leadership capabilities of advanced practice nurses using a qualitative descriptive study. Nurs Open. 2018; 5:(3)400-413 https://doi.org/10.1002/nop2.150
Better leadership for tomorrow: NHS leadership review. 2015. https://tinyurl.com/ev7thw68 (accessed 24 February 2021)
Royal College of Nursing. Royal College of Nursing standards for advanced level nursing practice. 2018. https://www.rcn.org.uk/library/subject-guides/advanced-nursing-practice (accessed 24 February 2021)
Scott ES, Miles J. Advancing leadership capacity in nursing. Nurs Adm Q. 2013; 37:(1)77-82 https://doi.org/10.1097/NAQ.0b013e3182751998
Sheer B, Wong FK. The development of advanced nursing practice globally. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2008; 40:(3)204-11 https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1547-5069.2008.00242.x
Skår R. The meaning of autonomy in nursing practice. J Clin Nurs. 2010; 19:(15-16)2226-2234 https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2009.02804.x
Stanley JM, Gannon J, Gabuat J The clinical nurse leader: a catalyst for improving quality and patient safety. J Nurs Manag. 2008; 16:(5)614-622 https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2834.2008.00899.x
Swanwick T, Varnam R. Leadership development and primary care. BMJ. 2019; 3:59-61 https://doi.org/10.1136/leader-2019-000145
Leadership and management for nurses working at an advanced level
Senior Lecturer, Leadership and Management: Public Health, Birmingham City University
View articles
Leadership and management form a key part of advanced clinical practice (ACP) and work in synergy with the other pillars of advanced practice. Advanced clinical practitioners focus on improving patient outcomes, and with application of evidence-based practice, using extended and expanded skills, they can provide cost-effective care. They are equipped with skills and knowledge, allowing for the expansion of their scope of practice by performing at an advanced level to assist in meeting the needs of people across all healthcare settings and can shape healthcare reform. Advanced practice can be described as a level of practice, rather than a type of practice. There are four leadership domains of advanced nursing practice: clinical leadership, professional leadership, health system leadership and health policy leadership, each requiring a specific skill set, but with some overlaps. All nurses should demonstrate their leadership competencies—collectively as a profession and individually in all settings where they practice.
Leadership and management form an essential part of advanced clinical practice, as outlined by Health Education England (HEE) in 2017:
‘Advanced clinical practice is delivered by experienced, registered health and care practitioners. It is a level of practice characterised by a high degree of autonomy and complex decision making. This is underpinned by a master's level award or equivalent that encompasses the four pillars of clinical practice, leadership and management, education and research, with demonstration of core capabilities and area specific clinical competence …’
There is an appreciation that leadership and management skills work in synergy with the other pillars of advanced practice. Stanley et al (2008) advised that advanced clinical practitioners (ACPs) can shape healthcare reform, are trained to focus on improved patient outcomes, and with application of evidence-based practice, using extended and expanded skills, they can provide cost-effective care. ACPs are equipped with skills and knowledge, allowing for the expansion of their scope of practice by performing at an advanced level to assist in meeting the needs of people across all healthcare settings.
When considering a nursing context, the Royal College of Nursing (RCN) defined advanced practice as:
‘A level of practice, rather than a type of practice. Advanced nurse practitioners are educated at master's level in clinical practice and have been assessed as competent in practice using their expert clinical knowledge and skills. They have the freedom and authority to act, making autonomous decisions in the assessment, diagnosis and treatment of patients.’
Rose (2015) advocated that ACPs also need to respond to, inform and influence policy, and political and practice changes, while being aware of the complex needs of patients and new healthcare demands. Hamric et al (2014) delineated four leadership domains of advanced nursing practice:
- Clinical leadership
- Professional leadership
- Health system leadership
- Health policy leadership.
Each requires a specific skill set, but with some overlaps. These four leadership domains will guide the discussion that follows, with a focus on advanced nurse leadership.
Background: leadership and autonomy
Revisiting the HEE (2021) use of the word ‘leadership’ and the RCN's (2018) use of the term ‘autonomy’ as part of the definition of advanced nurse practitioners will set the scene and enable these two terms to be briefly examined. Naively, or perhaps traditionally and historically, we tend to put administrator and manager roles into a metaphorical box that considers them as formal leaders, while nurses in clinical roles are either not considered as leaders or they are identified as in formal or clinical leaders. As Scott and Miles (2013) stated, leadership is an expected attribute of all registered nurses, and, yet, leadership in the profession is often considered to be role dependent. All nurses—from student to consultant—are leaders, yet defined clinical leadership competencies are often not reflected in undergraduate nurse education. Research examining the impact of leadership demonstrated by nurses on patients, fellow nurses and other professionals and the broader health and care system is deficient ( Cummings, 2011 ). Nurses need to accept that leadership is a core activity of their role at all levels—once this is acknowledged the transition to advanced roles will be easier. Frequently, nurses approach the topic of leadership when studying for advanced practice as if it is something that they have never done and know little about. Yet they already have an enhanced leadership skill set developed throughout their careers, although they often fail to appreciate this. A solid foundation and affirmation that all nurses are leaders should form the basis of advanced practice.
Despite a blurring of boundaries between management and leadership, the two activities are different ( Bass, 2010 ). Working out who leads and who manages is difficult, with the added anomaly that not all managers are leaders, and some people who lead work in management positions. Kotter's seminal interpretation articulated that leadership processes involve setting a direction, aligning people, motivating and inspiring, and that management relates to organisational aspects such as planning, staffing, budgeting, controlling and solving problems ( Kotter, 1996 ). So leaders cope with new challenges and transform organisations, while managers maintain functional operations using resources effectively.
These explanations direct us to consider what is meant by the allied term of autonomy from the individual and organisational perspective. The Cambridge Dictionary (2020) defines autonomy for an individual as ‘independent and having the power to make your own decisions’ and for a group of people as ‘an autonomous organization, country, or region [that] is independent and has the freedom to govern itself’ (https://tinyurl.com/2h5canfa). In nursing, the concept of autonomy has a range of definitions. Skår defined professional autonomy as:
‘Having the authority to make decisions and the freedom to act in accordance with one's professional knowledge base.’
Skår, 2010:2226
In a clinical practice setting, Kramer et al (2006) outlined three dimensions of autonomy: clinical or practice autonomy, organisational autonomy, and work autonomy. However, they also advised caution with the use of the term autonomy because it has different meanings across the literature. Nevertheless, it has a place within advanced nursing roles, especially in connection with leadership.
Leadership and management for advanced practice
Recent research has examined leadership in advanced nursing practice. Hamric et al (2014) delineated four leadership domains. These link with the findings of Heinen et al (2019) in their review of leadership competencies and attributes in advanced nursing practice. The purpose of their research was to establish which leadership competencies are expected of master's level-educated nurses, such as advanced practice nurses and clinical nurse leaders, as described in the international literature. Note that in North America ‘advanced practice nurse’ is used as an umbrella term to include nurse practitioners and clinical nurse specialists ( Sheer and Wong, 2008 ).
Boxes 1 to 4 are based on the competencies identified by Heinen et al (2019) for the four leadership domains ( Hamric et al, 2014 ), and Box 5 gives some generic competencies that span each of these.
Box 1.Clinical leadership
- Provides leadership for evidence-based practice for a range of conditions and specialties
- Promotes health, facilitates self-care management, optimises patient engagement and progression to higher levels of care and readmissions
- Acts as a resource person, preceptor, mentor/coach, and role model demonstrating critical and reflective thinking
- Acts as a clinical expert, a leadership role in establishing and monitoring standards of practice to improve client care, including intra- and interdisciplinary peer supervision and review
- Analyses organisational systems for barriers and promotes enhancements that affect client healthcare status
- Identifies current relevant scientific health information, the translation of research in practice, the evaluation of practice, improvement of the reliability of healthcare practice and outcomes, and participation in collaborative research
- Acts as a liaison with other health agencies and professionals, and participates in assessing and evaluating healthcare services to optimise outcomes for patients/clients/communities
- Collaborates with health professionals, including physicians, advanced practice nurses, nurse managers and others, to plan, implement and evaluate improvement opportunities
- Aligns practice with overall organisational/contextual goals
- Guides, initiates and leads the development and implementation of standards, practice guidelines, quality assurance, education and research initiatives
Source: adapted from Heinen et al, 2019
Box 2.Professional leadership
- Assumes responsibility for own professional development by education, professional committees and work groups, and contributes to a work environment where continual improvements in practice are pursued
- Participates in professional organisations and activities that influence advanced practice nursing
- Participates in relevant networks: regional, national and international
- Develops leadership in and integrates the role of the nurse practitioner within the healthcare system
- Employs consultative and leadership skills with intraprofessional and interprofessional teams to create change in health care and within complex healthcare delivery systems
- Participates in peer-review activities, eg publications, research and practice
Box 3.Health system leadership
- Contributes to the development, implementation and monitoring of organisational performance standards
- Lead an interprofessional healthcare team with a focus on the delivery of patient-centred care and the evaluation of quality and cost-effectiveness across the healthcare continuum
- Enhances group dynamics, and manages group conflicts within the organisation
- Plans and implements training and provides technical assistance and nursing consultation to health department staff, health providers, policymakers and personnel in other community and governmental agencies and organisations
- Delegates and supervises tasks assigned to allied professional staff
- Creates a culture of ethical standards within organisations and communities
- Identifies internal and external issues that may impact delivery of essential medical and public health services
- Possesses a working knowledge of the healthcare system and its component parts (sites of care, delivery models, payment models and the roles of healthcare professionals, patients, caregivers and unlicensed professionals)
Box 4.Health policy
- Guides, initiates and provides leadership in policy-related activities to influence practice, health services and public policy
- Articulates the value of nursing to key stakeholders and policymakers
Source: Heinen et al, 2019
Box 5.Generic competencies spanning the four domains
- Possesses advanced communication skills/processes to lead quality improvement and patient safety initiatives in healthcare systems
- Uses principles of business, finance, economics, and health policy to develop and implement effective plans for practice-level and/or system-wide practice initiatives that will improve the quality of care delivery
- Advocates for and participates in creating an organisational environment that supports safe client care, collaborative practice and professional growth
- Creates positive healthy (work) environments and maintains a climate in which team members feel heard and safe
- Uses mentoring and coaching to prepare future generations of nurse leaders
- Provides evaluation and resolution of ethical and legal issues within healthcare systems relating to the use of information, information technology, communication networks, and patient care technology
The findings presented in Boxes 1 to 5 provide a research-based scoping of the international literature to identify aspects of leadership competencies connected with advanced nursing practice ( Heinen et al, 2019 ). Revisiting the theoretical differences between leadership and management ( Kotter, 1996 ), it can be appreciated that many of these competencies are blurred, with both existing as part of advanced roles. The clinical, professional and health system domains dominate the number of competencies recorded, giving an idea of the weight given by nurses to different areas of leadership. Competencies relating to the health policy domain were minimal. This is supported by a study describing the leadership capabilities of a sample of 14 advanced practice nurses in Canada using a qualitative descriptive study ( Lamb et al, 2018 ). Two overarching themes describing leadership were identified: ‘patient-focused leadership’ and ‘organisation and system-focused leadership’. Patient-focused leadership comprised capabilities intended to have an impact on patients and families. Organisation and system-focused leadership included capabilities intended to impact nurses, other healthcare providers, the organisation or larger healthcare system. Figure 1 summarises the leadership themes and capability domains identified in Lamb et al's study (2018) .
