Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
How to Write a Literature Review

As every student knows, writing informative essay and research papers is an integral part of the educational program. You create a thesis, support it using valid sources, and formulate systematic ideas surrounding it. However, not all students know that they will also have to face another type of paper known as a Literature Review in college. Let's take a closer look at this with our custom essay writer .
Literature Review Definition
As this is a less common academic writing type, students often ask: "What is a literature review?" According to the definition, a literature review is a body of work that explores various publications within a specific subject area and sometimes within a set timeframe.
This type of writing requires you to read and analyze various sources that relate to the main subject and present each unique comprehension of the publications. Lastly, a literature review should combine a summary with a synthesis of the documents used. A summary is a brief overview of the important information in the publication; a synthesis is a re-organization of the information that gives the writing a new and unique meaning.
Typically, a literature review is a part of a larger paper, such as a thesis or dissertation. However, you may also be given it as a stand-alone assignment.
The Purpose
The main purpose of a literature review is to summarize and synthesize the ideas created by previous authors without implementing personal opinions or other additional information.
However, a literature review objective is not just to list summaries of sources; rather, it is to notice a central trend or principle in all of the publications. Just like a research paper has a thesis that guides it on rails, a literature review has the main organizing principle (MOP). The goal of this type of academic writing is to identify the MOP and show how it exists in all of your supporting documents.
Why is a literature review important? The value of such work is explained by the following goals it pursues:
- Highlights the significance of the main topic within a specific subject area.
- Demonstrates and explains the background of research for a particular subject matter.
- Helps to find out the key themes, principles, concepts, and researchers that exist within a topic.
- Helps to reveal relationships between existing ideas/studies on a topic.
- Reveals the main points of controversy and gaps within a topic.
- Suggests questions to drive primary research based on previous studies.
Here are some example topics for writing literature reviews:
- Exploring racism in "To Kill a Mockingbird," "The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn," and "Uncle Tom's Cabin."
- Isolationism in "The Catcher in the Rye," "Frankenstein," and "1984"
- Understanding Moral Dilemmas in "Crime and Punishment," "The Scarlet Letter," and "The Lifeboat"
- Corruption of Power in "Macbeth," "All the King's Men," and "Animal Farm"
- Emotional and Physical survival in "Lord of the Flies," "Hatchet," and "Congo."
How Long Is a Literature Review?
When facing the need to write a literature review, students tend to wonder, "how long should a literature review be?" In some cases, the length of your paper's body may be determined by your instructor. Be sure to read the guidelines carefully to learn what is expected from you.
Keeping your literature review around 15-30% of your entire paper is recommended if you haven't been provided with specific guidelines. To give you a rough idea, that is about 2-3 pages for a 15-page paper. In case you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, its length should be specified in the instructions provided.
Literature Review Format: APA, MLA, and Chicago
The essay format you use should adhere to the citation style preferred by your instructor. Seek clarification from your instructor for several other components as well to establish a desired literature review format:
- How many sources should you review, and what kind of sources should they be (published materials, journal articles, or websites)?
- What format should you use to cite the sources?
- How long should the review be?
- Should your review consist of a summary, synthesis, or a personal critique?
- Should your review include subheadings or background information for your sources?
If you want to format your paper in APA style, then follow these rules:
- Use 1-inch page margins.
- Unless provided with other instructions, use double-spacing throughout the whole text.
- Make sure you choose a readable font. The preferred font for APA papers is Times New Roman set to 12-point size.
- Include a header at the top of every page (in capital letters). The page header must be a shortened version of your essay title and limited to 50 characters, including spacing and punctuation.
- Put page numbers in the upper right corner of every page.
- When shaping your literature review outline in APA, don't forget to include a title page. This page should include the paper's name, the author's name, and the institutional affiliation. Your title must be typed with upper and lowercase letters and centered in the upper part of the page; use no more than 12 words, and avoid using abbreviations and useless words.
For MLA style text, apply the following guidelines:
- Double your spacing across the entire paper.
- Set ½-inch indents for each new paragraph.
- The preferred font for MLA papers is Times New Roman set to 12-point size.
- Include a header at the top of your paper's first page or on the title page (note that MLA style does not require you to have a title page, but you are allowed to decide to include one). A header in this format should include your full name; the name of your instructor; the name of the class, course, or section number; and the due date of the assignment.
- Include a running head in the top right corner of each page in your paper. Place it one inch from the page's right margin and half an inch from the top margin. Only include your last name and the page number separated by a space in the running head. Do not put the abbreviation p. before page numbers.
Finally, if you are required to write a literature review in Chicago style, here are the key rules to follow:
- Set page margins to no less than 1 inch.
- Use double spacing across the entire text, except when it comes to table titles, figure captions, notes, blockquotes, and entries within the bibliography or References.
- Do not put spaces between paragraphs.
- Make sure you choose a clear and easily-readable font. The preferred fonts for Chicago papers are Times New Roman and Courier, set to no less than 10-point size, but preferably to 12-point size.
- A cover (title) page should include your full name, class information, and the date. Center the cover page and place it one-third below the top of the page.
- Place page numbers in the upper right corner of each page, including the cover page.
Read also about harvard format - popular style used in papers.
Structure of a Literature Review
How to structure a literature review: Like many other types of academic writing, a literature review follows a typical intro-body-conclusion style with 5 paragraphs overall. Now, let’s look at each component of the basic literature review structure in detail:

- Introduction
You should direct your reader(s) towards the MOP (main organizing principle). This means that your information must start from a broad perspective and gradually narrow down until it reaches your focal point.
Start by presenting your general concept (Corruption, for example). After the initial presentation, narrow your introduction's focus towards the MOP by mentioning the criteria you used to select the literature sources you have chosen (Macbeth, All the King's Men, and Animal Farm). Finally, the introduction will end with the presentation of your MOP that should directly link it to all three literature sources.
Body Paragraphs
Generally, each body paragraph will focus on a specific source of literature laid out in the essay's introduction. As each source has its own frame of reference for the MOP, it is crucial to structure the review in the most logically consistent way possible. This means the writing should be structured chronologically, thematically or methodologically.
Chronologically
Breaking down your sources based on their publication date is a solid way to keep a correct historical timeline. If applied properly, it can present the development of a certain concept over time and provide examples in the form of literature. However, sometimes there are better alternatives we can use to structure the body.
Thematically
Instead of taking the "timeline approach," another option can be looking at the link between your MOP and your sources. Sometimes, the main idea will just glare from a piece of literature. Other times, the author may have to seek examples to prove their point. An experienced writer will usually present their sources by order of strength. For example, in "To Kill A Mockingbird," the entire novel was centralized around racism; in "The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn," racism was one of many themes.
Methodologically
As made obvious by the terminology, this type of structuring focuses on the methods used to present the central concept. For example, in "1984", George Orwell uses the law-and-order approach and shows the dangers of a dystopia for a social species.
In "Frankenstein," Mary Shelley exposes the character's physical traits as repulsive and horrifying, forcing him to suffer in an isolated environment. By showcasing the various methods used to portray the MOP, the writer can compare them based on things like severity, ethicality, and overall impact.
After presenting your key findings in the body paragraphs, there are 3 final objectives to complete in the essay's conclusion. First, the author should summarize the findings they have made or found, in other words, and briefly answer the question: "What have you learned?"
After discussing that information, the next step is to present the significance of the information about our current world today. In other words, how can the reader take the information and apply it to today's society? From that point, we finish off with a breadcrumb trail.
As the author, you want to leave the readers' trail of thought within the actual essay topic. This provides them with a means of further investigation—meaning that the reader may consider where the discussion will go next.
Writing an Outline for a Literature Review
Students often underestimate the importance of planning the structure of their papers in advance. However, this is not a wise approach. Having a rough APA literature review outline (or other style outlines) will not only help you follow the right format and structure but will also make the writing process simpler and help ensure that you include all of the important information without missing anything.
How to write a literature review outline: As you already know from the Structure section of this guide, every part of your literature review performs its own important role. Therefore, you should create your outline while keeping the general introduction-body-conclusion structure in mind and ensuring that each section meets its own objectives. However, it is important to remember that a literature review outline is slightly different from outlines of other types of essays because it does not provide new information. Instead, it focuses on existing studies relevant to the main topic.
Here is a literature review outline example on the subject of the Ebola virus to help you get it right:
- Introduce the general topic. Provide background information on the Ebola virus: genome, pathogenesis, transmission, epidemiology, treatment, etc.
- Shape the main research question: What is the potential role of arthropods (mechanical or biological vectors) in the distribution of the Ebola virus?
- Methodology: For example, the information was searched through X databases to find relevant research articles about the Ebola virus and arthropods' role in its spreading. The data was extracted using a standardized form.
- Expected outcomes
- Overall trends in the literature on this topic: While the natural reservoir of the virus is still not known with certainty, many researchers believe that arthropods (and fruit bats, in particular) pay a significant role in the distribution of the virus.
- Subject 1: A brief overview of the particular piece of literature in general terms; an analysis of the key aspects of the study; a review of the research questions, methods, procedures, and outcomes; and an overview of the strong and weak points, gaps, and contradictions.
- Subject 2: A brief overview of the particular piece of literature in general terms; an analysis of the key aspects of the study; a review of the research questions, methods, procedures, and outcomes; and an overview of the strong and weak points, gaps, and contradictions.
- Subject 3: A brief overview of the particular piece of literature in general terms; an analysis of the key aspects of the study; a review of the research questions, methods, procedures, and outcomes; and an overview of the strong and weak points, gaps, and contradictions.
- Indicate the relationships between the pieces of literature discussed. Emphasize key themes, common patterns, and trends. Talk about the pros and cons of the different approaches taken by the authors/researchers.
- State which studies seem to be the most influential.
- Emphasize the major contradictions and points of disagreement. Define the gaps still to be covered (if any).
- If applicable: define how your own study will contribute to further disclosure of the topic.
Hopefully, this sample outline will help you to structure your own paper. However, if you feel like you need some more advice on how to organize your review, don’t hesitate to search for more literature review outline examples in APA or other styles on the Web, or simply ask our writers to get a dissertation help .
Need Help With LITERATURE REVIEW?
Count on our literature review writing service to get it done! We will make your literature essay, we only need your paper requirements to save your precious time and nerves from writing it on your own!
How to Write a Good Literature Review
Whether you are writing a literature review within the framework of a large research project (e.g. thesis, dissertation, or other) or as a stand-alone assignment, the approach you should take to writing generally remains the same.

Whether you are writing a literature review within the framework of a large research project (e.g., thesis, dissertation, or other) or as a stand-alone assignment, the approach you should take to writing generally remains the same.
Now, as you know about the general rules and have a basic literature review outline template, let's define the steps to take to handle this task right with our service:
Step 1: Identifying the Topic
This is probably the only matter you may approach differently depending on whether your literature review comes within a research paper or a separate assignment altogether. If you are creating a literature review as a part of another work, you need to search for literature related to your main research questions and problems. Respectively, if you are writing it as a stand-alone task, you will have to pick a relevant topic and central question upon which you will collect the literature. Earlier in this guide, we suggested some engaging topics to guide your search.
Step 2: Conducting Research
When you have a clearly defined topic, it is time to start collecting literature for your review. We recommend starting by compiling a list of relevant keywords related to your central question—to make the entire research process much simpler and help you find relevant publications faster.
When you have a list of keywords, use them to search for valid and relevant sources. At this point, be sure to use only trusted sources, such as ones from university libraries, online scientific databases, etc.
Once you have found some sources, be sure to define whether or not they are actually relevant to your topic and research question. To save time, you can read abstracts to get general ideas of what the papers are about instead of the whole thing.
Pro Tip: When you finally find a few valid publications, take a look at their bibliographies to discover other relevant sources as well.
Step 3: Assess and Prioritize Sources
Throughout your research, you will likely find plenty of relevant literature to include in your literature review. At this point, students often make the mistake of trying to fit all the collected sources into their reviews. Instead, we suggest looking at what you've collected once more, evaluating the available sources, and selecting the most relevant ones. You most likely won't be able to read everything you find on a given topic and then be able to synthesize all of the sources into a single literature review. That's why prioritizing them is important.
To evaluate which sources are worth including in your review, keep in mind the following criteria:
- Credibility;
- Innovation;
- Key insights;
Furthermore, as you read the sources, don’t forget to take notes on everything you can incorporate into the review later. And be sure to get your citations in place early on. If you cite the selected sources at the initial stage, you will find it easier to create your annotated bibliography later on.
Step 4: Identify Relationships, Key Ideas, and Gaps
Before you can move on to outlining and writing your literature review, the final step is determining the relationships between the studies that already exist. Identifying the relationships will help you organize the existing knowledge, build a solid literature outline, and (if necessary) indicate your own research contribution to a specific field.
Some of the key points to keep an eye out for are:
- Main themes;
- Contradictions and debates;
- Influential studies or theories;
- Trends and patterns;
Here are a few examples: Common trends may include a focus on specific groups of people across different studies. Most researchers may have increased interest in certain aspects of the topic regarding key themes. Contradictions may include some disagreement concerning the theories and outcomes of a study. And finally, gaps most often refer to a lack of research on certain aspects of a topic.
Step 5: Make an Outline
Although students tend to neglect this stage, outlining is one of the most important steps in writing every academic paper. This is the easiest way to organize the body of your text and ensure that you haven't missed anything important. Besides, having a rough idea of what you will write about in the paper will help you get it right faster and more easily. Earlier in this guide, we already discussed the basic structure of a literature review and gave you an example of a good outline. At this workflow stage, you can use all of the knowledge you've gained from us to build your own outline.
Step 6: Move on to Writing
Having found and created all of your sources, notes, citations, and a detailed outline, you can finally get to the writing part of the process. At this stage, all you need to do is follow the plan you've created and keep in mind the overall structure and format defined in your professor's instructions.
Step 7: Adding the Final Touches
Most students make a common mistake and skip the final stage of the process, which includes proofreading and editing. We recommend taking enough time for these steps to ensure that your work will be worth the highest score. Do not underestimate the importance of proofreading and editing, and allocate enough time for these steps.
Pro Tip: Before moving on to proofreading and editing, be sure to set your literature review aside for a day or two. This will give you a chance to take your mind off it and then get back to proofreading with a fresh perspective. This tip will ensure that you won't miss out on any gaps or errors that might be present in your text.
These steps will help you create a top-notch literature review with ease! Want to get more advice on how to handle this body of work? Here are the top 3 tips you need to keep in mind when writing a literature review:
1. Good Sources
When working on a literature review, the most important thing any writer should remember is to find the best possible sources for their MOP. This means that you should select and filter through about 5-10 different options while doing initial research.
The stronger a piece of literature showcases the central point, the better the quality of the entire review.
2. Synthesize The Literature
Make sure to structure the review in the most effective way possible, whether it be chronologically, thematically, or methodologically. Understand what exactly you would like to say, and structure the source comparison accordingly.
3. Avoid Generalizations
Remember that each piece of literature will approach the MOP from a different angle. As the author, make sure to present the contrasts in approaches clearly and don't include general statements that offer no value.
Literature Review Examples
You can find two well-written literature reviews by the EssayPro writing team below. They will help you understand what the final product of a literature review should ideally look like.
The first literature review compares monolingual and bilingual language acquisition skills and uses various sources to prove its point:
The second literature review compares the impact of fear and pain on a protagonist’s overall development in various settings:
Both reviews will help you sharpen your skills and provide good guidelines for writing high-quality papers.
Get Help from an Essay Writer
Still aren’t sure whether you can handle literature review writing on your own? No worries because you can pay for essay writing and our service has got you covered! Boost your grades is to place an order in a few quick clicks and we will satisfy your write my paper request.
Related Articles
.webp)
How To Write An A-Grade Literature Review
3 straightforward steps (with examples) + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2019
Quality research is about building onto the existing work of others , “standing on the shoulders of giants”, as Newton put it. The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.
Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure you get it right . In this post, I’ll show you exactly how to write a literature review in three straightforward steps, so you can conquer this vital chapter (the smart way).
Overview: The Literature Review Process
- Understanding the “ why “
- Finding the relevant literature
- Cataloguing and synthesising the information
- Outlining & writing up your literature review
- Example of a literature review
But first, the “why”…
Before we unpack how to write the literature review chapter, we’ve got to look at the why . To put it bluntly, if you don’t understand the function and purpose of the literature review process, there’s no way you can pull it off well. So, what exactly is the purpose of the literature review?
Well, there are (at least) four core functions:
- For you to gain an understanding (and demonstrate this understanding) of where the research is at currently, what the key arguments and disagreements are.
- For you to identify the gap(s) in the literature and then use this as justification for your own research topic.
- To help you build a conceptual framework for empirical testing (if applicable to your research topic).
- To inform your methodological choices and help you source tried and tested questionnaires (for interviews ) and measurement instruments (for surveys ).
Most students understand the first point but don’t give any thought to the rest. To get the most from the literature review process, you must keep all four points front of mind as you review the literature (more on this shortly), or you’ll land up with a wonky foundation.
Okay – with the why out the way, let’s move on to the how . As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I’ll break down into three steps:
- Finding the most suitable literature
- Understanding , distilling and organising the literature
- Planning and writing up your literature review chapter
Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter. I know it’s very tempting, but don’t try to kill two birds with one stone and write as you read. You’ll invariably end up wasting huge amounts of time re-writing and re-shaping, or you’ll just land up with a disjointed, hard-to-digest mess . Instead, you need to read first and distil the information, then plan and execute the writing.

Step 1: Find the relevant literature
Naturally, the first step in the literature review journey is to hunt down the existing research that’s relevant to your topic. While you probably already have a decent base of this from your research proposal , you need to expand on this substantially in the dissertation or thesis itself.
Essentially, you need to be looking for any existing literature that potentially helps you answer your research question (or develop it, if that’s not yet pinned down). There are numerous ways to find relevant literature, but I’ll cover my top four tactics here. I’d suggest combining all four methods to ensure that nothing slips past you:
Method 1 – Google Scholar Scrubbing
Google’s academic search engine, Google Scholar , is a great starting point as it provides a good high-level view of the relevant journal articles for whatever keyword you throw at it. Most valuably, it tells you how many times each article has been cited, which gives you an idea of how credible (or at least, popular) it is. Some articles will be free to access, while others will require an account, which brings us to the next method.
Method 2 – University Database Scrounging
Generally, universities provide students with access to an online library, which provides access to many (but not all) of the major journals.
So, if you find an article using Google Scholar that requires paid access (which is quite likely), search for that article in your university’s database – if it’s listed there, you’ll have access. Note that, generally, the search engine capabilities of these databases are poor, so make sure you search for the exact article name, or you might not find it.
Method 3 – Journal Article Snowballing
At the end of every academic journal article, you’ll find a list of references. As with any academic writing, these references are the building blocks of the article, so if the article is relevant to your topic, there’s a good chance a portion of the referenced works will be too. Do a quick scan of the titles and see what seems relevant, then search for the relevant ones in your university’s database.
Method 4 – Dissertation Scavenging
Similar to Method 3 above, you can leverage other students’ dissertations. All you have to do is skim through literature review chapters of existing dissertations related to your topic and you’ll find a gold mine of potential literature. Usually, your university will provide you with access to previous students’ dissertations, but you can also find a much larger selection in the following databases:
- Open Access Theses & Dissertations
- Stanford SearchWorks
Keep in mind that dissertations and theses are not as academically sound as published, peer-reviewed journal articles (because they’re written by students, not professionals), so be sure to check the credibility of any sources you find using this method. You can do this by assessing the citation count of any given article in Google Scholar. If you need help with assessing the credibility of any article, or with finding relevant research in general, you can chat with one of our Research Specialists .
Alright – with a good base of literature firmly under your belt, it’s time to move onto the next step.
Need a helping hand?
Step 2: Log, catalogue and synthesise
Once you’ve built a little treasure trove of articles, it’s time to get reading and start digesting the information – what does it all mean?
While I present steps one and two (hunting and digesting) as sequential, in reality, it’s more of a back-and-forth tango – you’ll read a little , then have an idea, spot a new citation, or a new potential variable, and then go back to searching for articles. This is perfectly natural – through the reading process, your thoughts will develop , new avenues might crop up, and directional adjustments might arise. This is, after all, one of the main purposes of the literature review process (i.e. to familiarise yourself with the current state of research in your field).
As you’re working through your treasure chest, it’s essential that you simultaneously start organising the information. There are three aspects to this:
- Logging reference information
- Building an organised catalogue
- Distilling and synthesising the information
I’ll discuss each of these below:
2.1 – Log the reference information
As you read each article, you should add it to your reference management software. I usually recommend Mendeley for this purpose (see the Mendeley 101 video below), but you can use whichever software you’re comfortable with. Most importantly, make sure you load EVERY article you read into your reference manager, even if it doesn’t seem very relevant at the time.
2.2 – Build an organised catalogue
In the beginning, you might feel confident that you can remember who said what, where, and what their main arguments were. Trust me, you won’t. If you do a thorough review of the relevant literature (as you must!), you’re going to read many, many articles, and it’s simply impossible to remember who said what, when, and in what context . Also, without the bird’s eye view that a catalogue provides, you’ll miss connections between various articles, and have no view of how the research developed over time. Simply put, it’s essential to build your own catalogue of the literature.
I would suggest using Excel to build your catalogue, as it allows you to run filters, colour code and sort – all very useful when your list grows large (which it will). How you lay your spreadsheet out is up to you, but I’d suggest you have the following columns (at minimum):
- Author, date, title – Start with three columns containing this core information. This will make it easy for you to search for titles with certain words, order research by date, or group by author.
- Categories or keywords – You can either create multiple columns, one for each category/theme and then tick the relevant categories, or you can have one column with keywords.
- Key arguments/points – Use this column to succinctly convey the essence of the article, the key arguments and implications thereof for your research.
- Context – Note the socioeconomic context in which the research was undertaken. For example, US-based, respondents aged 25-35, lower- income, etc. This will be useful for making an argument about gaps in the research.
- Methodology – Note which methodology was used and why. Also, note any issues you feel arise due to the methodology. Again, you can use this to make an argument about gaps in the research.
- Quotations – Note down any quoteworthy lines you feel might be useful later.
- Notes – Make notes about anything not already covered. For example, linkages to or disagreements with other theories, questions raised but unanswered, shortcomings or limitations, and so forth.
If you’d like, you can try out our free catalog template here (see screenshot below).

2.3 – Digest and synthesise
Most importantly, as you work through the literature and build your catalogue, you need to synthesise all the information in your own mind – how does it all fit together? Look for links between the various articles and try to develop a bigger picture view of the state of the research. Some important questions to ask yourself are:
- What answers does the existing research provide to my own research questions ?
- Which points do the researchers agree (and disagree) on?
- How has the research developed over time?
- Where do the gaps in the current research lie?
To help you develop a big-picture view and synthesise all the information, you might find mind mapping software such as Freemind useful. Alternatively, if you’re a fan of physical note-taking, investing in a large whiteboard might work for you.