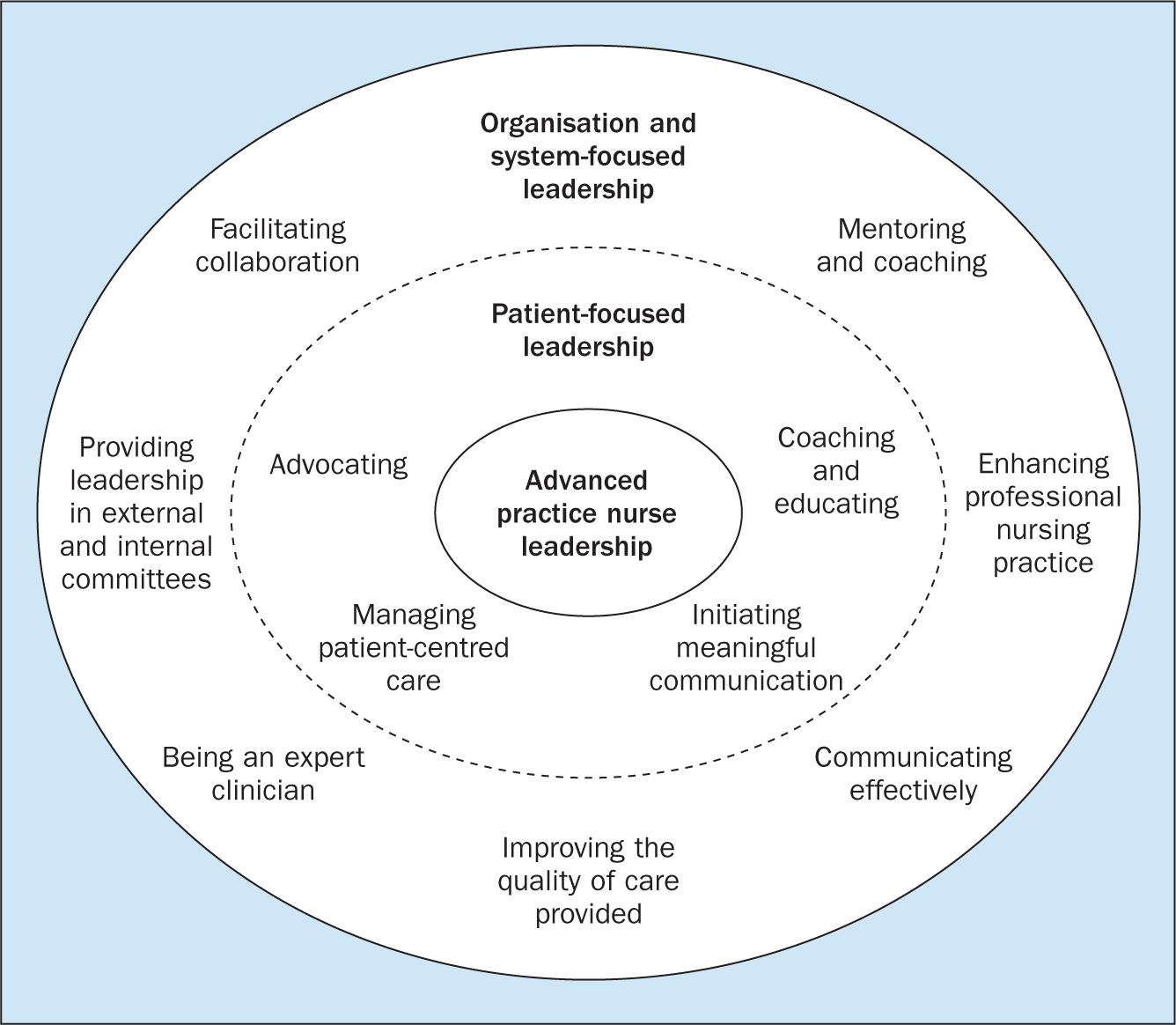
These findings also support the theory that advanced nurses do not recognise their wide reach as a major leadership part of their roles. In addition, it should be stated that all advanced nursing roles have their own idiosyncrasies based upon the individual practitioner, the environment and organisational needs; there is no ‘one size fits all’.
Multiprofessional working, leadership and the ACP role
With a move in the UK to multiprofessional working, especially in England, and changes towards core advanced practice skills crossing professional boundaries ( HEE, 2021 ) ACPs need proactive skills in cementing their leadership roles within teams. Anderson (2018) advised that successful multiprofessional working needs the individual professional to know the ‘standpoint’ of other professionals to enable their own understanding of complex problems. Edwards (2010) cautioned that professionals may work together and share personal values, but rarely do they work inter-professionally. The ACP role is complex, requiring autonomy and leadership of self within various aspects of the roles required of the individual in distinctive settings, in addition to performing and leading in teams often with professionals from other specialties.
What overt leadership skills may assist in delivery multiprofessional integrated care? Writing from a UK primary care perspective, Swanwick and Varnam (2019) described a necessary shift from the traditional individualistic hierarchical leader, working within and for single teams, to collective leadership encouraging a compassionate and inclusive culture. De Meyer (2011) also advised providing responsible collaborative leadership using the skills of co-operation, listening, influencing, and flexible adaptation, in contrast to what he terms the traditional ‘command and control’ top-down hierarchical approach. It could be suggested that this ‘way of being’ is aligned with the core skills of nurses but these may not be recognised by them as ‘real’ leading.
To ensure the success of the ACP role across the four pillars framework ( HEE, 2021 ) requires that the educational pathway and role has clarity, consistency and standardisation ( Dover et al, 2019 ) so that everyone will feel that they are entering on a level playing field. The framework ( HEE, 2021 ) represents a step forward by providing an overarching structure to align practice and education and creating greater consistency across ACP workforce developments. As the framework is implemented, it will be imperative to have an evaluation of its impact ( Evans et al, 2020 ).
The ACP is tasked with operating at an autonomous advanced level across the four pillars of education, leadership, research and clinical practice, and to be competent in the core capabilities for each pillar. Understanding the ACP role as a level of practice rather than a specific role with the distinguishing feature of autonomy may add clarification. Leadership is a crucial part of the ACP role and advanced nurses therefore need to conduct themselves as leaders so that others can recognise that they embody these skills. Yet, the time has come for all nurses to demonstrate their leadership competencies, collectively as a profession and individually in all settings where they practice. If every nurse is recognised as a leader, the transition to advanced practice will be fluid, streamlined and less of big deal.
Effective Leadership and Management in Nursing
Introduction.
Leadership is reflected as a comprehensive process that is used to realize goals, motivate other members to work, and providing support and inspiration to accomplish communally negotiated goals. In the nursing profession, leadership is the process of coordinating day and night shifts, and controlling the nursing team to ensure that the activities and practices within the health care organization are accomplished successfully. Leadership incorporates the perception, opinion, skills and attitude of an individual concerning certain issues concerning health and protection.
Leadership skills are very indispensable in the nursing profession as they facilitate to the effectiveness of the services offered by the nurses, such as caring for the patients and maintaining a sustainable, and health workforce in the organization’s environment (Burns, 1978). It is of immense connotation to note that nursing leadership roles are different from the managerial functions. The most crucial roles of professional nurse are managing of care, designing of care and coordination of care while management functions are about responsibilities. Nursing leadership skills are determined by the attributes that an effective leader have such as being visionary, and always equipped with approaches and strategies that are aimed at achieving future goal of the Health Organization.
My preceptor has the ability to incorporate and apply the attributes of an effective leader, such as being visionary and able to direct their workmates and services to a future mutual goal of the research or experiment (Sullivan & Decker, 2001). The preceptor is able to use problem-solving processes and maintain the effectiveness of the group, as well as developing team identification. This is possible due to dynamic and motivational authority they have on the group members under their guidance and supervision.
For effectiveness in their practice, the preceptor is manifested to be solution-focused and have the potential to devise approaches that are fundamental in inspiring and motivating the team which they lead. Preceptor initiates effective leadership styles that enable them to influence successful improvement of the teams or groups they lead. This is achieved by ensuring that they accomplish and maintain professional standards in their line of operation. The preceptors act as source of inspiration to the nurses and other teams that they monitor, supervise and instruct (Marriner-Tomey, 1993).
Nursing Leadership Skills Incorporated by the Preceptor within the following Professional Nursing Roles
Considering the three professional nursing roles within the practicum, preceptor incorporates the nursing proficiency and skills in the following forum:
Designer of care
As a designer of care, the preceptor makes decisions on what should be done by the team or group in the practicum in order to accomplish the task that is assigned to them. They incorporate the nursing leadership skill of acting with integrity, truthfulness and honesty as this helps them to be competitive and proficiency designers of care. The preceptor handles each team member as an independent individual, which is a trait of an effective nurse leader. This enables them to recognize the unique set of the needs of the members and address them in accordance to the nature and the existing surroundings within the practicum (Sullivan & Decker, 2001).
Coordinator of care
The preceptor is able to integrate management skills to resolves conflicts, and control the emotions of people depending on the nature of the predicaments that have contributed to the misunderstanding. Leaders are assumed to have the distinctiveness of seeking attention from the group that they direct. This way, the preceptor is able to request for concentration from the conflicting parties, allow them to explain their views towards the issues bringing misunderstanding, and draw a conclusion that is based on evidence derived from consideration of the opinions from both differing sides (Burns, 1978).
The preceptor adopts the supportive leadership style, as well as incorporating the core values of leadership which are mentorship and regulation, in order to be able to manage the teams and groups they are responsible for successfully. This is essential as it enables the preceptor to reduce and manage emotional exhaustion of the team and control cushioned pessimistic effects of the activities within the practicum.
Manager of care
A manager is assumed to have the obligation to delegate duties and responsibilities to the junior staff or the team to which they are instructors. The preceptor therefore, assumes the duty of providing intentional succession planning and appropriately promoting the teams’ value of clinical competency. The preceptor applies mechanisms for supervision and monitoring the progress of the practices and activities carried out by the team (Marriner-Tomey, 1993).
As a manager of care, the preceptor determines the nature of the activity or practice under investigation, its strengths, weaknesses, and threats that are associated with the activity and the instructing interventions. This enables them to formulate the future goals that are maintained by the team.
Generally, the nursing leadership roles are very crucial in offering instructions and guidelines to any group or team involved in an investigation or research within a practicum. Preceptors are facilitators in a nursing workshop or practicum, as they give directions to be followed by the members, offer supervision and monitor the progress of the team members. Incorporation of nursing leadership skills in carrying out the three professional nursing roles helps in attainment of completeness and effectiveness in the practice as all the activities and practices are done appropriately and to the plan.
Burns, J.M. (1978). Leadership . New York: Harper and Row.
Marriner-Tomey, A. (1993) Transformational Leadership in Nursing . London: Mosby.
Sullivan, E.J. & Decker, P.J. (2001). Effective Leadership and Management in Nursing (5 th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, June 1). Effective Leadership and Management in Nursing. https://studycorgi.com/effective-leadership-and-management-in-nursing/
"Effective Leadership and Management in Nursing." StudyCorgi , 1 June 2022, studycorgi.com/effective-leadership-and-management-in-nursing/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) 'Effective Leadership and Management in Nursing'. 1 June.
1. StudyCorgi . "Effective Leadership and Management in Nursing." June 1, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/effective-leadership-and-management-in-nursing/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Effective Leadership and Management in Nursing." June 1, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/effective-leadership-and-management-in-nursing/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "Effective Leadership and Management in Nursing." June 1, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/effective-leadership-and-management-in-nursing/.
This paper, “Effective Leadership and Management in Nursing”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: June 1, 2022 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essay Examples >
- Essays Topics >
- Essay on Nursing
Inspiring Essay About Nursing Leadership And Management
Type of paper: Essay
Topic: Nursing , Health , Leadership , Care , Breastfeeding , Health Care , Patient , Nursing Leadership
Words: 2250
Published: 03/08/2023
ORDER PAPER LIKE THIS
Impact of Nursing Leadership on Patient Care
Introduction Management and leadership are distinct and interconnected concepts that govern the organizational aspects of planning, organizing, and monitoring the provision of service. Effective management requires ideal leadership qualities; these aspects develop a shared sense of mission that helps achieve the organizational goals while minimizing any organization, political, and resource barrier (Kotter, 1996). Nursing leadership and management are primary and integral aspects of the provision of innovative, quality, and cost-efficient patient care. In particular, nursing leadership and management encompass a wide range of leadership qualities including delivering clinical care, enhancing patient care coordination, as well as boosting quality improvement and safety in the health care system. This paper explains precisely the relevance of nurse leadership and management in the healthcare system. Primarily, it highlights some important aspects that are involved in enhancing nursing leadership and management. Next, the paper describes a range of leadership qualities that are recognized in the provision of effective healthcare based in the context of International and New Zealand report. The paper winds up by analyzing how positive nurse leadership and management influence the delivery of quality health services. In essence, the section describes the importance of leadership and management and how it impacts on Patient Care.
Nursing leadership and management are powerful organization systems for shaping various health policies both at the health systems levels and globally. Nursing leadership has been incorporated in government agencies, healthcare regulatory bodies, and health advocacy groups and departments. As the international health systems advocate for the provision of innovative, quality, and cost-efficient patient care, the nursing leadership has been recognized as the most influential factor in shaping the healthcare organizations to ensure the realization of required patient care (Shariff, 2014). In particular, nursing leadership has a broad knowledge of the societal, economic, and political aspects influencing the healthcare system. Also, they are in a position to identify and reform various cultural, societal and financial barriers facing different levels of the healthcare system. Additionally, the nurse leaders have a pool of understanding of the health research as well as the education systems which are important in the current healthcare systems. They are equipped with knowledge on health care education and its relationship with the practice of healthcare research. Most importantly, nurse leaders operating at this level of the health system are well-informed with the perspectives and values of their nursing profession; thus, they are influential contributors of patient-centred health care delivery (Machell, Gough, & Steward, 2009). With this professional and environmental knowledge, they are well placed in advocating for ideal policies and models of care at the nursing unit and in the wider health care. All these aspects of nursing leadership work together to boost quality improvement, patient care coordination, as well as delivering clinical care and safety in the health care system.
Nursing Leadership and Management Qualities and its Impacts on Patient Care
Based on International and New Zealand literature, nursing leadership strategies and qualities significantly influence the delivery of health services and patient care improvement. These qualities are required for providing ideal cultures that promote safe, high quality and compassionate patient care. This section analyzes some of the crucial qualities of nursing leadership at all levels of health care system.
Staff Engagement and Satisfaction
The level of staff engagement in making major decisions that affect their welfare determines the overall delivery of service. The international literature data suggests that where the nursing leadership stipulates well-laid procedures of staff engagement and emotional capacity to care one another, there are reduced and declining cases of patient death. High-quality patient care is also experienced when the nursing leadership observes a high level of staff satisfaction coupled with integrated, coherent, and supportive people management practices. Thus, for a healthcare care organization to achieve quality patient care, leaders must create a positive environment that incorporates staff engagement and satisfactions platforms.
Learning, Innovation, and Quality Improvement
The collapse of Staffordshire NHS Agency advocated for culture change in health care organizations. The leadership had to stipulate strong emphasis based on learning, innovation and quality improvement as the key elements required to revive healthcare performance (West et al., 1992). Besides, they had to adopt a culture of ethical learning to ensure that needs of the patients were fulfilled. In effect, the leadership had to incorporate innovations aspects with strong emphasis on transparency, accountability. This action would ensure that all information on the quality of healthcare and safety of patients was made accessible to every health unit and sector in the service.
Clear Objectives
Strategic Narrative and Compelling Visions Leaders in best healthcare organizations focus on strategic narrative and vision geared towards high quality and compassionate health care. According to Dixon-Woods et al. (2013), these aspects serve as the core purpose and priority of an efficient nursing organization. On the same note, the message that is passed by leaders must prioritize actions based visions to achieve the intended results. A strategic narrative and prioritized vision create a mechanism to monitor, measure, reinforce, and reward the working staffs, which influences the delivery of services to the patient.
Team Working
Apparently, follow-up data and report intended to assess the existence of essential elements of teamwork shows that only about 40% of healthcare staffs work as a team (Walsworth‐Bell et al., 1992). Analysis of such organizations has revealed extreme cases of staff harassment, high levels of errors, staff absenteeism, which have translated to high patient mortality rate. Contrasting reports from NHS where teamwork was highly upheld (91%) revealed that high reduction in such vices. Therefore, as the co-morbidity becomes highly common and complexity of health care intensifies, the nursing leadership must uphold teamwork as a crucial contributor to healthcare quality. Leaders must ensure that all departments of the healthcare organization work closely together and even integrate the wider health care system to ensure the provision of quality healthcare. Essential elements of teamwork should include team objectives, regular meetings, and interdependent working.
How Positive Nursing Leadership and Management Impact on Patient Care
Nursing leadership is an integral part of the provision of effective nursing care. Fundamentally, it is highly recognized in the implementation of systematic and goal prioritized interventions, which aims to promote the health conditions and comfort of the patient. Since nurses are high involved in the provision of essential care, their role in the nursing leadership and management system is clearly manifested. Nurses motivate and coordinate various medical care teams and patient care to ensure support and well- being of the patient and their family (James, 2010). As their careers progress, they take their role of leadership within the health care organizations as well as beyond the nursing domain or even the entire health care system. They conduct healthcare research and education needed in all health care settings and management. In this regards, Nurse Leadership is essential for various reasons; thus, their contribution should always be fully recognized and understood. This section analyzes the importance of nursing leadership in the health care system and how it impacts on patient care.
Coordinating Patient Outcomes and Safety
The provision of safety for the patients is a vital requirement in every health care organization. Nursing leadership has an essential role in promoting positive patient outcomes as well as promoting the high-quality patient care and safety. It coordinates the patient care system, medication management, infection control, assistance with daily living activities, and general social support. Notably, patient outcome and their safety are greatly influenced by other health care providers ranging from the nursing unit manager to the national healthcare sector. A positive leadership formulates best care practices that ensure efficient interaction of these health care systems. According to Wong et al. (2013), a strong leadership style is directly linked with patient outcomes, patient safety, and the entire range of clinical settings. For instance, strong leadership is directly correlated with reduced rates of pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and brain hemorrhage (Capuano, Bokovoy, Hitchings, & Houser, 2005). On the same note, effective leadership is linked with low rates of patient falls and medication errors (Capuano et al., 2005)
Positive Work Environment
The scope in which the nurses experience empowerment depends, to a greater extent, on the nature and behaviour of nursing leadership; in particular, positive leadership behaviours instil healthy transformational practices that create practical and empowering work conditions (Laschinger et al., 2012). Research have pointed that efficient transformational and nurse empowering environment is translated into enhanced patient care and patient-based healthcare provision.

Employ and Retain Appropriate Nursing Workforce
The retention of a highly skilled workforce is critical to the healthcare system. The nursing leadership ensures that the workforce is highly skilled and qualified, which have an impact on patient outcomes. Primarily, appropriate staffing relates directly to the quality of healthcare provided and this, in turn, influences the patient care and recovery. In particular, the quality of the workforce influences other behaviours in the workplace including access to professional skills, organizational culture, interpersonal interaction, and lateral regulation over nursing activities. All these aspects influence the overall experience and outcome of patients. Most importantly, effective leadership influence staff retention and movement in the healthcare system. All these aspects influence the overall experience and outcome of patients. Most importantly, effective leadership influence staff retention and movement in the healthcare system. As well, this impact on the overall cohesion in the staff team and also influence the continuous existence of patient care and outcomes (Smith et al., 2009).