Step 3: Outline and write it up!
Once you’re satisfied that you have digested and distilled all the relevant literature in your mind, it’s time to put pen to paper (or rather, fingers to keyboard). There are two steps here – outlining and writing:
3.1 – Draw up your outline
Having spent so much time reading, it might be tempting to just start writing up without a clear structure in mind. However, it’s critically important to decide on your structure and develop a detailed outline before you write anything. Your literature review chapter needs to present a clear, logical and an easy to follow narrative – and that requires some planning. Don’t try to wing it!
Naturally, you won’t always follow the plan to the letter, but without a detailed outline, you’re more than likely going to end up with a disjointed pile of waffle , and then you’re going to spend a far greater amount of time re-writing, hacking and patching. The adage, “measure twice, cut once” is very suitable here.
In terms of structure, the first decision you’ll have to make is whether you’ll lay out your review thematically (into themes) or chronologically (by date/period). The right choice depends on your topic, research objectives and research questions, which we discuss in this article .
Once that’s decided, you need to draw up an outline of your entire chapter in bullet point format. Try to get as detailed as possible, so that you know exactly what you’ll cover where, how each section will connect to the next, and how your entire argument will develop throughout the chapter. Also, at this stage, it’s a good idea to allocate rough word count limits for each section, so that you can identify word count problems before you’ve spent weeks or months writing!
PS – check out our free literature review chapter template…
3.2 – Get writing
With a detailed outline at your side, it’s time to start writing up (finally!). At this stage, it’s common to feel a bit of writer’s block and find yourself procrastinating under the pressure of finally having to put something on paper. To help with this, remember that the objective of the first draft is not perfection – it’s simply to get your thoughts out of your head and onto paper, after which you can refine them. The structure might change a little, the word count allocations might shift and shuffle, and you might add or remove a section – that’s all okay. Don’t worry about all this on your first draft – just get your thoughts down on paper.

Once you’ve got a full first draft (however rough it may be), step away from it for a day or two (longer if you can) and then come back at it with fresh eyes. Pay particular attention to the flow and narrative – does it fall fit together and flow from one section to another smoothly? Now’s the time to try to improve the linkage from each section to the next, tighten up the writing to be more concise, trim down word count and sand it down into a more digestible read.
Once you’ve done that, give your writing to a friend or colleague who is not a subject matter expert and ask them if they understand the overall discussion. The best way to assess this is to ask them to explain the chapter back to you. This technique will give you a strong indication of which points were clearly communicated and which weren’t. If you’re working with Grad Coach, this is a good time to have your Research Specialist review your chapter.
Finally, tighten it up and send it off to your supervisor for comment. Some might argue that you should be sending your work to your supervisor sooner than this (indeed your university might formally require this), but in my experience, supervisors are extremely short on time (and often patience), so, the more refined your chapter is, the less time they’ll waste on addressing basic issues (which you know about already) and the more time they’ll spend on valuable feedback that will increase your mark-earning potential.
Literature Review Example
In the video below, we unpack an actual literature review so that you can see how all the core components come together in reality.
Let’s Recap
In this post, we’ve covered how to research and write up a high-quality literature review chapter. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- It is essential to understand the WHY of the literature review before you read or write anything. Make sure you understand the 4 core functions of the process.
- The first step is to hunt down the relevant literature . You can do this using Google Scholar, your university database, the snowballing technique and by reviewing other dissertations and theses.
- Next, you need to log all the articles in your reference manager , build your own catalogue of literature and synthesise all the research.
- Following that, you need to develop a detailed outline of your entire chapter – the more detail the better. Don’t start writing without a clear outline (on paper, not in your head!)
- Write up your first draft in rough form – don’t aim for perfection. Remember, done beats perfect.
- Refine your second draft and get a layman’s perspective on it . Then tighten it up and submit it to your supervisor.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

37 Comments
Thank you very much. This page is an eye opener and easy to comprehend.
This is awesome!
I wish I come across GradCoach earlier enough.
But all the same I’ll make use of this opportunity to the fullest.
Thank you for this good job.
Keep it up!
You’re welcome, Yinka. Thank you for the kind words. All the best writing your literature review.
Thank you for a very useful literature review session. Although I am doing most of the steps…it being my first masters an Mphil is a self study and one not sure you are on the right track. I have an amazing supervisor but one also knows they are super busy. So not wanting to bother on the minutae. Thank you.
You’re most welcome, Renee. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This has been really helpful. Will make full use of it. 🙂
Thank you Gradcoach.
Really agreed. Admirable effort
thank you for this beautiful well explained recap.
Thank you so much for your guide of video and other instructions for the dissertation writing.
It is instrumental. It encouraged me to write a dissertation now.
Thank you the video was great – from someone that knows nothing thankyou
an amazing and very constructive way of presetting a topic, very useful, thanks for the effort,
It is timely
It is very good video of guidance for writing a research proposal and a dissertation. Since I have been watching and reading instructions, I have started my research proposal to write. I appreciate to Mr Jansen hugely.
I learn a lot from your videos. Very comprehensive and detailed.
Thank you for sharing your knowledge. As a research student, you learn better with your learning tips in research
I was really stuck in reading and gathering information but after watching these things are cleared thanks, it is so helpful.
Really helpful, Thank you for the effort in showing such information
This is super helpful thank you very much.
Thank you for this whole literature writing review.You have simplified the process.
I’m so glad I found GradCoach. Excellent information, Clear explanation, and Easy to follow, Many thanks Derek!
You’re welcome, Maithe. Good luck writing your literature review 🙂
Thank you Coach, you have greatly enriched and improved my knowledge
Great piece, so enriching and it is going to help me a great lot in my project and thesis, thanks so much
This is THE BEST site for ANYONE doing a masters or doctorate! Thank you for the sound advice and templates. You rock!
Thanks, Stephanie 🙂
This is mind blowing, the detailed explanation and simplicity is perfect.
I am doing two papers on my final year thesis, and I must stay I feel very confident to face both headlong after reading this article.
thank you so much.
if anyone is to get a paper done on time and in the best way possible, GRADCOACH is certainly the go to area!
This is very good video which is well explained with detailed explanation
Thank you excellent piece of work and great mentoring
Thanks, it was useful
Thank you very much. the video and the information were very helpful.
Good morning scholar. I’m delighted coming to know you even before the commencement of my dissertation which hopefully is expected in not more than six months from now. I would love to engage my study under your guidance from the beginning to the end. I love to know how to do good job
Thank you so much Derek for such useful information on writing up a good literature review. I am at a stage where I need to start writing my one. My proposal was accepted late last year but I honestly did not know where to start
Like the name of your YouTube implies you are GRAD (great,resource person, about dissertation). In short you are smart enough in coaching research work.
This is a very well thought out webpage. Very informative and a great read.
Very comprehensive and eye opener for me as beginner in postgraduate study. Well explained and easy to understand. Appreciate and good reference in guiding me in my research journey. Thank you
Thank you. I requested to download the free literature review template, however, your website wouldn’t allow me to complete the request or complete a download. May I request that you email me the free template? Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Evidence-Based Practice (EBP)
- The EBP Process
- Forming a Clinical Question
- Inclusion & Exclusion Criteria
- Acquiring Evidence
- Appraising the Quality of the Evidence
- Writing a Literature Review
- Finding Psychological Tests & Assessment Instruments
What Is a Literature Review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis of scholarly writings that are related directly to your research question. Put simply, it's a critical evaluation of what's already been written on a particular topic . It represents the literature that provides background information on your topic and shows a connection between those writings and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand-alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
What a Literature Review Is Not:
- A list or summary of sources
- An annotated bibliography
- A grouping of broad, unrelated sources
- A compilation of everything that has been written on a particular topic
- Literary criticism (think English) or a book review
Why Literature Reviews Are Important
- They explain the background of research on a topic
- They demonstrate why a topic is significant to a subject area
- They discover relationships between research studies/ideas
- They identify major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic
- They identify critical gaps and points of disagreement
- They discuss further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies
To Learn More about Conducting and Writing a Lit Review . . .
Monash University (in Australia) has created several extremely helpful, interactive tutorials.
- The Stand-Alone Literature Review, https://www.monash.edu/rlo/assignment-samples/science/stand-alone-literature-review
- Researching for Your Literature Review, https://guides.lib.monash.edu/researching-for-your-literature-review/home
- Writing a Literature Review, https://www.monash.edu/rlo/graduate-research-writing/write-the-thesis/writing-a-literature-review
Keep Track of Your Sources!
A citation manager can be helpful way to work with large numbers of citations. See UMSL Libraries' Citing Sources guide for more information. Personally, I highly recommend Zotero —it's free, easy to use, and versatile. If you need help getting started with Zotero or one of the other citation managers, please contact a librarian.
- << Previous: Appraising the Quality of the Evidence
- Next: Finding Psychological Tests & Assessment Instruments >>
- Last Updated: Nov 15, 2023 11:47 AM
- URL: https://libguides.umsl.edu/ebp
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 8 March 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE : Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: Mar 8, 2024 1:02 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

Show off your science in Nature’s photo competition
Career News 08 MAR 24

Academic workplaces are still failing Black women; they must do better
World View 08 MAR 24

How sacked whistle-blower Susanne Täuber’s career fared after she spoke out
Career Column 07 MAR 24

Nature publishes too few papers from women researchers — that must change
Editorial 06 MAR 24

Artificial intelligence and illusions of understanding in scientific research
Perspective 06 MAR 24

What science says about hybrid working — and how to make it a success
News Feature 04 MAR 24

Superconductivity scandal: the inside story of deception in a rising star’s physics lab
News Feature 08 MAR 24

China has a list of suspect journals and it’s just been updated
News Q&A 06 MAR 24
Southeast University Future Technology Institute Recruitment Notice
Professor openings in mechanical engineering, control science and engineering, and integrating emerging interdisciplinary majors
Nanjing, Jiangsu (CN)
Southeast University
Faculty Positions at SUSTech School of Medicine
SUSTech School of Medicine offers equal opportunities and welcome applicants from the world with all ethnic backgrounds.
Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
Southern University of Science and Technology, School of Medicine
Postdoc recruitment 2024, SUSTech Proteomics Research Group
Postdoctoral fellows or research assistant professors to join Prof. Ruijun Tian's team for MS-based proteomics and cell signal transduction.
Shenzhen, Guangdong (CN)
Faculty Positions at SUSTech Department of Biomedical Engineering
We seek outstanding applicants for full-time tenure-track/tenured faculty positions. Positions are available for both junior and senior-level.
Southern University of Science and Technology (Biomedical Engineering)
Leading Talents Position in Shandong Institute of Brain Science and Brain-inspired Research
Shandong Institute of Brain Science and Brain-inspired Research is a strategic scientific initiative of Shandong Province, P.R. China.
Jinan, Shandong (CN)
Shandong First Medical University
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on January 30, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on August 14, 2023.
Literary analysis means closely studying a text, interpreting its meanings, and exploring why the author made certain choices. It can be applied to novels, short stories, plays, poems, or any other form of literary writing.
A literary analysis essay is not a rhetorical analysis , nor is it just a summary of the plot or a book review. Instead, it is a type of argumentative essay where you need to analyze elements such as the language, perspective, and structure of the text, and explain how the author uses literary devices to create effects and convey ideas.
Before beginning a literary analysis essay, it’s essential to carefully read the text and c ome up with a thesis statement to keep your essay focused. As you write, follow the standard structure of an academic essay :
- An introduction that tells the reader what your essay will focus on.
- A main body, divided into paragraphs , that builds an argument using evidence from the text.
- A conclusion that clearly states the main point that you have shown with your analysis.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: reading the text and identifying literary devices, step 2: coming up with a thesis, step 3: writing a title and introduction, step 4: writing the body of the essay, step 5: writing a conclusion, other interesting articles.
The first step is to carefully read the text(s) and take initial notes. As you read, pay attention to the things that are most intriguing, surprising, or even confusing in the writing—these are things you can dig into in your analysis.
Your goal in literary analysis is not simply to explain the events described in the text, but to analyze the writing itself and discuss how the text works on a deeper level. Primarily, you’re looking out for literary devices —textual elements that writers use to convey meaning and create effects. If you’re comparing and contrasting multiple texts, you can also look for connections between different texts.
To get started with your analysis, there are several key areas that you can focus on. As you analyze each aspect of the text, try to think about how they all relate to each other. You can use highlights or notes to keep track of important passages and quotes.
Language choices
Consider what style of language the author uses. Are the sentences short and simple or more complex and poetic?
What word choices stand out as interesting or unusual? Are words used figuratively to mean something other than their literal definition? Figurative language includes things like metaphor (e.g. “her eyes were oceans”) and simile (e.g. “her eyes were like oceans”).
Also keep an eye out for imagery in the text—recurring images that create a certain atmosphere or symbolize something important. Remember that language is used in literary texts to say more than it means on the surface.
Narrative voice
Ask yourself:
- Who is telling the story?
- How are they telling it?
Is it a first-person narrator (“I”) who is personally involved in the story, or a third-person narrator who tells us about the characters from a distance?
Consider the narrator’s perspective . Is the narrator omniscient (where they know everything about all the characters and events), or do they only have partial knowledge? Are they an unreliable narrator who we are not supposed to take at face value? Authors often hint that their narrator might be giving us a distorted or dishonest version of events.
The tone of the text is also worth considering. Is the story intended to be comic, tragic, or something else? Are usually serious topics treated as funny, or vice versa ? Is the story realistic or fantastical (or somewhere in between)?
Consider how the text is structured, and how the structure relates to the story being told.
- Novels are often divided into chapters and parts.
- Poems are divided into lines, stanzas, and sometime cantos.
- Plays are divided into scenes and acts.
Think about why the author chose to divide the different parts of the text in the way they did.
There are also less formal structural elements to take into account. Does the story unfold in chronological order, or does it jump back and forth in time? Does it begin in medias res —in the middle of the action? Does the plot advance towards a clearly defined climax?
With poetry, consider how the rhyme and meter shape your understanding of the text and your impression of the tone. Try reading the poem aloud to get a sense of this.
In a play, you might consider how relationships between characters are built up through different scenes, and how the setting relates to the action. Watch out for dramatic irony , where the audience knows some detail that the characters don’t, creating a double meaning in their words, thoughts, or actions.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Your thesis in a literary analysis essay is the point you want to make about the text. It’s the core argument that gives your essay direction and prevents it from just being a collection of random observations about a text.
If you’re given a prompt for your essay, your thesis must answer or relate to the prompt. For example:
Essay question example
Is Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” a religious parable?
Your thesis statement should be an answer to this question—not a simple yes or no, but a statement of why this is or isn’t the case:
Thesis statement example
Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” is not a religious parable, but a story about bureaucratic alienation.
Sometimes you’ll be given freedom to choose your own topic; in this case, you’ll have to come up with an original thesis. Consider what stood out to you in the text; ask yourself questions about the elements that interested you, and consider how you might answer them.
Your thesis should be something arguable—that is, something that you think is true about the text, but which is not a simple matter of fact. It must be complex enough to develop through evidence and arguments across the course of your essay.
Say you’re analyzing the novel Frankenstein . You could start by asking yourself:
Your initial answer might be a surface-level description:
The character Frankenstein is portrayed negatively in Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein .
However, this statement is too simple to be an interesting thesis. After reading the text and analyzing its narrative voice and structure, you can develop the answer into a more nuanced and arguable thesis statement:
Mary Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as.
Remember that you can revise your thesis statement throughout the writing process , so it doesn’t need to be perfectly formulated at this stage. The aim is to keep you focused as you analyze the text.
Finding textual evidence
To support your thesis statement, your essay will build an argument using textual evidence —specific parts of the text that demonstrate your point. This evidence is quoted and analyzed throughout your essay to explain your argument to the reader.
It can be useful to comb through the text in search of relevant quotations before you start writing. You might not end up using everything you find, and you may have to return to the text for more evidence as you write, but collecting textual evidence from the beginning will help you to structure your arguments and assess whether they’re convincing.
To start your literary analysis paper, you’ll need two things: a good title, and an introduction.
Your title should clearly indicate what your analysis will focus on. It usually contains the name of the author and text(s) you’re analyzing. Keep it as concise and engaging as possible.
A common approach to the title is to use a relevant quote from the text, followed by a colon and then the rest of your title.
If you struggle to come up with a good title at first, don’t worry—this will be easier once you’ve begun writing the essay and have a better sense of your arguments.
“Fearful symmetry” : The violence of creation in William Blake’s “The Tyger”

The introduction
The essay introduction provides a quick overview of where your argument is going. It should include your thesis statement and a summary of the essay’s structure.
A typical structure for an introduction is to begin with a general statement about the text and author, using this to lead into your thesis statement. You might refer to a commonly held idea about the text and show how your thesis will contradict it, or zoom in on a particular device you intend to focus on.
Then you can end with a brief indication of what’s coming up in the main body of the essay. This is called signposting. It will be more elaborate in longer essays, but in a short five-paragraph essay structure, it shouldn’t be more than one sentence.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, protagonist Victor Frankenstein is a stable representation of the callous ambition of modern science throughout the novel. This essay, however, argues that far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as. This essay begins by exploring the positive portrayal of Frankenstein in the first volume, then moves on to the creature’s perception of him, and finally discusses the third volume’s narrative shift toward viewing Frankenstein as the creature views him.
Some students prefer to write the introduction later in the process, and it’s not a bad idea. After all, you’ll have a clearer idea of the overall shape of your arguments once you’ve begun writing them!
If you do write the introduction first, you should still return to it later to make sure it lines up with what you ended up writing, and edit as necessary.
The body of your essay is everything between the introduction and conclusion. It contains your arguments and the textual evidence that supports them.
Paragraph structure
A typical structure for a high school literary analysis essay consists of five paragraphs : the three paragraphs of the body, plus the introduction and conclusion.
Each paragraph in the main body should focus on one topic. In the five-paragraph model, try to divide your argument into three main areas of analysis, all linked to your thesis. Don’t try to include everything you can think of to say about the text—only analysis that drives your argument.
In longer essays, the same principle applies on a broader scale. For example, you might have two or three sections in your main body, each with multiple paragraphs. Within these sections, you still want to begin new paragraphs at logical moments—a turn in the argument or the introduction of a new idea.
Robert’s first encounter with Gil-Martin suggests something of his sinister power. Robert feels “a sort of invisible power that drew me towards him.” He identifies the moment of their meeting as “the beginning of a series of adventures which has puzzled myself, and will puzzle the world when I am no more in it” (p. 89). Gil-Martin’s “invisible power” seems to be at work even at this distance from the moment described; before continuing the story, Robert feels compelled to anticipate at length what readers will make of his narrative after his approaching death. With this interjection, Hogg emphasizes the fatal influence Gil-Martin exercises from his first appearance.
Topic sentences
To keep your points focused, it’s important to use a topic sentence at the beginning of each paragraph.
A good topic sentence allows a reader to see at a glance what the paragraph is about. It can introduce a new line of argument and connect or contrast it with the previous paragraph. Transition words like “however” or “moreover” are useful for creating smooth transitions:
… The story’s focus, therefore, is not upon the divine revelation that may be waiting beyond the door, but upon the mundane process of aging undergone by the man as he waits.
Nevertheless, the “radiance” that appears to stream from the door is typically treated as religious symbolism.
This topic sentence signals that the paragraph will address the question of religious symbolism, while the linking word “nevertheless” points out a contrast with the previous paragraph’s conclusion.
Using textual evidence
A key part of literary analysis is backing up your arguments with relevant evidence from the text. This involves introducing quotes from the text and explaining their significance to your point.
It’s important to contextualize quotes and explain why you’re using them; they should be properly introduced and analyzed, not treated as self-explanatory:
It isn’t always necessary to use a quote. Quoting is useful when you’re discussing the author’s language, but sometimes you’ll have to refer to plot points or structural elements that can’t be captured in a short quote.
In these cases, it’s more appropriate to paraphrase or summarize parts of the text—that is, to describe the relevant part in your own words:
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The conclusion of your analysis shouldn’t introduce any new quotations or arguments. Instead, it’s about wrapping up the essay. Here, you summarize your key points and try to emphasize their significance to the reader.
A good way to approach this is to briefly summarize your key arguments, and then stress the conclusion they’ve led you to, highlighting the new perspective your thesis provides on the text as a whole:
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
By tracing the depiction of Frankenstein through the novel’s three volumes, I have demonstrated how the narrative structure shifts our perception of the character. While the Frankenstein of the first volume is depicted as having innocent intentions, the second and third volumes—first in the creature’s accusatory voice, and then in his own voice—increasingly undermine him, causing him to appear alternately ridiculous and vindictive. Far from the one-dimensional villain he is often taken to be, the character of Frankenstein is compelling because of the dynamic narrative frame in which he is placed. In this frame, Frankenstein’s narrative self-presentation responds to the images of him we see from others’ perspectives. This conclusion sheds new light on the novel, foregrounding Shelley’s unique layering of narrative perspectives and its importance for the depiction of character.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, August 14). How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved March 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/literary-analysis/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to write a narrative essay | example & tips, what is your plagiarism score.