Financial Performance
A strong and efficient nursing leadership impacts on overall patient care regarding its financial performance. In all health systems, patient oriented services take the largest cost share. Therefore, the nursing leadership is required to formulate realistic financial approaches and decisions without compromising the quality of patient care (Ribelin, 2003). A stable financial system that upholds accountability and transparency can access quality medical facilities to its patients. Besides, a sound nursing leadership both at the unit and national levels leads to an enhanced sense on financial goals ownership within the nursing teams. This creates staff satisfaction and improved motivation among healthcare workforce, which results in patient care and service delivery (Ribelin, 2003).
Nursing leadership and management are fundamental aspects in the provision of innovative, quality, and cost-effective care. In essence, these aspects consist of a broad range of leadership ideas needed in the delivery of patient care, enhancing patient care coordination among staff, as well as boosting quality improvement and safety in the health care system. Since nursing leadership is an integral part in the provision of quality nursing care, their role should always be fully recognized and understood. Nursing leadership is involved in recruiting and retaining an appropriate nursing workforce, coordinating patient outcomes and safety, creating a positive working environment, and promoting financial performance. These roles influence the overall healthcare performance and outcome of patients Nursing leadership needs to be adaptable and possesses ideal qualities towards the realization of its goals. These qualities encompass inspiring visions prioritized at all health care levels, aligned and clear objectives in the organization of the nursing care systems and departments. Also, quality leadership advocate for the supportive environment and staff involvement, efficient working teams, and innovative, learning, and quality improvement geared in the delivery of effective medical care to the patients.
Aiken, L. H., Cimiotti, J. P., Sloane, D. M., Smith, H. L., Flynn, L., & Neff, D. F. (2011). Effects of nurse staffing and nurse education on patient deaths in hospitals with different nurse work environments. Medical Care, 49(12), 1047–1053. Capuano, T., Bokovoy, J., Hitchings, K., & Houser, J. (2005). Use of a validated model to evaluate the impact of the work environment on outcomes at a magnet hospital. Health Care Management Review, 30(3), 229–236. Dixon-Woods, M., Baker, R., Charles, K., Dawson, J., Jerzembek, G., Martin, G., & West, M. (2013). Culture and behaviour in the English national health service: Overview of lessons from a large multimethod study. BMJ Quality & Safety, 23(2), 106–115. Hinno, S., Partanen, P., & Vehviläinen-Julkunen, K. (2011). Nursing activities, nurse staffing and adverse patient outcomes as perceived by hospital nurses. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 21(11-12), 1584–1593. James, K. M. G. (2010). Incorporating complexity science theory into nursing curricula. Creative Nursing, 16(3), 137–142. Kotter J.P. (1996) Leading Change.Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Press. Laschinger, H. K. S., Wong, C. A., & Grau, A. L. (2012). Authentic leadership, empowerment and burnout: A comparison in new graduates and experienced nurses. Journal of Nursing Management, 21(3), 541–552. Machell, S., Gough, P., & Steward, K. (2009). From ward to board: Identifying good practice in the business of caring. United Kingdom: King’s Fund Ribelin, P. J. (2003). Retention reflects leadership style. Nursing Management (Springhouse), 34(8), 18–19. Shariff, N. (2014). Factors that act as facilitators and barriers to nurse leaders’ participation in health policy development. BMC Nursing, 13(1), 20. Smith, P., Pearson, P. H., & Ross, F. (2009). Emotions at work: What is the link to patient and staff safety? Implications for nurse managers in the NHS. Journal of Nursing Management, 17(2), 230–237. Walsworth‐Bell, J. P., Theaker, T., & Amir, Z. (1992). Survey of NHS staff Health‐related Behaviours. Journal of Management in Medicine, 6(4), 47–55. West, M. A., & Anderson, N. (1992). Innovation, cultural values, and the management of change in British hospitals. Work & Stress, 6(3), 293–310. Wong, C. A., & Laschinger, H. K. S. (2012). Authentic leadership, performance, and job satisfaction: The mediating role of empowerment. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 69(4), 947–959.

Cite this page
Share with friends using:
Removal Request

Finished papers: 1929
This paper is created by writer with
ID 277320874
If you want your paper to be:
Well-researched, fact-checked, and accurate
Original, fresh, based on current data
Eloquently written and immaculately formatted
275 words = 1 page double-spaced

Get your papers done by pros!
Other Pages
Goodacre essays, school psychology essays, first position essays, ex machina essays, media relations essays, bed space essays, american poetry essays, miles to go essays, ipv6 essays, ipv4 essays, roy cohn essays, thorium essays, example of genetically engineered foods research paper, example of essay on budhism two jewels other than budha, example of article review on critique of articles, research proposal on lost in gps augmented spaces and drift, report on benefits of a social media presence, good example of essay on standardizing regulations, good example of essay on james burke the day the universe changed, ufp chemistry lab practical 1 report examples, research review article reviews example, example of american history essay 3, good essay about the gay gene and homosexuality, rotating unbalance report examples, example of research paper on history of vogue magazine, ethics and values between for profit and not for profit organizations essays example, example of the odyssey essay, biomedical diagnostics degree personal statement example, christopher columbus book review examples, critique of a quantitative research report research paper example, ocean of trash essay example, good example of report on ethics privacy and information security, good letter to the parents report example, intellectual property term papers, inferior term papers, fare term papers, net profit term papers, preschool term papers, inference term papers, healing term papers, bargaining term papers, deciding term papers, interrogation term papers.
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline
Inspiring Leadership in Nursing: Key Topics to Empower the Next Generation of Nurse Leaders

This article was written in collaboration with Christine T. and ChatGPT, our little helper developed by OpenAI.

Nursing leadership plays a crucial role in the healthcare industry, influencing the quality of patient care and the overall performance of healthcare organizations. As the nursing profession continues to evolve, aspiring nurse leaders must stay informed about the latest developments and best practices in nursing leadership. This comprehensive guide explores essential nursing leadership topics, offering valuable insights and strategies for success.
The Importance of Nursing Leadership
Impact on patient care.
Effective nursing leadership directly impacts patient care, ensuring that nurses provide safe, high-quality, and evidence-based care. Nurse leaders play a critical role in developing and implementing policies, protocols, and standards of practice that promote positive patient outcomes.
Topic Examples
- The role of nurse leaders in reducing hospital-acquired infections
- How nurse leaders can improve patient satisfaction
- The effect of nursing leadership on patient safety initiatives
- Combating health care-associated infections: a community-based approach
- Nurse leaders’ impact on the reduction of medication errors
- Promoting patient-centered care through nursing leadership
- The role of nurse leaders in implementing evidence-based practices to improve patient outcomes
- How transformational leadership can positively impact patient satisfaction
- The impact of nurse leaders on patient safety and error reduction initiatives
Medical Studies Overwhelming?
Delegate Your Nursing Papers to the Pros!
Get 15% Discount
+ Plagiarism Report for FREE
Influence on Organizational Performance
Nurse leaders contribute to the overall performance of healthcare organizations by guiding and supporting nursing teams, managing resources, and participating in decision-making processes. Their leadership helps create a positive work environment, reduce staff turnover, and improve patient satisfaction.
- How nurse leaders can contribute to reducing staff turnover
- The role of nurse leaders in improving the hospital’s financial performance
- Nurse leaders as drivers of organizational culture
- The integral role of nurses in healthcare systems: the importance of education and experience
- The relationship between nurse leadership and hospital readmission rates
- How nurse leaders can contribute to reducing healthcare costs
- The role of nurse leaders in promoting interprofessional collaboration to improve organizational performance
- Strategies for nurse leaders to foster a positive work environment
- The impact of nursing leadership on employee engagement and satisfaction
Advancement of the Nursing Profession
Nurse leaders advocate for nursing, promoting professional development, innovation, and research. They also work to elevate the nursing profession’s status, fostering collaboration and interdisciplinary partnerships.
- The role of nurse leaders in shaping the future of nursing education
- How nurse leaders can advocate for the nursing profession
- The impact of nurse leaders on the development of nursing standards and policies
- Encouraging research and evidence-based practice among nursing teams
- The role of nurse leaders in promoting interprofessional collaboration
- Encouraging the pursuit of advanced nursing degrees and certifications among nursing staff
- The impact of nurse leaders on shaping healthcare policies and regulations
- How nurse leaders can advocate for improved working conditions and fair compensation for nursing staff
Essential Nursing Leadership Skills
Communication and interpersonal skills.
Effective communication and interpersonal skills are crucial for nursing leaders. They must listen actively, express themselves clearly, and demonstrate empathy and understanding when interacting with colleagues, patients, and families.
- Active listening skills for nurse leaders
- Developing emotional intelligence in nursing leadership
- The role of nonverbal communication in nursing leadership
- Strategies for nurse leaders to improve communication with their teams
- How nurse leaders can facilitate open and honest feedback
- The importance of emotional intelligence in nurse leadership
- Strategies for nurse leaders to improve their communication skills with diverse populations
- The role of nurse leaders in fostering effective communication within interdisciplinary healthcare teams
Decision-Making and Problem-Solving Abilities
Nurse leaders must be skilled in making informed decisions and solving complex problems. They should be able to analyze situations, weigh the pros and cons of various options, and choose the best course of action.
- Critical thinking skills for nurse leaders
- Ethical decision-making in nursing leadership
- The role of evidence-based practice in nursing leadership decisions
- Strategies for nurse leaders to develop effective problem-solving skills
- The importance of collaboration and teamwork in decision-making for nurse leaders
- The role of nurse leaders in crisis management and emergency preparedness
- How nurse leaders can develop effective problem-solving strategies to address complex healthcare challenges
Time Management and Organization
Managing time and resources effectively is essential for nurse leaders. They must be able to prioritize tasks, delegate responsibilities, and balance competing demands to ensure the smooth operation of their teams and organizations.
- Prioritization techniques for nurse leaders
- The role of delegation in effective time management for nursing managers
- Strategies for nurse leaders to manage workload and reduce stress
- Balancing clinical and administrative responsibilities as a nurse leader
- Time management tools and techniques for nurse leaders
- The importance of delegation in nurse leadership
- Strategies for nurse leaders to effectively manage their workload and prioritize tasks
- The role of nurse leaders in creating efficient workflows and processes within nursing teams
Embracing Diversity and Inclusivity in Nursing Leadership
The value of a diverse nursing workforce.