- Schools & departments

Literature review
A general guide on how to conduct and write a literature review.
Please check course or programme information and materials provided by teaching staff , including your project supervisor, for subject-specific guidance.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a piece of academic writing demonstrating knowledge and understanding of the academic literature on a specific topic placed in context. A literature review also includes a critical evaluation of the material; this is why it is called a literature review rather than a literature report. It is a process of reviewing the literature, as well as a form of writing.
To illustrate the difference between reporting and reviewing, think about television or film review articles. These articles include content such as a brief synopsis or the key points of the film or programme plus the critic’s own evaluation. Similarly the two main objectives of a literature review are firstly the content covering existing research, theories and evidence, and secondly your own critical evaluation and discussion of this content.
Usually a literature review forms a section or part of a dissertation, research project or long essay. However, it can also be set and assessed as a standalone piece of work.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
…your task is to build an argument, not a library. Rudestam, K.E. and Newton, R.R. (1992) Surviving your dissertation: A comprehensive guide to content and process. California: Sage, p49.
In a larger piece of written work, such as a dissertation or project, a literature review is usually one of the first tasks carried out after deciding on a topic. Reading combined with critical analysis can help to refine a topic and frame research questions. Conducting a literature review establishes your familiarity with and understanding of current research in a particular field before carrying out a new investigation. After doing a literature review, you should know what research has already been done and be able to identify what is unknown within your topic.
When doing and writing a literature review, it is good practice to:
- summarise and analyse previous research and theories;
- identify areas of controversy and contested claims;
- highlight any gaps that may exist in research to date.
Conducting a literature review
Focusing on different aspects of your literature review can be useful to help plan, develop, refine and write it. You can use and adapt the prompt questions in our worksheet below at different points in the process of researching and writing your review. These are suggestions to get you thinking and writing.
Developing and refining your literature review (pdf)
Developing and refining your literature review (Word)
Developing and refining your literature review (Word rtf)
Writing a literature review has a lot in common with other assignment tasks. There is advice on our other pages about thinking critically, reading strategies and academic writing. Our literature review top tips suggest some specific things you can do to help you submit a successful review.
Literature review top tips (pdf)
Literature review top tips (Word rtf)
Our reading page includes strategies and advice on using books and articles and a notes record sheet grid you can use.
Reading at university
The Academic writing page suggests ways to organise and structure information from a range of sources and how you can develop your argument as you read and write.
Academic writing
The Critical thinking page has advice on how to be a more critical researcher and a form you can use to help you think and break down the stages of developing your argument.
Critical thinking
As with other forms of academic writing, your literature review needs to demonstrate good academic practice by following the Code of Student Conduct and acknowledging the work of others through citing and referencing your sources.
Good academic practice
As with any writing task, you will need to review, edit and rewrite sections of your literature review. The Editing and proofreading page includes tips on how to do this and strategies for standing back and thinking about your structure and checking the flow of your argument.
Editing and proofreading
Guidance on literature searching from the University Library
The Academic Support Librarians have developed LibSmart I and II, Learn courses to help you develop and enhance your digital research skills and capabilities; from getting started with the Library to managing data for your dissertation.
Searching using the library’s DiscoverEd tool: DiscoverEd
Finding resources in your subject: Subject guides
The Academic Support Librarians also provide one-to-one appointments to help you develop your research strategies.
1 to 1 support for literature searching and systematic reviews
Advice to help you optimise use of Google Scholar, Google Books and Google for your research and study: Using Google
Managing and curating your references
A referencing management tool can help you to collect and organise and your source material to produce a bibliography or reference list.
Referencing and reference management
Information Services provide access to Cite them right online which is a guide to the main referencing systems and tells you how to reference just about any source (EASE log-in may be required).
Cite them right
Published study guides
There are a number of scholarship skills books and guides available which can help with writing a literature review. Our Resource List of study skills guides includes sections on Referencing, Dissertation and project writing and Literature reviews.
Study skills guides
- Undergraduate courses
- Postgraduate courses
- January starts
- Foundation courses
- Apprenticeships
- Part-time and short courses
- Apply undergraduate
- Apply postgraduate
Search for a course
Search by course name, subject, and more
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- (suspended) - Available in Clearing Not available in Clearing location-sign UCAS
Fees and funding
- Tuition fees
- Scholarships
- Funding your studies
- Student finance
- Cost of living support
Why study at Kent
Student life.
- Careers and employability
- Student support and wellbeing
- Our locations
- Placements and internships
- Year abroad
- Student stories
- Schools and colleges
- International
- International students
- Your country
- Applicant FAQs
- International scholarships
- University of Kent International College
- Campus Tours
- Applicant Events
- Postgraduate events
- Maps and directions
- Research strengths
- Research centres
- Research impact
Research institutes
- Durrell Institute of Conservation and Ecology
- Institute of Cyber Security for Society
- Institute of Cultural and Creative Industries
- Institute of Health, Social Care and Wellbeing
Research students
- Graduate and Researcher College
- Research degrees
- Find a supervisor
- How to apply
Popular searches
- Visits and Open Days
- Jobs and vacancies
- Accommodation
- Student guide
- Library and IT
- Research highlights
- Signature themes
- Partner with us
- Student Guide
- Student Help
- Health & wellbeing
- Student voice
- Living at Kent
- Careers & volunteering
- Diversity at Kent
- Finance & funding
- Life after graduation
Literature reviews
Writing a literature review.
The following guide has been created for you by the Student Learning Advisory Service . For more detailed guidance and to speak to one of our advisers, please book an appointment or join one of our workshops . Alternatively, have a look at our SkillBuilder skills videos.
Preparing a literature review involves:
- Searching for reliable, accurate and up-to-date material on a topic or subject
- Reading and summarising the key points from this literature
- Synthesising these key ideas, theories and concepts into a summary of what is known
- Discussing and evaluating these ideas, theories and concepts
- Identifying particular areas of debate or controversy
- Preparing the ground for the application of these ideas to new research
Finding and choosing material
Ensure you are clear on what you are looking for. ask yourself:.
- What is the specific question, topic or focus of my assignment?
- What kind of material do I need (e.g. theory, policy, empirical data)?
- What type of literature is available (e.g. journals, books, government documents)?
What kind of literature is particularly authoritative in this academic discipline (e.g. psychology, sociology, pharmacy)?
How much do you need?
This will depend on the length of the dissertation, the nature of the subject, and the level of study (undergraduate, Masters, PhD). As a very rough rule of thumb – you may choose 8-10 significant pieces (books and/or articles) for an 8,000 word dissertation, up to 20 major pieces of work for 12-15,000 words, and so on. Bear in mind that if your dissertation is based mainly around an interaction with existing scholarship you will need a longer literature review than if it is there as a prelude to new empirical research. Use your judgement or ask your supervisor for guidance.
Where to find suitable material
Your literature review should include a balance between substantial academic books, journal articles and other scholarly publications. All these sources should be as up-to-date as possible, with the exception of ‘classic texts’ such as major works written by leading scholars setting out formative ideas and theories central to your subject. There are several ways to locate suitable material:
Module bibliography: for undergraduate dissertations, look first at the bibliography provided with the module documentation. Choose one or two likely looking books or articles and then scan through the bibliographies provided by these authors. Skim read some of this material looking for clues: can you use these leads to identify key theories and authors or track down other appropriate material?
Library catalogue search engine: enter a few key words to capture a range of items, but avoid over-generalisations; if you type in something as broad as ‘social theory’ you are likely to get several thousand results. Be more specific: for example, ‘Heidegger, existentialism’. Ideally, you should narrow the field to obtain just a few dozen results. Skim through these quickly to identity texts which are most likely to contribute to your study.
Library bookshelves: browse the library shelves in the relevant subject area and examine the books that catch your eye. Check the contents and index pages, or skim through the introductions (or abstracts, in the case of journal articles) to see if they contain relevant material, and replace them if not. Don’t be afraid to ask one of the subject librarians for further help. Your supervisor may also be able to point you in the direction of some of the important literature , but remember this is your literature search, not theirs.
Online: for recent journal articles you will almost certainly need to use one of the online search engines. These can be found on the ‘Indexing Services’ button on the Templeman Library website. Kent students based at Medway still need to use the Templeman pages to access online journals, although you can get to these pages through the Drill Hall Library catalogue. Take a look as well at the Subject Guides on both the Templeman and DHL websites.
Check that you have made the right selection by asking:
- Has my search been wide enough to ensure that I have identified all the relevant material, but narrow enough to exclude irrelevant material?
- Is there a good enough sample of literature for the level (PhD, Masters, undergraduate) of my dissertation or thesis?
- Have I considered as many alternative points of view as possible?
- Will the reader find my literature review relevant and useful?
Assessing the literature
Read the material you have chosen carefully, considering the following:
- The key point discussed by the author: is this clearly defined
- What evidence has the author produced to support this central idea?
- How convincing are the reasons given for the author’s point of view?
- Could the evidence be interpreted in other ways?
- What is the author's research method (e.g. qualitative, quantitative, experimental, etc.)?
- What is the author's theoretical framework (e.g. psychological, developmental, feminist)?
- What is the relationship assumed by the author between theory and practice?
- Has the author critically evaluated the other literature in the field?
- Does the author include literature opposing their point of view?
- Is the research data based on a reliable method and accurate information?
- Can you ‘deconstruct’ the argument – identify the gaps or jumps in the logic?
- What are the strengths and limitations of this study?
- What does this book or article contribute to the field or topic?
- What does this book or article contribute to my own topic or thesis?
As you note down the key content of each book or journal article (together with the reference details of each source) record your responses to these questions. You will then be able to summarise each piece of material from two perspectives:
Content: a brief description of the content of the book or article. Remember, an author will often make just one key point; so, what is the point they are making, and how does it relate to your own research project or assignment?
Critical analysis: an assessment of the relative strengths and weaknesses of the evidence used, and the arguments presented. Has anything conveniently been left out or skated over? Is there a counter-argument, and has the author dealt with this adequately? Can the evidence presented be interpreted another way? Does the author demonstrate any obvious bias which could affect their reliability? Overall, based on the above analysis of the author’s work, how do you evaluate its contribution to the scholarly understanding and knowledge surrounding the topic?
Structuring the literature review
In a PhD thesis, the literature review typically comprises one chapter (perhaps 8-10,000 words), for a Masters dissertation it may be around 2-3,000 words, and for an undergraduate dissertation it may be no more than 2,000 words. In each case the word count can vary depending on a range of factors and it is always best, if in doubt, to ask your supervisor.
The overall structure of the section or chapter should be like any other: it should have a beginning, middle and end. You will need to guide the reader through the literature review, outlining the strategy you have adopted for selecting the books or articles, presenting the topic theme for the review, then using most of the word limit to analyse the chosen books or articles thoroughly before pulling everything together briefly in the conclusion.
Some people prefer a less linear approach. Instead of simply working through a list of 8-20 items on your book review list, you might want to try a thematic approach, grouping key ideas, facts, concepts or approaches together and then bouncing the ideas off each other. This is a slightly more creative (and interesting) way of producing the review, but a little more risky as it is harder to establish coherence and logical sequencing.
Whichever approach you adopt, make sure everything flows smoothly – that one idea or book leads neatly to the next. Take your reader effortlessly through a sequence of thought that is clear, accurate, precise and interesting.
Writing up your literature review
As with essays generally, only attempt to write up the literature review when you have completed all the reading and note-taking, and carefully planned its content and structure. Find an appropriate way of introducing the review, then guide the reader through the material clearly and directly, bearing in mind the following:
- Be selective in the number of points you draw out from each piece of literature; remember that one of your objectives is to demonstrate that you can use your judgement to identify what is central and what is secondary.
- Summarise and synthesise – use your own words to sum up what you think is important or controversial about the book or article.
- Never claim more than the evidence will support. Too many dissertations and theses are let down by sweeping generalisations. Be tentative and careful in the way you interpret the evidence.
- Keep your own voice – you are entitled to your own point of view provided it is based on evidence and clear argument.
- At the same time, aim to project an objective and tentative tone by using the 3rd person, (for example, ‘this tends to suggest’, ‘it could be argued’ and so on).
- Even with a literature review you should avoid using too many, or overlong, quotes. Summarise material in your own words as much as possible. Save the quotes for ‘punch-lines’ to drive a particular point home.
- Revise, revise, revise: refine and edit the draft as much as you can. Check for fluency, structure, evidence, criticality and referencing, and don’t forget the basics of good grammar, punctuation and spelling.
15 Literature Review Examples
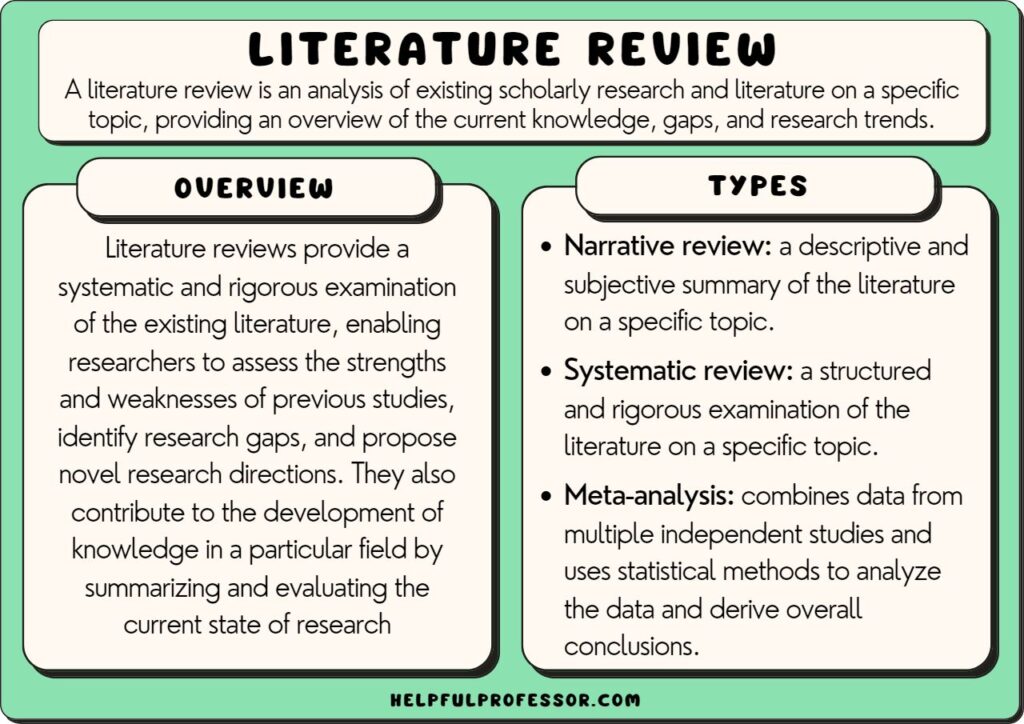
Literature reviews are a necessary step in a research process and often required when writing your research proposal . They involve gathering, analyzing, and evaluating existing knowledge about a topic in order to find gaps in the literature where future studies will be needed.
Ideally, once you have completed your literature review, you will be able to identify how your research project can build upon and extend existing knowledge in your area of study.
Generally, for my undergraduate research students, I recommend a narrative review, where themes can be generated in order for the students to develop sufficient understanding of the topic so they can build upon the themes using unique methods or novel research questions.
If you’re in the process of writing a literature review, I have developed a literature review template for you to use – it’s a huge time-saver and walks you through how to write a literature review step-by-step:
Get your time-saving templates here to write your own literature review.
Literature Review Examples
For the following types of literature review, I present an explanation and overview of the type, followed by links to some real-life literature reviews on the topics.
1. Narrative Review Examples
Also known as a traditional literature review, the narrative review provides a broad overview of the studies done on a particular topic.
It often includes both qualitative and quantitative studies and may cover a wide range of years.
The narrative review’s purpose is to identify commonalities, gaps, and contradictions in the literature .
I recommend to my students that they should gather their studies together, take notes on each study, then try to group them by themes that form the basis for the review (see my step-by-step instructions at the end of the article).
Example Study
Title: Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations
Citation: Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/ijcp.12686
Overview: This narrative review analyzed themes emerging from 69 articles about communication in healthcare contexts. Five key themes were found in the literature: poor communication can lead to various negative outcomes, discontinuity of care, compromise of patient safety, patient dissatisfaction, and inefficient use of resources. After presenting the key themes, the authors recommend that practitioners need to approach healthcare communication in a more structured way, such as by ensuring there is a clear understanding of who is in charge of ensuring effective communication in clinical settings.
Other Examples
- Burnout in United States Healthcare Professionals: A Narrative Review (Reith, 2018) – read here
- Examining the Presence, Consequences, and Reduction of Implicit Bias in Health Care: A Narrative Review (Zestcott, Blair & Stone, 2016) – read here
- A Narrative Review of School-Based Physical Activity for Enhancing Cognition and Learning (Mavilidi et al., 2018) – read here
- A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents (Dyrbye & Shanafelt, 2015) – read here
2. Systematic Review Examples
This type of literature review is more structured and rigorous than a narrative review. It involves a detailed and comprehensive plan and search strategy derived from a set of specified research questions.
The key way you’d know a systematic review compared to a narrative review is in the methodology: the systematic review will likely have a very clear criteria for how the studies were collected, and clear explanations of exclusion/inclusion criteria.
The goal is to gather the maximum amount of valid literature on the topic, filter out invalid or low-quality reviews, and minimize bias. Ideally, this will provide more reliable findings, leading to higher-quality conclusions and recommendations for further research.
You may note from the examples below that the ‘method’ sections in systematic reviews tend to be much more explicit, often noting rigid inclusion/exclusion criteria and exact keywords used in searches.
Title: The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review
Citation: Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092422441730122X
Overview: This systematic review included 72 studies of food naturalness to explore trends in the literature about its importance for consumers. Keywords used in the data search included: food, naturalness, natural content, and natural ingredients. Studies were included if they examined consumers’ preference for food naturalness and contained empirical data. The authors found that the literature lacks clarity about how naturalness is defined and measured, but also found that food consumption is significantly influenced by perceived naturalness of goods.
- A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018 (Martin, Sun & Westine, 2020) – read here
- Where Is Current Research on Blockchain Technology? (Yli-Huumo et al., 2016) – read here
- Universities—industry collaboration: A systematic review (Ankrah & Al-Tabbaa, 2015) – read here
- Internet of Things Applications: A Systematic Review (Asghari, Rahmani & Javadi, 2019) – read here
3. Meta-analysis
This is a type of systematic review that uses statistical methods to combine and summarize the results of several studies.
Due to its robust methodology, a meta-analysis is often considered the ‘gold standard’ of secondary research , as it provides a more precise estimate of a treatment effect than any individual study contributing to the pooled analysis.
Furthermore, by aggregating data from a range of studies, a meta-analysis can identify patterns, disagreements, or other interesting relationships that may have been hidden in individual studies.
This helps to enhance the generalizability of findings, making the conclusions drawn from a meta-analysis particularly powerful and informative for policy and practice.
Title: Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s Disease Risk: A Meta-Meta-Analysis
Citation: Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Source: https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060386
O verview: This study examines the relationship between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Researchers conducted a systematic search of meta-analyses and reviewed several databases, collecting 100 primary studies and five meta-analyses to analyze the connection between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease. They find that the literature compellingly demonstrates that low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels significantly influence the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
- The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research (Wisniewski, Zierer & Hattie, 2020) – read here
- How Much Does Education Improve Intelligence? A Meta-Analysis (Ritchie & Tucker-Drob, 2018) – read here
- A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling (Geiger et al., 2019) – read here
- Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits (Patterson, Chung & Swan, 2014) – read here
Other Types of Reviews
- Scoping Review: This type of review is used to map the key concepts underpinning a research area and the main sources and types of evidence available. It can be undertaken as stand-alone projects in their own right, or as a precursor to a systematic review.
- Rapid Review: This type of review accelerates the systematic review process in order to produce information in a timely manner. This is achieved by simplifying or omitting stages of the systematic review process.
- Integrative Review: This review method is more inclusive than others, allowing for the simultaneous inclusion of experimental and non-experimental research. The goal is to more comprehensively understand a particular phenomenon.
- Critical Review: This is similar to a narrative review but requires a robust understanding of both the subject and the existing literature. In a critical review, the reviewer not only summarizes the existing literature, but also evaluates its strengths and weaknesses. This is common in the social sciences and humanities .
- State-of-the-Art Review: This considers the current level of advancement in a field or topic and makes recommendations for future research directions. This type of review is common in technological and scientific fields but can be applied to any discipline.
How to Write a Narrative Review (Tips for Undergrad Students)
Most undergraduate students conducting a capstone research project will be writing narrative reviews. Below is a five-step process for conducting a simple review of the literature for your project.
- Search for Relevant Literature: Use scholarly databases related to your field of study, provided by your university library, along with appropriate search terms to identify key scholarly articles that have been published on your topic.
- Evaluate and Select Sources: Filter the source list by selecting studies that are directly relevant and of sufficient quality, considering factors like credibility , objectivity, accuracy, and validity.
- Analyze and Synthesize: Review each source and summarize the main arguments in one paragraph (or more, for postgrad). Keep these summaries in a table.
- Identify Themes: With all studies summarized, group studies that share common themes, such as studies that have similar findings or methodologies.
- Write the Review: Write your review based upon the themes or subtopics you have identified. Give a thorough overview of each theme, integrating source data, and conclude with a summary of the current state of knowledge then suggestions for future research based upon your evaluation of what is lacking in the literature.
Literature reviews don’t have to be as scary as they seem. Yes, they are difficult and require a strong degree of comprehension of academic studies. But it can be feasibly done through following a structured approach to data collection and analysis. With my undergraduate research students (who tend to conduct small-scale qualitative studies ), I encourage them to conduct a narrative literature review whereby they can identify key themes in the literature. Within each theme, students can critique key studies and their strengths and limitations , in order to get a lay of the land and come to a point where they can identify ways to contribute new insights to the existing academic conversation on their topic.
Ankrah, S., & Omar, A. T. (2015). Universities–industry collaboration: A systematic review. Scandinavian Journal of Management, 31(3), 387-408.
Asghari, P., Rahmani, A. M., & Javadi, H. H. S. (2019). Internet of Things applications: A systematic review. Computer Networks , 148 , 241-261.
Dyrbye, L., & Shanafelt, T. (2016). A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents. Medical education , 50 (1), 132-149.
Geiger, J. L., Steg, L., Van Der Werff, E., & Ünal, A. B. (2019). A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling. Journal of environmental psychology , 64 , 78-97.
Martin, F., Sun, T., & Westine, C. D. (2020). A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018. Computers & education , 159 , 104009.
Mavilidi, M. F., Ruiter, M., Schmidt, M., Okely, A. D., Loyens, S., Chandler, P., & Paas, F. (2018). A narrative review of school-based physical activity for enhancing cognition and learning: The importance of relevancy and integration. Frontiers in psychology , 2079.
Patterson, G. T., Chung, I. W., & Swan, P. W. (2014). Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits: A meta-analysis. Journal of experimental criminology , 10 , 487-513.
Reith, T. P. (2018). Burnout in United States healthcare professionals: a narrative review. Cureus , 10 (12).
Ritchie, S. J., & Tucker-Drob, E. M. (2018). How much does education improve intelligence? A meta-analysis. Psychological science , 29 (8), 1358-1369.
Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Wisniewski, B., Zierer, K., & Hattie, J. (2020). The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research. Frontiers in Psychology , 10 , 3087.
Yli-Huumo, J., Ko, D., Choi, S., Park, S., & Smolander, K. (2016). Where is current research on blockchain technology?—a systematic review. PloS one , 11 (10), e0163477.
Zestcott, C. A., Blair, I. V., & Stone, J. (2016). Examining the presence, consequences, and reduction of implicit bias in health care: a narrative review. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations , 19 (4), 528-542

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 17 Adversity Examples (And How to Overcome Them)
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- UWF Libraries
Literature Review: Conducting & Writing
- Sample Literature Reviews
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review
- Finding "The Literature"
- Organizing/Writing
- APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window
- MLA Style This link opens in a new window
Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts
Have an exemplary literature review.
- Literature Review Sample 1
- Literature Review Sample 2
- Literature Review Sample 3
Have you written a stellar literature review you care to share for teaching purposes?
Are you an instructor who has received an exemplary literature review and have permission from the student to post?
Please contact Britt McGowan at [email protected] for inclusion in this guide. All disciplines welcome and encouraged.
- << Previous: MLA Style
- Next: Get Help! >>
- Last Updated: Feb 26, 2024 2:04 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uwf.edu/litreview

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
The Literature Review
30 Understanding the Difference Between a Literature Review and an Essay
So now that you know what a literature review is and how to write it, it is important to understand how a literature review is different from an essay. First of all, it is necessary to point out that many students struggle with understanding the difference between a literature review and an essay. This is particularly so because a student can use the exact same resources to create a literature review or an essay; however, what is different about the two is where the emphasis in the writing is placed (Thomas 2012).
A discussed previously, a literature review focuses on everything that has been written about a particular topic, theory, or research. It is focused on the research and the researchers who have undertaken research on your topic. In contrast, an essay focuses on proving a point. It does not need to provide an extensive coverage of all of the material on the topic. In fact, the writer chooses only those sources that prove the point. Most professors will expect to see you discuss a few different perspectives from the materials that run contrary to the point you are trying to make. For example, suppose you want to write an essay about the negative effects of shiftwork on nurses. You would gather material to show that shiftwork negatively affects nurses, and the various ways it affects nurses. Now in this case, you might find the odd research paper that states shiftwork has no effect – although, I doubt it, because it has been extensively documented to have a negative affect. However, the point is that with an essay you are focused on providing information on your topic and proving your point.
Understanding the difference between a literature review and an annotated bibliography
There is a third type of academic writing that can also confuse students who are attempting to write a literature review … and that is an annotated bibliography. An annotated bibliography provides all of the reference details of a bibliography, but it goes one step further and provides a short (approximately 150 words) description of the reference. An annotated bibliography is not to be confused with a bibliography. A bibliography is a list of journal articles, books, and other resources that someone has utilized in writing. The bibliography, provides a list of all resources that someone used to write a research paper and, unlike a reference list, includes references that may not appear in the body of the paper. No doubt you have had to create many bibliographies in your academic studies. Here is a link to a website where you can learn more about annotated bibliographies and also to see a sample of an annotated bibliography: Annotated Bibliographies
An Introduction to Research Methods in Sociology by Valerie A. Sheppard is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.

Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet].
Chapter 9 methods for literature reviews.
Guy Paré and Spyros Kitsiou .
9.1. Introduction
Literature reviews play a critical role in scholarship because science remains, first and foremost, a cumulative endeavour ( vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). As in any academic discipline, rigorous knowledge syntheses are becoming indispensable in keeping up with an exponentially growing eHealth literature, assisting practitioners, academics, and graduate students in finding, evaluating, and synthesizing the contents of many empirical and conceptual papers. Among other methods, literature reviews are essential for: (a) identifying what has been written on a subject or topic; (b) determining the extent to which a specific research area reveals any interpretable trends or patterns; (c) aggregating empirical findings related to a narrow research question to support evidence-based practice; (d) generating new frameworks and theories; and (e) identifying topics or questions requiring more investigation ( Paré, Trudel, Jaana, & Kitsiou, 2015 ).
Literature reviews can take two major forms. The most prevalent one is the “literature review” or “background” section within a journal paper or a chapter in a graduate thesis. This section synthesizes the extant literature and usually identifies the gaps in knowledge that the empirical study addresses ( Sylvester, Tate, & Johnstone, 2013 ). It may also provide a theoretical foundation for the proposed study, substantiate the presence of the research problem, justify the research as one that contributes something new to the cumulated knowledge, or validate the methods and approaches for the proposed study ( Hart, 1998 ; Levy & Ellis, 2006 ).
The second form of literature review, which is the focus of this chapter, constitutes an original and valuable work of research in and of itself ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Rather than providing a base for a researcher’s own work, it creates a solid starting point for all members of the community interested in a particular area or topic ( Mulrow, 1987 ). The so-called “review article” is a journal-length paper which has an overarching purpose to synthesize the literature in a field, without collecting or analyzing any primary data ( Green, Johnson, & Adams, 2006 ).
When appropriately conducted, review articles represent powerful information sources for practitioners looking for state-of-the art evidence to guide their decision-making and work practices ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Further, high-quality reviews become frequently cited pieces of work which researchers seek out as a first clear outline of the literature when undertaking empirical studies ( Cooper, 1988 ; Rowe, 2014 ). Scholars who track and gauge the impact of articles have found that review papers are cited and downloaded more often than any other type of published article ( Cronin, Ryan, & Coughlan, 2008 ; Montori, Wilczynski, Morgan, Haynes, & Hedges, 2003 ; Patsopoulos, Analatos, & Ioannidis, 2005 ). The reason for their popularity may be the fact that reading the review enables one to have an overview, if not a detailed knowledge of the area in question, as well as references to the most useful primary sources ( Cronin et al., 2008 ). Although they are not easy to conduct, the commitment to complete a review article provides a tremendous service to one’s academic community ( Paré et al., 2015 ; Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). Most, if not all, peer-reviewed journals in the fields of medical informatics publish review articles of some type.
The main objectives of this chapter are fourfold: (a) to provide an overview of the major steps and activities involved in conducting a stand-alone literature review; (b) to describe and contrast the different types of review articles that can contribute to the eHealth knowledge base; (c) to illustrate each review type with one or two examples from the eHealth literature; and (d) to provide a series of recommendations for prospective authors of review articles in this domain.
9.2. Overview of the Literature Review Process and Steps
As explained in Templier and Paré (2015) , there are six generic steps involved in conducting a review article:
- formulating the research question(s) and objective(s),
- searching the extant literature,
- screening for inclusion,
- assessing the quality of primary studies,
- extracting data, and
- analyzing data.
Although these steps are presented here in sequential order, one must keep in mind that the review process can be iterative and that many activities can be initiated during the planning stage and later refined during subsequent phases ( Finfgeld-Connett & Johnson, 2013 ; Kitchenham & Charters, 2007 ).
Formulating the research question(s) and objective(s): As a first step, members of the review team must appropriately justify the need for the review itself ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ), identify the review’s main objective(s) ( Okoli & Schabram, 2010 ), and define the concepts or variables at the heart of their synthesis ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ; Webster & Watson, 2002 ). Importantly, they also need to articulate the research question(s) they propose to investigate ( Kitchenham & Charters, 2007 ). In this regard, we concur with Jesson, Matheson, and Lacey (2011) that clearly articulated research questions are key ingredients that guide the entire review methodology; they underscore the type of information that is needed, inform the search for and selection of relevant literature, and guide or orient the subsequent analysis. Searching the extant literature: The next step consists of searching the literature and making decisions about the suitability of material to be considered in the review ( Cooper, 1988 ). There exist three main coverage strategies. First, exhaustive coverage means an effort is made to be as comprehensive as possible in order to ensure that all relevant studies, published and unpublished, are included in the review and, thus, conclusions are based on this all-inclusive knowledge base. The second type of coverage consists of presenting materials that are representative of most other works in a given field or area. Often authors who adopt this strategy will search for relevant articles in a small number of top-tier journals in a field ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In the third strategy, the review team concentrates on prior works that have been central or pivotal to a particular topic. This may include empirical studies or conceptual papers that initiated a line of investigation, changed how problems or questions were framed, introduced new methods or concepts, or engendered important debate ( Cooper, 1988 ). Screening for inclusion: The following step consists of evaluating the applicability of the material identified in the preceding step ( Levy & Ellis, 2006 ; vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). Once a group of potential studies has been identified, members of the review team must screen them to determine their relevance ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). A set of predetermined rules provides a basis for including or excluding certain studies. This exercise requires a significant investment on the part of researchers, who must ensure enhanced objectivity and avoid biases or mistakes. As discussed later in this chapter, for certain types of reviews there must be at least two independent reviewers involved in the screening process and a procedure to resolve disagreements must also be in place ( Liberati et al., 2009 ; Shea et al., 2009 ). Assessing the quality of primary studies: In addition to screening material for inclusion, members of the review team may need to assess the scientific quality of the selected studies, that is, appraise the rigour of the research design and methods. Such formal assessment, which is usually conducted independently by at least two coders, helps members of the review team refine which studies to include in the final sample, determine whether or not the differences in quality may affect their conclusions, or guide how they analyze the data and interpret the findings ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). Ascribing quality scores to each primary study or considering through domain-based evaluations which study components have or have not been designed and executed appropriately makes it possible to reflect on the extent to which the selected study addresses possible biases and maximizes validity ( Shea et al., 2009 ). Extracting data: The following step involves gathering or extracting applicable information from each primary study included in the sample and deciding what is relevant to the problem of interest ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ). Indeed, the type of data that should be recorded mainly depends on the initial research questions ( Okoli & Schabram, 2010 ). However, important information may also be gathered about how, when, where and by whom the primary study was conducted, the research design and methods, or qualitative/quantitative results ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ). Analyzing and synthesizing data : As a final step, members of the review team must collate, summarize, aggregate, organize, and compare the evidence extracted from the included studies. The extracted data must be presented in a meaningful way that suggests a new contribution to the extant literature ( Jesson et al., 2011 ). Webster and Watson (2002) warn researchers that literature reviews should be much more than lists of papers and should provide a coherent lens to make sense of extant knowledge on a given topic. There exist several methods and techniques for synthesizing quantitative (e.g., frequency analysis, meta-analysis) and qualitative (e.g., grounded theory, narrative analysis, meta-ethnography) evidence ( Dixon-Woods, Agarwal, Jones, Young, & Sutton, 2005 ; Thomas & Harden, 2008 ).
9.3. Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations
EHealth researchers have at their disposal a number of approaches and methods for making sense out of existing literature, all with the purpose of casting current research findings into historical contexts or explaining contradictions that might exist among a set of primary research studies conducted on a particular topic. Our classification scheme is largely inspired from Paré and colleagues’ (2015) typology. Below we present and illustrate those review types that we feel are central to the growth and development of the eHealth domain.
9.3.1. Narrative Reviews
The narrative review is the “traditional” way of reviewing the extant literature and is skewed towards a qualitative interpretation of prior knowledge ( Sylvester et al., 2013 ). Put simply, a narrative review attempts to summarize or synthesize what has been written on a particular topic but does not seek generalization or cumulative knowledge from what is reviewed ( Davies, 2000 ; Green et al., 2006 ). Instead, the review team often undertakes the task of accumulating and synthesizing the literature to demonstrate the value of a particular point of view ( Baumeister & Leary, 1997 ). As such, reviewers may selectively ignore or limit the attention paid to certain studies in order to make a point. In this rather unsystematic approach, the selection of information from primary articles is subjective, lacks explicit criteria for inclusion and can lead to biased interpretations or inferences ( Green et al., 2006 ). There are several narrative reviews in the particular eHealth domain, as in all fields, which follow such an unstructured approach ( Silva et al., 2015 ; Paul et al., 2015 ).
Despite these criticisms, this type of review can be very useful in gathering together a volume of literature in a specific subject area and synthesizing it. As mentioned above, its primary purpose is to provide the reader with a comprehensive background for understanding current knowledge and highlighting the significance of new research ( Cronin et al., 2008 ). Faculty like to use narrative reviews in the classroom because they are often more up to date than textbooks, provide a single source for students to reference, and expose students to peer-reviewed literature ( Green et al., 2006 ). For researchers, narrative reviews can inspire research ideas by identifying gaps or inconsistencies in a body of knowledge, thus helping researchers to determine research questions or formulate hypotheses. Importantly, narrative reviews can also be used as educational articles to bring practitioners up to date with certain topics of issues ( Green et al., 2006 ).
Recently, there have been several efforts to introduce more rigour in narrative reviews that will elucidate common pitfalls and bring changes into their publication standards. Information systems researchers, among others, have contributed to advancing knowledge on how to structure a “traditional” review. For instance, Levy and Ellis (2006) proposed a generic framework for conducting such reviews. Their model follows the systematic data processing approach comprised of three steps, namely: (a) literature search and screening; (b) data extraction and analysis; and (c) writing the literature review. They provide detailed and very helpful instructions on how to conduct each step of the review process. As another methodological contribution, vom Brocke et al. (2009) offered a series of guidelines for conducting literature reviews, with a particular focus on how to search and extract the relevant body of knowledge. Last, Bandara, Miskon, and Fielt (2011) proposed a structured, predefined and tool-supported method to identify primary studies within a feasible scope, extract relevant content from identified articles, synthesize and analyze the findings, and effectively write and present the results of the literature review. We highly recommend that prospective authors of narrative reviews consult these useful sources before embarking on their work.
Darlow and Wen (2015) provide a good example of a highly structured narrative review in the eHealth field. These authors synthesized published articles that describe the development process of mobile health ( m-health ) interventions for patients’ cancer care self-management. As in most narrative reviews, the scope of the research questions being investigated is broad: (a) how development of these systems are carried out; (b) which methods are used to investigate these systems; and (c) what conclusions can be drawn as a result of the development of these systems. To provide clear answers to these questions, a literature search was conducted on six electronic databases and Google Scholar . The search was performed using several terms and free text words, combining them in an appropriate manner. Four inclusion and three exclusion criteria were utilized during the screening process. Both authors independently reviewed each of the identified articles to determine eligibility and extract study information. A flow diagram shows the number of studies identified, screened, and included or excluded at each stage of study selection. In terms of contributions, this review provides a series of practical recommendations for m-health intervention development.
9.3.2. Descriptive or Mapping Reviews
The primary goal of a descriptive review is to determine the extent to which a body of knowledge in a particular research topic reveals any interpretable pattern or trend with respect to pre-existing propositions, theories, methodologies or findings ( King & He, 2005 ; Paré et al., 2015 ). In contrast with narrative reviews, descriptive reviews follow a systematic and transparent procedure, including searching, screening and classifying studies ( Petersen, Vakkalanka, & Kuzniarz, 2015 ). Indeed, structured search methods are used to form a representative sample of a larger group of published works ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Further, authors of descriptive reviews extract from each study certain characteristics of interest, such as publication year, research methods, data collection techniques, and direction or strength of research outcomes (e.g., positive, negative, or non-significant) in the form of frequency analysis to produce quantitative results ( Sylvester et al., 2013 ). In essence, each study included in a descriptive review is treated as the unit of analysis and the published literature as a whole provides a database from which the authors attempt to identify any interpretable trends or draw overall conclusions about the merits of existing conceptualizations, propositions, methods or findings ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In doing so, a descriptive review may claim that its findings represent the state of the art in a particular domain ( King & He, 2005 ).
In the fields of health sciences and medical informatics, reviews that focus on examining the range, nature and evolution of a topic area are described by Anderson, Allen, Peckham, and Goodwin (2008) as mapping reviews . Like descriptive reviews, the research questions are generic and usually relate to publication patterns and trends. There is no preconceived plan to systematically review all of the literature although this can be done. Instead, researchers often present studies that are representative of most works published in a particular area and they consider a specific time frame to be mapped.
An example of this approach in the eHealth domain is offered by DeShazo, Lavallie, and Wolf (2009). The purpose of this descriptive or mapping review was to characterize publication trends in the medical informatics literature over a 20-year period (1987 to 2006). To achieve this ambitious objective, the authors performed a bibliometric analysis of medical informatics citations indexed in medline using publication trends, journal frequencies, impact factors, Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) term frequencies, and characteristics of citations. Findings revealed that there were over 77,000 medical informatics articles published during the covered period in numerous journals and that the average annual growth rate was 12%. The MeSH term analysis also suggested a strong interdisciplinary trend. Finally, average impact scores increased over time with two notable growth periods. Overall, patterns in research outputs that seem to characterize the historic trends and current components of the field of medical informatics suggest it may be a maturing discipline (DeShazo et al., 2009).
9.3.3. Scoping Reviews
Scoping reviews attempt to provide an initial indication of the potential size and nature of the extant literature on an emergent topic (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005; Daudt, van Mossel, & Scott, 2013 ; Levac, Colquhoun, & O’Brien, 2010). A scoping review may be conducted to examine the extent, range and nature of research activities in a particular area, determine the value of undertaking a full systematic review (discussed next), or identify research gaps in the extant literature ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In line with their main objective, scoping reviews usually conclude with the presentation of a detailed research agenda for future works along with potential implications for both practice and research.
Unlike narrative and descriptive reviews, the whole point of scoping the field is to be as comprehensive as possible, including grey literature (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005). Inclusion and exclusion criteria must be established to help researchers eliminate studies that are not aligned with the research questions. It is also recommended that at least two independent coders review abstracts yielded from the search strategy and then the full articles for study selection ( Daudt et al., 2013 ). The synthesized evidence from content or thematic analysis is relatively easy to present in tabular form (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005; Thomas & Harden, 2008 ).
One of the most highly cited scoping reviews in the eHealth domain was published by Archer, Fevrier-Thomas, Lokker, McKibbon, and Straus (2011) . These authors reviewed the existing literature on personal health record ( phr ) systems including design, functionality, implementation, applications, outcomes, and benefits. Seven databases were searched from 1985 to March 2010. Several search terms relating to phr s were used during this process. Two authors independently screened titles and abstracts to determine inclusion status. A second screen of full-text articles, again by two independent members of the research team, ensured that the studies described phr s. All in all, 130 articles met the criteria and their data were extracted manually into a database. The authors concluded that although there is a large amount of survey, observational, cohort/panel, and anecdotal evidence of phr benefits and satisfaction for patients, more research is needed to evaluate the results of phr implementations. Their in-depth analysis of the literature signalled that there is little solid evidence from randomized controlled trials or other studies through the use of phr s. Hence, they suggested that more research is needed that addresses the current lack of understanding of optimal functionality and usability of these systems, and how they can play a beneficial role in supporting patient self-management ( Archer et al., 2011 ).
9.3.4. Forms of Aggregative Reviews
Healthcare providers, practitioners, and policy-makers are nowadays overwhelmed with large volumes of information, including research-based evidence from numerous clinical trials and evaluation studies, assessing the effectiveness of health information technologies and interventions ( Ammenwerth & de Keizer, 2004 ; Deshazo et al., 2009 ). It is unrealistic to expect that all these disparate actors will have the time, skills, and necessary resources to identify the available evidence in the area of their expertise and consider it when making decisions. Systematic reviews that involve the rigorous application of scientific strategies aimed at limiting subjectivity and bias (i.e., systematic and random errors) can respond to this challenge.
Systematic reviews attempt to aggregate, appraise, and synthesize in a single source all empirical evidence that meet a set of previously specified eligibility criteria in order to answer a clearly formulated and often narrow research question on a particular topic of interest to support evidence-based practice ( Liberati et al., 2009 ). They adhere closely to explicit scientific principles ( Liberati et al., 2009 ) and rigorous methodological guidelines (Higgins & Green, 2008) aimed at reducing random and systematic errors that can lead to deviations from the truth in results or inferences. The use of explicit methods allows systematic reviews to aggregate a large body of research evidence, assess whether effects or relationships are in the same direction and of the same general magnitude, explain possible inconsistencies between study results, and determine the strength of the overall evidence for every outcome of interest based on the quality of included studies and the general consistency among them ( Cook, Mulrow, & Haynes, 1997 ). The main procedures of a systematic review involve:
- Formulating a review question and developing a search strategy based on explicit inclusion criteria for the identification of eligible studies (usually described in the context of a detailed review protocol).
- Searching for eligible studies using multiple databases and information sources, including grey literature sources, without any language restrictions.
- Selecting studies, extracting data, and assessing risk of bias in a duplicate manner using two independent reviewers to avoid random or systematic errors in the process.
- Analyzing data using quantitative or qualitative methods.
- Presenting results in summary of findings tables.
- Interpreting results and drawing conclusions.
Many systematic reviews, but not all, use statistical methods to combine the results of independent studies into a single quantitative estimate or summary effect size. Known as meta-analyses , these reviews use specific data extraction and statistical techniques (e.g., network, frequentist, or Bayesian meta-analyses) to calculate from each study by outcome of interest an effect size along with a confidence interval that reflects the degree of uncertainty behind the point estimate of effect ( Borenstein, Hedges, Higgins, & Rothstein, 2009 ; Deeks, Higgins, & Altman, 2008 ). Subsequently, they use fixed or random-effects analysis models to combine the results of the included studies, assess statistical heterogeneity, and calculate a weighted average of the effect estimates from the different studies, taking into account their sample sizes. The summary effect size is a value that reflects the average magnitude of the intervention effect for a particular outcome of interest or, more generally, the strength of a relationship between two variables across all studies included in the systematic review. By statistically combining data from multiple studies, meta-analyses can create more precise and reliable estimates of intervention effects than those derived from individual studies alone, when these are examined independently as discrete sources of information.
The review by Gurol-Urganci, de Jongh, Vodopivec-Jamsek, Atun, and Car (2013) on the effects of mobile phone messaging reminders for attendance at healthcare appointments is an illustrative example of a high-quality systematic review with meta-analysis. Missed appointments are a major cause of inefficiency in healthcare delivery with substantial monetary costs to health systems. These authors sought to assess whether mobile phone-based appointment reminders delivered through Short Message Service ( sms ) or Multimedia Messaging Service ( mms ) are effective in improving rates of patient attendance and reducing overall costs. To this end, they conducted a comprehensive search on multiple databases using highly sensitive search strategies without language or publication-type restrictions to identify all rct s that are eligible for inclusion. In order to minimize the risk of omitting eligible studies not captured by the original search, they supplemented all electronic searches with manual screening of trial registers and references contained in the included studies. Study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessments were performed independently by two coders using standardized methods to ensure consistency and to eliminate potential errors. Findings from eight rct s involving 6,615 participants were pooled into meta-analyses to calculate the magnitude of effects that mobile text message reminders have on the rate of attendance at healthcare appointments compared to no reminders and phone call reminders.
Meta-analyses are regarded as powerful tools for deriving meaningful conclusions. However, there are situations in which it is neither reasonable nor appropriate to pool studies together using meta-analytic methods simply because there is extensive clinical heterogeneity between the included studies or variation in measurement tools, comparisons, or outcomes of interest. In these cases, systematic reviews can use qualitative synthesis methods such as vote counting, content analysis, classification schemes and tabulations, as an alternative approach to narratively synthesize the results of the independent studies included in the review. This form of review is known as qualitative systematic review.