A diverse nursing workforce brings unique perspectives, experiences, and skills to the healthcare environment, benefiting patient care. By embracing diversity, nurse leaders can foster a more inclusive and supportive work environment that encourages collaboration and innovation.
- The benefits of diverse nursing teams for patient care
- The role of nurse leaders in recruiting and retaining diverse nursing staff
- Addressing health disparities through a diverse nursing workforce
- The impact of cultural competence on nursing practice and leadership
- Encouraging diverse perspectives and experiences in nursing teams
- Global health learning in nursing and health care disparities
- The benefits of having a diverse nursing workforce on patient outcomes and satisfaction
- Addressing health disparities through culturally competent nursing leadership
Strategies for Promoting Diversity and Inclusion
Nurse leaders can promote diversity and inclusion by implementing hiring and promotion practices that support equal opportunities, offering cultural competency training, and actively addressing discrimination and bias within their organizations.
- Overcoming unconscious bias in nursing leadership
- The role of nurse leaders in fostering an inclusive work environment
- Strategies for promoting diversity and inclusion in nursing education
- The impact of diversity and inclusion on nursing team performance
- Encouraging cultural competence and sensitivity among nursing staff
- Implementing diversity and inclusion training programs for nursing staff
- The role of nurse leaders in fostering a culture of respect and inclusivity within nursing teams
- Strategies for nurse leaders to address unconscious bias and promote equity in the workplace
Developing and Mentoring Future Nurse Leaders
Identifying and nurturing leadership potential.
Nurse leaders play an essential role in identifying and nurturing the leadership potential of their staff. By offering guidance, encouragement, and opportunities for growth, they can help prepare the next generation of nurse leaders.
- Recognizing leadership potential in nursing staff
- Strategies for nurse leaders to develop their team’s leadership skills
- The importance of succession planning in nursing leadership
- Encouraging a growth mindset among nursing teams
- The role of mentorship and coaching in nurturing future nurse leaders
- Strategies for nurse leaders to identify and develop emerging nurse leaders within their teams
- The role of nurse leaders in creating leadership development programs for nursing staff
Mentorship and Coaching
Mentorship and coaching are invaluable for aspiring nurse leaders. By sharing their knowledge, experience, and insights, experienced nurse leaders can help guide and support those looking to advance in nursing.
- The benefits of mentorship for both mentors and mentees in nursing
- Developing effective mentoring relationships in nursing
- The role of nurse leaders in fostering a mentoring culture
- Strategies for providing constructive feedback and coaching to nursing staff
- Encouraging professional growth and development through mentorship
- The benefits of mentorship relationships for both mentors and mentees in nursing
- Strategies for nurse leaders to establish effective mentorship programs within their organizations
- The role of nurse leaders in providing coaching and feedback to nursing staff for professional growth
Promoting Teamwork and Collaboration in Nursing
The importance of teamwork in healthcare.
Teamwork is crucial for delivering safe, high-quality patient care. Nurse leaders must foster a culture of collaboration, encouraging open communication, mutual support, and shared decision-making among their teams.
- The role of nurse leaders in promoting effective teamwork
- Strategies for building trust and collaboration among nursing teams
- The impact of teamwork on patient care and safety
- The benefits of interprofessional collaboration in healthcare
- The role of nurse leaders in fostering a positive team culture
- The role of nurse leaders in promoting collaboration and teamwork among nursing staff
- Strategies for nurse leaders to address and resolve conflicts within nursing teams
- The impact of effective teamwork on patient outcomes and staff satisfaction in healthcare settings
Strategies for Building Effective Nursing Teams
Nurse leaders can build effective nursing teams by promoting shared goals and values, providing clear expectations and feedback, and recognizing and celebrating team achievements. Additionally, they should facilitate team-building activities and opportunities for professional development, which can strengthen team cohesion and performance.
- The importance of clear communication and expectations in nursing teams
- Strategies for addressing and resolving conflicts within nursing teams
- The role of team-building activities in fostering collaboration and trust among nursing staff
- The impact of shared decision-making on nursing team performance
- Encouraging a culture of continuous improvement and learning within nursing teams
- The role of nurse leaders in selecting and retaining top nursing talent
- Strategies for nurse leaders to create a positive work environment that fosters teamwork and collaboration
- The importance of team-building activities and exercises for nursing staff
Advocating for Nursing and Improving Patient Care
Policy and advocacy.
Nurse leaders are responsible for advocating for policies and initiatives that support the nursing profession and improve patient care. They should be informed about healthcare legislation, engage in advocacy efforts, and encourage their teams to participate in policy-making.
- The role of nurse leaders in shaping healthcare policy
- Strategies for nurse leaders to advocate for the nursing profession at the local, state, and national levels
- The impact of nursing leadership on the development and implementation of healthcare policies and regulations
- Engaging nursing staff in policy discussions and advocacy efforts
- The importance of staying informed about current healthcare policy issues for nurse leaders
- The role of nurse leaders in advocating for policies that improve patient care and support the nursing profession
- Strategies for nurse leaders to effectively engage with policymakers and stakeholders
- The impact of nurse leaders on shaping healthcare policies at the local, state, and national levels
Driving Quality Improvement and Innovation
Nurse leaders must be committed to continuous quality improvement and innovation in patient care. By staying informed about evidence-based practices and encouraging their teams to adopt innovative approaches, they can drive positive change within their organizations and the healthcare industry.
- The role of nurse leaders in promoting a culture of continuous quality improvement
- Strategies for nurse leaders to identify and address areas for improvement in patient care
- The impact of nursing leadership on the implementation of evidence-based practices and innovations
- Encouraging a culture of creativity and innovation among nursing teams
- The role of nurse leaders in driving change and improvement in healthcare organizations
- The role of nurse leaders in leading quality improvement initiatives within their organizations
- Strategies for nurse leaders to foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation among nursing staff
- The impact of nurse-led quality improvement projects on patient care and organizational performance
Fostering a Positive Work Environment
Creating a supportive and respectful culture.
A positive work environment is essential for nursing staff satisfaction, retention, and performance. Nurse leaders should foster a culture of support and respect where staff feels valued, empowered, and motivated to provide the best possible care.
- The role of nurse leaders in fostering a positive work environment
- Strategies for nurse leaders to promote a culture of support and respect among nursing staff
- The importance of addressing and preventing workplace bullying and incivility in nursing
- Encouraging open and honest communication within nursing teams
- The role of nurse leaders in promoting work-life balance and well-being among nursing staff
Addressing Workplace Challenges and Conflicts
Nurse leaders must be proactive in addressing workplace challenges and conflicts. They can maintain a healthy and productive work environment by developing and implementing strategies to manage issues such as workload, burnout, and interpersonal conflicts.
- The role of nurse leaders in conflict resolution within nursing teams
- Strategies for nurse leaders to address common workplace challenges, such as staffing shortages and burnout
- The importance of developing a proactive approach to addressing conflicts and challenges in nursing
- Promoting a culture of accountability and responsibility among nursing staff
- The role of nurse leaders in providing support and resources for nursing staff facing challenges and conflicts
- Conflict resolution strategies for nurse leaders
- The role of nurse leaders in mediating and resolving interprofessional conflicts within healthcare teams
- Strategies for nurse leaders to prevent and address workplace burnout among nursing staff
Lifelong Learning and Professional Development
Commitment to continuing education.
Lifelong learning is essential for nurse leaders to stay current with healthcare and nursing practice advances. They should pursue continuing education opportunities, research, and stay informed about industry trends and best practices.
- The importance of lifelong learning for nurse leaders and nursing staff
- Strategies for nurse leaders to promote a culture of continuous education and professional development within their teams
- The impact of continuing education on nursing practice and leadership
- Encouraging nursing staff to engage in professional development opportunities
- Transforming advanced nursing practice: embracing IOM recommendations and higher education
- The role of nurse leaders in staying informed about current nursing research and best practices
- The impact of continuing education on nursing practice and patient outcomes
- Strategies for nurse leaders to support and encourage continuing education among their nursing staff
- The role of nurse leaders in staying up-to-date with the latest nursing research, guidelines, and best practices
Encouraging Professional Development in Nursing Teams
Nurse leaders should support and encourage the professional development of their nursing teams. By providing resources, opportunities, and encouragement, they can help their staff grow professionally and contribute to advancing the nursing profession.
- The role of nurse leaders in identifying professional development opportunities for nursing staff
- Strategies for nurse leaders to create individualized professional development plans for their team members
- The importance of fostering a growth mindset among nursing staff
- Encouraging nursing staff to participate in conferences, workshops, and other professional development activities
- The role of nurse leaders in providing mentorship and guidance for nursing staff seeking career advancement
- The benefits of ongoing professional development for nursing staff and healthcare organizations
- Strategies for nurse leaders to create professional development opportunities within their organizations
- The role of nurse leaders in developing and implementing career advancement pathways for nursing staff
The Power of Inspiring Leadership in Nursing
Nursing leadership is a critical component of the healthcare industry, impacting patient care, organizational performance, and the advancement of the nursing profession. By mastering essential leadership skills, embracing diversity, promoting teamwork, and fostering a positive work environment, aspiring nurse leaders can make a meaningful difference in the lives of their patients, colleagues, and organizations. Committing to lifelong learning and professional development will ensure that nurse leaders remain at the forefront of their field, inspiring and empowering the next generation of nursing professionals.
Table of content
Crafted with Care:
Nursing Essays!
Precision, Passion, & Professionalism in Every Page.
Director of Harvard Global Nursing Leadership Program to be 2024 Penn Nursing Commencement Speaker
20210305093594.png)
Stephanie Ferguson, PhD, RN, FAAN, the Director of the Harvard Global Nursing Leadership Program and Professor of the Practice of Health Policy and Management, will serve as the 2024 Penn Nursing commencement speaker.
PHILADELPHIA (March 21, 2024) – Stephanie Ferguson, PhD, RN, FAAN , the Director of the Harvard Global Nursing Leadership Program and Professor of the Practice of Health Policy and Management at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health , will serve as the 2024 Penn Nursing commencement speaker. The event will take place at 3:00 PM EST on Monday, May 20, 2024, at the Kimmel Center for the Performing Arts .