A rigorous example of one such review in the eHealth domain is presented by Mickan, Atherton, Roberts, Heneghan, and Tilson (2014) on the use of handheld computers by healthcare professionals and their impact on access to information and clinical decision-making. In line with the methodological guidelines for systematic reviews, these authors: (a) developed and registered with prospero ( www.crd.york.ac.uk/ prospero / ) an a priori review protocol; (b) conducted comprehensive searches for eligible studies using multiple databases and other supplementary strategies (e.g., forward searches); and (c) subsequently carried out study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessments in a duplicate manner to eliminate potential errors in the review process. Heterogeneity between the included studies in terms of reported outcomes and measures precluded the use of meta-analytic methods. To this end, the authors resorted to using narrative analysis and synthesis to describe the effectiveness of handheld computers on accessing information for clinical knowledge, adherence to safety and clinical quality guidelines, and diagnostic decision-making.
In recent years, the number of systematic reviews in the field of health informatics has increased considerably. Systematic reviews with discordant findings can cause great confusion and make it difficult for decision-makers to interpret the review-level evidence ( Moher, 2013 ). Therefore, there is a growing need for appraisal and synthesis of prior systematic reviews to ensure that decision-making is constantly informed by the best available accumulated evidence. Umbrella reviews , also known as overviews of systematic reviews, are tertiary types of evidence synthesis that aim to accomplish this; that is, they aim to compare and contrast findings from multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses ( Becker & Oxman, 2008 ). Umbrella reviews generally adhere to the same principles and rigorous methodological guidelines used in systematic reviews. However, the unit of analysis in umbrella reviews is the systematic review rather than the primary study ( Becker & Oxman, 2008 ). Unlike systematic reviews that have a narrow focus of inquiry, umbrella reviews focus on broader research topics for which there are several potential interventions ( Smith, Devane, Begley, & Clarke, 2011 ). A recent umbrella review on the effects of home telemonitoring interventions for patients with heart failure critically appraised, compared, and synthesized evidence from 15 systematic reviews to investigate which types of home telemonitoring technologies and forms of interventions are more effective in reducing mortality and hospital admissions ( Kitsiou, Paré, & Jaana, 2015 ).
9.3.5. Realist Reviews
Realist reviews are theory-driven interpretative reviews developed to inform, enhance, or supplement conventional systematic reviews by making sense of heterogeneous evidence about complex interventions applied in diverse contexts in a way that informs policy decision-making ( Greenhalgh, Wong, Westhorp, & Pawson, 2011 ). They originated from criticisms of positivist systematic reviews which centre on their “simplistic” underlying assumptions ( Oates, 2011 ). As explained above, systematic reviews seek to identify causation. Such logic is appropriate for fields like medicine and education where findings of randomized controlled trials can be aggregated to see whether a new treatment or intervention does improve outcomes. However, many argue that it is not possible to establish such direct causal links between interventions and outcomes in fields such as social policy, management, and information systems where for any intervention there is unlikely to be a regular or consistent outcome ( Oates, 2011 ; Pawson, 2006 ; Rousseau, Manning, & Denyer, 2008 ).
To circumvent these limitations, Pawson, Greenhalgh, Harvey, and Walshe (2005) have proposed a new approach for synthesizing knowledge that seeks to unpack the mechanism of how “complex interventions” work in particular contexts. The basic research question — what works? — which is usually associated with systematic reviews changes to: what is it about this intervention that works, for whom, in what circumstances, in what respects and why? Realist reviews have no particular preference for either quantitative or qualitative evidence. As a theory-building approach, a realist review usually starts by articulating likely underlying mechanisms and then scrutinizes available evidence to find out whether and where these mechanisms are applicable ( Shepperd et al., 2009 ). Primary studies found in the extant literature are viewed as case studies which can test and modify the initial theories ( Rousseau et al., 2008 ).
The main objective pursued in the realist review conducted by Otte-Trojel, de Bont, Rundall, and van de Klundert (2014) was to examine how patient portals contribute to health service delivery and patient outcomes. The specific goals were to investigate how outcomes are produced and, most importantly, how variations in outcomes can be explained. The research team started with an exploratory review of background documents and research studies to identify ways in which patient portals may contribute to health service delivery and patient outcomes. The authors identified six main ways which represent “educated guesses” to be tested against the data in the evaluation studies. These studies were identified through a formal and systematic search in four databases between 2003 and 2013. Two members of the research team selected the articles using a pre-established list of inclusion and exclusion criteria and following a two-step procedure. The authors then extracted data from the selected articles and created several tables, one for each outcome category. They organized information to bring forward those mechanisms where patient portals contribute to outcomes and the variation in outcomes across different contexts.
9.3.6. Critical Reviews
Lastly, critical reviews aim to provide a critical evaluation and interpretive analysis of existing literature on a particular topic of interest to reveal strengths, weaknesses, contradictions, controversies, inconsistencies, and/or other important issues with respect to theories, hypotheses, research methods or results ( Baumeister & Leary, 1997 ; Kirkevold, 1997 ). Unlike other review types, critical reviews attempt to take a reflective account of the research that has been done in a particular area of interest, and assess its credibility by using appraisal instruments or critical interpretive methods. In this way, critical reviews attempt to constructively inform other scholars about the weaknesses of prior research and strengthen knowledge development by giving focus and direction to studies for further improvement ( Kirkevold, 1997 ).
Kitsiou, Paré, and Jaana (2013) provide an example of a critical review that assessed the methodological quality of prior systematic reviews of home telemonitoring studies for chronic patients. The authors conducted a comprehensive search on multiple databases to identify eligible reviews and subsequently used a validated instrument to conduct an in-depth quality appraisal. Results indicate that the majority of systematic reviews in this particular area suffer from important methodological flaws and biases that impair their internal validity and limit their usefulness for clinical and decision-making purposes. To this end, they provide a number of recommendations to strengthen knowledge development towards improving the design and execution of future reviews on home telemonitoring.
9.4. Summary
Table 9.1 outlines the main types of literature reviews that were described in the previous sub-sections and summarizes the main characteristics that distinguish one review type from another. It also includes key references to methodological guidelines and useful sources that can be used by eHealth scholars and researchers for planning and developing reviews.
Typology of Literature Reviews (adapted from Paré et al., 2015).
As shown in Table 9.1 , each review type addresses different kinds of research questions or objectives, which subsequently define and dictate the methods and approaches that need to be used to achieve the overarching goal(s) of the review. For example, in the case of narrative reviews, there is greater flexibility in searching and synthesizing articles ( Green et al., 2006 ). Researchers are often relatively free to use a diversity of approaches to search, identify, and select relevant scientific articles, describe their operational characteristics, present how the individual studies fit together, and formulate conclusions. On the other hand, systematic reviews are characterized by their high level of systematicity, rigour, and use of explicit methods, based on an “a priori” review plan that aims to minimize bias in the analysis and synthesis process (Higgins & Green, 2008). Some reviews are exploratory in nature (e.g., scoping/mapping reviews), whereas others may be conducted to discover patterns (e.g., descriptive reviews) or involve a synthesis approach that may include the critical analysis of prior research ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Hence, in order to select the most appropriate type of review, it is critical to know before embarking on a review project, why the research synthesis is conducted and what type of methods are best aligned with the pursued goals.
9.5. Concluding Remarks
In light of the increased use of evidence-based practice and research generating stronger evidence ( Grady et al., 2011 ; Lyden et al., 2013 ), review articles have become essential tools for summarizing, synthesizing, integrating or critically appraising prior knowledge in the eHealth field. As mentioned earlier, when rigorously conducted review articles represent powerful information sources for eHealth scholars and practitioners looking for state-of-the-art evidence. The typology of literature reviews we used herein will allow eHealth researchers, graduate students and practitioners to gain a better understanding of the similarities and differences between review types.
We must stress that this classification scheme does not privilege any specific type of review as being of higher quality than another ( Paré et al., 2015 ). As explained above, each type of review has its own strengths and limitations. Having said that, we realize that the methodological rigour of any review — be it qualitative, quantitative or mixed — is a critical aspect that should be considered seriously by prospective authors. In the present context, the notion of rigour refers to the reliability and validity of the review process described in section 9.2. For one thing, reliability is related to the reproducibility of the review process and steps, which is facilitated by a comprehensive documentation of the literature search process, extraction, coding and analysis performed in the review. Whether the search is comprehensive or not, whether it involves a methodical approach for data extraction and synthesis or not, it is important that the review documents in an explicit and transparent manner the steps and approach that were used in the process of its development. Next, validity characterizes the degree to which the review process was conducted appropriately. It goes beyond documentation and reflects decisions related to the selection of the sources, the search terms used, the period of time covered, the articles selected in the search, and the application of backward and forward searches ( vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). In short, the rigour of any review article is reflected by the explicitness of its methods (i.e., transparency) and the soundness of the approach used. We refer those interested in the concepts of rigour and quality to the work of Templier and Paré (2015) which offers a detailed set of methodological guidelines for conducting and evaluating various types of review articles.
To conclude, our main objective in this chapter was to demystify the various types of literature reviews that are central to the continuous development of the eHealth field. It is our hope that our descriptive account will serve as a valuable source for those conducting, evaluating or using reviews in this important and growing domain.
- Ammenwerth E., de Keizer N. An inventory of evaluation studies of information technology in health care. Trends in evaluation research, 1982-2002. International Journal of Medical Informatics. 2004; 44 (1):44–56. [ PubMed : 15778794 ]
- Anderson S., Allen P., Peckham S., Goodwin N. Asking the right questions: scoping studies in the commissioning of research on the organisation and delivery of health services. Health Research Policy and Systems. 2008; 6 (7):1–12. [ PMC free article : PMC2500008 ] [ PubMed : 18613961 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Archer N., Fevrier-Thomas U., Lokker C., McKibbon K. A., Straus S.E. Personal health records: a scoping review. Journal of American Medical Informatics Association. 2011; 18 (4):515–522. [ PMC free article : PMC3128401 ] [ PubMed : 21672914 ]
- Arksey H., O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology. 2005; 8 (1):19–32.
- A systematic, tool-supported method for conducting literature reviews in information systems. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 19th European Conference on Information Systems ( ecis 2011); June 9 to 11; Helsinki, Finland. 2011.
- Baumeister R. F., Leary M.R. Writing narrative literature reviews. Review of General Psychology. 1997; 1 (3):311–320.
- Becker L. A., Oxman A.D. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2008. Overviews of reviews; pp. 607–631.
- Borenstein M., Hedges L., Higgins J., Rothstein H. Introduction to meta-analysis. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons Inc; 2009.
- Cook D. J., Mulrow C. D., Haynes B. Systematic reviews: Synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1997; 126 (5):376–380. [ PubMed : 9054282 ]
- Cooper H., Hedges L.V. In: The handbook of research synthesis and meta-analysis. 2nd ed. Cooper H., Hedges L. V., Valentine J. C., editors. New York: Russell Sage Foundation; 2009. Research synthesis as a scientific process; pp. 3–17.
- Cooper H. M. Organizing knowledge syntheses: A taxonomy of literature reviews. Knowledge in Society. 1988; 1 (1):104–126.
- Cronin P., Ryan F., Coughlan M. Undertaking a literature review: a step-by-step approach. British Journal of Nursing. 2008; 17 (1):38–43. [ PubMed : 18399395 ]
- Darlow S., Wen K.Y. Development testing of mobile health interventions for cancer patient self-management: A review. Health Informatics Journal. 2015 (online before print). [ PubMed : 25916831 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Daudt H. M., van Mossel C., Scott S.J. Enhancing the scoping study methodology: a large, inter-professional team’s experience with Arksey and O’Malley’s framework. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2013; 13 :48. [ PMC free article : PMC3614526 ] [ PubMed : 23522333 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Davies P. The relevance of systematic reviews to educational policy and practice. Oxford Review of Education. 2000; 26 (3-4):365–378.
- Deeks J. J., Higgins J. P. T., Altman D.G. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2008. Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses; pp. 243–296.
- Deshazo J. P., Lavallie D. L., Wolf F.M. Publication trends in the medical informatics literature: 20 years of “Medical Informatics” in mesh . bmc Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2009; 9 :7. [ PMC free article : PMC2652453 ] [ PubMed : 19159472 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dixon-Woods M., Agarwal S., Jones D., Young B., Sutton A. Synthesising qualitative and quantitative evidence: a review of possible methods. Journal of Health Services Research and Policy. 2005; 10 (1):45–53. [ PubMed : 15667704 ]
- Finfgeld-Connett D., Johnson E.D. Literature search strategies for conducting knowledge-building and theory-generating qualitative systematic reviews. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2013; 69 (1):194–204. [ PMC free article : PMC3424349 ] [ PubMed : 22591030 ]
- Grady B., Myers K. M., Nelson E. L., Belz N., Bennett L., Carnahan L. … Guidelines Working Group. Evidence-based practice for telemental health. Telemedicine Journal and E Health. 2011; 17 (2):131–148. [ PubMed : 21385026 ]
- Green B. N., Johnson C. D., Adams A. Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: secrets of the trade. Journal of Chiropractic Medicine. 2006; 5 (3):101–117. [ PMC free article : PMC2647067 ] [ PubMed : 19674681 ]
- Greenhalgh T., Wong G., Westhorp G., Pawson R. Protocol–realist and meta-narrative evidence synthesis: evolving standards ( rameses ). bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2011; 11 :115. [ PMC free article : PMC3173389 ] [ PubMed : 21843376 ]
- Gurol-Urganci I., de Jongh T., Vodopivec-Jamsek V., Atun R., Car J. Mobile phone messaging reminders for attendance at healthcare appointments. Cochrane Database System Review. 2013; 12 cd 007458. [ PMC free article : PMC6485985 ] [ PubMed : 24310741 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hart C. Doing a literature review: Releasing the social science research imagination. London: SAGE Publications; 1998.
- Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions: Cochrane book series. Hoboken, nj : Wiley-Blackwell; 2008.
- Jesson J., Matheson L., Lacey F.M. Doing your literature review: traditional and systematic techniques. Los Angeles & London: SAGE Publications; 2011.
- King W. R., He J. Understanding the role and methods of meta-analysis in IS research. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2005; 16 :1.
- Kirkevold M. Integrative nursing research — an important strategy to further the development of nursing science and nursing practice. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 1997; 25 (5):977–984. [ PubMed : 9147203 ]
- Kitchenham B., Charters S. ebse Technical Report Version 2.3. Keele & Durham. uk : Keele University & University of Durham; 2007. Guidelines for performing systematic literature reviews in software engineering.
- Kitsiou S., Paré G., Jaana M. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of home telemonitoring interventions for patients with chronic diseases: a critical assessment of their methodological quality. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2013; 15 (7):e150. [ PMC free article : PMC3785977 ] [ PubMed : 23880072 ]
- Kitsiou S., Paré G., Jaana M. Effects of home telemonitoring interventions on patients with chronic heart failure: an overview of systematic reviews. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2015; 17 (3):e63. [ PMC free article : PMC4376138 ] [ PubMed : 25768664 ]
- Levac D., Colquhoun H., O’Brien K. K. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implementation Science. 2010; 5 (1):69. [ PMC free article : PMC2954944 ] [ PubMed : 20854677 ]
- Levy Y., Ellis T.J. A systems approach to conduct an effective literature review in support of information systems research. Informing Science. 2006; 9 :181–211.
- Liberati A., Altman D. G., Tetzlaff J., Mulrow C., Gøtzsche P. C., Ioannidis J. P. A. et al. Moher D. The prisma statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2009; 151 (4):W-65. [ PubMed : 19622512 ]
- Lyden J. R., Zickmund S. L., Bhargava T. D., Bryce C. L., Conroy M. B., Fischer G. S. et al. McTigue K. M. Implementing health information technology in a patient-centered manner: Patient experiences with an online evidence-based lifestyle intervention. Journal for Healthcare Quality. 2013; 35 (5):47–57. [ PubMed : 24004039 ]
- Mickan S., Atherton H., Roberts N. W., Heneghan C., Tilson J.K. Use of handheld computers in clinical practice: a systematic review. bmc Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2014; 14 :56. [ PMC free article : PMC4099138 ] [ PubMed : 24998515 ]
- Moher D. The problem of duplicate systematic reviews. British Medical Journal. 2013; 347 (5040) [ PubMed : 23945367 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Montori V. M., Wilczynski N. L., Morgan D., Haynes R. B., Hedges T. Systematic reviews: a cross-sectional study of location and citation counts. bmc Medicine. 2003; 1 :2. [ PMC free article : PMC281591 ] [ PubMed : 14633274 ]
- Mulrow C. D. The medical review article: state of the science. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1987; 106 (3):485–488. [ PubMed : 3813259 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Evidence-based information systems: A decade later. Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Systems ; 2011. Retrieved from http://aisel .aisnet.org/cgi/viewcontent .cgi?article =1221&context =ecis2011 .
- Okoli C., Schabram K. A guide to conducting a systematic literature review of information systems research. ssrn Electronic Journal. 2010
- Otte-Trojel T., de Bont A., Rundall T. G., van de Klundert J. How outcomes are achieved through patient portals: a realist review. Journal of American Medical Informatics Association. 2014; 21 (4):751–757. [ PMC free article : PMC4078283 ] [ PubMed : 24503882 ]
- Paré G., Trudel M.-C., Jaana M., Kitsiou S. Synthesizing information systems knowledge: A typology of literature reviews. Information & Management. 2015; 52 (2):183–199.
- Patsopoulos N. A., Analatos A. A., Ioannidis J.P. A. Relative citation impact of various study designs in the health sciences. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2005; 293 (19):2362–2366. [ PubMed : 15900006 ]
- Paul M. M., Greene C. M., Newton-Dame R., Thorpe L. E., Perlman S. E., McVeigh K. H., Gourevitch M.N. The state of population health surveillance using electronic health records: A narrative review. Population Health Management. 2015; 18 (3):209–216. [ PubMed : 25608033 ]
- Pawson R. Evidence-based policy: a realist perspective. London: SAGE Publications; 2006.
- Pawson R., Greenhalgh T., Harvey G., Walshe K. Realist review—a new method of systematic review designed for complex policy interventions. Journal of Health Services Research & Policy. 2005; 10 (Suppl 1):21–34. [ PubMed : 16053581 ]
- Petersen K., Vakkalanka S., Kuzniarz L. Guidelines for conducting systematic mapping studies in software engineering: An update. Information and Software Technology. 2015; 64 :1–18.
- Petticrew M., Roberts H. Systematic reviews in the social sciences: A practical guide. Malden, ma : Blackwell Publishing Co; 2006.
- Rousseau D. M., Manning J., Denyer D. Evidence in management and organizational science: Assembling the field’s full weight of scientific knowledge through syntheses. The Academy of Management Annals. 2008; 2 (1):475–515.
- Rowe F. What literature review is not: diversity, boundaries and recommendations. European Journal of Information Systems. 2014; 23 (3):241–255.
- Shea B. J., Hamel C., Wells G. A., Bouter L. M., Kristjansson E., Grimshaw J. et al. Boers M. amstar is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 2009; 62 (10):1013–1020. [ PubMed : 19230606 ]
- Shepperd S., Lewin S., Straus S., Clarke M., Eccles M. P., Fitzpatrick R. et al. Sheikh A. Can we systematically review studies that evaluate complex interventions? PLoS Medicine. 2009; 6 (8):e1000086. [ PMC free article : PMC2717209 ] [ PubMed : 19668360 ]
- Silva B. M., Rodrigues J. J., de la Torre Díez I., López-Coronado M., Saleem K. Mobile-health: A review of current state in 2015. Journal of Biomedical Informatics. 2015; 56 :265–272. [ PubMed : 26071682 ]
- Smith V., Devane D., Begley C., Clarke M. Methodology in conducting a systematic review of systematic reviews of healthcare interventions. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2011; 11 (1):15. [ PMC free article : PMC3039637 ] [ PubMed : 21291558 ]
- Sylvester A., Tate M., Johnstone D. Beyond synthesis: re-presenting heterogeneous research literature. Behaviour & Information Technology. 2013; 32 (12):1199–1215.
- Templier M., Paré G. A framework for guiding and evaluating literature reviews. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2015; 37 (6):112–137.
- Thomas J., Harden A. Methods for the thematic synthesis of qualitative research in systematic reviews. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2008; 8 (1):45. [ PMC free article : PMC2478656 ] [ PubMed : 18616818 ]
- Reconstructing the giant: on the importance of rigour in documenting the literature search process. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Information Systems ( ecis 2009); Verona, Italy. 2009.
- Webster J., Watson R.T. Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: Writing a literature review. Management Information Systems Quarterly. 2002; 26 (2):11.
- Whitlock E. P., Lin J. S., Chou R., Shekelle P., Robinson K.A. Using existing systematic reviews in complex systematic reviews. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2008; 148 (10):776–782. [ PubMed : 18490690 ]
This publication is licensed under a Creative Commons License, Attribution-Noncommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0): see https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- Cite this Page Paré G, Kitsiou S. Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews. In: Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.
- PDF version of this title (4.5M)
- Disable Glossary Links
In this Page
- Introduction
- Overview of the Literature Review Process and Steps
- Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations
- Concluding Remarks
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Recent Activity
- Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Ev... Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
Advertisement
An automated essay scoring systems: a systematic literature review
- Published: 23 September 2021
- Volume 55 , pages 2495–2527, ( 2022 )
Cite this article
- Dadi Ramesh ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3967-8914 1 , 2 &
- Suresh Kumar Sanampudi 3
32k Accesses
73 Citations
6 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Assessment in the Education system plays a significant role in judging student performance. The present evaluation system is through human assessment. As the number of teachers' student ratio is gradually increasing, the manual evaluation process becomes complicated. The drawback of manual evaluation is that it is time-consuming, lacks reliability, and many more. This connection online examination system evolved as an alternative tool for pen and paper-based methods. Present Computer-based evaluation system works only for multiple-choice questions, but there is no proper evaluation system for grading essays and short answers. Many researchers are working on automated essay grading and short answer scoring for the last few decades, but assessing an essay by considering all parameters like the relevance of the content to the prompt, development of ideas, Cohesion, and Coherence is a big challenge till now. Few researchers focused on Content-based evaluation, while many of them addressed style-based assessment. This paper provides a systematic literature review on automated essay scoring systems. We studied the Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning techniques used to evaluate automatic essay scoring and analyzed the limitations of the current studies and research trends. We observed that the essay evaluation is not done based on the relevance of the content and coherence.
Similar content being viewed by others