Dr. Ferguson is a global health care leader who has worked in more than 100 nations as a technical advisor, consultant, and facilitator for organizations including the World Health Organization (WHO), the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), the International Council of Nurses (ICN), and the National Council of State Boards of Nursing (NCSBN).
“Dr. Ferguson’s exemplary career as a global health leader has influenced policy at the highest levels, both nationally and internationally. She is a great inspiration as our students look ahead to their careers in nursing,” said Penn Nursing Dean Antonia M. Villarruel . “Penn Nursing develops innovative leaders who are prepared to address looming challenges as opportunities to promote health, wherever they practice. Having Dr. Ferguson address our graduating class this year speaks to the drive I see in our students to expand the boundaries of what society typically thinks nurses do.”
For more than 20 years at WHO’s headquarters, regional offices, and PAHO, Ferguson developed strategic plans and initiatives to strengthen and evaluate health care delivery systems, human resources for health and regulations, population health outcomes, and nursing and other health professional education, leadership programs and services. During her ten-plus years at ICN, she directed the ICN Leadership for Change Programä, the ICN-Burdett Global Nursing Leadership Instituteä, and served as an ICN Consultant for Nursing and Health Policy.
Ferguson is an elected member of the National Academy of Medicine (NAM) and served on the NAM Nominating Committee. She was an appointed member on the NAM’s recent Consensus Study on Global Health and the Future Role of the USA. She is an elected Fellow of the American Academy of Nursing (AAN) and chaired the AAN’s International Task Force. She is a former chair of the Advisory Council for the AAN’s Institute for Nursing Leadership. Ferguson is a Distinguished Practitioner and Fellow in the National Academies of Practice and was a White House Fellow in 1996-97 in President Clinton’s Administration and served at the US Department of Health and Human Services in the Office of the Secretary.
Her many board appointments, honors and awards include the 2014 HRH Princess Muna Al Hussein Award from the American Nurses Credentialing Center, which recognized her significant contributions to health care across borders and exceptional dedication to nursing. She is also the recipient of the American Academy of Nursing’s 2020 Civitas Award for her extraordinary dedication to excellence in promoting quality care in nursing worldwide.
Dr. Ferguson received her PhD in 1996 and her BSN in 1985 from the University of Virginia in Charlottesville, VA. Her MS/Nursing degree in 1987 is from the Virginia Commonwealth University, Medical College of Virginia, in Richmond, VA.
About the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing
The University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing is one of the world’s leading schools of nursing. For the eighth year in a row, it is ranked the #1 nursing school in the world by QS University. For the second year in a row, our Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) program is ranked # 1 in the 2023 U.S. News & World Report’s Best Colleges rankings. Penn Nursing is also consistently ranked highly in the U.S. News & World Report annual list of best graduate schools and is ranked as one of the top schools of nursing in funding from the National Institutes of Health. Penn Nursing prepares nurse scientists and nurse leaders to meet the health needs of a global society through innovation in research, education, and practice. Follow Penn Nursing on: Facebook , X , LinkedIn , YouTube , & Instagram .
MEDIA CONTACT
Type of article.
- Experts keyboard_arrow_right Expert Pitch Expert Query Expert Directory
- Journalists
- About keyboard_arrow_right Member Services Accessibility Statement Newswise Live Invoice Lookup Services for Journalists Archived Wires Participating Institutions Media Subscribers Sample Effectiveness Reports Terms of Service Privacy Policy Our Staff Contact Newswise
- Blog FAQ Help
Leadership & Management in Nursing: Personal Experience Personal Essay
In my interactions with the preceptor, I have come to realize that the most fundamental issues about leadership and management in homecare settings do not necessarily revolve around endowments in financial aspects and material resources; rather, effective leadership and management involve collaboration and establishment of mutually fulfilling relationships with colleagues and patients. It is clear how my preceptor collaborates with other nursing officers in certain responsibilities and functions, and how she influences the process of care to achieve positive outcomes for patients and staff. My preceptor, above all things, teaches me that collaboration and establishment of fulfilling relationships with patients and colleagues must increasingly rely on trust, clinical expertise, and professional autonomy. Indeed, through my interactions with the preceptor, I have come to realize that nurses are the face of the care of which the patients are most aware, but continue to be regarded as subordinate and passive recipients of the leader’s influence because most nursing leaders within the institutional setting do not indulge them on collaborative and mutually fulfilling relationships. Now, I can boldly suggest that collaboration and the establishment of mutually fulfilling relationships are, in my view, critical for the health institution’s patient care objectives and the nurses’ personal and professional development and management skills.
Identified Concepts about Leadership and/or Management
As a direct consequence of my constant interactions with my preceptor in my clinical experience, I have come to identify many concepts, processes, and principles about leadership and/or management that will shape and develop my nursing practice. Some of the most dominant are explained as follows:
Leading Change (Chapter 17)
My constant interactions with my preceptor, who happens to be the Director of Nursing Practice and Hospital Education, have demonstrated that nurses are not only agents of change but visionaries and active participants in learning as well as in the process of giving care. As agents of change, I have come to realize that we also ought to be in the frontline in advocating for the needs of our patients, profession, institutions, and the standards of competency anticipated of registered nurses (RNs). As agents of change, we are not only expected to deal with and enhance the lives of patients struggling with various health-related challenges, but we should go an extra mile to assist colleagues to understand the importance, necessity, and process of change, and to support each other during times of difficult transitions such as those involved in major hospital reorganizations.
Delegation of Authority (Chapter 10)
As demonstrated by my preceptor, delegation of authority in the management of case loads within the homecare setting is extremely important not only because of the recurrent need for skilled nursing care and management to meet complex healthcare needs emerging in communities, but also due to the urge to reconceptualise and manage care in ways that bring economies of scale and successfully meet the needs and expectations of people. I have successfully internalized the facts that delegation of authority not only results in successful caseload analysis, care coordination and prioritization, but ensures that the healthcare needs and expectations of patients and their families are being addressed by the appropriate person at the appropriate time.
Building teams through Empowerment & Partnerships (Chapter 18 and Chapter 10)
My interactions with my preceptor have illuminated an important premise that teams can be developed through communications, but effective teams need to be grounded in empowering the nursing staff and involving them in practice-related decision making processes. It has indeed dawned on me that partnerships and teams can be achieved and enhanced by structurally empowering the nursing staff through availing means to access information, resources, supports and opportunities via formal or informal trajectories of power. My preceptor is particularly effective in using networks among peers and colleagues (informal means) not only to build empowered and satisfied work teams, but also to establish partnerships that draw on increased decision involvement and trust to achieve positive perceptions of an effective patient safety climate.
Staffing & Scheduling (Chapter 14)
Perhaps the most important things I have observed regarding staffing and scheduling of roles is that both processes must be evidence-based but not grounded in popular opinion or tradition, and that the effectiveness of staffing and scheduling of roles in homecare settings has considerable business, patient safety, and quality ramifications that sit at the heart of the nurse manager’s role. The wisdom and experience of the nurse leader, as demonstrated by my preceptor during my clinical trials, has the capacity to influence success in staffing and scheduling.
Evaluating Staff (Chapter 15)
From my clinical experience with my preceptor, I have observed that evaluation of nursing staff by their superiors is a standard managerial practice due, in large part, to the fact that it assists them to select the right staff members for diverse care-related duties. Perhaps this is the major reason why my preceptor always keeps a note pad by her side to note both negative and positive behaviours of nursing trainees with the view to provide a much more focused and accurate assessment of their performance during the clinical trials. The preceptor uses her notes not only to mentor me on my weak point, but also to reinforce my strengths.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, May 19). Leadership & Management in Nursing: Personal Experience. https://ivypanda.com/essays/leadership-amp-management-in-nursing-personal-experience/
"Leadership & Management in Nursing: Personal Experience." IvyPanda , 19 May 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/leadership-amp-management-in-nursing-personal-experience/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Leadership & Management in Nursing: Personal Experience'. 19 May.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Leadership & Management in Nursing: Personal Experience." May 19, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/leadership-amp-management-in-nursing-personal-experience/.
1. IvyPanda . "Leadership & Management in Nursing: Personal Experience." May 19, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/leadership-amp-management-in-nursing-personal-experience/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Leadership & Management in Nursing: Personal Experience." May 19, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/leadership-amp-management-in-nursing-personal-experience/.
- Business Ethics in Leadership & Management Development
- Global Leadership & Management: Expansion to France
- Leadership & Management in International Healthcare
- Islamic Law and Shariah: Leadership & Management
- Changes in Healthcare, Nursing Leadership & Management
- Boeing’s e-Enabled Advantage
- Homecare Systems for Elderly Individuals
- Homecare Service for the Elderly
- Preceptor & Graduate Nursing Student Relationships
- Nursing Preceptor Orientation Program
- Nurses' Perceptions of Empowerment and Patient Satisfaction
- Chapters 5, 11, 12, 14, 16, 20 of "Leading and Managing in Nursing" by Yoder-Wise
- Research Importance to Current Nursing Practice
- Registered Nurses Choosing to Stay for Long-Term Employment
- Workplace Violence in Emergency Department
The Philippines economy in 2024: Stronger for longer?
The Philippines ended 2023 on a high note, being the fastest growing economy across Southeast Asia with a growth rate of 5.6 percent—just shy of the government's target of 6.0 to 7.0 percent. 1 “National accounts,” Philippine Statistics Authority, January 31, 2024; "Philippine economic updates,” Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas, November 16, 2023. Should projections hold, the Philippines is expected to, once again, show significant growth in 2024, demonstrating its resilience despite various global economic pressures (Exhibit 1). 2 “Economic forecast 2024,” International Monetary Fund, November 1, 2023; McKinsey analysis.
The growth in the Philippine economy in 2023 was driven by a resumption in commercial activities, public infrastructure spending, and growth in digital financial services. Most sectors grew, with transportation and storage (13 percent), construction (9 percent), and financial services (9 percent), performing the best (Exhibit 2). 3 “National accounts,” Philippine Statistics Authority, January 31, 2024. While the country's trade deficit narrowed in 2023, it remains elevated at $52 billion due to slowing global demand and geopolitical uncertainties. 4 “Highlights of the Philippine export and import statistics,” Philippine Statistics Authority, January 28, 2024. Looking ahead to 2024, the current economic forecast for the Philippines projects a GDP growth of between 5 and 6 percent.