Automated Essay Scoring Systems

Automated Essay Scoring System Based on Rubric
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Due to COVID 19 outbreak, an online educational system has become inevitable. In the present scenario, almost all the educational institutions ranging from schools to colleges adapt the online education system. The assessment plays a significant role in measuring the learning ability of the student. Most automated evaluation is available for multiple-choice questions, but assessing short and essay answers remain a challenge. The education system is changing its shift to online-mode, like conducting computer-based exams and automatic evaluation. It is a crucial application related to the education domain, which uses natural language processing (NLP) and Machine Learning techniques. The evaluation of essays is impossible with simple programming languages and simple techniques like pattern matching and language processing. Here the problem is for a single question, we will get more responses from students with a different explanation. So, we need to evaluate all the answers concerning the question.
Automated essay scoring (AES) is a computer-based assessment system that automatically scores or grades the student responses by considering appropriate features. The AES research started in 1966 with the Project Essay Grader (PEG) by Ajay et al. ( 1973 ). PEG evaluates the writing characteristics such as grammar, diction, construction, etc., to grade the essay. A modified version of the PEG by Shermis et al. ( 2001 ) was released, which focuses on grammar checking with a correlation between human evaluators and the system. Foltz et al. ( 1999 ) introduced an Intelligent Essay Assessor (IEA) by evaluating content using latent semantic analysis to produce an overall score. Powers et al. ( 2002 ) proposed E-rater and Intellimetric by Rudner et al. ( 2006 ) and Bayesian Essay Test Scoring System (BESTY) by Rudner and Liang ( 2002 ), these systems use natural language processing (NLP) techniques that focus on style and content to obtain the score of an essay. The vast majority of the essay scoring systems in the 1990s followed traditional approaches like pattern matching and a statistical-based approach. Since the last decade, the essay grading systems started using regression-based and natural language processing techniques. AES systems like Dong et al. ( 2017 ) and others developed from 2014 used deep learning techniques, inducing syntactic and semantic features resulting in better results than earlier systems.
Ohio, Utah, and most US states are using AES systems in school education, like Utah compose tool, Ohio standardized test (an updated version of PEG), evaluating millions of student's responses every year. These systems work for both formative, summative assessments and give feedback to students on the essay. Utah provided basic essay evaluation rubrics (six characteristics of essay writing): Development of ideas, organization, style, word choice, sentence fluency, conventions. Educational Testing Service (ETS) has been conducting significant research on AES for more than a decade and designed an algorithm to evaluate essays on different domains and providing an opportunity for test-takers to improve their writing skills. In addition, they are current research content-based evaluation.
The evaluation of essay and short answer scoring should consider the relevance of the content to the prompt, development of ideas, Cohesion, Coherence, and domain knowledge. Proper assessment of the parameters mentioned above defines the accuracy of the evaluation system. But all these parameters cannot play an equal role in essay scoring and short answer scoring. In a short answer evaluation, domain knowledge is required, like the meaning of "cell" in physics and biology is different. And while evaluating essays, the implementation of ideas with respect to prompt is required. The system should also assess the completeness of the responses and provide feedback.
Several studies examined AES systems, from the initial to the latest AES systems. In which the following studies on AES systems are Blood ( 2011 ) provided a literature review from PEG 1984–2010. Which has covered only generalized parts of AES systems like ethical aspects, the performance of the systems. Still, they have not covered the implementation part, and it’s not a comparative study and has not discussed the actual challenges of AES systems.
Burrows et al. ( 2015 ) Reviewed AES systems on six dimensions like dataset, NLP techniques, model building, grading models, evaluation, and effectiveness of the model. They have not covered feature extraction techniques and challenges in features extractions. Covered only Machine Learning models but not in detail. This system not covered the comparative analysis of AES systems like feature extraction, model building, and level of relevance, cohesion, and coherence not covered in this review.
Ke et al. ( 2019 ) provided a state of the art of AES system but covered very few papers and not listed all challenges, and no comparative study of the AES model. On the other hand, Hussein et al. in ( 2019 ) studied two categories of AES systems, four papers from handcrafted features for AES systems, and four papers from the neural networks approach, discussed few challenges, and did not cover feature extraction techniques, the performance of AES models in detail.
Klebanov et al. ( 2020 ). Reviewed 50 years of AES systems, listed and categorized all essential features that need to be extracted from essays. But not provided a comparative analysis of all work and not discussed the challenges.
This paper aims to provide a systematic literature review (SLR) on automated essay grading systems. An SLR is an Evidence-based systematic review to summarize the existing research. It critically evaluates and integrates all relevant studies' findings and addresses the research domain's specific research questions. Our research methodology uses guidelines given by Kitchenham et al. ( 2009 ) for conducting the review process; provide a well-defined approach to identify gaps in current research and to suggest further investigation.
We addressed our research method, research questions, and the selection process in Sect. 2 , and the results of the research questions have discussed in Sect. 3 . And the synthesis of all the research questions addressed in Sect. 4 . Conclusion and possible future work discussed in Sect. 5 .
2 Research method
We framed the research questions with PICOC criteria.
Population (P) Student essays and answers evaluation systems.
Intervention (I) evaluation techniques, data sets, features extraction methods.
Comparison (C) Comparison of various approaches and results.
Outcomes (O) Estimate the accuracy of AES systems,
Context (C) NA.
2.1 Research questions
To collect and provide research evidence from the available studies in the domain of automated essay grading, we framed the following research questions (RQ):
RQ1 what are the datasets available for research on automated essay grading?
The answer to the question can provide a list of the available datasets, their domain, and access to the datasets. It also provides a number of essays and corresponding prompts.
RQ2 what are the features extracted for the assessment of essays?
The answer to the question can provide an insight into various features so far extracted, and the libraries used to extract those features.
RQ3, which are the evaluation metrics available for measuring the accuracy of algorithms?
The answer will provide different evaluation metrics for accurate measurement of each Machine Learning approach and commonly used measurement technique.
RQ4 What are the Machine Learning techniques used for automatic essay grading, and how are they implemented?
It can provide insights into various Machine Learning techniques like regression models, classification models, and neural networks for implementing essay grading systems. The response to the question can give us different assessment approaches for automated essay grading systems.
RQ5 What are the challenges/limitations in the current research?
The answer to the question provides limitations of existing research approaches like cohesion, coherence, completeness, and feedback.
2.2 Search process
We conducted an automated search on well-known computer science repositories like ACL, ACM, IEEE Explore, Springer, and Science Direct for an SLR. We referred to papers published from 2010 to 2020 as much of the work during these years focused on advanced technologies like deep learning and natural language processing for automated essay grading systems. Also, the availability of free data sets like Kaggle (2012), Cambridge Learner Corpus-First Certificate in English exam (CLC-FCE) by Yannakoudakis et al. ( 2011 ) led to research this domain.
Search Strings : We used search strings like “Automated essay grading” OR “Automated essay scoring” OR “short answer scoring systems” OR “essay scoring systems” OR “automatic essay evaluation” and searched on metadata.
2.3 Selection criteria
After collecting all relevant documents from the repositories, we prepared selection criteria for inclusion and exclusion of documents. With the inclusion and exclusion criteria, it becomes more feasible for the research to be accurate and specific.
Inclusion criteria 1 Our approach is to work with datasets comprise of essays written in English. We excluded the essays written in other languages.
Inclusion criteria 2 We included the papers implemented on the AI approach and excluded the traditional methods for the review.
Inclusion criteria 3 The study is on essay scoring systems, so we exclusively included the research carried out on only text data sets rather than other datasets like image or speech.
Exclusion criteria We removed the papers in the form of review papers, survey papers, and state of the art papers.
2.4 Quality assessment
In addition to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, we assessed each paper by quality assessment questions to ensure the article's quality. We included the documents that have clearly explained the approach they used, the result analysis and validation.
The quality checklist questions are framed based on the guidelines from Kitchenham et al. ( 2009 ). Each quality assessment question was graded as either 1 or 0. The final score of the study range from 0 to 3. A cut off score for excluding a study from the review is 2 points. Since the papers scored 2 or 3 points are included in the final evaluation. We framed the following quality assessment questions for the final study.
Quality Assessment 1: Internal validity.
Quality Assessment 2: External validity.
Quality Assessment 3: Bias.
The two reviewers review each paper to select the final list of documents. We used the Quadratic Weighted Kappa score to measure the final agreement between the two reviewers. The average resulted from the kappa score is 0.6942, a substantial agreement between the reviewers. The result of evolution criteria shown in Table 1 . After Quality Assessment, the final list of papers for review is shown in Table 2 . The complete selection process is shown in Fig. 1 . The total number of selected papers in year wise as shown in Fig. 2 .
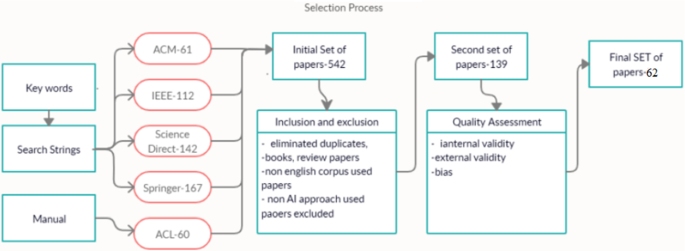
Selection process
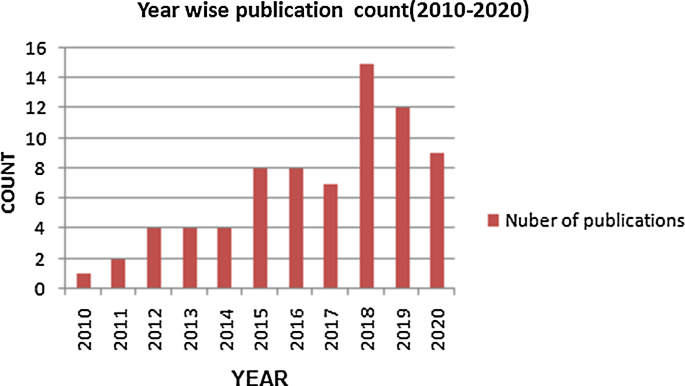
Year wise publications
3.1 What are the datasets available for research on automated essay grading?
To work with problem statement especially in Machine Learning and deep learning domain, we require considerable amount of data to train the models. To answer this question, we listed all the data sets used for training and testing for automated essay grading systems. The Cambridge Learner Corpus-First Certificate in English exam (CLC-FCE) Yannakoudakis et al. ( 2011 ) developed corpora that contain 1244 essays and ten prompts. This corpus evaluates whether a student can write the relevant English sentences without any grammatical and spelling mistakes. This type of corpus helps to test the models built for GRE and TOFEL type of exams. It gives scores between 1 and 40.
Bailey and Meurers ( 2008 ), Created a dataset (CREE reading comprehension) for language learners and automated short answer scoring systems. The corpus consists of 566 responses from intermediate students. Mohler and Mihalcea ( 2009 ). Created a dataset for the computer science domain consists of 630 responses for data structure assignment questions. The scores are range from 0 to 5 given by two human raters.
Dzikovska et al. ( 2012 ) created a Student Response Analysis (SRA) corpus. It consists of two sub-groups: the BEETLE corpus consists of 56 questions and approximately 3000 responses from students in the electrical and electronics domain. The second one is the SCIENTSBANK(SemEval-2013) (Dzikovska et al. 2013a ; b ) corpus consists of 10,000 responses on 197 prompts on various science domains. The student responses ladled with "correct, partially correct incomplete, Contradictory, Irrelevant, Non-domain."
In the Kaggle (2012) competition, released total 3 types of corpuses on an Automated Student Assessment Prize (ASAP1) (“ https://www.kaggle.com/c/asap-sas/ ” ) essays and short answers. It has nearly 17,450 essays, out of which it provides up to 3000 essays for each prompt. It has eight prompts that test 7th to 10th grade US students. It gives scores between the [0–3] and [0–60] range. The limitations of these corpora are: (1) it has a different score range for other prompts. (2) It uses statistical features such as named entities extraction and lexical features of words to evaluate essays. ASAP + + is one more dataset from Kaggle. It is with six prompts, and each prompt has more than 1000 responses total of 10,696 from 8th-grade students. Another corpus contains ten prompts from science, English domains and a total of 17,207 responses. Two human graders evaluated all these responses.
Correnti et al. ( 2013 ) created a Response-to-Text Assessment (RTA) dataset used to check student writing skills in all directions like style, mechanism, and organization. 4–8 grade students give the responses to RTA. Basu et al. ( 2013 ) created a power grading dataset with 700 responses for ten different prompts from US immigration exams. It contains all short answers for assessment.
The TOEFL11 corpus Blanchard et al. ( 2013 ) contains 1100 essays evenly distributed over eight prompts. It is used to test the English language skills of a candidate attending the TOFEL exam. It scores the language proficiency of a candidate as low, medium, and high.
International Corpus of Learner English (ICLE) Granger et al. ( 2009 ) built a corpus of 3663 essays covering different dimensions. It has 12 prompts with 1003 essays that test the organizational skill of essay writing, and13 prompts, each with 830 essays that examine the thesis clarity and prompt adherence.
Argument Annotated Essays (AAE) Stab and Gurevych ( 2014 ) developed a corpus that contains 102 essays with 101 prompts taken from the essayforum2 site. It tests the persuasive nature of the student essay. The SCIENTSBANK corpus used by Sakaguchi et al. ( 2015 ) available in git-hub, containing 9804 answers to 197 questions in 15 science domains. Table 3 illustrates all datasets related to AES systems.
3.2 RQ2 what are the features extracted for the assessment of essays?
Features play a major role in the neural network and other supervised Machine Learning approaches. The automatic essay grading systems scores student essays based on different types of features, which play a prominent role in training the models. Based on their syntax and semantics and they are categorized into three groups. 1. statistical-based features Contreras et al. ( 2018 ); Kumar et al. ( 2019 ); Mathias and Bhattacharyya ( 2018a ; b ) 2. Style-based (Syntax) features Cummins et al. ( 2016 ); Darwish and Mohamed ( 2020 ); Ke et al. ( 2019 ). 3. Content-based features Dong et al. ( 2017 ). A good set of features appropriate models evolved better AES systems. The vast majority of the researchers are using regression models if features are statistical-based. For Neural Networks models, researches are using both style-based and content-based features. The following table shows the list of various features used in existing AES Systems. Table 4 represents all set of features used for essay grading.
We studied all the feature extracting NLP libraries as shown in Fig. 3 . that are used in the papers. The NLTK is an NLP tool used to retrieve statistical features like POS, word count, sentence count, etc. With NLTK, we can miss the essay's semantic features. To find semantic features Word2Vec Mikolov et al. ( 2013 ), GloVe Jeffrey Pennington et al. ( 2014 ) is the most used libraries to retrieve the semantic text from the essays. And in some systems, they directly trained the model with word embeddings to find the score. From Fig. 4 as observed that non-content-based feature extraction is higher than content-based.
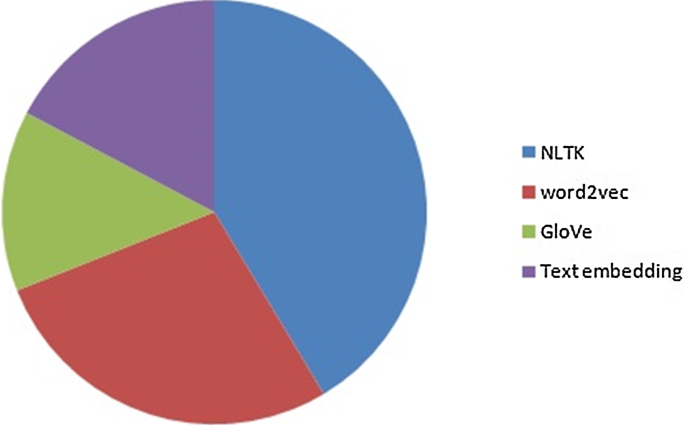
Usages of tools
Number of papers on content based features
3.3 RQ3 which are the evaluation metrics available for measuring the accuracy of algorithms?
The majority of the AES systems are using three evaluation metrics. They are (1) quadrated weighted kappa (QWK) (2) Mean Absolute Error (MAE) (3) Pearson Correlation Coefficient (PCC) Shehab et al. ( 2016 ). The quadratic weighted kappa will find agreement between human evaluation score and system evaluation score and produces value ranging from 0 to 1. And the Mean Absolute Error is the actual difference between human-rated score to system-generated score. The mean square error (MSE) measures the average squares of the errors, i.e., the average squared difference between the human-rated and the system-generated scores. MSE will always give positive numbers only. Pearson's Correlation Coefficient (PCC) finds the correlation coefficient between two variables. It will provide three values (0, 1, − 1). "0" represents human-rated and system scores that are not related. "1" represents an increase in the two scores. "− 1" illustrates a negative relationship between the two scores.
3.4 RQ4 what are the Machine Learning techniques being used for automatic essay grading, and how are they implemented?
After scrutinizing all documents, we categorize the techniques used in automated essay grading systems into four baskets. 1. Regression techniques. 2. Classification model. 3. Neural networks. 4. Ontology-based approach.
All the existing AES systems developed in the last ten years employ supervised learning techniques. Researchers using supervised methods viewed the AES system as either regression or classification task. The goal of the regression task is to predict the score of an essay. The classification task is to classify the essays belonging to (low, medium, or highly) relevant to the question's topic. Since the last three years, most AES systems developed made use of the concept of the neural network.
3.4.1 Regression based models
Mohler and Mihalcea ( 2009 ). proposed text-to-text semantic similarity to assign a score to the student essays. There are two text similarity measures like Knowledge-based measures, corpus-based measures. There eight knowledge-based tests with all eight models. They found the similarity. The shortest path similarity determines based on the length, which shortest path between two contexts. Leacock & Chodorow find the similarity based on the shortest path's length between two concepts using node-counting. The Lesk similarity finds the overlap between the corresponding definitions, and Wu & Palmer algorithm finds similarities based on the depth of two given concepts in the wordnet taxonomy. Resnik, Lin, Jiang&Conrath, Hirst& St-Onge find the similarity based on different parameters like the concept, probability, normalization factor, lexical chains. In corpus-based likeness, there LSA BNC, LSA Wikipedia, and ESA Wikipedia, latent semantic analysis is trained on Wikipedia and has excellent domain knowledge. Among all similarity scores, correlation scores LSA Wikipedia scoring accuracy is more. But these similarity measure algorithms are not using NLP concepts. These models are before 2010 and basic concept models to continue the research automated essay grading with updated algorithms on neural networks with content-based features.
Adamson et al. ( 2014 ) proposed an automatic essay grading system which is a statistical-based approach in this they retrieved features like POS, Character count, Word count, Sentence count, Miss spelled words, n-gram representation of words to prepare essay vector. They formed a matrix with these all vectors in that they applied LSA to give a score to each essay. It is a statistical approach that doesn’t consider the semantics of the essay. The accuracy they got when compared to the human rater score with the system is 0.532.
Cummins et al. ( 2016 ). Proposed Timed Aggregate Perceptron vector model to give ranking to all the essays, and later they converted the rank algorithm to predict the score of the essay. The model trained with features like Word unigrams, bigrams, POS, Essay length, grammatical relation, Max word length, sentence length. It is multi-task learning, gives ranking to the essays, and predicts the score for the essay. The performance evaluated through QWK is 0.69, a substantial agreement between the human rater and the system.
Sultan et al. ( 2016 ). Proposed a Ridge regression model to find short answer scoring with Question Demoting. Question Demoting is the new concept included in the essay's final assessment to eliminate duplicate words from the essay. The extracted features are Text Similarity, which is the similarity between the student response and reference answer. Question Demoting is the number of repeats in a student response. With inverse document frequency, they assigned term weight. The sentence length Ratio is the number of words in the student response, is another feature. With these features, the Ridge regression model was used, and the accuracy they got 0.887.
Contreras et al. ( 2018 ). Proposed Ontology based on text mining in this model has given a score for essays in phases. In phase-I, they generated ontologies with ontoGen and SVM to find the concept and similarity in the essay. In phase II from ontologies, they retrieved features like essay length, word counts, correctness, vocabulary, and types of word used, domain information. After retrieving statistical data, they used a linear regression model to find the score of the essay. The accuracy score is the average of 0.5.
Darwish and Mohamed ( 2020 ) proposed the fusion of fuzzy Ontology with LSA. They retrieve two types of features, like syntax features and semantic features. In syntax features, they found Lexical Analysis with tokens, and they construct a parse tree. If the parse tree is broken, the essay is inconsistent—a separate grade assigned to the essay concerning syntax features. The semantic features are like similarity analysis, Spatial Data Analysis. Similarity analysis is to find duplicate sentences—Spatial Data Analysis for finding Euclid distance between the center and part. Later they combine syntax features and morphological features score for the final score. The accuracy they achieved with the multiple linear regression model is 0.77, mostly on statistical features.
Süzen Neslihan et al. ( 2020 ) proposed a text mining approach for short answer grading. First, their comparing model answers with student response by calculating the distance between two sentences. By comparing the model answer with student response, they find the essay's completeness and provide feedback. In this approach, model vocabulary plays a vital role in grading, and with this model vocabulary, the grade will be assigned to the student's response and provides feedback. The correlation between the student answer to model answer is 0.81.
3.4.2 Classification based Models
Persing and Ng ( 2013 ) used a support vector machine to score the essay. The features extracted are OS, N-gram, and semantic text to train the model and identified the keywords from the essay to give the final score.
Sakaguchi et al. ( 2015 ) proposed two methods: response-based and reference-based. In response-based scoring, the extracted features are response length, n-gram model, and syntactic elements to train the support vector regression model. In reference-based scoring, features such as sentence similarity using word2vec is used to find the cosine similarity of the sentences that is the final score of the response. First, the scores were discovered individually and later combined two features to find a final score. This system gave a remarkable increase in performance by combining the scores.
Mathias and Bhattacharyya ( 2018a ; b ) Proposed Automated Essay Grading Dataset with Essay Attribute Scores. The first concept features selection depends on the essay type. So the common attributes are Content, Organization, Word Choice, Sentence Fluency, Conventions. In this system, each attribute is scored individually, with the strength of each attribute identified. The model they used is a random forest classifier to assign scores to individual attributes. The accuracy they got with QWK is 0.74 for prompt 1 of the ASAS dataset ( https://www.kaggle.com/c/asap-sas/ ).
Ke et al. ( 2019 ) used a support vector machine to find the response score. In this method, features like Agreeability, Specificity, Clarity, Relevance to prompt, Conciseness, Eloquence, Confidence, Direction of development, Justification of opinion, and Justification of importance. First, the individual parameter score obtained was later combined with all scores to give a final response score. The features are used in the neural network to find whether the sentence is relevant to the topic or not.
Salim et al. ( 2019 ) proposed an XGBoost Machine Learning classifier to assess the essays. The algorithm trained on features like word count, POS, parse tree depth, and coherence in the articles with sentence similarity percentage; cohesion and coherence are considered for training. And they implemented K-fold cross-validation for a result the average accuracy after specific validations is 68.12.
3.4.3 Neural network models
Shehab et al. ( 2016 ) proposed a neural network method that used learning vector quantization to train human scored essays. After training, the network can provide a score to the ungraded essays. First, we should process the essay to remove Spell checking and then perform preprocessing steps like Document Tokenization, stop word removal, Stemming, and submit it to the neural network. Finally, the model will provide feedback on the essay, whether it is relevant to the topic. And the correlation coefficient between human rater and system score is 0.7665.
Kopparapu and De ( 2016 ) proposed the Automatic Ranking of Essays using Structural and Semantic Features. This approach constructed a super essay with all the responses. Next, ranking for a student essay is done based on the super-essay. The structural and semantic features derived helps to obtain the scores. In a paragraph, 15 Structural features like an average number of sentences, the average length of sentences, and the count of words, nouns, verbs, adjectives, etc., are used to obtain a syntactic score. A similarity score is used as semantic features to calculate the overall score.
Dong and Zhang ( 2016 ) proposed a hierarchical CNN model. The model builds two layers with word embedding to represents the words as the first layer. The second layer is a word convolution layer with max-pooling to find word vectors. The next layer is a sentence-level convolution layer with max-pooling to find the sentence's content and synonyms. A fully connected dense layer produces an output score for an essay. The accuracy with the hierarchical CNN model resulted in an average QWK of 0.754.
Taghipour and Ng ( 2016 ) proposed a first neural approach for essay scoring build in which convolution and recurrent neural network concepts help in scoring an essay. The network uses a lookup table with the one-hot representation of the word vector of an essay. The final efficiency of the network model with LSTM resulted in an average QWK of 0.708.
Dong et al. ( 2017 ). Proposed an Attention-based scoring system with CNN + LSTM to score an essay. For CNN, the input parameters were character embedding and word embedding, and it has attention pooling layers and used NLTK to obtain word and character embedding. The output gives a sentence vector, which provides sentence weight. After CNN, it will have an LSTM layer with an attention pooling layer, and this final layer results in the final score of the responses. The average QWK score is 0.764.
Riordan et al. ( 2017 ) proposed a neural network with CNN and LSTM layers. Word embedding, given as input to a neural network. An LSTM network layer will retrieve the window features and delivers them to the aggregation layer. The aggregation layer is a superficial layer that takes a correct window of words and gives successive layers to predict the answer's sore. The accuracy of the neural network resulted in a QWK of 0.90.
Zhao et al. ( 2017 ) proposed a new concept called Memory-Augmented Neural network with four layers, input representation layer, memory addressing layer, memory reading layer, and output layer. An input layer represents all essays in a vector form based on essay length. After converting the word vector, the memory addressing layer takes a sample of the essay and weighs all the terms. The memory reading layer takes the input from memory addressing segment and finds the content to finalize the score. Finally, the output layer will provide the final score of the essay. The accuracy of essay scores is 0.78, which is far better than the LSTM neural network.
Mathias and Bhattacharyya ( 2018a ; b ) proposed deep learning networks using LSTM with the CNN layer and GloVe pre-trained word embeddings. For this, they retrieved features like Sentence count essays, word count per sentence, Number of OOVs in the sentence, Language model score, and the text's perplexity. The network predicted the goodness scores of each essay. The higher the goodness scores, means higher the rank and vice versa.
Nguyen and Dery ( 2016 ). Proposed Neural Networks for Automated Essay Grading. In this method, a single layer bi-directional LSTM accepting word vector as input. Glove vectors used in this method resulted in an accuracy of 90%.
Ruseti et al. ( 2018 ) proposed a recurrent neural network that is capable of memorizing the text and generate a summary of an essay. The Bi-GRU network with the max-pooling layer molded on the word embedding of each document. It will provide scoring to the essay by comparing it with a summary of the essay from another Bi-GRU network. The result obtained an accuracy of 0.55.
Wang et al. ( 2018a ; b ) proposed an automatic scoring system with the bi-LSTM recurrent neural network model and retrieved the features using the word2vec technique. This method generated word embeddings from the essay words using the skip-gram model. And later, word embedding is used to train the neural network to find the final score. The softmax layer in LSTM obtains the importance of each word. This method used a QWK score of 0.83%.
Dasgupta et al. ( 2018 ) proposed a technique for essay scoring with augmenting textual qualitative Features. It extracted three types of linguistic, cognitive, and psychological features associated with a text document. The linguistic features are Part of Speech (POS), Universal Dependency relations, Structural Well-formedness, Lexical Diversity, Sentence Cohesion, Causality, and Informativeness of the text. The psychological features derived from the Linguistic Information and Word Count (LIWC) tool. They implemented a convolution recurrent neural network that takes input as word embedding and sentence vector, retrieved from the GloVe word vector. And the second layer is the Convolution Layer to find local features. The next layer is the recurrent neural network (LSTM) to find corresponding of the text. The accuracy of this method resulted in an average QWK of 0.764.
Liang et al. ( 2018 ) proposed a symmetrical neural network AES model with Bi-LSTM. They are extracting features from sample essays and student essays and preparing an embedding layer as input. The embedding layer output is transfer to the convolution layer from that LSTM will be trained. Hear the LSRM model has self-features extraction layer, which will find the essay's coherence. The average QWK score of SBLSTMA is 0.801.
Liu et al. ( 2019 ) proposed two-stage learning. In the first stage, they are assigning a score based on semantic data from the essay. The second stage scoring is based on some handcrafted features like grammar correction, essay length, number of sentences, etc. The average score of the two stages is 0.709.
Pedro Uria Rodriguez et al. ( 2019 ) proposed a sequence-to-sequence learning model for automatic essay scoring. They used BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), which extracts the semantics from a sentence from both directions. And XLnet sequence to sequence learning model to extract features like the next sentence in an essay. With this pre-trained model, they attained coherence from the essay to give the final score. The average QWK score of the model is 75.5.
Xia et al. ( 2019 ) proposed a two-layer Bi-directional LSTM neural network for the scoring of essays. The features extracted with word2vec to train the LSTM and accuracy of the model in an average of QWK is 0.870.
Kumar et al. ( 2019 ) Proposed an AutoSAS for short answer scoring. It used pre-trained Word2Vec and Doc2Vec models trained on Google News corpus and Wikipedia dump, respectively, to retrieve the features. First, they tagged every word POS and they found weighted words from the response. It also found prompt overlap to observe how the answer is relevant to the topic, and they defined lexical overlaps like noun overlap, argument overlap, and content overlap. This method used some statistical features like word frequency, difficulty, diversity, number of unique words in each response, type-token ratio, statistics of the sentence, word length, and logical operator-based features. This method uses a random forest model to train the dataset. The data set has sample responses with their associated score. The model will retrieve the features from both responses like graded and ungraded short answers with questions. The accuracy of AutoSAS with QWK is 0.78. It will work on any topics like Science, Arts, Biology, and English.
Jiaqi Lun et al. ( 2020 ) proposed an automatic short answer scoring with BERT. In this with a reference answer comparing student responses and assigning scores. The data augmentation is done with a neural network and with one correct answer from the dataset classifying reaming responses as correct or incorrect.
Zhu and Sun ( 2020 ) proposed a multimodal Machine Learning approach for automated essay scoring. First, they count the grammar score with the spaCy library and numerical count as the number of words and sentences with the same library. With this input, they trained a single and Bi LSTM neural network for finding the final score. For the LSTM model, they prepared sentence vectors with GloVe and word embedding with NLTK. Bi-LSTM will check each sentence in both directions to find semantic from the essay. The average QWK score with multiple models is 0.70.
3.4.4 Ontology based approach
Mohler et al. ( 2011 ) proposed a graph-based method to find semantic similarity in short answer scoring. For the ranking of answers, they used the support vector regression model. The bag of words is the main feature extracted in the system.
Ramachandran et al. ( 2015 ) also proposed a graph-based approach to find lexical based semantics. Identified phrase patterns and text patterns are the features to train a random forest regression model to score the essays. The accuracy of the model in a QWK is 0.78.
Zupanc et al. ( 2017 ) proposed sentence similarity networks to find the essay's score. Ajetunmobi and Daramola ( 2017 ) recommended an ontology-based information extraction approach and domain-based ontology to find the score.
3.4.5 Speech response scoring
Automatic scoring is in two ways one is text-based scoring, other is speech-based scoring. This paper discussed text-based scoring and its challenges, and now we cover speech scoring and common points between text and speech-based scoring. Evanini and Wang ( 2013 ), Worked on speech scoring of non-native school students, extracted features with speech ratter, and trained a linear regression model, concluding that accuracy varies based on voice pitching. Loukina et al. ( 2015 ) worked on feature selection from speech data and trained SVM. Malinin et al. ( 2016 ) used neural network models to train the data. Loukina et al. ( 2017 ). Proposed speech and text-based automatic scoring. Extracted text-based features, speech-based features and trained a deep neural network for speech-based scoring. They extracted 33 types of features based on acoustic signals. Malinin et al. ( 2017 ). Wu Xixin et al. ( 2020 ) Worked on deep neural networks for spoken language assessment. Incorporated different types of models and tested them. Ramanarayanan et al. ( 2017 ) worked on feature extraction methods and extracted punctuation, fluency, and stress and trained different Machine Learning models for scoring. Knill et al. ( 2018 ). Worked on Automatic speech recognizer and its errors how its impacts the speech assessment.
3.4.5.1 The state of the art
This section provides an overview of the existing AES systems with a comparative study w. r. t models, features applied, datasets, and evaluation metrics used for building the automated essay grading systems. We divided all 62 papers into two sets of the first set of review papers in Table 5 with a comparative study of the AES systems.
3.4.6 Comparison of all approaches
In our study, we divided major AES approaches into three categories. Regression models, classification models, and neural network models. The regression models failed to find cohesion and coherence from the essay because it trained on BoW(Bag of Words) features. In processing data from input to output, the regression models are less complicated than neural networks. There are unable to find many intricate patterns from the essay and unable to find sentence connectivity. If we train the model with BoW features in the neural network approach, the model never considers the essay's coherence and coherence.
First, to train a Machine Learning algorithm with essays, all the essays are converted to vector form. We can form a vector with BoW and Word2vec, TF-IDF. The BoW and Word2vec vector representation of essays represented in Table 6 . The vector representation of BoW with TF-IDF is not incorporating the essays semantic, and it’s just statistical learning from a given vector. Word2vec vector comprises semantic of essay in a unidirectional way.
In BoW, the vector contains the frequency of word occurrences in the essay. The vector represents 1 and more based on the happenings of words in the essay and 0 for not present. So, in BoW, the vector does not maintain the relationship with adjacent words; it’s just for single words. In word2vec, the vector represents the relationship between words with other words and sentences prompt in multiple dimensional ways. But word2vec prepares vectors in a unidirectional way, not in a bidirectional way; word2vec fails to find semantic vectors when a word has two meanings, and the meaning depends on adjacent words. Table 7 represents a comparison of Machine Learning models and features extracting methods.
In AES, cohesion and coherence will check the content of the essay concerning the essay prompt these can be extracted from essay in the vector from. Two more parameters are there to access an essay is completeness and feedback. Completeness will check whether student’s response is sufficient or not though the student wrote correctly. Table 8 represents all four parameters comparison for essay grading. Table 9 illustrates comparison of all approaches based on various features like grammar, spelling, organization of essay, relevance.
3.5 What are the challenges/limitations in the current research?
From our study and results discussed in the previous sections, many researchers worked on automated essay scoring systems with numerous techniques. We have statistical methods, classification methods, and neural network approaches to evaluate the essay automatically. The main goal of the automated essay grading system is to reduce human effort and improve consistency.
The vast majority of essay scoring systems are dealing with the efficiency of the algorithm. But there are many challenges in automated essay grading systems. One should assess the essay by following parameters like the relevance of the content to the prompt, development of ideas, Cohesion, Coherence, and domain knowledge.
No model works on the relevance of content, which means whether student response or explanation is relevant to the given prompt or not if it is relevant to how much it is appropriate, and there is no discussion about the cohesion and coherence of the essays. All researches concentrated on extracting the features using some NLP libraries, trained their models, and testing the results. But there is no explanation in the essay evaluation system about consistency and completeness, But Palma and Atkinson ( 2018 ) explained coherence-based essay evaluation. And Zupanc and Bosnic ( 2014 ) also used the word coherence to evaluate essays. And they found consistency with latent semantic analysis (LSA) for finding coherence from essays, but the dictionary meaning of coherence is "The quality of being logical and consistent."
Another limitation is there is no domain knowledge-based evaluation of essays using Machine Learning models. For example, the meaning of a cell is different from biology to physics. Many Machine Learning models extract features with WordVec and GloVec; these NLP libraries cannot convert the words into vectors when they have two or more meanings.
3.5.1 Other challenges that influence the Automated Essay Scoring Systems.
All these approaches worked to improve the QWK score of their models. But QWK will not assess the model in terms of features extraction and constructed irrelevant answers. The QWK is not evaluating models whether the model is correctly assessing the answer or not. There are many challenges concerning students' responses to the Automatic scoring system. Like in evaluating approach, no model has examined how to evaluate the constructed irrelevant and adversarial answers. Especially the black box type of approaches like deep learning models provides more options to the students to bluff the automated scoring systems.
The Machine Learning models that work on statistical features are very vulnerable. Based on Powers et al. ( 2001 ) and Bejar Isaac et al. ( 2014 ), the E-rater was failed on Constructed Irrelevant Responses Strategy (CIRS). From the study of Bejar et al. ( 2013 ), Higgins and Heilman ( 2014 ), observed that when student response contain irrelevant content or shell language concurring to prompt will influence the final score of essays in an automated scoring system.
In deep learning approaches, most of the models automatically read the essay's features, and some methods work on word-based embedding and other character-based embedding features. From the study of Riordan Brain et al. ( 2019 ), The character-based embedding systems do not prioritize spelling correction. However, it is influencing the final score of the essay. From the study of Horbach and Zesch ( 2019 ), Various factors are influencing AES systems. For example, there are data set size, prompt type, answer length, training set, and human scorers for content-based scoring.
Ding et al. ( 2020 ) reviewed that the automated scoring system is vulnerable when a student response contains more words from prompt, like prompt vocabulary repeated in the response. Parekh et al. ( 2020 ) and Kumar et al. ( 2020 ) tested various neural network models of AES by iteratively adding important words, deleting unimportant words, shuffle the words, and repeating sentences in an essay and found that no change in the final score of essays. These neural network models failed to recognize common sense in adversaries' essays and give more options for the students to bluff the automated systems.
Other than NLP and ML techniques for AES. From Wresch ( 1993 ) to Madnani and Cahill ( 2018 ). discussed the complexity of AES systems, standards need to be followed. Like assessment rubrics to test subject knowledge, irrelevant responses, and ethical aspects of an algorithm like measuring the fairness of student response.
Fairness is an essential factor for automated systems. For example, in AES, fairness can be measure in an agreement between human score to machine score. Besides this, From Loukina et al. ( 2019 ), the fairness standards include overall score accuracy, overall score differences, and condition score differences between human and system scores. In addition, scoring different responses in the prospect of constructive relevant and irrelevant will improve fairness.
Madnani et al. ( 2017a ; b ). Discussed the fairness of AES systems for constructed responses and presented RMS open-source tool for detecting biases in the models. With this, one can change fairness standards according to their analysis of fairness.
From Berzak et al.'s ( 2018 ) approach, behavior factors are a significant challenge in automated scoring systems. That helps to find language proficiency, word characteristics (essential words from the text), predict the critical patterns from the text, find related sentences in an essay, and give a more accurate score.
Rupp ( 2018 ), has discussed the designing, evaluating, and deployment methodologies for AES systems. They provided notable characteristics of AES systems for deployment. They are like model performance, evaluation metrics for a model, threshold values, dynamically updated models, and framework.
First, we should check the model performance on different datasets and parameters for operational deployment. Selecting Evaluation metrics for AES models are like QWK, correlation coefficient, or sometimes both. Kelley and Preacher ( 2012 ) have discussed three categories of threshold values: marginal, borderline, and acceptable. The values can be varied based on data size, model performance, type of model (single scoring, multiple scoring models). Once a model is deployed and evaluates millions of responses every time for optimal responses, we need a dynamically updated model based on prompt and data. Finally, framework designing of AES model, hear a framework contains prompts where test-takers can write the responses. One can design two frameworks: a single scoring model for a single methodology and multiple scoring models for multiple concepts. When we deploy multiple scoring models, each prompt could be trained separately, or we can provide generalized models for all prompts with this accuracy may vary, and it is challenging.
4 Synthesis
Our Systematic literature review on the automated essay grading system first collected 542 papers with selected keywords from various databases. After inclusion and exclusion criteria, we left with 139 articles; on these selected papers, we applied Quality assessment criteria with two reviewers, and finally, we selected 62 writings for final review.
Our observations on automated essay grading systems from 2010 to 2020 are as followed:
The implementation techniques of automated essay grading systems are classified into four buckets; there are 1. regression models 2. Classification models 3. Neural networks 4. Ontology-based methodology, but using neural networks, the researchers are more accurate than other techniques, and all the methods state of the art provided in Table 3 .
The majority of the regression and classification models on essay scoring used statistical features to find the final score. It means the systems or models trained on such parameters as word count, sentence count, etc. though the parameters extracted from the essay, the algorithm are not directly training on essays. The algorithms trained on some numbers obtained from the essay and hear if numbers matched the composition will get a good score; otherwise, the rating is less. In these models, the evaluation process is entirely on numbers, irrespective of the essay. So, there is a lot of chance to miss the coherence, relevance of the essay if we train our algorithm on statistical parameters.
In the neural network approach, the models trained on Bag of Words (BoW) features. The BoW feature is missing the relationship between a word to word and the semantic meaning of the sentence. E.g., Sentence 1: John killed bob. Sentence 2: bob killed John. In these two sentences, the BoW is "John," "killed," "bob."
In the Word2Vec library, if we are prepared a word vector from an essay in a unidirectional way, the vector will have a dependency with other words and finds the semantic relationship with other words. But if a word has two or more meanings like "Bank loan" and "River Bank," hear bank has two implications, and its adjacent words decide the sentence meaning; in this case, Word2Vec is not finding the real meaning of the word from the sentence.
The features extracted from essays in the essay scoring system are classified into 3 type's features like statistical features, style-based features, and content-based features, which are explained in RQ2 and Table 3 . But statistical features, are playing a significant role in some systems and negligible in some systems. In Shehab et al. ( 2016 ); Cummins et al. ( 2016 ). Dong et al. ( 2017 ). Dong and Zhang ( 2016 ). Mathias and Bhattacharyya ( 2018a ; b ) Systems the assessment is entirely on statistical and style-based features they have not retrieved any content-based features. And in other systems that extract content from the essays, the role of statistical features is for only preprocessing essays but not included in the final grading.
In AES systems, coherence is the main feature to be considered while evaluating essays. The actual meaning of coherence is to stick together. That is the logical connection of sentences (local level coherence) and paragraphs (global level coherence) in a story. Without coherence, all sentences in a paragraph are independent and meaningless. In an Essay, coherence is a significant feature that is explaining everything in a flow and its meaning. It is a powerful feature in AES system to find the semantics of essay. With coherence, one can assess whether all sentences are connected in a flow and all paragraphs are related to justify the prompt. Retrieving the coherence level from an essay is a critical task for all researchers in AES systems.
In automatic essay grading systems, the assessment of essays concerning content is critical. That will give the actual score for the student. Most of the researches used statistical features like sentence length, word count, number of sentences, etc. But according to collected results, 32% of the systems used content-based features for the essay scoring. Example papers which are on content-based assessment are Taghipour and Ng ( 2016 ); Persing and Ng ( 2013 ); Wang et al. ( 2018a , 2018b ); Zhao et al. ( 2017 ); Kopparapu and De ( 2016 ), Kumar et al. ( 2019 ); Mathias and Bhattacharyya ( 2018a ; b ); Mohler and Mihalcea ( 2009 ) are used content and statistical-based features. The results are shown in Fig. 3 . And mainly the content-based features extracted with word2vec NLP library, but word2vec is capable of capturing the context of a word in a document, semantic and syntactic similarity, relation with other terms, but word2vec is capable of capturing the context word in a uni-direction either left or right. If a word has multiple meanings, there is a chance of missing the context in the essay. After analyzing all the papers, we found that content-based assessment is a qualitative assessment of essays.
On the other hand, Horbach and Zesch ( 2019 ); Riordan Brain et al. ( 2019 ); Ding et al. ( 2020 ); Kumar et al. ( 2020 ) proved that neural network models are vulnerable when a student response contains constructed irrelevant, adversarial answers. And a student can easily bluff an automated scoring system by submitting different responses like repeating sentences and repeating prompt words in an essay. From Loukina et al. ( 2019 ), and Madnani et al. ( 2017b ). The fairness of an algorithm is an essential factor to be considered in AES systems.
While talking about speech assessment, the data set contains audios of duration up to one minute. Feature extraction techniques are entirely different from text assessment, and accuracy varies based on speaking fluency, pitching, male to female voice and boy to adult voice. But the training algorithms are the same for text and speech assessment.
Once an AES system evaluates essays and short answers accurately in all directions, there is a massive demand for automated systems in the educational and related world. Now AES systems are deployed in GRE, TOEFL exams; other than these, we can deploy AES systems in massive open online courses like Coursera(“ https://coursera.org/learn//machine-learning//exam ”), NPTEL ( https://swayam.gov.in/explorer ), etc. still they are assessing student performance with multiple-choice questions. In another perspective, AES systems can be deployed in information retrieval systems like Quora, stack overflow, etc., to check whether the retrieved response is appropriate to the question or not and can give ranking to the retrieved answers.
5 Conclusion and future work
As per our Systematic literature review, we studied 62 papers. There exist significant challenges for researchers in implementing automated essay grading systems. Several researchers are working rigorously on building a robust AES system despite its difficulty in solving this problem. All evaluating methods are not evaluated based on coherence, relevance, completeness, feedback, and knowledge-based. And 90% of essay grading systems are used Kaggle ASAP (2012) dataset, which has general essays from students and not required any domain knowledge, so there is a need for domain-specific essay datasets to train and test. Feature extraction is with NLTK, WordVec, and GloVec NLP libraries; these libraries have many limitations while converting a sentence into vector form. Apart from feature extraction and training Machine Learning models, no system is accessing the essay's completeness. No system provides feedback to the student response and not retrieving coherence vectors from the essay—another perspective the constructive irrelevant and adversarial student responses still questioning AES systems.