Inflation rates are expected to temper between 3.2 and 3.6 percent in 2024 after ending 2023 at 6.0 percent, above the 2.0 to 4.0 percent target range set by the government. 5 “Nomura downgrades Philippine 2024 growth forecast,” Nomura, September 11, 2023; “IMF raises Philippine growth rate forecast,” International Monetary Fund, July 16, 2023.
For the purposes of this article, most of the statistics used for our analysis have come from a common thread of sources. These include the Central Bank of the Philippines (Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas); the Department of Energy Philippines; the IT and Business Process Association of the Philippines (IBPAP); and the Philippines Statistics Authority.
The state of the Philippine economy across seven major sectors and themes
In the article, we explore the 2024 outlook for seven key sectors and themes, what may affect each of them in the coming year, and what could potentially unlock continued growth.
Financial services
The recovery of the financial services sector appears on track as year-on-year growth rates stabilize. 6 Philippines Statistics Authority, November 2023; McKinsey in partnership with Oxford Economics, November 2023. In 2024, this sector will likely continue to grow, though at a slower pace of about 5 percent.
Financial inclusion and digitalization are contributing to growth in this sector in 2024, even if new challenges emerge. Various factors are expected to impact this sector:
- Inclusive finance: Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas continues to invest in financial inclusion initiatives. For example, basic deposit accounts (BDAs) reached $22 million in 2023 and banking penetration improved, with the proportion of adults with formal bank accounts increasing from 29 percent in 2019 to 56 percent in 2021. 7 “Financial inclusion dashboard: First quarter 2023,” Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas, February 6, 2024.
- Digital adoption: Digital channels are expected to continue to grow, with data showing that 60 percent of adults who have a mobile phone and internet access have done a digital financial transaction. 8 “Financial inclusion dashboard: First quarter 2023,” Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas, February 6, 2024. Businesses in this sector, however, will need to remain vigilant in navigating cybersecurity and fraud risks.
- Unsecured lending growth: Growth in unsecured lending is expected to continue, but at a slower pace than the past two to three years. For example, unsecured retail lending for the banking system alone grew by 27 percent annually from 2020 to 2022. 9 “Loan accounts: As of first quarter 2023,” Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas, February 6, 2024; "Global banking pools,” McKinsey, November 2023. Businesses in this field are, however, expected to recalibrate their risk profiling models as segments with high nonperforming loans emerge.
- High interest rates: Key interest rates are expected to decline in the second half of 2024, creating more accommodating borrowing conditions that could boost wholesale and corporate loans.
Supportive frameworks have a pivotal role to play in unlocking growth in this sector to meet the ever-increasing demand from the financially underserved. For example, financial literacy programs and easier-to-access accounts—such as BDAs—are some measures that can help widen market access to financial services. Continued efforts are being made to build an open finance framework that could serve the needs of the unbanked population, as well as a unified credit scoring mechanism to increase the ability of historically under-financed segments, such as small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), to access formal credit. 10 “BSP launches credit scoring model,” Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas, April 26, 2023.
Energy and Power
The outlook for the energy sector seems positive, with the potential to grow by 7 percent in 2024 as the country focuses on renewable energy generation. 11 McKinsey analysis based on input from industry experts. Currently, stakeholders are focused on increasing energy security, particularly on importing liquefied natural gas (LNG) to meet power plants’ requirements as production in one of the country’s main sources of natural gas, the Malampaya gas field, declines. 12 Myrna M. Velasco, “Malampaya gas field prod’n declines steeply in 2021,” Manila Bulletin , July 9, 2022. High global inflation and the fact that the Philippines is a net fuel importer are impacting electricity prices and the build-out of planned renewable energy projects. Recent regulatory moves to remove foreign ownership limits on exploration, development, and utilization of renewable energy resources could possibly accelerate growth in the country’s energy and power sector. 13 “RA 11659,” Department of Energy Philippines, June 8, 2023.
Gas, renewables, and transmission are potential growth drivers for the sector. Upgrading power grids so that they become more flexible and better able to cope with the intermittent electricity supply that comes with renewables will be critical as the sector pivots toward renewable energy. A recent coal moratorium may position natural gas as a transition fuel—this could stimulate exploration and production investments for new, indigenous natural gas fields, gas pipeline infrastructure, and LNG import terminal projects. 14 Philippine energy plan 2020–2040, Department of Energy Philippines, June 10, 2022; Power development plan 2020–2040 , Department of Energy Philippines, 2021. The increasing momentum of green energy auctions could facilitate the development of renewables at scale, as the country targets 35 percent share of renewables by 2030. 15 Power development plan 2020–2040 , 2022.
Growth in the healthcare industry may slow to 2.8 percent in 2024, while pharmaceuticals manufacturing is expected to rebound with 5.2 percent growth in 2024. 16 McKinsey analysis in partnership with Oxford Economics.
Healthcare demand could grow, although the quality of care may be strained as the health worker shortage is projected to increase over the next five years. 17 McKinsey analysis. The supply-and-demand gap in nursing alone is forecast to reach a shortage of approximately 90,000 nurses by 2028. 18 McKinsey analysis. Another compounding factor straining healthcare is the higher than anticipated benefit utilization and rising healthcare costs, which, while helping to meet people's healthcare budgets, may continue to drive down profitability for health insurers.
Meanwhile, pharmaceutical companies are feeling varying effects of people becoming increasingly health conscious. Consumers are using more over the counter (OTC) medication and placing more beneficial value on organic health products, such as vitamins and supplements made from natural ingredients, which could impact demand for prescription drugs. 19 “Consumer health in the Philippines 2023,” Euromonitor, October 2023.
Businesses operating in this field may end up benefiting from universal healthcare policies. If initiatives are implemented that integrate healthcare systems, rationalize copayments, attract and retain talent, and incentivize investments, they could potentially help to strengthen healthcare provision and quality.
Businesses may also need to navigate an increasingly complex landscape of diverse health needs, digitization, and price controls. Digital and data transformations are being seen to facilitate improvements in healthcare delivery and access, with leading digital health apps getting more than one million downloads. 20 Google Play Store, September 27, 2023. Digitization may create an opportunity to develop healthcare ecosystems that unify touchpoints along the patient journey and provide offline-to-online care, as well as potentially realizing cost efficiencies.
Consumer and retail
Growth in the retail and wholesale trade and consumer goods sectors is projected to remain stable in 2024, at 4 percent and 5 percent, respectively.
Inflation, however, continues to put consumers under pressure. While inflation rates may fall—predicted to reach 4 percent in 2024—commodity prices may still remain elevated in the near term, a top concern for Filipinos. 21 “IMF raises Philippine growth forecast,” July 26, 2023; “Nomura downgrades Philippines 2024 growth forecast,” September 11, 2023. In response to challenging economic conditions, 92 percent of consumers have changed their shopping behaviors, and approximately 50 percent indicate that they are switching brands or retail providers in seek of promotions and better prices. 22 “Philippines consumer pulse survey, 2023,” McKinsey, November 2023.
Online shopping has become entrenched in Filipino consumers, as they find that they get access to a wider range of products, can compare prices more easily, and can shop with more convenience. For example, a McKinsey Philippines consumer sentiment survey in 2023 found that 80 percent of respondents, on average, use online and omnichannel to purchase footwear, toys, baby supplies, apparel, and accessories. To capture the opportunity that this shift in Filipino consumer preferences brings and to unlock growth in this sector, retail organizations could turn to omnichannel strategies to seamlessly integrate online and offline channels. Businesses may need to explore investments that increase resilience across the supply chain, alongside researching and developing new products that serve emerging consumer preferences, such as that for natural ingredients and sustainable sources.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is a key contributor to the Philippine economy, contributing approximately 19 percent of GDP in 2022, employing about 7 percent of the country’s labor force, and growing in line with GDP at approximately 6 percent between 2023 and 2024. 23 McKinsey analysis based on input from industry experts.
Some changes could be seen in 2024 that might affect the sector moving forward. The focus toward building resilient supply chains and increasing self-sufficiency is growing. The Philippines also is likely to benefit from increasing regional trade, as well as the emerging trend of nearshoring or onshoring as countries seek to make their supply chains more resilient. With semiconductors driving approximately 45 percent of Philippine exports, the transfer of knowledge and technology, as well as the development of STEM capabilities, could help attract investments into the sector and increase the relevance of the country as a manufacturing hub. 24 McKinsey analysis based on input from industry experts.
To secure growth, public and private sector support could bolster investments in R&D and upskill the labor force. In addition, strategies to attract investment may be integral to the further development of supply chain infrastructure and manufacturing bases. Government programs to enable digital transformation and R&D, along with a strategic approach to upskilling the labor force, could help boost industry innovation in line with Industry 4.0 demand. 25 Industry 4.0 is also referred to as the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Priority products to which manufacturing industries could pivot include more complex, higher value chain electronic components in the semiconductor segment; generic OTC drugs and nature-based pharmaceuticals in the pharmaceutical sector; and, for green industries, products such as EVs, batteries, solar panels, and biomass production.
Information technology business process outsourcing
The information technology business process outsourcing (IT-BPO) sector is on track to reach its long-term targets, with $38 billion in forecast revenues in 2024. 26 Khriscielle Yalao, “WHF flexibility key to achieving growth targets—IBPAP,” Manila Bulletin , January 23, 2024. Emerging innovations in service delivery and work models are being observed, which could drive further growth in the sector.
The industry continues to outperform headcount and revenue targets, shaping its position as a country leader for employment and services. 27 McKinsey analysis based in input from industry experts. Demand from global companies for offshoring is expected to increase, due to cost containment strategies and preference for Philippine IT-BPO providers. New work setups continue to emerge, ranging from remote-first to office-first, which could translate to potential net benefits. These include a 10 to 30 percent increase in employee retention; a three- to four-hour reduction in commute times; an increase in enabled talent of 350,000; and a potential reduction in greenhouse gas emissions of 1.4 to 1.5 million tons of CO 2 per year. 28 McKinsey analysis based in input from industry experts. It is becoming increasingly more important that the IT-BPO sector adapts to new technologies as businesses begin to harness automation and generative AI (gen AI) to unlock productivity.
Talent and technology are clear areas where growth in this sector can be unlocked. The growing complexity of offshoring requirements necessitates building a proper talent hub to help bridge employee gaps and better match local talent to employers’ needs. Businesses in the industry could explore developing facilities and digital infrastructure to enable industry expansion outside the metros, especially in future “digital cities” nationwide. Introducing new service areas could capture latent demand from existing clients with evolving needs as well as unserved clients. BPO centers could explore the potential of offering higher-value services by cultivating technology-focused capabilities, such as using gen AI to unlock revenue, deliver sales excellence, and reduce general administrative costs.
Sustainability
The Philippines is considered to be the fourth most vulnerable country to climate change in the world as, due to its geographic location, the country has a higher risk of exposure to natural disasters, such as rising sea levels. 29 “The Philippines has been ranked the fourth most vulnerable country to climate change,” Global Climate Risk Index, January 2021. Approximately $3.2 billion, on average, in economic loss could occur annually because of natural disasters over the next five decades, translating to up to 7 to 8 percent of the country’s nominal GDP. 30 “The Philippines has been ranked the fourth most vulnerable country to climate change,” Global Climate Risk Index, January 2021.
The Philippines could capitalize on five green growth opportunities to operate in global value chains and catalyze growth for the nation:
- Renewable energy: The country could aim to generate 50 percent of its energy from renewables by 2040, building on its high renewable energy potential and the declining cost of producing renewable energy.
- Solar photovoltaic (PV) manufacturing: More than a twofold increase in annual output from 2023 to 2030 could be achieved, enabled by lower production costs.
- Battery production: The Philippines could aim for a $1.5 billion domestic market by 2030, capitalizing on its vast nickel reserves (the second largest globally). 31 “MineSpans,” McKinsey, November 2023.
- Electric mobility: Electric vehicles could account for 15 percent of the country’s vehicle sales by 2030 (from less than 1 percent currently), driven by incentives, local distribution, and charging infrastructure. 32 McKinsey analysis based on input from industry experts.
- Nature-based solutions: The country’s largely untapped total abatement potential could reach up to 200 to 300 metric tons of CO 2 , enabled by its biodiversity and strong demand.
The Philippine economy: Three scenarios for growth
Having grown faster than other economies in Southeast Asia in 2023 to end the year with 5.6 percent growth, the Philippines can expect a similarly healthy growth outlook for 2024. Based on our analysis, there are three potential scenarios for the country’s growth. 33 McKinsey analysis in partnership with Oxford Economics.
Slower growth: The first scenario projects GDP growth of 4.8 percent if there are challenging conditions—such as declining trade and accelerated inflation—which could keep key policy rates high at about 6.5 percent and dampen private consumption, leading to slower long-term growth.
Soft landing: The second scenario projects GDP growth of 5.2 percent if inflation moderates and global conditions turn out to be largely favorable due to a stable investment environment and regional trade demand.
Accelerated growth: In the third scenario, GDP growth is projected to reach 6.1 percent if inflation slows and public policies accommodate aspects such as loosening key policy rates and offering incentive programs to boost productivity.
Focusing on factors that could unlock growth in its seven critical sectors and themes, while adapting to the macro-economic scenario that plays out, would allow the Philippines to materialize its growth potential in 2024 and take steps towards achieving longer-term, sustainable economic growth.
Jon Canto is a partner in McKinsey’s Manila office, where Frauke Renz is an associate partner, and Vicah Villanueva is a consultant.
The authors wish to thank Charlene Chua, Charlie del Rosario, Ryan delos Reyes, Debadrita Dhara, Evelyn C. Fong, Krzysztof Kwiatkowski, Frances Lee, Aaron Ong, and Liane Tan for their contributions to this article.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

The Philippines Growth Dialogues

What does 2023 hold for the Philippines’ economy?

On the verge of a digital banking revolution in the Philippines

COMMENTS
Reflection On Leadership And Management Skills. This essay will be used as a tool to critique and improve my leadership and management skills as this is essential to the changes that are needed in the NHS improvement plan. In this process I have identified my leadership strengths as well as my development needs.
A nurse leader must have a variety of leadership styles depending on the situation. Leaders are sought after for their expertise in their respective specialties and staff nurses look up to these individuals for guidance. Management is defined as a process about an improvement in knowledge skills, habits and attitudes of the employee in an ...
Delivering safe, quality client care often requires registered nurses (RN) to manage care provided by the nursing team. Making assignments, delegating tasks, and supervising nursing team members are essential managerial components of an entry-level staff RN role. As previously discussed, nursing team members include RNs, licensed practical/vocational nurses (LPN/VN), and assistive personnel ...
It is interesting to observe that most of these factors are a part of leadership management, focusing on providing training and support and addressing the issues affecting nurses. ... Manojlovich 45 identified that strong nursing leadership behavior can contribute to the empowerment and self-efficacy on practice behaviors of the nurses, ...
Management & Team Working in Nursing Peter Ellis 4E 00_ELLIS_LMTWN_4E_FM.indd 3 25/10/2021 3:01:53 PM. 170 Chapter 9 Developing confidence as a manager and leader ... move from practising nurse through to leadership and management roles. Causer and Exworthy (2003) classically identify six stages on the path from practice to manage- ...
This essay explores the similarities and differences between leadership and management in the nursing profession. It specifically focuses on how nurse leaders and managers perceive continuous quality improvement and patient satisfaction. We will write a custom essay on your topic tailored to your instructions! 308 experts online.
The link to nursing leadership is obvious—ethics, positive change, purpose, growth, and social connection are all part of who we are as nurses and nurse leaders. The most common relational leadership styles are transformational, authentic, and servant. All three leadership styles have connections to healthy work environments and staff ...
Background: Nursing leadership plays a vital role in shaping outcomes for healthcare organizations, personnel and patients. With much of the leadership workforce set to retire in the near future, identifying factors that positively contribute to the development of leadership in nurses is of utmost importance.
7 Leadership Styles in Nursing. Nursing leadership styles can impact job satisfaction, nurse retention rates, quality of care, and patient outcomes. The nurse's educational background, personality, and work environment may influence their nursing leadership style. Each type of nurse leader role can be valuable when utilized in the right setting.
Abstract. Leadership and management form a key part of advanced clinical practice (ACP) and work in synergy with the other pillars of advanced practice. Advanced clinical practitioners focus on improving patient outcomes, and with application of evidence-based practice, using extended and expanded skills, they can provide cost-effective care.
Sullivan, J. (2012). Effective leadership and management in nursing (8th ed.). Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson. This essay, "Effective Leadership and Management in Nursing" is published exclusively on IvyPanda's free essay examples database. You can use it for research and reference purposes to write your own paper.
In a nursing organization, improving the quality of healthcare delivered by the department to be equal with the organizational performance is a key role of leadership (Marquis and Huston, 2015). Nursing leadership is essential in the clinical setting and plays an important role in the development of the nurse as an individual or as a professional.
An empowerment framework for nursing leadership development: supporting evidence. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 68(1), pp.159-169. Malloy, T. (2010). Nursing leadership style and psychosocial work environment. Journal of Nursing Management, 18(6), pp.715-725. Marriner, A. (2009). Nursing leadership and management effects work environments.
In the nursing profession, leadership is the process of coordinating day and night shifts, and controlling the nursing team to ensure that the activities and practices within the health care organization are accomplished successfully. Leadership incorporates the perception, opinion, skills and attitude of an individual concerning certain issues ...
Hospital and Health Networks, 78 (7), 86-112. This essay, "Leadership and Management in Nursing" is published exclusively on IvyPanda's free essay examples database. You can use it for research and reference purposes to write your own paper. However, you must cite it accordingly . Donate a paper.
Nursing leadership and management are primary and integral aspects of the provision of innovative, quality, and cost-efficient patient care. In particular, nursing leadership and management encompass a wide range of leadership qualities including delivering clinical care, enhancing patient care coordination, as well as boosting quality ...
Navigating Nursing Leadership: Your Journey as a Nurse Manager Considering a Career as a Nurse Manager 4 min • February, 13 2024 Aspiring to become a Nurse Manager means stepping into a dynamic leadership role crucial for the success of a unit, program, or department. Your primary responsibility will be to inspire and motivate staff towards ...
Finally, personal qualities determine the nurses' ability to lead. My personal skills have a significant impact on my leadership skills. I am very persistent, determined and communicative. My persistent nature has enabled me to stay focused on achieving my goals. My determination has kept me going even when faced with challenges.
The role of nurse leaders in fostering a positive work environment. Strategies for nurse leaders to promote a culture of support and respect among nursing staff. The importance of addressing and preventing workplace bullying and incivility in nursing. Encouraging open and honest communication within nursing teams.
A clinical nursing leader is one who is involved in direct patient care and who continuously improves the care that is afforded to such persons by influencing the treatment provision delivered by others (Cook, 2001). Leadership is not merely a series of skills or tasks; rather, it is an attitude that informs behaviour (Cook, 2001).
Leadership can use this tool to evaluate quality assurance and performance improvement (QAPI) progress. Nursing Home Survey on Patient Safety Culture This survey is designed specifically for nursing home providers and other staff and asks for their opinions about the culture of patient safety and healthcare quality in their nursing home.
Weiss, S. A., Tappen, R. M., & Grimley, K. (2019). Essentials of nursing leadership & management (7 th ed.). F. A. Davis Company. This essay, "Nursing Leadership and Management Issues" is published exclusively on IvyPanda's free essay examples database. You can use it for research and reference purposes to write your own paper.
Emily received her Bachelor's of Science in Nursing from Molloy College and accepted a role as a new graduate nurse in a critical care fellowship. During this time, she developed a passion for nursing leadership and management thus enrolling in a BSN to DNP program in nursing leadership and management at The George Washington University.
PHILADELPHIA (March 21, 2024) - Stephanie Ferguson, PhD, RN, FAAN, the Director of the Harvard Global Nursing Leadership Program and Professor of the Practice of Health Policy and Management at ...
SOUTH PLAINFIELD, NJ - The South Plainfield Womens Leadership Team is seeking submissions for its 2024 essay contest.
Leading Change (Chapter 17) My constant interactions with my preceptor, who happens to be the Director of Nursing Practice and Hospital Education, have demonstrated that nurses are not only agents of change but visionaries and active participants in learning as well as in the process of giving care. As agents of change, I have come to realize ...
The Philippines ended 2023 on a high note, being the fastest growing economy across Southeast Asia with a growth rate of 5.6 percent—just shy of the government's target of 6.0 to 7.0 percent. 1 "National accounts," Philippine Statistics Authority, January 31, 2024; "Philippine economic updates," Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas, November 16, 2023. ...