Our proposed research work will go on the content-based assessment of essays with domain knowledge and find a score for the essays with internal and external consistency. And we will create a new dataset concerning one domain. And another area in which we can improve is the feature extraction techniques.
This study includes only four digital databases for study selection may miss some functional studies on the topic. However, we hope that we covered most of the significant studies as we manually collected some papers published in useful journals.
Adamson, A., Lamb, A., & December, R. M. (2014). Automated Essay Grading.
Ajay HB, Tillett PI, Page EB (1973) Analysis of essays by computer (AEC-II) (No. 8-0102). Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, Office of Education, National Center for Educational Research and Development
Ajetunmobi SA, Daramola O (2017) Ontology-based information extraction for subject-focussed automatic essay evaluation. In: 2017 International Conference on Computing Networking and Informatics (ICCNI) p 1–6. IEEE
Alva-Manchego F, et al. (2019) EASSE: Easier Automatic Sentence Simplification Evaluation.” ArXiv abs/1908.04567 (2019): n. pag
Bailey S, Meurers D (2008) Diagnosing meaning errors in short answers to reading comprehension questions. In: Proceedings of the Third Workshop on Innovative Use of NLP for Building Educational Applications (Columbus), p 107–115
Basu S, Jacobs C, Vanderwende L (2013) Powergrading: a clustering approach to amplify human effort for short answer grading. Trans Assoc Comput Linguist (TACL) 1:391–402
Article Google Scholar
Bejar, I. I., Flor, M., Futagi, Y., & Ramineni, C. (2014). On the vulnerability of automated scoring to construct-irrelevant response strategies (CIRS): An illustration. Assessing Writing, 22, 48-59.
Bejar I, et al. (2013) Length of Textual Response as a Construct-Irrelevant Response Strategy: The Case of Shell Language. Research Report. ETS RR-13-07.” ETS Research Report Series (2013): n. pag
Berzak Y, et al. (2018) “Assessing Language Proficiency from Eye Movements in Reading.” ArXiv abs/1804.07329 (2018): n. pag
Blanchard D, Tetreault J, Higgins D, Cahill A, Chodorow M (2013) TOEFL11: A corpus of non-native English. ETS Research Report Series, 2013(2):i–15, 2013
Blood, I. (2011). Automated essay scoring: a literature review. Studies in Applied Linguistics and TESOL, 11(2).
Burrows S, Gurevych I, Stein B (2015) The eras and trends of automatic short answer grading. Int J Artif Intell Educ 25:60–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-014-0026-8
Cader, A. (2020, July). The Potential for the Use of Deep Neural Networks in e-Learning Student Evaluation with New Data Augmentation Method. In International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education (pp. 37–42). Springer, Cham.
Cai C (2019) Automatic essay scoring with recurrent neural network. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on High Performance Compilation, Computing and Communications (2019): n. pag.
Chen M, Li X (2018) "Relevance-Based Automated Essay Scoring via Hierarchical Recurrent Model. In: 2018 International Conference on Asian Language Processing (IALP), Bandung, Indonesia, 2018, p 378–383, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/IALP.2018.8629256
Chen Z, Zhou Y (2019) "Research on Automatic Essay Scoring of Composition Based on CNN and OR. In: 2019 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Big Data (ICAIBD), Chengdu, China, p 13–18, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICAIBD.2019.8837007
Contreras JO, Hilles SM, Abubakar ZB (2018) Automated essay scoring with ontology based on text mining and NLTK tools. In: 2018 International Conference on Smart Computing and Electronic Enterprise (ICSCEE), 1-6
Correnti R, Matsumura LC, Hamilton L, Wang E (2013) Assessing students’ skills at writing analytically in response to texts. Elem Sch J 114(2):142–177
Cummins, R., Zhang, M., & Briscoe, E. (2016, August). Constrained multi-task learning for automated essay scoring. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Darwish SM, Mohamed SK (2020) Automated essay evaluation based on fusion of fuzzy ontology and latent semantic analysis. In: Hassanien A, Azar A, Gaber T, Bhatnagar RF, Tolba M (eds) The International Conference on Advanced Machine Learning Technologies and Applications
Dasgupta T, Naskar A, Dey L, Saha R (2018) Augmenting textual qualitative features in deep convolution recurrent neural network for automatic essay scoring. In: Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Natural Language Processing Techniques for Educational Applications p 93–102
Ding Y, et al. (2020) "Don’t take “nswvtnvakgxpm” for an answer–The surprising vulnerability of automatic content scoring systems to adversarial input." In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics
Dong F, Zhang Y (2016) Automatic features for essay scoring–an empirical study. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing p 1072–1077
Dong F, Zhang Y, Yang J (2017) Attention-based recurrent convolutional neural network for automatic essay scoring. In: Proceedings of the 21st Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning (CoNLL 2017) p 153–162
Dzikovska M, Nielsen R, Brew C, Leacock C, Gi ampiccolo D, Bentivogli L, Clark P, Dagan I, Dang HT (2013a) Semeval-2013 task 7: The joint student response analysis and 8th recognizing textual entailment challenge
Dzikovska MO, Nielsen R, Brew C, Leacock C, Giampiccolo D, Bentivogli L, Clark P, Dagan I, Trang Dang H (2013b) SemEval-2013 Task 7: The Joint Student Response Analysis and 8th Recognizing Textual Entailment Challenge. *SEM 2013: The First Joint Conference on Lexical and Computational Semantics
Educational Testing Service (2008) CriterionSM online writing evaluation service. Retrieved from http://www.ets.org/s/criterion/pdf/9286_CriterionBrochure.pdf .
Evanini, K., & Wang, X. (2013, August). Automated speech scoring for non-native middle school students with multiple task types. In INTERSPEECH (pp. 2435–2439).
Foltz PW, Laham D, Landauer TK (1999) The Intelligent Essay Assessor: Applications to Educational Technology. Interactive Multimedia Electronic Journal of Computer-Enhanced Learning, 1, 2, http://imej.wfu.edu/articles/1999/2/04/ index.asp
Granger, S., Dagneaux, E., Meunier, F., & Paquot, M. (Eds.). (2009). International corpus of learner English. Louvain-la-Neuve: Presses universitaires de Louvain.
Higgins, D., & Heilman, M. (2014). Managing what we can measure: Quantifying the susceptibility of automated scoring systems to gaming behavior. Educational Measurement: Issues and Practice, 33(3), 36–46.
Horbach A, Zesch T (2019) The influence of variance in learner answers on automatic content scoring. Front Educ 4:28. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2019.00028
https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning/exam/7pytE/linear-regression-with-multiple-variables/attempt
Hussein, M. A., Hassan, H., & Nassef, M. (2019). Automated language essay scoring systems: A literature review. PeerJ Computer Science, 5, e208.
Ke Z, Ng V (2019) “Automated essay scoring: a survey of the state of the art.” IJCAI
Ke, Z., Inamdar, H., Lin, H., & Ng, V. (2019, July). Give me more feedback II: Annotating thesis strength and related attributes in student essays. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 3994-4004).
Kelley K, Preacher KJ (2012) On effect size. Psychol Methods 17(2):137–152
Kitchenham B, Brereton OP, Budgen D, Turner M, Bailey J, Linkman S (2009) Systematic literature reviews in software engineering–a systematic literature review. Inf Softw Technol 51(1):7–15
Klebanov, B. B., & Madnani, N. (2020, July). Automated evaluation of writing–50 years and counting. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 7796–7810).
Knill K, Gales M, Kyriakopoulos K, et al. (4 more authors) (2018) Impact of ASR performance on free speaking language assessment. In: Interspeech 2018.02–06 Sep 2018, Hyderabad, India. International Speech Communication Association (ISCA)
Kopparapu SK, De A (2016) Automatic ranking of essays using structural and semantic features. In: 2016 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), p 519–523
Kumar, Y., Aggarwal, S., Mahata, D., Shah, R. R., Kumaraguru, P., & Zimmermann, R. (2019, July). Get it scored using autosas—an automated system for scoring short answers. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Vol. 33, No. 01, pp. 9662–9669).
Kumar Y, et al. (2020) “Calling out bluff: attacking the robustness of automatic scoring systems with simple adversarial testing.” ArXiv abs/2007.06796
Li X, Chen M, Nie J, Liu Z, Feng Z, Cai Y (2018) Coherence-Based Automated Essay Scoring Using Self-attention. In: Sun M, Liu T, Wang X, Liu Z, Liu Y (eds) Chinese Computational Linguistics and Natural Language Processing Based on Naturally Annotated Big Data. CCL 2018, NLP-NABD 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 11221. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01716-3_32
Liang G, On B, Jeong D, Kim H, Choi G (2018) Automated essay scoring: a siamese bidirectional LSTM neural network architecture. Symmetry 10:682
Liua, H., Yeb, Y., & Wu, M. (2018, April). Ensemble Learning on Scoring Student Essay. In 2018 International Conference on Management and Education, Humanities and Social Sciences (MEHSS 2018). Atlantis Press.
Liu J, Xu Y, Zhao L (2019) Automated Essay Scoring based on Two-Stage Learning. ArXiv, abs/1901.07744
Loukina A, et al. (2015) Feature selection for automated speech scoring.” BEA@NAACL-HLT
Loukina A, et al. (2017) “Speech- and Text-driven Features for Automated Scoring of English-Speaking Tasks.” SCNLP@EMNLP 2017
Loukina A, et al. (2019) The many dimensions of algorithmic fairness in educational applications. BEA@ACL
Lun J, Zhu J, Tang Y, Yang M (2020) Multiple data augmentation strategies for improving performance on automatic short answer scoring. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 34(09): 13389-13396
Madnani, N., & Cahill, A. (2018, August). Automated scoring: Beyond natural language processing. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Computational Linguistics (pp. 1099–1109).
Madnani N, et al. (2017b) “Building better open-source tools to support fairness in automated scoring.” EthNLP@EACL
Malinin A, et al. (2016) “Off-topic response detection for spontaneous spoken english assessment.” ACL
Malinin A, et al. (2017) “Incorporating uncertainty into deep learning for spoken language assessment.” ACL
Mathias S, Bhattacharyya P (2018a) Thank “Goodness”! A Way to Measure Style in Student Essays. In: Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Natural Language Processing Techniques for Educational Applications p 35–41
Mathias S, Bhattacharyya P (2018b) ASAP++: Enriching the ASAP automated essay grading dataset with essay attribute scores. In: Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2018).
Mikolov T, et al. (2013) “Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space.” ICLR
Mohler M, Mihalcea R (2009) Text-to-text semantic similarity for automatic short answer grading. In: Proceedings of the 12th Conference of the European Chapter of the ACL (EACL 2009) p 567–575
Mohler M, Bunescu R, Mihalcea R (2011) Learning to grade short answer questions using semantic similarity measures and dependency graph alignments. In: Proceedings of the 49th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics: Human language technologies p 752–762
Muangkammuen P, Fukumoto F (2020) Multi-task Learning for Automated Essay Scoring with Sentiment Analysis. In: Proceedings of the 1st Conference of the Asia-Pacific Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 10th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing: Student Research Workshop p 116–123
Nguyen, H., & Dery, L. (2016). Neural networks for automated essay grading. CS224d Stanford Reports, 1–11.
Palma D, Atkinson J (2018) Coherence-based automatic essay assessment. IEEE Intell Syst 33(5):26–36
Parekh S, et al (2020) My Teacher Thinks the World Is Flat! Interpreting Automatic Essay Scoring Mechanism.” ArXiv abs/2012.13872 (2020): n. pag
Pennington, J., Socher, R., & Manning, C. D. (2014, October). Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP) (pp. 1532–1543).
Persing I, Ng V (2013) Modeling thesis clarity in student essays. In:Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers) p 260–269
Powers DE, Burstein JC, Chodorow M, Fowles ME, Kukich K (2001) Stumping E-Rater: challenging the validity of automated essay scoring. ETS Res Rep Ser 2001(1):i–44
Google Scholar
Powers, D. E., Burstein, J. C., Chodorow, M., Fowles, M. E., & Kukich, K. (2002). Stumping e-rater: challenging the validity of automated essay scoring. Computers in Human Behavior, 18(2), 103–134.
Ramachandran L, Cheng J, Foltz P (2015) Identifying patterns for short answer scoring using graph-based lexico-semantic text matching. In: Proceedings of the Tenth Workshop on Innovative Use of NLP for Building Educational Applications p 97–106
Ramanarayanan V, et al. (2017) “Human and Automated Scoring of Fluency, Pronunciation and Intonation During Human-Machine Spoken Dialog Interactions.” INTERSPEECH
Riordan B, Horbach A, Cahill A, Zesch T, Lee C (2017) Investigating neural architectures for short answer scoring. In: Proceedings of the 12th Workshop on Innovative Use of NLP for Building Educational Applications p 159–168
Riordan B, Flor M, Pugh R (2019) "How to account for misspellings: Quantifying the benefit of character representations in neural content scoring models."In: Proceedings of the Fourteenth Workshop on Innovative Use of NLP for Building Educational Applications
Rodriguez P, Jafari A, Ormerod CM (2019) Language models and Automated Essay Scoring. ArXiv, abs/1909.09482
Rudner, L. M., & Liang, T. (2002). Automated essay scoring using Bayes' theorem. The Journal of Technology, Learning and Assessment, 1(2).
Rudner, L. M., Garcia, V., & Welch, C. (2006). An evaluation of IntelliMetric™ essay scoring system. The Journal of Technology, Learning and Assessment, 4(4).
Rupp A (2018) Designing, evaluating, and deploying automated scoring systems with validity in mind: methodological design decisions. Appl Meas Educ 31:191–214
Ruseti S, Dascalu M, Johnson AM, McNamara DS, Balyan R, McCarthy KS, Trausan-Matu S (2018) Scoring summaries using recurrent neural networks. In: International Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems p 191–201. Springer, Cham
Sakaguchi K, Heilman M, Madnani N (2015) Effective feature integration for automated short answer scoring. In: Proceedings of the 2015 conference of the North American Chapter of the association for computational linguistics: Human language technologies p 1049–1054
Salim, Y., Stevanus, V., Barlian, E., Sari, A. C., & Suhartono, D. (2019, December). Automated English Digital Essay Grader Using Machine Learning. In 2019 IEEE International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Education (TALE) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Shehab A, Elhoseny M, Hassanien AE (2016) A hybrid scheme for Automated Essay Grading based on LVQ and NLP techniques. In: 12th International Computer Engineering Conference (ICENCO), Cairo, 2016, p 65-70
Shermis MD, Mzumara HR, Olson J, Harrington S (2001) On-line grading of student essays: PEG goes on the World Wide Web. Assess Eval High Educ 26(3):247–259
Stab C, Gurevych I (2014) Identifying argumentative discourse structures in persuasive essays. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) p 46–56
Sultan MA, Salazar C, Sumner T (2016) Fast and easy short answer grading with high accuracy. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies p 1070–1075
Süzen, N., Gorban, A. N., Levesley, J., & Mirkes, E. M. (2020). Automatic short answer grading and feedback using text mining methods. Procedia Computer Science, 169, 726–743.
Taghipour K, Ng HT (2016) A neural approach to automated essay scoring. In: Proceedings of the 2016 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing p 1882–1891
Tashu TM (2020) "Off-Topic Essay Detection Using C-BGRU Siamese. In: 2020 IEEE 14th International Conference on Semantic Computing (ICSC), San Diego, CA, USA, p 221–225, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSC.2020.00046
Tashu TM, Horváth T (2019) A layered approach to automatic essay evaluation using word-embedding. In: McLaren B, Reilly R, Zvacek S, Uhomoibhi J (eds) Computer Supported Education. CSEDU 2018. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1022. Springer, Cham
Tashu TM, Horváth T (2020) Semantic-Based Feedback Recommendation for Automatic Essay Evaluation. In: Bi Y, Bhatia R, Kapoor S (eds) Intelligent Systems and Applications. IntelliSys 2019. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1038. Springer, Cham
Uto M, Okano M (2020) Robust Neural Automated Essay Scoring Using Item Response Theory. In: Bittencourt I, Cukurova M, Muldner K, Luckin R, Millán E (eds) Artificial Intelligence in Education. AIED 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 12163. Springer, Cham
Wang Z, Liu J, Dong R (2018a) Intelligent Auto-grading System. In: 2018 5th IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing and Intelligence Systems (CCIS) p 430–435. IEEE.
Wang Y, et al. (2018b) “Automatic Essay Scoring Incorporating Rating Schema via Reinforcement Learning.” EMNLP
Zhu W, Sun Y (2020) Automated essay scoring system using multi-model Machine Learning, david c. wyld et al. (eds): mlnlp, bdiot, itccma, csity, dtmn, aifz, sigpro
Wresch W (1993) The Imminence of Grading Essays by Computer-25 Years Later. Comput Compos 10:45–58
Wu, X., Knill, K., Gales, M., & Malinin, A. (2020). Ensemble approaches for uncertainty in spoken language assessment.
Xia L, Liu J, Zhang Z (2019) Automatic Essay Scoring Model Based on Two-Layer Bi-directional Long-Short Term Memory Network. In: Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence p 133–137
Yannakoudakis H, Briscoe T, Medlock B (2011) A new dataset and method for automatically grading ESOL texts. In: Proceedings of the 49th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics: human language technologies p 180–189
Zhao S, Zhang Y, Xiong X, Botelho A, Heffernan N (2017) A memory-augmented neural model for automated grading. In: Proceedings of the Fourth (2017) ACM Conference on Learning@ Scale p 189–192
Zupanc K, Bosnic Z (2014) Automated essay evaluation augmented with semantic coherence measures. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining p 1133–1138. IEEE.
Zupanc K, Savić M, Bosnić Z, Ivanović M (2017) Evaluating coherence of essays using sentence-similarity networks. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Computer Systems and Technologies p 65–72
Dzikovska, M. O., Nielsen, R., & Brew, C. (2012, June). Towards effective tutorial feedback for explanation questions: A dataset and baselines. In Proceedings of the 2012 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (pp. 200-210).
Kumar, N., & Dey, L. (2013, November). Automatic Quality Assessment of documents with application to essay grading. In 2013 12th Mexican International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (pp. 216–222). IEEE.
Wu, S. H., & Shih, W. F. (2018, July). A short answer grading system in chinese by support vector approach. In Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Natural Language Processing Techniques for Educational Applications (pp. 125-129).
Agung Putri Ratna, A., Lalita Luhurkinanti, D., Ibrahim I., Husna D., Dewi Purnamasari P. (2018). Automatic Essay Grading System for Japanese Language Examination Using Winnowing Algorithm, 2018 International Seminar on Application for Technology of Information and Communication, 2018, pp. 565–569. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISEMANTIC.2018.8549789 .
Sharma A., & Jayagopi D. B. (2018). Automated Grading of Handwritten Essays 2018 16th International Conference on Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition (ICFHR), 2018, pp 279–284. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICFHR-2018.2018.00056
Download references
Not Applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence, SR University, Warangal, TS, India
Dadi Ramesh
Research Scholar, JNTU, Hyderabad, India
Department of Information Technology, JNTUH College of Engineering, Nachupally, Kondagattu, Jagtial, TS, India
Suresh Kumar Sanampudi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Dadi Ramesh .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (XLSX 80 KB)
Rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Ramesh, D., Sanampudi, S.K. An automated essay scoring systems: a systematic literature review. Artif Intell Rev 55 , 2495–2527 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-021-10068-2
Download citation
Published : 23 September 2021
Issue Date : March 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-021-10068-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Short answer scoring
- Essay grading
- Natural language processing
- Deep learning
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say "literature review" or refer to "the literature," we are talking about the research (scholarship) in a given field. You will often see the terms "the research," "the ...
Here are the top 3 tips you need to keep in mind when writing a literature review: 1. Good Sources. When working on a literature review, the most important thing any writer should remember is to find the best possible sources for their MOP. This means that you should select and filter through about 5-10 different options while doing initial ...
Okay - with the why out the way, let's move on to the how. As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I'll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter.
A formal literature review is an evidence-based, in-depth analysis of a subject. There are many reasons for writing one and these will influence the length and style of your review, but in essence a literature review is a critical appraisal of the current collective knowledge on a subject. Rather than just being an exhaustive list of all that ...
A literature review is an integrated analysis of scholarly writings that are related directly to your research question. Put simply, it's a critical evaluation of what's already been written on a particular topic.It represents the literature that provides background information on your topic and shows a connection between those writings and your research question.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
Whatever stage you are at in your academic life, you will have to review the literature and write about it. You will be asked to do this as a student when you write essays, dissertations and theses. Later, whenever you write an academic paper, there will usually be some element of literature review in the introduction. And if you have to
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Reading the text and identifying literary devices. Step 2: Coming up with a thesis. Step 3: Writing a title and introduction. Step 4: Writing the body of the essay. Step 5: Writing a conclusion. Other interesting articles.
A literature review also includes a critical evaluation of the material; this is why it is called a literature review rather than a literature report. It is a process of reviewing the literature, as well as a form of writing. To illustrate the difference between reporting and reviewing, think about television or film review articles.
Essay Writing versus Writing a Literature Review Essay writing is a process that communicates ideas to an intended reader, and is usually written according to pre-determined academic conventions. ... (Shields, 2010). The reflective essay is based on the premise that learning occurs and is enhanced through reflection. While reflective essays ...
Preparing a literature review involves: Searching for reliable, accurate and up-to-date material on a topic or subject. Synthesising these key ideas, theories and concepts into a summary of what is known. Discussing and evaluating these ideas, theories and concepts. Preparing the ground for the application of these ideas to new research.
15 Literature Review Examples. Literature reviews are a necessary step in a research process and often required when writing your research proposal. They involve gathering, analyzing, and evaluating existing knowledge about a topic in order to find gaps in the literature where future studies will be needed. Ideally, once you have completed your ...
Steps for Conducting a Lit Review; Finding "The Literature" Organizing/Writing; APA Style This link opens in a new window; Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window; MLA Style This link opens in a new window; Sample Literature Reviews. Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts; Have an exemplary literature review? Get Help!
As mentioned previously, there are a number of existing guidelines for literature reviews. Depending on the methodology needed to achieve the purpose of the review, all types can be helpful and appropriate to reach a specific goal (for examples, please see Table 1).These approaches can be qualitative, quantitative, or have a mixed design depending on the phase of the review.
5. With the class as a whole, try to formulate a thesis statement for a literature review essay based on the information up on the board. Give students Handouts IV and V, and if time permits, discuss how to formulate an outline for a paper based on the thesis statement that the class formulated, referring to Handouts IV and V as appropriate. (6 ...
First of all, it is necessary to point out that many students struggle with understanding the difference between a literature review and an essay. This is particularly so because a student can use the exact same resources to create a literature review or an essay; however, what is different about the two is where the emphasis in the writing is ...
Literature reviews play a critical role in scholarship because science remains, first and foremost, a cumulative endeavour (vom Brocke et al., 2009). As in any academic discipline, rigorous knowledge syntheses are becoming indispensable in keeping up with an exponentially growing eHealth literature, assisting practitioners, academics, and graduate students in finding, evaluating, and ...
In this essay, we focus on the use of AI-based tools in the conduct of literature reviews. Advancing knowledge in this area is particularly promising since (1) standalone review projects require substantial efforts over months and years (Larsen et al., 2019), (2) the volume of reviews published in IS journals has been rising steadily (Schryen et al., 2020), and (3) literature reviews involve ...
This paper aims to provide a systematic literature review (SLR) on automated essay grading systems. An SLR is an Evidence-based systematic review to summarize the existing research. It critically evaluates and integrates all relevant studies' findings and addresses the research domain's specific research questions.
The assignment requires students to research a contemporary social issue, do a rhetorical analysis of a scholarly article, a literature review, and a research-based analysis of a piece of media pertaining to the issue. Citations for two scholarly articles